Design and Modeling of Nanodevices Compact Modeling of Nano MOSFETs
|
|
|
- Shannon Preston
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 : Design and Modeling of Nanodevices Design and Modeling of Nanodevices Compact Modeling of Nano MOSFETs Dr Zhou Xing Office: S1-B1c-95 Phone: Web: X. ZHOU 1 18
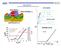
2 Top-down vs Bottom-up sand Lithography Top-down History: ICs have been designed by SPICE using BSIM over the past 3 years. 1 m 1 m 1 m 1 nm 1 nm 1 nm BSIM/SPICE for IC designs ~3yrs Minimum Feature Size Microelectronics SPICE models TG NW EDA tools for nanodevice ~yrs Nanoelectronics CNT Mol.Ele. Single atom 1 pm Motivation: New models for future nano-devices at the atomic scale. Bottom-up device Assembly X. ZHOU 18
3 Moore s Law Compact Model Parameters Chip complexity will double about every 18 months. M. Chan, et al., Microelectronics Reliability, vol. 43, pp , 3. A disturbing version of Moore s law the number of compact-model parameters doubles about every decade (as a result of evolutionary development) X. ZHOU 3 18
4 Approaches to Analyzing Microelectronic Systems X. ZHOU 4 18
5 Process Device Circuit Block System Block Gate Circuit Interconnect Analog and Digital Subcircuit expansion acceleration Motivation Compact multi-level technology/transistor/ subsystem modeling System performance Centered at transistor-level compact model Transistor optimization Device Process Parameter extraction Process/structural variations Technology development Process effects on device/circuit X. ZHOU 5 18
6 Paradigm Shift in IC Chip Design and Manufacturing ertically -integrated giant semiconductor manufacturers Horizontally -strong foundries and fabless design houses IC Chip Manufacturer Design Fab Fabless Design House Wafer Fab Foundry CAD EDA endor X. ZHOU 6 18
7 Design Fabrication Paradigm: Ideality & Reality Design House Ideality EDA endor Reality SPICE Wafer Fab Circuit designer CAD developer CM Process engineer Model developer X. ZHOU 7 18
8 Model Developer s Dilemma Design House I won t use it unless it s been implemented in my SPICE simulator Circuit designer Do you want to try my new model? EDA endor I won t code it unless fab can provide data and model CAD developer CM Can you implement my new model? 1 3 Model developer Wafer Fab I won t extract your model unless my customer (designer) wants it Process engineer Will you support my new model? X. ZHOU 8 18
9 Models and Modeling Groups NGSOI/MG Model BSIM EK HiSIM ULTRA-SOI/MG ACM Xsim Technology-dependent predictive model DG/MG SiNW/CNT PCMOS ISNE III-/Si X. ZHOU 9 18
10 Accuracy Speed Tradeoff: History & Future Accuracy & Speed (No demand for 3+ yrs) (High demand for analog) PSP M11 HiS SP Central concern for CM: accuracy speed tradeoff Determined by demand/supply M9 P S M1 M M3 B1 B B3 t -based s -based Q i -based EK ACM B4 U (Not as slow with HPC) SPP B5 X Iterative: can be costly for digital 1 Future: how to tradeoff? Scalable (non-binnable): accuracy over geometry Single-piece across all regions Selectable accuracy within the same core model Extension to non-bulk FETs Time X. ZHOU 1 18
11 Role of Compact Model (Courtesy: M. Chan) Ultimate goal: towards accuracy and simplicity X. ZHOU 11 18
12 SPICE Circuit Simulation: (Modified) Nodal Analysis KL/KCL: I R R R R R R3 DC: R1 R R 1 I R R R 3 Transient: companion 1 1 C1 1 C1 R R h R h I i 1 1 C1 1 C1 1 1 C i 1 C i 1 C R h R R h 3 AC: jc jc 1 1 j R1 R R 1 Ie jc1 jc 1 R R R 3 f(x) I I e nv th 1 x x x 3 1 x Nonlinear: N R iteration x x x n1 n f f ' x x n n X. ZHOU 1 18
13 What Is a Model, and Modeling? John von Neumann The sciences do not try to explain, they hardly even try to interpret, they mainly make models. By a model is meant a mathematical construct which, with the addition of certain verbal interpretations, describes observed phenomena. The justification of such a mathematical construct is solely and precisely that it is expected to work. A model is a mental image of reality One can have many different images of the same reality. Correct physical approximations and correct mathematical formulations to emulate ideal device physical behaviors and corroborate with real device characteristics. What does compact mean? What is physical of a model? X. ZHOU 13 18
14 Perspective: Compact Modeling for Circuit Simulation Monte Carlo: (6-D, t) I D (k,r,t) t I D () = I ds + I b + I g S G I g D I D Compact: (-D, t) I = Qv Q C ij = Q i / j r I ds Ib G ij = I i / j Q + Q(t) SPICE (nodal analysis) k B Age Numerical: (3-D, t) I D (r,t,) mental image t r(x,y,z) L,W,(Z) DC (n sets = unphysical ) T g, d, b, s f, (t) X. ZHOU 14 18
15 Ideal vs Real MOSFET To Be Modeled But we need to model this This is what the core model deals with. (R. Rios, WCM5) X. ZHOU 15 18
16 Binning vs Meshing Binning = piece-wise (in geometry) Infinite number of bins = single-device model = nonscalable (= unphysical?) Key difference: binnable (transistor-based) vs non-binnable (technology-based) model Binnable model: parameters extracted by fitting electrical data at fixed geometry Non-binnable model: parameters extracted by fitting data over geometry at fixed bias Compare: Meshing necessary? and physical? Numerical: meshing t Compact: binning N Homogeneous: Meshing unnecessary, 1 mesh n mesh ( s -model numerical) 1 bin n bin N(x,y) Inhomogeneous: Meshing necessary, and physical ( s -model less physical ) Necessary and physical for non-binnable model Binnable model: n sets = unphysical L X. ZHOU 16 18
17 MOSFET Compact Models: History and Future Classical bulk-cmos ~4 yrs Poisson + GCA Sah Pao (input) oltage Equation Pao Sah (output) Current Equation Q b linearization Charge Sheet Model (Q sc =Q b +Q i ) t -based Q i linearization Iterative / explicit Q i -based s -based Non-classical CMOS SOI Partially-Depleted (PD) Bulk oltage/current Equations, CSM nontrivial Fully-Depleted (FD), Ultra-Thin Body (UTB) Non-Charge-Sheet MG New oltage/current Equations Body Contact/Floating Body Symmetric/Asymmetric Double Gate (s-dg/a-dg) Tri-gate, GAA, Schottky-barrier, DSS, TFET, X. ZHOU 17 18
18 Conceptual Core Bulk-MOS at arious Body Doping G N A (cm 3 ) S L g D s s n + n + N sd T ox s o d N g d X j Bulk FinFET/SiNW (unintentional doped) C) Intrinsic (7 C) o X dm (m) (N A = N D = : undoped = pure Si) T Si Bulk: T Si >> X dm, with B : o = b = B SOI: T Si > X dm, without B : o floating o b B N A N D DG/GAA: T Si /R << X dm : volume inversion ( o : virtual electrode ) X. ZHOU 18 18
19 Need for an Extendable Core Model for Future Generation S Pao Sah G I ds D I D S t -based models History has witnessed generations of MOS models and efforts required from one generation to the next Need for a core model extendable to future generations, and with less duplicating efforts G (B) D I D Q i -based models S s -based models G D I D S G1 Time HEMT leveraging on MOS models MG/FinFET is just a special case D I D B Sub Sub G Bulk PD-SOI FD-UTB/SOI DG/GAA/SB/DSS X. ZHOU 19 18
20 Seamless Transformation and Unification of MOSFETs (a) g (b) g b (c) g ' b oxf t oxf s t Si s d s d s d b b oxb t oxb t Si t oxb = t oxf a-dg (f) b PD-SOI g ' b = b = b FD-UTB/SOI t oxb ' = (e) g (d) b = g g ' = s = b s d s d s d t Si 'Bulk-UTB' half s-dg g s-dg b PD-SOI FD-UTB/SOI a-dg s-dg UTB Bulk Bulk X. ZHOU 18
21 The Generic SOI/DG/GAA MOSFET Zero-field potential: o [ o' (X o ) = ] Imref-split: cr = Fn Fp = c r r = b (BC: body-contacted) r = min = min( s, d ) ( FB : w/o BC) Bulk: special case of s-dg SOI: special case of ia-dg Common/symmetric-DG [GAA] g1 = g = g : two gates with one bias C ox1 = C ox : s-dg (X o = T Si /; [R]) Full-depletion: FD = g (X d =T Si /) C ox1 C ox : ca-dg (X o < T Si ) Independent/asymmetric-DG g1 g : ia-dg, biased independently Zero-field location may be outside body Consider two independent gates; linked through full-depletion condition: X d1 + X d = T Si GAA SOI ia-dg ca-dg s-dg bulk Unification of MOS X. ZHOU 1 18
22 Generic Double-Gate MOSFET with Any Body Doping S n + x r T ox1 R X o1 ( g1 ) L g p1 s1 o1 G1 N g1 ( ox1 ) o1 = o = r = (at gi = FBi, s = d =) D n + y N A (cm 3 ) Bulk FinFET/SiNW (unintentional doped) C) Intrinsic doping (7 C) (< 6 m) X dm (m) (N A = N D = : undoped = pure Si) X o ( g ) o Bulk: T Si >> X dm, with BC: o = b = B T Si x 1 T ox s G N g p ( ox ) N sd y SOI: T Si > X dm, without BC: o floating DG/GAA: T Si /R << X dm : volume inversion ( o : virtual electrode ) X. ZHOU 18
23 PD/FD at arious Body Doping/Thickness L g G S = D = G S = D = n + T ox o X dm o s N g PD n + y T Si n + n + o X dm s FD T Si o o = r G = FB, S = D = 1 14 G S = D = T Si N A N D (cm 3 ) K ox s N sd n + n + o PD T X dm Si o FD s x G X. ZHOU 3 18
24 Dynamic Depletion (DD) at arious Body Thickness S = L g G D = DD S = G D = DD n + T ox X dm,s s N g n + y T Si n + n + X dm,c s FD X dm,d T Si o PD S = G D = DD T Si N A N D (1 17 cm 3 ) K ox s N sd n + T Si X dm,s s DD X dm,d n + x G X. ZHOU 4 18
25 Symmetric Charge Linearization Symmetric bulk/inversion charge linearization dqi Q y Q C q A i i s s ox i b s s ss ds I q Av q Av ds i b th s i b th ds, eff W L eff Cox eff eff, s eff, d s 1 s Long-channel symmetric current model sc, F cb vth v e C ox eff, c 1 Lc, eff b LEsat, c gt, c sc, b th sc, b W L 1 gt gt, s gt, d q i gb FB s s b 1 s s, s s, d A b 1,, ds s eff ds d eff,, s sd ss F db F sb ds,, ;, ; ', c s d c d s ceff, c csat, cc', sat cs, d d, eff s, eff ds, eff E C n ox b eff gt s b Si n s b LE gt, s sat, s ds, sat d, sat s gt, s Ab, slesat, s Ab, svth LE gt, d sat, d sd, sat s, sat d gt, d Ab, d LEsat, d Ab, dvth E sat, c v sat, c X. ZHOU 5 18
26 Symmetric Linearization of Bulk-Charge Factor for DD PD FD DD Due to the use of ds and f ( gf ), no singularity occurs at flatband X. ZHOU 6 18
27 The Poisson Boltzmann Equation and Solution X. ZHOU 7 18
28 The Complete ( Sah Pao ) oltage Equation X. ZHOU 8 18
29 Drain Current: Pao Sah Double Integral J x, y qn E qd n y ny n y n kt n qnn y qn y kt n qnn ln y q ni qnnfn y qn d dy n cb d t cb Si Ids yw qnx, y n x, ydx dy W y Q y d dy const. J qn d dx nx n cb s i cb Ey D n v y kt q ln n n Fn th i Fcb vth dx s n, cb qn s A e Qiyq nx, ydxq, n cb d q d d 1 s d E, F cb vth x cb qn A Si ve th 1 Fcb vth vth th e v v th e e qn F cb qn A Ex x, ysgn 1 vth 1 sgn A Si, Si s ti ti,,, y n x y n x y dx n x y dx db sb db y Q y d Q y d s i cb i cb sb A Ex n N e x n y y cb Fn F F cb v th W db W db s e ds i cb ox 1 cb L sb L sb Fcb v th ve th v F cb th I Q d C dd,, F F cb di cb ve th v F cb th X. ZHOU 9 18
30 CSM: Charge-Sheet Model vth, s 1, qn, dx N p qn e Q y q N p dx q N p d q d d s A cb A b A A s d E x cb F A Si cb Depletion approximation (n = p = ; also N D = ): qn 1 Q y d C y s A, b ox s s qn A Si Potential/charge balance: Q y C y Q g ox gb FB s ox Qi Qb Qox Qg Charge-sheet model (CSM): Qi y Qg y Qox Qb y Cox gb FB s y s y Sah Pao ( S P ) voltage equation ( s > 3v th ): sy F cb y vth gb FB s y s y vthe gb FB s y gb FB s s dcb y 1v th ds y y i y Cox vc Q th ox vc th ox C ox Qiy Qi y Qb y Qi y Qb y CSM dq i d s d s Cox d s C ox Cox 1 dy dy dy Q s b dy I y W y Q y ds s i drift s i s th diff dcb y ds d dy ds W yq y W yv dy I y I y s dq i y dy X. ZHOU 3 18
31 Drain Current Model: s -based vs Q i -based W L d I Q d s cb ds i s s L s ds s I W Q db i Qid cb ds Qi dcb L Ids Qi dqi sb L Q is dqi W d CSM: Q C i ox gb FB s s S P: 3v s th y y v e gb FB s s th y y v s F cb th q Q C v i i ox th q Q C v b b ox th s I dqi ds Idrift I Idiff y Ws yv UCCM: diff th dy q v i q i gb vfb d s W sl I ln vcb n1 drift y Ws y Qi y I n q n dy diff vth dqi q nq L v s W sl W 1 1 Idrift Qd i s L Cox v th sl s sl s s L From S P: W 1 3 3, Cox gb FB sl s sl s sl s L 3 L, L y q q q q q ln v v v i i b i b gb fb F cb Q i linearization v v gb gb th v v FB FB th s s cb sb sl s cb db th X. ZHOU 31 18
32 Q i -based Current Model CSM / S P: Q C C i ox gb FB s ox s s y Fcb y vth ox s th ox s C v e C Q i linearization: dqi nc q dy d cb Ids y WsQi dy ox ds dy CSM / D+D: d v dq s th i WsQi dy Q i dy i qn n C s q ox s sa n 1C C 1 v th dqi WsQi nc q ox Q i dy q b ox Qip Qi s p C, Q y q n x y dx qn y s b Cox nc sa UCCM: 1 th q ox i W W d I Q d Q dq v Q db Qid cb ds i cb i i L sb L Q is dqi I W Q 1 v dq Qid th ds i i L Qis nqcox Q i W Q Q W v Q Q L n C L I I I ds drift diff id is q ox dqi d Qip Q i Q i v ln nc q ox Q ip cb th p cb th id is I I I ds f r q Q C v s is ox th q Q C v d id ox th I C W v q q q q s d ds ox th s d L nq I ds q s q d qs qd I s n q n q From UCCM: I v, C W L s n th n ox X. ZHOU 3 18
33 t -based Model: Linear (Drift) Current Source-referenced threshold condition ( pinned surface potential): y y y y y, s s cb F sb cb ds s F Bulk-charge linearization: y Q C C y b ox s ox F sb Cox F sb F Q C Q i ox gb FB s b sb y Cox gb FB F sb y F sb F C ox gs t A b y Linear (drift) current: ( gs > t ) Threshold voltage: Bulk-charge factor: sb t FB F F sb A b 1 1 (For fixed bulk-charge: A b = 1),, I y W Q y d dy WQ y v v E E d dy d dy ds s i s i s y y s W ds W 1 I I Q d C A L L ds drift i ox gs t b ds ds F sb X. ZHOU 33 18
34 t -based Model: Subthreshold (Diffusion) Current Q Subthreshold surface potential: C b ox dd Q C gb FB dd b ox CSM / S P: s y dd 4 dd gb FB dd F cb y vth i ox dd th b Q C v e Q v Q C 1 e C th dd F cb vth i ox dd ox dd dd vth dd F cb v th Cox dd 1 e Cox dd dd vth dd F cb vth Cox e dd Subthreshold (diffusion) current: ( gs < t ), 1.5 ' ' t t off s F sb Q C d W L Q I id v dq v Q Q is ds th i th id is Q Q Q Q Q W L is i id i cb sb cb db W Ids Cdvth e 1 e L dd C q N X dd F sb vth ds vth ox Si A Si Qb dd Q dd Q b dd b s dd s b s d gb FB dd dd s Cox Cox n dd F sb gs t s -based dd C s F sb ' W Cd Ids Idiff Cox vth e e L C ox dm X ' ' gs t nv th ds th 1 v dm Qb dd C n1 Cd Cox 1 F d sb Si dd qn A X. ZHOU 34 18
35 elocity Saturation and Saturation Current v ertical-field mobility (empirical) Qi Coxgs t Qb Coxt v sat E eff Qb Qi Si n Piecewise model 1 E Bulk-Si eff E crit gs t ne 6T E E n property (.5) ox sat Saturation field v 1 EEsat n E sat v sa t vsat E Esat v E sat Esat sat 1 Esat Esat n Saturation current CSM: Lateral-field mobility Idsat WvsatQsat WvsatCox gs t A b dsat n 1 eff Ab 1 1 ds EsatLeff F sb EsatLeff gs t (1)( dsat ) = (): dsat Linear current gs t AbEsatLeff (3) (): W 1 I C A L ds eff ox gs t b ds ds ~1 7 cm/s (1) gs t Idsat WvsatCox gs t A b E sat L eff L (Amplitude) gs () (3) Linear! E Qi Cox gs t A b y t X. ZHOU 35 18
36 Charge-Sharing Model: t Roll-Off Charge-sharing model ( triangle ) Without charge-sharing Q C t FB bm ox F With charge-sharing Q C ' ' t FB ox F bm ' t t t 1 C Q C L bm qn AX dm X dm Si F sbtox T L L X t ' Q Q Q X bm bm bm dm ox ox eff ox ox eff ox g j t C ox ox Tox Qbm qnaxdm X qn dm Si F sb A Short-channel effect (SCE): t roll-off (L eff ) ds L g L L X eff g j T ox X j n + X. ZHOU s o Total bulk charge: X dm Bulk charge per unit area: W o L g Q' b Q b o g b L eff Simple Triangle Model n + d Charge shared by the gate/drain o Q qn W L X X ' B A eff d d Q qn W L X B A eff d ' ' Qb QB X 1 Q Q L b B eff d N sd
37 Charge-Sharing Model: t DIBL Charge-sharing model ( trapezoidal ) Source-end (linear): ( ds = d ) Drain-end (saturation): ( ds = dd ) Average depletion width: (any ds ) X X, qn dm dm s Si F sb A X dm, s dm, d qn Si A X, qn dm d Si F db A X s F sb d F db DIBL: Drain-Induced Barrier Lowering L L L DIBL g t g ts g db sb ds Trapezoidal area = box t s o T ox X j n + ' Q qn b A XdmLeff t t ts X dm,s Dynamic depletion (DD) W qn A ts b, ds T L o L g Q' b Q b o g b L eff X dm,d n + d o Charge shared by the drain y L g N sd X F sb dm T s d F db Si ox L X ox ox eff ox g d j ~ 6 /.7 / d. ts DIBL t FB F F sb t t t ds ts t t ds d dd X. ZHOU 37 18
38 Reverse Short-Channel Effect: t Roll-Up & Halo Empirical RSCE model ( halo ) N eff N Halo pile-up: () N pile A N N pile cosh L l Halo lateral spread: () A Replacing all previous N A by N eff eff.5 l F sb F kt qln N A ni Halo N eff s o T ox X j n + X dm,s W o Q b N A o g d L g o L eff y n + N sd X dm,d Q' b b Gaussian halo model p N y N e pile yl l t Reverse SCE: Halo Halo dose, tilt, energy y t L g N eff L eff N y dy N L l l erf l l l p pile eff N A erf Leff Le ff X. ZHOU 38 18
39 Summary of Important (Simple) Equations Effective body doping and related equations Halo doping F vth ln N A ni Physical quantities L N N l.5 eff Lg d X N pile eff N A A N pile cosh L l Neff q SiNeff F vthln ni Cox Threshold voltage Long-channel (1D theoretical model) eff F sb t gs FB F F sb s F sb Any channel-length and body/drain-bias v th kt C T ox ox ox Q C E qn C C FB MS ox ox M g F ss ox X d Si dm X dm Si F s b qn eff ox ox o n 1 Cd Cox SiTox tsb, ds t t tneff, Tox F sb F sb ox q.59 s d ds L g d X j Linear t : Saturation ts : Si Si o (Physical constants) Physical parameters: L, T, X,, N, T g ox j M ss t t t ds d j sb ts t t ds dd sb X. ZHOU 39 18
40 Summary of Important (Simple) Equations Drain current Bulk-charge factor 1 Ab 1 F sb Linear W 1 Idlin gs, s b, eff Cox gs t Ab L Saturation I dsat gs, s, ds Subthreshold b ds ds ds eff Wv sat Fitting parameters: C ox gs gs t A E t b sat W I C v e e L eff gs t eff ertical-field N 6T A,,, d, s/ d ox v E sat n vsat,, Ecrit,, sat 1 Eeff Ecrit n X. ZHOU 4 18 gs t nvth ds vth dsub gs, sb, ds n d th 1 Leff (TCAD: W = 1 m) E I I I I dsat dsat dlin gs,,,, d dlin dd ds I I gs dd,,,, dd ds dsub gs d dsubs gs,,,, dd Mobility Lateral-field eff 1 ds Drive current I on : I I n E L sat eff dd,, d on dsat d Leakage current I off : I I,, off dsub dd
Virtual Device Simulation. Virtual Process Integration
 : CMOS Process and Device Simulation Virtual Device Simulation Virtual Process Integration Dr Zhou Xing Office: S1-B1c-95 Phone: 6790-4532 Email: exzhou@ntu.edu.sg Web: http://www.ntu.edu.sg/home/exzhou/teaching//
: CMOS Process and Device Simulation Virtual Device Simulation Virtual Process Integration Dr Zhou Xing Office: S1-B1c-95 Phone: 6790-4532 Email: exzhou@ntu.edu.sg Web: http://www.ntu.edu.sg/home/exzhou/teaching//
Advanced Compact Models for MOSFETs
 Advanced Compact Models for MOSFETs Christian Enz, Carlos Galup-Montoro, Gennady Gildenblat, Chenming Hu, Ronald van Langevelde, Mitiko Miura-Mattausch, Rafael Rios, Chih-Tang (Tom) Sah Josef Watts (editor)
Advanced Compact Models for MOSFETs Christian Enz, Carlos Galup-Montoro, Gennady Gildenblat, Chenming Hu, Ronald van Langevelde, Mitiko Miura-Mattausch, Rafael Rios, Chih-Tang (Tom) Sah Josef Watts (editor)
Unified Compact Model for Generic Double-Gate
 WCM-MSM007 Workshop on Compact Modeling 10th International Conference on Modeling and Simulation of Microsystems Santa Clara, California, USA Unified Compact Model for Generic Double-Gate MOSFETs Xing
WCM-MSM007 Workshop on Compact Modeling 10th International Conference on Modeling and Simulation of Microsystems Santa Clara, California, USA Unified Compact Model for Generic Double-Gate MOSFETs Xing
MOS Transistors. Prof. Krishna Saraswat. Department of Electrical Engineering Stanford University Stanford, CA
 MOS Transistors Prof. Krishna Saraswat Department of Electrical Engineering S Stanford, CA 94305 saraswat@stanford.edu 1 1930: Patent on the Field-Effect Transistor! Julius Lilienfeld filed a patent describing
MOS Transistors Prof. Krishna Saraswat Department of Electrical Engineering S Stanford, CA 94305 saraswat@stanford.edu 1 1930: Patent on the Field-Effect Transistor! Julius Lilienfeld filed a patent describing
Unified Approach to Bulk/SOI/UTB/s-DG MOSFET Compact Modeling
 WCM-MSM2006 Workshop on Compact Modeling 9th International Conference on Modeling and Simulation of Microsystems Boston, Massachusetts, USA Unified Approach to Bulk/SOI/UTB/s-DG MOSFET Compact Modeling
WCM-MSM2006 Workshop on Compact Modeling 9th International Conference on Modeling and Simulation of Microsystems Boston, Massachusetts, USA Unified Approach to Bulk/SOI/UTB/s-DG MOSFET Compact Modeling
Lecture 11: MOSFET Modeling
 Digital Integrated Circuits (83-313) Lecture 11: MOSFET ing Semester B, 2016-17 Lecturer: Dr. Adam Teman TAs: Itamar Levi, Robert Giterman 18 June 2017 Disclaimer: This course was prepared, in its entirety,
Digital Integrated Circuits (83-313) Lecture 11: MOSFET ing Semester B, 2016-17 Lecturer: Dr. Adam Teman TAs: Itamar Levi, Robert Giterman 18 June 2017 Disclaimer: This course was prepared, in its entirety,
Chapter 5 MOSFET Theory for Submicron Technology
 Chapter 5 MOSFET Theory for Submicron Technology Short channel effects Other small geometry effects Parasitic components Velocity saturation/overshoot Hot carrier effects ** Majority of these notes are
Chapter 5 MOSFET Theory for Submicron Technology Short channel effects Other small geometry effects Parasitic components Velocity saturation/overshoot Hot carrier effects ** Majority of these notes are
The Devices: MOS Transistors
 The Devices: MOS Transistors References: Semiconductor Device Fundamentals, R. F. Pierret, Addison-Wesley Digital Integrated Circuits: A Design Perspective, J. Rabaey et.al. Prentice Hall NMOS Transistor
The Devices: MOS Transistors References: Semiconductor Device Fundamentals, R. F. Pierret, Addison-Wesley Digital Integrated Circuits: A Design Perspective, J. Rabaey et.al. Prentice Hall NMOS Transistor
V t vs. N A at Various T ox
 V t vs. N A at Various T ox Threshold Voltage, V t 0.9 0.8 0.7 0.6 0.5 0.4 T ox = 5.5 nm T ox = 5 nm T ox = 6 nm m = 4.35 ev, Q ox = 0; V sb = 0 V 0.3 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0 3.5 4.0 4.5 Body Doping, N
V t vs. N A at Various T ox Threshold Voltage, V t 0.9 0.8 0.7 0.6 0.5 0.4 T ox = 5.5 nm T ox = 5 nm T ox = 6 nm m = 4.35 ev, Q ox = 0; V sb = 0 V 0.3 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0 3.5 4.0 4.5 Body Doping, N
MOSFET: Introduction
 E&CE 437 Integrated VLSI Systems MOS Transistor 1 of 30 MOSFET: Introduction Metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistor (MOSFET) or MOS is widely used for implementing digital designs Its major
E&CE 437 Integrated VLSI Systems MOS Transistor 1 of 30 MOSFET: Introduction Metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistor (MOSFET) or MOS is widely used for implementing digital designs Its major
EE5311- Digital IC Design
 EE5311- Digital IC Design Module 1 - The Transistor Janakiraman V Assistant Professor Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Madras Chennai October 28, 2017 Janakiraman, IITM
EE5311- Digital IC Design Module 1 - The Transistor Janakiraman V Assistant Professor Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Madras Chennai October 28, 2017 Janakiraman, IITM
MOSFET Capacitance Model
 MOSFET Capacitance Model So far we discussed the MOSFET DC models. In real circuit operation, the device operates under time varying terminal voltages and the device operation can be described by: 1 small
MOSFET Capacitance Model So far we discussed the MOSFET DC models. In real circuit operation, the device operates under time varying terminal voltages and the device operation can be described by: 1 small
nmosfet Schematic Four structural masks: Field, Gate, Contact, Metal. Reverse doping polarities for pmosfet in N-well.
 nmosfet Schematic Four structural masks: Field, Gate, Contact, Metal. Reverse doping polarities for pmosfet in N-well. nmosfet Schematic 0 y L n + source n + drain depletion region polysilicon gate x z
nmosfet Schematic Four structural masks: Field, Gate, Contact, Metal. Reverse doping polarities for pmosfet in N-well. nmosfet Schematic 0 y L n + source n + drain depletion region polysilicon gate x z
LECTURE 3 MOSFETS II. MOS SCALING What is Scaling?
 LECTURE 3 MOSFETS II Lecture 3 Goals* * Understand constant field and constant voltage scaling and their effects. Understand small geometry effects for MOS transistors and their implications modeling and
LECTURE 3 MOSFETS II Lecture 3 Goals* * Understand constant field and constant voltage scaling and their effects. Understand small geometry effects for MOS transistors and their implications modeling and
The Critical Role of Quantum Capacitance in Compact Modeling of Nano-Scaled and Nanoelectronic Devices
 The Critical Role of Quantum Capacitance in Compact Modeling of Nano-Scaled and Nanoelectronic Devices Zhiping Yu and Jinyu Zhang Institute of Microelectronics Tsinghua University, Beijing, China yuzhip@tsinghua.edu.cn
The Critical Role of Quantum Capacitance in Compact Modeling of Nano-Scaled and Nanoelectronic Devices Zhiping Yu and Jinyu Zhang Institute of Microelectronics Tsinghua University, Beijing, China yuzhip@tsinghua.edu.cn
ELEC 3908, Physical Electronics, Lecture 23. The MOSFET Square Law Model
 ELEC 3908, Physical Electronics, Lecture 23 The MOSFET Square Law Model Lecture Outline As with the diode and bipolar, have looked at basic structure of the MOSFET and now turn to derivation of a current
ELEC 3908, Physical Electronics, Lecture 23 The MOSFET Square Law Model Lecture Outline As with the diode and bipolar, have looked at basic structure of the MOSFET and now turn to derivation of a current
The Devices. Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective. Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic. July 30, 2002
 Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic The Devices July 30, 2002 Goal of this chapter Present intuitive understanding of device operation Introduction
Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic The Devices July 30, 2002 Goal of this chapter Present intuitive understanding of device operation Introduction
Nanoscale CMOS Design Issues
 Nanoscale CMOS Design Issues Jaydeep P. Kulkarni Assistant Professor, ECE Department The University of Texas at Austin jaydeep@austin.utexas.edu Fall, 2017, VLSI-1 Class Transistor I-V Review Agenda Non-ideal
Nanoscale CMOS Design Issues Jaydeep P. Kulkarni Assistant Professor, ECE Department The University of Texas at Austin jaydeep@austin.utexas.edu Fall, 2017, VLSI-1 Class Transistor I-V Review Agenda Non-ideal
N Channel MOSFET level 3
 N Channel MOSFET level 3 mosn3 NSource NBulk NSource NBulk NSource NBulk NSource (a) (b) (c) (d) NBulk Figure 1: MOSFET Types Form: mosn3: instance name n 1 n n 3 n n 1 is the drain node, n is the gate
N Channel MOSFET level 3 mosn3 NSource NBulk NSource NBulk NSource NBulk NSource (a) (b) (c) (d) NBulk Figure 1: MOSFET Types Form: mosn3: instance name n 1 n n 3 n n 1 is the drain node, n is the gate
Microelectronics Part 1: Main CMOS circuits design rules
 GBM8320 Dispositifs Médicaux telligents Microelectronics Part 1: Main CMOS circuits design rules Mohamad Sawan et al. Laboratoire de neurotechnologies Polystim! http://www.cours.polymtl.ca/gbm8320/! med-amine.miled@polymtl.ca!
GBM8320 Dispositifs Médicaux telligents Microelectronics Part 1: Main CMOS circuits design rules Mohamad Sawan et al. Laboratoire de neurotechnologies Polystim! http://www.cours.polymtl.ca/gbm8320/! med-amine.miled@polymtl.ca!
The Future of CMOS. David Pulfrey. CHRONOLOGY of the FET. Lecture Lilienfeld s patent (BG FET) 1965 Commercialization (Fairchild)
 The Future of CMOS David Pulfrey 1 CHRONOLOGY of the FET 1933 Lilienfeld s patent (BG FET) 1965 Commercialization (Fairchild) 1991 The most abundant object made by mankind (C.T. Sah) 2003 The 10 nm FET
The Future of CMOS David Pulfrey 1 CHRONOLOGY of the FET 1933 Lilienfeld s patent (BG FET) 1965 Commercialization (Fairchild) 1991 The most abundant object made by mankind (C.T. Sah) 2003 The 10 nm FET
MOS Transistor Theory
 CHAPTER 3 MOS Transistor Theory Outline 2 1. Introduction 2. Ideal I-V Characteristics 3. Nonideal I-V Effects 4. C-V Characteristics 5. DC Transfer Characteristics 6. Switch-level RC Delay Models MOS
CHAPTER 3 MOS Transistor Theory Outline 2 1. Introduction 2. Ideal I-V Characteristics 3. Nonideal I-V Effects 4. C-V Characteristics 5. DC Transfer Characteristics 6. Switch-level RC Delay Models MOS
Lecture #27. The Short Channel Effect (SCE)
 Lecture #27 ANNOUNCEMENTS Design Project: Your BJT design should meet the performance specifications to within 10% at both 300K and 360K. ( β dc > 45, f T > 18 GHz, V A > 9 V and V punchthrough > 9 V )
Lecture #27 ANNOUNCEMENTS Design Project: Your BJT design should meet the performance specifications to within 10% at both 300K and 360K. ( β dc > 45, f T > 18 GHz, V A > 9 V and V punchthrough > 9 V )
ECE-305: Fall 2017 MOS Capacitors and Transistors
 ECE-305: Fall 2017 MOS Capacitors and Transistors Pierret, Semiconductor Device Fundamentals (SDF) Chapters 15+16 (pp. 525-530, 563-599) Professor Peter Bermel Electrical and Computer Engineering Purdue
ECE-305: Fall 2017 MOS Capacitors and Transistors Pierret, Semiconductor Device Fundamentals (SDF) Chapters 15+16 (pp. 525-530, 563-599) Professor Peter Bermel Electrical and Computer Engineering Purdue
ECEN474/704: (Analog) VLSI Circuit Design Spring 2018
 ECEN474/704: (Analog) SI Circuit Design Spring 2018 ecture 2: MOS ransistor Modeling Sam Palermo Analog & Mixed-Signal Center exas A&M University Announcements If you haven t already, turn in your 0.18um
ECEN474/704: (Analog) SI Circuit Design Spring 2018 ecture 2: MOS ransistor Modeling Sam Palermo Analog & Mixed-Signal Center exas A&M University Announcements If you haven t already, turn in your 0.18um
MOSFET. Id-Vd curve. I DS Transfer curve V G. Lec. 8. Vd=1V. Saturation region. V Th
 MOSFET Id-Vd curve Saturation region I DS Transfer curve Vd=1V V Th V G 1 0 < V GS < V T V GS > V T V Gs >V T & Small V D > 0 I DS WQ inv WC v WC i V V VDS V V G i T G n T L n I D g V D (g conductance
MOSFET Id-Vd curve Saturation region I DS Transfer curve Vd=1V V Th V G 1 0 < V GS < V T V GS > V T V Gs >V T & Small V D > 0 I DS WQ inv WC v WC i V V VDS V V G i T G n T L n I D g V D (g conductance
EE 560 MOS TRANSISTOR THEORY PART 2. Kenneth R. Laker, University of Pennsylvania
 1 EE 560 MOS TRANSISTOR THEORY PART nmos TRANSISTOR IN LINEAR REGION V S = 0 V G > V T0 channel SiO V D = small 4 C GC C BC substrate depletion region or bulk B p nmos TRANSISTOR AT EDGE OF SATURATION
1 EE 560 MOS TRANSISTOR THEORY PART nmos TRANSISTOR IN LINEAR REGION V S = 0 V G > V T0 channel SiO V D = small 4 C GC C BC substrate depletion region or bulk B p nmos TRANSISTOR AT EDGE OF SATURATION
This article has been accepted and published on J-STAGE in advance of copyediting. Content is final as presented.
 This article has been accepted and published on J-STAGE in advance of copyediting. Content is final as presented. References IEICE Electronics Express, Vol.* No.*,*-* Effects of Gamma-ray radiation on
This article has been accepted and published on J-STAGE in advance of copyediting. Content is final as presented. References IEICE Electronics Express, Vol.* No.*,*-* Effects of Gamma-ray radiation on
Zuhui Chen, Xing Zhou, Guan Huei See, Zhaomin Zhu, and Guojun Zhu
 Zuhui Chen, Xing Zhou, Guan Huei See, Zhaomin Zhu, and Guojun Zhu School of EEE, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore Slide No.1/18 Outline Motivations. Theory of interface traps. Theory of unified
Zuhui Chen, Xing Zhou, Guan Huei See, Zhaomin Zhu, and Guojun Zhu School of EEE, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore Slide No.1/18 Outline Motivations. Theory of interface traps. Theory of unified
CMPEN 411 VLSI Digital Circuits. Lecture 03: MOS Transistor
 CMPEN 411 VLSI Digital Circuits Lecture 03: MOS Transistor Kyusun Choi [Adapted from Rabaey s Digital Integrated Circuits, Second Edition, 2003 J. Rabaey, A. Chandrakasan, B. Nikolic] CMPEN 411 L03 S.1
CMPEN 411 VLSI Digital Circuits Lecture 03: MOS Transistor Kyusun Choi [Adapted from Rabaey s Digital Integrated Circuits, Second Edition, 2003 J. Rabaey, A. Chandrakasan, B. Nikolic] CMPEN 411 L03 S.1
EE 560 MOS TRANSISTOR THEORY
 1 EE 560 MOS TRANSISTOR THEORY PART 1 TWO TERMINAL MOS STRUCTURE V G (GATE VOLTAGE) 2 GATE OXIDE SiO 2 SUBSTRATE p-type doped Si (N A = 10 15 to 10 16 cm -3 ) t ox V B (SUBSTRATE VOLTAGE) EQUILIBRIUM:
1 EE 560 MOS TRANSISTOR THEORY PART 1 TWO TERMINAL MOS STRUCTURE V G (GATE VOLTAGE) 2 GATE OXIDE SiO 2 SUBSTRATE p-type doped Si (N A = 10 15 to 10 16 cm -3 ) t ox V B (SUBSTRATE VOLTAGE) EQUILIBRIUM:
Semiconductor Physics Problems 2015
 Semiconductor Physics Problems 2015 Page and figure numbers refer to Semiconductor Devices Physics and Technology, 3rd edition, by SM Sze and M-K Lee 1. The purest semiconductor crystals it is possible
Semiconductor Physics Problems 2015 Page and figure numbers refer to Semiconductor Devices Physics and Technology, 3rd edition, by SM Sze and M-K Lee 1. The purest semiconductor crystals it is possible
ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals
 ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 4: January 23, 2018 MOS Transistor Theory, MOS Model Penn ESE 570 Spring 2018 Khanna Lecture Outline! CMOS Process Enhancements! Semiconductor
ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 4: January 23, 2018 MOS Transistor Theory, MOS Model Penn ESE 570 Spring 2018 Khanna Lecture Outline! CMOS Process Enhancements! Semiconductor
MOS Transistor I-V Characteristics and Parasitics
 ECEN454 Digital Integrated Circuit Design MOS Transistor I-V Characteristics and Parasitics ECEN 454 Facts about Transistors So far, we have treated transistors as ideal switches An ON transistor passes
ECEN454 Digital Integrated Circuit Design MOS Transistor I-V Characteristics and Parasitics ECEN 454 Facts about Transistors So far, we have treated transistors as ideal switches An ON transistor passes
Lecture 8: Ballistic FET I-V
 Lecture 8: Ballistic FET I-V 1 Lecture 1: Ballistic FETs Jena: 61-70 Diffusive Field Effect Transistor Source Gate L g >> l Drain Source V GS Gate Drain I D Mean free path much shorter than channel length
Lecture 8: Ballistic FET I-V 1 Lecture 1: Ballistic FETs Jena: 61-70 Diffusive Field Effect Transistor Source Gate L g >> l Drain Source V GS Gate Drain I D Mean free path much shorter than channel length
Lecture 5: CMOS Transistor Theory
 Lecture 5: CMOS Transistor Theory Slides courtesy of Deming Chen Slides based on the initial set from David Harris CMOS VLSI Design Outline q q q q q q q Introduction MOS Capacitor nmos I-V Characteristics
Lecture 5: CMOS Transistor Theory Slides courtesy of Deming Chen Slides based on the initial set from David Harris CMOS VLSI Design Outline q q q q q q q Introduction MOS Capacitor nmos I-V Characteristics
Microelectronic Devices and Circuits Lecture 13 - Linear Equivalent Circuits - Outline Announcements Exam Two -
 6.012 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits Lecture 13 Linear Equivalent Circuits Outline Announcements Exam Two Coming next week, Nov. 5, 7:309:30 p.m. Review Subthreshold operation of MOSFETs Review Large
6.012 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits Lecture 13 Linear Equivalent Circuits Outline Announcements Exam Two Coming next week, Nov. 5, 7:309:30 p.m. Review Subthreshold operation of MOSFETs Review Large
Scaling Issues in Planar FET: Dual Gate FET and FinFETs
 Scaling Issues in Planar FET: Dual Gate FET and FinFETs Lecture 12 Dr. Amr Bayoumi Fall 2014 Advanced Devices (EC760) Arab Academy for Science and Technology - Cairo 1 Outline Scaling Issues for Planar
Scaling Issues in Planar FET: Dual Gate FET and FinFETs Lecture 12 Dr. Amr Bayoumi Fall 2014 Advanced Devices (EC760) Arab Academy for Science and Technology - Cairo 1 Outline Scaling Issues for Planar
Chapter 4 Field-Effect Transistors
 Chapter 4 Field-Effect Transistors Microelectronic Circuit Design Richard C. Jaeger Travis N. Blalock 5/5/11 Chap 4-1 Chapter Goals Describe operation of MOSFETs. Define FET characteristics in operation
Chapter 4 Field-Effect Transistors Microelectronic Circuit Design Richard C. Jaeger Travis N. Blalock 5/5/11 Chap 4-1 Chapter Goals Describe operation of MOSFETs. Define FET characteristics in operation
Device Models (PN Diode, MOSFET )
 Device Models (PN Diode, MOSFET ) Instructor: Steven P. Levitan steve@ece.pitt.edu TA: Gayatri Mehta, José Martínez Book: Digital Integrated Circuits: A Design Perspective; Jan Rabaey Lab Notes: Handed
Device Models (PN Diode, MOSFET ) Instructor: Steven P. Levitan steve@ece.pitt.edu TA: Gayatri Mehta, José Martínez Book: Digital Integrated Circuits: A Design Perspective; Jan Rabaey Lab Notes: Handed
A Multi-Gate CMOS Compact Model BSIMMG
 A Multi-Gate CMOS Compact Model BSIMMG Darsen Lu, Sriramkumar Venugopalan, Tanvir Morshed, Yogesh Singh Chauhan, Chung-Hsun Lin, Mohan Dunga, Ali Niknejad and Chenming Hu University of California, Berkeley
A Multi-Gate CMOS Compact Model BSIMMG Darsen Lu, Sriramkumar Venugopalan, Tanvir Morshed, Yogesh Singh Chauhan, Chung-Hsun Lin, Mohan Dunga, Ali Niknejad and Chenming Hu University of California, Berkeley
Simple and accurate modeling of the 3D structural variations in FinFETs
 Simple and accurate modeling of the 3D structural variations in FinFETs Donghu Kim Electrical Engineering Program Graduate school of UNIST 2013 Simple and accurate modeling of the 3D structural variations
Simple and accurate modeling of the 3D structural variations in FinFETs Donghu Kim Electrical Engineering Program Graduate school of UNIST 2013 Simple and accurate modeling of the 3D structural variations
Lecture 04 Review of MOSFET
 ECE 541/ME 541 Microelectronic Fabrication Techniques Lecture 04 Review of MOSFET Zheng Yang (ERF 3017, email: yangzhen@uic.edu) What is a Transistor? A Switch! An MOS Transistor V GS V T V GS S Ron D
ECE 541/ME 541 Microelectronic Fabrication Techniques Lecture 04 Review of MOSFET Zheng Yang (ERF 3017, email: yangzhen@uic.edu) What is a Transistor? A Switch! An MOS Transistor V GS V T V GS S Ron D
Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective. Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic. The Devices. July 30, Devices.
 Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic The July 30, 2002 1 Goal of this chapter Present intuitive understanding of device operation Introduction
Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic The July 30, 2002 1 Goal of this chapter Present intuitive understanding of device operation Introduction
SOI/SOTB Compact Models
 MOS-AK 2017 An Overview of the HiSIM SOI/SOTB Compact Models Marek Mierzwinski*, Dondee Navarro**, and Mitiko Miura-Mattausch** *Keysight Technologies **Hiroshima University Agenda Introduction Model overview
MOS-AK 2017 An Overview of the HiSIM SOI/SOTB Compact Models Marek Mierzwinski*, Dondee Navarro**, and Mitiko Miura-Mattausch** *Keysight Technologies **Hiroshima University Agenda Introduction Model overview
Semiconductor Integrated Process Design (MS 635)
 Semiconductor Integrated Process Design (MS 635) Instructor: Prof. Keon Jae Lee - Office: 응용공학동 #4306, Tel: #3343 - Email: keonlee@kaist.ac.kr Lecture: (Tu, Th), 1:00-2:15 #2425 Office hour: Tues & Thur
Semiconductor Integrated Process Design (MS 635) Instructor: Prof. Keon Jae Lee - Office: 응용공학동 #4306, Tel: #3343 - Email: keonlee@kaist.ac.kr Lecture: (Tu, Th), 1:00-2:15 #2425 Office hour: Tues & Thur
EE105 - Fall 2006 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits
 EE105 - Fall 2006 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits Prof. Jan M. Rabaey (jan@eecs) Lecture 7: MOS Transistor Some Administrative Issues Lab 2 this week Hw 2 due on We Hw 3 will be posted same day MIDTERM
EE105 - Fall 2006 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits Prof. Jan M. Rabaey (jan@eecs) Lecture 7: MOS Transistor Some Administrative Issues Lab 2 this week Hw 2 due on We Hw 3 will be posted same day MIDTERM
ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals
 ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 4: January 29, 2019 MOS Transistor Theory, MOS Model Penn ESE 570 Spring 2019 Khanna Lecture Outline! CMOS Process Enhancements! Semiconductor
ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 4: January 29, 2019 MOS Transistor Theory, MOS Model Penn ESE 570 Spring 2019 Khanna Lecture Outline! CMOS Process Enhancements! Semiconductor
Introduction and Background
 Analog CMOS Integrated Circuit Design Introduction and Background Dr. Jawdat Abu-Taha Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Islamic University of Gaza jtaha@iugaza.edu.ps 1 Marking Assignments
Analog CMOS Integrated Circuit Design Introduction and Background Dr. Jawdat Abu-Taha Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Islamic University of Gaza jtaha@iugaza.edu.ps 1 Marking Assignments
CHAPTER 5 EFFECT OF GATE ELECTRODE WORK FUNCTION VARIATION ON DC AND AC PARAMETERS IN CONVENTIONAL AND JUNCTIONLESS FINFETS
 98 CHAPTER 5 EFFECT OF GATE ELECTRODE WORK FUNCTION VARIATION ON DC AND AC PARAMETERS IN CONVENTIONAL AND JUNCTIONLESS FINFETS In this chapter, the effect of gate electrode work function variation on DC
98 CHAPTER 5 EFFECT OF GATE ELECTRODE WORK FUNCTION VARIATION ON DC AND AC PARAMETERS IN CONVENTIONAL AND JUNCTIONLESS FINFETS In this chapter, the effect of gate electrode work function variation on DC
ECE 305: Fall MOSFET Energy Bands
 ECE 305: Fall 2016 MOSFET Energy Bands Professor Peter Bermel Electrical and Computer Engineering Purdue University, West Lafayette, IN USA pbermel@purdue.edu Pierret, Semiconductor Device Fundamentals
ECE 305: Fall 2016 MOSFET Energy Bands Professor Peter Bermel Electrical and Computer Engineering Purdue University, West Lafayette, IN USA pbermel@purdue.edu Pierret, Semiconductor Device Fundamentals
Lecture 29 - The Long Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor (cont.) April 20, 2007
 6.720J/3.43J - Integrated Microelectronic Devices - Spring 2007 Lecture 29-1 Lecture 29 - The Long Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor (cont.) April 20, 2007 Contents: 1. Non-ideal and second-order
6.720J/3.43J - Integrated Microelectronic Devices - Spring 2007 Lecture 29-1 Lecture 29 - The Long Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor (cont.) April 20, 2007 Contents: 1. Non-ideal and second-order
II III IV V VI B C N. Al Si P S. Zn Ga Ge As Se Cd In Sn Sb Te. Silicon (Si) the dominating material in IC manufacturing
 II III IV V VI B N Al Si P S Zn Ga Ge As Se d In Sn Sb Te Silicon (Si) the dominating material in I manufacturing ompound semiconductors III - V group: GaAs GaN GaSb GaP InAs InP InSb... The Energy Band
II III IV V VI B N Al Si P S Zn Ga Ge As Se d In Sn Sb Te Silicon (Si) the dominating material in I manufacturing ompound semiconductors III - V group: GaAs GaN GaSb GaP InAs InP InSb... The Energy Band
! MOS Capacitances. " Extrinsic. " Intrinsic. ! Lumped Capacitance Model. ! First Order Capacitor Summary. ! Capacitance Implications
 ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 7: February, 07 MOS SPICE Models, MOS Parasitic Details Lecture Outline! MOS Capacitances " Extrinsic " Intrinsic! Lumped Capacitance Model!
ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 7: February, 07 MOS SPICE Models, MOS Parasitic Details Lecture Outline! MOS Capacitances " Extrinsic " Intrinsic! Lumped Capacitance Model!
6.012 Electronic Devices and Circuits
 Page 1 of 10 YOUR NAME Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Massachusetts Institute of Technology 6.012 Electronic Devices and Circuits Exam No. 2 Thursday, November 5, 2009 7:30 to
Page 1 of 10 YOUR NAME Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Massachusetts Institute of Technology 6.012 Electronic Devices and Circuits Exam No. 2 Thursday, November 5, 2009 7:30 to
Lecture 30 The Short Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor. November 15, 2002
 6.720J/3.43J Integrated Microelectronic Devices Fall 2002 Lecture 30 1 Lecture 30 The Short Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor November 15, 2002 Contents: 1. Short channel effects Reading
6.720J/3.43J Integrated Microelectronic Devices Fall 2002 Lecture 30 1 Lecture 30 The Short Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor November 15, 2002 Contents: 1. Short channel effects Reading
EEC 118 Lecture #2: MOSFET Structure and Basic Operation. Rajeevan Amirtharajah University of California, Davis Jeff Parkhurst Intel Corporation
 EEC 118 Lecture #2: MOSFET Structure and Basic Operation Rajeevan Amirtharajah University of California, Davis Jeff Parkhurst Intel Corporation Announcements Lab 1 this week, report due next week Bring
EEC 118 Lecture #2: MOSFET Structure and Basic Operation Rajeevan Amirtharajah University of California, Davis Jeff Parkhurst Intel Corporation Announcements Lab 1 this week, report due next week Bring
EE105 - Fall 2005 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits
 EE105 - Fall 005 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits ecture 7 MOS Transistor Announcements Homework 3, due today Homework 4 due next week ab this week Reading: Chapter 4 1 ecture Material ast lecture
EE105 - Fall 005 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits ecture 7 MOS Transistor Announcements Homework 3, due today Homework 4 due next week ab this week Reading: Chapter 4 1 ecture Material ast lecture
Device Models (PN Diode, MOSFET )
 Device Models (PN Diode, MOSFET ) Instructor: Steven P. Levitan steve@ece.pitt.edu TA: Gayatri Mehta, José Martínez Book: Digital Integrated Circuits: A Design Perspective; Jan Rabaey Lab Notes: Handed
Device Models (PN Diode, MOSFET ) Instructor: Steven P. Levitan steve@ece.pitt.edu TA: Gayatri Mehta, José Martínez Book: Digital Integrated Circuits: A Design Perspective; Jan Rabaey Lab Notes: Handed
Section 12: Intro to Devices
 Section 12: Intro to Devices Extensive reading materials on reserve, including Robert F. Pierret, Semiconductor Device Fundamentals Bond Model of Electrons and Holes Si Si Si Si Si Si Si Si Si Silicon
Section 12: Intro to Devices Extensive reading materials on reserve, including Robert F. Pierret, Semiconductor Device Fundamentals Bond Model of Electrons and Holes Si Si Si Si Si Si Si Si Si Silicon
MOSFET SCALING ECE 663
 MOSFET SCALING Scaling of switches Moore s Law economics Moore s Law - #DRAM Bits per chip doubles every 18 months ~5% bigger chips/wafers ~5% design improvements ~50 % Lithography ability to print smaller
MOSFET SCALING Scaling of switches Moore s Law economics Moore s Law - #DRAM Bits per chip doubles every 18 months ~5% bigger chips/wafers ~5% design improvements ~50 % Lithography ability to print smaller
MOS Capacitor MOSFET Devices. MOSFET s. INEL Solid State Electronics. Manuel Toledo Quiñones. ECE Dept. UPRM.
 INEL 6055 - Solid State Electronics ECE Dept. UPRM 20th March 2006 Definitions MOS Capacitor Isolated Metal, SiO 2, Si Threshold Voltage qφ m metal d vacuum level SiO qχ 2 E g /2 qφ F E C E i E F E v qφ
INEL 6055 - Solid State Electronics ECE Dept. UPRM 20th March 2006 Definitions MOS Capacitor Isolated Metal, SiO 2, Si Threshold Voltage qφ m metal d vacuum level SiO qχ 2 E g /2 qφ F E C E i E F E v qφ
The PSP compact MOSFET model An update
 The PSP compact MOSFET model An update Gert-Jan Smit, Andries Scholten, D.B.M. Klaassen NXP Semiconductors Ronald van Langevelde Philips Research Europe Gennady Gildenblat, Weimin Wu, Xin Li, Amit Jha,
The PSP compact MOSFET model An update Gert-Jan Smit, Andries Scholten, D.B.M. Klaassen NXP Semiconductors Ronald van Langevelde Philips Research Europe Gennady Gildenblat, Weimin Wu, Xin Li, Amit Jha,
The Devices. Devices
 The The MOS Transistor Gate Oxyde Gate Source n+ Polysilicon Drain n+ Field-Oxyde (SiO 2 ) p-substrate p+ stopper Bulk Contact CROSS-SECTION of NMOS Transistor Cross-Section of CMOS Technology MOS transistors
The The MOS Transistor Gate Oxyde Gate Source n+ Polysilicon Drain n+ Field-Oxyde (SiO 2 ) p-substrate p+ stopper Bulk Contact CROSS-SECTION of NMOS Transistor Cross-Section of CMOS Technology MOS transistors
R. Ludwig and G. Bogdanov RF Circuit Design: Theory and Applications 2 nd edition. Figures for Chapter 6
 R. Ludwig and G. Bogdanov RF Circuit Design: Theory and Applications 2 nd edition Figures for Chapter 6 Free electron Conduction band Hole W g W C Forbidden Band or Bandgap W V Electron energy Hole Valence
R. Ludwig and G. Bogdanov RF Circuit Design: Theory and Applications 2 nd edition Figures for Chapter 6 Free electron Conduction band Hole W g W C Forbidden Band or Bandgap W V Electron energy Hole Valence
Lecture 12: MOSFET Devices
 Lecture 12: MOSFET Devices Gu-Yeon Wei Division of Engineering and Applied Sciences Harvard University guyeon@eecs.harvard.edu Wei 1 Overview Reading S&S: Chapter 5.1~5.4 Supplemental Reading Background
Lecture 12: MOSFET Devices Gu-Yeon Wei Division of Engineering and Applied Sciences Harvard University guyeon@eecs.harvard.edu Wei 1 Overview Reading S&S: Chapter 5.1~5.4 Supplemental Reading Background
ECE 497 JS Lecture - 12 Device Technologies
 ECE 497 JS Lecture - 12 Device Technologies Spring 2004 Jose E. Schutt-Aine Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Illinois jose@emlab.uiuc.edu 1 NMOS Transistor 2 ρ Source channel charge density
ECE 497 JS Lecture - 12 Device Technologies Spring 2004 Jose E. Schutt-Aine Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Illinois jose@emlab.uiuc.edu 1 NMOS Transistor 2 ρ Source channel charge density
Ultimately Scaled CMOS: DG FinFETs?
 Ultimately Scaled CMOS: DG FinFETs? Jerry G. Fossum SOI Group Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Florida Gainesville, FL 32611-6130 J. G. Fossum / 1 Outline Introduction -
Ultimately Scaled CMOS: DG FinFETs? Jerry G. Fossum SOI Group Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Florida Gainesville, FL 32611-6130 J. G. Fossum / 1 Outline Introduction -
The Gradual Channel Approximation for the MOSFET:
 6.01 - Electronic Devices and Circuits Fall 003 The Gradual Channel Approximation for the MOSFET: We are modeling the terminal characteristics of a MOSFET and thus want i D (v DS, v GS, v BS ), i B (v
6.01 - Electronic Devices and Circuits Fall 003 The Gradual Channel Approximation for the MOSFET: We are modeling the terminal characteristics of a MOSFET and thus want i D (v DS, v GS, v BS ), i B (v
Semiconductor Physics fall 2012 problems
 Semiconductor Physics fall 2012 problems 1. An n-type sample of silicon has a uniform density N D = 10 16 atoms cm -3 of arsenic, and a p-type silicon sample has N A = 10 15 atoms cm -3 of boron. For each
Semiconductor Physics fall 2012 problems 1. An n-type sample of silicon has a uniform density N D = 10 16 atoms cm -3 of arsenic, and a p-type silicon sample has N A = 10 15 atoms cm -3 of boron. For each
Quantitative MOSFET. Step 1. Connect the MOS capacitor results for the electron charge in the inversion layer Q N to the drain current.
 Quantitative MOSFET Step 1. Connect the MOS capacitor results for the electron charge in the inversion layer Q N to the drain current. V DS _ n source polysilicon gate y = y * 0 x metal interconnect to
Quantitative MOSFET Step 1. Connect the MOS capacitor results for the electron charge in the inversion layer Q N to the drain current. V DS _ n source polysilicon gate y = y * 0 x metal interconnect to
Integrated Circuits & Systems
 Federal University of Santa Catarina Center for Technology Computer Science & Electronics Engineering Integrated Circuits & Systems INE 5442 Lecture 10 MOSFET part 1 guntzel@inf.ufsc.br ual-well Trench-Isolated
Federal University of Santa Catarina Center for Technology Computer Science & Electronics Engineering Integrated Circuits & Systems INE 5442 Lecture 10 MOSFET part 1 guntzel@inf.ufsc.br ual-well Trench-Isolated
ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals
 ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 4: January 24, 2017 MOS Transistor Theory, MOS Model Penn ESE 570 Spring 2017 Khanna Lecture Outline! Semiconductor Physics " Band gaps "
ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 4: January 24, 2017 MOS Transistor Theory, MOS Model Penn ESE 570 Spring 2017 Khanna Lecture Outline! Semiconductor Physics " Band gaps "
FIELD-EFFECT TRANSISTORS
 FIEL-EFFECT TRANSISTORS 1 Semiconductor review 2 The MOS capacitor 2 The enhancement-type N-MOS transistor 3 I-V characteristics of enhancement MOSFETS 4 The output characteristic of the MOSFET in saturation
FIEL-EFFECT TRANSISTORS 1 Semiconductor review 2 The MOS capacitor 2 The enhancement-type N-MOS transistor 3 I-V characteristics of enhancement MOSFETS 4 The output characteristic of the MOSFET in saturation
ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals
 ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 7: February 4, 2016 MOS SPICE Models, MOS Parasitic Details Lecture Outline! MOS Capacitances " Extrinsic " Intrinsic! Lumped Capacitance
ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 7: February 4, 2016 MOS SPICE Models, MOS Parasitic Details Lecture Outline! MOS Capacitances " Extrinsic " Intrinsic! Lumped Capacitance
Introduction to compact modeling. Sivakumar Mudanai Intel Corp.
 Introduction to compact modeling Sivakumar Mudanai Intel Corp. Outline What is a compact model Why do we need compact models Requirements on a compact model Building the core long channel compact model
Introduction to compact modeling Sivakumar Mudanai Intel Corp. Outline What is a compact model Why do we need compact models Requirements on a compact model Building the core long channel compact model
ECE606: Solid State Devices Lecture 23 MOSFET I-V Characteristics MOSFET non-idealities
 ECE66: Solid State evices Lecture 3 MOSFET I- Characteristics MOSFET non-idealities Gerhard Klimeck gekco@purdue.edu Outline 1) Square law/ simplified bulk charge theory ) elocity saturation in simplified
ECE66: Solid State evices Lecture 3 MOSFET I- Characteristics MOSFET non-idealities Gerhard Klimeck gekco@purdue.edu Outline 1) Square law/ simplified bulk charge theory ) elocity saturation in simplified
VLSI Design The MOS Transistor
 VLSI Design The MOS Transistor Frank Sill Torres Universidade Federal de Minas Gerais (UFMG), Brazil VLSI Design: CMOS Technology 1 Outline Introduction MOS Capacitor nmos I-V Characteristics pmos I-V
VLSI Design The MOS Transistor Frank Sill Torres Universidade Federal de Minas Gerais (UFMG), Brazil VLSI Design: CMOS Technology 1 Outline Introduction MOS Capacitor nmos I-V Characteristics pmos I-V
The Devices. Jan M. Rabaey
 The Devices Jan M. Rabaey Goal of this chapter Present intuitive understanding of device operation Introduction of basic device equations Introduction of models for manual analysis Introduction of models
The Devices Jan M. Rabaey Goal of this chapter Present intuitive understanding of device operation Introduction of basic device equations Introduction of models for manual analysis Introduction of models
MOS Transistor Theory MOSFET Symbols Current Characteristics of MOSFET. MOS Symbols and Characteristics. nmos Enhancement Transistor
 MOS Transistor Theory MOSFET Symbols Current Characteristics of MOSFET Calculation of t and Important 2 nd Order Effects SmallSignal Signal MOSFET Model Summary Material from: CMOS LSI Design By Weste
MOS Transistor Theory MOSFET Symbols Current Characteristics of MOSFET Calculation of t and Important 2 nd Order Effects SmallSignal Signal MOSFET Model Summary Material from: CMOS LSI Design By Weste
Analysis of Transconductances in Deep Submicron CMOS with EKV 3.0
 MOS Models & Parameter Extraction Workgroup Arbeitskreis MOS Modelle & Parameterextraktion XFAB, Erfurt, Germany, October 2, 2002 Analysis of Transconductances in Deep Submicron CMOS with EKV 3.0 Matthias
MOS Models & Parameter Extraction Workgroup Arbeitskreis MOS Modelle & Parameterextraktion XFAB, Erfurt, Germany, October 2, 2002 Analysis of Transconductances in Deep Submicron CMOS with EKV 3.0 Matthias
Lecture 28 - The Long Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor (cont.) April 18, 2007
 6.720J/3.43J - Integrated Microelectronic Devices - Spring 2007 Lecture 28-1 Lecture 28 - The Long Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor (cont.) April 18, 2007 Contents: 1. Second-order and
6.720J/3.43J - Integrated Microelectronic Devices - Spring 2007 Lecture 28-1 Lecture 28 - The Long Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor (cont.) April 18, 2007 Contents: 1. Second-order and
! CMOS Process Enhancements. ! Semiconductor Physics. " Band gaps. " Field Effects. ! MOS Physics. " Cut-off. " Depletion.
 ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 4: January 3, 018 MOS Transistor Theory, MOS Model Lecture Outline! CMOS Process Enhancements! Semiconductor Physics " Band gaps " Field Effects!
ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 4: January 3, 018 MOS Transistor Theory, MOS Model Lecture Outline! CMOS Process Enhancements! Semiconductor Physics " Band gaps " Field Effects!
ECE-305: Spring 2016 MOSFET IV
 ECE-305: Spring 2016 MOSFET IV Professor Mark Lundstrom Electrical and Computer Engineering Purdue University, West Lafayette, IN USA lundstro@purdue.edu Lundstrom s lecture notes: Lecture 4 4/7/16 outline
ECE-305: Spring 2016 MOSFET IV Professor Mark Lundstrom Electrical and Computer Engineering Purdue University, West Lafayette, IN USA lundstro@purdue.edu Lundstrom s lecture notes: Lecture 4 4/7/16 outline
Electronic Devices and Circuits Lecture 15 - Digital Circuits: Inverter Basics - Outline Announcements. = total current; I D
 6.012 - Electronic Devices and Circuits Lecture 15 - Digital Circuits: Inverter asics - Outline Announcements Handout - Lecture Outline and Summary The MOSFET alpha factor - use definition in lecture,
6.012 - Electronic Devices and Circuits Lecture 15 - Digital Circuits: Inverter asics - Outline Announcements Handout - Lecture Outline and Summary The MOSFET alpha factor - use definition in lecture,
JFET/MESFET. JFET: small gate current (reverse leakage of the gate-to-channel junction) More gate leakage than MOSFET, less than bipolar.
 JFET/MESFET JFET: small gate current (reverse leakage of the gate-to-channel junction) More gate leakage than MOSFET, less than bipolar. JFET has higher transconductance than the MOSFET. Used in low-noise,
JFET/MESFET JFET: small gate current (reverse leakage of the gate-to-channel junction) More gate leakage than MOSFET, less than bipolar. JFET has higher transconductance than the MOSFET. Used in low-noise,
Section 12: Intro to Devices
 Section 12: Intro to Devices Extensive reading materials on reserve, including Robert F. Pierret, Semiconductor Device Fundamentals EE143 Ali Javey Bond Model of Electrons and Holes Si Si Si Si Si Si Si
Section 12: Intro to Devices Extensive reading materials on reserve, including Robert F. Pierret, Semiconductor Device Fundamentals EE143 Ali Javey Bond Model of Electrons and Holes Si Si Si Si Si Si Si
RFIC2017 MO2B-2. A Simplified CMOS FET Model using Surface Potential Equations For Inter-modulation Simulations of Passive-Mixer-Like Circuits
 A Simplified CMOS FET Model using Surface Potential Equations For Inter-modulation Simulations of Passive-Mixer-Like Circuits M. Baraani Dastjerdi and H. Krishnaswamy CoSMIC Lab, Columbia University, New
A Simplified CMOS FET Model using Surface Potential Equations For Inter-modulation Simulations of Passive-Mixer-Like Circuits M. Baraani Dastjerdi and H. Krishnaswamy CoSMIC Lab, Columbia University, New
! CMOS Process Enhancements. ! Semiconductor Physics. " Band gaps. " Field Effects. ! MOS Physics. " Cut-off. " Depletion.
 ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 4: January 9, 019 MOS Transistor Theory, MOS Model Lecture Outline CMOS Process Enhancements Semiconductor Physics Band gaps Field Effects
ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 4: January 9, 019 MOS Transistor Theory, MOS Model Lecture Outline CMOS Process Enhancements Semiconductor Physics Band gaps Field Effects
Practice 3: Semiconductors
 Practice 3: Semiconductors Digital Electronic Circuits Semester A 2012 VLSI Fabrication Process VLSI Very Large Scale Integration The ability to fabricate many devices on a single substrate within a given
Practice 3: Semiconductors Digital Electronic Circuits Semester A 2012 VLSI Fabrication Process VLSI Very Large Scale Integration The ability to fabricate many devices on a single substrate within a given
Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Cornell University. ECE 3150: Microelectronics. Spring Exam 1 ` March 22, 2018
 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Cornell University ECE 3150: Microelectronics Spring 2018 Exam 1 ` March 22, 2018 INSTRUCTIONS: Every problem must be done in the separate booklet Only
Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Cornell University ECE 3150: Microelectronics Spring 2018 Exam 1 ` March 22, 2018 INSTRUCTIONS: Every problem must be done in the separate booklet Only
6.012 MICROELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.012 MICROELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS Answers to Exam 2 Spring 2008 Problem 1: Graded by Prof. Fonstad
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.012 MICROELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS Answers to Exam 2 Spring 2008 Problem 1: Graded by Prof. Fonstad
Lecture 15: MOS Transistor models: Body effects, SPICE models. Context. In the last lecture, we discussed the modes of operation of a MOS FET:
 Lecture 15: MOS Transistor models: Body effects, SPICE models Context In the last lecture, we discussed the modes of operation of a MOS FET: oltage controlled resistor model I- curve (Square-Law Model)
Lecture 15: MOS Transistor models: Body effects, SPICE models Context In the last lecture, we discussed the modes of operation of a MOS FET: oltage controlled resistor model I- curve (Square-Law Model)
Extensive reading materials on reserve, including
 Section 12: Intro to Devices Extensive reading materials on reserve, including Robert F. Pierret, Semiconductor Device Fundamentals EE143 Ali Javey Bond Model of Electrons and Holes Si Si Si Si Si Si Si
Section 12: Intro to Devices Extensive reading materials on reserve, including Robert F. Pierret, Semiconductor Device Fundamentals EE143 Ali Javey Bond Model of Electrons and Holes Si Si Si Si Si Si Si
1 Name: Student number: DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS AND PHYSICAL OCEANOGRAPHY MEMORIAL UNIVERSITY OF NEWFOUNDLAND. Fall :00-11:00
 1 Name: DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS AND PHYSICAL OCEANOGRAPHY MEMORIAL UNIVERSITY OF NEWFOUNDLAND Final Exam Physics 3000 December 11, 2012 Fall 2012 9:00-11:00 INSTRUCTIONS: 1. Answer all seven (7) questions.
1 Name: DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS AND PHYSICAL OCEANOGRAPHY MEMORIAL UNIVERSITY OF NEWFOUNDLAND Final Exam Physics 3000 December 11, 2012 Fall 2012 9:00-11:00 INSTRUCTIONS: 1. Answer all seven (7) questions.
MOS Transistor Properties Review
 MOS Transistor Properties Review 1 VLSI Chip Manufacturing Process Photolithography: transfer of mask patterns to the chip Diffusion or ion implantation: selective doping of Si substrate Oxidation: SiO
MOS Transistor Properties Review 1 VLSI Chip Manufacturing Process Photolithography: transfer of mask patterns to the chip Diffusion or ion implantation: selective doping of Si substrate Oxidation: SiO
Part 4: Heterojunctions - MOS Devices. MOSFET Current Voltage Characteristics
 MOS Device Uses: Part 4: Heterojunctions - MOS Devices MOSCAP capacitor: storing charge, charge-coupled device (CCD), etc. MOSFET transistor: switch, current amplifier, dynamic random access memory (DRAM-volatile),
MOS Device Uses: Part 4: Heterojunctions - MOS Devices MOSCAP capacitor: storing charge, charge-coupled device (CCD), etc. MOSFET transistor: switch, current amplifier, dynamic random access memory (DRAM-volatile),
Lecture 12: MOS Capacitors, transistors. Context
 Lecture 12: MOS Capacitors, transistors Context In the last lecture, we discussed PN diodes, and the depletion layer into semiconductor surfaces. Small signal models In this lecture, we will apply those
Lecture 12: MOS Capacitors, transistors Context In the last lecture, we discussed PN diodes, and the depletion layer into semiconductor surfaces. Small signal models In this lecture, we will apply those
Lecture 3: Transistor as an thermonic switch
 Lecture 3: Transistor as an thermonic switch 2016-01-21 Lecture 3, High Speed Devices 2016 1 Lecture 3: Transistors as an thermionic switch Reading Guide: 54-57 in Jena Transistor metrics Reservoir equilibrium
Lecture 3: Transistor as an thermonic switch 2016-01-21 Lecture 3, High Speed Devices 2016 1 Lecture 3: Transistors as an thermionic switch Reading Guide: 54-57 in Jena Transistor metrics Reservoir equilibrium
The Intrinsic Silicon
 The Intrinsic ilicon Thermally generated electrons and holes Carrier concentration p i =n i ni=1.45x10 10 cm-3 @ room temp Generally: n i = 3.1X10 16 T 3/2 e -1.21/2KT cm -3 T= temperature in K o (egrees
The Intrinsic ilicon Thermally generated electrons and holes Carrier concentration p i =n i ni=1.45x10 10 cm-3 @ room temp Generally: n i = 3.1X10 16 T 3/2 e -1.21/2KT cm -3 T= temperature in K o (egrees
