Switching Circuits & Logic Design
|
|
|
- Meagan Boone
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Switching ircuits & Logic esign Jieong Roland Jiang 江介宏 epartment of lectrical ngineering National Taiwan University Fall 22 6 Sequential ircuit esign homsky ierarchy 2
2 Outline Summary of design procedure for sequential circuits esign eample code converter esign of iterative circuits esign of sequential circuits using ROs and PLs 3 Summary of esign Procedure for Sequential ircuits. erive state table (and/or state graph) Given the problem statement, determine the required relationship between the input and output sequences and derive a state table For many problems, it is easiest to first construct a state graph 2. Reduce state table minimization by row matching or using an implication table 3. Perform state assignment log 2 m flipflops are needed to encode m states 4. Form transition table Substitute the assigned flipflop states for each state in the reduced state table 5. erive flipflop input equations and output functions Plot netstate maps and input maps for each flipflop to derive the flipflop input equations 6. Realize flipflop input equations and output functions using available logic gates 7. heck design Use signal tracing, computer simulation, or lab testing 4
3 esign ample ode onverter onvert to ecess3 code dd 3 to a binarycodeddecimal digit in the range to 9 ssume serial input and output with the least significant bit first Reset to initial state after receiving every 4 inputs () ode onverter (ecess3) an the converter be realized without delaying the output? t t = () () (2) (3) = () () (2) (3) Input () t t other codes Output (ecess3) t 5 t esign ample ode onverter Step : derive state table and state graph Time t t Input Sequence Received (LS first) reset F G I J K L N P Net = I J K F G L N P Output () = t / t / / / F / / / G / / / / / / / L J N I K P / / / / // / / / / 6
4 esign ample ode onverter Time t t Step 2: Reduce state table Input Sequence Received (LS first) reset F G I J K L N P Net = I J K F G L N P Output () = t Net The matching assumes, under =, the net state is and = The matching imposes no particular condition on these don t cares Output () Time = = t 7 esign ample ode onverter In reducing a state table by row matching, sometimes there can be multiple incompatible choices in matching a row ample R S Net = S S Output () = R can be matched with either or S, but not both 8
5 esign ample ode onverter Step 3: Perform state assignment Need 3 flipflops for 7 states Reduced state table Net Output () Time = = t t ssignment map n even better assignment? 9 esign ample ode onverter Step 4: Form transition table Transition table = = = = t Net Output () Time = = t
6 esign ample ode onverter Step 5: erive flipflop input equations and output functions 2 3 = = 2 = = 3 = = = esign ample ode onverter Step 6: Realize circuit Flipflop input functions I G G2 2 FF FF Output function 5 G5 G3 3 G4 3 LK FF G6 6 G7 2
7 esign of Iterative ircuits any of the design procedures used for sequential circuits can be applied to the design of iterative circuits.g., the design procedure used for the (sequential) serial adder of Uni can be applied to the design of the parallel adder of Unit 4 Unilateral iterative circuit is the simplest form of an iterative circuit linear array of combinational cells with signals between cells traveling in only one direction 2 3 i n ell a ell a ell a a ell a a a ell a i i n n 2 3 i n 2 3 i n i and i are the primary input and output, respectively, of cell i a i and a i resemble the present state and net state, respectively, of cell i 3 esign of Iterative ircuits esign of a omparator ompare two nbit binary numbers = 2 n and Y = y y 2 y n and determine if they are equal or which one is larger if they are not equal ssume and y are the most significant bits (we plan to do the comparison from left to right) y 2 y 2 i y i n y n a a 2 a 3 a i a i a n a n b ell ell ell ell b b 2 b 2 3 i b i i b n b n n Output Network (<Y) 2(=Y) 3(>Y) 4
8 esign of Iterative ircuits esign of a omparator Steps,2: derive and reduce state table S i =Y >Y <Y S i S S S 2 i y i = S S S 2 S 2 S S 2 S S S 2 S S S :<Y 2 :=Y 3 :>Y Steps 3,4: Perform state assignment and form transition table a i b i a b i i y i = state assignment i 2 3 S = S = S 2 = 5 esign of Iterative ircuits esign of a omparator Steps 5,6: derive and realize cell input and output functions Typical cell for comparator y i i i y i a i b i i y i a i b i a i a i a i b i a i =a i i y i b i b i =b i i y i a i Output circuit for comparator b i b i a n b n a n b n a n b n a n (<Y) 2 (=Y) =an b n 3 (>Y) 2 =a n b n 3 =b n 6
9 esign of Iterative ircuits esign of a omparator Sequential comparator i y i a i a i a a i (<Y) Typical ell lock K 2 (=Y) b i b i b b i 3 (>Y) lock K t t n time = 2 n Y = y y 2 y n 7 esign of Sequential ircuits Using ROs and PLs For a ealy sequential circuit, the combinational part can be realized using a RO (PL) For the circuit with m inputs, n outputs, and k state variables, we need k flipflops and a RO with mk inputs (2 mk words) and nk outputs Similarly, for a oore sequential circuit, the netstate and output combinational subcircuits can be realized using two ROs (PLs) or, alternatively, a single RO (PL) 8
10 esign of Sequential ircuits Using ROs ample Realize the prior to ecess3 code converter using a RO and FFs table Transition table state Net = Output () = = = = = 9 esign of Sequential ircuits Using ROs ample (cont d) Realize the prior to ecess3 code converter using a RO and FFs Truth table input lines RO 6 Words 4 its output lines 2
11 esign of Sequential ircuits Using ROs ample (cont d) Realize the prior to ecess3 code converter using a RO and FFs RO 6 Words 4 its 2 3 K 2 K 3 lock K 2 esign of Sequential ircuits Using PLs ample Realize the prior to ecess3 code converter using a PL and FFs ssignment map Transition table = = = = 22
12 esign of Sequential ircuits Using PLs ample (cont d) Realize the prior to ecess3 code converter using a PL and FFs = = 2 = = 3 = = = 23 esign of Sequential ircuits Using PLs ample (cont d) Realize the prior to ecess3 code converter using a PL and FFs PL table 2 3 = = 2 = = 3 = = = N plane OR plane 24
13 esign of Sequential ircuits Using PLs ample segment of a sequential PL realizing the netstate equation = = lock n Inverting Tri Output uffer Programmable N rray 25
UNIT III Design of Combinational Logic Circuits. Department of Computer Science SRM UNIVERSITY
 UNIT III Design of ombinational Logic ircuits Department of omputer Science SRM UNIVERSITY Introduction to ombinational ircuits Logic circuits for digital systems may be ombinational Sequential combinational
UNIT III Design of ombinational Logic ircuits Department of omputer Science SRM UNIVERSITY Introduction to ombinational ircuits Logic circuits for digital systems may be ombinational Sequential combinational
Unit 9. Multiplexers, Decoders, and Programmable Logic Devices. Unit 9 1
 Unit 9 Multiplexers, ecoders, and Programmable Logic evices Unit 9 Outline Multiplexers Three state buffers ecoders Encoders Read Only Memories (ROMs) Programmable logic devices ield Programmable Gate
Unit 9 Multiplexers, ecoders, and Programmable Logic evices Unit 9 Outline Multiplexers Three state buffers ecoders Encoders Read Only Memories (ROMs) Programmable logic devices ield Programmable Gate
:3 2 D e c o de r S ubs ys te m "0 " One "1 " Ze ro "0 " "0 " One I 1 "0 " One "1 " Ze ro "1 " Ze ro "0 " "0 "
 dvanced igital Logic esign EES 303 http://ziyang.eecs.northwestern.edu/eecs303/ 5:32 decoder/demultiplexer Teacher: Robert ick Office: L477 Tech Email: dickrp@northwestern.edu Phone: 847 467 2298 \EN 5:32
dvanced igital Logic esign EES 303 http://ziyang.eecs.northwestern.edu/eecs303/ 5:32 decoder/demultiplexer Teacher: Robert ick Office: L477 Tech Email: dickrp@northwestern.edu Phone: 847 467 2298 \EN 5:32
Show that the dual of the exclusive-or is equal to its compliment. 7
 Darshan Institute of ngineering and Technology, Rajkot, Subject: Digital lectronics (2300) GTU Question ank Unit Group Questions Do as directed : I. Given that (6)0 = (00)x, find the value of x. II. dd
Darshan Institute of ngineering and Technology, Rajkot, Subject: Digital lectronics (2300) GTU Question ank Unit Group Questions Do as directed : I. Given that (6)0 = (00)x, find the value of x. II. dd
EE40 Lec 15. Logic Synthesis and Sequential Logic Circuits
 EE40 Lec 15 Logic Synthesis and Sequential Logic Circuits Prof. Nathan Cheung 10/20/2009 Reading: Hambley Chapters 7.4-7.6 Karnaugh Maps: Read following before reading textbook http://www.facstaff.bucknell.edu/mastascu/elessonshtml/logic/logic3.html
EE40 Lec 15 Logic Synthesis and Sequential Logic Circuits Prof. Nathan Cheung 10/20/2009 Reading: Hambley Chapters 7.4-7.6 Karnaugh Maps: Read following before reading textbook http://www.facstaff.bucknell.edu/mastascu/elessonshtml/logic/logic3.html
Logic. Basic Logic Functions. Switches in series (AND) Truth Tables. Switches in Parallel (OR) Alternative view for OR
 TOPIS: Logic Logic Expressions Logic Gates Simplifying Logic Expressions Sequential Logic (Logic with a Memory) George oole (85-864), English mathematician, oolean logic used in digital computers since
TOPIS: Logic Logic Expressions Logic Gates Simplifying Logic Expressions Sequential Logic (Logic with a Memory) George oole (85-864), English mathematician, oolean logic used in digital computers since
Combinational Logic Design
 PEN 35 - igital System esign ombinational Logic esign hapter 3 Logic and omputer esign Fundamentals, 4 rd Ed., Mano 2008 Pearson Prentice Hall esign oncepts and utomation top-down design proceeds from
PEN 35 - igital System esign ombinational Logic esign hapter 3 Logic and omputer esign Fundamentals, 4 rd Ed., Mano 2008 Pearson Prentice Hall esign oncepts and utomation top-down design proceeds from
The logic is straightforward. Adding two 0s will result in 0. Adding two 1s results in 10 where 1 is the carry bit and 0 is the sum bit.
 Adders Half adders Half adders represent the smallest block for adding in digital computers. What they do is very simple: they add two bits, producing a sum and a carry. The logic is straightforward. Adding
Adders Half adders Half adders represent the smallest block for adding in digital computers. What they do is very simple: they add two bits, producing a sum and a carry. The logic is straightforward. Adding
DESIGN AND IMPLEMENTATION OF ENCODERS AND DECODERS. To design and implement encoders and decoders using logic gates.
 DESIGN AND IMPLEMENTATION OF ENCODERS AND DECODERS AIM To design and implement encoders and decoders using logic gates. COMPONENTS REQUIRED S.No Components Specification Quantity 1. Digital IC Trainer
DESIGN AND IMPLEMENTATION OF ENCODERS AND DECODERS AIM To design and implement encoders and decoders using logic gates. COMPONENTS REQUIRED S.No Components Specification Quantity 1. Digital IC Trainer
S.E. Sem. III [ETRX] Digital Circuit Design. t phl. Fig.: Input and output voltage waveforms to define propagation delay times.
![S.E. Sem. III [ETRX] Digital Circuit Design. t phl. Fig.: Input and output voltage waveforms to define propagation delay times. S.E. Sem. III [ETRX] Digital Circuit Design. t phl. Fig.: Input and output voltage waveforms to define propagation delay times.](/thumbs/93/111090909.jpg) S.E. Sem. III [ETRX] Digital ircuit Design Time : 3 Hrs.] Prelim Paper Solution [Marks : 80. Solve following : [20].(a) Explain characteristics of logic families. [5] haracteristics of logic families are
S.E. Sem. III [ETRX] Digital ircuit Design Time : 3 Hrs.] Prelim Paper Solution [Marks : 80. Solve following : [20].(a) Explain characteristics of logic families. [5] haracteristics of logic families are
CARLETON UNIVERSITY Final EXAMINATION April 16, 2003
 LTN UNIVSIT Final MINTIN pril 6, 23 Name: Number: Signature: UTIN: HUS No. of Student: epartment Name & ourse Number: ourse Instructor(s) UTHI MMN 3 4 lectronic ngineering L267, and Profs. N. Tait and
LTN UNIVSIT Final MINTIN pril 6, 23 Name: Number: Signature: UTIN: HUS No. of Student: epartment Name & ourse Number: ourse Instructor(s) UTHI MMN 3 4 lectronic ngineering L267, and Profs. N. Tait and
CARLETON UNIVERSITY Final rev EXAMINATION Fri, April 22, 2005, 14:00
 LTON UNIVSITY Final rev MINTION Fri, pril 22, 25, 4: Name: Number: Signature: UTION: 3 HOUS No. of Students: 258 epartment Name & ourse Number: lectronics L 267, and ourse Instructor(s) T..ay and J. Knight
LTON UNIVSITY Final rev MINTION Fri, pril 22, 25, 4: Name: Number: Signature: UTION: 3 HOUS No. of Students: 258 epartment Name & ourse Number: lectronics L 267, and ourse Instructor(s) T..ay and J. Knight
Chapter 7. Synchronous Sequential Networks. Excitation for
 Chapter 7 Excitation for Synchronous Sequential Networks J. C. Huang, 2004 igital Logic esign 1 Structure of a clocked synchronous sequential network Mealy model of a clocked synchronous sequential network
Chapter 7 Excitation for Synchronous Sequential Networks J. C. Huang, 2004 igital Logic esign 1 Structure of a clocked synchronous sequential network Mealy model of a clocked synchronous sequential network
CMSC 313 Lecture 19 Combinational Logic Components Programmable Logic Arrays Karnaugh Maps
 CMSC 33 Lecture 9 Combinational Logic Components Programmable Logic rrays Karnaugh Maps UMC, CMSC33, Richard Chang Last Time & efore Returned midterm exam Half adders & full adders Ripple
CMSC 33 Lecture 9 Combinational Logic Components Programmable Logic rrays Karnaugh Maps UMC, CMSC33, Richard Chang Last Time & efore Returned midterm exam Half adders & full adders Ripple
CMSC 313 Lecture 19 Homework 4 Questions Combinational Logic Components Programmable Logic Arrays Introduction to Circuit Simplification
 CMSC 33 Lecture 9 Homework 4 Questions Combinational Logic Components Programmable Logic rrays Introduction to Circuit Simplification UMC, CMSC33, Richard Chang CMSC 33, Computer Organization
CMSC 33 Lecture 9 Homework 4 Questions Combinational Logic Components Programmable Logic rrays Introduction to Circuit Simplification UMC, CMSC33, Richard Chang CMSC 33, Computer Organization
XI STANDARD [ COMPUTER SCIENCE ] 5 MARKS STUDY MATERIAL.
![XI STANDARD [ COMPUTER SCIENCE ] 5 MARKS STUDY MATERIAL. XI STANDARD [ COMPUTER SCIENCE ] 5 MARKS STUDY MATERIAL.](/thumbs/81/84726747.jpg) 2017-18 XI STANDARD [ COMPUTER SCIENCE ] 5 MARKS STUDY MATERIAL HALF ADDER 1. The circuit that performs addition within the Arithmetic and Logic Unit of the CPU are called adders. 2. A unit that adds two
2017-18 XI STANDARD [ COMPUTER SCIENCE ] 5 MARKS STUDY MATERIAL HALF ADDER 1. The circuit that performs addition within the Arithmetic and Logic Unit of the CPU are called adders. 2. A unit that adds two
Combinational Logic. By : Ali Mustafa
 Combinational Logic By : Ali Mustafa Contents Adder Subtractor Multiplier Comparator Decoder Encoder Multiplexer How to Analyze any combinational circuit like this? Analysis Procedure To obtain the output
Combinational Logic By : Ali Mustafa Contents Adder Subtractor Multiplier Comparator Decoder Encoder Multiplexer How to Analyze any combinational circuit like this? Analysis Procedure To obtain the output
Figure 1-1 Basic Gates
 Figure - Basic Gates B ND: = B B OR: = + B NOT: = ' B ELUSIVE OR: = + B Figure -2 Full dder Y in FULL DDER (a) Full adder module out Sum Y in outsum (b) Truth Table Sum = 'Y'in + 'Yin' + Y'in' + Yin =
Figure - Basic Gates B ND: = B B OR: = + B NOT: = ' B ELUSIVE OR: = + B Figure -2 Full dder Y in FULL DDER (a) Full adder module out Sum Y in outsum (b) Truth Table Sum = 'Y'in + 'Yin' + Y'in' + Yin =
15.1 Elimination of Redundant States
 15.1 Elimination of Redundant States In Ch. 14 we tried not to have unnecessary states What if we have extra states in the state graph/table? Complete the table then eliminate the redundant states Chapter
15.1 Elimination of Redundant States In Ch. 14 we tried not to have unnecessary states What if we have extra states in the state graph/table? Complete the table then eliminate the redundant states Chapter
Chapter 2. Review of Digital Systems Design
 x 2-4 = 42.625. Chapter 2 Review of Digital Systems Design Numbering Systems Decimal number may be expressed as powers of 10. For example, consider a six digit decimal number 987654, which can be represented
x 2-4 = 42.625. Chapter 2 Review of Digital Systems Design Numbering Systems Decimal number may be expressed as powers of 10. For example, consider a six digit decimal number 987654, which can be represented
12/31/2010. Overview. 10-Combinational Circuit Design Text: Unit 8. Limited Fan-in. Limited Fan-in. Limited Fan-in. Limited Fan-in
 Overview 10-ombinational ircuit esign Text: Unit 8 Gates with elays and Timing Other Hazards GR/ISS 201 igital Operations and omputations Winter 2011 r. Louie 2 Practical logic gates are limited by the
Overview 10-ombinational ircuit esign Text: Unit 8 Gates with elays and Timing Other Hazards GR/ISS 201 igital Operations and omputations Winter 2011 r. Louie 2 Practical logic gates are limited by the
ELE2120 Digital Circuits and Systems. Tutorial Note 9
 ELE2120 Digital Circuits and Systems Tutorial Note 9 Outline 1. Exercise(1) Sequential Circuit Analysis 2. Exercise (2) Sequential Circuit Analysis 3. Exercise (3) Sequential Circuit Analysis 4. Ref. Construction
ELE2120 Digital Circuits and Systems Tutorial Note 9 Outline 1. Exercise(1) Sequential Circuit Analysis 2. Exercise (2) Sequential Circuit Analysis 3. Exercise (3) Sequential Circuit Analysis 4. Ref. Construction
Analysis of clocked sequential networks
 Analysis of clocked sequential networks keywords: Mealy, Moore Consider : a sequential parity checker an 8th bit is added to each group of 7 bits such that the total # of 1 bits is odd for odd parity if
Analysis of clocked sequential networks keywords: Mealy, Moore Consider : a sequential parity checker an 8th bit is added to each group of 7 bits such that the total # of 1 bits is odd for odd parity if
COMP2611: Computer Organization. Introduction to Digital Logic
 1 OMP2611: omputer Organization ombinational Logic OMP2611 Fall 2015 asics of Logic ircuits 2 its are the basis for binary number representation in digital computers ombining bits into patterns following
1 OMP2611: omputer Organization ombinational Logic OMP2611 Fall 2015 asics of Logic ircuits 2 its are the basis for binary number representation in digital computers ombining bits into patterns following
Appendix A: Digital Logic. Principles of Computer Architecture. Principles of Computer Architecture by M. Murdocca and V. Heuring
 - Principles of Computer rchitecture Miles Murdocca and Vincent Heuring 999 M. Murdocca and V. Heuring -2 Chapter Contents. Introduction.2 Combinational Logic.3 Truth Tables.4 Logic Gates.5 Properties
- Principles of Computer rchitecture Miles Murdocca and Vincent Heuring 999 M. Murdocca and V. Heuring -2 Chapter Contents. Introduction.2 Combinational Logic.3 Truth Tables.4 Logic Gates.5 Properties
Chapter # 4: Programmable and Steering Logic
 hapter # : Programmable and teering Logic ontemporary Logic esign Randy H. Katz University of alifornia, erkeley June 993 No. - PLs and PLs Pre-fabricated building block of many N/OR gates (or NOR, NN)
hapter # : Programmable and teering Logic ontemporary Logic esign Randy H. Katz University of alifornia, erkeley June 993 No. - PLs and PLs Pre-fabricated building block of many N/OR gates (or NOR, NN)
CMSC 313 Lecture 15 Good-bye Assembly Language Programming Overview of second half on Digital Logic DigSim Demo
 CMSC 33 Lecture 5 Good-bye ssembly Language Programming Overview of second half on Digital Logic DigSim Demo UMC, CMSC33, Richard Chang Good-bye ssembly Language What a pain! Understand
CMSC 33 Lecture 5 Good-bye ssembly Language Programming Overview of second half on Digital Logic DigSim Demo UMC, CMSC33, Richard Chang Good-bye ssembly Language What a pain! Understand
EE141- Spring 2004 Digital Integrated Circuits
 EE141- pring 2004 Digital Integrated ircuits Lecture 19 Dynamic Logic - Adders (that is wrap-up) 1 Administrative tuff Hw 6 due on Th No lab this week Midterm 2 next week Project 2 to be launched week
EE141- pring 2004 Digital Integrated ircuits Lecture 19 Dynamic Logic - Adders (that is wrap-up) 1 Administrative tuff Hw 6 due on Th No lab this week Midterm 2 next week Project 2 to be launched week
Principles of Computer Architecture. Appendix B: Reduction of Digital Logic. Chapter Contents
 B-1 Principles of Computer Architecture Miles Murdocca and Vincent Heuring Appendix B: Reduction of Digital Logic B-2 Chapter Contents B.1 Reduction of Combinational Logic and Sequential Logic B.2 Reduction
B-1 Principles of Computer Architecture Miles Murdocca and Vincent Heuring Appendix B: Reduction of Digital Logic B-2 Chapter Contents B.1 Reduction of Combinational Logic and Sequential Logic B.2 Reduction
Sequential Circuit Analysis
 Sequential Circuit Analysis Last time we started talking about latches and flip-flops, which are basic one-bit memory units. Today we ll talk about sequential circuit analysis and design. First, we ll
Sequential Circuit Analysis Last time we started talking about latches and flip-flops, which are basic one-bit memory units. Today we ll talk about sequential circuit analysis and design. First, we ll
Combinational Logic Design Combinational Functions and Circuits
 Combinational Logic Design Combinational Functions and Circuits Overview Combinational Circuits Design Procedure Generic Example Example with don t cares: BCD-to-SevenSegment converter Binary Decoders
Combinational Logic Design Combinational Functions and Circuits Overview Combinational Circuits Design Procedure Generic Example Example with don t cares: BCD-to-SevenSegment converter Binary Decoders
Working with Combinational Logic. Design example: 2x2-bit multiplier
 Working with ombinational Logic Simplification two-level simplification exploiting don t cares algorithm for simplification Logic realization two-level logic and canonical forms realized with NNs and NORs
Working with ombinational Logic Simplification two-level simplification exploiting don t cares algorithm for simplification Logic realization two-level logic and canonical forms realized with NNs and NORs
ELEC Digital Logic Circuits Fall 2014 Sequential Circuits (Chapter 6) Finite State Machines (Ch. 7-10)
 ELEC 2200-002 Digital Logic Circuits Fall 2014 Sequential Circuits (Chapter 6) Finite State Machines (Ch. 7-10) Vishwani D. Agrawal James J. Danaher Professor Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
ELEC 2200-002 Digital Logic Circuits Fall 2014 Sequential Circuits (Chapter 6) Finite State Machines (Ch. 7-10) Vishwani D. Agrawal James J. Danaher Professor Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
ECEN 248: INTRODUCTION TO DIGITAL SYSTEMS DESIGN. Week 9 Dr. Srinivas Shakkottai Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering
 ECEN 248: INTRODUCTION TO DIGITAL SYSTEMS DESIGN Week 9 Dr. Srinivas Shakkottai Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering TIMING ANALYSIS Overview Circuits do not respond instantaneously to input changes
ECEN 248: INTRODUCTION TO DIGITAL SYSTEMS DESIGN Week 9 Dr. Srinivas Shakkottai Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering TIMING ANALYSIS Overview Circuits do not respond instantaneously to input changes
Fundamentals of Digital Design
 Fundamentals of Digital Design Digital Radiation Measurement and Spectroscopy NE/RHP 537 1 Binary Number System The binary numeral system, or base-2 number system, is a numeral system that represents numeric
Fundamentals of Digital Design Digital Radiation Measurement and Spectroscopy NE/RHP 537 1 Binary Number System The binary numeral system, or base-2 number system, is a numeral system that represents numeric
The Design Procedure. Output Equation Determination - Derive output equations from the state table
 The Design Procedure Specification Formulation - Obtain a state diagram or state table State Assignment - Assign binary codes to the states Flip-Flop Input Equation Determination - Select flipflop types
The Design Procedure Specification Formulation - Obtain a state diagram or state table State Assignment - Assign binary codes to the states Flip-Flop Input Equation Determination - Select flipflop types
Section 001. Read this before starting!
 Points missed: Student's Name: Total score: / points East Tennessee State University epartment of omputer and Information Sciences SI 25 (Tarnoff) omputer Organization TEST 2 for Fall Semester, 24 Section
Points missed: Student's Name: Total score: / points East Tennessee State University epartment of omputer and Information Sciences SI 25 (Tarnoff) omputer Organization TEST 2 for Fall Semester, 24 Section
LOGIC CIRCUITS. Basic Experiment and Design of Electronics
 Basic Experiment and Design of Electronics LOGIC CIRCUITS Ho Kyung Kim, Ph.D. hokyung@pusan.ac.kr School of Mechanical Engineering Pusan National University Outline Combinational logic circuits Output
Basic Experiment and Design of Electronics LOGIC CIRCUITS Ho Kyung Kim, Ph.D. hokyung@pusan.ac.kr School of Mechanical Engineering Pusan National University Outline Combinational logic circuits Output
Chapter 6 Introduction to state machines
 9..7 hapter 6 Introduction to state machines Dr.-Ing. Stefan Werner Table of content hapter : Switching Algebra hapter : Logical Levels, Timing & Delays hapter 3: Karnaugh-Veitch-Maps hapter 4: ombinational
9..7 hapter 6 Introduction to state machines Dr.-Ing. Stefan Werner Table of content hapter : Switching Algebra hapter : Logical Levels, Timing & Delays hapter 3: Karnaugh-Veitch-Maps hapter 4: ombinational
L10 State Machine Design Topics
 L State Machine Design Topics States Machine Design Other topics on state machine design Equivalent sequential machines Incompletely specified machines One Hot State Machines Ref: text Unit 15.4, 15.5,
L State Machine Design Topics States Machine Design Other topics on state machine design Equivalent sequential machines Incompletely specified machines One Hot State Machines Ref: text Unit 15.4, 15.5,
Appendix A: Digital Logic. CPSC 352- Computer Organization
 - CPSC 352- Computer Organization -2 Chapter Contents. Introduction.2 Combinational Logic.3 Truth Tables.4 Logic Gates.5 Properties of oolean lgebra.6 The Sum-of-Products Form, and Logic Diagrams.7 The
- CPSC 352- Computer Organization -2 Chapter Contents. Introduction.2 Combinational Logic.3 Truth Tables.4 Logic Gates.5 Properties of oolean lgebra.6 The Sum-of-Products Form, and Logic Diagrams.7 The
Digital Logic: Boolean Algebra and Gates. Textbook Chapter 3
 Digital Logic: Boolean Algebra and Gates Textbook Chapter 3 Basic Logic Gates XOR CMPE12 Summer 2009 02-2 Truth Table The most basic representation of a logic function Lists the output for all possible
Digital Logic: Boolean Algebra and Gates Textbook Chapter 3 Basic Logic Gates XOR CMPE12 Summer 2009 02-2 Truth Table The most basic representation of a logic function Lists the output for all possible
Combinational Logic. Jee-Hwan Ryu. School of Mechanical Engineering Korea University of Technology and Education
 MEC5 디지털공학 Combinational Logic Jee-Hwan Ryu School of Mechanical Engineering Combinational circuits Outputs are determined from the present inputs Consist of input/output variables and logic gates inary
MEC5 디지털공학 Combinational Logic Jee-Hwan Ryu School of Mechanical Engineering Combinational circuits Outputs are determined from the present inputs Consist of input/output variables and logic gates inary
Sequential Circuit Design
 Sequential Circuit esign esign Procedure. Specification 2. Formulation Obtain a state diagram or state table 3. State Assignment Assign binary codes to the states 4. Flip-Flop Input Equation etermination
Sequential Circuit esign esign Procedure. Specification 2. Formulation Obtain a state diagram or state table 3. State Assignment Assign binary codes to the states 4. Flip-Flop Input Equation etermination
LOGIC CIRCUITS. Basic Experiment and Design of Electronics. Ho Kyung Kim, Ph.D.
 Basic Experiment and Design of Electronics LOGIC CIRCUITS Ho Kyung Kim, Ph.D. hokyung@pusan.ac.kr School of Mechanical Engineering Pusan National University Digital IC packages TTL (transistor-transistor
Basic Experiment and Design of Electronics LOGIC CIRCUITS Ho Kyung Kim, Ph.D. hokyung@pusan.ac.kr School of Mechanical Engineering Pusan National University Digital IC packages TTL (transistor-transistor
Digital Electronics. Part A
 Digital Electronics Final Examination Part A Winter 2004-05 Student Name: Date: lass Period: Total Points: Multiple hoice Directions: Select the letter of the response which best completes the item or
Digital Electronics Final Examination Part A Winter 2004-05 Student Name: Date: lass Period: Total Points: Multiple hoice Directions: Select the letter of the response which best completes the item or
Decoding A Counter. svbitec.wordpress.com 1
 ecoding A ounter ecoding a counter involves determining which state in the sequence the counter is in. ifferentiate between active-high and active-low decoding. Active-HIGH decoding: output HIGH if the
ecoding A ounter ecoding a counter involves determining which state in the sequence the counter is in. ifferentiate between active-high and active-low decoding. Active-HIGH decoding: output HIGH if the
COMBINATIONAL LOGIC FUNCTIONS
 COMBINATIONAL LOGIC FUNCTIONS Digital logic circuits can be classified as either combinational or sequential circuits. A combinational circuit is one where the output at any time depends only on the present
COMBINATIONAL LOGIC FUNCTIONS Digital logic circuits can be classified as either combinational or sequential circuits. A combinational circuit is one where the output at any time depends only on the present
Computer organization
 Computer organization Levels of abstraction Assembler Simulator Applications C C++ Java High-level language SOFTWARE add lw ori Assembly language Goal 0000 0001 0000 1001 0101 Machine instructions/data
Computer organization Levels of abstraction Assembler Simulator Applications C C++ Java High-level language SOFTWARE add lw ori Assembly language Goal 0000 0001 0000 1001 0101 Machine instructions/data
Appendix A: Digital Logic. Principles of Computer Architecture. Principles of Computer Architecture by M. Murdocca and V. Heuring
 - Principles of Computer rchitecture Miles Murdocca and Vincent Heuring 999 M. Murdocca and V. Heuring -2 Chapter Contents. Introduction.2 Combinational Logic.3 Truth Tables.4 Logic Gates.5 Properties
- Principles of Computer rchitecture Miles Murdocca and Vincent Heuring 999 M. Murdocca and V. Heuring -2 Chapter Contents. Introduction.2 Combinational Logic.3 Truth Tables.4 Logic Gates.5 Properties
Simplification of State Machines
 T3 Lecture Notes State Reduction hapter 9 - of Simplification of State Machines This semester has been spent developing the techniques needed to design digital circuits. Now we can compile a list of just
T3 Lecture Notes State Reduction hapter 9 - of Simplification of State Machines This semester has been spent developing the techniques needed to design digital circuits. Now we can compile a list of just
CprE 281: Digital Logic
 CprE 281: Digital Logic Instructor: Alexander Stoytchev http://www.ece.iastate.edu/~alexs/classes/ Synchronous Sequential Circuits Basic Design Steps CprE 281: Digital Logic Iowa State University, Ames,
CprE 281: Digital Logic Instructor: Alexander Stoytchev http://www.ece.iastate.edu/~alexs/classes/ Synchronous Sequential Circuits Basic Design Steps CprE 281: Digital Logic Iowa State University, Ames,
SRC Language Conventions. Class 6: Intro to SRC Simulator Register Transfers and Logic Circuits. SRC Simulator Demo. cond_br.asm.
 Fall 2006 S333: omputer rchitecture University of Virginia omputer Science Michele o SR Language onventions lass 6: Intro to SR Simulator Register Transfers and Logic ircuits hapter 2, ppendix.5 2 SR Simulator
Fall 2006 S333: omputer rchitecture University of Virginia omputer Science Michele o SR Language onventions lass 6: Intro to SR Simulator Register Transfers and Logic ircuits hapter 2, ppendix.5 2 SR Simulator
ECE/Comp Sci 352 Digital Systems Fundamentals. Charles R. Kime Section 2 Fall Logic and Computer Design Fundamentals
 University of Wisconsin - Madison ECE/Comp Sci 352 Digital Systems Fundamentals Charles R. Kime Section 2 Fall 2001 Lecture 5 Registers & Counters Part 2 Charles Kime Counters Counters are sequential circuits
University of Wisconsin - Madison ECE/Comp Sci 352 Digital Systems Fundamentals Charles R. Kime Section 2 Fall 2001 Lecture 5 Registers & Counters Part 2 Charles Kime Counters Counters are sequential circuits
Logic. Combinational. inputs. outputs. the result. system can
 Digital Electronics Combinational Logic Functions Digital logic circuits can be classified as either combinational or sequential circuits. A combinational circuit is one where the output at any time depends
Digital Electronics Combinational Logic Functions Digital logic circuits can be classified as either combinational or sequential circuits. A combinational circuit is one where the output at any time depends
PGT104 Digital Electronics. PGT104 Digital Electronics
 1 Part 6 Sequential Logic ircuits Disclaimer: Most of the contents (if not all) are extracted from resources available for Digital Fundamentals 10 th Edition 2 Basic Shift Register Operations A shift register
1 Part 6 Sequential Logic ircuits Disclaimer: Most of the contents (if not all) are extracted from resources available for Digital Fundamentals 10 th Edition 2 Basic Shift Register Operations A shift register
Lecture 3 Review on Digital Logic (Part 2)
 Lecture 3 Review on Digital Logic (Part 2) Xuan Silvia Zhang Washington University in St. Louis http://classes.engineering.wustl.edu/ese461/ ircuit Optimization Simplest implementation ost criterion literal
Lecture 3 Review on Digital Logic (Part 2) Xuan Silvia Zhang Washington University in St. Louis http://classes.engineering.wustl.edu/ese461/ ircuit Optimization Simplest implementation ost criterion literal
Ch 7. Finite State Machines. VII - Finite State Machines Contemporary Logic Design 1
 Ch 7. Finite State Machines VII - Finite State Machines Contemporary Logic esign 1 Finite State Machines Sequential circuits primitive sequential elements combinational logic Models for representing sequential
Ch 7. Finite State Machines VII - Finite State Machines Contemporary Logic esign 1 Finite State Machines Sequential circuits primitive sequential elements combinational logic Models for representing sequential
Theory of Logic Circuits. Laboratory manual. Exercise 1
 Zakład Mikroinformatyki i Teorii utomatów Cyfrowych Theory of Logic Circuits Laboratory manual Eercise Combinational switching circuits 008 Urszula Stańczyk, Piotr Czekalski (edt. E.. Combinational switching
Zakład Mikroinformatyki i Teorii utomatów Cyfrowych Theory of Logic Circuits Laboratory manual Eercise Combinational switching circuits 008 Urszula Stańczyk, Piotr Czekalski (edt. E.. Combinational switching
Exercise booklet - Logic
 Name: Class: Date:......... Exercise booklet Logic BCD Counter Worksheet with excercises and repetitive tasks for students and learners Find the seven logic gates in the puzzle. The words can be hidden
Name: Class: Date:......... Exercise booklet Logic BCD Counter Worksheet with excercises and repetitive tasks for students and learners Find the seven logic gates in the puzzle. The words can be hidden
Chapter #7: Sequential Logic Case Studies Contemporary Logic Design
 hapter #7: Sequential Logic ase Studies ontemporary Logic Design No. 7- Storage egister Group of storage elements read/written as a unit 4-bit register constructed from 4 D FFs Shared clock and clear lines
hapter #7: Sequential Logic ase Studies ontemporary Logic Design No. 7- Storage egister Group of storage elements read/written as a unit 4-bit register constructed from 4 D FFs Shared clock and clear lines
University of Toronto Faculty of Applied Science and Engineering Final Examination
 University of Toronto Faculty of Applied Science and Engineering Final Examination ECE 24S - Digital Systems Examiner: Belinda Wang, Jianwen Zhu 2: - 4:3pm, April 26th, 24 Duration: 5 minutes (2.5 hours)
University of Toronto Faculty of Applied Science and Engineering Final Examination ECE 24S - Digital Systems Examiner: Belinda Wang, Jianwen Zhu 2: - 4:3pm, April 26th, 24 Duration: 5 minutes (2.5 hours)
Lab 3 Revisited. Zener diodes IAP 2008 Lecture 4 1
 Lab 3 Revisited Zener diodes R C 6.091 IAP 2008 Lecture 4 1 Lab 3 Revisited +15 Voltage regulators 555 timers 270 1N758 0.1uf 5K pot V+ V- 2N2222 0.1uf V o. V CC V Vin s = 5 V Vc V c Vs 1 e t = RC Threshold
Lab 3 Revisited Zener diodes R C 6.091 IAP 2008 Lecture 4 1 Lab 3 Revisited +15 Voltage regulators 555 timers 270 1N758 0.1uf 5K pot V+ V- 2N2222 0.1uf V o. V CC V Vin s = 5 V Vc V c Vs 1 e t = RC Threshold
CMSC 313 Lecture 16 Announcement: no office hours today. Good-bye Assembly Language Programming Overview of second half on Digital Logic DigSim Demo
 CMSC 33 Lecture 6 nnouncement: no office hours today. Good-bye ssembly Language Programming Overview of second half on Digital Logic DigSim Demo UMC, CMSC33, Richard Chang Good-bye ssembly
CMSC 33 Lecture 6 nnouncement: no office hours today. Good-bye ssembly Language Programming Overview of second half on Digital Logic DigSim Demo UMC, CMSC33, Richard Chang Good-bye ssembly
Week-5. Sequential Circuit Design. Acknowledgement: Most of the following slides are adapted from Prof. Kale's slides at UIUC, USA.
 Week-5 Sequential Circuit Design Acknowledgement: Most of the following slides are adapted from Prof. Kale's slides at UIUC, USA. Storing a value: SR = 00 What if S = 0 and R = 0? The equations on the
Week-5 Sequential Circuit Design Acknowledgement: Most of the following slides are adapted from Prof. Kale's slides at UIUC, USA. Storing a value: SR = 00 What if S = 0 and R = 0? The equations on the
EEL 3701 Fall Multiply out the following logic expressions to obtain the Sum of Products.
 Page 1/5 Version: 7/30/17 1. Multiply out the following logic expressions to obtain the Sum of Products.. (/W /X Y) (W /Z) (/W X /Z) (W X) (W Y /Z). (/W /Y Z) (/W Y) (X /Y /Z) (/W X Y) (Y Z) 2. Using oolean
Page 1/5 Version: 7/30/17 1. Multiply out the following logic expressions to obtain the Sum of Products.. (/W /X Y) (W /Z) (/W X /Z) (W X) (W Y /Z). (/W /Y Z) (/W Y) (X /Y /Z) (/W X Y) (Y Z) 2. Using oolean
Clocked Sequential Circuits UNIT 13 ANALYSIS OF CLOCKED SEQUENTIAL CIRCUITS. Analysis of Clocked Sequential Circuits. Signal Tracing and Timing Charts
 ed Sequential Circuits 2 Contents nalysis by signal tracing & timing charts State tables and graphs General models for sequential circuits sequential parity checker Reading Unit 3 asic unit Unit : Latch
ed Sequential Circuits 2 Contents nalysis by signal tracing & timing charts State tables and graphs General models for sequential circuits sequential parity checker Reading Unit 3 asic unit Unit : Latch
Boolean Algebra and Logic Simplification
 S302 Digital Logic Design Boolean Algebra and Logic Simplification Boolean Analysis of Logic ircuits, evaluating of Boolean expressions, representing the operation of Logic circuits and Boolean expressions
S302 Digital Logic Design Boolean Algebra and Logic Simplification Boolean Analysis of Logic ircuits, evaluating of Boolean expressions, representing the operation of Logic circuits and Boolean expressions
Department of Electrical & Electronics EE-333 DIGITAL SYSTEMS
 Department of Electrical & Electronics EE-333 DIGITAL SYSTEMS 1) Given the two binary numbers X = 1010100 and Y = 1000011, perform the subtraction (a) X -Y and (b) Y - X using 2's complements. a) X = 1010100
Department of Electrical & Electronics EE-333 DIGITAL SYSTEMS 1) Given the two binary numbers X = 1010100 and Y = 1000011, perform the subtraction (a) X -Y and (b) Y - X using 2's complements. a) X = 1010100
Digital Logic Design. Midterm #2
 EECS: igital Logic esign r. nthony. Johnson s7m2s_dild7.fm - igital Logic esign Midterm #2 Problems Points. 5 2. 4 3. 6 Total 5 Was the exam fair? yes no EECS: igital Logic esign r. nthony. Johnson s7m2s_dild7.fm
EECS: igital Logic esign r. nthony. Johnson s7m2s_dild7.fm - igital Logic esign Midterm #2 Problems Points. 5 2. 4 3. 6 Total 5 Was the exam fair? yes no EECS: igital Logic esign r. nthony. Johnson s7m2s_dild7.fm
Why digital? Overview. Number Systems. Binary to Decimal conversion
 Why digital? Overview It has the following advantages over analog. It can be processed and transmitted efficiently and reliably. It can be stored and retrieved with greater accuracy. Noise level does not
Why digital? Overview It has the following advantages over analog. It can be processed and transmitted efficiently and reliably. It can be stored and retrieved with greater accuracy. Noise level does not
Sequential Logic Circuits
 Chapter 4 Sequential Logic Circuits 4 1 The defining characteristic of a combinational circuit is that its output depends only on the current inputs applied to the circuit. The output of a sequential circuit,
Chapter 4 Sequential Logic Circuits 4 1 The defining characteristic of a combinational circuit is that its output depends only on the current inputs applied to the circuit. The output of a sequential circuit,
Ch 4. Combinational Logic Technologies. IV - Combinational Logic Technologies Contemporary Logic Design 1
 h 4. ombinational Logic Technologies Technologies ontemporary Logic Design 1 History - From Switches to Integrated ircuits The underlying implementation technologies for digital systems Technologies ontemporary
h 4. ombinational Logic Technologies Technologies ontemporary Logic Design 1 History - From Switches to Integrated ircuits The underlying implementation technologies for digital systems Technologies ontemporary
Combinational Logic (mostly review!)
 ombinational Logic (mostly review!)! Logic functions, truth tables, and switches " NOT, N, OR, NN, NOR, OR,... " Minimal set! xioms and theorems of oolean algebra " Proofs by re-writing " Proofs by perfect
ombinational Logic (mostly review!)! Logic functions, truth tables, and switches " NOT, N, OR, NN, NOR, OR,... " Minimal set! xioms and theorems of oolean algebra " Proofs by re-writing " Proofs by perfect
Digital Electronics Circuits 2017
 JSS SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY UNIVERSITY Digital Electronics Circuits (EC37L) Lab in-charge: Dr. Shankraiah Course outcomes: After the completion of laboratory the student will be able to, 1. Simplify, design
JSS SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY UNIVERSITY Digital Electronics Circuits (EC37L) Lab in-charge: Dr. Shankraiah Course outcomes: After the completion of laboratory the student will be able to, 1. Simplify, design
Digital- or Logic Circuits. Outline Logic Circuits. Logic Voltage Levels. Binary Representation
 Outline Logic ircuits Introduction Logic Systems TTL MOS Logic Gates NOT, OR, N NOR, NN, XOR Implementation oolean lgebra ombinatorial ircuits Multipleer emultipleer rithmetic ircuits Simplifying Logic
Outline Logic ircuits Introduction Logic Systems TTL MOS Logic Gates NOT, OR, N NOR, NN, XOR Implementation oolean lgebra ombinatorial ircuits Multipleer emultipleer rithmetic ircuits Simplifying Logic
ELCT201: DIGITAL LOGIC DESIGN
 ELCT201: DIGITAL LOGIC DESIGN Dr. Eng. Haitham Omran, haitham.omran@guc.edu.eg Dr. Eng. Wassim Alexan, wassim.joseph@guc.edu.eg Following the slides of Dr. Ahmed H. Madian Lecture 10 محرم 1439 ه Winter
ELCT201: DIGITAL LOGIC DESIGN Dr. Eng. Haitham Omran, haitham.omran@guc.edu.eg Dr. Eng. Wassim Alexan, wassim.joseph@guc.edu.eg Following the slides of Dr. Ahmed H. Madian Lecture 10 محرم 1439 ه Winter
Random Number Generator Digital Design - Demo
 Understanding Digital Design The Digital Electronics 2014 Digital Design - Demo This presentation will Review the oard Game Counter block diagram. Review the circuit design of the sequential logic section
Understanding Digital Design The Digital Electronics 2014 Digital Design - Demo This presentation will Review the oard Game Counter block diagram. Review the circuit design of the sequential logic section
Z = F(X) Combinational circuit. A combinational circuit can be specified either by a truth table. Truth Table
 Lesson Objectives In this lesson, you will learn about What are combinational circuits Design procedure of combinational circuits Examples of combinational circuit design Combinational Circuits Logic circuit
Lesson Objectives In this lesson, you will learn about What are combinational circuits Design procedure of combinational circuits Examples of combinational circuit design Combinational Circuits Logic circuit
211: Computer Architecture Summer 2016
 211: Computer Architecture Summer 2016 Liu Liu Topic: Storage Project3 Digital Logic - Storage: Recap - Review: cache hit rate - Project3 - Digital Logic: - truth table => SOP - simplification: Boolean
211: Computer Architecture Summer 2016 Liu Liu Topic: Storage Project3 Digital Logic - Storage: Recap - Review: cache hit rate - Project3 - Digital Logic: - truth table => SOP - simplification: Boolean
Logic Synthesis and Verification
 Logic Synthesis and Verification Jie-Hong Roland Jiang 江介宏 Department of Electrical Engineering National Taiwan University Fall Timing Analysis & Optimization Reading: Logic Synthesis in a Nutshell Sections
Logic Synthesis and Verification Jie-Hong Roland Jiang 江介宏 Department of Electrical Engineering National Taiwan University Fall Timing Analysis & Optimization Reading: Logic Synthesis in a Nutshell Sections
Digital Electronics Sequential Logic
 /5/27 igital Electronics Sequential Logic r. I. J. Wassell Sequential Logic The logic circuits discussed previously are known as combinational, in that the output depends only on the condition of the latest
/5/27 igital Electronics Sequential Logic r. I. J. Wassell Sequential Logic The logic circuits discussed previously are known as combinational, in that the output depends only on the condition of the latest
 vidyarthiplus.com vidyarthiplus.com vidyarthiplus.com ANNA UNIVERSITY- COMBATORE B.E./ B.TECH. DEGREE EXAMINATION - JUNE 2009. ELECTRICAL & ELECTONICS ENGG. - FOURTH SEMESTER DIGITAL LOGIC CIRCUITS PART-A
vidyarthiplus.com vidyarthiplus.com vidyarthiplus.com ANNA UNIVERSITY- COMBATORE B.E./ B.TECH. DEGREE EXAMINATION - JUNE 2009. ELECTRICAL & ELECTONICS ENGG. - FOURTH SEMESTER DIGITAL LOGIC CIRCUITS PART-A
A B D 1 Y D 2 D 3. Truth table for 4 to 1 MUX: A B Y 0 0 D D D D 3
 . What is a multiplexer? esign a 4 to multiplexer using logic gates. Write the truth table and explain its working principle. Answer: is a circuit with many inputs but only one output. esigning of 4 to
. What is a multiplexer? esign a 4 to multiplexer using logic gates. Write the truth table and explain its working principle. Answer: is a circuit with many inputs but only one output. esigning of 4 to
CE Optimized State Machines
 C 1911 Optimized State Machines Un-used states o we care about un-used states? YS! Start-up Bit errors 2 tj Un-used states Mod 5 counter reset 000 001 010 100 011 101 111 110 3 tj Un-used states Mod 5
C 1911 Optimized State Machines Un-used states o we care about un-used states? YS! Start-up Bit errors 2 tj Un-used states Mod 5 counter reset 000 001 010 100 011 101 111 110 3 tj Un-used states Mod 5
COSC 243. Introduction to Logic And Combinatorial Logic. Lecture 4 - Introduction to Logic and Combinatorial Logic. COSC 243 (Computer Architecture)
 COSC 243 Introduction to Logic And Combinatorial Logic 1 Overview This Lecture Introduction to Digital Logic Gates Boolean algebra Combinatorial Logic Source: Chapter 11 (10 th edition) Source: J.R. Gregg,
COSC 243 Introduction to Logic And Combinatorial Logic 1 Overview This Lecture Introduction to Digital Logic Gates Boolean algebra Combinatorial Logic Source: Chapter 11 (10 th edition) Source: J.R. Gregg,
LOGIC GATES (PRACTICE PROBLEMS)
 LOGIC GTES (PRCTICE PROLEMS) Key points and summary First set of problems from Q. Nos. 1 to 9 are based on the logic gates like ND, OR, NOT, NND & NOR etc. First four problems are basic in nature. Problems
LOGIC GTES (PRCTICE PROLEMS) Key points and summary First set of problems from Q. Nos. 1 to 9 are based on the logic gates like ND, OR, NOT, NND & NOR etc. First four problems are basic in nature. Problems
Systems I: Computer Organization and Architecture
 Systems I: Computer Organization and Architecture Lecture 6 - Combinational Logic Introduction A combinational circuit consists of input variables, logic gates, and output variables. The logic gates accept
Systems I: Computer Organization and Architecture Lecture 6 - Combinational Logic Introduction A combinational circuit consists of input variables, logic gates, and output variables. The logic gates accept
COSC3330 Computer Architecture Lecture 2. Combinational Logic
 COSC333 Computer rchitecture Lecture 2. Combinational Logic Instructor: Weidong Shi (Larry), PhD Computer Science Department University of Houston Today Combinational Logic oolean lgebra Mux, DeMux, Decoder
COSC333 Computer rchitecture Lecture 2. Combinational Logic Instructor: Weidong Shi (Larry), PhD Computer Science Department University of Houston Today Combinational Logic oolean lgebra Mux, DeMux, Decoder
SYNCHRONOUS SEQUENTIAL CIRCUITS
 CHAPTER SYNCHRONOUS SEUENTIAL CIRCUITS Registers an counters, two very common synchronous sequential circuits, are introuce in this chapter. Register is a igital circuit for storing information. Contents
CHAPTER SYNCHRONOUS SEUENTIAL CIRCUITS Registers an counters, two very common synchronous sequential circuits, are introuce in this chapter. Register is a igital circuit for storing information. Contents
Reg. No. Question Paper Code : B.E./B.Tech. DEGREE EXAMINATION, NOVEMBER/DECEMBER Second Semester. Computer Science and Engineering
 Sp 6 Reg. No. Question Paper Code : 27156 B.E./B.Tech. DEGREE EXAMINATION, NOVEMBER/DECEMBER 2015. Second Semester Computer Science and Engineering CS 6201 DIGITAL PRINCIPLES AND SYSTEM DESIGN (Common
Sp 6 Reg. No. Question Paper Code : 27156 B.E./B.Tech. DEGREE EXAMINATION, NOVEMBER/DECEMBER 2015. Second Semester Computer Science and Engineering CS 6201 DIGITAL PRINCIPLES AND SYSTEM DESIGN (Common
Overview. Multiplexor. cs281: Introduction to Computer Systems Lab02 Basic Combinational Circuits: The Mux and the Adder
 cs281: Introduction to Computer Systems Lab02 Basic Combinational Circuits: The Mux and the Adder Overview The objective of this lab is to understand two basic combinational circuits the multiplexor and
cs281: Introduction to Computer Systems Lab02 Basic Combinational Circuits: The Mux and the Adder Overview The objective of this lab is to understand two basic combinational circuits the multiplexor and
UNIVERSITY OF BOLTON SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING BENG (HONS) ELECTRICAL & ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING EXAMINATION SEMESTER /2017
 UNIVERSITY OF BOLTON TW35 SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING BENG (HONS) ELECTRICAL & ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING EXAMINATION SEMESTER 2-2016/2017 INTERMEDIATE DIGITAL ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATIONS MODULE NO: EEE5002
UNIVERSITY OF BOLTON TW35 SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING BENG (HONS) ELECTRICAL & ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING EXAMINATION SEMESTER 2-2016/2017 INTERMEDIATE DIGITAL ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATIONS MODULE NO: EEE5002
Learning Objectives:
 Learning Objectives: t the end of this topic you will be able to; draw a block diagram showing how -type flip-flops can be connected to form a synchronous counter to meet a given specification; explain
Learning Objectives: t the end of this topic you will be able to; draw a block diagram showing how -type flip-flops can be connected to form a synchronous counter to meet a given specification; explain
L4: Sequential Building Blocks (Flip-flops, Latches and Registers)
 L4: Sequential Building Blocks (Flip-flops, Latches and Registers) Acknowledgements:., Materials in this lecture are courtesy of the following people and used with permission. - Randy H. Katz (University
L4: Sequential Building Blocks (Flip-flops, Latches and Registers) Acknowledgements:., Materials in this lecture are courtesy of the following people and used with permission. - Randy H. Katz (University
Combinatorial Logic Design Principles
 Combinatorial Logic Design Principles ECGR2181 Chapter 4 Notes Logic System Design I 4-1 Boolean algebra a.k.a. switching algebra deals with boolean values -- 0, 1 Positive-logic convention analog voltages
Combinatorial Logic Design Principles ECGR2181 Chapter 4 Notes Logic System Design I 4-1 Boolean algebra a.k.a. switching algebra deals with boolean values -- 0, 1 Positive-logic convention analog voltages
Overview. Programmable logic (PLAs & PALs ) Short-hand notation. Programming the wire connections
 Overview Programmable logic (PLs & PLs ) Last lecture "Switching-network" logic blocks Multiplexers/selectors emultiplexers/decoders Programmable logic devices (PLs) Regular structures for 2-level logic
Overview Programmable logic (PLs & PLs ) Last lecture "Switching-network" logic blocks Multiplexers/selectors emultiplexers/decoders Programmable logic devices (PLs) Regular structures for 2-level logic
10/12/2016. An FSM with No Inputs Moves from State to State. ECE 120: Introduction to Computing. Eventually, the States Form a Loop
 University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering An FSM with No Inputs Moves from State to State What happens if an FSM has no inputs? ECE 120: Introduction to Computing
University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering An FSM with No Inputs Moves from State to State What happens if an FSM has no inputs? ECE 120: Introduction to Computing
Introduction to Computer Engineering. CS/ECE 252, Fall 2012 Prof. Guri Sohi Computer Sciences Department University of Wisconsin Madison
 Introduction to Computer Engineering CS/ECE 252, Fall 2012 Prof. Guri Sohi Computer Sciences Department University of Wisconsin Madison Chapter 3 Digital Logic Structures Slides based on set prepared by
Introduction to Computer Engineering CS/ECE 252, Fall 2012 Prof. Guri Sohi Computer Sciences Department University of Wisconsin Madison Chapter 3 Digital Logic Structures Slides based on set prepared by
Looking at a two binary digit sum shows what we need to extend addition to multiple binary digits.
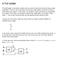 A Full Adder The half-adder is extremely useful until you want to add more that one binary digit quantities. The slow way to develop a two binary digit adders would be to make a truth table and reduce
A Full Adder The half-adder is extremely useful until you want to add more that one binary digit quantities. The slow way to develop a two binary digit adders would be to make a truth table and reduce
