Sequential vs. Combinational
|
|
|
- Wendy Campbell
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Sequential Circuits
2 Sequential vs. Combinational Combinational Logic: Output depends only on current input TV channel selector (-9) inputs system outputs Sequential Logic: Output depends not only on current input but also on current state of the system (which depends on past input values) TV channel selector (up-down) Need some type of memory to remember the current state 2
3 Sequential Logic Sequential Logic circuits Remember past inputs and past circuit state. Outputs from the system are fed back as new inputs. The storage elements are circuits that are capable of storing binary information: memory. 3
4 Feedback Loop Feedback: A signal s depends on another signal whose value depends on s (perhaps with several intermediate signals). s 4
5 Base of Memory Consider the following circuit: It can differentiate between two different states as it has only one feedback line that can keep one of two values, or. A circuit with n feedback lines has 2 n potential states, and that the memory of our circuit depends on the number of its feedback lines: 5
6 Synchronous vs. Asynch. Synchronous sequential circuit: the behavior can be defined from knowledge of its signal at discrete instants of time. achieves synchronization by using a timing signal called the clock. Asynchronous sequential circuit: the behavior is dependent on the order of input signal changes over continuous time, and output can change at any time (clockless). 6
7 Clock Signal Rising Clock Edge Clock generator: Periodic train of clock pulses Different duty cycles Falling Clock Edge 7
8 Clock Signal Clock is distributed throughout the whole design All components synchronizes itself with it. 8
9 Synchronous Circuits Combinational Logic clk time 9
10 SR latch (NOR version) R Q R S S Q Truth Table: Next State = F(S, R, Current State) S(t) R(t) Q(t) Q(t+) (hold) (Hold) (reset) (reset) (set) (set) Not allowed Not allowed
11 SR Latch Truth Table: Next State = F(S, R, Current State) Derived K-Map: S(t) R(t) Q(t) Q(t+) (hold) (Hold) (reset) (reset) (set) (set) Not allowed Not allowed Characteristic Equation: S R R-S Latch Q+ Q+ = S + R Q t Q
12 R=S=?? Illegal output, because When S=R=, both outputs go to zero. If both inputs now go to, the state of the SR flip flop is depends on which input remains a longer before making transition to. Hence, undefined state. MUST be avoided. 2
13 Timing Diagram Reset Hold Set Reset Set Race R S Q Q Forbidden State Forbidden State 3
14 Timing Diagram of SR Latch 4
15 SR Latch State Diagram Observed State Diagram Q Q Q Q Q Q Very difficult to observe R-S Latch in the - state Ambiguously returns to state - or - 5
16 S R Latch (NAND version) S R Q Q S R Q Q Set S R R-S Latch Q Q X Y NAND 6
17 S R Latch (NAND version) S R Q Q S R Q Q Set Hold X Y NAND 7
18 S R Latch (NAND version) S R Q Q S R Q Q Set Reset Hold X Y NAND 8
19 S R Latch (NAND version) S R Q Q X Y NAND S R Q Q Set Reset Hold Hold 9
20 S R Latch (NAND version) S R Q Q X Y NAND S R Q Q Disallowed Set Reset Hold Hold 2
21 SR Latch with Control (Enable) S S Q C R R Q S R C S R Q Q Q Q Store Reset Set Disallowed X X Q Q Store 2
22 D Latch S-R latches are useful in control applications, where we often think in terms of setting a flag in response to some condition, and resetting it when conditions change We often need latches simply to store bits presented on a signal line D latch Can eliminate the undesirable indeterminate state in the RS flip flop: ensure that inputs S and R are never simultaneously. This is done in the D latch: D C D Latch Q Q 22
23 D Latch (cont.) D S S Q C R R Q D C Q Q X Q Q S R C Q Q Q Q Store Reset Set Disallowed X X Q Q Store 23
24 D Latch Timing Diagram D C D Latch Q Q C 24
25 D-Latch Circuit D C D Latch Q Q C D Q Q+ C D Q Q C D Q+ = C.Q + C.D 25
26 D Latch with Transmission Gates 2 C= TG closes and TG2 opens Q =D and Q=D C= TG opens and TG2 closes Hold Q and Q 26
27 JK Latch J Q J, K both one yields toggle K Q J(t) K(t) Q(t) Q(t+) (hold) (Hold) (reset) (reset) (set) (set) (toggle) (toggle) J K Q Q Derived K-Map: JK Q ( t ) J-K Latch K Characteristic Equation: Q+ = Q K + Q J J 27
28 JK Latch Using SR Latch How to eliminate the forbidden state in SR? Idea: use output feedback to guarantee that R and S are never both one J, K both one yields toggle J K S R R-S latch Q Q Q Q J(t) K(t) Q(t) Q(t+ ) HOLD RESET SET Characteristic Equation: Q+ = Q K + Q J TOGGLE 28
29 JK Latch Race Condition Set Reset Toggle Toggle Correctness: Single State change per clocking event Solution: Master/Slave Flipflop 29
30 Flip-Flops Latches are transparent (= any change on the inputs is seen at the outputs immediately). This causes synchronization problems! Solution: use latches to create flipflops that can respond (update) ONLY on SPECIFIC times (instead of ANY time). 3
31 Alternatives in FF choice Type of FF RS D JK T 3
32 D-FF Timing for D Flip-Flop (Falling-Edge Trigger) Truth table 32
33 Symbols 33
34 Compare 3 Types 34
35 Rising Edge D-FF What About Falling-Edge Circuit? 35
36 Setup & Hold Time and Propagation Delay Setup time: D input must be stable for a certain amount of time before the active edge of clock cycle Hold time: D input must be stable for a certain amount of time after the active edge of the clock Propagation Delay (Clock-to-Output): from the time the clock changes to the time the output changes Propagation Delay (Data-to-Output): from the time the data changes to the time the output changes 36
37 Setup & Hold Time and Propagation Delay Setup and Hold Times for an Edge-Triggered D Flip-Flop t plh may be different from t phl t p clock-to-output vs. t p D-to-output 37
38 Timing Parameters of a D-Latch t su not met in D-latch there may be SR-like metastability. 38
39 Edge-Triggered D Flip-Flop Determination of Minimum Clock Period 39
40 Master-Slave FF configuration using SR latches Enables level-triggered behavior 4
41 S R CLK Q Q Master-Slave FF configuration using SR latches (cont.) Q Q Store Reset Set Disallowed X X Q Q Store When C=, master is enabled and stores new data, slave stores old data. When C=, master s state passes to enabled slave (Q=Y), master not sensitive to new data (disabled). Master Slave 4
42 Master-Slave J-K Flip-Flop 42
43 Master-Slave J-K Flip-Flop P P Sample inputs while clock high J Sample inputs while clock low Uses time to break feedback path from outputs to inputs! 's Set Reset Catch T oggle K C P P Q Q Master outputs Slave outputs Correct Toggle Operation 43
44 Edge-Triggered FF 's Catching: a -- glitch on the J or K inputs leads to a state change! forces designer to use hazard-free logic Solution: edge-triggered logic Negative Edge-Triggered D flipflop 4-5 gate delays setup, hold times necessary to successfully latch the input Negative edge-triggered FF when clock is high Characteristic Equation: Q+ = D 44
45 T Flip-Flop T Flip-Flop Timing Diagram for T Flip-Flop (Falling-Edge Trigger) 45
46 Implementation of T-FF Implementation of T Flip-Flop 46
47 FFs with Additional Inputs D Flip-Flop with Clock Enable The characteristic equation : The MUX output : 47
48 Asynchronous Preset/Clear Many times it is desirable to asynchronously (i.e., independent of the clock) set or reset FFs. D S Q Example: At power-up to that we can start from a known state. C R Q Asynchronous set == direct set == Preset Asynchronous reset == direct reset == Clear There may be synchronous preset and clear. 48
49 Asynchronous Set/Reset S J K R C IEEE standard graphics symbol for JK- FF with direct set & reset Cn indicates that Cn controls all other inputs whose label starts with n. In this case, C controls J and K. Function Table S R C J K Q(t+) X X X Preset X X X Clear X X X Undefined Q(t) Hold Reset Set Q(t) -- Complement 49
50 Asynchronous Inputs 5
51 Synchronous Reset 5
ECEN 248: INTRODUCTION TO DIGITAL SYSTEMS DESIGN. Week 7 Dr. Srinivas Shakkottai Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering
 ECEN 248: INTRODUCTION TO DIGITAL SYSTEMS DESIGN Week 7 Dr. Srinivas Shakkottai Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering SEQUENTIAL CIRCUITS: LATCHES Overview Circuits require memory to store intermediate
ECEN 248: INTRODUCTION TO DIGITAL SYSTEMS DESIGN Week 7 Dr. Srinivas Shakkottai Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering SEQUENTIAL CIRCUITS: LATCHES Overview Circuits require memory to store intermediate
ELCT201: DIGITAL LOGIC DESIGN
 ELCT201: DIGITAL LOGIC DESIGN Dr. Eng. Haitham Omran, haitham.omran@guc.edu.eg Dr. Eng. Wassim Alexan, wassim.joseph@guc.edu.eg Lecture 6 Following the slides of Dr. Ahmed H. Madian محرم 1439 ه Winter
ELCT201: DIGITAL LOGIC DESIGN Dr. Eng. Haitham Omran, haitham.omran@guc.edu.eg Dr. Eng. Wassim Alexan, wassim.joseph@guc.edu.eg Lecture 6 Following the slides of Dr. Ahmed H. Madian محرم 1439 ه Winter
Synchronous Sequential Logic
 1 IT 201 DIGITAL SYSTEMS DESIGN MODULE4 NOTES Synchronous Sequential Logic Sequential Circuits - A sequential circuit consists of a combinational circuit and a feedback through the storage elements in
1 IT 201 DIGITAL SYSTEMS DESIGN MODULE4 NOTES Synchronous Sequential Logic Sequential Circuits - A sequential circuit consists of a combinational circuit and a feedback through the storage elements in
L4: Sequential Building Blocks (Flip-flops, Latches and Registers)
 L4: Sequential Building Blocks (Flip-flops, Latches and Registers) Acknowledgements: Lecture material adapted from R. Katz, G. Borriello, Contemporary Logic esign (second edition), Prentice-Hall/Pearson
L4: Sequential Building Blocks (Flip-flops, Latches and Registers) Acknowledgements: Lecture material adapted from R. Katz, G. Borriello, Contemporary Logic esign (second edition), Prentice-Hall/Pearson
Chapter 7 Sequential Logic
 Chapter 7 Sequential Logic SKEE2263 Digital Systems Mun im/ismahani/izam {munim@utm.my,e-izam@utm.my,ismahani@fke.utm.my} March 28, 2016 Table of Contents 1 Intro 2 Bistable Circuits 3 FF Characteristics
Chapter 7 Sequential Logic SKEE2263 Digital Systems Mun im/ismahani/izam {munim@utm.my,e-izam@utm.my,ismahani@fke.utm.my} March 28, 2016 Table of Contents 1 Intro 2 Bistable Circuits 3 FF Characteristics
Sequential Logic. Rab Nawaz Khan Jadoon DCS. Lecturer COMSATS Lahore Pakistan. Department of Computer Science
 Sequential Logic Rab Nawaz Khan Jadoon DCS COMSATS Institute of Information Technology Lecturer COMSATS Lahore Pakistan Digital Logic and Computer Design Sequential Logic Combinational circuits with memory
Sequential Logic Rab Nawaz Khan Jadoon DCS COMSATS Institute of Information Technology Lecturer COMSATS Lahore Pakistan Digital Logic and Computer Design Sequential Logic Combinational circuits with memory
L4: Sequential Building Blocks (Flip-flops, Latches and Registers)
 L4: Sequential Building Blocks (Flip-flops, Latches and Registers) Acknowledgements:., Materials in this lecture are courtesy of the following people and used with permission. - Randy H. Katz (University
L4: Sequential Building Blocks (Flip-flops, Latches and Registers) Acknowledgements:., Materials in this lecture are courtesy of the following people and used with permission. - Randy H. Katz (University
Chapter #6: Sequential Logic Design
 Chapter #6: equential Logic esign Contemporary Logic esign No. 6- Cross-Coupled NO Gates ust like cascaded inverters, with capability to force output to (reset) or (set) \ eset Hold et eset et ace \ Forbidden
Chapter #6: equential Logic esign Contemporary Logic esign No. 6- Cross-Coupled NO Gates ust like cascaded inverters, with capability to force output to (reset) or (set) \ eset Hold et eset et ace \ Forbidden
Topic 8: Sequential Circuits
 Topic 8: Sequential Circuits Readings : Patterson & Hennesy, Appendix B.4 - B.6 Goals Basic Principles behind Memory Elements Clocks Applications of sequential circuits Introduction to the concept of the
Topic 8: Sequential Circuits Readings : Patterson & Hennesy, Appendix B.4 - B.6 Goals Basic Principles behind Memory Elements Clocks Applications of sequential circuits Introduction to the concept of the
Sequential Circuit Analysis
 Sequential Circuit Analysis Last time we started talking about latches and flip-flops, which are basic one-bit memory units. Today we ll talk about sequential circuit analysis and design. First, we ll
Sequential Circuit Analysis Last time we started talking about latches and flip-flops, which are basic one-bit memory units. Today we ll talk about sequential circuit analysis and design. First, we ll
Lecture 14: State Tables, Diagrams, Latches, and Flip Flop
 EE210: Switching Systems Lecture 14: State Tables, Diagrams, Latches, and Flip Flop Prof. YingLi Tian Nov. 6, 2017 Department of Electrical Engineering The City College of New York The City University
EE210: Switching Systems Lecture 14: State Tables, Diagrams, Latches, and Flip Flop Prof. YingLi Tian Nov. 6, 2017 Department of Electrical Engineering The City College of New York The City University
Overview of Chapter 4
 Overview of hapter 4 Types of Sequential ircuits Storage Elements Latches Flip-Flops Sequential ircuit Analysis State Tables State Diagrams Sequential ircuit Design Specification Assignment of State odes
Overview of hapter 4 Types of Sequential ircuits Storage Elements Latches Flip-Flops Sequential ircuit Analysis State Tables State Diagrams Sequential ircuit Design Specification Assignment of State odes
Vidyalankar S.E. Sem. III [ETRX] Digital Circuits and Design Prelim Question Paper Solution
![Vidyalankar S.E. Sem. III [ETRX] Digital Circuits and Design Prelim Question Paper Solution Vidyalankar S.E. Sem. III [ETRX] Digital Circuits and Design Prelim Question Paper Solution](/thumbs/79/79145081.jpg) S.E. Sem. III [ETRX] Digital Circuits and Design Prelim uestion Paper Solution. (a) Static Hazard Static hazards have two cases: static and static. static- hazard exists when the output variable should
S.E. Sem. III [ETRX] Digital Circuits and Design Prelim uestion Paper Solution. (a) Static Hazard Static hazards have two cases: static and static. static- hazard exists when the output variable should
LOGIC CIRCUITS. Basic Experiment and Design of Electronics
 Basic Experiment and Design of Electronics LOGIC CIRCUITS Ho Kyung Kim, Ph.D. hokyung@pusan.ac.kr School of Mechanical Engineering Pusan National University Outline Combinational logic circuits Output
Basic Experiment and Design of Electronics LOGIC CIRCUITS Ho Kyung Kim, Ph.D. hokyung@pusan.ac.kr School of Mechanical Engineering Pusan National University Outline Combinational logic circuits Output
S.Y. Diploma : Sem. III [CO/CM/IF/CD/CW] Digital Techniques
![S.Y. Diploma : Sem. III [CO/CM/IF/CD/CW] Digital Techniques S.Y. Diploma : Sem. III [CO/CM/IF/CD/CW] Digital Techniques](/thumbs/90/103932933.jpg) S.Y. Diploma : Sem. III [CO/CM/IF/CD/CW] Digital Techniques Time: 3 Hrs.] Prelim Question Paper Solution [Marks : 100 Q.1(a) Attempt any SIX of the following : [12] Q.1(a) (i) Derive AND gate and OR gate
S.Y. Diploma : Sem. III [CO/CM/IF/CD/CW] Digital Techniques Time: 3 Hrs.] Prelim Question Paper Solution [Marks : 100 Q.1(a) Attempt any SIX of the following : [12] Q.1(a) (i) Derive AND gate and OR gate
Sequential Logic Circuits
 Chapter 4 Sequential Logic Circuits 4 1 The defining characteristic of a combinational circuit is that its output depends only on the current inputs applied to the circuit. The output of a sequential circuit,
Chapter 4 Sequential Logic Circuits 4 1 The defining characteristic of a combinational circuit is that its output depends only on the current inputs applied to the circuit. The output of a sequential circuit,
Chapter 14 Sequential logic, Latches and Flip-Flops
 Chapter 14 Sequential logic, Latches and Flip-Flops Flops Lesson 4 JK Flip Flop Ch14L4-"Digital Principles and Design", Raj Kamal, Pearson Education, 2006 2 JK Flip-Flop ve edge triggered Output Q and
Chapter 14 Sequential logic, Latches and Flip-Flops Flops Lesson 4 JK Flip Flop Ch14L4-"Digital Principles and Design", Raj Kamal, Pearson Education, 2006 2 JK Flip-Flop ve edge triggered Output Q and
Introduction to Digital Logic
 Introduction to Digital Logic Lecture 17: Latches Flip-Flops Problem w/ Bistables Output should have been at end of sequence Problem: Glitch was remembered Need some way to ignore inputs until they are
Introduction to Digital Logic Lecture 17: Latches Flip-Flops Problem w/ Bistables Output should have been at end of sequence Problem: Glitch was remembered Need some way to ignore inputs until they are
Chapter 4. Sequential Logic Circuits
 Chapter 4 Sequential Logic Circuits 1 2 Chapter 4 4 1 The defining characteristic of a combinational circuit is that its output depends only on the current inputs applied to the circuit. The output of
Chapter 4 Sequential Logic Circuits 1 2 Chapter 4 4 1 The defining characteristic of a combinational circuit is that its output depends only on the current inputs applied to the circuit. The output of
LOGIC CIRCUITS. Basic Experiment and Design of Electronics. Ho Kyung Kim, Ph.D.
 Basic Experiment and Design of Electronics LOGIC CIRCUITS Ho Kyung Kim, Ph.D. hokyung@pusan.ac.kr School of Mechanical Engineering Pusan National University Digital IC packages TTL (transistor-transistor
Basic Experiment and Design of Electronics LOGIC CIRCUITS Ho Kyung Kim, Ph.D. hokyung@pusan.ac.kr School of Mechanical Engineering Pusan National University Digital IC packages TTL (transistor-transistor
P2 (10 points): Given the circuit below, answer the following questions:
 P1 (10 points): Given the function f(a, b, c, d) = m(3,4,5,10,14) + D(6,7): A: Fill in the timing diagram for f. B: Implement f using only 2-1 MUXes. Your circuit should not include more than four 2-1
P1 (10 points): Given the function f(a, b, c, d) = m(3,4,5,10,14) + D(6,7): A: Fill in the timing diagram for f. B: Implement f using only 2-1 MUXes. Your circuit should not include more than four 2-1
S.Y. Diploma : Sem. III [DE/ED/EI/EJ/EN/ET/EV/EX/IC/IE/IS/IU/MU] Principles of Digital Techniques
![S.Y. Diploma : Sem. III [DE/ED/EI/EJ/EN/ET/EV/EX/IC/IE/IS/IU/MU] Principles of Digital Techniques S.Y. Diploma : Sem. III [DE/ED/EI/EJ/EN/ET/EV/EX/IC/IE/IS/IU/MU] Principles of Digital Techniques](/thumbs/82/86792063.jpg) S.Y. Diploma : Sem. III [DE/ED/EI/EJ/EN/ET/EV/EX/IC/IE/IS/IU/MU] Principles of Digital Techniques Time: 3 Hrs.] Prelim Question Paper Solution [Marks : 100 Q.1(a) Attempt any SIX of the following : [12]
S.Y. Diploma : Sem. III [DE/ED/EI/EJ/EN/ET/EV/EX/IC/IE/IS/IU/MU] Principles of Digital Techniques Time: 3 Hrs.] Prelim Question Paper Solution [Marks : 100 Q.1(a) Attempt any SIX of the following : [12]
Topic 8: Sequential Circuits. Bistable Devices. S-R Latches. Consider the following element. Readings : Patterson & Hennesy, Appendix B.4 - B.
 Topic 8: Sequential Circuits Bistable Devices Readings : Consider the following element Patterson & Hennesy, Appendix B.4 - B.6 Goals Basic Principles behind Memory Elements Clocks Applications of sequential
Topic 8: Sequential Circuits Bistable Devices Readings : Consider the following element Patterson & Hennesy, Appendix B.4 - B.6 Goals Basic Principles behind Memory Elements Clocks Applications of sequential
CMPEN 411. Spring Lecture 18: Static Sequential Circuits
 CMPEN 411 VLSI Digital Circuits Spring 2011 Lecture 18: Static Sequential Circuits [Adapted from Rabaey s Digital Integrated Circuits, Second Edition, 2003 J. Rabaey, A. Chandrakasan, B. Nikolic] Sp11
CMPEN 411 VLSI Digital Circuits Spring 2011 Lecture 18: Static Sequential Circuits [Adapted from Rabaey s Digital Integrated Circuits, Second Edition, 2003 J. Rabaey, A. Chandrakasan, B. Nikolic] Sp11
Integrated Circuits & Systems
 Federal University of Santa Catarina Center for Technology Computer Science & Electronics Engineering Integrated Circuits & Systems INE 5442 Lecture 18 CMOS Sequential Circuits - 1 guntzel@inf.ufsc.br
Federal University of Santa Catarina Center for Technology Computer Science & Electronics Engineering Integrated Circuits & Systems INE 5442 Lecture 18 CMOS Sequential Circuits - 1 guntzel@inf.ufsc.br
Using the NOT realization from the NAND, we can NOT the output of the NAND gate making it a NOT NOT AND or simply an AND gate.
 CSC 216 NAND/NOR Equivalents and Flip/Flops Dr. Anthony S. Pyzdrowski 10/28/2016 The NAND gate is a NOT AND gate. It is false when all inputs are true and true otherwise. The NOR gate is a NOT OR gate.
CSC 216 NAND/NOR Equivalents and Flip/Flops Dr. Anthony S. Pyzdrowski 10/28/2016 The NAND gate is a NOT AND gate. It is false when all inputs are true and true otherwise. The NOR gate is a NOT OR gate.
Synchronous Sequential Circuit
 Synchronous Sequential Circuit The change of internal state occurs in response to the synchronized clock pulses. Data are read during the clock pulse (e.g. rising-edge triggered) It is supposed to wait
Synchronous Sequential Circuit The change of internal state occurs in response to the synchronized clock pulses. Data are read during the clock pulse (e.g. rising-edge triggered) It is supposed to wait
Memory Elements I. CS31 Pascal Van Hentenryck. CS031 Lecture 6 Page 1
 Memory Elements I CS31 Pascal Van Hentenryck CS031 Lecture 6 Page 1 Memory Elements (I) Combinational devices are good for computing Boolean functions pocket calculator Computers also need to remember
Memory Elements I CS31 Pascal Van Hentenryck CS031 Lecture 6 Page 1 Memory Elements (I) Combinational devices are good for computing Boolean functions pocket calculator Computers also need to remember
I. Motivation & Examples
 I. Motivation & Examples Output depends on current input and past history of inputs. State embodies all the information about the past needed to predict current output based on current input. State variables,
I. Motivation & Examples Output depends on current input and past history of inputs. State embodies all the information about the past needed to predict current output based on current input. State variables,
Gates and Flip-Flops
 Gates and Flip-Flops Chris Kervick (11355511) With Evan Sheridan and Tom Power December 2012 On a scale of 1 to 10, how likely is it that this question is using binary?...4? What s a 4? Abstract The operation
Gates and Flip-Flops Chris Kervick (11355511) With Evan Sheridan and Tom Power December 2012 On a scale of 1 to 10, how likely is it that this question is using binary?...4? What s a 4? Abstract The operation
Fundamentals of Digital Design
 Fundamentals of Digital Design Digital Radiation Measurement and Spectroscopy NE/RHP 537 1 Binary Number System The binary numeral system, or base-2 number system, is a numeral system that represents numeric
Fundamentals of Digital Design Digital Radiation Measurement and Spectroscopy NE/RHP 537 1 Binary Number System The binary numeral system, or base-2 number system, is a numeral system that represents numeric
ELEC Digital Logic Circuits Fall 2014 Sequential Circuits (Chapter 6) Finite State Machines (Ch. 7-10)
 ELEC 2200-002 Digital Logic Circuits Fall 2014 Sequential Circuits (Chapter 6) Finite State Machines (Ch. 7-10) Vishwani D. Agrawal James J. Danaher Professor Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
ELEC 2200-002 Digital Logic Circuits Fall 2014 Sequential Circuits (Chapter 6) Finite State Machines (Ch. 7-10) Vishwani D. Agrawal James J. Danaher Professor Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
CHAPTER 9: SEQUENTIAL CIRCUITS
 CHAPTER 9: ASYNCHRONOUS SEUENTIAL CIRCUITS Chapter Objectives 2 Sequential circuits that are not snchronized b a clock Asnchronous circuits Analsis of Asnchronous circuits Snthesis of Asnchronous circuits
CHAPTER 9: ASYNCHRONOUS SEUENTIAL CIRCUITS Chapter Objectives 2 Sequential circuits that are not snchronized b a clock Asnchronous circuits Analsis of Asnchronous circuits Snthesis of Asnchronous circuits
ELEN Electronique numérique
 ELEN0040 - Electronique numérique Patricia ROUSSEAUX Année académique 2014-2015 CHAPITRE 3 Combinational Logic Circuits ELEN0040 3-4 1 Combinational Functional Blocks 1.1 Rudimentary Functions 1.2 Functions
ELEN0040 - Electronique numérique Patricia ROUSSEAUX Année académique 2014-2015 CHAPITRE 3 Combinational Logic Circuits ELEN0040 3-4 1 Combinational Functional Blocks 1.1 Rudimentary Functions 1.2 Functions
CSE140: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems. Midterm Information. Instructor: Mohsen Imani. Sources: TSR, Katz, Boriello & Vahid
 CSE140: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems Midterm Information Instructor: Mohsen Imani Midterm Topics In general: everything that was covered in homework 1 and 2 and related lectures,
CSE140: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems Midterm Information Instructor: Mohsen Imani Midterm Topics In general: everything that was covered in homework 1 and 2 and related lectures,
EET 310 Flip-Flops 11/17/2011 1
 EET 310 Flip-Flops 11/17/2011 1 FF s and some Definitions Clock Input: FF s are controlled by a trigger or Clock signal. All FF s have a clock input. If a device which attempts to do a FF s task does not
EET 310 Flip-Flops 11/17/2011 1 FF s and some Definitions Clock Input: FF s are controlled by a trigger or Clock signal. All FF s have a clock input. If a device which attempts to do a FF s task does not
ALU, Latches and Flip-Flops
 CSE14: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems ALU, Latches and Flip-Flops Tajana Simunic Rosing Where we are. Last time: ALUs Plan for today: ALU example, latches and flip flops Exam #1 grades
CSE14: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems ALU, Latches and Flip-Flops Tajana Simunic Rosing Where we are. Last time: ALUs Plan for today: ALU example, latches and flip flops Exam #1 grades
EE141- Spring 2007 Digital Integrated Circuits
 EE141- Spring 27 igital Integrated Circuits Lecture 19 Sequential Circuits 1 Administrative Stuff Project Ph. 2 due Tu. 5pm 24 Cory box + email ee141- project@bwrc.eecs.berkeley.edu Hw 8 Posts this Fr.,
EE141- Spring 27 igital Integrated Circuits Lecture 19 Sequential Circuits 1 Administrative Stuff Project Ph. 2 due Tu. 5pm 24 Cory box + email ee141- project@bwrc.eecs.berkeley.edu Hw 8 Posts this Fr.,
CPE/EE 422/522. Chapter 1 - Review of Logic Design Fundamentals. Dr. Rhonda Kay Gaede UAH. 1.1 Combinational Logic
 CPE/EE 422/522 Chapter - Review of Logic Design Fundamentals Dr. Rhonda Kay Gaede UAH UAH Chapter CPE/EE 422/522. Combinational Logic Combinational Logic has no control inputs. When the inputs to a combinational
CPE/EE 422/522 Chapter - Review of Logic Design Fundamentals Dr. Rhonda Kay Gaede UAH UAH Chapter CPE/EE 422/522. Combinational Logic Combinational Logic has no control inputs. When the inputs to a combinational
Chapter 5 Synchronous Sequential Logic
 Chapter 5 Synchronous Sequential Logic Sequential circuit: A circuit that includes memory elements. In this case the output depends not only on the current input but also on the past inputs. Memory A synchronous
Chapter 5 Synchronous Sequential Logic Sequential circuit: A circuit that includes memory elements. In this case the output depends not only on the current input but also on the past inputs. Memory A synchronous
Sequential Circuits Sequential circuits combinational circuits state gate delay
 Sequential Circuits Sequential circuits are those with memory, also called feedback. In this, they differ from combinational circuits, which have no memory. The stable output of a combinational circuit
Sequential Circuits Sequential circuits are those with memory, also called feedback. In this, they differ from combinational circuits, which have no memory. The stable output of a combinational circuit
Digital Electronics Sequential Logic
 /5/27 igital Electronics Sequential Logic r. I. J. Wassell Sequential Logic The logic circuits discussed previously are known as combinational, in that the output depends only on the condition of the latest
/5/27 igital Electronics Sequential Logic r. I. J. Wassell Sequential Logic The logic circuits discussed previously are known as combinational, in that the output depends only on the condition of the latest
Lecture 9: Sequential Logic Circuits. Reading: CH 7
 Lecture 9: Sequential Logic Circuits Reading: CH 7 Sequential Logic FSM (Finite-state machine) Inputs Current State COMBINATIONAL LOGIC Registers Outputs = f(current, inputs) Next state 2 storage mechanisms
Lecture 9: Sequential Logic Circuits Reading: CH 7 Sequential Logic FSM (Finite-state machine) Inputs Current State COMBINATIONAL LOGIC Registers Outputs = f(current, inputs) Next state 2 storage mechanisms
Computers also need devices capable of Storing data and information Performing mathematical operations on such data
 Sequential Machines Introduction Logic devices examined so far Combinational Output function of input only Output valid as long as input true Change input change output Computers also need devices capable
Sequential Machines Introduction Logic devices examined so far Combinational Output function of input only Output valid as long as input true Change input change output Computers also need devices capable
Unit II Chapter 4:- Digital Logic Contents 4.1 Introduction... 4
 Unit II Chapter 4:- Digital Logic Contents 4.1 Introduction... 4 4.1.1 Signal... 4 4.1.2 Comparison of Analog and Digital Signal... 7 4.2 Number Systems... 7 4.2.1 Decimal Number System... 7 4.2.2 Binary
Unit II Chapter 4:- Digital Logic Contents 4.1 Introduction... 4 4.1.1 Signal... 4 4.1.2 Comparison of Analog and Digital Signal... 7 4.2 Number Systems... 7 4.2.1 Decimal Number System... 7 4.2.2 Binary
MODULE 5 Chapter 7. Clocked Storage Elements
 MODULE 5 Chapter 7 Clocked Storage Elements 3/9/2015 1 Outline Background Clocked Storage Elements Timing, terminology, classification Static CSEs Latches Registers Dynamic CSEs Latches Registers 3/9/2015
MODULE 5 Chapter 7 Clocked Storage Elements 3/9/2015 1 Outline Background Clocked Storage Elements Timing, terminology, classification Static CSEs Latches Registers Dynamic CSEs Latches Registers 3/9/2015
Problem Set 9 Solutions
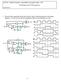 CSE 26 Digital Computers: Organization and Logical Design - 27 Jon Turner Problem Set 9 Solutions. For each of the sequential circuits shown below, draw in the missing parts of the timing diagrams. You
CSE 26 Digital Computers: Organization and Logical Design - 27 Jon Turner Problem Set 9 Solutions. For each of the sequential circuits shown below, draw in the missing parts of the timing diagrams. You
Different encodings generate different circuits
 FSM State Encoding Different encodings generate different circuits no easy way to find best encoding with fewest logic gates or shortest propagation delay. Binary encoding: K states need log 2 K bits i.e.,
FSM State Encoding Different encodings generate different circuits no easy way to find best encoding with fewest logic gates or shortest propagation delay. Binary encoding: K states need log 2 K bits i.e.,
Digital Logic: Boolean Algebra and Gates. Textbook Chapter 3
 Digital Logic: Boolean Algebra and Gates Textbook Chapter 3 Basic Logic Gates XOR CMPE12 Summer 2009 02-2 Truth Table The most basic representation of a logic function Lists the output for all possible
Digital Logic: Boolean Algebra and Gates Textbook Chapter 3 Basic Logic Gates XOR CMPE12 Summer 2009 02-2 Truth Table The most basic representation of a logic function Lists the output for all possible
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION (Autonomous) (ISO/IEC Certified) State any two Boolean laws. (Any 2 laws 1 mark each)
 Subject Code: 17333 Model Answer Page 1/ 27 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model
Subject Code: 17333 Model Answer Page 1/ 27 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model
Fundamentals of Computer Systems
 Fundamentals of Computer Systems Sequential Logic Stephen A. Edwards Columbia University Summer 2017 State-Holding Elements Bistable Elements S Latch Latch Positive-Edge-Triggered Flip-Flop Flip-Flop with
Fundamentals of Computer Systems Sequential Logic Stephen A. Edwards Columbia University Summer 2017 State-Holding Elements Bistable Elements S Latch Latch Positive-Edge-Triggered Flip-Flop Flip-Flop with
Chapter 9 Asynchronous Sequential Logic
 9.1 Introduction EEA051 - Digital Logic 數位邏輯 Chapter 9 Asynchronous Sequential Logic 吳俊興高雄大學資訊工程學系 December 2004 Two major types of sequential circuits: depending on timing of their signals Asynchronous
9.1 Introduction EEA051 - Digital Logic 數位邏輯 Chapter 9 Asynchronous Sequential Logic 吳俊興高雄大學資訊工程學系 December 2004 Two major types of sequential circuits: depending on timing of their signals Asynchronous
Digital Design. Sequential Logic
 Principles Of igital esign Chapter 6 Sequential Logic Chapter preview Boolean algebra 3 Logic gates and flip-flops 3 Finite-state machine 6 Logic design techniques 4 Sequential design techniques 6 Binary
Principles Of igital esign Chapter 6 Sequential Logic Chapter preview Boolean algebra 3 Logic gates and flip-flops 3 Finite-state machine 6 Logic design techniques 4 Sequential design techniques 6 Binary
ELE2120 Digital Circuits and Systems. Tutorial Note 9
 ELE2120 Digital Circuits and Systems Tutorial Note 9 Outline 1. Exercise(1) Sequential Circuit Analysis 2. Exercise (2) Sequential Circuit Analysis 3. Exercise (3) Sequential Circuit Analysis 4. Ref. Construction
ELE2120 Digital Circuits and Systems Tutorial Note 9 Outline 1. Exercise(1) Sequential Circuit Analysis 2. Exercise (2) Sequential Circuit Analysis 3. Exercise (3) Sequential Circuit Analysis 4. Ref. Construction
Topics. CMOS Design Multi-input delay analysis. John A. Chandy Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Connecticut
 Topics CMO Design Multi-input delay analysis pring 25 Transmission Gate OUT Z OUT Z pring 25 Transmission Gate OUT When is low, the output is at high impedance When is high, the output follows However,
Topics CMO Design Multi-input delay analysis pring 25 Transmission Gate OUT Z OUT Z pring 25 Transmission Gate OUT When is low, the output is at high impedance When is high, the output follows However,
Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective
 Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic Designing Sequential Logic Circuits November 2002 Sequential Logic Inputs Current State COMBINATIONAL
Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic Designing Sequential Logic Circuits November 2002 Sequential Logic Inputs Current State COMBINATIONAL
Introduction EE 224: INTRODUCTION TO DIGITAL CIRCUITS & COMPUTER DESIGN. Lecture 6: Sequential Logic 3 Registers & Counters 5/9/2010
 EE 224: INTROUCTION TO IGITAL CIRCUITS & COMPUTER ESIGN Lecture 6: Sequential Logic 3 Registers & Counters 05/10/2010 Avinash Kodi, kodi@ohio.edu Introduction 2 A Flip-Flop stores one bit of information
EE 224: INTROUCTION TO IGITAL CIRCUITS & COMPUTER ESIGN Lecture 6: Sequential Logic 3 Registers & Counters 05/10/2010 Avinash Kodi, kodi@ohio.edu Introduction 2 A Flip-Flop stores one bit of information
Digital Circuits ECS 371
 Digital Circuits ECS 371 Dr. Prapun Suksompong prapun@siit.tu.ac.th Lecture 18 Office Hours: BKD 3601-7 Monday 9:00-10:30, 1:30-3:30 Tuesday 10:30-11:30 1 Announcement Reading Assignment: Chapter 7: 7-1,
Digital Circuits ECS 371 Dr. Prapun Suksompong prapun@siit.tu.ac.th Lecture 18 Office Hours: BKD 3601-7 Monday 9:00-10:30, 1:30-3:30 Tuesday 10:30-11:30 1 Announcement Reading Assignment: Chapter 7: 7-1,
 vidyarthiplus.com vidyarthiplus.com vidyarthiplus.com ANNA UNIVERSITY- COMBATORE B.E./ B.TECH. DEGREE EXAMINATION - JUNE 2009. ELECTRICAL & ELECTONICS ENGG. - FOURTH SEMESTER DIGITAL LOGIC CIRCUITS PART-A
vidyarthiplus.com vidyarthiplus.com vidyarthiplus.com ANNA UNIVERSITY- COMBATORE B.E./ B.TECH. DEGREE EXAMINATION - JUNE 2009. ELECTRICAL & ELECTONICS ENGG. - FOURTH SEMESTER DIGITAL LOGIC CIRCUITS PART-A
MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE TIRUCHIRAPALLI
 DEPARTMENT: ECE MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE TIRUCHIRAPALLI 6 QUESTION BANK SUBJECT NAME: DIGITAL ELECTRONICS UNIT : Design of Sequential Circuits PART A ( Marks). Draw the logic diagram 4: Multiplexer.(AUC
DEPARTMENT: ECE MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE TIRUCHIRAPALLI 6 QUESTION BANK SUBJECT NAME: DIGITAL ELECTRONICS UNIT : Design of Sequential Circuits PART A ( Marks). Draw the logic diagram 4: Multiplexer.(AUC
Sample Test Paper - I
 Scheme G Sample Test Paper - I Course Name : Computer Engineering Group Marks : 25 Hours: 1 Hrs. Q.1) Attempt any THREE: 09 Marks a) Define i) Propagation delay ii) Fan-in iii) Fan-out b) Convert the following:
Scheme G Sample Test Paper - I Course Name : Computer Engineering Group Marks : 25 Hours: 1 Hrs. Q.1) Attempt any THREE: 09 Marks a) Define i) Propagation delay ii) Fan-in iii) Fan-out b) Convert the following:
I. Motivation & Examples
 I. Motivation & Examples Output depends on current input and past history of inputs. State embodies all the information about the past needed to predict current output based on current input. State variables,
I. Motivation & Examples Output depends on current input and past history of inputs. State embodies all the information about the past needed to predict current output based on current input. State variables,
Synchronous Sequential Logic Part I. BME208 Logic Circuits Yalçın İŞLER
 Synchronous Sequential Logic Part I BME28 Logic Circuits Yalçın İŞLER islerya@yahoo.com http://me.islerya.com Sequential Logic Digital circuits we have learned, so far, have been combinational no memory,
Synchronous Sequential Logic Part I BME28 Logic Circuits Yalçın İŞLER islerya@yahoo.com http://me.islerya.com Sequential Logic Digital circuits we have learned, so far, have been combinational no memory,
Sequential Logic Worksheet
 Sequential Logic Worksheet Concept Inventory: Notes: D-latch & the Dynamic Discipline D-register Timing constraints for sequential circuits Set-up and hold times for sequential circuits 6.004 Worksheet
Sequential Logic Worksheet Concept Inventory: Notes: D-latch & the Dynamic Discipline D-register Timing constraints for sequential circuits Set-up and hold times for sequential circuits 6.004 Worksheet
Digital Logic and Design (Course Code: EE222) Lecture 19: Sequential Circuits Contd..
 Indian Institute of Technology Jodhpur, Year 2017-2018 Digital Logic and Design (Course Code: EE222) Lecture 19: Sequential Circuits Contd.. Course Instructor: Shree Prakash Tiwari Email: sptiwari@iitj.ac.in
Indian Institute of Technology Jodhpur, Year 2017-2018 Digital Logic and Design (Course Code: EE222) Lecture 19: Sequential Circuits Contd.. Course Instructor: Shree Prakash Tiwari Email: sptiwari@iitj.ac.in
Latches. October 13, 2003 Latches 1
 Latches The second part of CS231 focuses on sequential circuits, where we add memory to the hardware that we ve already seen. Our schedule will be very similar to before: We first show how primitive memory
Latches The second part of CS231 focuses on sequential circuits, where we add memory to the hardware that we ve already seen. Our schedule will be very similar to before: We first show how primitive memory
CS221: Digital Design. Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati
 CS221: Digital Design FlipFlop&Register Flop Dr. A. Sahu DeptofComp.Sc.&Engg. Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati Outline Level Sensitive (Latch) vsedge Sensitive (Flip Flop) Master Slave Flip Flop
CS221: Digital Design FlipFlop&Register Flop Dr. A. Sahu DeptofComp.Sc.&Engg. Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati Outline Level Sensitive (Latch) vsedge Sensitive (Flip Flop) Master Slave Flip Flop
Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective
 igital Integrated Circuits A esign Perspective Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic esigning Sequential Logic Circuits November 2002 Naming Conventions In our text: a latch is level sensitive
igital Integrated Circuits A esign Perspective Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic esigning Sequential Logic Circuits November 2002 Naming Conventions In our text: a latch is level sensitive
Chapter 5 Synchronous Sequential Logic
 Chapter 5 Synchronous Sequential Logic Sequential Circuits Latches and Flip Flops Analysis of Clocked Sequential Circuits HDL Optimization Design Procedure Sequential Circuits Various definitions Combinational
Chapter 5 Synchronous Sequential Logic Sequential Circuits Latches and Flip Flops Analysis of Clocked Sequential Circuits HDL Optimization Design Procedure Sequential Circuits Various definitions Combinational
UMBC. At the system level, DFT includes boundary scan and analog test bus. The DFT techniques discussed focus on improving testability of SAFs.
 Overview Design for testability(dft) makes it possible to: Assure the detection of all faults in a circuit. Reduce the cost and time associated with test development. Reduce the execution time of performing
Overview Design for testability(dft) makes it possible to: Assure the detection of all faults in a circuit. Reduce the cost and time associated with test development. Reduce the execution time of performing
Digital Electronics Circuits 2017
 JSS SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY UNIVERSITY Digital Electronics Circuits (EC37L) Lab in-charge: Dr. Shankraiah Course outcomes: After the completion of laboratory the student will be able to, 1. Simplify, design
JSS SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY UNIVERSITY Digital Electronics Circuits (EC37L) Lab in-charge: Dr. Shankraiah Course outcomes: After the completion of laboratory the student will be able to, 1. Simplify, design
GMU, ECE 680 Physical VLSI Design
 ECE680: Physical VLSI esign Chapter IV esigning Sequential Logic Circuits (Chapter 7) 1 Sequential Logic Inputs Current State COMBINATIONAL LOGIC Registers Outputs Next state 2 storage mechanisms positive
ECE680: Physical VLSI esign Chapter IV esigning Sequential Logic Circuits (Chapter 7) 1 Sequential Logic Inputs Current State COMBINATIONAL LOGIC Registers Outputs Next state 2 storage mechanisms positive
PGT104 Digital Electronics. PGT104 Digital Electronics
 1 Part 6 Sequential Logic ircuits Disclaimer: Most of the contents (if not all) are extracted from resources available for Digital Fundamentals 10 th Edition 2 Basic Shift Register Operations A shift register
1 Part 6 Sequential Logic ircuits Disclaimer: Most of the contents (if not all) are extracted from resources available for Digital Fundamentals 10 th Edition 2 Basic Shift Register Operations A shift register
9/18/2008 GMU, ECE 680 Physical VLSI Design
 ECE680: Physical VLSI esign Chapter IV esigning Sequential Logic Circuits (Chapter 7) 1 Sequential Logic Inputs Current State COMBINATIONAL LOGIC Registers Outputs Next state 2 storage mechanisms positive
ECE680: Physical VLSI esign Chapter IV esigning Sequential Logic Circuits (Chapter 7) 1 Sequential Logic Inputs Current State COMBINATIONAL LOGIC Registers Outputs Next state 2 storage mechanisms positive
Boolean Algebra and Digital Logic 2009, University of Colombo School of Computing
 IT 204 Section 3.0 Boolean Algebra and Digital Logic Boolean Algebra 2 Logic Equations to Truth Tables X = A. B + A. B + AB A B X 0 0 0 0 3 Sum of Products The OR operation performed on the products of
IT 204 Section 3.0 Boolean Algebra and Digital Logic Boolean Algebra 2 Logic Equations to Truth Tables X = A. B + A. B + AB A B X 0 0 0 0 3 Sum of Products The OR operation performed on the products of
Chapter 13. Clocked Circuits SEQUENTIAL VS. COMBINATIONAL CMOS TG LATCHES, FLIP FLOPS. Baker Ch. 13 Clocked Circuits. Introduction to VLSI
 Chapter 13 Clocked Circuits SEQUENTIAL VS. COMBINATIONAL CMOS TG LATCHES, FLIP FLOPS SET-RESET (SR) ARBITER LATCHES FLIP FLOPS EDGE TRIGGERED DFF FF TIMING Joseph A. Elias, Ph.D. Adjunct Professor, University
Chapter 13 Clocked Circuits SEQUENTIAL VS. COMBINATIONAL CMOS TG LATCHES, FLIP FLOPS SET-RESET (SR) ARBITER LATCHES FLIP FLOPS EDGE TRIGGERED DFF FF TIMING Joseph A. Elias, Ph.D. Adjunct Professor, University
Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective
 igital Integrated Circuits A esign Perspective Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic esigning Sequential Logic Circuits November 2002 Sequential Logic Inputs Current State COMBINATIONAL LOGIC
igital Integrated Circuits A esign Perspective Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic esigning Sequential Logic Circuits November 2002 Sequential Logic Inputs Current State COMBINATIONAL LOGIC
Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic. November Digital Integrated Circuits 2nd Sequential Circuits
 igital Integrated Circuits A esign Perspective Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic esigning i Sequential Logic Circuits November 2002 Sequential Logic Inputs Current State COMBINATIONAL
igital Integrated Circuits A esign Perspective Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic esigning i Sequential Logic Circuits November 2002 Sequential Logic Inputs Current State COMBINATIONAL
Lecture 7: Sequential Networks
 CSE 140: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems Lecture 7: Sequential Networks CK Cheng Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering University of California, San Diego 1 Part II: Sequential
CSE 140: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems Lecture 7: Sequential Networks CK Cheng Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering University of California, San Diego 1 Part II: Sequential
Homework Assignment #1 Solutions EE 477 Spring 2017 Professor Parker
 Homework Assignment #1 Solutions EE 477 Spring 2017 Professor Parker Note: + implies OR,. implies AND, ~ implies NOT Question 1: a) (4%) Use transmission gates to design a 3-input OR gate Note: There are
Homework Assignment #1 Solutions EE 477 Spring 2017 Professor Parker Note: + implies OR,. implies AND, ~ implies NOT Question 1: a) (4%) Use transmission gates to design a 3-input OR gate Note: There are
Lecture 3 Review on Digital Logic (Part 2)
 Lecture 3 Review on Digital Logic (Part 2) Xuan Silvia Zhang Washington University in St. Louis http://classes.engineering.wustl.edu/ese461/ ircuit Optimization Simplest implementation ost criterion literal
Lecture 3 Review on Digital Logic (Part 2) Xuan Silvia Zhang Washington University in St. Louis http://classes.engineering.wustl.edu/ese461/ ircuit Optimization Simplest implementation ost criterion literal
Synchronous Sequential Logic Part I
 Synchronous Sequential Logic Part I Mantıksal Tasarım BBM23 section instructor: Ufuk Çelikcan Sequential Logic Digital circuits we have learned, so far, have been combinational no memory, outputs are entirely
Synchronous Sequential Logic Part I Mantıksal Tasarım BBM23 section instructor: Ufuk Çelikcan Sequential Logic Digital circuits we have learned, so far, have been combinational no memory, outputs are entirely
6. Finite State Machines
 6. Finite State Machines 6.4x Computation Structures Part Digital Circuits Copyright 25 MIT EECS 6.4 Computation Structures L6: Finite State Machines, Slide # Our New Machine Clock State Registers k Current
6. Finite State Machines 6.4x Computation Structures Part Digital Circuits Copyright 25 MIT EECS 6.4 Computation Structures L6: Finite State Machines, Slide # Our New Machine Clock State Registers k Current
Adders, subtractors comparators, multipliers and other ALU elements
 CSE4: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems Adders, subtractors comparators, multipliers and other ALU elements Adders 2 Circuit Delay Transistors have instrinsic resistance and capacitance
CSE4: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems Adders, subtractors comparators, multipliers and other ALU elements Adders 2 Circuit Delay Transistors have instrinsic resistance and capacitance
Synchronous 4 Bit Counters; Binary, Direct Reset
 Synchronous 4 Bit Counters; Binary, Direct Reset This synchronous, presettable counter features an internal carry look-ahead for application in high-speed counting designs. Synchronous operation is provided
Synchronous 4 Bit Counters; Binary, Direct Reset This synchronous, presettable counter features an internal carry look-ahead for application in high-speed counting designs. Synchronous operation is provided
EE40 Lec 15. Logic Synthesis and Sequential Logic Circuits
 EE40 Lec 15 Logic Synthesis and Sequential Logic Circuits Prof. Nathan Cheung 10/20/2009 Reading: Hambley Chapters 7.4-7.6 Karnaugh Maps: Read following before reading textbook http://www.facstaff.bucknell.edu/mastascu/elessonshtml/logic/logic3.html
EE40 Lec 15 Logic Synthesis and Sequential Logic Circuits Prof. Nathan Cheung 10/20/2009 Reading: Hambley Chapters 7.4-7.6 Karnaugh Maps: Read following before reading textbook http://www.facstaff.bucknell.edu/mastascu/elessonshtml/logic/logic3.html
University of Minnesota Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
 University of Minnesota Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering EE2301 Fall 2008 Introduction to Digital System Design L. L. Kinney Final Eam (Closed Book) Solutions Please enter your name, ID
University of Minnesota Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering EE2301 Fall 2008 Introduction to Digital System Design L. L. Kinney Final Eam (Closed Book) Solutions Please enter your name, ID
CPE100: Digital Logic Design I
 Chapter 3 Professor Brendan Morris, SEB 3216, brendan.morris@unlv.edu http://www.ee.unlv.edu/~b1morris/cpe1/ CPE1: Digital Logic Design I Section 14: Dr. Morris Sequential Logic Design Chapter 3 Chapter
Chapter 3 Professor Brendan Morris, SEB 3216, brendan.morris@unlv.edu http://www.ee.unlv.edu/~b1morris/cpe1/ CPE1: Digital Logic Design I Section 14: Dr. Morris Sequential Logic Design Chapter 3 Chapter
ECEN 248: INTRODUCTION TO DIGITAL SYSTEMS DESIGN. Week 9 Dr. Srinivas Shakkottai Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering
 ECEN 248: INTRODUCTION TO DIGITAL SYSTEMS DESIGN Week 9 Dr. Srinivas Shakkottai Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering TIMING ANALYSIS Overview Circuits do not respond instantaneously to input changes
ECEN 248: INTRODUCTION TO DIGITAL SYSTEMS DESIGN Week 9 Dr. Srinivas Shakkottai Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering TIMING ANALYSIS Overview Circuits do not respond instantaneously to input changes
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 23 - FFs revisited, FIFOs, ECCs, LSFRs. Cross-coupled NOR gates
 EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 23 - FFs revisited, FIFOs, ECCs, LSFRs April 16, 2009 John Wawrzynek Spring 2009 EECS150 - Lec24-blocks Page 1 Cross-coupled NOR gates remember, If both R=0 & S=0, then
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 23 - FFs revisited, FIFOs, ECCs, LSFRs April 16, 2009 John Wawrzynek Spring 2009 EECS150 - Lec24-blocks Page 1 Cross-coupled NOR gates remember, If both R=0 & S=0, then
Fundamentals of Boolean Algebra
 UNIT-II 1 Fundamentals of Boolean Algebra Basic Postulates Postulate 1 (Definition): A Boolean algebra is a closed algebraic system containing a set K of two or more elements and the two operators and
UNIT-II 1 Fundamentals of Boolean Algebra Basic Postulates Postulate 1 (Definition): A Boolean algebra is a closed algebraic system containing a set K of two or more elements and the two operators and
Week-5. Sequential Circuit Design. Acknowledgement: Most of the following slides are adapted from Prof. Kale's slides at UIUC, USA.
 Week-5 Sequential Circuit Design Acknowledgement: Most of the following slides are adapted from Prof. Kale's slides at UIUC, USA. Storing a value: SR = 00 What if S = 0 and R = 0? The equations on the
Week-5 Sequential Circuit Design Acknowledgement: Most of the following slides are adapted from Prof. Kale's slides at UIUC, USA. Storing a value: SR = 00 What if S = 0 and R = 0? The equations on the
Fundamentals of Computer Systems
 Fundamentals of Computer Systems Review for the Midterm Stephen A. Edwards Columbia University Spring 22 The Midterm 75 minutes 4 5 problems Closed book Simple calculators are OK, but unnecessary One double-sided
Fundamentals of Computer Systems Review for the Midterm Stephen A. Edwards Columbia University Spring 22 The Midterm 75 minutes 4 5 problems Closed book Simple calculators are OK, but unnecessary One double-sided
Module - 19 Gated Latches
 Digital Circuits and Systems Prof. Shankar Balachandran Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay And Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of
Digital Circuits and Systems Prof. Shankar Balachandran Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay And Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of
MOSIS REPORT. Spring MOSIS Report 1. MOSIS Report 2. MOSIS Report 3
 MOSIS REPORT Spring 2010 MOSIS Report 1 MOSIS Report 2 MOSIS Report 3 MOSIS Report 1 Design of 4-bit counter using J-K flip flop I. Objective The purpose of this project is to design one 4-bit counter
MOSIS REPORT Spring 2010 MOSIS Report 1 MOSIS Report 2 MOSIS Report 3 MOSIS Report 1 Design of 4-bit counter using J-K flip flop I. Objective The purpose of this project is to design one 4-bit counter
5. Sequential Logic x Computation Structures Part 1 Digital Circuits. Copyright 2015 MIT EECS
 5. Sequential Logic 6.004x Computation Structures Part 1 igital Circuits Copyright 2015 MIT EECS 6.004 Computation Structures L5: Sequential Logic, Slide #1 Something We Can t Build (Yet) What if you were
5. Sequential Logic 6.004x Computation Structures Part 1 igital Circuits Copyright 2015 MIT EECS 6.004 Computation Structures L5: Sequential Logic, Slide #1 Something We Can t Build (Yet) What if you were
EE 209 Logic Cumulative Exam Name:
 EE 209 Logic Cumulative Exam Name: 1.) Answer the following questions as True or False a.) A 4-to-1 multiplexer requires at least 4 select lines: true / false b.) An 8-to-1 mux and no other logi can be
EE 209 Logic Cumulative Exam Name: 1.) Answer the following questions as True or False a.) A 4-to-1 multiplexer requires at least 4 select lines: true / false b.) An 8-to-1 mux and no other logi can be
PAST EXAM PAPER & MEMO N3 ABOUT THE QUESTION PAPERS:
 EKURHULENI TECH COLLEGE. No. 3 Mogale Square, Krugersdorp. Website: www. ekurhulenitech.co.za Email: info@ekurhulenitech.co.za TEL: 011 040 7343 CELL: 073 770 3028/060 715 4529 PAST EXAM PAPER & MEMO N3
EKURHULENI TECH COLLEGE. No. 3 Mogale Square, Krugersdorp. Website: www. ekurhulenitech.co.za Email: info@ekurhulenitech.co.za TEL: 011 040 7343 CELL: 073 770 3028/060 715 4529 PAST EXAM PAPER & MEMO N3
DIGITAL LOGIC CIRCUITS
 DIGITAL LOGIC CIRCUITS Introduction Logic Gates Boolean Algebra Map Specification Combinational Circuits Flip-Flops Sequential Circuits Memory Components Integrated Circuits Digital Computers 2 LOGIC GATES
DIGITAL LOGIC CIRCUITS Introduction Logic Gates Boolean Algebra Map Specification Combinational Circuits Flip-Flops Sequential Circuits Memory Components Integrated Circuits Digital Computers 2 LOGIC GATES
ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals
 ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 17: March 23, 2017 Energy and Power Optimization, Design Space Exploration, Synchronous MOS Logic Lecture Outline! Energy and Power Optimization
ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 17: March 23, 2017 Energy and Power Optimization, Design Space Exploration, Synchronous MOS Logic Lecture Outline! Energy and Power Optimization
