Full Length Test Electronics and Communication Engineering
|
|
|
- Garey Wright
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1 [Ans A] PQRS P PQRSS P S QR P S Q QR Q P S R Q P S R (Q P S ) SPQ Full Length Test Electronics and Communication Engineering Answer Keys and Eplanations 2 [Ans A] Green s theorem and stokes theorem convert line integral to surface integral and vice versa Whereas Gauss s ivergence theorem converts from surface to volume and vice versa 3 [Ans *] Range: 5 to 5 y ( ) y( ) y( ) y 4 [Ans A] Maimum value of y over the interval 2 to 5 will be at = 5 Let S n r n / d sin 5 [Ans ] : , info@thegateacademycom Copyright reserved Web:wwwthegateacademycom 1
2 Given ( ) sin y sin sin sin cos sin sin (sin ) sin 6 [Ans C] By KL i 7 [Ans *] Range: 015 to 016 Bandwidth of series RLC circuit R rad sec L rad sec z z 8 [Ans B] n T e n n ( e e ) n (y) n () e e 9 [Ans C] Since, thermal run away is due to minority charge carriers and in FET, the conduction is due to majority carriers, so as temperature increases, mobility decreases and thus no trouble of thermal stability : , info@thegateacademycom Copyright reserved Web:wwwthegateacademycom 2
3 10 [Ans *] Range to L cm cm N cm and N cm L R where qn (N N N ) -cm R 11 [Ans *] Range: 0008 to 001 Open loop gain A da d d d ( ) ( ) : , info@thegateacademycom Copyright reserved Web:wwwthegateacademycom 3
4 12 [Ans *] Range: 32 to 31 k k O Using KCL k k k [ [ ] ] 13 [Ans *] Range: 55 to 58 R R r R Where, ( g R ) and R R and R r R R R k ( ) p k R sec f M z : , info@thegateacademycom Copyright reserved Web:wwwthegateacademycom 4
5 14 [Ans ] X X X X X Minimised form is 15 [Ans ] f X y y 1 st nd rd th f X y nd f X y after clock X 16 [Ans ] MUX M S S M J K = XOR (J, K) J k : , info@thegateacademycom Copyright reserved Web:wwwthegateacademycom 5
6 17 [Ans B] (t) t Since the wave has odd symmetry, hence a 18 [Ans A] h(n), (n) (n )- (z), z - Put z e (e ) [ e ] e [e e ] (e ) e cos (e ) e cos cos 19 [Ans *] Range: 6 to 6 y(t) ( t) (t) ( t) f (t) is band limited to f z Then ( t) is band limited to f Hz Nyquist rate f f a 20 [Ans C] Maimum occurs at n where n is odd ence first maimum occurs at s s s s omparing and : , info@thegateacademycom Copyright reserved Web:wwwthegateacademycom 6
7 21 [Ans ] u S u S S u u [ ] [ ] [ ] [ ] 0 u u 1 One can denote any state by any name; changing and So, that answer is d dt [ ] [ ] ( ) [ ] u u / 22 [Ans *] Range: 4391 to 44 SQNR log ( ) d s log SQNR log d log s 23 [Ans *] Range: 2 to 2 cos t cos t cos t cos t [ cos t] or envelope detection Should be atleast : , info@thegateacademycom Copyright reserved Web:wwwthegateacademycom 7
8 24 [Ans A] e cos y e sin y ( ) at ( )is m harge enclosed ( ) 25 [Ans *] Range: 9 to 9 cos( t ) elocity of EM wave in a los-less medium, - m sec 26 [Ans ], Multiplying both sides by b 0 1 [ (b b ) ( b) ] [ ( b ) ( b b ) b ] 27 [Ans ] Given that a > 0 So, a ( ) nd also g() So a ( ) g() for all R a ( ) g() Has no solution 28 [Ans A] z e ( iy) e ( ) ( y y)(e )(cos y i sin y) (e ),( y ) cos y y sin y- : , info@thegateacademycom Copyright reserved Web:wwwthegateacademycom 8
9 29 [Ans C] or T mode f u Since the wave guide is air filled u c a ence f z G z As f = 4 GHz f, the T mode will propagated u m s / / u ( ) phase velocity group velocity m s 30 [Ans*] Range: 4 to 4 urrent at node e (sin t cos t) d dt e (sin t cos t) e (cos t sin t) d dt *e (cos t sin t)+ L di dt e sin t e cos t k k k k 31 [Ans *] Range: 24 to 24 By KCL at output node So ( ) S M S M : , info@thegateacademycom Copyright reserved Web:wwwthegateacademycom 9
10 32 [Ans *] Range: i i ( ) i ( ) t t ( ) 33 [Ans B] Means : , info@thegateacademycom Copyright reserved Web:wwwthegateacademycom 10
11 34 [Ans B] Effective density of states Function (N ) = Therefore, the electron conduction is given by cm n N ep [ kt ] ep ( cm ) 35 [Ans *] Range: 13 to 13 cm sec cm sec So, diffusion length of holes, L m cm 36 [Ans A] Case I: CB configuration mitter injection efficiency ase transport factor input current n Case II: CE configuration T K T T / ( ) m ( ) ( ) : , info@thegateacademycom Copyright reserved Web:wwwthegateacademycom 11
12 37 [Ans *]Range 450 to 500 k i i and k i ( k ) for and for Regulation Regulation : , info@thegateacademycom Copyright reserved Web:wwwthegateacademycom 12
13 38 [Ans *] Range: 25 to 30 For current through the 3k resistance connected in the collector terminal of pnp transistor is O ( ) m k Therefore, emitter potential of the pnp transistor oltage drop across k Resistor m k current through k resistor m k k Now for Base of npn transistor is grounded ie at 0 Therefore oltage drop across R = ( ) Current through R = 2mA Required value of R m k m k m k Q Q m k m R 39 [Ans C] f R R or R R R R ( )( ) z : , info@thegateacademycom Copyright reserved Web:wwwthegateacademycom 13
14 40 [Ans *]Range: 37 to 4 For proper functioning the clock period should be equal to or greater than all t MO 12 s ns t of N N ns Total t ns s f z M z 41 [Ans *] Range: 1 to 1 A Q X X Y J K Q A = 0 A = 1 A = 0 Q = 0 Q = 1 A = 1 State changes when A = 1 : , info@thegateacademycom Copyright reserved Web:wwwthegateacademycom 14
15 42 [Ans B] LX B, 2100 H LX, 0200 H LX SP, 2700 PUSH B PUSH LX H, 0100 XTHL A L L HLT,E pair remains unchanged L : , info@thegateacademycom Copyright reserved Web:wwwthegateacademycom 15
16 43 [Ans B] (t) (n) { } t h(t) h(n) * + t (n) h(n) y(t) y(n) { } t y(t)dt (from the figure) 44 [Ans *] Range: 79 to 81 To solve this problem we could compute the analytical epression for the inverse Z-T, and then we could evaluate that epression at k=3 An alternative method to recall that (z) f, - f, -z f, -z f, -z f, -z ie, f[k] can be computed by epanding the fraction in power of z This can be done by dividing n(z) by d(z) upto the term z, its coefficient is equal to f[3] z z z z ) z z z z ( z z z z z z z z So, coefficient is 8 z z z z z z z z z z z z z z z z : , info@thegateacademycom Copyright reserved Web:wwwthegateacademycom 16
17 45 [Ans C] y stokes theorem ( ) ds dr i j k y z y z yz i(z ) k( z ),i(z ) k( z )- k (z ) (z )ds (z ) ds 46 [Ans ] ( ( ))u ( ( ))u z ( ( ))u [ ] [ ] [ ] [ ],u- y 47 [Ans *] Range: 30 to 30 Standard form of Phase Lead ompensator G (s) Or T T T T by comparing equation and T s T s sin [ ] = sin [ ] rad : , info@thegateacademycom Copyright reserved Web:wwwthegateacademycom 17
18 48 [Ans ] For stable system s should have roots in left half s plane s s s y (s ),(s y)(s ) - s (s ),s s( y) y- The roots to lie in left hand plane, y And y y y and y 49 [Ans ] For a single tone SSB-SC signal the waveform after carrier reinsertion becomes s (t) s(t) c(l) cos( t t) cos t ( cos t) cos t sin t sin t The output of the demodulation is given by [the envelope will be] (t), cos t-,sin t- cos t [ cos t] [ cos t], inomial epansion- cos t Neglecting dc component the normalized power of detected signal will be P [ ] Given P [ ] : , info@thegateacademycom Copyright reserved Web:wwwthegateacademycom 18
19 50 [Ans A] X (t), (t)- os t S, (t)- f ()d ( )d For m=1, ( S N ) S S ( S N ) / / ( S N ) ( S N ) / ( ) ( ) =31 m 51 [Ans *] Range: 247 to 247 Let the image frequency rejection ratio of the RF amplifier to be added be The rejection ratio ( ) at 1100 khz: f f f k z f f f f Q ( ) ( ) The rejection ratio ( ) at 25 MHz: f k z f f f f Q ( ) ( ) According to requirement ( ) ( ) So, loaded Q required for the RF stage Q (Q ) (Q ) ( ) : , info@thegateacademycom Copyright reserved Web:wwwthegateacademycom 19
20 52 [Ans C] BW of voice signal z The number of quantizing levels Number of bits required for sampling + supervision Number of the bits in each frame For synchronization Required W k z 53 [Ans *] Range: 240 to 240 ( t) cos( t ) verage power density ( )( ) ( ) verage power r ( ) ( ) ( ) watts 54 [Ans ] Airline can be regarded as a loss less line R G R L L rad m ividing by equation R and R ( ) rom equation L R ( ) ( ) n m p m : , info@thegateacademycom Copyright reserved Web:wwwthegateacademycom 20
21 55 [Ans *] Range: 881 to 886 dv d d d ( ) m negry nergy density volume nergy ( ) volume nergy ( ), d- mj J, - 56 [Ans ] They will chime together after the time in minutes equal to L M of L M min hrs min 57 [Ans C] According to the statement, 80% of the total runs were made by spinners So, conclusion I does not follow Nothing about the opening batsmen is mentioned in the statement So, conclusion II also does not follow 58 [Ans ] 1 km = 1000 meter 1 min = 60 second verage speed Total distance Total time Total distance = 12 km = meter Total time = minute = = 1440 seconds verage speed m s 59 [Ans A] 60 [Ans C] CEPQS - E cannot go with S AEPQS - C and P have to be together E cannot go with S ACPRS -It satisfies all the conditions and also there are two boys in the team BPRS - C and P have to be together Hence, C : , info@thegateacademycom Copyright reserved Web:wwwthegateacademycom 21
22 61 [Ans A] Number of males in U P [ of ( of N)] N Total population N Number of males in M P [ of ( of N)] N Number of males in Goa [ of ( of N)] N N N N Total males in these states ( )N N Required ( N ) 62 [Ans C] A cube is cut into 125 smaller cubes Length of cube = l = 5 unit Let upper face be coloured red Then bottom face will be coloured green, two adjacent faces are coloured yellow and blue respectively Two faces are uncoloured Number of cubes uncoloured on all faces = (n ) ( ) Now there are two surfaces which are not coloured There will be 9 cubes at centre on both the uncoloured surfaces each 3 cubes at the common edge of both uncoloured surfaces Total number of uncoloured cubes = = [Ans C] 64 [Ans B] The passage clearly states the unawareness of teachers regarding population education Thus, the teachers should be given a proper orientation on the same : , info@thegateacademycom Copyright reserved Web:wwwthegateacademycom 22
23 65 [Ans C] In statement I nothing is given about c Hence it is not enough to answer the question In statement II nothing is mentioned about a Hence this statement alone cannot answer the question Combining both the statements we get a : b : c = 3 : 15 : 10 a : c = 3 :10 a c a c c Question can be answered using both the statements Hence, C : , info@thegateacademycom Copyright reserved Web:wwwthegateacademycom 23
GATE-2019 Full Length Test Electrical Engineering Test ID: EE-FLT-2019
 Name:... GATE-2019 Full Length Test Electrical Engineering Duration: 3 hours Maimum marks : 100 Please read the following instructions carefully General nstructions 1. Total duration of eamination is 180
Name:... GATE-2019 Full Length Test Electrical Engineering Duration: 3 hours Maimum marks : 100 Please read the following instructions carefully General nstructions 1. Total duration of eamination is 180
Full Length Test Civil Engineering
 Full ength Test ivil Engineering nswer Keys and Explanations 1 [ns ] Green s theorem and stokes theorem convert line integral to surface integral and vice versa Whereas Gauss s Divergence theorem converts
Full ength Test ivil Engineering nswer Keys and Explanations 1 [ns ] Green s theorem and stokes theorem convert line integral to surface integral and vice versa Whereas Gauss s Divergence theorem converts
Homework Assignment 08
 Homework Assignment 08 Question 1 (Short Takes) Two points each unless otherwise indicated. 1. Give one phrase/sentence that describes the primary advantage of an active load. Answer: Large effective resistance
Homework Assignment 08 Question 1 (Short Takes) Two points each unless otherwise indicated. 1. Give one phrase/sentence that describes the primary advantage of an active load. Answer: Large effective resistance
GATE 2017 ECE Session 3 Answer Key
 1. Three pair cubical dice are thrown simultaneously. What is the probability that all three dice have same number is... Ans. ( 1 36 ). The one of the eigen value is real, rest are imaginary the real value
1. Three pair cubical dice are thrown simultaneously. What is the probability that all three dice have same number is... Ans. ( 1 36 ). The one of the eigen value is real, rest are imaginary the real value
Chapter 9 Bipolar Junction Transistor
 hapter 9 ipolar Junction Transistor hapter 9 - JT ipolar Junction Transistor JT haracteristics NPN, PNP JT D iasing ollector haracteristic and Load Line ipolar Junction Transistor (JT) JT is a three-terminal
hapter 9 ipolar Junction Transistor hapter 9 - JT ipolar Junction Transistor JT haracteristics NPN, PNP JT D iasing ollector haracteristic and Load Line ipolar Junction Transistor (JT) JT is a three-terminal
Quick Review. ESE319 Introduction to Microelectronics. and Q1 = Q2, what is the value of V O-dm. If R C1 = R C2. s.t. R C1. Let Q1 = Q2 and R C1
 Quick Review If R C1 = R C2 and Q1 = Q2, what is the value of V O-dm? Let Q1 = Q2 and R C1 R C2 s.t. R C1 > R C2, express R C1 & R C2 in terms R C and ΔR C. If V O-dm is the differential output offset
Quick Review If R C1 = R C2 and Q1 = Q2, what is the value of V O-dm? Let Q1 = Q2 and R C1 R C2 s.t. R C1 > R C2, express R C1 & R C2 in terms R C and ΔR C. If V O-dm is the differential output offset
BJT - Mode of Operations
 JT - Mode of Operations JTs can be modeled by two back-to-back diodes. N+ P N- N+ JTs are operated in four modes. HO #6: LN 251 - JT M Models Page 1 1) Forward active / normal junction forward biased junction
JT - Mode of Operations JTs can be modeled by two back-to-back diodes. N+ P N- N+ JTs are operated in four modes. HO #6: LN 251 - JT M Models Page 1 1) Forward active / normal junction forward biased junction
Electronic Circuits 1. Transistor Devices. Contents BJT and FET Characteristics Operations. Prof. C.K. Tse: Transistor devices
 Electronic Circuits 1 Transistor Devices Contents BJT and FET Characteristics Operations 1 What is a transistor? Three-terminal device whose voltage-current relationship is controlled by a third voltage
Electronic Circuits 1 Transistor Devices Contents BJT and FET Characteristics Operations 1 What is a transistor? Three-terminal device whose voltage-current relationship is controlled by a third voltage
Q. 1 Q. 25 carry one mark each.
 Q. Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q. Consider a system of linear equations: x y 3z =, x 3y 4z =, and x 4y 6 z = k. The value of k for which the system has infinitely many solutions is. Q. A function 3 = is
Q. Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q. Consider a system of linear equations: x y 3z =, x 3y 4z =, and x 4y 6 z = k. The value of k for which the system has infinitely many solutions is. Q. A function 3 = is
figure shows a pnp transistor biased to operate in the active mode
 Lecture 10b EE-215 Electronic Devices and Circuits Asst Prof Muhammad Anis Chaudhary BJT: Device Structure and Physical Operation The pnp Transistor figure shows a pnp transistor biased to operate in the
Lecture 10b EE-215 Electronic Devices and Circuits Asst Prof Muhammad Anis Chaudhary BJT: Device Structure and Physical Operation The pnp Transistor figure shows a pnp transistor biased to operate in the
GATE : , Copyright reserved. Web:www.thegateacademy.com
 GATE-2016 Index 1. Question Paper Analysis 2. Question Paper & Answer keys : 080-617 66 222, info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web:www.thegateacademy.com ANALYSIS OF GATE 2016 Electrical Engineering
GATE-2016 Index 1. Question Paper Analysis 2. Question Paper & Answer keys : 080-617 66 222, info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web:www.thegateacademy.com ANALYSIS OF GATE 2016 Electrical Engineering
Introduction to Transistors. Semiconductors Diodes Transistors
 Introduction to Transistors Semiconductors Diodes Transistors 1 Semiconductors Typical semiconductors, like silicon and germanium, have four valence electrons which form atomic bonds with neighboring atoms
Introduction to Transistors Semiconductors Diodes Transistors 1 Semiconductors Typical semiconductors, like silicon and germanium, have four valence electrons which form atomic bonds with neighboring atoms
Forward-Active Terminal Currents
 Forward-Active Terminal Currents Collector current: (electron diffusion current density) x (emitter area) diff J n AE qd n n po A E V E V th ------------------------------ e W (why minus sign? is by def.
Forward-Active Terminal Currents Collector current: (electron diffusion current density) x (emitter area) diff J n AE qd n n po A E V E V th ------------------------------ e W (why minus sign? is by def.
Q. 1 Q. 25 carry one mark each.
 GATE 5 SET- ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING - EC Q. Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q. The bilateral Laplace transform of a function is if a t b f() t = otherwise (A) a b s (B) s e ( a b) s (C) e as
GATE 5 SET- ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING - EC Q. Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q. The bilateral Laplace transform of a function is if a t b f() t = otherwise (A) a b s (B) s e ( a b) s (C) e as
Conventional Paper I-2010
 Conventional Paper I-010 1. (a) Sketch the covalent bonding of Si atoms in a intrinsic Si crystal Illustrate with sketches the formation of bonding in presence of donor and acceptor atoms. Sketch the energy
Conventional Paper I-010 1. (a) Sketch the covalent bonding of Si atoms in a intrinsic Si crystal Illustrate with sketches the formation of bonding in presence of donor and acceptor atoms. Sketch the energy
55:041 Electronic Circuits The University of Iowa Fall Exam 2
 Exam 2 Name: Score /60 Question 1 One point unless indicated otherwise. 1. An engineer measures the (step response) rise time of an amplifier as t r = 0.35 μs. Estimate the 3 db bandwidth of the amplifier.
Exam 2 Name: Score /60 Question 1 One point unless indicated otherwise. 1. An engineer measures the (step response) rise time of an amplifier as t r = 0.35 μs. Estimate the 3 db bandwidth of the amplifier.
ECE Branch GATE Paper The order of the differential equation + + = is (A) 1 (B) 2
 Question 1 Question 20 carry one mark each. 1. The order of the differential equation + + = is (A) 1 (B) 2 (C) 3 (D) 4 2. The Fourier series of a real periodic function has only P. Cosine terms if it is
Question 1 Question 20 carry one mark each. 1. The order of the differential equation + + = is (A) 1 (B) 2 (C) 3 (D) 4 2. The Fourier series of a real periodic function has only P. Cosine terms if it is
Electronics II. Midterm II
 The University of Toledo su7ms_elct7.fm - Electronics II Midterm II Problems Points. 7. 7 3. 6 Total 0 Was the exam fair? yes no The University of Toledo su7ms_elct7.fm - Problem 7 points Equation (-)
The University of Toledo su7ms_elct7.fm - Electronics II Midterm II Problems Points. 7. 7 3. 6 Total 0 Was the exam fair? yes no The University of Toledo su7ms_elct7.fm - Problem 7 points Equation (-)
Final Examination EE 130 December 16, 1997 Time allotted: 180 minutes
 Final Examination EE 130 December 16, 1997 Time allotted: 180 minutes Problem 1: Semiconductor Fundamentals [30 points] A uniformly doped silicon sample of length 100µm and cross-sectional area 100µm 2
Final Examination EE 130 December 16, 1997 Time allotted: 180 minutes Problem 1: Semiconductor Fundamentals [30 points] A uniformly doped silicon sample of length 100µm and cross-sectional area 100µm 2
At point G V = = = = = = RB B B. IN RB f
 Common Emitter At point G CE RC 0. 4 12 0. 4 116. I C RC 116. R 1k C 116. ma I IC 116. ma β 100 F 116µ A I R ( 116µ A)( 20kΩ) 2. 3 R + 2. 3 + 0. 7 30. IN R f Gain in Constant Current Region I I I C F
Common Emitter At point G CE RC 0. 4 12 0. 4 116. I C RC 116. R 1k C 116. ma I IC 116. ma β 100 F 116µ A I R ( 116µ A)( 20kΩ) 2. 3 R + 2. 3 + 0. 7 30. IN R f Gain in Constant Current Region I I I C F
ANALYSIS OF GATE 2018* (Memory Based) Electronics and Communication Engineering
 ANALYSS OF GATE 2018* (Memory Based) Electronics and Communication Engineering Electromagnetic Theory 8% Electronic Device Circuits 12% General Aptitude 15% Engineering Mathematics 14% Network Theory 7%
ANALYSS OF GATE 2018* (Memory Based) Electronics and Communication Engineering Electromagnetic Theory 8% Electronic Device Circuits 12% General Aptitude 15% Engineering Mathematics 14% Network Theory 7%
ELEN 610 Data Converters
 Spring 04 S. Hoyos - EEN-60 ELEN 60 Data onverters Sebastian Hoyos Texas A&M University Analog and Mixed Signal Group Spring 04 S. Hoyos - EEN-60 Electronic Noise Signal to Noise ratio SNR Signal Power
Spring 04 S. Hoyos - EEN-60 ELEN 60 Data onverters Sebastian Hoyos Texas A&M University Analog and Mixed Signal Group Spring 04 S. Hoyos - EEN-60 Electronic Noise Signal to Noise ratio SNR Signal Power
SOME USEFUL NETWORK THEOREMS
 APPENDIX D SOME USEFUL NETWORK THEOREMS Introduction In this appendix we review three network theorems that are useful in simplifying the analysis of electronic circuits: Thévenin s theorem Norton s theorem
APPENDIX D SOME USEFUL NETWORK THEOREMS Introduction In this appendix we review three network theorems that are useful in simplifying the analysis of electronic circuits: Thévenin s theorem Norton s theorem
Electronics and Communication Exercise 1
 Electronics and Communication Exercise 1 1. For matrices of same dimension M, N and scalar c, which one of these properties DOES NOT ALWAYS hold? (A) (M T ) T = M (C) (M + N) T = M T + N T (B) (cm)+ =
Electronics and Communication Exercise 1 1. For matrices of same dimension M, N and scalar c, which one of these properties DOES NOT ALWAYS hold? (A) (M T ) T = M (C) (M + N) T = M T + N T (B) (cm)+ =
1.1 An excitation is applied to a system at t = T and its response is zero for < t < T. Such a system is (a) non-causal system.
 . An excitation is applied to a system at t = T and its response is zero for < t < T. Such a system is (a) non-causal system x(t) (b) stable system (c) causal system (d) unstable system t=t t. In a series
. An excitation is applied to a system at t = T and its response is zero for < t < T. Such a system is (a) non-causal system x(t) (b) stable system (c) causal system (d) unstable system t=t t. In a series
Device Physics: The Bipolar Transistor
 Monolithic Amplifier Circuits: Device Physics: The Bipolar Transistor Chapter 4 Jón Tómas Guðmundsson tumi@hi.is 2. Week Fall 2010 1 Introduction In analog design the transistors are not simply switches
Monolithic Amplifier Circuits: Device Physics: The Bipolar Transistor Chapter 4 Jón Tómas Guðmundsson tumi@hi.is 2. Week Fall 2010 1 Introduction In analog design the transistors are not simply switches
Microelectronic Circuit Design Fourth Edition - Part I Solutions to Exercises
 Page Microelectronic Circuit esign Fourth Edition - Part I Solutions to Exercises CHAPTER V LSB 5.V 0 bits 5.V 04bits 5.00 mv V 5.V MSB.560V 000000 9 + 8 + 4 + 0 785 0 V O 785 5.00mV or ) 5.V 3.95 V V
Page Microelectronic Circuit esign Fourth Edition - Part I Solutions to Exercises CHAPTER V LSB 5.V 0 bits 5.V 04bits 5.00 mv V 5.V MSB.560V 000000 9 + 8 + 4 + 0 785 0 V O 785 5.00mV or ) 5.V 3.95 V V
Nyquist-Rate A/D Converters
 IsLab Analog Integrated ircuit Design AD-51 Nyquist-ate A/D onverters כ Kyungpook National University IsLab Analog Integrated ircuit Design AD-1 Nyquist-ate MOS A/D onverters Nyquist-rate : oversampling
IsLab Analog Integrated ircuit Design AD-51 Nyquist-ate A/D onverters כ Kyungpook National University IsLab Analog Integrated ircuit Design AD-1 Nyquist-ate MOS A/D onverters Nyquist-rate : oversampling
Vidyalankar S.E. Sem. III [EXTC] Analog Electronics - I Prelim Question Paper Solution
![Vidyalankar S.E. Sem. III [EXTC] Analog Electronics - I Prelim Question Paper Solution Vidyalankar S.E. Sem. III [EXTC] Analog Electronics - I Prelim Question Paper Solution](/thumbs/90/101612294.jpg) . (a) S.E. Sem. [EXTC] Analog Electronics - Prelim Question Paper Solution Comparison between BJT and JFET BJT JFET ) BJT is a bipolar device, both majority JFET is an unipolar device, electron and minority
. (a) S.E. Sem. [EXTC] Analog Electronics - Prelim Question Paper Solution Comparison between BJT and JFET BJT JFET ) BJT is a bipolar device, both majority JFET is an unipolar device, electron and minority
Homework Assignment 09
 Homework Assignment 09 Question 1 (Short Takes) Two points each unless otherwise indicated. 1. What is the 3-dB bandwidth of the amplifier shown below if r π = 2.5K, r o = 100K, g m = 40 ms, and C L =
Homework Assignment 09 Question 1 (Short Takes) Two points each unless otherwise indicated. 1. What is the 3-dB bandwidth of the amplifier shown below if r π = 2.5K, r o = 100K, g m = 40 ms, and C L =
EE 330 Lecture 20. Bipolar Device Modeling
 330 Lecture 20 ipolar Device Modeling xam 2 Friday March 9 xam 3 Friday April 13 Review from Last Lecture ipolar Transistors npn stack pnp stack ipolar Devices Show asic Symmetry lectrical Properties not
330 Lecture 20 ipolar Device Modeling xam 2 Friday March 9 xam 3 Friday April 13 Review from Last Lecture ipolar Transistors npn stack pnp stack ipolar Devices Show asic Symmetry lectrical Properties not
CMOS Comparators. Kyungpook National University. Integrated Systems Lab, Kyungpook National University. Comparators
 IsLab Analog Integrated ircuit Design OMP-21 MOS omparators כ Kyungpook National University IsLab Analog Integrated ircuit Design OMP-1 omparators A comparator is used to detect whether a signal is greater
IsLab Analog Integrated ircuit Design OMP-21 MOS omparators כ Kyungpook National University IsLab Analog Integrated ircuit Design OMP-1 omparators A comparator is used to detect whether a signal is greater
S.E. Sem. III [ETRX] Electronic Circuits and Design I
![S.E. Sem. III [ETRX] Electronic Circuits and Design I S.E. Sem. III [ETRX] Electronic Circuits and Design I](/thumbs/95/124107626.jpg) S.E. Sem. [ETRX] Electronic ircuits and Design Time : 3 Hrs.] Prelim Paper Solution [Marks : 80 Q.1(a) What happens when diode is operated at high frequency? [5] Ans.: Diode High Frequency Model : This
S.E. Sem. [ETRX] Electronic ircuits and Design Time : 3 Hrs.] Prelim Paper Solution [Marks : 80 Q.1(a) What happens when diode is operated at high frequency? [5] Ans.: Diode High Frequency Model : This
ECE 304: Design Issues for Voltage Follower as Output Stage S&S Chapter 14, pp
 ECE 34: Design Issues for oltage Follower as Output Stage S&S Chapter 14, pp. 131133 Introduction The voltage follower provides a good buffer between a differential amplifier and a load in two ways: 1.
ECE 34: Design Issues for oltage Follower as Output Stage S&S Chapter 14, pp. 131133 Introduction The voltage follower provides a good buffer between a differential amplifier and a load in two ways: 1.
INDIAN SPACE RESEARCH ORGANISATION. Recruitment Entrance Test for Scientist/Engineer SC 2017
 1. The signal m (t) as shown is applied both to a phase modulator (with kp as the phase constant) and a frequency modulator with ( kf as the frequency constant) having the same carrier frequency. The ratio
1. The signal m (t) as shown is applied both to a phase modulator (with kp as the phase constant) and a frequency modulator with ( kf as the frequency constant) having the same carrier frequency. The ratio
SWITCHED CAPACITOR AMPLIFIERS
 SWITCHED CAPACITOR AMPLIFIERS AO 0V 4. AO 0V 4.2 i Q AO 0V 4.3 Q AO 0V 4.4 Q i AO 0V 4.5 AO 0V 4.6 i Q AO 0V 4.7 Q AO 0V 4.8 i Q AO 0V 4.9 Simple amplifier First approach: A 0 = infinite. C : V C = V s
SWITCHED CAPACITOR AMPLIFIERS AO 0V 4. AO 0V 4.2 i Q AO 0V 4.3 Q AO 0V 4.4 Q i AO 0V 4.5 AO 0V 4.6 i Q AO 0V 4.7 Q AO 0V 4.8 i Q AO 0V 4.9 Simple amplifier First approach: A 0 = infinite. C : V C = V s
ECE-342 Test 2 Solutions, Nov 4, :00-8:00pm, Closed Book (one page of notes allowed)
 ECE-342 Test 2 Solutions, Nov 4, 2008 6:00-8:00pm, Closed Book (one page of notes allowed) Please use the following physical constants in your calculations: Boltzmann s Constant: Electron Charge: Free
ECE-342 Test 2 Solutions, Nov 4, 2008 6:00-8:00pm, Closed Book (one page of notes allowed) Please use the following physical constants in your calculations: Boltzmann s Constant: Electron Charge: Free
ECE-343 Test 2: Mar 21, :00-8:00, Closed Book. Name : SOLUTION
 ECE-343 Test 2: Mar 21, 2012 6:00-8:00, Closed Book Name : SOLUTION 1. (25 pts) (a) Draw a circuit diagram for a differential amplifier designed under the following constraints: Use only BJTs. (You may
ECE-343 Test 2: Mar 21, 2012 6:00-8:00, Closed Book Name : SOLUTION 1. (25 pts) (a) Draw a circuit diagram for a differential amplifier designed under the following constraints: Use only BJTs. (You may
EECE 2150 Circuits and Signals Final Exam Fall 2016 Dec 16
 EECE 2150 Circuits and Signals Final Exam Fall 2016 Dec 16 Instructions: Write your name and section number on all pages Closed book, closed notes; Computers and cell phones are not allowed You can use
EECE 2150 Circuits and Signals Final Exam Fall 2016 Dec 16 Instructions: Write your name and section number on all pages Closed book, closed notes; Computers and cell phones are not allowed You can use
Electronic Circuits Summary
 Electronic Circuits Summary Andreas Biri, D-ITET 6.06.4 Constants (@300K) ε 0 = 8.854 0 F m m 0 = 9. 0 3 kg k =.38 0 3 J K = 8.67 0 5 ev/k kt q = 0.059 V, q kt = 38.6, kt = 5.9 mev V Small Signal Equivalent
Electronic Circuits Summary Andreas Biri, D-ITET 6.06.4 Constants (@300K) ε 0 = 8.854 0 F m m 0 = 9. 0 3 kg k =.38 0 3 J K = 8.67 0 5 ev/k kt q = 0.059 V, q kt = 38.6, kt = 5.9 mev V Small Signal Equivalent
ONE MARK QUESTIONS. 1. The condition on R, L and C such that the step response y(t) in the figure has no oscillations, is
 ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING ONE MARK QUESTIONS. The condition on R, L and C such that the step response y(t) in the figure has no oscillations, is (a.) R L C (b.) R L C (c.) R L C (d.) R LC
ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING ONE MARK QUESTIONS. The condition on R, L and C such that the step response y(t) in the figure has no oscillations, is (a.) R L C (b.) R L C (c.) R L C (d.) R LC
Chapter 13 Small-Signal Modeling and Linear Amplification
 Chapter 13 Small-Signal Modeling and Linear Amplification Microelectronic Circuit Design Richard C. Jaeger Travis N. Blalock 1/4/12 Chap 13-1 Chapter Goals Understanding of concepts related to: Transistors
Chapter 13 Small-Signal Modeling and Linear Amplification Microelectronic Circuit Design Richard C. Jaeger Travis N. Blalock 1/4/12 Chap 13-1 Chapter Goals Understanding of concepts related to: Transistors
GATE Question Paper & Answer Keys
 Question Paper & Answer Keys Index 1 Question Paper Analysis 2 Question Paper & Answer keys : 080-617 66 222, info@thegateacademycom Copyright reserved Web:wwwthegateacademycom ANALSIS OF GATE 2010 Electrical
Question Paper & Answer Keys Index 1 Question Paper Analysis 2 Question Paper & Answer keys : 080-617 66 222, info@thegateacademycom Copyright reserved Web:wwwthegateacademycom ANALSIS OF GATE 2010 Electrical
1 P a g e.
 1. Choose the most appropriate word from the options given below to complete the following sentence. Communication and interpersonal skills are important in their own ways. each B. both C. all either.
1. Choose the most appropriate word from the options given below to complete the following sentence. Communication and interpersonal skills are important in their own ways. each B. both C. all either.
WORKBOOK. Try Yourself Questions. Electrical Engineering Digital Electronics. Detailed Explanations of
 27 WORKBOOK Detailed Eplanations of Try Yourself Questions Electrical Engineering Digital Electronics Number Systems and Codes T : Solution Converting into decimal number system 2 + 3 + 5 + 8 2 + 4 8 +
27 WORKBOOK Detailed Eplanations of Try Yourself Questions Electrical Engineering Digital Electronics Number Systems and Codes T : Solution Converting into decimal number system 2 + 3 + 5 + 8 2 + 4 8 +
Institute of Solid State Physics. Technische Universität Graz. Exam. Feb 2, 10:00-11:00 P2
 Technische Universität Graz nstitute of Solid State Physics Exam Feb 2, 10:00-11:00 P2 Exam Four questions, two from the online list. Calculator is ok. No notes. Explain some concept: (tunnel contact,
Technische Universität Graz nstitute of Solid State Physics Exam Feb 2, 10:00-11:00 P2 Exam Four questions, two from the online list. Calculator is ok. No notes. Explain some concept: (tunnel contact,
GATE : , Copyright reserved. Web:www.thegateacademy.com
 Index. Question Paper Analysis 2. Question Paper & Answer keys : 080-67 66 222, info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web:www.thegateacademy.com ANALYSIS OF GATE 206 Electrical Engineering CN Mathematics
Index. Question Paper Analysis 2. Question Paper & Answer keys : 080-67 66 222, info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web:www.thegateacademy.com ANALYSIS OF GATE 206 Electrical Engineering CN Mathematics
Final Exam. 55:041 Electronic Circuits. The University of Iowa. Fall 2013.
 Final Exam Name: Max: 130 Points Question 1 In the circuit shown, the op-amp is ideal, except for an input bias current I b = 1 na. Further, R F = 10K, R 1 = 100 Ω and C = 1 μf. The switch is opened at
Final Exam Name: Max: 130 Points Question 1 In the circuit shown, the op-amp is ideal, except for an input bias current I b = 1 na. Further, R F = 10K, R 1 = 100 Ω and C = 1 μf. The switch is opened at
(Refer Slide Time: 1:49)
 Analog Electronic Circuits Professor S. C. Dutta Roy Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Delhi Lecture no 14 Module no 01 Midband analysis of FET Amplifiers (Refer Slide
Analog Electronic Circuits Professor S. C. Dutta Roy Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Delhi Lecture no 14 Module no 01 Midband analysis of FET Amplifiers (Refer Slide
The BJT Differential Amplifier. Basic Circuit. DC Solution
 c Copyright 010. W. Marshall Leach, Jr., Professor, Georgia Institute of Technology, School of Electrical and Computer Engineering. The BJT Differential Amplifier Basic Circuit Figure 1 shows the circuit
c Copyright 010. W. Marshall Leach, Jr., Professor, Georgia Institute of Technology, School of Electrical and Computer Engineering. The BJT Differential Amplifier Basic Circuit Figure 1 shows the circuit
Homework Assignment 11
 Homework Assignment Question State and then explain in 2 3 sentences, the advantage of switched capacitor filters compared to continuous-time active filters. (3 points) Continuous time filters use resistors
Homework Assignment Question State and then explain in 2 3 sentences, the advantage of switched capacitor filters compared to continuous-time active filters. (3 points) Continuous time filters use resistors
(Refer Slide Time: 1:22)
 Analog Electronic Circuits Professor S. C. Dutta Roy Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Delhi Lecture no 19 Module no 01 Problem Session 5 on Frequency Response of Small
Analog Electronic Circuits Professor S. C. Dutta Roy Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Delhi Lecture no 19 Module no 01 Problem Session 5 on Frequency Response of Small
OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER ª Differential-input, Single-Ended (or Differential) output, DC-coupled, High-Gain amplifier
 à OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS à OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS (Introduction and Properties) Phase relationships: Non-inverting input to output is 0 Inverting input to output is 180 OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER ª Differential-input,
à OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS à OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS (Introduction and Properties) Phase relationships: Non-inverting input to output is 0 Inverting input to output is 180 OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER ª Differential-input,
EC Objective Paper I (Set - D)
 EC-Objective Paper-I ESE-5 www.gateforum.com EC Objective Paper I (Set - D). If a system produces frequencies in the output are not present in the input, then the system cannot be Minimum phase system
EC-Objective Paper-I ESE-5 www.gateforum.com EC Objective Paper I (Set - D). If a system produces frequencies in the output are not present in the input, then the system cannot be Minimum phase system
Section 5.4 BJT Circuits at DC
 12/3/2004 section 5_4 JT Circuits at DC 1/1 Section 5.4 JT Circuits at DC Reading Assignment: pp. 421-436 To analyze a JT circuit, we follow the same boring procedure as always: ASSUME, ENFORCE, ANALYZE
12/3/2004 section 5_4 JT Circuits at DC 1/1 Section 5.4 JT Circuits at DC Reading Assignment: pp. 421-436 To analyze a JT circuit, we follow the same boring procedure as always: ASSUME, ENFORCE, ANALYZE
ELEC 3908, Physical Electronics, Lecture 18. The Early Effect, Breakdown and Self-Heating
 ELEC 3908, Physical Electronics, Lecture 18 The Early Effect, Breakdown and Self-Heating Lecture Outline Previous 2 lectures analyzed fundamental static (dc) carrier transport in the bipolar transistor
ELEC 3908, Physical Electronics, Lecture 18 The Early Effect, Breakdown and Self-Heating Lecture Outline Previous 2 lectures analyzed fundamental static (dc) carrier transport in the bipolar transistor
Poynting Vector and Energy Flow W14D1
 Poynting Vector and Energy Flow W14D1 1 Announcements Week 14 Prepset due online Friday 8:30 am PS 11 due Week 14 Friday at 9 pm in boxes outside 26-152 Sunday Tutoring 1-5 pm in 26-152 2 Outline Poynting
Poynting Vector and Energy Flow W14D1 1 Announcements Week 14 Prepset due online Friday 8:30 am PS 11 due Week 14 Friday at 9 pm in boxes outside 26-152 Sunday Tutoring 1-5 pm in 26-152 2 Outline Poynting
Notes for course EE1.1 Circuit Analysis TOPIC 10 2-PORT CIRCUITS
 Objectives: Introduction Notes for course EE1.1 Circuit Analysis 4-5 Re-examination of 1-port sub-circuits Admittance parameters for -port circuits TOPIC 1 -PORT CIRCUITS Gain and port impedance from -port
Objectives: Introduction Notes for course EE1.1 Circuit Analysis 4-5 Re-examination of 1-port sub-circuits Admittance parameters for -port circuits TOPIC 1 -PORT CIRCUITS Gain and port impedance from -port
CE/CS Amplifier Response at High Frequencies
 .. CE/CS Amplifier Response at High Frequencies INEL 4202 - Manuel Toledo August 20, 2012 INEL 4202 - Manuel Toledo CE/CS High Frequency Analysis 1/ 24 Outline.1 High Frequency Models.2 Simplified Method.3
.. CE/CS Amplifier Response at High Frequencies INEL 4202 - Manuel Toledo August 20, 2012 INEL 4202 - Manuel Toledo CE/CS High Frequency Analysis 1/ 24 Outline.1 High Frequency Models.2 Simplified Method.3
Oversampling Converters
 Oversampling Converters David Johns and Ken Martin (johns@eecg.toronto.edu) (martin@eecg.toronto.edu) slide 1 of 56 Motivation Popular approach for medium-to-low speed A/D and D/A applications requiring
Oversampling Converters David Johns and Ken Martin (johns@eecg.toronto.edu) (martin@eecg.toronto.edu) slide 1 of 56 Motivation Popular approach for medium-to-low speed A/D and D/A applications requiring
ESE319 Introduction to Microelectronics Bode Plot Review High Frequency BJT Model
 Bode Plot Review High Frequency BJT Model 1 Logarithmic Frequency Response Plots (Bode Plots) Generic form of frequency response rational polynomial, where we substitute jω for s: H s=k sm a m 1 s m 1
Bode Plot Review High Frequency BJT Model 1 Logarithmic Frequency Response Plots (Bode Plots) Generic form of frequency response rational polynomial, where we substitute jω for s: H s=k sm a m 1 s m 1
ELECTRONICS IA 2017 SCHEME
 ELECTRONICS IA 2017 SCHEME CONTENTS 1 [ 5 marks ]...4 2...5 a. [ 2 marks ]...5 b. [ 2 marks ]...5 c. [ 5 marks ]...5 d. [ 2 marks ]...5 3...6 a. [ 3 marks ]...6 b. [ 3 marks ]...6 4 [ 7 marks ]...7 5...8
ELECTRONICS IA 2017 SCHEME CONTENTS 1 [ 5 marks ]...4 2...5 a. [ 2 marks ]...5 b. [ 2 marks ]...5 c. [ 5 marks ]...5 d. [ 2 marks ]...5 3...6 a. [ 3 marks ]...6 b. [ 3 marks ]...6 4 [ 7 marks ]...7 5...8
Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each.
 GATE 2019 General Aptitude (GA) Set-3 Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q.1 I am not sure if the bus that has been booked will be able to all the students. (A) sit (B) deteriorate (C) fill (D) accommodate
GATE 2019 General Aptitude (GA) Set-3 Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q.1 I am not sure if the bus that has been booked will be able to all the students. (A) sit (B) deteriorate (C) fill (D) accommodate
ANALYSIS OF GATE 2017* Electrical Engineering
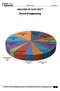 ANALYSS OF GATE 2017* Electrical Engineering Power Systems 10% General Aptitude 15% Engineering Mathematics 11% Network Theory 9% Signals & Systems 7% Electrical Machines 12% Control Systems 11% Power
ANALYSS OF GATE 2017* Electrical Engineering Power Systems 10% General Aptitude 15% Engineering Mathematics 11% Network Theory 9% Signals & Systems 7% Electrical Machines 12% Control Systems 11% Power
Circle the one best answer for each question. Five points per question.
 ID # NAME EE-255 EXAM 3 November 8, 2001 Instructor (circle one) Talavage Gray This exam consists of 16 multiple choice questions and one workout problem. Record all answers to the multiple choice questions
ID # NAME EE-255 EXAM 3 November 8, 2001 Instructor (circle one) Talavage Gray This exam consists of 16 multiple choice questions and one workout problem. Record all answers to the multiple choice questions
Basic Electronics. Introductory Lecture Course for. Technology and Instrumentation in Particle Physics Chicago, Illinois June 9-14, 2011
 Basic Electronics Introductory Lecture Course for Technology and Instrumentation in Particle Physics 2011 Chicago, Illinois June 9-14, 2011 Presented By Gary Drake Argonne National Laboratory drake@anl.gov
Basic Electronics Introductory Lecture Course for Technology and Instrumentation in Particle Physics 2011 Chicago, Illinois June 9-14, 2011 Presented By Gary Drake Argonne National Laboratory drake@anl.gov
Switching circuits: basics and switching speed
 ECE137B notes; copyright 2018 Switching circuits: basics and switching speed Mark Rodwell, University of California, Santa Barbara Amplifiers vs. switching circuits Some transistor circuit might have V
ECE137B notes; copyright 2018 Switching circuits: basics and switching speed Mark Rodwell, University of California, Santa Barbara Amplifiers vs. switching circuits Some transistor circuit might have V
CHAPTER 7 - CD COMPANION
 Chapter 7 - CD companion 1 CHAPTER 7 - CD COMPANION CD-7.2 Biasing of Single-Stage Amplifiers This companion section to the text contains detailed treatments of biasing circuits for both bipolar and field-effect
Chapter 7 - CD companion 1 CHAPTER 7 - CD COMPANION CD-7.2 Biasing of Single-Stage Amplifiers This companion section to the text contains detailed treatments of biasing circuits for both bipolar and field-effect
CHEM*3440. Current Convention. Charge. Potential Energy. Chemical Instrumentation. Rudimentary Electronics. Topic 3
 urrent onvention HEM*3440 hemical nstrumentation Topic 3 udimentary Electronics ONENTON: Electrical current flows from a region of positive potential energy to a region of more negative (or less positive)
urrent onvention HEM*3440 hemical nstrumentation Topic 3 udimentary Electronics ONENTON: Electrical current flows from a region of positive potential energy to a region of more negative (or less positive)
EE105 - Fall 2006 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits
 EE105 - Fall 2006 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits Prof. Jan M. Rabaey (jan@eecs) Lecture 21: Bipolar Junction Transistor Administrative Midterm Th 6:30-8pm in Sibley Auditorium Covering everything
EE105 - Fall 2006 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits Prof. Jan M. Rabaey (jan@eecs) Lecture 21: Bipolar Junction Transistor Administrative Midterm Th 6:30-8pm in Sibley Auditorium Covering everything
Bipolar junction transistors
 Bipolar junction transistors Find parameters of te BJT in CE configuration at BQ 40 µa and CBQ V. nput caracteristic B / µa 40 0 00 80 60 40 0 0 0, 0,5 0,3 0,35 0,4 BE / V Output caracteristics C / ma
Bipolar junction transistors Find parameters of te BJT in CE configuration at BQ 40 µa and CBQ V. nput caracteristic B / µa 40 0 00 80 60 40 0 0 0, 0,5 0,3 0,35 0,4 BE / V Output caracteristics C / ma
6.1 Introduction
 6. Introduction A.C Circuits made up of resistors, inductors and capacitors are said to be resonant circuits when the current drawn from the supply is in phase with the impressed sinusoidal voltage. Then.
6. Introduction A.C Circuits made up of resistors, inductors and capacitors are said to be resonant circuits when the current drawn from the supply is in phase with the impressed sinusoidal voltage. Then.
The Common-Emitter Amplifier
 c Copyright 2009. W. Marshall Leach, Jr., Professor, Georgia Institute of Technology, School of Electrical and Computer Engineering. The Common-Emitter Amplifier Basic Circuit Fig. shows the circuit diagram
c Copyright 2009. W. Marshall Leach, Jr., Professor, Georgia Institute of Technology, School of Electrical and Computer Engineering. The Common-Emitter Amplifier Basic Circuit Fig. shows the circuit diagram
Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT) - Introduction
 Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT) - Introduction It was found in 1948 at the Bell Telephone Laboratories. It is a three terminal device and has three semiconductor regions. It can be used in signal amplification
Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT) - Introduction It was found in 1948 at the Bell Telephone Laboratories. It is a three terminal device and has three semiconductor regions. It can be used in signal amplification
GATE 2009 Electronics and Communication Engineering
 GATE 2009 Electronics and Communication Engineering Question 1 Question 20 carry one mark each. 1. The order of the differential equation + + y =e (A) 1 (B) 2 (C) 3 (D) 4 is 2. The Fourier series of a
GATE 2009 Electronics and Communication Engineering Question 1 Question 20 carry one mark each. 1. The order of the differential equation + + y =e (A) 1 (B) 2 (C) 3 (D) 4 is 2. The Fourier series of a
EE105 Fall 2014 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits
 EE05 Fall 204 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits Prof. Ming C. Wu wu@eecs.berkeley.edu 5 Sutardja Dai Hall (SDH) Terminal Gain and I/O Resistances of BJT Amplifiers Emitter (CE) Collector (CC) Base (CB)
EE05 Fall 204 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits Prof. Ming C. Wu wu@eecs.berkeley.edu 5 Sutardja Dai Hall (SDH) Terminal Gain and I/O Resistances of BJT Amplifiers Emitter (CE) Collector (CC) Base (CB)
RIB. ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Analog Electronics. 8 Electrical Engineering RIB-R T7. Detailed Explanations. Rank Improvement Batch ANSWERS.
 8 Electrical Engineering RIB-R T7 Session 08-9 S.No. : 9078_LS RIB Rank Improvement Batch ELECTRICL ENGINEERING nalog Electronics NSWERS. (d) 7. (a) 3. (c) 9. (a) 5. (d). (d) 8. (c) 4. (c) 0. (c) 6. (b)
8 Electrical Engineering RIB-R T7 Session 08-9 S.No. : 9078_LS RIB Rank Improvement Batch ELECTRICL ENGINEERING nalog Electronics NSWERS. (d) 7. (a) 3. (c) 9. (a) 5. (d). (d) 8. (c) 4. (c) 0. (c) 6. (b)
Sinusoidal Steady State Analysis (AC Analysis) Part II
 Sinusoidal Steady State Analysis (AC Analysis) Part II Amin Electronics and Electrical Communications Engineering Department (EECE) Cairo University elc.n102.eng@gmail.com http://scholar.cu.edu.eg/refky/
Sinusoidal Steady State Analysis (AC Analysis) Part II Amin Electronics and Electrical Communications Engineering Department (EECE) Cairo University elc.n102.eng@gmail.com http://scholar.cu.edu.eg/refky/
Whereas the diode was a 1-junction device, the transistor contains two junctions. This leads to two possibilities:
 Part Recall: two types of charge carriers in semiconductors: electrons & holes two types of doped semiconductors: n-type (favor e-), p-type (favor holes) for conduction Whereas the diode was a -junction
Part Recall: two types of charge carriers in semiconductors: electrons & holes two types of doped semiconductors: n-type (favor e-), p-type (favor holes) for conduction Whereas the diode was a -junction
Chapter 10 Instructor Notes
 G. izzoni, Principles and Applications of lectrical ngineering Problem solutions, hapter 10 hapter 10 nstructor Notes hapter 10 introduces bipolar junction transistors. The material on transistors has
G. izzoni, Principles and Applications of lectrical ngineering Problem solutions, hapter 10 hapter 10 nstructor Notes hapter 10 introduces bipolar junction transistors. The material on transistors has
Switched Capacitor Circuits I. Prof. Paul Hasler Georgia Institute of Technology
 Switched Capacitor Circuits I Prof. Paul Hasler Georgia Institute of Technology Switched Capacitor Circuits Making a resistor using a capacitor and switches; therefore resistance is set by a digital clock
Switched Capacitor Circuits I Prof. Paul Hasler Georgia Institute of Technology Switched Capacitor Circuits Making a resistor using a capacitor and switches; therefore resistance is set by a digital clock
EE 230 Lecture 33. Nonlinear Circuits and Nonlinear Devices. Diode BJT MOSFET
 EE 230 Lecture 33 Nonlinear Circuits and Nonlinear Devices Diode BJT MOSFET Review from Last Time: n-channel MOSFET Source Gate L Drain W L EFF Poly Gate oxide n-active p-sub depletion region (electrically
EE 230 Lecture 33 Nonlinear Circuits and Nonlinear Devices Diode BJT MOSFET Review from Last Time: n-channel MOSFET Source Gate L Drain W L EFF Poly Gate oxide n-active p-sub depletion region (electrically
R. Ludwig and G. Bogdanov RF Circuit Design: Theory and Applications 2 nd edition. Figures for Chapter 6
 R. Ludwig and G. Bogdanov RF Circuit Design: Theory and Applications 2 nd edition Figures for Chapter 6 Free electron Conduction band Hole W g W C Forbidden Band or Bandgap W V Electron energy Hole Valence
R. Ludwig and G. Bogdanov RF Circuit Design: Theory and Applications 2 nd edition Figures for Chapter 6 Free electron Conduction band Hole W g W C Forbidden Band or Bandgap W V Electron energy Hole Valence
FE Review 2/2/2011. Electric Charge. Electric Energy ELECTRONICS # 1 FUNDAMENTALS
 FE eview ELECONICS # FUNDAMENALS Electric Charge 2 In an electric circuit there is a conservation of charge. he net electric charge is constant. here are positive and negative charges. Like charges repel
FE eview ELECONICS # FUNDAMENALS Electric Charge 2 In an electric circuit there is a conservation of charge. he net electric charge is constant. here are positive and negative charges. Like charges repel
Lecture 23: NorCal 40A Power Amplifier. Thermal Modeling.
 Whites, EE 322 Lecture 23 Page 1 of 13 Lecture 23: NorCal 40A Power Amplifier. Thermal Modeling. Recall from the last lecture that the NorCal 40A uses a Class C power amplifier. From Fig. 10.3(b) the collector
Whites, EE 322 Lecture 23 Page 1 of 13 Lecture 23: NorCal 40A Power Amplifier. Thermal Modeling. Recall from the last lecture that the NorCal 40A uses a Class C power amplifier. From Fig. 10.3(b) the collector
Sinusoidal Steady-State Analysis
 Chapter 4 Sinusoidal Steady-State Analysis In this unit, we consider circuits in which the sources are sinusoidal in nature. The review section of this unit covers most of section 9.1 9.9 of the text.
Chapter 4 Sinusoidal Steady-State Analysis In this unit, we consider circuits in which the sources are sinusoidal in nature. The review section of this unit covers most of section 9.1 9.9 of the text.
Electronics II. Final Examination
 The University of Toledo f17fs_elct27.fm 1 Electronics II Final Examination Problems Points 1. 11 2. 14 3. 15 Total 40 Was the exam fair? yes no The University of Toledo f17fs_elct27.fm 2 Problem 1 11
The University of Toledo f17fs_elct27.fm 1 Electronics II Final Examination Problems Points 1. 11 2. 14 3. 15 Total 40 Was the exam fair? yes no The University of Toledo f17fs_elct27.fm 2 Problem 1 11
Assignment 3 ELEC 312/Winter 12 R.Raut, Ph.D.
 Page 1 of 3 ELEC 312: ELECTRONICS II : ASSIGNMENT-3 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Winter 2012 1. A common-emitter amplifier that can be represented by the following equivalent circuit,
Page 1 of 3 ELEC 312: ELECTRONICS II : ASSIGNMENT-3 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Winter 2012 1. A common-emitter amplifier that can be represented by the following equivalent circuit,
To discuss this question paper visit Navigate to the Discussion Forum.
 GATE-2019 Full Length Test Civil Engineering Name:... Test ID: CE-FLT- 2019 Duration: 3 hours Maximum marks : 100 Please read the following instructions carefully General Instructions 1. Total duration
GATE-2019 Full Length Test Civil Engineering Name:... Test ID: CE-FLT- 2019 Duration: 3 hours Maximum marks : 100 Please read the following instructions carefully General Instructions 1. Total duration
Exercise The determinant of matrix A is 5 and the determinant of matrix B is 40. The determinant of matrix AB is.
 Exercise 1. The determinant of matrix A is 5 and the determinant of matrix B is 40. The determinant of matrix AB is.. Let X be a random variable which is uniformly chosen from the set of positive odd numbers
Exercise 1. The determinant of matrix A is 5 and the determinant of matrix B is 40. The determinant of matrix AB is.. Let X be a random variable which is uniformly chosen from the set of positive odd numbers
DEPARTMENT OF ECE UNIT VII BIASING & STABILIZATION AMPLIFIER:
 UNIT VII IASING & STAILIZATION AMPLIFIE: - A circuit that increases the amplitude of given signal is an amplifier - Small ac signal applied to an amplifier is obtained as large a.c. signal of same frequency
UNIT VII IASING & STAILIZATION AMPLIFIE: - A circuit that increases the amplitude of given signal is an amplifier - Small ac signal applied to an amplifier is obtained as large a.c. signal of same frequency
Spring Semester 2012 Final Exam
 Spring Semester 2012 Final Exam Note: Show your work, underline results, and always show units. Official exam time: 2.0 hours; an extension of at least 1.0 hour will be granted to anyone. Materials parameters
Spring Semester 2012 Final Exam Note: Show your work, underline results, and always show units. Official exam time: 2.0 hours; an extension of at least 1.0 hour will be granted to anyone. Materials parameters
Chapter 2. - DC Biasing - BJTs
 Chapter 2. - DC Biasing - BJTs Objectives To Understand : Concept of Operating point and stability Analyzing Various biasing circuits and their comparison with respect to stability BJT A Review Invented
Chapter 2. - DC Biasing - BJTs Objectives To Understand : Concept of Operating point and stability Analyzing Various biasing circuits and their comparison with respect to stability BJT A Review Invented
ID # NAME. EE-255 EXAM 3 April 7, Instructor (circle one) Ogborn Lundstrom
 ID # NAME EE-255 EXAM 3 April 7, 1998 Instructor (circle one) Ogborn Lundstrom This exam consists of 20 multiple choice questions. Record all answers on this page, but you must turn in the entire exam.
ID # NAME EE-255 EXAM 3 April 7, 1998 Instructor (circle one) Ogborn Lundstrom This exam consists of 20 multiple choice questions. Record all answers on this page, but you must turn in the entire exam.
Tutorial #4: Bias Point Analysis in Multisim
 SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING AND APPLIED SCIENCE DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING ECE 2115: ENGINEERING ELECTRONICS LABORATORY Tutorial #4: Bias Point Analysis in Multisim INTRODUCTION When BJTs
SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING AND APPLIED SCIENCE DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING ECE 2115: ENGINEERING ELECTRONICS LABORATORY Tutorial #4: Bias Point Analysis in Multisim INTRODUCTION When BJTs
EE 230 Lecture 31. THE MOS TRANSISTOR Model Simplifcations THE Bipolar Junction TRANSISTOR
 EE 23 Lecture 3 THE MOS TRANSISTOR Model Simplifcations THE Bipolar Junction TRANSISTOR Quiz 3 Determine I X. Assume W=u, L=2u, V T =V, uc OX = - 4 A/V 2, λ= And the number is? 3 8 5 2? 6 4 9 7 Quiz 3
EE 23 Lecture 3 THE MOS TRANSISTOR Model Simplifcations THE Bipolar Junction TRANSISTOR Quiz 3 Determine I X. Assume W=u, L=2u, V T =V, uc OX = - 4 A/V 2, λ= And the number is? 3 8 5 2? 6 4 9 7 Quiz 3
pickup from external sources unwanted feedback RF interference from system or elsewhere, power supply fluctuations ground currents
 Noise What is NOISE? A definition: Any unwanted signal obscuring signal to be observed two main origins EXTRINSIC NOISE examples... pickup from external sources unwanted feedback RF interference from system
Noise What is NOISE? A definition: Any unwanted signal obscuring signal to be observed two main origins EXTRINSIC NOISE examples... pickup from external sources unwanted feedback RF interference from system
Chapter 9 Frequency Response. PART C: High Frequency Response
 Chapter 9 Frequency Response PART C: High Frequency Response Discrete Common Source (CS) Amplifier Goal: find high cut-off frequency, f H 2 f H is dependent on internal capacitances V o Load Resistance
Chapter 9 Frequency Response PART C: High Frequency Response Discrete Common Source (CS) Amplifier Goal: find high cut-off frequency, f H 2 f H is dependent on internal capacitances V o Load Resistance
Nyquist-Rate D/A Converters. D/A Converter Basics.
 Nyquist-Rate D/A Converters David Johns and Ken Martin (johns@eecg.toronto.edu) (martin@eecg.toronto.edu) slide 1 of 20 D/A Converter Basics. B in D/A is a digital signal (or word), B in b i B in = 2 1
Nyquist-Rate D/A Converters David Johns and Ken Martin (johns@eecg.toronto.edu) (martin@eecg.toronto.edu) slide 1 of 20 D/A Converter Basics. B in D/A is a digital signal (or word), B in b i B in = 2 1
Operational Amplifier (Op-Amp) Operational Amplifiers. OP-Amp: Components. Internal Design of LM741
 (Op-Amp) s Prof. Dr. M. Zahurul Haq zahurul@me.buet.ac.bd http://teacher.buet.ac.bd/zahurul/ Department of Mechanical Engineering Bangladesh University of Engineering & Technology ME 475: Mechatronics
(Op-Amp) s Prof. Dr. M. Zahurul Haq zahurul@me.buet.ac.bd http://teacher.buet.ac.bd/zahurul/ Department of Mechanical Engineering Bangladesh University of Engineering & Technology ME 475: Mechatronics
