ONE MARK QUESTIONS. 1. The condition on R, L and C such that the step response y(t) in the figure has no oscillations, is
|
|
|
- Dale Gallagher
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING ONE MARK QUESTIONS. The condition on R, L and C such that the step response y(t) in the figure has no oscillations, is (a.) R L C (b.) R L C (c.) R L C (d.) R LC n 0. The ABCD parameters of an ideal n: transformer shown in the figure are. The value of X 0 X will be (a.) n (b.) n (c.) n (d.) n 3. In a series RLC circuit, R = kω, L = H, and C = (a.) 0 4 Hz 400 μ F. The resonant frequency is Graduate Aptitude Test in Engineering- Previous Paper - ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING of 30
2 (b.) 0 4 Hz π (c.) 0 4 Hz (d.) 4 π 0 Hz 4. The maximum power that can be transferred to the load resistor R L from the voltage source in the figure is (a.) W (b.) 0 W (c.) 0.5 W (d.) 0.5 W 5. The first and the last critical frequency of an RC-driving point impedance function must respectively be (a.) a zero and a pole (b.) a zero and a zero (c.) a pole and a pole (d.) a pole and a zero 6. The bandgap of Silicon at room temperature is (a.).3 ev (b.) 0.7 ev (c.). ev (d.).4ev 7. A Silicon PN junction at a temperature of 0 C has a reverse saturation current of 0 pico-amperes (pa). The reverse saturation current at 40 C for the same bias is approximately (a.) 30 pa (b.) 40 pa (c.) 50 pa (d.) 60 pa 8. The primary reason for the widespread use of Silicon in semiconductor device technology is (a.) abundance of Silicon on the surface of the Earth. (b.) larger bandgap of Silicon in comparison to Germanium Graduate Aptitude Test in Engineering- Previous Paper - ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING of 30
3 (c.) favorable properties of Silicon-dioxide (SiO ). (d.) lower melting point 9. The effect of current shunt feedback in an amplifier is to (a.) increase the input resistance and decrease the output resistance (b.) increase both input and output resistances (c.) decrease both input and output resistances. (d.) decrease the input resistance and increase the output resistance 0. The input resistance R i of the amplifier shown in the figure is (a.) 30 4 kω (b.) 0 kω (c.) 40 kω (d.) infinite. The cascade amplifier is a multistage configuration of (a.) CC-CB (b.) CE-CB (c.) CB-CC (d.) CE-CC. Decimal 43 in Hexadecimal and BCD number system is respectively (a.) B, 0l0000 (b.) B, 00000l (c.) B, 00l000 (d.) B, The Boolean function f implemented in the figure using two input multiplexers is (a.) ABC + ABC (b.) ABC + ABC (c.) ABC + ABC (d.) ABC + ABC Graduate Aptitude Test in Engineering- Previous Paper - ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING3 of 30
4 4. Choose the function f ( t); (a.) 3sin( 5t ) (b.) 4cos( 0t+ 3) + sin ( 70t) (c.) exp( t ) sin ( 5t) (d.) < t <, for which a Fourier series cannot be defined. 5. The function x(t) is shown in the figure. Even and odd parts of a unit-step function u(t) are respectively, (a.), () x t (b.), ( ) x t (c.), ( ) x t (d.), () x t 6. The region of convergence of Z-transform of the sequence n 5 6 un 6 5 u n 5 (a.) z < 6 5 (b.) z > 6 (c.) 5 < z < 5 (d.) 6 5 ( ) = ( ) 6 6 < z < n must be 7. Which of the following can b impulse response of a causal system? (a.) (b.) (c.) Graduate Aptitude Test in Engineering- Previous Paper - ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING4 of 30
5 (d.) 8. Let x ( n) = u( n), y( n) = x ( ) (a.) 4 (b.) (c.) 4 (d.) 4 3 n j n and ( ) 9. The power in the signal ( t) = 8cos 0πt + 4sin ( 5πt) (a.) 40 (b.) 4 (c.) 4 (d.) 8 Y e ω be the Fourier transform of ( ) π s is 0. A linear system is equivalently represented by two sets of state equations. X = AX + BU and W = CW + DU 0 y n. Then Y( e j ) is The eigen values of the representations are also computed as [λ] and [μ]. Which one of the following statements is true? (a.) [λ] = [μ] and X = W (b.) [λ] = [μ] and X W (c.) [λ] [μ] and X = W (d.) [λ] [μ] and X W. Which one of the following polar diagrams corresponds to a lag network? (a.) Graduate Aptitude Test in Engineering- Previous Paper - ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING5 of 30
6 (b.) (c.) (d.). Despite the presence of negative feedback, control systems still have problems of instability because the (a.) components used have nonlinearities (b.) dynamic equations of the systems are not known exactly (c.) mathematical analysis involves approximations (d.) System has large negative phase angle at high frequencies. 3. Find the correct match between group and group. Group A. { + km(t)} A sin ( ω c t) B. C. D. ( ) sin ( ωct) { ω c + ( )} km t A Asin t km t t Asin ωct+ k m( t) dt Group. Phase modulation. Frequency modulation 3. Amplitude modulation 4. DSB-SC modulation Codes; Graduate Aptitude Test in Engineering- Previous Paper - ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING6 of 30
7 A B C D (a.) 4 3 (b.) 3 4 (c.) 4 3 (d.) Which of the following analog modulation scheme requires the minimum transmitted power and minimum channel bandwidth? (a.) VSB (b.) DSB-SC (c.) SSB (d.) AM 5. Refractive index of glass is.5. Find the wavelength of a beam of light with frequency of 0 4 Hz in glass. Assume velocity of light is m/s in vacuum (a.) 3 μm (b.) 3 mm (c.) μm (d.) μm 6. The magnetic field intensity vector of a plane wave is given by H(x, y, z, t) = 0sin(50000t x + 30â y ), where â y denotes the unit vector in y direction. The wave is propagating with a phase velocity (a.) m/s (b.) m/s (c.) m/s (d.) m/s 7. The following differential equation has (a.) degree =, order (b.) degree =, order = (c.) degree = 4, order = 3 (d.) degree =, order = 3 3 d y dy 3 4 y = x dt dt 8. A fair dice is rolled twice. The probability that an odd number will follow an even number is (a.) (b.) 6 Graduate Aptitude Test in Engineering- Previous Paper - ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING7 of 30
8 (c.) 3 (d.) 4 9. A solution of the following differential equation is given by (a.) y = e x + e -3x (b.) y = e x + e 3x (c.) y = e -x + e 3x (d.) y = e -x + e -3x d y dy 5 + 6y = 0 dx dx TWO MARKS QUESTIONS 30. For the circuit shown in the figure, the instantaneous current i i (t) is 0 3 (a.) (b.) 90 0 (c.) 5 60 Amps. (d.) Amps. 3. Impedance Z as shown in the given figure is (a.) j9 Ω (b.) j9 Ω (c.) j9 Ω (d.) j 39 Ω 3. For the circuit shown in the figure, Thevenin s voltage and Thevenin s equivalent resistance at terminals a - b is Graduate Aptitude Test in Engineering- Previous Paper - ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING8 of 30
9 (a.) 5V and Ω (b.) 7.5V and.5ω (c.) 4V and Ω (d.) 3V and.5ω 33. If R = R = R 4 = R and R 3 =.R in the bridge circuit shown in the figure, then the reading in the ideal voltmeter connected between a and b is (a.) 0.38 V (b.) 0.38 V (c.) 0.38 V (d.) V 34. The h parameters of the circuit shown in the figure are (a.) (b.) (c.) (d.) A square pulse of 3 volts amplitude is applied to C-R circuit shown in the figure. The capacitor is initially uncharged. The output voltage V at time t = sec is Graduate Aptitude Test in Engineering- Previous Paper - ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING9 of 30
10 (a.) 3V (b.) -3V (c.) 4V (d.) -4V 36. A Silicon sample A is doped with 0 8 atoms / cm 3 of Boron. Another sample B of identical dimensions is doped with 0 8 atoms / cm 3 of Phosphorus. The ratio of electron to hole mobility is 3. The ratio of conductivity of the sample A to B is (a.) 3 (b.) 3 (c.) 3 (d.) Silicon PN junction diode under reverse bias has depletion region of width 0μm. The relative permittivity of Silicon, ε =.7 and the permittivity of free space ε 0 = 8.85 x 0 F/m. The depletion capacitance of the diode per square meter is (a.) 00 μf (b.) 0 μf (c.) μf (d.) 0 μf 38. A MOS capacitor made using p type substrate is in the accumulation mode. The dominant charge in the channel is due to the presence of (a.) holes (b.) electrons (c.) positively charged ions (d.) negatively charged ions 39. For an npn transistor connected as shown in the figure, V BE = 0.7 volts. Given that reverse saturation current of the junction at room temperature 300 K is 0-3 A, the emitter current is Graduate Aptitude Test in Engineering- Previous Paper - ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERIN0 G of 30
11 (a.) 30 ma (b.) 39 ma (c.) 49 ma (d.) 0 ma 40. The voltage e 0 indicated in the figure has been measured by an ideal voltmeter. Which of the following can be calculated? (a.) Bias current of the inverting input only (b.) Bias current of the inverting and non-inverting inputs only (c.) Input offset current only (d.) Both the bias currents and the input offset current 4. The OP-amp circuit shown in the figure is a filter. The type of filter and its cut-off frequency are respectively (a.) high pass, 000 rad/sec. (b.) low pass, 000 rad/sec. (c.) high pass, 0000 rad/sec. (d.) low pass, 0000 rad/sec. 4. In an ideal differential amplifier shown in the figure, a large value of (R E ). Graduate Aptitude Test in Engineering- Previous Paper - ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERIN G of 30
12 B GATE-005 (a.) increases both the differential and common-mode gains. (b.) increases the common-mode gain only. (c.) decreases the differential-mode gain only (d.) decreases the common-mode gain only 43. For an n-channel MOSFET and its transfer curve shown in the figure, the threshold voltage is (a.) V and the device is in active region (b.)-l V and the device is in saturation region (c.) V and the device is in saturation region (d.)-l V and the device is in active region 44. The circuit using a BJT with β = 50 and V BE = 0.7 V is shown in the figure. The base current I B and collector voltage VC are respectively (a.) 43 μa and.4 Volts (b.) 40 μa and 6 Volts (c.) 45 μa and Volts (d.) 50 μa and 0 Volts 45. The zener diode in the regulator circuit shown in the figure has a Zener voltage of 5.8 volts and a Zener knee current of 0.5 ma. The maximum load current drawn from this circuit ensuring proper functioning over the input voltage range between 0 and 30 volts, is Graduate Aptitude Test in Engineering- Previous Paper - ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERIN G of 30
13 (a.) 3.7 ma (b.) 4. ma (c.) 3.7 ma (d.) 4. ma 46. Given the ideal operational amplifier circuit shown in the figure indicate the correct transfer characteristics assuming ideal diodes with zero cut-in voltage. (a.) (b.) (c.) (d.) 47. Z i and Z 0 of the circuit are respectively (Given, r d = 0 kω, I DSS = 0mA, V p =-8A) Graduate Aptitude Test in Engineering- Previous Paper - ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERIN3 G of 30
14 (a.) MΩ and kω (b.) MΩ and 0 kω (c.) infinity and MΩ (d.) infinity and 0 kω 48. I D and V DS under DC conditions are respectively (Given, r d = 0 kω, I DSS = 0mA, V p =-8A) (a.) 5.65 ma and 8.75 V (b.) ma and 5.00 V (c.) ma and.00 V (d.) ma and.00 V 49. Trans-conductance in milli-siemens (ms) and voltage gain of the amplifier are respectively (Given, r d = 0 kω, I DSS = 0mA, V p =-8A) Graduate Aptitude Test in Engineering- Previous Paper - ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERIN4 G of 30
15 (a.).875 ms and 3.4 (b.).875 ms and -3.4 (c.) 3.3 ms and -6 (d.) 3.3 ms and The transistors used in a portion of the TTL gate shown in the figure have a β = 00. The baseemitter voltage of is 0.7V for a transistor in active region and 0.75 V for a transistor in saturation. If the sink current I = ma and the output is at logic 0, then the current I R will be equal to (a.) 0.65 ma (b.) 0.70 ma (c.) 0.75 ma (d.).00 ma 5. The Boolean expression for the truth table shown is (a.) B( A + C) ( A+ C) (b.) B( A+ C) ( A+ C) (c.) B( A+ C) ( A+ C) (d.) B( A+ C) ( A+ C) 5. Both transistors T and T show in the figure, have a threshold voltage of Volts. The device parameters K and K of T and T are, respectively, 36μA/V and 9μA/V. The output voltage V 0 is Graduate Aptitude Test in Engineering- Previous Paper - ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERIN5 G of 30
16 (a.) V (b.) V (c.) 3V (d.) 4V 53. The present output Q n of an edge triggered JK flip-flop is logic 0. If J =, then Q n+ (a.) cannot be determined (b.) will be logic 0 (c.) will be logic (d.) will race around 54. The given figure shows a ripple counter using positive edge triggered flip-flops. If the present state of the counter is Q Q Q 0 = 0, then its next state (Q Q Q 0 ) will be (a.) 00 (b.) 00 (c.) (d.) What memory address range is NOT represented by chip # and chip # in the figure. A 0 to A 5 in this figure are the address lines and CS means Chip Select. Graduate Aptitude Test in Engineering- Previous Paper - ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERIN6 G of 30
17 (a.) FF (b.) FF (c.) F900-FAFF (d.) F800-F9FF 56. The output y(t) of a linear time invariant system is related to its input x(t) by the following equation: ( ) 0.5 ( ) ( ) 0.5 ( ) yt = xt td + T + xt td + xt td T The filter transfer function H(ω) of such a system is given by (a.) ( + cosω ) j td T e ω (b.) ( + 0.5cosω ) (c.) ( + cosω ) j td T e ω j td T e ω (d.) ( + 0.5cosω ) j td T e ω 57. Match the following and choose the correct combination. Group A. continuous and aperiodic signal B. continuous and periodic signal C. Discrete and aperiodic signal D. Discrete and periodic signal Group. Fourier representation is continuous and aperiodic. Fourier representation is discrete and aperiodic 3. Fourier representation is continuous and periodic 4. Fouriere representation is discrete and periodic Codes; A B C D (a.) 3 4 Graduate Aptitude Test in Engineering- Previous Paper - ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERIN7 G of 30
18 (b.) 3 4 (c.) 3 4 (d.) A signal x( n) sin( ω n φ) j response ( ) will be = + is the input to a linear time-invariant system having a frequency 0 H e ω. If the output of the system ( ) (a.) n ω + β for any arbitrary real β 0 0 (b.) n ω + πk for any arbitrary integer k. 0 0 (c.) n ω + πk for any arbitrary integer k. 0 0 (d.) n0ω0 + πk Ax n n 0 j, then the most general form of H ( e ω ) 59. For a signal x(t) the Fourier transform is X(f). Then the inverse Fourier transform of X(3t + ) is given by (a.) t x t (b.) x e 3 3 j3 t e π j 4 (c.) ( ) 3x 3t e (d.) x( 3t+ ) j 4 π t/3 π t Statement of Linked Answer Questions 60 and 6: A sequence x(n) has non-zero values as shown in the figure 60. The sequence ( ) y n (a.) n x = 0, for n even will be for n odd Graduate Aptitude Test in Engineering- Previous Paper - ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERIN8 G of 30
19 (b.) (c.) (d.) 6. The Fourier transform of y(n) will be (a.) e [ cos 4 + cos + ] j ω ω ω (b.) [ cosω+ cosω+ ] (c.) e [ cos + cos + ] jω ω ω j ω (d.) e [ cos ω+ cosω+ ] 6. The polar diagram of a conditionally stable system for open loop gain K = is shown in the figure. The open loop transfer function of the system is known to be stable. The closed loop system is stable for (a.) K < 5 and < K < 8 Graduate Aptitude Test in Engineering- Previous Paper - ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERIN9 G of 30
20 (b.) K < and < K < 5 8 (c.) K < and 5 < K 8 (d.) K < and K < In the derivation of expression for peak percent overshoot, of the following conditions is not required? (a.) System is linear and time invariant M p πξ = exp 00%, which one ξ (b.) The system transfer function has a pair of complex conjugate poles and no zeroes. (c.) There is no transportation delay in the system. (d.) The system has zero initial conditions. 64. A ramp input applied to an unity feedback system results in 5% steady state error. The type number and zero frequency gain of the system are respectively (a.) and 0 (b.) 0 and 0 (c.) 0 and 0 (d.) and 0 K =, = is to be compensated to achieve the damping ratio s ξ = 0.5, and an undamped natural frequency, ω n = 5 rad/s. Which one of the following compensator s will be suitable? 65. A double integrator plant, G( s) H( s) Ge (a.) ( ) s + 3 s s (b.) s + 3 s 6 (c.) s (d.) s + 6 s 66. An unity feedback system is given as, G( s) Indicate the correct root locus diagram (a.) K = s s ( s) ( + 3) Graduate Aptitude Test in Engineering- Previous Paper - ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERIN0 G of 30
21 (b.) (c.) (d.) Common Data for Questions 67 and 68: The open loop transfer function of a unity feedback system is given by G( s) = 3e s s s ( + ) 67. The gain and phase crossover frequencies in rad/sec are, respectively (a.) 0.63 and.6 (b.) 0.63 and (c.) and 0.63 (d.).6 and 0.63h 68. Based on the above results, the gain and phase margins of the system will be (a.) and 87.5 (b.) 7.09 and 87.5 (c.) 7.09 db and 87.5 Graduate Aptitude Test in Engineering- Previous Paper - ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERIN G of 30
22 (d.) db and A device with input x(t) and output y(t) is characterized by: y( t) = x ( t) An FM signal with frequency deviation of 90 khz and modulating signal bandwidth of 5 khz is applied to this device. The bandwidth of the output signal is (a.) 370 khz (b.) 90 khz (c.) 380 khz (d.) 95 khz 70. A signal as shown in the figure is applied to a matched filter. Which of the following does represent the output of this matched filter? (a.) (b.) (c.) (d.) Graduate Aptitude Test in Engineering- Previous Paper - ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERIN G of 30
23 7. Noise with uniform power spectral density of N 0 W/Hz is passed through a filter H (ω) = exp (- jωt d ) followed by an ideal low pass filter of bandwidth B Hz. The output noise power in Watts is (a.) N 0 B (b.) 4 N 0 B (c.) 8 N 0 B (d.) 6 N 0 B 7. A carrier is phase modulated (PM) with frequency deviation of 0 khz by a single tone frequency of khz. If the single tone frequency is increased to khz, assuming that phase deviation remains unchanged, the bandwidth of the PM signal is (a.) khz (b.) khz (c.) 4 khz (d.) 44 khz 73. An output of a communication channel is a random variable v with the probability density function as shown in the figure. The mean square value of v is (a.) 4 (b.) 6 (c.) 8 (d.) 9 Common Data for Questions 74 and 75: Asymmetric three-level midtread quantizer is to be designed assuming equiprobable occurrence of all quantization levels. 74. If the probability density function is divided into three regions as shown in the figure, the value of a in the figure is (a.) 3 (b.) 3 Graduate Aptitude Test in Engineering- Previous Paper - ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERIN3 G of 30
24 (c.) (d.) The quantization noise power for the quantization region between - a and +a in the figure is (a.) 4 8 (b.) 9 (c.) 5 8 (d.) Which one of the following does represent the electric field lines for the TE 0 mode in the crosssection of a hollow rectangular metallic waveguide? (a.) (b.) (c.) (d.) Graduate Aptitude Test in Engineering- Previous Paper - ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERIN4 G of 30
25 77. Characteristic impedance of a transmission line is 50Ω. Input impedance of the open- circuited line is Z 0C = 00 + j50ω. When the transmission line is short-circuited, then value of the input impedance will be (a.) 50Ω (b.) 00 + j5oω (c.) j.54ω (d.) 7.69 j.54ω 78. Two identical and parallel dipole antennas are kept apart by a distance of 4 λ in the H-plane. They are fed with equal currents but the right most antenna has a phase shift of The radiation pattern is given as (a.) (b.) (c.) (d.) Common Data for Questions 79 and 80: Voltage standing wave pattern in a lossless transmission line with characteristic impedance 50Q and a resistive load is shown in the figure. Graduate Aptitude Test in Engineering- Previous Paper - ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERIN5 G of 30
26 79. The value of the load resistance is (a.) 50Ω (b.) 00Ω (c.).5ω (d.) 0Ω 80. The reflection coefficient is given by (a.) 0.6 (b.) l (c.) 0.6 (d.) 0 8. Many circles are drawn in a Smith chart used for transmission line calculations. The circles shown in the figure represent (a.) unit circles (b.) constant resistance circles (c.) constant reactance circles (d.) constant reflection coefficient circles Common Data for Questions 8 and 83: Consider an 8085 microprocessor system 8. The following program starts at location 000H. LXI SP, 00FF LXI H, 007 MVI A, 0 SUB M Graduate Aptitude Test in Engineering- Previous Paper - ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERIN6 G of 30
27 The content of accumulator when the program counter reaches 009H is (a.) 0 H (b.) 0 H (c.) 00 H (d.) FFH 83. If in addition following code exists from 009H onwards, ORI 40 H ADDM What will be the result in the accumulator after the last instruction is executed? (a.) 40 H (b.) 0 H (c.) 60 H (d.) 4 H 84. In what range should Re(s) remain so that the Laplace transform of the function e (a+)t+5 exits. (a.) Re(s) > a + (b.) Re(s) > a + 7 (c.) Re(s) < (d.) Re(s) > a Given the matrix, the eigenvector is 4 3 (a.) 3 4 (b.) 3 (c.) (d.) Let, A = 0 3 and A- = 0 a. Then (a + b) = b (a.) 7 0 (b.) 3 0 Graduate Aptitude Test in Engineering- Previous Paper - ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERIN7 G of 30
28 (c.) 9 60 (d.) The value of the integral (a.) (b.) π (c.) (d.) π x I = exp dx π 0 8 is 88. The derivative of the symmetric function drawn in given figure will look like (a.) (b.) (c.) (d.) Graduate Aptitude Test in Engineering- Previous Paper - ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERIN8 G of 30
29 89. Match the following and choose the correct combination: Group A. Newton-Raphso method B. Rung-kutta method C. Simpson s Rule D. Gauss elimination Group. Solving nonlinear equations. Solving linear simultaneous equations 3. Solving ordinary differential equations 4. Numerical integration 5. Interpolation 6. Calculation of Eigenvalues Codes: A B C D (a.) (b.) (c.) 3 4 (d.) Given an orthogonal matrix A = T AA is (a.) Graduate Aptitude Test in Engineering- Previous Paper - ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERIN9 G of 30
30 Graduate Aptitude Test in Engineering- Previous Paper - ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERIN30 of 30 GATE-005 (b.) (c.) (d.) G 0
Q. 1 Q. 25 carry one mark each.
 GATE 5 SET- ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING - EC Q. Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q. The bilateral Laplace transform of a function is if a t b f() t = otherwise (A) a b s (B) s e ( a b) s (C) e as
GATE 5 SET- ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING - EC Q. Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q. The bilateral Laplace transform of a function is if a t b f() t = otherwise (A) a b s (B) s e ( a b) s (C) e as
ONE MARK QUESTIONS. 1. Consider the network graph shown in the figure. Which one of the following is NOT a tree of this graph?
 ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING ONE MARK QUESTIONS 1. Consider the network graph shown in the figure. Which one of the following is NOT a tree of this graph? (a.) (b.) (c.) (d.). The equivalent
ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING ONE MARK QUESTIONS 1. Consider the network graph shown in the figure. Which one of the following is NOT a tree of this graph? (a.) (b.) (c.) (d.). The equivalent
ECE Branch GATE Paper The order of the differential equation + + = is (A) 1 (B) 2
 Question 1 Question 20 carry one mark each. 1. The order of the differential equation + + = is (A) 1 (B) 2 (C) 3 (D) 4 2. The Fourier series of a real periodic function has only P. Cosine terms if it is
Question 1 Question 20 carry one mark each. 1. The order of the differential equation + + = is (A) 1 (B) 2 (C) 3 (D) 4 2. The Fourier series of a real periodic function has only P. Cosine terms if it is
GATE EC Question 1-30 Carry One Mark Each. The following differential equation has. (B) degree = 1, order = 2 (C) degree = 4, order = 3
 GATE EC 5 Question - 3 Carry One Mark Each MCQ. SOL. The following differential equation has dy dy 3 3c 4 y m+ c + + dt dt m x (A) degree, order (B) degree, order (C) degree 4, order 3 (D) degree, order
GATE EC 5 Question - 3 Carry One Mark Each MCQ. SOL. The following differential equation has dy dy 3 3c 4 y m+ c + + dt dt m x (A) degree, order (B) degree, order (C) degree 4, order 3 (D) degree, order
Q. 1 Q. 25 carry one mark each.
 Q. Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q. Consider a system of linear equations: x y 3z =, x 3y 4z =, and x 4y 6 z = k. The value of k for which the system has infinitely many solutions is. Q. A function 3 = is
Q. Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q. Consider a system of linear equations: x y 3z =, x 3y 4z =, and x 4y 6 z = k. The value of k for which the system has infinitely many solutions is. Q. A function 3 = is
GATE 2009 Electronics and Communication Engineering
 GATE 2009 Electronics and Communication Engineering Question 1 Question 20 carry one mark each. 1. The order of the differential equation + + y =e (A) 1 (B) 2 (C) 3 (D) 4 is 2. The Fourier series of a
GATE 2009 Electronics and Communication Engineering Question 1 Question 20 carry one mark each. 1. The order of the differential equation + + y =e (A) 1 (B) 2 (C) 3 (D) 4 is 2. The Fourier series of a
Electronics and Communication Exercise 1
 Electronics and Communication Exercise 1 1. For matrices of same dimension M, N and scalar c, which one of these properties DOES NOT ALWAYS hold? (A) (M T ) T = M (C) (M + N) T = M T + N T (B) (cm)+ =
Electronics and Communication Exercise 1 1. For matrices of same dimension M, N and scalar c, which one of these properties DOES NOT ALWAYS hold? (A) (M T ) T = M (C) (M + N) T = M T + N T (B) (cm)+ =
1.1 An excitation is applied to a system at t = T and its response is zero for < t < T. Such a system is (a) non-causal system.
 . An excitation is applied to a system at t = T and its response is zero for < t < T. Such a system is (a) non-causal system x(t) (b) stable system (c) causal system (d) unstable system t=t t. In a series
. An excitation is applied to a system at t = T and its response is zero for < t < T. Such a system is (a) non-causal system x(t) (b) stable system (c) causal system (d) unstable system t=t t. In a series
GATE 2007 Electronics and Communication Engineering
 GATE 2007 Electronics and Communication Engineering Q.1 to Q.20 carry one mark each 1. If E denotes expectation, the variance of a random variable X is given by (A) E[X ] E [X] (C) E[X ] (B) E[X ] E [X]
GATE 2007 Electronics and Communication Engineering Q.1 to Q.20 carry one mark each 1. If E denotes expectation, the variance of a random variable X is given by (A) E[X ] E [X] (C) E[X ] (B) E[X ] E [X]
Exercise The determinant of matrix A is 5 and the determinant of matrix B is 40. The determinant of matrix AB is.
 Exercise 1. The determinant of matrix A is 5 and the determinant of matrix B is 40. The determinant of matrix AB is.. Let X be a random variable which is uniformly chosen from the set of positive odd numbers
Exercise 1. The determinant of matrix A is 5 and the determinant of matrix B is 40. The determinant of matrix AB is.. Let X be a random variable which is uniformly chosen from the set of positive odd numbers
INDIAN SPACE RESEARCH ORGANISATION. Recruitment Entrance Test for Scientist/Engineer SC 2017
 1. The signal m (t) as shown is applied both to a phase modulator (with kp as the phase constant) and a frequency modulator with ( kf as the frequency constant) having the same carrier frequency. The ratio
1. The signal m (t) as shown is applied both to a phase modulator (with kp as the phase constant) and a frequency modulator with ( kf as the frequency constant) having the same carrier frequency. The ratio
B. Both A and R are correct but R is not correct explanation of A. C. A is true, R is false. D. A is false, R is true
 1. Assertion (A): A demultiplexer can be used as a decode r. Reason (R): A demultiplexer can be built by using AND gates only. A. Both A and R are correct and R is correct explanation of A B. Both A and
1. Assertion (A): A demultiplexer can be used as a decode r. Reason (R): A demultiplexer can be built by using AND gates only. A. Both A and R are correct and R is correct explanation of A B. Both A and
Exercise: 4. 1 converges. 1. The series. (D) e. (A) 2 ln 2 (C) 2 (B) 2. equal to. 4. If. a and b equation. d x 2. (D) ae 2t. (A) ae t.
 Exercise: 4 1. The series n 1 = 0 n! converges to (A) ln (B) (C) (D) e. The magnitude of the gradient for the function f(x, y, z) = x =3y +z 3 at the point (1, 1, 1) is. 3. Let X be a zero mean unit variance
Exercise: 4 1. The series n 1 = 0 n! converges to (A) ln (B) (C) (D) e. The magnitude of the gradient for the function f(x, y, z) = x =3y +z 3 at the point (1, 1, 1) is. 3. Let X be a zero mean unit variance
Homework Assignment 08
 Homework Assignment 08 Question 1 (Short Takes) Two points each unless otherwise indicated. 1. Give one phrase/sentence that describes the primary advantage of an active load. Answer: Large effective resistance
Homework Assignment 08 Question 1 (Short Takes) Two points each unless otherwise indicated. 1. Give one phrase/sentence that describes the primary advantage of an active load. Answer: Large effective resistance
SESSION - 1. Auhippo.com
 SESSION - 03 Question Booklet Code EC : ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING A Duration: Three Hours Maximum Marks: 00 Read the following instructions carefully.. Do not open the seal of the Question
SESSION - 03 Question Booklet Code EC : ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING A Duration: Three Hours Maximum Marks: 00 Read the following instructions carefully.. Do not open the seal of the Question
Conventional Paper-I Part A. 1. (a) Define intrinsic wave impedance for a medium and derive the equation for intrinsic vy
 EE-Conventional Paper-I IES-01 www.gateforum.com Conventional Paper-I-01 Part A 1. (a) Define intrinsic wave impedance for a medium and derive the equation for intrinsic vy impedance for a lossy dielectric
EE-Conventional Paper-I IES-01 www.gateforum.com Conventional Paper-I-01 Part A 1. (a) Define intrinsic wave impedance for a medium and derive the equation for intrinsic vy impedance for a lossy dielectric
mywbut.com GATE SOLVED PAPER - EC Q Carry One Mark Each (D) degree = 2, order = 3 (B) degree = 1, order = 2 (C) degree = 4, order = 3
 GATE OLVED PAPER EC 5 Q. 3 Carry One Mark Each Q. The following differential equation has dy dy 3 3c y m+ c + + dt dt m x (A) degree, order (B) degree, order ol. (C) degree, order 3 (D) degree, order 3
GATE OLVED PAPER EC 5 Q. 3 Carry One Mark Each Q. The following differential equation has dy dy 3 3c y m+ c + + dt dt m x (A) degree, order (B) degree, order ol. (C) degree, order 3 (D) degree, order 3
3. (a) Figure 3(a) shows a Bridge T network used in control systems. The element values are clearly marked in the figure.
 I.E.S.-(Conv.) 1987 ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING PAPER - I PART A 1. (a) Define precisely unit step and unit impulse functions. Sketch the following function from t = 0 to t = 10 units, indicating all salient
I.E.S.-(Conv.) 1987 ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING PAPER - I PART A 1. (a) Define precisely unit step and unit impulse functions. Sketch the following function from t = 0 to t = 10 units, indicating all salient
Conventional Paper-I-2011 PART-A
 Conventional Paper-I-0 PART-A.a Give five properties of static magnetic field intensity. What are the different methods by which it can be calculated? Write a Maxwell s equation relating this in integral
Conventional Paper-I-0 PART-A.a Give five properties of static magnetic field intensity. What are the different methods by which it can be calculated? Write a Maxwell s equation relating this in integral
1 P a g e.
 1. Choose the most appropriate word from the options given below to complete the following sentence. Communication and interpersonal skills are important in their own ways. each B. both C. all either.
1. Choose the most appropriate word from the options given below to complete the following sentence. Communication and interpersonal skills are important in their own ways. each B. both C. all either.
EE Branch GATE Paper 2010
 Q.1 Q.25 carry one mark each 1. The value of the quantity P, where, is equal to 0 1 e 1/e 2. Divergence of the three-dimensional radial vector field is 3 1/r 3. The period of the signal x(t) = 8 is 0.4
Q.1 Q.25 carry one mark each 1. The value of the quantity P, where, is equal to 0 1 e 1/e 2. Divergence of the three-dimensional radial vector field is 3 1/r 3. The period of the signal x(t) = 8 is 0.4
6.012 Electronic Devices and Circuits Spring 2005
 6.012 Electronic Devices and Circuits Spring 2005 May 16, 2005 Final Exam (200 points) -OPEN BOOK- Problem NAME RECITATION TIME 1 2 3 4 5 Total General guidelines (please read carefully before starting):
6.012 Electronic Devices and Circuits Spring 2005 May 16, 2005 Final Exam (200 points) -OPEN BOOK- Problem NAME RECITATION TIME 1 2 3 4 5 Total General guidelines (please read carefully before starting):
`EC : ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING
 03 Question Booklet Code B `EC : ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING Duration: Three Hours Maximum Marks: 00 Read the following instructions carefully.. Do not open the seal of the Question Booklet
03 Question Booklet Code B `EC : ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING Duration: Three Hours Maximum Marks: 00 Read the following instructions carefully.. Do not open the seal of the Question Booklet
2013 Question Booklet Code EC : ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING
 013 Question Booklet Code EC : ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING A Duration: Three Hours Maximum Marks: 100 Read the following instructions carefully. 1. Do not open the seal of the Question Booklet
013 Question Booklet Code EC : ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING A Duration: Three Hours Maximum Marks: 100 Read the following instructions carefully. 1. Do not open the seal of the Question Booklet
GATE 2017 ECE Session 3 Answer Key
 1. Three pair cubical dice are thrown simultaneously. What is the probability that all three dice have same number is... Ans. ( 1 36 ). The one of the eigen value is real, rest are imaginary the real value
1. Three pair cubical dice are thrown simultaneously. What is the probability that all three dice have same number is... Ans. ( 1 36 ). The one of the eigen value is real, rest are imaginary the real value
INSTRUMENTAL ENGINEERING
 INSTRUMENTAL ENGINEERING Subject Code: IN Course Structure Sections/Units Section A Unit 1 Unit 2 Unit 3 Unit 4 Unit 5 Unit 6 Section B Section C Section D Section E Section F Section G Section H Section
INSTRUMENTAL ENGINEERING Subject Code: IN Course Structure Sections/Units Section A Unit 1 Unit 2 Unit 3 Unit 4 Unit 5 Unit 6 Section B Section C Section D Section E Section F Section G Section H Section
Studio 9 Review Operational Amplifier Stability Compensation Miller Effect Phase Margin Unity Gain Frequency Slew Rate Limiting Reading: Text sec 5.
 Studio 9 Review Operational Amplifier Stability Compensation Miller Effect Phase Margin Unity Gain Frequency Slew Rate Limiting Reading: Text sec 5.2 pp. 232-242 Two-stage op-amp Analysis Strategy Recognize
Studio 9 Review Operational Amplifier Stability Compensation Miller Effect Phase Margin Unity Gain Frequency Slew Rate Limiting Reading: Text sec 5.2 pp. 232-242 Two-stage op-amp Analysis Strategy Recognize
Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each.
 GATE 2019 General Aptitude (GA) Set-3 Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q.1 I am not sure if the bus that has been booked will be able to all the students. (A) sit (B) deteriorate (C) fill (D) accommodate
GATE 2019 General Aptitude (GA) Set-3 Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q.1 I am not sure if the bus that has been booked will be able to all the students. (A) sit (B) deteriorate (C) fill (D) accommodate
GATE 2010 Electronics and Communication Engineering
 GATE 2010 Electronics and Communication Engineering Q.1 Q.25 carry one mark each. Q1. The eigen values of a skew-symmetric matrix are (A) Always zero (B) Always pure imaginary (C) Either zero or pure imaginary
GATE 2010 Electronics and Communication Engineering Q.1 Q.25 carry one mark each. Q1. The eigen values of a skew-symmetric matrix are (A) Always zero (B) Always pure imaginary (C) Either zero or pure imaginary
GATE 2008 Electrical Engineering
 GATE 2008 Electrical Engineering Q.1 Q. 20 carry one mark each. 1. The number of chords in the graph of the given circuit will be + _ (A) 3 (B) 4 (C) 5 (D) 6 2. The Thevenin'a equivalent of a circuit operating
GATE 2008 Electrical Engineering Q.1 Q. 20 carry one mark each. 1. The number of chords in the graph of the given circuit will be + _ (A) 3 (B) 4 (C) 5 (D) 6 2. The Thevenin'a equivalent of a circuit operating
Chapter 4 Field-Effect Transistors
 Chapter 4 Field-Effect Transistors Microelectronic Circuit Design Richard C. Jaeger Travis N. Blalock 5/5/11 Chap 4-1 Chapter Goals Describe operation of MOSFETs. Define FET characteristics in operation
Chapter 4 Field-Effect Transistors Microelectronic Circuit Design Richard C. Jaeger Travis N. Blalock 5/5/11 Chap 4-1 Chapter Goals Describe operation of MOSFETs. Define FET characteristics in operation
Electronic Circuits Summary
 Electronic Circuits Summary Andreas Biri, D-ITET 6.06.4 Constants (@300K) ε 0 = 8.854 0 F m m 0 = 9. 0 3 kg k =.38 0 3 J K = 8.67 0 5 ev/k kt q = 0.059 V, q kt = 38.6, kt = 5.9 mev V Small Signal Equivalent
Electronic Circuits Summary Andreas Biri, D-ITET 6.06.4 Constants (@300K) ε 0 = 8.854 0 F m m 0 = 9. 0 3 kg k =.38 0 3 J K = 8.67 0 5 ev/k kt q = 0.059 V, q kt = 38.6, kt = 5.9 mev V Small Signal Equivalent
 GATE 2016 General Aptitude - GA Set-3 Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q.1 Based on the given statements, select the appropriate option with respect to grammar and usage. Statements (i) The height of Mr.
GATE 2016 General Aptitude - GA Set-3 Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q.1 Based on the given statements, select the appropriate option with respect to grammar and usage. Statements (i) The height of Mr.
I.E.S-(Conv.)-2005 Values of the following constants may be used wherever Necessary:
 I.E.S-(Conv.)-2005 ELECTRONICS AND TELECOMMUNICATION ENGINEERING PAPER - I Time Allowed: 3 hours Maximum Marks: 200 Candidates should attempt any FIVE questions. Assume suitable data, if found necessary
I.E.S-(Conv.)-2005 ELECTRONICS AND TELECOMMUNICATION ENGINEERING PAPER - I Time Allowed: 3 hours Maximum Marks: 200 Candidates should attempt any FIVE questions. Assume suitable data, if found necessary
EE105 Fall 2014 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits
 EE05 Fall 204 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits Prof. Ming C. Wu wu@eecs.berkeley.edu 5 Sutardja Dai Hall (SDH) Terminal Gain and I/O Resistances of BJT Amplifiers Emitter (CE) Collector (CC) Base (CB)
EE05 Fall 204 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits Prof. Ming C. Wu wu@eecs.berkeley.edu 5 Sutardja Dai Hall (SDH) Terminal Gain and I/O Resistances of BJT Amplifiers Emitter (CE) Collector (CC) Base (CB)
MICROELECTRONIC CIRCUIT DESIGN Second Edition
 MICROELECTRONIC CIRCUIT DESIGN Second Edition Richard C. Jaeger and Travis N. Blalock Answers to Selected Problems Updated 10/23/06 Chapter 1 1.3 1.52 years, 5.06 years 1.5 2.00 years, 6.65 years 1.8 113
MICROELECTRONIC CIRCUIT DESIGN Second Edition Richard C. Jaeger and Travis N. Blalock Answers to Selected Problems Updated 10/23/06 Chapter 1 1.3 1.52 years, 5.06 years 1.5 2.00 years, 6.65 years 1.8 113
55:041 Electronic Circuits The University of Iowa Fall Final Exam
 Final Exam Name: Score Max: 135 Question 1 (1 point unless otherwise noted) a. What is the maximum theoretical efficiency for a class-b amplifier? Answer: 78% b. The abbreviation/term ESR is often encountered
Final Exam Name: Score Max: 135 Question 1 (1 point unless otherwise noted) a. What is the maximum theoretical efficiency for a class-b amplifier? Answer: 78% b. The abbreviation/term ESR is often encountered
Switched-Capacitor Circuits David Johns and Ken Martin University of Toronto
 Switched-Capacitor Circuits David Johns and Ken Martin University of Toronto (johns@eecg.toronto.edu) (martin@eecg.toronto.edu) University of Toronto 1 of 60 Basic Building Blocks Opamps Ideal opamps usually
Switched-Capacitor Circuits David Johns and Ken Martin University of Toronto (johns@eecg.toronto.edu) (martin@eecg.toronto.edu) University of Toronto 1 of 60 Basic Building Blocks Opamps Ideal opamps usually
6.012 Electronic Devices and Circuits
 Page 1 of 10 YOUR NAME Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Massachusetts Institute of Technology 6.012 Electronic Devices and Circuits Exam No. 2 Thursday, November 5, 2009 7:30 to
Page 1 of 10 YOUR NAME Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Massachusetts Institute of Technology 6.012 Electronic Devices and Circuits Exam No. 2 Thursday, November 5, 2009 7:30 to
Solved Problems. Electric Circuits & Components. 1-1 Write the KVL equation for the circuit shown.
 Solved Problems Electric Circuits & Components 1-1 Write the KVL equation for the circuit shown. 1-2 Write the KCL equation for the principal node shown. 1-2A In the DC circuit given in Fig. 1, find (i)
Solved Problems Electric Circuits & Components 1-1 Write the KVL equation for the circuit shown. 1-2 Write the KCL equation for the principal node shown. 1-2A In the DC circuit given in Fig. 1, find (i)
GATE 2010 Electrical Engineering
 GATE 2010 Electrical Engineering Q.1 Q.25 carry one mark each 1. The value of the quantity P, where P = xe dx, is equal to (A) 0 (B) 1 (C) e (D) 1/e 2. Divergence of the three-dimensional radial vector
GATE 2010 Electrical Engineering Q.1 Q.25 carry one mark each 1. The value of the quantity P, where P = xe dx, is equal to (A) 0 (B) 1 (C) e (D) 1/e 2. Divergence of the three-dimensional radial vector
CBSE Physics Set I Outer Delhi Board 2012
 Q28. a) In Young s double slit experiment, derive the condition for (I) constructive interference and (II) destructive interference at a point on the screen. b) A beam of light consisting of two wavelengths,
Q28. a) In Young s double slit experiment, derive the condition for (I) constructive interference and (II) destructive interference at a point on the screen. b) A beam of light consisting of two wavelengths,
ECE-342 Test 2 Solutions, Nov 4, :00-8:00pm, Closed Book (one page of notes allowed)
 ECE-342 Test 2 Solutions, Nov 4, 2008 6:00-8:00pm, Closed Book (one page of notes allowed) Please use the following physical constants in your calculations: Boltzmann s Constant: Electron Charge: Free
ECE-342 Test 2 Solutions, Nov 4, 2008 6:00-8:00pm, Closed Book (one page of notes allowed) Please use the following physical constants in your calculations: Boltzmann s Constant: Electron Charge: Free
ID # NAME. EE-255 EXAM 3 April 7, Instructor (circle one) Ogborn Lundstrom
 ID # NAME EE-255 EXAM 3 April 7, 1998 Instructor (circle one) Ogborn Lundstrom This exam consists of 20 multiple choice questions. Record all answers on this page, but you must turn in the entire exam.
ID # NAME EE-255 EXAM 3 April 7, 1998 Instructor (circle one) Ogborn Lundstrom This exam consists of 20 multiple choice questions. Record all answers on this page, but you must turn in the entire exam.
Chapter 13 Small-Signal Modeling and Linear Amplification
 Chapter 13 Small-Signal Modeling and Linear Amplification Microelectronic Circuit Design Richard C. Jaeger Travis N. Blalock 1/4/12 Chap 13-1 Chapter Goals Understanding of concepts related to: Transistors
Chapter 13 Small-Signal Modeling and Linear Amplification Microelectronic Circuit Design Richard C. Jaeger Travis N. Blalock 1/4/12 Chap 13-1 Chapter Goals Understanding of concepts related to: Transistors
Homework Assignment 09
 Homework Assignment 09 Question 1 (Short Takes) Two points each unless otherwise indicated. 1. What is the 3-dB bandwidth of the amplifier shown below if r π = 2.5K, r o = 100K, g m = 40 ms, and C L =
Homework Assignment 09 Question 1 (Short Takes) Two points each unless otherwise indicated. 1. What is the 3-dB bandwidth of the amplifier shown below if r π = 2.5K, r o = 100K, g m = 40 ms, and C L =
Final Exam. 55:041 Electronic Circuits. The University of Iowa. Fall 2013.
 Final Exam Name: Max: 130 Points Question 1 In the circuit shown, the op-amp is ideal, except for an input bias current I b = 1 na. Further, R F = 10K, R 1 = 100 Ω and C = 1 μf. The switch is opened at
Final Exam Name: Max: 130 Points Question 1 In the circuit shown, the op-amp is ideal, except for an input bias current I b = 1 na. Further, R F = 10K, R 1 = 100 Ω and C = 1 μf. The switch is opened at
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, BERKELEY College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences
 UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, BERKELEY College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences EECS 40 Spring 2000 Introduction to Microelectronic Devices Prof. King MIDTERM EXAMINATION
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, BERKELEY College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences EECS 40 Spring 2000 Introduction to Microelectronic Devices Prof. King MIDTERM EXAMINATION
II/IV B.Tech (Regular/Supplementary) DEGREE EXAMINATION. Answer ONE question from each unit.
 14ECEI302/EC 212 1. Answer all questions (1X12=12 Marks) a What are the applications of linked list? b Compare singly linked list and doubly linked list. c Define ADT. d What are the basic operations of
14ECEI302/EC 212 1. Answer all questions (1X12=12 Marks) a What are the applications of linked list? b Compare singly linked list and doubly linked list. c Define ADT. d What are the basic operations of
4. Given a range of frequencies, which of the following systems is best for transmission line load matching?
 IES-00- Paper-I. Consider the following statements: For a rectangular waveguide with dimensions a b where b is the narrow dimension, small value of b. Gives a larger separation between cutoff frequencies
IES-00- Paper-I. Consider the following statements: For a rectangular waveguide with dimensions a b where b is the narrow dimension, small value of b. Gives a larger separation between cutoff frequencies
GATE : , Copyright reserved. Web:www.thegateacademy.com
 GATE-2016 Index 1. Question Paper Analysis 2. Question Paper & Answer keys : 080-617 66 222, info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web:www.thegateacademy.com ANALYSIS OF GATE 2016 Electrical Engineering
GATE-2016 Index 1. Question Paper Analysis 2. Question Paper & Answer keys : 080-617 66 222, info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web:www.thegateacademy.com ANALYSIS OF GATE 2016 Electrical Engineering
6.012 Electronic Devices and Circuits
 Page 1 of 12 YOUR NAME Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Massachusetts Institute of Technology 6.012 Electronic Devices and Circuits FINAL EXAMINATION Open book. Notes: 1. Unless
Page 1 of 12 YOUR NAME Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Massachusetts Institute of Technology 6.012 Electronic Devices and Circuits FINAL EXAMINATION Open book. Notes: 1. Unless
DEPARTMENT OF ECE UNIT VII BIASING & STABILIZATION AMPLIFIER:
 UNIT VII IASING & STAILIZATION AMPLIFIE: - A circuit that increases the amplitude of given signal is an amplifier - Small ac signal applied to an amplifier is obtained as large a.c. signal of same frequency
UNIT VII IASING & STAILIZATION AMPLIFIE: - A circuit that increases the amplitude of given signal is an amplifier - Small ac signal applied to an amplifier is obtained as large a.c. signal of same frequency
Lecture 23: Negative Resistance Osc, Differential Osc, and VCOs
 EECS 142 Lecture 23: Negative Resistance Osc, Differential Osc, and VCOs Prof. Ali M. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley Copyright c 2005 by Ali M. Niknejad A. M. Niknejad University of California,
EECS 142 Lecture 23: Negative Resistance Osc, Differential Osc, and VCOs Prof. Ali M. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley Copyright c 2005 by Ali M. Niknejad A. M. Niknejad University of California,
1 Name: Student number: DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS AND PHYSICAL OCEANOGRAPHY MEMORIAL UNIVERSITY OF NEWFOUNDLAND. Fall :00-11:00
 1 Name: DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS AND PHYSICAL OCEANOGRAPHY MEMORIAL UNIVERSITY OF NEWFOUNDLAND Final Exam Physics 3000 December 11, 2012 Fall 2012 9:00-11:00 INSTRUCTIONS: 1. Answer all seven (7) questions.
1 Name: DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS AND PHYSICAL OCEANOGRAPHY MEMORIAL UNIVERSITY OF NEWFOUNDLAND Final Exam Physics 3000 December 11, 2012 Fall 2012 9:00-11:00 INSTRUCTIONS: 1. Answer all seven (7) questions.
Biasing the CE Amplifier
 Biasing the CE Amplifier Graphical approach: plot I C as a function of the DC base-emitter voltage (note: normally plot vs. base current, so we must return to Ebers-Moll): I C I S e V BE V th I S e V th
Biasing the CE Amplifier Graphical approach: plot I C as a function of the DC base-emitter voltage (note: normally plot vs. base current, so we must return to Ebers-Moll): I C I S e V BE V th I S e V th
Final Examination EE 130 December 16, 1997 Time allotted: 180 minutes
 Final Examination EE 130 December 16, 1997 Time allotted: 180 minutes Problem 1: Semiconductor Fundamentals [30 points] A uniformly doped silicon sample of length 100µm and cross-sectional area 100µm 2
Final Examination EE 130 December 16, 1997 Time allotted: 180 minutes Problem 1: Semiconductor Fundamentals [30 points] A uniformly doped silicon sample of length 100µm and cross-sectional area 100µm 2
ECE-343 Test 2: Mar 21, :00-8:00, Closed Book. Name : SOLUTION
 ECE-343 Test 2: Mar 21, 2012 6:00-8:00, Closed Book Name : SOLUTION 1. (25 pts) (a) Draw a circuit diagram for a differential amplifier designed under the following constraints: Use only BJTs. (You may
ECE-343 Test 2: Mar 21, 2012 6:00-8:00, Closed Book Name : SOLUTION 1. (25 pts) (a) Draw a circuit diagram for a differential amplifier designed under the following constraints: Use only BJTs. (You may
Electronic Circuits. Prof. Dr. Qiuting Huang Integrated Systems Laboratory
 Electronic Circuits Prof. Dr. Qiuting Huang 6. Transimpedance Amplifiers, Voltage Regulators, Logarithmic Amplifiers, Anti-Logarithmic Amplifiers Transimpedance Amplifiers Sensing an input current ii in
Electronic Circuits Prof. Dr. Qiuting Huang 6. Transimpedance Amplifiers, Voltage Regulators, Logarithmic Amplifiers, Anti-Logarithmic Amplifiers Transimpedance Amplifiers Sensing an input current ii in
EECE 2150 Circuits and Signals Final Exam Fall 2016 Dec 16
 EECE 2150 Circuits and Signals Final Exam Fall 2016 Dec 16 Instructions: Write your name and section number on all pages Closed book, closed notes; Computers and cell phones are not allowed You can use
EECE 2150 Circuits and Signals Final Exam Fall 2016 Dec 16 Instructions: Write your name and section number on all pages Closed book, closed notes; Computers and cell phones are not allowed You can use
EC- Objective Paper-I IES IES Paper-I
 EC- Objective Paper-I IES-03 www.gateforum.com IES-03- Paper-I. The resistances of two coils of a watt meter are 0.0Ω and 00 Ω respectively and both are non-inclusive. The current through a resistance
EC- Objective Paper-I IES-03 www.gateforum.com IES-03- Paper-I. The resistances of two coils of a watt meter are 0.0Ω and 00 Ω respectively and both are non-inclusive. The current through a resistance
Shared on QualifyGate.com
 1 Section - I (General Aptitude) Q.1 Choose the correct verb to fill in the blank below: Let us. introvert alternate atheist (d) altruist Q.2 Choose the most appropriate word from the options given below
1 Section - I (General Aptitude) Q.1 Choose the correct verb to fill in the blank below: Let us. introvert alternate atheist (d) altruist Q.2 Choose the most appropriate word from the options given below
ECE3050 Assignment 7
 ECE3050 Assignment 7. Sketch and label the Bode magnitude and phase plots for the transfer functions given. Use loglog scales for the magnitude plots and linear-log scales for the phase plots. On the magnitude
ECE3050 Assignment 7. Sketch and label the Bode magnitude and phase plots for the transfer functions given. Use loglog scales for the magnitude plots and linear-log scales for the phase plots. On the magnitude
Conventional Paper I-2010
 Conventional Paper I-010 1. (a) Sketch the covalent bonding of Si atoms in a intrinsic Si crystal Illustrate with sketches the formation of bonding in presence of donor and acceptor atoms. Sketch the energy
Conventional Paper I-010 1. (a) Sketch the covalent bonding of Si atoms in a intrinsic Si crystal Illustrate with sketches the formation of bonding in presence of donor and acceptor atoms. Sketch the energy
Frequency Dependent Aspects of Op-amps
 Frequency Dependent Aspects of Op-amps Frequency dependent feedback circuits The arguments that lead to expressions describing the circuit gain of inverting and non-inverting amplifier circuits with resistive
Frequency Dependent Aspects of Op-amps Frequency dependent feedback circuits The arguments that lead to expressions describing the circuit gain of inverting and non-inverting amplifier circuits with resistive
Graduate Diploma in Engineering Circuits and waves
 9210-112 Graduate Diploma in Engineering Circuits and waves You should have the following for this examination one answer book non-programmable calculator pen, pencil, ruler No additional data is attached
9210-112 Graduate Diploma in Engineering Circuits and waves You should have the following for this examination one answer book non-programmable calculator pen, pencil, ruler No additional data is attached
Answer Key. Electronics Engineering GATE Forenoon Session 31st Jan, Write us at Phone: ,
 Answer Key of Electronics Engineering GATE-2015 Forenoon Session 31st Jan, 2015 Write us at info@madeeasy.in Phone: 011-45124612, 9958995830 www.madeeasy.in Page 1 Section - I (General Aptitude) Q.1 Choose
Answer Key of Electronics Engineering GATE-2015 Forenoon Session 31st Jan, 2015 Write us at info@madeeasy.in Phone: 011-45124612, 9958995830 www.madeeasy.in Page 1 Section - I (General Aptitude) Q.1 Choose
ELECTRONICS IA 2017 SCHEME
 ELECTRONICS IA 2017 SCHEME CONTENTS 1 [ 5 marks ]...4 2...5 a. [ 2 marks ]...5 b. [ 2 marks ]...5 c. [ 5 marks ]...5 d. [ 2 marks ]...5 3...6 a. [ 3 marks ]...6 b. [ 3 marks ]...6 4 [ 7 marks ]...7 5...8
ELECTRONICS IA 2017 SCHEME CONTENTS 1 [ 5 marks ]...4 2...5 a. [ 2 marks ]...5 b. [ 2 marks ]...5 c. [ 5 marks ]...5 d. [ 2 marks ]...5 3...6 a. [ 3 marks ]...6 b. [ 3 marks ]...6 4 [ 7 marks ]...7 5...8
Operational Amplifiers
 Operational Amplifiers A Linear IC circuit Operational Amplifier (op-amp) An op-amp is a high-gain amplifier that has high input impedance and low output impedance. An ideal op-amp has infinite gain and
Operational Amplifiers A Linear IC circuit Operational Amplifier (op-amp) An op-amp is a high-gain amplifier that has high input impedance and low output impedance. An ideal op-amp has infinite gain and
CARLETON UNIVERSITY. FINAL EXAMINATION December DURATION 3 HOURS No. of Students 130
 ALETON UNIVESITY FINAL EXAMINATION December 005 DUATION 3 HOUS No. of Students 130 Department Name & ourse Number: Electronics ELE 3509 ourse Instructor(s): Prof. John W. M. ogers and alvin Plett AUTHOIZED
ALETON UNIVESITY FINAL EXAMINATION December 005 DUATION 3 HOUS No. of Students 130 Department Name & ourse Number: Electronics ELE 3509 ourse Instructor(s): Prof. John W. M. ogers and alvin Plett AUTHOIZED
EC Objective Paper I (Set - D)
 EC-Objective Paper-I ESE-5 www.gateforum.com EC Objective Paper I (Set - D). If a system produces frequencies in the output are not present in the input, then the system cannot be Minimum phase system
EC-Objective Paper-I ESE-5 www.gateforum.com EC Objective Paper I (Set - D). If a system produces frequencies in the output are not present in the input, then the system cannot be Minimum phase system
Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each.
 GATE 2016 General Aptitude - GA Set-6 Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q.1 The man who is now Municipal Commissioner worked as. (A) the security guard at a university (B) a security guard at the university
GATE 2016 General Aptitude - GA Set-6 Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q.1 The man who is now Municipal Commissioner worked as. (A) the security guard at a university (B) a security guard at the university
ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING
 ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Subject Code: EE Course Structure Sections/Units Section A Unit 1 Unit 2 Unit 3 Unit 4 Unit 5 Unit 6 Unit 7 Section B Section C Section D Section E Section F Section G Section H
ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Subject Code: EE Course Structure Sections/Units Section A Unit 1 Unit 2 Unit 3 Unit 4 Unit 5 Unit 6 Unit 7 Section B Section C Section D Section E Section F Section G Section H
Assignment 3 ELEC 312/Winter 12 R.Raut, Ph.D.
 Page 1 of 3 ELEC 312: ELECTRONICS II : ASSIGNMENT-3 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Winter 2012 1. A common-emitter amplifier that can be represented by the following equivalent circuit,
Page 1 of 3 ELEC 312: ELECTRONICS II : ASSIGNMENT-3 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Winter 2012 1. A common-emitter amplifier that can be represented by the following equivalent circuit,
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, BERKELEY College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences
 UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, BERKELEY College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences EE 105: Microelectronic Devices and Circuits Spring 2008 MIDTERM EXAMINATION #1 Time
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, BERKELEY College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences EE 105: Microelectronic Devices and Circuits Spring 2008 MIDTERM EXAMINATION #1 Time
Chapter 1 Fundamental Concepts
 Chapter 1 Fundamental Concepts 1 Signals A signal is a pattern of variation of a physical quantity, often as a function of time (but also space, distance, position, etc). These quantities are usually the
Chapter 1 Fundamental Concepts 1 Signals A signal is a pattern of variation of a physical quantity, often as a function of time (but also space, distance, position, etc). These quantities are usually the
and V DS V GS V T (the saturation region) I DS = k 2 (V GS V T )2 (1+ V DS )
 ECE 4420 Spring 2005 Page 1 FINAL EXAMINATION NAME SCORE /100 Problem 1O 2 3 4 5 6 7 Sum Points INSTRUCTIONS: This exam is closed book. You are permitted four sheets of notes (three of which are your sheets
ECE 4420 Spring 2005 Page 1 FINAL EXAMINATION NAME SCORE /100 Problem 1O 2 3 4 5 6 7 Sum Points INSTRUCTIONS: This exam is closed book. You are permitted four sheets of notes (three of which are your sheets
Microelectronic Circuit Design 4th Edition Errata - Updated 4/4/14
 Chapter Text # Inside back cover: Triode region equation should not be squared! i D = K n v GS "V TN " v & DS % ( v DS $ 2 ' Page 49, first exercise, second answer: -1.35 x 10 6 cm/s Page 58, last exercise,
Chapter Text # Inside back cover: Triode region equation should not be squared! i D = K n v GS "V TN " v & DS % ( v DS $ 2 ' Page 49, first exercise, second answer: -1.35 x 10 6 cm/s Page 58, last exercise,
Refinements to Incremental Transistor Model
 Refinements to Incremental Transistor Model This section presents modifications to the incremental models that account for non-ideal transistor behavior Incremental output port resistance Incremental changes
Refinements to Incremental Transistor Model This section presents modifications to the incremental models that account for non-ideal transistor behavior Incremental output port resistance Incremental changes
Feedback design for the Buck Converter
 Feedback design for the Buck Converter Portland State University Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Portland, Oregon, USA December 30, 2009 Abstract In this paper we explore two compensation
Feedback design for the Buck Converter Portland State University Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Portland, Oregon, USA December 30, 2009 Abstract In this paper we explore two compensation
Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT) - Introduction
 Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT) - Introduction It was found in 1948 at the Bell Telephone Laboratories. It is a three terminal device and has three semiconductor regions. It can be used in signal amplification
Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT) - Introduction It was found in 1948 at the Bell Telephone Laboratories. It is a three terminal device and has three semiconductor regions. It can be used in signal amplification
Mod. Sim. Dyn. Sys. Amplifiers page 1
 AMPLIFIERS A circuit containing only capacitors, amplifiers (transistors) and resistors may resonate. A circuit containing only capacitors and resistors may not. Why does amplification permit resonance
AMPLIFIERS A circuit containing only capacitors, amplifiers (transistors) and resistors may resonate. A circuit containing only capacitors and resistors may not. Why does amplification permit resonance
I PUC ELECTRONICS MODEL QUESTION PAPER -1 ( For new syllabus 2013)
 Max Mark: 70] I UC ELECTRONICS MODEL QUESTION AER - ( For new syllabus 0) [ Max Time : hrs 5 min Note: i. Question paper contains four parts. ii. art-a is compulsory, art-d contains two sub parts (a) problems
Max Mark: 70] I UC ELECTRONICS MODEL QUESTION AER - ( For new syllabus 0) [ Max Time : hrs 5 min Note: i. Question paper contains four parts. ii. art-a is compulsory, art-d contains two sub parts (a) problems
GATE 2007 Electrical Engineering
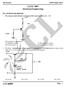 Q.1 Q. 20 carry one mark each GATE 2007 Electrical Engineering 1. The common emitter forward current gain of the transistor shown is β F = 100. 10V 1kΩ 270kΩ 1kΩ The transistor is operating in (A) Saturation
Q.1 Q. 20 carry one mark each GATE 2007 Electrical Engineering 1. The common emitter forward current gain of the transistor shown is β F = 100. 10V 1kΩ 270kΩ 1kΩ The transistor is operating in (A) Saturation
PGVES ENTRANCE EXAM SYLLABUS Pattern: objective type
 SYLLABUS FOR ENTRANCE EXAM FOR PG & PD COURSES PGTD/PGCTE: Work shop Technology, Metrology, Dies & Moulds, and allied.. Design of Machine Members, Material Science, Heat Treatment and Testing, Metrology
SYLLABUS FOR ENTRANCE EXAM FOR PG & PD COURSES PGTD/PGCTE: Work shop Technology, Metrology, Dies & Moulds, and allied.. Design of Machine Members, Material Science, Heat Treatment and Testing, Metrology
Examination paper for TFY4185 Measurement Technique/ Måleteknikk
 Page 1 of 14 Department of Physics Examination paper for TFY4185 Measurement Technique/ Måleteknikk Academic contact during examination: Patrick Espy Phone: +47 41 38 65 78 Examination date: 15 August
Page 1 of 14 Department of Physics Examination paper for TFY4185 Measurement Technique/ Måleteknikk Academic contact during examination: Patrick Espy Phone: +47 41 38 65 78 Examination date: 15 August
Mod. Sim. Dyn. Sys. Amplifiers page 1
 AMPLIFIERS A circuit containing only capacitors, amplifiers (transistors) and resistors may resonate. A circuit containing only capacitors and resistors may not. Why does amplification permit resonance
AMPLIFIERS A circuit containing only capacitors, amplifiers (transistors) and resistors may resonate. A circuit containing only capacitors and resistors may not. Why does amplification permit resonance
Lecture 7: Transistors and Amplifiers
 Lecture 7: Transistors and Amplifiers Hybrid Transistor Model for small AC : The previous model for a transistor used one parameter (β, the current gain) to describe the transistor. doesn't explain many
Lecture 7: Transistors and Amplifiers Hybrid Transistor Model for small AC : The previous model for a transistor used one parameter (β, the current gain) to describe the transistor. doesn't explain many
Physics (Theory) There are 30 questions in total. Question Nos. 1 to 8 are very short answer type questions and carry one mark each.
 Physics (Theory) Time allowed: 3 hours] [Maximum marks:70 General Instructions: (i) All questions are compulsory. (ii) (iii) (iii) (iv) (v) There are 30 questions in total. Question Nos. to 8 are very
Physics (Theory) Time allowed: 3 hours] [Maximum marks:70 General Instructions: (i) All questions are compulsory. (ii) (iii) (iii) (iv) (v) There are 30 questions in total. Question Nos. to 8 are very
ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS SUMMARY
 ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS SUMMARY Classification of Materials: Insulator: An insulator is a material that offers a very low level (or negligible) of conductivity when voltage is applied. Eg: Paper,
ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS SUMMARY Classification of Materials: Insulator: An insulator is a material that offers a very low level (or negligible) of conductivity when voltage is applied. Eg: Paper,
Digital Electronics Final Examination. Part A
 Digital Electronics Final Examination Part A Spring 2009 Student Name: Date: Class Period: Total Points: /50 Converted Score: /40 Page 1 of 13 Directions: This is a CLOSED BOOK/CLOSED NOTES exam. Select
Digital Electronics Final Examination Part A Spring 2009 Student Name: Date: Class Period: Total Points: /50 Converted Score: /40 Page 1 of 13 Directions: This is a CLOSED BOOK/CLOSED NOTES exam. Select
Lecture 37: Frequency response. Context
 EECS 05 Spring 004, Lecture 37 Lecture 37: Frequency response Prof J. S. Smith EECS 05 Spring 004, Lecture 37 Context We will figure out more of the design parameters for the amplifier we looked at in
EECS 05 Spring 004, Lecture 37 Lecture 37: Frequency response Prof J. S. Smith EECS 05 Spring 004, Lecture 37 Context We will figure out more of the design parameters for the amplifier we looked at in
First and Second Order Circuits. Claudio Talarico, Gonzaga University Spring 2015
 First and Second Order Circuits Claudio Talarico, Gonzaga University Spring 2015 Capacitors and Inductors intuition: bucket of charge q = Cv i = C dv dt Resist change of voltage DC open circuit Store voltage
First and Second Order Circuits Claudio Talarico, Gonzaga University Spring 2015 Capacitors and Inductors intuition: bucket of charge q = Cv i = C dv dt Resist change of voltage DC open circuit Store voltage
Prof. Anyes Taffard. Physics 120/220. Voltage Divider Capacitor RC circuits
 Prof. Anyes Taffard Physics 120/220 Voltage Divider Capacitor RC circuits Voltage Divider The figure is called a voltage divider. It s one of the most useful and important circuit elements we will encounter.
Prof. Anyes Taffard Physics 120/220 Voltage Divider Capacitor RC circuits Voltage Divider The figure is called a voltage divider. It s one of the most useful and important circuit elements we will encounter.
SOME USEFUL NETWORK THEOREMS
 APPENDIX D SOME USEFUL NETWORK THEOREMS Introduction In this appendix we review three network theorems that are useful in simplifying the analysis of electronic circuits: Thévenin s theorem Norton s theorem
APPENDIX D SOME USEFUL NETWORK THEOREMS Introduction In this appendix we review three network theorems that are useful in simplifying the analysis of electronic circuits: Thévenin s theorem Norton s theorem
PHYS225 Lecture 9. Electronic Circuits
 PHYS225 Lecture 9 Electronic Circuits Last lecture Field Effect Transistors Voltage controlled resistor Various FET circuits Switch Source follower Current source Similar to BJT Draws no input current
PHYS225 Lecture 9 Electronic Circuits Last lecture Field Effect Transistors Voltage controlled resistor Various FET circuits Switch Source follower Current source Similar to BJT Draws no input current
Chapter wise Theoretical Important Questions in Physics for Class-XII
 Electrostatics- 1. Derive an expression for the electric field at a point on the axial position of an electric dipole. 2. Derive an expression for the electric field at a point on the equatorial position
Electrostatics- 1. Derive an expression for the electric field at a point on the axial position of an electric dipole. 2. Derive an expression for the electric field at a point on the equatorial position
Whereas the diode was a 1-junction device, the transistor contains two junctions. This leads to two possibilities:
 Part Recall: two types of charge carriers in semiconductors: electrons & holes two types of doped semiconductors: n-type (favor e-), p-type (favor holes) for conduction Whereas the diode was a -junction
Part Recall: two types of charge carriers in semiconductors: electrons & holes two types of doped semiconductors: n-type (favor e-), p-type (favor holes) for conduction Whereas the diode was a -junction
Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each.
 General Aptitude (GA) Set-5 Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q.1 By giving him the last of the cake, you will ensure lasting in our house today. The words that best fill the blanks in the above sentence
General Aptitude (GA) Set-5 Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q.1 By giving him the last of the cake, you will ensure lasting in our house today. The words that best fill the blanks in the above sentence
Microelectronic Circuit Design Fourth Edition - Part I Solutions to Exercises
 Page Microelectronic Circuit esign Fourth Edition - Part I Solutions to Exercises CHAPTER V LSB 5.V 0 bits 5.V 04bits 5.00 mv V 5.V MSB.560V 000000 9 + 8 + 4 + 0 785 0 V O 785 5.00mV or ) 5.V 3.95 V V
Page Microelectronic Circuit esign Fourth Edition - Part I Solutions to Exercises CHAPTER V LSB 5.V 0 bits 5.V 04bits 5.00 mv V 5.V MSB.560V 000000 9 + 8 + 4 + 0 785 0 V O 785 5.00mV or ) 5.V 3.95 V V
