BSIM4.3.0 Model. Enhancements and Improvements Relative to BSIM4.2.1
|
|
|
- Winifred Cummings
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 BSIM4.3.0 Model Enhancements and Improvements Relative to BSIM4.. Xuemei (Jane) Xi, Jin He, Mohan Dunga, Ali Niknejad, Chenming Hu University of California, Berkeley
2 OUTLINE New Features of BSIM4.3.0 beta release Stress ect model New temperature model Holistic ise model enhancement Unified current saturation model Velocity saturation Velocity overshoot Source injection thermal velocity limit New document for multi-layer gate tunneling Forward body bias
3 Model for Isolation-induced Stress Effects Trench isolation edge L SA SB W LOD SD Instance parameters added: SA, SB, SD SD is neighbour finger distance which is constant throughout all the fingers. Stress ect calculation only if: ) both SA and SB are given and are larger than 0 for finger number NF=; ) SA, SB and SD are all given and are larger than 0 for NF > Intermediate geometry definitions : LOD = SA + SB + NF L + ( NF ) SD 3
4 Mobility Model With STI Stress Define : r m = m / mo = ( m mo ) / m = m m o o (relative mobility change due to stress) So, m m o =+ r m (Vth insensitive to Lod, SA and/or SB) 4
5 Stress Effects Model-/LOD Model Simple stress distribution function: /(SA+L/), /(SB+L/) ρ µ Inv _ sa = SA expression with LOD, L, W, and T dependence ku0 Kstress _u0 L drawn ( Inv _ sa Inv _sb) r = + m Inv _sb = SB L drawn LKU0 WKU0 Kstress _u0 = + + LLODKU0 WLODKU0 ( Ldrawn + XL ) (Wdrawn + XW + WLOD ) + PKU0 Temperatur e + TKU TNOM LLODKU0 WLODKU0 ( Ldrawn XL ) (Wdrawn XW WLOD ) Inv _sa = All data can be fitted well with only one set of parameters (ie. Global model for LOD ect) and do t need extra binning parameters if binning is desired. For multi-finger device: NF NF Inv _ sa = i= 0 SA L + i ( SD + L ) NF i= 0 SB L + i ( SD + L ) drawn drawn drawn drawn NF S = For irregular LOD device: n n sw i swi = = W sa L SB L i= W sb L A Ldrawn i drawn i drawn drawn drawn i 5 drawn
6 Stress Effect m, u sat Model m + r = + r m m ( ( SA,SB ) SA ref,sb ref ) m o u sat + = + K K r r m m ( ( SA, SB ) SA ref, SB ref u ) sato u µ sato Where o, are low field mobility, saturation velocity at SA ref, SB ref 6
7 Stress Effect Model to VTH0, K, ETA0 Kstress _vth0 = + ( L + LKVTH0 LLODKVTH drawn + XL ) (Wdrawn + XW + LLODKVTH ( Ldrawn + XL ) (Wdrawn + XW + + PKVTH0 WKVTH0 WLOD ) WLOD) WLODKVTH WLODKVTH VTH 0 = VTH 0 K = K original ETA0 = ETA0 original original KVTH0 + Kstress_vth0 STK + Kstress_vth0 LODK STETA0 + Kstress_vth0 ( Inv _ sa + Inv _ sb Inv _ sa Inv _ sb ) ( Inv _ sa + Inv _ sb Inv _ sa Inv _ sb ) LODETA0 ref ( Inv _ sa + Inv _ sb Inv _ sa Inv _ sb ) ref ref ref ref ref 7
8 Stress Effect Model Verification Drain current relative change (%) with SAref=5mm SA=SB 8
9 Stress Effect Model Verification 9
10 Stress Effect Model Verification Drain current relative change (%) with SAref=5mm 0
11 Temperature Model Enhancement Temperature mode TEMPMOD created: TEMPMOD = 0: current model with VFB enhancement TEMPMOD = : New format for vsat, prt, ua, ub, uc: PARAM (T ) = PARAM (TNOM ) [ + TEMP _COEFF ( T TNOM) ]
12 Holistic Thermal Noise Model Enhancement q ti b ti Refer to Chapter 9 of BSIM4 manual = RNOIB + TNOIB L = RNOIA + TNOIA L V E gst sat V E sat L gst L (9..5) (9..6) Default RNOIA=0.577; RNOIB=0.37
13 Unified Current Saturation -Velocity Overshoot Model Price s approximation to HD model: l E y J = qnme y( + ) + qd me x y n x Approximate solution of Price s equation yields unified current expression that includes velocity saturation and velocity overshoot: I DS 0 I DS,HD = V where E + L ds Vds Vds + LAMBDA Esat litl + L Vds Vds + Esat litl E OV sat + OV V = E sat sat m = + ds I DS 0 I DS ( BSIM 4.. ) L Esat 3
14 Unified Current Saturation: -Source end Velocity Limit HD transport source carrier velocity: and Quasi-Ballistic Transport v = shd I DS,HD Wq s Ballistic transport source carrier velocity: where VTL: thermal velocity, r = r v sbt = VTL + r L XN L + LC XN 3.0 Unified current expression with velocity saturation, velocity overshoot and source velocity limit: DS,HD I DS = / MM [ ( ) ] MM + v / v shd I sbt 4
15 Direct Tunneling through Multiple- Layer Gate Stacks Gate Current modeled as For a single layer For two layer case a double = a f + a T J G = Q exp( at T exp( ( f ) + f ( oxe a new INV t ) Vox f ) 3h oxe f K IMP T ) where qm f B K qm f B α is the tunneling attenuation coicient already modeled in BSIM4, f = Toxe / Toxe Stands for multiple layers(n ) as well. Using new tunneling attenuation coicient and interpreted with tunneling equations in BSIM4, BSIM4 is w capable of modeling multi-layer gate tunneling. 5
16 Verification Verified with data of existing gate stack of HfO and silicon oxynitride. Very good fit observed using BSIM model. BSIM4 direct tunneling equation thus models the multi-layer case. Gate st layer nd layer 6
17 Forward Body Bias To ensure a good model behavior of body ect, body bias is usually bounded between (Vbsc, and f s0 where f s0 = 0.95 f s ). BSIM4.. already has the smooth function for Vbs low bound. Following is the upper bound smooth function: Where: ' ( 0. 95Φ V d ) Φ ' Vbs 0. 95Φ s Φ s Vbs d + s bs d. 95 = s ( V V δ ) + ( V V δ ) V bs bc bs bc 4δ Vbs = Vbc bc Is the low bound smooth function. d = 0.00V, and V bc is the maximum allowable V bs and found from dv th /dv bs = 0 to be V bc K = 0.9 Φ s 4K 7
18 Gate Current Partition Bugfix From Original: PIGCD Vds + exp Igcs = Igc PIGCD ( PIGCD V ) V ds ds +. 0e e 4 and Igcd = Igc ( PIGCD V + ) exp( PIGCD V ) ds PIGCD V ds +. 0e 4 ds +. 0e 4 To: PIGCD V Igcs = Igc Igcd = Igc ds + exp PIGCD ( PIGCD V + ) exp( PIGCD V ) ds PIGCD ( PIGCD V ) V ds V ds ds +. 0e e e 4 ds +. 0e 4 8
19 Gate Current Partition Bugfix.0x0 -.8x0 -.6x0 - Igc with bugfix Original Igc I GC (A).4x0 -.x0 -.0x0 - VDS increase 8.0x0-6.0x V GS (V) Effect of gate current bug fix Comparison with experimental data 9
20 New Parameters in BSIM Stress Effect Parameter Name Description Default Value Binnab le? Note SA INSTANCE parameter: Distance between OD edge to Poly from one side 0.0 If t given or ( 0.0), stress ect will be turned off SB INSTANCE parameter: Distance between OD edge to Poly from the other side 0.0 If t given or ( 0.0), stress ect will be turned off SD INSTANCE parameter: Distance between neighbour fingers 0.0 for NF >: if t given or ( 0.0), stress ect will be turned off saref Reference distance between OD edge to poly of one side.e-06[m] >0.0 sbref Reference distance between OD edge to poly of the other side.e-06[m] >0.0 wlod Width parameter for stress ect 0.0 [m] ku0 Mobility degradation/enhancement coicient for stress ect 0.0 [m] kvsat Saturation velocity degradation/enhancement parameter for stress ect 0.0[m] - kvsat tku0 Temperature coicient of ku0 0.0 lku0 Length dependence of ku0 0.0 [m llodku0 ] 0
21 New Parameters in BSIM Stress Effect Parameter Name Description Default Value Binnable? Note wku0 Width dependence of ku0 0.0 [m wlodku0 ] pku0 Cross-term dependence of ku0 0.0[m llodku0+wlodku0 ] llodku0 Length parameter for u0 stress ect 0.0 >0 wlodkuo Width parameter for u0 stress ect 0.0 >0 kvth0 Threshold shift parameter for stress ect 0.0[V*m] lkvth0 Length dependence of kvth0 0.0[V*m llodku0 ] wkvth0 Width dependence of kvth0 0.0[V*m wlodku0 ] pkvth0 Cross-term dependence of kvth0 0.0[V*m llodku0+wlodku0 ] llodvth Length parameter for Vth stress ect 0.0 >0 wlodvth Width parameter for Vth stress ect 0.0 >0 stk K shift factor related to Vth0 change 0.0[m] lodk K shift modification factor for stress ect.0 >0 steta0 eta0 shift factor related to Vth0 change 0.0[m] lodeta0 eta0 shift modification factor for stress ect.0 >0
22 New Model Parameters in BSIM4.3.0 Parameter Name Description -Unified Current Saturation Default Value Binnable? Note LAMBDA Velocity overshoot coicient 0.0 yes If t given or ( 0.0), velocity overshoot will be turned off VTL LC Thermal velocity Velocity back scattering coicient.0e5 [m/s] 0.0[m] yes If t given or ( 0.0), source end thermal velocity limit will be turned off ~5e-9(m) at room temperature XN Velocity back scattering coicient 3.0 yes Temperature Model TEMPMOD Temperature mode selector 0 If=0, original model will be used If=, new format will be used Holistic Thermal Noise RNOIA Thermal ise coicient RNOIB Thermal ise coicient 0.37
MOSFET. Id-Vd curve. I DS Transfer curve V G. Lec. 8. Vd=1V. Saturation region. V Th
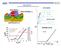 MOSFET Id-Vd curve Saturation region I DS Transfer curve Vd=1V V Th V G 1 0 < V GS < V T V GS > V T V Gs >V T & Small V D > 0 I DS WQ inv WC v WC i V V VDS V V G i T G n T L n I D g V D (g conductance
MOSFET Id-Vd curve Saturation region I DS Transfer curve Vd=1V V Th V G 1 0 < V GS < V T V GS > V T V Gs >V T & Small V D > 0 I DS WQ inv WC v WC i V V VDS V V G i T G n T L n I D g V D (g conductance
Enhancement and Technical Notes
 BSIM4.4.0 Release Enhancement and Technical Notes BSIM group University of California, Berkeley BSIM4.4.0 March 004 1 OUTLINE New Features of BSIM4.4.0 release Trap-assisted tunneling and recombination
BSIM4.4.0 Release Enhancement and Technical Notes BSIM group University of California, Berkeley BSIM4.4.0 March 004 1 OUTLINE New Features of BSIM4.4.0 release Trap-assisted tunneling and recombination
A Multi-Gate CMOS Compact Model BSIMMG
 A Multi-Gate CMOS Compact Model BSIMMG Darsen Lu, Sriramkumar Venugopalan, Tanvir Morshed, Yogesh Singh Chauhan, Chung-Hsun Lin, Mohan Dunga, Ali Niknejad and Chenming Hu University of California, Berkeley
A Multi-Gate CMOS Compact Model BSIMMG Darsen Lu, Sriramkumar Venugopalan, Tanvir Morshed, Yogesh Singh Chauhan, Chung-Hsun Lin, Mohan Dunga, Ali Niknejad and Chenming Hu University of California, Berkeley
EECS130 Integrated Circuit Devices
 EECS130 Integrated Circuit Devices Professor Ali Javey 10/30/2007 MOSFETs Lecture 4 Reading: Chapter 17, 19 Announcements The next HW set is due on Thursday. Midterm 2 is next week!!!! Threshold and Subthreshold
EECS130 Integrated Circuit Devices Professor Ali Javey 10/30/2007 MOSFETs Lecture 4 Reading: Chapter 17, 19 Announcements The next HW set is due on Thursday. Midterm 2 is next week!!!! Threshold and Subthreshold
N Channel MOSFET level 3
 N Channel MOSFET level 3 mosn3 NSource NBulk NSource NBulk NSource NBulk NSource (a) (b) (c) (d) NBulk Figure 1: MOSFET Types Form: mosn3: instance name n 1 n n 3 n n 1 is the drain node, n is the gate
N Channel MOSFET level 3 mosn3 NSource NBulk NSource NBulk NSource NBulk NSource (a) (b) (c) (d) NBulk Figure 1: MOSFET Types Form: mosn3: instance name n 1 n n 3 n n 1 is the drain node, n is the gate
Integrated Circuits & Systems
 Federal University of Santa Catarina Center for Technology Computer Science & Electronics Engineering Integrated Circuits & Systems INE 5442 Lecture 10 MOSFET part 1 guntzel@inf.ufsc.br ual-well Trench-Isolated
Federal University of Santa Catarina Center for Technology Computer Science & Electronics Engineering Integrated Circuits & Systems INE 5442 Lecture 10 MOSFET part 1 guntzel@inf.ufsc.br ual-well Trench-Isolated
Microelectronic Devices and Circuits Lecture 9 - MOS Capacitors I - Outline Announcements Problem set 5 -
 6.012 - Microelectronic Devices and Circuits Lecture 9 - MOS Capacitors I - Outline Announcements Problem set 5 - Posted on Stellar. Due net Wednesday. Qualitative description - MOS in thermal equilibrium
6.012 - Microelectronic Devices and Circuits Lecture 9 - MOS Capacitors I - Outline Announcements Problem set 5 - Posted on Stellar. Due net Wednesday. Qualitative description - MOS in thermal equilibrium
nmosfet Schematic Four structural masks: Field, Gate, Contact, Metal. Reverse doping polarities for pmosfet in N-well.
 nmosfet Schematic Four structural masks: Field, Gate, Contact, Metal. Reverse doping polarities for pmosfet in N-well. nmosfet Schematic 0 y L n + source n + drain depletion region polysilicon gate x z
nmosfet Schematic Four structural masks: Field, Gate, Contact, Metal. Reverse doping polarities for pmosfet in N-well. nmosfet Schematic 0 y L n + source n + drain depletion region polysilicon gate x z
APPENDIX D: Binning BSIM3v3 Parameters
 APPENDIX D: Binning BSIM3v3 Parameters Below is a list of all BSIM3v3 model parameters which can or cannot be binned. All model parameters which can be binned follow the following implementation: P L P
APPENDIX D: Binning BSIM3v3 Parameters Below is a list of all BSIM3v3 model parameters which can or cannot be binned. All model parameters which can be binned follow the following implementation: P L P
APPENDIX A: Parameter List
 APPENDIX A: Parameter List A.1 BSIM3v3 Model Control Parameters none level BSIMv3 model selector 8 none Mobmod mobmod Mobility model selector 1 none Capmod capmod Flag for the short channel 1 none capacitance
APPENDIX A: Parameter List A.1 BSIM3v3 Model Control Parameters none level BSIMv3 model selector 8 none Mobmod mobmod Mobility model selector 1 none Capmod capmod Flag for the short channel 1 none capacitance
The Devices. Devices
 The The MOS Transistor Gate Oxyde Gate Source n+ Polysilicon Drain n+ Field-Oxyde (SiO 2 ) p-substrate p+ stopper Bulk Contact CROSS-SECTION of NMOS Transistor Cross-Section of CMOS Technology MOS transistors
The The MOS Transistor Gate Oxyde Gate Source n+ Polysilicon Drain n+ Field-Oxyde (SiO 2 ) p-substrate p+ stopper Bulk Contact CROSS-SECTION of NMOS Transistor Cross-Section of CMOS Technology MOS transistors
BSIM-CMG Model. Berkeley Common-Gate Multi-Gate MOSFET Model
 BSIM-CMG Model Why BSIM-CMG Model When we reach the end of the technology roadmap for the classical CMOS, multigate (MG) CMOS structures will likely take up the baton. Numerous efforts are underway to
BSIM-CMG Model Why BSIM-CMG Model When we reach the end of the technology roadmap for the classical CMOS, multigate (MG) CMOS structures will likely take up the baton. Numerous efforts are underway to
EE5311- Digital IC Design
 EE5311- Digital IC Design Module 1 - The Transistor Janakiraman V Assistant Professor Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Madras Chennai October 28, 2017 Janakiraman, IITM
EE5311- Digital IC Design Module 1 - The Transistor Janakiraman V Assistant Professor Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Madras Chennai October 28, 2017 Janakiraman, IITM
APPENDIX A: Parameter List
 APPENDIX A: Parameter List A.1 BSIM3v3 Model Control Parameters none level BSIMv3 model selector 8 none Mobmod mobmod Mobility model selector 1 none Capmod capmod Flag for the short channel 2 none capacitance
APPENDIX A: Parameter List A.1 BSIM3v3 Model Control Parameters none level BSIMv3 model selector 8 none Mobmod mobmod Mobility model selector 1 none Capmod capmod Flag for the short channel 2 none capacitance
MOS Transistor Theory
 CHAPTER 3 MOS Transistor Theory Outline 2 1. Introduction 2. Ideal I-V Characteristics 3. Nonideal I-V Effects 4. C-V Characteristics 5. DC Transfer Characteristics 6. Switch-level RC Delay Models MOS
CHAPTER 3 MOS Transistor Theory Outline 2 1. Introduction 2. Ideal I-V Characteristics 3. Nonideal I-V Effects 4. C-V Characteristics 5. DC Transfer Characteristics 6. Switch-level RC Delay Models MOS
CHAPTER 3: Unified I-V Model
 CHAPTER 3: Unified - Model The development of separate model expressions for such device operation regimes as subthreshold and strong inversion were discussed in Chapter 2. Although these expressions can
CHAPTER 3: Unified - Model The development of separate model expressions for such device operation regimes as subthreshold and strong inversion were discussed in Chapter 2. Although these expressions can
NEW VERSION OF LETI-UTSOI2 FEATURING FURTHER IMPROVED PREDICTABILITY, AND A NEW STRESS MODEL FOR FDSOI TECHNOLOGY
 NEW VERSION OF LETI-UTSOI2 FEATURING FURTHER IMPROVED PREDICTABILITY, AND A NEW STRESS MODEL FOR FDSOI TECHNOLOGY T. Poiroux, P. Scheer*, O. Rozeau, B. de Salvo, A. Juge*, J. C. Barbé, M. Vinet CEA-Leti,
NEW VERSION OF LETI-UTSOI2 FEATURING FURTHER IMPROVED PREDICTABILITY, AND A NEW STRESS MODEL FOR FDSOI TECHNOLOGY T. Poiroux, P. Scheer*, O. Rozeau, B. de Salvo, A. Juge*, J. C. Barbé, M. Vinet CEA-Leti,
The Devices. Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective. Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic. July 30, 2002
 Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic The Devices July 30, 2002 Goal of this chapter Present intuitive understanding of device operation Introduction
Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic The Devices July 30, 2002 Goal of this chapter Present intuitive understanding of device operation Introduction
MOSFET Model with Simple Extraction Procedures, Suitable for Sensitive Analog Simulations
 ROMANIAN JOURNAL OF INFORMATION SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY Volume 10, Number 2, 2007, 189 197 MOSFET Model with Simple Extraction Procedures, Suitable for Sensitive Analog Simulations S. EFTIMIE 1, ALEX. RUSU
ROMANIAN JOURNAL OF INFORMATION SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY Volume 10, Number 2, 2007, 189 197 MOSFET Model with Simple Extraction Procedures, Suitable for Sensitive Analog Simulations S. EFTIMIE 1, ALEX. RUSU
ELEC 3908, Physical Electronics, Lecture 23. The MOSFET Square Law Model
 ELEC 3908, Physical Electronics, Lecture 23 The MOSFET Square Law Model Lecture Outline As with the diode and bipolar, have looked at basic structure of the MOSFET and now turn to derivation of a current
ELEC 3908, Physical Electronics, Lecture 23 The MOSFET Square Law Model Lecture Outline As with the diode and bipolar, have looked at basic structure of the MOSFET and now turn to derivation of a current
(S&S ) PMOS: holes flow from Source to Drain. from Source to Drain. W.-Y. Choi. Electronic Circuits 2 (09/1)
 (S&S 4.1 4.3) NMOS: electrons flow from Source to Drain PMOS: holes flow from Source to Drain In cut-off ( v < V ), i = 0 GS t D NMOS I-V Characteristics In triode, ( v > V but v v v ) GS t DS GS T W 1
(S&S 4.1 4.3) NMOS: electrons flow from Source to Drain PMOS: holes flow from Source to Drain In cut-off ( v < V ), i = 0 GS t D NMOS I-V Characteristics In triode, ( v > V but v v v ) GS t DS GS T W 1
APPENDIX D: Model Parameter Binning
 APPENDIX D: Model Parameter Binning Below is the information on parameter binning regarding which model parameters can or cannot be binned. All those parameters which can be binned follow this implementation:
APPENDIX D: Model Parameter Binning Below is the information on parameter binning regarding which model parameters can or cannot be binned. All those parameters which can be binned follow this implementation:
Long-channel MOSFET IV Corrections
 Long-channel MOSFET IV orrections Three MITs of the Day The body ect and its influence on long-channel V th. Long-channel subthreshold conduction and control (subthreshold slope S) Scattering components
Long-channel MOSFET IV orrections Three MITs of the Day The body ect and its influence on long-channel V th. Long-channel subthreshold conduction and control (subthreshold slope S) Scattering components
CMOS Digital Integrated Circuits Analysis and Design
 MOS igital ntegrated ircuits Analysis and esign hapter 4 Modeling of MOS ransistors Using SPE 1 ntroduction he SPE software that was distributed by U Berkeley beginning in the late 1970s had three built-in
MOS igital ntegrated ircuits Analysis and esign hapter 4 Modeling of MOS ransistors Using SPE 1 ntroduction he SPE software that was distributed by U Berkeley beginning in the late 1970s had three built-in
The PSP compact MOSFET model An update
 The PSP compact MOSFET model An update Gert-Jan Smit, Andries Scholten, D.B.M. Klaassen NXP Semiconductors Ronald van Langevelde Philips Research Europe Gennady Gildenblat, Weimin Wu, Xin Li, Amit Jha,
The PSP compact MOSFET model An update Gert-Jan Smit, Andries Scholten, D.B.M. Klaassen NXP Semiconductors Ronald van Langevelde Philips Research Europe Gennady Gildenblat, Weimin Wu, Xin Li, Amit Jha,
Lecture 11: MOSFET Modeling
 Digital Integrated Circuits (83-313) Lecture 11: MOSFET ing Semester B, 2016-17 Lecturer: Dr. Adam Teman TAs: Itamar Levi, Robert Giterman 18 June 2017 Disclaimer: This course was prepared, in its entirety,
Digital Integrated Circuits (83-313) Lecture 11: MOSFET ing Semester B, 2016-17 Lecturer: Dr. Adam Teman TAs: Itamar Levi, Robert Giterman 18 June 2017 Disclaimer: This course was prepared, in its entirety,
Advanced Compact Models for MOSFETs
 Advanced Compact Models for MOSFETs Christian Enz, Carlos Galup-Montoro, Gennady Gildenblat, Chenming Hu, Ronald van Langevelde, Mitiko Miura-Mattausch, Rafael Rios, Chih-Tang (Tom) Sah Josef Watts (editor)
Advanced Compact Models for MOSFETs Christian Enz, Carlos Galup-Montoro, Gennady Gildenblat, Chenming Hu, Ronald van Langevelde, Mitiko Miura-Mattausch, Rafael Rios, Chih-Tang (Tom) Sah Josef Watts (editor)
MOSFET Capacitance Model
 MOSFET Capacitance Model So far we discussed the MOSFET DC models. In real circuit operation, the device operates under time varying terminal voltages and the device operation can be described by: 1 small
MOSFET Capacitance Model So far we discussed the MOSFET DC models. In real circuit operation, the device operates under time varying terminal voltages and the device operation can be described by: 1 small
USC-ISI. The MOSIS Service. BSIM3v3.1 Model. Parameters Extraction and Optimization. October 2000
 USC-ISI The MOSIS Service BSIM3v3.1 Model Parameters Extraction and Optimization October 000 Henok Abebe ance C.Tyree Table of Contents 1. Introduction and Motivation: -----------------------------------------------1.
USC-ISI The MOSIS Service BSIM3v3.1 Model Parameters Extraction and Optimization October 000 Henok Abebe ance C.Tyree Table of Contents 1. Introduction and Motivation: -----------------------------------------------1.
EE115C Winter 2017 Digital Electronic Circuits. Lecture 2: MOS Transistor: IV Model
 EE115C Winter 2017 Digital Electronic Circuits Lecture 2: MOS Transistor: IV Model Levels of Modeling Analytical CAD analytical Switch-level sim Transistor-level sim complexity Different complexity, accuracy,
EE115C Winter 2017 Digital Electronic Circuits Lecture 2: MOS Transistor: IV Model Levels of Modeling Analytical CAD analytical Switch-level sim Transistor-level sim complexity Different complexity, accuracy,
2D-2D tunneling field effect transistors using
 2D-2D tunneling field effect transistors using WSe 2 /SnSe 2 heterostructures Tania Roy, 1,2,3 Mahmut Tosun, 1,2,3 Mark Hettick, 1,2,3, Geun Ho Ahn, 1,2,3 Chenming Hu 1, and Ali Javey 1,2,3, 1 Electrical
2D-2D tunneling field effect transistors using WSe 2 /SnSe 2 heterostructures Tania Roy, 1,2,3 Mahmut Tosun, 1,2,3 Mark Hettick, 1,2,3, Geun Ho Ahn, 1,2,3 Chenming Hu 1, and Ali Javey 1,2,3, 1 Electrical
LEVEL 61 RPI a-si TFT Model
 LEVEL 61 RPI a-si TFT Model Star-Hspice LEVEL 61 is an AIM-SPICE MOS15 amorphous silicon (a-si) thin-film transistor (TFT) model. Model Features AIM-SPICE MOS15 a-si TFT model features include: Modified
LEVEL 61 RPI a-si TFT Model Star-Hspice LEVEL 61 is an AIM-SPICE MOS15 amorphous silicon (a-si) thin-film transistor (TFT) model. Model Features AIM-SPICE MOS15 a-si TFT model features include: Modified
Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective. Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic. The Devices. July 30, Devices.
 Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic The July 30, 2002 1 Goal of this chapter Present intuitive understanding of device operation Introduction
Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic The July 30, 2002 1 Goal of this chapter Present intuitive understanding of device operation Introduction
Nanometer Transistors and Their Models. Jan M. Rabaey
 Nanometer Transistors and Their Models Jan M. Rabaey Chapter Outline Nanometer transistor behavior and models Sub-threshold currents and leakage Variability Device and technology innovations Nanometer
Nanometer Transistors and Their Models Jan M. Rabaey Chapter Outline Nanometer transistor behavior and models Sub-threshold currents and leakage Variability Device and technology innovations Nanometer
MOSFET: Introduction
 E&CE 437 Integrated VLSI Systems MOS Transistor 1 of 30 MOSFET: Introduction Metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistor (MOSFET) or MOS is widely used for implementing digital designs Its major
E&CE 437 Integrated VLSI Systems MOS Transistor 1 of 30 MOSFET: Introduction Metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistor (MOSFET) or MOS is widely used for implementing digital designs Its major
ECE 415/515 ANALOG INTEGRATED CIRCUIT DESIGN
 ECE 415/515 ANALOG INTEGRATED CIRCUIT DESIGN CMOS PROCESS CHARACTERIZATION VISHAL SAXENA VSAXENA@UIDAHO.EDU Vishal Saxena DESIGN PARAMETERS Analog circuit designers care about: Open-loop Gain: g m r o
ECE 415/515 ANALOG INTEGRATED CIRCUIT DESIGN CMOS PROCESS CHARACTERIZATION VISHAL SAXENA VSAXENA@UIDAHO.EDU Vishal Saxena DESIGN PARAMETERS Analog circuit designers care about: Open-loop Gain: g m r o
Device Models (PN Diode, MOSFET )
 Device Models (PN Diode, MOSFET ) Instructor: Steven P. Levitan steve@ece.pitt.edu TA: Gayatri Mehta, José Martínez Book: Digital Integrated Circuits: A Design Perspective; Jan Rabaey Lab Notes: Handed
Device Models (PN Diode, MOSFET ) Instructor: Steven P. Levitan steve@ece.pitt.edu TA: Gayatri Mehta, José Martínez Book: Digital Integrated Circuits: A Design Perspective; Jan Rabaey Lab Notes: Handed
Content. MIS Capacitor. Accumulation Depletion Inversion MOS CAPACITOR. A Cantoni Digital Switching
 Content MIS Capacitor Accumulation Depletion Inversion MOS CAPACITOR 1 MIS Capacitor Metal Oxide C ox p-si C s Components of a capacitance model for the MIS structure 2 MIS Capacitor- Accumulation ρ( x)
Content MIS Capacitor Accumulation Depletion Inversion MOS CAPACITOR 1 MIS Capacitor Metal Oxide C ox p-si C s Components of a capacitance model for the MIS structure 2 MIS Capacitor- Accumulation ρ( x)
Virtual Device Simulation. Virtual Process Integration
 : CMOS Process and Device Simulation Virtual Device Simulation Virtual Process Integration Dr Zhou Xing Office: S1-B1c-95 Phone: 6790-4532 Email: exzhou@ntu.edu.sg Web: http://www.ntu.edu.sg/home/exzhou/teaching//
: CMOS Process and Device Simulation Virtual Device Simulation Virtual Process Integration Dr Zhou Xing Office: S1-B1c-95 Phone: 6790-4532 Email: exzhou@ntu.edu.sg Web: http://www.ntu.edu.sg/home/exzhou/teaching//
MOS Transistor I-V Characteristics and Parasitics
 ECEN454 Digital Integrated Circuit Design MOS Transistor I-V Characteristics and Parasitics ECEN 454 Facts about Transistors So far, we have treated transistors as ideal switches An ON transistor passes
ECEN454 Digital Integrated Circuit Design MOS Transistor I-V Characteristics and Parasitics ECEN 454 Facts about Transistors So far, we have treated transistors as ideal switches An ON transistor passes
Chapter 5 MOSFET Theory for Submicron Technology
 Chapter 5 MOSFET Theory for Submicron Technology Short channel effects Other small geometry effects Parasitic components Velocity saturation/overshoot Hot carrier effects ** Majority of these notes are
Chapter 5 MOSFET Theory for Submicron Technology Short channel effects Other small geometry effects Parasitic components Velocity saturation/overshoot Hot carrier effects ** Majority of these notes are
ECE-305: Spring 2016 MOSFET IV
 ECE-305: Spring 2016 MOSFET IV Professor Mark Lundstrom Electrical and Computer Engineering Purdue University, West Lafayette, IN USA lundstro@purdue.edu Lundstrom s lecture notes: Lecture 4 4/7/16 outline
ECE-305: Spring 2016 MOSFET IV Professor Mark Lundstrom Electrical and Computer Engineering Purdue University, West Lafayette, IN USA lundstro@purdue.edu Lundstrom s lecture notes: Lecture 4 4/7/16 outline
The Devices. Jan M. Rabaey
 The Devices Jan M. Rabaey Goal of this chapter Present intuitive understanding of device operation Introduction of basic device equations Introduction of models for manual analysis Introduction of models
The Devices Jan M. Rabaey Goal of this chapter Present intuitive understanding of device operation Introduction of basic device equations Introduction of models for manual analysis Introduction of models
The Critical Role of Quantum Capacitance in Compact Modeling of Nano-Scaled and Nanoelectronic Devices
 The Critical Role of Quantum Capacitance in Compact Modeling of Nano-Scaled and Nanoelectronic Devices Zhiping Yu and Jinyu Zhang Institute of Microelectronics Tsinghua University, Beijing, China yuzhip@tsinghua.edu.cn
The Critical Role of Quantum Capacitance in Compact Modeling of Nano-Scaled and Nanoelectronic Devices Zhiping Yu and Jinyu Zhang Institute of Microelectronics Tsinghua University, Beijing, China yuzhip@tsinghua.edu.cn
ECE315 / ECE515 Lecture-2 Date:
 Lecture-2 Date: 04.08.2016 NMOS I/V Characteristics Discussion on I/V Characteristics MOSFET Second Order Effect NMOS I-V Characteristics ECE315 / ECE515 Gradual Channel Approximation: Cut-off Linear/Triode
Lecture-2 Date: 04.08.2016 NMOS I/V Characteristics Discussion on I/V Characteristics MOSFET Second Order Effect NMOS I-V Characteristics ECE315 / ECE515 Gradual Channel Approximation: Cut-off Linear/Triode
Lecture 12: MOSFET Devices
 Lecture 12: MOSFET Devices Gu-Yeon Wei Division of Engineering and Applied Sciences Harvard University guyeon@eecs.harvard.edu Wei 1 Overview Reading S&S: Chapter 5.1~5.4 Supplemental Reading Background
Lecture 12: MOSFET Devices Gu-Yeon Wei Division of Engineering and Applied Sciences Harvard University guyeon@eecs.harvard.edu Wei 1 Overview Reading S&S: Chapter 5.1~5.4 Supplemental Reading Background
Microsystems Technology Laboratories, MIT. Teledyne Scientific Company (TSC)
 Extraction of Virtual-Source Injection Velocity in sub-100 nm III-V HFETs 1,2) D.-H. Kim, 1) J. A. del Alamo, 1) D. A. Antoniadis and 2) B. Brar 1) Microsystems Technology Laboratories, MIT 2) Teledyne
Extraction of Virtual-Source Injection Velocity in sub-100 nm III-V HFETs 1,2) D.-H. Kim, 1) J. A. del Alamo, 1) D. A. Antoniadis and 2) B. Brar 1) Microsystems Technology Laboratories, MIT 2) Teledyne
The Devices: MOS Transistors
 The Devices: MOS Transistors References: Semiconductor Device Fundamentals, R. F. Pierret, Addison-Wesley Digital Integrated Circuits: A Design Perspective, J. Rabaey et.al. Prentice Hall NMOS Transistor
The Devices: MOS Transistors References: Semiconductor Device Fundamentals, R. F. Pierret, Addison-Wesley Digital Integrated Circuits: A Design Perspective, J. Rabaey et.al. Prentice Hall NMOS Transistor
Lecture 8: Ballistic FET I-V
 Lecture 8: Ballistic FET I-V 1 Lecture 1: Ballistic FETs Jena: 61-70 Diffusive Field Effect Transistor Source Gate L g >> l Drain Source V GS Gate Drain I D Mean free path much shorter than channel length
Lecture 8: Ballistic FET I-V 1 Lecture 1: Ballistic FETs Jena: 61-70 Diffusive Field Effect Transistor Source Gate L g >> l Drain Source V GS Gate Drain I D Mean free path much shorter than channel length
ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals
 ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 5: January 25, 2018 MOS Operating Regions, pt. 1 Lecture Outline! 3 Regions of operation for MOSFET " Subthreshold " Linear " Saturation!
ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 5: January 25, 2018 MOS Operating Regions, pt. 1 Lecture Outline! 3 Regions of operation for MOSFET " Subthreshold " Linear " Saturation!
Device Models (PN Diode, MOSFET )
 Device Models (PN Diode, MOSFET ) Instructor: Steven P. Levitan steve@ece.pitt.edu TA: Gayatri Mehta, José Martínez Book: Digital Integrated Circuits: A Design Perspective; Jan Rabaey Lab Notes: Handed
Device Models (PN Diode, MOSFET ) Instructor: Steven P. Levitan steve@ece.pitt.edu TA: Gayatri Mehta, José Martínez Book: Digital Integrated Circuits: A Design Perspective; Jan Rabaey Lab Notes: Handed
Zuhui Chen, Xing Zhou, Guan Huei See, Zhaomin Zhu, and Guojun Zhu
 Zuhui Chen, Xing Zhou, Guan Huei See, Zhaomin Zhu, and Guojun Zhu School of EEE, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore Slide No.1/18 Outline Motivations. Theory of interface traps. Theory of unified
Zuhui Chen, Xing Zhou, Guan Huei See, Zhaomin Zhu, and Guojun Zhu School of EEE, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore Slide No.1/18 Outline Motivations. Theory of interface traps. Theory of unified
Effects of Scaling on Modeling of Analog RF MOS Devices
 Effects of Scaling on Modeling of Analog RF MOS Devices Y. Liu, S. Cao, T.-Y. Oh 1, B. Wu, O. Tornblad 2, R. Dutton Center for Integrated Systems, Stanford University 1 LG Electronics 2 Infineon Technologies
Effects of Scaling on Modeling of Analog RF MOS Devices Y. Liu, S. Cao, T.-Y. Oh 1, B. Wu, O. Tornblad 2, R. Dutton Center for Integrated Systems, Stanford University 1 LG Electronics 2 Infineon Technologies
Introduction to compact modeling. Sivakumar Mudanai Intel Corp.
 Introduction to compact modeling Sivakumar Mudanai Intel Corp. Outline What is a compact model Why do we need compact models Requirements on a compact model Building the core long channel compact model
Introduction to compact modeling Sivakumar Mudanai Intel Corp. Outline What is a compact model Why do we need compact models Requirements on a compact model Building the core long channel compact model
EE 330 Lecture 16. MOS Device Modeling p-channel n-channel comparisons Model consistency and relationships CMOS Process Flow
 EE 330 Lecture 16 MOS Device Modeling p-channel n-channel comparisons Model consistency and relationships CMOS Process Flow Review from Last Time Operation Regions by Applications Id I D 300 250 200 150
EE 330 Lecture 16 MOS Device Modeling p-channel n-channel comparisons Model consistency and relationships CMOS Process Flow Review from Last Time Operation Regions by Applications Id I D 300 250 200 150
EE 560 MOS TRANSISTOR THEORY PART 2. Kenneth R. Laker, University of Pennsylvania
 1 EE 560 MOS TRANSISTOR THEORY PART nmos TRANSISTOR IN LINEAR REGION V S = 0 V G > V T0 channel SiO V D = small 4 C GC C BC substrate depletion region or bulk B p nmos TRANSISTOR AT EDGE OF SATURATION
1 EE 560 MOS TRANSISTOR THEORY PART nmos TRANSISTOR IN LINEAR REGION V S = 0 V G > V T0 channel SiO V D = small 4 C GC C BC substrate depletion region or bulk B p nmos TRANSISTOR AT EDGE OF SATURATION
Towards a Scalable EKV Compact Model Including Ballistic and Quasi-Ballistic Transport
 2011 Workshop on Compact Modeling Towards a Scalable EKV Compact Model Including Ballistic and Quasi-Ballistic Transport Christian Enz 1,2, A. Mangla 2 and J.-M. Sallese 2 1) Swiss Center for Electronics
2011 Workshop on Compact Modeling Towards a Scalable EKV Compact Model Including Ballistic and Quasi-Ballistic Transport Christian Enz 1,2, A. Mangla 2 and J.-M. Sallese 2 1) Swiss Center for Electronics
6.012 Electronic Devices and Circuits Spring 2005
 6.012 Electronic Devices and Circuits Spring 2005 May 16, 2005 Final Exam (200 points) -OPEN BOOK- Problem NAME RECITATION TIME 1 2 3 4 5 Total General guidelines (please read carefully before starting):
6.012 Electronic Devices and Circuits Spring 2005 May 16, 2005 Final Exam (200 points) -OPEN BOOK- Problem NAME RECITATION TIME 1 2 3 4 5 Total General guidelines (please read carefully before starting):
This article has been accepted and published on J-STAGE in advance of copyediting. Content is final as presented.
 This article has been accepted and published on J-STAGE in advance of copyediting. Content is final as presented. References IEICE Electronics Express, Vol.* No.*,*-* Effects of Gamma-ray radiation on
This article has been accepted and published on J-STAGE in advance of copyediting. Content is final as presented. References IEICE Electronics Express, Vol.* No.*,*-* Effects of Gamma-ray radiation on
Practice 3: Semiconductors
 Practice 3: Semiconductors Digital Electronic Circuits Semester A 2012 VLSI Fabrication Process VLSI Very Large Scale Integration The ability to fabricate many devices on a single substrate within a given
Practice 3: Semiconductors Digital Electronic Circuits Semester A 2012 VLSI Fabrication Process VLSI Very Large Scale Integration The ability to fabricate many devices on a single substrate within a given
LECTURE 3 MOSFETS II. MOS SCALING What is Scaling?
 LECTURE 3 MOSFETS II Lecture 3 Goals* * Understand constant field and constant voltage scaling and their effects. Understand small geometry effects for MOS transistors and their implications modeling and
LECTURE 3 MOSFETS II Lecture 3 Goals* * Understand constant field and constant voltage scaling and their effects. Understand small geometry effects for MOS transistors and their implications modeling and
Introduction to Reliability Simulation with EKV Device Model
 Introduction to Reliability Simulation with Device Model Benoît Mongellaz Laboratoire IXL ENSEIRB - Université Bordeaux 1 - UMR CNRS 5818 Workshop november 4-5th, Lausanne 1 Motivation & Goal Introduced
Introduction to Reliability Simulation with Device Model Benoît Mongellaz Laboratoire IXL ENSEIRB - Université Bordeaux 1 - UMR CNRS 5818 Workshop november 4-5th, Lausanne 1 Motivation & Goal Introduced
Quantum-size effects in sub-10 nm fin width InGaAs finfets
 Quantum-size effects in sub-10 nm fin width InGaAs finfets Alon Vardi, Xin Zhao, and Jesús A. del Alamo Microsystems Technology Laboratories, MIT December 9, 2015 Sponsors: DTRA NSF (E3S STC) Northrop
Quantum-size effects in sub-10 nm fin width InGaAs finfets Alon Vardi, Xin Zhao, and Jesús A. del Alamo Microsystems Technology Laboratories, MIT December 9, 2015 Sponsors: DTRA NSF (E3S STC) Northrop
ECEN474/704: (Analog) VLSI Circuit Design Spring 2018
 ECEN474/704: (Analog) SI Circuit Design Spring 2018 ecture 2: MOS ransistor Modeling Sam Palermo Analog & Mixed-Signal Center exas A&M University Announcements If you haven t already, turn in your 0.18um
ECEN474/704: (Analog) SI Circuit Design Spring 2018 ecture 2: MOS ransistor Modeling Sam Palermo Analog & Mixed-Signal Center exas A&M University Announcements If you haven t already, turn in your 0.18um
EE 330 Lecture 17. MOSFET Modeling CMOS Process Flow
 EE 330 Lecture 17 MOSFET Modeling CMOS Process Flow Review from Last Lecture Limitations of Existing Models V DD V OUT V OUT V DD?? V IN V OUT V IN V IN V DD Switch-Level Models V DD Simple square-law
EE 330 Lecture 17 MOSFET Modeling CMOS Process Flow Review from Last Lecture Limitations of Existing Models V DD V OUT V OUT V DD?? V IN V OUT V IN V IN V DD Switch-Level Models V DD Simple square-law
L ECE 4211 UConn F. Jain Scaling Laws for NanoFETs Chapter 10 Logic Gate Scaling
 L13 04202017 ECE 4211 UConn F. Jain Scaling Laws for NanoFETs Chapter 10 Logic Gate Scaling Scaling laws: Generalized scaling (GS) p. 610 Design steps p.613 Nanotransistor issues (page 626) Degradation
L13 04202017 ECE 4211 UConn F. Jain Scaling Laws for NanoFETs Chapter 10 Logic Gate Scaling Scaling laws: Generalized scaling (GS) p. 610 Design steps p.613 Nanotransistor issues (page 626) Degradation
Lecture 3: CMOS Transistor Theory
 Lecture 3: CMOS Transistor Theory Outline Introduction MOS Capacitor nmos I-V Characteristics pmos I-V Characteristics Gate and Diffusion Capacitance 2 Introduction So far, we have treated transistors
Lecture 3: CMOS Transistor Theory Outline Introduction MOS Capacitor nmos I-V Characteristics pmos I-V Characteristics Gate and Diffusion Capacitance 2 Introduction So far, we have treated transistors
Simple Theory of the Ballistic Nanotransistor
 Simple Theory of the Ballistic Nanotransistor Mark Lundstrom Purdue University Network for Computational Nanoechnology outline I) Traditional MOS theory II) A bottom-up approach III) The ballistic nanotransistor
Simple Theory of the Ballistic Nanotransistor Mark Lundstrom Purdue University Network for Computational Nanoechnology outline I) Traditional MOS theory II) A bottom-up approach III) The ballistic nanotransistor
MOS Transistor. EE141-Fall 2007 Digital Integrated Circuits. Review: What is a Transistor? Announcements. Class Material
 EE-Fall 7 igital Integrated Circuits MO Transistor Lecture MO Transistor Model Announcements Review: hat is a Transistor? Lab this week! Lab next week Homework # is due Thurs. Homework # due next Thurs.
EE-Fall 7 igital Integrated Circuits MO Transistor Lecture MO Transistor Model Announcements Review: hat is a Transistor? Lab this week! Lab next week Homework # is due Thurs. Homework # due next Thurs.
Quarter-micrometre surface and buried channel PMOSFET modelling for circuit simulation
 Semicond. Sci. Technol. 11 1996) 1763 1769. Printed in the UK Quarter-micrometre surface and buried channel PMOSFET modelling for circuit simulation Yuhua Cheng, Min-chie Jeng, Zhihong Liu, Kai Chen, Bin
Semicond. Sci. Technol. 11 1996) 1763 1769. Printed in the UK Quarter-micrometre surface and buried channel PMOSFET modelling for circuit simulation Yuhua Cheng, Min-chie Jeng, Zhihong Liu, Kai Chen, Bin
P-MOS Device and CMOS Inverters
 Lecture 23 P-MOS Device and CMOS Inverters A) P-MOS Device Structure and Oeration B) Relation of Current to t OX, µ V LIMIT C) CMOS Device Equations and Use D) CMOS Inverter V OUT vs. V IN E) CMOS Short
Lecture 23 P-MOS Device and CMOS Inverters A) P-MOS Device Structure and Oeration B) Relation of Current to t OX, µ V LIMIT C) CMOS Device Equations and Use D) CMOS Inverter V OUT vs. V IN E) CMOS Short
ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals
 ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 6: January 30, 2018 MOS Operating Regions, pt. 2 Lecture Outline! Operating Regions (review) " Subthreshold " Resistive " Saturation! Intro.
ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 6: January 30, 2018 MOS Operating Regions, pt. 2 Lecture Outline! Operating Regions (review) " Subthreshold " Resistive " Saturation! Intro.
EE 330 Lecture 16. MOSFET Modeling CMOS Process Flow
 EE 330 Lecture 16 MOSFET Modeling CMOS Process Flow Model Extensions 300 Id 250 200 150 100 50 300 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 Vds Existing Model 250 200 Id 150 100 50 Slope is not 0 0 0 1 2 3 4 Actual Device Vds Model
EE 330 Lecture 16 MOSFET Modeling CMOS Process Flow Model Extensions 300 Id 250 200 150 100 50 300 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 Vds Existing Model 250 200 Id 150 100 50 Slope is not 0 0 0 1 2 3 4 Actual Device Vds Model
Unified Compact Model for Generic Double-Gate
 WCM-MSM007 Workshop on Compact Modeling 10th International Conference on Modeling and Simulation of Microsystems Santa Clara, California, USA Unified Compact Model for Generic Double-Gate MOSFETs Xing
WCM-MSM007 Workshop on Compact Modeling 10th International Conference on Modeling and Simulation of Microsystems Santa Clara, California, USA Unified Compact Model for Generic Double-Gate MOSFETs Xing
Lecture 11: MOS Transistor
 Lecture 11: MOS Transistor Prof. Niknejad Lecture Outline Review: MOS Capacitors Regions MOS Capacitors (3.8 3.9) CV Curve Threshold Voltage MOS Transistors (4.1 4.3): Overview Cross-section and layout
Lecture 11: MOS Transistor Prof. Niknejad Lecture Outline Review: MOS Capacitors Regions MOS Capacitors (3.8 3.9) CV Curve Threshold Voltage MOS Transistors (4.1 4.3): Overview Cross-section and layout
BSIM3v3 Manual. (Final Version) Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences. University of California, Berkeley, CA 94720
 BSIM3v3 Manual (Final Version) Yuhua Cheng, Mansun Chan, Kelvin Hui, Min-chie Jeng, Zhihong Liu, Jianhui Huang, Kai Chen, James Chen, Robert Tu, Ping K. Ko, Chenming Hu Department of Electrical Engineering
BSIM3v3 Manual (Final Version) Yuhua Cheng, Mansun Chan, Kelvin Hui, Min-chie Jeng, Zhihong Liu, Jianhui Huang, Kai Chen, James Chen, Robert Tu, Ping K. Ko, Chenming Hu Department of Electrical Engineering
University of Pennsylvania Department of Electrical Engineering. ESE 570 Midterm Exam March 14, 2013 FORMULAS AND DATA
 University of Pennsylvania Department of Electrical Engineering ESE 570 Midterm Exam March 4, 03 FORMULAS AND DATA. PHYSICAL CONSTANTS: n i = intrinsic concentration undoped) silicon =.45 x 0 0 cm -3 @
University of Pennsylvania Department of Electrical Engineering ESE 570 Midterm Exam March 4, 03 FORMULAS AND DATA. PHYSICAL CONSTANTS: n i = intrinsic concentration undoped) silicon =.45 x 0 0 cm -3 @
HW 5 posted due in two weeks Lab this week Midterm graded Project to be launched in week 7
 HW 5 posted due in two weeks Lab this week Midterm graded Project to be launched in week 7 2 What do digital IC designers need to know? 5 EE4 EECS4 6 3 0< V GS - V T < V DS Pinch-off 7 For (V GS V T )
HW 5 posted due in two weeks Lab this week Midterm graded Project to be launched in week 7 2 What do digital IC designers need to know? 5 EE4 EECS4 6 3 0< V GS - V T < V DS Pinch-off 7 For (V GS V T )
Lecture 15 OUTLINE. MOSFET structure & operation (qualitative) Review of electrostatics The (N)MOS capacitor
 Lecture 15 OUTLINE MOSFET structure & operation (qualitative) Review of electrostatics The (N)MOS capacitor Electrostatics t ti Charge vs. voltage characteristic Reading: Chapter 6.1 6.2.1 EE105 Fall 2007
Lecture 15 OUTLINE MOSFET structure & operation (qualitative) Review of electrostatics The (N)MOS capacitor Electrostatics t ti Charge vs. voltage characteristic Reading: Chapter 6.1 6.2.1 EE105 Fall 2007
BSIM4.6.4 MOSFET Model
 BSIM4.6.4 MOSFET Model -User s Manual Tanvir Hasan Morshed, Wenwei (Morgan) Yang, Mohan V. Dunga, Xuemei (Jane) Xi, Jin He, Weidong Liu, Kanyu, M. Cao, Xiaodong Jin, Jeff J. Ou, Mansun Chan, Ali M. Niknejad,
BSIM4.6.4 MOSFET Model -User s Manual Tanvir Hasan Morshed, Wenwei (Morgan) Yang, Mohan V. Dunga, Xuemei (Jane) Xi, Jin He, Weidong Liu, Kanyu, M. Cao, Xiaodong Jin, Jeff J. Ou, Mansun Chan, Ali M. Niknejad,
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences. EECS 130 Professor Ali Javey Fall 2006
 UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences EECS 130 Professor Ali Javey Fall 2006 Midterm 2 Name: SID: Closed book. Two sheets of notes are
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences EECS 130 Professor Ali Javey Fall 2006 Midterm 2 Name: SID: Closed book. Two sheets of notes are
Microelectronics Part 1: Main CMOS circuits design rules
 GBM8320 Dispositifs Médicaux telligents Microelectronics Part 1: Main CMOS circuits design rules Mohamad Sawan et al. Laboratoire de neurotechnologies Polystim! http://www.cours.polymtl.ca/gbm8320/! med-amine.miled@polymtl.ca!
GBM8320 Dispositifs Médicaux telligents Microelectronics Part 1: Main CMOS circuits design rules Mohamad Sawan et al. Laboratoire de neurotechnologies Polystim! http://www.cours.polymtl.ca/gbm8320/! med-amine.miled@polymtl.ca!
BSIM4v4.7 MOSFET Model
 BSIM4v4.7 MOSFET Model -User s Manual Tanvir Hasan Morshed, Darsen D. Lu, Wenwei (Morgan) Yang, Mohan V. Dunga, Xuemei (Jane) Xi, Jin He, Weidong Liu, Kanyu, M. Cao, Xiaodong Jin, Jeff J. Ou, Mansun Chan,
BSIM4v4.7 MOSFET Model -User s Manual Tanvir Hasan Morshed, Darsen D. Lu, Wenwei (Morgan) Yang, Mohan V. Dunga, Xuemei (Jane) Xi, Jin He, Weidong Liu, Kanyu, M. Cao, Xiaodong Jin, Jeff J. Ou, Mansun Chan,
Non Ideal Transistor Behavior
 Non Ideal Transistor Behavior Slides adapted from: N. Weste, D. Harris, CMOS VLSI Design, Addison- Wesley, 3/e, 2004 1 Non-ideal Transistor I-V effects Non ideal transistor Behavior Channel Length ModulaJon
Non Ideal Transistor Behavior Slides adapted from: N. Weste, D. Harris, CMOS VLSI Design, Addison- Wesley, 3/e, 2004 1 Non-ideal Transistor I-V effects Non ideal transistor Behavior Channel Length ModulaJon
CMPEN 411 VLSI Digital Circuits. Lecture 03: MOS Transistor
 CMPEN 411 VLSI Digital Circuits Lecture 03: MOS Transistor Kyusun Choi [Adapted from Rabaey s Digital Integrated Circuits, Second Edition, 2003 J. Rabaey, A. Chandrakasan, B. Nikolic] CMPEN 411 L03 S.1
CMPEN 411 VLSI Digital Circuits Lecture 03: MOS Transistor Kyusun Choi [Adapted from Rabaey s Digital Integrated Circuits, Second Edition, 2003 J. Rabaey, A. Chandrakasan, B. Nikolic] CMPEN 411 L03 S.1
EE115C Winter 2017 Digital Electronic Circuits. Lecture 3: MOS RC Model, CMOS Manufacturing
 EE115C Winter 2017 Digital Electronic Circuits Lecture 3: MOS RC Model, CMOS Manufacturing Agenda MOS Transistor: RC Model (pp. 104-113) S R on D CMOS Manufacturing Process (pp. 36-46) S S C GS G G C GD
EE115C Winter 2017 Digital Electronic Circuits Lecture 3: MOS RC Model, CMOS Manufacturing Agenda MOS Transistor: RC Model (pp. 104-113) S R on D CMOS Manufacturing Process (pp. 36-46) S S C GS G G C GD
MOS Transistors Models
 MOS Transistors Models Andreas G. Andreou Pedro Julian Electrical and Computer Engineering Johns Hopkins University http://andreoulab.net The MOS transistor Levels of Abstraction- Model Equations If V
MOS Transistors Models Andreas G. Andreou Pedro Julian Electrical and Computer Engineering Johns Hopkins University http://andreoulab.net The MOS transistor Levels of Abstraction- Model Equations If V
Self-heat Modeling of Multi-finger n-mosfets for RF-CMOS Applications
 Self-heat Modeling of Multi-finger n-mosfets for RF-CMOS Applications Hitoshi Aoki and Haruo Kobayashi Faculty of Science and Technology, Gunma University (RMO2D-3) Outline Research Background Purposes
Self-heat Modeling of Multi-finger n-mosfets for RF-CMOS Applications Hitoshi Aoki and Haruo Kobayashi Faculty of Science and Technology, Gunma University (RMO2D-3) Outline Research Background Purposes
P. R. Nelson 1 ECE418 - VLSI. Midterm Exam. Solutions
 P. R. Nelson 1 ECE418 - VLSI Midterm Exam Solutions 1. (8 points) Draw the cross-section view for A-A. The cross-section view is as shown below.. ( points) Can you tell which of the metal1 regions is the
P. R. Nelson 1 ECE418 - VLSI Midterm Exam Solutions 1. (8 points) Draw the cross-section view for A-A. The cross-section view is as shown below.. ( points) Can you tell which of the metal1 regions is the
1. The MOS Transistor. Electrical Conduction in Solids
 Electrical Conduction in Solids!The band diagram describes the energy levels for electron in solids.!the lower filled band is named Valence Band.!The upper vacant band is named conduction band.!the distance
Electrical Conduction in Solids!The band diagram describes the energy levels for electron in solids.!the lower filled band is named Valence Band.!The upper vacant band is named conduction band.!the distance
Lecture Outline. ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals. Review: MOS Capacitor with External Bias
 ESE 57: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 5: Januar 6, 17 MOS Operating Regions, pt. 1 Lecture Outline! 3 Regions of operation for MOSFET " Subthreshold " Linear " Saturation! Level
ESE 57: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 5: Januar 6, 17 MOS Operating Regions, pt. 1 Lecture Outline! 3 Regions of operation for MOSFET " Subthreshold " Linear " Saturation! Level
Semiconductor Devices. C. Hu: Modern Semiconductor Devices for Integrated Circuits Chapter 5
 Semiconductor Devices C. Hu: Modern Semiconductor Devices for Integrated Circuits Chapter 5 Global leader in environmental and industrial measurement Wednesday 3.2. afternoon Tour around facilities & lecture
Semiconductor Devices C. Hu: Modern Semiconductor Devices for Integrated Circuits Chapter 5 Global leader in environmental and industrial measurement Wednesday 3.2. afternoon Tour around facilities & lecture
Today s lecture. EE141- Spring 2003 Lecture 4. Design Rules CMOS Inverter MOS Transistor Model
 - Spring 003 Lecture 4 Design Rules CMOS Inverter MOS Transistor Model Today s lecture Design Rules The CMOS inverter at a glance An MOS transistor model for manual analysis Important! Labs start next
- Spring 003 Lecture 4 Design Rules CMOS Inverter MOS Transistor Model Today s lecture Design Rules The CMOS inverter at a glance An MOS transistor model for manual analysis Important! Labs start next
EE 330 Lecture 16. Devices in Semiconductor Processes. MOS Transistors
 EE 330 Lecture 16 Devices in Semiconductor Processes MOS Transistors Review from Last Time Model Summary I D I V DS V S I B V BS = 0 0 VS VT W VDS ID = μcox VS VT VDS VS V VDS VS VT L T < W μc ( V V )
EE 330 Lecture 16 Devices in Semiconductor Processes MOS Transistors Review from Last Time Model Summary I D I V DS V S I B V BS = 0 0 VS VT W VDS ID = μcox VS VT VDS VS V VDS VS VT L T < W μc ( V V )
DKDT: A Performance Aware Dual Dielectric Assignment for Tunneling Current Reduction
 DKDT: A Performance Aware Dual Dielectric Assignment for Tunneling Current Reduction Saraju P. Mohanty Dept of Computer Science and Engineering University of North Texas smohanty@cs.unt.edu http://www.cs.unt.edu/~smohanty/
DKDT: A Performance Aware Dual Dielectric Assignment for Tunneling Current Reduction Saraju P. Mohanty Dept of Computer Science and Engineering University of North Texas smohanty@cs.unt.edu http://www.cs.unt.edu/~smohanty/
Appendix 1: List of symbols
 Appendix 1: List of symbols Symbol Description MKS Units a Acceleration m/s 2 a 0 Bohr radius m A Area m 2 A* Richardson constant m/s A C Collector area m 2 A E Emitter area m 2 b Bimolecular recombination
Appendix 1: List of symbols Symbol Description MKS Units a Acceleration m/s 2 a 0 Bohr radius m A Area m 2 A* Richardson constant m/s A C Collector area m 2 A E Emitter area m 2 b Bimolecular recombination
EE105 Fall 2014 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits. NMOS Transistor Capacitances: Saturation Region
 EE105 Fall 014 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits Prof. Ming C. Wu wu@eecs.berkeley.edu 511 Sutardja Dai Hall (SDH) 1 NMOS Transistor Capacitances: Saturation Region Drain no longer connected to channel
EE105 Fall 014 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits Prof. Ming C. Wu wu@eecs.berkeley.edu 511 Sutardja Dai Hall (SDH) 1 NMOS Transistor Capacitances: Saturation Region Drain no longer connected to channel
Spring Semester 2012 Final Exam
 Spring Semester 2012 Final Exam Note: Show your work, underline results, and always show units. Official exam time: 2.0 hours; an extension of at least 1.0 hour will be granted to anyone. Materials parameters
Spring Semester 2012 Final Exam Note: Show your work, underline results, and always show units. Official exam time: 2.0 hours; an extension of at least 1.0 hour will be granted to anyone. Materials parameters
The HV-EKV MOSFET Model
 The HV-EKV MOSFET Model Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL), Switzerland EPFL Team Yogesh Singh Chauhan, Costin Anghel, Francois Krummenacher, Adrian Mihai Ionescu and Michel Declercq CMC Meeting,
The HV-EKV MOSFET Model Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL), Switzerland EPFL Team Yogesh Singh Chauhan, Costin Anghel, Francois Krummenacher, Adrian Mihai Ionescu and Michel Declercq CMC Meeting,
ECEN474/704: (Analog) VLSI Circuit Design Spring 2018
 ECEN474/704: (Analog) VLSI Circuit Design Spring 2018 Lecture 4: MOS ransistor Modeling Sam Palermo Analog & Mixed-Signal Center exas A&M University Agenda MOS ransistor Modeling MOS Spice Models MOS High-Order
ECEN474/704: (Analog) VLSI Circuit Design Spring 2018 Lecture 4: MOS ransistor Modeling Sam Palermo Analog & Mixed-Signal Center exas A&M University Agenda MOS ransistor Modeling MOS Spice Models MOS High-Order
