EE 560 MOS TRANSISTOR THEORY PART 2. Kenneth R. Laker, University of Pennsylvania
|
|
|
- Aldous Allen
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1 EE 560 MOS TRANSISTOR THEORY PART
2 nmos TRANSISTOR IN LINEAR REGION V S = 0 V G > V T0 channel SiO V D = small 4 C GC C BC substrate depletion region or bulk B p nmos TRANSISTOR AT EDGE OF SATURATION REGION V S = 0 channel V G > V T0 SiO V D = V DSAT C GC C BC substrate or bulk B p depletion region pinch-off point
3 5 nmos TRANSISTOR IN SATURATION REGION V S = 0 channel V G > V T0 SIO V D > V DSAT C GC substrate or bulk B p C BC depletion region pinch-off point
4 MOSFET CURRENT - VOLTAGE CHARACTERISTICS V S = V B = 0 V G > V T0 6 V DS C GC substrate or bulk B p x C BC y y = 0 y = L y = 0 y Channel length = L y = L Channel width = Source side inversion layer (channel) dy Drain side
5 MOSFET CURRENT - VOLTAGE CHARACTERISTICS V S = V B = 0 V G > V T0 7 V DS C GC substrate or bulk B Boundary conditions: V CS (y = 0) = V S = 0 V CS (y = L) = V DS p x y = 0 C BC y V CS (y) y = L Assumptions: V T0 (y) = V T0 > V T0 Mobile charge in channel: V GD = - V DS > V T0 Q I (y) = C ox [ V CS (y) V T 0 ] dr = dy 1 µ n Q I (y) µ n = electron mobility = cm /Vsec [µ > U0 in SPICE]
6 MOSFET CURRENT - VOLTAGE CHARACTERISTICS Boundary conditions: Q I (y) = C ox [ V CS (y) V T 0 ] V CS (y = 0) = V S = 0 V CS (y = L) = V DS dr = dy 1 µ n Q I (y) 8 dv CS = dr = L dy = µ n 0 µ n Q I (y) dy Integrating along the channel 0 < y < L and 0 < V CS < V DS : i.e. V DS Q I (y) 0 dv CS = µ n C ox [( V T 0 )V DS V DS / ] = µ C n ox L [(V V )V V GS T 0 DS DS]
7 MOSFET CURRENT - VOLTAGE CHARACTERISTICS 9 = µ C n ox = k' L [(V V )V V GS T 0 DS DS] L [( V T 0 )V DS V DS = k [(V V )V V GS T 0 DS DS] ] k' = µ n C ox [k' -> KP in SPICE] k = k' L
8 MOSFET CURRENT - VOLTAGE CHARACTERISTICS 30 EXAMPLE 3.4 For an n-mos transistor with µ n = 600 cm /Vsec, C ox = 7 x 10-8 F/cm = 0 µm, L = µm, V T0 = 1.0 V, plot the relationship between and V DS,. = k [(V V )V V GS T 0 DS DS] where k = µ n C ox L F = C/V k = µ n C ox L = (600 cm /Vsec)(7x10 8 F/cm ) 0µ m = 0.4 ma/v µ m = 0.1mA/V [( 1.0) V DS V DS ] LINEAR OR TRIODE REGION (ma) V DS = - V T0 VDS V T0 = 5V Assumptions: = 4V > V T0 V = 3V GD = V DS > V T0 V DS (V)
9 MOSFET CURRENT - VOLTAGE CHARACTERISTICS V DS - V T0 = V DSAT SATURATION REGION 31 = µ n C ox = µ n C ox L [(V V )V V GS T 0 DS = V = V - V DSAT GS T0 L [( V T 0 )( V T 0 ) ( V T 0 ) ] (sat) = µ n C ox L ( V T 0 ) 4.0 V (ma) DS = - V T0 LINEAR SAT.0 = 5V = 4V 0 = 3V V DS (V) (sat) V T0
10 MOSFET CURRENT - VOLTAGE CHARACTERISTICS CHANNEL LENGTH MODULATION Boundary conditions: V CS (y = 0) = V S = 0 V CS (y = L) = V DS Q I (y) = C ox [ V CS (y) V T 0 ] Q I (y = 0) = C ox [ V T 0 ] Q 1 (y = L) = C ox [ V DS V T 0 ] 3 V S = 0 V G > V T0 = V DS = V DSAT V D > V DSAT substrate or bulk B p C GC C BC L' L L L' = L L effective channel length V CS (y = L') = V DSAT
11 MOSFET CURRENT - VOLTAGE CHARACTERISTICS V S = 0 V G > V T0 V D > V DSAT 33 substrate or bulk B p C GC C BC L' L L (sat) = µ n C ox where L L' (V T 0 ) = µ C n ox V DS V DSAT L(1 L (V V ) L ) GS T 0 emperical relation: 1 1 L = 1 + λv DS [λ -> LAMBDA in SPICE] L λ = channel length modulation coefficent (V -1 )
12 MOSFET CURRENT - VOLTAGE CHARACTERISTICS L' (V T 0 ) = µ C n ox (sat) = µ n C ox 1 1 L L = 1 + λ V DS (sat) = µ n C ox L(1 L (V V ) L ) GS T 0 L ( V T 0 ) (1 + λ V DS ) V (ma) DS = - V T0 λ 0 λ 0 λ = 5V = 4V = 3V V DS (V)
13 MOSFET CURRENT - VOLTAGE CHARACTERISTICS 35 SUBSTRATE BIAS EFFECT = f(, V DS, V SB )
14 MOSFET CURRENT - VOLTAGE CHARACTERISTICS n-mos G + n-mos = 0 D + V DS - + S for V T S B G - - B V SB p-mos + D V SB V DS 36 > V T, V DS < - V T > V T, V DS > - V T p-mos = 0 for V T < V T, V DS > - V T < V T, V DS < - V T
15 MOSFET CURRENT - VOLTAGE CHARACTERISTICS MEASUREMENT OF PARAMETERS (V T0, γ, λ, k n, k p ) k n = µ n C ox k L p = µ p C ox L 37 D G S B + V SB + V DS = (sat) = k n ( V T 0 ) k n (sat) = (V V ) GS T 0 V SB = 0 V SB > 0 Gamma V T0 V T1
16 MOSFET CURRENT - VOLTAGE CHARACTERISTICS 38 Lambda = V T G D S B + V DS > - V T0 1 V BS = 0 = V T0 + 1 (sat) = k n ( V T 0 ) (1+ λ V DS ) = V T0 + 1 V DS1 V DS V DS 1 = 1+ λv DS 1 + λ V DS1
17 EFFECTIVE CHANNEL LENGTH AND IDTH B S C GC C GC G D 39 substrate or pbulk B n + C BC BC n + n + n + p LD LD L L eff L M SPICE Parameters L eff = L M - LD - DL LD -> under diffusion DL -> error in photolith and etch eff = M - D SPICE Parameters D -> error in photolith and etch
18 MOSFET - SCALING SCALING -> refers to ordered reduction in dimensions of the MOSFET and other VLSI features Reduce Size of VLSI chips. Change operational charateristics of MOSFETs and parasitics. Phyiscal limits restrict degree of scaling that can be achieved. SCALING FACTOR = α > 1 --> S First-order "constant field" MOS scaling theory: The electric field E is kept constant, and the scaled device is obtained by applying a dimensionless scale-factor α to (such that E is unchanged): a. All dimensions, including those vertical to the surface (1/α) b. device voltages (1/α) c. the concentration densities (α). (1/α)/(1/α) = 1 <=> α(1/α) = 1 40
19 MOSFET - SCALING Alternative Scaling Rules: Constant Voltage Scaling, i.e. V DD is kept constant, while the process is scaled. a. All dimensions, including those vertical to the surface (1/α) b. device voltages (1) c. the concentration densities (α ). 1/(1/α) = α <=> α (1/α) = α 41 Lateral Scaling: only the gate length is scaled L = 1/α (gate-shrink). Year Feature Size(µm) Historical reduction in min feature size for typical CMOS Process
20 Influence of Scaling on MOS Device Performance PARAMETER SCALING MODEL Constant Field Constant Voltage Lateral 4 Length (L) 1/α 1/α 1/α idth () 1/α 1/α 1 Supply Voltage (V) 1/α 1 1 Gate Oxide thickness (t ox ) 1/α 1/α 1 Junction depth (X j ) 1/α 1/α 1 Substrate Doping (N A ) α α 1 Current (I) - (/L) (1/t ox )V 1/α α α Power Dissipation (P) - IV 1/α α α Electric Field Across Gate Oxide - V/t ox 1 α 1 Load Capacitance (C) - L (1/t ox ) 1/α 1/α 1/α Gate Delay (T) - VC/I 1/α 1/α 1/α
21 p B MOSFET CAPACITANCES S n + C GC C GC C BC BC n + n + G D n + 43 substrate or p bulk B LD LD L eff substrate or bulk B p L M L D L D n + n + Y
22 MOSFET CAPACITANCES 44 C gb D C gd C db G MOSFET (DC MODEL) B C gs C sb S C gd, C gs, C gb -> Oxide Capacitances C db, C sb -> Junction Capacitances
23 MOSFET CAPACITANCES 45 OXIDE Capacitances a. Overlap Caps C ox = ε ox t ox C GS (overlap) = C ox L D C GD (overlap) = C ox L D b. Gate - Channel MOSFET - Cut-off Region ALL MOSFET OPERATION REGIONS C gb = C ox L C gs = C gd = 0 p
24 MOSFET CAPACITANCES b. Gate - Channel MOSFET - Linear Region 46 C gb = 0 p C gs = (1/) C ox L C gd = (1/) C ox L p C gb = 0 C gs = (/3) C ox L C gd = 0
25 Capacitance Cut-off Linear Saturation 47 1 /3 1/ C gb (total) C gd (total) C gs (total) (C/C ox L) Cut-off C gb C ox L C ox L D 0 +C ox L D Saturation C gs 0.5C ox L + C ox L D 0.5C ox L + C ox L D Linear C gd 0 + C ox L D (/3)C L ox + C ox L D Gate -to Channel/Bulk Cap Contribution V T V T + V DS
26 JUNCTION Capacitances -> C db, C sb 48 x j p x d Y x j n + Channel n + 4 Source Drain
27 JUNCTION Capacitances -> C db, C sb Y 49 1 n + Channel n + 4 [x j -> XJ in SPICE] Source Drain Junction Area Type x j Y x j x j Y x j Y n + /p n + /p + n + /p + n + /p + n + /p 5 3 x j p - Substrate -> N A p + - Channel-stop -> 10N A
28 JUNCTION Capacitances -> C db, C sb 50 n +, p junctions p N A x d N D x j x d = ε Si q N A N D (φ V) V = Ext bias --> V DB, V SB 0 φ 0 = kt q ln N N built-in junction A D n i potential [φ Depletion-region charge 0 -> PB in SPICE] Q j = Aq N N A D N A + N D x = A ε q N A N D d Si N A + N D (φ V) 0 C j = dq j dv = A ε Si q N A N D N A + N D 1 φ 0 V = AC j 0 1 V φ 0 1/ A = junction area [AS, AD -> Source, Drain Areas in SPICE]
29 C j = dq j dv = A ε q 51 Si N A N D 1 N A + N D φ 0 V = AC j 0 1 V 1/ (F) φ 0 m = grading coefficent C (F/cm j0 = ε q Si N A N D ) N m = 1/ for abrubt junction A + N 1 D φ 0 [m = MJ in SPICE] C j = C j0 when V = 0 [C j0 -> CJ in SPICE] [φ 0 -> PB in SPICE] EQUIVALENT LARGE SIGNAL CAPACTIANCE = AC j 0 φ 0 ( 1) 1 V (V V 1 )(1 m) φ 0 1 m 1 V 1 φ 0 1 m m = 1/ C eq = AC j0 K eq 0 < K eq < 1 --> Voltage Equiv Factor
30 n +, p + junctions (Sidewalls) 5 C j0sw = ε Si q N A (sw)n D N A (sw) + N D 1 φ 0sw (F/cm ) Since all sidewalls have depth = x j : [x j -> XJ in SPICE] C jsw = C j0sw x j (F/cm) [C jsw -> CJS in SPICE] EQUIVALENT LARGE SIGNAL CAPACTIANCE C eq (sw) = P C jsw K eq (sw) P = sidewall perimeter [PS, PD -> Source, Drain Perimeters in SPICE] K eq (sw) = φ 0sw (V V 1 ) 1 V φ 0sw 1/ 1 V 1 φ 0sw [m(sw) -> MJS in SPICE] 1/ m(sw) = 1/
31 EXAMPLE 3-8 Determine the total junction capacitance at the drain, i.e. C db, for the n-channel enhancement MOSFET in Fig. 1. The process parameters are Substrate doping N A = x cm -3 Source/drain (n+) doping N D = 10 0 cm -3 Sidewall (p+) doping N A (sw) = 4 x cm -3 Gate oxide thickness t ox = 45 nm Junction depth x j = 1.0 µm 10 µm G 53 5 µm D S n + n + Figure 1 µm Source, Drain are surrounded by p + channel-stop. The substrate is biased at 0V. Assume the drain voltage range is 0.5 V to 5.0 V.
32 54 where C j0 = ε Si q N A N D N A + N 1 D φ 0 C j0sw = ε Si q N A (sw)n D N A (sw) + N D 1 φ 0sw
33 5 µm 10 µm D S n + n + Figure 1 µm φ 0, φ 0sw φ 0 = kt q ln N N A D n i = 0.06Vln ( x1015 )10 0.1x10 0 G N A = x cm -3 N D = 10 0 cm -3 N A (sw) = 4 x cm -3 t ox = 45 nm x j = 1.0 µm = 0.896V φ 0sw = kt q ln N (sw)n A D n i = 0.06Vln (4x1016 )10 0.1x10 0 = 0.975V 55 C j0, C j0sw C j0 = ε Si q N A N D N A + N D 1 φ 0 = (1.04 x10 1 F/cm)(1.6x10 19 C) = 1.35x10 8 F/cm ( x10 15 )10 0 x V
34 C j0sw = ε Si q N A (sw)n D N A (sw) + N D 1 φ 0sw 56 = (1.04 x10 1 F/cm)(1.6x10 19 C) = 5.83x10 8 F/cm (4x10 16 )10 0 4x V C jsw C jsw = C j0sw x j = (5.83x10 8 F/cm )(10 4 cm) = 5.83pF/cm K eq, K eq (sw) V BD1 = V B - V D1 = 0-0.5V = -0.5V V BD = V B - V D = 0-5V = -5V
35 57 Area, Perimeter Y n + Channel P D n + 4 Source Drain A D : n + /p junctions: 5 µm A D = (5 x 1) µm + (10 x 5) µm = 55 µm P D : n + /p + + junctions: P D = Y + = 0 µm + 5 µm = 5 µm x j Figure 1 10 µm C db = A D C j 0 K eq + P D C j0sw K eq (sw) = 11.6fF G D S n + n + µm
36 Mobility Degradation due to Longitudinal Electric Field: VELOSITY SATURATION (very small channel lengths + high supply voltages) v Dsat velosity(v D ) slope = µ 0 E crit slope µ s µ 0 = v sat /E crit E Note µ s < µ 0 [SPICE Parameters: U0 -> µ 0, UCRIT -> E crit, VMAX -> v sat ] (sat) = v DSAT Q I = v DSAT C ox V DSAT = v DSAT C ox ( - V T ) Note: (sat) = linear f( - V T ), independent of L E y 58
37 Mobility Degradation due to Tranverse Electric Field: (due to gate voltage across very thin oxide-depletion layer) 59 µ n (eff) = µ n 0 1+ Θ E x µ n0 1+η( V T ) E x Short Channel Effect - V T0 (short channel) = V T0 - V T0 L eff --> x j L L S L D x j V T 0 = 1 x ds qε Si N A φ F x j L C ox x dd gate induced 1 + x ds 1 x j + 1+ x dd x j 1
38 60 Narrow Channel Effect - V T0 (narrow channel) = V T0 + V T0 --> x dm Thick Ox L Q NC Drain Poly Gate x dm Source Q NC Thin Ox V T 0 = 1 C ox qε Si N A φ F κ x dm
39 SPICE MODELING OF MOS CAPACITANCES 61 M NFET =4U L=1U AS=15P AD=15P PS=11.5U PD=11.5U. m. m m. U = 10.MODEL NFET NMOS -6 cm + TOX=00E-8 F/m P = CGBO=00P CGSO=300P CGDO=300P + CJ=00U CJS=400P MJ=0.5 MJS=0.3 PB=0.7 V F/m F/m M NFET =4U L=1U AS=15P AD=15P PS=11.5U PD=11.5U D G S B C gb = L C ox = pf = pf
40 M NFET =4U L=1U AS=15P AD=15P PS=11.5U PD=11.5U..MODEL NFET NMOS + TOX=00E-8 + CGBO=00P CGSO=300P CGDO=300P + CJ=00U CJS=400P MJ=0.5 MJS=0.3 PB=0.7 6 C j = Area CJ 1 + V -MJ j V - + Periphery CJS j PB PB CJ = zero-bias junction capacitance per junction area -MJS ( F/m = 10-4 pf/µm ) CJS = zero-bias junction capacitance per junction periphery ( F/m = pf/µm) MJ = grading coefficient of junction bottom (0.5) MJS = grading coefficient of junction side-wall (0.3) VJ = the junction potential (V sb, V db for n-channel, V bs, V bd for p-channel) PB = the built-in voltage (+0.7 V) Area = AS or AD, the area of source or drain ( m = 15 µm ) Periphery = PS or PD, the periphery of source or drain ( m = 11.5 µm)
The Devices. Devices
 The The MOS Transistor Gate Oxyde Gate Source n+ Polysilicon Drain n+ Field-Oxyde (SiO 2 ) p-substrate p+ stopper Bulk Contact CROSS-SECTION of NMOS Transistor Cross-Section of CMOS Technology MOS transistors
The The MOS Transistor Gate Oxyde Gate Source n+ Polysilicon Drain n+ Field-Oxyde (SiO 2 ) p-substrate p+ stopper Bulk Contact CROSS-SECTION of NMOS Transistor Cross-Section of CMOS Technology MOS transistors
University of Pennsylvania Department of Electrical Engineering. ESE 570 Midterm Exam March 14, 2013 FORMULAS AND DATA
 University of Pennsylvania Department of Electrical Engineering ESE 570 Midterm Exam March 4, 03 FORMULAS AND DATA. PHYSICAL CONSTANTS: n i = intrinsic concentration undoped) silicon =.45 x 0 0 cm -3 @
University of Pennsylvania Department of Electrical Engineering ESE 570 Midterm Exam March 4, 03 FORMULAS AND DATA. PHYSICAL CONSTANTS: n i = intrinsic concentration undoped) silicon =.45 x 0 0 cm -3 @
MOSFET: Introduction
 E&CE 437 Integrated VLSI Systems MOS Transistor 1 of 30 MOSFET: Introduction Metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistor (MOSFET) or MOS is widely used for implementing digital designs Its major
E&CE 437 Integrated VLSI Systems MOS Transistor 1 of 30 MOSFET: Introduction Metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistor (MOSFET) or MOS is widely used for implementing digital designs Its major
EE 560 MOS TRANSISTOR THEORY
 1 EE 560 MOS TRANSISTOR THEORY PART 1 TWO TERMINAL MOS STRUCTURE V G (GATE VOLTAGE) 2 GATE OXIDE SiO 2 SUBSTRATE p-type doped Si (N A = 10 15 to 10 16 cm -3 ) t ox V B (SUBSTRATE VOLTAGE) EQUILIBRIUM:
1 EE 560 MOS TRANSISTOR THEORY PART 1 TWO TERMINAL MOS STRUCTURE V G (GATE VOLTAGE) 2 GATE OXIDE SiO 2 SUBSTRATE p-type doped Si (N A = 10 15 to 10 16 cm -3 ) t ox V B (SUBSTRATE VOLTAGE) EQUILIBRIUM:
! MOS Capacitances. " Extrinsic. " Intrinsic. ! Lumped Capacitance Model. ! First Order Capacitor Summary. ! Capacitance Implications
 ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 7: February, 07 MOS SPICE Models, MOS Parasitic Details Lecture Outline! MOS Capacitances " Extrinsic " Intrinsic! Lumped Capacitance Model!
ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 7: February, 07 MOS SPICE Models, MOS Parasitic Details Lecture Outline! MOS Capacitances " Extrinsic " Intrinsic! Lumped Capacitance Model!
The Devices. Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective. Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic. July 30, 2002
 Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic The Devices July 30, 2002 Goal of this chapter Present intuitive understanding of device operation Introduction
Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic The Devices July 30, 2002 Goal of this chapter Present intuitive understanding of device operation Introduction
LECTURE 3 MOSFETS II. MOS SCALING What is Scaling?
 LECTURE 3 MOSFETS II Lecture 3 Goals* * Understand constant field and constant voltage scaling and their effects. Understand small geometry effects for MOS transistors and their implications modeling and
LECTURE 3 MOSFETS II Lecture 3 Goals* * Understand constant field and constant voltage scaling and their effects. Understand small geometry effects for MOS transistors and their implications modeling and
EE115C Winter 2017 Digital Electronic Circuits. Lecture 3: MOS RC Model, CMOS Manufacturing
 EE115C Winter 2017 Digital Electronic Circuits Lecture 3: MOS RC Model, CMOS Manufacturing Agenda MOS Transistor: RC Model (pp. 104-113) S R on D CMOS Manufacturing Process (pp. 36-46) S S C GS G G C GD
EE115C Winter 2017 Digital Electronic Circuits Lecture 3: MOS RC Model, CMOS Manufacturing Agenda MOS Transistor: RC Model (pp. 104-113) S R on D CMOS Manufacturing Process (pp. 36-46) S S C GS G G C GD
ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals
 ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 7: February 4, 2016 MOS SPICE Models, MOS Parasitic Details Lecture Outline! MOS Capacitances " Extrinsic " Intrinsic! Lumped Capacitance
ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 7: February 4, 2016 MOS SPICE Models, MOS Parasitic Details Lecture Outline! MOS Capacitances " Extrinsic " Intrinsic! Lumped Capacitance
Device Models (PN Diode, MOSFET )
 Device Models (PN Diode, MOSFET ) Instructor: Steven P. Levitan steve@ece.pitt.edu TA: Gayatri Mehta, José Martínez Book: Digital Integrated Circuits: A Design Perspective; Jan Rabaey Lab Notes: Handed
Device Models (PN Diode, MOSFET ) Instructor: Steven P. Levitan steve@ece.pitt.edu TA: Gayatri Mehta, José Martínez Book: Digital Integrated Circuits: A Design Perspective; Jan Rabaey Lab Notes: Handed
Lecture 4: CMOS Transistor Theory
 Introduction to CMOS VLSI Design Lecture 4: CMOS Transistor Theory David Harris, Harvey Mudd College Kartik Mohanram and Steven Levitan University of Pittsburgh Outline q Introduction q MOS Capacitor q
Introduction to CMOS VLSI Design Lecture 4: CMOS Transistor Theory David Harris, Harvey Mudd College Kartik Mohanram and Steven Levitan University of Pittsburgh Outline q Introduction q MOS Capacitor q
MOS Transistor I-V Characteristics and Parasitics
 ECEN454 Digital Integrated Circuit Design MOS Transistor I-V Characteristics and Parasitics ECEN 454 Facts about Transistors So far, we have treated transistors as ideal switches An ON transistor passes
ECEN454 Digital Integrated Circuit Design MOS Transistor I-V Characteristics and Parasitics ECEN 454 Facts about Transistors So far, we have treated transistors as ideal switches An ON transistor passes
N Channel MOSFET level 3
 N Channel MOSFET level 3 mosn3 NSource NBulk NSource NBulk NSource NBulk NSource (a) (b) (c) (d) NBulk Figure 1: MOSFET Types Form: mosn3: instance name n 1 n n 3 n n 1 is the drain node, n is the gate
N Channel MOSFET level 3 mosn3 NSource NBulk NSource NBulk NSource NBulk NSource (a) (b) (c) (d) NBulk Figure 1: MOSFET Types Form: mosn3: instance name n 1 n n 3 n n 1 is the drain node, n is the gate
Device Models (PN Diode, MOSFET )
 Device Models (PN Diode, MOSFET ) Instructor: Steven P. Levitan steve@ece.pitt.edu TA: Gayatri Mehta, José Martínez Book: Digital Integrated Circuits: A Design Perspective; Jan Rabaey Lab Notes: Handed
Device Models (PN Diode, MOSFET ) Instructor: Steven P. Levitan steve@ece.pitt.edu TA: Gayatri Mehta, José Martínez Book: Digital Integrated Circuits: A Design Perspective; Jan Rabaey Lab Notes: Handed
Lecture 3: CMOS Transistor Theory
 Lecture 3: CMOS Transistor Theory Outline Introduction MOS Capacitor nmos I-V Characteristics pmos I-V Characteristics Gate and Diffusion Capacitance 2 Introduction So far, we have treated transistors
Lecture 3: CMOS Transistor Theory Outline Introduction MOS Capacitor nmos I-V Characteristics pmos I-V Characteristics Gate and Diffusion Capacitance 2 Introduction So far, we have treated transistors
VLSI Design and Simulation
 VLSI Design and Simulation Performance Characterization Topics Performance Characterization Resistance Estimation Capacitance Estimation Inductance Estimation Performance Characterization Inverter Voltage
VLSI Design and Simulation Performance Characterization Topics Performance Characterization Resistance Estimation Capacitance Estimation Inductance Estimation Performance Characterization Inverter Voltage
ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals
 ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 6: January 30, 2018 MOS Operating Regions, pt. 2 Lecture Outline! Operating Regions (review) " Subthreshold " Resistive " Saturation! Intro.
ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 6: January 30, 2018 MOS Operating Regions, pt. 2 Lecture Outline! Operating Regions (review) " Subthreshold " Resistive " Saturation! Intro.
ELEC 3908, Physical Electronics, Lecture 26. MOSFET Small Signal Modelling
 ELEC 3908, Physical Electronics, Lecture 26 MOSFET Small Signal Modelling Lecture Outline MOSFET small signal behavior will be considered in the same way as for the diode and BJT Capacitances will be considered
ELEC 3908, Physical Electronics, Lecture 26 MOSFET Small Signal Modelling Lecture Outline MOSFET small signal behavior will be considered in the same way as for the diode and BJT Capacitances will be considered
P. R. Nelson 1 ECE418 - VLSI. Midterm Exam. Solutions
 P. R. Nelson 1 ECE418 - VLSI Midterm Exam Solutions 1. (8 points) Draw the cross-section view for A-A. The cross-section view is as shown below.. ( points) Can you tell which of the metal1 regions is the
P. R. Nelson 1 ECE418 - VLSI Midterm Exam Solutions 1. (8 points) Draw the cross-section view for A-A. The cross-section view is as shown below.. ( points) Can you tell which of the metal1 regions is the
The Devices: MOS Transistors
 The Devices: MOS Transistors References: Semiconductor Device Fundamentals, R. F. Pierret, Addison-Wesley Digital Integrated Circuits: A Design Perspective, J. Rabaey et.al. Prentice Hall NMOS Transistor
The Devices: MOS Transistors References: Semiconductor Device Fundamentals, R. F. Pierret, Addison-Wesley Digital Integrated Circuits: A Design Perspective, J. Rabaey et.al. Prentice Hall NMOS Transistor
EEC 118 Lecture #2: MOSFET Structure and Basic Operation. Rajeevan Amirtharajah University of California, Davis Jeff Parkhurst Intel Corporation
 EEC 118 Lecture #2: MOSFET Structure and Basic Operation Rajeevan Amirtharajah University of California, Davis Jeff Parkhurst Intel Corporation Announcements Lab 1 this week, report due next week Bring
EEC 118 Lecture #2: MOSFET Structure and Basic Operation Rajeevan Amirtharajah University of California, Davis Jeff Parkhurst Intel Corporation Announcements Lab 1 this week, report due next week Bring
Circuits. L2: MOS Models-2 (1 st Aug. 2013) B. Mazhari Dept. of EE, IIT Kanpur. B. Mazhari, IITK. G-Number
 EE610: CMOS Analog Circuits L: MOS Models- (1 st Aug. 013) B. Mazhari Dept. of EE, IIT Kanpur 3 NMOS Models MOS MODEL Above Threshold Subthreshold ( GS > TN ) ( GS < TN ) Saturation ti Ti Triode ( DS >
EE610: CMOS Analog Circuits L: MOS Models- (1 st Aug. 013) B. Mazhari Dept. of EE, IIT Kanpur 3 NMOS Models MOS MODEL Above Threshold Subthreshold ( GS > TN ) ( GS < TN ) Saturation ti Ti Triode ( DS >
MOS Transistor Properties Review
 MOS Transistor Properties Review 1 VLSI Chip Manufacturing Process Photolithography: transfer of mask patterns to the chip Diffusion or ion implantation: selective doping of Si substrate Oxidation: SiO
MOS Transistor Properties Review 1 VLSI Chip Manufacturing Process Photolithography: transfer of mask patterns to the chip Diffusion or ion implantation: selective doping of Si substrate Oxidation: SiO
Lecture 10 MOSFET (III) MOSFET Equivalent Circuit Models
 Lecture 10 MOSFET (III) MOSFET Equivalent Circuit Models Outline Lowfrequency smallsignal equivalent circuit model Highfrequency smallsignal equivalent circuit model Reading Assignment: Howe and Sodini;
Lecture 10 MOSFET (III) MOSFET Equivalent Circuit Models Outline Lowfrequency smallsignal equivalent circuit model Highfrequency smallsignal equivalent circuit model Reading Assignment: Howe and Sodini;
EE105 - Fall 2006 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits
 EE105 - Fall 2006 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits Prof. Jan M. Rabaey (jan@eecs) Lecture 7: MOS Transistor Some Administrative Issues Lab 2 this week Hw 2 due on We Hw 3 will be posted same day MIDTERM
EE105 - Fall 2006 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits Prof. Jan M. Rabaey (jan@eecs) Lecture 7: MOS Transistor Some Administrative Issues Lab 2 this week Hw 2 due on We Hw 3 will be posted same day MIDTERM
Chapter 4 Field-Effect Transistors
 Chapter 4 Field-Effect Transistors Microelectronic Circuit Design Richard C. Jaeger Travis N. Blalock 5/5/11 Chap 4-1 Chapter Goals Describe operation of MOSFETs. Define FET characteristics in operation
Chapter 4 Field-Effect Transistors Microelectronic Circuit Design Richard C. Jaeger Travis N. Blalock 5/5/11 Chap 4-1 Chapter Goals Describe operation of MOSFETs. Define FET characteristics in operation
EE5311- Digital IC Design
 EE5311- Digital IC Design Module 1 - The Transistor Janakiraman V Assistant Professor Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Madras Chennai October 28, 2017 Janakiraman, IITM
EE5311- Digital IC Design Module 1 - The Transistor Janakiraman V Assistant Professor Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Madras Chennai October 28, 2017 Janakiraman, IITM
Lecture 5: CMOS Transistor Theory
 Lecture 5: CMOS Transistor Theory Slides courtesy of Deming Chen Slides based on the initial set from David Harris CMOS VLSI Design Outline q q q q q q q Introduction MOS Capacitor nmos I-V Characteristics
Lecture 5: CMOS Transistor Theory Slides courtesy of Deming Chen Slides based on the initial set from David Harris CMOS VLSI Design Outline q q q q q q q Introduction MOS Capacitor nmos I-V Characteristics
The transistor is not in the cutoff region. the transistor is in the saturation region. To see this, recognize that in a long-channel transistor ifv
 ECE 440 Spring 005 Page 1 Homework Assignment No. Solutions P.4 For each transistor, first determine if the transistor is in cutoff by checking to see if GS is less than or greater than. may have to be
ECE 440 Spring 005 Page 1 Homework Assignment No. Solutions P.4 For each transistor, first determine if the transistor is in cutoff by checking to see if GS is less than or greater than. may have to be
ESE 570 MOS TRANSISTOR THEORY Part 2
 ESE 570 MOS TRANSISTOR THEORY Part 2 GCA (gradual channel approximation) MOS Transistor Model Strong Inversion Operation CMOS = NMOS + PMOS 2 TwoTerminal MOS Capacitor > nmos Transistor VGS
ESE 570 MOS TRANSISTOR THEORY Part 2 GCA (gradual channel approximation) MOS Transistor Model Strong Inversion Operation CMOS = NMOS + PMOS 2 TwoTerminal MOS Capacitor > nmos Transistor VGS
VLSI Design The MOS Transistor
 VLSI Design The MOS Transistor Frank Sill Torres Universidade Federal de Minas Gerais (UFMG), Brazil VLSI Design: CMOS Technology 1 Outline Introduction MOS Capacitor nmos I-V Characteristics pmos I-V
VLSI Design The MOS Transistor Frank Sill Torres Universidade Federal de Minas Gerais (UFMG), Brazil VLSI Design: CMOS Technology 1 Outline Introduction MOS Capacitor nmos I-V Characteristics pmos I-V
EE105 Fall 2014 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits. NMOS Transistor Capacitances: Saturation Region
 EE105 Fall 014 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits Prof. Ming C. Wu wu@eecs.berkeley.edu 511 Sutardja Dai Hall (SDH) 1 NMOS Transistor Capacitances: Saturation Region Drain no longer connected to channel
EE105 Fall 014 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits Prof. Ming C. Wu wu@eecs.berkeley.edu 511 Sutardja Dai Hall (SDH) 1 NMOS Transistor Capacitances: Saturation Region Drain no longer connected to channel
MOS Transistor Theory
 CHAPTER 3 MOS Transistor Theory Outline 2 1. Introduction 2. Ideal I-V Characteristics 3. Nonideal I-V Effects 4. C-V Characteristics 5. DC Transfer Characteristics 6. Switch-level RC Delay Models MOS
CHAPTER 3 MOS Transistor Theory Outline 2 1. Introduction 2. Ideal I-V Characteristics 3. Nonideal I-V Effects 4. C-V Characteristics 5. DC Transfer Characteristics 6. Switch-level RC Delay Models MOS
ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals
 ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 5: January 25, 2018 MOS Operating Regions, pt. 1 Lecture Outline! 3 Regions of operation for MOSFET " Subthreshold " Linear " Saturation!
ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 5: January 25, 2018 MOS Operating Regions, pt. 1 Lecture Outline! 3 Regions of operation for MOSFET " Subthreshold " Linear " Saturation!
EE105 - Fall 2005 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits
 EE105 - Fall 005 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits ecture 7 MOS Transistor Announcements Homework 3, due today Homework 4 due next week ab this week Reading: Chapter 4 1 ecture Material ast lecture
EE105 - Fall 005 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits ecture 7 MOS Transistor Announcements Homework 3, due today Homework 4 due next week ab this week Reading: Chapter 4 1 ecture Material ast lecture
MOS Transistors. Prof. Krishna Saraswat. Department of Electrical Engineering Stanford University Stanford, CA
 MOS Transistors Prof. Krishna Saraswat Department of Electrical Engineering S Stanford, CA 94305 saraswat@stanford.edu 1 1930: Patent on the Field-Effect Transistor! Julius Lilienfeld filed a patent describing
MOS Transistors Prof. Krishna Saraswat Department of Electrical Engineering S Stanford, CA 94305 saraswat@stanford.edu 1 1930: Patent on the Field-Effect Transistor! Julius Lilienfeld filed a patent describing
EEC 116 Lecture #3: CMOS Inverters MOS Scaling. Rajeevan Amirtharajah University of California, Davis Jeff Parkhurst Intel Corporation
 EEC 116 Lecture #3: CMOS Inverters MOS Scaling Rajeevan Amirtharajah University of California, Davis Jeff Parhurst Intel Corporation Outline Review: Inverter Transfer Characteristics Lecture 3: Noise Margins,
EEC 116 Lecture #3: CMOS Inverters MOS Scaling Rajeevan Amirtharajah University of California, Davis Jeff Parhurst Intel Corporation Outline Review: Inverter Transfer Characteristics Lecture 3: Noise Margins,
MOS Transistor Theory
 MOS Transistor Theory So far, we have viewed a MOS transistor as an ideal switch (digital operation) Reality: less than ideal EE 261 Krish Chakrabarty 1 Introduction So far, we have treated transistors
MOS Transistor Theory So far, we have viewed a MOS transistor as an ideal switch (digital operation) Reality: less than ideal EE 261 Krish Chakrabarty 1 Introduction So far, we have treated transistors
ELEC 3908, Physical Electronics, Lecture 23. The MOSFET Square Law Model
 ELEC 3908, Physical Electronics, Lecture 23 The MOSFET Square Law Model Lecture Outline As with the diode and bipolar, have looked at basic structure of the MOSFET and now turn to derivation of a current
ELEC 3908, Physical Electronics, Lecture 23 The MOSFET Square Law Model Lecture Outline As with the diode and bipolar, have looked at basic structure of the MOSFET and now turn to derivation of a current
Today s lecture. EE141- Spring 2003 Lecture 4. Design Rules CMOS Inverter MOS Transistor Model
 - Spring 003 Lecture 4 Design Rules CMOS Inverter MOS Transistor Model Today s lecture Design Rules The CMOS inverter at a glance An MOS transistor model for manual analysis Important! Labs start next
- Spring 003 Lecture 4 Design Rules CMOS Inverter MOS Transistor Model Today s lecture Design Rules The CMOS inverter at a glance An MOS transistor model for manual analysis Important! Labs start next
ECE321 Electronics I
 EE31 Electronics I Lecture 8: MOSET Threshold Voltage and Parasitic apacitances Payman Zarkesh-Ha Office: EE Bldg. 3B Office hours: Tuesday :-3:PM or by appointment E-mail: payman@ece.unm.edu Slide: 1
EE31 Electronics I Lecture 8: MOSET Threshold Voltage and Parasitic apacitances Payman Zarkesh-Ha Office: EE Bldg. 3B Office hours: Tuesday :-3:PM or by appointment E-mail: payman@ece.unm.edu Slide: 1
CMPEN 411 VLSI Digital Circuits. Lecture 03: MOS Transistor
 CMPEN 411 VLSI Digital Circuits Lecture 03: MOS Transistor Kyusun Choi [Adapted from Rabaey s Digital Integrated Circuits, Second Edition, 2003 J. Rabaey, A. Chandrakasan, B. Nikolic] CMPEN 411 L03 S.1
CMPEN 411 VLSI Digital Circuits Lecture 03: MOS Transistor Kyusun Choi [Adapted from Rabaey s Digital Integrated Circuits, Second Edition, 2003 J. Rabaey, A. Chandrakasan, B. Nikolic] CMPEN 411 L03 S.1
MOSFET Capacitance Model
 MOSFET Capacitance Model So far we discussed the MOSFET DC models. In real circuit operation, the device operates under time varying terminal voltages and the device operation can be described by: 1 small
MOSFET Capacitance Model So far we discussed the MOSFET DC models. In real circuit operation, the device operates under time varying terminal voltages and the device operation can be described by: 1 small
Practice 3: Semiconductors
 Practice 3: Semiconductors Digital Electronic Circuits Semester A 2012 VLSI Fabrication Process VLSI Very Large Scale Integration The ability to fabricate many devices on a single substrate within a given
Practice 3: Semiconductors Digital Electronic Circuits Semester A 2012 VLSI Fabrication Process VLSI Very Large Scale Integration The ability to fabricate many devices on a single substrate within a given
Lecture 10 MOSFET (III) MOSFET Equivalent Circuit Models
 Lecture 1 MOSFET (III) MOSFET Equivalent Circuit Models Outline Lowfrequency smallsignal equivalent circuit model Highfrequency smallsignal equivalent circuit model Reading Assignment: Howe and Sodini;
Lecture 1 MOSFET (III) MOSFET Equivalent Circuit Models Outline Lowfrequency smallsignal equivalent circuit model Highfrequency smallsignal equivalent circuit model Reading Assignment: Howe and Sodini;
Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective. Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic. The Devices. July 30, Devices.
 Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic The July 30, 2002 1 Goal of this chapter Present intuitive understanding of device operation Introduction
Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic The July 30, 2002 1 Goal of this chapter Present intuitive understanding of device operation Introduction
Integrated Circuits & Systems
 Federal University of Santa Catarina Center for Technology Computer Science & Electronics Engineering Integrated Circuits & Systems INE 5442 Lecture 10 MOSFET part 1 guntzel@inf.ufsc.br ual-well Trench-Isolated
Federal University of Santa Catarina Center for Technology Computer Science & Electronics Engineering Integrated Circuits & Systems INE 5442 Lecture 10 MOSFET part 1 guntzel@inf.ufsc.br ual-well Trench-Isolated
II III IV V VI B C N. Al Si P S. Zn Ga Ge As Se Cd In Sn Sb Te. Silicon (Si) the dominating material in IC manufacturing
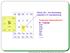 II III IV V VI B N Al Si P S Zn Ga Ge As Se d In Sn Sb Te Silicon (Si) the dominating material in I manufacturing ompound semiconductors III - V group: GaAs GaN GaSb GaP InAs InP InSb... The Energy Band
II III IV V VI B N Al Si P S Zn Ga Ge As Se d In Sn Sb Te Silicon (Si) the dominating material in I manufacturing ompound semiconductors III - V group: GaAs GaN GaSb GaP InAs InP InSb... The Energy Band
The Devices. Jan M. Rabaey
 The Devices Jan M. Rabaey Goal of this chapter Present intuitive understanding of device operation Introduction of basic device equations Introduction of models for manual analysis Introduction of models
The Devices Jan M. Rabaey Goal of this chapter Present intuitive understanding of device operation Introduction of basic device equations Introduction of models for manual analysis Introduction of models
Chapter 2 CMOS Transistor Theory. Jin-Fu Li Department of Electrical Engineering National Central University Jungli, Taiwan
 Chapter 2 CMOS Transistor Theory Jin-Fu Li Department of Electrical Engineering National Central University Jungli, Taiwan Outline Introduction MOS Device Design Equation Pass Transistor Jin-Fu Li, EE,
Chapter 2 CMOS Transistor Theory Jin-Fu Li Department of Electrical Engineering National Central University Jungli, Taiwan Outline Introduction MOS Device Design Equation Pass Transistor Jin-Fu Li, EE,
Microelectronics Part 1: Main CMOS circuits design rules
 GBM8320 Dispositifs Médicaux telligents Microelectronics Part 1: Main CMOS circuits design rules Mohamad Sawan et al. Laboratoire de neurotechnologies Polystim! http://www.cours.polymtl.ca/gbm8320/! med-amine.miled@polymtl.ca!
GBM8320 Dispositifs Médicaux telligents Microelectronics Part 1: Main CMOS circuits design rules Mohamad Sawan et al. Laboratoire de neurotechnologies Polystim! http://www.cours.polymtl.ca/gbm8320/! med-amine.miled@polymtl.ca!
ECEN474/704: (Analog) VLSI Circuit Design Spring 2018
 ECEN474/704: (Analog) SI Circuit Design Spring 2018 ecture 2: MOS ransistor Modeling Sam Palermo Analog & Mixed-Signal Center exas A&M University Announcements If you haven t already, turn in your 0.18um
ECEN474/704: (Analog) SI Circuit Design Spring 2018 ecture 2: MOS ransistor Modeling Sam Palermo Analog & Mixed-Signal Center exas A&M University Announcements If you haven t already, turn in your 0.18um
Lecture 12: MOS Capacitors, transistors. Context
 Lecture 12: MOS Capacitors, transistors Context In the last lecture, we discussed PN diodes, and the depletion layer into semiconductor surfaces. Small signal models In this lecture, we will apply those
Lecture 12: MOS Capacitors, transistors Context In the last lecture, we discussed PN diodes, and the depletion layer into semiconductor surfaces. Small signal models In this lecture, we will apply those
ECE 497 JS Lecture - 12 Device Technologies
 ECE 497 JS Lecture - 12 Device Technologies Spring 2004 Jose E. Schutt-Aine Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Illinois jose@emlab.uiuc.edu 1 NMOS Transistor 2 ρ Source channel charge density
ECE 497 JS Lecture - 12 Device Technologies Spring 2004 Jose E. Schutt-Aine Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Illinois jose@emlab.uiuc.edu 1 NMOS Transistor 2 ρ Source channel charge density
Lecture 11: MOS Transistor
 Lecture 11: MOS Transistor Prof. Niknejad Lecture Outline Review: MOS Capacitors Regions MOS Capacitors (3.8 3.9) CV Curve Threshold Voltage MOS Transistors (4.1 4.3): Overview Cross-section and layout
Lecture 11: MOS Transistor Prof. Niknejad Lecture Outline Review: MOS Capacitors Regions MOS Capacitors (3.8 3.9) CV Curve Threshold Voltage MOS Transistors (4.1 4.3): Overview Cross-section and layout
The Devices. Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective. Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic. July 30, 2002
 igital Integrated Circuits A esign Perspective Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic The evices July 30, 2002 Goal of this chapter Present intuitive understanding of device operation Introduction
igital Integrated Circuits A esign Perspective Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic The evices July 30, 2002 Goal of this chapter Present intuitive understanding of device operation Introduction
Lecture 29 - The Long Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor (cont.) April 20, 2007
 6.720J/3.43J - Integrated Microelectronic Devices - Spring 2007 Lecture 29-1 Lecture 29 - The Long Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor (cont.) April 20, 2007 Contents: 1. Non-ideal and second-order
6.720J/3.43J - Integrated Microelectronic Devices - Spring 2007 Lecture 29-1 Lecture 29 - The Long Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor (cont.) April 20, 2007 Contents: 1. Non-ideal and second-order
Lecture 12: MOSFET Devices
 Lecture 12: MOSFET Devices Gu-Yeon Wei Division of Engineering and Applied Sciences Harvard University guyeon@eecs.harvard.edu Wei 1 Overview Reading S&S: Chapter 5.1~5.4 Supplemental Reading Background
Lecture 12: MOSFET Devices Gu-Yeon Wei Division of Engineering and Applied Sciences Harvard University guyeon@eecs.harvard.edu Wei 1 Overview Reading S&S: Chapter 5.1~5.4 Supplemental Reading Background
ELEC 3908, Physical Electronics, Lecture 27. MOSFET Scaling and Velocity Saturation
 ELEC 3908, Physical Electronics, Lecture 27 MOSFET Scaling and Velocity Saturation Lecture Outline Industry push is always to pack more devices on a chip to increase functionality, which requires making
ELEC 3908, Physical Electronics, Lecture 27 MOSFET Scaling and Velocity Saturation Lecture Outline Industry push is always to pack more devices on a chip to increase functionality, which requires making
MOS Transistor Theory MOSFET Symbols Current Characteristics of MOSFET. MOS Symbols and Characteristics. nmos Enhancement Transistor
 MOS Transistor Theory MOSFET Symbols Current Characteristics of MOSFET Calculation of t and Important 2 nd Order Effects SmallSignal Signal MOSFET Model Summary Material from: CMOS LSI Design By Weste
MOS Transistor Theory MOSFET Symbols Current Characteristics of MOSFET Calculation of t and Important 2 nd Order Effects SmallSignal Signal MOSFET Model Summary Material from: CMOS LSI Design By Weste
The Physical Structure (NMOS)
 The Physical Structure (NMOS) Al SiO2 Field Oxide Gate oxide S n+ Polysilicon Gate Al SiO2 SiO2 D n+ L channel P Substrate Field Oxide contact Metal (S) n+ (G) L W n+ (D) Poly 1 Transistor Resistance Two
The Physical Structure (NMOS) Al SiO2 Field Oxide Gate oxide S n+ Polysilicon Gate Al SiO2 SiO2 D n+ L channel P Substrate Field Oxide contact Metal (S) n+ (G) L W n+ (D) Poly 1 Transistor Resistance Two
6.012 Electronic Devices and Circuits Spring 2005
 6.012 Electronic Devices and Circuits Spring 2005 May 16, 2005 Final Exam (200 points) -OPEN BOOK- Problem NAME RECITATION TIME 1 2 3 4 5 Total General guidelines (please read carefully before starting):
6.012 Electronic Devices and Circuits Spring 2005 May 16, 2005 Final Exam (200 points) -OPEN BOOK- Problem NAME RECITATION TIME 1 2 3 4 5 Total General guidelines (please read carefully before starting):
and V DS V GS V T (the saturation region) I DS = k 2 (V GS V T )2 (1+ V DS )
 ECE 4420 Spring 2005 Page 1 FINAL EXAMINATION NAME SCORE /100 Problem 1O 2 3 4 5 6 7 Sum Points INSTRUCTIONS: This exam is closed book. You are permitted four sheets of notes (three of which are your sheets
ECE 4420 Spring 2005 Page 1 FINAL EXAMINATION NAME SCORE /100 Problem 1O 2 3 4 5 6 7 Sum Points INSTRUCTIONS: This exam is closed book. You are permitted four sheets of notes (three of which are your sheets
ENEE 359a Digital VLSI Design
 SLIDE 1 ENEE 359a Digital VLSI Design & Logical Effort Prof. blj@ece.umd.edu Credit where credit is due: Slides contain original artwork ( Jacob 2004) as well as material taken liberally from Irwin & Vijay
SLIDE 1 ENEE 359a Digital VLSI Design & Logical Effort Prof. blj@ece.umd.edu Credit where credit is due: Slides contain original artwork ( Jacob 2004) as well as material taken liberally from Irwin & Vijay
FIELD-EFFECT TRANSISTORS
 FIEL-EFFECT TRANSISTORS 1 Semiconductor review 2 The MOS capacitor 2 The enhancement-type N-MOS transistor 3 I-V characteristics of enhancement MOSFETS 4 The output characteristic of the MOSFET in saturation
FIEL-EFFECT TRANSISTORS 1 Semiconductor review 2 The MOS capacitor 2 The enhancement-type N-MOS transistor 3 I-V characteristics of enhancement MOSFETS 4 The output characteristic of the MOSFET in saturation
Check course home page periodically for announcements. Homework 2 is due TODAY by 5pm In 240 Cory
 EE141 Fall 005 Lecture 6 MOS Capacitances, Propagation elay Important! Check course home page periodically for announcements Homework is due TOAY by 5pm In 40 Cory Homework 3 will be posted TOAY ue Thursday
EE141 Fall 005 Lecture 6 MOS Capacitances, Propagation elay Important! Check course home page periodically for announcements Homework is due TOAY by 5pm In 40 Cory Homework 3 will be posted TOAY ue Thursday
ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals
 ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 4: January 23, 2018 MOS Transistor Theory, MOS Model Penn ESE 570 Spring 2018 Khanna Lecture Outline! CMOS Process Enhancements! Semiconductor
ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 4: January 23, 2018 MOS Transistor Theory, MOS Model Penn ESE 570 Spring 2018 Khanna Lecture Outline! CMOS Process Enhancements! Semiconductor
ECE 342 Electronic Circuits. 3. MOS Transistors
 ECE 342 Electronic Circuits 3. MOS Transistors Jose E. Schutt-Aine Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Illinois jschutt@emlab.uiuc.edu 1 NMOS Transistor Typically L = 0.1 to 3 m, W = 0.2 to
ECE 342 Electronic Circuits 3. MOS Transistors Jose E. Schutt-Aine Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Illinois jschutt@emlab.uiuc.edu 1 NMOS Transistor Typically L = 0.1 to 3 m, W = 0.2 to
CMOS Digital Integrated Circuits Analysis and Design
 MOS igital ntegrated ircuits Analysis and esign hapter 4 Modeling of MOS ransistors Using SPE 1 ntroduction he SPE software that was distributed by U Berkeley beginning in the late 1970s had three built-in
MOS igital ntegrated ircuits Analysis and esign hapter 4 Modeling of MOS ransistors Using SPE 1 ntroduction he SPE software that was distributed by U Berkeley beginning in the late 1970s had three built-in
Introduction to CMOS VLSI. Chapter 2: CMOS Transistor Theory. Harris, 2004 Updated by Li Chen, Outline
 Introduction to MOS VLSI Design hapter : MOS Transistor Theory copyright@david Harris, 004 Updated by Li hen, 010 Outline Introduction MOS apacitor nmos IV haracteristics pmos IV haracteristics Gate and
Introduction to MOS VLSI Design hapter : MOS Transistor Theory copyright@david Harris, 004 Updated by Li hen, 010 Outline Introduction MOS apacitor nmos IV haracteristics pmos IV haracteristics Gate and
CMOS INVERTER. Last Lecture. Metrics for qualifying digital circuits. »Cost» Reliability» Speed (delay)»performance
 CMOS INVERTER Last Lecture Metrics for qualifying digital circuits»cost» Reliability» Speed (delay)»performance 1 Today s lecture The CMOS inverter at a glance An MOS transistor model for manual analysis
CMOS INVERTER Last Lecture Metrics for qualifying digital circuits»cost» Reliability» Speed (delay)»performance 1 Today s lecture The CMOS inverter at a glance An MOS transistor model for manual analysis
EE 330 Lecture 16. Devices in Semiconductor Processes. MOS Transistors
 EE 330 Lecture 16 Devices in Semiconductor Processes MOS Transistors Review from Last Time Model Summary I D I V DS V S I B V BS = 0 0 VS VT W VDS ID = μcox VS VT VDS VS V VDS VS VT L T < W μc ( V V )
EE 330 Lecture 16 Devices in Semiconductor Processes MOS Transistors Review from Last Time Model Summary I D I V DS V S I B V BS = 0 0 VS VT W VDS ID = μcox VS VT VDS VS V VDS VS VT L T < W μc ( V V )
ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals
 ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 4: January 24, 2017 MOS Transistor Theory, MOS Model Penn ESE 570 Spring 2017 Khanna Lecture Outline! Semiconductor Physics " Band gaps "
ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 4: January 24, 2017 MOS Transistor Theory, MOS Model Penn ESE 570 Spring 2017 Khanna Lecture Outline! Semiconductor Physics " Band gaps "
HW 5 posted due in two weeks Lab this week Midterm graded Project to be launched in week 7
 HW 5 posted due in two weeks Lab this week Midterm graded Project to be launched in week 7 2 What do digital IC designers need to know? 5 EE4 EECS4 6 3 0< V GS - V T < V DS Pinch-off 7 For (V GS V T )
HW 5 posted due in two weeks Lab this week Midterm graded Project to be launched in week 7 2 What do digital IC designers need to know? 5 EE4 EECS4 6 3 0< V GS - V T < V DS Pinch-off 7 For (V GS V T )
MOSFET. Id-Vd curve. I DS Transfer curve V G. Lec. 8. Vd=1V. Saturation region. V Th
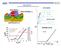 MOSFET Id-Vd curve Saturation region I DS Transfer curve Vd=1V V Th V G 1 0 < V GS < V T V GS > V T V Gs >V T & Small V D > 0 I DS WQ inv WC v WC i V V VDS V V G i T G n T L n I D g V D (g conductance
MOSFET Id-Vd curve Saturation region I DS Transfer curve Vd=1V V Th V G 1 0 < V GS < V T V GS > V T V Gs >V T & Small V D > 0 I DS WQ inv WC v WC i V V VDS V V G i T G n T L n I D g V D (g conductance
Introduction and Background
 Analog CMOS Integrated Circuit Design Introduction and Background Dr. Jawdat Abu-Taha Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Islamic University of Gaza jtaha@iugaza.edu.ps 1 Marking Assignments
Analog CMOS Integrated Circuit Design Introduction and Background Dr. Jawdat Abu-Taha Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Islamic University of Gaza jtaha@iugaza.edu.ps 1 Marking Assignments
Lecture Outline. ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals. Review: MOS Capacitor with External Bias
 ESE 57: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 5: Januar 6, 17 MOS Operating Regions, pt. 1 Lecture Outline! 3 Regions of operation for MOSFET " Subthreshold " Linear " Saturation! Level
ESE 57: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 5: Januar 6, 17 MOS Operating Regions, pt. 1 Lecture Outline! 3 Regions of operation for MOSFET " Subthreshold " Linear " Saturation! Level
Quantitative MOSFET. Step 1. Connect the MOS capacitor results for the electron charge in the inversion layer Q N to the drain current.
 Quantitative MOSFET Step 1. Connect the MOS capacitor results for the electron charge in the inversion layer Q N to the drain current. V DS _ n source polysilicon gate y = y * 0 x metal interconnect to
Quantitative MOSFET Step 1. Connect the MOS capacitor results for the electron charge in the inversion layer Q N to the drain current. V DS _ n source polysilicon gate y = y * 0 x metal interconnect to
EE 330 Lecture 16. MOS Device Modeling p-channel n-channel comparisons Model consistency and relationships CMOS Process Flow
 EE 330 Lecture 16 MOS Device Modeling p-channel n-channel comparisons Model consistency and relationships CMOS Process Flow Review from Last Time Operation Regions by Applications Id I D 300 250 200 150
EE 330 Lecture 16 MOS Device Modeling p-channel n-channel comparisons Model consistency and relationships CMOS Process Flow Review from Last Time Operation Regions by Applications Id I D 300 250 200 150
ECE 546 Lecture 10 MOS Transistors
 ECE 546 Lecture 10 MOS Transistors Spring 2018 Jose E. Schutt-Aine Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Illinois jesa@illinois.edu NMOS Transistor NMOS Transistor N-Channel MOSFET Built on p-type
ECE 546 Lecture 10 MOS Transistors Spring 2018 Jose E. Schutt-Aine Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Illinois jesa@illinois.edu NMOS Transistor NMOS Transistor N-Channel MOSFET Built on p-type
Nanoscale CMOS Design Issues
 Nanoscale CMOS Design Issues Jaydeep P. Kulkarni Assistant Professor, ECE Department The University of Texas at Austin jaydeep@austin.utexas.edu Fall, 2017, VLSI-1 Class Transistor I-V Review Agenda Non-ideal
Nanoscale CMOS Design Issues Jaydeep P. Kulkarni Assistant Professor, ECE Department The University of Texas at Austin jaydeep@austin.utexas.edu Fall, 2017, VLSI-1 Class Transistor I-V Review Agenda Non-ideal
Chapter 5 MOSFET Theory for Submicron Technology
 Chapter 5 MOSFET Theory for Submicron Technology Short channel effects Other small geometry effects Parasitic components Velocity saturation/overshoot Hot carrier effects ** Majority of these notes are
Chapter 5 MOSFET Theory for Submicron Technology Short channel effects Other small geometry effects Parasitic components Velocity saturation/overshoot Hot carrier effects ** Majority of these notes are
Lecture 15: MOS Transistor models: Body effects, SPICE models. Context. In the last lecture, we discussed the modes of operation of a MOS FET:
 Lecture 15: MOS Transistor models: Body effects, SPICE models Context In the last lecture, we discussed the modes of operation of a MOS FET: oltage controlled resistor model I- curve (Square-Law Model)
Lecture 15: MOS Transistor models: Body effects, SPICE models Context In the last lecture, we discussed the modes of operation of a MOS FET: oltage controlled resistor model I- curve (Square-Law Model)
Class 05: Device Physics II
 Topics: 1. Introduction 2. NFET Model and Cross Section with Parasitics 3. NFET as a Capacitor 4. Capacitance vs. Voltage Curves 5. NFET as a Capacitor - Band Diagrams at V=0 6. NFET as a Capacitor - Accumulation
Topics: 1. Introduction 2. NFET Model and Cross Section with Parasitics 3. NFET as a Capacitor 4. Capacitance vs. Voltage Curves 5. NFET as a Capacitor - Band Diagrams at V=0 6. NFET as a Capacitor - Accumulation
Section 12: Intro to Devices
 Section 12: Intro to Devices Extensive reading materials on reserve, including Robert F. Pierret, Semiconductor Device Fundamentals EE143 Ali Javey Bond Model of Electrons and Holes Si Si Si Si Si Si Si
Section 12: Intro to Devices Extensive reading materials on reserve, including Robert F. Pierret, Semiconductor Device Fundamentals EE143 Ali Javey Bond Model of Electrons and Holes Si Si Si Si Si Si Si
ECE-305: Fall 2017 MOS Capacitors and Transistors
 ECE-305: Fall 2017 MOS Capacitors and Transistors Pierret, Semiconductor Device Fundamentals (SDF) Chapters 15+16 (pp. 525-530, 563-599) Professor Peter Bermel Electrical and Computer Engineering Purdue
ECE-305: Fall 2017 MOS Capacitors and Transistors Pierret, Semiconductor Device Fundamentals (SDF) Chapters 15+16 (pp. 525-530, 563-599) Professor Peter Bermel Electrical and Computer Engineering Purdue
Non Ideal Transistor Behavior
 Non Ideal Transistor Behavior Slides adapted from: N. Weste, D. Harris, CMOS VLSI Design, Addison- Wesley, 3/e, 2004 1 Non-ideal Transistor I-V effects Non ideal transistor Behavior Channel Length ModulaJon
Non Ideal Transistor Behavior Slides adapted from: N. Weste, D. Harris, CMOS VLSI Design, Addison- Wesley, 3/e, 2004 1 Non-ideal Transistor I-V effects Non ideal transistor Behavior Channel Length ModulaJon
! CMOS Process Enhancements. ! Semiconductor Physics. " Band gaps. " Field Effects. ! MOS Physics. " Cut-off. " Depletion.
 ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 4: January 3, 018 MOS Transistor Theory, MOS Model Lecture Outline! CMOS Process Enhancements! Semiconductor Physics " Band gaps " Field Effects!
ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 4: January 3, 018 MOS Transistor Theory, MOS Model Lecture Outline! CMOS Process Enhancements! Semiconductor Physics " Band gaps " Field Effects!
Conduction in Semiconductors -Review
 Conduction in Semiconductors Review Intrinsic (undoped) Semiconductors intrinsic carrier concentration n i =.45x0 0 cm 3, at room temp. n = p = n i, in intrinsic (undoped) material n number of electrons,
Conduction in Semiconductors Review Intrinsic (undoped) Semiconductors intrinsic carrier concentration n i =.45x0 0 cm 3, at room temp. n = p = n i, in intrinsic (undoped) material n number of electrons,
ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals
 ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 4: January 29, 2019 MOS Transistor Theory, MOS Model Penn ESE 570 Spring 2019 Khanna Lecture Outline! CMOS Process Enhancements! Semiconductor
ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 4: January 29, 2019 MOS Transistor Theory, MOS Model Penn ESE 570 Spring 2019 Khanna Lecture Outline! CMOS Process Enhancements! Semiconductor
MOSFET Physics: The Long Channel Approximation
 MOSFET Physics: The ong Channel Approximation A basic n-channel MOSFET (Figure 1) consists of two heavily-doped n-type regions, the Source and Drain, that comprise the main terminals of the device. The
MOSFET Physics: The ong Channel Approximation A basic n-channel MOSFET (Figure 1) consists of two heavily-doped n-type regions, the Source and Drain, that comprise the main terminals of the device. The
Chapter 2 MOS Transistor theory
 Chapter MOS Transistor theory.1 Introduction An MOS transistor is a majority-carrier device, which the current a conductg channel between the source and the dra is modulated by a voltage applied to the
Chapter MOS Transistor theory.1 Introduction An MOS transistor is a majority-carrier device, which the current a conductg channel between the source and the dra is modulated by a voltage applied to the
Topics to be Covered. capacitance inductance transmission lines
 Topics to be Covered Circuit Elements Switching Characteristics Power Dissipation Conductor Sizes Charge Sharing Design Margins Yield resistance capacitance inductance transmission lines Resistance of
Topics to be Covered Circuit Elements Switching Characteristics Power Dissipation Conductor Sizes Charge Sharing Design Margins Yield resistance capacitance inductance transmission lines Resistance of
Microelectronics Main CMOS design rules & basic circuits
 GBM8320 Dispositifs médicaux intelligents Microelectronics Main CMOS design rules & basic circuits Mohamad Sawan et al. Laboratoire de neurotechnologies Polystim mohamad.sawan@polymtl.ca M5418 6 & 7 September
GBM8320 Dispositifs médicaux intelligents Microelectronics Main CMOS design rules & basic circuits Mohamad Sawan et al. Laboratoire de neurotechnologies Polystim mohamad.sawan@polymtl.ca M5418 6 & 7 September
Chapter 13 Small-Signal Modeling and Linear Amplification
 Chapter 13 Small-Signal Modeling and Linear Amplification Microelectronic Circuit Design Richard C. Jaeger Travis N. Blalock 1/4/12 Chap 13-1 Chapter Goals Understanding of concepts related to: Transistors
Chapter 13 Small-Signal Modeling and Linear Amplification Microelectronic Circuit Design Richard C. Jaeger Travis N. Blalock 1/4/12 Chap 13-1 Chapter Goals Understanding of concepts related to: Transistors
Integrated Circuits & Systems
 Federal University of Santa Catarina Center for Technology Computer Science & Electronics Engineering Integrated Circuits & Systems INE 5442 Lecture 13 The CMOS Inverter: dynamic behavior (delay) guntzel@inf.ufsc.br
Federal University of Santa Catarina Center for Technology Computer Science & Electronics Engineering Integrated Circuits & Systems INE 5442 Lecture 13 The CMOS Inverter: dynamic behavior (delay) guntzel@inf.ufsc.br
EE 330 Lecture 16. MOSFET Modeling CMOS Process Flow
 EE 330 Lecture 16 MOSFET Modeling CMOS Process Flow Model Extensions 300 Id 250 200 150 100 50 300 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 Vds Existing Model 250 200 Id 150 100 50 Slope is not 0 0 0 1 2 3 4 Actual Device Vds Model
EE 330 Lecture 16 MOSFET Modeling CMOS Process Flow Model Extensions 300 Id 250 200 150 100 50 300 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 Vds Existing Model 250 200 Id 150 100 50 Slope is not 0 0 0 1 2 3 4 Actual Device Vds Model
Step 1. Finding V M. Goal: Þnd V M = input voltage for the output = V M both transistors are saturated at V IN = V M since
 Step 1. Finding V M Goal: Þnd V M = input voltage for the output = V M both transistors are saturated at V IN = V M since V DSn = V M - 0 > V M - V Tn V SDp = V DD - V M = (V DD - V M ) V Tp Equate drain
Step 1. Finding V M Goal: Þnd V M = input voltage for the output = V M both transistors are saturated at V IN = V M since V DSn = V M - 0 > V M - V Tn V SDp = V DD - V M = (V DD - V M ) V Tp Equate drain
Lecture 9 MOSFET(II) MOSFET I V CHARACTERISTICS(contd.)
 Lecture 9 MOSFET(II) MOSFET I V CHARACTERISTICS(contd.) Outline 1. The saturation region 2. Backgate characteristics Reading Assignment: Howe and Sodini, Chapter 4, Section 4.4 6.012 Spring 2009 Lecture
Lecture 9 MOSFET(II) MOSFET I V CHARACTERISTICS(contd.) Outline 1. The saturation region 2. Backgate characteristics Reading Assignment: Howe and Sodini, Chapter 4, Section 4.4 6.012 Spring 2009 Lecture
EECS 141: FALL 05 MIDTERM 1
 University of California College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences D. Markovic TuTh 11-1:3 Thursday, October 6, 6:3-8:pm EECS 141: FALL 5 MIDTERM 1 NAME Last SOLUTION
University of California College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences D. Markovic TuTh 11-1:3 Thursday, October 6, 6:3-8:pm EECS 141: FALL 5 MIDTERM 1 NAME Last SOLUTION
