Semiconductor Devices and Models
|
|
|
- Amberlynn Mills
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Prof. Tai-Haur Kuo, EE, NKU, Tainan iy, Taiwan - 郭泰豪, nalog I Design, 07 Semiconducor Devices and Models Resisor apacior Diode Bipolar Transisor MOSFET SPIE Model ppendix
2 Prof. Tai-Haur Kuo, EE, NKU, Tainan iy, Taiwan - 郭泰豪, nalog I Design, 07 Resisors Maerial Diffusion layers: e.g. n+, p+, well onducors : e.g. polysilicon, meal meal SiO SiO n + p-subsrae Resisance calculaion R=ρ/=ρ/W= R /W R =ρ/ is shee resisance Resisiviy W ross-secion area, Resisiviy=ρ R Shee resisance W Shee resisance = R R口 R W
3 Prof. Tai-Haur Kuo, EE, NKU, Tainan iy, Taiwan -3 郭泰豪, nalog I Design, 07 Resisors (on.) Graphical calculaions from shee resisance W R W W W W ½ 7.5R W W W W/.5 R R (volage coefficien) and T (emperaure coefficien) of R (or ) nonlineariy THD
4 Prof. Tai-Haur Kuo, EE, NKU, Tainan iy, Taiwan -4 郭泰豪, nalog I Design, 07 apaciors Meal-or polysilicon-over-diffusion is volage dependen meal SiO SiO n + meal l Meal-Insulaor-meal High lineariy meal n meal n- p - Iner-meal and inra-meal Iner: differen layer Inra: same layer meal n ia meal n- ia
5 Prof. Tai-Haur Kuo, EE, NKU, Tainan iy, Taiwan -5 郭泰豪, nalog I Design, 07 Resiser raio-maching consideraions Resisor onac Meal R w R w 3 R3 w R4 w
6 Prof. Tai-Haur Kuo, EE, NKU, Tainan iy, Taiwan -6 郭泰豪, nalog I Design, 07 apacior raio-maching consideraions X 3 4 X 7 7 X X X X
7 Prof. Tai-Haur Kuo, EE, NKU, Tainan iy, Taiwan -7 郭泰豪, nalog I Design, 07 Diode ccepor ions Donor ions I O Holes Elecrons I S p-ype -Xp 0 Xn n-ype x T O Depleion Region I I S (exp T ) kt where T q I S sauraion curren K Xp [ K Xn [ ( q ) S 0 0 R D / ] ( q ) N N (N N S 0 0 R / ] N D N (N N K S relaive permiivi y of silicon 0 buli in poenial reverse bias volage R D D ) )
8 Prof. Tai-Haur Kuo, EE, NKU, Tainan iy, Taiwan 郭泰豪, nalog I Design, 07-8 Juncion apaciance For abrup juncion: For graded juncion / D D R 0 0 S ] N N N N ) ( [qk Q Q 0 R j0 / D D R 0 0 S R j ] N N N N ) ( qk [ d dq ] ] N N N N qk [ [ / D D 0 0 S j0 m D D R 0 0 S ] ) N (N N N ) ( [qk Q Q m 0 R j0 m R 0 m D D 0 S R j ) ( ) ( ] N N N N m)[qk ( d dq ] ] N N N N m)[qk ( [ m 0 m D D 0 S j0 m depend on he doping profile m /3 for a linearly graded juncion
9 Prof. Tai-Haur Kuo, EE, NKU, Tainan iy, Taiwan -9 郭泰豪, nalog I Design, 07 Diode Model D Model For < r (off) For > r (on) R f di ( d ) D I e S T / T I T D I S I D r O I D + - R f r Small Signal Model For forward-biased diode rd I T D Diffusion capaciance: Juncion capaciance: d r T d j j0 r d d j Normally, d >> j ( d 00 j ) j0 : apaciance a 0- bias T : Diode ransi ime
10 Prof. Tai-Haur Kuo, EE, NKU, Tainan iy, Taiwan -0 郭泰豪, nalog I Design, 07 Bipolar Process erical and laeral ransisor in a bipolar process collecor base base collecor emier emier n n + n + n + p p p p n + + n n + n + n p + n p erical PNP or NPN high β aeral PNP or NPN low β verical npn ransisor laeral pnp ransisor
11 Prof. Tai-Haur Kuo, EE, NKU, Tainan iy, Taiwan - 郭泰豪, nalog I Design, 07 BJT Model: Ebers-Moll model (D Model) α R I R α F I F NPN PNP I E E EB I F - - I R B I B I B B BE I E B I B B BE I E I B B E I E E I E I I E I S -I α e S R e BB BB T T - I α -I S S R e e B B T T
12 Prof. Tai-Haur Kuo, EE, NKU, Tainan iy, Taiwan - 郭泰豪, nalog I Design, 07 Small Signal BJT Model Emier luminum conacs ollecor P n + n + P n P + Base Isolaion island p subsrae
13 Prof. Tai-Haur Kuo, EE, NKU, Tainan iy, Taiwan -3 郭泰豪, nalog I Design, 07 Small Signal BJT Model (on.) Sub r μ BS B r b + B R r n BE v be g m v be r o S - R E Sub E
14 Prof. Tai-Haur Kuo, EE, NKU, Tainan iy, Taiwan -4 郭泰豪, nalog I Design, 07 MOS Transisors MOS srucure NMOS GTE ONDUTOR INSUTOR symbol DRIN GTE SOURE n n P - DOPED SEMIONDUTOR SUBSTRTE DRIN SUBSTRTE SOURE PMOS ONDUTOR symbol DRIN GTE INSUTOR GTE p n - DOPED p SOURE DRIN SUBSTRTE SOURE SEMIONDUTOR SUBSTRTE
15 Prof. Tai-Haur Kuo, EE, NKU, Tainan iy, Taiwan -5 郭泰豪, nalog I Design, 07 MOS Transisors (on.) -Enhancemen NMOS Source Gae Drain s gs D P Source Gae Drain Meal Polysilicon Oxide n-diffusion p-diffusion -Depleion NMOS P Implan p-subsrae n-depleion subsrae -Enhancemen PMOS Source Gae Drain -Depleion PMOS Source Gae Drain n n Implan
16 Prof. Tai-Haur Kuo, EE, NKU, Tainan iy, Taiwan -6 郭泰豪, nalog I Design, 07 MOS Transisor Symbol (on.) nmos enhancemen nmos depleion pmos enhancemen
17 Prof. Tai-Haur Kuo, EE, NKU, Tainan iy, Taiwan -7 郭泰豪, nalog I Design, 07 Example : nmos MOS Transisor Operaion gs >, ds = 0 (linear region) GND (0 ) gs v d gae ( inversion layer) 0 hannel ( inversion layer) gs >, ds = gs - GND (0 ) gs 0
18 Prof. Tai-Haur Kuo, EE, NKU, Tainan iy, Taiwan -8 郭泰豪, nalog I Design, 07 MOS Transisor Operaion (on.) Example : nmos gs >, ds > gs - (sauraion region) GND (0 ) 0 Pinch off, Xd I- characerisic of nmos INER REGION gs - = ds STURTION REGION gs4 I ds gs3 gs gs ds
19 arge Signal Behavior of MOSFETs Threshold volage arge-signal I- I 0 0 qε W SiO f where γ GS N SB qε - SiO f f N kw SB and - GS OX f k ε 0 ε If depleion-layer widh X d is considered eff = -X d I kw GS hannel lengh modulaion I kw d GS d e I eff r o eff I I eff Prof. Tai-Haur Kuo, EE, NKU, Tainan iy, Taiwan -9 郭泰豪, nalog I Design, 07 I eff dx d eff d dx d d I kw GS
20 Prof. Tai-Haur Kuo, EE, NKU, Tainan iy, Taiwan -0 郭泰豪, nalog I Design, 07 Small Signal Model of MOSFETs in Sauraion Equivalen circui model G + gd D v gs g m v gs g mb v bs r ds - gs - S v bs + sb gb db B
21 Prof. Tai-Haur Kuo, EE, NKU, Tainan iy, Taiwan - 郭泰豪, nalog I Design, 07 Small Signal Model of MOSFETs in Sauraion (on.) gm I ' W W k GS k I GS I W gmb k GS g o f SB f m BS BS BS BS f BS r o I - I eff dx ( d d ) - λi I sb db gs f sb0 SB 0 db0 Q gm π T GS gs 0 3 W W K OX ( GS W 3 - ) 3 f GS Derivaion of gs Toal charge sored in he channel Q T gs W 3 Q W T GS 0 [ 3 GS GS W - (y) W - ]dy I D μ GS Q T - - d
22 Prof. Tai-Haur Kuo, EE, NKU, Tainan iy, Taiwan - 郭泰豪, nalog I Design, 07 Example Small Signal Model Derive he complee small-signal model for an NMOS ransisor wih I =00μ, SB =0.5, =0.6. Device parameers are f = 0.65, W=.5 μm, =45 nm, γ= 0.45 /, μ n = 80μ/, λ =. -, =. nm, Ψ 0 = 0.69, sb0 = db0 =.5 ff. Overlap capaciance from gae o source and gae o drain is.5 ff. ssume gb =5fF. g m = μ n W I D = =.76m g mb n W I f D SB r o I D.. k
23 Prof. Tai-Haur Kuo, EE, NKU, Tainan iy, Taiwan -3 郭泰豪, nalog I Design, 07 Example Small Signal Model (on.) Wih SB =0.5,we find The volage from drain o body is.5 sb sb / / SB DB SB ff ff Hence,.5 db db / / DB.. ff.85ff The ide capaciance per uni area is.. F r SiO cm 8.7 ff 9. m The inrinsic porion of he gae source capaciance is gs fF.5fF m
24 Prof. Tai-Haur Kuo, EE, NKU, Tainan iy, Taiwan -4 郭泰豪, nalog I Design, 07 Example Small Signal Model (on.) The addiion of overlap capaciance gives gs =.4 ff Gae-drain capaciance is overlap capaciance gd =.5 ff The complee small-signal equivalen circui is shown below G v gs + - ff ff. 76 v gs 44 v bs.k D S v bs - + ff 5fF.85fF The f T of he device can be calculaed wih gb = 5fF giving f T gs g m gd gb B Hz 3.GHz
25 Prof. Tai-Haur Kuo, EE, NKU, Tainan iy, Taiwan -5 郭泰豪, nalog I Design, 07 Subhreshold onducion in MOSFETs I GS W n n k exp x - exp where k depends on process I x n.5 ( ) parameers = 5 W = 0 μ m = 0μm GS ( )
26 Prof. Tai-Haur Kuo, EE, NKU, Tainan iy, Taiwan -6 郭泰豪, nalog I Design, 07 Subhreshold onducion in MOSFET (con.) Ploed on linear scales as characerisic. I versus GS,showing he square-law I ( / ) = 5 W = 0 μm = 0μm GS ( ) Exrapolaed = 0.7
27 Prof. Tai-Haur Kuo, EE, NKU, Tainan iy, Taiwan -7 郭泰豪, nalog I Design, 07 Subhreshold onducion in MOSFET (con.) Ploed on log-linear scales showing he exponenial characerisic in he subhreshold region. I ( ) Square-law region = 5 W = 0 μ m = 0μm 0-0 Subhreshold exponenial region GS ( )
28 Prof. Tai-Haur Kuo, EE, NKU, Tainan iy, Taiwan -8 郭泰豪, nalog I Design, 07 Mobiliy Degradaion arge laeral elecric fields accelerae carriers up o a maximum velociy arger verical elecric fields effecive channel deph collisions These effecs can be modeled by an effecive carrier mobiliy I n,eff D where θ [ ( n and W n eff ) ] m / m eff ( [ ( eff m are device parameers ) ] m / m ) I D n W eff, This effec can also expressed as α-law model from curve-fiing Source Gae Drain I D () Wihou mobiliy degradaion Wih mobiliy degradaion n + aeral Elecric Field p-subsrae n + ()
29 Prof. Tai-Haur Kuo, EE, NKU, Tainan iy, Taiwan -9 郭泰豪, nalog I Design, 07 Subsrae urren Flow in MOSFETs I DB k ( - sa )I exp - ( k - sa ) k k where and are process-dependen parameers and sa is he value of where he drain characerisics ener he sauraion region g db I DB DB k - I DB sa
30 Prof. Tai-Haur Kuo, EE, NKU, Tainan iy, Taiwan -30 郭泰豪, nalog I Design, 07 Example (/) alculae rdb /g db for and 4, and compare wih he device. r o ssume I = 00μ, λ = , (sa) = 0.3, K = 5 -, and K = 30. For =, we have I g DB db exp and hus r db g db G
31 Prof. Tai-Haur Kuo, EE, NKU, Tainan iy, Taiwan -3 郭泰豪, nalog I Design, 07 Example (/) This resul is negligibly large compared wih ro. k λid.4 However, for IDB exp The subsrae leakage curren is now abou 0.5% of he drain curren. We find gdb and hus r db g db Ω 833 This parasiic resisor is now comparable o and can have a dominan effec on high-oupu-impedance MOS curren mirrors. kω r o
32 Prof. Tai-Haur Kuo, EE, NKU, Tainan iy, Taiwan -3 郭泰豪, nalog I Design, 07 Summary of MOSFET Parameers arge-signal Operaion Quaniy Drain curren (sauraion region) I μ Formula W ( - ds gs ) Drain curren (riode region) I ds μ W [( gs - ) ds - ds ] Threshold volage 0 γ[ φ f - sb - φ f ] Threshold volage parameer γ qn Oxide capaciance ε 3.45 ff m for 00 ο
33 Prof. Tai-Haur Kuo, EE, NKU, Tainan iy, Taiwan -33 郭泰豪, nalog I Design, 07 Summary of MOSFET Parameers arge-signal Operaion Quaniy Formula Top-gae ransconducance g m μ W ( GS - ) I W Transconducance-o-curren raio g I m GS - Body-effec ransconducance g mb φ f γ SB g m χg m hannel-lengh modulaion parameer λ eff dx d d Oupu resisance r o λi I eff dx d d
34 Prof. Tai-Haur Kuo, EE, NKU, Tainan iy, Taiwan -34 郭泰豪, nalog I Design, 07 Summary of MOSFET Parameers Quaniy Formula Effecive channel lengh eff drwn - d - X d Maximum gain g m r o λ GS - - GS Source-body depleion capaciance sb sb0 ψ SB Drain-body depleion capaciance db db0 ψ DB Gae-source capaciance Transiion frequency f 3 gs W T π gs gm gd gb
35 SPIE MOSFET Model Parameers of Typical NMOS Process (MOSIS) Prof. Tai-Haur Kuo, EE, NKU, Tainan iy, Taiwan -35 郭泰豪, nalog I Design, 07 Parameer (evel model) Enhancemen Depleion Unis TO KP μ/ GMM PHI MBD 3.E-.00E-6 GSO.60E-4.60E-4 widh GDO.60E-4.60E-4 widh GBO.70E-4.70E-4 widh RSH J.E-4.E-4 MJ JSW 5.0E-4 5.0E-4 pf/μ perimeer MJSW TOX ff/ ff/ ff/ Ω/ pf/μ
36 SPIE MOSFET Model Parameers of Typical NMOS Process (MOSIS) (on.) (evel model) Enhancemen Depleion Unis /cm NSUB.09E5.0E6 NSS 0 0 /cm NFS.90E 4.3E /cm TPG XJ D UO URIT.0E E6 cm UEXP.00E-3.00E-3 MX.0E5 6.75E5 m/s NEFF.00E-.00E- DET.6.80 The SPIE parameers: Empirical parameers Fiing measured device characerisics o he mahemaical equaions Using a numerical opimizaion algorihm This approach gives good fi o he model bu causes a deviaion from he ypical parameers. Parameer relaionships may no be self-consisen wih some of he fundamenal relaionships. *Please refer o he chapers abou SPIE model in he HSPIE documen suggesed in assignmen Prof. Tai-Haur Kuo, EE, NKU, Tainan iy, Taiwan -36 郭泰豪, nalog I Design, 07 3 /(v s) /cm
37 ppendix Resisance Esimaion apaciance Esimaion Inducance Esimaion PP- -37 Prof. Tai-Haur Kuo, EE, NKU, Tainan iy, Taiwan 郭泰豪, nalog I Design, 07
38 Shee Resisance R=ρ/=ρ/W= R /W R =ρ/ Resisance Esimaion : resisivi y W : hicknes s :conducor lengh W : conducor R widh :shee resisance ohm/square, / urren PP- -38 Prof. Tai-Haur Kuo, EE, NKU, Tainan iy, Taiwan 郭泰豪, nalog I Design, 07
39 Resisance Esimaion (con.) Typical shee resisance for conducors Maerial Min. Typical Max. Inermaal (meal-meal) Top-meal(meal3) Polysilicon Silicide 3 6 Diffusion(n +, p + ) Silicided diffusion 4 0 N-well K K 5K PP-3-39 Prof. Tai-Haur Kuo, EE, NKU, Tainan iy, Taiwan 郭泰豪, nalog I Design, 07
40 Resisance Esimaion of Nonrecangular Shapes Direc esimaion W urren urren R = /W W Table-assised esimaion W RTIO = W 4 R = + 4W W W W D W W W W W W RTIO = W B W W W RTIO = W W W R = + W W R = /W W W RTIO = W W W W E W W RTIO = W W Shape Raio Resisance 5 5 B 5 5 B.5 B.55 B D. D.5.3 D.3 D 3.6 E.5.45 E.8 E 3.3 E 4.65 PP-4-40 Prof. Tai-Haur Kuo, EE, NKU, Tainan iy, Taiwan 郭泰豪, nalog I Design, 07
41 onac and ia Resisance Proporional o he area of he conac e.g. feaure size =>Rconac 0.5Ω ~ a few ens of Ωs Muliple conacs o obain low-resisance inerlayer connecions PP-5-4 Prof. Tai-Haur Kuo, EE, NKU, Tainan iy, Taiwan 郭泰豪, nalog I Design, 07
42 MOS-apacior haracerisics - plo accumulaion depleion inversion.0 low frequency high frequency min Three regions in he plo (i)ccumulaion region (ii)depleion region (iii)inversion region 0 gs ccumulaion region ε ε o :gae area o o SiO : permiivi y of free space : gae capacianc e ε SiO : dielecric ε SiO ε o ε o consan of SiO ( 3.9) :gae capacianc e per uni area PP Prof. Tai-Haur Kuo, EE, NKU, Tainan iy, Taiwan 郭泰豪, nalog I Design, 07 o gae gae g < p-subsrae +
43 Depleion region εsiεo dep d d : depleion layer deph ε Si gb : dielecric o Where o o dep beween gae and surface Inversion region gb min dep For MOS-apacior haracerisics (con.) consan of Si( ) dep :gae capacianc e per uni is low frequency o o o capacianc e area :saic (i.e. low frequency, 00Hz) dep dep O 00 ~ 00, min min :dynamic o varies (i.e. high depends on he deph of he depleoin region, i.e. depends on subsrae doping for subsrae doping densiy va ries from 0 / densiy. frequency) from 0.0 ~ PP-7-43 o dep Prof. Tai-Haur Kuo, EE, NKU, Tainan iy, Taiwan 郭泰豪, nalog I Design, 07 cm -3 o 50-5 o dep cm -3 gae gae + gae depleion layer p-subsrae gae p-subsrae h > g > 0 g > h channel depleion layer d d
44 MOS Device apaciance ross secion of MOS device GTE gs gb gd SOURE HNNE DRIN DEPETION YER sb db Equivalen circui SUBSTRTE d gd db g GTE DRIN SOURE SUBSTRT be gs s sb gb PP-8-44 Prof. Tai-Haur Kuo, EE, NKU, Tainan iy, Taiwan 郭泰豪, nalog I Design, 07
45 MOS Device apaciance (con.) pprimaion of gae capaciance Self-aligned process is assumed (i.e. overlap caps. are negligible) Parameer off Non-sauraed Sauraed gb gs gd g = gb + gs + gd (finie for shor channel devices) 0.9 (shor channel) PP-9-45 Prof. Tai-Haur Kuo, EE, NKU, Tainan iy, Taiwan 郭泰豪, nalog I Design, 07
46 gs,gd and Example : W=49. m, =4.5 m (long channel) gs and gd *large g & small gd (in sauraion region) g gd large 0 ( gd is due o channel side fringing fields beween gae and drain.) gs, gd W gs gs ds (vols) gs gd PP-0-46 Prof. Tai-Haur Kuo, EE, NKU, Tainan iy, Taiwan 郭泰豪, nalog I Design, 07
47 gs,gd and (con.) Example : =0.75 m (shor channel) gs and gd small *small g & small gd (in sauraion region) gd gs gs 0. ( gd is due o channel side fringing fields beween gae and drain.) g gs, gd W gs ds (vols) gd PP- -47 Prof. Tai-Haur Kuo, EE, NKU, Tainan iy, Taiwan 郭泰豪, nalog I Design, 07
48 = ε SiO e.g., gae capaciance per uni area ε Uni ransisor I is he same widh as a meal-diffusion conac o ; where o ε SiO and ε 0-3 o pf/μf 4 ff/μf W 4 Minimum-size ransisor 5 W 4 PP Prof. Tai-Haur Kuo, EE, NKU, Tainan iy, Taiwan 郭泰豪, nalog I Design, 07
49 Diffusion apaciance rea and periphery d=ja*(ab)+jp*(a+b) ja: juncion capaciance per μm jp: periphery capaciance per μm a: widh of diffusion region b: lengh of diffusion region Typical value (μm n-well process) ja: *0-4 pf/μm (n+ diffusion) 5*0-4 pf/μm (p+ diffusion) jp: 4*0-4 pf/μm (n+ diffusion) 4*0-4 pf/μm (p+ diffusion) olage dependen j j j0 j b m j b jp j0 a m ja Diffusion rea b is juncion abrup poly volage isbuil -in juncion is zero bias capaciance graded juncion juncion poenial ~ ~ 0.6 PP-3-49 Prof. Tai-Haur Kuo, EE, NKU, Tainan iy, Taiwan 郭泰豪, nalog I Design, 07
50 SPIE example. SPIE Modeling of MOS apaciances M NFET W 4U U S 5P D 5P PS.5U PD.5U...MODE NFET NMOS TOX 00E - 8 GBO 00P GSO 600P GDO 600P J 00U JSW 400P MJ 0.5 MJSW 0.3 PB o node4 - drain TOX 00 node3 - gae node5 - source node0 - subsrae channel widh 4m channel lengh m source area S 5m drain area D 5m - beyond he channel. 000 F/M gbo gso occours due o he polysilicon exesion and represen he gae - o - source/drain source periphery PS.5m capaciance due o overlap in he physical drain periphery PD.5m - srucure of he ransisor F/M gdo PP-4-50 Prof. Tai-Haur Kuo, EE, NKU, Tainan iy, Taiwan 郭泰豪, nalog I Design, 07
51 SPIE Modeling of MOS apaciances (con.) apaciance gae capaciance g(inrinsic) g(exrinsic) g(oal) W j rea j where W gs0 W gd0 gb PF g(inrinsic) OX g(exrinsic) source and drain capaciance rea j S or D, he PF J J PB J he juncion poenial PB he buil -in volage PF J MJ 4 0.0PF MJSW he grading coefficien of he PF 0.04PF 0 4 periphery JSW he zero -bias capaciance per juncion MJ he grading coefficien of he juncion boom ~ vols juncion area of he souce or drain.5 is assumed.5 is assumed area PF JSW he zero -bias capaciance per juncion periphery sidewall Periphery PS or PD, he periphery of he source or drain j(drain) j(source) PP-5-5 Prof. Tai-Haur Kuo, EE, NKU, Tainan iy, Taiwan 郭泰豪, nalog I Design, 07 J PB MJSW
52 Single wire capaciance Rouing apaciance Parallel-plae effec and fringing effec Fringing field W T Insulaor(Oxide) H Subsrae ccurae capaciance evaluaion : use compuer Hand calculaion : use simple model (less han 0% error) Half cylinders w Parallel plae h ε w h w h 0.5 PP Prof. Tai-Haur Kuo, EE, NKU, Tainan iy, Taiwan 郭泰豪, nalog I Design, 07 h 0.5
53 Rouing apaciance (con.) Muliple conducor capaciances Three-layer example c 3 c c layer3 layer layer apaciance calculaion is very complex refer o exbook Typical dielecric and conducor hicknesses Thin ide o 00 Meal o 6000 Field ide o 6000 M M ide o 6000 Polysilicon o 3000 Meal o 000 M poly ide o 6000 Passivaion o 0000 PP-7-53 Prof. Tai-Haur Kuo, EE, NKU, Tainan iy, Taiwan 郭泰豪, nalog I Design, 07
54 Disribued R Effecs Transmission line l Subsrae conducor layer isolaion layer Delay ime from one end o he oher end rc l r : resisance c : capacianc e per uni l :lengh of per uni he wire lengh lengh PP-8-54 Prof. Tai-Haur Kuo, EE, NKU, Tainan iy, Taiwan 郭泰豪, nalog I Design, 07
55 Disribued R Effecs (con.) Disadvanages of long wire: ong delay Reducion in sensiiviy o noise PP-9-55 Prof. Tai-Haur Kuo, EE, NKU, Tainan iy, Taiwan 郭泰豪, nalog I Design, 07
56 Disribued R Effecs (con.) Mehod o improve disadvanages menioned previously g delay rcl If g, more buffers In acual design, if possible, rcl rc τ g l g l rc rcl g 4 rcl If g, delay ime 4 rc g is l reduced should be used PP-0-56 Prof. Tai-Haur Kuo, EE, NKU, Tainan iy, Taiwan 郭泰豪, nalog I Design, 07
57 Disribued R Effecs (con.) Transmission line effec is paricularly severe in poly wire because of he relaively high resisance of his layer. Gae poly layer is he wors one because of is high capaciance o subsrae. Sraegies Use meal line : small r Use wider meal for signal disribuion line (e.g. clock disribuion line) : small r, a iny bi large PP- -57 Prof. Tai-Haur Kuo, EE, NKU, Tainan iy, Taiwan 郭泰豪, nalog I Design, 07
58 Inducance On-chip inducance are normally small. Bond-wire inducance is larger. Inducance of bonding wires and he pins on packages : he magneic permeabiliy of h : he heigh d: he 4h ln H/cm d (ypically.57 0 diameer above of he he H/cm) ground wire Inducance of on-chip wires ln 8h w w : conducor h : he heigh w 4h widh above he -8 H/cm subsrae he plane wire PP- -58 Prof. Tai-Haur Kuo, EE, NKU, Tainan iy, Taiwan 郭泰豪, nalog I Design, 07
Chapter 6 MOSFET in the On-state
 Chaper 6 MOSFET in he On-sae The MOSFET (MOS Field-Effec Transisor) is he building block of Gb memory chips, GHz microprocessors, analog, and RF circuis. Mach he following MOSFET characerisics wih heir
Chaper 6 MOSFET in he On-sae The MOSFET (MOS Field-Effec Transisor) is he building block of Gb memory chips, GHz microprocessors, analog, and RF circuis. Mach he following MOSFET characerisics wih heir
Introduction to Digital Circuits
 The NMOS nerer The NMOS Depleion oad 50 [ D ] µ A GS.0 + 40 30 0 0 Resisance characerisic of Q 3 4 5 6 GS 0.5 GS 0 GS 0.5 GS.0 GS.5 [ ] DS GS i 0 Q Q Depleion load Enhancemen drier Drain characerisic of
The NMOS nerer The NMOS Depleion oad 50 [ D ] µ A GS.0 + 40 30 0 0 Resisance characerisic of Q 3 4 5 6 GS 0.5 GS 0 GS 0.5 GS.0 GS.5 [ ] DS GS i 0 Q Q Depleion load Enhancemen drier Drain characerisic of
Semiconductor Devices. C. Hu: Modern Semiconductor Devices for Integrated Circuits Chapter 6
 Semiconducor Devices C. Hu: Modern Semiconducor Devices for Inegraed Circuis Chaper 6 For hose of you who are sudying a bachelor level and need he old course S-69.2111 Mikro- ja nanoelekroniikan perusee
Semiconducor Devices C. Hu: Modern Semiconducor Devices for Inegraed Circuis Chaper 6 For hose of you who are sudying a bachelor level and need he old course S-69.2111 Mikro- ja nanoelekroniikan perusee
Chapter 4. Circuit Characterization and Performance Estimation
 VLSI Design Chaper 4 Circui Characerizaion and Performance Esimaion Jin-Fu Li Chaper 4 Circui Characerizaion and Performance Esimaion Resisance & Capaciance Esimaion Swiching Characerisics Transisor Sizing
VLSI Design Chaper 4 Circui Characerizaion and Performance Esimaion Jin-Fu Li Chaper 4 Circui Characerizaion and Performance Esimaion Resisance & Capaciance Esimaion Swiching Characerisics Transisor Sizing
EE 560 MOS INVERTERS: DYNAMIC CHARACTERISTICS. Kenneth R. Laker, University of Pennsylvania
 1 EE 560 MOS INVERTERS: DYNAMIC CHARACTERISTICS C gsp V DD C sbp C gd, C gs, C gb -> Oxide Caps C db, C sb -> Juncion Caps 2 S C in -> Ineconnec Cap G B D C dbp V in C gdp V ou C gdn D C dbn G B S C in
1 EE 560 MOS INVERTERS: DYNAMIC CHARACTERISTICS C gsp V DD C sbp C gd, C gs, C gb -> Oxide Caps C db, C sb -> Juncion Caps 2 S C in -> Ineconnec Cap G B D C dbp V in C gdp V ou C gdn D C dbn G B S C in
CHAP.4 Circuit Characteristics and Performance Estimation
 HAP.4 ircui haracerisics and Performance Esimaion 4. Resisance esimaion R ρ l w (ohms) where ρ Resisiviy Thickness l onducor lengh w onducor widh l R Rs w where Rs Shee resisance (Ω/square) in 0.5µm o
HAP.4 ircui haracerisics and Performance Esimaion 4. Resisance esimaion R ρ l w (ohms) where ρ Resisiviy Thickness l onducor lengh w onducor widh l R Rs w where Rs Shee resisance (Ω/square) in 0.5µm o
The Devices. Devices
 The The MOS Transistor Gate Oxyde Gate Source n+ Polysilicon Drain n+ Field-Oxyde (SiO 2 ) p-substrate p+ stopper Bulk Contact CROSS-SECTION of NMOS Transistor Cross-Section of CMOS Technology MOS transistors
The The MOS Transistor Gate Oxyde Gate Source n+ Polysilicon Drain n+ Field-Oxyde (SiO 2 ) p-substrate p+ stopper Bulk Contact CROSS-SECTION of NMOS Transistor Cross-Section of CMOS Technology MOS transistors
Outline. Chapter 2: DC & Transient Response. Introduction to CMOS VLSI. DC Response. Transient Response Delay Estimation
 Inroducion o CMOS VLSI Design Chaper : DC & Transien Response David Harris, 004 Updaed by Li Chen, 010 Ouline DC Response Logic Levels and Noise Margins Transien Response Delay Esimaion Slide 1 Aciviy
Inroducion o CMOS VLSI Design Chaper : DC & Transien Response David Harris, 004 Updaed by Li Chen, 010 Ouline DC Response Logic Levels and Noise Margins Transien Response Delay Esimaion Slide 1 Aciviy
EE 560 MOS TRANSISTOR THEORY PART 2. Kenneth R. Laker, University of Pennsylvania
 1 EE 560 MOS TRANSISTOR THEORY PART nmos TRANSISTOR IN LINEAR REGION V S = 0 V G > V T0 channel SiO V D = small 4 C GC C BC substrate depletion region or bulk B p nmos TRANSISTOR AT EDGE OF SATURATION
1 EE 560 MOS TRANSISTOR THEORY PART nmos TRANSISTOR IN LINEAR REGION V S = 0 V G > V T0 channel SiO V D = small 4 C GC C BC substrate depletion region or bulk B p nmos TRANSISTOR AT EDGE OF SATURATION
Capacitors & Inductors
 apaciors & Inducors EEE5 Elecric ircuis Anawach Sangswang Dep. of Elecrical Engineering KMUTT Elecric Field Elecric flux densiy Elecric field srengh E Elecric flux lines always exend from a posiively charged
apaciors & Inducors EEE5 Elecric ircuis Anawach Sangswang Dep. of Elecrical Engineering KMUTT Elecric Field Elecric flux densiy Elecric field srengh E Elecric flux lines always exend from a posiively charged
Type Marking Pin Configuration Package SMBT3904/MMBT3904 SOT23 SMBT3904S 2=E 1=B 3=C 1=E1 2=B1 3=C2
 SMBT94...MMBT94 NPN Silicon Swiching Transisors High D curren gain:. ma o ma Low collecoremier sauraion volage For SMBT94S: Two (galvanic) inernal isolaed ransisors wih good maching in one package omplemenary
SMBT94...MMBT94 NPN Silicon Swiching Transisors High D curren gain:. ma o ma Low collecoremier sauraion volage For SMBT94S: Two (galvanic) inernal isolaed ransisors wih good maching in one package omplemenary
dv 7. Voltage-current relationship can be obtained by integrating both sides of i = C :
 EECE202 NETWORK ANALYSIS I Dr. Charles J. Kim Class Noe 22: Capaciors, Inducors, and Op Amp Circuis A. Capaciors. A capacior is a passive elemen designed o sored energy in is elecric field. 2. A capacior
EECE202 NETWORK ANALYSIS I Dr. Charles J. Kim Class Noe 22: Capaciors, Inducors, and Op Amp Circuis A. Capaciors. A capacior is a passive elemen designed o sored energy in is elecric field. 2. A capacior
Capacitors. C d. An electrical component which stores charge. parallel plate capacitor. Scale in cm
 apaciors An elecrical componen which sores charge E 2 2 d A 2 parallel plae capacior Scale in cm Leyden Jars I was invened independenly by German cleric Ewald Georg von Kleis on Ocober 745 and by Duch
apaciors An elecrical componen which sores charge E 2 2 d A 2 parallel plae capacior Scale in cm Leyden Jars I was invened independenly by German cleric Ewald Georg von Kleis on Ocober 745 and by Duch
EECS 141: FALL 00 MIDTERM 2
 Universiy of California College of Engineering Deparmen of Elecrical Engineering and Compuer Science J. M. Rabaey TuTh9:30-11am ee141@eecs EECS 141: FALL 00 MIDTERM 2 For all problems, you can assume he
Universiy of California College of Engineering Deparmen of Elecrical Engineering and Compuer Science J. M. Rabaey TuTh9:30-11am ee141@eecs EECS 141: FALL 00 MIDTERM 2 For all problems, you can assume he
3~ Rectifier Bridge, half-controlled (high-side) + Brake Unit + NTC /20 NTC. Features / Advantages: Applications: Package: E2-Pack
 ZB3-6ioX hyrisor Module M = 6 I = D FSM = 7 I 3~ ecifier Brake hopper ES = 2 I = 2 2 E(sa) =,8 3~ ecifier Bridge, half-conrolled (high-side) + Brake Uni + N Par number ZB3-6ioX Backside: isolaed / 3 2
ZB3-6ioX hyrisor Module M = 6 I = D FSM = 7 I 3~ ecifier Brake hopper ES = 2 I = 2 2 E(sa) =,8 3~ ecifier Bridge, half-conrolled (high-side) + Brake Uni + N Par number ZB3-6ioX Backside: isolaed / 3 2
NDS332P P-Channel Logic Level Enhancement Mode Field Effect Transistor
 June 997 NS33P P-Channel Logic Level Enhancemen Mode Field Effec Transisor General escripion Feaures These P-Channel logic level enhancemen mode power field effec ransisors are produced using Fairchild's
June 997 NS33P P-Channel Logic Level Enhancemen Mode Field Effec Transisor General escripion Feaures These P-Channel logic level enhancemen mode power field effec ransisors are produced using Fairchild's
Standard Rectifier Module
 UB2-6NOX Sandard ecifier Module M = 6 I = 8 D 3~ ecifier I SM = Brake hopper ES = 2 I = 8 25 E(sa) =.7 3~ ecifier Bridge + Brake Uni Par number UB2-6NOX M/O S Backside: isolaed ~6 ~E6 ~K6 U/ W M/O W U
UB2-6NOX Sandard ecifier Module M = 6 I = 8 D 3~ ecifier I SM = Brake hopper ES = 2 I = 8 25 E(sa) =.7 3~ ecifier Bridge + Brake Uni Par number UB2-6NOX M/O S Backside: isolaed ~6 ~E6 ~K6 U/ W M/O W U
University of Cyprus Biomedical Imaging and Applied Optics. Appendix. DC Circuits Capacitors and Inductors AC Circuits Operational Amplifiers
 Universiy of Cyprus Biomedical Imaging and Applied Opics Appendix DC Circuis Capaciors and Inducors AC Circuis Operaional Amplifiers Circui Elemens An elecrical circui consiss of circui elemens such as
Universiy of Cyprus Biomedical Imaging and Applied Opics Appendix DC Circuis Capaciors and Inducors AC Circuis Operaional Amplifiers Circui Elemens An elecrical circui consiss of circui elemens such as
EECE251. Circuit Analysis I. Set 4: Capacitors, Inductors, and First-Order Linear Circuits
 EEE25 ircui Analysis I Se 4: apaciors, Inducors, and Firs-Order inear ircuis Shahriar Mirabbasi Deparmen of Elecrical and ompuer Engineering Universiy of Briish olumbia shahriar@ece.ubc.ca Overview Passive
EEE25 ircui Analysis I Se 4: apaciors, Inducors, and Firs-Order inear ircuis Shahriar Mirabbasi Deparmen of Elecrical and ompuer Engineering Universiy of Briish olumbia shahriar@ece.ubc.ca Overview Passive
Chapter 4 AC Network Analysis
 haper 4 A Nework Analysis Jaesung Jang apaciance Inducance and Inducion Time-Varying Signals Sinusoidal Signals Reference: David K. heng, Field and Wave Elecromagneics. Energy Sorage ircui Elemens Energy
haper 4 A Nework Analysis Jaesung Jang apaciance Inducance and Inducion Time-Varying Signals Sinusoidal Signals Reference: David K. heng, Field and Wave Elecromagneics. Energy Sorage ircui Elemens Energy
NDP4050L / NDB4050L N-Channel Logic Level Enhancement Mode Field Effect Transistor
 April 996 NP45L / NB45L N-Channel Logic Level Enhancemen Mode Field Effec Transisor General escripion Feaures These logic level N-Channel enhancemen mode power field effec ransisors are produced using
April 996 NP45L / NB45L N-Channel Logic Level Enhancemen Mode Field Effec Transisor General escripion Feaures These logic level N-Channel enhancemen mode power field effec ransisors are produced using
University of Pennsylvania Department of Electrical Engineering. ESE 570 Midterm Exam March 14, 2013 FORMULAS AND DATA
 University of Pennsylvania Department of Electrical Engineering ESE 570 Midterm Exam March 4, 03 FORMULAS AND DATA. PHYSICAL CONSTANTS: n i = intrinsic concentration undoped) silicon =.45 x 0 0 cm -3 @
University of Pennsylvania Department of Electrical Engineering ESE 570 Midterm Exam March 4, 03 FORMULAS AND DATA. PHYSICAL CONSTANTS: n i = intrinsic concentration undoped) silicon =.45 x 0 0 cm -3 @
VLSI Design and Simulation
 VLSI Design and Simulation Performance Characterization Topics Performance Characterization Resistance Estimation Capacitance Estimation Inductance Estimation Performance Characterization Inverter Voltage
VLSI Design and Simulation Performance Characterization Topics Performance Characterization Resistance Estimation Capacitance Estimation Inductance Estimation Performance Characterization Inverter Voltage
MOSFET: Introduction
 E&CE 437 Integrated VLSI Systems MOS Transistor 1 of 30 MOSFET: Introduction Metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistor (MOSFET) or MOS is widely used for implementing digital designs Its major
E&CE 437 Integrated VLSI Systems MOS Transistor 1 of 30 MOSFET: Introduction Metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistor (MOSFET) or MOS is widely used for implementing digital designs Its major
NDS356P P-Channel Logic Level Enhancement Mode Field Effect Transistor
 March 996 NS356P P-Channel Logic Level Enhancemen Mode Field Effec Transisor General escripion These P-Channel logic level enhancemen mode power field effec ransisors are produced using Fairchild's proprieary,
March 996 NS356P P-Channel Logic Level Enhancemen Mode Field Effec Transisor General escripion These P-Channel logic level enhancemen mode power field effec ransisors are produced using Fairchild's proprieary,
XPT IGBT Module MIXA450PF1200TSF. Phase leg + free wheeling Diodes + NTC MIXA450PF1200TSF. Part number
 XPT IGBT Module CS 2x 12 I C25 1.8 C(sa) Phase leg + free wheeling Diodes + NTC Par number Backside: isolaed 5 2 1 8 7 9 3 4 /11 Feaures / dvanages: pplicaions: Package: SimBus F High level of inegraion
XPT IGBT Module CS 2x 12 I C25 1.8 C(sa) Phase leg + free wheeling Diodes + NTC Par number Backside: isolaed 5 2 1 8 7 9 3 4 /11 Feaures / dvanages: pplicaions: Package: SimBus F High level of inegraion
NDH834P P-Channel Enhancement Mode Field Effect Transistor
 May 997 NH834P P-Channel Enhancemen Mode Field Effec Transisor General escripion Feaures SuperSOT TM -8 P-Channel enhancemen mode power field effec ransisors are produced using Fairchild's proprieary,
May 997 NH834P P-Channel Enhancemen Mode Field Effec Transisor General escripion Feaures SuperSOT TM -8 P-Channel enhancemen mode power field effec ransisors are produced using Fairchild's proprieary,
Lecture 28: Single Stage Frequency response. Context
 Lecure 28: Single Sage Frequency response Prof J. S. Sih Conex In oday s lecure, we will coninue o look a he frequency response of single sage aplifiers, saring wih a ore coplee discussion of he CS aplifier,
Lecure 28: Single Sage Frequency response Prof J. S. Sih Conex In oday s lecure, we will coninue o look a he frequency response of single sage aplifiers, saring wih a ore coplee discussion of he CS aplifier,
EE105 Fall 2014 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits. NMOS Transistor Capacitances: Saturation Region
 EE105 Fall 014 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits Prof. Ming C. Wu wu@eecs.berkeley.edu 511 Sutardja Dai Hall (SDH) 1 NMOS Transistor Capacitances: Saturation Region Drain no longer connected to channel
EE105 Fall 014 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits Prof. Ming C. Wu wu@eecs.berkeley.edu 511 Sutardja Dai Hall (SDH) 1 NMOS Transistor Capacitances: Saturation Region Drain no longer connected to channel
Reading. Lecture 28: Single Stage Frequency response. Lecture Outline. Context
 Reading Lecure 28: Single Sage Frequency response Prof J. S. Sih Reading: We are discussing he frequency response of single sage aplifiers, which isn reaed in he ex unil afer uli-sae aplifiers (beginning
Reading Lecure 28: Single Sage Frequency response Prof J. S. Sih Reading: We are discussing he frequency response of single sage aplifiers, which isn reaed in he ex unil afer uli-sae aplifiers (beginning
Features / Advantages: Applications: Package: Y4
 IGBT (NPT) Module CES = 12 I C25 = 16 = 2.2 CE(sa) Buck Chopper + free wheeling Diode Par number MDI145-123 Backside: isolaed 1 7 6 3 2 Feaures / dvanages: pplicaions: Package: Y4 NPT IGBT echnology low
IGBT (NPT) Module CES = 12 I C25 = 16 = 2.2 CE(sa) Buck Chopper + free wheeling Diode Par number MDI145-123 Backside: isolaed 1 7 6 3 2 Feaures / dvanages: pplicaions: Package: Y4 NPT IGBT echnology low
Features / Advantages: Applications: Package: Y4
 IGBT (NPT) Module CES = 12 I C2 = 16 = 2.2 CE(sa) Boos Chopper + free wheeling Diode Par number MID14-123 Backside: isolaed 1 3 4 2 Feaures / dvanages: pplicaions: Package: Y4 NPT IGBT echnology low sauraion
IGBT (NPT) Module CES = 12 I C2 = 16 = 2.2 CE(sa) Boos Chopper + free wheeling Diode Par number MID14-123 Backside: isolaed 1 3 4 2 Feaures / dvanages: pplicaions: Package: Y4 NPT IGBT echnology low sauraion
EEC 118 Lecture #15: Interconnect. Rajeevan Amirtharajah University of California, Davis
 EEC 118 Lecure #15: Inerconnec Rajeevan Amiraraja Universiy of California, Davis Ouline Review and Finis: Low Power Design Inerconnec Effecs: Rabaey C. 4 and C. 9 (Kang & Leblebici, 6.5-6.6) Amiraraja,
EEC 118 Lecure #15: Inerconnec Rajeevan Amiraraja Universiy of California, Davis Ouline Review and Finis: Low Power Design Inerconnec Effecs: Rabaey C. 4 and C. 9 (Kang & Leblebici, 6.5-6.6) Amiraraja,
II III IV V VI B C N. Al Si P S. Zn Ga Ge As Se Cd In Sn Sb Te. Silicon (Si) the dominating material in IC manufacturing
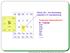 II III IV V VI B N Al Si P S Zn Ga Ge As Se d In Sn Sb Te Silicon (Si) the dominating material in I manufacturing ompound semiconductors III - V group: GaAs GaN GaSb GaP InAs InP InSb... The Energy Band
II III IV V VI B N Al Si P S Zn Ga Ge As Se d In Sn Sb Te Silicon (Si) the dominating material in I manufacturing ompound semiconductors III - V group: GaAs GaN GaSb GaP InAs InP InSb... The Energy Band
! MOS Capacitances. " Extrinsic. " Intrinsic. ! Lumped Capacitance Model. ! First Order Capacitor Summary. ! Capacitance Implications
 ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 7: February, 07 MOS SPICE Models, MOS Parasitic Details Lecture Outline! MOS Capacitances " Extrinsic " Intrinsic! Lumped Capacitance Model!
ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 7: February, 07 MOS SPICE Models, MOS Parasitic Details Lecture Outline! MOS Capacitances " Extrinsic " Intrinsic! Lumped Capacitance Model!
AO V Complementary Enhancement Mode Field Effect Transistor
 AO46 6V Complemenary Enhancemen Mode Field Effec Transisor General Descripion The AO46 uses advanced rench echnology MOSFETs o provide excellen and low gae charge. The complemenary MOSFETs may be used
AO46 6V Complemenary Enhancemen Mode Field Effec Transisor General Descripion The AO46 uses advanced rench echnology MOSFETs o provide excellen and low gae charge. The complemenary MOSFETs may be used
Topics to be Covered. capacitance inductance transmission lines
 Topics to be Covered Circuit Elements Switching Characteristics Power Dissipation Conductor Sizes Charge Sharing Design Margins Yield resistance capacitance inductance transmission lines Resistance of
Topics to be Covered Circuit Elements Switching Characteristics Power Dissipation Conductor Sizes Charge Sharing Design Margins Yield resistance capacitance inductance transmission lines Resistance of
NDS355AN N-Channel Logic Level Enhancement Mode Field Effect Transistor
 January 997 NS3AN N-Channel Logic Level Enhancemen Mode Field Effec Transisor General escripion Feaures SuperSOT TM -3 N-Channel logic level enhancemen mode power field effec ransisors are produced using
January 997 NS3AN N-Channel Logic Level Enhancemen Mode Field Effec Transisor General escripion Feaures SuperSOT TM -3 N-Channel logic level enhancemen mode power field effec ransisors are produced using
EEC 118 Lecture #2: MOSFET Structure and Basic Operation. Rajeevan Amirtharajah University of California, Davis Jeff Parkhurst Intel Corporation
 EEC 118 Lecture #2: MOSFET Structure and Basic Operation Rajeevan Amirtharajah University of California, Davis Jeff Parkhurst Intel Corporation Announcements Lab 1 this week, report due next week Bring
EEC 118 Lecture #2: MOSFET Structure and Basic Operation Rajeevan Amirtharajah University of California, Davis Jeff Parkhurst Intel Corporation Announcements Lab 1 this week, report due next week Bring
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA AT BERKELEY
 Homework #10 Soluions EECS 40, Fall 2006 Prof. Chang-Hasnain Due a 6 pm in 240 Cory on Wednesday, 04/18/07 oal Poins: 100 Pu (1) your name and (2) discussion secion number on your homework. You need o
Homework #10 Soluions EECS 40, Fall 2006 Prof. Chang-Hasnain Due a 6 pm in 240 Cory on Wednesday, 04/18/07 oal Poins: 100 Pu (1) your name and (2) discussion secion number on your homework. You need o
Analysis of Microstrip Coupling Gap to Estimate Polymer Permittivity
 Analysis of Microsrip Couplin Gap o Esimae Polymer Permiiviy Chanchal Yadav Deparmen of Physics & Elecronics Rajdhani Collee, Universiy of Delhi Delhi, India Absrac A ap in he microsrip line can be modeled
Analysis of Microsrip Couplin Gap o Esimae Polymer Permiiviy Chanchal Yadav Deparmen of Physics & Elecronics Rajdhani Collee, Universiy of Delhi Delhi, India Absrac A ap in he microsrip line can be modeled
EE 330 Lecture 41. Digital Circuits. Propagation Delay With Multiple Levels of Logic Overdrive
 EE 330 Lecure 41 Digial ircuis Propagaion Delay Wih Muliple Levels of Logic Overdrive Review from Las Time The Reference Inverer Reference Inverer V DD R =R PD PU = IN= 4OX WMIN LMIN V IN M 2 M 1 L VTn.2VDD
EE 330 Lecure 41 Digial ircuis Propagaion Delay Wih Muliple Levels of Logic Overdrive Review from Las Time The Reference Inverer Reference Inverer V DD R =R PD PU = IN= 4OX WMIN LMIN V IN M 2 M 1 L VTn.2VDD
Mobile Ion Effects on SiC MOS Bias- Temperature Instability Measurements
 14-15 Aug 2014 1 U.S. Army Research, Developmen and Engineering Command Mobile Ion Effecs on SiC MOS Bias- Temperaure Insabiliy Measuremens Daniel B. Habersa Neil Goldsman (UMD), and Aivars Lelis 14-15
14-15 Aug 2014 1 U.S. Army Research, Developmen and Engineering Command Mobile Ion Effecs on SiC MOS Bias- Temperaure Insabiliy Measuremens Daniel B. Habersa Neil Goldsman (UMD), and Aivars Lelis 14-15
EE 330 Lecture 23. Small Signal Analysis Small Signal Modelling
 EE 330 Lecure 23 Small Signal Analysis Small Signal Modelling Exam 2 Friday March 9 Exam 3 Friday April 13 Review Session for Exam 2: 6:00 p.m. on Thursday March 8 in Room Sweeney 1116 Review from Las
EE 330 Lecure 23 Small Signal Analysis Small Signal Modelling Exam 2 Friday March 9 Exam 3 Friday April 13 Review Session for Exam 2: 6:00 p.m. on Thursday March 8 in Room Sweeney 1116 Review from Las
Features / Advantages: Applications: Package: Y4
 IGBT (NPT) Module CES = x 1 I C = 9 =. CE(sa) Phase leg Par number MII7-13 1 Backside: isolaed 7 3 Feaures / dvanages: pplicaions: Package: Y NPT IGBT echnology low sauraion volage low swiching losses
IGBT (NPT) Module CES = x 1 I C = 9 =. CE(sa) Phase leg Par number MII7-13 1 Backside: isolaed 7 3 Feaures / dvanages: pplicaions: Package: Y NPT IGBT echnology low sauraion volage low swiching losses
Introduction to AC Power, RMS RMS. ECE 2210 AC Power p1. Use RMS in power calculations. AC Power P =? DC Power P =. V I = R =. I 2 R. V p.
 ECE MS I DC Power P I = Inroducion o AC Power, MS I AC Power P =? A Solp //9, // // correced p4 '4 v( ) = p cos( ω ) v( ) p( ) Couldn' we define an "effecive" volage ha would allow us o use he same relaionships
ECE MS I DC Power P I = Inroducion o AC Power, MS I AC Power P =? A Solp //9, // // correced p4 '4 v( ) = p cos( ω ) v( ) p( ) Couldn' we define an "effecive" volage ha would allow us o use he same relaionships
Chapter 7 Response of First-order RL and RC Circuits
 Chaper 7 Response of Firs-order RL and RC Circuis 7.- The Naural Response of RL and RC Circuis 7.3 The Sep Response of RL and RC Circuis 7.4 A General Soluion for Sep and Naural Responses 7.5 Sequenial
Chaper 7 Response of Firs-order RL and RC Circuis 7.- The Naural Response of RL and RC Circuis 7.3 The Sep Response of RL and RC Circuis 7.4 A General Soluion for Sep and Naural Responses 7.5 Sequenial
Physics for Scientists & Engineers 2
 Direc Curren Physics for Scieniss & Engineers 2 Spring Semeser 2005 Lecure 16 This week we will sudy charges in moion Elecric charge moving from one region o anoher is called elecric curren Curren is all
Direc Curren Physics for Scieniss & Engineers 2 Spring Semeser 2005 Lecure 16 This week we will sudy charges in moion Elecric charge moving from one region o anoher is called elecric curren Curren is all
ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals
 ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 7: February 4, 2016 MOS SPICE Models, MOS Parasitic Details Lecture Outline! MOS Capacitances " Extrinsic " Intrinsic! Lumped Capacitance
ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 7: February 4, 2016 MOS SPICE Models, MOS Parasitic Details Lecture Outline! MOS Capacitances " Extrinsic " Intrinsic! Lumped Capacitance
MOS Transistor I-V Characteristics and Parasitics
 ECEN454 Digital Integrated Circuit Design MOS Transistor I-V Characteristics and Parasitics ECEN 454 Facts about Transistors So far, we have treated transistors as ideal switches An ON transistor passes
ECEN454 Digital Integrated Circuit Design MOS Transistor I-V Characteristics and Parasitics ECEN 454 Facts about Transistors So far, we have treated transistors as ideal switches An ON transistor passes
Designing Information Devices and Systems I Spring 2019 Lecture Notes Note 17
 EES 16A Designing Informaion Devices and Sysems I Spring 019 Lecure Noes Noe 17 17.1 apaciive ouchscreen In he las noe, we saw ha a capacior consiss of wo pieces on conducive maerial separaed by a nonconducive
EES 16A Designing Informaion Devices and Sysems I Spring 019 Lecure Noes Noe 17 17.1 apaciive ouchscreen In he las noe, we saw ha a capacior consiss of wo pieces on conducive maerial separaed by a nonconducive
Circuits. L2: MOS Models-2 (1 st Aug. 2013) B. Mazhari Dept. of EE, IIT Kanpur. B. Mazhari, IITK. G-Number
 EE610: CMOS Analog Circuits L: MOS Models- (1 st Aug. 013) B. Mazhari Dept. of EE, IIT Kanpur 3 NMOS Models MOS MODEL Above Threshold Subthreshold ( GS > TN ) ( GS < TN ) Saturation ti Ti Triode ( DS >
EE610: CMOS Analog Circuits L: MOS Models- (1 st Aug. 013) B. Mazhari Dept. of EE, IIT Kanpur 3 NMOS Models MOS MODEL Above Threshold Subthreshold ( GS > TN ) ( GS < TN ) Saturation ti Ti Triode ( DS >
Technology Scaling. 9nm. Advanced Digital IC-Design. Content. What happens when technology is scaled? Progress: Described by Gordon Moore
 Advanced Digial IC-Design Conen 0.μm Wha happens when echnology is scaled? Technology caling 9nm ource Gae Drain ource Gae Drain ubsrae ubsrae IC Design pace Progress: Described by Gordon Moore peed Tradiional
Advanced Digial IC-Design Conen 0.μm Wha happens when echnology is scaled? Technology caling 9nm ource Gae Drain ource Gae Drain ubsrae ubsrae IC Design pace Progress: Described by Gordon Moore peed Tradiional
High Voltage Standard Rectifier Module
 UB35-22NO High olage Sandard ecifier Module M = 22 I = 5 D 3~ ecifier I SM = Brake hopper ES = 7 I = 3 25 E(sa) =.9 3~ ecifier Bridge + Brake Uni + NT Par number UB35-22NO Backside: isolaed 24+25 29 3
UB35-22NO High olage Sandard ecifier Module M = 22 I = 5 D 3~ ecifier I SM = Brake hopper ES = 7 I = 3 25 E(sa) =.9 3~ ecifier Bridge + Brake Uni + NT Par number UB35-22NO Backside: isolaed 24+25 29 3
CoolMOS 1) Power MOSFET with Series Schottky Diode and Ultra Fast Antiparallel Diode
 IXKF 4N6SCD1 CoolMOS 1) Power MOSFET wih Series Schoky Diode and Ulra Fas niparallel Diode in High olage ISOPLUS i4-pc S = 6 2 = 41 yp. = 6 mω rr = 7 ISOPLUS i4-pc Preliminary daa 1 D S T D F 1 2 E72873
IXKF 4N6SCD1 CoolMOS 1) Power MOSFET wih Series Schoky Diode and Ulra Fas niparallel Diode in High olage ISOPLUS i4-pc S = 6 2 = 41 yp. = 6 mω rr = 7 ISOPLUS i4-pc Preliminary daa 1 D S T D F 1 2 E72873
EE 330 Lecture 40. Digital Circuits. Propagation Delay With Multiple Levels of Logic Overdrive
 EE 330 Lecure 0 Digial ircuis Propagaion Delay Wih Muliple Levels of Logic Overdrive Review from Las Time Propagaion Delay in Saic MOS Family F Propagaion hrough k levels of logic + + + + HL HLn LH(n-1)
EE 330 Lecure 0 Digial ircuis Propagaion Delay Wih Muliple Levels of Logic Overdrive Review from Las Time Propagaion Delay in Saic MOS Family F Propagaion hrough k levels of logic + + + + HL HLn LH(n-1)
KEYWORDS: FD SOI MOSFET, charge pumping, geometric component, rise and fall time method, DC reverse bias, pulse reverse bias
 Jpn. J. ppl. Phys. Vol. 38 (1999) pp. 2496 25 Par 1, No. 4B, pril 1999 c 1999 Publicaion Board, Japanese Journal of pplied Physics Measuremen of Energeic and Laeral Disribuion of Inerface Sae Densiy in
Jpn. J. ppl. Phys. Vol. 38 (1999) pp. 2496 25 Par 1, No. 4B, pril 1999 c 1999 Publicaion Board, Japanese Journal of pplied Physics Measuremen of Energeic and Laeral Disribuion of Inerface Sae Densiy in
Chapter 1 Fundamental Concepts
 Chaper 1 Fundamenal Conceps 1 Signals A signal is a paern of variaion of a physical quaniy, ofen as a funcion of ime (bu also space, disance, posiion, ec). These quaniies are usually he independen variables
Chaper 1 Fundamenal Conceps 1 Signals A signal is a paern of variaion of a physical quaniy, ofen as a funcion of ime (bu also space, disance, posiion, ec). These quaniies are usually he independen variables
Inductor Energy Storage
 School of Compuer Science and Elecrical Engineering 5/5/ nducor Energy Sorage Boh capaciors and inducors are energy sorage devices They do no dissipae energy like a resisor, bu sore and reurn i o he circui
School of Compuer Science and Elecrical Engineering 5/5/ nducor Energy Sorage Boh capaciors and inducors are energy sorage devices They do no dissipae energy like a resisor, bu sore and reurn i o he circui
U(t) (t) -U T 1. (t) (t)
 Prof. Dr.-ng. F. Schuber Digial ircuis Exercise. () () A () - T T The highpass is driven by he square pulse (). alculae and skech A (). = µf, = KΩ, = 5 V, T = T = ms. Exercise. () () A () T T The highpass
Prof. Dr.-ng. F. Schuber Digial ircuis Exercise. () () A () - T T The highpass is driven by he square pulse (). alculae and skech A (). = µf, = KΩ, = 5 V, T = T = ms. Exercise. () () A () T T The highpass
Digital Integrated Circuits
 Digial Inegraed ircuis YuZhuo Fu conac:fuyuzhuo@ic.sju.edu.cn Office locaion:47 room WeiDianZi building,no 800 Donghuan road,minhang amus Inroducion Digial I 3.MOS Inverer Inroducion Digial I ouline MOS
Digial Inegraed ircuis YuZhuo Fu conac:fuyuzhuo@ic.sju.edu.cn Office locaion:47 room WeiDianZi building,no 800 Donghuan road,minhang amus Inroducion Digial I 3.MOS Inverer Inroducion Digial I ouline MOS
Top View. Top View S2 G2 S1 G1
 AO49 3V Complemenary MOSFET General Descripion AO49 uses advanced rench echnology o provide excellen R DS(ON) and low gae charge. This complemenary N and P channel MOSFET configuraion is ideal for low
AO49 3V Complemenary MOSFET General Descripion AO49 uses advanced rench echnology o provide excellen R DS(ON) and low gae charge. This complemenary N and P channel MOSFET configuraion is ideal for low
The problem with linear regulators
 he problem wih linear regulaors i in P in = i in V REF R a i ref i q i C v CE P o = i o i B ie P = v i o o in R 1 R 2 i o i f η = P o P in iref is small ( 0). iq (quiescen curren) is small (probably).
he problem wih linear regulaors i in P in = i in V REF R a i ref i q i C v CE P o = i o i B ie P = v i o o in R 1 R 2 i o i f η = P o P in iref is small ( 0). iq (quiescen curren) is small (probably).
ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals
 ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 6: January 30, 2018 MOS Operating Regions, pt. 2 Lecture Outline! Operating Regions (review) " Subthreshold " Resistive " Saturation! Intro.
ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 6: January 30, 2018 MOS Operating Regions, pt. 2 Lecture Outline! Operating Regions (review) " Subthreshold " Resistive " Saturation! Intro.
Chapter 4 Field-Effect Transistors
 Chapter 4 Field-Effect Transistors Microelectronic Circuit Design Richard C. Jaeger Travis N. Blalock 5/5/11 Chap 4-1 Chapter Goals Describe operation of MOSFETs. Define FET characteristics in operation
Chapter 4 Field-Effect Transistors Microelectronic Circuit Design Richard C. Jaeger Travis N. Blalock 5/5/11 Chap 4-1 Chapter Goals Describe operation of MOSFETs. Define FET characteristics in operation
Lecture Outline. Introduction Transmission Line Equations Transmission Line Wave Equations 8/10/2018. EE 4347 Applied Electromagnetics.
 8/10/018 Course Insrucor Dr. Raymond C. Rumpf Office: A 337 Phone: (915) 747 6958 E Mail: rcrumpf@uep.edu EE 4347 Applied Elecromagneics Topic 4a Transmission Line Equaions Transmission These Line noes
8/10/018 Course Insrucor Dr. Raymond C. Rumpf Office: A 337 Phone: (915) 747 6958 E Mail: rcrumpf@uep.edu EE 4347 Applied Elecromagneics Topic 4a Transmission Line Equaions Transmission These Line noes
EE650R: Reliability Physics of Nanoelectronic Devices Lecture 9:
 EE65R: Reliabiliy Physics of anoelecronic Devices Lecure 9: Feaures of Time-Dependen BTI Degradaion Dae: Sep. 9, 6 Classnoe Lufe Siddique Review Animesh Daa 9. Background/Review: BTI is observed when he
EE65R: Reliabiliy Physics of anoelecronic Devices Lecure 9: Feaures of Time-Dependen BTI Degradaion Dae: Sep. 9, 6 Classnoe Lufe Siddique Review Animesh Daa 9. Background/Review: BTI is observed when he
6.012 Electronic Devices and Circuits Spring 2005
 6.012 Electronic Devices and Circuits Spring 2005 May 16, 2005 Final Exam (200 points) -OPEN BOOK- Problem NAME RECITATION TIME 1 2 3 4 5 Total General guidelines (please read carefully before starting):
6.012 Electronic Devices and Circuits Spring 2005 May 16, 2005 Final Exam (200 points) -OPEN BOOK- Problem NAME RECITATION TIME 1 2 3 4 5 Total General guidelines (please read carefully before starting):
1. Introduction. Rawid Banchuin
 011 Inernaional Conerence on Inormaion and Elecronics Engineering IPCSIT vol.6 (011 (011 IACSIT Press, Singapore Process Induced Random Variaion Models o Nanoscale MOS Perormance: Eicien ool or he nanoscale
011 Inernaional Conerence on Inormaion and Elecronics Engineering IPCSIT vol.6 (011 (011 IACSIT Press, Singapore Process Induced Random Variaion Models o Nanoscale MOS Perormance: Eicien ool or he nanoscale
Chapter 10 INDUCTANCE Recommended Problems:
 Chaper 0 NDUCTANCE Recommended Problems: 3,5,7,9,5,6,7,8,9,,,3,6,7,9,3,35,47,48,5,5,69, 7,7. Self nducance Consider he circui shown in he Figure. When he swich is closed, he curren, and so he magneic field,
Chaper 0 NDUCTANCE Recommended Problems: 3,5,7,9,5,6,7,8,9,,,3,6,7,9,3,35,47,48,5,5,69, 7,7. Self nducance Consider he circui shown in he Figure. When he swich is closed, he curren, and so he magneic field,
3. Alternating Current
 3. Alernaing Curren TOPCS Definiion and nroducion AC Generaor Componens of AC Circuis Series LRC Circuis Power in AC Circuis Transformers & AC Transmission nroducion o AC The elecric power ou of a home
3. Alernaing Curren TOPCS Definiion and nroducion AC Generaor Componens of AC Circuis Series LRC Circuis Power in AC Circuis Transformers & AC Transmission nroducion o AC The elecric power ou of a home
Silicon Diffused Power Transistor
 Philips Semiconducors Silicon Diffused Power Transisor Produc specificaion GENERAL DESCRIPTION Enhanced performance, new generaion, high-volage, high-speed swiching npn ransisor wih an inegraed damper
Philips Semiconducors Silicon Diffused Power Transisor Produc specificaion GENERAL DESCRIPTION Enhanced performance, new generaion, high-volage, high-speed swiching npn ransisor wih an inegraed damper
EE115C Winter 2017 Digital Electronic Circuits. Lecture 3: MOS RC Model, CMOS Manufacturing
 EE115C Winter 2017 Digital Electronic Circuits Lecture 3: MOS RC Model, CMOS Manufacturing Agenda MOS Transistor: RC Model (pp. 104-113) S R on D CMOS Manufacturing Process (pp. 36-46) S S C GS G G C GD
EE115C Winter 2017 Digital Electronic Circuits Lecture 3: MOS RC Model, CMOS Manufacturing Agenda MOS Transistor: RC Model (pp. 104-113) S R on D CMOS Manufacturing Process (pp. 36-46) S S C GS G G C GD
IE1206 Embedded Electronics
 E06 Embedded Elecronics Le Le3 Le4 Le Ex Ex P-block Documenaion, Seriecom Pulse sensors,, R, P, serial and parallel K LAB Pulse sensors, Menu program Sar of programing ask Kirchhoffs laws Node analysis
E06 Embedded Elecronics Le Le3 Le4 Le Ex Ex P-block Documenaion, Seriecom Pulse sensors,, R, P, serial and parallel K LAB Pulse sensors, Menu program Sar of programing ask Kirchhoffs laws Node analysis
Hall effect. Formulae :- 1) Hall coefficient RH = cm / Coulumb. 2) Magnetic induction BY 2
 Page of 6 all effec Aim :- ) To deermine he all coefficien (R ) ) To measure he unknown magneic field (B ) and o compare i wih ha measured by he Gaussmeer (B ). Apparaus :- ) Gauss meer wih probe ) Elecromagne
Page of 6 all effec Aim :- ) To deermine he all coefficien (R ) ) To measure he unknown magneic field (B ) and o compare i wih ha measured by he Gaussmeer (B ). Apparaus :- ) Gauss meer wih probe ) Elecromagne
S G V DS V GS Pulsed Drain Current B -15 Schottky reverse voltage Continuous Forward Current A F I DM V KA
 ON473 2V PChannel MOSFET wih Schoky Diode General Descripion The ON473 uses advanced rench echnology o provide excellen R DS(ON) and low gae charge. Schoky diode is provided o faciliae he implemenaion
ON473 2V PChannel MOSFET wih Schoky Diode General Descripion The ON473 uses advanced rench echnology o provide excellen R DS(ON) and low gae charge. Schoky diode is provided o faciliae he implemenaion
Top View. Top View. V DS Gate-Source Voltage ±8 ±8 Continuous Drain Current Pulsed Drain Current C V GS I D -2.5 I DM P D 0.
 V Complemenary MOSFET General Descripion The AO664 combines advanced rench MOSFET echnology wih a low resisance package o provide exremely low R DS(ON). This device is ideal for load swich and baery proecion
V Complemenary MOSFET General Descripion The AO664 combines advanced rench MOSFET echnology wih a low resisance package o provide exremely low R DS(ON). This device is ideal for load swich and baery proecion
Module 10 SCR. 2. To understand two Transistor Static and Transient Models. 3. To learn the SCR Turn-on and Turn-off methods
 1 Module 1 SR 1. Inroducion 2. SR characerisics 3. Two ransisor saic and ransien models 4. SR urnon mehods 5. SR urnoff mehods 6. SR proecion and Triggering circuis 7. ae proecion circuis 8. Summary Learning
1 Module 1 SR 1. Inroducion 2. SR characerisics 3. Two ransisor saic and ransien models 4. SR urnon mehods 5. SR urnoff mehods 6. SR proecion and Triggering circuis 7. ae proecion circuis 8. Summary Learning
Characteristics of Active Devices
 007/Oct/17 1 haracteristics of Active Devices Review of MOSFET Physics MOS ircuit Applications Review of JT Physics MOS Noise JT Noise MS/RF Technology Roadmap MS MOS 1., 1.0, 0.8µm 0.60, 0.50µm 0.45,
007/Oct/17 1 haracteristics of Active Devices Review of MOSFET Physics MOS ircuit Applications Review of JT Physics MOS Noise JT Noise MS/RF Technology Roadmap MS MOS 1., 1.0, 0.8µm 0.60, 0.50µm 0.45,
Chapter 16: Summary. Instructor: Jean-François MILLITHALER.
 Chaper 16: Summary Insrucor: Jean-François MILLITHALER hp://faculy.uml.edu/jeanfrancois_millihaler/funelec/spring2017 Slide 1 Curren & Charge Elecric curren is he ime rae of change of charge, measured
Chaper 16: Summary Insrucor: Jean-François MILLITHALER hp://faculy.uml.edu/jeanfrancois_millihaler/funelec/spring2017 Slide 1 Curren & Charge Elecric curren is he ime rae of change of charge, measured
O10 W10. Features / Advantages: Applications: Package: V2-Pack. 3~ Rectifier with brake unit for drive inverters
 ZB-ioX hyrisor Module M = = 8 D SM = 7 3~ ecifier Brake hopper ES = = 8 5 E(sa) =.7 3~ ecifier Bridge, half-conrolled (high-side) + Brake Uni Par number ZB-ioX Backside: isolaed O S E M L7 G7 7 O eaures
ZB-ioX hyrisor Module M = = 8 D SM = 7 3~ ecifier Brake hopper ES = = 8 5 E(sa) =.7 3~ ecifier Bridge, half-conrolled (high-side) + Brake Uni Par number ZB-ioX Backside: isolaed O S E M L7 G7 7 O eaures
The Devices: MOS Transistors
 The Devices: MOS Transistors References: Semiconductor Device Fundamentals, R. F. Pierret, Addison-Wesley Digital Integrated Circuits: A Design Perspective, J. Rabaey et.al. Prentice Hall NMOS Transistor
The Devices: MOS Transistors References: Semiconductor Device Fundamentals, R. F. Pierret, Addison-Wesley Digital Integrated Circuits: A Design Perspective, J. Rabaey et.al. Prentice Hall NMOS Transistor
EEC 116 Lecture #3: CMOS Inverters MOS Scaling. Rajeevan Amirtharajah University of California, Davis Jeff Parkhurst Intel Corporation
 EEC 116 Lecture #3: CMOS Inverters MOS Scaling Rajeevan Amirtharajah University of California, Davis Jeff Parhurst Intel Corporation Outline Review: Inverter Transfer Characteristics Lecture 3: Noise Margins,
EEC 116 Lecture #3: CMOS Inverters MOS Scaling Rajeevan Amirtharajah University of California, Davis Jeff Parhurst Intel Corporation Outline Review: Inverter Transfer Characteristics Lecture 3: Noise Margins,
SOTiny Gate STX. Input. Descriptio n. Features. Block Diagram. Pin Configuration. Recommended Operating Conditions (1) Pin Description.
 PI74STXG08 4567890456789045678904567890456789045678904567890456789045678904567890456789045678904567890 4567890456789045678904567890456789045678904567890456789045678904567890456789045678904567890 - Feaures
PI74STXG08 4567890456789045678904567890456789045678904567890456789045678904567890456789045678904567890 4567890456789045678904567890456789045678904567890456789045678904567890456789045678904567890 - Feaures
Section 2.2 Charge and Current 2.6 b) The current direction is designated as the direction of the movement of positive charges.
 Chaper Soluions Secion. Inroducion. Curren source. Volage source. esisor.4 Capacior.5 Inducor Secion. Charge and Curren.6 b) The curren direcion is designaed as he direcion of he movemen of posiive charges..7
Chaper Soluions Secion. Inroducion. Curren source. Volage source. esisor.4 Capacior.5 Inducor Secion. Charge and Curren.6 b) The curren direcion is designaed as he direcion of he movemen of posiive charges..7
Lecture -14: Chopper fed DC Drives
 Lecure -14: Chopper fed DC Drives Chopper fed DC drives o A chopper is a saic device ha convers fixed DC inpu volage o a variable dc oupu volage direcly o A chopper is a high speed on/off semiconducor
Lecure -14: Chopper fed DC Drives Chopper fed DC drives o A chopper is a saic device ha convers fixed DC inpu volage o a variable dc oupu volage direcly o A chopper is a high speed on/off semiconducor
ENEE 359a Digital VLSI Design
 SLIDE 1 ENEE 359a Digital VLSI Design & Logical Effort Prof. blj@ece.umd.edu Credit where credit is due: Slides contain original artwork ( Jacob 2004) as well as material taken liberally from Irwin & Vijay
SLIDE 1 ENEE 359a Digital VLSI Design & Logical Effort Prof. blj@ece.umd.edu Credit where credit is due: Slides contain original artwork ( Jacob 2004) as well as material taken liberally from Irwin & Vijay
V DS. 100% UIS Tested 100% R g Tested. Top View. Top View S2 G2
 3V Dual PChannel MOSFET General Descripion The AO483 uses advanced rench echnology o provide excellen R DS(ON) wih low gae charge. This device is suiable for use as a load swich or in PWM applicaions.
3V Dual PChannel MOSFET General Descripion The AO483 uses advanced rench echnology o provide excellen R DS(ON) wih low gae charge. This device is suiable for use as a load swich or in PWM applicaions.
7. Capacitors and Inductors
 7. Capaciors and Inducors 7. The Capacior The ideal capacior is a passive elemen wih circui symbol The curren-volage relaion is i=c dv where v and i saisfy he convenions for a passive elemen The capacior
7. Capaciors and Inducors 7. The Capacior The ideal capacior is a passive elemen wih circui symbol The curren-volage relaion is i=c dv where v and i saisfy he convenions for a passive elemen The capacior
CHAPTER 12 DIRECT CURRENT CIRCUITS
 CHAPTER 12 DIRECT CURRENT CIUITS DIRECT CURRENT CIUITS 257 12.1 RESISTORS IN SERIES AND IN PARALLEL When wo resisors are conneced ogeher as shown in Figure 12.1 we said ha hey are conneced in series. As
CHAPTER 12 DIRECT CURRENT CIUITS DIRECT CURRENT CIUITS 257 12.1 RESISTORS IN SERIES AND IN PARALLEL When wo resisors are conneced ogeher as shown in Figure 12.1 we said ha hey are conneced in series. As
MOS Transistor Theory
 CHAPTER 3 MOS Transistor Theory Outline 2 1. Introduction 2. Ideal I-V Characteristics 3. Nonideal I-V Effects 4. C-V Characteristics 5. DC Transfer Characteristics 6. Switch-level RC Delay Models MOS
CHAPTER 3 MOS Transistor Theory Outline 2 1. Introduction 2. Ideal I-V Characteristics 3. Nonideal I-V Effects 4. C-V Characteristics 5. DC Transfer Characteristics 6. Switch-level RC Delay Models MOS
L1, L2, N1 N2. + Vout. C out. Figure 2.1.1: Flyback converter
 page 11 Flyback converer The Flyback converer belongs o he primary swiched converer family, which means here is isolaion beween in and oupu. Flyback converers are used in nearly all mains supplied elecronic
page 11 Flyback converer The Flyback converer belongs o he primary swiched converer family, which means here is isolaion beween in and oupu. Flyback converers are used in nearly all mains supplied elecronic
p h a s e - o u t Three phase full Bridge with Trench MOSFETs in DCB isolated high current package GWM X2
 GWM 18-4X2 Three phase full Bridge wih Trench MOSFETs in DCB isolaed high curren package S = 4 V 25 = 18 R DSon yp. = 1.9 mw Preliminary daa G1 G3 G5 L+ S1 G2 S3 G4 S5 G6 L1 L2 L3 Sraigh leads Surface
GWM 18-4X2 Three phase full Bridge wih Trench MOSFETs in DCB isolaed high curren package S = 4 V 25 = 18 R DSon yp. = 1.9 mw Preliminary daa G1 G3 G5 L+ S1 G2 S3 G4 S5 G6 L1 L2 L3 Sraigh leads Surface
PI74STX1G126. SOTiny Gate STX Buffer with 3-State Output. Features. Descriptio n. Block Diagram. Pin Configuration
 PI74STXG6 4567890456789045678904567890456789045678904567890456789045678904567890456789045678904567890 4567890456789045678904567890456789045678904567890456789045678904567890456789045678904567890 SOTiny
PI74STXG6 4567890456789045678904567890456789045678904567890456789045678904567890456789045678904567890 4567890456789045678904567890456789045678904567890456789045678904567890456789045678904567890 SOTiny
Converter - Brake - Inverter Module (CBI2)
 Converer - Brake - Inverer Module (CBI2) 21 22 D11 D13 D1 1 2 3 7 D7 16 1 T1 D1 T3 D3 T D 18 2 6 17 19 4 D12 D14 D16 T7 T2 D2 T4 D4 T6 D6 23 14 24 11 1 12 13 NTC 8 9 Three Phase Brake Chopper Three Phase
Converer - Brake - Inverer Module (CBI2) 21 22 D11 D13 D1 1 2 3 7 D7 16 1 T1 D1 T3 D3 T D 18 2 6 17 19 4 D12 D14 D16 T7 T2 D2 T4 D4 T6 D6 23 14 24 11 1 12 13 NTC 8 9 Three Phase Brake Chopper Three Phase
Cosmic Feb 06, 2007 by Raja Reddy P
 osmic ircuis@iisc, Feb 6, 7 by aja eddy P. ou() i() alculae ou(s)/(s). plo o(). calculae ime consan and pole frequency. ou ( e τ ) ou (s) ( s) Time consan (/) Pole frequency : ω p. i() n he above circui
osmic ircuis@iisc, Feb 6, 7 by aja eddy P. ou() i() alculae ou(s)/(s). plo o(). calculae ime consan and pole frequency. ou ( e τ ) ou (s) ( s) Time consan (/) Pole frequency : ω p. i() n he above circui
Mechanical Fatigue and Load-Induced Aging of Loudspeaker Suspension. Wolfgang Klippel,
 Mechanical Faigue and Load-Induced Aging of Loudspeaker Suspension Wolfgang Klippel, Insiue of Acousics and Speech Communicaion Dresden Universiy of Technology presened a he ALMA Symposium 2012, Las Vegas
Mechanical Faigue and Load-Induced Aging of Loudspeaker Suspension Wolfgang Klippel, Insiue of Acousics and Speech Communicaion Dresden Universiy of Technology presened a he ALMA Symposium 2012, Las Vegas
p h a s e - o u t Three Phase Rectifier Bridge with IGBT and Fast Recovery Diode for Braking System VVZB 135 = 1600 V = 135 A Recommended replacement:
 VVZB 5 Three Phase Recifier Bridge wih IGBT and Fas Recovery Diode for Braking Sysem V RRM I dvm = 6 V = 5 V RRM Type + 6 5 4 NTC 9 + V 6 VVZB 5-6 NO 6+7 4+5 + Symbol Condiions Maximum Raings V RRM 6 V
VVZB 5 Three Phase Recifier Bridge wih IGBT and Fas Recovery Diode for Braking Sysem V RRM I dvm = 6 V = 5 V RRM Type + 6 5 4 NTC 9 + V 6 VVZB 5-6 NO 6+7 4+5 + Symbol Condiions Maximum Raings V RRM 6 V
Physical Limitations of Logic Gates Week 10a
 Physical Limiaions of Logic Gaes Week 10a In a compuer we ll have circuis of logic gaes o perform specific funcions Compuer Daapah: Boolean algebraic funcions using binary variables Symbolic represenaion
Physical Limiaions of Logic Gaes Week 10a In a compuer we ll have circuis of logic gaes o perform specific funcions Compuer Daapah: Boolean algebraic funcions using binary variables Symbolic represenaion
Converter - Brake - Inverter Module (CBI2)
 MUBW 5-6 7 Converer - Brake - Inverer Module (CBI2) 2 22 D D3 D5 2 3 7 D7 6 5 T D T3 D3 T5 D5 8 2 6 7 5 9 4 D2 D4 D6 T7 T2 D2 T4 D4 T6 D6 23 4 24 2 3 NTC 8 9 Three Phase Brake Chopper Three Phase Recifier
MUBW 5-6 7 Converer - Brake - Inverer Module (CBI2) 2 22 D D3 D5 2 3 7 D7 6 5 T D T3 D3 T5 D5 8 2 6 7 5 9 4 D2 D4 D6 T7 T2 D2 T4 D4 T6 D6 23 4 24 2 3 NTC 8 9 Three Phase Brake Chopper Three Phase Recifier
