Simplification of State Machines
|
|
|
- Hilda Stanley
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 T3 Lecture Notes State Reduction hapter 9 - of Simplification of State Machines This semester has been spent developing the techniques needed to design digital circuits. Now we can compile a list of just what it takes to complete a successful digital design project. Specif the problem erive the state table and/or the state diagram Reduce the # of states to the minimum possible hoose an appropriate state assignment onstruct an appropriate transition table evelop the design equations Implement the circuit
2 T3 Lecture Notes State Reduction hapter 9 - of The onl topic in that list that is left to be discussed is that of minimiing the number of states. iscussion of State Reduction is normall divided into two different areas:. State Reduction in ompletel Specified ircuits. State Reduction in Incompletel Specified ircuits We will limit our discussion to the first area. This topic is epanded on in T 4 and usuall encompasses the second discussion area. The removal of redundant states is important for a number of reasons. () ost: The number of memor elements is directl related to the number of states. () ompleit: The more states the circuit contains, the more comple the design and its associated implementation becomes. (3) ids failure analsis: iagnostic routines are usuall based on the assumption that there are no redundant states. There are 3 major State reduction Methods: Reduction b (a) Inspection (b) Partitioning (c) Implication table. We will stud the st two methods and leave the Implication table method for T 4.
3 T3 Lecture Notes State Reduction hapter 9-3 of Reduction Inspection This is the easiest and most obvious technique. We can merge compatible states if we follow some simple rules.. Two states that have different outputs are not compatible and can t be merged.. Two states are compatible and can be merged if, under all possible input conditions, the net states and outputs are the same. 3. Two states are compatible and can be merged if, under all possible input conditions, the merging of the two states will make the net states compatible and the outputs the same.
4 T3 Lecture Notes State Reduction hapter 9-4 of The following is an eample from Professor Hackworth s T4 tet. (rule ) = = andidates for merging (rule ) Not a candidate (rule ) (rule ) = = Note the substitution of all s with s along with the merger. = = This application of rule 3 is quite often hard to notice. That s wh we need other methods of state reduction. (rule 3) if were merged with then we could replace with and then the Net states and the outputs would match. = = Note that with this final circuit we have made quite a hardware savings. We went from 5 states (3 ff) to states ( ff) along with a significant reduction in control circuitr.
5 T3 Lecture Notes State Reduction hapter 9-5 of Let s look at another small eample. In doing so, we will also look at a couple of new was to write state tables which will help us in our reductions. Y Z 7 7» Two groups of possible candidates for merging. 7»» If we merge and, would the results be the same? 7» = therefore the two states are not compatible. = therefore the two states are not compatible. 's outputs ( ) are different 's outputs ( ) are different
6 T3 Lecture Notes State Reduction hapter 9-6 of Let s do the same thing ecept this time, let s put the table into another form. = Y/ = Y/ = Y/ = Y/ / / / / - / / / / / / / / / / Note that since was redundant, we replaced ever with a. What did we save with this State Merger? Saved on gates, not on s. Let s rewrite the table another wa ON MOR TIM. Y = = = = = = = = -
7 T3 Lecture Notes State Reduction hapter 9-7 of Let s tr a second eample. We will use the Inspection method to reduce the following state table: Let s look at the instances where Z is equal to : Y Y = = = = State had a NT STT of and. ollowing the thread we get: State has NT STTS of and. definition, will be fine, but is not compatible because has an output of and has an output of. If one item in an thread of a state inspection is incompatible, the whole thread (and the state) is bad (fruit of the poison tree) as well!! We don t even have to look at the other thread coming off of but if ou like, note that the thread starts with which we have alread determined to be incompatible. is the other possibilit for Z =. Note that if we work thru the top thread, we get to which we have shown to be incompatible, therefore the entire tree is poisoned. ontinued on the net page:
8 T3 Lecture Notes State Reduction hapter 9-8 of ontinuing the eample, let s now look at the output condition of Z = This time, we will use less eplanation for the failures. Tr to follow wh each tree failed: Y Y = = = = Y Z = = = = Y Z = = = = Note that we replaced the single with an and all the occurrences of with. We reduced the circuit from 7 states (3 ) to 5 states (3). We still didn t save on flip-flops but we most likel saved on control circuitr.
9 T3 Lecture Notes State Reduction hapter 9-9 of Moore Reduction (also known as Partitioning) (page 58) = Y = = =. The st step is to assume that all states are compatible. P =(). Then we start grouping the states based on their outputs. P =()()() 3. Then we group these groups b Net State. or, =, The net state is. Note that in P, is in the same group () so can sta in the same group. However, is not in the same group as was so will have to be separated out into its own group. We now have partition (P ): P =()()()() or, =, The net state is which becomes. were in the same group in the last partition, P so the can still share a group in P 3. P 3 =()()()() or, =, Net state is. Obviousl the are in same group in P 3 so can remain grouped. P 4 =()()()() or, =, Net state is which are all in the same group in P 4, so we can keep together. P 5 =()()()()
10 T3 Lecture Notes State Reduction hapter 9 - of Once a partition repeats itself, ou are finished. So, for this group, we get: Reduced from 7 states (3 ff) to 4 states ( ff) + control circuitr. = = = = Y = = = = Y
11 T3 Lecture Notes State Reduction hapter 9 - of Let s redo our eample on page 7 b using Moore reduction. Y = = = =. ssume the all are compatible. P =(). roup b output. P =()() 3. roup b net state. P = ()()()() P 3 = ()()()()() P 4 = ()()()()() P 3 = P 4 thus reduced Y = = = = Y = = = = Same answer as before.
12 T3 Lecture Notes State Reduction hapter 9 - of (ample 9.3 in Nelson, et. al.) Reduce the following stable b appling Moore s Reduction. Y = = = = P =(H) H H P =()()()(H) P =()()()()(H) P 3 =()()()()(H) P 3 = P, Thus reduced Y = = = = Y = = = = H H H H
13 T3 Lecture Notes State Reduction hapter 9-3 of ample 9.4 (in Nelson, et. al.) / / / / / / / / / / / / P =(H) P =()(H) / / / / P =()()(H) / / / / / / / / / / / / P 3 =()()()()(H) P 4 =()()()()(H) H / / / / P 3 =P 4, Thus reduced / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / H / / / /
14 T3 Lecture Notes State Reduction hapter 9-4 of State ssignments State assignment procedures are concerned with methods for assigning binar values to states in such a wa as to reduce the cost of the combinational circuit which drives the flip-flops (memor elements). These methods are mainl useful when a circuit is viewed as a black bo. Such a circuit ma follow a sequence of internal states, but the binar values of the individual states ma be of no consequence outside of the bo as long as the circuit produces the required sequence of output bits for an sequence of input bits. this definition, this assignment procedure obviousl doesn t appl to circuits whose eternal outputs are taken directl from flip-flops with a particular binar sequence specified. There are man methods of optimiing the state assignments made to a given circuit. Most are etremel involved and are beond the scope of this course. However, one particular method of state assignment optimiation is essentiall simple and eas to follow.
15 T3 Lecture Notes State Reduction hapter 9-5 of In the following rules, there term adjacent assignments means that the state assignments made to a pair of states differ b onl bit, i.e. ra odes. Rule : Rule : Rule 3: States that have the same net states for a given input should be given logicall adjacent assignments. States that are the net states of a given present state, under logicall adjacent inputs, should be given logicall adjacent assignments. If there is a conflict between rule and, rule takes precedence. Let s appl these rules to an eample: ssign. # ssign. # ssign. #3 Y = = = = Using Rule #, the state pair (,) should be given adjacent assignments because both of them go to state for =. Similarl, state pairs (,), (,), and (,) all should be given adjacent assignments; the pair (,) appears twice.
16 T3 Lecture Notes State Reduction hapter 9-6 of The application of Rule # shows that the state pair (,) should be given adjacent assignments because the are net states of the present state. or similar reasons, state pairs (,) and (,) Rule : States that are the net states of a given present state, under logicall adjacent inputs, should be given logicall adjacent assignments. Rule : States that have the same net states for a given input should be given logicall adjacent should be adjacent with (,) appearing twice. 3 ssign. # 3 ssign. # 3 ssign. #3 The figure above demonstrates the three different choices for state assignments which attempt to meet as man of the adjacenc requirements as possible. It can hopefull be seen that ssignment 3 satisfies most of the adjacencies and hence produces a better result then the other assignments. It might be suggested that ssignment
17 T3 Lecture Notes State Reduction hapter 9-7 of produces the same number of adjacencies as #3, but it doesn t fulfill the adjacenc requirement for state pair (,) as determined b Rule. (Note that we don t bother here with an equation for since it is not affected b a state assignment.) Let s take a look at the logic equations produced b each assignment. The actual work to produce these equations follows but will not be covered in class. It is left up to the student to verif the equations for him or herself. s can be easil seen below, our choice of ssign. #3 is clearl the winner in the logic component simplicit contest. J K J K # gates N gate OR gate + wire and a choice between: # or + OR gate or OR gate additional N gates OR gate wire + and a choice between: # or + OR gate or additional OR gate additional N gates N gate # 3 3 wires
18 T3 Lecture Notes State Reduction hapter 9-8 of State ssignment # Y Y J J K K ssign # PS NS J K 3 J J J = + J = + = K K K = K = + =
19 T3 Lecture Notes State Reduction hapter 9-9 of State ssignment # Y Y J K J K ssign # PS NS J K 3 J J J = + = J = K K = + K K =
20 T3 Lecture Notes State Reduction hapter 9 - of State ssignment #3 Y Y J K J K ssign #3 PS NS J K 3 J J J = J = K K K = K =
ASYNCHRONOUS SEQUENTIAL CIRCUITS
 ASYNCHRONOUS SEQUENTIAL CIRCUITS Sequential circuits that are not snchronized b a clock Asnchronous circuits Analsis of Asnchronous circuits Snthesis of Asnchronous circuits Hazards that cause incorrect
ASYNCHRONOUS SEQUENTIAL CIRCUITS Sequential circuits that are not snchronized b a clock Asnchronous circuits Analsis of Asnchronous circuits Snthesis of Asnchronous circuits Hazards that cause incorrect
8.7 Systems of Non-Linear Equations and Inequalities
 8.7 Sstems of Non-Linear Equations and Inequalities 67 8.7 Sstems of Non-Linear Equations and Inequalities In this section, we stud sstems of non-linear equations and inequalities. Unlike the sstems of
8.7 Sstems of Non-Linear Equations and Inequalities 67 8.7 Sstems of Non-Linear Equations and Inequalities In this section, we stud sstems of non-linear equations and inequalities. Unlike the sstems of
Switching Circuits & Logic Design
 Switching ircuits & Logic esign Jieong Roland Jiang 江介宏 epartment of lectrical ngineering National Taiwan University Fall 22 6 Sequential ircuit esign homsky ierarchy http://www.cs.lmu.edu/~ray/notes/languagetheory/
Switching ircuits & Logic esign Jieong Roland Jiang 江介宏 epartment of lectrical ngineering National Taiwan University Fall 22 6 Sequential ircuit esign homsky ierarchy http://www.cs.lmu.edu/~ray/notes/languagetheory/
2.8 Implicit Differentiation
 .8 Implicit Differentiation Section.8 Notes Page 1 Before I tell ou what implicit differentiation is, let s start with an example: EXAMPLE: Find if x. This question is asking us to find the derivative
.8 Implicit Differentiation Section.8 Notes Page 1 Before I tell ou what implicit differentiation is, let s start with an example: EXAMPLE: Find if x. This question is asking us to find the derivative
Topic 3 Notes Jeremy Orloff
 Topic 3 Notes Jerem Orloff 3 Line integrals and auch s theorem 3.1 Introduction The basic theme here is that comple line integrals will mirror much of what we ve seen for multivariable calculus line integrals.
Topic 3 Notes Jerem Orloff 3 Line integrals and auch s theorem 3.1 Introduction The basic theme here is that comple line integrals will mirror much of what we ve seen for multivariable calculus line integrals.
Logical design of digital systems
 21062017 lectures Summer Semester 2017 Table of content 1 Combinational circuit design 2 Elementary combinatorial circuits for data transmission 3 Memory structures 4 Programmable logic devices 5 Algorithmic
21062017 lectures Summer Semester 2017 Table of content 1 Combinational circuit design 2 Elementary combinatorial circuits for data transmission 3 Memory structures 4 Programmable logic devices 5 Algorithmic
DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS First Order Differential Equations. Paul Dawkins
 DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS First Order Paul Dawkins Table of Contents Preface... First Order... 3 Introduction... 3 Linear... 4 Separable... 7 Eact... 8 Bernoulli... 39 Substitutions... 46 Intervals of Validit...
DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS First Order Paul Dawkins Table of Contents Preface... First Order... 3 Introduction... 3 Linear... 4 Separable... 7 Eact... 8 Bernoulli... 39 Substitutions... 46 Intervals of Validit...
8. BOOLEAN ALGEBRAS x x
 8. BOOLEAN ALGEBRAS 8.1. Definition of a Boolean Algebra There are man sstems of interest to computing scientists that have a common underling structure. It makes sense to describe such a mathematical
8. BOOLEAN ALGEBRAS 8.1. Definition of a Boolean Algebra There are man sstems of interest to computing scientists that have a common underling structure. It makes sense to describe such a mathematical
Chapter 4 Analytic Trigonometry
 Analtic Trigonometr Chapter Analtic Trigonometr Inverse Trigonometric Functions The trigonometric functions act as an operator on the variable (angle, resulting in an output value Suppose this process
Analtic Trigonometr Chapter Analtic Trigonometr Inverse Trigonometric Functions The trigonometric functions act as an operator on the variable (angle, resulting in an output value Suppose this process
L10 State Machine Design Topics
 L State Machine Design Topics States Machine Design Other topics on state machine design Equivalent sequential machines Incompletely specified machines One Hot State Machines Ref: text Unit 15.4, 15.5,
L State Machine Design Topics States Machine Design Other topics on state machine design Equivalent sequential machines Incompletely specified machines One Hot State Machines Ref: text Unit 15.4, 15.5,
3.7 InveRSe FUnCTIOnS
 CHAPTER functions learning ObjeCTIveS In this section, ou will: Verif inverse functions. Determine the domain and range of an inverse function, and restrict the domain of a function to make it one-to-one.
CHAPTER functions learning ObjeCTIveS In this section, ou will: Verif inverse functions. Determine the domain and range of an inverse function, and restrict the domain of a function to make it one-to-one.
CHAPTER 9: SEQUENTIAL CIRCUITS
 CHAPTER 9: ASYNCHRONOUS SEUENTIAL CIRCUITS Chapter Objectives 2 Sequential circuits that are not snchronized b a clock Asnchronous circuits Analsis of Asnchronous circuits Snthesis of Asnchronous circuits
CHAPTER 9: ASYNCHRONOUS SEUENTIAL CIRCUITS Chapter Objectives 2 Sequential circuits that are not snchronized b a clock Asnchronous circuits Analsis of Asnchronous circuits Snthesis of Asnchronous circuits
CS/EE 181a 2008/09 Lecture 4
 CS/EE 181a 28/9 Lecture 4 General topic of today s lecture: Logic Optimization Karnaugh maps. Quine-McCluskey tabulation method (not in detail). Non series-parallel networks (some care is required). Reference
CS/EE 181a 28/9 Lecture 4 General topic of today s lecture: Logic Optimization Karnaugh maps. Quine-McCluskey tabulation method (not in detail). Non series-parallel networks (some care is required). Reference
Foundations of Databases
 Foundations of Databases (Slides adapted from Thomas Eiter, Leonid Libkin and Werner Nutt) Foundations of Databases 1 Quer optimization: finding a good wa to evaluate a quer Queries are declarative, and
Foundations of Databases (Slides adapted from Thomas Eiter, Leonid Libkin and Werner Nutt) Foundations of Databases 1 Quer optimization: finding a good wa to evaluate a quer Queries are declarative, and
Methods for Advanced Mathematics (C3) Coursework Numerical Methods
 Woodhouse College 0 Page Introduction... 3 Terminolog... 3 Activit... 4 Wh use numerical methods?... Change of sign... Activit... 6 Interval Bisection... 7 Decimal Search... 8 Coursework Requirements on
Woodhouse College 0 Page Introduction... 3 Terminolog... 3 Activit... 4 Wh use numerical methods?... Change of sign... Activit... 6 Interval Bisection... 7 Decimal Search... 8 Coursework Requirements on
Introduction to CMOS VLSI Design. Logical Effort B. Original Lecture by Jay Brockman. University of Notre Dame Fall 2008
 Introduction to CMOS VLSI Design Logical Effort Part B Original Lecture b Ja Brockman Universit of Notre Dame Fall 2008 Modified b Peter Kogge Fall 2010,2011,2015, 2018 Based on lecture slides b David
Introduction to CMOS VLSI Design Logical Effort Part B Original Lecture b Ja Brockman Universit of Notre Dame Fall 2008 Modified b Peter Kogge Fall 2010,2011,2015, 2018 Based on lecture slides b David
CpE358/CS381. Switching Theory and Logical Design. Class 2
 CpE358/CS38 Switching Theor and Logical Design Class 2 CpE358/CS38 Switching Theor and Logical Design Summer- 24 Copright 24 Stevens Institute of Technolog -45 Toda s Material Fundamental concepts of digital
CpE358/CS38 Switching Theor and Logical Design Class 2 CpE358/CS38 Switching Theor and Logical Design Summer- 24 Copright 24 Stevens Institute of Technolog -45 Toda s Material Fundamental concepts of digital
Intermediate Algebra. Gregg Waterman Oregon Institute of Technology
 Intermediate Algebra Gregg Waterman Oregon Institute of Technolog c 2017 Gregg Waterman This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International license. The essence of the license
Intermediate Algebra Gregg Waterman Oregon Institute of Technolog c 2017 Gregg Waterman This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International license. The essence of the license
Problem Set 9 Solutions
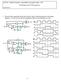 CSE 26 Digital Computers: Organization and Logical Design - 27 Jon Turner Problem Set 9 Solutions. For each of the sequential circuits shown below, draw in the missing parts of the timing diagrams. You
CSE 26 Digital Computers: Organization and Logical Design - 27 Jon Turner Problem Set 9 Solutions. For each of the sequential circuits shown below, draw in the missing parts of the timing diagrams. You
Menu. Binary Adder EEL3701 EEL3701. Add, Subtract, Compare, ALU
 Other MSI Circuit: Adders >Binar, Half & Full Canonical forms Binar Subtraction Full-Subtractor Magnitude Comparators >See Lam: Fig 4.8 ALU Menu Look into m... 1 Binar Adder Suppose we want to add two
Other MSI Circuit: Adders >Binar, Half & Full Canonical forms Binar Subtraction Full-Subtractor Magnitude Comparators >See Lam: Fig 4.8 ALU Menu Look into m... 1 Binar Adder Suppose we want to add two
1 GSW Gaussian Elimination
 Gaussian elimination is probabl the simplest technique for solving a set of simultaneous linear equations, such as: = A x + A x + A x +... + A x,,,, n n = A x + A x + A x +... + A x,,,, n n... m = Am,x
Gaussian elimination is probabl the simplest technique for solving a set of simultaneous linear equations, such as: = A x + A x + A x +... + A x,,,, n n = A x + A x + A x +... + A x,,,, n n... m = Am,x
Week 3 September 5-7.
 MA322 Weekl topics and quiz preparations Week 3 September 5-7. Topics These are alread partl covered in lectures. We collect the details for convenience.. Solutions of homogeneous equations AX =. 2. Using
MA322 Weekl topics and quiz preparations Week 3 September 5-7. Topics These are alread partl covered in lectures. We collect the details for convenience.. Solutions of homogeneous equations AX =. 2. Using
Physics Gravitational force. 2. Strong or color force. 3. Electroweak force
 Phsics 360 Notes on Griffths - pluses and minuses No tetbook is perfect, and Griffithsisnoeception. Themajorplusisthat it is prett readable. For minuses, see below. Much of what G sas about the del operator
Phsics 360 Notes on Griffths - pluses and minuses No tetbook is perfect, and Griffithsisnoeception. Themajorplusisthat it is prett readable. For minuses, see below. Much of what G sas about the del operator
LESSON 35: EIGENVALUES AND EIGENVECTORS APRIL 21, (1) We might also write v as v. Both notations refer to a vector.
 LESSON 5: EIGENVALUES AND EIGENVECTORS APRIL 2, 27 In this contet, a vector is a column matri E Note 2 v 2, v 4 5 6 () We might also write v as v Both notations refer to a vector (2) A vector can be man
LESSON 5: EIGENVALUES AND EIGENVECTORS APRIL 2, 27 In this contet, a vector is a column matri E Note 2 v 2, v 4 5 6 () We might also write v as v Both notations refer to a vector (2) A vector can be man
7.1. Unit 7. Minterm and Canonical Sums 2- and 3-Variable Boolean Algebra Theorems DeMorgan's Theorem Simplification using Boolean Algebra
 7.1 Unit 7 Minterm and Canonical Sums 2- and 3-Variable Boolean Algebra Theorems DeMorgan's Theorem Simplification using Boolean Algebra CHECKERS / DECODERS 7.2 7.3 Gates Gates can have more than 2 inputs
7.1 Unit 7 Minterm and Canonical Sums 2- and 3-Variable Boolean Algebra Theorems DeMorgan's Theorem Simplification using Boolean Algebra CHECKERS / DECODERS 7.2 7.3 Gates Gates can have more than 2 inputs
04. What is the Mod number of the counter circuit shown below? Assume initially reset.
 . Which of the following is the state diagram for the Meale machine shown below. 4. What is the Mod number of the counter circuit shown below? Assume initiall reset. input CLK D output D D a. b. / / /
. Which of the following is the state diagram for the Meale machine shown below. 4. What is the Mod number of the counter circuit shown below? Assume initiall reset. input CLK D output D D a. b. / / /
Math 123 Summary of Important Algebra & Trigonometry Concepts Chapter 1 & Appendix D, Stewart, Calculus Early Transcendentals
 Math Summar of Important Algebra & Trigonometr Concepts Chapter & Appendi D, Stewart, Calculus Earl Transcendentals Function a rule that assigns to each element in a set D eactl one element, called f (
Math Summar of Important Algebra & Trigonometr Concepts Chapter & Appendi D, Stewart, Calculus Earl Transcendentals Function a rule that assigns to each element in a set D eactl one element, called f (
1. For the following sub-problems, consider the following context-free grammar: S AB$ (1) A xax (2) A B (3) B yby (5) B A (6)
 ECE 468 & 573 Problem Set 2: Contet-free Grammars, Parsers 1. For the following sub-problems, consider the following contet-free grammar: S AB$ (1) A A (2) A B (3) A λ (4) B B (5) B A (6) B λ (7) (a) What
ECE 468 & 573 Problem Set 2: Contet-free Grammars, Parsers 1. For the following sub-problems, consider the following contet-free grammar: S AB$ (1) A A (2) A B (3) A λ (4) B B (5) B A (6) B λ (7) (a) What
Section 8.5 Parametric Equations
 504 Chapter 8 Section 8.5 Parametric Equations Man shapes, even ones as simple as circles, cannot be represented as an equation where is a function of. Consider, for eample, the path a moon follows as
504 Chapter 8 Section 8.5 Parametric Equations Man shapes, even ones as simple as circles, cannot be represented as an equation where is a function of. Consider, for eample, the path a moon follows as
Outcomes. Spiral 1 / Unit 2. Boolean Algebra BOOLEAN ALGEBRA INTRO. Basic Boolean Algebra Logic Functions Decoders Multiplexers
 -2. -2.2 piral / Unit 2 Basic Boolean Algebra Logic Functions Decoders Multipleers Mark Redekopp Outcomes I know the difference between combinational and sequential logic and can name eamples of each.
-2. -2.2 piral / Unit 2 Basic Boolean Algebra Logic Functions Decoders Multipleers Mark Redekopp Outcomes I know the difference between combinational and sequential logic and can name eamples of each.
Biostatistics in Research Practice - Regression I
 Biostatistics in Research Practice - Regression I Simon Crouch 30th Januar 2007 In scientific studies, we often wish to model the relationships between observed variables over a sample of different subjects.
Biostatistics in Research Practice - Regression I Simon Crouch 30th Januar 2007 In scientific studies, we often wish to model the relationships between observed variables over a sample of different subjects.
10.2 The Unit Circle: Cosine and Sine
 0. The Unit Circle: Cosine and Sine 77 0. The Unit Circle: Cosine and Sine In Section 0.., we introduced circular motion and derived a formula which describes the linear velocit of an object moving on
0. The Unit Circle: Cosine and Sine 77 0. The Unit Circle: Cosine and Sine In Section 0.., we introduced circular motion and derived a formula which describes the linear velocit of an object moving on
We have examined power functions like f (x) = x 2. Interchanging x
 CHAPTER 5 Eponential and Logarithmic Functions We have eamined power functions like f =. Interchanging and ields a different function f =. This new function is radicall different from a power function
CHAPTER 5 Eponential and Logarithmic Functions We have eamined power functions like f =. Interchanging and ields a different function f =. This new function is radicall different from a power function
ES.1803 Topic 16 Notes Jeremy Orloff
 ES803 Topic 6 Notes Jerem Orloff 6 Eigenalues, diagonalization, decoupling This note coers topics that will take us seeral classes to get through We will look almost eclusiel at 2 2 matrices These hae
ES803 Topic 6 Notes Jerem Orloff 6 Eigenalues, diagonalization, decoupling This note coers topics that will take us seeral classes to get through We will look almost eclusiel at 2 2 matrices These hae
Roberto s Notes on Integral Calculus Chapter 3: Basics of differential equations Section 3. Separable ODE s
 Roberto s Notes on Integral Calculus Chapter 3: Basics of differential equations Section 3 Separable ODE s What ou need to know alread: What an ODE is and how to solve an eponential ODE. What ou can learn
Roberto s Notes on Integral Calculus Chapter 3: Basics of differential equations Section 3 Separable ODE s What ou need to know alread: What an ODE is and how to solve an eponential ODE. What ou can learn
Learning From Data Lecture 7 Approximation Versus Generalization
 Learning From Data Lecture 7 Approimation Versus Generalization The VC Dimension Approimation Versus Generalization Bias and Variance The Learning Curve M. Magdon-Ismail CSCI 4100/6100 recap: The Vapnik-Chervonenkis
Learning From Data Lecture 7 Approimation Versus Generalization The VC Dimension Approimation Versus Generalization Bias and Variance The Learning Curve M. Magdon-Ismail CSCI 4100/6100 recap: The Vapnik-Chervonenkis
Mathematics 309 Conic sections and their applicationsn. Chapter 2. Quadric figures. ai,j x i x j + b i x i + c =0. 1. Coordinate changes
 Mathematics 309 Conic sections and their applicationsn Chapter 2. Quadric figures In this chapter want to outline quickl how to decide what figure associated in 2D and 3D to quadratic equations look like.
Mathematics 309 Conic sections and their applicationsn Chapter 2. Quadric figures In this chapter want to outline quickl how to decide what figure associated in 2D and 3D to quadratic equations look like.
FACULTY OF MATHEMATICAL STUDIES MATHEMATICS FOR PART I ENGINEERING. Lectures AB = BA = I,
 FACULTY OF MATHEMATICAL STUDIES MATHEMATICS FOR PART I ENGINEERING Lectures MODULE 7 MATRICES II Inverse of a matri Sstems of linear equations Solution of sets of linear equations elimination methods 4
FACULTY OF MATHEMATICAL STUDIES MATHEMATICS FOR PART I ENGINEERING Lectures MODULE 7 MATRICES II Inverse of a matri Sstems of linear equations Solution of sets of linear equations elimination methods 4
Functions. Introduction
 Functions,00 P,000 00 0 70 7 80 8 0 000 00 00 Figure Standard and Poor s Inde with dividends reinvested (credit "bull": modification of work b Praitno Hadinata; credit "graph": modification of work b MeasuringWorth)
Functions,00 P,000 00 0 70 7 80 8 0 000 00 00 Figure Standard and Poor s Inde with dividends reinvested (credit "bull": modification of work b Praitno Hadinata; credit "graph": modification of work b MeasuringWorth)
Green s Theorem Jeremy Orloff
 Green s Theorem Jerem Orloff Line integrals and Green s theorem. Vector Fields Vector notation. In 8.4 we will mostl use the notation (v) = (a, b) for vectors. The other common notation (v) = ai + bj runs
Green s Theorem Jerem Orloff Line integrals and Green s theorem. Vector Fields Vector notation. In 8.4 we will mostl use the notation (v) = (a, b) for vectors. The other common notation (v) = ai + bj runs
Ch 5 Alg 2 L2 Note Sheet Key Do Activity 1 on your Ch 5 Activity Sheet.
 Ch Alg L Note Sheet Ke Do Activit 1 on our Ch Activit Sheet. Chapter : Quadratic Equations and Functions.1 Modeling Data With Quadratic Functions You had three forms for linear equations, ou will have
Ch Alg L Note Sheet Ke Do Activit 1 on our Ch Activit Sheet. Chapter : Quadratic Equations and Functions.1 Modeling Data With Quadratic Functions You had three forms for linear equations, ou will have
8.1 Exponents and Roots
 Section 8. Eponents and Roots 75 8. Eponents and Roots Before defining the net famil of functions, the eponential functions, we will need to discuss eponent notation in detail. As we shall see, eponents
Section 8. Eponents and Roots 75 8. Eponents and Roots Before defining the net famil of functions, the eponential functions, we will need to discuss eponent notation in detail. As we shall see, eponents
Total time is: 1 setup, 2 AND, 3 XOR, 1 delay = (1*1) + (2*2) + (3*3) + (1*1) = 15ns
 Clock Period/ Delay Analysis: Find longest possible path (time-wise) between two flip-flops. If 2ns for AND and 3ns for XOR, with T delayff = 1ns and T setupff = 1 ns. So the total time is: 1 setupff +
Clock Period/ Delay Analysis: Find longest possible path (time-wise) between two flip-flops. If 2ns for AND and 3ns for XOR, with T delayff = 1ns and T setupff = 1 ns. So the total time is: 1 setupff +
CSE 140: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems. Lecture 9: Sequential Networks: Implementation
 CSE 4: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems Lecture 9: Sequential Networks: Implementation CK Cheng Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering University of California, San Diego Implementation
CSE 4: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems Lecture 9: Sequential Networks: Implementation CK Cheng Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering University of California, San Diego Implementation
Let s now begin to formalize our analysis of sequential machines Powerful methods for designing machines for System control Pattern recognition Etc.
 Finite State Machines Introduction Let s now begin to formalize our analysis of sequential machines Powerful methods for designing machines for System control Pattern recognition Etc. Such devices form
Finite State Machines Introduction Let s now begin to formalize our analysis of sequential machines Powerful methods for designing machines for System control Pattern recognition Etc. Such devices form
SOLVING SYSTEMS OF EQUATIONS
 SOLVING SYSTEMS OF EQUATIONS 4.. 4..4 Students have been solving equations even before Algebra. Now the focus on what a solution means, both algebraicall and graphicall. B understanding the nature of solutions,
SOLVING SYSTEMS OF EQUATIONS 4.. 4..4 Students have been solving equations even before Algebra. Now the focus on what a solution means, both algebraicall and graphicall. B understanding the nature of solutions,
5.4 dividing POlynOmIAlS
 SECTION 5.4 dividing PolNomiAls 3 9 3 learning ObjeCTIveS In this section, ou will: Use long division to divide polnomials. Use snthetic division to divide polnomials. 5.4 dividing POlnOmIAlS Figure 1
SECTION 5.4 dividing PolNomiAls 3 9 3 learning ObjeCTIveS In this section, ou will: Use long division to divide polnomials. Use snthetic division to divide polnomials. 5.4 dividing POlnOmIAlS Figure 1
Review Topics for MATH 1400 Elements of Calculus Table of Contents
 Math 1400 - Mano Table of Contents - Review - page 1 of 2 Review Topics for MATH 1400 Elements of Calculus Table of Contents MATH 1400 Elements of Calculus is one of the Marquette Core Courses for Mathematical
Math 1400 - Mano Table of Contents - Review - page 1 of 2 Review Topics for MATH 1400 Elements of Calculus Table of Contents MATH 1400 Elements of Calculus is one of the Marquette Core Courses for Mathematical
Solutions to Two Interesting Problems
 Solutions to Two Interesting Problems Save the Lemming On each square of an n n chessboard is an arrow pointing to one of its eight neighbors (or off the board, if it s an edge square). However, arrows
Solutions to Two Interesting Problems Save the Lemming On each square of an n n chessboard is an arrow pointing to one of its eight neighbors (or off the board, if it s an edge square). However, arrows
INTRODUCTION TO DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS
 INTRODUCTION TO DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS. Definitions and Terminolog. Initial-Value Problems.3 Differential Equations as Mathematical Models CHAPTER IN REVIEW The words differential and equations certainl
INTRODUCTION TO DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS. Definitions and Terminolog. Initial-Value Problems.3 Differential Equations as Mathematical Models CHAPTER IN REVIEW The words differential and equations certainl
Lecture 8: Sequential Networks and Finite State Machines
 Lecture 8: Sequential Networks and Finite State Machines CSE 140: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems Spring 2014 CK Cheng, Diba Mirza Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering University
Lecture 8: Sequential Networks and Finite State Machines CSE 140: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems Spring 2014 CK Cheng, Diba Mirza Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering University
Chapter 8 Notes SN AA U2C8
 Chapter 8 Notes SN AA U2C8 Name Period Section 8-: Eploring Eponential Models Section 8-2: Properties of Eponential Functions In Chapter 7, we used properties of eponents to determine roots and some of
Chapter 8 Notes SN AA U2C8 Name Period Section 8-: Eploring Eponential Models Section 8-2: Properties of Eponential Functions In Chapter 7, we used properties of eponents to determine roots and some of
Introduction to CMOS VLSI Design. Lecture 5: Logical Effort. David Harris. Harvey Mudd College Spring Outline
 Introduction to CMOS VLSI Design Lecture 5: Logical Effort David Harris Harve Mudd College Spring 00 Outline Introduction Dela in a Logic Gate Multistage Logic Networks Choosing the Best Number of Stages
Introduction to CMOS VLSI Design Lecture 5: Logical Effort David Harris Harve Mudd College Spring 00 Outline Introduction Dela in a Logic Gate Multistage Logic Networks Choosing the Best Number of Stages
Analytic Trigonometry
 CHAPTER 5 Analtic Trigonometr 5. Fundamental Identities 5. Proving Trigonometric Identities 5.3 Sum and Difference Identities 5.4 Multiple-Angle Identities 5.5 The Law of Sines 5.6 The Law of Cosines It
CHAPTER 5 Analtic Trigonometr 5. Fundamental Identities 5. Proving Trigonometric Identities 5.3 Sum and Difference Identities 5.4 Multiple-Angle Identities 5.5 The Law of Sines 5.6 The Law of Cosines It
Unit 2 Notes Packet on Quadratic Functions and Factoring
 Name: Period: Unit Notes Packet on Quadratic Functions and Factoring Notes #: Graphing quadratic equations in standard form, verte form, and intercept form. A. Intro to Graphs of Quadratic Equations: a
Name: Period: Unit Notes Packet on Quadratic Functions and Factoring Notes #: Graphing quadratic equations in standard form, verte form, and intercept form. A. Intro to Graphs of Quadratic Equations: a
Unit 3 NOTES Honors Common Core Math 2 1. Day 1: Properties of Exponents
 Unit NOTES Honors Common Core Math Da : Properties of Eponents Warm-Up: Before we begin toda s lesson, how much do ou remember about eponents? Use epanded form to write the rules for the eponents. OBJECTIVE
Unit NOTES Honors Common Core Math Da : Properties of Eponents Warm-Up: Before we begin toda s lesson, how much do ou remember about eponents? Use epanded form to write the rules for the eponents. OBJECTIVE
Mark Redekopp, All rights reserved. Lecture 4 Slides. Boolean Algebra Logic Functions Canonical Sums/Products
 Lecture 4 Slides Boolean Algebra Logic Functions Canonical Sums/Products LOGIC FUNCTION REPRESENTATION Logic Functions A logic function maps input combinations to an output value ( 1 or ) 3 possible representations
Lecture 4 Slides Boolean Algebra Logic Functions Canonical Sums/Products LOGIC FUNCTION REPRESENTATION Logic Functions A logic function maps input combinations to an output value ( 1 or ) 3 possible representations
ES.182A Topic 36 Notes Jeremy Orloff
 ES.82A Topic 36 Notes Jerem Orloff 36 Vector fields and line integrals in the plane 36. Vector analsis We now will begin our stud of the part of 8.2 called vector analsis. This is the stud of vector fields
ES.82A Topic 36 Notes Jerem Orloff 36 Vector fields and line integrals in the plane 36. Vector analsis We now will begin our stud of the part of 8.2 called vector analsis. This is the stud of vector fields
5.3.3 The general solution for plane waves incident on a layered halfspace. The general solution to the Helmholz equation in rectangular coordinates
 5.3.3 The general solution for plane waves incident on a laered halfspace The general solution to the elmhol equation in rectangular coordinates The vector propagation constant Vector relationships between
5.3.3 The general solution for plane waves incident on a laered halfspace The general solution to the elmhol equation in rectangular coordinates The vector propagation constant Vector relationships between
1.5. Analyzing Graphs of Functions. The Graph of a Function. What you should learn. Why you should learn it. 54 Chapter 1 Functions and Their Graphs
 0_005.qd /7/05 8: AM Page 5 5 Chapter Functions and Their Graphs.5 Analzing Graphs of Functions What ou should learn Use the Vertical Line Test for functions. Find the zeros of functions. Determine intervals
0_005.qd /7/05 8: AM Page 5 5 Chapter Functions and Their Graphs.5 Analzing Graphs of Functions What ou should learn Use the Vertical Line Test for functions. Find the zeros of functions. Determine intervals
2.2 Equations of Lines
 660_ch0pp07668.qd 10/16/08 4:1 PM Page 96 96 CHAPTER Linear Functions and Equations. Equations of Lines Write the point-slope and slope-intercept forms Find the intercepts of a line Write equations for
660_ch0pp07668.qd 10/16/08 4:1 PM Page 96 96 CHAPTER Linear Functions and Equations. Equations of Lines Write the point-slope and slope-intercept forms Find the intercepts of a line Write equations for
2.3 Quadratic Functions
 88 Linear and Quadratic Functions. Quadratic Functions You ma recall studing quadratic equations in Intermediate Algebra. In this section, we review those equations in the contet of our net famil of functions:
88 Linear and Quadratic Functions. Quadratic Functions You ma recall studing quadratic equations in Intermediate Algebra. In this section, we review those equations in the contet of our net famil of functions:
a. plotting points in Cartesian coordinates (Grade 9 and 10), b. using a graphing calculator such as the TI-83 Graphing Calculator,
 GRADE PRE-CALCULUS UNIT C: QUADRATIC FUNCTIONS CLASS NOTES FRAME. After linear functions, = m + b, and their graph the Quadratic Functions are the net most important equation or function. The Quadratic
GRADE PRE-CALCULUS UNIT C: QUADRATIC FUNCTIONS CLASS NOTES FRAME. After linear functions, = m + b, and their graph the Quadratic Functions are the net most important equation or function. The Quadratic
Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Wisconsin Madison. Fall Midterm Examination CLOSED BOOK
 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Wisconsin Madison ECE 553: Testing and Testable Design of Digital Systems Fall 203-204 Midterm Examination CLOSED OOK Kewal K. Saluja Date:
Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Wisconsin Madison ECE 553: Testing and Testable Design of Digital Systems Fall 203-204 Midterm Examination CLOSED OOK Kewal K. Saluja Date:
5.6 RATIOnAl FUnCTIOnS. Using Arrow notation. learning ObjeCTIveS
 CHAPTER PolNomiAl ANd rational functions learning ObjeCTIveS In this section, ou will: Use arrow notation. Solve applied problems involving rational functions. Find the domains of rational functions. Identif
CHAPTER PolNomiAl ANd rational functions learning ObjeCTIveS In this section, ou will: Use arrow notation. Solve applied problems involving rational functions. Find the domains of rational functions. Identif
Sequential Circuit Design
 Sequential Circuit esign esign Procedure. Specification 2. Formulation Obtain a state diagram or state table 3. State Assignment Assign binary codes to the states 4. Flip-Flop Input Equation etermination
Sequential Circuit esign esign Procedure. Specification 2. Formulation Obtain a state diagram or state table 3. State Assignment Assign binary codes to the states 4. Flip-Flop Input Equation etermination
Math-2. Lesson:1-2 Properties of Exponents
 Math- Lesson:- Properties of Eponents Properties of Eponents What is a power? Power: An epression formed b repeated multiplication of the same factor. Coefficient Base Eponent The eponent applies to the
Math- Lesson:- Properties of Eponents Properties of Eponents What is a power? Power: An epression formed b repeated multiplication of the same factor. Coefficient Base Eponent The eponent applies to the
UNIVERSITY OF BOLTON SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING BENG (HONS) ELECTRICAL & ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING EXAMINATION SEMESTER /2017
 UNIVERSITY OF BOLTON TW35 SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING BENG (HONS) ELECTRICAL & ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING EXAMINATION SEMESTER 2-2016/2017 INTERMEDIATE DIGITAL ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATIONS MODULE NO: EEE5002
UNIVERSITY OF BOLTON TW35 SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING BENG (HONS) ELECTRICAL & ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING EXAMINATION SEMESTER 2-2016/2017 INTERMEDIATE DIGITAL ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATIONS MODULE NO: EEE5002
Boolean Algebra and Logic Gates
 Boolean Algebra and Logic Gates Prof. Wangrok Oh Dept. of Information Communications Eng. Chungnam National Universit Prof. Wangrok Oh(CNU) / 5 Overview Aiomatic Definition of Boolean Algebra 2 Basic Theorems
Boolean Algebra and Logic Gates Prof. Wangrok Oh Dept. of Information Communications Eng. Chungnam National Universit Prof. Wangrok Oh(CNU) / 5 Overview Aiomatic Definition of Boolean Algebra 2 Basic Theorems
ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT, OAKLAND UNIVERSITY ECE-2700: Digital Logic Design Winter Notes - Unit 2
 ECE-7: Digital Logic Design Winter 8 Notes - Unit OPTIMIZED IMPLEMENTATION OF LOGIC FUNCTIONS BASIC TECHNIQUES: We can alas minimie logic unctions using the Boolean theorems. Hoever, more poerul methods
ECE-7: Digital Logic Design Winter 8 Notes - Unit OPTIMIZED IMPLEMENTATION OF LOGIC FUNCTIONS BASIC TECHNIQUES: We can alas minimie logic unctions using the Boolean theorems. Hoever, more poerul methods
Polynomial and Rational Functions
 Polnomial and Rational Functions 5 Figure 1 35-mm film, once the standard for capturing photographic images, has been made largel obsolete b digital photograph. (credit film : modification of work b Horia
Polnomial and Rational Functions 5 Figure 1 35-mm film, once the standard for capturing photographic images, has been made largel obsolete b digital photograph. (credit film : modification of work b Horia
10.5 Graphs of the Trigonometric Functions
 790 Foundations of Trigonometr 0.5 Graphs of the Trigonometric Functions In this section, we return to our discussion of the circular (trigonometric functions as functions of real numbers and pick up where
790 Foundations of Trigonometr 0.5 Graphs of the Trigonometric Functions In this section, we return to our discussion of the circular (trigonometric functions as functions of real numbers and pick up where
6 Synchronous State Machine Design
 Design of synchronous counters. Based on the description of the problem, determine the required number n of the FFs - the smallest value of n is such that the number of states N 2 n and the desired counting
Design of synchronous counters. Based on the description of the problem, determine the required number n of the FFs - the smallest value of n is such that the number of states N 2 n and the desired counting
Combinational Logic Design
 PEN 35 - igital System esign ombinational Logic esign hapter 3 Logic and omputer esign Fundamentals, 4 rd Ed., Mano 2008 Pearson Prentice Hall esign oncepts and utomation top-down design proceeds from
PEN 35 - igital System esign ombinational Logic esign hapter 3 Logic and omputer esign Fundamentals, 4 rd Ed., Mano 2008 Pearson Prentice Hall esign oncepts and utomation top-down design proceeds from
13.2 Solving Larger Systems by Gaussian Elimination
 . Solving Larger Sstems b Gaussian Elimination Now we want to learn how to solve sstems of equations that have more that two variables. We start with the following definition. Definition: Row echelon form
. Solving Larger Sstems b Gaussian Elimination Now we want to learn how to solve sstems of equations that have more that two variables. We start with the following definition. Definition: Row echelon form
CARLETON UNIVERSITY Final EXAMINATION April 16, 2003
 LTN UNIVSIT Final MINTIN pril 6, 23 Name: Number: Signature: UTIN: HUS No. of Student: epartment Name & ourse Number: ourse Instructor(s) UTHI MMN 3 4 lectronic ngineering L267, and Profs. N. Tait and
LTN UNIVSIT Final MINTIN pril 6, 23 Name: Number: Signature: UTIN: HUS No. of Student: epartment Name & ourse Number: ourse Instructor(s) UTHI MMN 3 4 lectronic ngineering L267, and Profs. N. Tait and
15.1 Elimination of Redundant States
 15.1 Elimination of Redundant States In Ch. 14 we tried not to have unnecessary states What if we have extra states in the state graph/table? Complete the table then eliminate the redundant states Chapter
15.1 Elimination of Redundant States In Ch. 14 we tried not to have unnecessary states What if we have extra states in the state graph/table? Complete the table then eliminate the redundant states Chapter
FYSE420 DIGITAL ELECTRONICS
 FYSE42 IGITAL ELECTRONICS Lecture 4 [] [2] [3] IGITAL LOGIC CIRCUIT ANALYSIS & ESIGN Nelson, Nagle, Irvin, Carrol ISBN -3-463894-8 IGITAL ESIGN Morris Mano Fourth edition ISBN -3-98924-3 igital esign Principles
FYSE42 IGITAL ELECTRONICS Lecture 4 [] [2] [3] IGITAL LOGIC CIRCUIT ANALYSIS & ESIGN Nelson, Nagle, Irvin, Carrol ISBN -3-463894-8 IGITAL ESIGN Morris Mano Fourth edition ISBN -3-98924-3 igital esign Principles
Chapter 5: Quadratic Equations and Functions 5.1 Modeling Data With Quadratic Functions Quadratic Functions and Their Graphs
 Ch 5 Alg Note Sheet Ke Chapter 5: Quadratic Equations and Functions 5.1 Modeling Data With Quadratic Functions Quadratic Functions and Their Graphs Definition: Standard Form of a Quadratic Function The
Ch 5 Alg Note Sheet Ke Chapter 5: Quadratic Equations and Functions 5.1 Modeling Data With Quadratic Functions Quadratic Functions and Their Graphs Definition: Standard Form of a Quadratic Function The
Linear Equation Theory - 2
 Algebra Module A46 Linear Equation Theor - Copright This publication The Northern Alberta Institute of Technolog 00. All Rights Reserved. LAST REVISED June., 009 Linear Equation Theor - Statement of Prerequisite
Algebra Module A46 Linear Equation Theor - Copright This publication The Northern Alberta Institute of Technolog 00. All Rights Reserved. LAST REVISED June., 009 Linear Equation Theor - Statement of Prerequisite
Lecture 10: Synchronous Sequential Circuits Design
 Lecture 0: Synchronous Sequential Circuits Design. General Form Input Combinational Flip-flops Combinational Output Circuit Circuit Clock.. Moore type has outputs dependent only on the state, e.g. ripple
Lecture 0: Synchronous Sequential Circuits Design. General Form Input Combinational Flip-flops Combinational Output Circuit Circuit Clock.. Moore type has outputs dependent only on the state, e.g. ripple
Ch 3 Alg 2 Note Sheet.doc 3.1 Graphing Systems of Equations
 Ch 3 Alg Note Sheet.doc 3.1 Graphing Sstems of Equations Sstems of Linear Equations A sstem of equations is a set of two or more equations that use the same variables. If the graph of each equation =.4
Ch 3 Alg Note Sheet.doc 3.1 Graphing Sstems of Equations Sstems of Linear Equations A sstem of equations is a set of two or more equations that use the same variables. If the graph of each equation =.4
5 State Minimisation. university of applied sciences hamburg. Digital Systems. Prof. Dr. J. Reichardt Prof. Dr. B. Schwarz
 5 State Minimisation In an early design phase when a word description of a sequential circuit's function is transformed into a FSM state diagram or state table redundant states may arise. State minimisation
5 State Minimisation In an early design phase when a word description of a sequential circuit's function is transformed into a FSM state diagram or state table redundant states may arise. State minimisation
ECEN 248: INTRODUCTION TO DIGITAL SYSTEMS DESIGN. Week 9 Dr. Srinivas Shakkottai Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering
 ECEN 248: INTRODUCTION TO DIGITAL SYSTEMS DESIGN Week 9 Dr. Srinivas Shakkottai Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering TIMING ANALYSIS Overview Circuits do not respond instantaneously to input changes
ECEN 248: INTRODUCTION TO DIGITAL SYSTEMS DESIGN Week 9 Dr. Srinivas Shakkottai Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering TIMING ANALYSIS Overview Circuits do not respond instantaneously to input changes
11.4 Polar Coordinates
 11. Polar Coordinates 917 11. Polar Coordinates In Section 1.1, we introduced the Cartesian coordinates of a point in the plane as a means of assigning ordered pairs of numbers to points in the plane.
11. Polar Coordinates 917 11. Polar Coordinates In Section 1.1, we introduced the Cartesian coordinates of a point in the plane as a means of assigning ordered pairs of numbers to points in the plane.
Section 3.1. ; X = (0, 1]. (i) f : R R R, f (x, y) = x y
![Section 3.1. ; X = (0, 1]. (i) f : R R R, f (x, y) = x y Section 3.1. ; X = (0, 1]. (i) f : R R R, f (x, y) = x y](/thumbs/83/88503328.jpg) Paul J. Bruillard MATH 0.970 Problem Set 6 An Introduction to Abstract Mathematics R. Bond and W. Keane Section 3.1: 3b,c,e,i, 4bd, 6, 9, 15, 16, 18c,e, 19a, 0, 1b Section 3.: 1f,i, e, 6, 1e,f,h, 13e,
Paul J. Bruillard MATH 0.970 Problem Set 6 An Introduction to Abstract Mathematics R. Bond and W. Keane Section 3.1: 3b,c,e,i, 4bd, 6, 9, 15, 16, 18c,e, 19a, 0, 1b Section 3.: 1f,i, e, 6, 1e,f,h, 13e,
DIGITAL LOGIC CIRCUITS
 DIGITAL LOGIC CIRCUITS Introduction Logic Gates Boolean Algebra Map Specification Combinational Circuits Flip-Flops Sequential Circuits Memor Components Integrated Circuits BASIC LOGIC BLOCK - GATE - Logic
DIGITAL LOGIC CIRCUITS Introduction Logic Gates Boolean Algebra Map Specification Combinational Circuits Flip-Flops Sequential Circuits Memor Components Integrated Circuits BASIC LOGIC BLOCK - GATE - Logic
Math Lesson 2-2 Properties of Exponents
 Math-00 Lesson - Properties of Eponents Properties of Eponents What is a power? Power: An epression formed b repeated multiplication of the base. Coefficient Base Eponent The eponent applies to the number
Math-00 Lesson - Properties of Eponents Properties of Eponents What is a power? Power: An epression formed b repeated multiplication of the base. Coefficient Base Eponent The eponent applies to the number
Conservation of Linear Momentum
 Conservation of Linear Momentum Once we have determined the continuit equation in di erential form we proceed to derive the momentum equation in di erential form. We start b writing the integral form of
Conservation of Linear Momentum Once we have determined the continuit equation in di erential form we proceed to derive the momentum equation in di erential form. We start b writing the integral form of
THE UNIVERSITY OF MICHIGAN. Timing Analysis of Domino Logic
 Timing Analsis of Domino Logic b David Van Campenhout, Trevor Mudge and Karem Sakallah CSE-T-296-96 THE UNIVESITY O MICHIGAN Computer Science and Engineering Division Department of Electrical Engineering
Timing Analsis of Domino Logic b David Van Campenhout, Trevor Mudge and Karem Sakallah CSE-T-296-96 THE UNIVESITY O MICHIGAN Computer Science and Engineering Division Department of Electrical Engineering
MATH Line integrals III Fall The fundamental theorem of line integrals. In general C
 MATH 255 Line integrals III Fall 216 In general 1. The fundamental theorem of line integrals v T ds depends on the curve between the starting point and the ending point. onsider two was to get from (1,
MATH 255 Line integrals III Fall 216 In general 1. The fundamental theorem of line integrals v T ds depends on the curve between the starting point and the ending point. onsider two was to get from (1,
Eigenvectors and Eigenvalues 1
 Ma 2015 page 1 Eigenvectors and Eigenvalues 1 In this handout, we will eplore eigenvectors and eigenvalues. We will begin with an eploration, then provide some direct eplanation and worked eamples, and
Ma 2015 page 1 Eigenvectors and Eigenvalues 1 In this handout, we will eplore eigenvectors and eigenvalues. We will begin with an eploration, then provide some direct eplanation and worked eamples, and
Linear Relationships
 Linear Relationships Curriculum Read www.mathletics.com Basics Page questions. Draw the following lines on the provided aes: a Line with -intercept and -intercept -. The -intercept is ( 0and, ) the -intercept
Linear Relationships Curriculum Read www.mathletics.com Basics Page questions. Draw the following lines on the provided aes: a Line with -intercept and -intercept -. The -intercept is ( 0and, ) the -intercept
Cubic and quartic functions
 3 Cubic and quartic functions 3A Epanding 3B Long division of polnomials 3C Polnomial values 3D The remainder and factor theorems 3E Factorising polnomials 3F Sum and difference of two cubes 3G Solving
3 Cubic and quartic functions 3A Epanding 3B Long division of polnomials 3C Polnomial values 3D The remainder and factor theorems 3E Factorising polnomials 3F Sum and difference of two cubes 3G Solving
Q: Examine the relationship between X and the Next state. How would you describe this circuit? A: An inverter which is synched with a clock signal.
 /2/2 OF 7 Next, let s reverse engineer a T-Flip flop Prob. (Pg 529) Note that whenever T is equal to, there is a state change, otherwise, there isn t. In this circuit, (x) determines whether the output
/2/2 OF 7 Next, let s reverse engineer a T-Flip flop Prob. (Pg 529) Note that whenever T is equal to, there is a state change, otherwise, there isn t. In this circuit, (x) determines whether the output
3.2 LOGARITHMIC FUNCTIONS AND THEIR GRAPHS
 Section. Logarithmic Functions and Their Graphs 7. LOGARITHMIC FUNCTIONS AND THEIR GRAPHS Ariel Skelle/Corbis What ou should learn Recognize and evaluate logarithmic functions with base a. Graph logarithmic
Section. Logarithmic Functions and Their Graphs 7. LOGARITHMIC FUNCTIONS AND THEIR GRAPHS Ariel Skelle/Corbis What ou should learn Recognize and evaluate logarithmic functions with base a. Graph logarithmic
Laurie s Notes. Overview of Section 3.5
 Overview of Section.5 Introduction Sstems of linear equations were solved in Algebra using substitution, elimination, and graphing. These same techniques are applied to nonlinear sstems in this lesson.
Overview of Section.5 Introduction Sstems of linear equations were solved in Algebra using substitution, elimination, and graphing. These same techniques are applied to nonlinear sstems in this lesson.
ES.182A Topic 41 Notes Jeremy Orloff. 41 Extensions and applications of Green s theorem
 ES.182A Topic 41 Notes Jerem Orloff 41 Etensions and applications of Green s theorem 41.1 eview of Green s theorem: Tangential (work) form: F T ds = curlf d d M d + N d = N M d d. Normal (flu) form: F
ES.182A Topic 41 Notes Jerem Orloff 41 Etensions and applications of Green s theorem 41.1 eview of Green s theorem: Tangential (work) form: F T ds = curlf d d M d + N d = N M d d. Normal (flu) form: F
Mealy & Moore Machines
 Mealy & Moore Machines Moore Machine is a finite-state machine whose output values are determined solely by its current state and can be defined as six elements (S, S 0, Σ, Λ, T, G), consisting of the
Mealy & Moore Machines Moore Machine is a finite-state machine whose output values are determined solely by its current state and can be defined as six elements (S, S 0, Σ, Λ, T, G), consisting of the
Higher. Polynomials and Quadratics. Polynomials and Quadratics 1
 Higher Mathematics Contents 1 1 Quadratics EF 1 The Discriminant EF 3 3 Completing the Square EF 4 4 Sketching Parabolas EF 7 5 Determining the Equation of a Parabola RC 9 6 Solving Quadratic Inequalities
Higher Mathematics Contents 1 1 Quadratics EF 1 The Discriminant EF 3 3 Completing the Square EF 4 4 Sketching Parabolas EF 7 5 Determining the Equation of a Parabola RC 9 6 Solving Quadratic Inequalities
