Computer Architecture 10. Fast Adders
|
|
|
- Clifford Underwood
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Computer Architecture 10 Fast s Ma d e wi t h Op e n Of f i c e. o r g 1
2 Carry Problem Addition is primary mechanism in implementing arithmetic operations Slow addition directly affects the total performance of the computer Complex (and fast) addition schemes increase the cost of the final implementation The choice for adder structure must be tailor- made to the potential applications Ma d e wi t h Op e n Of f i c e. o r g 2
3 RCA (Computer Architecture I) RCA Ripple Carry Simplest, Smallest and Slowest (SSS), but... Worst-case carry-propagation is Θ(k) k - digits Ma d e wi t h Op e n Of f i c e. o r g 3
4 Bit-Serial RCA VLSI implementation advantages: small pin count reduced wire length high clock rate small space low power consumption Alternative to pipeline units for parallel processing shift X Y c FA Bit-serial RCA implementation X+Y shift Ma d e wi t h Op e n Of f i c e. o r g 4
5 Coping with Carry Detect the end of carry propagation asynchronous adders Speed up the propagation (CPA Carry Propagate s) CLA / CSLA / CSKA Carry Lookahead / Select / s Limit the carry propagation CSA Carry Save Estimate & Parallel Carry s Eliminate the carry propagation Carry-free RNS operations Ma d e wi t h Op e n Of f i c e. o r g 5
6 s Overview Not complete 1-bit adders Half HA Full FA Bit Counter (m,k) CPA RCA CSKA CSLA CLA multi-operand adders 3-operand Array CSA Tree Ma d e wi t h Op e n Of f i c e. o r g 6
7 Asynchronous Based on RCA - detection of carry completion Average longest chain of propagation ~ log 2 k Not suitable for synchronous processing a i +b i d i+1 c i+1 a i *b i a i +b i d i carry (c, d) from previous stage c i Complete a i *b i from other bit positions (c,d) extended carry (0,0) Carry not yet known (0,1) Carry 0 (1,0) Carry 1 Ma d e wi t h Op e n Of f i c e. o r g 7
8 CLA (Computer Architecture I) CLA Carry Lookahead Fast but Complex Worst-case carry propagation is Θ(log k) LA LA LA LA Logic - 1 st level LA Logic - 2 nd level k - digits Ma d e wi t h Op e n Of f i c e. o r g 8
9 Carry Select (CSLA) The oldest logarithmic-time adder The additions are performed in parallel according to alternative scenarios: carry= 0 or 1 The final selection of results is made with the computed value of carry CLSAs have Θ(log k) addition time, but with high complexity of hardware c 0 Ma d e wi t h Op e n Of f i c e. o r g 9
10 One-Level CSLA k 1 ½k k/2 RCA 0 ½k 1 0 k 1 ½k k/2 RCA c 0 k/2 RCA 1 k/2 k/2 Mux 2 1 (k/2 buses) c k/2 k/2 k/2 c out + High k/2 bits of result Low k/2 bits of result Ma d e wi t h Op e n Of f i c e. o r g 10
11 Block Propagation in CSLA Not optimal due to block-carry propagation delay k-1 ¾k ¾k-1 ½k ½k-1 ¼k ¼k-1 0 k/4 RCA 1 k/4 RCA 1 k/4 RCA 1 k/4 RCA k/4 RCA 0 k/4 RCA k/4 RCA 0 0 c 0 c 3k/4 c k/2 c k/4 c k Res. k-1...¾k ¾k-1...½k ½k-1...¼k ¼k Ma d e wi t h Op e n Of f i c e. o r g 11
12 Two-Level CSLA Block-carry propagation is fast, but design complex k-1 ¾k ¾k-1 ½k ½k-1 ¼k ¼k-1 0 k/4 RCA 1 c 3k/4 k/4 RCA 1 k/4 RCA k/4 RCA 0 k/4 RCA 0 k/4 RCA 0 1 k/4 RCA c 0 c 3k/4 c k/4 c k/2 c k Result k-1...½k ½k-1...¼k ¼k Ma d e wi t h Op e n Of f i c e. o r g 12
13 Propagation Chains Carries can be generated, propagated or absorbed Propagation chains are evaluated in parallel How to speed up the worst-case propagation? worst-case carry propagation Ma d e wi t h Op e n Of f i c e. o r g 13
14 Carry (CSKA) Carry-in is propagated through n-stages if p=1 Propagate condition p is easily computable c i +1 FA FA FA FA p = p i *p i+1 *p i+2 *p i+3 propagation condition p i =a i +b i c i 4-bit RCA p Carry skip Ma d e wi t h Op e n Of f i c e. o r g 14
15 CSKA 16-bit CSKA 4-bit RCA 4-bit RCA 4-bit RCA 4-bit RCA p p p p c 16 Carry skip c 12 Carry skip c 8 Carry skip c 4 Carry skip c 0 carry-propagate carry-skip carry-propagate worst-case The longest delay due to carry propagation: propagation through bits 1-3 and OR skip bits 4-11 propagation through bits (block 0 and last do not contribute to carry-propagation delay) Ma d e wi t h Op e n Of f i c e. o r g 15
16 CSKA Delay Analysis Assume: 1 block skip-delay = 1 bit carry-propagation k bits, b bits in skip-block (fixed-size) T fixcska carry-propagation delay in fixed-block size CSKA (number of stages the carry must be propagated through) 4-bit RCA 4-bit RCA 4-bit RCA 4-bit RCA p p p p c 16 Carry skip c 12 Carry skip c 8 Carry skip c 4 Carry skip c 0 T fixcska = (b 1) (k/b 2) + (b 1) = 2b + k/b -3.5 in block 0 + OR gate + all skips + in last block e.g. 32-bit: T fixcska = 12.5 (b=4, k=32) Ma d e wi t h Op e n Of f i c e. o r g 16
17 Fixed-Size Blocks Optimal size of fixed-size skip blocks: dt fixcska /db = 0 d(2b + k/b -3.5)/db = 2 k/b 2 = 0 b opt = (k/2) 1/2 T fixcska-opt = 2(2k) 1/2 3.5 e.g. 16-bit adder b opt 3, T fixcska 8 e.g. 32-bit adder b opt = 4, T fixcska = 12.5 e.g. 64-bit adder b opt 6, T fixcska 19 Ma d e wi t h Op e n Of f i c e. o r g 17
18 Variable-Size Blocks Variable-size skip blocks shorten the propagation Optimal configuration is to have the longest block in the middle and the shortest at both ends t number of blocks (even number) b bits in smallest skip block b b+1... b+t/2-1 b+t/ b+1 b k = t*(b + t/4 1/2) b = k/t t/4 + 1/2 Ma d e wi t h Op e n Of f i c e. o r g 18
19 Variable-Size Blocks T varcska carry-propagation delay in fixed-block size CSKA (number of stages the carry must be propagated through) b 1 t b 1 T varcska = 2*(b 1) (t 2) = 2k/t + t/2 2.5 Optimal size of fixed-size skip blocks: dt varcska /db = 0 2k/t 2 + 1/2 = 0 t opt = 2 k 1/2 T varcska-opt = 2 k 1/2 2.5 Ma d e wi t h Op e n Of f i c e. o r g 19
20 Variable-Size Blocks T varcska-opt t opt = 2 k 1/2 varcska-opt = 2 k 1/2 2.5 b opt 1 e.g. 16-bit adder t opt = 8, T fixcska 5.5 e.g. 32-bit adder t opt 12, T fixcska 9 e.g. 64-bit adder t opt = 16, T fixcska 13.5 Ma d e wi t h Op e n Of f i c e. o r g 20
21 Multilevel CSKA First-level skip blocks get propagate-condition signal from block adders Second-level skip blocks get propagate-condition signal from first-level skip blocks Carry can be propagated over group of skip blocks Ma d e wi t h Op e n Of f i c e. o r g 21
22 Multilevel CSKA Multilevel structures are results of complex optimizations and usually are not regular adders first level skip blocks second level skip blocks Ma d e wi t h Op e n Of f i c e. o r g 22
23 Hybrid Fast s Combination of RCA, CLA, CSKA and others allows to satisfy various criteria: high performance cost-effectiveness low power consumption Ma d e wi t h Op e n Of f i c e. o r g 23
24 Example CSLA+CSKA+CLA CL Logic CSKA CSKA 0 1 CSKA CSKA 0 1 CSKA CSKA 0 1 CSKA Ma d e wi t h Op e n Of f i c e. o r g 24
25 Multioperand s Applications in multiplication, vector and matrix arithmetics and others x y x*y x y x*y Adding n-numbers of k-bits, total sum has k+log 2 n bits Ma d e wi t h Op e n Of f i c e. o r g 25
26 Serial Implementation Latency Θ(n Θ log k) faster than linear dependence on number of operands logarithmic dependence for scaling the operand size Partial sum k+log n bits n-operands k-bits Fast adder Θ(log k) Shift register Ma d e wi t h Op e n Of f i c e. o r g 26
27 Tree Implementation with CPA Tree of 2-operand adders (RCA are best here!) For n-operands, n-1 adders are needed (costly) Latency Θ(k+log Θ n) scales well with n n k-bit operands RCA RCA RCA k+1 k+1 k+1 RCA RCA k+2 k+2 RCA k+3 bit result Ma d e wi t h Op e n Of f i c e. o r g 27
28 Look into Tree of RCAs s at higher levels need not wait for full carry propagation from lower-level adders All adders start with just one FA-delay after previous level FA FA HA single RCA at level i FA HA single RCA at level i+1 Ma d e wi t h Op e n Of f i c e. o r g 28
29 Tree Implementation with CSA Tree of 3-operand carry-save adders CSA reduce n-operands to 2-operands, Θ(log n) Final fast CPA is needed, Θ(log k) Latency Θ(log Θ n + log k) scales well with n & k n k-bit operands CSA CSA CSA CSA CSA CPA Ma d e wi t h Op e n Of f i c e. o r g 29
Chapter 5. Digital Design and Computer Architecture, 2 nd Edition. David Money Harris and Sarah L. Harris. Chapter 5 <1>
 Chapter 5 Digital Design and Computer Architecture, 2 nd Edition David Money Harris and Sarah L. Harris Chapter 5 Chapter 5 :: Topics Introduction Arithmetic Circuits umber Systems Sequential Building
Chapter 5 Digital Design and Computer Architecture, 2 nd Edition David Money Harris and Sarah L. Harris Chapter 5 Chapter 5 :: Topics Introduction Arithmetic Circuits umber Systems Sequential Building
Part II Addition / Subtraction
 Part II Addition / Subtraction Parts Chapters I. Number Representation 1. 2. 3. 4. Numbers and Arithmetic Representing Signed Numbers Redundant Number Systems Residue Number Systems Elementary Operations
Part II Addition / Subtraction Parts Chapters I. Number Representation 1. 2. 3. 4. Numbers and Arithmetic Representing Signed Numbers Redundant Number Systems Residue Number Systems Elementary Operations
CMPEN 411 VLSI Digital Circuits Spring Lecture 19: Adder Design
 CMPEN 411 VLSI Digital Circuits Spring 2011 Lecture 19: Adder Design [Adapted from Rabaey s Digital Integrated Circuits, Second Edition, 2003 J. Rabaey, A. Chandrakasan, B. Nikolic] Sp11 CMPEN 411 L19
CMPEN 411 VLSI Digital Circuits Spring 2011 Lecture 19: Adder Design [Adapted from Rabaey s Digital Integrated Circuits, Second Edition, 2003 J. Rabaey, A. Chandrakasan, B. Nikolic] Sp11 CMPEN 411 L19
Chapter 5 Arithmetic Circuits
 Chapter 5 Arithmetic Circuits SKEE2263 Digital Systems Mun im/ismahani/izam {munim@utm.my,e-izam@utm.my,ismahani@fke.utm.my} February 11, 2016 Table of Contents 1 Iterative Designs 2 Adders 3 High-Speed
Chapter 5 Arithmetic Circuits SKEE2263 Digital Systems Mun im/ismahani/izam {munim@utm.my,e-izam@utm.my,ismahani@fke.utm.my} February 11, 2016 Table of Contents 1 Iterative Designs 2 Adders 3 High-Speed
Part II Addition / Subtraction
 Part II Addition / Subtraction Parts Chapters I. Number Representation 1. 2. 3. 4. Numbers and Arithmetic Representing Signed Numbers Redundant Number Systems Residue Number Systems Elementary Operations
Part II Addition / Subtraction Parts Chapters I. Number Representation 1. 2. 3. 4. Numbers and Arithmetic Representing Signed Numbers Redundant Number Systems Residue Number Systems Elementary Operations
VLSI Design. [Adapted from Rabaey s Digital Integrated Circuits, 2002, J. Rabaey et al.] ECE 4121 VLSI DEsign.1
![VLSI Design. [Adapted from Rabaey s Digital Integrated Circuits, 2002, J. Rabaey et al.] ECE 4121 VLSI DEsign.1 VLSI Design. [Adapted from Rabaey s Digital Integrated Circuits, 2002, J. Rabaey et al.] ECE 4121 VLSI DEsign.1](/thumbs/72/67474772.jpg) VLSI Design Adder Design [Adapted from Rabaey s Digital Integrated Circuits, 2002, J. Rabaey et al.] ECE 4121 VLSI DEsign.1 Major Components of a Computer Processor Devices Control Memory Input Datapath
VLSI Design Adder Design [Adapted from Rabaey s Digital Integrated Circuits, 2002, J. Rabaey et al.] ECE 4121 VLSI DEsign.1 Major Components of a Computer Processor Devices Control Memory Input Datapath
Lecture 8: Sequential Multipliers
 Lecture 8: Sequential Multipliers ECE 645 Computer Arithmetic 3/25/08 ECE 645 Computer Arithmetic Lecture Roadmap Sequential Multipliers Unsigned Signed Radix-2 Booth Recoding High-Radix Multiplication
Lecture 8: Sequential Multipliers ECE 645 Computer Arithmetic 3/25/08 ECE 645 Computer Arithmetic Lecture Roadmap Sequential Multipliers Unsigned Signed Radix-2 Booth Recoding High-Radix Multiplication
ECE 645: Lecture 2. Carry-Lookahead, Carry-Select, & Hybrid Adders
 ECE 645: Lecture 2 Carry-Lookahead, Carry-Select, & Hybrid Adders Required Reading Behrooz Parhami, Computer Arithmetic: Algorithms and Hardware Design Chapter 6, Carry-Lookahead Adders Sections 6.1-6.2.
ECE 645: Lecture 2 Carry-Lookahead, Carry-Select, & Hybrid Adders Required Reading Behrooz Parhami, Computer Arithmetic: Algorithms and Hardware Design Chapter 6, Carry-Lookahead Adders Sections 6.1-6.2.
CSE477 VLSI Digital Circuits Fall Lecture 20: Adder Design
 CSE477 VLSI Digital Circuits Fall 22 Lecture 2: Adder Design Mary Jane Irwin ( www.cse.psu.edu/~mji ) www.cse.psu.edu/~cg477 [Adapted from Rabaey s Digital Integrated Circuits, 22, J. Rabaey et al.] CSE477
CSE477 VLSI Digital Circuits Fall 22 Lecture 2: Adder Design Mary Jane Irwin ( www.cse.psu.edu/~mji ) www.cse.psu.edu/~cg477 [Adapted from Rabaey s Digital Integrated Circuits, 22, J. Rabaey et al.] CSE477
Cost/Performance Tradeoffs:
 Cost/Performance Tradeoffs: a case study Digital Systems Architecture I. L10 - Multipliers 1 Binary Multiplication x a b n bits n bits EASY PROBLEM: design combinational circuit to multiply tiny (1-, 2-,
Cost/Performance Tradeoffs: a case study Digital Systems Architecture I. L10 - Multipliers 1 Binary Multiplication x a b n bits n bits EASY PROBLEM: design combinational circuit to multiply tiny (1-, 2-,
Number representation
 Number representation A number can be represented in binary in many ways. The most common number types to be represented are: Integers, positive integers one-complement, two-complement, sign-magnitude
Number representation A number can be represented in binary in many ways. The most common number types to be represented are: Integers, positive integers one-complement, two-complement, sign-magnitude
VLSI Arithmetic. Lecture 9: Carry-Save and Multi-Operand Addition. Prof. Vojin G. Oklobdzija University of California
 VLSI Arithmetic Lecture 9: Carry-Save and Multi-Operand Addition Prof. Vojin G. Oklobdzija University of California http://www.ece.ucdavis.edu/acsel Carry-Save Addition* *from Parhami 2 June 18, 2003 Carry-Save
VLSI Arithmetic Lecture 9: Carry-Save and Multi-Operand Addition Prof. Vojin G. Oklobdzija University of California http://www.ece.ucdavis.edu/acsel Carry-Save Addition* *from Parhami 2 June 18, 2003 Carry-Save
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 24 - Arithmetic Blocks, Part 2 + Shifters
 EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 24 - Arithmetic Blocks, Part 2 + Shifters April 15, 2010 John Wawrzynek 1 Multiplication a 3 a 2 a 1 a 0 Multiplicand b 3 b 2 b 1 b 0 Multiplier X a 3 b 0 a 2 b 0 a 1 b
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 24 - Arithmetic Blocks, Part 2 + Shifters April 15, 2010 John Wawrzynek 1 Multiplication a 3 a 2 a 1 a 0 Multiplicand b 3 b 2 b 1 b 0 Multiplier X a 3 b 0 a 2 b 0 a 1 b
ARITHMETIC COMBINATIONAL MODULES AND NETWORKS
 ARITHMETIC COMBINATIONAL MODULES AND NETWORKS 1 SPECIFICATION OF ADDER MODULES FOR POSITIVE INTEGERS HALF-ADDER AND FULL-ADDER MODULES CARRY-RIPPLE AND CARRY-LOOKAHEAD ADDER MODULES NETWORKS OF ADDER MODULES
ARITHMETIC COMBINATIONAL MODULES AND NETWORKS 1 SPECIFICATION OF ADDER MODULES FOR POSITIVE INTEGERS HALF-ADDER AND FULL-ADDER MODULES CARRY-RIPPLE AND CARRY-LOOKAHEAD ADDER MODULES NETWORKS OF ADDER MODULES
A COMBINED 16-BIT BINARY AND DUAL GALOIS FIELD MULTIPLIER. Jesus Garcia and Michael J. Schulte
 A COMBINED 16-BIT BINARY AND DUAL GALOIS FIELD MULTIPLIER Jesus Garcia and Michael J. Schulte Lehigh University Department of Computer Science and Engineering Bethlehem, PA 15 ABSTRACT Galois field arithmetic
A COMBINED 16-BIT BINARY AND DUAL GALOIS FIELD MULTIPLIER Jesus Garcia and Michael J. Schulte Lehigh University Department of Computer Science and Engineering Bethlehem, PA 15 ABSTRACT Galois field arithmetic
ECEN 248: INTRODUCTION TO DIGITAL SYSTEMS DESIGN. Week 9 Dr. Srinivas Shakkottai Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering
 ECEN 248: INTRODUCTION TO DIGITAL SYSTEMS DESIGN Week 9 Dr. Srinivas Shakkottai Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering TIMING ANALYSIS Overview Circuits do not respond instantaneously to input changes
ECEN 248: INTRODUCTION TO DIGITAL SYSTEMS DESIGN Week 9 Dr. Srinivas Shakkottai Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering TIMING ANALYSIS Overview Circuits do not respond instantaneously to input changes
CS 140 Lecture 14 Standard Combinational Modules
 CS 14 Lecture 14 Standard Combinational Modules Professor CK Cheng CSE Dept. UC San Diego Some slides from Harris and Harris 1 Part III. Standard Modules A. Interconnect B. Operators. Adders Multiplier
CS 14 Lecture 14 Standard Combinational Modules Professor CK Cheng CSE Dept. UC San Diego Some slides from Harris and Harris 1 Part III. Standard Modules A. Interconnect B. Operators. Adders Multiplier
An Area Efficient Enhanced Carry Select Adder
 International Journal of Engineering Science Invention ISSN (Online): 2319 6734, ISSN (Print): 2319 6726 PP.06-12 An Area Efficient Enhanced Carry Select Adder 1, Gaandla.Anusha, 2, B.ShivaKumar 1, PG
International Journal of Engineering Science Invention ISSN (Online): 2319 6734, ISSN (Print): 2319 6726 PP.06-12 An Area Efficient Enhanced Carry Select Adder 1, Gaandla.Anusha, 2, B.ShivaKumar 1, PG
ISSN (PRINT): , (ONLINE): , VOLUME-4, ISSUE-10,
 A NOVEL DOMINO LOGIC DESIGN FOR EMBEDDED APPLICATION Dr.K.Sujatha Associate Professor, Department of Computer science and Engineering, Sri Krishna College of Engineering and Technology, Coimbatore, Tamilnadu,
A NOVEL DOMINO LOGIC DESIGN FOR EMBEDDED APPLICATION Dr.K.Sujatha Associate Professor, Department of Computer science and Engineering, Sri Krishna College of Engineering and Technology, Coimbatore, Tamilnadu,
Binary addition by hand. Adding two bits
 Chapter 3 Arithmetic is the most basic thing you can do with a computer We focus on addition, subtraction, multiplication and arithmetic-logic units, or ALUs, which are the heart of CPUs. ALU design Bit
Chapter 3 Arithmetic is the most basic thing you can do with a computer We focus on addition, subtraction, multiplication and arithmetic-logic units, or ALUs, which are the heart of CPUs. ALU design Bit
Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective. Arithmetic Circuits. Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic.
 Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic Arithmetic Circuits January, 2003 1 A Generic Digital Processor MEM ORY INPUT-OUTPUT CONTROL DATAPATH
Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic Arithmetic Circuits January, 2003 1 A Generic Digital Processor MEM ORY INPUT-OUTPUT CONTROL DATAPATH
Adders, subtractors comparators, multipliers and other ALU elements
 CSE4: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems Adders, subtractors comparators, multipliers and other ALU elements Instructor: Mohsen Imani UC San Diego Slides from: Prof.Tajana Simunic Rosing
CSE4: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems Adders, subtractors comparators, multipliers and other ALU elements Instructor: Mohsen Imani UC San Diego Slides from: Prof.Tajana Simunic Rosing
Sample Test Paper - I
 Scheme G Sample Test Paper - I Course Name : Computer Engineering Group Marks : 25 Hours: 1 Hrs. Q.1) Attempt any THREE: 09 Marks a) Define i) Propagation delay ii) Fan-in iii) Fan-out b) Convert the following:
Scheme G Sample Test Paper - I Course Name : Computer Engineering Group Marks : 25 Hours: 1 Hrs. Q.1) Attempt any THREE: 09 Marks a) Define i) Propagation delay ii) Fan-in iii) Fan-out b) Convert the following:
Midterm Exam Two is scheduled on April 8 in class. On March 27 I will help you prepare Midterm Exam Two.
 Announcements Midterm Exam Two is scheduled on April 8 in class. On March 27 I will help you prepare Midterm Exam Two. Chapter 5 1 Chapter 3: Part 3 Arithmetic Functions Iterative combinational circuits
Announcements Midterm Exam Two is scheduled on April 8 in class. On March 27 I will help you prepare Midterm Exam Two. Chapter 5 1 Chapter 3: Part 3 Arithmetic Functions Iterative combinational circuits
1 Short adders. t total_ripple8 = t first + 6*t middle + t last = 4t p + 6*2t p + 2t p = 18t p
 UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences Study Homework: Arithmetic NTU IC54CA (Fall 2004) SOLUTIONS Short adders A The delay of the ripple
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences Study Homework: Arithmetic NTU IC54CA (Fall 2004) SOLUTIONS Short adders A The delay of the ripple
What s the Deal? MULTIPLICATION. Time to multiply
 What s the Deal? MULTIPLICATION Time to multiply Multiplying two numbers requires a multiply Luckily, in binary that s just an AND gate! 0*0=0, 0*1=0, 1*0=0, 1*1=1 Generate a bunch of partial products
What s the Deal? MULTIPLICATION Time to multiply Multiplying two numbers requires a multiply Luckily, in binary that s just an AND gate! 0*0=0, 0*1=0, 1*0=0, 1*1=1 Generate a bunch of partial products
8. Design Tradeoffs x Computation Structures Part 1 Digital Circuits. Copyright 2015 MIT EECS
 8. Design Tradeoffs 6.004x Computation Structures Part 1 Digital Circuits Copyright 2015 MIT EECS 6.004 Computation Structures L08: Design Tradeoffs, Slide #1 There are a large number of implementations
8. Design Tradeoffs 6.004x Computation Structures Part 1 Digital Circuits Copyright 2015 MIT EECS 6.004 Computation Structures L08: Design Tradeoffs, Slide #1 There are a large number of implementations
9. Datapath Design. Jacob Abraham. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering The University of Texas at Austin VLSI Design Fall 2017
 9. Datapath Design Jacob Abraham Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering The University of Texas at Austin VLSI Design Fall 2017 October 2, 2017 ECE Department, University of Texas at Austin
9. Datapath Design Jacob Abraham Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering The University of Texas at Austin VLSI Design Fall 2017 October 2, 2017 ECE Department, University of Texas at Austin
Arithmetic in Integer Rings and Prime Fields
 Arithmetic in Integer Rings and Prime Fields A 3 B 3 A 2 B 2 A 1 B 1 A 0 B 0 FA C 3 FA C 2 FA C 1 FA C 0 C 4 S 3 S 2 S 1 S 0 http://koclab.org Çetin Kaya Koç Spring 2018 1 / 71 Contents Arithmetic in Integer
Arithmetic in Integer Rings and Prime Fields A 3 B 3 A 2 B 2 A 1 B 1 A 0 B 0 FA C 3 FA C 2 FA C 1 FA C 0 C 4 S 3 S 2 S 1 S 0 http://koclab.org Çetin Kaya Koç Spring 2018 1 / 71 Contents Arithmetic in Integer
8. Design Tradeoffs x Computation Structures Part 1 Digital Circuits. Copyright 2015 MIT EECS
 8. Design Tradeoffs 6.004x Computation Structures Part 1 Digital Circuits Copyright 2015 MIT EECS 6.004 Computation Structures L08: Design Tradeoffs, Slide #1 There are a large number of implementations
8. Design Tradeoffs 6.004x Computation Structures Part 1 Digital Circuits Copyright 2015 MIT EECS 6.004 Computation Structures L08: Design Tradeoffs, Slide #1 There are a large number of implementations
Tree and Array Multipliers Ivor Page 1
 Tree and Array Multipliers 1 Tree and Array Multipliers Ivor Page 1 11.1 Tree Multipliers In Figure 1 seven input operands are combined by a tree of CSAs. The final level of the tree is a carry-completion
Tree and Array Multipliers 1 Tree and Array Multipliers Ivor Page 1 11.1 Tree Multipliers In Figure 1 seven input operands are combined by a tree of CSAs. The final level of the tree is a carry-completion
Logic and Computer Design Fundamentals. Chapter 5 Arithmetic Functions and Circuits
 Logic and Computer Design Fundamentals Chapter 5 Arithmetic Functions and Circuits Arithmetic functions Operate on binary vectors Use the same subfunction in each bit position Can design functional block
Logic and Computer Design Fundamentals Chapter 5 Arithmetic Functions and Circuits Arithmetic functions Operate on binary vectors Use the same subfunction in each bit position Can design functional block
COE 202: Digital Logic Design Sequential Circuits Part 4. Dr. Ahmad Almulhem ahmadsm AT kfupm Phone: Office:
 COE 202: Digital Logic Design Sequential Circuits Part 4 Dr. Ahmad Almulhem Email: ahmadsm AT kfupm Phone: 860-7554 Office: 22-324 Objectives Registers Counters Registers 0 1 n-1 A register is a group
COE 202: Digital Logic Design Sequential Circuits Part 4 Dr. Ahmad Almulhem Email: ahmadsm AT kfupm Phone: 860-7554 Office: 22-324 Objectives Registers Counters Registers 0 1 n-1 A register is a group
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 22 - Arithmetic Blocks, Part 1
 EECS150 - igital esign Lecture 22 - Arithmetic Blocks, Part 1 April 10, 2011 John Wawrzynek Spring 2011 EECS150 - Lec23-arith1 Page 1 Each cell: r i = a i XOR b i XOR c in Carry-ripple Adder Revisited
EECS150 - igital esign Lecture 22 - Arithmetic Blocks, Part 1 April 10, 2011 John Wawrzynek Spring 2011 EECS150 - Lec23-arith1 Page 1 Each cell: r i = a i XOR b i XOR c in Carry-ripple Adder Revisited
EFFICIENT MULTIOUTPUT CARRY LOOK-AHEAD ADDERS
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF RESEARCH IN COMPUTER APPLICATIONS AND ROBOTICS ISSN 2320-7345 EFFICIENT MULTIOUTPUT CARRY LOOK-AHEAD ADDERS B. Venkata Sreecharan 1, C. Venkata Sudhakar 2 1 M.TECH (VLSI DESIGN)
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF RESEARCH IN COMPUTER APPLICATIONS AND ROBOTICS ISSN 2320-7345 EFFICIENT MULTIOUTPUT CARRY LOOK-AHEAD ADDERS B. Venkata Sreecharan 1, C. Venkata Sudhakar 2 1 M.TECH (VLSI DESIGN)
Hardware Design I Chap. 4 Representative combinational logic
 Hardware Design I Chap. 4 Representative combinational logic E-mail: shimada@is.naist.jp Already optimized circuits There are many optimized circuits which are well used You can reduce your design workload
Hardware Design I Chap. 4 Representative combinational logic E-mail: shimada@is.naist.jp Already optimized circuits There are many optimized circuits which are well used You can reduce your design workload
Lecture 8. Sequential Multipliers
 Lecture 8 Sequential Multipliers Required Reading Behrooz Parhami, Computer Arithmetic: Algorithms and Hardware Design Chapter 9, Basic Multiplication Scheme Chapter 10, High-Radix Multipliers Chapter
Lecture 8 Sequential Multipliers Required Reading Behrooz Parhami, Computer Arithmetic: Algorithms and Hardware Design Chapter 9, Basic Multiplication Scheme Chapter 10, High-Radix Multipliers Chapter
DIGITAL TECHNICS. Dr. Bálint Pődör. Óbuda University, Microelectronics and Technology Institute
 DIGITAL TECHNICS Dr. Bálint Pődör Óbuda University, Microelectronics and Technology Institute 4. LECTURE: COMBINATIONAL LOGIC DESIGN: ARITHMETICS (THROUGH EXAMPLES) 2016/2017 COMBINATIONAL LOGIC DESIGN:
DIGITAL TECHNICS Dr. Bálint Pődör Óbuda University, Microelectronics and Technology Institute 4. LECTURE: COMBINATIONAL LOGIC DESIGN: ARITHMETICS (THROUGH EXAMPLES) 2016/2017 COMBINATIONAL LOGIC DESIGN:
Adders allow computers to add numbers 2-bit ripple-carry adder
 Lecture 12 Logistics HW was due yesterday HW5 was out yesterday (due next Wednesday) Feedback: thank you! Things to work on: ig picture, ook chapters, Exam comments Last lecture dders Today Clarification
Lecture 12 Logistics HW was due yesterday HW5 was out yesterday (due next Wednesday) Feedback: thank you! Things to work on: ig picture, ook chapters, Exam comments Last lecture dders Today Clarification
Homework 4 due today Quiz #4 today In class (80min) final exam on April 29 Project reports due on May 4. Project presentations May 5, 1-4pm
 EE241 - Spring 2010 Advanced Digital Integrated Circuits Lecture 25: Digital Arithmetic Adders Announcements Homework 4 due today Quiz #4 today In class (80min) final exam on April 29 Project reports due
EE241 - Spring 2010 Advanced Digital Integrated Circuits Lecture 25: Digital Arithmetic Adders Announcements Homework 4 due today Quiz #4 today In class (80min) final exam on April 29 Project reports due
Problem Set 6 Solutions
 CS/EE 260 Digital Computers: Organization and Logical Design Problem Set 6 Solutions Jon Turner Quiz on 2/21/02 1. The logic diagram at left below shows a 5 bit ripple-carry decrement circuit. Draw a logic
CS/EE 260 Digital Computers: Organization and Logical Design Problem Set 6 Solutions Jon Turner Quiz on 2/21/02 1. The logic diagram at left below shows a 5 bit ripple-carry decrement circuit. Draw a logic
Digital Electronics II Mike Brookes Please pick up: Notes from the front desk
 NOTATION.PPT(10/8/2010) 1.1 Digital Electronics II Mike Brookes Please pick up: Notes from the front desk 1. What does Digital mean? 2. Where is it used? 3. Why is it used? 4. What are the important features
NOTATION.PPT(10/8/2010) 1.1 Digital Electronics II Mike Brookes Please pick up: Notes from the front desk 1. What does Digital mean? 2. Where is it used? 3. Why is it used? 4. What are the important features
Area-Time Optimal Adder with Relative Placement Generator
 Area-Time Optimal Adder with Relative Placement Generator Abstract: This paper presents the design of a generator, for the production of area-time-optimal adders. A unique feature of this generator is
Area-Time Optimal Adder with Relative Placement Generator Abstract: This paper presents the design of a generator, for the production of area-time-optimal adders. A unique feature of this generator is
Overview. Arithmetic circuits. Binary half adder. Binary full adder. Last lecture PLDs ROMs Tristates Design examples
 Overview rithmetic circuits Last lecture PLDs ROMs Tristates Design examples Today dders Ripple-carry Carry-lookahead Carry-select The conclusion of combinational logic!!! General-purpose building blocks
Overview rithmetic circuits Last lecture PLDs ROMs Tristates Design examples Today dders Ripple-carry Carry-lookahead Carry-select The conclusion of combinational logic!!! General-purpose building blocks
Chapter 4. Combinational: Circuits with logic gates whose outputs depend on the present combination of the inputs. elements. Dr.
 Chapter 4 Dr. Panos Nasiopoulos Combinational: Circuits with logic gates whose outputs depend on the present combination of the inputs. Sequential: In addition, they include storage elements Combinational
Chapter 4 Dr. Panos Nasiopoulos Combinational: Circuits with logic gates whose outputs depend on the present combination of the inputs. Sequential: In addition, they include storage elements Combinational
Digital Electronics. Part A
 Digital Electronics Final Examination Part A Winter 2004-05 Student Name: Date: lass Period: Total Points: Multiple hoice Directions: Select the letter of the response which best completes the item or
Digital Electronics Final Examination Part A Winter 2004-05 Student Name: Date: lass Period: Total Points: Multiple hoice Directions: Select the letter of the response which best completes the item or
Computer Architecture. ESE 345 Computer Architecture. Design Process. CA: Design process
 Computer Architecture ESE 345 Computer Architecture Design Process 1 The Design Process "To Design Is To Represent" Design activity yields description/representation of an object -- Traditional craftsman
Computer Architecture ESE 345 Computer Architecture Design Process 1 The Design Process "To Design Is To Represent" Design activity yields description/representation of an object -- Traditional craftsman
Arithmetic Circuits How to add and subtract using combinational logic Setting flags Adding faster
 rithmetic Circuits Didn t I learn how to do addition in second grade? UNC courses aren t what they used to be... 01011 +00101 10000 Finally; time to build some serious functional blocks We ll need a lot
rithmetic Circuits Didn t I learn how to do addition in second grade? UNC courses aren t what they used to be... 01011 +00101 10000 Finally; time to build some serious functional blocks We ll need a lot
Arithmetic Circuits-2
 Arithmetic Circuits-2 Multipliers Array multipliers Shifters Barrel shifter Logarithmic shifter ECE 261 Krish Chakrabarty 1 Binary Multiplication M-1 X = X i 2 i i=0 Multiplicand N-1 Y = Y i 2 i i=0 Multiplier
Arithmetic Circuits-2 Multipliers Array multipliers Shifters Barrel shifter Logarithmic shifter ECE 261 Krish Chakrabarty 1 Binary Multiplication M-1 X = X i 2 i i=0 Multiplicand N-1 Y = Y i 2 i i=0 Multiplier
CPE100: Digital Logic Design I
 Professor Brendan Morris, SEB 3216, brendan.morris@unlv.edu CPE100: Digital Logic Design I Final Review http://www.ee.unlv.edu/~b1morris/cpe100/ 2 Logistics Tuesday Dec 12 th 13:00-15:00 (1-3pm) 2 hour
Professor Brendan Morris, SEB 3216, brendan.morris@unlv.edu CPE100: Digital Logic Design I Final Review http://www.ee.unlv.edu/~b1morris/cpe100/ 2 Logistics Tuesday Dec 12 th 13:00-15:00 (1-3pm) 2 hour
Lecture 7: Logic design. Combinational logic circuits
 /24/28 Lecture 7: Logic design Binary digital circuits: Two voltage levels: and (ground and supply voltage) Built from transistors used as on/off switches Analog circuits not very suitable for generic
/24/28 Lecture 7: Logic design Binary digital circuits: Two voltage levels: and (ground and supply voltage) Built from transistors used as on/off switches Analog circuits not very suitable for generic
Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective. Arithmetic Circuits. Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic.
 Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic Arithmetic Circuits January, 2003 1 A Generic Digital Processor MEMORY INPUT-OUTPUT CONTROL DATAPATH
Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic Arithmetic Circuits January, 2003 1 A Generic Digital Processor MEMORY INPUT-OUTPUT CONTROL DATAPATH
Sequential Logic Worksheet
 Sequential Logic Worksheet Concept Inventory: Notes: D-latch & the Dynamic Discipline D-register Timing constraints for sequential circuits Set-up and hold times for sequential circuits 6.004 Worksheet
Sequential Logic Worksheet Concept Inventory: Notes: D-latch & the Dynamic Discipline D-register Timing constraints for sequential circuits Set-up and hold times for sequential circuits 6.004 Worksheet
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 10 - Combinational Logic Circuits Part 1
 EECS5 - Digital Design Lecture - Combinational Logic Circuits Part Feburary 26, 22 John Wawrzynek Spring 22 EECS5 - Lec-cl Page Combinational Logic (CL) Defined y i = f i (x,...., xn-), where x, y are
EECS5 - Digital Design Lecture - Combinational Logic Circuits Part Feburary 26, 22 John Wawrzynek Spring 22 EECS5 - Lec-cl Page Combinational Logic (CL) Defined y i = f i (x,...., xn-), where x, y are
Radix-4 Vectoring CORDIC Algorithm and Architectures. July 1998 Technical Report No: UMA-DAC-98/20
 Radix-4 Vectoring CORDIC Algorithm and Architectures J. Villalba E. Antelo J.D. Bruguera E.L. Zapata July 1998 Technical Report No: UMA-DAC-98/20 Published in: J. of VLSI Signal Processing Systems for
Radix-4 Vectoring CORDIC Algorithm and Architectures J. Villalba E. Antelo J.D. Bruguera E.L. Zapata July 1998 Technical Report No: UMA-DAC-98/20 Published in: J. of VLSI Signal Processing Systems for
14:332:231 DIGITAL LOGIC DESIGN
 4:332:23 DIGITAL LOGIC DEIGN Ivan Marsic, Rutgers University Electrical & Computer Engineering Fall 23 Lecture #4: Adders, ubtracters, and ALUs Vector Binary Adder [Wakerly 4 th Ed., ec. 6., p. 474] ingle
4:332:23 DIGITAL LOGIC DEIGN Ivan Marsic, Rutgers University Electrical & Computer Engineering Fall 23 Lecture #4: Adders, ubtracters, and ALUs Vector Binary Adder [Wakerly 4 th Ed., ec. 6., p. 474] ingle
LOGIC CIRCUITS. Basic Experiment and Design of Electronics. Ho Kyung Kim, Ph.D.
 Basic Experiment and Design of Electronics LOGIC CIRCUITS Ho Kyung Kim, Ph.D. hokyung@pusan.ac.kr School of Mechanical Engineering Pusan National University Digital IC packages TTL (transistor-transistor
Basic Experiment and Design of Electronics LOGIC CIRCUITS Ho Kyung Kim, Ph.D. hokyung@pusan.ac.kr School of Mechanical Engineering Pusan National University Digital IC packages TTL (transistor-transistor
Cost/Performance Tradeoff of n-select Square Root Implementations
 Australian Computer Science Communications, Vol.22, No.4, 2, pp.9 6, IEEE Comp. Society Press Cost/Performance Tradeoff of n-select Square Root Implementations Wanming Chu and Yamin Li Computer Architecture
Australian Computer Science Communications, Vol.22, No.4, 2, pp.9 6, IEEE Comp. Society Press Cost/Performance Tradeoff of n-select Square Root Implementations Wanming Chu and Yamin Li Computer Architecture
Arithmetic Circuits-2
 Arithmetic Circuits-2 Multipliers Array multipliers Shifters Barrel shifter Logarithmic shifter ECE 261 Krish Chakrabarty 1 Binary Multiplication M-1 X = X i 2 i i=0 Multiplicand N-1 Y = Y i 2 i i=0 Multiplier
Arithmetic Circuits-2 Multipliers Array multipliers Shifters Barrel shifter Logarithmic shifter ECE 261 Krish Chakrabarty 1 Binary Multiplication M-1 X = X i 2 i i=0 Multiplicand N-1 Y = Y i 2 i i=0 Multiplier
Looking at a two binary digit sum shows what we need to extend addition to multiple binary digits.
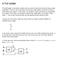 A Full Adder The half-adder is extremely useful until you want to add more that one binary digit quantities. The slow way to develop a two binary digit adders would be to make a truth table and reduce
A Full Adder The half-adder is extremely useful until you want to add more that one binary digit quantities. The slow way to develop a two binary digit adders would be to make a truth table and reduce
Multiplication Ivor Page 1
 Multiplication 1 Multiplication Ivor Page 1 10.1 Shift/Add Multiplication Algorithms We will adopt the notation, a Multiplicand a k 1 a k 2 a 1 a 0 b Multiplier x k 1 x k 2 x 1 x 0 p Product p 2k 1 p 2k
Multiplication 1 Multiplication Ivor Page 1 10.1 Shift/Add Multiplication Algorithms We will adopt the notation, a Multiplicand a k 1 a k 2 a 1 a 0 b Multiplier x k 1 x k 2 x 1 x 0 p Product p 2k 1 p 2k
Proposal to Improve Data Format Conversions for a Hybrid Number System Processor
 Proceedings of the 11th WSEAS International Conference on COMPUTERS, Agios Nikolaos, Crete Island, Greece, July 6-8, 007 653 Proposal to Improve Data Format Conversions for a Hybrid Number System Processor
Proceedings of the 11th WSEAS International Conference on COMPUTERS, Agios Nikolaos, Crete Island, Greece, July 6-8, 007 653 Proposal to Improve Data Format Conversions for a Hybrid Number System Processor
Carry Look Ahead Adders
 Carry Look Ahead Adders Lesson Objectives: The objectives of this lesson are to learn about: 1. Carry Look Ahead Adder circuit. 2. Binary Parallel Adder/Subtractor circuit. 3. BCD adder circuit. 4. Binary
Carry Look Ahead Adders Lesson Objectives: The objectives of this lesson are to learn about: 1. Carry Look Ahead Adder circuit. 2. Binary Parallel Adder/Subtractor circuit. 3. BCD adder circuit. 4. Binary
Design of Sequential Circuits
 Design of Sequential Circuits Seven Steps: Construct a state diagram (showing contents of flip flop and inputs with next state) Assign letter variables to each flip flop and each input and output variable
Design of Sequential Circuits Seven Steps: Construct a state diagram (showing contents of flip flop and inputs with next state) Assign letter variables to each flip flop and each input and output variable
Adders, subtractors comparators, multipliers and other ALU elements
 CSE4: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems Adders, subtractors comparators, multipliers and other ALU elements Adders 2 Circuit Delay Transistors have instrinsic resistance and capacitance
CSE4: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems Adders, subtractors comparators, multipliers and other ALU elements Adders 2 Circuit Delay Transistors have instrinsic resistance and capacitance
Lecture 4. Adders. Computer Systems Laboratory Stanford University
 Lecture 4 Adders Computer Systems Laboratory Stanford University horowitz@stanford.edu Copyright 2006 Mark Horowitz Some figures from High-Performance Microprocessor Design IEEE 1 Overview Readings Today
Lecture 4 Adders Computer Systems Laboratory Stanford University horowitz@stanford.edu Copyright 2006 Mark Horowitz Some figures from High-Performance Microprocessor Design IEEE 1 Overview Readings Today
A High-Speed Realization of Chinese Remainder Theorem
 Proceedings of the 2007 WSEAS Int. Conference on Circuits, Systems, Signal and Telecommunications, Gold Coast, Australia, January 17-19, 2007 97 A High-Speed Realization of Chinese Remainder Theorem Shuangching
Proceedings of the 2007 WSEAS Int. Conference on Circuits, Systems, Signal and Telecommunications, Gold Coast, Australia, January 17-19, 2007 97 A High-Speed Realization of Chinese Remainder Theorem Shuangching
VLSI Design I; A. Milenkovic 1
 The -bit inary dder CPE/EE 427, CPE 527 VLI Design I L2: dder Design Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of labama in Huntsville leksandar Milenkovic ( www. ece.uah.edu/~milenka
The -bit inary dder CPE/EE 427, CPE 527 VLI Design I L2: dder Design Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of labama in Huntsville leksandar Milenkovic ( www. ece.uah.edu/~milenka
Reg. No. Question Paper Code : B.E./B.Tech. DEGREE EXAMINATION, NOVEMBER/DECEMBER Second Semester. Computer Science and Engineering
 Sp 6 Reg. No. Question Paper Code : 27156 B.E./B.Tech. DEGREE EXAMINATION, NOVEMBER/DECEMBER 2015. Second Semester Computer Science and Engineering CS 6201 DIGITAL PRINCIPLES AND SYSTEM DESIGN (Common
Sp 6 Reg. No. Question Paper Code : 27156 B.E./B.Tech. DEGREE EXAMINATION, NOVEMBER/DECEMBER 2015. Second Semester Computer Science and Engineering CS 6201 DIGITAL PRINCIPLES AND SYSTEM DESIGN (Common
CMPUT 329. Circuits for binary addition
 CMPUT 329 Parallel Adder with Carry Lookahead and ALU Ioanis Nikolaidis (Katz & Borriello) rcuits for binary addition Full adder (carry-in to cascade for multi-bit adders) Sum = xor A xor B Cout = B +
CMPUT 329 Parallel Adder with Carry Lookahead and ALU Ioanis Nikolaidis (Katz & Borriello) rcuits for binary addition Full adder (carry-in to cascade for multi-bit adders) Sum = xor A xor B Cout = B +
L8/9: Arithmetic Structures
 L8/9: Arithmetic Structures Acknowledgements: Materials in this lecture are courtesy of the following sources and are used with permission. Rex Min Kevin Atkinson Prof. Randy Katz (Unified Microelectronics
L8/9: Arithmetic Structures Acknowledgements: Materials in this lecture are courtesy of the following sources and are used with permission. Rex Min Kevin Atkinson Prof. Randy Katz (Unified Microelectronics
Chapter 7. VLSI System Components
 VLSI Design Chapter 7 VLSI System Components Jin-Fu Li Chapter 7 VLSI System Components Introduction Datapath Operators Memory Elements Control Structures 2 System-Level Hierarchy System (Top) Complex
VLSI Design Chapter 7 VLSI System Components Jin-Fu Li Chapter 7 VLSI System Components Introduction Datapath Operators Memory Elements Control Structures 2 System-Level Hierarchy System (Top) Complex
ECE/Comp Sci 352 Digital Systems Fundamentals. Charles R. Kime Section 2 Fall Logic and Computer Design Fundamentals
 University of Wisconsin - Madison ECE/Comp Sci 352 Digital Systems Fundamentals Charles R. Kime Section 2 Fall 2001 Lecture 5 Registers & Counters Part 2 Charles Kime Counters Counters are sequential circuits
University of Wisconsin - Madison ECE/Comp Sci 352 Digital Systems Fundamentals Charles R. Kime Section 2 Fall 2001 Lecture 5 Registers & Counters Part 2 Charles Kime Counters Counters are sequential circuits
Proposal to Improve Data Format Conversions for a Hybrid Number System Processor
 Proposal to Improve Data Format Conversions for a Hybrid Number System Processor LUCIAN JURCA, DANIEL-IOAN CURIAC, AUREL GONTEAN, FLORIN ALEXA Department of Applied Electronics, Department of Automation
Proposal to Improve Data Format Conversions for a Hybrid Number System Processor LUCIAN JURCA, DANIEL-IOAN CURIAC, AUREL GONTEAN, FLORIN ALEXA Department of Applied Electronics, Department of Automation
A Suggestion for a Fast Residue Multiplier for a Family of Moduli of the Form (2 n (2 p ± 1))
 The Computer Journal, 47(1), The British Computer Society; all rights reserved A Suggestion for a Fast Residue Multiplier for a Family of Moduli of the Form ( n ( p ± 1)) Ahmad A. Hiasat Electronics Engineering
The Computer Journal, 47(1), The British Computer Society; all rights reserved A Suggestion for a Fast Residue Multiplier for a Family of Moduli of the Form ( n ( p ± 1)) Ahmad A. Hiasat Electronics Engineering
Computer Arithmetic Design
 Computer Arithmetic Design Instructor: Kuan Jen Lin E-Mail: kjlin@mails.fju.edu.tw Web: http://vlsi.ee.fju.edu.tw/teacher/kjlin/kjlin.htm Dept. of EE, FJU, Taiwan Room: SF 727B Computer Arithmetic 1, Dept.
Computer Arithmetic Design Instructor: Kuan Jen Lin E-Mail: kjlin@mails.fju.edu.tw Web: http://vlsi.ee.fju.edu.tw/teacher/kjlin/kjlin.htm Dept. of EE, FJU, Taiwan Room: SF 727B Computer Arithmetic 1, Dept.
EECS 427 Lecture 8: Adders Readings: EECS 427 F09 Lecture 8 1. Reminders. HW3 project initial proposal: due Wednesday 10/7
 EECS 427 Lecture 8: dders Readings: 11.1-11.3.3 3 EECS 427 F09 Lecture 8 1 Reminders HW3 project initial proposal: due Wednesday 10/7 You can schedule a half-hour hour appointment with me to discuss your
EECS 427 Lecture 8: dders Readings: 11.1-11.3.3 3 EECS 427 F09 Lecture 8 1 Reminders HW3 project initial proposal: due Wednesday 10/7 You can schedule a half-hour hour appointment with me to discuss your
Digital Design for Multiplication
 Digital Design for Multiplication Norman Matloff October 15, 2003 c 2003, N.S. Matloff 1 Overview A cottage industry exists in developing fast digital logic to perform arithmetic computations. Fast addition,
Digital Design for Multiplication Norman Matloff October 15, 2003 c 2003, N.S. Matloff 1 Overview A cottage industry exists in developing fast digital logic to perform arithmetic computations. Fast addition,
ECE 645: Lecture 3. Conditional-Sum Adders and Parallel Prefix Network Adders. FPGA Optimized Adders
 ECE 645: Lecture 3 Conditional-Sum Adders and Parallel Prefix Network Adders FPGA Optimized Adders Required Reading Behrooz Parhami, Computer Arithmetic: Algorithms and Hardware Design Chapter 7.4, Conditional-Sum
ECE 645: Lecture 3 Conditional-Sum Adders and Parallel Prefix Network Adders FPGA Optimized Adders Required Reading Behrooz Parhami, Computer Arithmetic: Algorithms and Hardware Design Chapter 7.4, Conditional-Sum
Design of Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) using Modified QCA Adder
 Design of Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) using Modified QCA Adder M.S.Navya Deepthi M.Tech (VLSI), Department of ECE, BVC College of Engineering, Rajahmundry. Abstract: Quantum cellular automata (QCA) is
Design of Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) using Modified QCA Adder M.S.Navya Deepthi M.Tech (VLSI), Department of ECE, BVC College of Engineering, Rajahmundry. Abstract: Quantum cellular automata (QCA) is
Design and Comparison of Wallace Multiplier Based on Symmetric Stacking and High speed counters
 International Journal of Engineering Research and Advanced Technology (IJERAT) DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.31695/IJERAT.2018.3271 E-ISSN : 2454-6135 Volume.4, Issue 6 June -2018 Design and Comparison of Wallace
International Journal of Engineering Research and Advanced Technology (IJERAT) DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.31695/IJERAT.2018.3271 E-ISSN : 2454-6135 Volume.4, Issue 6 June -2018 Design and Comparison of Wallace
Combinatorial circuits - arithmetics
 Combinatorial circuits - arithmetics Lionel Morel Département Informatique - INSA Lyon Automne 2016 AC - Arith Automne 2016 1 / 19 Numerical Functions Blackboard AC - Arith Automne 2016 3 / 19 Numerical
Combinatorial circuits - arithmetics Lionel Morel Département Informatique - INSA Lyon Automne 2016 AC - Arith Automne 2016 1 / 19 Numerical Functions Blackboard AC - Arith Automne 2016 3 / 19 Numerical
Lecture 3 Review on Digital Logic (Part 2)
 Lecture 3 Review on Digital Logic (Part 2) Xuan Silvia Zhang Washington University in St. Louis http://classes.engineering.wustl.edu/ese461/ ircuit Optimization Simplest implementation ost criterion literal
Lecture 3 Review on Digital Logic (Part 2) Xuan Silvia Zhang Washington University in St. Louis http://classes.engineering.wustl.edu/ese461/ ircuit Optimization Simplest implementation ost criterion literal
ECE 2300 Digital Logic & Computer Organization
 ECE 2300 Digital Logic & Computer Organization pring 201 More inary rithmetic LU 1 nnouncements Lab 4 prelab () due tomorrow Lab 5 to be released tonight 2 Example: Fixed ize 2 C ddition White stone =
ECE 2300 Digital Logic & Computer Organization pring 201 More inary rithmetic LU 1 nnouncements Lab 4 prelab () due tomorrow Lab 5 to be released tonight 2 Example: Fixed ize 2 C ddition White stone =
Novel Bit Adder Using Arithmetic Logic Unit of QCA Technology
 Novel Bit Adder Using Arithmetic Logic Unit of QCA Technology Uppoju Shiva Jyothi M.Tech (ES & VLSI Design), Malla Reddy Engineering College For Women, Secunderabad. Abstract: Quantum cellular automata
Novel Bit Adder Using Arithmetic Logic Unit of QCA Technology Uppoju Shiva Jyothi M.Tech (ES & VLSI Design), Malla Reddy Engineering College For Women, Secunderabad. Abstract: Quantum cellular automata
ECE 341. Lecture # 3
 ECE 341 Lecture # 3 Instructor: Zeshan Chishti zeshan@ece.pdx.edu October 7, 2013 Portland State University Lecture Topics Counters Finite State Machines Decoders Multiplexers Reference: Appendix A of
ECE 341 Lecture # 3 Instructor: Zeshan Chishti zeshan@ece.pdx.edu October 7, 2013 Portland State University Lecture Topics Counters Finite State Machines Decoders Multiplexers Reference: Appendix A of
DIGIT-SERIAL ARITHMETIC
 DIGIT-SERIAL ARITHMETIC 1 Modes of operation:lsdf and MSDF Algorithm and implementation models LSDF arithmetic MSDF: Online arithmetic TIMING PARAMETERS 2 radix-r number system: conventional and redundant
DIGIT-SERIAL ARITHMETIC 1 Modes of operation:lsdf and MSDF Algorithm and implementation models LSDF arithmetic MSDF: Online arithmetic TIMING PARAMETERS 2 radix-r number system: conventional and redundant
GALOP : A Generalized VLSI Architecture for Ultrafast Carry Originate-Propagate adders
 GALOP : A Generalized VLSI Architecture for Ultrafast Carry Originate-Propagate adders Dhananjay S. Phatak Electrical Engineering Department State University of New York, Binghamton, NY 13902-6000 Israel
GALOP : A Generalized VLSI Architecture for Ultrafast Carry Originate-Propagate adders Dhananjay S. Phatak Electrical Engineering Department State University of New York, Binghamton, NY 13902-6000 Israel
LOGIC CIRCUITS. Basic Experiment and Design of Electronics
 Basic Experiment and Design of Electronics LOGIC CIRCUITS Ho Kyung Kim, Ph.D. hokyung@pusan.ac.kr School of Mechanical Engineering Pusan National University Outline Combinational logic circuits Output
Basic Experiment and Design of Electronics LOGIC CIRCUITS Ho Kyung Kim, Ph.D. hokyung@pusan.ac.kr School of Mechanical Engineering Pusan National University Outline Combinational logic circuits Output
CMP 334: Seventh Class
 CMP 334: Seventh Class Performance HW 5 solution Averages and weighted averages (review) Amdahl's law Ripple-carry adder circuits Binary addition Half-adder circuits Full-adder circuits Subtraction, negative
CMP 334: Seventh Class Performance HW 5 solution Averages and weighted averages (review) Amdahl's law Ripple-carry adder circuits Binary addition Half-adder circuits Full-adder circuits Subtraction, negative
10/12/2016. An FSM with No Inputs Moves from State to State. ECE 120: Introduction to Computing. Eventually, the States Form a Loop
 University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering An FSM with No Inputs Moves from State to State What happens if an FSM has no inputs? ECE 120: Introduction to Computing
University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering An FSM with No Inputs Moves from State to State What happens if an FSM has no inputs? ECE 120: Introduction to Computing
per chip (approx) 1 SSI (Small Scale Integration) Up to 99
 Q.2 a. Classify the integration technology as per the scale of integration. Explain in brief the various steps involved in fabrication of monolithic IC. Scales of Integration (Basic) Various steps involved
Q.2 a. Classify the integration technology as per the scale of integration. Explain in brief the various steps involved in fabrication of monolithic IC. Scales of Integration (Basic) Various steps involved
Digital Electronics Final Examination. Part A
 Digital Electronics Final Examination Part A Spring 2009 Student Name: Date: Class Period: Total Points: /50 Converted Score: /40 Page 1 of 13 Directions: This is a CLOSED BOOK/CLOSED NOTES exam. Select
Digital Electronics Final Examination Part A Spring 2009 Student Name: Date: Class Period: Total Points: /50 Converted Score: /40 Page 1 of 13 Directions: This is a CLOSED BOOK/CLOSED NOTES exam. Select
DE58/DC58 LOGIC DESIGN DEC 2014
 Q.2 a. In a base-5 number system, 3 digit representations is used. Find out (i) Number of distinct quantities that can be represented.(ii) Representation of highest decimal number in base-5. Since, r=5
Q.2 a. In a base-5 number system, 3 digit representations is used. Find out (i) Number of distinct quantities that can be represented.(ii) Representation of highest decimal number in base-5. Since, r=5
An Approximate Parallel Multiplier with Deterministic Errors for Ultra-High Speed Integrated Optical Circuits
 An Approximate Parallel Multiplier with Deterministic Errors for Ultra-High Speed Integrated Optical Circuits Jun Shiomi 1, Tohru Ishihara 1, Hidetoshi Onodera 1, Akihiko Shinya 2, Masaya Notomi 2 1 Graduate
An Approximate Parallel Multiplier with Deterministic Errors for Ultra-High Speed Integrated Optical Circuits Jun Shiomi 1, Tohru Ishihara 1, Hidetoshi Onodera 1, Akihiko Shinya 2, Masaya Notomi 2 1 Graduate
Logic Design II (17.342) Spring Lecture Outline
 Logic Design II (17.342) Spring 2012 Lecture Outline Class # 10 April 12, 2012 Dohn Bowden 1 Today s Lecture First half of the class Circuits for Arithmetic Operations Chapter 18 Should finish at least
Logic Design II (17.342) Spring 2012 Lecture Outline Class # 10 April 12, 2012 Dohn Bowden 1 Today s Lecture First half of the class Circuits for Arithmetic Operations Chapter 18 Should finish at least
Lecture 11: Adders. Slides courtesy of Deming Chen. Slides based on the initial set from David Harris. 4th Ed.
 Lecture : dders Slides courtesy of Deming hen Slides based on the initial set from David Harris MOS VLSI Design Outline Single-bit ddition arry-ripple dder arry-skip dder arry-lookahead dder arry-select
Lecture : dders Slides courtesy of Deming hen Slides based on the initial set from David Harris MOS VLSI Design Outline Single-bit ddition arry-ripple dder arry-skip dder arry-lookahead dder arry-select
Serial Parallel Multiplier Design in Quantum-dot Cellular Automata
 Serial Parallel Multiplier Design in Quantum-dot Cellular Automata Heumpil Cho and Earl E. Swartzlander, Jr. Application Specific Processor Group Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering The University
Serial Parallel Multiplier Design in Quantum-dot Cellular Automata Heumpil Cho and Earl E. Swartzlander, Jr. Application Specific Processor Group Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering The University
ECE380 Digital Logic. Positional representation
 ECE380 Digital Logic Number Representation and Arithmetic Circuits: Number Representation and Unsigned Addition Dr. D. J. Jackson Lecture 16-1 Positional representation First consider integers Begin with
ECE380 Digital Logic Number Representation and Arithmetic Circuits: Number Representation and Unsigned Addition Dr. D. J. Jackson Lecture 16-1 Positional representation First consider integers Begin with
Arithmetic Circuits Didn t I learn how to do addition in the second grade? UNC courses aren t what they used to be...
 rithmetic Circuits Didn t I learn how to do addition in the second grade? UNC courses aren t what they used to be... + Finally; time to build some serious functional blocks We ll need a lot of boxes The
rithmetic Circuits Didn t I learn how to do addition in the second grade? UNC courses aren t what they used to be... + Finally; time to build some serious functional blocks We ll need a lot of boxes The
