Study of Carrier Transport in Strained and Unstrained SOI Tri-gate and Omega-gate Si Nanowire MOSFETs
|
|
|
- Nigel Golden
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 42nd ESSDERC, Bordeaux, France, Sept A2L-E, High Mobility Devices, 18 Sept. Study of Carrier Transport in Strained and Unstrained SOI Tri-gate and Omega-gate Si Nanowire MOSFETs M. Koyama 1,4, M. Cassé 1, R. Coquand 1,2,3, S. Barraud 1, H. Iwai 4, G. Ghibaudo 2, and G. Reimbold 1 1 CEA LETI, 2 IMEP-LAHC INPG-MINATEC, 3 STMicroelectronics, 4 FRC, Tokyo Institute of Technology
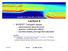
2 Introduction - Si nanowire MOSFETs FD-SOI/high-k/mid-gap MG (Undoped channel) Higher mobility Reduction of random dopant fluctuation (RDF) No poly-depletion Almost symmetrical Id-Vg curve for N- and PMOS Source Gate Gate Mid-gap MG High-k Undoped Si FD-SOI FET Drain Drain BOX Application Si nanowire MOSFETs High immunity to short channel effect (SCE) and drain induced barrier lowering (DIBL) Better electrostatic control Lower off-current (I OFF ) Steeper subthreshold slope (SS) Gate Source BOX Si Tri-gate NWFET Source BOX Si Drain Omega-gate NWFET Advantages in downscaling and power consumption 2
3 Issues and challenges Quantum confinement of carriers Downscaled cross-section of NW below 20nm 20nm Contributions of different crystallographic orientation Tri-gate: top surface and side-walls Ω-gate, GAA: rounded (omega-shaped, cylindrical) surface Stress engineering Improvement of device performance Promising solution to further scaling of CMOS technology Combination of NW architecture and stress 3
4 Purpose Understanding of carrier transport in SOI and ssoi Tri-gate and Omega-gate SiNW MOSFETs Influence on carrier transport - Channel shape Tri-gate vs Omega-gate - Width dimensions NW down to 10nm - Uniaxial tensile strain H Gate W Si Source BOX Si Drain Gate Si Source BOX Si Drain Measurement Carrier mobility on N- and PMOS NW FETs down to low temperature 4
5 Measured Si nanowires Gate stack: HfSiON(2nm)/ALD-TiN(5nm)/poly-Si(50nm) SOI and ssoi wafer Unstrained and strained NW - 50 channels NWs - Long channel transistors with Lg=10µm R.Coquand et al., Symp. VLSI Tech., p.13 (2012). Effective mobility extraction by conventional split C-V technique 5
6 Basic characteristics: Id-Vg curves I d /W tot (µa/µm) Vd=0.9V Vd=40mV W=10nm H=11nm Tri-gate Vd=40mV Vd=0.9V Ω gate Vd=40mV Vd=0.9V V g (V) No I ON difference Vd=0.9V Vd=40mV W=23nm H=10nm Unstrained TG vs ΩG NWs Vd=0.9V Vd=40mV ssoi-tg Vd=40mV Vd=0.9V SOI-TG Vd=40mV Vd=0.9V V g (V) Vd=0.9V Vd=40mV Vt shift Strained TG W=16nm H=10.5nm Unstrained vs strained TGNWs NMOS: I ON enhancement Vt shift ~ 40mV PMOS: I ON deterioration Subthreshold slope (SS) ~ 70mV/dec: Well behaved characteristics 6
7 Scattering-limited mobility in MOSFET Effective mobility, µ eff Coulomb scattering Low Surface roughness Phonon scattering scattering High Temperature Total mobility S.Takagi et al., Trans. Electron Dev., 41, 2357 (1994). Inversion charge density, Phonon scattering (PS) depends on temperature (T) Coulomb scattering (CS) Surface roughness scattering (SRS) T independent Carrier transport is limited by 3 scattering mechanisms 7
8 Temperature dependent mobility <TGNW vs Wide FET> Effective Mobility (cm²/vs) NMOS TGNW: W=10nm T=20K T=300K ( cm -2 ) TGNW Wide FET Wide FET Effective Mobility (cm²/vs) Wide FET: W=10µm PMOS K 300K ( cm -2 ) TGNW Wide FET High T=50K T=300K Tri-gate NW NMOS: Mobility high PMOS: Small mobility high Maximum peak position shift to lower 8
9 Contribution of surface orientation to effective mobility Maximum mobility in unstrained wide FET Si surface orientation Top surface () Side-walls (110) µ eff_max (cm 2 /Vs) in SOI Electron (NMOS) Hole (PMOS) Gate [110] Source BOX Si Drain Top Si() Side-wall Si(110) Advantage Si()//[110] (top surface): electron transport Si(110)//[110] (side-walls): hole transport H.Irie et al., IEDM Tech. Dig., 225 (4). Electron mobility degradation Hole mobility enhancement as the width decreases Nanowire: Increasing the contribution of (110)-oriented side-walls 9
10 Extracted top and surface mobility in Tri-gate NW Effective Mobility (cm²/vs) ~µ C TGNW: W=10nm µ top µ side-wall Tri-gate NW ( cm -2 ) NMOS ~µ SR_top T=K µ ~µ SR_side-wall total eff Effective Mobility (cm²/vs) = W top() 2H µ eff + W + 2H W + 2H µ µ top µ side-wall ( cm -2 ) Larger contribution of (110) side-wall PMOS ~µ SR_side-wall ~µ SR_top side wall(110) eff T=K Maximum mobility (Coulomb and Phonon) Surface roughness-limited mobility 10
11 Temperature dependent mobility <TGNW vs ΩGNW> TGNW: W=30nm ΩGNW: W=23nm Effective Mobility (cm²/vs) NMOS ΩGNW TGNW T=20K T=300K Effective Mobility (cm²/vs) T=20K T=300K N 13-2 inv ( cm -2 ) ( cm -2 ) PMOS ΩGNW TGNW ΩG N- and PMOS Maximum mobility low T Lower Coulomb scattering due to H 2 anneal process 11
12 Stress effect on carrier transport along [110] (b) lateral strain relaxation s-si [110] [110] BOX BoX Biaxial vs uniaxial stress (~1.4GPa) - Biaxial tensile stress (in () plane) - Uniaxial stress along channel direction (Lateral strain relaxation) Mobility enhancement (degradation) from strain effect - Repopulation of Si conduction valleys - Reduction of intervalley phonon scattering Strain NMOS PMOS (transport //[110]) () (110) () (110) no strain biaxial tensile + - / = uniaxial tensile // [110] Uniaxial tensile stress along [110] direction: Improving electron mobility 12
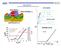
13 Top width (W top ) dependent effective mobility <TG vs WG> µ eff (cm 2 High Tri-gate +55% = cm % NW Wide W top (µm) ssoi SOI NMOS µ eff (cm 2 High Ω-gate +50% +65% NW Wide W top (µm) Electron mobility degradation as the width narrowing = cm -2 ssoi SOI Uniaxial strained NW with ~50% gain in µ eff Still enhanced TG and ΩG devices exhibit almost the same mobility improvement - Strain relaxation - Piezoresistive properties Same in both geometries 13
14 Top width (W top ) dependent effective mobility <TG vs WG> µ eff (cm 2 High Tri-gate -30% = cm -2 ssoi SOI W top (µm) PMOS Ω-gate TG and ΩGNW represent roughly the same mobility Strained NWs; No mobility improvement as W top decreases µ eff (cm 2 High -25% = cm -2 ssoi SOI W top (µm) Uniaxial tensile strain for PMOS Counterbalance of better mobility in unstrained Si(110) Large mobility degradation for Si() top surface Agreement with NMOS 14
15 Temperature dependent mobility <SOI vs strained-soi> µ eff (cm 2 High NMOS ~µ SR_wide Unstrained = cm -2 Strained Tri-gate Ω-gate Tri-gate Ω-gate W=10nm W=10µm W=23nm W=10µm W=16nm W=10µm W=33nm W=10µm Temperature (K) Wide FET ~µ SR_wide ~µ SR_NW ~µ SR_NW Temperature (K) T>K T<K Phonon-limited mobility: Improvement from strain effect Mobility saturation from surface roughness scattering (SRS) SR-limited mobility: Small enhancement by strain effect Roughly same properties in both TG and ΩG geometries 15
16 Temperature dependent mobility <SOI vs strained SOI> µ eff (cm 2 High PMOS ~µ SR_NW ~µ SR_wide Unstrained Wide FET 500 = cm -2 Strained Tri-gate Ω-gate Tri-gate Ω-gate W=30nm W=10µm W=23nm W=10µm W=36nm W=10µm W=33nm W=10µm Temperature (K) ~µ SR_wide ~µ SR_NW Temperature (K) Whole T range Stress influence to mobility (Phonon- and SR-limited) Enhancement: Wide FETs Degradation: TG and ΩG NWs Same in both NWs Biaxial stress (wide FET): Improvement Uniaxial stress (both NWs): Deterioration 16
17 Temperature dependent maximum mobility Influence of phonon scattering µ max ~ µ phonon T γ Values of power law exponent γ Tri-gate Wide (10µm) NMOS SOI ssoi PMOS SOI ssoi w/o H 2 anneal NW Ω-gate Wide (10µm) with H 2 anneal NW Larger stress influence for NMOS Phonon-limited mobility Dependent on the strain effect Independent on channel shape width dimension 17
18 Conclusions Carrier transport in strained and unstrained TG and ΩG NWs i) Transport properties in TGNWs (down to 10nm 10nm section) Agreement with the contribution of different orientation Larger Si(110) side-wall contribution ii) ΩGNWs (down to W top-view of 23 nm) Roughly same mobility behavior as TGNWs Lower Coulomb scattering iii) Uniaxial strain in both nanowire geometries Enhancing NMOS performance Diminishing PMOS performance Phonon-limited and SR-limited mobility No significant difference from the channel shape 18
19 Modifiez les styles du texte du masque Deuxième niveau > Troisième niveau Thank you for Merci de votre your kind attention attention 19
20 Backup slides 20
21 Temperature dependent mobility <TGNW vs ΩGNW> TGNW: W=10nm W=30nm ΩGNW: W=23nm Effective Mobility (cm²/vs) NMOS ΩGNW TGNW (30nm) T=20K T=300K Effective Mobility (cm²/vs) N 13-2 inv ( cm -2 ) ( cm -2 ) NMOS ΩGNW TGNW (10nm) T=20K T=300K ΩG NMOS Maximum mobility low T Lower Coulomb scattering due to H 2 anneal process 21
22 Temperature dependent mobility <TGNW> TGNW: W=10nm vs W=30nm Effective Mobility (cm²/vs) NMOS T=20K T=300K ( cm -2 ) W=10nm W=30nm Larger contribution of (110) side-wall 300K 250K K 150K K 50K 20K Maximum mobility (Coulomb and Phonon) Surface roughness-limited mobility 22
23 Temperature dependent mobility <SOI vs strained SOI> µ eff (cm 2 High NMOS Tri-gate W=10nm W=30nm W=10µm Unstrained Ω-gate W=23nm W=10µm Wide FET ~µ SR_NW ~µ SR_NW = cm -2 Tri-gate W=16nm W=36nm W=10µm Strained Ω-gate W=33nm W=10µm Difference between W top =10nm & 30nm TGNWs Contribution of (110) side-walls 23
24 Extraction of µ top and µ side-wall contribution for Tri-gate NW Contribution of surface orientation to effective mobility µ µ total eff = W top() 2H µ eff + W + 2H W + 2H µ side wall(110) eff = α µ total eff W µ 2H top() eff side wall(110) eff W + 2H α = 2H J. Chen et al., Symp., VLSI Tech., p.32 (8). R. Coquand et al., Proc., ULIS conf. (2012). Si surface orientation Top surface () Side-walls (110) Electron (NMOS) + - µ eff (cm 2 /Vs) Hole (PMOS) - + H Gate [110] W Source BOX Si Drain Top Si() Side-wall Si(110) Scattering behavior on µ top and µ side-wall? 24
25 Scattering influence in µ top and µ side-wall of Tri-gate NW Effective Mobility (cm²/vs) ~µ C NMOS T=K T=300K ( cm -2 ) ~µ SR_top ~µ SR_side-wall µ top µ side-wall µ Si(110) TGNW: W=10nm µ side-wall ~ referential µ Si(110) Mobility limit Scattering mechanism Coulomb (µ C ) Surface roughness (µ SR ) µ top () Strong Weak µ side-wall (110) Weak Strong 25
26 Scattering influence in µ top and µ side-wall of Tri-gate NW Effective Mobility (cm²/vs) ~µ C ~µ SR_side-wall ~µ SR_top ( cm -2 ) PMOS T=K T=300K µ top µ side-wall µ Si(110) TGNW: W=30nm µ side-wall ~ µ high Mobility limit Scattering mechanism Coulomb (µ C ) Surface roughness (µ SR ) µ top () No difference µ side-wall (110) Similar slope 26
27 H 2 anneal impact in wide device Effective Mobility (cm²/vs) Wide FET NMOS Wide FET: W=10µm ( cm -2 ) 300K 250K K 150K K 50K 20K Enhancement Coulomb-limited mobility SR-limited mobility ΩG_with H 2 (W=10µm) TG_w/o H 2 (W=10µm) PMOS ( cm -2 ) 300K 250K K 150K K 50K 20K Enhancement Coulomb-limited mobility 27
28 Mobility improvement from strain effect Mobility gain in Strained-Si nmosfet (tensile) Increase of the 2-fold valley occupancy (population) with lower conductivity mass Decrease the phonon scattering rate between the 2-fold and the 4-fold valleys (intervalley scattering) Strain effect for hole (tensile) Breking of the valence band degeneracy Reduction of conductivity mass 28
29 Fablication process Undoped FD-SOI wafer (Mesa isolation) - with or w/o biaxial tensile stress of ~1.4 GPa NW patterning (DUV lithography) - with or w/o H 2 anneal HfSiON(2nm)/ALD TiN(5nm)/poly-Si(50nm) gate stack Gate patterning Spacer 1 formation S/D epitaxy (T Si =18nm) LDD implantation Spacer 2 formation HDD implantation Silicidation Back-end 29
30 Basic characteristics: Id-Vg curves I d /W tot (µa/µm) Vd=40mV NMOS Vd=-40mV PMOS Tri-gate Omega-gate strained-tg strained-ωg I d /W tot (µa/µm) Vd=0.9V d tot Vd=-0.9V 6 4 Tri-gate Omega-gate strained-tg strained-ωg V g (V) V g (V) 0 30
Enhanced Mobility CMOS
 Enhanced Mobility CMOS Judy L. Hoyt I. Åberg, C. Ni Chléirigh, O. Olubuyide, J. Jung, S. Yu, E.A. Fitzgerald, and D.A. Antoniadis Microsystems Technology Laboratory MIT, Cambridge, MA 02139 Acknowledge
Enhanced Mobility CMOS Judy L. Hoyt I. Åberg, C. Ni Chléirigh, O. Olubuyide, J. Jung, S. Yu, E.A. Fitzgerald, and D.A. Antoniadis Microsystems Technology Laboratory MIT, Cambridge, MA 02139 Acknowledge
Lecture 9. Strained-Si Technology I: Device Physics
 Strain Analysis in Daily Life Lecture 9 Strained-Si Technology I: Device Physics Background Planar MOSFETs FinFETs Reading: Y. Sun, S. Thompson, T. Nishida, Strain Effects in Semiconductors, Springer,
Strain Analysis in Daily Life Lecture 9 Strained-Si Technology I: Device Physics Background Planar MOSFETs FinFETs Reading: Y. Sun, S. Thompson, T. Nishida, Strain Effects in Semiconductors, Springer,
Tri-Gate Fully-Depleted CMOS Transistors: Fabrication, Design and Layout
 Tri-Gate Fully-Depleted CMOS Transistors: Fabrication, Design and Layout B.Doyle, J.Kavalieros, T. Linton, R.Rios B.Boyanov, S.Datta, M. Doczy, S.Hareland, B. Jin, R.Chau Logic Technology Development Intel
Tri-Gate Fully-Depleted CMOS Transistors: Fabrication, Design and Layout B.Doyle, J.Kavalieros, T. Linton, R.Rios B.Boyanov, S.Datta, M. Doczy, S.Hareland, B. Jin, R.Chau Logic Technology Development Intel
Recent Development of FinFET Technology for CMOS Logic and Memory
 Recent Development of FinFET Technology for CMOS Logic and Memory Chung-Hsun Lin EECS Department University of California at Berkeley Why FinFET Outline FinFET process Unique features of FinFET Mobility,
Recent Development of FinFET Technology for CMOS Logic and Memory Chung-Hsun Lin EECS Department University of California at Berkeley Why FinFET Outline FinFET process Unique features of FinFET Mobility,
EE410 vs. Advanced CMOS Structures
 EE410 vs. Advanced CMOS Structures Prof. Krishna S Department of Electrical Engineering S 1 EE410 CMOS Structure P + poly-si N + poly-si Al/Si alloy LPCVD PSG P + P + N + N + PMOS N-substrate NMOS P-well
EE410 vs. Advanced CMOS Structures Prof. Krishna S Department of Electrical Engineering S 1 EE410 CMOS Structure P + poly-si N + poly-si Al/Si alloy LPCVD PSG P + P + N + N + PMOS N-substrate NMOS P-well
Multiple Gate CMOS and Beyond
 Multiple CMOS and Beyond Dept. of EECS, KAIST Yang-Kyu Choi Outline 1. Ultimate Scaling of MOSFETs - 3nm Nanowire FET - 8nm Non-Volatile Memory Device 2. Multiple Functions of MOSFETs 3. Summary 2 CMOS
Multiple CMOS and Beyond Dept. of EECS, KAIST Yang-Kyu Choi Outline 1. Ultimate Scaling of MOSFETs - 3nm Nanowire FET - 8nm Non-Volatile Memory Device 2. Multiple Functions of MOSFETs 3. Summary 2 CMOS
EECS130 Integrated Circuit Devices
 EECS130 Integrated Circuit Devices Professor Ali Javey 10/30/2007 MOSFETs Lecture 4 Reading: Chapter 17, 19 Announcements The next HW set is due on Thursday. Midterm 2 is next week!!!! Threshold and Subthreshold
EECS130 Integrated Circuit Devices Professor Ali Javey 10/30/2007 MOSFETs Lecture 4 Reading: Chapter 17, 19 Announcements The next HW set is due on Thursday. Midterm 2 is next week!!!! Threshold and Subthreshold
High Mobility Materials and Novel Device Structures for High Performance Nanoscale MOSFETs
 High Mobility Materials and Novel Device Structures for High Performance Nanoscale MOSFETs Prof. (Dr.) Tejas Krishnamohan Department of Electrical Engineering Stanford University, CA & Intel Corporation
High Mobility Materials and Novel Device Structures for High Performance Nanoscale MOSFETs Prof. (Dr.) Tejas Krishnamohan Department of Electrical Engineering Stanford University, CA & Intel Corporation
Comparison of Ultra-Thin InAs and InGaAs Quantum Wells and Ultra-Thin-Body Surface-Channel MOSFETs
 Comparison of Ultra-Thin InAs and InGaAs Quantum Wells and Ultra-Thin-Body Surface-Channel MOSFETs Cheng-Ying Huang 1, Sanghoon Lee 1, Evan Wilson 3, Pengyu Long 3, Michael Povolotskyi 3, Varistha Chobpattana
Comparison of Ultra-Thin InAs and InGaAs Quantum Wells and Ultra-Thin-Body Surface-Channel MOSFETs Cheng-Ying Huang 1, Sanghoon Lee 1, Evan Wilson 3, Pengyu Long 3, Michael Povolotskyi 3, Varistha Chobpattana
A final review session will be offered on Thursday, May 10 from 10AM to 12noon in 521 Cory (the Hogan Room).
 A final review session will be offered on Thursday, May 10 from 10AM to 12noon in 521 Cory (the Hogan Room). The Final Exam will take place from 12:30PM to 3:30PM on Saturday May 12 in 60 Evans.» All of
A final review session will be offered on Thursday, May 10 from 10AM to 12noon in 521 Cory (the Hogan Room). The Final Exam will take place from 12:30PM to 3:30PM on Saturday May 12 in 60 Evans.» All of
A Multi-Gate CMOS Compact Model BSIMMG
 A Multi-Gate CMOS Compact Model BSIMMG Darsen Lu, Sriramkumar Venugopalan, Tanvir Morshed, Yogesh Singh Chauhan, Chung-Hsun Lin, Mohan Dunga, Ali Niknejad and Chenming Hu University of California, Berkeley
A Multi-Gate CMOS Compact Model BSIMMG Darsen Lu, Sriramkumar Venugopalan, Tanvir Morshed, Yogesh Singh Chauhan, Chung-Hsun Lin, Mohan Dunga, Ali Niknejad and Chenming Hu University of California, Berkeley
The Pennsylvania State University. Kurt J. Lesker Company. North Carolina State University. Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company 1
 Enhancement Mode Strained (1.3%) Germanium Quantum Well FinFET (W fin =20nm) with High Mobility (μ Hole =700 cm 2 /Vs), Low EOT (~0.7nm) on Bulk Silicon Substrate A. Agrawal 1, M. Barth 1, G. B. Rayner
Enhancement Mode Strained (1.3%) Germanium Quantum Well FinFET (W fin =20nm) with High Mobility (μ Hole =700 cm 2 /Vs), Low EOT (~0.7nm) on Bulk Silicon Substrate A. Agrawal 1, M. Barth 1, G. B. Rayner
This is the author s final accepted version.
 Al-Ameri, T., Georgiev, V.P., Adamu-Lema, F. and Asenov, A. (2017) Does a Nanowire Transistor Follow the Golden Ratio? A 2D Poisson- Schrödinger/3D Monte Carlo Simulation Study. In: 2017 International
Al-Ameri, T., Georgiev, V.P., Adamu-Lema, F. and Asenov, A. (2017) Does a Nanowire Transistor Follow the Golden Ratio? A 2D Poisson- Schrödinger/3D Monte Carlo Simulation Study. In: 2017 International
The Future of CMOS. David Pulfrey. CHRONOLOGY of the FET. Lecture Lilienfeld s patent (BG FET) 1965 Commercialization (Fairchild)
 The Future of CMOS David Pulfrey 1 CHRONOLOGY of the FET 1933 Lilienfeld s patent (BG FET) 1965 Commercialization (Fairchild) 1991 The most abundant object made by mankind (C.T. Sah) 2003 The 10 nm FET
The Future of CMOS David Pulfrey 1 CHRONOLOGY of the FET 1933 Lilienfeld s patent (BG FET) 1965 Commercialization (Fairchild) 1991 The most abundant object made by mankind (C.T. Sah) 2003 The 10 nm FET
Performance Enhancement of P-channel InGaAs Quantum-well FETs by Superposition of Process-induced Uniaxial Strain and Epitaxially-grown Biaxial Strain
 Performance Enhancement of P-channel InGaAs Quantum-well FETs by Superposition of Process-induced Uniaxial Strain and Epitaxially-grown Biaxial Strain Ling Xia 1, Vadim Tokranov 2, Serge R. Oktyabrsky
Performance Enhancement of P-channel InGaAs Quantum-well FETs by Superposition of Process-induced Uniaxial Strain and Epitaxially-grown Biaxial Strain Ling Xia 1, Vadim Tokranov 2, Serge R. Oktyabrsky
Modeling and Computation of Gate Tunneling Current through Ultra Thin Gate Oxides in Double Gate MOSFETs with Ultra Thin Body Silicon Channel
 Modeling and Computation of Gate Tunneling Current through Ultra Thin Gate Oxides in Double Gate MOSFETs with Ultra Thin Body Silicon Channel Bhadrinarayana L V 17 th July 2008 Microelectronics Lab, Indian
Modeling and Computation of Gate Tunneling Current through Ultra Thin Gate Oxides in Double Gate MOSFETs with Ultra Thin Body Silicon Channel Bhadrinarayana L V 17 th July 2008 Microelectronics Lab, Indian
Ultimately Scaled CMOS: DG FinFETs?
 Ultimately Scaled CMOS: DG FinFETs? Jerry G. Fossum SOI Group Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Florida Gainesville, FL 32611-6130 J. G. Fossum / 1 Outline Introduction -
Ultimately Scaled CMOS: DG FinFETs? Jerry G. Fossum SOI Group Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Florida Gainesville, FL 32611-6130 J. G. Fossum / 1 Outline Introduction -
Single Electron Devices and Circuits
 Single Electron Devices and Circuits M. F. Gonzalez-Zalba 1, S. Kaxiras 2, R.D. Levine 3, F. Remacle 4, S. Rogge 5, M. Sanquer 6 1 Hitachi Cambridge Laboratory, Cambridge, UK 2 Division of Computer Systems,
Single Electron Devices and Circuits M. F. Gonzalez-Zalba 1, S. Kaxiras 2, R.D. Levine 3, F. Remacle 4, S. Rogge 5, M. Sanquer 6 1 Hitachi Cambridge Laboratory, Cambridge, UK 2 Division of Computer Systems,
Simple Theory of the Ballistic Nanotransistor
 Simple Theory of the Ballistic Nanotransistor Mark Lundstrom Purdue University Network for Computational Nanoechnology outline I) Traditional MOS theory II) A bottom-up approach III) The ballistic nanotransistor
Simple Theory of the Ballistic Nanotransistor Mark Lundstrom Purdue University Network for Computational Nanoechnology outline I) Traditional MOS theory II) A bottom-up approach III) The ballistic nanotransistor
Components Research, TMG Intel Corporation *QinetiQ. Contact:
 1 High-Performance 4nm Gate Length InSb P-Channel Compressively Strained Quantum Well Field Effect Transistors for Low-Power (V CC =.5V) Logic Applications M. Radosavljevic,, T. Ashley*, A. Andreev*, S.
1 High-Performance 4nm Gate Length InSb P-Channel Compressively Strained Quantum Well Field Effect Transistors for Low-Power (V CC =.5V) Logic Applications M. Radosavljevic,, T. Ashley*, A. Andreev*, S.
Lecture 5: CMOS Transistor Theory
 Lecture 5: CMOS Transistor Theory Slides courtesy of Deming Chen Slides based on the initial set from David Harris CMOS VLSI Design Outline q q q q q q q Introduction MOS Capacitor nmos I-V Characteristics
Lecture 5: CMOS Transistor Theory Slides courtesy of Deming Chen Slides based on the initial set from David Harris CMOS VLSI Design Outline q q q q q q q Introduction MOS Capacitor nmos I-V Characteristics
ECE 342 Electronic Circuits. Lecture 6 MOS Transistors
 ECE 342 Electronic Circuits Lecture 6 MOS Transistors Jose E. Schutt-Aine Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Illinois jesa@illinois.edu 1 NMOS Transistor Typically L = 0.1 to 3 m, W = 0.2
ECE 342 Electronic Circuits Lecture 6 MOS Transistors Jose E. Schutt-Aine Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Illinois jesa@illinois.edu 1 NMOS Transistor Typically L = 0.1 to 3 m, W = 0.2
Courtesy of S. Salahuddin (UC Berkeley) Lecture 4
 Courtesy of S. Salahuddin (UC Berkeley) Lecture 4 MOSFET Transport Issues semiconductor band structure quantum confinement effects low-field mobility and high-field saturation Reading: - M. Lundstrom,
Courtesy of S. Salahuddin (UC Berkeley) Lecture 4 MOSFET Transport Issues semiconductor band structure quantum confinement effects low-field mobility and high-field saturation Reading: - M. Lundstrom,
Towards Atomistic Simulations of the Electro-Thermal Properties of Nanowire Transistors Mathieu Luisier and Reto Rhyner
 Towards Atomistic Simulations of the Electro-Thermal Properties of Nanowire Transistors Mathieu Luisier and Reto Rhyner Integrated Systems Laboratory ETH Zurich, Switzerland Outline Motivation Electron
Towards Atomistic Simulations of the Electro-Thermal Properties of Nanowire Transistors Mathieu Luisier and Reto Rhyner Integrated Systems Laboratory ETH Zurich, Switzerland Outline Motivation Electron
Split-gate charge trap memories: impact of scaling on performances and consumption for low-power embedded applications
 Split-gate charge trap memories: impact of scaling on performances and consumption for low-power embedded applications Lia Masoero lia.masoero@cea.fr Outline Introduction Technological details Basics of
Split-gate charge trap memories: impact of scaling on performances and consumption for low-power embedded applications Lia Masoero lia.masoero@cea.fr Outline Introduction Technological details Basics of
Prospects for Ge MOSFETs
 Prospects for Ge MOSFETs Sematech Workshop December 4, 2005 Dimitri A. Antoniadis Microsystems Technology Laboratories MIT Sematech Workshop 2005 1 Channel Transport - I D I D =WQ i (x 0 )v xo v xo : carrier
Prospects for Ge MOSFETs Sematech Workshop December 4, 2005 Dimitri A. Antoniadis Microsystems Technology Laboratories MIT Sematech Workshop 2005 1 Channel Transport - I D I D =WQ i (x 0 )v xo v xo : carrier
Introduction and Background
 Analog CMOS Integrated Circuit Design Introduction and Background Dr. Jawdat Abu-Taha Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Islamic University of Gaza jtaha@iugaza.edu.ps 1 Marking Assignments
Analog CMOS Integrated Circuit Design Introduction and Background Dr. Jawdat Abu-Taha Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Islamic University of Gaza jtaha@iugaza.edu.ps 1 Marking Assignments
MONTE CARLO SIMULATION OF THE ELECTRON MOBILITY IN STRAINED SILICON
 MONTE CARLO SIMULATION OF THE ELECTRON MOBILITY IN STRAINED SILICON Siddhartha Dhar*, Enzo Ungersböck*, Mihail Nedjalkov, Vassil Palankovski Advanced Materials and Device Analysis Group, at * *Institute
MONTE CARLO SIMULATION OF THE ELECTRON MOBILITY IN STRAINED SILICON Siddhartha Dhar*, Enzo Ungersböck*, Mihail Nedjalkov, Vassil Palankovski Advanced Materials and Device Analysis Group, at * *Institute
Classification of Solids
 Classification of Solids Classification by conductivity, which is related to the band structure: (Filled bands are shown dark; D(E) = Density of states) Class Electron Density Density of States D(E) Examples
Classification of Solids Classification by conductivity, which is related to the band structure: (Filled bands are shown dark; D(E) = Density of states) Class Electron Density Density of States D(E) Examples
The Evolution of Theory on Drain Current Saturation Mechanism of MOSFETs from the Early Days to the Present Day
 The Evolution of Theory on Drain Current Saturation Mechanism of MOSFETs from the Early Days to the Present Day Peizhen Yang 1, W.S. Lau 1, Seow Wei Lai 2, V.L. Lo 2, S.Y. Siah 2 and L. Chan 2 3 1 Nanyang
The Evolution of Theory on Drain Current Saturation Mechanism of MOSFETs from the Early Days to the Present Day Peizhen Yang 1, W.S. Lau 1, Seow Wei Lai 2, V.L. Lo 2, S.Y. Siah 2 and L. Chan 2 3 1 Nanyang
Nanoscale CMOS Design Issues
 Nanoscale CMOS Design Issues Jaydeep P. Kulkarni Assistant Professor, ECE Department The University of Texas at Austin jaydeep@austin.utexas.edu Fall, 2017, VLSI-1 Class Transistor I-V Review Agenda Non-ideal
Nanoscale CMOS Design Issues Jaydeep P. Kulkarni Assistant Professor, ECE Department The University of Texas at Austin jaydeep@austin.utexas.edu Fall, 2017, VLSI-1 Class Transistor I-V Review Agenda Non-ideal
The Devices: MOS Transistors
 The Devices: MOS Transistors References: Semiconductor Device Fundamentals, R. F. Pierret, Addison-Wesley Digital Integrated Circuits: A Design Perspective, J. Rabaey et.al. Prentice Hall NMOS Transistor
The Devices: MOS Transistors References: Semiconductor Device Fundamentals, R. F. Pierret, Addison-Wesley Digital Integrated Circuits: A Design Perspective, J. Rabaey et.al. Prentice Hall NMOS Transistor
Lecture 11: MOSFET Modeling
 Digital Integrated Circuits (83-313) Lecture 11: MOSFET ing Semester B, 2016-17 Lecturer: Dr. Adam Teman TAs: Itamar Levi, Robert Giterman 18 June 2017 Disclaimer: This course was prepared, in its entirety,
Digital Integrated Circuits (83-313) Lecture 11: MOSFET ing Semester B, 2016-17 Lecturer: Dr. Adam Teman TAs: Itamar Levi, Robert Giterman 18 June 2017 Disclaimer: This course was prepared, in its entirety,
OMEN an atomistic and full-band quantum transport simulator for post-cmos nanodevices
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs Other Nanotechnology Publications Birck Nanotechnology Center 8-18-28 OMEN an atomistic and full-band quantum transport simulator for post-cmos nanodevices Mathieu Luisier
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs Other Nanotechnology Publications Birck Nanotechnology Center 8-18-28 OMEN an atomistic and full-band quantum transport simulator for post-cmos nanodevices Mathieu Luisier
STRAIN EFFECTS ON THE VALENCE BAND OF SILICON: PIEZORESISTANCE IN P-TYPE SILICON AND MOBILITY ENHANCEMENT IN STRAINED SILICON PMOSFET
 STRAIN EFFECTS ON THE VALENCE BAND OF SILICON: PIEZORESISTANCE IN P-TYPE SILICON AND MOBILITY ENHANCEMENT IN STRAINED SILICON PMOSFET By KEHUEY WU A DISSERTATION PRESENTED TO THE GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE
STRAIN EFFECTS ON THE VALENCE BAND OF SILICON: PIEZORESISTANCE IN P-TYPE SILICON AND MOBILITY ENHANCEMENT IN STRAINED SILICON PMOSFET By KEHUEY WU A DISSERTATION PRESENTED TO THE GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE
Comparative studies of Ge and Si p-channel metal oxide semiconductor field-effect-transistors with HfSiON dielectric and TaN metal gate
 Comparative studies of Ge and Si p-channel metal oxide semiconductor field-effect-transistors with HfSiON dielectric and TaN metal gate Hu Ai-Bin( 胡爱斌 ) and Xu Qiu-Xia( 徐秋霞 ) Institute of Microelectronics,
Comparative studies of Ge and Si p-channel metal oxide semiconductor field-effect-transistors with HfSiON dielectric and TaN metal gate Hu Ai-Bin( 胡爱斌 ) and Xu Qiu-Xia( 徐秋霞 ) Institute of Microelectronics,
Fabrication and Analysis of Deep Submicron Strained-Si N-MOSFET s
 1406 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON ELECTRON DEVICES, VOL. 47, NO. 7, JULY 2000 Fabrication and Analysis of Deep Submicron Strained-Si N-MOSFET s Kern (Ken) Rim, Member, IEEE, Judy L. Hoyt, Member, IEEE, and James
1406 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON ELECTRON DEVICES, VOL. 47, NO. 7, JULY 2000 Fabrication and Analysis of Deep Submicron Strained-Si N-MOSFET s Kern (Ken) Rim, Member, IEEE, Judy L. Hoyt, Member, IEEE, and James
NEW VERSION OF LETI-UTSOI2 FEATURING FURTHER IMPROVED PREDICTABILITY, AND A NEW STRESS MODEL FOR FDSOI TECHNOLOGY
 NEW VERSION OF LETI-UTSOI2 FEATURING FURTHER IMPROVED PREDICTABILITY, AND A NEW STRESS MODEL FOR FDSOI TECHNOLOGY T. Poiroux, P. Scheer*, O. Rozeau, B. de Salvo, A. Juge*, J. C. Barbé, M. Vinet CEA-Leti,
NEW VERSION OF LETI-UTSOI2 FEATURING FURTHER IMPROVED PREDICTABILITY, AND A NEW STRESS MODEL FOR FDSOI TECHNOLOGY T. Poiroux, P. Scheer*, O. Rozeau, B. de Salvo, A. Juge*, J. C. Barbé, M. Vinet CEA-Leti,
MOSFET. Id-Vd curve. I DS Transfer curve V G. Lec. 8. Vd=1V. Saturation region. V Th
 MOSFET Id-Vd curve Saturation region I DS Transfer curve Vd=1V V Th V G 1 0 < V GS < V T V GS > V T V Gs >V T & Small V D > 0 I DS WQ inv WC v WC i V V VDS V V G i T G n T L n I D g V D (g conductance
MOSFET Id-Vd curve Saturation region I DS Transfer curve Vd=1V V Th V G 1 0 < V GS < V T V GS > V T V Gs >V T & Small V D > 0 I DS WQ inv WC v WC i V V VDS V V G i T G n T L n I D g V D (g conductance
Microelectronics Part 1: Main CMOS circuits design rules
 GBM8320 Dispositifs Médicaux telligents Microelectronics Part 1: Main CMOS circuits design rules Mohamad Sawan et al. Laboratoire de neurotechnologies Polystim! http://www.cours.polymtl.ca/gbm8320/! med-amine.miled@polymtl.ca!
GBM8320 Dispositifs Médicaux telligents Microelectronics Part 1: Main CMOS circuits design rules Mohamad Sawan et al. Laboratoire de neurotechnologies Polystim! http://www.cours.polymtl.ca/gbm8320/! med-amine.miled@polymtl.ca!
MOSFET SCALING ECE 663
 MOSFET SCALING Scaling of switches Moore s Law economics Moore s Law - #DRAM Bits per chip doubles every 18 months ~5% bigger chips/wafers ~5% design improvements ~50 % Lithography ability to print smaller
MOSFET SCALING Scaling of switches Moore s Law economics Moore s Law - #DRAM Bits per chip doubles every 18 months ~5% bigger chips/wafers ~5% design improvements ~50 % Lithography ability to print smaller
Characteristics of MOSFET with Non-overlapped Source-Drain to Gate
 IEICE TRANS. ELECTRON., VOL.E85 C, NO.5 MAY 2002 1079 PAPER Special Issue on Advanced Sub-0.1 µm CMOS Devices Characteristics of MOSFET with Non-overlapped Source-Drain to Gate Hyunjin LEE a), Nonmember,
IEICE TRANS. ELECTRON., VOL.E85 C, NO.5 MAY 2002 1079 PAPER Special Issue on Advanced Sub-0.1 µm CMOS Devices Characteristics of MOSFET with Non-overlapped Source-Drain to Gate Hyunjin LEE a), Nonmember,
Overview of Modeling and Simulation TCAD - FLOOPS / FLOODS
 Overview of Modeling and Simulation TCAD - FLOOPS / FLOODS Modeling Overview Strain Effects Thermal Modeling TCAD Modeling Outline FLOOPS / FLOODS Introduction Progress on GaN Devices Prospects for Reliability
Overview of Modeling and Simulation TCAD - FLOOPS / FLOODS Modeling Overview Strain Effects Thermal Modeling TCAD Modeling Outline FLOOPS / FLOODS Introduction Progress on GaN Devices Prospects for Reliability
Low Frequency Noise in MoS 2 Negative Capacitance Field-effect Transistor
 Low Frequency Noise in MoS Negative Capacitance Field-effect Transistor Sami Alghamdi, Mengwei Si, Lingming Yang, and Peide D. Ye* School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Purdue University West Lafayette,
Low Frequency Noise in MoS Negative Capacitance Field-effect Transistor Sami Alghamdi, Mengwei Si, Lingming Yang, and Peide D. Ye* School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Purdue University West Lafayette,
The Devices. Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective. Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic. July 30, 2002
 Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic The Devices July 30, 2002 Goal of this chapter Present intuitive understanding of device operation Introduction
Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic The Devices July 30, 2002 Goal of this chapter Present intuitive understanding of device operation Introduction
MOSFET: Introduction
 E&CE 437 Integrated VLSI Systems MOS Transistor 1 of 30 MOSFET: Introduction Metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistor (MOSFET) or MOS is widely used for implementing digital designs Its major
E&CE 437 Integrated VLSI Systems MOS Transistor 1 of 30 MOSFET: Introduction Metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistor (MOSFET) or MOS is widely used for implementing digital designs Its major
L ECE 4211 UConn F. Jain Scaling Laws for NanoFETs Chapter 10 Logic Gate Scaling
 L13 04202017 ECE 4211 UConn F. Jain Scaling Laws for NanoFETs Chapter 10 Logic Gate Scaling Scaling laws: Generalized scaling (GS) p. 610 Design steps p.613 Nanotransistor issues (page 626) Degradation
L13 04202017 ECE 4211 UConn F. Jain Scaling Laws for NanoFETs Chapter 10 Logic Gate Scaling Scaling laws: Generalized scaling (GS) p. 610 Design steps p.613 Nanotransistor issues (page 626) Degradation
Metallic: 2n 1. +n 2. =3q Armchair structure always metallic = 2
 Properties of CNT d = 2.46 n 2 2 1 + n1n2 + n2 2π Metallic: 2n 1 +n 2 =3q Armchair structure always metallic a) Graphite Valence(π) and Conduction(π*) states touch at six points(fermi points) Carbon Nanotube:
Properties of CNT d = 2.46 n 2 2 1 + n1n2 + n2 2π Metallic: 2n 1 +n 2 =3q Armchair structure always metallic a) Graphite Valence(π) and Conduction(π*) states touch at six points(fermi points) Carbon Nanotube:
CMPEN 411 VLSI Digital Circuits. Lecture 03: MOS Transistor
 CMPEN 411 VLSI Digital Circuits Lecture 03: MOS Transistor Kyusun Choi [Adapted from Rabaey s Digital Integrated Circuits, Second Edition, 2003 J. Rabaey, A. Chandrakasan, B. Nikolic] CMPEN 411 L03 S.1
CMPEN 411 VLSI Digital Circuits Lecture 03: MOS Transistor Kyusun Choi [Adapted from Rabaey s Digital Integrated Circuits, Second Edition, 2003 J. Rabaey, A. Chandrakasan, B. Nikolic] CMPEN 411 L03 S.1
Scaling Issues in Planar FET: Dual Gate FET and FinFETs
 Scaling Issues in Planar FET: Dual Gate FET and FinFETs Lecture 12 Dr. Amr Bayoumi Fall 2014 Advanced Devices (EC760) Arab Academy for Science and Technology - Cairo 1 Outline Scaling Issues for Planar
Scaling Issues in Planar FET: Dual Gate FET and FinFETs Lecture 12 Dr. Amr Bayoumi Fall 2014 Advanced Devices (EC760) Arab Academy for Science and Technology - Cairo 1 Outline Scaling Issues for Planar
Quantum-size effects in sub-10 nm fin width InGaAs finfets
 Quantum-size effects in sub-10 nm fin width InGaAs finfets Alon Vardi, Xin Zhao, and Jesús A. del Alamo Microsystems Technology Laboratories, MIT December 9, 2015 Sponsors: DTRA NSF (E3S STC) Northrop
Quantum-size effects in sub-10 nm fin width InGaAs finfets Alon Vardi, Xin Zhao, and Jesús A. del Alamo Microsystems Technology Laboratories, MIT December 9, 2015 Sponsors: DTRA NSF (E3S STC) Northrop
Measurement and Modeling of the n-channel and p-channel MOSFET s Inversion Layer Mobility at Room and Low Temperature Operation
 Measurement and Modeling of the n-channel and p-channel MOSFET s Inversion Layer Mobility at Room and Low Temperature Operation B. Cheng, J. Woo To cite this version: B. Cheng, J. Woo. Measurement and
Measurement and Modeling of the n-channel and p-channel MOSFET s Inversion Layer Mobility at Room and Low Temperature Operation B. Cheng, J. Woo To cite this version: B. Cheng, J. Woo. Measurement and
The Critical Role of Quantum Capacitance in Compact Modeling of Nano-Scaled and Nanoelectronic Devices
 The Critical Role of Quantum Capacitance in Compact Modeling of Nano-Scaled and Nanoelectronic Devices Zhiping Yu and Jinyu Zhang Institute of Microelectronics Tsinghua University, Beijing, China yuzhip@tsinghua.edu.cn
The Critical Role of Quantum Capacitance in Compact Modeling of Nano-Scaled and Nanoelectronic Devices Zhiping Yu and Jinyu Zhang Institute of Microelectronics Tsinghua University, Beijing, China yuzhip@tsinghua.edu.cn
Lecture #27. The Short Channel Effect (SCE)
 Lecture #27 ANNOUNCEMENTS Design Project: Your BJT design should meet the performance specifications to within 10% at both 300K and 360K. ( β dc > 45, f T > 18 GHz, V A > 9 V and V punchthrough > 9 V )
Lecture #27 ANNOUNCEMENTS Design Project: Your BJT design should meet the performance specifications to within 10% at both 300K and 360K. ( β dc > 45, f T > 18 GHz, V A > 9 V and V punchthrough > 9 V )
Keywords MOSFET, FinFET, Silicon, Germanium, InGaAs, Monte Carlo, Drift Diffusion.
 Predicting Future Technology Performance Asen Asenov and Craig Alexander Gold Standard Simulations The Rankine Building, Oakfield Avenue Glasgow G12 8LT +44 ()141 33 479 a.asenov@goldstandardsimulations.com
Predicting Future Technology Performance Asen Asenov and Craig Alexander Gold Standard Simulations The Rankine Building, Oakfield Avenue Glasgow G12 8LT +44 ()141 33 479 a.asenov@goldstandardsimulations.com
Solid-State Electronics
 Solid-State Electronics 52 (2008) 1884 1888 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Solid-State Electronics journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/sse Analysis of STI-induced mechanical stress-related
Solid-State Electronics 52 (2008) 1884 1888 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Solid-State Electronics journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/sse Analysis of STI-induced mechanical stress-related
High hole and electron mobilities using Strained Si/Strained Ge heterostructures
 High hole and electron mobilities using Strained Si/Strained Ge heterostructures Saurabh Gupta, Minjoo L. Lee, Chris W. Leitz and E.A. Fitzgerald Department of Materials Science and Engineering, MIT, Cambridge,
High hole and electron mobilities using Strained Si/Strained Ge heterostructures Saurabh Gupta, Minjoo L. Lee, Chris W. Leitz and E.A. Fitzgerald Department of Materials Science and Engineering, MIT, Cambridge,
Semiconductor Physics Problems 2015
 Semiconductor Physics Problems 2015 Page and figure numbers refer to Semiconductor Devices Physics and Technology, 3rd edition, by SM Sze and M-K Lee 1. The purest semiconductor crystals it is possible
Semiconductor Physics Problems 2015 Page and figure numbers refer to Semiconductor Devices Physics and Technology, 3rd edition, by SM Sze and M-K Lee 1. The purest semiconductor crystals it is possible
Si Nanowire FET Modeling and Technology
 Si Nanowire FET Modeling and Technology November 8, 2010 @ Peking University H. Iwai Tokyo Inst. Tech. 1 First Computer Eniac: made of huge number of vacuum tubes 1946 Big size, huge power, short life
Si Nanowire FET Modeling and Technology November 8, 2010 @ Peking University H. Iwai Tokyo Inst. Tech. 1 First Computer Eniac: made of huge number of vacuum tubes 1946 Big size, huge power, short life
THE END OF simple scaling for a solid-state device technology
 1010 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON ELECTRON DEVICES, VOL. 53, NO. 5, MAY 2006 Uniaxial-Process-Induced Strained-Si: Extending the CMOS Roadmap Scott E. Thompson, Senior Member, IEEE, Guangyu Sun, Youn Sung Choi,
1010 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON ELECTRON DEVICES, VOL. 53, NO. 5, MAY 2006 Uniaxial-Process-Induced Strained-Si: Extending the CMOS Roadmap Scott E. Thompson, Senior Member, IEEE, Guangyu Sun, Youn Sung Choi,
Electronics with 2D Crystals: Scaling extender, or harbinger of new functions?
 Electronics with 2D Crystals: Scaling extender, or harbinger of new functions? 1 st Workshop on Data Abundant Systems Technology Stanford, April 2014 Debdeep Jena (djena@nd.edu) Electrical Engineering,
Electronics with 2D Crystals: Scaling extender, or harbinger of new functions? 1 st Workshop on Data Abundant Systems Technology Stanford, April 2014 Debdeep Jena (djena@nd.edu) Electrical Engineering,
Modeling Random Variability of 16nm Bulk FinFETs
 Modeling Random Variability of 16nm Bulk FinFETs Victor Moroz, Qiang Lu, and Munkang Choi September 9, 2010 1 Outline 2 Outline 3 16nm Bulk FinFETs for 16nm Node Simulation domain 24nm fin pitch 56nm gate
Modeling Random Variability of 16nm Bulk FinFETs Victor Moroz, Qiang Lu, and Munkang Choi September 9, 2010 1 Outline 2 Outline 3 16nm Bulk FinFETs for 16nm Node Simulation domain 24nm fin pitch 56nm gate
Objective and Outline. Acknowledgement. Objective: Power Components. Outline: 1) Acknowledgements. Section 4: Power Components
 Objective: Power Components Outline: 1) Acknowledgements 2) Objective and Outline 1 Acknowledgement This lecture note has been obtained from similar courses all over the world. I wish to thank all the
Objective: Power Components Outline: 1) Acknowledgements 2) Objective and Outline 1 Acknowledgement This lecture note has been obtained from similar courses all over the world. I wish to thank all the
!""#$%&'("')*+,%*-'$(,".,#-#,%'+,/' /.&$0#%#'/(1+,%&'.,',+,(&$+2#'3*24'5.' 6758!9&!
 Università di Pisa!""#$%&'("')*+,%*-'$(,".,#-#,%'+,/' /.&$#%#'/(1+,%&'.,',+,(&$+#'3*'5.' 758!9&!!"#$%&'#()"*+"( H%8*'/%I-+/&#J%#)+-+-'%*#J-55K)+&'I*L%&+-M#5-//'&+%,*(#)+&'I*/%,*(#N-5-,&I=+%,*L%&+%(# @+%O-'.%/P#J%#F%.*#!"&,-..-(/#$$#''*$-(
Università di Pisa!""#$%&'("')*+,%*-'$(,".,#-#,%'+,/' /.&$#%#'/(1+,%&'.,',+,(&$+#'3*'5.' 758!9&!!"#$%&'#()"*+"( H%8*'/%I-+/&#J%#)+-+-'%*#J-55K)+&'I*L%&+-M#5-//'&+%,*(#)+&'I*/%,*(#N-5-,&I=+%,*L%&+%(# @+%O-'.%/P#J%#F%.*#!"&,-..-(/#$$#''*$-(
Technische Universität Graz. Institute of Solid State Physics. 11. MOSFETs
 Technische Universität Graz Institute of Solid State Physics 11. MOSFETs Dec. 12, 2018 Gradual channel approximation accumulation depletion inversion http://lampx.tugraz.at/~hadley/psd/l10/gradualchannelapprox.php
Technische Universität Graz Institute of Solid State Physics 11. MOSFETs Dec. 12, 2018 Gradual channel approximation accumulation depletion inversion http://lampx.tugraz.at/~hadley/psd/l10/gradualchannelapprox.php
ECE 342 Electronic Circuits. 3. MOS Transistors
 ECE 342 Electronic Circuits 3. MOS Transistors Jose E. Schutt-Aine Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Illinois jschutt@emlab.uiuc.edu 1 NMOS Transistor Typically L = 0.1 to 3 m, W = 0.2 to
ECE 342 Electronic Circuits 3. MOS Transistors Jose E. Schutt-Aine Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Illinois jschutt@emlab.uiuc.edu 1 NMOS Transistor Typically L = 0.1 to 3 m, W = 0.2 to
Indium arsenide quantum wire trigate metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistor
 JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS 99, 054503 2006 Indium arsenide quantum wire trigate metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistor M. J. Gilbert a and D. K. Ferry Department of Electrical Engineering and
JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS 99, 054503 2006 Indium arsenide quantum wire trigate metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistor M. J. Gilbert a and D. K. Ferry Department of Electrical Engineering and
MOS Transistor I-V Characteristics and Parasitics
 ECEN454 Digital Integrated Circuit Design MOS Transistor I-V Characteristics and Parasitics ECEN 454 Facts about Transistors So far, we have treated transistors as ideal switches An ON transistor passes
ECEN454 Digital Integrated Circuit Design MOS Transistor I-V Characteristics and Parasitics ECEN 454 Facts about Transistors So far, we have treated transistors as ideal switches An ON transistor passes
InGaAs Double-Gate Fin-Sidewall MOSFET
 InGaAs Double-Gate Fin-Sidewall MOSFET Alon Vardi, Xin Zhao and Jesús del Alamo Microsystems Technology Laboratories, MIT June 25, 214 Sponsors: Sematech, Technion-MIT Fellowship, and NSF E3S Center (#939514)
InGaAs Double-Gate Fin-Sidewall MOSFET Alon Vardi, Xin Zhao and Jesús del Alamo Microsystems Technology Laboratories, MIT June 25, 214 Sponsors: Sematech, Technion-MIT Fellowship, and NSF E3S Center (#939514)
Integrated Circuits & Systems
 Federal University of Santa Catarina Center for Technology Computer Science & Electronics Engineering Integrated Circuits & Systems INE 5442 Lecture 10 MOSFET part 1 guntzel@inf.ufsc.br ual-well Trench-Isolated
Federal University of Santa Catarina Center for Technology Computer Science & Electronics Engineering Integrated Circuits & Systems INE 5442 Lecture 10 MOSFET part 1 guntzel@inf.ufsc.br ual-well Trench-Isolated
A Compact Analytical Modelling of the Electrical Characteristics of Submicron Channel MOSFETs
 ROMANIAN JOURNAL OF INFORMATION SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY Volume 11, Number 4, 2008, 383 395 A Compact Analytical Modelling of the Electrical Characteristics of Submicron Channel MOSFETs Andrei SEVCENCO,
ROMANIAN JOURNAL OF INFORMATION SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY Volume 11, Number 4, 2008, 383 395 A Compact Analytical Modelling of the Electrical Characteristics of Submicron Channel MOSFETs Andrei SEVCENCO,
ESE370: Circuit-Level Modeling, Design, and Optimization for Digital Systems. Today. Refinement. Last Time. No Field. Body Contact
 ESE370: Circuit-Level Modeling, Design, and Optimization for Digital Systems Day 10: September 6, 01 MOS Transistor Basics Today MOS Transistor Topology Threshold Operating Regions Resistive Saturation
ESE370: Circuit-Level Modeling, Design, and Optimization for Digital Systems Day 10: September 6, 01 MOS Transistor Basics Today MOS Transistor Topology Threshold Operating Regions Resistive Saturation
Strained Si CMOS (SS CMOS) technology: opportunities and challenges
 Solid-State Electronics 47 (23) 1133 1139 www.elsevier.com/locate/sse Strained Si CMOS (SS CMOS) technology: opportunities and challenges K. Rim a, *, R. Anderson b, D. Boyd b, F. Cardone a, K. Chan a,
Solid-State Electronics 47 (23) 1133 1139 www.elsevier.com/locate/sse Strained Si CMOS (SS CMOS) technology: opportunities and challenges K. Rim a, *, R. Anderson b, D. Boyd b, F. Cardone a, K. Chan a,
Analytical modelling and performance analysis of Double-Gate MOSFET-based circuit including ballistic/quasi-ballistic effects
 Analytical modelling and performance analysis of Double-Gate MOSFET-based circuit including ballistic/quasi-ballistic effects Sebastien Martinie, Daniela Munteanu, Gilles Le Carval, Jean-Luc Autran To
Analytical modelling and performance analysis of Double-Gate MOSFET-based circuit including ballistic/quasi-ballistic effects Sebastien Martinie, Daniela Munteanu, Gilles Le Carval, Jean-Luc Autran To
MOS Transistor Theory
 CHAPTER 3 MOS Transistor Theory Outline 2 1. Introduction 2. Ideal I-V Characteristics 3. Nonideal I-V Effects 4. C-V Characteristics 5. DC Transfer Characteristics 6. Switch-level RC Delay Models MOS
CHAPTER 3 MOS Transistor Theory Outline 2 1. Introduction 2. Ideal I-V Characteristics 3. Nonideal I-V Effects 4. C-V Characteristics 5. DC Transfer Characteristics 6. Switch-level RC Delay Models MOS
EE105 Fall 2014 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits. NMOS Transistor Capacitances: Saturation Region
 EE105 Fall 014 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits Prof. Ming C. Wu wu@eecs.berkeley.edu 511 Sutardja Dai Hall (SDH) 1 NMOS Transistor Capacitances: Saturation Region Drain no longer connected to channel
EE105 Fall 014 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits Prof. Ming C. Wu wu@eecs.berkeley.edu 511 Sutardja Dai Hall (SDH) 1 NMOS Transistor Capacitances: Saturation Region Drain no longer connected to channel
Fig The electron mobility for a-si and poly-si TFT.
 Fig. 1-1-1 The electron mobility for a-si and poly-si TFT. Fig. 1-1-2 The aperture ratio for a-si and poly-si TFT. 33 Fig. 1-2-1 All kinds defect well. (a) is the Dirac well. (b) is the repulsive Columbic
Fig. 1-1-1 The electron mobility for a-si and poly-si TFT. Fig. 1-1-2 The aperture ratio for a-si and poly-si TFT. 33 Fig. 1-2-1 All kinds defect well. (a) is the Dirac well. (b) is the repulsive Columbic
The Devices. Devices
 The The MOS Transistor Gate Oxyde Gate Source n+ Polysilicon Drain n+ Field-Oxyde (SiO 2 ) p-substrate p+ stopper Bulk Contact CROSS-SECTION of NMOS Transistor Cross-Section of CMOS Technology MOS transistors
The The MOS Transistor Gate Oxyde Gate Source n+ Polysilicon Drain n+ Field-Oxyde (SiO 2 ) p-substrate p+ stopper Bulk Contact CROSS-SECTION of NMOS Transistor Cross-Section of CMOS Technology MOS transistors
Section 12: Intro to Devices
 Section 12: Intro to Devices Extensive reading materials on reserve, including Robert F. Pierret, Semiconductor Device Fundamentals Bond Model of Electrons and Holes Si Si Si Si Si Si Si Si Si Silicon
Section 12: Intro to Devices Extensive reading materials on reserve, including Robert F. Pierret, Semiconductor Device Fundamentals Bond Model of Electrons and Holes Si Si Si Si Si Si Si Si Si Silicon
GaN based transistors
 GaN based transistors S FP FP dielectric G SiO 2 Al x Ga 1-x N barrier i-gan Buffer i-sic D Transistors "The Transistor was probably the most important invention of the 20th Century The American Institute
GaN based transistors S FP FP dielectric G SiO 2 Al x Ga 1-x N barrier i-gan Buffer i-sic D Transistors "The Transistor was probably the most important invention of the 20th Century The American Institute
Nanometer Transistors and Their Models. Jan M. Rabaey
 Nanometer Transistors and Their Models Jan M. Rabaey Chapter Outline Nanometer transistor behavior and models Sub-threshold currents and leakage Variability Device and technology innovations Nanometer
Nanometer Transistors and Their Models Jan M. Rabaey Chapter Outline Nanometer transistor behavior and models Sub-threshold currents and leakage Variability Device and technology innovations Nanometer
Solid-State Electronics
 Solid-State Electronics 84 (2013) 147 154 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Solid-State Electronics journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/sse Progress in Z 2 -FET 1T-DRAM: Retention
Solid-State Electronics 84 (2013) 147 154 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Solid-State Electronics journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/sse Progress in Z 2 -FET 1T-DRAM: Retention
First-principles study of electronic properties of biaxially strained silicon: Effects on charge carrier mobility
 First-principles study of electronic properties of biaxially strained silicon: Effects on charge carrier mobility Decai Yu,* Yu Zhang, and Feng Liu Department of Materials Science and Engineering, University
First-principles study of electronic properties of biaxially strained silicon: Effects on charge carrier mobility Decai Yu,* Yu Zhang, and Feng Liu Department of Materials Science and Engineering, University
Physics an performance of III-V nanowire heterojunction TFETs including phonon and impurity band tails:
 Physics an performance of III-V nanowire heterojunction TFETs including phonon and impurity band tails: An atomistic mode space NEGF quantum transport study. A. Afzalian TSMC, Leuven, Belgium (Invited)
Physics an performance of III-V nanowire heterojunction TFETs including phonon and impurity band tails: An atomistic mode space NEGF quantum transport study. A. Afzalian TSMC, Leuven, Belgium (Invited)
MOSFET PIEZORESISTANCE COEFFICIENTS ON (100) SILICON NIDHI MOHTA
 MOSFET PIEZORESISTANCE COEFFICIENTS ON (1) SILICON By NIDHI MOHTA A THESIS PRESENTED TO THE GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE UNIVERSITY OF FLORIDA IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT OF THE REQUIREMENTS FOR THE DEGREE OF MASTER
MOSFET PIEZORESISTANCE COEFFICIENTS ON (1) SILICON By NIDHI MOHTA A THESIS PRESENTED TO THE GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE UNIVERSITY OF FLORIDA IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT OF THE REQUIREMENTS FOR THE DEGREE OF MASTER
EECS240 Spring Lecture 21: Matching. Elad Alon Dept. of EECS. V i+ V i-
 EECS40 Spring 010 Lecture 1: Matching Elad Alon Dept. of EECS Offset V i+ V i- To achieve zero offset, comparator devices must be perfectly matched to each other How well-matched can the devices be made?
EECS40 Spring 010 Lecture 1: Matching Elad Alon Dept. of EECS Offset V i+ V i- To achieve zero offset, comparator devices must be perfectly matched to each other How well-matched can the devices be made?
ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals
 ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 4: January 23, 2018 MOS Transistor Theory, MOS Model Penn ESE 570 Spring 2018 Khanna Lecture Outline! CMOS Process Enhancements! Semiconductor
ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 4: January 23, 2018 MOS Transistor Theory, MOS Model Penn ESE 570 Spring 2018 Khanna Lecture Outline! CMOS Process Enhancements! Semiconductor
Lecture 4: CMOS Transistor Theory
 Introduction to CMOS VLSI Design Lecture 4: CMOS Transistor Theory David Harris, Harvey Mudd College Kartik Mohanram and Steven Levitan University of Pittsburgh Outline q Introduction q MOS Capacitor q
Introduction to CMOS VLSI Design Lecture 4: CMOS Transistor Theory David Harris, Harvey Mudd College Kartik Mohanram and Steven Levitan University of Pittsburgh Outline q Introduction q MOS Capacitor q
Investigation of the band gap widening effect in thin silicon double gate MOSFETs
 Investigation of the band gap widening effect in thin silicon double gate MOSFETs Master thesis September 12, 2006 Report number: 068.030/2006 Author J.L.P.J. van der Steen Supervisors dr. ir. R.J.E. Hueting
Investigation of the band gap widening effect in thin silicon double gate MOSFETs Master thesis September 12, 2006 Report number: 068.030/2006 Author J.L.P.J. van der Steen Supervisors dr. ir. R.J.E. Hueting
CHAPTER 5 EFFECT OF GATE ELECTRODE WORK FUNCTION VARIATION ON DC AND AC PARAMETERS IN CONVENTIONAL AND JUNCTIONLESS FINFETS
 98 CHAPTER 5 EFFECT OF GATE ELECTRODE WORK FUNCTION VARIATION ON DC AND AC PARAMETERS IN CONVENTIONAL AND JUNCTIONLESS FINFETS In this chapter, the effect of gate electrode work function variation on DC
98 CHAPTER 5 EFFECT OF GATE ELECTRODE WORK FUNCTION VARIATION ON DC AND AC PARAMETERS IN CONVENTIONAL AND JUNCTIONLESS FINFETS In this chapter, the effect of gate electrode work function variation on DC
Effect of Remote-Surface-Roughness Scattering on Electron Mobility in MOSFETs with High-k Dielectrics. Technology, Yokohama , Japan
 Effect of Remote-Surface-Roughness Scattering on Electron Mobility in MOSFETs with High-k Dielectrics M. Mamatrishat a, M. Kouda a, T. Kawanago a, K. Kakushima b, P. Ahmet a, A. Aierken c, K. Tsutsui b,
Effect of Remote-Surface-Roughness Scattering on Electron Mobility in MOSFETs with High-k Dielectrics M. Mamatrishat a, M. Kouda a, T. Kawanago a, K. Kakushima b, P. Ahmet a, A. Aierken c, K. Tsutsui b,
Fundamentals of Nanoelectronics: Basic Concepts
 Fundamentals of Nanoelectronics: Basic Concepts Sławomir Prucnal FWIM Page 1 Introduction Outline Electronics in nanoscale Transport Ohms law Optoelectronic properties of semiconductors Optics in nanoscale
Fundamentals of Nanoelectronics: Basic Concepts Sławomir Prucnal FWIM Page 1 Introduction Outline Electronics in nanoscale Transport Ohms law Optoelectronic properties of semiconductors Optics in nanoscale
ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals
 ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 4: January 29, 2019 MOS Transistor Theory, MOS Model Penn ESE 570 Spring 2019 Khanna Lecture Outline! CMOS Process Enhancements! Semiconductor
ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 4: January 29, 2019 MOS Transistor Theory, MOS Model Penn ESE 570 Spring 2019 Khanna Lecture Outline! CMOS Process Enhancements! Semiconductor
Journal of Electron Devices, Vol. 18, 2013, pp JED [ISSN: ]
![Journal of Electron Devices, Vol. 18, 2013, pp JED [ISSN: ] Journal of Electron Devices, Vol. 18, 2013, pp JED [ISSN: ]](/thumbs/86/93990983.jpg) DrainCurrent-Id in linearscale(a/um) Id in logscale Journal of Electron Devices, Vol. 18, 2013, pp. 1582-1586 JED [ISSN: 1682-3427 ] SUITABILITY OF HIGH-k GATE DIELECTRICS ON THE DEVICE PERFORMANCE AND
DrainCurrent-Id in linearscale(a/um) Id in logscale Journal of Electron Devices, Vol. 18, 2013, pp. 1582-1586 JED [ISSN: 1682-3427 ] SUITABILITY OF HIGH-k GATE DIELECTRICS ON THE DEVICE PERFORMANCE AND
Carbon Nanotube Electronics
 Carbon Nanotube Electronics Jeorg Appenzeller, Phaedon Avouris, Vincent Derycke, Stefan Heinz, Richard Martel, Marko Radosavljevic, Jerry Tersoff, Shalom Wind H.-S. Philip Wong hspwong@us.ibm.com IBM T.J.
Carbon Nanotube Electronics Jeorg Appenzeller, Phaedon Avouris, Vincent Derycke, Stefan Heinz, Richard Martel, Marko Radosavljevic, Jerry Tersoff, Shalom Wind H.-S. Philip Wong hspwong@us.ibm.com IBM T.J.
FLCC Seminar. Spacer Lithography for Reduced Variability in MOSFET Performance
 1 Seminar Spacer Lithography for Reduced Variability in MOSFET Performance Prof. Tsu-Jae King Liu Electrical Engineering & Computer Sciences Dept. University of California at Berkeley Graduate Student:
1 Seminar Spacer Lithography for Reduced Variability in MOSFET Performance Prof. Tsu-Jae King Liu Electrical Engineering & Computer Sciences Dept. University of California at Berkeley Graduate Student:
Long-channel MOSFET IV Corrections
 Long-channel MOSFET IV orrections Three MITs of the Day The body ect and its influence on long-channel V th. Long-channel subthreshold conduction and control (subthreshold slope S) Scattering components
Long-channel MOSFET IV orrections Three MITs of the Day The body ect and its influence on long-channel V th. Long-channel subthreshold conduction and control (subthreshold slope S) Scattering components
Simple and accurate modeling of the 3D structural variations in FinFETs
 Simple and accurate modeling of the 3D structural variations in FinFETs Donghu Kim Electrical Engineering Program Graduate school of UNIST 2013 Simple and accurate modeling of the 3D structural variations
Simple and accurate modeling of the 3D structural variations in FinFETs Donghu Kim Electrical Engineering Program Graduate school of UNIST 2013 Simple and accurate modeling of the 3D structural variations
Analytical Modeling of Threshold Voltage for a. Biaxial Strained-Si-MOSFET
 Contemporary Engineering Sciences, Vol. 4, 2011, no. 6, 249 258 Analytical Modeling of Threshold Voltage for a Biaxial Strained-Si-MOSFET Amit Chaudhry Faculty of University Institute of Engineering and
Contemporary Engineering Sciences, Vol. 4, 2011, no. 6, 249 258 Analytical Modeling of Threshold Voltage for a Biaxial Strained-Si-MOSFET Amit Chaudhry Faculty of University Institute of Engineering and
An Analytical Model for a Gate-Induced-Drain-Leakage Current in a Buried-Channel PMOSFET
 Journal of the Korean Physical Society, Vol. 4, No. 5, November 00, pp. 86 867 An Analytical Model for a Gate-Induced-Drain-Leakage Current in a Buried-Channel PMOSFET Seong-Ho Kim, Sung-Eun Kim, Joo-Han
Journal of the Korean Physical Society, Vol. 4, No. 5, November 00, pp. 86 867 An Analytical Model for a Gate-Induced-Drain-Leakage Current in a Buried-Channel PMOSFET Seong-Ho Kim, Sung-Eun Kim, Joo-Han
