Logical design of digital systems
|
|
|
- Edith Jacobs
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 lectures Summer Semester 2017 Table of content 1 Combinational circuit design 2 Elementary combinatorial circuits for data transmission 3 Memory structures 4 Programmable logic devices 5 Algorithmic minimization approaches 51 Minimization of combinational Functions 52 State machine minimization 521 Characteristics of State Machines 522 Trivial state machine Simplification 523 Minimization according to Huffman & Mealy 524 The Moore Algorithm 6 Sequential circuit design 7 Testing digital circuits 2 1
2 State machine minimization 521 Characteristics of state machines Characteristics of state machines - Moore and Mealy Machines - 4 2
3 Characteristics of state machines - Synthesis of sequential circuits - Specify the problem, circuit behaviour Definition of In- and Output variables Derive state diagram/ state table/ type of state machine (Moore, Mealy, ) => Result: uncoded state table of a certain type of machine; eg Moore Machine State coding Calculate FF equations Design circuit for the output function Choose type of flip flop and calculate flip-flops flops input functions Design of the circuit for the state transition function Eventual transformation of the logical expressions into suitable structured expressions Application in the circuit diagram Characteristics of state machines - State machine tables - Transition Table Output Table x 1 x 2 x i x k x 1 X 2 x i x k z 1 n +1 z 2 z ij =g(x i,z j ) z j z l z 1 y ij=f(x i,z j ) z 2 z j z l 6 3
4 Characteristics of state machines - State machine tables - State transition table - of a Mealy-Machine - of a Moore Machine x 1 x 2 x i x k z 1 n+1 z 2 z ij / y ij z j z l z 1 x 1 x 2 x i x k zn+1 ij y 1 z 2 y 2 z j y u z l y v Characteristics of state machines - State transition diagramm - State tranistion table of JK-FF 1X Present State S1 S2 Input JK Out put 00 0I I0 II Q S1 S2 S2 S1 S2 S2 S1 S1 I 0 00 S1 0 X1 S J = don t care K=1 J = 0 K=0 Note, that an input that does not have any influence on a certain transition is marked with an X at the according arrow (don t care) 8 4
5 Characteristics of state machines - Timing diagrams - Z0 Z1 Z2 Z3 Z Trivial state machine minimization 10 5
6 Trivial state machine Simplification State machine minimization 523 Minimization according to Huffman & Mealy 12 6
7 State machine minimization 523 Minimization according to Huffman & Mealy Z n Z n+1 Y n Y n+1 X X State machine minimization 523 Minimization according to Huffman & Mealy 14 7
8 State machine minimization 524 Minimization according to Huffman & Mealy State machine minimization 523 Minimization according to Huffman & Mealy Z n Z n+1 Y n Y n+1 X X 0 0 I P I I I I I I I I I I I 0 Z n Z n+1 Y n Y n+1 X X 16 8
9 State machine minimization 523 Minimization according to Huffman & Mealy State machine minimization 523 Minimization according to Huffman & Mealy Z n Z n+1 Y n Y n+1 Z n Z n+1 Y n Y n+1 X X X X 18 9
Chapter 6 Introduction to state machines
 9..7 hapter 6 Introduction to state machines Dr.-Ing. Stefan Werner Table of content hapter : Switching Algebra hapter : Logical Levels, Timing & Delays hapter 3: Karnaugh-Veitch-Maps hapter 4: ombinational
9..7 hapter 6 Introduction to state machines Dr.-Ing. Stefan Werner Table of content hapter : Switching Algebra hapter : Logical Levels, Timing & Delays hapter 3: Karnaugh-Veitch-Maps hapter 4: ombinational
UNIVERSITY OF BOLTON SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING BENG (HONS) ELECTRICAL & ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING EXAMINATION SEMESTER /2017
 UNIVERSITY OF BOLTON TW35 SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING BENG (HONS) ELECTRICAL & ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING EXAMINATION SEMESTER 2-2016/2017 INTERMEDIATE DIGITAL ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATIONS MODULE NO: EEE5002
UNIVERSITY OF BOLTON TW35 SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING BENG (HONS) ELECTRICAL & ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING EXAMINATION SEMESTER 2-2016/2017 INTERMEDIATE DIGITAL ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATIONS MODULE NO: EEE5002
Finite State Machine. By : Ali Mustafa
 Finite State Machine By : Ali Mustafa So Far We have covered the memory elements issue and we are ready to implement the sequential circuits. We need to know how to Deal(analyze) with a sequential circuit?
Finite State Machine By : Ali Mustafa So Far We have covered the memory elements issue and we are ready to implement the sequential circuits. We need to know how to Deal(analyze) with a sequential circuit?
ECE380 Digital Logic. Synchronous sequential circuits
 ECE38 Digital Logic Synchronous Sequential Circuits: State Diagrams, State Tables Dr. D. J. Jackson Lecture 27- Synchronous sequential circuits Circuits here a clock signal is used to control operation
ECE38 Digital Logic Synchronous Sequential Circuits: State Diagrams, State Tables Dr. D. J. Jackson Lecture 27- Synchronous sequential circuits Circuits here a clock signal is used to control operation
Lecture 10: Synchronous Sequential Circuits Design
 Lecture 0: Synchronous Sequential Circuits Design. General Form Input Combinational Flip-flops Combinational Output Circuit Circuit Clock.. Moore type has outputs dependent only on the state, e.g. ripple
Lecture 0: Synchronous Sequential Circuits Design. General Form Input Combinational Flip-flops Combinational Output Circuit Circuit Clock.. Moore type has outputs dependent only on the state, e.g. ripple
CSE 140: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems. Lecture 9: Sequential Networks: Implementation
 CSE 4: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems Lecture 9: Sequential Networks: Implementation CK Cheng Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering University of California, San Diego Implementation
CSE 4: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems Lecture 9: Sequential Networks: Implementation CK Cheng Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering University of California, San Diego Implementation
Lecture 8: Sequential Networks and Finite State Machines
 Lecture 8: Sequential Networks and Finite State Machines CSE 140: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems Spring 2014 CK Cheng, Diba Mirza Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering University
Lecture 8: Sequential Networks and Finite State Machines CSE 140: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems Spring 2014 CK Cheng, Diba Mirza Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering University
Digital Circuits and Systems
 EE201: Digital Circuits and Systems 4 Sequential Circuits page 1 of 11 EE201: Digital Circuits and Systems Section 4 Sequential Circuits 4.1 Overview of Sequential Circuits: Definition The circuit whose
EE201: Digital Circuits and Systems 4 Sequential Circuits page 1 of 11 EE201: Digital Circuits and Systems Section 4 Sequential Circuits 4.1 Overview of Sequential Circuits: Definition The circuit whose
Fundamentals of Digital Design
 Fundamentals of Digital Design Digital Radiation Measurement and Spectroscopy NE/RHP 537 1 Binary Number System The binary numeral system, or base-2 number system, is a numeral system that represents numeric
Fundamentals of Digital Design Digital Radiation Measurement and Spectroscopy NE/RHP 537 1 Binary Number System The binary numeral system, or base-2 number system, is a numeral system that represents numeric
Sequential Circuit Analysis
 Sequential Circuit Analysis Last time we started talking about latches and flip-flops, which are basic one-bit memory units. Today we ll talk about sequential circuit analysis and design. First, we ll
Sequential Circuit Analysis Last time we started talking about latches and flip-flops, which are basic one-bit memory units. Today we ll talk about sequential circuit analysis and design. First, we ll
Chapter 15 SEQUENTIAL CIRCUITS ANALYSIS, STATE- MINIMIZATION, ASSIGNMENT AND CIRCUIT IMPLEMENTATION
 Chapter 15 SEQUENTIAL CIRCUITS ANALYSIS, STATE- MINIMIZATION, ASSIGNMENT AND CIRCUIT IMPLEMENTATION Lesson 2 ANALYSIS OF CLOCKED SEQUENTIAL CIRCUIT Ch15L2- "Digital Principles and Design", Raj Kamal, Pearson
Chapter 15 SEQUENTIAL CIRCUITS ANALYSIS, STATE- MINIMIZATION, ASSIGNMENT AND CIRCUIT IMPLEMENTATION Lesson 2 ANALYSIS OF CLOCKED SEQUENTIAL CIRCUIT Ch15L2- "Digital Principles and Design", Raj Kamal, Pearson
Digital Logic and Design (Course Code: EE222) Lecture 19: Sequential Circuits Contd..
 Indian Institute of Technology Jodhpur, Year 2017-2018 Digital Logic and Design (Course Code: EE222) Lecture 19: Sequential Circuits Contd.. Course Instructor: Shree Prakash Tiwari Email: sptiwari@iitj.ac.in
Indian Institute of Technology Jodhpur, Year 2017-2018 Digital Logic and Design (Course Code: EE222) Lecture 19: Sequential Circuits Contd.. Course Instructor: Shree Prakash Tiwari Email: sptiwari@iitj.ac.in
CprE 281: Digital Logic
 CprE 281: Digital Logic Instructor: Alexander Stoytchev http://www.ece.iastate.edu/~alexs/classes/ Synchronous Sequential Circuits Basic Design Steps CprE 281: Digital Logic Iowa State University, Ames,
CprE 281: Digital Logic Instructor: Alexander Stoytchev http://www.ece.iastate.edu/~alexs/classes/ Synchronous Sequential Circuits Basic Design Steps CprE 281: Digital Logic Iowa State University, Ames,
Logical Design of Digital Systems
 Lecture 4 Table of Content 1. Combinational circuit design 2. Elementary combinatorial circuits for data transmission 3. Memory structures 4. Programmable logic devices 5. Algorithmic minimization approaches
Lecture 4 Table of Content 1. Combinational circuit design 2. Elementary combinatorial circuits for data transmission 3. Memory structures 4. Programmable logic devices 5. Algorithmic minimization approaches
The Design Procedure. Output Equation Determination - Derive output equations from the state table
 The Design Procedure Specification Formulation - Obtain a state diagram or state table State Assignment - Assign binary codes to the states Flip-Flop Input Equation Determination - Select flipflop types
The Design Procedure Specification Formulation - Obtain a state diagram or state table State Assignment - Assign binary codes to the states Flip-Flop Input Equation Determination - Select flipflop types
FSM model for sequential circuits
 1 FSM model for sequential circuits The mathematical model of a sequential circuit is called finite-state machine. FSM is fully characterized by: S Finite set of states ( state ~ contents of FFs) I Finite
1 FSM model for sequential circuits The mathematical model of a sequential circuit is called finite-state machine. FSM is fully characterized by: S Finite set of states ( state ~ contents of FFs) I Finite
CpE358/CS381. Switching Theory and Logical Design. Class 16
 CpE358/CS38 Switching Theory and Logical Design Class 6 CpE358/CS38 Summer- 24 Copyright 24-585 Today Fundamental concepts of digital systems (Mano Chapter ) inary codes, number systems, and arithmetic
CpE358/CS38 Switching Theory and Logical Design Class 6 CpE358/CS38 Summer- 24 Copyright 24-585 Today Fundamental concepts of digital systems (Mano Chapter ) inary codes, number systems, and arithmetic
ELCT201: DIGITAL LOGIC DESIGN
 ELCT201: DIGITAL LOGIC DESIGN Dr. Eng. Haitham Omran, haitham.omran@guc.edu.eg Dr. Eng. Wassim Alexan, wassim.joseph@guc.edu.eg Following the slides of Dr. Ahmed H. Madian Lecture 10 محرم 1439 ه Winter
ELCT201: DIGITAL LOGIC DESIGN Dr. Eng. Haitham Omran, haitham.omran@guc.edu.eg Dr. Eng. Wassim Alexan, wassim.joseph@guc.edu.eg Following the slides of Dr. Ahmed H. Madian Lecture 10 محرم 1439 ه Winter
Lecture 14: State Tables, Diagrams, Latches, and Flip Flop
 EE210: Switching Systems Lecture 14: State Tables, Diagrams, Latches, and Flip Flop Prof. YingLi Tian Nov. 6, 2017 Department of Electrical Engineering The City College of New York The City University
EE210: Switching Systems Lecture 14: State Tables, Diagrams, Latches, and Flip Flop Prof. YingLi Tian Nov. 6, 2017 Department of Electrical Engineering The City College of New York The City University
Lecture (08) Synchronous Sequential Logic
 Lecture (08) Synchronous Sequential Logic By: Dr. Ahmed ElShafee ١ Dr. Ahmed ElShafee, ACU : Spring 2018, CSE303 Logic design II Analysis of Clocked Sequential Circuits The behavior of a clocked sequential
Lecture (08) Synchronous Sequential Logic By: Dr. Ahmed ElShafee ١ Dr. Ahmed ElShafee, ACU : Spring 2018, CSE303 Logic design II Analysis of Clocked Sequential Circuits The behavior of a clocked sequential
FYSE420 DIGITAL ELECTRONICS
 FYSE42 IGITAL ELECTRONICS Lecture 4 [] [2] [3] IGITAL LOGIC CIRCUIT ANALYSIS & ESIGN Nelson, Nagle, Irvin, Carrol ISBN -3-463894-8 IGITAL ESIGN Morris Mano Fourth edition ISBN -3-98924-3 igital esign Principles
FYSE42 IGITAL ELECTRONICS Lecture 4 [] [2] [3] IGITAL LOGIC CIRCUIT ANALYSIS & ESIGN Nelson, Nagle, Irvin, Carrol ISBN -3-463894-8 IGITAL ESIGN Morris Mano Fourth edition ISBN -3-98924-3 igital esign Principles
ELE2120 Digital Circuits and Systems. Tutorial Note 9
 ELE2120 Digital Circuits and Systems Tutorial Note 9 Outline 1. Exercise(1) Sequential Circuit Analysis 2. Exercise (2) Sequential Circuit Analysis 3. Exercise (3) Sequential Circuit Analysis 4. Ref. Construction
ELE2120 Digital Circuits and Systems Tutorial Note 9 Outline 1. Exercise(1) Sequential Circuit Analysis 2. Exercise (2) Sequential Circuit Analysis 3. Exercise (3) Sequential Circuit Analysis 4. Ref. Construction
Mealy & Moore Machines
 Mealy & Moore Machines Moore Machine is a finite-state machine whose output values are determined solely by its current state and can be defined as six elements (S, S 0, Σ, Λ, T, G), consisting of the
Mealy & Moore Machines Moore Machine is a finite-state machine whose output values are determined solely by its current state and can be defined as six elements (S, S 0, Σ, Λ, T, G), consisting of the
 vidyarthiplus.com vidyarthiplus.com vidyarthiplus.com ANNA UNIVERSITY- COMBATORE B.E./ B.TECH. DEGREE EXAMINATION - JUNE 2009. ELECTRICAL & ELECTONICS ENGG. - FOURTH SEMESTER DIGITAL LOGIC CIRCUITS PART-A
vidyarthiplus.com vidyarthiplus.com vidyarthiplus.com ANNA UNIVERSITY- COMBATORE B.E./ B.TECH. DEGREE EXAMINATION - JUNE 2009. ELECTRICAL & ELECTONICS ENGG. - FOURTH SEMESTER DIGITAL LOGIC CIRCUITS PART-A
Chapter 14 Sequential logic, Latches and Flip-Flops
 Chapter 14 Sequential logic, Latches and Flip-Flops Flops Lesson 4 JK Flip Flop Ch14L4-"Digital Principles and Design", Raj Kamal, Pearson Education, 2006 2 JK Flip-Flop ve edge triggered Output Q and
Chapter 14 Sequential logic, Latches and Flip-Flops Flops Lesson 4 JK Flip Flop Ch14L4-"Digital Principles and Design", Raj Kamal, Pearson Education, 2006 2 JK Flip-Flop ve edge triggered Output Q and
Chapter 5 Synchronous Sequential Logic
 Chapter 5 Synchronous Sequential Logic Sequential circuit: A circuit that includes memory elements. In this case the output depends not only on the current input but also on the past inputs. Memory A synchronous
Chapter 5 Synchronous Sequential Logic Sequential circuit: A circuit that includes memory elements. In this case the output depends not only on the current input but also on the past inputs. Memory A synchronous
ECEN 248: INTRODUCTION TO DIGITAL SYSTEMS DESIGN. Week 7 Dr. Srinivas Shakkottai Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering
 ECEN 248: INTRODUCTION TO DIGITAL SYSTEMS DESIGN Week 7 Dr. Srinivas Shakkottai Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering SEQUENTIAL CIRCUITS: LATCHES Overview Circuits require memory to store intermediate
ECEN 248: INTRODUCTION TO DIGITAL SYSTEMS DESIGN Week 7 Dr. Srinivas Shakkottai Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering SEQUENTIAL CIRCUITS: LATCHES Overview Circuits require memory to store intermediate
ELEC Digital Logic Circuits Fall 2014 Sequential Circuits (Chapter 6) Finite State Machines (Ch. 7-10)
 ELEC 2200-002 Digital Logic Circuits Fall 2014 Sequential Circuits (Chapter 6) Finite State Machines (Ch. 7-10) Vishwani D. Agrawal James J. Danaher Professor Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
ELEC 2200-002 Digital Logic Circuits Fall 2014 Sequential Circuits (Chapter 6) Finite State Machines (Ch. 7-10) Vishwani D. Agrawal James J. Danaher Professor Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
14:332:231 DIGITAL LOGIC DESIGN
 14:332:231 IGITL LOGI ESIGN Ivan Marsic, Rutgers University Electrical & omputer Engineering all 2013 Lecture #17: locked Synchronous -Machine nalysis locked Synchronous Sequential ircuits lso known as
14:332:231 IGITL LOGI ESIGN Ivan Marsic, Rutgers University Electrical & omputer Engineering all 2013 Lecture #17: locked Synchronous -Machine nalysis locked Synchronous Sequential ircuits lso known as
Sequential logic and design
 Principles Of Digital Design Sequential logic and design Analysis State-based (Moore) Input-based (Mealy) FSM definition Synthesis State minimization Encoding Optimization and timing Copyright 20-20by
Principles Of Digital Design Sequential logic and design Analysis State-based (Moore) Input-based (Mealy) FSM definition Synthesis State minimization Encoding Optimization and timing Copyright 20-20by
EE 209 Logic Cumulative Exam Name:
 EE 209 Logic Cumulative Exam Name: 1.) Answer the following questions as True or False a.) A 4-to-1 multiplexer requires at least 4 select lines: true / false b.) An 8-to-1 mux and no other logi can be
EE 209 Logic Cumulative Exam Name: 1.) Answer the following questions as True or False a.) A 4-to-1 multiplexer requires at least 4 select lines: true / false b.) An 8-to-1 mux and no other logi can be
Lecture 14 Finite state machines
 Lecture 14 Finite state machines Finite state machines are the foundation of nearly all digital computation. The state diagram captures the desired system behavior A formulaic process turns this diagram
Lecture 14 Finite state machines Finite state machines are the foundation of nearly all digital computation. The state diagram captures the desired system behavior A formulaic process turns this diagram
Models for representing sequential circuits
 Sequential Circuits Models for representing sequential circuits Finite-state machines (Moore and Mealy) Representation of memory (states) Changes in state (transitions) Design procedure State diagrams
Sequential Circuits Models for representing sequential circuits Finite-state machines (Moore and Mealy) Representation of memory (states) Changes in state (transitions) Design procedure State diagrams
EEE2135 Digital Logic Design
 EEE2135 Digital Logic Design Chapter 7. Sequential Circuits Design 서강대학교 전자공학과 1. Model of Sequential Circuits 1) Sequential vs. Combinational Circuits a. Sequential circuits: Outputs depend on both the
EEE2135 Digital Logic Design Chapter 7. Sequential Circuits Design 서강대학교 전자공학과 1. Model of Sequential Circuits 1) Sequential vs. Combinational Circuits a. Sequential circuits: Outputs depend on both the
Analysis and Design of Sequential Circuits: Examples
 COSC3410 Analysis and Design of Sequential Circuits: Examples J. C. Huang Department of Computer Science University of Houston Sequential machine slide 1 inputs combinational circuit outputs memory elements
COSC3410 Analysis and Design of Sequential Circuits: Examples J. C. Huang Department of Computer Science University of Houston Sequential machine slide 1 inputs combinational circuit outputs memory elements
(Boolean Algebra, combinational circuits) (Binary Codes and -arithmetics)
 Task 1. Exercises: Logical Design of Digital Systems Seite: 1 Self Study (Boolean Algebra, combinational circuits) 1.1 Minimize the function f 1 a ab ab by the help of Boolean algebra and give an implementation
Task 1. Exercises: Logical Design of Digital Systems Seite: 1 Self Study (Boolean Algebra, combinational circuits) 1.1 Minimize the function f 1 a ab ab by the help of Boolean algebra and give an implementation
Counters. We ll look at different kinds of counters and discuss how to build them
 Counters We ll look at different kinds of counters and discuss how to build them These are not only examples of sequential analysis and design, but also real devices used in larger circuits 1 Introducing
Counters We ll look at different kinds of counters and discuss how to build them These are not only examples of sequential analysis and design, but also real devices used in larger circuits 1 Introducing
Analysis of Clocked Sequential Circuits
 Objectives Analysis of Clocked Sequential Circuits The objectives of this lesson are as follows: Analysis of clocked sequential circuits with an example State Reduction with an example State assignment
Objectives Analysis of Clocked Sequential Circuits The objectives of this lesson are as follows: Analysis of clocked sequential circuits with an example State Reduction with an example State assignment
Appendix B. Review of Digital Logic. Baback Izadi Division of Engineering Programs
 Appendix B Review of Digital Logic Baback Izadi Division of Engineering Programs bai@engr.newpaltz.edu Elect. & Comp. Eng. 2 DeMorgan Symbols NAND (A.B) = A +B NOR (A+B) = A.B AND A.B = A.B = (A +B ) OR
Appendix B Review of Digital Logic Baback Izadi Division of Engineering Programs bai@engr.newpaltz.edu Elect. & Comp. Eng. 2 DeMorgan Symbols NAND (A.B) = A +B NOR (A+B) = A.B AND A.B = A.B = (A +B ) OR
L10 State Machine Design Topics
 L State Machine Design Topics States Machine Design Other topics on state machine design Equivalent sequential machines Incompletely specified machines One Hot State Machines Ref: text Unit 15.4, 15.5,
L State Machine Design Topics States Machine Design Other topics on state machine design Equivalent sequential machines Incompletely specified machines One Hot State Machines Ref: text Unit 15.4, 15.5,
Clocked Synchronous State-machine Analysis
 Clocked Synchronous State-machine Analysis Given the circuit diagram of a state machine: Analyze the combinational logic to determine flip-flop input (excitation) equations: D i = F i (Q, inputs) The input
Clocked Synchronous State-machine Analysis Given the circuit diagram of a state machine: Analyze the combinational logic to determine flip-flop input (excitation) equations: D i = F i (Q, inputs) The input
ENGG 1203 Tutorial _03 Laboratory 3 Build a ball counter. Lab 3. Lab 3 Gate Timing. Lab 3 Steps in designing a State Machine. Timing diagram of a DFF
 ENGG 1203 Tutorial _03 Laboratory 3 Build a ball counter Timing diagram of a DFF Lab 3 Gate Timing difference timing for difference kind of gate, cost dependence (1) Setup Time = t2-t1 (2) Propagation
ENGG 1203 Tutorial _03 Laboratory 3 Build a ball counter Timing diagram of a DFF Lab 3 Gate Timing difference timing for difference kind of gate, cost dependence (1) Setup Time = t2-t1 (2) Propagation
Philadelphia University Student Name: Student Number:
 Philadelphia University Student Name: Student Number: Faculty of Engineering Serial Number: Final Exam, Second Semester: 2015/2016 Dept. of Computer Engineering Course Title: Logic Circuits Date: 08/06/2016
Philadelphia University Student Name: Student Number: Faculty of Engineering Serial Number: Final Exam, Second Semester: 2015/2016 Dept. of Computer Engineering Course Title: Logic Circuits Date: 08/06/2016
Digital Design 2010 DE2 1
 1 Underviser: D. M. Akbar Hussain Litteratur: Digital Design Principles & Practices 4 th Edition by yj John F. Wakerly 2 DE2 1 3 4 DE2 2 To enable students to apply analysis, synthesis and implementation
1 Underviser: D. M. Akbar Hussain Litteratur: Digital Design Principles & Practices 4 th Edition by yj John F. Wakerly 2 DE2 1 3 4 DE2 2 To enable students to apply analysis, synthesis and implementation
Final Exam. ECE 25, Spring 2008 Thursday, June 12, Problem Points Score Total 90
 Final Exam ECE 25, Spring 2008 Thursday, June 12, 2008 Name: PID: Problem Points Score 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 10 5 10 6 10 7 10 8 10 9 10 Total 90 1) Number representation (10 pts) a) For each binary vector
Final Exam ECE 25, Spring 2008 Thursday, June 12, 2008 Name: PID: Problem Points Score 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 10 5 10 6 10 7 10 8 10 9 10 Total 90 1) Number representation (10 pts) a) For each binary vector
COE 202: Digital Logic Design Sequential Circuits Part 3. Dr. Ahmad Almulhem ahmadsm AT kfupm Phone: Office:
 COE 202: Digital Logic Design Sequential Circuits Part 3 Dr. Ahmad Almulhem Email: ahmadsm AT kfupm Phone: 860-7554 Office: 22-324 Objectives State Reduction and Assignment Design of Synchronous Sequential
COE 202: Digital Logic Design Sequential Circuits Part 3 Dr. Ahmad Almulhem Email: ahmadsm AT kfupm Phone: 860-7554 Office: 22-324 Objectives State Reduction and Assignment Design of Synchronous Sequential
Total time is: 1 setup, 2 AND, 3 XOR, 1 delay = (1*1) + (2*2) + (3*3) + (1*1) = 15ns
 Clock Period/ Delay Analysis: Find longest possible path (time-wise) between two flip-flops. If 2ns for AND and 3ns for XOR, with T delayff = 1ns and T setupff = 1 ns. So the total time is: 1 setupff +
Clock Period/ Delay Analysis: Find longest possible path (time-wise) between two flip-flops. If 2ns for AND and 3ns for XOR, with T delayff = 1ns and T setupff = 1 ns. So the total time is: 1 setupff +
Sequential Logic. Rab Nawaz Khan Jadoon DCS. Lecturer COMSATS Lahore Pakistan. Department of Computer Science
 Sequential Logic Rab Nawaz Khan Jadoon DCS COMSATS Institute of Information Technology Lecturer COMSATS Lahore Pakistan Digital Logic and Computer Design Sequential Logic Combinational circuits with memory
Sequential Logic Rab Nawaz Khan Jadoon DCS COMSATS Institute of Information Technology Lecturer COMSATS Lahore Pakistan Digital Logic and Computer Design Sequential Logic Combinational circuits with memory
3. Complete the following table of equivalent values. Use binary numbers with a sign bit and 7 bits for the value
 EGC22 Digital Logic Fundamental Additional Practice Problems. Complete the following table of equivalent values. Binary. Octal 35.77 33.23.875 29.99 27 9 64 Hexadecimal B.3 D.FD B.4C 2. Calculate the following
EGC22 Digital Logic Fundamental Additional Practice Problems. Complete the following table of equivalent values. Binary. Octal 35.77 33.23.875 29.99 27 9 64 Hexadecimal B.3 D.FD B.4C 2. Calculate the following
Problem Set 9 Solutions
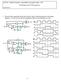 CSE 26 Digital Computers: Organization and Logical Design - 27 Jon Turner Problem Set 9 Solutions. For each of the sequential circuits shown below, draw in the missing parts of the timing diagrams. You
CSE 26 Digital Computers: Organization and Logical Design - 27 Jon Turner Problem Set 9 Solutions. For each of the sequential circuits shown below, draw in the missing parts of the timing diagrams. You
Synchronous Sequential Logic Part I. BME208 Logic Circuits Yalçın İŞLER
 Synchronous Sequential Logic Part I BME28 Logic Circuits Yalçın İŞLER islerya@yahoo.com http://me.islerya.com Sequential Logic Digital circuits we have learned, so far, have been combinational no memory,
Synchronous Sequential Logic Part I BME28 Logic Circuits Yalçın İŞLER islerya@yahoo.com http://me.islerya.com Sequential Logic Digital circuits we have learned, so far, have been combinational no memory,
CPE/EE 422/522. Chapter 1 - Review of Logic Design Fundamentals. Dr. Rhonda Kay Gaede UAH. 1.1 Combinational Logic
 CPE/EE 422/522 Chapter - Review of Logic Design Fundamentals Dr. Rhonda Kay Gaede UAH UAH Chapter CPE/EE 422/522. Combinational Logic Combinational Logic has no control inputs. When the inputs to a combinational
CPE/EE 422/522 Chapter - Review of Logic Design Fundamentals Dr. Rhonda Kay Gaede UAH UAH Chapter CPE/EE 422/522. Combinational Logic Combinational Logic has no control inputs. When the inputs to a combinational
King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals College of Computer Science and Engineering Computer Engineering Department
 King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals College of Computer Science and Engineering Computer Engineering Department Page 1 of 13 COE 202: Digital Logic Design (3-0-3) Term 112 (Spring 2012) Final
King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals College of Computer Science and Engineering Computer Engineering Department Page 1 of 13 COE 202: Digital Logic Design (3-0-3) Term 112 (Spring 2012) Final
Philadelphia University Student Name: Student Number:
 Philadelphia University Student Name: Student Number: Faculty of Engineering Serial Number: Final Exam, First Semester: 2017/2018 Dept. of Computer Engineering Course Title: Logic Circuits Date: 29/01/2018
Philadelphia University Student Name: Student Number: Faculty of Engineering Serial Number: Final Exam, First Semester: 2017/2018 Dept. of Computer Engineering Course Title: Logic Circuits Date: 29/01/2018
Example: vending machine
 Example: vending machine Release item after 15 cents are deposited Single coin slot for dimes, nickels o change Reset Coin Sensor Vending Machine FSM Open Release Mechanism Clock Spring 2005 CSE370 - guest
Example: vending machine Release item after 15 cents are deposited Single coin slot for dimes, nickels o change Reset Coin Sensor Vending Machine FSM Open Release Mechanism Clock Spring 2005 CSE370 - guest
CPE100: Digital Logic Design I
 Professor Brendan Morris, SEB 3216, brendan.morris@unlv.edu CPE100: Digital Logic Design I Midterm02 Review http://www.ee.unlv.edu/~b1morris/cpe100/ 2 Logistics Thursday Nov. 16 th In normal lecture (13:00-14:15)
Professor Brendan Morris, SEB 3216, brendan.morris@unlv.edu CPE100: Digital Logic Design I Midterm02 Review http://www.ee.unlv.edu/~b1morris/cpe100/ 2 Logistics Thursday Nov. 16 th In normal lecture (13:00-14:15)
Synchronous Sequential Circuit Design
 Synchronous Sequential Circuit Design 1 Sequential circuit design In sequential circuit design, we turn some description into a working circuit We first make a state table or diagram to express the computation
Synchronous Sequential Circuit Design 1 Sequential circuit design In sequential circuit design, we turn some description into a working circuit We first make a state table or diagram to express the computation
Sequential Synchronous Circuit Analysis
 Sequential Synchronous Circuit Analysis General Model Current State at time (t) is stored in an array of flip-flops. Next State at time (t+1) is a Boolean function of State and Inputs. Outputs at time
Sequential Synchronous Circuit Analysis General Model Current State at time (t) is stored in an array of flip-flops. Next State at time (t+1) is a Boolean function of State and Inputs. Outputs at time
or 0101 Machine
 Synchronous State Graph or Synchronous State Graph or Detector Design a state graph for a machine with: One input X, one output Z. Z= after receiving the complete sequence or Overlapped sequences are detected.
Synchronous State Graph or Synchronous State Graph or Detector Design a state graph for a machine with: One input X, one output Z. Z= after receiving the complete sequence or Overlapped sequences are detected.
COE 202: Digital Logic Design Sequential Circuits Part 3. Dr. Ahmad Almulhem ahmadsm AT kfupm Phone: Office:
 COE 202: Digital Logic Design Sequential Circuits Part 3 Dr. Ahmad Almulhem Email: ahmadsm AT kfupm Phone: 860-7554 Office: 22-324 Objectives Important Design Concepts State Reduction and Assignment Design
COE 202: Digital Logic Design Sequential Circuits Part 3 Dr. Ahmad Almulhem Email: ahmadsm AT kfupm Phone: 860-7554 Office: 22-324 Objectives Important Design Concepts State Reduction and Assignment Design
Parity Checker Example. EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 9 - Finite State Machines 1. Formal Design Process. Formal Design Process
 Parity Checker Example A string of bits has even parity if the number of 1 s in the string is even. Design a circuit that accepts a bit-serial stream of bits and outputs a 0 if the parity thus far is even
Parity Checker Example A string of bits has even parity if the number of 1 s in the string is even. Design a circuit that accepts a bit-serial stream of bits and outputs a 0 if the parity thus far is even
Simplify the following Boolean expressions and minimize the number of literals:
 Boolean Algebra Task 1 Simplify the following Boolean expressions and minimize the number of literals: 1.1 1.2 1.3 Task 2 Convert the following expressions into sum of products and product of sums: 2.1
Boolean Algebra Task 1 Simplify the following Boolean expressions and minimize the number of literals: 1.1 1.2 1.3 Task 2 Convert the following expressions into sum of products and product of sums: 2.1
Digital Logic Design. Midterm #2
 EECS: igital Logic esign r. nthony. Johnson s7m2s_dild7.fm - igital Logic esign Midterm #2 Problems Points. 5 2. 4 3. 6 Total 5 Was the exam fair? yes no EECS: igital Logic esign r. nthony. Johnson s7m2s_dild7.fm
EECS: igital Logic esign r. nthony. Johnson s7m2s_dild7.fm - igital Logic esign Midterm #2 Problems Points. 5 2. 4 3. 6 Total 5 Was the exam fair? yes no EECS: igital Logic esign r. nthony. Johnson s7m2s_dild7.fm
Sequential Circuit Design
 Sequential Circuit esign esign Procedure. Specification 2. Formulation Obtain a state diagram or state table 3. State Assignment Assign binary codes to the states 4. Flip-Flop Input Equation etermination
Sequential Circuit esign esign Procedure. Specification 2. Formulation Obtain a state diagram or state table 3. State Assignment Assign binary codes to the states 4. Flip-Flop Input Equation etermination
Lecture 17: Designing Sequential Systems Using Flip Flops
 EE210: Switching Systems Lecture 17: Designing Sequential Systems Using Flip Flops Prof. YingLi Tian April 11, 2019 Department of Electrical Engineering The City College of New York The City University
EE210: Switching Systems Lecture 17: Designing Sequential Systems Using Flip Flops Prof. YingLi Tian April 11, 2019 Department of Electrical Engineering The City College of New York The City University
Different encodings generate different circuits
 FSM State Encoding Different encodings generate different circuits no easy way to find best encoding with fewest logic gates or shortest propagation delay. Binary encoding: K states need log 2 K bits i.e.,
FSM State Encoding Different encodings generate different circuits no easy way to find best encoding with fewest logic gates or shortest propagation delay. Binary encoding: K states need log 2 K bits i.e.,
ELE2120 Digital Circuits and Systems. Tutorial Note 10
 ELE2120 Digital Circuits and Systems Tutorial Note 10 Outline 1. 1. Sequential Circuit Design 2. 2. Design procedure: a complete example illustration Sequential circuit analysis & design In sequential
ELE2120 Digital Circuits and Systems Tutorial Note 10 Outline 1. 1. Sequential Circuit Design 2. 2. Design procedure: a complete example illustration Sequential circuit analysis & design In sequential
14.1. Unit 14. State Machine Design
 4. Unit 4 State Machine Design 4.2 Outcomes I can create a state diagram to solve a sequential problem I can implement a working state machine given a state diagram STATE MACHINES OVERVIEW 4.3 4.4 Review
4. Unit 4 State Machine Design 4.2 Outcomes I can create a state diagram to solve a sequential problem I can implement a working state machine given a state diagram STATE MACHINES OVERVIEW 4.3 4.4 Review
Synchronous Sequential Logic Part I
 Synchronous Sequential Logic Part I Mantıksal Tasarım BBM23 section instructor: Ufuk Çelikcan Sequential Logic Digital circuits we have learned, so far, have been combinational no memory, outputs are entirely
Synchronous Sequential Logic Part I Mantıksal Tasarım BBM23 section instructor: Ufuk Çelikcan Sequential Logic Digital circuits we have learned, so far, have been combinational no memory, outputs are entirely
IE1204 Digital Design. L10: State Machines (Part 2) Masoumeh (Azin) Ebrahimi Elena Dubrova
 IE1204 Digital Design L10: State Machines (Part 2) Masoumeh (Azin) Ebrahimi (masebr@kth.se) Elena Dubrova (dubrova@kth.se) KTH / ICT / ES This lecture BV pp. 528-532, 557-567 IE1204 Digital Design, Autumn2015
IE1204 Digital Design L10: State Machines (Part 2) Masoumeh (Azin) Ebrahimi (masebr@kth.se) Elena Dubrova (dubrova@kth.se) KTH / ICT / ES This lecture BV pp. 528-532, 557-567 IE1204 Digital Design, Autumn2015
Ch 7. Finite State Machines. VII - Finite State Machines Contemporary Logic Design 1
 Ch 7. Finite State Machines VII - Finite State Machines Contemporary Logic esign 1 Finite State Machines Sequential circuits primitive sequential elements combinational logic Models for representing sequential
Ch 7. Finite State Machines VII - Finite State Machines Contemporary Logic esign 1 Finite State Machines Sequential circuits primitive sequential elements combinational logic Models for representing sequential
Review for B33DV2-Digital Design. Digital Design
 Review for B33DV2 The Elements of Modern Behaviours Design Representations Blocks Waveforms Gates Truth Tables Boolean Algebra Switches Rapid Prototyping Technologies Circuit Technologies TTL MOS Simulation
Review for B33DV2 The Elements of Modern Behaviours Design Representations Blocks Waveforms Gates Truth Tables Boolean Algebra Switches Rapid Prototyping Technologies Circuit Technologies TTL MOS Simulation
EE40 Lec 15. Logic Synthesis and Sequential Logic Circuits
 EE40 Lec 15 Logic Synthesis and Sequential Logic Circuits Prof. Nathan Cheung 10/20/2009 Reading: Hambley Chapters 7.4-7.6 Karnaugh Maps: Read following before reading textbook http://www.facstaff.bucknell.edu/mastascu/elessonshtml/logic/logic3.html
EE40 Lec 15 Logic Synthesis and Sequential Logic Circuits Prof. Nathan Cheung 10/20/2009 Reading: Hambley Chapters 7.4-7.6 Karnaugh Maps: Read following before reading textbook http://www.facstaff.bucknell.edu/mastascu/elessonshtml/logic/logic3.html
ECEN 248: INTRODUCTION TO DIGITAL SYSTEMS DESIGN. Week 9 Dr. Srinivas Shakkottai Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering
 ECEN 248: INTRODUCTION TO DIGITAL SYSTEMS DESIGN Week 9 Dr. Srinivas Shakkottai Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering TIMING ANALYSIS Overview Circuits do not respond instantaneously to input changes
ECEN 248: INTRODUCTION TO DIGITAL SYSTEMS DESIGN Week 9 Dr. Srinivas Shakkottai Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering TIMING ANALYSIS Overview Circuits do not respond instantaneously to input changes
15.1 Elimination of Redundant States
 15.1 Elimination of Redundant States In Ch. 14 we tried not to have unnecessary states What if we have extra states in the state graph/table? Complete the table then eliminate the redundant states Chapter
15.1 Elimination of Redundant States In Ch. 14 we tried not to have unnecessary states What if we have extra states in the state graph/table? Complete the table then eliminate the redundant states Chapter
Finite State Machine (FSM)
 Finite State Machine (FSM) Consists of: State register Stores current state Loads next state at clock edge Combinational logic Computes the next state Computes the outputs S S Next State CLK Current State
Finite State Machine (FSM) Consists of: State register Stores current state Loads next state at clock edge Combinational logic Computes the next state Computes the outputs S S Next State CLK Current State
Computers also need devices capable of Storing data and information Performing mathematical operations on such data
 Sequential Machines Introduction Logic devices examined so far Combinational Output function of input only Output valid as long as input true Change input change output Computers also need devices capable
Sequential Machines Introduction Logic devices examined so far Combinational Output function of input only Output valid as long as input true Change input change output Computers also need devices capable
EECS Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems. FSMs 9/11/2007
 EECS 150 - Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems FSMs 9/11/2007 Sarah Bird Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California, Berkeley Slides borrowed from David Culler
EECS 150 - Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems FSMs 9/11/2007 Sarah Bird Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California, Berkeley Slides borrowed from David Culler
Chapter 4 Part 2 Sequential Circuits
 University of Wisconsin - Madison ECE/Comp Sci 352 Digital Systems Fundamentals Kewal K. Saluja and Yu Hen Hu Spring 2002 Chapter 4 Part 2 Sequential Circuits Originals by: Charles R. Kime and Tom Kamisnski
University of Wisconsin - Madison ECE/Comp Sci 352 Digital Systems Fundamentals Kewal K. Saluja and Yu Hen Hu Spring 2002 Chapter 4 Part 2 Sequential Circuits Originals by: Charles R. Kime and Tom Kamisnski
Present Next state Output state w = 0 w = 1 z A A B 0 B A C 0 C A C 1
 W Combinational circuit Flip-flops Combinational circuit Z cycle: t t t 2 t 3 t 4 t 5 t 6 t 7 t 8 t 9 t : : Figure 8.. The general form of a sequential circuit. Figure 8.2. Sequences of input and output
W Combinational circuit Flip-flops Combinational circuit Z cycle: t t t 2 t 3 t 4 t 5 t 6 t 7 t 8 t 9 t : : Figure 8.. The general form of a sequential circuit. Figure 8.2. Sequences of input and output
Department of Electrical & Electronics EE-333 DIGITAL SYSTEMS
 Department of Electrical & Electronics EE-333 DIGITAL SYSTEMS 1) Given the two binary numbers X = 1010100 and Y = 1000011, perform the subtraction (a) X -Y and (b) Y - X using 2's complements. a) X = 1010100
Department of Electrical & Electronics EE-333 DIGITAL SYSTEMS 1) Given the two binary numbers X = 1010100 and Y = 1000011, perform the subtraction (a) X -Y and (b) Y - X using 2's complements. a) X = 1010100
Chapter 7 Sequential Logic
 Chapter 7 Sequential Logic SKEE2263 Digital Systems Mun im/ismahani/izam {munim@utm.my,e-izam@utm.my,ismahani@fke.utm.my} March 28, 2016 Table of Contents 1 Intro 2 Bistable Circuits 3 FF Characteristics
Chapter 7 Sequential Logic SKEE2263 Digital Systems Mun im/ismahani/izam {munim@utm.my,e-izam@utm.my,ismahani@fke.utm.my} March 28, 2016 Table of Contents 1 Intro 2 Bistable Circuits 3 FF Characteristics
ENGG 1203 Tutorial_9 - Review. Boolean Algebra. Simplifying Logic Circuits. Combinational Logic. 1. Combinational & Sequential Logic
 ENGG 1203 Tutorial_9 - Review Boolean Algebra 1. Combinational & Sequential Logic 2. Computer Systems 3. Electronic Circuits 4. Signals, Systems, and Control Remark : Multiple Choice Questions : ** Check
ENGG 1203 Tutorial_9 - Review Boolean Algebra 1. Combinational & Sequential Logic 2. Computer Systems 3. Electronic Circuits 4. Signals, Systems, and Control Remark : Multiple Choice Questions : ** Check
Memory Elements I. CS31 Pascal Van Hentenryck. CS031 Lecture 6 Page 1
 Memory Elements I CS31 Pascal Van Hentenryck CS031 Lecture 6 Page 1 Memory Elements (I) Combinational devices are good for computing Boolean functions pocket calculator Computers also need to remember
Memory Elements I CS31 Pascal Van Hentenryck CS031 Lecture 6 Page 1 Memory Elements (I) Combinational devices are good for computing Boolean functions pocket calculator Computers also need to remember
Topic 8: Sequential Circuits
 Topic 8: Sequential Circuits Readings : Patterson & Hennesy, Appendix B.4 - B.6 Goals Basic Principles behind Memory Elements Clocks Applications of sequential circuits Introduction to the concept of the
Topic 8: Sequential Circuits Readings : Patterson & Hennesy, Appendix B.4 - B.6 Goals Basic Principles behind Memory Elements Clocks Applications of sequential circuits Introduction to the concept of the
DIGITAL LOGIC CIRCUITS
 DIGITAL LOGIC CIRCUITS Introduction Logic Gates Boolean Algebra Map Specification Combinational Circuits Flip-Flops Sequential Circuits Memory Components Integrated Circuits Digital Computers 2 LOGIC GATES
DIGITAL LOGIC CIRCUITS Introduction Logic Gates Boolean Algebra Map Specification Combinational Circuits Flip-Flops Sequential Circuits Memory Components Integrated Circuits Digital Computers 2 LOGIC GATES
Synchronous Sequential Circuit Design. Digital Computer Design
 Synchronous Sequential Circuit Design Digital Computer Design Races and Instability Combinational logic has no cyclic paths and no races If inputs are applied to combinational logic, the outputs will always
Synchronous Sequential Circuit Design Digital Computer Design Races and Instability Combinational logic has no cyclic paths and no races If inputs are applied to combinational logic, the outputs will always
5 State Minimisation. university of applied sciences hamburg. Digital Systems. Prof. Dr. J. Reichardt Prof. Dr. B. Schwarz
 5 State Minimisation In an early design phase when a word description of a sequential circuit's function is transformed into a FSM state diagram or state table redundant states may arise. State minimisation
5 State Minimisation In an early design phase when a word description of a sequential circuit's function is transformed into a FSM state diagram or state table redundant states may arise. State minimisation
Digital Control of Electric Drives
 Digital Control of Electric Drives Logic Circuits - equential Description Form, Finite tate Machine (FM) Czech Technical University in Prague Faculty of Electrical Engineering Ver.. J. Zdenek 27 Logic
Digital Control of Electric Drives Logic Circuits - equential Description Form, Finite tate Machine (FM) Czech Technical University in Prague Faculty of Electrical Engineering Ver.. J. Zdenek 27 Logic
University of Guelph School of Engineering ENG 2410 Digital Design Fall There are 7 questions, answer all questions.
 Final Examination Instructor: Shawki M. Areibi Co-examiner: Medhat Moussa. Location: UOG Date: Wednesday, December 5th, 2007 Time: 8:30-10:30 AM Duration: 2 hours. Type: R Closed Book. Instructions: University
Final Examination Instructor: Shawki M. Areibi Co-examiner: Medhat Moussa. Location: UOG Date: Wednesday, December 5th, 2007 Time: 8:30-10:30 AM Duration: 2 hours. Type: R Closed Book. Instructions: University
Sequential Logic Circuits
 Chapter 4 Sequential Logic Circuits 4 1 The defining characteristic of a combinational circuit is that its output depends only on the current inputs applied to the circuit. The output of a sequential circuit,
Chapter 4 Sequential Logic Circuits 4 1 The defining characteristic of a combinational circuit is that its output depends only on the current inputs applied to the circuit. The output of a sequential circuit,
Let s now begin to formalize our analysis of sequential machines Powerful methods for designing machines for System control Pattern recognition Etc.
 Finite State Machines Introduction Let s now begin to formalize our analysis of sequential machines Powerful methods for designing machines for System control Pattern recognition Etc. Such devices form
Finite State Machines Introduction Let s now begin to formalize our analysis of sequential machines Powerful methods for designing machines for System control Pattern recognition Etc. Such devices form
ECE/Comp Sci 352 Digital Systems Fundamentals. Charles R. Kime Section 2 Fall Logic and Computer Design Fundamentals
 University of Wisconsin - Madison ECE/Comp Sci 352 Digital Systems Fundamentals Charles R. Kime Section 2 Fall 2001 Lecture 5 Registers & Counters Part 2 Charles Kime Counters Counters are sequential circuits
University of Wisconsin - Madison ECE/Comp Sci 352 Digital Systems Fundamentals Charles R. Kime Section 2 Fall 2001 Lecture 5 Registers & Counters Part 2 Charles Kime Counters Counters are sequential circuits
Chapter 6. Synchronous Sequential Circuits
 Chapter 6 Synchronous Sequential Circuits In a combinational circuit, the values of the outputs are determined solely by the present values of its inputs. In a sequential circuit, the values of the outputs
Chapter 6 Synchronous Sequential Circuits In a combinational circuit, the values of the outputs are determined solely by the present values of its inputs. In a sequential circuit, the values of the outputs
6 Synchronous State Machine Design
 Design of synchronous counters. Based on the description of the problem, determine the required number n of the FFs - the smallest value of n is such that the number of states N 2 n and the desired counting
Design of synchronous counters. Based on the description of the problem, determine the required number n of the FFs - the smallest value of n is such that the number of states N 2 n and the desired counting
Lecture 9: Digital Electronics
 Introduction: We can classify the building blocks of a circuit or system as being either analog or digital in nature. If we focus on voltage as the circuit parameter of interest: nalog: The voltage can
Introduction: We can classify the building blocks of a circuit or system as being either analog or digital in nature. If we focus on voltage as the circuit parameter of interest: nalog: The voltage can
Clocked Sequential Circuits UNIT 13 ANALYSIS OF CLOCKED SEQUENTIAL CIRCUITS. Analysis of Clocked Sequential Circuits. Signal Tracing and Timing Charts
 ed Sequential Circuits 2 Contents nalysis by signal tracing & timing charts State tables and graphs General models for sequential circuits sequential parity checker Reading Unit 3 asic unit Unit : Latch
ed Sequential Circuits 2 Contents nalysis by signal tracing & timing charts State tables and graphs General models for sequential circuits sequential parity checker Reading Unit 3 asic unit Unit : Latch
Menu. Master-Slave Flip-Flop
 Menu Clocks and Master-lave Flip-Flops J-K and other Flip-Flops Truth table & excitation table Adders (see [Lam: pg 130]) Counters Look into my... 1 CLK Master-lave Flip-Flop Master-lave Latch/Flip-Flop
Menu Clocks and Master-lave Flip-Flops J-K and other Flip-Flops Truth table & excitation table Adders (see [Lam: pg 130]) Counters Look into my... 1 CLK Master-lave Flip-Flop Master-lave Latch/Flip-Flop
CE1911 LECTURE FSM DESIGN PRACTICE DAY 1
 REVIEW MATERIAL 1. Combinational circuits do not have memory. They calculate instantaneous outputs based only on current inputs. They implement basic arithmetic and logic functions. 2. Sequential circuits
REVIEW MATERIAL 1. Combinational circuits do not have memory. They calculate instantaneous outputs based only on current inputs. They implement basic arithmetic and logic functions. 2. Sequential circuits
Principles of Computer Architecture. Appendix B: Reduction of Digital Logic. Chapter Contents
 B-1 Principles of Computer Architecture Miles Murdocca and Vincent Heuring Appendix B: Reduction of Digital Logic B-2 Chapter Contents B.1 Reduction of Combinational Logic and Sequential Logic B.2 Reduction
B-1 Principles of Computer Architecture Miles Murdocca and Vincent Heuring Appendix B: Reduction of Digital Logic B-2 Chapter Contents B.1 Reduction of Combinational Logic and Sequential Logic B.2 Reduction
