1 Short adders. t total_ripple8 = t first + 6*t middle + t last = 4t p + 6*2t p + 2t p = 18t p
|
|
|
- Mariah Park
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences Study Homework: Arithmetic NTU IC54CA (Fall 2004) SOLUTIONS Short adders A The delay of the ripple carry adder can be split into three parts: the first bit, the middle six bits, and the last bit. For the first bit, the critical path for the c out is one XOR, one AND, and one OR gate. Then for the next 6 bits, since p has had plenty of time to be computed already, we need only one AND and one OR gate to get from c in to c out. In the final stage, the important path is from c in to the s output, which is one XOR delay. Therefore, the delays are: t first = 0.5*2 2 *t p + 2*0.25*2 2 *t p = 4t p t middle = 2*0.25*2 2 *t p = 2t p t last = 0.5*2 2 *t p = 2t p t total_ripple8 = t first + 6*t middle + t last = 4t p + 6*2t p + 2t p = 8t p B The CLA logic functions implemented are c o3 = g 3 + p 3 g 2 +p 3 p 2 g +p 3 p 2 p g 0 +p 3 p 2 p p 0 c in c o2 = g 2 + p 2 g + p 2 p g 0 + p 2 p p 0 c in c o = g + p g 0 + p p 0 c in c o0 = g 0 + p 0 c in cin 4bit CLA c o3 4bit CLA Figure. Carry look-ahead architecture. For the first 4-bit CLA group, the important path is from c in to c o3. After one XOR delay, all the g i s and p i s are computed. In the most straightforward implementation, the worst-case path is then through one 5-input AND gate and a 5-input OR gate (other topologies are possible) which takes a total of: t firstcla = 0.5*2 2 *t p *5 2 *t p *5 2 *t p = 4.5t p For the second 4-bit CLA group, the important path is from c in to c o2 to the final sum bit. Again using the most straightforward implementation, c in to c o2 takes one 4-input AND gate and one 4- input OR gate. From c o2 to sum goes through one XOR gate: t secondcla = 0.25*4 2 *t p *4 2 *t p + 0.5*2 2 *t p = 0t p The total delay is then the sum of these two groups: t total_cla8 = t firstcla + t secondcla = 24.5t p C In the analysis of a 32-bit ripple carry adder, the same delays calculated for the 8-bit case can be reused:
2 t total_ripple32 = t first + 30*t middle + t last = 4t p + 30*2t p + 2t p = 66t p For the 32-bit CLA using a hierarchical propagate/generate scheme, refer to the figure for the worst-case path through the entire adder. Calculate the sum bit 2t p +2t p Pass the carry back 2t p + 2t p Obtain p i,g i (2t p ) Obtain P,G block propagate generates 8t p +8t p It takes one XOR delay to get the propagate/generate terms for each bit, which is 2t p. The propagate/generate terms in the second- and third-levels are computed as: P middle = P top0 *P top *P top2 *P top3 G middle = G top3 + G top2 *P top3 + G top *P top3 *P top2 + G top0 *P top3 *P top2 *P top So the worst-case path to make these P and G terms is one 4-input AND gate followed by a 4- input OR gate, which totals 8t p for each level. Traversing back up the tree, the groups can compute their carry-outs using the simple c o = G + P*c i so it only takes one 2-input AND gate and one 2-input OR gate, which is 2t p for each level. Once the top level is reached, the final carry takes 2t p and the sum requires an additional 2-input XOR, adding another 2t p. Totaling all the delays yields a critical path delay of t total_cla32 = 2t p + (8t p + 8t p ) + (2t p + 2t p ) + (2t p + 2t p ) = 26t p As the as the number of bits increases, the carry look ahead adder has a distinct advantage. However, for adders with less than 0-bits, it is usually faster to implement the simpler ripple carry architecture.
3 2 Comparator design 2A The simplest implementation calculates the (B-A). If the resulting is negative (ie. if the sign bit is one), then A is greater than B. If the sign bit is zero, then A <= B. The implementation would simply bitwise complement B and compute OUT = A + (~B) +. The output of the N-bit comparator would simply be the last bit of this result, ie. OUT[N-]. A N B N N OUT OUT[N-] A>B Assuming the adder is a ripple carry adder, the worst case delay of the comparator would be of the same form as A: 4*t p +(N-2)*2t p +2*t p = (N+)*2t p
4 3 Signed Multiplication This solution implements Baugh-Wooley multiplier technique. As an illustrative example, extend the traditional binary notation to allow bits to be negative (similar to the carry-save technique). In this case, the failing example can be transformed to: Extended binary Decimal equivalent (-8)+4 = (-4) x (-8)+ = (-7) (-8)+4 = (-4) (0) (0) (-32)= (-32)+(-8)+4=28 So, this wacky method appears to give the correct answer (at least for this example). It is left as an exercise to prove that it works for all numbers. Now, consider how to implement this multiplier. In the general case, the following partial products are required (parentheses signify the negative weighted bits). (a 3 ) a 2 a a 0 (b 3 ) b 2 b b 0 (a 3 b 0 ) a 2 b 0 ab 0 a 0 b 0 (a 3 b ) a 2 b a b a 0 b (a 3 b 2 ) a 2 b 2 a b 2 a 0 b 2 a 3 b 3 (a 2 b 3 ) (a b 3 ) (a 0 b 3 ) P 7 p 6 p 5 p 4 p 3 p 2 p p0 The bits in the partial products can be reordered to form more useful groups consisting of positive and negative terms: (a 3 ) a 2 a a 0 (b 3 ) b 2 b b 0 a 2 b 0 ab 0 a 0 b 0 a 2 b a b a 0 b a 3 b 3 0 a 2 b 2 a b 2 a 0 b 2 (a 3 b 2 ) (a 3 b ) (a 3 b 0 ) (a 2 b 3 ) (a b 3 ) (a 0 b 3 ) P 7 p 6 p 5 p 4 p 3 p 2 p p 0 We are trying to add the positive partial products (above dashed line) and subtract the negative partial products (those below the dashed line). The negatively weighted partial products can be interpreted as two numbers that can be negated, allowing the whole array to be added together. Note that blank entries in the table are implicit zeros.
5 Consider the first negative row. Negation is tricky here because we only want to negate if a 3 is one. If a 3 is zero, we want the entire row to be zero. The logic function for each bit is then a 3 bi. For the entire number [0 0 (a 3 b 2 ) (a 3 b ) (a 3 b 0 )], the result would be the following sum: a 3 a b a a b a b a 3 where the extra a 3 terms sprinkled around are for sign-extension and for the + in the two s complement conversion. As another simplification, the leading two positions can be interpreted is either as: [0 0] = 0 [a 4 a 3 ] = [a 3 a 3 ] = [] = or equivalently as: [ a 4 ] + = [ a 3 ] + = [] + [ 0] + = 0 [0 0] = = [] a a 3 3 = 0 = If the above methods are also use to negate the partial products starting with b 3, the resulting the initial partial sum array would be: (a 3 ) a 2 a a 0 (b 3 ) b 2 b b 0 a 2 b 0 ab 0 a 0 b 0 a 2 b a b a 0 b a 3 b 3 0 a 2 b 2 a b 2 a 0 b 2 a a b a b a b b a b a b a b P 7 P 6 p 5 p 4 p 3 p 2 p p 0 Merging the constant one s together, yields the final partial sum array: a 3 b 3 0 a 2 b 2 a b 2 a 0 b 2 a a b a b a b b a b a b a b (a 3 ) a 2 a a 0 (b 3 ) b 2 b b 0 a 2 b 0 ab 0 a 0 b 0 a 2 b a b a 0 b P 7 P 6 p 5 p 4 p 3 p 2 p p 0
6 We can implement this array in the following way. Using the block below as the processing element of the main array we can obtain the result p[7:0] sin a sin a b b cout cin cout FA cin sout sout a2 a a0 b0 b b2 ~ ~b4 p7 p6 p5 p4 p3 p2 p p0
Chapter 5 Arithmetic Circuits
 Chapter 5 Arithmetic Circuits SKEE2263 Digital Systems Mun im/ismahani/izam {munim@utm.my,e-izam@utm.my,ismahani@fke.utm.my} February 11, 2016 Table of Contents 1 Iterative Designs 2 Adders 3 High-Speed
Chapter 5 Arithmetic Circuits SKEE2263 Digital Systems Mun im/ismahani/izam {munim@utm.my,e-izam@utm.my,ismahani@fke.utm.my} February 11, 2016 Table of Contents 1 Iterative Designs 2 Adders 3 High-Speed
CS 140 Lecture 14 Standard Combinational Modules
 CS 14 Lecture 14 Standard Combinational Modules Professor CK Cheng CSE Dept. UC San Diego Some slides from Harris and Harris 1 Part III. Standard Modules A. Interconnect B. Operators. Adders Multiplier
CS 14 Lecture 14 Standard Combinational Modules Professor CK Cheng CSE Dept. UC San Diego Some slides from Harris and Harris 1 Part III. Standard Modules A. Interconnect B. Operators. Adders Multiplier
Midterm Exam Two is scheduled on April 8 in class. On March 27 I will help you prepare Midterm Exam Two.
 Announcements Midterm Exam Two is scheduled on April 8 in class. On March 27 I will help you prepare Midterm Exam Two. Chapter 5 1 Chapter 3: Part 3 Arithmetic Functions Iterative combinational circuits
Announcements Midterm Exam Two is scheduled on April 8 in class. On March 27 I will help you prepare Midterm Exam Two. Chapter 5 1 Chapter 3: Part 3 Arithmetic Functions Iterative combinational circuits
Carry Look Ahead Adders
 Carry Look Ahead Adders Lesson Objectives: The objectives of this lesson are to learn about: 1. Carry Look Ahead Adder circuit. 2. Binary Parallel Adder/Subtractor circuit. 3. BCD adder circuit. 4. Binary
Carry Look Ahead Adders Lesson Objectives: The objectives of this lesson are to learn about: 1. Carry Look Ahead Adder circuit. 2. Binary Parallel Adder/Subtractor circuit. 3. BCD adder circuit. 4. Binary
Binary addition by hand. Adding two bits
 Chapter 3 Arithmetic is the most basic thing you can do with a computer We focus on addition, subtraction, multiplication and arithmetic-logic units, or ALUs, which are the heart of CPUs. ALU design Bit
Chapter 3 Arithmetic is the most basic thing you can do with a computer We focus on addition, subtraction, multiplication and arithmetic-logic units, or ALUs, which are the heart of CPUs. ALU design Bit
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 10 - Combinational Logic Circuits Part 1
 EECS5 - Digital Design Lecture - Combinational Logic Circuits Part Feburary 26, 22 John Wawrzynek Spring 22 EECS5 - Lec-cl Page Combinational Logic (CL) Defined y i = f i (x,...., xn-), where x, y are
EECS5 - Digital Design Lecture - Combinational Logic Circuits Part Feburary 26, 22 John Wawrzynek Spring 22 EECS5 - Lec-cl Page Combinational Logic (CL) Defined y i = f i (x,...., xn-), where x, y are
Logic and Computer Design Fundamentals. Chapter 5 Arithmetic Functions and Circuits
 Logic and Computer Design Fundamentals Chapter 5 Arithmetic Functions and Circuits Arithmetic functions Operate on binary vectors Use the same subfunction in each bit position Can design functional block
Logic and Computer Design Fundamentals Chapter 5 Arithmetic Functions and Circuits Arithmetic functions Operate on binary vectors Use the same subfunction in each bit position Can design functional block
ARITHMETIC COMBINATIONAL MODULES AND NETWORKS
 ARITHMETIC COMBINATIONAL MODULES AND NETWORKS 1 SPECIFICATION OF ADDER MODULES FOR POSITIVE INTEGERS HALF-ADDER AND FULL-ADDER MODULES CARRY-RIPPLE AND CARRY-LOOKAHEAD ADDER MODULES NETWORKS OF ADDER MODULES
ARITHMETIC COMBINATIONAL MODULES AND NETWORKS 1 SPECIFICATION OF ADDER MODULES FOR POSITIVE INTEGERS HALF-ADDER AND FULL-ADDER MODULES CARRY-RIPPLE AND CARRY-LOOKAHEAD ADDER MODULES NETWORKS OF ADDER MODULES
CprE 281: Digital Logic
 CprE 281: Digital Logic Instructor: Alexander Stoytchev http://www.ece.iastate.edu/~alexs/classes/ Multiplication CprE 281: Digital Logic Iowa State University, Ames, IA Copyright Alexander Stoytchev HW
CprE 281: Digital Logic Instructor: Alexander Stoytchev http://www.ece.iastate.edu/~alexs/classes/ Multiplication CprE 281: Digital Logic Iowa State University, Ames, IA Copyright Alexander Stoytchev HW
COE 202: Digital Logic Design Combinational Circuits Part 2. Dr. Ahmad Almulhem ahmadsm AT kfupm Phone: Office:
 COE 202: Digital Logic Design Combinational Circuits Part 2 Dr. Ahmad Almulhem Email: ahmadsm AT kfupm Phone: 860-7554 Office: 22-324 Objectives Arithmetic Circuits Adder Subtractor Carry Look Ahead Adder
COE 202: Digital Logic Design Combinational Circuits Part 2 Dr. Ahmad Almulhem Email: ahmadsm AT kfupm Phone: 860-7554 Office: 22-324 Objectives Arithmetic Circuits Adder Subtractor Carry Look Ahead Adder
Chapter 5. Digital Design and Computer Architecture, 2 nd Edition. David Money Harris and Sarah L. Harris. Chapter 5 <1>
 Chapter 5 Digital Design and Computer Architecture, 2 nd Edition David Money Harris and Sarah L. Harris Chapter 5 Chapter 5 :: Topics Introduction Arithmetic Circuits umber Systems Sequential Building
Chapter 5 Digital Design and Computer Architecture, 2 nd Edition David Money Harris and Sarah L. Harris Chapter 5 Chapter 5 :: Topics Introduction Arithmetic Circuits umber Systems Sequential Building
14:332:231 DIGITAL LOGIC DESIGN
 4:332:23 DIGITAL LOGIC DEIGN Ivan Marsic, Rutgers University Electrical & Computer Engineering Fall 23 Lecture #4: Adders, ubtracters, and ALUs Vector Binary Adder [Wakerly 4 th Ed., ec. 6., p. 474] ingle
4:332:23 DIGITAL LOGIC DEIGN Ivan Marsic, Rutgers University Electrical & Computer Engineering Fall 23 Lecture #4: Adders, ubtracters, and ALUs Vector Binary Adder [Wakerly 4 th Ed., ec. 6., p. 474] ingle
Hardware Design I Chap. 4 Representative combinational logic
 Hardware Design I Chap. 4 Representative combinational logic E-mail: shimada@is.naist.jp Already optimized circuits There are many optimized circuits which are well used You can reduce your design workload
Hardware Design I Chap. 4 Representative combinational logic E-mail: shimada@is.naist.jp Already optimized circuits There are many optimized circuits which are well used You can reduce your design workload
CprE 281: Digital Logic
 CprE 281: Digital Logic Instructor: Alexander Stoytchev http://www.ece.iastate.edu/~alexs/classes/ Fast Adders CprE 281: Digital Logic Iowa State University, Ames, IA Copyright Alexander Stoytchev HW5
CprE 281: Digital Logic Instructor: Alexander Stoytchev http://www.ece.iastate.edu/~alexs/classes/ Fast Adders CprE 281: Digital Logic Iowa State University, Ames, IA Copyright Alexander Stoytchev HW5
Chapter 03: Computer Arithmetic. Lesson 03: Arithmetic Operations Adder and Subtractor circuits Design
 Chapter 03: Computer Arithmetic Lesson 03: Arithmetic Operations Adder and Subtractor circuits Design Objective To understand adder circuit Subtractor circuit Fast adder circuit 2 Adder Circuit 3 Full
Chapter 03: Computer Arithmetic Lesson 03: Arithmetic Operations Adder and Subtractor circuits Design Objective To understand adder circuit Subtractor circuit Fast adder circuit 2 Adder Circuit 3 Full
Number representation
 Number representation A number can be represented in binary in many ways. The most common number types to be represented are: Integers, positive integers one-complement, two-complement, sign-magnitude
Number representation A number can be represented in binary in many ways. The most common number types to be represented are: Integers, positive integers one-complement, two-complement, sign-magnitude
Adders, subtractors comparators, multipliers and other ALU elements
 CSE4: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems Adders, subtractors comparators, multipliers and other ALU elements Adders 2 Circuit Delay Transistors have instrinsic resistance and capacitance
CSE4: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems Adders, subtractors comparators, multipliers and other ALU elements Adders 2 Circuit Delay Transistors have instrinsic resistance and capacitance
CSE140: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems. Decoders, adders, comparators, multipliers and other ALU elements. Tajana Simunic Rosing
 CSE4: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems Decoders, adders, comparators, multipliers and other ALU elements Tajana Simunic Rosing Mux, Demux Encoder, Decoder 2 Transmission Gate: Mux/Tristate
CSE4: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems Decoders, adders, comparators, multipliers and other ALU elements Tajana Simunic Rosing Mux, Demux Encoder, Decoder 2 Transmission Gate: Mux/Tristate
Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective. Arithmetic Circuits. Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic.
 Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic Arithmetic Circuits January, 2003 1 A Generic Digital Processor MEM ORY INPUT-OUTPUT CONTROL DATAPATH
Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic Arithmetic Circuits January, 2003 1 A Generic Digital Processor MEM ORY INPUT-OUTPUT CONTROL DATAPATH
Adders, subtractors comparators, multipliers and other ALU elements
 CSE4: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems Adders, subtractors comparators, multipliers and other ALU elements Instructor: Mohsen Imani UC San Diego Slides from: Prof.Tajana Simunic Rosing
CSE4: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems Adders, subtractors comparators, multipliers and other ALU elements Instructor: Mohsen Imani UC San Diego Slides from: Prof.Tajana Simunic Rosing
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 22 - Arithmetic Blocks, Part 1
 EECS150 - igital esign Lecture 22 - Arithmetic Blocks, Part 1 April 10, 2011 John Wawrzynek Spring 2011 EECS150 - Lec23-arith1 Page 1 Each cell: r i = a i XOR b i XOR c in Carry-ripple Adder Revisited
EECS150 - igital esign Lecture 22 - Arithmetic Blocks, Part 1 April 10, 2011 John Wawrzynek Spring 2011 EECS150 - Lec23-arith1 Page 1 Each cell: r i = a i XOR b i XOR c in Carry-ripple Adder Revisited
Computer Science 324 Computer Architecture Mount Holyoke College Fall Topic Notes: Digital Logic
 Computer Science 324 Computer Architecture Mount Holyoke College Fall 2007 Topic Notes: Digital Logic Our goal for the next few weeks is to paint a a reasonably complete picture of how we can go from transistor
Computer Science 324 Computer Architecture Mount Holyoke College Fall 2007 Topic Notes: Digital Logic Our goal for the next few weeks is to paint a a reasonably complete picture of how we can go from transistor
Module 2. Basic Digital Building Blocks. Binary Arithmetic & Arithmetic Circuits Comparators, Decoders, Encoders, Multiplexors Flip-Flops
 Module 2 asic Digital uilding locks Lecturer: Dr. Yongsheng Gao Office: Tech 3.25 Email: Web: Structure: Textbook: yongsheng.gao@griffith.edu.au maxwell.me.gu.edu.au 6 lecturers 1 tutorial 1 laboratory
Module 2 asic Digital uilding locks Lecturer: Dr. Yongsheng Gao Office: Tech 3.25 Email: Web: Structure: Textbook: yongsheng.gao@griffith.edu.au maxwell.me.gu.edu.au 6 lecturers 1 tutorial 1 laboratory
CMPUT 329. Circuits for binary addition
 CMPUT 329 Parallel Adder with Carry Lookahead and ALU Ioanis Nikolaidis (Katz & Borriello) rcuits for binary addition Full adder (carry-in to cascade for multi-bit adders) Sum = xor A xor B Cout = B +
CMPUT 329 Parallel Adder with Carry Lookahead and ALU Ioanis Nikolaidis (Katz & Borriello) rcuits for binary addition Full adder (carry-in to cascade for multi-bit adders) Sum = xor A xor B Cout = B +
Tree and Array Multipliers Ivor Page 1
 Tree and Array Multipliers 1 Tree and Array Multipliers Ivor Page 1 11.1 Tree Multipliers In Figure 1 seven input operands are combined by a tree of CSAs. The final level of the tree is a carry-completion
Tree and Array Multipliers 1 Tree and Array Multipliers Ivor Page 1 11.1 Tree Multipliers In Figure 1 seven input operands are combined by a tree of CSAs. The final level of the tree is a carry-completion
CSEE 3827: Fundamentals of Computer Systems. Combinational Circuits
 CSEE 3827: Fundamentals of Computer Systems Combinational Circuits Outline (M&K 3., 3.3, 3.6-3.9, 4.-4.2, 4.5, 9.4) Combinational Circuit Design Standard combinational circuits enabler decoder encoder
CSEE 3827: Fundamentals of Computer Systems Combinational Circuits Outline (M&K 3., 3.3, 3.6-3.9, 4.-4.2, 4.5, 9.4) Combinational Circuit Design Standard combinational circuits enabler decoder encoder
Adders - Subtractors
 Adders - Subtractors Lesson Objectives: The objectives of this lesson are to learn about: 1. Half adder circuit. 2. Full adder circuit. 3. Binary parallel adder circuit. 4. Half subtractor circuit. 5.
Adders - Subtractors Lesson Objectives: The objectives of this lesson are to learn about: 1. Half adder circuit. 2. Full adder circuit. 3. Binary parallel adder circuit. 4. Half subtractor circuit. 5.
L8/9: Arithmetic Structures
 L8/9: Arithmetic Structures Acknowledgements: Materials in this lecture are courtesy of the following sources and are used with permission. Rex Min Kevin Atkinson Prof. Randy Katz (Unified Microelectronics
L8/9: Arithmetic Structures Acknowledgements: Materials in this lecture are courtesy of the following sources and are used with permission. Rex Min Kevin Atkinson Prof. Randy Katz (Unified Microelectronics
Digital Design for Multiplication
 Digital Design for Multiplication Norman Matloff October 15, 2003 c 2003, N.S. Matloff 1 Overview A cottage industry exists in developing fast digital logic to perform arithmetic computations. Fast addition,
Digital Design for Multiplication Norman Matloff October 15, 2003 c 2003, N.S. Matloff 1 Overview A cottage industry exists in developing fast digital logic to perform arithmetic computations. Fast addition,
We are here. Assembly Language. Processors Arithmetic Logic Units. Finite State Machines. Circuits Gates. Transistors
 CSC258 Week 3 1 Logistics If you cannot login to MarkUs, email me your UTORID and name. Check lab marks on MarkUs, if it s recorded wrong, contact Larry within a week after the lab. Quiz 1 average: 86%
CSC258 Week 3 1 Logistics If you cannot login to MarkUs, email me your UTORID and name. Check lab marks on MarkUs, if it s recorded wrong, contact Larry within a week after the lab. Quiz 1 average: 86%
The logic is straightforward. Adding two 0s will result in 0. Adding two 1s results in 10 where 1 is the carry bit and 0 is the sum bit.
 Adders Half adders Half adders represent the smallest block for adding in digital computers. What they do is very simple: they add two bits, producing a sum and a carry. The logic is straightforward. Adding
Adders Half adders Half adders represent the smallest block for adding in digital computers. What they do is very simple: they add two bits, producing a sum and a carry. The logic is straightforward. Adding
UNSIGNED BINARY NUMBERS DIGITAL ELECTRONICS SYSTEM DESIGN WHAT ABOUT NEGATIVE NUMBERS? BINARY ADDITION 11/9/2018
 DIGITAL ELECTRONICS SYSTEM DESIGN LL 2018 PROFS. IRIS BAHAR & ROD BERESFORD NOVEMBER 9, 2018 LECTURE 19: BINARY ADDITION, UNSIGNED BINARY NUMBERS For the binary number b n-1 b n-2 b 1 b 0. b -1 b -2 b
DIGITAL ELECTRONICS SYSTEM DESIGN LL 2018 PROFS. IRIS BAHAR & ROD BERESFORD NOVEMBER 9, 2018 LECTURE 19: BINARY ADDITION, UNSIGNED BINARY NUMBERS For the binary number b n-1 b n-2 b 1 b 0. b -1 b -2 b
What s the Deal? MULTIPLICATION. Time to multiply
 What s the Deal? MULTIPLICATION Time to multiply Multiplying two numbers requires a multiply Luckily, in binary that s just an AND gate! 0*0=0, 0*1=0, 1*0=0, 1*1=1 Generate a bunch of partial products
What s the Deal? MULTIPLICATION Time to multiply Multiplying two numbers requires a multiply Luckily, in binary that s just an AND gate! 0*0=0, 0*1=0, 1*0=0, 1*1=1 Generate a bunch of partial products
Combinational Logic. By : Ali Mustafa
 Combinational Logic By : Ali Mustafa Contents Adder Subtractor Multiplier Comparator Decoder Encoder Multiplexer How to Analyze any combinational circuit like this? Analysis Procedure To obtain the output
Combinational Logic By : Ali Mustafa Contents Adder Subtractor Multiplier Comparator Decoder Encoder Multiplexer How to Analyze any combinational circuit like this? Analysis Procedure To obtain the output
ISSN (PRINT): , (ONLINE): , VOLUME-4, ISSUE-10,
 A NOVEL DOMINO LOGIC DESIGN FOR EMBEDDED APPLICATION Dr.K.Sujatha Associate Professor, Department of Computer science and Engineering, Sri Krishna College of Engineering and Technology, Coimbatore, Tamilnadu,
A NOVEL DOMINO LOGIC DESIGN FOR EMBEDDED APPLICATION Dr.K.Sujatha Associate Professor, Department of Computer science and Engineering, Sri Krishna College of Engineering and Technology, Coimbatore, Tamilnadu,
Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective. Arithmetic Circuits. Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic.
 Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic Arithmetic Circuits January, 2003 1 A Generic Digital Processor MEMORY INPUT-OUTPUT CONTROL DATAPATH
Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic Arithmetic Circuits January, 2003 1 A Generic Digital Processor MEMORY INPUT-OUTPUT CONTROL DATAPATH
Arithmetic Circuits-2
 Arithmetic Circuits-2 Multipliers Array multipliers Shifters Barrel shifter Logarithmic shifter ECE 261 Krish Chakrabarty 1 Binary Multiplication M-1 X = X i 2 i i=0 Multiplicand N-1 Y = Y i 2 i i=0 Multiplier
Arithmetic Circuits-2 Multipliers Array multipliers Shifters Barrel shifter Logarithmic shifter ECE 261 Krish Chakrabarty 1 Binary Multiplication M-1 X = X i 2 i i=0 Multiplicand N-1 Y = Y i 2 i i=0 Multiplier
EECS150. Arithmetic Circuits
 EE5 ection 8 Arithmetic ircuits Fall 2 Arithmetic ircuits Excellent Examples of ombinational Logic Design Time vs. pace Trade-offs Doing things fast may require more logic and thus more space Example:
EE5 ection 8 Arithmetic ircuits Fall 2 Arithmetic ircuits Excellent Examples of ombinational Logic Design Time vs. pace Trade-offs Doing things fast may require more logic and thus more space Example:
Carry Look-ahead Adders. EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 12 - Combinational Logic & Arithmetic Circuits Part 2. Carry Look-ahead Adders
 EECS5 - Digital Design Leture 2 - Combinational Logi & Arithmeti Ciruits Part 2 Otober 3, 22 John Wawrzynek In general, for n-bit addition best we an ahieve is delay α log(n) How do we arrange this? (think
EECS5 - Digital Design Leture 2 - Combinational Logi & Arithmeti Ciruits Part 2 Otober 3, 22 John Wawrzynek In general, for n-bit addition best we an ahieve is delay α log(n) How do we arrange this? (think
Review. EECS Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems. Lec 18 Arithmetic II (Multiplication) Computer Number Systems
 Review EE 5 - omponents and Design Techniques for Digital ystems Lec 8 rithmetic II (Multiplication) David uller Electrical Engineering and omputer ciences University of alifornia, Berkeley http://www.eecs.berkeley.edu/~culler
Review EE 5 - omponents and Design Techniques for Digital ystems Lec 8 rithmetic II (Multiplication) David uller Electrical Engineering and omputer ciences University of alifornia, Berkeley http://www.eecs.berkeley.edu/~culler
VLSI Design. [Adapted from Rabaey s Digital Integrated Circuits, 2002, J. Rabaey et al.] ECE 4121 VLSI DEsign.1
![VLSI Design. [Adapted from Rabaey s Digital Integrated Circuits, 2002, J. Rabaey et al.] ECE 4121 VLSI DEsign.1 VLSI Design. [Adapted from Rabaey s Digital Integrated Circuits, 2002, J. Rabaey et al.] ECE 4121 VLSI DEsign.1](/thumbs/72/67474772.jpg) VLSI Design Adder Design [Adapted from Rabaey s Digital Integrated Circuits, 2002, J. Rabaey et al.] ECE 4121 VLSI DEsign.1 Major Components of a Computer Processor Devices Control Memory Input Datapath
VLSI Design Adder Design [Adapted from Rabaey s Digital Integrated Circuits, 2002, J. Rabaey et al.] ECE 4121 VLSI DEsign.1 Major Components of a Computer Processor Devices Control Memory Input Datapath
EECS 141 Due 04/19/02, 5pm, in 558 Cory
 UIVERSITY OF CALIFORIA College of Engineering Deprtment of Electricl Engineering nd Computer Sciences Lst modified on April 8, 2002 y Tufn Krlr (tufn@eecs.erkeley.edu) Jn M. Rey, Andrei Vldemirescu Homework
UIVERSITY OF CALIFORIA College of Engineering Deprtment of Electricl Engineering nd Computer Sciences Lst modified on April 8, 2002 y Tufn Krlr (tufn@eecs.erkeley.edu) Jn M. Rey, Andrei Vldemirescu Homework
DIGITAL TECHNICS. Dr. Bálint Pődör. Óbuda University, Microelectronics and Technology Institute
 DIGITAL TECHNICS Dr. Bálint Pődör Óbuda University, Microelectronics and Technology Institute 4. LECTURE: COMBINATIONAL LOGIC DESIGN: ARITHMETICS (THROUGH EXAMPLES) 2016/2017 COMBINATIONAL LOGIC DESIGN:
DIGITAL TECHNICS Dr. Bálint Pődör Óbuda University, Microelectronics and Technology Institute 4. LECTURE: COMBINATIONAL LOGIC DESIGN: ARITHMETICS (THROUGH EXAMPLES) 2016/2017 COMBINATIONAL LOGIC DESIGN:
Hw 6 due Thursday, Nov 3, 5pm No lab this week
 EE141 Fall 2005 Lecture 18 dders nnouncements Hw 6 due Thursday, Nov 3, 5pm No lab this week Midterm 2 Review: Tue Nov 8, North Gate Hall, Room 105, 6:30-8:30pm Exam: Thu Nov 10, Morgan, Room 101, 6:30-8:00pm
EE141 Fall 2005 Lecture 18 dders nnouncements Hw 6 due Thursday, Nov 3, 5pm No lab this week Midterm 2 Review: Tue Nov 8, North Gate Hall, Room 105, 6:30-8:30pm Exam: Thu Nov 10, Morgan, Room 101, 6:30-8:00pm
EFFICIENT MULTIOUTPUT CARRY LOOK-AHEAD ADDERS
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF RESEARCH IN COMPUTER APPLICATIONS AND ROBOTICS ISSN 2320-7345 EFFICIENT MULTIOUTPUT CARRY LOOK-AHEAD ADDERS B. Venkata Sreecharan 1, C. Venkata Sudhakar 2 1 M.TECH (VLSI DESIGN)
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF RESEARCH IN COMPUTER APPLICATIONS AND ROBOTICS ISSN 2320-7345 EFFICIENT MULTIOUTPUT CARRY LOOK-AHEAD ADDERS B. Venkata Sreecharan 1, C. Venkata Sudhakar 2 1 M.TECH (VLSI DESIGN)
3. Combinational Circuit Design
 CSEE 3827: Fundamentals of Computer Systems, Spring 2 3. Combinational Circuit Design Prof. Martha Kim (martha@cs.columbia.edu) Web: http://www.cs.columbia.edu/~martha/courses/3827/sp/ Outline (H&H 2.8,
CSEE 3827: Fundamentals of Computer Systems, Spring 2 3. Combinational Circuit Design Prof. Martha Kim (martha@cs.columbia.edu) Web: http://www.cs.columbia.edu/~martha/courses/3827/sp/ Outline (H&H 2.8,
Combinational Logic Design Arithmetic Functions and Circuits
 Combinational Logic Design Arithmetic Functions and Circuits Overview Binary Addition Half Adder Full Adder Ripple Carry Adder Carry Look-ahead Adder Binary Subtraction Binary Subtractor Binary Adder-Subtractor
Combinational Logic Design Arithmetic Functions and Circuits Overview Binary Addition Half Adder Full Adder Ripple Carry Adder Carry Look-ahead Adder Binary Subtraction Binary Subtractor Binary Adder-Subtractor
Class Website:
 ECE 20B, Winter 2003 Introduction to Electrical Engineering, II LECTURE NOTES #5 Instructor: Andrew B. Kahng (lecture) Email: abk@ece.ucsd.edu Telephone: 858-822-4884 office, 858-353-0550 cell Office:
ECE 20B, Winter 2003 Introduction to Electrical Engineering, II LECTURE NOTES #5 Instructor: Andrew B. Kahng (lecture) Email: abk@ece.ucsd.edu Telephone: 858-822-4884 office, 858-353-0550 cell Office:
Computer Architecture. ESE 345 Computer Architecture. Design Process. CA: Design process
 Computer Architecture ESE 345 Computer Architecture Design Process 1 The Design Process "To Design Is To Represent" Design activity yields description/representation of an object -- Traditional craftsman
Computer Architecture ESE 345 Computer Architecture Design Process 1 The Design Process "To Design Is To Represent" Design activity yields description/representation of an object -- Traditional craftsman
Computer Architecture 10. Fast Adders
 Computer Architecture 10 Fast s Ma d e wi t h Op e n Of f i c e. o r g 1 Carry Problem Addition is primary mechanism in implementing arithmetic operations Slow addition directly affects the total performance
Computer Architecture 10 Fast s Ma d e wi t h Op e n Of f i c e. o r g 1 Carry Problem Addition is primary mechanism in implementing arithmetic operations Slow addition directly affects the total performance
Total Time = 90 Minutes, Total Marks = 100. Total /10 /25 /20 /10 /15 /20
 University of Waterloo Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering E&CE 223 Digital Circuits and Systems Midterm Examination Instructor: M. Sachdev October 30th, 2006 Total Time = 90 Minutes, Total
University of Waterloo Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering E&CE 223 Digital Circuits and Systems Midterm Examination Instructor: M. Sachdev October 30th, 2006 Total Time = 90 Minutes, Total
Looking at a two binary digit sum shows what we need to extend addition to multiple binary digits.
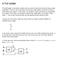 A Full Adder The half-adder is extremely useful until you want to add more that one binary digit quantities. The slow way to develop a two binary digit adders would be to make a truth table and reduce
A Full Adder The half-adder is extremely useful until you want to add more that one binary digit quantities. The slow way to develop a two binary digit adders would be to make a truth table and reduce
CSE140: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems. Logic minimization algorithm summary. Instructor: Mohsen Imani UC San Diego
 CSE4: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems Logic minimization algorithm summary Instructor: Mohsen Imani UC San Diego Slides from: Prof.Tajana Simunic Rosing & Dr.Pietro Mercati Definition
CSE4: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems Logic minimization algorithm summary Instructor: Mohsen Imani UC San Diego Slides from: Prof.Tajana Simunic Rosing & Dr.Pietro Mercati Definition
Arithmetic Circuits-2
 Arithmetic Circuits-2 Multipliers Array multipliers Shifters Barrel shifter Logarithmic shifter ECE 261 Krish Chakrabarty 1 Binary Multiplication M-1 X = X i 2 i i=0 Multiplicand N-1 Y = Y i 2 i i=0 Multiplier
Arithmetic Circuits-2 Multipliers Array multipliers Shifters Barrel shifter Logarithmic shifter ECE 261 Krish Chakrabarty 1 Binary Multiplication M-1 X = X i 2 i i=0 Multiplicand N-1 Y = Y i 2 i i=0 Multiplier
Building a Computer Adder
 Logic Gates are used to translate Boolean logic into circuits. In the abstract it is clear that we can build AND gates that perform the AND function and OR gates that perform the OR function and so on.
Logic Gates are used to translate Boolean logic into circuits. In the abstract it is clear that we can build AND gates that perform the AND function and OR gates that perform the OR function and so on.
Dual-Field Arithmetic Unit for GF(p) and GF(2 m ) *
 Institute for Applied Information Processing and Communications Graz University of Technology Dual-Field Arithmetic Unit for GF(p) and GF(2 m ) * CHES 2002 Workshop on Cryptographic Hardware and Embedded
Institute for Applied Information Processing and Communications Graz University of Technology Dual-Field Arithmetic Unit for GF(p) and GF(2 m ) * CHES 2002 Workshop on Cryptographic Hardware and Embedded
Arithmetic in Integer Rings and Prime Fields
 Arithmetic in Integer Rings and Prime Fields A 3 B 3 A 2 B 2 A 1 B 1 A 0 B 0 FA C 3 FA C 2 FA C 1 FA C 0 C 4 S 3 S 2 S 1 S 0 http://koclab.org Çetin Kaya Koç Spring 2018 1 / 71 Contents Arithmetic in Integer
Arithmetic in Integer Rings and Prime Fields A 3 B 3 A 2 B 2 A 1 B 1 A 0 B 0 FA C 3 FA C 2 FA C 1 FA C 0 C 4 S 3 S 2 S 1 S 0 http://koclab.org Çetin Kaya Koç Spring 2018 1 / 71 Contents Arithmetic in Integer
I. INTRODUCTION. CMOS Technology: An Introduction to QCA Technology As an. T. Srinivasa Padmaja, C. M. Sri Priya
 International Journal of Scientific Research in Computer Science, Engineering and Information Technology 2018 IJSRCSEIT Volume 3 Issue 5 ISSN : 2456-3307 Design and Implementation of Carry Look Ahead Adder
International Journal of Scientific Research in Computer Science, Engineering and Information Technology 2018 IJSRCSEIT Volume 3 Issue 5 ISSN : 2456-3307 Design and Implementation of Carry Look Ahead Adder
Arithmetic Circuits How to add and subtract using combinational logic Setting flags Adding faster
 rithmetic Circuits Didn t I learn how to do addition in second grade? UNC courses aren t what they used to be... 01011 +00101 10000 Finally; time to build some serious functional blocks We ll need a lot
rithmetic Circuits Didn t I learn how to do addition in second grade? UNC courses aren t what they used to be... 01011 +00101 10000 Finally; time to build some serious functional blocks We ll need a lot
UNIT II COMBINATIONAL CIRCUITS:
 UNIT II COMBINATIONAL CIRCUITS: INTRODUCTION: The digital system consists of two types of circuits, namely (i) (ii) Combinational circuits Sequential circuits Combinational circuit consists of logic gates
UNIT II COMBINATIONAL CIRCUITS: INTRODUCTION: The digital system consists of two types of circuits, namely (i) (ii) Combinational circuits Sequential circuits Combinational circuit consists of logic gates
Low Latency Architectures of a Comparator for Binary Signed Digits in a 28-nm CMOS Technology
 Low Latency Architectures of a Comparator for Binary Signed Digits in a 28-nm CMOS Technology Martin Schmidt, Thomas Veigel, Sebastian Haug, Markus Grözing, Manfred Berroth Stuttgart, Germany 1 Outline
Low Latency Architectures of a Comparator for Binary Signed Digits in a 28-nm CMOS Technology Martin Schmidt, Thomas Veigel, Sebastian Haug, Markus Grözing, Manfred Berroth Stuttgart, Germany 1 Outline
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 24 - Arithmetic Blocks, Part 2 + Shifters
 EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 24 - Arithmetic Blocks, Part 2 + Shifters April 15, 2010 John Wawrzynek 1 Multiplication a 3 a 2 a 1 a 0 Multiplicand b 3 b 2 b 1 b 0 Multiplier X a 3 b 0 a 2 b 0 a 1 b
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 24 - Arithmetic Blocks, Part 2 + Shifters April 15, 2010 John Wawrzynek 1 Multiplication a 3 a 2 a 1 a 0 Multiplicand b 3 b 2 b 1 b 0 Multiplier X a 3 b 0 a 2 b 0 a 1 b
CMPEN 411 VLSI Digital Circuits Spring Lecture 19: Adder Design
 CMPEN 411 VLSI Digital Circuits Spring 2011 Lecture 19: Adder Design [Adapted from Rabaey s Digital Integrated Circuits, Second Edition, 2003 J. Rabaey, A. Chandrakasan, B. Nikolic] Sp11 CMPEN 411 L19
CMPEN 411 VLSI Digital Circuits Spring 2011 Lecture 19: Adder Design [Adapted from Rabaey s Digital Integrated Circuits, Second Edition, 2003 J. Rabaey, A. Chandrakasan, B. Nikolic] Sp11 CMPEN 411 L19
Homework 4 due today Quiz #4 today In class (80min) final exam on April 29 Project reports due on May 4. Project presentations May 5, 1-4pm
 EE241 - Spring 2010 Advanced Digital Integrated Circuits Lecture 25: Digital Arithmetic Adders Announcements Homework 4 due today Quiz #4 today In class (80min) final exam on April 29 Project reports due
EE241 - Spring 2010 Advanced Digital Integrated Circuits Lecture 25: Digital Arithmetic Adders Announcements Homework 4 due today Quiz #4 today In class (80min) final exam on April 29 Project reports due
Lecture 18: Datapath Functional Units
 Lecture 8: Datapath Functional Unit Outline Comparator Shifter Multi-input Adder Multiplier 8: Datapath Functional Unit CMOS VLSI Deign 4th Ed. 2 Comparator 0 detector: A = 00 000 detector: A = Equality
Lecture 8: Datapath Functional Unit Outline Comparator Shifter Multi-input Adder Multiplier 8: Datapath Functional Unit CMOS VLSI Deign 4th Ed. 2 Comparator 0 detector: A = 00 000 detector: A = Equality
Boolean Algebra and Digital Logic 2009, University of Colombo School of Computing
 IT 204 Section 3.0 Boolean Algebra and Digital Logic Boolean Algebra 2 Logic Equations to Truth Tables X = A. B + A. B + AB A B X 0 0 0 0 3 Sum of Products The OR operation performed on the products of
IT 204 Section 3.0 Boolean Algebra and Digital Logic Boolean Algebra 2 Logic Equations to Truth Tables X = A. B + A. B + AB A B X 0 0 0 0 3 Sum of Products The OR operation performed on the products of
Lecture 12: Datapath Functional Units
 Lecture 2: Datapath Functional Unit Slide courtey of Deming Chen Slide baed on the initial et from David Harri CMOS VLSI Deign Outline Comparator Shifter Multi-input Adder Multiplier Reading:.3-4;.8-9
Lecture 2: Datapath Functional Unit Slide courtey of Deming Chen Slide baed on the initial et from David Harri CMOS VLSI Deign Outline Comparator Shifter Multi-input Adder Multiplier Reading:.3-4;.8-9
A B OUT_0 OUT_1 OUT_2 OUT_
 A B OUT_0 OUT_1 OUT_2 OUT_3 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 1 0 0 0 1 A Decoder is something that does the opposite of encoding; it converts the data back into its original form. This decoder converts
A B OUT_0 OUT_1 OUT_2 OUT_3 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 1 0 0 0 1 A Decoder is something that does the opposite of encoding; it converts the data back into its original form. This decoder converts
Residue Number Systems Ivor Page 1
 Residue Number Systems 1 Residue Number Systems Ivor Page 1 7.1 Arithmetic in a modulus system The great speed of arithmetic in Residue Number Systems (RNS) comes from a simple theorem from number theory:
Residue Number Systems 1 Residue Number Systems Ivor Page 1 7.1 Arithmetic in a modulus system The great speed of arithmetic in Residue Number Systems (RNS) comes from a simple theorem from number theory:
ELCT201: DIGITAL LOGIC DESIGN
 ELCT2: DIGITAL LOGIC DESIGN Dr. Eng. Haitham Omran, haitham.omran@guc.edu.eg Dr. Eng. Wassim Alexan, wassim.joseph@guc.edu.eg Lecture 4 Following the slides of Dr. Ahmed H. Madian محرم 439 ه Winter 28
ELCT2: DIGITAL LOGIC DESIGN Dr. Eng. Haitham Omran, haitham.omran@guc.edu.eg Dr. Eng. Wassim Alexan, wassim.joseph@guc.edu.eg Lecture 4 Following the slides of Dr. Ahmed H. Madian محرم 439 ه Winter 28
An Area Efficient Enhanced Carry Select Adder
 International Journal of Engineering Science Invention ISSN (Online): 2319 6734, ISSN (Print): 2319 6726 PP.06-12 An Area Efficient Enhanced Carry Select Adder 1, Gaandla.Anusha, 2, B.ShivaKumar 1, PG
International Journal of Engineering Science Invention ISSN (Online): 2319 6734, ISSN (Print): 2319 6726 PP.06-12 An Area Efficient Enhanced Carry Select Adder 1, Gaandla.Anusha, 2, B.ShivaKumar 1, PG
A COMBINED 16-BIT BINARY AND DUAL GALOIS FIELD MULTIPLIER. Jesus Garcia and Michael J. Schulte
 A COMBINED 16-BIT BINARY AND DUAL GALOIS FIELD MULTIPLIER Jesus Garcia and Michael J. Schulte Lehigh University Department of Computer Science and Engineering Bethlehem, PA 15 ABSTRACT Galois field arithmetic
A COMBINED 16-BIT BINARY AND DUAL GALOIS FIELD MULTIPLIER Jesus Garcia and Michael J. Schulte Lehigh University Department of Computer Science and Engineering Bethlehem, PA 15 ABSTRACT Galois field arithmetic
CSE 20 DISCRETE MATH. Fall
 CSE 20 DISCRETE MATH Fall 2017 http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/classes/fa17/cse20-ab/ Today's learning goals Describe and use algorithms for integer operations based on their expansions Relate algorithms for integer
CSE 20 DISCRETE MATH Fall 2017 http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/classes/fa17/cse20-ab/ Today's learning goals Describe and use algorithms for integer operations based on their expansions Relate algorithms for integer
Number System. Decimal to binary Binary to Decimal Binary to octal Binary to hexadecimal Hexadecimal to binary Octal to binary
 Number System Decimal to binary Binary to Decimal Binary to octal Binary to hexadecimal Hexadecimal to binary Octal to binary BOOLEAN ALGEBRA BOOLEAN LOGIC OPERATIONS Logical AND Logical OR Logical COMPLEMENTATION
Number System Decimal to binary Binary to Decimal Binary to octal Binary to hexadecimal Hexadecimal to binary Octal to binary BOOLEAN ALGEBRA BOOLEAN LOGIC OPERATIONS Logical AND Logical OR Logical COMPLEMENTATION
DESIGN AND ANALYSIS OF A FULL ADDER USING VARIOUS REVERSIBLE GATES
 DESIGN AND ANALYSIS OF A FULL ADDER USING VARIOUS REVERSIBLE GATES Sudhir Dakey Faculty,Department of E.C.E., MVSR Engineering College Abstract The goal of VLSI has remained unchanged since many years
DESIGN AND ANALYSIS OF A FULL ADDER USING VARIOUS REVERSIBLE GATES Sudhir Dakey Faculty,Department of E.C.E., MVSR Engineering College Abstract The goal of VLSI has remained unchanged since many years
mith College Computer Science CSC270 Spring 16 Circuits and Systems Lecture Notes Week 2 Dominique Thiébaut
 mith College Computer Science CSC270 Spring 16 Circuits and Systems Lecture Notes Week 2 Dominique Thiébaut dthiebaut@smith.edu Lab 1: Lessons Learned a0 b0 adder c0 S0 a1 b1 a0 b0 adder adder S1 S0 a31
mith College Computer Science CSC270 Spring 16 Circuits and Systems Lecture Notes Week 2 Dominique Thiébaut dthiebaut@smith.edu Lab 1: Lessons Learned a0 b0 adder c0 S0 a1 b1 a0 b0 adder adder S1 S0 a31
Review for Test 1 : Ch1 5
 Review for Test 1 : Ch1 5 October 5, 2006 Typeset by FoilTEX Positional Numbers 527.46 10 = (5 10 2 )+(2 10 1 )+(7 10 0 )+(4 10 1 )+(6 10 2 ) 527.46 8 = (5 8 2 ) + (2 8 1 ) + (7 8 0 ) + (4 8 1 ) + (6 8
Review for Test 1 : Ch1 5 October 5, 2006 Typeset by FoilTEX Positional Numbers 527.46 10 = (5 10 2 )+(2 10 1 )+(7 10 0 )+(4 10 1 )+(6 10 2 ) 527.46 8 = (5 8 2 ) + (2 8 1 ) + (7 8 0 ) + (4 8 1 ) + (6 8
Chapter 4. Combinational: Circuits with logic gates whose outputs depend on the present combination of the inputs. elements. Dr.
 Chapter 4 Dr. Panos Nasiopoulos Combinational: Circuits with logic gates whose outputs depend on the present combination of the inputs. Sequential: In addition, they include storage elements Combinational
Chapter 4 Dr. Panos Nasiopoulos Combinational: Circuits with logic gates whose outputs depend on the present combination of the inputs. Sequential: In addition, they include storage elements Combinational
CMSC 313 Lecture 17. Focus Groups. Announcement: in-class lab Thu 10/30 Homework 3 Questions Circuits for Addition Midterm Exam returned
 Focus Groups CMSC 33 Lecture 7 Need good sample of all types of CS students Mon /7 & Thu /2, 2:3p-2:p & 6:p-7:3p Announcement: in-class lab Thu /3 Homework 3 Questions Circuits for Addition Midterm Exam
Focus Groups CMSC 33 Lecture 7 Need good sample of all types of CS students Mon /7 & Thu /2, 2:3p-2:p & 6:p-7:3p Announcement: in-class lab Thu /3 Homework 3 Questions Circuits for Addition Midterm Exam
Lecture 5: Arithmetic
 Lecture 5: Arithmetic COS / ELE 375 Computer Architecture and Organization Princeton University Fall 2015 Prof. David August 1 5 Binary Representation of Integers Two physical states: call these 1 and
Lecture 5: Arithmetic COS / ELE 375 Computer Architecture and Organization Princeton University Fall 2015 Prof. David August 1 5 Binary Representation of Integers Two physical states: call these 1 and
9. Datapath Design. Jacob Abraham. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering The University of Texas at Austin VLSI Design Fall 2017
 9. Datapath Design Jacob Abraham Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering The University of Texas at Austin VLSI Design Fall 2017 October 2, 2017 ECE Department, University of Texas at Austin
9. Datapath Design Jacob Abraham Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering The University of Texas at Austin VLSI Design Fall 2017 October 2, 2017 ECE Department, University of Texas at Austin
Reduced-Area Constant-Coefficient and Multiple-Constant Multipliers for Xilinx FPGAs with 6-Input LUTs
 Article Reduced-Area Constant-Coefficient and Multiple-Constant Multipliers for Xilinx FPGAs with 6-Input LUTs E. George Walters III Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Penn State Erie,
Article Reduced-Area Constant-Coefficient and Multiple-Constant Multipliers for Xilinx FPGAs with 6-Input LUTs E. George Walters III Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Penn State Erie,
CS221: Digital Design Data Path Components Adder
 CS221: Digital Design Data Path Coponents Adder Dr. A. Sahu DeptofCop.Sc.&Engg. Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati Outline Adder: Basic Model Carry Propagation and Generation MachesterAdder Carry
CS221: Digital Design Data Path Coponents Adder Dr. A. Sahu DeptofCop.Sc.&Engg. Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati Outline Adder: Basic Model Carry Propagation and Generation MachesterAdder Carry
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 4 - Boolean Algebra I (Representations of Combinational Logic Circuits)
 EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 4 - Boolean Algebra I (Representations of Combinational Logic Circuits) September 5, 2002 John Wawrzynek Fall 2002 EECS150 Lec4-bool1 Page 1, 9/5 9am Outline Review of
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 4 - Boolean Algebra I (Representations of Combinational Logic Circuits) September 5, 2002 John Wawrzynek Fall 2002 EECS150 Lec4-bool1 Page 1, 9/5 9am Outline Review of
ECE/CS 552: Introduction To Computer Architecture 1. Instructor:Mikko H Lipasti. Fall 2010 University i of Wisconsin-Madison
 ECE/CS 552: Arithmetic I Instructor:Mikko H Lipasti Fall 2010 Univsity i of Wisconsin-Madison i Lecture notes partially based on set created by Mark Hill. Basic Arithmetic and the ALU Numb representations:
ECE/CS 552: Arithmetic I Instructor:Mikko H Lipasti Fall 2010 Univsity i of Wisconsin-Madison i Lecture notes partially based on set created by Mark Hill. Basic Arithmetic and the ALU Numb representations:
Chapter 4: Designing Combinational Systems Uchechukwu Ofoegbu
 Chapter 4: Designing Combinational Systems Uchechukwu Ofoegbu Temple University Gate Delay ((1.1).1) ((1.0).0) ((0.1).1) ((0.1).0) ((1.1) = 1 0 s = sum c out carry-out a, b = added bits C = carry in a
Chapter 4: Designing Combinational Systems Uchechukwu Ofoegbu Temple University Gate Delay ((1.1).1) ((1.0).0) ((0.1).1) ((0.1).0) ((1.1) = 1 0 s = sum c out carry-out a, b = added bits C = carry in a
Reversible ALU Implementation using Kogge-Stone Adder
 Reversible ALU Implementation using Kogge-Stone Adder K.Ravitejakhanna Student, Department of ECE SR Engineering College, Ch.Sridevi Reddy Asst.Professor, Department of ECE SR Engineering College, Abstract
Reversible ALU Implementation using Kogge-Stone Adder K.Ravitejakhanna Student, Department of ECE SR Engineering College, Ch.Sridevi Reddy Asst.Professor, Department of ECE SR Engineering College, Abstract
Outline. EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 4 - Boolean Algebra I (Representations of Combinational Logic Circuits) Combinational Logic (CL) Defined
 EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 4 - Boolean Algebra I (Representations of Combinational Logic Circuits) January 30, 2003 John Wawrzynek Outline Review of three representations for combinational logic:
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 4 - Boolean Algebra I (Representations of Combinational Logic Circuits) January 30, 2003 John Wawrzynek Outline Review of three representations for combinational logic:
Systems I: Computer Organization and Architecture
 Systems I: Computer Organization and Architecture Lecture 6 - Combinational Logic Introduction A combinational circuit consists of input variables, logic gates, and output variables. The logic gates accept
Systems I: Computer Organization and Architecture Lecture 6 - Combinational Logic Introduction A combinational circuit consists of input variables, logic gates, and output variables. The logic gates accept
ALUs and Data Paths. Subtitle: How to design the data path of a processor. 1/8/ L3 Data Path Design Copyright Joanne DeGroat, ECE, OSU 1
 ALUs and Data Paths Subtitle: How to design the data path of a processor. Copyright 2006 - Joanne DeGroat, ECE, OSU 1 Lecture overview General Data Path of a multifunction ALU Copyright 2006 - Joanne DeGroat,
ALUs and Data Paths Subtitle: How to design the data path of a processor. Copyright 2006 - Joanne DeGroat, ECE, OSU 1 Lecture overview General Data Path of a multifunction ALU Copyright 2006 - Joanne DeGroat,
Computer Architecture. ECE 361 Lecture 5: The Design Process & ALU Design. 361 design.1
 Computer Architecture ECE 361 Lecture 5: The Design Process & Design 361 design.1 Quick Review of Last Lecture 361 design.2 MIPS ISA Design Objectives and Implications Support general OS and C- style language
Computer Architecture ECE 361 Lecture 5: The Design Process & Design 361 design.1 Quick Review of Last Lecture 361 design.2 MIPS ISA Design Objectives and Implications Support general OS and C- style language
Lecture 8: Sequential Multipliers
 Lecture 8: Sequential Multipliers ECE 645 Computer Arithmetic 3/25/08 ECE 645 Computer Arithmetic Lecture Roadmap Sequential Multipliers Unsigned Signed Radix-2 Booth Recoding High-Radix Multiplication
Lecture 8: Sequential Multipliers ECE 645 Computer Arithmetic 3/25/08 ECE 645 Computer Arithmetic Lecture Roadmap Sequential Multipliers Unsigned Signed Radix-2 Booth Recoding High-Radix Multiplication
Review for Final Exam
 CSE140: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems Review for Final Exam Mohsen Imani CAPE Please submit your evaluations!!!! RTL design Use the RTL design process to design a system that has
CSE140: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems Review for Final Exam Mohsen Imani CAPE Please submit your evaluations!!!! RTL design Use the RTL design process to design a system that has
Overview. Arithmetic circuits. Binary half adder. Binary full adder. Last lecture PLDs ROMs Tristates Design examples
 Overview rithmetic circuits Last lecture PLDs ROMs Tristates Design examples Today dders Ripple-carry Carry-lookahead Carry-select The conclusion of combinational logic!!! General-purpose building blocks
Overview rithmetic circuits Last lecture PLDs ROMs Tristates Design examples Today dders Ripple-carry Carry-lookahead Carry-select The conclusion of combinational logic!!! General-purpose building blocks
ECE 2300 Digital Logic & Computer Organization
 ECE 2300 Digital Logic & Computer Organization pring 201 More inary rithmetic LU 1 nnouncements Lab 4 prelab () due tomorrow Lab 5 to be released tonight 2 Example: Fixed ize 2 C ddition White stone =
ECE 2300 Digital Logic & Computer Organization pring 201 More inary rithmetic LU 1 nnouncements Lab 4 prelab () due tomorrow Lab 5 to be released tonight 2 Example: Fixed ize 2 C ddition White stone =
Every time has a value associated with it, not just some times. A variable can take on any value within a range
 Digital Logic Circuits Binary Logic and Gates Logic Simulation Boolean Algebra NAND/NOR and XOR gates Decoder fundamentals Half Adder, Full Adder, Ripple Carry Adder Analog vs Digital Analog Continuous»
Digital Logic Circuits Binary Logic and Gates Logic Simulation Boolean Algebra NAND/NOR and XOR gates Decoder fundamentals Half Adder, Full Adder, Ripple Carry Adder Analog vs Digital Analog Continuous»
Binary Multipliers. Reading: Study Chapter 3. The key trick of multiplication is memorizing a digit-to-digit table Everything else was just adding
 Binary Multipliers The key trick of multiplication is memorizing a digit-to-digit table Everything else was just adding 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 2 2 4 6 8 2 4 6 8 3 3 6 9 2 5 8 2 24 27 4 4 8 2 6
Binary Multipliers The key trick of multiplication is memorizing a digit-to-digit table Everything else was just adding 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 2 2 4 6 8 2 4 6 8 3 3 6 9 2 5 8 2 24 27 4 4 8 2 6
1 Boolean Algebra Simplification
 cs281: Computer Organization Lab3 Prelab Our objective in this prelab is to lay the groundwork for simplifying boolean expressions in order to minimize the complexity of the resultant digital logic circuit.
cs281: Computer Organization Lab3 Prelab Our objective in this prelab is to lay the groundwork for simplifying boolean expressions in order to minimize the complexity of the resultant digital logic circuit.
Arithmetic and Logic Unit First Part
 Arithmetic and Logic Unit First Part Arquitectura de Computadoras Arturo Díaz D PérezP Centro de Investigación n y de Estudios Avanzados del IPN adiaz@cinvestav.mx Arquitectura de Computadoras ALU1-1 Typical
Arithmetic and Logic Unit First Part Arquitectura de Computadoras Arturo Díaz D PérezP Centro de Investigación n y de Estudios Avanzados del IPN adiaz@cinvestav.mx Arquitectura de Computadoras ALU1-1 Typical
Logic. Combinational. inputs. outputs. the result. system can
 Digital Electronics Combinational Logic Functions Digital logic circuits can be classified as either combinational or sequential circuits. A combinational circuit is one where the output at any time depends
Digital Electronics Combinational Logic Functions Digital logic circuits can be classified as either combinational or sequential circuits. A combinational circuit is one where the output at any time depends
