Nanoscale CMOS Design Issues
|
|
|
- Eleanore Hodge
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Nanoscale CMOS Design Issues Jaydeep P. Kulkarni Assistant Professor, ECE Department The University of Texas at Austin Fall, 2017, VLSI-1 Class
2 Transistor I-V Review Agenda Non-ideal Transistor Behavior Velocity Saturation Channel Length Modulation Body Effect Leakage Temperature Sensitivity Process and Environmental Variations Process Corners 6T SRAM scaling challenges and design techniques Summary University of Texas, Austin Jaydeep P. Kulkarni 2
3 Ideal Transistor I-V 0 Vgs Vt cutoff V I ds ds Vgs V t V linear 2 ds Vds Vdsat V 2 gs Vt Vds Vdsat saturation 2 Shockley 1 st order transistor models 180 nm TSMC process Ideal Models β = 155(W/L) ma/v 2 V t = 0.4 V V DD = 1.8 V University of Texas, Austin Jaydeep P. Kulkarni 3
4 Simulated nmos I-V Plot 180 nm TSMC process BSIM 3v3 SPICE models What differs? Less ON current No square law Current increases in saturation I ds (A) 250 V gs = V gs = 1.5 V gs = V gs = V gs = V ds University of Texas, Austin Jaydeep P. Kulkarni 4
5 Velocity Saturation We assumed carrier velocity is proportional to E-field v = μe lat = μv ds /L At high fields, this ceases to be true Carriers scatter off atoms Velocity reaches v sat Electrons: 6-10 x 10 6 cm/s Holes: 4-8 x 10 6 cm/s Better model sat sat / 2 μe lat v vsat μesat Elat 1 E sat 0 0 slope = E sat E lat 2E sat 3E sat University of Texas, Austin Jaydeep P. Kulkarni 5
6 Velocity saturation I-V Effects Ideal transistor ON current increases with V DD 2 W V V I C V V L 2 2 gs t ds ox gs t Velocity-saturated ON current increases with V DD I C W V V v ds ox gs t Real transistors are partially velocity saturated Approximate with α -power law model I ds V DD α 1 < α < 2 determined empirically 2 max 2 University of Texas, Austin Jaydeep P. Kulkarni 6
7 a-power Model 0 Vgs Vt cutoff Vds Ids Idsat Vds Vdsat linear Vdsat Idsat Vds Vdsat saturation I P V V 2 dsat c gs t a /2 V P V V dsat v gs t a I ds (A) 400 Simulated a-law Shockley V gs = 1.8 V gs = 1.5 V gs = 1.2 V gs = 0.9 V gs = 0.6 V ds University of Texas, Austin Jaydeep P. Kulkarni 7
8 Channel Length Modulation Reverse-biased p-n junctions form a depletion region Region between n and p with no carriers Width of depletion L d region grows with reverse bias L eff = L L d Shorter L eff gives more current I ds increases with V ds Even in saturation GND Source V DD Gate V DD Drain Depletion Region Width: L d n+ L L eff n+ p GND bulk Si University of Texas, Austin Jaydeep P. Kulkarni 8
9 Channel Length Modulation I-V I ds (A) 400 I V V lv ds gs t ds l = channel length modulation coefficient not feature size Empirically fit to I-V characteristics V gs = 1.2 V gs = 1.8 V gs = 1.5 V gs = 0.9 V gs = V ds λ calculated by substituting I DS = 0, and finding the 1/V DS X- intercept University of Texas, Austin Jaydeep P. Kulkarni 9
10 Body Effect V t : gate voltage necessary to invert channel Increases if source voltage increases because source is connected to the channel Increase in V t with V s is called the body effect University of Texas, Austin Jaydeep P. Kulkarni 10
11 Body Effect Model V V g f V f t t0 s sb s f s = surface potential at threshold N A fs 2vT ln n i Depends on doping level N A And intrinsic carrier concentration n i g = body effect coefficient g t ox ox 2q N si A 2q N C si ox A University of Texas, Austin Jaydeep P. Kulkarni 11
12 OFF Transistor Behavior What about current in cutoff? Simulated results don t match measurements What differs? Current doesn t go to 0 in cutoff I ds 1 ma 100 A 10 A 1 A 100 na 10 na 1 na 100 pa 10 pa Subthreshold Region Subthreshold Slope V t Saturation Region V ds = 1.8 Sub-threshold region very attractive for low voltage operation but process variation sensitive V gs University of Texas, Austin Jaydeep P. Kulkarni 12
13 Leakage Sources Subthreshold conduction Transistors can t abruptly turn ON or OFF Junction leakage Reverse-biased PN junction diode current Gate leakage Tunneling through ultrathin gate dielectric Subthreshold leakage is the biggest source in modern transistors University of Texas, Austin Jaydeep P. Kulkarni 13
14 Subthreshold Leakage Subthreshold leakage exponential with V gs I ds I ds e nvt 1 e 0 V V V v gs t ds T ds0 vte η is process dependent, typically , increases with temp. Subthreshold Swing: inverse of sub-threshold slope MOSFETs: Minimum S.S. limit is 60mV/Decade I 1 ma 100 A 10 A 1 A 100 na 10 na 1 na 100 pa 10 pa I ds Subthreshold Region Subthreshold Slope V t Saturation Region V ds = Higher S.S. slope translates to higher OFF state leakage, lower I ON /I OFF Quest to develop Steep sub-threshold slope transistors (e.g. Tunnel FETs) V gs University of Texas, Austin Jaydeep P. Kulkarni 14
15 DIBL (Drain Induced Barrier Lowering) Drain-Induced Barrier Lowering Drain voltage lowers V t V t Vt V ds High drain voltage causes subthreshold leakage to increase. DIBL due to increase in depletion region width near the drain junction with drain voltage increase DIBL is quantified in terms of mv of change in V T for 1V change in V DS. Although unitless, it is typically measured as mv/v University of Texas, Austin Jaydeep P. Kulkarni 15
16 Junction Leakage Reverse-biased p-n junctions have some leakage VD T I e v D I S 1 I s depends on doping levels And area and perimeter of diffusion regions Typically < 1 fa/m 2 p+ n+ n+ p+ p+ n+ p substrate n well University of Texas, Austin Jaydeep P. Kulkarni 16
17 Gate Leakage Carriers may tunnel thorough very thin gate oxides Predicted tunneling current (from [Song01]) Negligible for older processes Critically important for advanced process nodes 10 9 t ox JG (A/cm 2 ) V DD trend 0.6 nm 0.8 nm 1.0 nm 1.2 nm 1.5 nm 1.9 nm V DD Source: Intel University of Texas, Austin Jaydeep P. Kulkarni 17
18 Temperature Dependence Linear region current ZTC Saturation region current ITD Effect of temperature on mobility and threshold voltage Ring oscillator frequency variation Ref: M. Cho, CICC, 2012 Elevated temperature reduces both mobility and threshold voltage At high Vcc, Vt change has less impact on gate overdrive, so mobility degradation dominates lower current with temperature increase (in relatively old technology) At lower Vcc, Vt reduction increases (Vgs-Vt) term more than the mobility degradation higher current with temperature increase (known as Inverse Temperature Dependence) University of Texas, Austin Jaydeep P. Kulkarni 18
19 pmos slow fast Process Variations Transistors have uncertainty in parameters Process: L eff, V t, t ox of nmos and pmos Vary around typical (T) values Fast (F) L eff : short V t : low t ox : thin SF SS TT FF FS Slow (S): opposite Not all parameters are independent slow nmos fast for nmos and pmos University of Texas, Austin Jaydeep P. Kulkarni 19
20 Environmental Variation V DD and T also vary in time and space Fast: V DD : high T: low Corner Voltage Temperature F C T C S C University of Texas, Austin Jaydeep P. Kulkarni 20
21 Important Corners Some critical simulation corners include Purpose nmos pmos V DD Temp Cycle time S S S S Power F F F F Subthrehold leakage F F F S University of Texas, Austin Jaydeep P. Kulkarni 21
22 What is the effect of non-ideal transistor behavior in real life designs? University of Texas, Austin Jaydeep P. Kulkarni 22
23 A case study: Advanced SRAM 75% of the die area occupied by SRAMs Key enabler for logic technology scaling Ref: Springer Book on Nanometer Variation Tolerant SRAM Intel EX Xeon server processor (E7 V3): 18 Cores in 22nm technology 5.6 Billion transistors 45 Mega Bytes of L3 cache 45*8*6*1024*1024 = 2.26 Billion transistors to realize 6T SRAM bitcells Ref: ~40% total transistors in just L3 bit cells University of Texas, Austin Jaydeep P. Kulkarni 23
24 6T SRAM bitcell scaling Innovation in both process technology and circuit techniques University of Texas, Austin Jaydeep P. Kulkarni 24
25 6T SRAM density scaling 1.8X every process generation including assist circuits for Vmin and leakage reduction University of Texas, Austin Jaydeep P. Kulkarni 25
26 6T SRAM V T variation and Vmin window Conflicting read vs. write design requirements in 6T SRAM Shrinking VT optimization window with process scaling University of Texas, Austin Jaydeep P. Kulkarni 26
27 Source of variations University of Texas, Austin Jaydeep P. Kulkarni 27
28 Random process variations University of Texas, Austin Jaydeep P. Kulkarni 28
29 6T SRAM Vmin SRAM Vmin distribution affected by global systematic and local random variations. University of Texas, Austin Jaydeep P. Kulkarni 29
30 6T SRAM design trade-offs University of Texas, Austin Jaydeep P. Kulkarni 30
31 6T SRAM read and write margin University of Texas, Austin Jaydeep P. Kulkarni 31
32 Read vs. write stability University of Texas, Austin Jaydeep P. Kulkarni 32
33 Restricted design rules University of Texas, Austin Jaydeep P. Kulkarni 33
34 Read stability assist techniques University of Texas, Austin Jaydeep P. Kulkarni 34
35 Read stability bitline voltage tuning University of Texas, Austin Jaydeep P. Kulkarni 35
36 Strong PMOS affects write-ability University of Texas, Austin Jaydeep P. Kulkarni 36
37 Write-assist techniques Effectiveness of circuit write assist technique depends on transistor technology and SRAM application University of Texas, Austin Jaydeep P. Kulkarni 37
38 Write assist lowering the supply voltage University of Texas, Austin Jaydeep P. Kulkarni 38
39 Transient Voltage Collapse University of Texas, Austin Jaydeep P. Kulkarni 39
40 Other considerations in advanced SRAMs University of Texas, Austin Jaydeep P. Kulkarni 40
41 Summary: Nano-scale CMOS design issues Non-ideal Transistor Behavior Velocity saturation: alpha power model Channel length modulation : I DS increases with V DS in saturation Body Effect: V t increases with body bias DIBL: V t lowers due to V DS increase Leakage: Subthreshold current dominates, 60mV/decade Gate leakage: High-K gate dielectrics Temperature sensitivity: depends on Vcc, μ, and Vt dependance Case study: Advanced nano-scale SRAMs Impact of process variations Vmin read/write failure mechanisms Overview of read and write assist techniques Considerations for energy efficient memory designs University of Texas, Austin Jaydeep P. Kulkarni 41
Lecture 5: CMOS Transistor Theory
 Lecture 5: CMOS Transistor Theory Slides courtesy of Deming Chen Slides based on the initial set from David Harris CMOS VLSI Design Outline q q q q q q q Introduction MOS Capacitor nmos I-V Characteristics
Lecture 5: CMOS Transistor Theory Slides courtesy of Deming Chen Slides based on the initial set from David Harris CMOS VLSI Design Outline q q q q q q q Introduction MOS Capacitor nmos I-V Characteristics
VLSI Design The MOS Transistor
 VLSI Design The MOS Transistor Frank Sill Torres Universidade Federal de Minas Gerais (UFMG), Brazil VLSI Design: CMOS Technology 1 Outline Introduction MOS Capacitor nmos I-V Characteristics pmos I-V
VLSI Design The MOS Transistor Frank Sill Torres Universidade Federal de Minas Gerais (UFMG), Brazil VLSI Design: CMOS Technology 1 Outline Introduction MOS Capacitor nmos I-V Characteristics pmos I-V
MOS Transistor I-V Characteristics and Parasitics
 ECEN454 Digital Integrated Circuit Design MOS Transistor I-V Characteristics and Parasitics ECEN 454 Facts about Transistors So far, we have treated transistors as ideal switches An ON transistor passes
ECEN454 Digital Integrated Circuit Design MOS Transistor I-V Characteristics and Parasitics ECEN 454 Facts about Transistors So far, we have treated transistors as ideal switches An ON transistor passes
MOS Transistor Theory
 CHAPTER 3 MOS Transistor Theory Outline 2 1. Introduction 2. Ideal I-V Characteristics 3. Nonideal I-V Effects 4. C-V Characteristics 5. DC Transfer Characteristics 6. Switch-level RC Delay Models MOS
CHAPTER 3 MOS Transistor Theory Outline 2 1. Introduction 2. Ideal I-V Characteristics 3. Nonideal I-V Effects 4. C-V Characteristics 5. DC Transfer Characteristics 6. Switch-level RC Delay Models MOS
EE5311- Digital IC Design
 EE5311- Digital IC Design Module 1 - The Transistor Janakiraman V Assistant Professor Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Madras Chennai October 28, 2017 Janakiraman, IITM
EE5311- Digital IC Design Module 1 - The Transistor Janakiraman V Assistant Professor Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Madras Chennai October 28, 2017 Janakiraman, IITM
MOSFET: Introduction
 E&CE 437 Integrated VLSI Systems MOS Transistor 1 of 30 MOSFET: Introduction Metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistor (MOSFET) or MOS is widely used for implementing digital designs Its major
E&CE 437 Integrated VLSI Systems MOS Transistor 1 of 30 MOSFET: Introduction Metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistor (MOSFET) or MOS is widely used for implementing digital designs Its major
The Devices: MOS Transistors
 The Devices: MOS Transistors References: Semiconductor Device Fundamentals, R. F. Pierret, Addison-Wesley Digital Integrated Circuits: A Design Perspective, J. Rabaey et.al. Prentice Hall NMOS Transistor
The Devices: MOS Transistors References: Semiconductor Device Fundamentals, R. F. Pierret, Addison-Wesley Digital Integrated Circuits: A Design Perspective, J. Rabaey et.al. Prentice Hall NMOS Transistor
MOS Transistor Theory
 MOS Transistor Theory So far, we have viewed a MOS transistor as an ideal switch (digital operation) Reality: less than ideal EE 261 Krish Chakrabarty 1 Introduction So far, we have treated transistors
MOS Transistor Theory So far, we have viewed a MOS transistor as an ideal switch (digital operation) Reality: less than ideal EE 261 Krish Chakrabarty 1 Introduction So far, we have treated transistors
Non Ideal Transistor Behavior
 Non Ideal Transistor Behavior Slides adapted from: N. Weste, D. Harris, CMOS VLSI Design, Addison- Wesley, 3/e, 2004 1 Non-ideal Transistor I-V effects Non ideal transistor Behavior Channel Length ModulaJon
Non Ideal Transistor Behavior Slides adapted from: N. Weste, D. Harris, CMOS VLSI Design, Addison- Wesley, 3/e, 2004 1 Non-ideal Transistor I-V effects Non ideal transistor Behavior Channel Length ModulaJon
EE105 Fall 2014 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits. NMOS Transistor Capacitances: Saturation Region
 EE105 Fall 014 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits Prof. Ming C. Wu wu@eecs.berkeley.edu 511 Sutardja Dai Hall (SDH) 1 NMOS Transistor Capacitances: Saturation Region Drain no longer connected to channel
EE105 Fall 014 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits Prof. Ming C. Wu wu@eecs.berkeley.edu 511 Sutardja Dai Hall (SDH) 1 NMOS Transistor Capacitances: Saturation Region Drain no longer connected to channel
The Devices. Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective. Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic. July 30, 2002
 Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic The Devices July 30, 2002 Goal of this chapter Present intuitive understanding of device operation Introduction
Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic The Devices July 30, 2002 Goal of this chapter Present intuitive understanding of device operation Introduction
CMPEN 411 VLSI Digital Circuits. Lecture 03: MOS Transistor
 CMPEN 411 VLSI Digital Circuits Lecture 03: MOS Transistor Kyusun Choi [Adapted from Rabaey s Digital Integrated Circuits, Second Edition, 2003 J. Rabaey, A. Chandrakasan, B. Nikolic] CMPEN 411 L03 S.1
CMPEN 411 VLSI Digital Circuits Lecture 03: MOS Transistor Kyusun Choi [Adapted from Rabaey s Digital Integrated Circuits, Second Edition, 2003 J. Rabaey, A. Chandrakasan, B. Nikolic] CMPEN 411 L03 S.1
Lecture 4: CMOS Transistor Theory
 Introduction to CMOS VLSI Design Lecture 4: CMOS Transistor Theory David Harris, Harvey Mudd College Kartik Mohanram and Steven Levitan University of Pittsburgh Outline q Introduction q MOS Capacitor q
Introduction to CMOS VLSI Design Lecture 4: CMOS Transistor Theory David Harris, Harvey Mudd College Kartik Mohanram and Steven Levitan University of Pittsburgh Outline q Introduction q MOS Capacitor q
EECS130 Integrated Circuit Devices
 EECS130 Integrated Circuit Devices Professor Ali Javey 10/30/2007 MOSFETs Lecture 4 Reading: Chapter 17, 19 Announcements The next HW set is due on Thursday. Midterm 2 is next week!!!! Threshold and Subthreshold
EECS130 Integrated Circuit Devices Professor Ali Javey 10/30/2007 MOSFETs Lecture 4 Reading: Chapter 17, 19 Announcements The next HW set is due on Thursday. Midterm 2 is next week!!!! Threshold and Subthreshold
MOS Transistors. Prof. Krishna Saraswat. Department of Electrical Engineering Stanford University Stanford, CA
 MOS Transistors Prof. Krishna Saraswat Department of Electrical Engineering S Stanford, CA 94305 saraswat@stanford.edu 1 1930: Patent on the Field-Effect Transistor! Julius Lilienfeld filed a patent describing
MOS Transistors Prof. Krishna Saraswat Department of Electrical Engineering S Stanford, CA 94305 saraswat@stanford.edu 1 1930: Patent on the Field-Effect Transistor! Julius Lilienfeld filed a patent describing
Lecture 11: MOSFET Modeling
 Digital Integrated Circuits (83-313) Lecture 11: MOSFET ing Semester B, 2016-17 Lecturer: Dr. Adam Teman TAs: Itamar Levi, Robert Giterman 18 June 2017 Disclaimer: This course was prepared, in its entirety,
Digital Integrated Circuits (83-313) Lecture 11: MOSFET ing Semester B, 2016-17 Lecturer: Dr. Adam Teman TAs: Itamar Levi, Robert Giterman 18 June 2017 Disclaimer: This course was prepared, in its entirety,
Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective. Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic. The Devices. July 30, Devices.
 Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic The July 30, 2002 1 Goal of this chapter Present intuitive understanding of device operation Introduction
Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic The July 30, 2002 1 Goal of this chapter Present intuitive understanding of device operation Introduction
Lecture 3: CMOS Transistor Theory
 Lecture 3: CMOS Transistor Theory Outline Introduction MOS Capacitor nmos I-V Characteristics pmos I-V Characteristics Gate and Diffusion Capacitance 2 Introduction So far, we have treated transistors
Lecture 3: CMOS Transistor Theory Outline Introduction MOS Capacitor nmos I-V Characteristics pmos I-V Characteristics Gate and Diffusion Capacitance 2 Introduction So far, we have treated transistors
Integrated Circuits & Systems
 Federal University of Santa Catarina Center for Technology Computer Science & Electronics Engineering Integrated Circuits & Systems INE 5442 Lecture 10 MOSFET part 1 guntzel@inf.ufsc.br ual-well Trench-Isolated
Federal University of Santa Catarina Center for Technology Computer Science & Electronics Engineering Integrated Circuits & Systems INE 5442 Lecture 10 MOSFET part 1 guntzel@inf.ufsc.br ual-well Trench-Isolated
The Devices. Jan M. Rabaey
 The Devices Jan M. Rabaey Goal of this chapter Present intuitive understanding of device operation Introduction of basic device equations Introduction of models for manual analysis Introduction of models
The Devices Jan M. Rabaey Goal of this chapter Present intuitive understanding of device operation Introduction of basic device equations Introduction of models for manual analysis Introduction of models
The Devices. Devices
 The The MOS Transistor Gate Oxyde Gate Source n+ Polysilicon Drain n+ Field-Oxyde (SiO 2 ) p-substrate p+ stopper Bulk Contact CROSS-SECTION of NMOS Transistor Cross-Section of CMOS Technology MOS transistors
The The MOS Transistor Gate Oxyde Gate Source n+ Polysilicon Drain n+ Field-Oxyde (SiO 2 ) p-substrate p+ stopper Bulk Contact CROSS-SECTION of NMOS Transistor Cross-Section of CMOS Technology MOS transistors
ECE 342 Electronic Circuits. 3. MOS Transistors
 ECE 342 Electronic Circuits 3. MOS Transistors Jose E. Schutt-Aine Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Illinois jschutt@emlab.uiuc.edu 1 NMOS Transistor Typically L = 0.1 to 3 m, W = 0.2 to
ECE 342 Electronic Circuits 3. MOS Transistors Jose E. Schutt-Aine Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Illinois jschutt@emlab.uiuc.edu 1 NMOS Transistor Typically L = 0.1 to 3 m, W = 0.2 to
Scaling Issues in Planar FET: Dual Gate FET and FinFETs
 Scaling Issues in Planar FET: Dual Gate FET and FinFETs Lecture 12 Dr. Amr Bayoumi Fall 2014 Advanced Devices (EC760) Arab Academy for Science and Technology - Cairo 1 Outline Scaling Issues for Planar
Scaling Issues in Planar FET: Dual Gate FET and FinFETs Lecture 12 Dr. Amr Bayoumi Fall 2014 Advanced Devices (EC760) Arab Academy for Science and Technology - Cairo 1 Outline Scaling Issues for Planar
Lecture #27. The Short Channel Effect (SCE)
 Lecture #27 ANNOUNCEMENTS Design Project: Your BJT design should meet the performance specifications to within 10% at both 300K and 360K. ( β dc > 45, f T > 18 GHz, V A > 9 V and V punchthrough > 9 V )
Lecture #27 ANNOUNCEMENTS Design Project: Your BJT design should meet the performance specifications to within 10% at both 300K and 360K. ( β dc > 45, f T > 18 GHz, V A > 9 V and V punchthrough > 9 V )
CMOS INVERTER. Last Lecture. Metrics for qualifying digital circuits. »Cost» Reliability» Speed (delay)»performance
 CMOS INVERTER Last Lecture Metrics for qualifying digital circuits»cost» Reliability» Speed (delay)»performance 1 Today s lecture The CMOS inverter at a glance An MOS transistor model for manual analysis
CMOS INVERTER Last Lecture Metrics for qualifying digital circuits»cost» Reliability» Speed (delay)»performance 1 Today s lecture The CMOS inverter at a glance An MOS transistor model for manual analysis
Device Models (PN Diode, MOSFET )
 Device Models (PN Diode, MOSFET ) Instructor: Steven P. Levitan steve@ece.pitt.edu TA: Gayatri Mehta, José Martínez Book: Digital Integrated Circuits: A Design Perspective; Jan Rabaey Lab Notes: Handed
Device Models (PN Diode, MOSFET ) Instructor: Steven P. Levitan steve@ece.pitt.edu TA: Gayatri Mehta, José Martínez Book: Digital Integrated Circuits: A Design Perspective; Jan Rabaey Lab Notes: Handed
L ECE 4211 UConn F. Jain Scaling Laws for NanoFETs Chapter 10 Logic Gate Scaling
 L13 04202017 ECE 4211 UConn F. Jain Scaling Laws for NanoFETs Chapter 10 Logic Gate Scaling Scaling laws: Generalized scaling (GS) p. 610 Design steps p.613 Nanotransistor issues (page 626) Degradation
L13 04202017 ECE 4211 UConn F. Jain Scaling Laws for NanoFETs Chapter 10 Logic Gate Scaling Scaling laws: Generalized scaling (GS) p. 610 Design steps p.613 Nanotransistor issues (page 626) Degradation
Device Models (PN Diode, MOSFET )
 Device Models (PN Diode, MOSFET ) Instructor: Steven P. Levitan steve@ece.pitt.edu TA: Gayatri Mehta, José Martínez Book: Digital Integrated Circuits: A Design Perspective; Jan Rabaey Lab Notes: Handed
Device Models (PN Diode, MOSFET ) Instructor: Steven P. Levitan steve@ece.pitt.edu TA: Gayatri Mehta, José Martínez Book: Digital Integrated Circuits: A Design Perspective; Jan Rabaey Lab Notes: Handed
MOSFET. Id-Vd curve. I DS Transfer curve V G. Lec. 8. Vd=1V. Saturation region. V Th
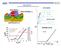 MOSFET Id-Vd curve Saturation region I DS Transfer curve Vd=1V V Th V G 1 0 < V GS < V T V GS > V T V Gs >V T & Small V D > 0 I DS WQ inv WC v WC i V V VDS V V G i T G n T L n I D g V D (g conductance
MOSFET Id-Vd curve Saturation region I DS Transfer curve Vd=1V V Th V G 1 0 < V GS < V T V GS > V T V Gs >V T & Small V D > 0 I DS WQ inv WC v WC i V V VDS V V G i T G n T L n I D g V D (g conductance
ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals
 ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 5: January 25, 2018 MOS Operating Regions, pt. 1 Lecture Outline! 3 Regions of operation for MOSFET " Subthreshold " Linear " Saturation!
ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 5: January 25, 2018 MOS Operating Regions, pt. 1 Lecture Outline! 3 Regions of operation for MOSFET " Subthreshold " Linear " Saturation!
Practice 3: Semiconductors
 Practice 3: Semiconductors Digital Electronic Circuits Semester A 2012 VLSI Fabrication Process VLSI Very Large Scale Integration The ability to fabricate many devices on a single substrate within a given
Practice 3: Semiconductors Digital Electronic Circuits Semester A 2012 VLSI Fabrication Process VLSI Very Large Scale Integration The ability to fabricate many devices on a single substrate within a given
EE 330 Lecture 16. MOSFET Modeling CMOS Process Flow
 EE 330 Lecture 16 MOSFET Modeling CMOS Process Flow Model Extensions 300 Id 250 200 150 100 50 300 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 Vds Existing Model 250 200 Id 150 100 50 Slope is not 0 0 0 1 2 3 4 Actual Device Vds Model
EE 330 Lecture 16 MOSFET Modeling CMOS Process Flow Model Extensions 300 Id 250 200 150 100 50 300 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 Vds Existing Model 250 200 Id 150 100 50 Slope is not 0 0 0 1 2 3 4 Actual Device Vds Model
Introduction to CMOS VLSI. Chapter 2: CMOS Transistor Theory. Harris, 2004 Updated by Li Chen, Outline
 Introduction to MOS VLSI Design hapter : MOS Transistor Theory copyright@david Harris, 004 Updated by Li hen, 010 Outline Introduction MOS apacitor nmos IV haracteristics pmos IV haracteristics Gate and
Introduction to MOS VLSI Design hapter : MOS Transistor Theory copyright@david Harris, 004 Updated by Li hen, 010 Outline Introduction MOS apacitor nmos IV haracteristics pmos IV haracteristics Gate and
P. R. Nelson 1 ECE418 - VLSI. Midterm Exam. Solutions
 P. R. Nelson 1 ECE418 - VLSI Midterm Exam Solutions 1. (8 points) Draw the cross-section view for A-A. The cross-section view is as shown below.. ( points) Can you tell which of the metal1 regions is the
P. R. Nelson 1 ECE418 - VLSI Midterm Exam Solutions 1. (8 points) Draw the cross-section view for A-A. The cross-section view is as shown below.. ( points) Can you tell which of the metal1 regions is the
ECE315 / ECE515 Lecture-2 Date:
 Lecture-2 Date: 04.08.2016 NMOS I/V Characteristics Discussion on I/V Characteristics MOSFET Second Order Effect NMOS I-V Characteristics ECE315 / ECE515 Gradual Channel Approximation: Cut-off Linear/Triode
Lecture-2 Date: 04.08.2016 NMOS I/V Characteristics Discussion on I/V Characteristics MOSFET Second Order Effect NMOS I-V Characteristics ECE315 / ECE515 Gradual Channel Approximation: Cut-off Linear/Triode
ECE 305 Exam 5 SOLUTIONS: Spring 2015 April 17, 2015 Mark Lundstrom Purdue University
 NAME: PUID: : ECE 305 Exam 5 SOLUTIONS: April 17, 2015 Mark Lundstrom Purdue University This is a closed book exam. You may use a calculator and the formula sheet at the end of this exam. Following the
NAME: PUID: : ECE 305 Exam 5 SOLUTIONS: April 17, 2015 Mark Lundstrom Purdue University This is a closed book exam. You may use a calculator and the formula sheet at the end of this exam. Following the
N Channel MOSFET level 3
 N Channel MOSFET level 3 mosn3 NSource NBulk NSource NBulk NSource NBulk NSource (a) (b) (c) (d) NBulk Figure 1: MOSFET Types Form: mosn3: instance name n 1 n n 3 n n 1 is the drain node, n is the gate
N Channel MOSFET level 3 mosn3 NSource NBulk NSource NBulk NSource NBulk NSource (a) (b) (c) (d) NBulk Figure 1: MOSFET Types Form: mosn3: instance name n 1 n n 3 n n 1 is the drain node, n is the gate
Chapter 4 Field-Effect Transistors
 Chapter 4 Field-Effect Transistors Microelectronic Circuit Design Richard C. Jaeger Travis N. Blalock 5/5/11 Chap 4-1 Chapter Goals Describe operation of MOSFETs. Define FET characteristics in operation
Chapter 4 Field-Effect Transistors Microelectronic Circuit Design Richard C. Jaeger Travis N. Blalock 5/5/11 Chap 4-1 Chapter Goals Describe operation of MOSFETs. Define FET characteristics in operation
Objective and Outline. Acknowledgement. Objective: Power Components. Outline: 1) Acknowledgements. Section 4: Power Components
 Objective: Power Components Outline: 1) Acknowledgements 2) Objective and Outline 1 Acknowledgement This lecture note has been obtained from similar courses all over the world. I wish to thank all the
Objective: Power Components Outline: 1) Acknowledgements 2) Objective and Outline 1 Acknowledgement This lecture note has been obtained from similar courses all over the world. I wish to thank all the
Tri-Gate Fully-Depleted CMOS Transistors: Fabrication, Design and Layout
 Tri-Gate Fully-Depleted CMOS Transistors: Fabrication, Design and Layout B.Doyle, J.Kavalieros, T. Linton, R.Rios B.Boyanov, S.Datta, M. Doczy, S.Hareland, B. Jin, R.Chau Logic Technology Development Intel
Tri-Gate Fully-Depleted CMOS Transistors: Fabrication, Design and Layout B.Doyle, J.Kavalieros, T. Linton, R.Rios B.Boyanov, S.Datta, M. Doczy, S.Hareland, B. Jin, R.Chau Logic Technology Development Intel
ESE370: Circuit-Level Modeling, Design, and Optimization for Digital Systems. Today. Refinement. Last Time. No Field. Body Contact
 ESE370: Circuit-Level Modeling, Design, and Optimization for Digital Systems Day 10: September 6, 01 MOS Transistor Basics Today MOS Transistor Topology Threshold Operating Regions Resistive Saturation
ESE370: Circuit-Level Modeling, Design, and Optimization for Digital Systems Day 10: September 6, 01 MOS Transistor Basics Today MOS Transistor Topology Threshold Operating Regions Resistive Saturation
MOS Transistor Theory MOSFET Symbols Current Characteristics of MOSFET. MOS Symbols and Characteristics. nmos Enhancement Transistor
 MOS Transistor Theory MOSFET Symbols Current Characteristics of MOSFET Calculation of t and Important 2 nd Order Effects SmallSignal Signal MOSFET Model Summary Material from: CMOS LSI Design By Weste
MOS Transistor Theory MOSFET Symbols Current Characteristics of MOSFET Calculation of t and Important 2 nd Order Effects SmallSignal Signal MOSFET Model Summary Material from: CMOS LSI Design By Weste
Semiconductor Physics fall 2012 problems
 Semiconductor Physics fall 2012 problems 1. An n-type sample of silicon has a uniform density N D = 10 16 atoms cm -3 of arsenic, and a p-type silicon sample has N A = 10 15 atoms cm -3 of boron. For each
Semiconductor Physics fall 2012 problems 1. An n-type sample of silicon has a uniform density N D = 10 16 atoms cm -3 of arsenic, and a p-type silicon sample has N A = 10 15 atoms cm -3 of boron. For each
EE 330 Lecture 16. Devices in Semiconductor Processes. MOS Transistors
 EE 330 Lecture 16 Devices in Semiconductor Processes MOS Transistors Review from Last Time Model Summary I D I V DS V S I B V BS = 0 0 VS VT W VDS ID = μcox VS VT VDS VS V VDS VS VT L T < W μc ( V V )
EE 330 Lecture 16 Devices in Semiconductor Processes MOS Transistors Review from Last Time Model Summary I D I V DS V S I B V BS = 0 0 VS VT W VDS ID = μcox VS VT VDS VS V VDS VS VT L T < W μc ( V V )
Lecture 12: MOSFET Devices
 Lecture 12: MOSFET Devices Gu-Yeon Wei Division of Engineering and Applied Sciences Harvard University guyeon@eecs.harvard.edu Wei 1 Overview Reading S&S: Chapter 5.1~5.4 Supplemental Reading Background
Lecture 12: MOSFET Devices Gu-Yeon Wei Division of Engineering and Applied Sciences Harvard University guyeon@eecs.harvard.edu Wei 1 Overview Reading S&S: Chapter 5.1~5.4 Supplemental Reading Background
Today s lecture. EE141- Spring 2003 Lecture 4. Design Rules CMOS Inverter MOS Transistor Model
 - Spring 003 Lecture 4 Design Rules CMOS Inverter MOS Transistor Model Today s lecture Design Rules The CMOS inverter at a glance An MOS transistor model for manual analysis Important! Labs start next
- Spring 003 Lecture 4 Design Rules CMOS Inverter MOS Transistor Model Today s lecture Design Rules The CMOS inverter at a glance An MOS transistor model for manual analysis Important! Labs start next
The Devices. Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective. Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic. July 30, 2002
 igital Integrated Circuits A esign Perspective Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic The evices July 30, 2002 Goal of this chapter Present intuitive understanding of device operation Introduction
igital Integrated Circuits A esign Perspective Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic The evices July 30, 2002 Goal of this chapter Present intuitive understanding of device operation Introduction
LECTURE 3 MOSFETS II. MOS SCALING What is Scaling?
 LECTURE 3 MOSFETS II Lecture 3 Goals* * Understand constant field and constant voltage scaling and their effects. Understand small geometry effects for MOS transistors and their implications modeling and
LECTURE 3 MOSFETS II Lecture 3 Goals* * Understand constant field and constant voltage scaling and their effects. Understand small geometry effects for MOS transistors and their implications modeling and
Fundamentals of the Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor
 Triode Working FET Fundamentals of the Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor The characteristics of energy bands as a function of applied voltage. Surface inversion. The expression for the
Triode Working FET Fundamentals of the Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor The characteristics of energy bands as a function of applied voltage. Surface inversion. The expression for the
Lecture 6 Power Zhuo Feng. Z. Feng MTU EE4800 CMOS Digital IC Design & Analysis 2010
 EE4800 CMOS Digital IC Design & Analysis Lecture 6 Power Zhuo Feng 6.1 Outline Power and Energy Dynamic Power Static Power 6.2 Power and Energy Power is drawn from a voltage source attached to the V DD
EE4800 CMOS Digital IC Design & Analysis Lecture 6 Power Zhuo Feng 6.1 Outline Power and Energy Dynamic Power Static Power 6.2 Power and Energy Power is drawn from a voltage source attached to the V DD
ECE 342 Electronic Circuits. Lecture 6 MOS Transistors
 ECE 342 Electronic Circuits Lecture 6 MOS Transistors Jose E. Schutt-Aine Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Illinois jesa@illinois.edu 1 NMOS Transistor Typically L = 0.1 to 3 m, W = 0.2
ECE 342 Electronic Circuits Lecture 6 MOS Transistors Jose E. Schutt-Aine Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Illinois jesa@illinois.edu 1 NMOS Transistor Typically L = 0.1 to 3 m, W = 0.2
Nanometer Transistors and Their Models. Jan M. Rabaey
 Nanometer Transistors and Their Models Jan M. Rabaey Chapter Outline Nanometer transistor behavior and models Sub-threshold currents and leakage Variability Device and technology innovations Nanometer
Nanometer Transistors and Their Models Jan M. Rabaey Chapter Outline Nanometer transistor behavior and models Sub-threshold currents and leakage Variability Device and technology innovations Nanometer
SECTION: Circle one: Alam Lundstrom. ECE 305 Exam 5 SOLUTIONS: Spring 2016 April 18, 2016 M. A. Alam and M.S. Lundstrom Purdue University
 NAME: PUID: SECTION: Circle one: Alam Lundstrom ECE 305 Exam 5 SOLUTIONS: April 18, 2016 M A Alam and MS Lundstrom Purdue University This is a closed book exam You may use a calculator and the formula
NAME: PUID: SECTION: Circle one: Alam Lundstrom ECE 305 Exam 5 SOLUTIONS: April 18, 2016 M A Alam and MS Lundstrom Purdue University This is a closed book exam You may use a calculator and the formula
Long-channel MOSFET IV Corrections
 Long-channel MOSFET IV orrections Three MITs of the Day The body ect and its influence on long-channel V th. Long-channel subthreshold conduction and control (subthreshold slope S) Scattering components
Long-channel MOSFET IV orrections Three MITs of the Day The body ect and its influence on long-channel V th. Long-channel subthreshold conduction and control (subthreshold slope S) Scattering components
ECE-305: Fall 2017 MOS Capacitors and Transistors
 ECE-305: Fall 2017 MOS Capacitors and Transistors Pierret, Semiconductor Device Fundamentals (SDF) Chapters 15+16 (pp. 525-530, 563-599) Professor Peter Bermel Electrical and Computer Engineering Purdue
ECE-305: Fall 2017 MOS Capacitors and Transistors Pierret, Semiconductor Device Fundamentals (SDF) Chapters 15+16 (pp. 525-530, 563-599) Professor Peter Bermel Electrical and Computer Engineering Purdue
Chapter 2 CMOS Transistor Theory. Jin-Fu Li Department of Electrical Engineering National Central University Jungli, Taiwan
 Chapter 2 CMOS Transistor Theory Jin-Fu Li Department of Electrical Engineering National Central University Jungli, Taiwan Outline Introduction MOS Device Design Equation Pass Transistor Jin-Fu Li, EE,
Chapter 2 CMOS Transistor Theory Jin-Fu Li Department of Electrical Engineering National Central University Jungli, Taiwan Outline Introduction MOS Device Design Equation Pass Transistor Jin-Fu Li, EE,
Lecture 04 Review of MOSFET
 ECE 541/ME 541 Microelectronic Fabrication Techniques Lecture 04 Review of MOSFET Zheng Yang (ERF 3017, email: yangzhen@uic.edu) What is a Transistor? A Switch! An MOS Transistor V GS V T V GS S Ron D
ECE 541/ME 541 Microelectronic Fabrication Techniques Lecture 04 Review of MOSFET Zheng Yang (ERF 3017, email: yangzhen@uic.edu) What is a Transistor? A Switch! An MOS Transistor V GS V T V GS S Ron D
EE 330 Lecture 16. MOS Device Modeling p-channel n-channel comparisons Model consistency and relationships CMOS Process Flow
 EE 330 Lecture 16 MOS Device Modeling p-channel n-channel comparisons Model consistency and relationships CMOS Process Flow Review from Last Time Operation Regions by Applications Id I D 300 250 200 150
EE 330 Lecture 16 MOS Device Modeling p-channel n-channel comparisons Model consistency and relationships CMOS Process Flow Review from Last Time Operation Regions by Applications Id I D 300 250 200 150
ECEN474/704: (Analog) VLSI Circuit Design Spring 2018
 ECEN474/704: (Analog) SI Circuit Design Spring 2018 ecture 2: MOS ransistor Modeling Sam Palermo Analog & Mixed-Signal Center exas A&M University Announcements If you haven t already, turn in your 0.18um
ECEN474/704: (Analog) SI Circuit Design Spring 2018 ecture 2: MOS ransistor Modeling Sam Palermo Analog & Mixed-Signal Center exas A&M University Announcements If you haven t already, turn in your 0.18um
EE 560 MOS TRANSISTOR THEORY PART 2. Kenneth R. Laker, University of Pennsylvania
 1 EE 560 MOS TRANSISTOR THEORY PART nmos TRANSISTOR IN LINEAR REGION V S = 0 V G > V T0 channel SiO V D = small 4 C GC C BC substrate depletion region or bulk B p nmos TRANSISTOR AT EDGE OF SATURATION
1 EE 560 MOS TRANSISTOR THEORY PART nmos TRANSISTOR IN LINEAR REGION V S = 0 V G > V T0 channel SiO V D = small 4 C GC C BC substrate depletion region or bulk B p nmos TRANSISTOR AT EDGE OF SATURATION
Technische Universität Graz. Institute of Solid State Physics. 11. MOSFETs
 Technische Universität Graz Institute of Solid State Physics 11. MOSFETs Dec. 12, 2018 Gradual channel approximation accumulation depletion inversion http://lampx.tugraz.at/~hadley/psd/l10/gradualchannelapprox.php
Technische Universität Graz Institute of Solid State Physics 11. MOSFETs Dec. 12, 2018 Gradual channel approximation accumulation depletion inversion http://lampx.tugraz.at/~hadley/psd/l10/gradualchannelapprox.php
Long Channel MOS Transistors
 Long Channel MOS Transistors The theory developed for MOS capacitor (HO #2) can be directly extended to Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect transistors (MOSFET) by considering the following structure:
Long Channel MOS Transistors The theory developed for MOS capacitor (HO #2) can be directly extended to Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect transistors (MOSFET) by considering the following structure:
DC and Transient Responses (i.e. delay) (some comments on power too!)
 DC and Transient Responses (i.e. delay) (some comments on power too!) Michael Niemier (Some slides based on lecture notes by David Harris) 1 Lecture 02 - CMOS Transistor Theory & the Effects of Scaling
DC and Transient Responses (i.e. delay) (some comments on power too!) Michael Niemier (Some slides based on lecture notes by David Harris) 1 Lecture 02 - CMOS Transistor Theory & the Effects of Scaling
EE 560 MOS TRANSISTOR THEORY
 1 EE 560 MOS TRANSISTOR THEORY PART 1 TWO TERMINAL MOS STRUCTURE V G (GATE VOLTAGE) 2 GATE OXIDE SiO 2 SUBSTRATE p-type doped Si (N A = 10 15 to 10 16 cm -3 ) t ox V B (SUBSTRATE VOLTAGE) EQUILIBRIUM:
1 EE 560 MOS TRANSISTOR THEORY PART 1 TWO TERMINAL MOS STRUCTURE V G (GATE VOLTAGE) 2 GATE OXIDE SiO 2 SUBSTRATE p-type doped Si (N A = 10 15 to 10 16 cm -3 ) t ox V B (SUBSTRATE VOLTAGE) EQUILIBRIUM:
Microelectronics Part 1: Main CMOS circuits design rules
 GBM8320 Dispositifs Médicaux telligents Microelectronics Part 1: Main CMOS circuits design rules Mohamad Sawan et al. Laboratoire de neurotechnologies Polystim! http://www.cours.polymtl.ca/gbm8320/! med-amine.miled@polymtl.ca!
GBM8320 Dispositifs Médicaux telligents Microelectronics Part 1: Main CMOS circuits design rules Mohamad Sawan et al. Laboratoire de neurotechnologies Polystim! http://www.cours.polymtl.ca/gbm8320/! med-amine.miled@polymtl.ca!
ECE 546 Lecture 10 MOS Transistors
 ECE 546 Lecture 10 MOS Transistors Spring 2018 Jose E. Schutt-Aine Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Illinois jesa@illinois.edu NMOS Transistor NMOS Transistor N-Channel MOSFET Built on p-type
ECE 546 Lecture 10 MOS Transistors Spring 2018 Jose E. Schutt-Aine Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Illinois jesa@illinois.edu NMOS Transistor NMOS Transistor N-Channel MOSFET Built on p-type
Lecture 13 MOSFET as an amplifier with an introduction to MOSFET small-signal model and small-signal schematics. Lena Peterson
 Lecture 13 MOSFET as an amplifier with an introduction to MOSFET small-signal model and small-signal schematics Lena Peterson 2015-10-13 Outline (1) Why is the CMOS inverter gain not infinite? Large-signal
Lecture 13 MOSFET as an amplifier with an introduction to MOSFET small-signal model and small-signal schematics Lena Peterson 2015-10-13 Outline (1) Why is the CMOS inverter gain not infinite? Large-signal
The Future of CMOS. David Pulfrey. CHRONOLOGY of the FET. Lecture Lilienfeld s patent (BG FET) 1965 Commercialization (Fairchild)
 The Future of CMOS David Pulfrey 1 CHRONOLOGY of the FET 1933 Lilienfeld s patent (BG FET) 1965 Commercialization (Fairchild) 1991 The most abundant object made by mankind (C.T. Sah) 2003 The 10 nm FET
The Future of CMOS David Pulfrey 1 CHRONOLOGY of the FET 1933 Lilienfeld s patent (BG FET) 1965 Commercialization (Fairchild) 1991 The most abundant object made by mankind (C.T. Sah) 2003 The 10 nm FET
CHAPTER 5 EFFECT OF GATE ELECTRODE WORK FUNCTION VARIATION ON DC AND AC PARAMETERS IN CONVENTIONAL AND JUNCTIONLESS FINFETS
 98 CHAPTER 5 EFFECT OF GATE ELECTRODE WORK FUNCTION VARIATION ON DC AND AC PARAMETERS IN CONVENTIONAL AND JUNCTIONLESS FINFETS In this chapter, the effect of gate electrode work function variation on DC
98 CHAPTER 5 EFFECT OF GATE ELECTRODE WORK FUNCTION VARIATION ON DC AND AC PARAMETERS IN CONVENTIONAL AND JUNCTIONLESS FINFETS In this chapter, the effect of gate electrode work function variation on DC
Lecture 15: MOS Transistor models: Body effects, SPICE models. Context. In the last lecture, we discussed the modes of operation of a MOS FET:
 Lecture 15: MOS Transistor models: Body effects, SPICE models Context In the last lecture, we discussed the modes of operation of a MOS FET: oltage controlled resistor model I- curve (Square-Law Model)
Lecture 15: MOS Transistor models: Body effects, SPICE models Context In the last lecture, we discussed the modes of operation of a MOS FET: oltage controlled resistor model I- curve (Square-Law Model)
! MOS Capacitances. " Extrinsic. " Intrinsic. ! Lumped Capacitance Model. ! First Order Capacitor Summary. ! Capacitance Implications
 ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 7: February, 07 MOS SPICE Models, MOS Parasitic Details Lecture Outline! MOS Capacitances " Extrinsic " Intrinsic! Lumped Capacitance Model!
ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 7: February, 07 MOS SPICE Models, MOS Parasitic Details Lecture Outline! MOS Capacitances " Extrinsic " Intrinsic! Lumped Capacitance Model!
Semiconductor Physics Problems 2015
 Semiconductor Physics Problems 2015 Page and figure numbers refer to Semiconductor Devices Physics and Technology, 3rd edition, by SM Sze and M-K Lee 1. The purest semiconductor crystals it is possible
Semiconductor Physics Problems 2015 Page and figure numbers refer to Semiconductor Devices Physics and Technology, 3rd edition, by SM Sze and M-K Lee 1. The purest semiconductor crystals it is possible
A Multi-Gate CMOS Compact Model BSIMMG
 A Multi-Gate CMOS Compact Model BSIMMG Darsen Lu, Sriramkumar Venugopalan, Tanvir Morshed, Yogesh Singh Chauhan, Chung-Hsun Lin, Mohan Dunga, Ali Niknejad and Chenming Hu University of California, Berkeley
A Multi-Gate CMOS Compact Model BSIMMG Darsen Lu, Sriramkumar Venugopalan, Tanvir Morshed, Yogesh Singh Chauhan, Chung-Hsun Lin, Mohan Dunga, Ali Niknejad and Chenming Hu University of California, Berkeley
ECE 497 JS Lecture - 12 Device Technologies
 ECE 497 JS Lecture - 12 Device Technologies Spring 2004 Jose E. Schutt-Aine Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Illinois jose@emlab.uiuc.edu 1 NMOS Transistor 2 ρ Source channel charge density
ECE 497 JS Lecture - 12 Device Technologies Spring 2004 Jose E. Schutt-Aine Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Illinois jose@emlab.uiuc.edu 1 NMOS Transistor 2 ρ Source channel charge density
The Physical Structure (NMOS)
 The Physical Structure (NMOS) Al SiO2 Field Oxide Gate oxide S n+ Polysilicon Gate Al SiO2 SiO2 D n+ L channel P Substrate Field Oxide contact Metal (S) n+ (G) L W n+ (D) Poly 1 Transistor Resistance Two
The Physical Structure (NMOS) Al SiO2 Field Oxide Gate oxide S n+ Polysilicon Gate Al SiO2 SiO2 D n+ L channel P Substrate Field Oxide contact Metal (S) n+ (G) L W n+ (D) Poly 1 Transistor Resistance Two
Microsystems Technology Laboratories, MIT. Teledyne Scientific Company (TSC)
 Extraction of Virtual-Source Injection Velocity in sub-100 nm III-V HFETs 1,2) D.-H. Kim, 1) J. A. del Alamo, 1) D. A. Antoniadis and 2) B. Brar 1) Microsystems Technology Laboratories, MIT 2) Teledyne
Extraction of Virtual-Source Injection Velocity in sub-100 nm III-V HFETs 1,2) D.-H. Kim, 1) J. A. del Alamo, 1) D. A. Antoniadis and 2) B. Brar 1) Microsystems Technology Laboratories, MIT 2) Teledyne
EEC 118 Lecture #2: MOSFET Structure and Basic Operation. Rajeevan Amirtharajah University of California, Davis Jeff Parkhurst Intel Corporation
 EEC 118 Lecture #2: MOSFET Structure and Basic Operation Rajeevan Amirtharajah University of California, Davis Jeff Parkhurst Intel Corporation Announcements Lab 1 this week, report due next week Bring
EEC 118 Lecture #2: MOSFET Structure and Basic Operation Rajeevan Amirtharajah University of California, Davis Jeff Parkhurst Intel Corporation Announcements Lab 1 this week, report due next week Bring
EECS 427 Lecture 11: Power and Energy Reading: EECS 427 F09 Lecture Reminders
 EECS 47 Lecture 11: Power and Energy Reading: 5.55 [Adapted from Irwin and Narayanan] 1 Reminders CAD5 is due Wednesday 10/8 You can submit it by Thursday 10/9 at noon Lecture on 11/ will be taught by
EECS 47 Lecture 11: Power and Energy Reading: 5.55 [Adapted from Irwin and Narayanan] 1 Reminders CAD5 is due Wednesday 10/8 You can submit it by Thursday 10/9 at noon Lecture on 11/ will be taught by
Chapter 20. Current Mirrors. Basics. Cascoding. Biasing Circuits. Baker Ch. 20 Current Mirrors. Introduction to VLSI
 Chapter 20 Current Mirrors Basics Long Channel Matching Biasing Short Channel Temperature Subthreshold Cascoding Simple Low Voltage, Wide Swing Wide Swing, Short Channel Regulated Drain Biasing Circuits
Chapter 20 Current Mirrors Basics Long Channel Matching Biasing Short Channel Temperature Subthreshold Cascoding Simple Low Voltage, Wide Swing Wide Swing, Short Channel Regulated Drain Biasing Circuits
ESE570 Spring University of Pennsylvania Department of Electrical and System Engineering Digital Integrated Cicruits AND VLSI Fundamentals
 University of Pennsylvania Department of Electrical and System Engineering Digital Integrated Cicruits AND VLSI Fundamentals ESE570, Spring 2018 Final Monday, Apr 0 5 Problems with point weightings shown.
University of Pennsylvania Department of Electrical and System Engineering Digital Integrated Cicruits AND VLSI Fundamentals ESE570, Spring 2018 Final Monday, Apr 0 5 Problems with point weightings shown.
EE 466/586 VLSI Design. Partha Pande School of EECS Washington State University
 EE 466/586 VLSI Design Partha Pande School of EECS Washington State University pande@eecs.wsu.edu Lecture 8 Power Dissipation in CMOS Gates Power in CMOS gates Dynamic Power Capacitance switching Crowbar
EE 466/586 VLSI Design Partha Pande School of EECS Washington State University pande@eecs.wsu.edu Lecture 8 Power Dissipation in CMOS Gates Power in CMOS gates Dynamic Power Capacitance switching Crowbar
ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals
 ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 6: January 30, 2018 MOS Operating Regions, pt. 2 Lecture Outline! Operating Regions (review) " Subthreshold " Resistive " Saturation! Intro.
ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 6: January 30, 2018 MOS Operating Regions, pt. 2 Lecture Outline! Operating Regions (review) " Subthreshold " Resistive " Saturation! Intro.
EE105 - Fall 2006 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits
 EE105 - Fall 2006 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits Prof. Jan M. Rabaey (jan@eecs) Lecture 7: MOS Transistor Some Administrative Issues Lab 2 this week Hw 2 due on We Hw 3 will be posted same day MIDTERM
EE105 - Fall 2006 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits Prof. Jan M. Rabaey (jan@eecs) Lecture 7: MOS Transistor Some Administrative Issues Lab 2 this week Hw 2 due on We Hw 3 will be posted same day MIDTERM
ELEC 3908, Physical Electronics, Lecture 23. The MOSFET Square Law Model
 ELEC 3908, Physical Electronics, Lecture 23 The MOSFET Square Law Model Lecture Outline As with the diode and bipolar, have looked at basic structure of the MOSFET and now turn to derivation of a current
ELEC 3908, Physical Electronics, Lecture 23 The MOSFET Square Law Model Lecture Outline As with the diode and bipolar, have looked at basic structure of the MOSFET and now turn to derivation of a current
HW 5 posted due in two weeks Lab this week Midterm graded Project to be launched in week 7
 HW 5 posted due in two weeks Lab this week Midterm graded Project to be launched in week 7 2 What do digital IC designers need to know? 5 EE4 EECS4 6 3 0< V GS - V T < V DS Pinch-off 7 For (V GS V T )
HW 5 posted due in two weeks Lab this week Midterm graded Project to be launched in week 7 2 What do digital IC designers need to know? 5 EE4 EECS4 6 3 0< V GS - V T < V DS Pinch-off 7 For (V GS V T )
EE105 - Fall 2005 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits
 EE105 - Fall 005 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits ecture 7 MOS Transistor Announcements Homework 3, due today Homework 4 due next week ab this week Reading: Chapter 4 1 ecture Material ast lecture
EE105 - Fall 005 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits ecture 7 MOS Transistor Announcements Homework 3, due today Homework 4 due next week ab this week Reading: Chapter 4 1 ecture Material ast lecture
ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals
 ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 7: February 4, 2016 MOS SPICE Models, MOS Parasitic Details Lecture Outline! MOS Capacitances " Extrinsic " Intrinsic! Lumped Capacitance
ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 7: February 4, 2016 MOS SPICE Models, MOS Parasitic Details Lecture Outline! MOS Capacitances " Extrinsic " Intrinsic! Lumped Capacitance
FIELD-EFFECT TRANSISTORS
 FIEL-EFFECT TRANSISTORS 1 Semiconductor review 2 The MOS capacitor 2 The enhancement-type N-MOS transistor 3 I-V characteristics of enhancement MOSFETS 4 The output characteristic of the MOSFET in saturation
FIEL-EFFECT TRANSISTORS 1 Semiconductor review 2 The MOS capacitor 2 The enhancement-type N-MOS transistor 3 I-V characteristics of enhancement MOSFETS 4 The output characteristic of the MOSFET in saturation
MOS Transistor Properties Review
 MOS Transistor Properties Review 1 VLSI Chip Manufacturing Process Photolithography: transfer of mask patterns to the chip Diffusion or ion implantation: selective doping of Si substrate Oxidation: SiO
MOS Transistor Properties Review 1 VLSI Chip Manufacturing Process Photolithography: transfer of mask patterns to the chip Diffusion or ion implantation: selective doping of Si substrate Oxidation: SiO
V t vs. N A at Various T ox
 V t vs. N A at Various T ox Threshold Voltage, V t 0.9 0.8 0.7 0.6 0.5 0.4 T ox = 5.5 nm T ox = 5 nm T ox = 6 nm m = 4.35 ev, Q ox = 0; V sb = 0 V 0.3 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0 3.5 4.0 4.5 Body Doping, N
V t vs. N A at Various T ox Threshold Voltage, V t 0.9 0.8 0.7 0.6 0.5 0.4 T ox = 5.5 nm T ox = 5 nm T ox = 6 nm m = 4.35 ev, Q ox = 0; V sb = 0 V 0.3 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0 3.5 4.0 4.5 Body Doping, N
Chapter 5 MOSFET Theory for Submicron Technology
 Chapter 5 MOSFET Theory for Submicron Technology Short channel effects Other small geometry effects Parasitic components Velocity saturation/overshoot Hot carrier effects ** Majority of these notes are
Chapter 5 MOSFET Theory for Submicron Technology Short channel effects Other small geometry effects Parasitic components Velocity saturation/overshoot Hot carrier effects ** Majority of these notes are
Announcements. EE141- Fall 2002 Lecture 7. MOS Capacitances Inverter Delay Power
 - Fall 2002 Lecture 7 MOS Capacitances Inverter Delay Power Announcements Wednesday 12-3pm lab cancelled Lab 4 this week Homework 2 due today at 5pm Homework 3 posted tonight Today s lecture MOS capacitances
- Fall 2002 Lecture 7 MOS Capacitances Inverter Delay Power Announcements Wednesday 12-3pm lab cancelled Lab 4 this week Homework 2 due today at 5pm Homework 3 posted tonight Today s lecture MOS capacitances
Chapter 2 MOS Transistor theory
 Chapter MOS Transistor theory.1 Introduction An MOS transistor is a majority-carrier device, which the current a conductg channel between the source and the dra is modulated by a voltage applied to the
Chapter MOS Transistor theory.1 Introduction An MOS transistor is a majority-carrier device, which the current a conductg channel between the source and the dra is modulated by a voltage applied to the
Lecture Outline. ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals. Review: MOS Capacitor with External Bias
 ESE 57: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 5: Januar 6, 17 MOS Operating Regions, pt. 1 Lecture Outline! 3 Regions of operation for MOSFET " Subthreshold " Linear " Saturation! Level
ESE 57: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 5: Januar 6, 17 MOS Operating Regions, pt. 1 Lecture Outline! 3 Regions of operation for MOSFET " Subthreshold " Linear " Saturation! Level
Introduction and Background
 Analog CMOS Integrated Circuit Design Introduction and Background Dr. Jawdat Abu-Taha Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Islamic University of Gaza jtaha@iugaza.edu.ps 1 Marking Assignments
Analog CMOS Integrated Circuit Design Introduction and Background Dr. Jawdat Abu-Taha Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Islamic University of Gaza jtaha@iugaza.edu.ps 1 Marking Assignments
Power Dissipation. Where Does Power Go in CMOS?
 Power Dissipation [Adapted from Chapter 5 of Digital Integrated Circuits, 2003, J. Rabaey et al.] Where Does Power Go in CMOS? Dynamic Power Consumption Charging and Discharging Capacitors Short Circuit
Power Dissipation [Adapted from Chapter 5 of Digital Integrated Circuits, 2003, J. Rabaey et al.] Where Does Power Go in CMOS? Dynamic Power Consumption Charging and Discharging Capacitors Short Circuit
The Intrinsic Silicon
 The Intrinsic ilicon Thermally generated electrons and holes Carrier concentration p i =n i ni=1.45x10 10 cm-3 @ room temp Generally: n i = 3.1X10 16 T 3/2 e -1.21/2KT cm -3 T= temperature in K o (egrees
The Intrinsic ilicon Thermally generated electrons and holes Carrier concentration p i =n i ni=1.45x10 10 cm-3 @ room temp Generally: n i = 3.1X10 16 T 3/2 e -1.21/2KT cm -3 T= temperature in K o (egrees
CSE493/593. Designing for Low Power
 CSE493/593 Designing for Low Power Mary Jane Irwin [Adapted from Rabaey s Digital Integrated Circuits, 2002, J. Rabaey et al.].1 Why Power Matters Packaging costs Power supply rail design Chip and system
CSE493/593 Designing for Low Power Mary Jane Irwin [Adapted from Rabaey s Digital Integrated Circuits, 2002, J. Rabaey et al.].1 Why Power Matters Packaging costs Power supply rail design Chip and system
Operation and Modeling of. The MOS Transistor. Second Edition. Yannis Tsividis Columbia University. New York Oxford OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS
 Operation and Modeling of The MOS Transistor Second Edition Yannis Tsividis Columbia University New York Oxford OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS CONTENTS Chapter 1 l.l 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 Chapter 2 2.1 2.2
Operation and Modeling of The MOS Transistor Second Edition Yannis Tsividis Columbia University New York Oxford OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS CONTENTS Chapter 1 l.l 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 Chapter 2 2.1 2.2
EEC 116 Lecture #3: CMOS Inverters MOS Scaling. Rajeevan Amirtharajah University of California, Davis Jeff Parkhurst Intel Corporation
 EEC 116 Lecture #3: CMOS Inverters MOS Scaling Rajeevan Amirtharajah University of California, Davis Jeff Parhurst Intel Corporation Outline Review: Inverter Transfer Characteristics Lecture 3: Noise Margins,
EEC 116 Lecture #3: CMOS Inverters MOS Scaling Rajeevan Amirtharajah University of California, Davis Jeff Parhurst Intel Corporation Outline Review: Inverter Transfer Characteristics Lecture 3: Noise Margins,
