Towards a Scalable EKV Compact Model Including Ballistic and Quasi-Ballistic Transport
|
|
|
- Emma McDonald
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 2011 Workshop on Compact Modeling Towards a Scalable EKV Compact Model Including Ballistic and Quasi-Ballistic Transport Christian Enz 1,2, A. Mangla 2 and J.-M. Sallese 2 1) Swiss Center for Electronics and Microtechnology (CSEM), Neuchâtel, Switzerland 2) Swiss Federal Institute of Technology, Lausanne (EPFL), Switzerland
2 Outline Introduction State of the Art Behavior of the Continuous Model Conclusions Slide 2
3 Introduction Carrier Transport Mechanisms in MOSFETs L >> λ (carrier mean-free-path) Diffusive transport (drift and diffusion) Collision dominated Well described by conventional mobility theory L ~ λ Quasi-Ballistic transport where carriers encounter limited amount of scattering from source and drain Mobility theory no longer describes transport L < λ Ballistic transport Collision free Controlled by carrier injection from source into the channel source source source L drain drain drain K. Natori, Ballistic/quasi-ballistic transport in nanoscale transistor, Applied Surface Science, Jul Slide 3
4 Coefficients Introduction The Ballistic MOSFET r b r 0.6 b Rb r Te Channel Length [nm] The ballistic transistor remains an ideal device that represents the limit of scalability of a real device. Below 10nm, quasi-ballistic transport needs to be accounted for K. Natori, Ballistic/quasi-ballistic transport in nanoscale transistor, Applied Surface Science, Jul r: Back-scattering coefficient b: Ballisticity Te: Fraction of injected carriers reaching the drain without energy relaxation Rb: Portion of injected flux that rebounds from the drain to the channel due to scattering inside the drain Slide 4
5 Outline Introduction State of the Art Behavior of the Continuous Model Conclusions Slide 5
6 State-of-the-Art Lundstrom s Flux Scattering Theory Transmission view of the device where carriers injected into the channel from the source, across an energy barrier whose height is controlled by the gateto-source voltage The positive directed flux is injected over the source-channel barrier The negative flux is composed of two components: Backscattered flux, and Fraction of flux injected from drain The drain injected flux is suppressed at high drain bias Source Virtual Source Drain 0 L Position Along the Channel Source injected flux Drain injected flux Backscattered flux K. Natori, Ballistic metal-oxide-semiconductor field effect transistor, Journal of Applied Physics, J. McKelvey, R. Longini et al., Alternative Approach to the Solution of Added Carrier Transport Problems in Semiconductors, Physical Review, M. Lundstrom, Elementary scattering theory of the Si MOSFET, IEEE Electron Device Letters, Jul Slide 6 Electron Potential
7 Introduction Lundstrom s Flux Scattering Theory Assuming current continuity, evaluated at the virtual source ID Q 0 0 for V U W v 1 r vx(0) vt b vt 1 r i x DS T 0: inversion charge density at the virtual source 0: average carrier velocity at the virtual source : thermal velocity of electrons 01: back-scattering coefficient function of the gate and drain bias voltages Electron Potential Source Virtual Source Drain 0 L Position Along the Channel Source injected flux Drain injected flux Backscattered flux M. Lundstrom and Z. Ren, Essential Physics of Carrier Transport in Nanoscale MOSFETs, IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, Slide 7
8 Introduction Lundstrom s Model The drain current including the flux injected from the drain and reaching the source is given by ID 0 1 r 1 e Qi vt W 1 r 1 r 1 1 r V where non-degenerate conditions have been assumed. In a fully ballistic device 0, and the current simplifies to e DS V U DS T U T I W D V U 1 e DS T Q 0v Q 0v for V U V 1 DS U e T i T i T DS T A. Rahman and M.S. Lundstrom, A compact scattering model for the nanoscale double-gate MOSFET, IEEE TED, Mar Slide 8
9 State-of-the-Art Lundstrom s Model: The Backscattering Coefficient The backscattering coefficient,, defined as the ratio of the backscattered flux to the injected flux, captures the scattering occurring in the channel r where l is the length across which the potential drops by a few U T s, which depends on the potential profile in the channel and is the carrier mean-free-path, which depends on the field-dependent mobility In Lundstrom s theory, the source-to-drain and drain-to-source backscattering coefficients are assumed to be equal Even though attempts have been made to evaluate it analytically, it remains largely empirical Slide 9
10 State-of-the-Art Scalable Models from Ballistic to Drift-Diffusion The classical approach to Ballistic modeling is quite simple However, it is not seamlessly scalable It cannot be directly scaled up to result in the conventional drift-diffusion model Designers would need to use different models for short and long channel devices at the same technology node It is apparent then that we need a compact model that either Extends the ballistic model to include the drift-diffusion model, or Extends the drift-diffusion model to include the ballistic case. Slide 10
11 State-of-the-Art Khakifirooz s Semi-empirical Model Follows Lundstrom s transport over the barrier approach. The drain current in the virtual source model is given by ID Q 0 0 F W v i x s Avoids expressing 0, which becomes a model parameter The model is very simple since it uses only 6 measured and 4 fitting parameters 0 is log-exp function including a suitable inversion transition function for continuity between weak and strong inversion V (0) ln 1 exp GS V T U T F Q f i Ceff nut nu T F f 1 V V U 1 exp U GS T T T 2 A. Khakifirooz, O. M. Nayfeh, and D. Antoniadis, A Simple Semiempirical Short-Channel MOSFET Current Voltage Model Continuous Across All Regions of Operation and Employing Only Physical Parameters, IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, Aug Slide 11
12 State-of-the-Art Khakifirooz s Semi-empirical Model Comparison of electrostatics with the EKV model Normalized source charge density q i (0) Khakifirooz EKV Normalized overdrive voltage (v g -v t ) Slide 12
13 State-of-the-Art Khakifirooz s Semi-empirical Model An empirical saturation function modifies the velocity term to model the transition between saturation and linear regions according to ID Q 0 0 F W v i x s F s V DS V DSAT 1 V 1 DS VDSAT L c =35 nm L c =32 nm A. Khakifirooz, O. M. Nayfeh, and D. Antoniadis, A Simple Semiempirical Short-Channel MOSFET Current Voltage Model Continuous Across All Regions of Operation and Employing Only Physical Parameters, IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, Aug Slide 13
14 State-of-the-Art Chain of Ballistic Transistors VG VD VS B B B Virtual reservoirs B It has been proposed that a Drift-Diffusion transistor can be represented as a chain of ballistic transistors At each node, the electrons are thermalized in accordance with the Buttiker virtual probe approach There are N-1 Fermi levels but the drain current continuity is ensured G. Mugnaini and G. Iannaccone, Physics-Based Compact Model of Nanoscale MOSFETs Part I: Transition From Drift-Diffusion to Ballistic Transport, IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, Aug Slide 14
15 State-of-the-Art Chain of Ballistic Transistors The electrostatics formulation of the chain turns out to be similar to the EKV electrostatics Also, the drain current formulation is similar in structure to EKV A nonlinear term accounts for velocity saturation, similar to the field-dependent mobility term G. Mugnaini and G. Iannaccone, Physics-Based Compact Model of Nanoscale MOSFETs Part I: Transition From Drift-Diffusion to Ballistic Transport, IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, Aug Slide 15
16 State-of-the-Art The Unified Model Whatever be the transport mechanism, there is always a limiting velocity: vlim min vsat, v The drain current can be expressed as a Mathiessen s rule : inj I I min I, I D dd bal sat : drift-diffusion component : ballistic component : velocity saturated component D. Fleury, G. Bidal, A. Cros, F. Boeuf, T. Skotnicki, and G. Ghibaudo, New Experimental Insight into Ballisticity of Transport in Strained Bulk MOSFETs, Symposium on VLSI Technology, Slide 16
17 State-of-the-Art The Unified Model Results of thermal measurements on 22nm strained-si devices Velocity limiting the current is the saturation velocity (due to collisions) and not the thermal injection velocity Even in 22nm effective length devices, the transport is scattering dominated D. Fleury, G. Bidal, A. Cros, F. Boeuf, T. Skotnicki, and G. Ghibaudo, New Experimental Insight into Ballisticity of Transport in Strained Bulk MOSFETs, Symposium on VLSI Technology, Slide 17
18 Outline Introduction State of the Art Behavior of the Continuous Model Conclusions Slide 18
19 Behavior of the Continuous Model EKV Continuous Model The classical DD EKV model has been extended to include ballistic transport The electrostatic is identical to the classical EKV model The ballistic behavior is added following a similar approach to Mugnaini, but with a simpler implementation Still early work and requires additional improvement and validation The characteristics of our continuous model at various channel lengths is shown, and the results are compared with the Ballistic (B) model and Drift-Diffusion (DD) model (without velocity saturation) G. Mugnaini and G. Iannaccone, Physics-Based Compact Model of Nanoscale MOSFETs Part I: Transition From Drift-Diffusion to Ballistic Transport, IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, Aug Slide 19
20 Behavior of the Continuous Model Behavior of a Continuous Model Very Short Channel For very short devices (L=2nm), the model mostly follows the ballistic model Output Characteristics Transfer Characteristics L=2nm, V G -V T =1V, V S =0 10 L=2nm, V D =1V, V S =0, V T =0 I D.L/W [ma] This model Ballistic model EKV drift-diffusion model I D.L/W [ma] This model Ballistic model EKV drift-diffusion model V DS [V] V GS [V] Slide 20
21 Behavior of the Continuous Model Behavior of a Continuous Model Short Channel For short-channel devices (L=20nm), the model operates as quasi-ballistic, it follows the DD model at low bias and switches to B at higher bias Output Characteristics Transfer Characteristics I D.L/W [ma] L=20nm, V G -V T =1V, V S = This model Ballistic model EKV drift-diffusion model I D.L/W [ma] L=20nm, V D =1V, V S =0, V T = This model Ballistic model EKV drift-diffusion model V DS [V] V GS [V] Slide 21
22 Behavior of the Continuous Model Behavior of a Continuous Model Long Channel For long-channel devices (L=200nm), the model follows the DD model Output Characteristics Transfer Characteristics L=200nm, V G -V T =1V, V S =0 1 L=200nm, V D =1V, V S =0, V T =0 I D.L/W [ma] This model Ballistic model EKV drift-diffusion model I D.L/W [ma] This model Ballistic model EKV drift-diffusion model V DS [V] V GS [V] Slide 22
23 Behavior of the Continuous Model Saturation in Ballistic Transistors Ballistic: ID C W v V V ox T GS T DD in strong inversion: ID C V V W v ox sat GS T Saturation current expression of B is similar to that of DD velocity saturation in SI Saturation occurs because of velocity saturation at the source Velocity overshoot appears in the high field region close to the drain Similar to ballistic transistor, saturation of DD transistor current in weak inversion occurs for Do we also have velocity saturation in DD transistor biased in weak inversion? M. Lundstrom and Z. Ren, Essential physics of carrier transport in nanoscale MOSFETs, IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, Slide 23
24 Behavior of the Continuous Model Effect of Velocity Saturation on the Current in WI Velocity saturation also affects the current in weak inversion (WI) in saturation i d 20 UT 2U T v L E L The normalized source transconductance is then given by c sat Gms q Ispec g s i with G 2n U G 1 2 U ms d spec T spec c T The G ms /I D ratio is not affected by velocity saturation and remains equal to unity as for the long channel case 0 I 2 D qs Qi Ispec nu where qs with I 1 2 Q Q 2nC U spec c spec spec ox T Velocity saturation parameter c 2 T Slide 24
25 Behavior of the Continuous Model G m / I D Characteristic Including VS c 20 UT 2U T v L E L sat c 1 g ms /i d 0.1 IC I I D spec (saturation) 1 c c 2 1 c Inversion Coefficient, IC A. Mangla, J.-M. Sallese and C. Enz, MIXDES 2011 Slide 25
26 Behavior of the Continuous Model Figure-of-Merit for Low Power RF Design Moderate inversion is a good trade-off for having at the same time high current efficiency and maximum gain at RF for a given current 1 FoM g ms i d f t id 1 i d WI SI FoM 0.1 moderate inversion c Inversion Coefficient, IC 20 UT 2U T c v L E L sat c A. Shameli and P. Heydari, ISLPED 2006 A. Mangla, J.-M. Sallese and C. Enz, MIXDES 2011 Slide 26
27 Outline Introduction State of the Art Behavior of the Continuous Model Conclusions Slide 27
28 Conclusion With the scaling of CMOS, the devices would soon start approaching the ballistic limit Significant advances have been made to model the ballistic and quasi-ballistic behavior in devices. However, a design oriented compact model, scalable from extremely short to long channel lengths and continuous at all inversion levels, is still elusive We are working towards a scalable EKV compact model which includes ballistic transport. The preliminary results look promising Our analysis shows that velocity saturation not only strongly affects the current in strong inversion but has also an impact in weak inversion For short channel devices operating at high frequencies, the optimum operating point lies in moderate inversion and would eventually shift towards weak inversion for nanoscale devices Slide 28
MOSFET. Id-Vd curve. I DS Transfer curve V G. Lec. 8. Vd=1V. Saturation region. V Th
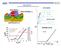 MOSFET Id-Vd curve Saturation region I DS Transfer curve Vd=1V V Th V G 1 0 < V GS < V T V GS > V T V Gs >V T & Small V D > 0 I DS WQ inv WC v WC i V V VDS V V G i T G n T L n I D g V D (g conductance
MOSFET Id-Vd curve Saturation region I DS Transfer curve Vd=1V V Th V G 1 0 < V GS < V T V GS > V T V Gs >V T & Small V D > 0 I DS WQ inv WC v WC i V V VDS V V G i T G n T L n I D g V D (g conductance
Simple Theory of the Ballistic Nanotransistor
 Simple Theory of the Ballistic Nanotransistor Mark Lundstrom Purdue University Network for Computational Nanoechnology outline I) Traditional MOS theory II) A bottom-up approach III) The ballistic nanotransistor
Simple Theory of the Ballistic Nanotransistor Mark Lundstrom Purdue University Network for Computational Nanoechnology outline I) Traditional MOS theory II) A bottom-up approach III) The ballistic nanotransistor
Microsystems Technology Laboratories, MIT. Teledyne Scientific Company (TSC)
 Extraction of Virtual-Source Injection Velocity in sub-100 nm III-V HFETs 1,2) D.-H. Kim, 1) J. A. del Alamo, 1) D. A. Antoniadis and 2) B. Brar 1) Microsystems Technology Laboratories, MIT 2) Teledyne
Extraction of Virtual-Source Injection Velocity in sub-100 nm III-V HFETs 1,2) D.-H. Kim, 1) J. A. del Alamo, 1) D. A. Antoniadis and 2) B. Brar 1) Microsystems Technology Laboratories, MIT 2) Teledyne
The Devices. Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective. Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic. July 30, 2002
 Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic The Devices July 30, 2002 Goal of this chapter Present intuitive understanding of device operation Introduction
Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic The Devices July 30, 2002 Goal of this chapter Present intuitive understanding of device operation Introduction
Cryogenic Characterization of 28 nm Bulk CMOS Technology for Quantum Computing
 Cryogenic Characterization of 8 nm Bulk CMOS Technology for Quantum Computing Arnout Beckers, Farzan Jazaeri, Andrea Ruffino, Claudio Bruschini, Andrea Baschirotto, and Christian Enz Integrated Circuits
Cryogenic Characterization of 8 nm Bulk CMOS Technology for Quantum Computing Arnout Beckers, Farzan Jazaeri, Andrea Ruffino, Claudio Bruschini, Andrea Baschirotto, and Christian Enz Integrated Circuits
MOS Transistors. Prof. Krishna Saraswat. Department of Electrical Engineering Stanford University Stanford, CA
 MOS Transistors Prof. Krishna Saraswat Department of Electrical Engineering S Stanford, CA 94305 saraswat@stanford.edu 1 1930: Patent on the Field-Effect Transistor! Julius Lilienfeld filed a patent describing
MOS Transistors Prof. Krishna Saraswat Department of Electrical Engineering S Stanford, CA 94305 saraswat@stanford.edu 1 1930: Patent on the Field-Effect Transistor! Julius Lilienfeld filed a patent describing
Analysis of Transconductances in Deep Submicron CMOS with EKV 3.0
 MOS Models & Parameter Extraction Workgroup Arbeitskreis MOS Modelle & Parameterextraktion XFAB, Erfurt, Germany, October 2, 2002 Analysis of Transconductances in Deep Submicron CMOS with EKV 3.0 Matthias
MOS Models & Parameter Extraction Workgroup Arbeitskreis MOS Modelle & Parameterextraktion XFAB, Erfurt, Germany, October 2, 2002 Analysis of Transconductances in Deep Submicron CMOS with EKV 3.0 Matthias
ECE-305: Spring 2016 MOSFET IV
 ECE-305: Spring 2016 MOSFET IV Professor Mark Lundstrom Electrical and Computer Engineering Purdue University, West Lafayette, IN USA lundstro@purdue.edu Lundstrom s lecture notes: Lecture 4 4/7/16 outline
ECE-305: Spring 2016 MOSFET IV Professor Mark Lundstrom Electrical and Computer Engineering Purdue University, West Lafayette, IN USA lundstro@purdue.edu Lundstrom s lecture notes: Lecture 4 4/7/16 outline
Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective. Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic. The Devices. July 30, Devices.
 Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic The July 30, 2002 1 Goal of this chapter Present intuitive understanding of device operation Introduction
Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic The July 30, 2002 1 Goal of this chapter Present intuitive understanding of device operation Introduction
Integrated Circuits & Systems
 Federal University of Santa Catarina Center for Technology Computer Science & Electronics Engineering Integrated Circuits & Systems INE 5442 Lecture 10 MOSFET part 1 guntzel@inf.ufsc.br ual-well Trench-Isolated
Federal University of Santa Catarina Center for Technology Computer Science & Electronics Engineering Integrated Circuits & Systems INE 5442 Lecture 10 MOSFET part 1 guntzel@inf.ufsc.br ual-well Trench-Isolated
Nanoscale CMOS Design Issues
 Nanoscale CMOS Design Issues Jaydeep P. Kulkarni Assistant Professor, ECE Department The University of Texas at Austin jaydeep@austin.utexas.edu Fall, 2017, VLSI-1 Class Transistor I-V Review Agenda Non-ideal
Nanoscale CMOS Design Issues Jaydeep P. Kulkarni Assistant Professor, ECE Department The University of Texas at Austin jaydeep@austin.utexas.edu Fall, 2017, VLSI-1 Class Transistor I-V Review Agenda Non-ideal
MOSFET: Introduction
 E&CE 437 Integrated VLSI Systems MOS Transistor 1 of 30 MOSFET: Introduction Metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistor (MOSFET) or MOS is widely used for implementing digital designs Its major
E&CE 437 Integrated VLSI Systems MOS Transistor 1 of 30 MOSFET: Introduction Metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistor (MOSFET) or MOS is widely used for implementing digital designs Its major
SECTION: Circle one: Alam Lundstrom. ECE 305 Exam 5 SOLUTIONS: Spring 2016 April 18, 2016 M. A. Alam and M.S. Lundstrom Purdue University
 NAME: PUID: SECTION: Circle one: Alam Lundstrom ECE 305 Exam 5 SOLUTIONS: April 18, 2016 M A Alam and MS Lundstrom Purdue University This is a closed book exam You may use a calculator and the formula
NAME: PUID: SECTION: Circle one: Alam Lundstrom ECE 305 Exam 5 SOLUTIONS: April 18, 2016 M A Alam and MS Lundstrom Purdue University This is a closed book exam You may use a calculator and the formula
Lecture 5: CMOS Transistor Theory
 Lecture 5: CMOS Transistor Theory Slides courtesy of Deming Chen Slides based on the initial set from David Harris CMOS VLSI Design Outline q q q q q q q Introduction MOS Capacitor nmos I-V Characteristics
Lecture 5: CMOS Transistor Theory Slides courtesy of Deming Chen Slides based on the initial set from David Harris CMOS VLSI Design Outline q q q q q q q Introduction MOS Capacitor nmos I-V Characteristics
The Devices: MOS Transistors
 The Devices: MOS Transistors References: Semiconductor Device Fundamentals, R. F. Pierret, Addison-Wesley Digital Integrated Circuits: A Design Perspective, J. Rabaey et.al. Prentice Hall NMOS Transistor
The Devices: MOS Transistors References: Semiconductor Device Fundamentals, R. F. Pierret, Addison-Wesley Digital Integrated Circuits: A Design Perspective, J. Rabaey et.al. Prentice Hall NMOS Transistor
CMPEN 411 VLSI Digital Circuits. Lecture 03: MOS Transistor
 CMPEN 411 VLSI Digital Circuits Lecture 03: MOS Transistor Kyusun Choi [Adapted from Rabaey s Digital Integrated Circuits, Second Edition, 2003 J. Rabaey, A. Chandrakasan, B. Nikolic] CMPEN 411 L03 S.1
CMPEN 411 VLSI Digital Circuits Lecture 03: MOS Transistor Kyusun Choi [Adapted from Rabaey s Digital Integrated Circuits, Second Edition, 2003 J. Rabaey, A. Chandrakasan, B. Nikolic] CMPEN 411 L03 S.1
MOS Transistor I-V Characteristics and Parasitics
 ECEN454 Digital Integrated Circuit Design MOS Transistor I-V Characteristics and Parasitics ECEN 454 Facts about Transistors So far, we have treated transistors as ideal switches An ON transistor passes
ECEN454 Digital Integrated Circuit Design MOS Transistor I-V Characteristics and Parasitics ECEN 454 Facts about Transistors So far, we have treated transistors as ideal switches An ON transistor passes
Lecture 11: MOSFET Modeling
 Digital Integrated Circuits (83-313) Lecture 11: MOSFET ing Semester B, 2016-17 Lecturer: Dr. Adam Teman TAs: Itamar Levi, Robert Giterman 18 June 2017 Disclaimer: This course was prepared, in its entirety,
Digital Integrated Circuits (83-313) Lecture 11: MOSFET ing Semester B, 2016-17 Lecturer: Dr. Adam Teman TAs: Itamar Levi, Robert Giterman 18 June 2017 Disclaimer: This course was prepared, in its entirety,
Physics-based compact model for ultimate FinFETs
 Physics-based compact model for ultimate FinFETs Ashkhen YESAYAN, Nicolas CHEVILLON, Fabien PREGALDINY, Morgan MADEC, Christophe LALLEMENT, Jean-Michel SALLESE nicolas.chevillon@iness.c-strasbourg.fr Research
Physics-based compact model for ultimate FinFETs Ashkhen YESAYAN, Nicolas CHEVILLON, Fabien PREGALDINY, Morgan MADEC, Christophe LALLEMENT, Jean-Michel SALLESE nicolas.chevillon@iness.c-strasbourg.fr Research
MOSFET Model with Simple Extraction Procedures, Suitable for Sensitive Analog Simulations
 ROMANIAN JOURNAL OF INFORMATION SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY Volume 10, Number 2, 2007, 189 197 MOSFET Model with Simple Extraction Procedures, Suitable for Sensitive Analog Simulations S. EFTIMIE 1, ALEX. RUSU
ROMANIAN JOURNAL OF INFORMATION SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY Volume 10, Number 2, 2007, 189 197 MOSFET Model with Simple Extraction Procedures, Suitable for Sensitive Analog Simulations S. EFTIMIE 1, ALEX. RUSU
Lecture #27. The Short Channel Effect (SCE)
 Lecture #27 ANNOUNCEMENTS Design Project: Your BJT design should meet the performance specifications to within 10% at both 300K and 360K. ( β dc > 45, f T > 18 GHz, V A > 9 V and V punchthrough > 9 V )
Lecture #27 ANNOUNCEMENTS Design Project: Your BJT design should meet the performance specifications to within 10% at both 300K and 360K. ( β dc > 45, f T > 18 GHz, V A > 9 V and V punchthrough > 9 V )
AS METAL OXIDE SEMICONDUCTOR field-effect
 2410 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON ELECTRON DEVICES, VOL. 60, NO. 7, JULY 2013 Quasi-Ballistic Transport Model for Graphene Field-Effect Transistor Guangxi Hu, Member, IEEE, Shuyan Hu, Ran Liu, Lingli Wang, Member,
2410 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON ELECTRON DEVICES, VOL. 60, NO. 7, JULY 2013 Quasi-Ballistic Transport Model for Graphene Field-Effect Transistor Guangxi Hu, Member, IEEE, Shuyan Hu, Ran Liu, Lingli Wang, Member,
Today s lecture. EE141- Spring 2003 Lecture 4. Design Rules CMOS Inverter MOS Transistor Model
 - Spring 003 Lecture 4 Design Rules CMOS Inverter MOS Transistor Model Today s lecture Design Rules The CMOS inverter at a glance An MOS transistor model for manual analysis Important! Labs start next
- Spring 003 Lecture 4 Design Rules CMOS Inverter MOS Transistor Model Today s lecture Design Rules The CMOS inverter at a glance An MOS transistor model for manual analysis Important! Labs start next
Lecture 29 - The Long Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor (cont.) April 20, 2007
 6.720J/3.43J - Integrated Microelectronic Devices - Spring 2007 Lecture 29-1 Lecture 29 - The Long Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor (cont.) April 20, 2007 Contents: 1. Non-ideal and second-order
6.720J/3.43J - Integrated Microelectronic Devices - Spring 2007 Lecture 29-1 Lecture 29 - The Long Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor (cont.) April 20, 2007 Contents: 1. Non-ideal and second-order
Lecture 3: CMOS Transistor Theory
 Lecture 3: CMOS Transistor Theory Outline Introduction MOS Capacitor nmos I-V Characteristics pmos I-V Characteristics Gate and Diffusion Capacitance 2 Introduction So far, we have treated transistors
Lecture 3: CMOS Transistor Theory Outline Introduction MOS Capacitor nmos I-V Characteristics pmos I-V Characteristics Gate and Diffusion Capacitance 2 Introduction So far, we have treated transistors
Practice 3: Semiconductors
 Practice 3: Semiconductors Digital Electronic Circuits Semester A 2012 VLSI Fabrication Process VLSI Very Large Scale Integration The ability to fabricate many devices on a single substrate within a given
Practice 3: Semiconductors Digital Electronic Circuits Semester A 2012 VLSI Fabrication Process VLSI Very Large Scale Integration The ability to fabricate many devices on a single substrate within a given
Operation and Modeling of. The MOS Transistor. Second Edition. Yannis Tsividis Columbia University. New York Oxford OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS
 Operation and Modeling of The MOS Transistor Second Edition Yannis Tsividis Columbia University New York Oxford OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS CONTENTS Chapter 1 l.l 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 Chapter 2 2.1 2.2
Operation and Modeling of The MOS Transistor Second Edition Yannis Tsividis Columbia University New York Oxford OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS CONTENTS Chapter 1 l.l 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 Chapter 2 2.1 2.2
Device Models (PN Diode, MOSFET )
 Device Models (PN Diode, MOSFET ) Instructor: Steven P. Levitan steve@ece.pitt.edu TA: Gayatri Mehta, José Martínez Book: Digital Integrated Circuits: A Design Perspective; Jan Rabaey Lab Notes: Handed
Device Models (PN Diode, MOSFET ) Instructor: Steven P. Levitan steve@ece.pitt.edu TA: Gayatri Mehta, José Martínez Book: Digital Integrated Circuits: A Design Perspective; Jan Rabaey Lab Notes: Handed
Advanced Compact Models for MOSFETs
 Advanced Compact Models for MOSFETs Christian Enz, Carlos Galup-Montoro, Gennady Gildenblat, Chenming Hu, Ronald van Langevelde, Mitiko Miura-Mattausch, Rafael Rios, Chih-Tang (Tom) Sah Josef Watts (editor)
Advanced Compact Models for MOSFETs Christian Enz, Carlos Galup-Montoro, Gennady Gildenblat, Chenming Hu, Ronald van Langevelde, Mitiko Miura-Mattausch, Rafael Rios, Chih-Tang (Tom) Sah Josef Watts (editor)
The HV-EKV MOSFET Model
 The HV-EKV MOSFET Model Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL), Switzerland EPFL Team Yogesh Singh Chauhan, Costin Anghel, Francois Krummenacher, Adrian Mihai Ionescu and Michel Declercq CMC Meeting,
The HV-EKV MOSFET Model Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL), Switzerland EPFL Team Yogesh Singh Chauhan, Costin Anghel, Francois Krummenacher, Adrian Mihai Ionescu and Michel Declercq CMC Meeting,
VLSI Design The MOS Transistor
 VLSI Design The MOS Transistor Frank Sill Torres Universidade Federal de Minas Gerais (UFMG), Brazil VLSI Design: CMOS Technology 1 Outline Introduction MOS Capacitor nmos I-V Characteristics pmos I-V
VLSI Design The MOS Transistor Frank Sill Torres Universidade Federal de Minas Gerais (UFMG), Brazil VLSI Design: CMOS Technology 1 Outline Introduction MOS Capacitor nmos I-V Characteristics pmos I-V
Lecture 28 - The Long Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor (cont.) April 18, 2007
 6.720J/3.43J - Integrated Microelectronic Devices - Spring 2007 Lecture 28-1 Lecture 28 - The Long Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor (cont.) April 18, 2007 Contents: 1. Second-order and
6.720J/3.43J - Integrated Microelectronic Devices - Spring 2007 Lecture 28-1 Lecture 28 - The Long Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor (cont.) April 18, 2007 Contents: 1. Second-order and
Lecture 30 The Short Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor. November 15, 2002
 6.720J/3.43J Integrated Microelectronic Devices Fall 2002 Lecture 30 1 Lecture 30 The Short Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor November 15, 2002 Contents: 1. Short channel effects Reading
6.720J/3.43J Integrated Microelectronic Devices Fall 2002 Lecture 30 1 Lecture 30 The Short Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor November 15, 2002 Contents: 1. Short channel effects Reading
Lecture 4: CMOS Transistor Theory
 Introduction to CMOS VLSI Design Lecture 4: CMOS Transistor Theory David Harris, Harvey Mudd College Kartik Mohanram and Steven Levitan University of Pittsburgh Outline q Introduction q MOS Capacitor q
Introduction to CMOS VLSI Design Lecture 4: CMOS Transistor Theory David Harris, Harvey Mudd College Kartik Mohanram and Steven Levitan University of Pittsburgh Outline q Introduction q MOS Capacitor q
EKV MOS Transistor Modelling & RF Application
 HP-RF MOS Modelling Workshop, Munich, February 15-16, 1999 EKV MOS Transistor Modelling & RF Application Matthias Bucher, Wladek Grabinski Electronics Laboratory (LEG) Swiss Federal Institute of Technology,
HP-RF MOS Modelling Workshop, Munich, February 15-16, 1999 EKV MOS Transistor Modelling & RF Application Matthias Bucher, Wladek Grabinski Electronics Laboratory (LEG) Swiss Federal Institute of Technology,
Lecture 12: MOSFET Devices
 Lecture 12: MOSFET Devices Gu-Yeon Wei Division of Engineering and Applied Sciences Harvard University guyeon@eecs.harvard.edu Wei 1 Overview Reading S&S: Chapter 5.1~5.4 Supplemental Reading Background
Lecture 12: MOSFET Devices Gu-Yeon Wei Division of Engineering and Applied Sciences Harvard University guyeon@eecs.harvard.edu Wei 1 Overview Reading S&S: Chapter 5.1~5.4 Supplemental Reading Background
N Channel MOSFET level 3
 N Channel MOSFET level 3 mosn3 NSource NBulk NSource NBulk NSource NBulk NSource (a) (b) (c) (d) NBulk Figure 1: MOSFET Types Form: mosn3: instance name n 1 n n 3 n n 1 is the drain node, n is the gate
N Channel MOSFET level 3 mosn3 NSource NBulk NSource NBulk NSource NBulk NSource (a) (b) (c) (d) NBulk Figure 1: MOSFET Types Form: mosn3: instance name n 1 n n 3 n n 1 is the drain node, n is the gate
The Evolution of Theory on Drain Current Saturation Mechanism of MOSFETs from the Early Days to the Present Day
 The Evolution of Theory on Drain Current Saturation Mechanism of MOSFETs from the Early Days to the Present Day Peizhen Yang 1, W.S. Lau 1, Seow Wei Lai 2, V.L. Lo 2, S.Y. Siah 2 and L. Chan 2 3 1 Nanyang
The Evolution of Theory on Drain Current Saturation Mechanism of MOSFETs from the Early Days to the Present Day Peizhen Yang 1, W.S. Lau 1, Seow Wei Lai 2, V.L. Lo 2, S.Y. Siah 2 and L. Chan 2 3 1 Nanyang
Essential Physics of Carrier Transport in Nanoscale MOSFETs
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON ELECTRON DEVICES, VOL. 49, NO. 1, JANUARY 2002 133 Essential Physics of Carrier Transport in Nanoscale MOSFETs Mark Lundstrom, Fellow, IEEE, and Zhibin Ren Abstract The device physics
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON ELECTRON DEVICES, VOL. 49, NO. 1, JANUARY 2002 133 Essential Physics of Carrier Transport in Nanoscale MOSFETs Mark Lundstrom, Fellow, IEEE, and Zhibin Ren Abstract The device physics
MOS Transistor Theory
 CHAPTER 3 MOS Transistor Theory Outline 2 1. Introduction 2. Ideal I-V Characteristics 3. Nonideal I-V Effects 4. C-V Characteristics 5. DC Transfer Characteristics 6. Switch-level RC Delay Models MOS
CHAPTER 3 MOS Transistor Theory Outline 2 1. Introduction 2. Ideal I-V Characteristics 3. Nonideal I-V Effects 4. C-V Characteristics 5. DC Transfer Characteristics 6. Switch-level RC Delay Models MOS
EKV based L-DMOS Model update including internal temperatures
 ROBUSPIC (IST-507653) Deliverable D1.2 EKV based L-DMOS Model update including internal temperatures Yogesh Singh Chauhan, Costin Anghel, Francois Krummenacher, Adrian Ionescu and Michel Declercq Ecole
ROBUSPIC (IST-507653) Deliverable D1.2 EKV based L-DMOS Model update including internal temperatures Yogesh Singh Chauhan, Costin Anghel, Francois Krummenacher, Adrian Ionescu and Michel Declercq Ecole
nmosfet Schematic Four structural masks: Field, Gate, Contact, Metal. Reverse doping polarities for pmosfet in N-well.
 nmosfet Schematic Four structural masks: Field, Gate, Contact, Metal. Reverse doping polarities for pmosfet in N-well. nmosfet Schematic 0 y L n + source n + drain depletion region polysilicon gate x z
nmosfet Schematic Four structural masks: Field, Gate, Contact, Metal. Reverse doping polarities for pmosfet in N-well. nmosfet Schematic 0 y L n + source n + drain depletion region polysilicon gate x z
Physics of Nanoscale Transistors
 Physics of Nanoscale ransistors Mark Electrical and Computer Engineering University, West Lafayette, IN 1. Introduction 2. he Ballistic MOSFE 3. Scattering heory of the MOSFE 4. Beyond the Si MOSFE 5.
Physics of Nanoscale ransistors Mark Electrical and Computer Engineering University, West Lafayette, IN 1. Introduction 2. he Ballistic MOSFE 3. Scattering heory of the MOSFE 4. Beyond the Si MOSFE 5.
ECE315 / ECE515 Lecture-2 Date:
 Lecture-2 Date: 04.08.2016 NMOS I/V Characteristics Discussion on I/V Characteristics MOSFET Second Order Effect NMOS I-V Characteristics ECE315 / ECE515 Gradual Channel Approximation: Cut-off Linear/Triode
Lecture-2 Date: 04.08.2016 NMOS I/V Characteristics Discussion on I/V Characteristics MOSFET Second Order Effect NMOS I-V Characteristics ECE315 / ECE515 Gradual Channel Approximation: Cut-off Linear/Triode
ECE 415/515 ANALOG INTEGRATED CIRCUIT DESIGN
 ECE 415/515 ANALOG INTEGRATED CIRCUIT DESIGN CMOS PROCESS CHARACTERIZATION VISHAL SAXENA VSAXENA@UIDAHO.EDU Vishal Saxena DESIGN PARAMETERS Analog circuit designers care about: Open-loop Gain: g m r o
ECE 415/515 ANALOG INTEGRATED CIRCUIT DESIGN CMOS PROCESS CHARACTERIZATION VISHAL SAXENA VSAXENA@UIDAHO.EDU Vishal Saxena DESIGN PARAMETERS Analog circuit designers care about: Open-loop Gain: g m r o
Device Models (PN Diode, MOSFET )
 Device Models (PN Diode, MOSFET ) Instructor: Steven P. Levitan steve@ece.pitt.edu TA: Gayatri Mehta, José Martínez Book: Digital Integrated Circuits: A Design Perspective; Jan Rabaey Lab Notes: Handed
Device Models (PN Diode, MOSFET ) Instructor: Steven P. Levitan steve@ece.pitt.edu TA: Gayatri Mehta, José Martínez Book: Digital Integrated Circuits: A Design Perspective; Jan Rabaey Lab Notes: Handed
ECE-305: Fall 2017 MOS Capacitors and Transistors
 ECE-305: Fall 2017 MOS Capacitors and Transistors Pierret, Semiconductor Device Fundamentals (SDF) Chapters 15+16 (pp. 525-530, 563-599) Professor Peter Bermel Electrical and Computer Engineering Purdue
ECE-305: Fall 2017 MOS Capacitors and Transistors Pierret, Semiconductor Device Fundamentals (SDF) Chapters 15+16 (pp. 525-530, 563-599) Professor Peter Bermel Electrical and Computer Engineering Purdue
A Compact Analytical Modelling of the Electrical Characteristics of Submicron Channel MOSFETs
 ROMANIAN JOURNAL OF INFORMATION SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY Volume 11, Number 4, 2008, 383 395 A Compact Analytical Modelling of the Electrical Characteristics of Submicron Channel MOSFETs Andrei SEVCENCO,
ROMANIAN JOURNAL OF INFORMATION SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY Volume 11, Number 4, 2008, 383 395 A Compact Analytical Modelling of the Electrical Characteristics of Submicron Channel MOSFETs Andrei SEVCENCO,
ECE 305: Fall MOSFET Energy Bands
 ECE 305: Fall 2016 MOSFET Energy Bands Professor Peter Bermel Electrical and Computer Engineering Purdue University, West Lafayette, IN USA pbermel@purdue.edu Pierret, Semiconductor Device Fundamentals
ECE 305: Fall 2016 MOSFET Energy Bands Professor Peter Bermel Electrical and Computer Engineering Purdue University, West Lafayette, IN USA pbermel@purdue.edu Pierret, Semiconductor Device Fundamentals
Lecture 8: Ballistic FET I-V
 Lecture 8: Ballistic FET I-V 1 Lecture 1: Ballistic FETs Jena: 61-70 Diffusive Field Effect Transistor Source Gate L g >> l Drain Source V GS Gate Drain I D Mean free path much shorter than channel length
Lecture 8: Ballistic FET I-V 1 Lecture 1: Ballistic FETs Jena: 61-70 Diffusive Field Effect Transistor Source Gate L g >> l Drain Source V GS Gate Drain I D Mean free path much shorter than channel length
ECE 342 Electronic Circuits. 3. MOS Transistors
 ECE 342 Electronic Circuits 3. MOS Transistors Jose E. Schutt-Aine Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Illinois jschutt@emlab.uiuc.edu 1 NMOS Transistor Typically L = 0.1 to 3 m, W = 0.2 to
ECE 342 Electronic Circuits 3. MOS Transistors Jose E. Schutt-Aine Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Illinois jschutt@emlab.uiuc.edu 1 NMOS Transistor Typically L = 0.1 to 3 m, W = 0.2 to
Analytical Modeling of Threshold Voltage for a. Biaxial Strained-Si-MOSFET
 Contemporary Engineering Sciences, Vol. 4, 2011, no. 6, 249 258 Analytical Modeling of Threshold Voltage for a Biaxial Strained-Si-MOSFET Amit Chaudhry Faculty of University Institute of Engineering and
Contemporary Engineering Sciences, Vol. 4, 2011, no. 6, 249 258 Analytical Modeling of Threshold Voltage for a Biaxial Strained-Si-MOSFET Amit Chaudhry Faculty of University Institute of Engineering and
MOSFET Physics: The Long Channel Approximation
 MOSFET Physics: The ong Channel Approximation A basic n-channel MOSFET (Figure 1) consists of two heavily-doped n-type regions, the Source and Drain, that comprise the main terminals of the device. The
MOSFET Physics: The ong Channel Approximation A basic n-channel MOSFET (Figure 1) consists of two heavily-doped n-type regions, the Source and Drain, that comprise the main terminals of the device. The
EECS130 Integrated Circuit Devices
 EECS130 Integrated Circuit Devices Professor Ali Javey 10/30/2007 MOSFETs Lecture 4 Reading: Chapter 17, 19 Announcements The next HW set is due on Thursday. Midterm 2 is next week!!!! Threshold and Subthreshold
EECS130 Integrated Circuit Devices Professor Ali Javey 10/30/2007 MOSFETs Lecture 4 Reading: Chapter 17, 19 Announcements The next HW set is due on Thursday. Midterm 2 is next week!!!! Threshold and Subthreshold
ASYMMETRICAL DOUBLE GATE (ADG) MOSFETs COMPACT MODELING. M. Reyboz, O. Rozeau, T. Poiroux, P. Martin
 ASYMMETRICAL DOUBLE GATE (ADG) MOSFETs COMPACT MODELING M. Reyboz, O. Rozeau, T. Poiroux, P. Martin 005 OUTLINE I INTRODUCTION II ADG ARCHITECTURE III MODELING DIFFICULTIES I DIFFERENT WAYS OF MODELING
ASYMMETRICAL DOUBLE GATE (ADG) MOSFETs COMPACT MODELING M. Reyboz, O. Rozeau, T. Poiroux, P. Martin 005 OUTLINE I INTRODUCTION II ADG ARCHITECTURE III MODELING DIFFICULTIES I DIFFERENT WAYS OF MODELING
High Mobility Materials and Novel Device Structures for High Performance Nanoscale MOSFETs
 High Mobility Materials and Novel Device Structures for High Performance Nanoscale MOSFETs Prof. (Dr.) Tejas Krishnamohan Department of Electrical Engineering Stanford University, CA & Intel Corporation
High Mobility Materials and Novel Device Structures for High Performance Nanoscale MOSFETs Prof. (Dr.) Tejas Krishnamohan Department of Electrical Engineering Stanford University, CA & Intel Corporation
MOS Transistor Properties Review
 MOS Transistor Properties Review 1 VLSI Chip Manufacturing Process Photolithography: transfer of mask patterns to the chip Diffusion or ion implantation: selective doping of Si substrate Oxidation: SiO
MOS Transistor Properties Review 1 VLSI Chip Manufacturing Process Photolithography: transfer of mask patterns to the chip Diffusion or ion implantation: selective doping of Si substrate Oxidation: SiO
Long Channel MOS Transistors
 Long Channel MOS Transistors The theory developed for MOS capacitor (HO #2) can be directly extended to Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect transistors (MOSFET) by considering the following structure:
Long Channel MOS Transistors The theory developed for MOS capacitor (HO #2) can be directly extended to Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect transistors (MOSFET) by considering the following structure:
COMPACT GRAPHENE FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTOR MODELING WITH QUANTUM CAPACITANCE EFFECTS
 COMPACT GRAPHENE FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTOR MODELING WITH QUANTUM CAPACITANCE EFFECTS Arya Raj K. and Bala Tripura Sundari B. Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering, Amrita Viswa Vidyapeetham,
COMPACT GRAPHENE FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTOR MODELING WITH QUANTUM CAPACITANCE EFFECTS Arya Raj K. and Bala Tripura Sundari B. Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering, Amrita Viswa Vidyapeetham,
ECE 546 Lecture 10 MOS Transistors
 ECE 546 Lecture 10 MOS Transistors Spring 2018 Jose E. Schutt-Aine Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Illinois jesa@illinois.edu NMOS Transistor NMOS Transistor N-Channel MOSFET Built on p-type
ECE 546 Lecture 10 MOS Transistors Spring 2018 Jose E. Schutt-Aine Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Illinois jesa@illinois.edu NMOS Transistor NMOS Transistor N-Channel MOSFET Built on p-type
Comparative Analysis of Practical Threshold Voltage Extraction Techniques for CMOS. Yu-Hsing Cheng ON Semiconductor October 15, 2018
 Comparative Analysis of Practical Threshold Voltage Extraction Techniques for CMOS and LDMOS Devices in 180 nm Technology Yu-Hsing Cheng ON Semiconductor October 15, 2018 Outline Overview and Background
Comparative Analysis of Practical Threshold Voltage Extraction Techniques for CMOS and LDMOS Devices in 180 nm Technology Yu-Hsing Cheng ON Semiconductor October 15, 2018 Outline Overview and Background
The Devices. Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective. Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic. July 30, 2002
 igital Integrated Circuits A esign Perspective Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic The evices July 30, 2002 Goal of this chapter Present intuitive understanding of device operation Introduction
igital Integrated Circuits A esign Perspective Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic The evices July 30, 2002 Goal of this chapter Present intuitive understanding of device operation Introduction
CMOS INVERTER. Last Lecture. Metrics for qualifying digital circuits. »Cost» Reliability» Speed (delay)»performance
 CMOS INVERTER Last Lecture Metrics for qualifying digital circuits»cost» Reliability» Speed (delay)»performance 1 Today s lecture The CMOS inverter at a glance An MOS transistor model for manual analysis
CMOS INVERTER Last Lecture Metrics for qualifying digital circuits»cost» Reliability» Speed (delay)»performance 1 Today s lecture The CMOS inverter at a glance An MOS transistor model for manual analysis
ANALYSIS AND MODELING OF 1/f NOISE IN IGZO TFTS
 ANALYSIS AND MODELING OF 1/f NOISE IN IGZO TFTS Gerard Uriarte, Wondwosen E. Muhea, Benjamin Iñiguez Dep. of Electronic Engineering, University Rovira i Virgili, Tarragona (Spain) Thomas Gneiting AdMOS
ANALYSIS AND MODELING OF 1/f NOISE IN IGZO TFTS Gerard Uriarte, Wondwosen E. Muhea, Benjamin Iñiguez Dep. of Electronic Engineering, University Rovira i Virgili, Tarragona (Spain) Thomas Gneiting AdMOS
Fundamentals of the Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor
 Triode Working FET Fundamentals of the Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor The characteristics of energy bands as a function of applied voltage. Surface inversion. The expression for the
Triode Working FET Fundamentals of the Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor The characteristics of energy bands as a function of applied voltage. Surface inversion. The expression for the
Lecture 04 Review of MOSFET
 ECE 541/ME 541 Microelectronic Fabrication Techniques Lecture 04 Review of MOSFET Zheng Yang (ERF 3017, email: yangzhen@uic.edu) What is a Transistor? A Switch! An MOS Transistor V GS V T V GS S Ron D
ECE 541/ME 541 Microelectronic Fabrication Techniques Lecture 04 Review of MOSFET Zheng Yang (ERF 3017, email: yangzhen@uic.edu) What is a Transistor? A Switch! An MOS Transistor V GS V T V GS S Ron D
Analytical modelling and performance analysis of Double-Gate MOSFET-based circuit including ballistic/quasi-ballistic effects
 Analytical modelling and performance analysis of Double-Gate MOSFET-based circuit including ballistic/quasi-ballistic effects Sebastien Martinie, Daniela Munteanu, Gilles Le Carval, Jean-Luc Autran To
Analytical modelling and performance analysis of Double-Gate MOSFET-based circuit including ballistic/quasi-ballistic effects Sebastien Martinie, Daniela Munteanu, Gilles Le Carval, Jean-Luc Autran To
The Devices. Jan M. Rabaey
 The Devices Jan M. Rabaey Goal of this chapter Present intuitive understanding of device operation Introduction of basic device equations Introduction of models for manual analysis Introduction of models
The Devices Jan M. Rabaey Goal of this chapter Present intuitive understanding of device operation Introduction of basic device equations Introduction of models for manual analysis Introduction of models
This article has been accepted and published on J-STAGE in advance of copyediting. Content is final as presented.
 This article has been accepted and published on J-STAGE in advance of copyediting. Content is final as presented. References IEICE Electronics Express, Vol.* No.*,*-* Effects of Gamma-ray radiation on
This article has been accepted and published on J-STAGE in advance of copyediting. Content is final as presented. References IEICE Electronics Express, Vol.* No.*,*-* Effects of Gamma-ray radiation on
ELEC 3908, Physical Electronics, Lecture 23. The MOSFET Square Law Model
 ELEC 3908, Physical Electronics, Lecture 23 The MOSFET Square Law Model Lecture Outline As with the diode and bipolar, have looked at basic structure of the MOSFET and now turn to derivation of a current
ELEC 3908, Physical Electronics, Lecture 23 The MOSFET Square Law Model Lecture Outline As with the diode and bipolar, have looked at basic structure of the MOSFET and now turn to derivation of a current
Lecture 9 MOSFET(II) MOSFET I V CHARACTERISTICS(contd.)
 Lecture 9 MOSFET(II) MOSFET I V CHARACTERISTICS(contd.) Outline 1. The saturation region 2. Backgate characteristics Reading Assignment: Howe and Sodini, Chapter 4, Section 4.4 6.012 Spring 2009 Lecture
Lecture 9 MOSFET(II) MOSFET I V CHARACTERISTICS(contd.) Outline 1. The saturation region 2. Backgate characteristics Reading Assignment: Howe and Sodini, Chapter 4, Section 4.4 6.012 Spring 2009 Lecture
EE 330 Lecture 16. Devices in Semiconductor Processes. MOS Transistors
 EE 330 Lecture 16 Devices in Semiconductor Processes MOS Transistors Review from Last Time Model Summary I D I V DS V S I B V BS = 0 0 VS VT W VDS ID = μcox VS VT VDS VS V VDS VS VT L T < W μc ( V V )
EE 330 Lecture 16 Devices in Semiconductor Processes MOS Transistors Review from Last Time Model Summary I D I V DS V S I B V BS = 0 0 VS VT W VDS ID = μcox VS VT VDS VS V VDS VS VT L T < W μc ( V V )
ECE 305 Exam 5 SOLUTIONS: Spring 2015 April 17, 2015 Mark Lundstrom Purdue University
 NAME: PUID: : ECE 305 Exam 5 SOLUTIONS: April 17, 2015 Mark Lundstrom Purdue University This is a closed book exam. You may use a calculator and the formula sheet at the end of this exam. Following the
NAME: PUID: : ECE 305 Exam 5 SOLUTIONS: April 17, 2015 Mark Lundstrom Purdue University This is a closed book exam. You may use a calculator and the formula sheet at the end of this exam. Following the
Spring Semester 2012 Final Exam
 Spring Semester 2012 Final Exam Note: Show your work, underline results, and always show units. Official exam time: 2.0 hours; an extension of at least 1.0 hour will be granted to anyone. Materials parameters
Spring Semester 2012 Final Exam Note: Show your work, underline results, and always show units. Official exam time: 2.0 hours; an extension of at least 1.0 hour will be granted to anyone. Materials parameters
MOS Transistor Theory
 MOS Transistor Theory So far, we have viewed a MOS transistor as an ideal switch (digital operation) Reality: less than ideal EE 261 Krish Chakrabarty 1 Introduction So far, we have treated transistors
MOS Transistor Theory So far, we have viewed a MOS transistor as an ideal switch (digital operation) Reality: less than ideal EE 261 Krish Chakrabarty 1 Introduction So far, we have treated transistors
A Multi-Gate CMOS Compact Model BSIMMG
 A Multi-Gate CMOS Compact Model BSIMMG Darsen Lu, Sriramkumar Venugopalan, Tanvir Morshed, Yogesh Singh Chauhan, Chung-Hsun Lin, Mohan Dunga, Ali Niknejad and Chenming Hu University of California, Berkeley
A Multi-Gate CMOS Compact Model BSIMMG Darsen Lu, Sriramkumar Venugopalan, Tanvir Morshed, Yogesh Singh Chauhan, Chung-Hsun Lin, Mohan Dunga, Ali Niknejad and Chenming Hu University of California, Berkeley
Scattering Theory of Carrier Transport in Semiconductor Devices
 Scattering Theory of Carrier Transport in Semiconductor Devices Mark Lundstrom, Carl Huster, Kausar Banoo, and Ramesh Venugopal Purdue University School of Electrical and Computer Engineering West Lafayette,
Scattering Theory of Carrier Transport in Semiconductor Devices Mark Lundstrom, Carl Huster, Kausar Banoo, and Ramesh Venugopal Purdue University School of Electrical and Computer Engineering West Lafayette,
Prospects for Ge MOSFETs
 Prospects for Ge MOSFETs Sematech Workshop December 4, 2005 Dimitri A. Antoniadis Microsystems Technology Laboratories MIT Sematech Workshop 2005 1 Channel Transport - I D I D =WQ i (x 0 )v xo v xo : carrier
Prospects for Ge MOSFETs Sematech Workshop December 4, 2005 Dimitri A. Antoniadis Microsystems Technology Laboratories MIT Sematech Workshop 2005 1 Channel Transport - I D I D =WQ i (x 0 )v xo v xo : carrier
EE105 - Fall 2005 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits
 EE105 - Fall 005 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits ecture 7 MOS Transistor Announcements Homework 3, due today Homework 4 due next week ab this week Reading: Chapter 4 1 ecture Material ast lecture
EE105 - Fall 005 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits ecture 7 MOS Transistor Announcements Homework 3, due today Homework 4 due next week ab this week Reading: Chapter 4 1 ecture Material ast lecture
The Critical Role of Quantum Capacitance in Compact Modeling of Nano-Scaled and Nanoelectronic Devices
 The Critical Role of Quantum Capacitance in Compact Modeling of Nano-Scaled and Nanoelectronic Devices Zhiping Yu and Jinyu Zhang Institute of Microelectronics Tsinghua University, Beijing, China yuzhip@tsinghua.edu.cn
The Critical Role of Quantum Capacitance in Compact Modeling of Nano-Scaled and Nanoelectronic Devices Zhiping Yu and Jinyu Zhang Institute of Microelectronics Tsinghua University, Beijing, China yuzhip@tsinghua.edu.cn
III-V CMOS: What have we learned from HEMTs? J. A. del Alamo, D.-H. Kim 1, T.-W. Kim, D. Jin, and D. A. Antoniadis
 III-V CMOS: What have we learned from HEMTs? J. A. del Alamo, D.-H. Kim 1, T.-W. Kim, D. Jin, and D. A. Antoniadis Microsystems Technology Laboratories, MIT 1 presently with Teledyne Scientific 23rd International
III-V CMOS: What have we learned from HEMTs? J. A. del Alamo, D.-H. Kim 1, T.-W. Kim, D. Jin, and D. A. Antoniadis Microsystems Technology Laboratories, MIT 1 presently with Teledyne Scientific 23rd International
6.012 MICROELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.012 MICROELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS Answers to Exam 2 Spring 2008 Problem 1: Graded by Prof. Fonstad
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.012 MICROELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS Answers to Exam 2 Spring 2008 Problem 1: Graded by Prof. Fonstad
Section 12: Intro to Devices
 Section 12: Intro to Devices Extensive reading materials on reserve, including Robert F. Pierret, Semiconductor Device Fundamentals Bond Model of Electrons and Holes Si Si Si Si Si Si Si Si Si Silicon
Section 12: Intro to Devices Extensive reading materials on reserve, including Robert F. Pierret, Semiconductor Device Fundamentals Bond Model of Electrons and Holes Si Si Si Si Si Si Si Si Si Silicon
OMEN an atomistic and full-band quantum transport simulator for post-cmos nanodevices
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs Other Nanotechnology Publications Birck Nanotechnology Center 8-18-28 OMEN an atomistic and full-band quantum transport simulator for post-cmos nanodevices Mathieu Luisier
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs Other Nanotechnology Publications Birck Nanotechnology Center 8-18-28 OMEN an atomistic and full-band quantum transport simulator for post-cmos nanodevices Mathieu Luisier
Technische Universität Graz. Institute of Solid State Physics. 11. MOSFETs
 Technische Universität Graz Institute of Solid State Physics 11. MOSFETs Dec. 12, 2018 Gradual channel approximation accumulation depletion inversion http://lampx.tugraz.at/~hadley/psd/l10/gradualchannelapprox.php
Technische Universität Graz Institute of Solid State Physics 11. MOSFETs Dec. 12, 2018 Gradual channel approximation accumulation depletion inversion http://lampx.tugraz.at/~hadley/psd/l10/gradualchannelapprox.php
The Devices. Devices
 The The MOS Transistor Gate Oxyde Gate Source n+ Polysilicon Drain n+ Field-Oxyde (SiO 2 ) p-substrate p+ stopper Bulk Contact CROSS-SECTION of NMOS Transistor Cross-Section of CMOS Technology MOS transistors
The The MOS Transistor Gate Oxyde Gate Source n+ Polysilicon Drain n+ Field-Oxyde (SiO 2 ) p-substrate p+ stopper Bulk Contact CROSS-SECTION of NMOS Transistor Cross-Section of CMOS Technology MOS transistors
HW 5 posted due in two weeks Lab this week Midterm graded Project to be launched in week 7
 HW 5 posted due in two weeks Lab this week Midterm graded Project to be launched in week 7 2 What do digital IC designers need to know? 5 EE4 EECS4 6 3 0< V GS - V T < V DS Pinch-off 7 For (V GS V T )
HW 5 posted due in two weeks Lab this week Midterm graded Project to be launched in week 7 2 What do digital IC designers need to know? 5 EE4 EECS4 6 3 0< V GS - V T < V DS Pinch-off 7 For (V GS V T )
EE 330 Lecture 16. MOS Device Modeling p-channel n-channel comparisons Model consistency and relationships CMOS Process Flow
 EE 330 Lecture 16 MOS Device Modeling p-channel n-channel comparisons Model consistency and relationships CMOS Process Flow Review from Last Time Operation Regions by Applications Id I D 300 250 200 150
EE 330 Lecture 16 MOS Device Modeling p-channel n-channel comparisons Model consistency and relationships CMOS Process Flow Review from Last Time Operation Regions by Applications Id I D 300 250 200 150
EE105 - Fall 2006 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits
 EE105 - Fall 2006 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits Prof. Jan M. Rabaey (jan@eecs) Lecture 7: MOS Transistor Some Administrative Issues Lab 2 this week Hw 2 due on We Hw 3 will be posted same day MIDTERM
EE105 - Fall 2006 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits Prof. Jan M. Rabaey (jan@eecs) Lecture 7: MOS Transistor Some Administrative Issues Lab 2 this week Hw 2 due on We Hw 3 will be posted same day MIDTERM
MIXDES 2001 Zakopane, POLAND June 2001
 8 th International Conference ADVANCEMENTS IN DC AND RF MOSFET MODELING WITH THE EPFL-EKV CHARGE BASED MODEL,;(' '(6,* J.-M. SALLESE *, W. GRABINSKI **, A.S. PORRET *, M. BUCHER +, C. LALLEMENT ++, F.
8 th International Conference ADVANCEMENTS IN DC AND RF MOSFET MODELING WITH THE EPFL-EKV CHARGE BASED MODEL,;(' '(6,* J.-M. SALLESE *, W. GRABINSKI **, A.S. PORRET *, M. BUCHER +, C. LALLEMENT ++, F.
Lecture 13 MOSFET as an amplifier with an introduction to MOSFET small-signal model and small-signal schematics. Lena Peterson
 Lecture 13 MOSFET as an amplifier with an introduction to MOSFET small-signal model and small-signal schematics Lena Peterson 2015-10-13 Outline (1) Why is the CMOS inverter gain not infinite? Large-signal
Lecture 13 MOSFET as an amplifier with an introduction to MOSFET small-signal model and small-signal schematics Lena Peterson 2015-10-13 Outline (1) Why is the CMOS inverter gain not infinite? Large-signal
Final Examination EE 130 December 16, 1997 Time allotted: 180 minutes
 Final Examination EE 130 December 16, 1997 Time allotted: 180 minutes Problem 1: Semiconductor Fundamentals [30 points] A uniformly doped silicon sample of length 100µm and cross-sectional area 100µm 2
Final Examination EE 130 December 16, 1997 Time allotted: 180 minutes Problem 1: Semiconductor Fundamentals [30 points] A uniformly doped silicon sample of length 100µm and cross-sectional area 100µm 2
EE5311- Digital IC Design
 EE5311- Digital IC Design Module 1 - The Transistor Janakiraman V Assistant Professor Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Madras Chennai October 28, 2017 Janakiraman, IITM
EE5311- Digital IC Design Module 1 - The Transistor Janakiraman V Assistant Professor Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Madras Chennai October 28, 2017 Janakiraman, IITM
ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals
 ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 5: January 25, 2018 MOS Operating Regions, pt. 1 Lecture Outline! 3 Regions of operation for MOSFET " Subthreshold " Linear " Saturation!
ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 5: January 25, 2018 MOS Operating Regions, pt. 1 Lecture Outline! 3 Regions of operation for MOSFET " Subthreshold " Linear " Saturation!
Investigation of the Thermal Noise of MOS Transistors under Analog and RF Operating Conditions
 Investigation of the Thermal Noise of MOS Transistors under Analog and RF Operating Conditions Ralf Brederlow 1, Georg Wenig 2, and Roland Thewes 1 1 Infineon Technologies, Corporate Research, 2 Technical
Investigation of the Thermal Noise of MOS Transistors under Analog and RF Operating Conditions Ralf Brederlow 1, Georg Wenig 2, and Roland Thewes 1 1 Infineon Technologies, Corporate Research, 2 Technical
EE 330 Lecture 16. MOSFET Modeling CMOS Process Flow
 EE 330 Lecture 16 MOSFET Modeling CMOS Process Flow Model Extensions 300 Id 250 200 150 100 50 300 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 Vds Existing Model 250 200 Id 150 100 50 Slope is not 0 0 0 1 2 3 4 Actual Device Vds Model
EE 330 Lecture 16 MOSFET Modeling CMOS Process Flow Model Extensions 300 Id 250 200 150 100 50 300 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 Vds Existing Model 250 200 Id 150 100 50 Slope is not 0 0 0 1 2 3 4 Actual Device Vds Model
Drift-diffusion model for single layer transition metal dichalcogenide field-effect transistors
 Drift-diffusion model for single layer transition metal dichalcogenide field-effect transistors David Jiménez Departament d'enginyeria Electrònica, Escola d'enginyeria, Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona,
Drift-diffusion model for single layer transition metal dichalcogenide field-effect transistors David Jiménez Departament d'enginyeria Electrònica, Escola d'enginyeria, Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona,
II III IV V VI B C N. Al Si P S. Zn Ga Ge As Se Cd In Sn Sb Te. Silicon (Si) the dominating material in IC manufacturing
 II III IV V VI B N Al Si P S Zn Ga Ge As Se d In Sn Sb Te Silicon (Si) the dominating material in I manufacturing ompound semiconductors III - V group: GaAs GaN GaSb GaP InAs InP InSb... The Energy Band
II III IV V VI B N Al Si P S Zn Ga Ge As Se d In Sn Sb Te Silicon (Si) the dominating material in I manufacturing ompound semiconductors III - V group: GaAs GaN GaSb GaP InAs InP InSb... The Energy Band
Section 12: Intro to Devices
 Section 12: Intro to Devices Extensive reading materials on reserve, including Robert F. Pierret, Semiconductor Device Fundamentals EE143 Ali Javey Bond Model of Electrons and Holes Si Si Si Si Si Si Si
Section 12: Intro to Devices Extensive reading materials on reserve, including Robert F. Pierret, Semiconductor Device Fundamentals EE143 Ali Javey Bond Model of Electrons and Holes Si Si Si Si Si Si Si
EE105 Fall 2014 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits. NMOS Transistor Capacitances: Saturation Region
 EE105 Fall 014 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits Prof. Ming C. Wu wu@eecs.berkeley.edu 511 Sutardja Dai Hall (SDH) 1 NMOS Transistor Capacitances: Saturation Region Drain no longer connected to channel
EE105 Fall 014 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits Prof. Ming C. Wu wu@eecs.berkeley.edu 511 Sutardja Dai Hall (SDH) 1 NMOS Transistor Capacitances: Saturation Region Drain no longer connected to channel
