Vending machine A design-example by Ingo Sander
|
|
|
- Ophelia Owen
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Vending machine A design-example by Ingo Sander
2 System ontrol We will design the block System ontrol OIN REEIVER OIN_PRESENT GT_1_EURO EQ_1_EURO LT_1_EURO SYSTEM ONTROL DROP DROP_READY DROP BOTTLE AUMU- LATOR DE_A LR_A RETURN_10_ENT HANGER_READY OIN RETURN Return only 10 cents coin.
3 oin Reciever The System ontrol unit controls a number of subsystems from other suppliers. oin Reciever. Drop Bottle. oin Return. OIN REEIVER OIN_PRESENT GT_1_EURO EQ_1_EURO LT_1_EURO SYSTEM ONTROL AUMU- LATOR DE_A LR_A A AUMULATOR counts up the amount of paid coins. Signal OIN_PRESENT indicates that there are coins and the amount is indicated by the signals GT_1_EURO, EQ_1_EURO, LT_1_EURO. With the signals DE_A and LR_A the systemcontrol unit can reduce the amount by 10 cents, or reset the AUMULATOR.
4 oin Return SYSTEM ONTROL RETURN_10_ENT HANGER_READY OIN RETURN With a pulse on RETURN_10_ENT the coin return unit will eject 10 cent, and signal HANGER_READY when this is done and the unit is ready for the next command.
5 Drop Bottle SYSTEM ONTROL DROP DROP_READY DROP BOTTLE With a pulse on DROP the drop bottle unit will eject a bottle, and signals DROP_READY when this is done and the unit is ready for the next command.
6 Block diagram OIN REEIVER OIN_PRESENT GT_1_EURO EQ_1_EURO LT_1_EURO SYSTEM ONTROL DROP DROP_READY DROP BOTTLE DE_A RETURN_10_ENT OIN RETURN LR_A HANGER_READY Signal properties DROP_READY is active for a clockperiod after the bottle is ejected HANGER_READY is active for a clockperiod after a 10 ent coin is ejected Because of the mechanical properties the following signals are active and inactive for several clock periods: OIN_PRESENT ( active for several clockperiods after the coin is inserted ) DROP_READY ( active for several clockperiods at bottle ejection ) HANGER_READY ( inactive for several clockperiods at coin ejection )
7 Use a Moore-machine State Inputsignals NEXT STATE DEODER STATE REGISTER OUTPUT DEODER Outputsignals lk onstruction of a state machine for the controller of a vending machine Assumptions - Moore-machine - Stateregister implemented with D-flip-flops
8 Function diagram for vending machine Nej no Sum < 1 Reset Myntinkast registrerat? Ja yes Summa? oin input 10 ent, 50 ent, 1 Euro oin return 10 ent Price of one bottle 1 Euro Sum= 1 Sum > 1 Mata ut flaskan Retur 10 ent Nollställ summan Minska summan
9 We draw a state diagram from the functional diagram : State diagram LT _1_ EURO DROP _ READY EQ _1_ EURO DROP _ READY (d) (a) (b) (c) DROP OIN _ PRESENT OIN _ PRESENT OIN _ PRESENT OIN _ PRESENT GT _1_ EURO (f) HANGER _ READY RETURN _10 _ ENT HANGER _ READY (e) LR _ A (g) DE _ A
10 State diagram (a) Wait for coin input (b) Register coin? (c) oin is registered (3 cases) (d) Eject bottle (e) Reset sum (f) Return 10 ent (g) Decrease sum 10 ent
11 Insignals Block schematic State register Outsignals OIN_PRESENT LT_I_EURO D A lk D A DROP EQ_I_EURO RETURN_I0_ENT GT_I_EURO DROP_READY HANGER_READY Next State Decoder D B lk D B Output Decoder LR_A A B D D DE_A lk
12 State encoding Idea: Let the states that are close together in the state diagram have codes with unit distance. (b) next to (c) (d) next to (e) (a) next to (b) (f) next to (g) 7 states 3 state variables A, B, are needed AB a Ø d f 1 b c e g (Ø = don t care) The number of inputs is large, 6, total there may be nine variables in Karnaugh maps???
13 LT _1_ EURO DROP _ READY EQ _1_ EURO DROP _ READY (d) (e) LR _ A B State encoding OIN _ PRESENT (a) 000 OIN _ PRESENT (b) (c) DROP (f) OIN _ PRESENT OIN _ PRESENT GT _1_ EURO HANGER _ READY RETURN _10 _ ENT HANGER _ READY (g) DE _ A A AB a Ø d f 1 b c e g (Ø = don t care) State variable AB, eg. in state (c) is A = 0, B = 1 and = 1
14 oded state table? From the state diagram, you can set up the following coded state table. How do we avoid the complexity of nine variables?
15 Variable-Entered Mapping (VEM) Variable-Entered Mapping can be helpful when you need Karnaugh diagrams with many variables. You write functional expression of Karnaugh diagrams. A + D A AB Ø EQ + GT 0 0 Variables
16 Next state - D A A + D A AB EQ : EQ_1_EURO GT : GT_1_EURO 0 0 Ø EQ + GT A = DA = A B EQ + A B GT + A
17 Next state - D B B + D B AB EQ : EQ_1_EURO P : OIN_PRESENT 0 0 Ø P EQ B = DB = A B EQ + B + B P + A B Easy to miss!
18 Next state - D + D AB P : OIN_PRESENT DR: DROP_READY R: HANGER_READY 0 P Ø DR R = D + A B R + B = A P + B DR
19 Output signals The output signals are the "pulses" which are generated when passing through the states d, f, e, g. DROP = AB LR _ A = AB RETURN _10 _ ENT DE _ A = AB = AB
20 Implementation of the vending machine students must master the the design of simple combinational and sequential digital systems You do that now! When they call from ocaola, it's just for you all Digital Designers to adopt the mission...
21
22 What will happen in state Φ? AB a Ø d f 1 b c e g Φ = (010) AB Φ + + A = A B EQ + A B GT + A A (010) AB = 1 1 EQ GT = EQ + GT B + + = A B EQ + B + B P + A B = A P + B DR + A B R + B + (010) AB = 1 1 P DR R = P + DR A B = 1 = 010,110, 011,111 Φ, d, c, e B + ( 010) = 1 1 EQ = 1 AB
23 What will happen in state Φ? A B = 1 = 010,110, 011,111 Φ, d, c, e Φ In Φ-state we are stuck, or we go to (c) and then on. Or we go to (d) and offers soft drinks, or we go to (e) and resets any previous payment. Obviously, we need to purchase a reset circuit that ensures that the machine always starts in (a) 000! Otherwise we will have legitimate complaints from the customers! RESET-generator
24
IE1204 Digital Design. L10: State Machines (Part 2) Masoumeh (Azin) Ebrahimi Elena Dubrova
 IE1204 Digital Design L10: State Machines (Part 2) Masoumeh (Azin) Ebrahimi (masebr@kth.se) Elena Dubrova (dubrova@kth.se) KTH / ICT / ES This lecture BV pp. 528-532, 557-567 IE1204 Digital Design, Autumn2015
IE1204 Digital Design L10: State Machines (Part 2) Masoumeh (Azin) Ebrahimi (masebr@kth.se) Elena Dubrova (dubrova@kth.se) KTH / ICT / ES This lecture BV pp. 528-532, 557-567 IE1204 Digital Design, Autumn2015
Lecture 14 Finite state machines
 Lecture 14 Finite state machines Finite state machines are the foundation of nearly all digital computation. The state diagram captures the desired system behavior A formulaic process turns this diagram
Lecture 14 Finite state machines Finite state machines are the foundation of nearly all digital computation. The state diagram captures the desired system behavior A formulaic process turns this diagram
Philadelphia University Student Name: Student Number:
 Philadelphia University Student Name: Student Number: Faculty of Engineering Serial Number: Final Exam, Second Semester: 2015/2016 Dept. of Computer Engineering Course Title: Logic Circuits Date: 08/06/2016
Philadelphia University Student Name: Student Number: Faculty of Engineering Serial Number: Final Exam, Second Semester: 2015/2016 Dept. of Computer Engineering Course Title: Logic Circuits Date: 08/06/2016
Symbolic State Minimization
 CSE 27 Introduction to igital Systems Supplementary Reading Symbolic State inimization and An Example Symbolic State inimization In constructing state diagrams, it often occurs that the number of symbolic
CSE 27 Introduction to igital Systems Supplementary Reading Symbolic State inimization and An Example Symbolic State inimization In constructing state diagrams, it often occurs that the number of symbolic
EGR224 F 18 Assignment #4
 EGR224 F 18 Assignment #4 ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Due Date: Friday (Section 10), October 19, by 5 pm (slide it under
EGR224 F 18 Assignment #4 ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Due Date: Friday (Section 10), October 19, by 5 pm (slide it under
Last lecture Counter design Finite state machine started vending machine example. Today Continue on the vending machine example Moore/Mealy machines
 Lecture 2 Logistics HW6 due Wednesday Lab 7 this week (Tuesday exception) Midterm 2 Friday (covers material up to simple FSM (today)) Review on Thursday Yoky office hour on Friday moved to Thursday 2-:2pm
Lecture 2 Logistics HW6 due Wednesday Lab 7 this week (Tuesday exception) Midterm 2 Friday (covers material up to simple FSM (today)) Review on Thursday Yoky office hour on Friday moved to Thursday 2-:2pm
Written exam with solutions IE1204/5 Digital Design Friday 13/
 Written eam with solutions IE204/5 Digital Design Friday / 207 08.00-2.00 General Information Eaminer: Ingo Sander. Teacher: Kista, William Sandqvist tel 08-7904487 Teacher: Valhallavägen, Ahmed Hemani
Written eam with solutions IE204/5 Digital Design Friday / 207 08.00-2.00 General Information Eaminer: Ingo Sander. Teacher: Kista, William Sandqvist tel 08-7904487 Teacher: Valhallavägen, Ahmed Hemani
Ch 7. Finite State Machines. VII - Finite State Machines Contemporary Logic Design 1
 Ch 7. Finite State Machines VII - Finite State Machines Contemporary Logic esign 1 Finite State Machines Sequential circuits primitive sequential elements combinational logic Models for representing sequential
Ch 7. Finite State Machines VII - Finite State Machines Contemporary Logic esign 1 Finite State Machines Sequential circuits primitive sequential elements combinational logic Models for representing sequential
Chapter 5 Synchronous Sequential Logic
 Chapter 5 Synchronous Sequential Logic Sequential circuit: A circuit that includes memory elements. In this case the output depends not only on the current input but also on the past inputs. Memory A synchronous
Chapter 5 Synchronous Sequential Logic Sequential circuit: A circuit that includes memory elements. In this case the output depends not only on the current input but also on the past inputs. Memory A synchronous
Synchronous Sequential Circuit Design. Digital Computer Design
 Synchronous Sequential Circuit Design Digital Computer Design Races and Instability Combinational logic has no cyclic paths and no races If inputs are applied to combinational logic, the outputs will always
Synchronous Sequential Circuit Design Digital Computer Design Races and Instability Combinational logic has no cyclic paths and no races If inputs are applied to combinational logic, the outputs will always
Written reexam with solutions for IE1204/5 Digital Design Monday 14/
 Written reexam with solutions for IE204/5 Digital Design Monday 4/3 206 4.-8. General Information Examiner: Ingo Sander. Teacher: William Sandqvist phone 08-7904487 Exam text does not have to be returned
Written reexam with solutions for IE204/5 Digital Design Monday 4/3 206 4.-8. General Information Examiner: Ingo Sander. Teacher: William Sandqvist phone 08-7904487 Exam text does not have to be returned
Sequential Circuit Design
 Sequential Circuit esign esign Procedure. Specification 2. Formulation Obtain a state diagram or state table 3. State Assignment Assign binary codes to the states 4. Flip-Flop Input Equation etermination
Sequential Circuit esign esign Procedure. Specification 2. Formulation Obtain a state diagram or state table 3. State Assignment Assign binary codes to the states 4. Flip-Flop Input Equation etermination
Synchronous Sequential Circuit Design
 Synchronous Sequential Circuit Design 1 Sequential circuit design In sequential circuit design, we turn some description into a working circuit We first make a state table or diagram to express the computation
Synchronous Sequential Circuit Design 1 Sequential circuit design In sequential circuit design, we turn some description into a working circuit We first make a state table or diagram to express the computation
ENGG 1203 Tutorial. Solution (b) Solution (a) Simplification using K-map. Combinational Logic (II) and Sequential Logic (I) 8 Feb Learning Objectives
 ENGG 23 Tutorial Simplification using K-map Combinational Logic (II) and Sequential Logic (I) 8 Feb Learning Objectives Apply Karnaugh map for logic simplification Design a finite state machine News HW
ENGG 23 Tutorial Simplification using K-map Combinational Logic (II) and Sequential Logic (I) 8 Feb Learning Objectives Apply Karnaugh map for logic simplification Design a finite state machine News HW
State Graphs FSMs. Page 1
 State Graphs FSMs Page 1 Binary Counter State Graph 00 Q1 Q0 N1 N0 0 0 0 1 0 1 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 11 01 State graphs are graphical representations of TT s They contain the same information: no more, no
State Graphs FSMs Page 1 Binary Counter State Graph 00 Q1 Q0 N1 N0 0 0 0 1 0 1 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 11 01 State graphs are graphical representations of TT s They contain the same information: no more, no
Computers also need devices capable of Storing data and information Performing mathematical operations on such data
 Sequential Machines Introduction Logic devices examined so far Combinational Output function of input only Output valid as long as input true Change input change output Computers also need devices capable
Sequential Machines Introduction Logic devices examined so far Combinational Output function of input only Output valid as long as input true Change input change output Computers also need devices capable
CprE 281: Digital Logic
 CprE 281: Digital Logic Instructor: Alexander Stoytchev http://www.ece.iastate.edu/~alexs/classes/ Synchronous Sequential Circuits Basic Design Steps CprE 281: Digital Logic Iowa State University, Ames,
CprE 281: Digital Logic Instructor: Alexander Stoytchev http://www.ece.iastate.edu/~alexs/classes/ Synchronous Sequential Circuits Basic Design Steps CprE 281: Digital Logic Iowa State University, Ames,
or 0101 Machine
 Synchronous State Graph or Synchronous State Graph or Detector Design a state graph for a machine with: One input X, one output Z. Z= after receiving the complete sequence or Overlapped sequences are detected.
Synchronous State Graph or Synchronous State Graph or Detector Design a state graph for a machine with: One input X, one output Z. Z= after receiving the complete sequence or Overlapped sequences are detected.
UNIVERSITY OF BOLTON SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING BENG (HONS) ELECTRICAL & ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING EXAMINATION SEMESTER /2017
 UNIVERSITY OF BOLTON TW35 SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING BENG (HONS) ELECTRICAL & ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING EXAMINATION SEMESTER 2-2016/2017 INTERMEDIATE DIGITAL ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATIONS MODULE NO: EEE5002
UNIVERSITY OF BOLTON TW35 SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING BENG (HONS) ELECTRICAL & ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING EXAMINATION SEMESTER 2-2016/2017 INTERMEDIATE DIGITAL ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATIONS MODULE NO: EEE5002
Written exam with solutions IE Digital Design Friday 21/
 Written exam with solutions IE204-5 Digital Design Friday 2/0 206 09.00-3.00 General Information Examiner: Ingo Sander. Teacher: Kista, William Sandvist tel 08-7904487, Elena Dubrova phone 08-790 4 4 Exam
Written exam with solutions IE204-5 Digital Design Friday 2/0 206 09.00-3.00 General Information Examiner: Ingo Sander. Teacher: Kista, William Sandvist tel 08-7904487, Elena Dubrova phone 08-790 4 4 Exam
Generalized FSM model: Moore and Mealy
 Lecture 18 Logistics HW7 is due on Monday (and topic included in midterm 2) Midterm 2 on Wednesday in lecture slot cover materials up to today s lecture Review session Tuesday 4:15pm in EEB125 Last lecture
Lecture 18 Logistics HW7 is due on Monday (and topic included in midterm 2) Midterm 2 on Wednesday in lecture slot cover materials up to today s lecture Review session Tuesday 4:15pm in EEB125 Last lecture
Asynchronous sequence circuits
 Asynchronous sequence circuits An asynchronous sequence machine is a sequence circuit without flip-flops Asynchronous sequence machines are based on combinational gates with feedback Upon analysis it is
Asynchronous sequence circuits An asynchronous sequence machine is a sequence circuit without flip-flops Asynchronous sequence machines are based on combinational gates with feedback Upon analysis it is
COEN 312 DIGITAL SYSTEMS DESIGN - LECTURE NOTES Concordia University
 1 OEN 312 DIGIAL SYSEMS DESIGN - LEURE NOES oncordia University hapter 6: Registers and ounters NOE: For more examples and detailed description of the material in the lecture notes, please refer to the
1 OEN 312 DIGIAL SYSEMS DESIGN - LEURE NOES oncordia University hapter 6: Registers and ounters NOE: For more examples and detailed description of the material in the lecture notes, please refer to the
Lecture 10: Synchronous Sequential Circuits Design
 Lecture 0: Synchronous Sequential Circuits Design. General Form Input Combinational Flip-flops Combinational Output Circuit Circuit Clock.. Moore type has outputs dependent only on the state, e.g. ripple
Lecture 0: Synchronous Sequential Circuits Design. General Form Input Combinational Flip-flops Combinational Output Circuit Circuit Clock.. Moore type has outputs dependent only on the state, e.g. ripple
Synchronous Sequential Circuit Design. Dr. Ehab A. H. AL-Hialy Page 1
 Synchronous Sequential Circuit Design Dr. Ehab A. H. AL-Hialy Page Motivation Analysis of a few simple circuits Generalizes to Synchronous Sequential Circuits (SSC) Outputs are Function of State (and Inputs)
Synchronous Sequential Circuit Design Dr. Ehab A. H. AL-Hialy Page Motivation Analysis of a few simple circuits Generalizes to Synchronous Sequential Circuits (SSC) Outputs are Function of State (and Inputs)
Chapter 6 Introduction to state machines
 9..7 hapter 6 Introduction to state machines Dr.-Ing. Stefan Werner Table of content hapter : Switching Algebra hapter : Logical Levels, Timing & Delays hapter 3: Karnaugh-Veitch-Maps hapter 4: ombinational
9..7 hapter 6 Introduction to state machines Dr.-Ing. Stefan Werner Table of content hapter : Switching Algebra hapter : Logical Levels, Timing & Delays hapter 3: Karnaugh-Veitch-Maps hapter 4: ombinational
Parity Checker Example. EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 9 - Finite State Machines 1. Formal Design Process. Formal Design Process
 Parity Checker Example A string of bits has even parity if the number of 1 s in the string is even. Design a circuit that accepts a bit-serial stream of bits and outputs a 0 if the parity thus far is even
Parity Checker Example A string of bits has even parity if the number of 1 s in the string is even. Design a circuit that accepts a bit-serial stream of bits and outputs a 0 if the parity thus far is even
CSE140: Design of Sequential Logic
 CSE4: Design of Sequential Logic Instructor: Mohsen Imani Flip Flops 2 Counter 3 Up counter 4 Up counter 5 FSM with JK-Flip Flop 6 State Table 7 State Table 8 Circuit Minimization 9 Circuit Timing Constraints
CSE4: Design of Sequential Logic Instructor: Mohsen Imani Flip Flops 2 Counter 3 Up counter 4 Up counter 5 FSM with JK-Flip Flop 6 State Table 7 State Table 8 Circuit Minimization 9 Circuit Timing Constraints
Written exam for IE1204/5 Digital Design with solutions Thursday 29/
 Written exam for IE4/5 Digital Design with solutions Thursday 9/ 5 9.-. General Information Examiner: Ingo Sander. Teacher: William Sandqvist phone 8-794487 Exam text does not have to be returned when
Written exam for IE4/5 Digital Design with solutions Thursday 9/ 5 9.-. General Information Examiner: Ingo Sander. Teacher: William Sandqvist phone 8-794487 Exam text does not have to be returned when
King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals College of Computer Science and Engineering Computer Engineering Department
 King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals College of Computer Science and Engineering Computer Engineering Department Page 1 of 13 COE 202: Digital Logic Design (3-0-3) Term 112 (Spring 2012) Final
King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals College of Computer Science and Engineering Computer Engineering Department Page 1 of 13 COE 202: Digital Logic Design (3-0-3) Term 112 (Spring 2012) Final
ELCT201: DIGITAL LOGIC DESIGN
 ELCT201: DIGITAL LOGIC DESIGN Dr. Eng. Haitham Omran, haitham.omran@guc.edu.eg Dr. Eng. Wassim Alexan, wassim.joseph@guc.edu.eg Following the slides of Dr. Ahmed H. Madian Lecture 10 محرم 1439 ه Winter
ELCT201: DIGITAL LOGIC DESIGN Dr. Eng. Haitham Omran, haitham.omran@guc.edu.eg Dr. Eng. Wassim Alexan, wassim.joseph@guc.edu.eg Following the slides of Dr. Ahmed H. Madian Lecture 10 محرم 1439 ه Winter
5 State Minimisation. university of applied sciences hamburg. Digital Systems. Prof. Dr. J. Reichardt Prof. Dr. B. Schwarz
 5 State Minimisation In an early design phase when a word description of a sequential circuit's function is transformed into a FSM state diagram or state table redundant states may arise. State minimisation
5 State Minimisation In an early design phase when a word description of a sequential circuit's function is transformed into a FSM state diagram or state table redundant states may arise. State minimisation
Written exam with solutions IE1204/5 Digital Design Monday 23/
 Written exam with solutions IE204/5 Digital Design Monday 23/0 207 4.00-8.00 General Information Examiner: Ingo Sander. Teacher: Kista, William Sandvist Exam text has to be returned when you hand in your
Written exam with solutions IE204/5 Digital Design Monday 23/0 207 4.00-8.00 General Information Examiner: Ingo Sander. Teacher: Kista, William Sandvist Exam text has to be returned when you hand in your
Philadelphia University Student Name: Student Number:
 Philadelphia University Student Name: Student Number: Faculty of Engineering Serial Number: Final Exam, First Semester: 2017/2018 Dept. of Computer Engineering Course Title: Logic Circuits Date: 29/01/2018
Philadelphia University Student Name: Student Number: Faculty of Engineering Serial Number: Final Exam, First Semester: 2017/2018 Dept. of Computer Engineering Course Title: Logic Circuits Date: 29/01/2018
CS/ECE 252: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER ENGINEERING COMPUTER SCIENCES DEPARTMENT UNIVERSITY OF WISCONSIN-MADISON
 CS/ECE 252: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER ENGINEERING COMPUTER SCIENCES DEPARTMENT UNIVERSITY OF WISCONSIN-MADISON Prof. Mark D. Hill & Prof. Mikko Lipasti TAs Sanghamitra Roy, Eric Hill, Samuel Javner, Natalie
CS/ECE 252: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER ENGINEERING COMPUTER SCIENCES DEPARTMENT UNIVERSITY OF WISCONSIN-MADISON Prof. Mark D. Hill & Prof. Mikko Lipasti TAs Sanghamitra Roy, Eric Hill, Samuel Javner, Natalie
The Design Procedure. Output Equation Determination - Derive output equations from the state table
 The Design Procedure Specification Formulation - Obtain a state diagram or state table State Assignment - Assign binary codes to the states Flip-Flop Input Equation Determination - Select flipflop types
The Design Procedure Specification Formulation - Obtain a state diagram or state table State Assignment - Assign binary codes to the states Flip-Flop Input Equation Determination - Select flipflop types
ELEC Digital Logic Circuits Fall 2014 Sequential Circuits (Chapter 6) Finite State Machines (Ch. 7-10)
 ELEC 2200-002 Digital Logic Circuits Fall 2014 Sequential Circuits (Chapter 6) Finite State Machines (Ch. 7-10) Vishwani D. Agrawal James J. Danaher Professor Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
ELEC 2200-002 Digital Logic Circuits Fall 2014 Sequential Circuits (Chapter 6) Finite State Machines (Ch. 7-10) Vishwani D. Agrawal James J. Danaher Professor Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
Example: vending machine
 Example: vending machine Release item after 15 cents are deposited Single coin slot for dimes, nickels o change Reset Coin Sensor Vending Machine FSM Open Release Mechanism Clock Spring 2005 CSE370 - guest
Example: vending machine Release item after 15 cents are deposited Single coin slot for dimes, nickels o change Reset Coin Sensor Vending Machine FSM Open Release Mechanism Clock Spring 2005 CSE370 - guest
ENEL Digital Circuit Design. Final Examination
 ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING ENEL 353 - Digital Circuit Design Final Examination Friday, December 17, 1999 Red Gymnasium, 3:30PM - 6:30 PM Instructions: Time allowed is 3 hours. The examination
ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING ENEL 353 - Digital Circuit Design Final Examination Friday, December 17, 1999 Red Gymnasium, 3:30PM - 6:30 PM Instructions: Time allowed is 3 hours. The examination
CPE100: Digital Logic Design I
 Professor Brendan Morris, SEB 3216, brendan.morris@unlv.edu CPE100: Digital Logic Design I Midterm02 Review http://www.ee.unlv.edu/~b1morris/cpe100/ 2 Logistics Thursday Nov. 16 th In normal lecture (13:00-14:15)
Professor Brendan Morris, SEB 3216, brendan.morris@unlv.edu CPE100: Digital Logic Design I Midterm02 Review http://www.ee.unlv.edu/~b1morris/cpe100/ 2 Logistics Thursday Nov. 16 th In normal lecture (13:00-14:15)
Chapter 6. Synchronous Sequential Circuits
 Chapter 6 Synchronous Sequential Circuits In a combinational circuit, the values of the outputs are determined solely by the present values of its inputs. In a sequential circuit, the values of the outputs
Chapter 6 Synchronous Sequential Circuits In a combinational circuit, the values of the outputs are determined solely by the present values of its inputs. In a sequential circuit, the values of the outputs
3. Complete the following table of equivalent values. Use binary numbers with a sign bit and 7 bits for the value
 EGC22 Digital Logic Fundamental Additional Practice Problems. Complete the following table of equivalent values. Binary. Octal 35.77 33.23.875 29.99 27 9 64 Hexadecimal B.3 D.FD B.4C 2. Calculate the following
EGC22 Digital Logic Fundamental Additional Practice Problems. Complete the following table of equivalent values. Binary. Octal 35.77 33.23.875 29.99 27 9 64 Hexadecimal B.3 D.FD B.4C 2. Calculate the following
Appendix A: Digital Logic. Principles of Computer Architecture. Principles of Computer Architecture by M. Murdocca and V. Heuring
 - Principles of Computer rchitecture Miles Murdocca and Vincent Heuring 999 M. Murdocca and V. Heuring -2 Chapter Contents. Introduction.2 Combinational Logic.3 Truth Tables.4 Logic Gates.5 Properties
- Principles of Computer rchitecture Miles Murdocca and Vincent Heuring 999 M. Murdocca and V. Heuring -2 Chapter Contents. Introduction.2 Combinational Logic.3 Truth Tables.4 Logic Gates.5 Properties
ECE380 Digital Logic. Synchronous sequential circuits
 ECE38 Digital Logic Synchronous Sequential Circuits: State Diagrams, State Tables Dr. D. J. Jackson Lecture 27- Synchronous sequential circuits Circuits here a clock signal is used to control operation
ECE38 Digital Logic Synchronous Sequential Circuits: State Diagrams, State Tables Dr. D. J. Jackson Lecture 27- Synchronous sequential circuits Circuits here a clock signal is used to control operation
Appendix B. Review of Digital Logic. Baback Izadi Division of Engineering Programs
 Appendix B Review of Digital Logic Baback Izadi Division of Engineering Programs bai@engr.newpaltz.edu Elect. & Comp. Eng. 2 DeMorgan Symbols NAND (A.B) = A +B NOR (A+B) = A.B AND A.B = A.B = (A +B ) OR
Appendix B Review of Digital Logic Baback Izadi Division of Engineering Programs bai@engr.newpaltz.edu Elect. & Comp. Eng. 2 DeMorgan Symbols NAND (A.B) = A +B NOR (A+B) = A.B AND A.B = A.B = (A +B ) OR
Analysis of Clocked Sequential Circuits
 Objectives Analysis of Clocked Sequential Circuits The objectives of this lesson are as follows: Analysis of clocked sequential circuits with an example State Reduction with an example State assignment
Objectives Analysis of Clocked Sequential Circuits The objectives of this lesson are as follows: Analysis of clocked sequential circuits with an example State Reduction with an example State assignment
Random Number Generator Digital Design - Demo
 Understanding Digital Design The Digital Electronics 2014 Digital Design - Demo This presentation will Review the oard Game Counter block diagram. Review the circuit design of the sequential logic section
Understanding Digital Design The Digital Electronics 2014 Digital Design - Demo This presentation will Review the oard Game Counter block diagram. Review the circuit design of the sequential logic section
University of Toronto Faculty of Applied Science and Engineering Edward S. Rogers Sr. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
 University of Toronto Faculty of Applied Science and Engineering Edward S. Rogers Sr. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Final Examination ECE 241F - Digital Systems Examiners: S. Brown,
University of Toronto Faculty of Applied Science and Engineering Edward S. Rogers Sr. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Final Examination ECE 241F - Digital Systems Examiners: S. Brown,
CHAPTER 9: SEQUENTIAL CIRCUITS
 CHAPTER 9: ASYNCHRONOUS SEUENTIAL CIRCUITS Chapter Objectives 2 Sequential circuits that are not snchronized b a clock Asnchronous circuits Analsis of Asnchronous circuits Snthesis of Asnchronous circuits
CHAPTER 9: ASYNCHRONOUS SEUENTIAL CIRCUITS Chapter Objectives 2 Sequential circuits that are not snchronized b a clock Asnchronous circuits Analsis of Asnchronous circuits Snthesis of Asnchronous circuits
CE1911 LECTURE FSM DESIGN PRACTICE DAY 1
 REVIEW MATERIAL 1. Combinational circuits do not have memory. They calculate instantaneous outputs based only on current inputs. They implement basic arithmetic and logic functions. 2. Sequential circuits
REVIEW MATERIAL 1. Combinational circuits do not have memory. They calculate instantaneous outputs based only on current inputs. They implement basic arithmetic and logic functions. 2. Sequential circuits
Combinational vs. Sequential. Summary of Combinational Logic. Combinational device/circuit: any circuit built using the basic gates Expressed as
 Summary of Combinational Logic : Computer Architecture I Instructor: Prof. Bhagi Narahari Dept. of Computer Science Course URL: www.seas.gwu.edu/~bhagiweb/cs3/ Combinational device/circuit: any circuit
Summary of Combinational Logic : Computer Architecture I Instructor: Prof. Bhagi Narahari Dept. of Computer Science Course URL: www.seas.gwu.edu/~bhagiweb/cs3/ Combinational device/circuit: any circuit
Digital Fundamentals
 Digital Fundamentals Tenth Edition Floyd hapter 8 Modified by Yuttapong Jiraraksopakun Floyd, Digital Fundamentals, 10 th 2008 Pearson Education ENE, KMUTT ed 2009 ounting in Binary As you know, the binary
Digital Fundamentals Tenth Edition Floyd hapter 8 Modified by Yuttapong Jiraraksopakun Floyd, Digital Fundamentals, 10 th 2008 Pearson Education ENE, KMUTT ed 2009 ounting in Binary As you know, the binary
Decoding A Counter. svbitec.wordpress.com 1
 ecoding A ounter ecoding a counter involves determining which state in the sequence the counter is in. ifferentiate between active-high and active-low decoding. Active-HIGH decoding: output HIGH if the
ecoding A ounter ecoding a counter involves determining which state in the sequence the counter is in. ifferentiate between active-high and active-low decoding. Active-HIGH decoding: output HIGH if the
ECE/Comp Sci 352 Digital Systems Fundamentals. Charles R. Kime Section 2 Fall Logic and Computer Design Fundamentals
 University of Wisconsin - Madison ECE/Comp Sci 352 Digital Systems Fundamentals Charles R. Kime Section 2 Fall 2001 Lecture 5 Registers & Counters Part 2 Charles Kime Counters Counters are sequential circuits
University of Wisconsin - Madison ECE/Comp Sci 352 Digital Systems Fundamentals Charles R. Kime Section 2 Fall 2001 Lecture 5 Registers & Counters Part 2 Charles Kime Counters Counters are sequential circuits
BER KELEY D AV IS IR VINE LOS AN GELES RIVERS IDE SAN D IEGO S AN FRANCISCO
 UN IVERSIT Y O F CA LIFO RNI A AT BERKELEY BER KELEY D AV IS IR VINE LOS AN GELES RIVERS IDE SAN D IEGO S AN FRANCISCO SAN TA BARBA RA S AN TA CRUZ De p a r tm en t of Ele ctr i ca l En gin e e rin g a
UN IVERSIT Y O F CA LIFO RNI A AT BERKELEY BER KELEY D AV IS IR VINE LOS AN GELES RIVERS IDE SAN D IEGO S AN FRANCISCO SAN TA BARBA RA S AN TA CRUZ De p a r tm en t of Ele ctr i ca l En gin e e rin g a
Problem Set 9 Solutions
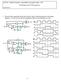 CSE 26 Digital Computers: Organization and Logical Design - 27 Jon Turner Problem Set 9 Solutions. For each of the sequential circuits shown below, draw in the missing parts of the timing diagrams. You
CSE 26 Digital Computers: Organization and Logical Design - 27 Jon Turner Problem Set 9 Solutions. For each of the sequential circuits shown below, draw in the missing parts of the timing diagrams. You
Finite State Machine. By : Ali Mustafa
 Finite State Machine By : Ali Mustafa So Far We have covered the memory elements issue and we are ready to implement the sequential circuits. We need to know how to Deal(analyze) with a sequential circuit?
Finite State Machine By : Ali Mustafa So Far We have covered the memory elements issue and we are ready to implement the sequential circuits. We need to know how to Deal(analyze) with a sequential circuit?
Different encodings generate different circuits
 FSM State Encoding Different encodings generate different circuits no easy way to find best encoding with fewest logic gates or shortest propagation delay. Binary encoding: K states need log 2 K bits i.e.,
FSM State Encoding Different encodings generate different circuits no easy way to find best encoding with fewest logic gates or shortest propagation delay. Binary encoding: K states need log 2 K bits i.e.,
ECEN 248: INTRODUCTION TO DIGITAL SYSTEMS DESIGN. Week 7 Dr. Srinivas Shakkottai Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering
 ECEN 248: INTRODUCTION TO DIGITAL SYSTEMS DESIGN Week 7 Dr. Srinivas Shakkottai Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering SEQUENTIAL CIRCUITS: LATCHES Overview Circuits require memory to store intermediate
ECEN 248: INTRODUCTION TO DIGITAL SYSTEMS DESIGN Week 7 Dr. Srinivas Shakkottai Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering SEQUENTIAL CIRCUITS: LATCHES Overview Circuits require memory to store intermediate
Sequential logic and design
 Principles Of Digital Design Sequential logic and design Analysis State-based (Moore) Input-based (Mealy) FSM definition Synthesis State minimization Encoding Optimization and timing Copyright 20-20by
Principles Of Digital Design Sequential logic and design Analysis State-based (Moore) Input-based (Mealy) FSM definition Synthesis State minimization Encoding Optimization and timing Copyright 20-20by
CARLETON UNIVERSITY Final EXAMINATION April 13, 2009: 14:00
 RLETON UNIVERSITY Final EXMINTION pril 3, 29: 4: Name: Number: Signature: URTION: 3 HOURS No. of Students: 250 epartment Name & ourse Number: Electronics ELE 2607, and ourse Instructor(s) J. W. Rogers
RLETON UNIVERSITY Final EXMINTION pril 3, 29: 4: Name: Number: Signature: URTION: 3 HOURS No. of Students: 250 epartment Name & ourse Number: Electronics ELE 2607, and ourse Instructor(s) J. W. Rogers
King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals College of Computer Science and Engineering Computer Engineering Department
 King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals College of Computer Science and Engineering Computer Engineering Department Page of COE 22: Digital Logic Design (3--3) Term (Fall 22) Final Exam Sunday January
King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals College of Computer Science and Engineering Computer Engineering Department Page of COE 22: Digital Logic Design (3--3) Term (Fall 22) Final Exam Sunday January
Design at the Register Transfer Level
 Week-7 Design at the Register Transfer Level Algorithmic State Machines Algorithmic State Machine (ASM) q Our design methodologies do not scale well to real-world problems. q 232 - Logic Design / Algorithmic
Week-7 Design at the Register Transfer Level Algorithmic State Machines Algorithmic State Machine (ASM) q Our design methodologies do not scale well to real-world problems. q 232 - Logic Design / Algorithmic
CPE100: Digital Logic Design I
 Chapter 3 Professor Brendan Morris, SEB 3216, brendan.morris@unlv.edu http://www.ee.unlv.edu/~b1morris/cpe1/ CPE1: Digital Logic Design I Section 14: Dr. Morris Sequential Logic Design Chapter 3 Chapter
Chapter 3 Professor Brendan Morris, SEB 3216, brendan.morris@unlv.edu http://www.ee.unlv.edu/~b1morris/cpe1/ CPE1: Digital Logic Design I Section 14: Dr. Morris Sequential Logic Design Chapter 3 Chapter
14.1. Unit 14. State Machine Design
 4. Unit 4 State Machine Design 4.2 Outcomes I can create a state diagram to solve a sequential problem I can implement a working state machine given a state diagram STATE MACHINES OVERVIEW 4.3 4.4 Review
4. Unit 4 State Machine Design 4.2 Outcomes I can create a state diagram to solve a sequential problem I can implement a working state machine given a state diagram STATE MACHINES OVERVIEW 4.3 4.4 Review
Digital Logic Design - Chapter 5
 Digital Logic Design - Chapter 5 S. Design a 2-bit binary up counter a) using positive-edge-triggered D flip-flops. b) using positive-edge-triggered T flip-flops. c) using positive-edge-triggered JK flip-flops.
Digital Logic Design - Chapter 5 S. Design a 2-bit binary up counter a) using positive-edge-triggered D flip-flops. b) using positive-edge-triggered T flip-flops. c) using positive-edge-triggered JK flip-flops.
Chapter 2. Review of Digital Systems Design
 x 2-4 = 42.625. Chapter 2 Review of Digital Systems Design Numbering Systems Decimal number may be expressed as powers of 10. For example, consider a six digit decimal number 987654, which can be represented
x 2-4 = 42.625. Chapter 2 Review of Digital Systems Design Numbering Systems Decimal number may be expressed as powers of 10. For example, consider a six digit decimal number 987654, which can be represented
Logical design of digital systems
 21062017 lectures Summer Semester 2017 Table of content 1 Combinational circuit design 2 Elementary combinatorial circuits for data transmission 3 Memory structures 4 Programmable logic devices 5 Algorithmic
21062017 lectures Summer Semester 2017 Table of content 1 Combinational circuit design 2 Elementary combinatorial circuits for data transmission 3 Memory structures 4 Programmable logic devices 5 Algorithmic
Let s now begin to formalize our analysis of sequential machines Powerful methods for designing machines for System control Pattern recognition Etc.
 Finite State Machines Introduction Let s now begin to formalize our analysis of sequential machines Powerful methods for designing machines for System control Pattern recognition Etc. Such devices form
Finite State Machines Introduction Let s now begin to formalize our analysis of sequential machines Powerful methods for designing machines for System control Pattern recognition Etc. Such devices form
Analysis and Design of Sequential Circuits: Examples
 COSC3410 Analysis and Design of Sequential Circuits: Examples J. C. Huang Department of Computer Science University of Houston Sequential machine slide 1 inputs combinational circuit outputs memory elements
COSC3410 Analysis and Design of Sequential Circuits: Examples J. C. Huang Department of Computer Science University of Houston Sequential machine slide 1 inputs combinational circuit outputs memory elements
Design of Sequential Circuits
 Design of Sequential Circuits Seven Steps: Construct a state diagram (showing contents of flip flop and inputs with next state) Assign letter variables to each flip flop and each input and output variable
Design of Sequential Circuits Seven Steps: Construct a state diagram (showing contents of flip flop and inputs with next state) Assign letter variables to each flip flop and each input and output variable
EE201l Homework # 6. Microprogrammed Control Unit Design
 EE201l Homework # 6 Microprogrammed ontrol Unit Design Instructor: G. Puvvada 1. Refer to the design of the microprogrammed control unit for the change dispenser discussed in your class notes Assume that
EE201l Homework # 6 Microprogrammed ontrol Unit Design Instructor: G. Puvvada 1. Refer to the design of the microprogrammed control unit for the change dispenser discussed in your class notes Assume that
SRC Language Conventions. Class 6: Intro to SRC Simulator Register Transfers and Logic Circuits. SRC Simulator Demo. cond_br.asm.
 Fall 2006 S333: omputer rchitecture University of Virginia omputer Science Michele o SR Language onventions lass 6: Intro to SR Simulator Register Transfers and Logic ircuits hapter 2, ppendix.5 2 SR Simulator
Fall 2006 S333: omputer rchitecture University of Virginia omputer Science Michele o SR Language onventions lass 6: Intro to SR Simulator Register Transfers and Logic ircuits hapter 2, ppendix.5 2 SR Simulator
FSM model for sequential circuits
 1 FSM model for sequential circuits The mathematical model of a sequential circuit is called finite-state machine. FSM is fully characterized by: S Finite set of states ( state ~ contents of FFs) I Finite
1 FSM model for sequential circuits The mathematical model of a sequential circuit is called finite-state machine. FSM is fully characterized by: S Finite set of states ( state ~ contents of FFs) I Finite
Synchronous Sequential Logic Part I. BME208 Logic Circuits Yalçın İŞLER
 Synchronous Sequential Logic Part I BME28 Logic Circuits Yalçın İŞLER islerya@yahoo.com http://me.islerya.com Sequential Logic Digital circuits we have learned, so far, have been combinational no memory,
Synchronous Sequential Logic Part I BME28 Logic Circuits Yalçın İŞLER islerya@yahoo.com http://me.islerya.com Sequential Logic Digital circuits we have learned, so far, have been combinational no memory,
Finite State Machine (FSM)
 Finite State Machine (FSM) Consists of: State register Stores current state Loads next state at clock edge Combinational logic Computes the next state Computes the outputs S S Next State CLK Current State
Finite State Machine (FSM) Consists of: State register Stores current state Loads next state at clock edge Combinational logic Computes the next state Computes the outputs S S Next State CLK Current State
CDA 3200 Digital Systems. Instructor: Dr. Janusz Zalewski Developed by: Dr. Dahai Guo Spring 2012
 CDA 3200 Digital Systems Instructor: Dr. Janusz Zalewski Developed by: Dr. Dahai Guo Spring 2012 Outline Registers and Register Transfers Shift Registers Design of Binary Counters Counters for Other Sequences
CDA 3200 Digital Systems Instructor: Dr. Janusz Zalewski Developed by: Dr. Dahai Guo Spring 2012 Outline Registers and Register Transfers Shift Registers Design of Binary Counters Counters for Other Sequences
CSE370 HW6 Solutions (Winter 2010)
 SE370 HW6 Solutions (Winter 2010) 1. L2e, 6.10 For this problem we are given a blank waveform with clock and input and asked to draw out the how different flip-flops and latches would behave. LK a) b)
SE370 HW6 Solutions (Winter 2010) 1. L2e, 6.10 For this problem we are given a blank waveform with clock and input and asked to draw out the how different flip-flops and latches would behave. LK a) b)
Clocked Sequential Circuits UNIT 13 ANALYSIS OF CLOCKED SEQUENTIAL CIRCUITS. Analysis of Clocked Sequential Circuits. Signal Tracing and Timing Charts
 ed Sequential Circuits 2 Contents nalysis by signal tracing & timing charts State tables and graphs General models for sequential circuits sequential parity checker Reading Unit 3 asic unit Unit : Latch
ed Sequential Circuits 2 Contents nalysis by signal tracing & timing charts State tables and graphs General models for sequential circuits sequential parity checker Reading Unit 3 asic unit Unit : Latch
Computer Science Final Examination Friday December 14 th 2001
 Computer Science 03 60 265 Final Examination Friday December 14 th 2001 Dr. Robert D. Kent and Dr. Alioune Ngom Last Name: First Name: Student Number: INSTRUCTIONS EXAM DURATION IS 3 HOURs. CALCULATORS,
Computer Science 03 60 265 Final Examination Friday December 14 th 2001 Dr. Robert D. Kent and Dr. Alioune Ngom Last Name: First Name: Student Number: INSTRUCTIONS EXAM DURATION IS 3 HOURs. CALCULATORS,
Module 10: Sequential Circuit Design
 Module : Sequential Circuit esign Wakerly: Chapter 7 (Part 3) : ECE 3233 r. Keith A. eague Spring 23 REA Chapter 7 (skipping references to HL) 23 -Machine esign and Synthesis he creative part, like writing
Module : Sequential Circuit esign Wakerly: Chapter 7 (Part 3) : ECE 3233 r. Keith A. eague Spring 23 REA Chapter 7 (skipping references to HL) 23 -Machine esign and Synthesis he creative part, like writing
COE 202: Digital Logic Design Sequential Circuits Part 3. Dr. Ahmad Almulhem ahmadsm AT kfupm Phone: Office:
 COE 202: Digital Logic Design Sequential Circuits Part 3 Dr. Ahmad Almulhem Email: ahmadsm AT kfupm Phone: 860-7554 Office: 22-324 Objectives State Reduction and Assignment Design of Synchronous Sequential
COE 202: Digital Logic Design Sequential Circuits Part 3 Dr. Ahmad Almulhem Email: ahmadsm AT kfupm Phone: 860-7554 Office: 22-324 Objectives State Reduction and Assignment Design of Synchronous Sequential
14:332:231 DIGITAL LOGIC DESIGN
 14:332:231 IGITL LOGI ESIGN Ivan Marsic, Rutgers University Electrical & omputer Engineering all 2013 Lecture #17: locked Synchronous -Machine nalysis locked Synchronous Sequential ircuits lso known as
14:332:231 IGITL LOGI ESIGN Ivan Marsic, Rutgers University Electrical & omputer Engineering all 2013 Lecture #17: locked Synchronous -Machine nalysis locked Synchronous Sequential ircuits lso known as
Review for B33DV2-Digital Design. Digital Design
 Review for B33DV2 The Elements of Modern Behaviours Design Representations Blocks Waveforms Gates Truth Tables Boolean Algebra Switches Rapid Prototyping Technologies Circuit Technologies TTL MOS Simulation
Review for B33DV2 The Elements of Modern Behaviours Design Representations Blocks Waveforms Gates Truth Tables Boolean Algebra Switches Rapid Prototyping Technologies Circuit Technologies TTL MOS Simulation
Show that the dual of the exclusive-or is equal to its compliment. 7
 Darshan Institute of ngineering and Technology, Rajkot, Subject: Digital lectronics (2300) GTU Question ank Unit Group Questions Do as directed : I. Given that (6)0 = (00)x, find the value of x. II. dd
Darshan Institute of ngineering and Technology, Rajkot, Subject: Digital lectronics (2300) GTU Question ank Unit Group Questions Do as directed : I. Given that (6)0 = (00)x, find the value of x. II. dd
CPE100: Digital Logic Design I
 Professor Brendan Morris, SEB 3216, brendan.morris@unlv.edu CPE100: Digital Logic Design I Final Review http://www.ee.unlv.edu/~b1morris/cpe100/ 2 Logistics Tuesday Dec 12 th 13:00-15:00 (1-3pm) 2 hour
Professor Brendan Morris, SEB 3216, brendan.morris@unlv.edu CPE100: Digital Logic Design I Final Review http://www.ee.unlv.edu/~b1morris/cpe100/ 2 Logistics Tuesday Dec 12 th 13:00-15:00 (1-3pm) 2 hour
Digital Circuit Engineering
 Digital Circuit Engineering 2nd Distributive ( A)( B) = AB Circuits that work in a sequence of steps Absorption A = A A= THESE CICUITS NEED STOAGE TO EMEMBE WHEE THEY AE STOAGE D MU G M MU G S CLK D Flip
Digital Circuit Engineering 2nd Distributive ( A)( B) = AB Circuits that work in a sequence of steps Absorption A = A A= THESE CICUITS NEED STOAGE TO EMEMBE WHEE THEY AE STOAGE D MU G M MU G S CLK D Flip
Analysis of clocked sequential networks
 Analysis of clocked sequential networks keywords: Mealy, Moore Consider : a sequential parity checker an 8th bit is added to each group of 7 bits such that the total # of 1 bits is odd for odd parity if
Analysis of clocked sequential networks keywords: Mealy, Moore Consider : a sequential parity checker an 8th bit is added to each group of 7 bits such that the total # of 1 bits is odd for odd parity if
ENGG 1203 Tutorial _03 Laboratory 3 Build a ball counter. Lab 3. Lab 3 Gate Timing. Lab 3 Steps in designing a State Machine. Timing diagram of a DFF
 ENGG 1203 Tutorial _03 Laboratory 3 Build a ball counter Timing diagram of a DFF Lab 3 Gate Timing difference timing for difference kind of gate, cost dependence (1) Setup Time = t2-t1 (2) Propagation
ENGG 1203 Tutorial _03 Laboratory 3 Build a ball counter Timing diagram of a DFF Lab 3 Gate Timing difference timing for difference kind of gate, cost dependence (1) Setup Time = t2-t1 (2) Propagation
Digital Circuits and Systems
 EE201: Digital Circuits and Systems 4 Sequential Circuits page 1 of 11 EE201: Digital Circuits and Systems Section 4 Sequential Circuits 4.1 Overview of Sequential Circuits: Definition The circuit whose
EE201: Digital Circuits and Systems 4 Sequential Circuits page 1 of 11 EE201: Digital Circuits and Systems Section 4 Sequential Circuits 4.1 Overview of Sequential Circuits: Definition The circuit whose
Fundamentals of Digital Design
 Fundamentals of Digital Design Digital Radiation Measurement and Spectroscopy NE/RHP 537 1 Binary Number System The binary numeral system, or base-2 number system, is a numeral system that represents numeric
Fundamentals of Digital Design Digital Radiation Measurement and Spectroscopy NE/RHP 537 1 Binary Number System The binary numeral system, or base-2 number system, is a numeral system that represents numeric
Digital Design. Sequential Logic
 Principles Of igital esign Chapter 6 Sequential Logic Chapter preview Boolean algebra 3 Logic gates and flip-flops 3 Finite-state machine 6 Logic design techniques 4 Sequential design techniques 6 Binary
Principles Of igital esign Chapter 6 Sequential Logic Chapter preview Boolean algebra 3 Logic gates and flip-flops 3 Finite-state machine 6 Logic design techniques 4 Sequential design techniques 6 Binary
University of Toronto Faculty of Applied Science and Engineering Edward S. Rogers Sr. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
 University of Toronto Faculty of Applied Science and Engineering Edward S. Rogers Sr. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Final Examination ECE 241F - Digital Systems Examiners: J. Rose and
University of Toronto Faculty of Applied Science and Engineering Edward S. Rogers Sr. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Final Examination ECE 241F - Digital Systems Examiners: J. Rose and
Counters. We ll look at different kinds of counters and discuss how to build them
 Counters We ll look at different kinds of counters and discuss how to build them These are not only examples of sequential analysis and design, but also real devices used in larger circuits 1 Introducing
Counters We ll look at different kinds of counters and discuss how to build them These are not only examples of sequential analysis and design, but also real devices used in larger circuits 1 Introducing
Example: A vending machine
 Lecture 22 Logistics HW8 due Monday (6/2), HW9 due Friday (6/6) Ant extra credit due 6/6 Take home extra credit final handed out 6/6 Final exam 6/9 8:30am Review? Last lecture Simplification Today State
Lecture 22 Logistics HW8 due Monday (6/2), HW9 due Friday (6/6) Ant extra credit due 6/6 Take home extra credit final handed out 6/6 Final exam 6/9 8:30am Review? Last lecture Simplification Today State
EE40 Lec 15. Logic Synthesis and Sequential Logic Circuits
 EE40 Lec 15 Logic Synthesis and Sequential Logic Circuits Prof. Nathan Cheung 10/20/2009 Reading: Hambley Chapters 7.4-7.6 Karnaugh Maps: Read following before reading textbook http://www.facstaff.bucknell.edu/mastascu/elessonshtml/logic/logic3.html
EE40 Lec 15 Logic Synthesis and Sequential Logic Circuits Prof. Nathan Cheung 10/20/2009 Reading: Hambley Chapters 7.4-7.6 Karnaugh Maps: Read following before reading textbook http://www.facstaff.bucknell.edu/mastascu/elessonshtml/logic/logic3.html
Hardware testing and design for testability. EE 3610 Digital Systems
 EE 3610: Digital Systems 1 Hardware testing and design for testability Introduction A Digital System requires testing before and after it is manufactured 2 Level 1: behavioral modeling and test benches
EE 3610: Digital Systems 1 Hardware testing and design for testability Introduction A Digital System requires testing before and after it is manufactured 2 Level 1: behavioral modeling and test benches
11.1 As mentioned in Experiment 10, sequential logic circuits are a type of logic circuit where the output of
 EE 2449 Experiment 11 Jack Levine and Nancy Warter-Perez CALIFORNIA STATE UNIVERSITY LOS ANGELES Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering EE-2449 Digital Logic Lab EXPERIMENT 11 SEQUENTIAL CIRCUITS
EE 2449 Experiment 11 Jack Levine and Nancy Warter-Perez CALIFORNIA STATE UNIVERSITY LOS ANGELES Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering EE-2449 Digital Logic Lab EXPERIMENT 11 SEQUENTIAL CIRCUITS
Logic Design II (17.342) Spring Lecture Outline
 Logic Design II (17.342) Spring 2012 Lecture Outline Class # 10 April 12, 2012 Dohn Bowden 1 Today s Lecture First half of the class Circuits for Arithmetic Operations Chapter 18 Should finish at least
Logic Design II (17.342) Spring 2012 Lecture Outline Class # 10 April 12, 2012 Dohn Bowden 1 Today s Lecture First half of the class Circuits for Arithmetic Operations Chapter 18 Should finish at least
Digital Logic Appendix A
 Digital Logic Appendix A Boolean Algebra Gates Combinatorial Circuits Sequential Circuits 1 Boolean Algebra George Boole ideas 1854 Claude Shannon, apply to circuit design, 1938 Describe digital circuitry
Digital Logic Appendix A Boolean Algebra Gates Combinatorial Circuits Sequential Circuits 1 Boolean Algebra George Boole ideas 1854 Claude Shannon, apply to circuit design, 1938 Describe digital circuitry
