Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor (MOSFET) Model
|
|
|
- Roberta Bell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor (MOSFET) Model Old Content - visit altium.com/documentation Modified by Phil Loughhead on 4-Mar-2014 Model Kind Transistor Model Sub-Kind MOSFET SPICE Prefix M SPICE Netlist Template %1 %2 %3 L=@LENGTH?WIDTH W=@WIDTH?"DRAIN AREA" AD=@"DRAIN AREA"?"SOURCE AREA" AS=@"SOURCE AREA"?"DRAIN PERIMETER" PD=@"DRAIN PERIMETER"?"SOURCE PERIMETER" PS=@"SOURCE PERIMETER"?NRD NRD=@NRD?NRS NRS=@NRS &"STARTING CONDITION"?"INITIAL D-S VOLTAGE" IC=@"INITIAL D-S G-S B-S VOLTAGE"?TEMPERATURE TEMP=@TEMPERATURE Parameters (definable at component level) The following component-level parameters are definable for this model type and are listed on the Parameters tab of the Sim Model dialog. To access this dialog, simply double-click on the entry for the simulation model link in the Models region of the Component Properties dialog. Length Width Drain Area Source Area channel length (in meters). channel width (in meters). area of the Drain diffusion (in sq.meters). area of the Source diffusion (in sq.meters). Drain Perimeter perimeter of drain junction (in meters). (Default = 0). Source Perimeter perimeter of source junction (in meters). (Default = 0). NRD equivalent number of squares of the drain diffusion (Default = 1). NRS equivalent number of squares of the source diffusion (Default = 1).
2 Starting Condition set to OFF to set terminal voltages to zero during operating point analysis. Can be useful as an aid in convergence. Initial D-S Voltage time-zero voltage across Drain-Source terminals (in Volts). Initial G-S Voltage time-zero voltage across Gate-Source terminals (in Volts). Initial B-S Voltage time-zero voltage across Bulk (substrate)-source terminals (in Volts). Temperature M temperature at which the device is to operate (in Degrees Celsius). If no value is specified, the default value assigned to TEMP on the SPICE Options page of the Analyses Setup dialog will be used (Default = 27). multiplication factor. (Default = 1). This parameter is only available when using the EKV model. Parameters (definable within model file) The following is a list of parameters that can be stored in the associated model file, when using the Shichman-Hodges, MOS2, MOS3 or MOS6 models: LEVEL model index (Default = 1). VTO zero-bias threshold voltage V TO (in Volts). (Default = 0). KP transconductance parameter (in A/V 2 ). (Default = 2.0e-5). GAMMA bulk threshold parameter γ (in V 1/2 ). (Default = 0). PHI surface potential φ (in Volts). (Default = 0.6). LAMBDA channel length modulation λ (in 1/V). This parameter is applicable to MOS1 and MOS2 model types only. (Default = 0). RD drain ohmic resistance (in Ohms). (Default = 0). RS source ohmic resistance (in Ohms). (Default = 0). CBD zero-bias B-D junction capacitance (in Farads). (Default = 0). CBS zero-bias B-S junction capacitance (in Farads). (Default = 0). IS bulk junction saturation current I S (in Amps). (Default = 1.0e-14). PB bulk junction potential (in Volts). (Default = 0.8). CGSO Gate-Source overlap capacitance per meter channel width (in Farads per meter). (Default = 0). CGDO Gate-Drain overlap capacitance per meter channel width (in Farads per meter). (Default = 0). CGBO Gate-Bulk overlap capacitance per meter channel length (in Farads per meter). (Default = 0). RSH Drain and Source diffusion sheet resistance (in Ohms). (Default = 0). CJ zero-bias bulk junction bottom capacitance per square meter of junction area (in Farads/m 2 ). (Default = 0). MJ bulk junction bottom grading coefficient (Default = 0.5). CJSW MJSW zero-bias bulk junction sidewall capacitance per meter of junction perimeter (in Farads/meter). (Default = 0). bulk junction sidewall grading coefficient (Default = LEVEL1; LEVEL2,3). JS bulk junction saturation current per square meter of junction area (in Amps/m 2 ). TOX oxide thickness (in meters). (Default = 1.0e-7).
3 NSUB substrate doping (in 1/cm 3 ). (Default = 0). NSS surface state density (in 1/cm 2 ). (Default = 0). NFS fast surface state density (in 1/cm 2 ). (Default = 0). TPG XJ type of gate material: +1 (default) = opposite to substrate -1 = same as substrate 0 = Al gate metallurgical junction depth (in meters). (Default = 0). This applies to Levels 2 (MOS2) and 3 (MOS3) only. LD lateral diffusion (in meters). (Default = 0). UO surface mobility (in cm 2 /Vs). (Default = 600). UCRIT UEXP UTRA critical field for mobility degradation (in V/cm). This parameter is applicable to the MOS2 model only. (Default = 1.0e4). critical field exponent in mobility degradation. This parameter is applicable to the MOS2 model only. (Default = 0). transverse field coefficient (mobility). This parameter has been deleted with respect to the MOS2 model. (Default = 0). VMAX maximum drift velocity of carriers (in m/s). (Default = 0). NEFF total channel-charge (fixed and mobile) coefficient. This parameter is applicable to the MOS2 model only. (Default = 1). KF flicker noise coefficient (Default = 0). AF flicker noise exponent (Default = 1). FC coefficient for forward-bias depletion capacitance formula (Default = 0.5). DELTA width effect on threshold voltage. This parameter is applicable to MOS2 and MOS3 model types only. (Default = 0). THETA mobility modulation (in 1/V). This parameter is applicable to the MOS3 model only. (Default = 0). ETA static feedback. This parameter is applicable to the MOS3 model only. (Default = 0). KAPPA saturation field factor. This parameter is applicable to the MOS3 model only. (Default = 0.2). TNOM parameter measurement temperature (in C) - If no value is specified, the default value assigned to TNOM on the SPICE Options page of the Analyses Setup dialog will be used (Default = 27). The following is a list of parameters that can be stored in the associated model file, when using the BSIM or BSIM2 models: LEVEL model index (Default = 1). VFB* PHI* flat-band voltage (in Volts). surface inversion potential (in Volts). K1* body effect coefficient (in V 1/2 ). K2* Drain/Source depletion charge-sharing coefficient. ETA* MUZ DL zero-bias drain-induced barrier-lowering coefficient. zero-bias mobility (in cm 2 /Vs). shortening of channel (in μm).
4 DW narrowing of channel (in μm). U0* zero-bias transverse-field mobility degradation coefficient (in V -1 ). U1* zer0-bias velocity saturation coefficient (in μm/v). X2MZ* sens. of mobility to substrate bias at V ds =0 (in cm 2 /V 2 s). X2E* sens. of drain-induced barrier lowering effect to substrate bias (in V -1 ). X3E* sens. of drain-induced barrier lowering effect to drain bias at V ds =V dd (in V -1 ). X2U0* sens. of transverse field mobility degradation effect to substrate bias (in V -2 ). X2U1* sens. of velocity saturation effect to substrate bias (in μmv -2 ). MUS X2MS* X3MS* mobility at zero substrate bias and at V ds =V dd (in cm 2 /V 2 s). sens. of mobility to substrate bias at V ds =V dd (in cm 2 /V 2 s). sens. of mobility to drain bias at V ds =V dd (in cm 2 /V 2 s). X3U1* sens. of velocity saturation effect on drain bias at V ds =V dd (in μmv -2 ). TOX TEMP VDD CGDO CGSO CGBO XPART gate oxide thickness (in μm). temperature at which parameters were measured (in C) measurement bias range (in Volts). gate-drain overlap capacitance per meter channel width (in F/m). gate-source overlap capacitance per meter channel width (in F/m). gate-bulk overlap capacitance per meter channel length (in F/m). gate-oxide capacitance-charge model flag. N0* zero-bias sub-threshold slope coefficient. NB* ND* RSH sens. of sub-threshold slope to substrate bias. sens. of sub-threshold slope to drain bias. drain and source diffusion sheet resistance (in Ohms). JS source drain junction current density (in A/m 2 ). PB MJ PBSW MJSW built-in potential of source drain junction (in Volts). grading coefficient of source drain junction. built-in potential of source drain junction sidewall (in Volts). grading coefficient of source drain junction sidewall. CJ source drain junction capacitance per unit area (in F/m 2 ). CJSW WDF DELL source drain junction sidewall capacitance per unit length (in F/m). source drain junction default width (in meters). source drain junction length reduction (in meters). The following is a list of parameters that can be stored in the associated model file, when using the BSIM3 model: LEVEL model index (Default = 1).
5 MOBMOD mobility model selector (Default = 1). CAPMOD flag for the short-channel capacitance model (Default = 2). NQSMOD flag for NQS model (Default = 0). NOIMOD flag for noise model (Default = 1). VTH0 K1 K2 threshold voltage (at V BS =0) for Large L (in Volts). (Default = NMOS; PMOS). (See BSIM3- Related notes). first-order body effect coefficient (in V 1/2 ). (Default = 0.5). (See BSIM3-Related notes). second-order body effect coefficient (Default = 0). (See BSIM3-Related notes). K3 narrow width coefficient (Default = 80). K3B body effect coefficient of K3 (in 1/V). (Default = 0). W0 NLX narrow width parameter (in meters) (Default = 2.5e-6). lateral non-uniform doping parameter (in meters). (Default = 1.74e-7). VBM maximum applied body bias in Vth calculation (in Volts). (Default = -3.0). DVT0 first coefficient of short-channel effect on Vth (Default = 2.2). DVT1 second coefficient of short-channel effect on Vth (Default = 0.53). DVT2 body-bias coefficient of short-channel effect on Vth (in 1/V). (Default = ). DVT0W first coefficient of narrow width effect on Vth for small channel length (in 1/m). (Default = 0). DVT1W second coefficient of narrow width effect on Vth for small channel length (in 1/m). (Default = 5.3e6). DVT2W body-bias coefficient of narrow width effect for small channel length (in 1/V). (Default = ). U0 UA UB UC VSAT mobility at TEMP = TNOM (in cm 2 /V/s). (Default = NMOSFET; PMOSFET). first-order mobility degradation coefficient (in m/v). (Default = 2.25e-9). second-order mobility degradation coefficient (in (m/v) 2 ). (Default = 5.87e-19). body-effect of mobility degradation coefficient. For MOBMOD = 1 or 2, measured in m/v 2, Default = -4.65e-11 For MOBMOD = 3, measured in 1/V, Default = saturation velocity at TEMP = TNOM (in m/sec). (Default = 8.0e4). A0 bulk charge effect coefficient for channel length (Default = 1.0). AGS gate bias coefficient of Abulk (in 1/V). (Default = 0). B0 bulk charge effect coefficient for channel width (in meters). (Default = 0). B1 bulk charge effect width offset (in meters). (Default = 0). KETA body-bias coefficient of bulk charge effect (in 1/V). (Default = ). A1 first non-saturation effect parameter (in 1/V). (Default = 0). A2 second non-saturation factor (Default = 1). RDSW parisitic resistance per unit width (in Ω-μm WR ). (Default = 0). PRWB body effect coefficient of RDSW (in V -1/2 ). (Default = 0). PRWG gate bias effect coefficient of RDSW (in 1/V). (Default = 0). WR width offset from Weff for RDS calculation (Default = 1). WINT width offset fitting parameter from I-V without bias (in meters). (Default = 0). LINT length offset fitting parameter from I-V without bias (in meters). (Default = 0).
6 DWG coefficient of Weff's gate dependence (in m/v). (Default = 0). DWB coefficient of Weff's substrate body-bias dependence (in m/v 1/2 ). (Default = 0). VOFF offset voltage in the subthreshold region at large W and L (in Volts). (Default = -0.08). NFACTOR subthreshold swing factor (Default = 1). ETA0 DIBL coefficient in subthreshold region (Default = 0.08). ETAB body-bias coefficient for the subthreshold DIBL effect (in 1/V). (Default = -0.07). DSUB DIBL coefficient exponent in subthreshold region (Default = DROUT). CIT interface trap capacitance (in F/m 2 ). (Default = 0). CDSC Drain/Source to channel coupling capacitance (in F/m 2 ). (Default = 2.4e-4). CDSCB body-bias sensitivity of CDSC (in F/Vm 2 ). (Default = 0). CDSCD Drain-bias sensitivity of CDSC (in F/Vm 2 ). (Default = 0). PCLM channel length modulation parameter (Default = 1.3). PDIBLC1 first output resistance DIBL effect correction parameter (Default = 0.39). PDIBLC2 second output resistance DIBL effect correction parameter (Default = ). PDIBLCB body-effect coefficient of DIBL correction parameters (in 1/V). (Default = 0). DROUT L dependence coefficient of the DIBL correction parameter in Rout (Default = 0.56). PSCBE1 PSCBE2 first substrate current body-effect parameter (in V/m). (Default = 4.24e8). second substrate current body-effect parameter (in m/v). (Default = 1.0e-5). PVAG gate dependence of Early voltage (Default = 0). DELTA Effective Vds parameter (in Volts). (Default = 0.01). NGATE poly gate doping concentration (in cm -3 ). (Default = 0). ALPHA0 the first parameter of impact ionization current (in m/v). (Default = 0). BETA0 the second parameter of impact ionization current (in Volts). (Default = 30). RSH source drain sheet resistance (in Ω/square). (Default = 0). JS source drain junction saturation current per unit area (in A/m 2 ). (Default = 1.0e-4). XPART charge partitioning rate flag (Default = 0). CGSO CGDO non LDD region source-gate overlap capacitance per channel length (in F/m). (See BSIM3-Related notes). non LDD region drain-gate overlap capacitance per channel length (in F/m). (See BSIM3-Related notes). CGBO gate bulk overlap capacitance per unit channel length (in F/m). (Default = 0). CJ bottom junction capacitance per unit area (in F/m 2 ). (Default = 5e-4). MJ bottom junction capacitance grating coefficient (Default = 0.5). MJSW Source/Drain side junction capacitance grading coefficient (Default = 0.33). CJSW CJSWG MJSWG Source/Drain side junction capacitance per unit area (in F/m). (Default = 5e-10). Source/Drain gate sidewall junction capacitance grading coefficient (in F/m). (Default = CJSW). Source/Drain gate sidewall junction capacitance coefficient. (Default = MJSW). PBSW Source/Drain side junction built-in potential (in Volts). (Default = 1.0). PB bottom built-in potential (in Volts). (Default = 1.0).
7 PBSWG Source/Drain gate sidewall junction built-in potential (in Volts). (Default = PBSW). CKAPPA coefficient for lightly doped region overlap capacitance (in F/m). (Default = 0.6). CF CLC Fringing field capacitance (in F/m). (See BSIM3-Related notes). constant term for the short channel model (in meters). (Default = 0.1e-6). CLE exponential term for the short channel model (Default = 0.6). DLC DWC length offset fitting parameter from C-V (in meters). (Default = LINT). width offset fitting parameter from C-V (in meters). (Default = WINT). ELM Elmore constant of the channel (Default = 5). WL coefficient of length dependence for width offset (in m WLN ). (Default = 0). WLN power of length dependence for width offset (Default = 1.0). WW coefficient of width dependence for width offset (in m WWN ). (Default = 0). WWN power of width dependence for width offset (Default = 1.0). WWL coefficient of length and width cross term for width offset (in m WWN+WLN ). (Default = 0). LL coefficient of length dependence for length offset (in m LLN ). (Default = 0). LLN power of length dependence for length offset (Default = 1.0). LW coefficient of width dependence for length offset (in m LWN ). (Default = 0). LWN power of width dependence for length offset (Default = 1.0). LWL coefficient of length and width cross term for length offset (in m LWN+LLN ). (Default = 0). TNOM parameter measurement temperature (in C) - If no value is specified, the default value assigned to TNOM on the SPICE Options page of the Analyses Setup dialog will be used (Default = 27). UTE mobility temperature exponent (Default = -1.5). KT1 temperature coefficient for threshold voltage (in Volts). (Default = -0.11). KT1L channel length dependence of the temperature coefficient for threshold voltage (in V*m). (Default = 0). KT2 body-bias coefficient of Vth temperature effect (Default = 0.022). UA1 UB1 UC1 AT temperature coefficient for UA (in m/v). (Default = 4.31e-9). temperature coefficient for UB (in (m/v) 2 ). (Default = -7.61e-18). temperature coefficient for UC. For MOBMOD = 1 or 2, measured in m/v 2, Default = -5.6e-11 For MOBMOD = 3, measured in 1/V, Default = temperature coefficient for saturation velocity (in m/s). (Default = 3.3e4). PRT temperature coefficient for RDSW (in Ω-μm). (Default = 0). NJ emission coefficient of junction (Default = 1). XTI junction current temperature exponent coefficient (Default = 3.0). NOIA NOIB NOIC EM noise parameter A (Default = 1e20 - NMOS; 9.9e18 - PMOS). noise parameter B (Default = 5e4 - NMOS; 2.4e3 - PMOS). noise parameter C (Default = -1.4e-12 - NMOS; 1.4e-12 - PMOS). saturation field (in V/m). (Default = 4.1e7). AF frequency exponent (Default = 1).
8 EF flicker exponent (Default = 1). KF flicker noise parameter (Default = 0). TOX XJ gate oxide thickness (in meters). (Default = 1.5e-8). junction depth (in meters). (Default = 1.5e-7). GAMMA1 body-effect coefficient near the surface (in V 1/2 ). (See BSIM3-Related notes). GAMMA2 body-effect coefficient in the bulk (in V 1/2 ). (See BSIM3-Related notes). NCH NSUB VBX XT channel doping concentration (in 1/cm 3 ). (Default = 1.7e17). (See BSIM3-Related notes). substrate doping concentration (in 1/cm 3 ). (Default = 6e16). Vbs at which the depletion region width equals XT (in Volts). (See BSIM3-Related notes). doping depth (in meters). (Default = 1.55e-7). LMIN minimum channel length (in meters). (Default = 0). LMAX maximum channel length (in meters). (Default = 1.0). WMIN minimum channel width (in meters). (Default = 0). WMAX maximum channel width (in meters). (Default = 1.0). BINUNIT Bin unit scale selector (Default = 1). The following is a list of parameters that can be stored in the associated model file, when using the EKV model: Process Related Parameters COX XJ gate oxide capacitance per unit area (in F/m 2 ). (Default = 0.7e-3). junction depth (in meters). (Default = 0.1e-6). DW channel width correction (in meters). (Default = 0). DL channel length correction (in meters). (Default = 0). Basic Intrinsic Model Parameters VTO long-channel threshold voltage (in Volts). (Default = 0.5). GAMMA body effect parameter (in V 1/2 ). (Default = 1.0). PHI bulk Fermi potential (*2) (in Volts). (Default = 0.7). KP E0 (EO) UCRIT transconductance parameter (in A/V 2 ). (Default = 50.0e-6). mobility reduction coefficient (in V/m). (Default = 1.0e12). longitudinal critical field (in V/m). (Default = 2.0e6). Optional Parameters TOX oxide thickness (in meters). NSUB channel doping (in cm -3 ). VFB UO VMAX flat-band voltage (in Volts). low-field mobility (in cm 2 /Vs). saturation velocity (in m/s). THETA mobility reduction coefficient (in 1/V). (Default = 0).
9 Channel Length Modulation and Charge Sharing Parameters LAMBDA depletion length coefficient (channel length modulation). (Default = 0.5). WETA narrow-channel effect coefficient. (Default = 0.25). LETA short-channel effect coefficient. (Default = 0.1). Reverse Short-Channel Effect Parameters Q0 (QO) reverse short-channel effect peak charge density (in As/m 2 ). (Default = 0). LK reverse short-channel effect characteristic length (in meters). (Default = 0.29e-6). Impact Ionization Related Parameters IBA first impact ionization coefficient (in 1/m). (Default = 0). IBB second impact ionization coefficient (in V/m). (Default = 3.0e8). IBN saturation voltage factor for impact ionization. (Default = 1.0). Intrinsic Model Temperature Parameters TCV threshold voltage temperature coefficient (in V/K). (Default = 1.0e-3). BEX mobility temperature exponent. (Default = -1.5). UCEX longitudinal critical field temperature exponent. (Default = 0.8). IBBT temperature coefficient for IBB (in 1/K). (Default = 9.0e-4). Flicker Noise Parameters KF flicker noise coefficient. (Default = 0). AF flicker noise exponent. (Default = 1). Setup Parameters NQS non-quasi-static (NQS) operation switch. (Default = 0). SATLIM ratio defining the saturation limit. (Default = exp(4)). Additional Parameters LEVEL model index (Default = 1). TNOM IS parameter measurement temperature (in C) - If no value is specified, the default value assigned to TNOM on the SPICE Options page of the Analyses Setup dialog will be used (Default = 27). bulk junction saturation current (in Amps). (Default = 1.0e-14). JS bulk junction saturation current per square meter of junction area (in Amps/m 2 ). JSW sidewall saturation current per unit length (in A/m). (Default = 0). N bulk p-n emission coefficient. (Default = 1). CBD zero-bias B-D junction capacitance (in Farads). (Default = 0). CBS zero-bias B-S junction capacitance (in Farads). (Default = 0). CJ CJSW zero-bias bulk junction bottom capacitance per square meter of junction area (in Farads/m 2 ). (Default = 0). zero-bias bulk junction sidewall capacitance per meter of junction perimeter (in Farads/meter). (Default = 0). MJ bulk junction bottom grading coefficient. (Default = 0.5). MJSW bulk junction sidewall grading coefficient. (Default = 0.33). FC coefficient for forward-bias depletion capacitance formula. (Default = 0.5).
10 PB bulk junction potential (in Volts). (Default = 0.8). PBSW built-in potential of source drain junction sidewall (in Volts). (Default = 1). TT bulk p-n transit time (in seconds). (Default = 0). CGSO Gate-Source overlap capacitance per meter channel width (in F/m). (Default = 0). CGDO Gate-Drain overlap capacitance per meter channel width (in F/m). (Default = 0). CGBO Gate-Bulk overlap capacitance per meter channel length (in F/m). (Default = 0). RD drain ohmic resistance (in Ohms). (Default = 0). RS source ohmic resistance (in Ohms). (Default = 0). RSH Drain and Source diffusion sheet resistance (in Ohms). (Default = 0). RSC source contact resistance (in Ohms). (Default = 0). RDC drain contact resistance (in Ohms). (Default = 0). XTI drain, source junction current temperature exponent. (Default = 0). TR1 first-order temperature coefficient for drain, source series resistance (in C -1 ). (Default = 0). TR2 second-order temperature coefficient for drain, source series resistance (in C -1 ). (Default = 0). ACM area calculation model. (Default = 0). CJGATE GEO HDIF zero-bias gate-edge sidewall junction capacitance (in F/m). If no value is specified, the value assigned to CJSW will be used. This parameter is only used when ACM = 3. It is ignored otherwise. shared geometry parameter. (Default = 0). This parameter is only used when ACM = 3. It is ignored otherwise. length of heavily doped diffusion (in m). (Default = 0). This parameter is only used when ACM = 2 or 3. It is ignored otherwise. LD lateral diffusion into channel (in m). (Default = 0). LDIF length of lightly doped diffusion near gate (in m). (Default = 0). SCALM model scaling factor. (Default = 1). UPDATE selects effective drain and source resistance model. (Default = 0). This parameter is only used when ACM = 1. It is ignored otherwise. WMLT width diffusion layer shrink reduction factor. (Default = 1). Notes General 1. The Simulator supports the following MOSFET device models, which differ only in their formulation of the I-V characteristic: Shichman-Hodges (LEVEL=1) MOS2 (LEVEL=2) MOS3 (LEVEL=3) BSIM (LEVEL=4) BSIM2 (LEVEL=5) MOS6 (LEVEL=6) BSIM3 (LEVEL=7) EKV (LEVEL=8) 2. The LEVEL parameter is used to specify which model to use. It is declared at the start of the
11 parameter values list, entered in the associated model file. If no LEVEL parameter is declared, the default Schichman-Hodges model will be used. The Bulk (substrate) node is connected, by default, to the Source node. If any of the component-level Length, Width, Drain Area or Source Area parameters are not specified, default values will be used. The values for the component-level NRD and NRS parameters are used to multiply the sheet resistance (RSH), in order to obtain an accurate representation of the parasitic series drain and source resistance of each transistor. The values for the component-level parameters Initial D-S Voltage, Initial G-S Voltage and Initial B-S Voltage only apply if the Use Initial Conditions option is enabled on the Transient/Fourier Analysis Setup page of the Analyses Setup dialog. The component-level Temperature parameter applies to LEVEL 1,2,3,6 & 8 MOSFET models (not BSIM type models). The link to the required model file (*.mdl) is specified on the Model Kind tab of the Sim Model dialog. The Model Name is used in the netlist to reference this file. Where a parameter has an indicated default (as part of the SPICE model definition), that default will be used if no value is specifically entered. The default should be applicable to most simulations. Generally you do not need to change this value. BSIM/BSIM2-Related 1. The BSIM and BSIM2 models are designed to be used with a process characterization system. This system is responsible for providing all parameter information (values) automatically through the use of a process file and therefore no default parameter values are specified. As a consequence, all parameters are required to be specified and the absence of any will result in an error. 2. If the XPART parameter is set to, a 40/60 drain/source charge partition in saturation is selected. If this parameter is set to 1, a 0/100 drain/source charge partition is selected. 3. Certain model parameters (those marked with an asterisk in the BSIM/BSIM2 list of parameters) also have corresponding parameters dependent on length and width. For more information on these and other aspects of the MOSFET models, consult the SPICE reference manual. BSIM3-Related 1. The following charge partition schemes are supported, selectable based on the value entered for the XPART parameter: XPART = 0 - a 0/100 drain/source charge partition os selected XPART = a 50/50 drain/source charge partition os selected XPART = 1 - a 40/60 drain/source charge partition os selected. 2. If no value is specified for one of the following parameters, it will be calculated: VTH0 K1 K2 CGSO CGDO CF GAMMA1 GAMMA2 NCH VBX
12 3. For details of the calculations involved, refer to the BSIM3v3 User Manual. 4. The following BSIM3 model parameters are not supported in Altium Designer: JSSW CGS1 CGD1 VFB side wall saturation current density. light doped source-gate region overlap capacitance. light doped drain-gate region overlap capacitance. flat-band volatge parameter. EKV-Related 1. The EKV MOSFET model was developed by the Electronics Laboratory (LEG) of the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology (EPFL). The model used in Altium Designer is version The following EKV model parameters are not supported in Altium Designer: M or NP N or NS AVTO AKP AGAMMA XQC parallel multiple device number. series multiple device number. area related threshold voltage mismatch parameter. area related gain mismatch parameter. area related body effect mismatch parameter. charge/capacitance model selector. For more detailed information on model equations associated with the EKV MOSFET, search the site for the document The EPFL-EKV MOSFET Model Equations for Simulation. Examples
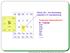
13 Consider the MOSFET in the above image, with the following characteristics: Pin1 (Drain) is connected to net D Pin2 (Gate) is connected to net G Pin3 (Source) is connected to net S The substrate node (Bulk) is connected to Pin3 (the Source node). Designator is Q1 The linked simulation model file is NMOS3.mdl. If no values are entered for the parameters in the Sim Model dialog, the entries in the SPICE netlist would be: *Schematic Netlist: MQ1 D G S S NMOS3.. *Models and Subcircuit:.MODEL NMOS3 NMOS(LEVEL=3) In this case, there are no parameter values specified in the Sim Model dialog. In the model file, there is only the LEVEL parameter specified, corresponding to the use of the MOS3 model. The default values for all other parameters inherent to the model will be used. PSpice Support Of the existing MOSFET device models, the following are not supported with respect to PSpice compatibility: BSIM3 model version 2.0 For the other supported MOSFET device models, many of the parameters that can be included in a linked model file are common to both Spice3f5 and PSpice. Those that are supported can be found in the previous section, Parameters (definable within model file). The following PSpice-based parameters are not supported for this device type. GDSNOI JSSW L N NLEV PBSW RB RDS RG TT W channel shot noise coefficient (use with NLEV=3) bulk p-n saturation sidewall current/length channel length bulk p-n emission coefficient noise equation selector bulk p-n sidewall potential bulk ohmic resistance drain-source shunt resistance gate ohmic resistance bulk p-n transit time channel width
14 Source URL:
APPENDIX D: Binning BSIM3v3 Parameters
 APPENDIX D: Binning BSIM3v3 Parameters Below is a list of all BSIM3v3 model parameters which can or cannot be binned. All model parameters which can be binned follow the following implementation: P L P
APPENDIX D: Binning BSIM3v3 Parameters Below is a list of all BSIM3v3 model parameters which can or cannot be binned. All model parameters which can be binned follow the following implementation: P L P
APPENDIX A: Parameter List
 APPENDIX A: Parameter List A.1 BSIM3v3 Model Control Parameters none level BSIMv3 model selector 8 none Mobmod mobmod Mobility model selector 1 none Capmod capmod Flag for the short channel 1 none capacitance
APPENDIX A: Parameter List A.1 BSIM3v3 Model Control Parameters none level BSIMv3 model selector 8 none Mobmod mobmod Mobility model selector 1 none Capmod capmod Flag for the short channel 1 none capacitance
APPENDIX A: Parameter List
 APPENDIX A: Parameter List A.1 BSIM3v3 Model Control Parameters none level BSIMv3 model selector 8 none Mobmod mobmod Mobility model selector 1 none Capmod capmod Flag for the short channel 2 none capacitance
APPENDIX A: Parameter List A.1 BSIM3v3 Model Control Parameters none level BSIMv3 model selector 8 none Mobmod mobmod Mobility model selector 1 none Capmod capmod Flag for the short channel 2 none capacitance
APPENDIX D: Model Parameter Binning
 APPENDIX D: Model Parameter Binning Below is the information on parameter binning regarding which model parameters can or cannot be binned. All those parameters which can be binned follow this implementation:
APPENDIX D: Model Parameter Binning Below is the information on parameter binning regarding which model parameters can or cannot be binned. All those parameters which can be binned follow this implementation:
(S&S ) PMOS: holes flow from Source to Drain. from Source to Drain. W.-Y. Choi. Electronic Circuits 2 (09/1)
 (S&S 4.1 4.3) NMOS: electrons flow from Source to Drain PMOS: holes flow from Source to Drain In cut-off ( v < V ), i = 0 GS t D NMOS I-V Characteristics In triode, ( v > V but v v v ) GS t DS GS T W 1
(S&S 4.1 4.3) NMOS: electrons flow from Source to Drain PMOS: holes flow from Source to Drain In cut-off ( v < V ), i = 0 GS t D NMOS I-V Characteristics In triode, ( v > V but v v v ) GS t DS GS T W 1
Study of MOSFET circuit
 ECE 570 Computer Aided Engineering for Integrated Circuits IC 752 - E Simulation Assignment No. 3 - Due: Oct. 30 (Th.), 2003 Study of MOSFET circuit Simulate the basic circuit of CMOS shift register shown
ECE 570 Computer Aided Engineering for Integrated Circuits IC 752 - E Simulation Assignment No. 3 - Due: Oct. 30 (Th.), 2003 Study of MOSFET circuit Simulate the basic circuit of CMOS shift register shown
EE 330 Homework 5 Spring 2017 (This assignment will not be collected or graded)
 EE 330 Homework 5 Spring 2017 (This assignment will not be collected or graded) Assume the CMOS process is characterized by model parameters V TH =1V and µc OX =100µA/V 2. If any other model parameters
EE 330 Homework 5 Spring 2017 (This assignment will not be collected or graded) Assume the CMOS process is characterized by model parameters V TH =1V and µc OX =100µA/V 2. If any other model parameters
Integrated Circuit Design: OTA in 0.5µm Technology
 Integrated Circuit Design: OTA in 0.5µm Technology Omar X. Avelar, Omar de la Mora & Diego I. Romero INTEGRATED CIRCUITS DESIGN (ESI108A) Instituto Tecnológico y de Estudios Superiores de Occidente (ITESO)
Integrated Circuit Design: OTA in 0.5µm Technology Omar X. Avelar, Omar de la Mora & Diego I. Romero INTEGRATED CIRCUITS DESIGN (ESI108A) Instituto Tecnológico y de Estudios Superiores de Occidente (ITESO)
EE 330 Homework 5 Fall 2018 (This assignment is due Wednesday Sept 19 at 12:00 noon)
 EE 330 Homework 5 Fall 2018 (This assignment is due Wednesday Sept 19 at 12:00 noon) Assume the CMOS process is characterized by model parameters VTH=1V and µcox=100µa/v 2. If any other model parameters
EE 330 Homework 5 Fall 2018 (This assignment is due Wednesday Sept 19 at 12:00 noon) Assume the CMOS process is characterized by model parameters VTH=1V and µcox=100µa/v 2. If any other model parameters
The Devices. Devices
 The The MOS Transistor Gate Oxyde Gate Source n+ Polysilicon Drain n+ Field-Oxyde (SiO 2 ) p-substrate p+ stopper Bulk Contact CROSS-SECTION of NMOS Transistor Cross-Section of CMOS Technology MOS transistors
The The MOS Transistor Gate Oxyde Gate Source n+ Polysilicon Drain n+ Field-Oxyde (SiO 2 ) p-substrate p+ stopper Bulk Contact CROSS-SECTION of NMOS Transistor Cross-Section of CMOS Technology MOS transistors
num1a ** num_1a.sp **SAM *circuit description * bias conditions vds vgs * Mosfet circuit M nch L=.5u w=8u R page 1
 ** num_1a.sp **SAM *circuit description vds 1 0 10 vgs 3 0 5 * Mosfet circuit M1 2 3 0 0 nch L=.5u w=8u R1 1 2 0 ~, Mosfet model.model nch nmos LEVEL = 1 TONS LST NODE POST.DC vds 0 10 100m vgs 0 1.PRNT
** num_1a.sp **SAM *circuit description vds 1 0 10 vgs 3 0 5 * Mosfet circuit M1 2 3 0 0 nch L=.5u w=8u R1 1 2 0 ~, Mosfet model.model nch nmos LEVEL = 1 TONS LST NODE POST.DC vds 0 10 100m vgs 0 1.PRNT
ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals
 ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 6: January 30, 2018 MOS Operating Regions, pt. 2 Lecture Outline! Operating Regions (review) " Subthreshold " Resistive " Saturation! Intro.
ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 6: January 30, 2018 MOS Operating Regions, pt. 2 Lecture Outline! Operating Regions (review) " Subthreshold " Resistive " Saturation! Intro.
EE115C Winter 2017 Digital Electronic Circuits. Lecture 2: MOS Transistor: IV Model
 EE115C Winter 2017 Digital Electronic Circuits Lecture 2: MOS Transistor: IV Model Levels of Modeling Analytical CAD analytical Switch-level sim Transistor-level sim complexity Different complexity, accuracy,
EE115C Winter 2017 Digital Electronic Circuits Lecture 2: MOS Transistor: IV Model Levels of Modeling Analytical CAD analytical Switch-level sim Transistor-level sim complexity Different complexity, accuracy,
Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT) Model. Model Kind. Model Sub-Kind. SPICE Prefix. SPICE Netlist Template Format
 Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT) Model Old Content - visit altiumcom/documentation Modified by Admin on Sep 13, 2017 Model Kind Transistor Model Sub-Kind BJT SPICE Prefix Q SPICE Netlist Template Format
Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT) Model Old Content - visit altiumcom/documentation Modified by Admin on Sep 13, 2017 Model Kind Transistor Model Sub-Kind BJT SPICE Prefix Q SPICE Netlist Template Format
N Channel MOSFET level 3
 N Channel MOSFET level 3 mosn3 NSource NBulk NSource NBulk NSource NBulk NSource (a) (b) (c) (d) NBulk Figure 1: MOSFET Types Form: mosn3: instance name n 1 n n 3 n n 1 is the drain node, n is the gate
N Channel MOSFET level 3 mosn3 NSource NBulk NSource NBulk NSource NBulk NSource (a) (b) (c) (d) NBulk Figure 1: MOSFET Types Form: mosn3: instance name n 1 n n 3 n n 1 is the drain node, n is the gate
ESE 570 MOS TRANSISTOR THEORY Part 2
 ESE 570 MOS TRANSISTOR THEORY Part 2 GCA (gradual channel approximation) MOS Transistor Model Strong Inversion Operation CMOS = NMOS + PMOS 2 TwoTerminal MOS Capacitor > nmos Transistor VGS
ESE 570 MOS TRANSISTOR THEORY Part 2 GCA (gradual channel approximation) MOS Transistor Model Strong Inversion Operation CMOS = NMOS + PMOS 2 TwoTerminal MOS Capacitor > nmos Transistor VGS
Page 1 of (2 pts) What is the purpose of the keeper transistor in a dynamic logic gate?
 Page 1 of 6 EE 434 Exam 2 Fall 2004 Name Instructions: nswer the following questions and solve the following problems. In problems relating to timing or delay calculations, assume you are working in a
Page 1 of 6 EE 434 Exam 2 Fall 2004 Name Instructions: nswer the following questions and solve the following problems. In problems relating to timing or delay calculations, assume you are working in a
! MOS Capacitances. " Extrinsic. " Intrinsic. ! Lumped Capacitance Model. ! First Order Capacitor Summary. ! Capacitance Implications
 ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 7: February, 07 MOS SPICE Models, MOS Parasitic Details Lecture Outline! MOS Capacitances " Extrinsic " Intrinsic! Lumped Capacitance Model!
ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 7: February, 07 MOS SPICE Models, MOS Parasitic Details Lecture Outline! MOS Capacitances " Extrinsic " Intrinsic! Lumped Capacitance Model!
MITLL Low-Power FDSOI CMOS Process
 MITLL Low-Power FDSOI CMOS Process Device Models Revision 2006:2 (September 2006) 2006 by MIT Lincoln Laboratory. All rights reserved. This work was sponsored by the United States Air Force under Air Force
MITLL Low-Power FDSOI CMOS Process Device Models Revision 2006:2 (September 2006) 2006 by MIT Lincoln Laboratory. All rights reserved. This work was sponsored by the United States Air Force under Air Force
ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals
 ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 7: February 4, 2016 MOS SPICE Models, MOS Parasitic Details Lecture Outline! MOS Capacitances " Extrinsic " Intrinsic! Lumped Capacitance
ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 7: February 4, 2016 MOS SPICE Models, MOS Parasitic Details Lecture Outline! MOS Capacitances " Extrinsic " Intrinsic! Lumped Capacitance
Chapter 5: BSIM3v3 Characterization
 5: BSIM3v3 Characterization The BSIM3 model (BSIM = Berkeley Short channel Insulated gate field effect transistor Model) was published by the University of California at Berkeley in July 1993. BSIM3 is
5: BSIM3v3 Characterization The BSIM3 model (BSIM = Berkeley Short channel Insulated gate field effect transistor Model) was published by the University of California at Berkeley in July 1993. BSIM3 is
University of Pennsylvania Department of Electrical Engineering. ESE 570 Midterm Exam March 14, 2013 FORMULAS AND DATA
 University of Pennsylvania Department of Electrical Engineering ESE 570 Midterm Exam March 4, 03 FORMULAS AND DATA. PHYSICAL CONSTANTS: n i = intrinsic concentration undoped) silicon =.45 x 0 0 cm -3 @
University of Pennsylvania Department of Electrical Engineering ESE 570 Midterm Exam March 4, 03 FORMULAS AND DATA. PHYSICAL CONSTANTS: n i = intrinsic concentration undoped) silicon =.45 x 0 0 cm -3 @
EKV MOS Transistor Modelling & RF Application
 HP-RF MOS Modelling Workshop, Munich, February 15-16, 1999 EKV MOS Transistor Modelling & RF Application Matthias Bucher, Wladek Grabinski Electronics Laboratory (LEG) Swiss Federal Institute of Technology,
HP-RF MOS Modelling Workshop, Munich, February 15-16, 1999 EKV MOS Transistor Modelling & RF Application Matthias Bucher, Wladek Grabinski Electronics Laboratory (LEG) Swiss Federal Institute of Technology,
USC-ISI. The MOSIS Service. BSIM3v3.1 Model. Parameters Extraction and Optimization. October 2000
 USC-ISI The MOSIS Service BSIM3v3.1 Model Parameters Extraction and Optimization October 000 Henok Abebe ance C.Tyree Table of Contents 1. Introduction and Motivation: -----------------------------------------------1.
USC-ISI The MOSIS Service BSIM3v3.1 Model Parameters Extraction and Optimization October 000 Henok Abebe ance C.Tyree Table of Contents 1. Introduction and Motivation: -----------------------------------------------1.
LECTURE 3 MOSFETS II. MOS SCALING What is Scaling?
 LECTURE 3 MOSFETS II Lecture 3 Goals* * Understand constant field and constant voltage scaling and their effects. Understand small geometry effects for MOS transistors and their implications modeling and
LECTURE 3 MOSFETS II Lecture 3 Goals* * Understand constant field and constant voltage scaling and their effects. Understand small geometry effects for MOS transistors and their implications modeling and
LEVEL 61 RPI a-si TFT Model
 LEVEL 61 RPI a-si TFT Model Star-Hspice LEVEL 61 is an AIM-SPICE MOS15 amorphous silicon (a-si) thin-film transistor (TFT) model. Model Features AIM-SPICE MOS15 a-si TFT model features include: Modified
LEVEL 61 RPI a-si TFT Model Star-Hspice LEVEL 61 is an AIM-SPICE MOS15 amorphous silicon (a-si) thin-film transistor (TFT) model. Model Features AIM-SPICE MOS15 a-si TFT model features include: Modified
Compact Modeling of Ultra Deep Submicron CMOS Devices
 Compact Modeling of Ultra Deep Submicron CMOS Devices Wladyslaw Grabinski*, Matthias Bucher, Jean-Michel Sallese, François Krummenacher Swiss Federal Institute of Technology (EPFL), Electronics Laboratory,
Compact Modeling of Ultra Deep Submicron CMOS Devices Wladyslaw Grabinski*, Matthias Bucher, Jean-Michel Sallese, François Krummenacher Swiss Federal Institute of Technology (EPFL), Electronics Laboratory,
ECEN474/704: (Analog) VLSI Circuit Design Spring 2018
 ECEN474/704: (Analog) VLSI Circuit Design Spring 2018 Lecture 4: MOS ransistor Modeling Sam Palermo Analog & Mixed-Signal Center exas A&M University Agenda MOS ransistor Modeling MOS Spice Models MOS High-Order
ECEN474/704: (Analog) VLSI Circuit Design Spring 2018 Lecture 4: MOS ransistor Modeling Sam Palermo Analog & Mixed-Signal Center exas A&M University Agenda MOS ransistor Modeling MOS Spice Models MOS High-Order
EE 560 MOS TRANSISTOR THEORY PART 2. Kenneth R. Laker, University of Pennsylvania
 1 EE 560 MOS TRANSISTOR THEORY PART nmos TRANSISTOR IN LINEAR REGION V S = 0 V G > V T0 channel SiO V D = small 4 C GC C BC substrate depletion region or bulk B p nmos TRANSISTOR AT EDGE OF SATURATION
1 EE 560 MOS TRANSISTOR THEORY PART nmos TRANSISTOR IN LINEAR REGION V S = 0 V G > V T0 channel SiO V D = small 4 C GC C BC substrate depletion region or bulk B p nmos TRANSISTOR AT EDGE OF SATURATION
Circuits. L2: MOS Models-2 (1 st Aug. 2013) B. Mazhari Dept. of EE, IIT Kanpur. B. Mazhari, IITK. G-Number
 EE610: CMOS Analog Circuits L: MOS Models- (1 st Aug. 013) B. Mazhari Dept. of EE, IIT Kanpur 3 NMOS Models MOS MODEL Above Threshold Subthreshold ( GS > TN ) ( GS < TN ) Saturation ti Ti Triode ( DS >
EE610: CMOS Analog Circuits L: MOS Models- (1 st Aug. 013) B. Mazhari Dept. of EE, IIT Kanpur 3 NMOS Models MOS MODEL Above Threshold Subthreshold ( GS > TN ) ( GS < TN ) Saturation ti Ti Triode ( DS >
ECE 342 Electronic Circuits. 3. MOS Transistors
 ECE 342 Electronic Circuits 3. MOS Transistors Jose E. Schutt-Aine Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Illinois jschutt@emlab.uiuc.edu 1 NMOS Transistor Typically L = 0.1 to 3 m, W = 0.2 to
ECE 342 Electronic Circuits 3. MOS Transistors Jose E. Schutt-Aine Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Illinois jschutt@emlab.uiuc.edu 1 NMOS Transistor Typically L = 0.1 to 3 m, W = 0.2 to
II III IV V VI B C N. Al Si P S. Zn Ga Ge As Se Cd In Sn Sb Te. Silicon (Si) the dominating material in IC manufacturing
 II III IV V VI B N Al Si P S Zn Ga Ge As Se d In Sn Sb Te Silicon (Si) the dominating material in I manufacturing ompound semiconductors III - V group: GaAs GaN GaSb GaP InAs InP InSb... The Energy Band
II III IV V VI B N Al Si P S Zn Ga Ge As Se d In Sn Sb Te Silicon (Si) the dominating material in I manufacturing ompound semiconductors III - V group: GaAs GaN GaSb GaP InAs InP InSb... The Energy Band
CHAPTER 3 - CMOS MODELS
 Lecture 04 Chapter 3 Introduction (4/15/02) Page 3.0-1 CHAPTER 3 - CMOS MODELS Chapter Outline 3.1 MOS Structure and Operation 3.2 Large signal MOS models suitable for hand calculations 3.3 Extensions
Lecture 04 Chapter 3 Introduction (4/15/02) Page 3.0-1 CHAPTER 3 - CMOS MODELS Chapter Outline 3.1 MOS Structure and Operation 3.2 Large signal MOS models suitable for hand calculations 3.3 Extensions
The Devices: MOS Transistors
 The Devices: MOS Transistors References: Semiconductor Device Fundamentals, R. F. Pierret, Addison-Wesley Digital Integrated Circuits: A Design Perspective, J. Rabaey et.al. Prentice Hall NMOS Transistor
The Devices: MOS Transistors References: Semiconductor Device Fundamentals, R. F. Pierret, Addison-Wesley Digital Integrated Circuits: A Design Perspective, J. Rabaey et.al. Prentice Hall NMOS Transistor
Generation and classification of Kerwin Huelsman Newcomb circuits using the DVCC
 INTENATIONAL JOUNAL OF CICUIT THEOY AND APPLICATIONS Int. J. Circ. Theor. Appl. 2009; 37:835 855 Published online 20 June 2008 in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI: 0.002/cta.503 Generation
INTENATIONAL JOUNAL OF CICUIT THEOY AND APPLICATIONS Int. J. Circ. Theor. Appl. 2009; 37:835 855 Published online 20 June 2008 in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI: 0.002/cta.503 Generation
MOSFET: Introduction
 E&CE 437 Integrated VLSI Systems MOS Transistor 1 of 30 MOSFET: Introduction Metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistor (MOSFET) or MOS is widely used for implementing digital designs Its major
E&CE 437 Integrated VLSI Systems MOS Transistor 1 of 30 MOSFET: Introduction Metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistor (MOSFET) or MOS is widely used for implementing digital designs Its major
Operation and Modeling of. The MOS Transistor. Second Edition. Yannis Tsividis Columbia University. New York Oxford OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS
 Operation and Modeling of The MOS Transistor Second Edition Yannis Tsividis Columbia University New York Oxford OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS CONTENTS Chapter 1 l.l 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 Chapter 2 2.1 2.2
Operation and Modeling of The MOS Transistor Second Edition Yannis Tsividis Columbia University New York Oxford OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS CONTENTS Chapter 1 l.l 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 Chapter 2 2.1 2.2
CMPEN 411 VLSI Digital Circuits. Lecture 03: MOS Transistor
 CMPEN 411 VLSI Digital Circuits Lecture 03: MOS Transistor Kyusun Choi [Adapted from Rabaey s Digital Integrated Circuits, Second Edition, 2003 J. Rabaey, A. Chandrakasan, B. Nikolic] CMPEN 411 L03 S.1
CMPEN 411 VLSI Digital Circuits Lecture 03: MOS Transistor Kyusun Choi [Adapted from Rabaey s Digital Integrated Circuits, Second Edition, 2003 J. Rabaey, A. Chandrakasan, B. Nikolic] CMPEN 411 L03 S.1
MOSFET Capacitance Model
 MOSFET Capacitance Model So far we discussed the MOSFET DC models. In real circuit operation, the device operates under time varying terminal voltages and the device operation can be described by: 1 small
MOSFET Capacitance Model So far we discussed the MOSFET DC models. In real circuit operation, the device operates under time varying terminal voltages and the device operation can be described by: 1 small
MOS Amplifiers Dr. Lynn Fuller Webpage:
 ROCHESTER INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY MICROELECTRONIC ENGINEERING Dr. Lynn Fuller Webpage: http://people.rit.edu/lffeee 82 Lomb Memorial Drive Rochester, NY 14623-5604 Email: Lynn.Fuller@rit.edu Department
ROCHESTER INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY MICROELECTRONIC ENGINEERING Dr. Lynn Fuller Webpage: http://people.rit.edu/lffeee 82 Lomb Memorial Drive Rochester, NY 14623-5604 Email: Lynn.Fuller@rit.edu Department
EE105 Fall 2014 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits. NMOS Transistor Capacitances: Saturation Region
 EE105 Fall 014 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits Prof. Ming C. Wu wu@eecs.berkeley.edu 511 Sutardja Dai Hall (SDH) 1 NMOS Transistor Capacitances: Saturation Region Drain no longer connected to channel
EE105 Fall 014 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits Prof. Ming C. Wu wu@eecs.berkeley.edu 511 Sutardja Dai Hall (SDH) 1 NMOS Transistor Capacitances: Saturation Region Drain no longer connected to channel
Transfer Gate and Dynamic Logic Dr. Lynn Fuller Webpage:
 ROCHESTER INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY MICROELECTRONIC ENGINEERING Transfer Gate and Dynamic Logic Dr. Lynn Fuller Webpage: http://people.rit.edu/lffeee 82 Lomb Memorial Drive Rochester, NY 14623-5604 Tel (585)
ROCHESTER INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY MICROELECTRONIC ENGINEERING Transfer Gate and Dynamic Logic Dr. Lynn Fuller Webpage: http://people.rit.edu/lffeee 82 Lomb Memorial Drive Rochester, NY 14623-5604 Tel (585)
EE 560 MOS TRANSISTOR THEORY
 1 EE 560 MOS TRANSISTOR THEORY PART 1 TWO TERMINAL MOS STRUCTURE V G (GATE VOLTAGE) 2 GATE OXIDE SiO 2 SUBSTRATE p-type doped Si (N A = 10 15 to 10 16 cm -3 ) t ox V B (SUBSTRATE VOLTAGE) EQUILIBRIUM:
1 EE 560 MOS TRANSISTOR THEORY PART 1 TWO TERMINAL MOS STRUCTURE V G (GATE VOLTAGE) 2 GATE OXIDE SiO 2 SUBSTRATE p-type doped Si (N A = 10 15 to 10 16 cm -3 ) t ox V B (SUBSTRATE VOLTAGE) EQUILIBRIUM:
The Devices. Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective. Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic. July 30, 2002
 Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic The Devices July 30, 2002 Goal of this chapter Present intuitive understanding of device operation Introduction
Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic The Devices July 30, 2002 Goal of this chapter Present intuitive understanding of device operation Introduction
The Devices. Jan M. Rabaey
 The Devices Jan M. Rabaey Goal of this chapter Present intuitive understanding of device operation Introduction of basic device equations Introduction of models for manual analysis Introduction of models
The Devices Jan M. Rabaey Goal of this chapter Present intuitive understanding of device operation Introduction of basic device equations Introduction of models for manual analysis Introduction of models
EEC 118 Lecture #2: MOSFET Structure and Basic Operation. Rajeevan Amirtharajah University of California, Davis Jeff Parkhurst Intel Corporation
 EEC 118 Lecture #2: MOSFET Structure and Basic Operation Rajeevan Amirtharajah University of California, Davis Jeff Parkhurst Intel Corporation Announcements Lab 1 this week, report due next week Bring
EEC 118 Lecture #2: MOSFET Structure and Basic Operation Rajeevan Amirtharajah University of California, Davis Jeff Parkhurst Intel Corporation Announcements Lab 1 this week, report due next week Bring
The simulated two volt performance of CMOS circuits with submicron transistors
 Lehigh University Lehigh Preserve Theses and Dissertations 1992 The simulated two volt performance of CMOS circuits with submicron transistors Christopher John Younger Lehigh University Follow this and
Lehigh University Lehigh Preserve Theses and Dissertations 1992 The simulated two volt performance of CMOS circuits with submicron transistors Christopher John Younger Lehigh University Follow this and
ECE 497 JS Lecture - 12 Device Technologies
 ECE 497 JS Lecture - 12 Device Technologies Spring 2004 Jose E. Schutt-Aine Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Illinois jose@emlab.uiuc.edu 1 NMOS Transistor 2 ρ Source channel charge density
ECE 497 JS Lecture - 12 Device Technologies Spring 2004 Jose E. Schutt-Aine Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Illinois jose@emlab.uiuc.edu 1 NMOS Transistor 2 ρ Source channel charge density
Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective. Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic. The Devices. July 30, Devices.
 Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic The July 30, 2002 1 Goal of this chapter Present intuitive understanding of device operation Introduction
Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic The July 30, 2002 1 Goal of this chapter Present intuitive understanding of device operation Introduction
ECE 546 Lecture 10 MOS Transistors
 ECE 546 Lecture 10 MOS Transistors Spring 2018 Jose E. Schutt-Aine Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Illinois jesa@illinois.edu NMOS Transistor NMOS Transistor N-Channel MOSFET Built on p-type
ECE 546 Lecture 10 MOS Transistors Spring 2018 Jose E. Schutt-Aine Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Illinois jesa@illinois.edu NMOS Transistor NMOS Transistor N-Channel MOSFET Built on p-type
MOS Transistor I-V Characteristics and Parasitics
 ECEN454 Digital Integrated Circuit Design MOS Transistor I-V Characteristics and Parasitics ECEN 454 Facts about Transistors So far, we have treated transistors as ideal switches An ON transistor passes
ECEN454 Digital Integrated Circuit Design MOS Transistor I-V Characteristics and Parasitics ECEN 454 Facts about Transistors So far, we have treated transistors as ideal switches An ON transistor passes
High Speed Logic Circuits Dr. Lynn Fuller Webpage:
 ROCHESTER INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY MICROELECTRONIC ENGINEERING Circuits Webpage: http://people.rit.edu/lffeee 82 Lomb Memorial Drive Rochester, NY 14623-5604 Tel (585) 475-2035 Fax (585) 475-5041 Email:
ROCHESTER INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY MICROELECTRONIC ENGINEERING Circuits Webpage: http://people.rit.edu/lffeee 82 Lomb Memorial Drive Rochester, NY 14623-5604 Tel (585) 475-2035 Fax (585) 475-5041 Email:
Lecture 12: MOS Capacitors, transistors. Context
 Lecture 12: MOS Capacitors, transistors Context In the last lecture, we discussed PN diodes, and the depletion layer into semiconductor surfaces. Small signal models In this lecture, we will apply those
Lecture 12: MOS Capacitors, transistors Context In the last lecture, we discussed PN diodes, and the depletion layer into semiconductor surfaces. Small signal models In this lecture, we will apply those
Chapter 4 Field-Effect Transistors
 Chapter 4 Field-Effect Transistors Microelectronic Circuit Design Richard C. Jaeger Travis N. Blalock 5/5/11 Chap 4-1 Chapter Goals Describe operation of MOSFETs. Define FET characteristics in operation
Chapter 4 Field-Effect Transistors Microelectronic Circuit Design Richard C. Jaeger Travis N. Blalock 5/5/11 Chap 4-1 Chapter Goals Describe operation of MOSFETs. Define FET characteristics in operation
Fundamentals of the Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor
 Triode Working FET Fundamentals of the Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor The characteristics of energy bands as a function of applied voltage. Surface inversion. The expression for the
Triode Working FET Fundamentals of the Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor The characteristics of energy bands as a function of applied voltage. Surface inversion. The expression for the
Diode Model (PN-Junction Diode Model)
 Diode Model (PN-Junction Diode Model) Diode_Model (PN-Junction Diode Model) Symbol Parameters Model parameters must be specified in SI units. Name Description Units Default Level Model level selector (1=standard,
Diode Model (PN-Junction Diode Model) Diode_Model (PN-Junction Diode Model) Symbol Parameters Model parameters must be specified in SI units. Name Description Units Default Level Model level selector (1=standard,
Chapter 5 MOSFET Theory for Submicron Technology
 Chapter 5 MOSFET Theory for Submicron Technology Short channel effects Other small geometry effects Parasitic components Velocity saturation/overshoot Hot carrier effects ** Majority of these notes are
Chapter 5 MOSFET Theory for Submicron Technology Short channel effects Other small geometry effects Parasitic components Velocity saturation/overshoot Hot carrier effects ** Majority of these notes are
Chapter 5 g m /I D -Based Design
 Chapter 5 g m /I D -Based Design Ross Walker ECE/CS 5720/6720 Fall 2017 University of Utah Partly adapted from Stanford s analog circuit design sequence Reading: See References at the end of this chapter
Chapter 5 g m /I D -Based Design Ross Walker ECE/CS 5720/6720 Fall 2017 University of Utah Partly adapted from Stanford s analog circuit design sequence Reading: See References at the end of this chapter
Modeling and Parameter Extraction Technique for Uni-Directional HV MOS Devices
 412 PAPER Special Section of Selected Papers from the 12th Workshop on Circuits and Systems in Karuizawa Modeling and Parameter Extraction Technique for Uni-Directional HV MOS Devices Takao MYONO, Member,
412 PAPER Special Section of Selected Papers from the 12th Workshop on Circuits and Systems in Karuizawa Modeling and Parameter Extraction Technique for Uni-Directional HV MOS Devices Takao MYONO, Member,
Lecture 3: CMOS Transistor Theory
 Lecture 3: CMOS Transistor Theory Outline Introduction MOS Capacitor nmos I-V Characteristics pmos I-V Characteristics Gate and Diffusion Capacitance 2 Introduction So far, we have treated transistors
Lecture 3: CMOS Transistor Theory Outline Introduction MOS Capacitor nmos I-V Characteristics pmos I-V Characteristics Gate and Diffusion Capacitance 2 Introduction So far, we have treated transistors
MOS Transistor Theory MOSFET Symbols Current Characteristics of MOSFET. MOS Symbols and Characteristics. nmos Enhancement Transistor
 MOS Transistor Theory MOSFET Symbols Current Characteristics of MOSFET Calculation of t and Important 2 nd Order Effects SmallSignal Signal MOSFET Model Summary Material from: CMOS LSI Design By Weste
MOS Transistor Theory MOSFET Symbols Current Characteristics of MOSFET Calculation of t and Important 2 nd Order Effects SmallSignal Signal MOSFET Model Summary Material from: CMOS LSI Design By Weste
VLSI Design and Simulation
 VLSI Design and Simulation Performance Characterization Topics Performance Characterization Resistance Estimation Capacitance Estimation Inductance Estimation Performance Characterization Inverter Voltage
VLSI Design and Simulation Performance Characterization Topics Performance Characterization Resistance Estimation Capacitance Estimation Inductance Estimation Performance Characterization Inverter Voltage
PSpice components for CAD
 PSpice components for CAD POLITEHNICA University of Bucharest, UPB-CETTI, Spl. Independentei 313, 060042-Bucharest, Romania, Phone: +40 21 3169633, Fax: +40 21 3169634, email: norocel.codreanu@cetti.ro
PSpice components for CAD POLITEHNICA University of Bucharest, UPB-CETTI, Spl. Independentei 313, 060042-Bucharest, Romania, Phone: +40 21 3169633, Fax: +40 21 3169634, email: norocel.codreanu@cetti.ro
VLSI Design The MOS Transistor
 VLSI Design The MOS Transistor Frank Sill Torres Universidade Federal de Minas Gerais (UFMG), Brazil VLSI Design: CMOS Technology 1 Outline Introduction MOS Capacitor nmos I-V Characteristics pmos I-V
VLSI Design The MOS Transistor Frank Sill Torres Universidade Federal de Minas Gerais (UFMG), Brazil VLSI Design: CMOS Technology 1 Outline Introduction MOS Capacitor nmos I-V Characteristics pmos I-V
Long Channel MOS Transistors
 Long Channel MOS Transistors The theory developed for MOS capacitor (HO #2) can be directly extended to Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect transistors (MOSFET) by considering the following structure:
Long Channel MOS Transistors The theory developed for MOS capacitor (HO #2) can be directly extended to Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect transistors (MOSFET) by considering the following structure:
Integrated Circuits & Systems
 Federal University of Santa Catarina Center for Technology Computer Science & Electronics Engineering Integrated Circuits & Systems INE 5442 Lecture 10 MOSFET part 1 guntzel@inf.ufsc.br ual-well Trench-Isolated
Federal University of Santa Catarina Center for Technology Computer Science & Electronics Engineering Integrated Circuits & Systems INE 5442 Lecture 10 MOSFET part 1 guntzel@inf.ufsc.br ual-well Trench-Isolated
ECE 342 Electronic Circuits. Lecture 6 MOS Transistors
 ECE 342 Electronic Circuits Lecture 6 MOS Transistors Jose E. Schutt-Aine Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Illinois jesa@illinois.edu 1 NMOS Transistor Typically L = 0.1 to 3 m, W = 0.2
ECE 342 Electronic Circuits Lecture 6 MOS Transistors Jose E. Schutt-Aine Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Illinois jesa@illinois.edu 1 NMOS Transistor Typically L = 0.1 to 3 m, W = 0.2
Combinatorial and Sequential CMOS Circuits Dr. Lynn Fuller Webpage:
 ROCHESTER INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY MICROELECTRONIC ENGINEERING Combinatorial and Sequential CMOS Circuits Webpage: http://people.rit.edu/lffeee 82 Lomb Memorial Drive Rochester, NY 14623-5604 Tel (585)
ROCHESTER INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY MICROELECTRONIC ENGINEERING Combinatorial and Sequential CMOS Circuits Webpage: http://people.rit.edu/lffeee 82 Lomb Memorial Drive Rochester, NY 14623-5604 Tel (585)
EE5311- Digital IC Design
 EE5311- Digital IC Design Module 1 - The Transistor Janakiraman V Assistant Professor Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Madras Chennai October 28, 2017 Janakiraman, IITM
EE5311- Digital IC Design Module 1 - The Transistor Janakiraman V Assistant Professor Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Madras Chennai October 28, 2017 Janakiraman, IITM
Lecture 5: CMOS Transistor Theory
 Lecture 5: CMOS Transistor Theory Slides courtesy of Deming Chen Slides based on the initial set from David Harris CMOS VLSI Design Outline q q q q q q q Introduction MOS Capacitor nmos I-V Characteristics
Lecture 5: CMOS Transistor Theory Slides courtesy of Deming Chen Slides based on the initial set from David Harris CMOS VLSI Design Outline q q q q q q q Introduction MOS Capacitor nmos I-V Characteristics
Nanoscale CMOS Design Issues
 Nanoscale CMOS Design Issues Jaydeep P. Kulkarni Assistant Professor, ECE Department The University of Texas at Austin jaydeep@austin.utexas.edu Fall, 2017, VLSI-1 Class Transistor I-V Review Agenda Non-ideal
Nanoscale CMOS Design Issues Jaydeep P. Kulkarni Assistant Professor, ECE Department The University of Texas at Austin jaydeep@austin.utexas.edu Fall, 2017, VLSI-1 Class Transistor I-V Review Agenda Non-ideal
Lab 1 Getting Started with EDA Tools
 Lab Getting Started with EDA Tools E3-238: Analog LSI Circuits INTRODUCTION The objective of this lab is to familiarize you with the Cadence irtuoso design environment. The irtuoso environment provides
Lab Getting Started with EDA Tools E3-238: Analog LSI Circuits INTRODUCTION The objective of this lab is to familiarize you with the Cadence irtuoso design environment. The irtuoso environment provides
MOS Transistor Theory
 CHAPTER 3 MOS Transistor Theory Outline 2 1. Introduction 2. Ideal I-V Characteristics 3. Nonideal I-V Effects 4. C-V Characteristics 5. DC Transfer Characteristics 6. Switch-level RC Delay Models MOS
CHAPTER 3 MOS Transistor Theory Outline 2 1. Introduction 2. Ideal I-V Characteristics 3. Nonideal I-V Effects 4. C-V Characteristics 5. DC Transfer Characteristics 6. Switch-level RC Delay Models MOS
Final Examination EE 130 December 16, 1997 Time allotted: 180 minutes
 Final Examination EE 130 December 16, 1997 Time allotted: 180 minutes Problem 1: Semiconductor Fundamentals [30 points] A uniformly doped silicon sample of length 100µm and cross-sectional area 100µm 2
Final Examination EE 130 December 16, 1997 Time allotted: 180 minutes Problem 1: Semiconductor Fundamentals [30 points] A uniformly doped silicon sample of length 100µm and cross-sectional area 100µm 2
The Physical Structure (NMOS)
 The Physical Structure (NMOS) Al SiO2 Field Oxide Gate oxide S n+ Polysilicon Gate Al SiO2 SiO2 D n+ L channel P Substrate Field Oxide contact Metal (S) n+ (G) L W n+ (D) Poly 1 Transistor Resistance Two
The Physical Structure (NMOS) Al SiO2 Field Oxide Gate oxide S n+ Polysilicon Gate Al SiO2 SiO2 D n+ L channel P Substrate Field Oxide contact Metal (S) n+ (G) L W n+ (D) Poly 1 Transistor Resistance Two
The Devices. Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective. Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic. July 30, 2002
 igital Integrated Circuits A esign Perspective Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic The evices July 30, 2002 Goal of this chapter Present intuitive understanding of device operation Introduction
igital Integrated Circuits A esign Perspective Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic The evices July 30, 2002 Goal of this chapter Present intuitive understanding of device operation Introduction
Device Models (PN Diode, MOSFET )
 Device Models (PN Diode, MOSFET ) Instructor: Steven P. Levitan steve@ece.pitt.edu TA: Gayatri Mehta, José Martínez Book: Digital Integrated Circuits: A Design Perspective; Jan Rabaey Lab Notes: Handed
Device Models (PN Diode, MOSFET ) Instructor: Steven P. Levitan steve@ece.pitt.edu TA: Gayatri Mehta, José Martínez Book: Digital Integrated Circuits: A Design Perspective; Jan Rabaey Lab Notes: Handed
Semiconductor Physics fall 2012 problems
 Semiconductor Physics fall 2012 problems 1. An n-type sample of silicon has a uniform density N D = 10 16 atoms cm -3 of arsenic, and a p-type silicon sample has N A = 10 15 atoms cm -3 of boron. For each
Semiconductor Physics fall 2012 problems 1. An n-type sample of silicon has a uniform density N D = 10 16 atoms cm -3 of arsenic, and a p-type silicon sample has N A = 10 15 atoms cm -3 of boron. For each
ANALYSIS OF THE BUMP PROBLEM IN BSIM3 USING NOR GATE CIRCUIT AND IMPLEMENTATION OF TECHNIQUES IN ORDER TO OVERCOME THEM
 ANALYSIS OF THE BUMP PROBLEM IN BSIM3 USING NOR GATE CIRCUIT AND IMPLEMENTATION OF TECHNIQUES IN ORDER TO OVERCOME THEM A Thesis SUBMITTED TO THE FACULTY OF UNIVERSITY OF MINNESOTA BY SUBRAMANIAM SANKARALINGAM
ANALYSIS OF THE BUMP PROBLEM IN BSIM3 USING NOR GATE CIRCUIT AND IMPLEMENTATION OF TECHNIQUES IN ORDER TO OVERCOME THEM A Thesis SUBMITTED TO THE FACULTY OF UNIVERSITY OF MINNESOTA BY SUBRAMANIAM SANKARALINGAM
MOS Transistor Theory
 MOS Transistor Theory So far, we have viewed a MOS transistor as an ideal switch (digital operation) Reality: less than ideal EE 261 Krish Chakrabarty 1 Introduction So far, we have treated transistors
MOS Transistor Theory So far, we have viewed a MOS transistor as an ideal switch (digital operation) Reality: less than ideal EE 261 Krish Chakrabarty 1 Introduction So far, we have treated transistors
Lecture #27. The Short Channel Effect (SCE)
 Lecture #27 ANNOUNCEMENTS Design Project: Your BJT design should meet the performance specifications to within 10% at both 300K and 360K. ( β dc > 45, f T > 18 GHz, V A > 9 V and V punchthrough > 9 V )
Lecture #27 ANNOUNCEMENTS Design Project: Your BJT design should meet the performance specifications to within 10% at both 300K and 360K. ( β dc > 45, f T > 18 GHz, V A > 9 V and V punchthrough > 9 V )
Lecture 4: CMOS Transistor Theory
 Introduction to CMOS VLSI Design Lecture 4: CMOS Transistor Theory David Harris, Harvey Mudd College Kartik Mohanram and Steven Levitan University of Pittsburgh Outline q Introduction q MOS Capacitor q
Introduction to CMOS VLSI Design Lecture 4: CMOS Transistor Theory David Harris, Harvey Mudd College Kartik Mohanram and Steven Levitan University of Pittsburgh Outline q Introduction q MOS Capacitor q
Device Models (PN Diode, MOSFET )
 Device Models (PN Diode, MOSFET ) Instructor: Steven P. Levitan steve@ece.pitt.edu TA: Gayatri Mehta, José Martínez Book: Digital Integrated Circuits: A Design Perspective; Jan Rabaey Lab Notes: Handed
Device Models (PN Diode, MOSFET ) Instructor: Steven P. Levitan steve@ece.pitt.edu TA: Gayatri Mehta, José Martínez Book: Digital Integrated Circuits: A Design Perspective; Jan Rabaey Lab Notes: Handed
ECE-305: Fall 2017 MOS Capacitors and Transistors
 ECE-305: Fall 2017 MOS Capacitors and Transistors Pierret, Semiconductor Device Fundamentals (SDF) Chapters 15+16 (pp. 525-530, 563-599) Professor Peter Bermel Electrical and Computer Engineering Purdue
ECE-305: Fall 2017 MOS Capacitors and Transistors Pierret, Semiconductor Device Fundamentals (SDF) Chapters 15+16 (pp. 525-530, 563-599) Professor Peter Bermel Electrical and Computer Engineering Purdue
Today s lecture. EE141- Spring 2003 Lecture 4. Design Rules CMOS Inverter MOS Transistor Model
 - Spring 003 Lecture 4 Design Rules CMOS Inverter MOS Transistor Model Today s lecture Design Rules The CMOS inverter at a glance An MOS transistor model for manual analysis Important! Labs start next
- Spring 003 Lecture 4 Design Rules CMOS Inverter MOS Transistor Model Today s lecture Design Rules The CMOS inverter at a glance An MOS transistor model for manual analysis Important! Labs start next
Charge-Storage Elements: Base-Charging Capacitance C b
 Charge-Storage Elements: Base-Charging Capacitance C b * Minority electrons are stored in the base -- this charge q NB is a function of the base-emitter voltage * base is still neutral... majority carriers
Charge-Storage Elements: Base-Charging Capacitance C b * Minority electrons are stored in the base -- this charge q NB is a function of the base-emitter voltage * base is still neutral... majority carriers
BSIM3v3 Manual. (Final Version) Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences. University of California, Berkeley, CA 94720
 BSIM3v3 Manual (Final Version) Yuhua Cheng, Mansun Chan, Kelvin Hui, Min-chie Jeng, Zhihong Liu, Jianhui Huang, Kai Chen, James Chen, Robert Tu, Ping K. Ko, Chenming Hu Department of Electrical Engineering
BSIM3v3 Manual (Final Version) Yuhua Cheng, Mansun Chan, Kelvin Hui, Min-chie Jeng, Zhihong Liu, Jianhui Huang, Kai Chen, James Chen, Robert Tu, Ping K. Ko, Chenming Hu Department of Electrical Engineering
The HV-EKV MOSFET Model
 The HV-EKV MOSFET Model Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL), Switzerland EPFL Team Yogesh Singh Chauhan, Costin Anghel, Francois Krummenacher, Adrian Mihai Ionescu and Michel Declercq CMC Meeting,
The HV-EKV MOSFET Model Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL), Switzerland EPFL Team Yogesh Singh Chauhan, Costin Anghel, Francois Krummenacher, Adrian Mihai Ionescu and Michel Declercq CMC Meeting,
MOS Transistors. Prof. Krishna Saraswat. Department of Electrical Engineering Stanford University Stanford, CA
 MOS Transistors Prof. Krishna Saraswat Department of Electrical Engineering S Stanford, CA 94305 saraswat@stanford.edu 1 1930: Patent on the Field-Effect Transistor! Julius Lilienfeld filed a patent describing
MOS Transistors Prof. Krishna Saraswat Department of Electrical Engineering S Stanford, CA 94305 saraswat@stanford.edu 1 1930: Patent on the Field-Effect Transistor! Julius Lilienfeld filed a patent describing
Lecture 12: MOSFET Devices
 Lecture 12: MOSFET Devices Gu-Yeon Wei Division of Engineering and Applied Sciences Harvard University guyeon@eecs.harvard.edu Wei 1 Overview Reading S&S: Chapter 5.1~5.4 Supplemental Reading Background
Lecture 12: MOSFET Devices Gu-Yeon Wei Division of Engineering and Applied Sciences Harvard University guyeon@eecs.harvard.edu Wei 1 Overview Reading S&S: Chapter 5.1~5.4 Supplemental Reading Background
CHAPTER 3 - CMOS MODELS
 CMOS Analog Circuit Design Page 3.-1 CHAPTER 3 - CMOS MODELS Chapter Outline 3.1 MOS Structure and Operation 3.2 Large signal MOS models suitable for hand calculations 3.3 Extensions of the large signal
CMOS Analog Circuit Design Page 3.-1 CHAPTER 3 - CMOS MODELS Chapter Outline 3.1 MOS Structure and Operation 3.2 Large signal MOS models suitable for hand calculations 3.3 Extensions of the large signal
FIELD-EFFECT TRANSISTORS
 FIEL-EFFECT TRANSISTORS 1 Semiconductor review 2 The MOS capacitor 2 The enhancement-type N-MOS transistor 3 I-V characteristics of enhancement MOSFETS 4 The output characteristic of the MOSFET in saturation
FIEL-EFFECT TRANSISTORS 1 Semiconductor review 2 The MOS capacitor 2 The enhancement-type N-MOS transistor 3 I-V characteristics of enhancement MOSFETS 4 The output characteristic of the MOSFET in saturation
CMOS Digital Integrated Circuits Analysis and Design
 MOS igital ntegrated ircuits Analysis and esign hapter 4 Modeling of MOS ransistors Using SPE 1 ntroduction he SPE software that was distributed by U Berkeley beginning in the late 1970s had three built-in
MOS igital ntegrated ircuits Analysis and esign hapter 4 Modeling of MOS ransistors Using SPE 1 ntroduction he SPE software that was distributed by U Berkeley beginning in the late 1970s had three built-in
Semiconductor Physics Problems 2015
 Semiconductor Physics Problems 2015 Page and figure numbers refer to Semiconductor Devices Physics and Technology, 3rd edition, by SM Sze and M-K Lee 1. The purest semiconductor crystals it is possible
Semiconductor Physics Problems 2015 Page and figure numbers refer to Semiconductor Devices Physics and Technology, 3rd edition, by SM Sze and M-K Lee 1. The purest semiconductor crystals it is possible
CMOS INVERTER. Last Lecture. Metrics for qualifying digital circuits. »Cost» Reliability» Speed (delay)»performance
 CMOS INVERTER Last Lecture Metrics for qualifying digital circuits»cost» Reliability» Speed (delay)»performance 1 Today s lecture The CMOS inverter at a glance An MOS transistor model for manual analysis
CMOS INVERTER Last Lecture Metrics for qualifying digital circuits»cost» Reliability» Speed (delay)»performance 1 Today s lecture The CMOS inverter at a glance An MOS transistor model for manual analysis
The PSP compact MOSFET model An update
 The PSP compact MOSFET model An update Gert-Jan Smit, Andries Scholten, D.B.M. Klaassen NXP Semiconductors Ronald van Langevelde Philips Research Europe Gennady Gildenblat, Weimin Wu, Xin Li, Amit Jha,
The PSP compact MOSFET model An update Gert-Jan Smit, Andries Scholten, D.B.M. Klaassen NXP Semiconductors Ronald van Langevelde Philips Research Europe Gennady Gildenblat, Weimin Wu, Xin Li, Amit Jha,
Technology file available in the CD-Rom length. Table 1-xxx: correspondence between technology and the value of lambda in µm
 A Design Rules This section gives information about the design rules used by Microwind2. You will find all the design rule values common to all CMOS processes. All that rules, as well as process parameters
A Design Rules This section gives information about the design rules used by Microwind2. You will find all the design rule values common to all CMOS processes. All that rules, as well as process parameters
MOSFET Physics: The Long Channel Approximation
 MOSFET Physics: The ong Channel Approximation A basic n-channel MOSFET (Figure 1) consists of two heavily-doped n-type regions, the Source and Drain, that comprise the main terminals of the device. The
MOSFET Physics: The ong Channel Approximation A basic n-channel MOSFET (Figure 1) consists of two heavily-doped n-type regions, the Source and Drain, that comprise the main terminals of the device. The
Stochastic Simulation Tool for VLSI
 Stochastic Simulation Tool for VLSI Mid-Project Report, Fall 2016 -Full Report- By Luis E. Martinez Sergio Graniello Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Colorado State University Fort Collins,
Stochastic Simulation Tool for VLSI Mid-Project Report, Fall 2016 -Full Report- By Luis E. Martinez Sergio Graniello Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Colorado State University Fort Collins,
SECTION: Circle one: Alam Lundstrom. ECE 305 Exam 5 SOLUTIONS: Spring 2016 April 18, 2016 M. A. Alam and M.S. Lundstrom Purdue University
 NAME: PUID: SECTION: Circle one: Alam Lundstrom ECE 305 Exam 5 SOLUTIONS: April 18, 2016 M A Alam and MS Lundstrom Purdue University This is a closed book exam You may use a calculator and the formula
NAME: PUID: SECTION: Circle one: Alam Lundstrom ECE 305 Exam 5 SOLUTIONS: April 18, 2016 M A Alam and MS Lundstrom Purdue University This is a closed book exam You may use a calculator and the formula
