Luleå Tekniska Universitet Kurskod SMD098 Tentamensdatum
|
|
|
- Berniece Payne
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Luleå Tekniska Universitet Kurskod SMD098 Tentamensdatum Skrivtid 4 timmar Tentamen i Beräkningsstrukturer Antal uppgifter: 6 Max poäng: 30 Betygsgränser: >20 poäng 4 >25 poäng 5 Betygsgränser kan komma att sänkas, dock ej höjas. Tentamen ger enbart betyget U, 4 eller 5. Har studenten fått godkänt på den praktiska delen av kursen ger detta betyget 3 även om resultatet på tentamen är ett U. Lärare: Tel: 2459 Jonas Thor Tillåtna hjälpmedel: Inga förutom skrivmaterial! Längst bak i tentamen hittar ni en guide till VHDL syntax. Frågorna besvaras på själva tentamen och lösblad. Lämna in tentamen och lösblad. Svaren skrives på svenska. Lycka till! 1
2 1. Xilinx XC4000 Configurable Logic Block (CLB) (5p) You have the following VHDL code library ieee; use ieee.std_logic_1164.all; entity Logic is port ( Clk : in std_logic; -- Clock Reset : in std_logic; -- Reset Enable : in std_logic; -- Clock Enable A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, I : in std_logic; -- Logic Inputs Y : out std_logic); -- Output end Logic; architecture RTL of Logic is process(clk, Reset) if Reset = 1 then Y <= 0 ; elsif rising_edge(clk) then if Enable = 1 then Y <= (A and B and C and D) xor E xor (F or G or H or I); end if; end if; end process; end RTL; a) Draw the schematics of the VHDL model below. (1p) 2
3 b) The modeled logic can be implemented in a single Xilinx XC4000 CLB. In the figure below, clearly indicate how the CLB is configured. Name the inputs/outputs as they are defined in the VHDL source. Use a pen to indicate what connections and resources are used. Show how the multiplexers are configured by drawing a line through them, from one input to the output. (2p) C 1 C 4 4 H 1 D IN /H 2 SR/H0 EC G 4 G 3 G 2 LOGIC FUNCTION G' OF G1-G4 DIN F' G' H' S/R CONTROL D SD Q Bypass YQ G 1 LOGIC FUNCTION OF H' F', G', AND H1 G' H' 1 EC RD Y F 4 F 3 F 2 LOGIC FUNCTION OF F1-F4 F' DIN F' G' H' S/R CONTROL D SD Q Bypass XQ F 1 K (CLOCK) H' F' 1 EC RD X Multiplexer Controlled by Configuration Program X6692 3
4 c) You probably used the Look-Up Tables (LUT) F, G and H in b). What are the contents of the LUTs, i.e. how are they programmed. Complete the tables below. (2p) F1 F2 F3 F4 F G1 G2 G3 G4 G F G H1 H
5 2. Manual synthesis (5p, 1p each) Here you are given five different VHDL models. Your task is to draw the schematics of the VHDL models. Use gates, multiplexers, flip-flops etc. Clearly mark the names of the inputs/outputs as indicated in the VHDL source. a) library ieee; use ieee.std_logic_1164.all; entity Signals is port ( Clk : in std_logic; -- Clock A, B, C : in std_logic; -- Inputs Y, X : out std_logic); -- Outputs end Signals; architecture RTL of Signals is signal S1, S2 : std_logic; process(clk) if rising_edge(clk) then S1 <= A and B; S2 <= S1 or C; X <= S1; Y <= S2; end if; end process; end RTL; 5
6 b) library ieee; use ieee.std_logic_1164.all; entity Variables is port ( Clk : in std_logic; -- Clock A, B, C : in std_logic; -- Inputs Y, X : out std_logic); -- Outputs end Variables; architecture RTL of Variables is process(clk) variable V1, V2 : std_logic; if rising_edge(clk) then V1 := A and B; V2 := V1 or C; X <= V1; Y <= V2; end if; end process; end RTL; 6
7 c) library ieee; use ieee.std_logic_1164.all; entity Logic is port ( A, B, C, D, E, F : in std_logic; Y : out std_logic ); end Logic; architecture RTL of Logic is Y <= A when D = 1 else Z ; Y <= B when E = 1 else Z ; Y <= C when F = 1 else Z ; end RTL; 7
8 d) library ieee; use ieee.std_logic_1164.all; entity Astrid is port ( Clk : in std_logic; -- Clock A : in std_logic; -- Inputs Y : out std_logic); -- Outputs end Astrid; architecture RTL of Astrid is signal B, C : std_logic; process(clk) if rising_edge(clk) then C <= B; Y <= C; B <= A; end if; end process; end RTL; 8
9 e) library ieee; use ieee.std_logic_1164.all; entity Kerstin is port ( Clk : in std_logic; -- Clock A : in std_logic; -- Inputs Y : out std_logic); -- Outputs end Kerstin; architecture RTL of Kerstin is process(clk) variable B, C : std_logic; if rising_edge(clk) then C := B; Y <= C; B := A; end if; end process; end RTL; 9
10 3. Synchronous design and timing (5p, 1p each) a) What does the acronym RTL stand for? Give a definition of RTL. b) Draw a timing diagram for a D flip-flop. The timing diagram must show the three important parameters, setup time, hold time and clock-to-output delay. 10
11 c) In the circuit shown below mark the short path and the long path also specify the delays for both paths. The delay of each gate is shown above the gate. Reg A 4 ns 2 ns Reg B 2 ns 1 ns Reg D Reg C Clock d) Now assume that the hold-time for the flip-flops in c) is.5 ns, the setup-time for the flip-flops are 1.5 ns and the clock-to-output delay for the flip-flops are.8 ns. Assuming that we have no clock skew, what is the minimum clock period? Explain and show your calculations 11
12 e) We have the same circuit, but there is clock skew between the input flip-flops and the output flip-flop as indicated in the figure below. The timing parameters for the flipflops are the same as in d). What is the maximum clock skew in order to guarantee failsafe operation? Explain and show your calculations. Reg A 4 ns 2 ns Reg B 2 ns 1 ns Reg D Reg C Clock t skew 12
13 4. State machine design (5 points) Here you will design a Moore finite state machine that controls three LEDs (sw: lysdioder). A simple block diagram of the design is shown in the figure below. Moore FSM L1 Control[1:0] L2 Reset L3 Clk The LEDs will be lit in different sequences depending on the Control input. Only one or zero LEDs are lit at the same time. When Reset is active, all LEDs will be off. The table below shows a functional description of the FSM. Reset (asynch) Control Sequence 1 -- All LEDs are off 0 00 L1 L2 L3 L1 L2 L L3 L2 L1 L3 L2 L L1 L2 L1 L2 L1 L L2 L3 L2 L3 L2 L3... For instance L1 L2 means that in the first clock cycle L1 is lit and in the next clock cycle L2 is lit. Draw a bubble diagram of your Moore FSM and write a VHDL model of the FSM using the entity declaration below. library ieee; use ieee.std_logic_1164.all; entity FSM is port ( Clk : in std_logic; -- Clock : in std_logic; -- Active high asynch reset Reset Control : in std_logic_vector(1 downto 0); L1, L2, L3 : out std_logic -- LED Outputs ); end FSM; 13
14 5. Various questions (5p, 1p each) 1. How are buses with multiple drivers modeled in VHDL? What is the difference between the std_u_logic and std_logic types? 2. The symbol for a 2 1 multiplexer is shown below. Use two tri-state buffers, with active high enable, and an inverter to implement the same functionality. Draw the schematics. A B Sel 0 1 Y 3. Write two VHDL processes, one describing the behavior of a 2-1 multiplexer implemented in gates or LUTs and one process that implements the 2-1 multiplexer with tri-state buffers. 4. Give three reasons why asynchronous designs are more complex than synchronous designs. 5. What is metastability? When can metastability occur? 14
15 6. Implementation technologies (5p) a) Describe the internal structure of a PAL. (0.5p) b) Name four technologies used to program programmable logic. (0.5p) c) FPGA, Full Custom, CPLD, PAL, Standard Cell and Gate Array are six technologies for programmable logic. i. Sort these in order of density (highest lowest). (0.5p) ii. Sort these in order of performance (highest lowest). (0.5p) d) Your company is manufacturing a simple digital circuit board, which needs new chip select logic. Which technology will you use to construct this? Motivate. (1p) e) You are in a hurry to create prototypes to an advanced digital chip. The prototype will be used as a base for a production run of a few thousand samples. Which technologies will you use for the prototypes and the production series respectively? Motivate. (1p) f) The new product to be ready for sale in two years is expected to sell large volumes. It requires handling of both digital and analog signals within a very small surface area. You want to realize this in one single chip. Which technology will you choose? Motivate. (1p) 15
ECE 448 Lecture 6. Finite State Machines. State Diagrams, State Tables, Algorithmic State Machine (ASM) Charts, and VHDL Code. George Mason University
 ECE 448 Lecture 6 Finite State Machines State Diagrams, State Tables, Algorithmic State Machine (ASM) Charts, and VHDL Code George Mason University Required reading P. Chu, FPGA Prototyping by VHDL Examples
ECE 448 Lecture 6 Finite State Machines State Diagrams, State Tables, Algorithmic State Machine (ASM) Charts, and VHDL Code George Mason University Required reading P. Chu, FPGA Prototyping by VHDL Examples
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences Introductory Digital Systems Lab (6.111) Quiz #1 - Spring 2003 Prof. Anantha Chandrakasan and Prof. Don
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences Introductory Digital Systems Lab (6.111) Quiz #1 - Spring 2003 Prof. Anantha Chandrakasan and Prof. Don
COE 328 Final Exam 2008
 COE 328 Final Exam 2008 1. Design a comparator that compares a 4 bit number A to a 4 bit number B and gives an Output F=1 if A is not equal B. You must use 2 input LUTs only. 2. Given the following logic
COE 328 Final Exam 2008 1. Design a comparator that compares a 4 bit number A to a 4 bit number B and gives an Output F=1 if A is not equal B. You must use 2 input LUTs only. 2. Given the following logic
Written exam with solutions IE1204/5 Digital Design Monday 23/
 Written exam with solutions IE204/5 Digital Design Monday 23/0 207 4.00-8.00 General Information Examiner: Ingo Sander. Teacher: Kista, William Sandvist Exam text has to be returned when you hand in your
Written exam with solutions IE204/5 Digital Design Monday 23/0 207 4.00-8.00 General Information Examiner: Ingo Sander. Teacher: Kista, William Sandvist Exam text has to be returned when you hand in your
Written reexam with solutions for IE1204/5 Digital Design Monday 14/
 Written reexam with solutions for IE204/5 Digital Design Monday 4/3 206 4.-8. General Information Examiner: Ingo Sander. Teacher: William Sandqvist phone 08-7904487 Exam text does not have to be returned
Written reexam with solutions for IE204/5 Digital Design Monday 4/3 206 4.-8. General Information Examiner: Ingo Sander. Teacher: William Sandqvist phone 08-7904487 Exam text does not have to be returned
Preparation of Examination Questions and Exercises: Solutions
 Questions Preparation of Examination Questions and Exercises: Solutions. -bit Subtraction: DIF = B - BI B BI BO DIF 2 DIF: B BI 4 6 BI 5 BO: BI BI 4 5 7 3 2 6 7 3 B B B B B DIF = B BI ; B = ( B) BI ( B),
Questions Preparation of Examination Questions and Exercises: Solutions. -bit Subtraction: DIF = B - BI B BI BO DIF 2 DIF: B BI 4 6 BI 5 BO: BI BI 4 5 7 3 2 6 7 3 B B B B B DIF = B BI ; B = ( B) BI ( B),
Experiment 4 Decoder Encoder Design using VHDL
 Objective: Experiment 4 Decoder Encoder Design using VHDL To learn how to write VHDL code To Learn how to do functional simulation To do study of the synthesis done by VHDL and the theoretical desin obtained
Objective: Experiment 4 Decoder Encoder Design using VHDL To learn how to write VHDL code To Learn how to do functional simulation To do study of the synthesis done by VHDL and the theoretical desin obtained
Dr. Nicola Nicolici COE/EE2DI4 Midterm Test #2 Nov 22, 2006
 COE/EE2DI4 Midterm Test #2 Fall 2006 Page 1 Dr. Nicola Nicolici COE/EE2DI4 Midterm Test #2 Nov 22, 2006 Instructions: This examination paper includes 12 pages and 20 multiple-choice questions starting
COE/EE2DI4 Midterm Test #2 Fall 2006 Page 1 Dr. Nicola Nicolici COE/EE2DI4 Midterm Test #2 Nov 22, 2006 Instructions: This examination paper includes 12 pages and 20 multiple-choice questions starting
Table of Content. Chapter 11 Dedicated Microprocessors Page 1 of 25
 Chapter 11 Dedicated Microprocessors Page 1 of 25 Table of Content Table of Content... 1 11 Dedicated Microprocessors... 2 11.1 Manual Construction of a Dedicated Microprocessor... 3 11.2 FSM + D Model
Chapter 11 Dedicated Microprocessors Page 1 of 25 Table of Content Table of Content... 1 11 Dedicated Microprocessors... 2 11.1 Manual Construction of a Dedicated Microprocessor... 3 11.2 FSM + D Model
Assignment # 3 - CSI 2111(Solutions)
 Assignment # 3 - CSI 2111(Solutions) Q1. Realize, using a suitable PLA, the following functions : [10 marks] f 1 (x,y,z) = Σm(0,1,5,7) f 2 (x,y,z) = Σm(2,5,6) f 3 (x,y,z) = Σm(1,4,5,7) f 4 (x,y,z) = Σm(0,3,6)
Assignment # 3 - CSI 2111(Solutions) Q1. Realize, using a suitable PLA, the following functions : [10 marks] f 1 (x,y,z) = Σm(0,1,5,7) f 2 (x,y,z) = Σm(2,5,6) f 3 (x,y,z) = Σm(1,4,5,7) f 4 (x,y,z) = Σm(0,3,6)
Example: vending machine
 Example: vending machine Release item after 15 cents are deposited Single coin slot for dimes, nickels o change Reset Coin Sensor Vending Machine FSM Open Release Mechanism Clock Spring 2005 CSE370 - guest
Example: vending machine Release item after 15 cents are deposited Single coin slot for dimes, nickels o change Reset Coin Sensor Vending Machine FSM Open Release Mechanism Clock Spring 2005 CSE370 - guest
Written exam for IE1204/5 Digital Design with solutions Thursday 29/
 Written exam for IE4/5 Digital Design with solutions Thursday 9/ 5 9.-. General Information Examiner: Ingo Sander. Teacher: William Sandqvist phone 8-794487 Exam text does not have to be returned when
Written exam for IE4/5 Digital Design with solutions Thursday 9/ 5 9.-. General Information Examiner: Ingo Sander. Teacher: William Sandqvist phone 8-794487 Exam text does not have to be returned when
Written exam with solutions IE1204/5 Digital Design Friday 13/
 Written eam with solutions IE204/5 Digital Design Friday / 207 08.00-2.00 General Information Eaminer: Ingo Sander. Teacher: Kista, William Sandqvist tel 08-7904487 Teacher: Valhallavägen, Ahmed Hemani
Written eam with solutions IE204/5 Digital Design Friday / 207 08.00-2.00 General Information Eaminer: Ingo Sander. Teacher: Kista, William Sandqvist tel 08-7904487 Teacher: Valhallavägen, Ahmed Hemani
Chapter 7 Sequential Logic
 Chapter 7 Sequential Logic SKEE2263 Digital Systems Mun im/ismahani/izam {munim@utm.my,e-izam@utm.my,ismahani@fke.utm.my} March 28, 2016 Table of Contents 1 Intro 2 Bistable Circuits 3 FF Characteristics
Chapter 7 Sequential Logic SKEE2263 Digital Systems Mun im/ismahani/izam {munim@utm.my,e-izam@utm.my,ismahani@fke.utm.my} March 28, 2016 Table of Contents 1 Intro 2 Bistable Circuits 3 FF Characteristics
Synchronous Sequential Circuit Design. Digital Computer Design
 Synchronous Sequential Circuit Design Digital Computer Design Races and Instability Combinational logic has no cyclic paths and no races If inputs are applied to combinational logic, the outputs will always
Synchronous Sequential Circuit Design Digital Computer Design Races and Instability Combinational logic has no cyclic paths and no races If inputs are applied to combinational logic, the outputs will always
Digital Control of Electric Drives
 Digital Control of Electric Drives Logic Circuits - equential Description Form, Finite tate Machine (FM) Czech Technical University in Prague Faculty of Electrical Engineering Ver.. J. Zdenek 27 Logic
Digital Control of Electric Drives Logic Circuits - equential Description Form, Finite tate Machine (FM) Czech Technical University in Prague Faculty of Electrical Engineering Ver.. J. Zdenek 27 Logic
Problem Set 6 Solutions
 CS/EE 260 Digital Computers: Organization and Logical Design Problem Set 6 Solutions Jon Turner Quiz on 2/21/02 1. The logic diagram at left below shows a 5 bit ripple-carry decrement circuit. Draw a logic
CS/EE 260 Digital Computers: Organization and Logical Design Problem Set 6 Solutions Jon Turner Quiz on 2/21/02 1. The logic diagram at left below shows a 5 bit ripple-carry decrement circuit. Draw a logic
Appendix B. Review of Digital Logic. Baback Izadi Division of Engineering Programs
 Appendix B Review of Digital Logic Baback Izadi Division of Engineering Programs bai@engr.newpaltz.edu Elect. & Comp. Eng. 2 DeMorgan Symbols NAND (A.B) = A +B NOR (A+B) = A.B AND A.B = A.B = (A +B ) OR
Appendix B Review of Digital Logic Baback Izadi Division of Engineering Programs bai@engr.newpaltz.edu Elect. & Comp. Eng. 2 DeMorgan Symbols NAND (A.B) = A +B NOR (A+B) = A.B AND A.B = A.B = (A +B ) OR
LECTURE 2: Delay models, std_ulogic and. EECS 316 CAD Computer Aided Design. with-select-when. Chris Papachristou Case Western Reserve University
 CAD Computer Aided Design LECTURE 2: Delay models, std_ulogic and with-select-when Instructor: Francis G. Wolff wolff@eecs.cwru.edu Chris Papachristou Case Western Reserve University Review: Full Adder:
CAD Computer Aided Design LECTURE 2: Delay models, std_ulogic and with-select-when Instructor: Francis G. Wolff wolff@eecs.cwru.edu Chris Papachristou Case Western Reserve University Review: Full Adder:
7 Multipliers and their VHDL representation
 7 Multipliers and their VHDL representation 7.1 Introduction to arithmetic algorithms If a is a number, then a vector of digits A n 1:0 = [a n 1... a 1 a 0 ] is a numeral representing the number in the
7 Multipliers and their VHDL representation 7.1 Introduction to arithmetic algorithms If a is a number, then a vector of digits A n 1:0 = [a n 1... a 1 a 0 ] is a numeral representing the number in the
ECE 3401 Lecture 23. Pipeline Design. State Table for 2-Cycle Instructions. Control Unit. ISA: Instruction Specifications (for reference)
 ECE 3401 Lecture 23 Pipeline Design Control State Register Combinational Control Logic New/ Modified Control Word ISA: Instruction Specifications (for reference) P C P C + 1 I N F I R M [ P C ] E X 0 PC
ECE 3401 Lecture 23 Pipeline Design Control State Register Combinational Control Logic New/ Modified Control Word ISA: Instruction Specifications (for reference) P C P C + 1 I N F I R M [ P C ] E X 0 PC
10/12/2016. An FSM with No Inputs Moves from State to State. ECE 120: Introduction to Computing. Eventually, the States Form a Loop
 University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering An FSM with No Inputs Moves from State to State What happens if an FSM has no inputs? ECE 120: Introduction to Computing
University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering An FSM with No Inputs Moves from State to State What happens if an FSM has no inputs? ECE 120: Introduction to Computing
Written exam with solutions IE Digital Design Friday 21/
 Written exam with solutions IE204-5 Digital Design Friday 2/0 206 09.00-3.00 General Information Examiner: Ingo Sander. Teacher: Kista, William Sandvist tel 08-7904487, Elena Dubrova phone 08-790 4 4 Exam
Written exam with solutions IE204-5 Digital Design Friday 2/0 206 09.00-3.00 General Information Examiner: Ingo Sander. Teacher: Kista, William Sandvist tel 08-7904487, Elena Dubrova phone 08-790 4 4 Exam
Ch 9. Sequential Logic Technologies. IX - Sequential Logic Technology Contemporary Logic Design 1
 Ch 9. Sequential Logic Technologies Technology Contemporary Logic Design Overview Basic Sequential Logic Components FSM Design with Counters FSM Design with Programmable Logic FSM Design with More Sophisticated
Ch 9. Sequential Logic Technologies Technology Contemporary Logic Design Overview Basic Sequential Logic Components FSM Design with Counters FSM Design with Programmable Logic FSM Design with More Sophisticated
Vidyalankar. S.E. Sem. III [EXTC] Digital System Design. Q.1 Solve following : [20] Q.1(a) Explain the following decimals in gray code form
![Vidyalankar. S.E. Sem. III [EXTC] Digital System Design. Q.1 Solve following : [20] Q.1(a) Explain the following decimals in gray code form Vidyalankar. S.E. Sem. III [EXTC] Digital System Design. Q.1 Solve following : [20] Q.1(a) Explain the following decimals in gray code form](/thumbs/96/126594189.jpg) S.E. Sem. III [EXTC] Digital System Design Time : 3 Hrs.] Prelim Paper Solution [Marks : 80 Q.1 Solve following : [20] Q.1(a) Explain the following decimals in gray code form [5] (i) (42) 10 (ii) (17)
S.E. Sem. III [EXTC] Digital System Design Time : 3 Hrs.] Prelim Paper Solution [Marks : 80 Q.1 Solve following : [20] Q.1(a) Explain the following decimals in gray code form [5] (i) (42) 10 (ii) (17)
Problem Set 9 Solutions
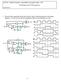 CSE 26 Digital Computers: Organization and Logical Design - 27 Jon Turner Problem Set 9 Solutions. For each of the sequential circuits shown below, draw in the missing parts of the timing diagrams. You
CSE 26 Digital Computers: Organization and Logical Design - 27 Jon Turner Problem Set 9 Solutions. For each of the sequential circuits shown below, draw in the missing parts of the timing diagrams. You
Programmable Logic Devices
 Programmable Logic Devices Mohammed Anvar P.K AP/ECE Al-Ameen Engineering College PLDs Programmable Logic Devices (PLD) General purpose chip for implementing circuits Can be customized using programmable
Programmable Logic Devices Mohammed Anvar P.K AP/ECE Al-Ameen Engineering College PLDs Programmable Logic Devices (PLD) General purpose chip for implementing circuits Can be customized using programmable
Digital Electronics Sequential Logic
 /5/27 igital Electronics Sequential Logic r. I. J. Wassell Sequential Logic The logic circuits discussed previously are known as combinational, in that the output depends only on the condition of the latest
/5/27 igital Electronics Sequential Logic r. I. J. Wassell Sequential Logic The logic circuits discussed previously are known as combinational, in that the output depends only on the condition of the latest
Introduction to the Xilinx Spartan-3E
 Introduction to the Xilinx Spartan-3E Nash Kaminski Instructor: Dr. Jafar Saniie ECE597 Illinois Institute of Technology Acknowledgment: I acknowledge that all of the work (including figures and code)
Introduction to the Xilinx Spartan-3E Nash Kaminski Instructor: Dr. Jafar Saniie ECE597 Illinois Institute of Technology Acknowledgment: I acknowledge that all of the work (including figures and code)
And Inverter Graphs. and and nand. inverter or nor xor
 And Inverter Graphs and and nand inverter or nor xor And Inverter Graphs A B gate 1 u gate 4 X C w gate 3 v gate 2 gate 5 Y A u B X w Y C v And Inverter Graphs Can represent any Boolean function: v i+1
And Inverter Graphs and and nand inverter or nor xor And Inverter Graphs A B gate 1 u gate 4 X C w gate 3 v gate 2 gate 5 Y A u B X w Y C v And Inverter Graphs Can represent any Boolean function: v i+1
MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE TIRUCHIRAPALLI
 MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE TIRUCHIRAPALLI 6 DEPARTMENT: EEE QUESTION BANK SUBJECT NAME: DIGITAL LOGIC CIRCUITS SUBJECT CODE: EE55 SEMESTER IV UNIT : Design of Synchronous Sequential Circuits PART
MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE TIRUCHIRAPALLI 6 DEPARTMENT: EEE QUESTION BANK SUBJECT NAME: DIGITAL LOGIC CIRCUITS SUBJECT CODE: EE55 SEMESTER IV UNIT : Design of Synchronous Sequential Circuits PART
ECEN 248: INTRODUCTION TO DIGITAL SYSTEMS DESIGN. Week 7 Dr. Srinivas Shakkottai Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering
 ECEN 248: INTRODUCTION TO DIGITAL SYSTEMS DESIGN Week 7 Dr. Srinivas Shakkottai Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering SEQUENTIAL CIRCUITS: LATCHES Overview Circuits require memory to store intermediate
ECEN 248: INTRODUCTION TO DIGITAL SYSTEMS DESIGN Week 7 Dr. Srinivas Shakkottai Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering SEQUENTIAL CIRCUITS: LATCHES Overview Circuits require memory to store intermediate
For smaller NRE cost For faster time to market For smaller high-volume manufacturing cost For higher performance
 University of California at Berkeley College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences EECS5 J. Wawrzynek Spring 22 2/22/2. [2 pts] Short Answers. Midterm Exam I a) [2 pts]
University of California at Berkeley College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences EECS5 J. Wawrzynek Spring 22 2/22/2. [2 pts] Short Answers. Midterm Exam I a) [2 pts]
Chapter 9. Counters and Shift Registers. Counters and Shift Registers
 Chapter 9 Counters and Shift Registers Counters and Shift Registers Counter: A Sequential Circuit that counts pulses. Used for Event Counting, Frequency Division, Timing, and Control Operations. Shift
Chapter 9 Counters and Shift Registers Counters and Shift Registers Counter: A Sequential Circuit that counts pulses. Used for Event Counting, Frequency Division, Timing, and Control Operations. Shift
University of Toronto Faculty of Applied Science and Engineering Edward S. Rogers Sr. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
 University of Toronto Faculty of Applied Science and Engineering Edward S. Rogers Sr. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Final Examination ECE 241F - Digital Systems Examiners: S. Brown,
University of Toronto Faculty of Applied Science and Engineering Edward S. Rogers Sr. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Final Examination ECE 241F - Digital Systems Examiners: S. Brown,
 vidyarthiplus.com vidyarthiplus.com vidyarthiplus.com ANNA UNIVERSITY- COMBATORE B.E./ B.TECH. DEGREE EXAMINATION - JUNE 2009. ELECTRICAL & ELECTONICS ENGG. - FOURTH SEMESTER DIGITAL LOGIC CIRCUITS PART-A
vidyarthiplus.com vidyarthiplus.com vidyarthiplus.com ANNA UNIVERSITY- COMBATORE B.E./ B.TECH. DEGREE EXAMINATION - JUNE 2009. ELECTRICAL & ELECTONICS ENGG. - FOURTH SEMESTER DIGITAL LOGIC CIRCUITS PART-A
Stop Watch (System Controller Approach)
 Stop Watch (System Controller Approach) Problem Design a stop watch that can measure times taken for two events Inputs CLK = 6 Hz RESET: Asynchronously reset everything X: comes from push button First
Stop Watch (System Controller Approach) Problem Design a stop watch that can measure times taken for two events Inputs CLK = 6 Hz RESET: Asynchronously reset everything X: comes from push button First
L4: Sequential Building Blocks (Flip-flops, Latches and Registers)
 L4: Sequential Building Blocks (Flip-flops, Latches and Registers) Acknowledgements: Lecture material adapted from R. Katz, G. Borriello, Contemporary Logic esign (second edition), Prentice-Hall/Pearson
L4: Sequential Building Blocks (Flip-flops, Latches and Registers) Acknowledgements: Lecture material adapted from R. Katz, G. Borriello, Contemporary Logic esign (second edition), Prentice-Hall/Pearson
Unit 16 Problem Solutions
 5.28 (contd) I. None II. (4, 7)ü (6, 7)ü (2, 4)ü (2, 6)ü Assignment: S =, =, =, =, = A B S Present ate Next ate W = Output S S S Present ate Next ate W = Output T input equations derived from the transition
5.28 (contd) I. None II. (4, 7)ü (6, 7)ü (2, 4)ü (2, 6)ü Assignment: S =, =, =, =, = A B S Present ate Next ate W = Output S S S Present ate Next ate W = Output T input equations derived from the transition
EECS Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems. FSMs 9/11/2007
 EECS 150 - Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems FSMs 9/11/2007 Sarah Bird Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California, Berkeley Slides borrowed from David Culler
EECS 150 - Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems FSMs 9/11/2007 Sarah Bird Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California, Berkeley Slides borrowed from David Culler
Shannon dekomposition
 Shannon dekomposition Claude Shannon matematiker/elektrotekniker 96 William Sandqvist illiam@kth.se ÖH 8.6 Visa hur en 4-to- multipleor kan användas som funktionsgenerator för att te. Generera OR-funktionen.
Shannon dekomposition Claude Shannon matematiker/elektrotekniker 96 William Sandqvist illiam@kth.se ÖH 8.6 Visa hur en 4-to- multipleor kan användas som funktionsgenerator för att te. Generera OR-funktionen.
Vidyalankar S.E. Sem. III [CMPN] Digital Logic Design and Analysis Prelim Question Paper Solution
![Vidyalankar S.E. Sem. III [CMPN] Digital Logic Design and Analysis Prelim Question Paper Solution Vidyalankar S.E. Sem. III [CMPN] Digital Logic Design and Analysis Prelim Question Paper Solution](/thumbs/90/103673562.jpg) . (a) (i) ( B C 5) H (A 2 B D) H S.E. Sem. III [CMPN] Digital Logic Design and Analysis Prelim Question Paper Solution ( B C 5) H (A 2 B D) H = (FFFF 698) H (ii) (2.3) 4 + (22.3) 4 2 2. 3 2. 3 2 3. 2 (2.3)
. (a) (i) ( B C 5) H (A 2 B D) H S.E. Sem. III [CMPN] Digital Logic Design and Analysis Prelim Question Paper Solution ( B C 5) H (A 2 B D) H = (FFFF 698) H (ii) (2.3) 4 + (22.3) 4 2 2. 3 2. 3 2 3. 2 (2.3)
Shannon decomposition
 Shannon decomposition Claude Shannon mathematician / electrical engineer 96 William Sandqvist illiam@kth.se E 8.6 Sho ho a 4-to- multipleer can e used as a "function generator" for eample to generate the
Shannon decomposition Claude Shannon mathematician / electrical engineer 96 William Sandqvist illiam@kth.se E 8.6 Sho ho a 4-to- multipleer can e used as a "function generator" for eample to generate the
Chapter 3. Digital Design and Computer Architecture, 2 nd Edition. David Money Harris and Sarah L. Harris. Chapter 3 <1>
 Chapter 3 Digital Design and Computer Architecture, 2 nd Edition David Money Harris and Sarah L. Harris Chapter 3 Chapter 3 :: Topics Introduction Latches and Flip-Flops Synchronous Logic Design Finite
Chapter 3 Digital Design and Computer Architecture, 2 nd Edition David Money Harris and Sarah L. Harris Chapter 3 Chapter 3 :: Topics Introduction Latches and Flip-Flops Synchronous Logic Design Finite
Pin Details of Digital Logic Gates:
 (1) (2) Pin Details of Digital Logic Gates: (3) Postulates and Theorems of Boolean algebra: S. No Postulate/Theorem Duality Remarks 1. X + 0 = X X.1 = X - 2. X + X = 1 X.X = 0-3. X + X = X X.X = X - 4.
(1) (2) Pin Details of Digital Logic Gates: (3) Postulates and Theorems of Boolean algebra: S. No Postulate/Theorem Duality Remarks 1. X + 0 = X X.1 = X - 2. X + X = 1 X.X = 0-3. X + X = X X.X = X - 4.
Different encodings generate different circuits
 FSM State Encoding Different encodings generate different circuits no easy way to find best encoding with fewest logic gates or shortest propagation delay. Binary encoding: K states need log 2 K bits i.e.,
FSM State Encoding Different encodings generate different circuits no easy way to find best encoding with fewest logic gates or shortest propagation delay. Binary encoding: K states need log 2 K bits i.e.,
CPE100: Digital Logic Design I
 Chapter 3 Professor Brendan Morris, SEB 3216, brendan.morris@unlv.edu http://www.ee.unlv.edu/~b1morris/cpe1/ CPE1: Digital Logic Design I Section 14: Dr. Morris Sequential Logic Design Chapter 3 Chapter
Chapter 3 Professor Brendan Morris, SEB 3216, brendan.morris@unlv.edu http://www.ee.unlv.edu/~b1morris/cpe1/ CPE1: Digital Logic Design I Section 14: Dr. Morris Sequential Logic Design Chapter 3 Chapter
Acknowledgment. DLD Lab. This set of slides on VHDL are due to Brown and Vranesic.
 Acknowledgment DLD Lab Thi et o lide on VHDL are due to Brown and Vraneic. Introduction to VHDL (Very High Speed Integrated Circuit Hardware Decription Language) 2 3 A imple logic unction and correponding
Acknowledgment DLD Lab Thi et o lide on VHDL are due to Brown and Vraneic. Introduction to VHDL (Very High Speed Integrated Circuit Hardware Decription Language) 2 3 A imple logic unction and correponding
Digital Logic and Design (Course Code: EE222) Lecture 19: Sequential Circuits Contd..
 Indian Institute of Technology Jodhpur, Year 2017-2018 Digital Logic and Design (Course Code: EE222) Lecture 19: Sequential Circuits Contd.. Course Instructor: Shree Prakash Tiwari Email: sptiwari@iitj.ac.in
Indian Institute of Technology Jodhpur, Year 2017-2018 Digital Logic and Design (Course Code: EE222) Lecture 19: Sequential Circuits Contd.. Course Instructor: Shree Prakash Tiwari Email: sptiwari@iitj.ac.in
Shannon decomposition
 Shannon decomposition Claude Shannon mathematician / electrical engineer 96 William Sandqvist illiam@kth.se E 8.6 Sho ho a 4-to- multipleer can e used as a "function generator" for eample to generate the
Shannon decomposition Claude Shannon mathematician / electrical engineer 96 William Sandqvist illiam@kth.se E 8.6 Sho ho a 4-to- multipleer can e used as a "function generator" for eample to generate the
L4: Sequential Building Blocks (Flip-flops, Latches and Registers)
 L4: Sequential Building Blocks (Flip-flops, Latches and Registers) Acknowledgements:., Materials in this lecture are courtesy of the following people and used with permission. - Randy H. Katz (University
L4: Sequential Building Blocks (Flip-flops, Latches and Registers) Acknowledgements:., Materials in this lecture are courtesy of the following people and used with permission. - Randy H. Katz (University
Ch 7. Finite State Machines. VII - Finite State Machines Contemporary Logic Design 1
 Ch 7. Finite State Machines VII - Finite State Machines Contemporary Logic esign 1 Finite State Machines Sequential circuits primitive sequential elements combinational logic Models for representing sequential
Ch 7. Finite State Machines VII - Finite State Machines Contemporary Logic esign 1 Finite State Machines Sequential circuits primitive sequential elements combinational logic Models for representing sequential
Vidyalankar S.E. Sem. III [ETRX] Digital Circuits and Design Prelim Question Paper Solution
![Vidyalankar S.E. Sem. III [ETRX] Digital Circuits and Design Prelim Question Paper Solution Vidyalankar S.E. Sem. III [ETRX] Digital Circuits and Design Prelim Question Paper Solution](/thumbs/79/79145081.jpg) S.E. Sem. III [ETRX] Digital Circuits and Design Prelim uestion Paper Solution. (a) Static Hazard Static hazards have two cases: static and static. static- hazard exists when the output variable should
S.E. Sem. III [ETRX] Digital Circuits and Design Prelim uestion Paper Solution. (a) Static Hazard Static hazards have two cases: static and static. static- hazard exists when the output variable should
EXPERIMENT Traffic Light Controller
 11.1 Objectives EXPERIMENT 11 11. Traffic Light Controller Practice on the design of clocked sequential circuits. Applications of sequential circuits. 11.2 Overview In this lab you are going to develop
11.1 Objectives EXPERIMENT 11 11. Traffic Light Controller Practice on the design of clocked sequential circuits. Applications of sequential circuits. 11.2 Overview In this lab you are going to develop
EE40 Lec 15. Logic Synthesis and Sequential Logic Circuits
 EE40 Lec 15 Logic Synthesis and Sequential Logic Circuits Prof. Nathan Cheung 10/20/2009 Reading: Hambley Chapters 7.4-7.6 Karnaugh Maps: Read following before reading textbook http://www.facstaff.bucknell.edu/mastascu/elessonshtml/logic/logic3.html
EE40 Lec 15 Logic Synthesis and Sequential Logic Circuits Prof. Nathan Cheung 10/20/2009 Reading: Hambley Chapters 7.4-7.6 Karnaugh Maps: Read following before reading textbook http://www.facstaff.bucknell.edu/mastascu/elessonshtml/logic/logic3.html
3. Complete the following table of equivalent values. Use binary numbers with a sign bit and 7 bits for the value
 EGC22 Digital Logic Fundamental Additional Practice Problems. Complete the following table of equivalent values. Binary. Octal 35.77 33.23.875 29.99 27 9 64 Hexadecimal B.3 D.FD B.4C 2. Calculate the following
EGC22 Digital Logic Fundamental Additional Practice Problems. Complete the following table of equivalent values. Binary. Octal 35.77 33.23.875 29.99 27 9 64 Hexadecimal B.3 D.FD B.4C 2. Calculate the following
RAO PAHALD SINGH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS BALANA(MOHINDER GARH)123029
 1 DIGITAL SYSTEM DESIGN LAB (EE-330-F) DIGITAL SYSTEM DESIGN LAB (EE-330-F) LAB MANUAL VI SEMESTER RAO PAHALD SINGH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS BALANA(MOHINDER GARH)123029 Department Of Electronics & Communication
1 DIGITAL SYSTEM DESIGN LAB (EE-330-F) DIGITAL SYSTEM DESIGN LAB (EE-330-F) LAB MANUAL VI SEMESTER RAO PAHALD SINGH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS BALANA(MOHINDER GARH)123029 Department Of Electronics & Communication
Clock Strategy. VLSI System Design NCKUEE-KJLEE
 Clock Strategy Clocked Systems Latch and Flip-flops System timing Clock skew High speed latch design Phase locked loop ynamic logic Multiple phase Clock distribution Clocked Systems Most VLSI systems are
Clock Strategy Clocked Systems Latch and Flip-flops System timing Clock skew High speed latch design Phase locked loop ynamic logic Multiple phase Clock distribution Clocked Systems Most VLSI systems are
Mealy & Moore Machines
 Mealy & Moore Machines Moore Machine is a finite-state machine whose output values are determined solely by its current state and can be defined as six elements (S, S 0, Σ, Λ, T, G), consisting of the
Mealy & Moore Machines Moore Machine is a finite-state machine whose output values are determined solely by its current state and can be defined as six elements (S, S 0, Σ, Λ, T, G), consisting of the
Synchronous Sequential Logic
 1 IT 201 DIGITAL SYSTEMS DESIGN MODULE4 NOTES Synchronous Sequential Logic Sequential Circuits - A sequential circuit consists of a combinational circuit and a feedback through the storage elements in
1 IT 201 DIGITAL SYSTEMS DESIGN MODULE4 NOTES Synchronous Sequential Logic Sequential Circuits - A sequential circuit consists of a combinational circuit and a feedback through the storage elements in
Faculty of Engineering. FINAL EXAMINATION FALL 2008 (December2008) ANSWER KEY
 1 McGill University Faculty of Engineering DIGITAL SYSTEM DESIGN ECSE-323 FINAL EXAMINATION FALL 2008 (December2008) ANSWER KEY STUDENT NAME McGILL I.D. NUMBER Examiner: Prof. J. Clark Signature: Associate
1 McGill University Faculty of Engineering DIGITAL SYSTEM DESIGN ECSE-323 FINAL EXAMINATION FALL 2008 (December2008) ANSWER KEY STUDENT NAME McGILL I.D. NUMBER Examiner: Prof. J. Clark Signature: Associate
ALU, Latches and Flip-Flops
 CSE14: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems ALU, Latches and Flip-Flops Tajana Simunic Rosing Where we are. Last time: ALUs Plan for today: ALU example, latches and flip flops Exam #1 grades
CSE14: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems ALU, Latches and Flip-Flops Tajana Simunic Rosing Where we are. Last time: ALUs Plan for today: ALU example, latches and flip flops Exam #1 grades
CprE 281: Digital Logic
 CprE 281: Digital Logic Instructor: Alexander Stoytchev http://www.ece.iastate.edu/~alexs/classes/ Synchronous Sequential Circuits Basic Design Steps CprE 281: Digital Logic Iowa State University, Ames,
CprE 281: Digital Logic Instructor: Alexander Stoytchev http://www.ece.iastate.edu/~alexs/classes/ Synchronous Sequential Circuits Basic Design Steps CprE 281: Digital Logic Iowa State University, Ames,
Sequential vs. Combinational
 Sequential Circuits Sequential vs. Combinational Combinational Logic: Output depends only on current input TV channel selector (-9) inputs system outputs Sequential Logic: Output depends not only on current
Sequential Circuits Sequential vs. Combinational Combinational Logic: Output depends only on current input TV channel selector (-9) inputs system outputs Sequential Logic: Output depends not only on current
CPE100: Digital Logic Design I
 Professor Brendan Morris, SEB 3216, brendan.morris@unlv.edu CPE100: Digital Logic Design I Final Review http://www.ee.unlv.edu/~b1morris/cpe100/ 2 Logistics Tuesday Dec 12 th 13:00-15:00 (1-3pm) 2 hour
Professor Brendan Morris, SEB 3216, brendan.morris@unlv.edu CPE100: Digital Logic Design I Final Review http://www.ee.unlv.edu/~b1morris/cpe100/ 2 Logistics Tuesday Dec 12 th 13:00-15:00 (1-3pm) 2 hour
Clocked Synchronous State-machine Analysis
 Clocked Synchronous State-machine Analysis Given the circuit diagram of a state machine: Analyze the combinational logic to determine flip-flop input (excitation) equations: D i = F i (Q, inputs) The input
Clocked Synchronous State-machine Analysis Given the circuit diagram of a state machine: Analyze the combinational logic to determine flip-flop input (excitation) equations: D i = F i (Q, inputs) The input
Konstruktion av Vippor och Latchar
 Konstruktion av Vippor och Latchar Datorarkitektur 1 (1DT038) Fördjupning November 2009 karl.marklund@it.uu.se Om du läser IT (1DT038) är detta material överkurs du bör dock redan vara bekant med hur det
Konstruktion av Vippor och Latchar Datorarkitektur 1 (1DT038) Fördjupning November 2009 karl.marklund@it.uu.se Om du läser IT (1DT038) är detta material överkurs du bör dock redan vara bekant med hur det
Sequential Circuits. CS/EE 3700 : Fundamentals of Digital System Design
 Sequential Circuits CS/EE 37 : Fundamentals of igital System esign Chris J. Myers Lecture 7: Flip-flops, Registers, Counters Chapter 7 Combinational output depends only on the input. Sequential output
Sequential Circuits CS/EE 37 : Fundamentals of igital System esign Chris J. Myers Lecture 7: Flip-flops, Registers, Counters Chapter 7 Combinational output depends only on the input. Sequential output
BER KELEY D AV IS IR VINE LOS AN GELES RIVERS IDE SAN D IEGO S AN FRANCISCO
 UN IVERSIT Y O F CA LIFO RNI A AT BERKELEY BER KELEY D AV IS IR VINE LOS AN GELES RIVERS IDE SAN D IEGO S AN FRANCISCO SAN TA BARBA RA S AN TA CRUZ De p a r tm en t of Ele ctr i ca l En gin e e rin g a
UN IVERSIT Y O F CA LIFO RNI A AT BERKELEY BER KELEY D AV IS IR VINE LOS AN GELES RIVERS IDE SAN D IEGO S AN FRANCISCO SAN TA BARBA RA S AN TA CRUZ De p a r tm en t of Ele ctr i ca l En gin e e rin g a
ECEN 248: INTRODUCTION TO DIGITAL SYSTEMS DESIGN. Week 9 Dr. Srinivas Shakkottai Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering
 ECEN 248: INTRODUCTION TO DIGITAL SYSTEMS DESIGN Week 9 Dr. Srinivas Shakkottai Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering TIMING ANALYSIS Overview Circuits do not respond instantaneously to input changes
ECEN 248: INTRODUCTION TO DIGITAL SYSTEMS DESIGN Week 9 Dr. Srinivas Shakkottai Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering TIMING ANALYSIS Overview Circuits do not respond instantaneously to input changes
Errata for Fundamentals of Logic Design, 5th ed, hardcover (1st printing)
 Errata for Fundamentals of Logic Design, 5th ed, hardcover (1st printing) Look on the back of the title page of the textbook (the copyright page) and you will find a line that reads either 3 4 5 6 7 06
Errata for Fundamentals of Logic Design, 5th ed, hardcover (1st printing) Look on the back of the title page of the textbook (the copyright page) and you will find a line that reads either 3 4 5 6 7 06
FSM model for sequential circuits
 1 FSM model for sequential circuits The mathematical model of a sequential circuit is called finite-state machine. FSM is fully characterized by: S Finite set of states ( state ~ contents of FFs) I Finite
1 FSM model for sequential circuits The mathematical model of a sequential circuit is called finite-state machine. FSM is fully characterized by: S Finite set of states ( state ~ contents of FFs) I Finite
Figure 6-1 Layout of Part of a Programmable Logic Cell Array
 Figure 6-1 Layout of Part of a Programmable Logic Cell Array Configurable Logic Block I/0 Block Interconnect Area Figure 6-2 Configuration Memory Cell Q WRITE DATA Q CONFIGURATION CONTROL Figure 6-3 Xilinx
Figure 6-1 Layout of Part of a Programmable Logic Cell Array Configurable Logic Block I/0 Block Interconnect Area Figure 6-2 Configuration Memory Cell Q WRITE DATA Q CONFIGURATION CONTROL Figure 6-3 Xilinx
MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE TIRUCHIRAPALLI
 DEPARTMENT: ECE MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE TIRUCHIRAPALLI 6 QUESTION BANK SUBJECT NAME: DIGITAL ELECTRONICS UNIT : Design of Sequential Circuits PART A ( Marks). Draw the logic diagram 4: Multiplexer.(AUC
DEPARTMENT: ECE MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE TIRUCHIRAPALLI 6 QUESTION BANK SUBJECT NAME: DIGITAL ELECTRONICS UNIT : Design of Sequential Circuits PART A ( Marks). Draw the logic diagram 4: Multiplexer.(AUC
Lab #10: Design of Finite State Machines
 Lab #10: Design of Finite State Machines ECE/COE 0501 Date of Experiment: 3/1/2017 Report Written: 3/4/2017 Submission Date: 3/15/2017 Nicholas Haver nicholas.haver@pitt.edu 1 H a v e r PURPOSE The purpose
Lab #10: Design of Finite State Machines ECE/COE 0501 Date of Experiment: 3/1/2017 Report Written: 3/4/2017 Submission Date: 3/15/2017 Nicholas Haver nicholas.haver@pitt.edu 1 H a v e r PURPOSE The purpose
Sequential Circuits. Circuits with state. Silvina Hanono Wachman Computer Science & Artificial Intelligence Lab M.I.T. L06-1
 Sequential Circuits Circuits with state Silvina Hanono Wachman Computer Science & Artificial Intelligence Lab M.I.T. L06-1 Combinational circuits A 0 A 1 A n-1. Sel lg(n) O Mux A B Comparator Result: LT,
Sequential Circuits Circuits with state Silvina Hanono Wachman Computer Science & Artificial Intelligence Lab M.I.T. L06-1 Combinational circuits A 0 A 1 A n-1. Sel lg(n) O Mux A B Comparator Result: LT,
Chapter 3. Chapter 3 :: Topics. Introduction. Sequential Circuits
 Chapter 3 Chapter 3 :: Topics igital esign and Computer Architecture, 2 nd Edition avid Money Harris and Sarah L. Harris Introduction Latches and Flip Flops Synchronous Logic esign Finite State Machines
Chapter 3 Chapter 3 :: Topics igital esign and Computer Architecture, 2 nd Edition avid Money Harris and Sarah L. Harris Introduction Latches and Flip Flops Synchronous Logic esign Finite State Machines
Parity Checker Example. EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 9 - Finite State Machines 1. Formal Design Process. Formal Design Process
 Parity Checker Example A string of bits has even parity if the number of 1 s in the string is even. Design a circuit that accepts a bit-serial stream of bits and outputs a 0 if the parity thus far is even
Parity Checker Example A string of bits has even parity if the number of 1 s in the string is even. Design a circuit that accepts a bit-serial stream of bits and outputs a 0 if the parity thus far is even
EXPERIMENT Bit Binary Sequential Multiplier
 12.1 Objectives EXPERIMENT 12 12. -Bit Binary Sequential Multiplier Introduction of large digital system design, i.e. data path and control path. To apply the above concepts to the design of a sequential
12.1 Objectives EXPERIMENT 12 12. -Bit Binary Sequential Multiplier Introduction of large digital system design, i.e. data path and control path. To apply the above concepts to the design of a sequential
Using Global Clock Networks
 Using Global Clock Networks Introduction Virtex-II devices support very high frequency designs and thus require low-skew advanced clock distribution. With device density up to 0 million system gates, numerous
Using Global Clock Networks Introduction Virtex-II devices support very high frequency designs and thus require low-skew advanced clock distribution. With device density up to 0 million system gates, numerous
HIGH RESOLUTIO TIME-I TERVAL MEASUREME T SYSTEMS APPLIED TO FLOW MEASUREME T. Sławomir Grzelak, Marcin Kowalski, Jarosław Czoków and Marek Zieliński
 Metrol. Meas. Syst., Vol. XXI (2014), No. 1, pp. 77 84. METROLOGY A D MEASUREME T SYSTEMS Index 330930, ISS 0860-8229 www.metrology.pg.gda.pl HIGH RESOLUTIO TIME-I TERVAL MEASUREME T SYSTEMS APPLIED TO
Metrol. Meas. Syst., Vol. XXI (2014), No. 1, pp. 77 84. METROLOGY A D MEASUREME T SYSTEMS Index 330930, ISS 0860-8229 www.metrology.pg.gda.pl HIGH RESOLUTIO TIME-I TERVAL MEASUREME T SYSTEMS APPLIED TO
University of Toronto Faculty of Applied Science and Engineering Edward S. Rogers Sr. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
 University of Toronto Faculty of Applied Science and Engineering Edward S. Rogers Sr. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Final Examination ECE 241F - Digital Systems Examiners: J. Rose and
University of Toronto Faculty of Applied Science and Engineering Edward S. Rogers Sr. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Final Examination ECE 241F - Digital Systems Examiners: J. Rose and
Fundamentals of Digital Design
 Fundamentals of Digital Design Digital Radiation Measurement and Spectroscopy NE/RHP 537 1 Binary Number System The binary numeral system, or base-2 number system, is a numeral system that represents numeric
Fundamentals of Digital Design Digital Radiation Measurement and Spectroscopy NE/RHP 537 1 Binary Number System The binary numeral system, or base-2 number system, is a numeral system that represents numeric
UNIVERSITY OF BOLTON SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING BENG (HONS) ELECTRICAL & ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING EXAMINATION SEMESTER /2017
 UNIVERSITY OF BOLTON TW35 SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING BENG (HONS) ELECTRICAL & ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING EXAMINATION SEMESTER 2-2016/2017 INTERMEDIATE DIGITAL ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATIONS MODULE NO: EEE5002
UNIVERSITY OF BOLTON TW35 SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING BENG (HONS) ELECTRICAL & ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING EXAMINATION SEMESTER 2-2016/2017 INTERMEDIATE DIGITAL ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATIONS MODULE NO: EEE5002
EGR224 F 18 Assignment #4
 EGR224 F 18 Assignment #4 ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Due Date: Friday (Section 10), October 19, by 5 pm (slide it under
EGR224 F 18 Assignment #4 ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Due Date: Friday (Section 10), October 19, by 5 pm (slide it under
CprE 281: Digital Logic
 CprE 28: Digital Logic Instructor: Alexander Stoytchev http://www.ece.iastate.edu/~alexs/classes/ Simple Processor CprE 28: Digital Logic Iowa State University, Ames, IA Copyright Alexander Stoytchev Digital
CprE 28: Digital Logic Instructor: Alexander Stoytchev http://www.ece.iastate.edu/~alexs/classes/ Simple Processor CprE 28: Digital Logic Iowa State University, Ames, IA Copyright Alexander Stoytchev Digital
Generalized FSM model: Moore and Mealy
 Lecture 18 Logistics HW7 is due on Monday (and topic included in midterm 2) Midterm 2 on Wednesday in lecture slot cover materials up to today s lecture Review session Tuesday 4:15pm in EEB125 Last lecture
Lecture 18 Logistics HW7 is due on Monday (and topic included in midterm 2) Midterm 2 on Wednesday in lecture slot cover materials up to today s lecture Review session Tuesday 4:15pm in EEB125 Last lecture
CSE140: Design of Sequential Logic
 CSE4: Design of Sequential Logic Instructor: Mohsen Imani Flip Flops 2 Counter 3 Up counter 4 Up counter 5 FSM with JK-Flip Flop 6 State Table 7 State Table 8 Circuit Minimization 9 Circuit Timing Constraints
CSE4: Design of Sequential Logic Instructor: Mohsen Imani Flip Flops 2 Counter 3 Up counter 4 Up counter 5 FSM with JK-Flip Flop 6 State Table 7 State Table 8 Circuit Minimization 9 Circuit Timing Constraints
EXAMINATION in Hardware Description and Verification
 Department of VT09 Computer Science and Engineering TDA956/DIT780 Chalmers and Gothenburg University 2009-05-27 EXAMINATION in Hardware Description and Verification DAY : 2009-05-27 TIME : 14:00-18:00
Department of VT09 Computer Science and Engineering TDA956/DIT780 Chalmers and Gothenburg University 2009-05-27 EXAMINATION in Hardware Description and Verification DAY : 2009-05-27 TIME : 14:00-18:00
Boolean Logic Continued Prof. James L. Frankel Harvard University
 Boolean Logic Continued Prof. James L. Frankel Harvard University Version of 10:18 PM 5-Sep-2017 Copyright 2017, 2016 James L. Frankel. All rights reserved. D Latch D R S Clk D Clk R S X 0 ~S 0 = R 0 ~R
Boolean Logic Continued Prof. James L. Frankel Harvard University Version of 10:18 PM 5-Sep-2017 Copyright 2017, 2016 James L. Frankel. All rights reserved. D Latch D R S Clk D Clk R S X 0 ~S 0 = R 0 ~R
Synchronous Sequential Circuit Design. Dr. Ehab A. H. AL-Hialy Page 1
 Synchronous Sequential Circuit Design Dr. Ehab A. H. AL-Hialy Page Motivation Analysis of a few simple circuits Generalizes to Synchronous Sequential Circuits (SSC) Outputs are Function of State (and Inputs)
Synchronous Sequential Circuit Design Dr. Ehab A. H. AL-Hialy Page Motivation Analysis of a few simple circuits Generalizes to Synchronous Sequential Circuits (SSC) Outputs are Function of State (and Inputs)
State Machines ELCTEC-131
 State Machines ELCTEC-131 Switch Debouncer A digital circuit that is used to remove the mechanical bounce from a switch contact. When a switch is closed, the contacts bounce from open to closed to cause
State Machines ELCTEC-131 Switch Debouncer A digital circuit that is used to remove the mechanical bounce from a switch contact. When a switch is closed, the contacts bounce from open to closed to cause
EEE2135 Digital Logic Design
 EEE2135 Digital Logic Design Chapter 7. Sequential Circuits Design 서강대학교 전자공학과 1. Model of Sequential Circuits 1) Sequential vs. Combinational Circuits a. Sequential circuits: Outputs depend on both the
EEE2135 Digital Logic Design Chapter 7. Sequential Circuits Design 서강대학교 전자공학과 1. Model of Sequential Circuits 1) Sequential vs. Combinational Circuits a. Sequential circuits: Outputs depend on both the
CSE140: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems. Midterm Information. Instructor: Mohsen Imani. Sources: TSR, Katz, Boriello & Vahid
 CSE140: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems Midterm Information Instructor: Mohsen Imani Midterm Topics In general: everything that was covered in homework 1 and 2 and related lectures,
CSE140: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems Midterm Information Instructor: Mohsen Imani Midterm Topics In general: everything that was covered in homework 1 and 2 and related lectures,
Lecture 7: Logic design. Combinational logic circuits
 /24/28 Lecture 7: Logic design Binary digital circuits: Two voltage levels: and (ground and supply voltage) Built from transistors used as on/off switches Analog circuits not very suitable for generic
/24/28 Lecture 7: Logic design Binary digital circuits: Two voltage levels: and (ground and supply voltage) Built from transistors used as on/off switches Analog circuits not very suitable for generic
CSC 322: Computer Organization Lab
 CSC 322: Computer Organization Lab Lecture 3: Logic Design Dr. Haidar M. Harmanani CSC 322: Computer Organization Lab Part I: Combinational Logic Dr. Haidar M. Harmanani Logical Design of Digital Systems
CSC 322: Computer Organization Lab Lecture 3: Logic Design Dr. Haidar M. Harmanani CSC 322: Computer Organization Lab Part I: Combinational Logic Dr. Haidar M. Harmanani Logical Design of Digital Systems
ENGG 1203 Tutorial _03 Laboratory 3 Build a ball counter. Lab 3. Lab 3 Gate Timing. Lab 3 Steps in designing a State Machine. Timing diagram of a DFF
 ENGG 1203 Tutorial _03 Laboratory 3 Build a ball counter Timing diagram of a DFF Lab 3 Gate Timing difference timing for difference kind of gate, cost dependence (1) Setup Time = t2-t1 (2) Propagation
ENGG 1203 Tutorial _03 Laboratory 3 Build a ball counter Timing diagram of a DFF Lab 3 Gate Timing difference timing for difference kind of gate, cost dependence (1) Setup Time = t2-t1 (2) Propagation
Programmable Logic Devices II
 Lecture 04: Efficient Design of Sequential Circuits Prof. Arliones Hoeller arliones.hoeller@ifsc.edu.br Prof. Marcos Moecke moecke@ifsc.edu.br 1 / 94 Reference These slides are based on the material made
Lecture 04: Efficient Design of Sequential Circuits Prof. Arliones Hoeller arliones.hoeller@ifsc.edu.br Prof. Marcos Moecke moecke@ifsc.edu.br 1 / 94 Reference These slides are based on the material made
Models for representing sequential circuits
 Sequential Circuits Models for representing sequential circuits Finite-state machines (Moore and Mealy) Representation of memory (states) Changes in state (transitions) Design procedure State diagrams
Sequential Circuits Models for representing sequential circuits Finite-state machines (Moore and Mealy) Representation of memory (states) Changes in state (transitions) Design procedure State diagrams
ELEC Digital Logic Circuits Fall 2014 Sequential Circuits (Chapter 6) Finite State Machines (Ch. 7-10)
 ELEC 2200-002 Digital Logic Circuits Fall 2014 Sequential Circuits (Chapter 6) Finite State Machines (Ch. 7-10) Vishwani D. Agrawal James J. Danaher Professor Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
ELEC 2200-002 Digital Logic Circuits Fall 2014 Sequential Circuits (Chapter 6) Finite State Machines (Ch. 7-10) Vishwani D. Agrawal James J. Danaher Professor Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
