Supplementary Information
|
|
|
- Bartholomew Cain
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Supplementary Information Rice APC/C TE controls tillering through mediating the degradation of MONOCULM 1 Qibing Lin 1*, Dan Wang 1*, Hui Dong 2*, Suhai Gu 1, Zhijun Cheng 1, Jie Gong 2, Ruizhen Qin 1, Ling Jiang 2, Gang Li 3, Jiu Lin Wang 1, Fuqing Wu 1, Xiuping Guo 1, Xin Zhang 1, Cailin Lei 1, Haiyang Wang 1, Jianmin Wan 1,2 1 National Key Facility for Crop Gene Resources and Genetic Improvement, Institute of Crop Science, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Beijing , China 2 National key Laboratory for Crop Genetics and Germplasm Enhancement, Jiangsu Plant Gene Engineering Research Center, Nanjing Agricultural University, Nanjing , China 3 Department of Molecular, Cellular, and Developmental Biology, Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut
2 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure S1 Protein sequence alignment of Cdh1-like proteins of S. pombe (SpSRW1), H. sapiens (HsCdh1), A. thaliana (AtCcs52A1, AtCcs52A2), M. truncatula (MtCcs52A, MtCcs52B), O. sativa (TE, OsCcs52B) and the truncated te protein. The conserved domains (seven WD-40 repeats) and motifs (C-box, CSM, IR, and RVL) are marked. In addition, the two degradation signals are also marked by two red boxes in the N-terminal region of HsCdh1. 2
3 Supplementary Figure S2 Phylogenetic analysis of TE protein. Protein sequences were aligned with CLUSTAL W in MEGA and the phylogenetic tree was analyzed by MEGA Accession numbers presented here are the following: SpSlp1, P78972; ScCdc20, P26309; SlCdc20-1, CBH19893; OsCDC20-2, BAF ; SlCdc20-2, CBH19894; MmCdc20-1, XP ; HsCdc20-1, NP ; HsCdc20-2, A56021; MmCdc20-2, NP ; RnCdc20, NP ; XlCdc20-1, AAH42288; XlCdc20-2, AAC41376; DmFzy, NP ; AtCdc20-1, At4g33260; AtCdc20-2, At4g33270; AtCdc20-3, At5g27570; ScHct1, P53197; UmCdh1, AY118173; SpSRW1, O ; 3
4 CeCdh1, NP ; XlCdh1, CAA74576; HsCdh1, NP ; HsFzr1, Q9UM11.2; MmCdh1, NP ; DmCdh1-2, NP ; OsCcs52B, LOC_Os01g74146; AtCcs52A2, At4g11920; AtCcs52A1, At4g22910; SlCcs52A, CBH19891; MtCcs52A, AF134835; TE, LOC_Os03g03150; ZmCcs52A, ACN36196; ZmCcs52B, ACG33710; AtCcs52B, At5g13840; MtCcs52B, AY357299; SpSrw1, O13286; SlCcs52B, CBH19892; LcjCcs52A, DQ ; PsCcs52A, DQ059036; MsCcs52A, AF079404; SbCcs52A, XP_ ; and SbCcs52B, XP_ Sp, S. pombe; Sc, S. cerevisiae; Sl, Solanum lycopersicum; Mm, Mus musculus; Hs, Homo sapiens; Rn, Rattus norvegicus; Xl, Xenopus laevis; Dm, D. melanogaster; At, A. thaliana; Um, Ustilago maydis; Ce, Caenorhabditis elegans; Os, Oryza sativa; Mt, M. truncatula; Zm, Zea mays; Lcj, Lotus corniculatus var. Japonicus; Ps, Pisum sativum; Ms, Medicago sativa; Sb, Sorghum bicolor. 4
5 Supplementary Figure S3 Phylogenetic and protein sequence analysis of MOC1 and OsCDC27. (a) Sequence alignment of MOC1, LAS and LS proteins. The conserved domains (LHRI, VHIID, LHRII, PFYRE and SAW) were marked. The typical degradation box (D-box) is marked by a green box in the N-terminal region of MOC1, LAS and LS. (b) Phylogenetic analysis showing that OsCDC27 is the rice homolog of HsCDC27, DmCDC27, AtCDC27a, AtCDC27b, and SpCDC27. Protein sequences were aligned with CLUSTAL W in MEGA and the phylogenetic tree was constructed by MEGA Accession numbers presented here are the following: HsCDC27, NP_ ; MmCDC27, NP_ ; RnCDC27, NP_ ; DmCDC27, NP_ ; SpCDC27, NP_ ; ScCDC27p, NP_ ; AtCDC27b, NP_ ; AtCDC27a, NP_ ; OsCDC27, NP_ ; NbCDC27b, BAF (c) OsCDC27 has the same conserved TPR domain (indicated as green boxes) as HsCDC27, DmCDC27, AtCDC27b, and SpCDC27 in their C-terminal region. 5
6 Supplementary Figure S4 Ubiquitination analysis of MOC1. In vitro ubiquitination assay showing that MOC1 is poly-ubiquitinated (represented by multiple up-shifted bands) by WT plant extracts and can be detected by antibodies against MOC1 or polyub antibodies on Western blots. 6
7 Supplementary Figure S5 Mapping of the moc1-5 allele. (a) Mapping of moc1-5. (b) Western blot analysis showing the absence of MOC1 proteins in moc1-5 plants (top). Rubisco staining showing a roughly equal loading of proteins (bottom). 7
8 Supplementary Tables Supplementary Table S1 Molecular markers used for mapping of the TE gene Primer sequences (5 3 ) Marker Type Forward primer Reverse primer g41 SSR CGCTCTGAAATCCGATATTTGC GGCTCTCTCCTCCTCGTTGC RM22 SSR GGTTTGGGAGCCCATAATCT CTGGGCTTCTTTCACTCGTC RM523 SSR AAGGCATTGCAGCTAGAAGC AAGGCATTGCAGCTAGAAGC g62 InDel GCATAACATCAAAGCCATGCTA GCTCCAATTCGATCTTCGTC g105 InDel GCCCTTCTCATTGCCTCG CTCTTCTCGCTTCTTCTTTTCG g118 InDel ATGTACAATAGTATTCCCACGTC AAAACAAGGTTTAATGGTAGTG 8
9 Supplementary Table S2 Molecular markers developed in this study for mapping of the moc1-5 allele Marker Type Primer sequences (5 3 ) Forward primer Reverse primer Indel 6-9 InDel GTGCGAATTCCTCCACCTC CGACATGGCTGGTCTCTCTC xs31 InDel TGCCAATTAGCTCGATTCTG TGGTCAAAATTTGTTCAAACTCA apo1 InDel CCGGTTTTGGTTTGTCTCAG ATTCCTTTGTGGGCTCCTTT RM3628 SSR GCCCTAGACACACCCGTACC TGCCAGATCAGAAATCATGC RM162 SSR GTGGTAGGGCGAAATGATCTGC ATCACGCGCTCCTACCTCACC xs30 InDel CAGCCGATTGGACTCGAT AACACCTTGCCGAACACC xs35 InDel TAAAAGAAAGGTTACTCATGGATTTTT TAATGCCTGCTGCATCTTAGG xs40 InDel TCCTCACACACAAGCACACA TCAAATTGGCATGCATTGAT xs51 InDel AAGTTCGCCGGAGAGAGAAG CAGCGTCATGGTTTCTGAAAGCCA xs44 InDel TTAATTAATCACCAATGCAATCTATGA CCAGCAACTTTTGCTTTGTG xs55 InDel CTTAGATTTGACACAACCTGCAC ATTCTGCAGTGCACGAGCTA xs56 InDel AACTATAGATCGGGATCGCTCA TTCAAAGAAACGAAAATCAACG 9
10 Supplementary Table S3 Primers used for construction of protein expression plasmids Fragment or plasmid Forward primer (5 3 ) Reverse primer(5 3 ) TE MOC1 pmal-c2x::mbp-moc1-m CTAGGAAGATCTATGGATC ACCACCACCACCAC CGCGGATCCATGCTCCGG TCACTCCACTCC GCGGACTTGGCGCTGGCG TGCGCGGACCTG CTAGATCTCGAGTCACCGGATGT AGCTCCTAACAAATG CGCAAGCTTCTACGACGACGACG GCTGCCA CGTCGACGGCGCCGCCGCCGCA ACGGCAC 10
11 Supplementary Table S4 plasmids Primers used for construction of yeast two-hybrid assay Fragment Forward primer (5' 3') Reverse primer (5' 3') OsCDC27 AGTGAATTCATGGAAACCCTAATGGTGGAC ATAGGATCCTTAAATCTCATCATCATCAT CATCATCATCC MOC1 AGTGAATTCATGCTCCGGTCACTCCACTCCTC AATGGATCCCTACGACGACGACGGCTGC MOC1-m AGTGAATTCATGCTCCGGTCACTCCACTCCTC AATGGATCCCTACGACGACGACGGCTGC MOC1d AGTGAATTCGGCCATGGCCACGTCGTC AATGGATCCCTACGACGACGACGGCTGC TE GGAATTCCATATGATGGATCACCACCACCACCA CCTG CTAGGAAGATCTTCACCGGATGTAGCTC CTAACAAATG 11
12 Supplementary Table S5 Primers used in Real time Quantitative RT-PCR Gene Primer sequences (5 3 ) Type Name Forward primer Reverse primer Actin qrt-pcr TCGTCTGCGATAATGGAACTG CCGACAATGCTGGGGAAG TE qrt-pcr TGGTCTTCGCATAATATCCTTG TGTCCCTACAGCAAGGTGAGT OsTB1 qrt-pcr CCTACCATGAGAGAAGAGACCA GTAGTGGGCTATGATCAGATGTG OSH1 qrt-pcr CTCAACACGCTCTCCATCTC GCTTGAGCTCCTGATCCAC 12
13 Supplementary Reference: 49. Tamura, K., Dudley, J., Nei, M. & Kumar, S. MEGA4: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol. Biol. Evol. 24, (2007). 13
Two Classes of the Cdh1-Type Activators of the Anaphase-Promoting Complex in Plants: Novel Functional Domains and Distinct Regulation W
 The Plant Cell, Vol. 16, 422 434, February 2004, www.plantcell.org ª 2004 American Society of Plant Biologists Two Classes of the Cdh1-Type Activators of the Anaphase-Promoting Complex in Plants: Novel
The Plant Cell, Vol. 16, 422 434, February 2004, www.plantcell.org ª 2004 American Society of Plant Biologists Two Classes of the Cdh1-Type Activators of the Anaphase-Promoting Complex in Plants: Novel
Small RNA in rice genome
 Vol. 45 No. 5 SCIENCE IN CHINA (Series C) October 2002 Small RNA in rice genome WANG Kai ( 1, ZHU Xiaopeng ( 2, ZHONG Lan ( 1,3 & CHEN Runsheng ( 1,2 1. Beijing Genomics Institute/Center of Genomics and
Vol. 45 No. 5 SCIENCE IN CHINA (Series C) October 2002 Small RNA in rice genome WANG Kai ( 1, ZHU Xiaopeng ( 2, ZHONG Lan ( 1,3 & CHEN Runsheng ( 1,2 1. Beijing Genomics Institute/Center of Genomics and
Supplemental Data. Perea-Resa et al. Plant Cell. (2012) /tpc
 Supplemental Data. Perea-Resa et al. Plant Cell. (22)..5/tpc.2.3697 Sm Sm2 Supplemental Figure. Sequence alignment of Arabidopsis LSM proteins. Alignment of the eleven Arabidopsis LSM proteins. Sm and
Supplemental Data. Perea-Resa et al. Plant Cell. (22)..5/tpc.2.3697 Sm Sm2 Supplemental Figure. Sequence alignment of Arabidopsis LSM proteins. Alignment of the eleven Arabidopsis LSM proteins. Sm and
Supplemental Table 1. Primers used for cloning and PCR amplification in this study
 Supplemental Table 1. Primers used for cloning and PCR amplification in this study Target Gene Primer sequence NATA1 (At2g393) forward GGG GAC AAG TTT GTA CAA AAA AGC AGG CTT CAT GGC GCC TCC AAC CGC AGC
Supplemental Table 1. Primers used for cloning and PCR amplification in this study Target Gene Primer sequence NATA1 (At2g393) forward GGG GAC AAG TTT GTA CAA AAA AGC AGG CTT CAT GGC GCC TCC AAC CGC AGC
Supplemental Figure 1. Comparison of Tiller Bud Formation between the Wild Type and d27. (A) and (B) Longitudinal sections of shoot apex in wild-type
 A B 2 3 3 2 1 1 Supplemental Figure 1. Comparison of Tiller Bud Formation between the Wild Type and d27. (A) and (B) Longitudinal sections of shoot apex in wild-type (A) and d27 (B) seedlings at the four
A B 2 3 3 2 1 1 Supplemental Figure 1. Comparison of Tiller Bud Formation between the Wild Type and d27. (A) and (B) Longitudinal sections of shoot apex in wild-type (A) and d27 (B) seedlings at the four
Supplemental Data. Yang et al. (2012). Plant Cell /tpc
 Supplemental Figure 1. Mature flowers of P. heterotricha. (A) An inflorescence of P. heterotricha showing the front view of a zygomorphic flower characterized by two small dorsal petals and only two fertile
Supplemental Figure 1. Mature flowers of P. heterotricha. (A) An inflorescence of P. heterotricha showing the front view of a zygomorphic flower characterized by two small dorsal petals and only two fertile
Supplementary text for the section Interactions conserved across species: can one select the conserved interactions?
 1 Supporting Information: What Evidence is There for the Homology of Protein-Protein Interactions? Anna C. F. Lewis, Nick S. Jones, Mason A. Porter, Charlotte M. Deane Supplementary text for the section
1 Supporting Information: What Evidence is There for the Homology of Protein-Protein Interactions? Anna C. F. Lewis, Nick S. Jones, Mason A. Porter, Charlotte M. Deane Supplementary text for the section
A novel laminin β gene BmLanB1-w regulates wing-specific cell adhesion in silkworm, Bombyx mori
 Supplementary information A novel laminin β gene BmLanB1-w regulates wing-specific cell adhesion in silkworm, Bombyx mori Xiaoling Tong*, Songzhen He *, Jun Chen, Hai Hu, Zhonghuai Xiang, Cheng Lu and
Supplementary information A novel laminin β gene BmLanB1-w regulates wing-specific cell adhesion in silkworm, Bombyx mori Xiaoling Tong*, Songzhen He *, Jun Chen, Hai Hu, Zhonghuai Xiang, Cheng Lu and
Procedure to Create NCBI KOGS
 Procedure to Create NCBI KOGS full details in: Tatusov et al (2003) BMC Bioinformatics 4:41. 1. Detect and mask typical repetitive domains Reason: masking prevents spurious lumping of non-orthologs based
Procedure to Create NCBI KOGS full details in: Tatusov et al (2003) BMC Bioinformatics 4:41. 1. Detect and mask typical repetitive domains Reason: masking prevents spurious lumping of non-orthologs based
Supplementary Figure 3
 Supplementary Figure 3 7.0 Col Kas-1 Line FTH1A 8.4 F3PII3 8.9 F26H11 ATQ1 T9I22 PLS8 F26B6-B 9.6 F27L4 9.81 F27D4 9.92 9.96 10.12 10.14 10.2 11.1 0.5 Mb T1D16 Col % RGR 83.3 101 227 93.5 75.9 132 90 375
Supplementary Figure 3 7.0 Col Kas-1 Line FTH1A 8.4 F3PII3 8.9 F26H11 ATQ1 T9I22 PLS8 F26B6-B 9.6 F27L4 9.81 F27D4 9.92 9.96 10.12 10.14 10.2 11.1 0.5 Mb T1D16 Col % RGR 83.3 101 227 93.5 75.9 132 90 375
Computational Structural Bioinformatics
 Computational Structural Bioinformatics ECS129 Instructor: Patrice Koehl http://koehllab.genomecenter.ucdavis.edu/teaching/ecs129 koehl@cs.ucdavis.edu Learning curve Math / CS Biology/ Chemistry Pre-requisite
Computational Structural Bioinformatics ECS129 Instructor: Patrice Koehl http://koehllab.genomecenter.ucdavis.edu/teaching/ecs129 koehl@cs.ucdavis.edu Learning curve Math / CS Biology/ Chemistry Pre-requisite
Duplication of an upstream silencer of FZP increases grain yield in rice
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Articles https://doi.org/10.1038/s41477-017-0042-4 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Duplication of an upstream silencer of FZP increases grain yield in rice
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Articles https://doi.org/10.1038/s41477-017-0042-4 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Duplication of an upstream silencer of FZP increases grain yield in rice
ECOL/MCB 320 and 320H Genetics
 ECOL/MCB 320 and 320H Genetics Instructors Dr. C. William Birky, Jr. Dept. of Ecology and Evolutionary Biology Lecturing on Molecular genetics Transmission genetics Population and evolutionary genetics
ECOL/MCB 320 and 320H Genetics Instructors Dr. C. William Birky, Jr. Dept. of Ecology and Evolutionary Biology Lecturing on Molecular genetics Transmission genetics Population and evolutionary genetics
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Fig. 1 Influences of crystal lattice contacts on Pol η structures. a. The dominant lattice contact between two hpol η molecules (silver and gold) in the type 1 crystals. b. A close-up view of the hydrophobic
Fig. 1 Influences of crystal lattice contacts on Pol η structures. a. The dominant lattice contact between two hpol η molecules (silver and gold) in the type 1 crystals. b. A close-up view of the hydrophobic
Mapping QTL for Seedling Root Traits in Common Wheat
 2005,38(10):1951-1957 Scientia Agricultura Sinica 1,2,3 1 1 1 2 1 / / 100081 2 050021 3 100039 DH 10 14 11 15 5A 4B 2D 6D 7D 3 2 3 3 2 2 2 3 2 1 3 1 3 DH Mapping for Seedling Root Traits in Common Wheat
2005,38(10):1951-1957 Scientia Agricultura Sinica 1,2,3 1 1 1 2 1 / / 100081 2 050021 3 100039 DH 10 14 11 15 5A 4B 2D 6D 7D 3 2 3 3 2 2 2 3 2 1 3 1 3 DH Mapping for Seedling Root Traits in Common Wheat
Regulatory Change in YABBY-like Transcription Factor Led to Evolution of Extreme Fruit Size during Tomato Domestication
 SUPPORTING ONLINE MATERIALS Regulatory Change in YABBY-like Transcription Factor Led to Evolution of Extreme Fruit Size during Tomato Domestication Bin Cong, Luz Barrero, & Steven Tanksley 1 SUPPORTING
SUPPORTING ONLINE MATERIALS Regulatory Change in YABBY-like Transcription Factor Led to Evolution of Extreme Fruit Size during Tomato Domestication Bin Cong, Luz Barrero, & Steven Tanksley 1 SUPPORTING
Illegitimate translation causes unexpected gene expression from on-target out-of-frame alleles
 Illegitimate translation causes unexpected gene expression from on-target out-of-frame alleles created by CRISPR-Cas9 Shigeru Makino, Ryutaro Fukumura, Yoichi Gondo* Mutagenesis and Genomics Team, RIKEN
Illegitimate translation causes unexpected gene expression from on-target out-of-frame alleles created by CRISPR-Cas9 Shigeru Makino, Ryutaro Fukumura, Yoichi Gondo* Mutagenesis and Genomics Team, RIKEN
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng Supplementary Figure 1. The phenotypes of PI , BR121, and Harosoy under short-day conditions.
 Supplementary Figure 1 The phenotypes of PI 159925, BR121, and Harosoy under short-day conditions. (a) Plant height. (b) Number of branches. (c) Average internode length. (d) Number of nodes. (e) Pods
Supplementary Figure 1 The phenotypes of PI 159925, BR121, and Harosoy under short-day conditions. (a) Plant height. (b) Number of branches. (c) Average internode length. (d) Number of nodes. (e) Pods
Title. Authors. Characterization of a major QTL for manganese accumulation in rice grain
 Title Characterization of a major QTL for manganese accumulation in rice grain Authors Chaolei Liu, Guang Chen, Yuanyuan Li, Youlin Peng, Anpeng Zhang, Kai Hong, Hongzhen Jiang, Banpu Ruan, Bin Zhang,
Title Characterization of a major QTL for manganese accumulation in rice grain Authors Chaolei Liu, Guang Chen, Yuanyuan Li, Youlin Peng, Anpeng Zhang, Kai Hong, Hongzhen Jiang, Banpu Ruan, Bin Zhang,
11/24/13. Science, then, and now. Computational Structural Bioinformatics. Learning curve. ECS129 Instructor: Patrice Koehl
 Computational Structural Bioinformatics ECS129 Instructor: Patrice Koehl http://www.cs.ucdavis.edu/~koehl/teaching/ecs129/index.html koehl@cs.ucdavis.edu Learning curve Math / CS Biology/ Chemistry Pre-requisite
Computational Structural Bioinformatics ECS129 Instructor: Patrice Koehl http://www.cs.ucdavis.edu/~koehl/teaching/ecs129/index.html koehl@cs.ucdavis.edu Learning curve Math / CS Biology/ Chemistry Pre-requisite
Genome-wide discovery of G-quadruplex forming sequences and their functional
 *Correspondence and requests for materials should be addressed to R.G. (rohini@nipgr.ac.in) Genome-wide discovery of G-quadruplex forming sequences and their functional relevance in plants Rohini Garg*,
*Correspondence and requests for materials should be addressed to R.G. (rohini@nipgr.ac.in) Genome-wide discovery of G-quadruplex forming sequences and their functional relevance in plants Rohini Garg*,
GATA family of transcription factors of vertebrates: phylogenetics and chromosomal synteny
 Phylogenetics and chromosomal synteny of the GATAs 1273 GATA family of transcription factors of vertebrates: phylogenetics and chromosomal synteny CHUNJIANG HE, HANHUA CHENG* and RONGJIA ZHOU* Department
Phylogenetics and chromosomal synteny of the GATAs 1273 GATA family of transcription factors of vertebrates: phylogenetics and chromosomal synteny CHUNJIANG HE, HANHUA CHENG* and RONGJIA ZHOU* Department
Application of new distance matrix to phylogenetic tree construction
 Application of new distance matrix to phylogenetic tree construction P.V.Lakshmi Computer Science & Engg Dept GITAM Institute of Technology GITAM University Andhra Pradesh India Allam Appa Rao Jawaharlal
Application of new distance matrix to phylogenetic tree construction P.V.Lakshmi Computer Science & Engg Dept GITAM Institute of Technology GITAM University Andhra Pradesh India Allam Appa Rao Jawaharlal
Supplementary Information. Recognition of the pre-mirna structure by Drosophila Dicer-1
 Supplementary Information Recognition of the pre-mirna structure by Drosophila Dicer-1 Akihisa Tsutsumi 1,2, Tomoko Kawamata 1, Natsuko Izumi 1 Hervé Seitz 3,4 and Yukihide Tomari 1,2 Nature Structural
Supplementary Information Recognition of the pre-mirna structure by Drosophila Dicer-1 Akihisa Tsutsumi 1,2, Tomoko Kawamata 1, Natsuko Izumi 1 Hervé Seitz 3,4 and Yukihide Tomari 1,2 Nature Structural
Supplemental Data. Fernández-Calvo et al. Plant Cell. (2011) /tpc
 Supplemental Data. Fernández-Calvo et al. Plant Cell. (2011). 10.1105/tpc.110.080788 Supplemental Figure S1. Phylogenetic tree of MYC2-related proteins from Arabidopsis and other plants. Phenogram representation
Supplemental Data. Fernández-Calvo et al. Plant Cell. (2011). 10.1105/tpc.110.080788 Supplemental Figure S1. Phylogenetic tree of MYC2-related proteins from Arabidopsis and other plants. Phenogram representation
Quantitative Measurement of Genome-wide Protein Domain Co-occurrence of Transcription Factors
 Quantitative Measurement of Genome-wide Protein Domain Co-occurrence of Transcription Factors Arli Parikesit, Peter F. Stadler, Sonja J. Prohaska Bioinformatics Group Institute of Computer Science University
Quantitative Measurement of Genome-wide Protein Domain Co-occurrence of Transcription Factors Arli Parikesit, Peter F. Stadler, Sonja J. Prohaska Bioinformatics Group Institute of Computer Science University
Enhancing hydrogen production of microalgae by redirecting electrons from photosystem I to hydrogenase
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Energy & Environmental Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supplementary information for Enhancing hydrogen production of microalgae
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Energy & Environmental Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supplementary information for Enhancing hydrogen production of microalgae
Penghui Li, Beibei Chen, Gaoyang Zhang, Longxiang Chen, Qiang Dong, Jiangqi Wen, Kirankumar S. Mysore and Jian Zhao
 New Phytologist Supporting Information Regulation of anthocyanin and proanthocyanidin biosynthesis by Medicago truncatula bhlh transcription factor MtTT8 Penghui Li, Beibei Chen, Gaoyang Zhang, Longxiang
New Phytologist Supporting Information Regulation of anthocyanin and proanthocyanidin biosynthesis by Medicago truncatula bhlh transcription factor MtTT8 Penghui Li, Beibei Chen, Gaoyang Zhang, Longxiang
Supplementary Table 1. Primers used in this study.
 Supplementary Tale 1. Primers used in this study. Name Primer sequence (5'-3') Primers of PCR-ased molecular markers developed in this study M1 F M1 R M2 F M2 R M3 F M3 R M4 F M4 R M5 F M5 R M6 F M6 R
Supplementary Tale 1. Primers used in this study. Name Primer sequence (5'-3') Primers of PCR-ased molecular markers developed in this study M1 F M1 R M2 F M2 R M3 F M3 R M4 F M4 R M5 F M5 R M6 F M6 R
Genetic dissection of chlorophyll content at different growth stages in common wheat
 c Indian Academy of Sciences RESEARCH ARTICLE Genetic dissection of chlorophyll content at different growth stages in common wheat KUNPU ZHANG 1,2, ZHIJUN FANG 3, YAN LIANG 1 and JICHUN TIAN 1 1 State
c Indian Academy of Sciences RESEARCH ARTICLE Genetic dissection of chlorophyll content at different growth stages in common wheat KUNPU ZHANG 1,2, ZHIJUN FANG 3, YAN LIANG 1 and JICHUN TIAN 1 1 State
Welcome to BIOL 572: Recombinant DNA techniques
 Lecture 1: 1 Welcome to BIOL 572: Recombinant DNA techniques Agenda 1: Introduce yourselves Agenda 2: Course introduction Agenda 3: Some logistics for BIOL 572 Agenda 4: Q&A section Agenda 1: Introduce
Lecture 1: 1 Welcome to BIOL 572: Recombinant DNA techniques Agenda 1: Introduce yourselves Agenda 2: Course introduction Agenda 3: Some logistics for BIOL 572 Agenda 4: Q&A section Agenda 1: Introduce
Pyrobayes: an improved base caller for SNP discovery in pyrosequences
 Pyrobayes: an improved base caller for SNP discovery in pyrosequences Aaron R Quinlan, Donald A Stewart, Michael P Strömberg & Gábor T Marth Supplementary figures and text: Supplementary Figure 1. The
Pyrobayes: an improved base caller for SNP discovery in pyrosequences Aaron R Quinlan, Donald A Stewart, Michael P Strömberg & Gábor T Marth Supplementary figures and text: Supplementary Figure 1. The
Effect of temperature on endogenous hormone levels and opposite phyllotaxy in maize leaf primordial
 Effect of temperature on endogenous hormone levels and opposite phyllotaxy in maize leaf primordial H. Ye, G.M. Han, Q. Ma, Y.Q. Tan, H.Y. Jiang, S.W. Zhu and B.J. Cheng School of Life Sciences, Anhui
Effect of temperature on endogenous hormone levels and opposite phyllotaxy in maize leaf primordial H. Ye, G.M. Han, Q. Ma, Y.Q. Tan, H.Y. Jiang, S.W. Zhu and B.J. Cheng School of Life Sciences, Anhui
Hereditary Hemochromatosis
 Hereditary Hemochromatosis The HFE gene Becky Reese What is hereditary hemochromatosis? Recessively inherited Iron overload disorder Inability to regulate iron absorption No cure http://www.consultant360.com/article/genetics-gastroenterology-what-you-need-know-part-1
Hereditary Hemochromatosis The HFE gene Becky Reese What is hereditary hemochromatosis? Recessively inherited Iron overload disorder Inability to regulate iron absorption No cure http://www.consultant360.com/article/genetics-gastroenterology-what-you-need-know-part-1
List of supplementary data
 List of supplementary data Figure S1 Amino acid alignment for GiNT Figure S2Amino acid alignment and phylogenetic analysis for GiGS1 and GiGS2 Figure S3 Amino acid alignment for GiGluS Figure S4 Amino
List of supplementary data Figure S1 Amino acid alignment for GiNT Figure S2Amino acid alignment and phylogenetic analysis for GiGS1 and GiGS2 Figure S3 Amino acid alignment for GiGluS Figure S4 Amino
Cryo-EM data collection, refinement and validation statistics
 1 Table S1 Cryo-EM data collection, refinement and validation statistics Data collection and processing CPSF-160 WDR33 (EMDB-7114) (PDB 6BM0) CPSF-160 WDR33 (EMDB-7113) (PDB 6BLY) CPSF-160 WDR33 CPSF-30
1 Table S1 Cryo-EM data collection, refinement and validation statistics Data collection and processing CPSF-160 WDR33 (EMDB-7114) (PDB 6BM0) CPSF-160 WDR33 (EMDB-7113) (PDB 6BLY) CPSF-160 WDR33 CPSF-30
CGS 5991 (2 Credits) Bioinformatics Tools
 CAP 5991 (3 Credits) Introduction to Bioinformatics CGS 5991 (2 Credits) Bioinformatics Tools Giri Narasimhan 8/26/03 CAP/CGS 5991: Lecture 1 1 Course Schedules CAP 5991 (3 credit) will meet every Tue
CAP 5991 (3 Credits) Introduction to Bioinformatics CGS 5991 (2 Credits) Bioinformatics Tools Giri Narasimhan 8/26/03 CAP/CGS 5991: Lecture 1 1 Course Schedules CAP 5991 (3 credit) will meet every Tue
Bioinformatics tools for phylogeny and visualization. Yanbin Yin
 Bioinformatics tools for phylogeny and visualization Yanbin Yin 1 Homework assignment 5 1. Take the MAFFT alignment http://cys.bios.niu.edu/yyin/teach/pbb/purdue.cellwall.list.lignin.f a.aln as input and
Bioinformatics tools for phylogeny and visualization Yanbin Yin 1 Homework assignment 5 1. Take the MAFFT alignment http://cys.bios.niu.edu/yyin/teach/pbb/purdue.cellwall.list.lignin.f a.aln as input and
AtTIL-P91V. AtTIL-P92V. AtTIL-P95V. AtTIL-P98V YFP-HPR
 Online Resource 1. Primers used to generate constructs AtTIL-P91V, AtTIL-P92V, AtTIL-P95V and AtTIL-P98V and YFP(HPR) using overlapping PCR. pentr/d- TOPO-AtTIL was used as template to generate the constructs
Online Resource 1. Primers used to generate constructs AtTIL-P91V, AtTIL-P92V, AtTIL-P95V and AtTIL-P98V and YFP(HPR) using overlapping PCR. pentr/d- TOPO-AtTIL was used as template to generate the constructs
Prof. Fahd M. Nasr. Lebanese university Faculty of sciences I Department of Natural Sciences.
 Prof. Fahd M. Nasr Lebanese university Faculty of sciences I Department of Natural Sciences fnasr@ul.edu.lb B3206 Microbial Genetics Eukaryotic M. G. The yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae as a genetic model
Prof. Fahd M. Nasr Lebanese university Faculty of sciences I Department of Natural Sciences fnasr@ul.edu.lb B3206 Microbial Genetics Eukaryotic M. G. The yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae as a genetic model
Fig. S1. Proliferation and cell cycle exit are affected by the med mutation. (A,B) M-phase nuclei are visualized by a-ph3 labeling in wild-type (A)
 Fig. S1. Proliferation and cell cycle exit are affected by the med mutation. (A,B) M-phase nuclei are visualized by a-ph3 labeling in wild-type (A) and mutant (B) 4 dpf retinae. The central retina of the
Fig. S1. Proliferation and cell cycle exit are affected by the med mutation. (A,B) M-phase nuclei are visualized by a-ph3 labeling in wild-type (A) and mutant (B) 4 dpf retinae. The central retina of the
. Supplementary Information
 . Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure S1. Mature embryo sac observations. Supplementary Figure S2. STT observations. Supplementary Figure S3. Comparison of the PTB1 cdna with that of the mutant.
. Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure S1. Mature embryo sac observations. Supplementary Figure S2. STT observations. Supplementary Figure S3. Comparison of the PTB1 cdna with that of the mutant.
Protein function studies: history, current status and future trends
 19 3 2007 6 Chinese Bulletin of Life Sciences Vol. 19, No. 3 Jun., 2007 1004-0374(2007)03-0294-07 ( 100871) Q51A Protein function studies: history, current status and future trends MA Jing, GE Xi, CHANG
19 3 2007 6 Chinese Bulletin of Life Sciences Vol. 19, No. 3 Jun., 2007 1004-0374(2007)03-0294-07 ( 100871) Q51A Protein function studies: history, current status and future trends MA Jing, GE Xi, CHANG
Slovene Plant Gene Bank (SPGB) and Genetic Resources Programme
 Slovene Plant Gene Bank (SPGB) and Genetic Resources Programme Second Meeting of the ECPGR Working Group on Leafy Vegetables 8 9 October, Ljubljana, Slovenia Vladimir MEGLIČ, Jelka ŠUŠTAR VOZLIČ Slovene
Slovene Plant Gene Bank (SPGB) and Genetic Resources Programme Second Meeting of the ECPGR Working Group on Leafy Vegetables 8 9 October, Ljubljana, Slovenia Vladimir MEGLIČ, Jelka ŠUŠTAR VOZLIČ Slovene
Using Base Pairing Probabilities for MiRNA Recognition. Yet Another SVM for MiRNA Recognition: yasmir
 0. Using Base Pairing Probabilities for MiRNA Recognition Yet Another SVM for MiRNA Recognition: yasmir Daniel Pasailă, Irina Mohorianu, Liviu Ciortuz Department of Computer Science Al. I. Cuza University,
0. Using Base Pairing Probabilities for MiRNA Recognition Yet Another SVM for MiRNA Recognition: yasmir Daniel Pasailă, Irina Mohorianu, Liviu Ciortuz Department of Computer Science Al. I. Cuza University,
Model building and validation for cryo-em maps at low resolution
 International Workshop of Advanced Image Processing of Cryo-Electron Microscopy 2015 Tsinghua University, Beijing, China June 3-7, 2015 Model building and validation for cryo-em maps at low resolution
International Workshop of Advanced Image Processing of Cryo-Electron Microscopy 2015 Tsinghua University, Beijing, China June 3-7, 2015 Model building and validation for cryo-em maps at low resolution
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng Supplementary Figure 1. ssp mutant phenotypes in a functional SP background.
 Supplementary Figure 1 ssp mutant phenotypes in a functional SP background. (a,b) Statistical comparisons of primary and sympodial shoot flowering times as determined by mean values for leaf number on
Supplementary Figure 1 ssp mutant phenotypes in a functional SP background. (a,b) Statistical comparisons of primary and sympodial shoot flowering times as determined by mean values for leaf number on
Title: A novel mechanism of protein thermostability: a unique N-terminal domain confers
 1 2 Title: A novel mechanism of protein thermostability: a unique N-terminal domain confers heat resistance to Fe/Mn-SODs 3 4 Running Title: Thermostability-improving peptide for SODs 5 6 7 8 Authors Wei
1 2 Title: A novel mechanism of protein thermostability: a unique N-terminal domain confers heat resistance to Fe/Mn-SODs 3 4 Running Title: Thermostability-improving peptide for SODs 5 6 7 8 Authors Wei
** LCA LCN PCA
 % of wild type value % of wild type value a 12 1 8 2 b 12 1 8 2 LCA LCN PCA Col- sod3-1 Supplementary Figure 1 sod3-1 influences cell proliferation. (a) Fifth leaf cell area (LCA) and leaf cell number
% of wild type value % of wild type value a 12 1 8 2 b 12 1 8 2 LCA LCN PCA Col- sod3-1 Supplementary Figure 1 sod3-1 influences cell proliferation. (a) Fifth leaf cell area (LCA) and leaf cell number
Multiple Sequence Alignment. Sequences
 Multiple Sequence Alignment Sequences > YOR020c mstllksaksivplmdrvlvqrikaqaktasglylpe knveklnqaevvavgpgftdangnkvvpqvkvgdqvl ipqfggstiklgnddevilfrdaeilakiakd > crassa mattvrsvksliplldrvlvqrvkaeaktasgiflpe
Multiple Sequence Alignment Sequences > YOR020c mstllksaksivplmdrvlvqrikaqaktasglylpe knveklnqaevvavgpgftdangnkvvpqvkvgdqvl ipqfggstiklgnddevilfrdaeilakiakd > crassa mattvrsvksliplldrvlvqrvkaeaktasgiflpe
Supplementary Methods
 Supplementary Methods Microarray analysis Grains of 7 DAP of the wild-type and gif1 were harvested for RNA preparation. Microarray analysis was performed with the Affymetrix (Santa Clara, CA) GeneChip
Supplementary Methods Microarray analysis Grains of 7 DAP of the wild-type and gif1 were harvested for RNA preparation. Microarray analysis was performed with the Affymetrix (Santa Clara, CA) GeneChip
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1. HSP21 expression in 35S:HSP21 and hsp21 knockdown plants. (a) Since no T- DNA insertion line for HSP21 is available in the publicly available T-DNA collections,
Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1. HSP21 expression in 35S:HSP21 and hsp21 knockdown plants. (a) Since no T- DNA insertion line for HSP21 is available in the publicly available T-DNA collections,
Supplementary Figure 1. Nature Biotechnology: doi: /nbt.4067
 Supplementary Figure 1 Phylogenetic tree of GAUT Protein Family and gene model, RNAi construct, and relative transcript abundance of GAUT4 in switchgrass, rice and poplar knockdown (KD) lines. Phylogenetic
Supplementary Figure 1 Phylogenetic tree of GAUT Protein Family and gene model, RNAi construct, and relative transcript abundance of GAUT4 in switchgrass, rice and poplar knockdown (KD) lines. Phylogenetic
ACTA AGRONOMICA SINICA SSR. Classification for Some Sterile Lines and Their Restorers of Hybrid Rice with SSR Markers
 32 2 2006 2 169 175 ACTA AGRONOMICA SINICA Vol132, No12 pp1 169-175 Feb1, 2006 SSR 1 1,2, # 1 1 1 1, 3 2 2 Ξ ( 1, 330045 ; 2,,100094) : ( Oryza sativa L. ) 12 36 SSR(simple sequence repeats), 5 7 54 300,
32 2 2006 2 169 175 ACTA AGRONOMICA SINICA Vol132, No12 pp1 169-175 Feb1, 2006 SSR 1 1,2, # 1 1 1 1, 3 2 2 Ξ ( 1, 330045 ; 2,,100094) : ( Oryza sativa L. ) 12 36 SSR(simple sequence repeats), 5 7 54 300,
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Zn 2+ -binding sites in USP18. (a) The two molecules of USP18 present in the asymmetric unit are shown. Chain A is shown in blue, chain B in green. Bound Zn 2+ ions are shown as
Supplementary Figure 1 Zn 2+ -binding sites in USP18. (a) The two molecules of USP18 present in the asymmetric unit are shown. Chain A is shown in blue, chain B in green. Bound Zn 2+ ions are shown as
FSC-W FSC-H CD4 CD62-L
 Supplementary Fig. 1 a SSC-A FSC-A FSC-W FSC-H SSC-W SSC-H CD4 CD62-L b SSC-A FSC-A FSC-W FSC-A FSC-A 7-AAD FSC-A CD4 IL-9 CD4 c SSC-A FSC-A FSC-W FSC-H SSC-W SSC-H 7-AAD KI67 Annexin-V 7-AAD d I L -5
Supplementary Fig. 1 a SSC-A FSC-A FSC-W FSC-H SSC-W SSC-H CD4 CD62-L b SSC-A FSC-A FSC-W FSC-A FSC-A 7-AAD FSC-A CD4 IL-9 CD4 c SSC-A FSC-A FSC-W FSC-H SSC-W SSC-H 7-AAD KI67 Annexin-V 7-AAD d I L -5
Multiple Sequence Alignments
 Multiple Sequence Alignments...... Elements of Bioinformatics Spring, 2003 Tom Carter http://astarte.csustan.edu/ tom/ March, 2003 1 Sequence Alignments Often, we would like to make direct comparisons
Multiple Sequence Alignments...... Elements of Bioinformatics Spring, 2003 Tom Carter http://astarte.csustan.edu/ tom/ March, 2003 1 Sequence Alignments Often, we would like to make direct comparisons
DNA Phylogeny. Signals and Systems in Biology Kushal EE, IIT Delhi
 DNA Phylogeny Signals and Systems in Biology Kushal Shah @ EE, IIT Delhi Phylogenetics Grouping and Division of organisms Keeps changing with time Splitting, hybridization and termination Cladistics :
DNA Phylogeny Signals and Systems in Biology Kushal Shah @ EE, IIT Delhi Phylogenetics Grouping and Division of organisms Keeps changing with time Splitting, hybridization and termination Cladistics :
Bioinformatics tools to analyze complex genomes. Yves Van de Peer Ghent University/VIB
 Bioinformatics tools to analyze complex genomes Yves Van de Peer Ghent University/VIB Detecting colinearity and large-scale gene duplications A 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Speciation/Duplicatio n S1 S2 1
Bioinformatics tools to analyze complex genomes Yves Van de Peer Ghent University/VIB Detecting colinearity and large-scale gene duplications A 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Speciation/Duplicatio n S1 S2 1
Quantitative trait locus analysis for ear height in maize based on a recombinant inbred line population
 Quantitative trait locus analysis for ear height in maize based on a recombinant inbred line population Z.Q. Li 4,5, H.M. Zhang 1,4, X.P. Wu 1,4, Y. Sun 3,4 and X.H. Liu 2 1 Maize Research Institute, Shanxi
Quantitative trait locus analysis for ear height in maize based on a recombinant inbred line population Z.Q. Li 4,5, H.M. Zhang 1,4, X.P. Wu 1,4, Y. Sun 3,4 and X.H. Liu 2 1 Maize Research Institute, Shanxi
Supplemental Data. Chen and Thelen (2010). Plant Cell /tpc
 Supplemental Data. Chen and Thelen (2010). Plant Cell 10.1105/tpc.109.071837 1 C Total 5 kg 20 kg 100 kg Transmission Image 100 kg soluble pdtpi-gfp Plastid (PDH-alpha) Mito (PDH-alpha) GFP Image vector
Supplemental Data. Chen and Thelen (2010). Plant Cell 10.1105/tpc.109.071837 1 C Total 5 kg 20 kg 100 kg Transmission Image 100 kg soluble pdtpi-gfp Plastid (PDH-alpha) Mito (PDH-alpha) GFP Image vector
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature13082 Supplementary Table 1. Examination of nectar production in wild-type and atsweet9 flowers. No. of flowers with detectable nectar out of the total observed
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature13082 Supplementary Table 1. Examination of nectar production in wild-type and atsweet9 flowers. No. of flowers with detectable nectar out of the total observed
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:1.138/nature111 cytosol Model: PILS function in cellular auxin homeostasis ER nucleus IAA degradation? sequestration? conjugation? storage? signalling? PILS IAA ER cytosol Supplemental Figure 1 Model
doi:1.138/nature111 cytosol Model: PILS function in cellular auxin homeostasis ER nucleus IAA degradation? sequestration? conjugation? storage? signalling? PILS IAA ER cytosol Supplemental Figure 1 Model
Table S1 List of primers used for genotyping and qrt-pcr.
 Table S1 List of primers used for genotyping and qrt-pcr. genotyping! allele! ligomer*! 5'-sequence-3'! rice! d10-2! F! TTGGCTTTGCCTCGTTTC!!! R! AGCCTCCACTTGTACTGTG! Arabidopsis! max2-3, max2-4! F! ACTCTCTCCGACCTCCCTGACG!!!
Table S1 List of primers used for genotyping and qrt-pcr. genotyping! allele! ligomer*! 5'-sequence-3'! rice! d10-2! F! TTGGCTTTGCCTCGTTTC!!! R! AGCCTCCACTTGTACTGTG! Arabidopsis! max2-3, max2-4! F! ACTCTCTCCGACCTCCCTGACG!!!
Pomegranate-Like N, P-Doped Nanospheres as Highly Active Electrocatalysts for Alkaline Hydrogen Evolution
 Supporting Information Pomegranate-Like N, P-Doped Mo2C@C Nanospheres as Highly Active Electrocatalysts for Alkaline Hydrogen Evolution Yu-Yun Chen,,,# Yun Zhang,,# Wen-Jie Jiang,, Xing Zhang,, Zhihui
Supporting Information Pomegranate-Like N, P-Doped Mo2C@C Nanospheres as Highly Active Electrocatalysts for Alkaline Hydrogen Evolution Yu-Yun Chen,,,# Yun Zhang,,# Wen-Jie Jiang,, Xing Zhang,, Zhihui
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11510 Supplementary Table 1. Indel Index Removal Gene Number of Starting Sequences Number of Final Sequences Percentage of Sequences Removed based on the Indel
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11510 Supplementary Table 1. Indel Index Removal Gene Number of Starting Sequences Number of Final Sequences Percentage of Sequences Removed based on the Indel
Genetic structure and eco-geographical differentiation of cultivated Hsien rice (Oryza sativa L. subsp. indica) in China revealed by microsatellites
 Article Crop Germplasm Resources January 2013 Vol.58 No.3: 344 352 doi: 10.1007/s11434-012-5396-4 Genetic structure and eco-geographical differentiation of cultivated Hsien rice (Oryza sativa L. subsp.
Article Crop Germplasm Resources January 2013 Vol.58 No.3: 344 352 doi: 10.1007/s11434-012-5396-4 Genetic structure and eco-geographical differentiation of cultivated Hsien rice (Oryza sativa L. subsp.
SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION Identification and validation of circrnas Ribo-minus RNA-seq data sets used in identification of circrnas in Oryza sativa and Arabidopsis thaliana were downloaded from NCBI (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/).
SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION Identification and validation of circrnas Ribo-minus RNA-seq data sets used in identification of circrnas in Oryza sativa and Arabidopsis thaliana were downloaded from NCBI (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/).
Structure and RNA-binding properties. of the Not1 Not2 Not5 module of the yeast Ccr4 Not complex
 Structure and RNA-binding properties of the Not1 Not2 Not5 module of the yeast Ccr4 Not complex Varun Bhaskar 1, Vladimir Roudko 2,3, Jerome Basquin 1, Kundan Sharma 4, Henning Urlaub 4, Bertrand Seraphin
Structure and RNA-binding properties of the Not1 Not2 Not5 module of the yeast Ccr4 Not complex Varun Bhaskar 1, Vladimir Roudko 2,3, Jerome Basquin 1, Kundan Sharma 4, Henning Urlaub 4, Bertrand Seraphin
Supplemental material
 Supplemental material Table 1- Segregation analysis of sgt1a sgt1b double mutant plants Parental genotype No. of lines Normal seeds Phenotype Abnormal seeds Ratio of abnormal seeds (%) WT 3 171 2 1.16
Supplemental material Table 1- Segregation analysis of sgt1a sgt1b double mutant plants Parental genotype No. of lines Normal seeds Phenotype Abnormal seeds Ratio of abnormal seeds (%) WT 3 171 2 1.16
Variation, Evolution, and Correlation Analysis of C+G Content and Genome or Chromosome Size in Different Kingdoms and Phyla
 Variation, Evolution, and Correlation Analysis of C+G Content and Genome or Chromosome Size in Different Kingdoms and Phyla Xiu-Qing Li 1 *, Donglei Du 2 1 Molecular Genetics Laboratory, Potato Research
Variation, Evolution, and Correlation Analysis of C+G Content and Genome or Chromosome Size in Different Kingdoms and Phyla Xiu-Qing Li 1 *, Donglei Du 2 1 Molecular Genetics Laboratory, Potato Research
Prospecting for Green Revolution Genes
 Learning Objectives: Prospecting for Green Revolution Genes 1) Discover how changes in individual genes produce phenotypic change 2) Learn to apply bioinformatics tools to identify groups of related genes
Learning Objectives: Prospecting for Green Revolution Genes 1) Discover how changes in individual genes produce phenotypic change 2) Learn to apply bioinformatics tools to identify groups of related genes
Comparing Genomes! Homologies and Families! Sequence Alignments!
 Comparing Genomes! Homologies and Families! Sequence Alignments! Allows us to achieve a greater understanding of vertebrate evolution! Tells us what is common and what is unique between different species
Comparing Genomes! Homologies and Families! Sequence Alignments! Allows us to achieve a greater understanding of vertebrate evolution! Tells us what is common and what is unique between different species
EVOLUTIONARY DISTANCE MODEL BASED ON DIFFERENTIAL EQUATION AND MARKOV PROCESS
 August 0 Vol 4 No 005-0 JATIT & LLS All rights reserved ISSN: 99-8645 wwwjatitorg E-ISSN: 87-95 EVOLUTIONAY DISTANCE MODEL BASED ON DIFFEENTIAL EUATION AND MAKOV OCESS XIAOFENG WANG College of Mathematical
August 0 Vol 4 No 005-0 JATIT & LLS All rights reserved ISSN: 99-8645 wwwjatitorg E-ISSN: 87-95 EVOLUTIONAY DISTANCE MODEL BASED ON DIFFEENTIAL EUATION AND MAKOV OCESS XIAOFENG WANG College of Mathematical
Unique variations of SRY gene result in distinct patrilineal phylogeny of Capra hircus and other domestic Bovidae*
 Animal Science Papers and Reports vol. 30 (2013), no. 3, 219-227 Institute of Genetics and Animal Breeding, Jastrzębiec, Poland Unique variations of SRY gene result in distinct patrilineal phylogeny of
Animal Science Papers and Reports vol. 30 (2013), no. 3, 219-227 Institute of Genetics and Animal Breeding, Jastrzębiec, Poland Unique variations of SRY gene result in distinct patrilineal phylogeny of
Genomics and bioinformatics summary. Finding genes -- computer searches
 Genomics and bioinformatics summary 1. Gene finding: computer searches, cdnas, ESTs, 2. Microarrays 3. Use BLAST to find homologous sequences 4. Multiple sequence alignments (MSAs) 5. Trees quantify sequence
Genomics and bioinformatics summary 1. Gene finding: computer searches, cdnas, ESTs, 2. Microarrays 3. Use BLAST to find homologous sequences 4. Multiple sequence alignments (MSAs) 5. Trees quantify sequence
7.06 Problem Set #4, Spring 2005
 7.06 Problem Set #4, Spring 2005 1. You re doing a mutant hunt in S. cerevisiae (budding yeast), looking for temperaturesensitive mutants that are defective in the cell cycle. You discover a mutant strain
7.06 Problem Set #4, Spring 2005 1. You re doing a mutant hunt in S. cerevisiae (budding yeast), looking for temperaturesensitive mutants that are defective in the cell cycle. You discover a mutant strain
Camello, a novel family of Histone Acetyltransferases that acetylate histone H4 and is essential for zebrafish development
 Supplementary Information: Camello, a novel family of Histone Acetyltransferases that acetylate histone H4 and is essential for zebrafish development Krishanpal Karmodiya 1, Krishanpal Anamika 1,2, Vijaykumar
Supplementary Information: Camello, a novel family of Histone Acetyltransferases that acetylate histone H4 and is essential for zebrafish development Krishanpal Karmodiya 1, Krishanpal Anamika 1,2, Vijaykumar
Giri Narasimhan. CAP 5510: Introduction to Bioinformatics CGS 5166: Bioinformatics Tools. Evaluation. Course Homepage.
 CAP 5510: Introduction to Bioinformatics CGS 5166: Bioinformatics Tools Giri Narasimhan ECS 389; Phone: x3748 giri@cis.fiu.edu www.cis.fiu.edu/~giri/teach/bioinfs06.html 1/12/06 CAP5510/CGS5166 1 Evaluation
CAP 5510: Introduction to Bioinformatics CGS 5166: Bioinformatics Tools Giri Narasimhan ECS 389; Phone: x3748 giri@cis.fiu.edu www.cis.fiu.edu/~giri/teach/bioinfs06.html 1/12/06 CAP5510/CGS5166 1 Evaluation
Molecular Coevolution of the Vertebrate Cytochrome c 1 and Rieske Iron Sulfur Protein in the Cytochrome bc 1 Complex
 Molecular Coevolution of the Vertebrate Cytochrome c 1 and Rieske Iron Sulfur Protein in the Cytochrome bc 1 Complex Kimberly Baer *, David McClellan Department of Integrative Biology, Brigham Young University,
Molecular Coevolution of the Vertebrate Cytochrome c 1 and Rieske Iron Sulfur Protein in the Cytochrome bc 1 Complex Kimberly Baer *, David McClellan Department of Integrative Biology, Brigham Young University,
MULTIPLE SEQUENCE ALIGNMENT FOR CONSTRUCTION OF PHYLOGENETIC TREE
 MULTIPLE SEQUENCE ALIGNMENT FOR CONSTRUCTION OF PHYLOGENETIC TREE Manmeet Kaur 1, Navneet Kaur Bawa 2 1 M-tech research scholar (CSE Dept) ACET, Manawala,Asr 2 Associate Professor (CSE Dept) ACET, Manawala,Asr
MULTIPLE SEQUENCE ALIGNMENT FOR CONSTRUCTION OF PHYLOGENETIC TREE Manmeet Kaur 1, Navneet Kaur Bawa 2 1 M-tech research scholar (CSE Dept) ACET, Manawala,Asr 2 Associate Professor (CSE Dept) ACET, Manawala,Asr
Time allowed: 2 hours Answer ALL questions in Section A, ALL PARTS of the question in Section B and ONE question from Section C.
 UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Biological Sciences Main Series UG Examination 2017-2018 GENETICS BIO-5009A Time allowed: 2 hours Answer ALL questions in Section A, ALL PARTS of the question in Section
UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Biological Sciences Main Series UG Examination 2017-2018 GENETICS BIO-5009A Time allowed: 2 hours Answer ALL questions in Section A, ALL PARTS of the question in Section
Gene mention normalization in full texts using GNAT and LINNAEUS
 Gene mention normalization in full texts using GNAT and LINNAEUS Illés Solt 1,2, Martin Gerner 3, Philippe Thomas 2, Goran Nenadic 4, Casey M. Bergman 3, Ulf Leser 2, Jörg Hakenberg 5 1 Department of Telecommunications
Gene mention normalization in full texts using GNAT and LINNAEUS Illés Solt 1,2, Martin Gerner 3, Philippe Thomas 2, Goran Nenadic 4, Casey M. Bergman 3, Ulf Leser 2, Jörg Hakenberg 5 1 Department of Telecommunications
Supplemental Data. Lermontova et al. (2013). Plant Cell /tpc
 Supplemental Figure 1. Multiple alignment of the N-terminal parts of plant KNL2 orthologs. Multiple sequence alignment was performed by the MUSCLE method and visualized by the JalView program. Highly conserved
Supplemental Figure 1. Multiple alignment of the N-terminal parts of plant KNL2 orthologs. Multiple sequence alignment was performed by the MUSCLE method and visualized by the JalView program. Highly conserved
Supplementary Information for: The genome of the extremophile crucifer Thellungiella parvula
 Supplementary Information for: The genome of the extremophile crucifer Thellungiella parvula Maheshi Dassanayake 1,9, Dong-Ha Oh 1,9, Jeffrey S. Haas 1,2, Alvaro Hernandez 3, Hyewon Hong 1,4, Shahjahan
Supplementary Information for: The genome of the extremophile crucifer Thellungiella parvula Maheshi Dassanayake 1,9, Dong-Ha Oh 1,9, Jeffrey S. Haas 1,2, Alvaro Hernandez 3, Hyewon Hong 1,4, Shahjahan
In silico analysis of the NBS protein family in Ectocarpus siliculosus
 Indian Journal of Biotechnology Vol 12, January 2013, pp 98-102 In silico analysis of the NBS protein family in Ectocarpus siliculosus Niaz Mahmood 1 * and Mahdi Muhammad Moosa 1,2 1 Molecular Biology
Indian Journal of Biotechnology Vol 12, January 2013, pp 98-102 In silico analysis of the NBS protein family in Ectocarpus siliculosus Niaz Mahmood 1 * and Mahdi Muhammad Moosa 1,2 1 Molecular Biology
Supplementary Material. stress responsive genes providing protection of wheat from salinity stress
 Supplementary Material Plant growth promoting rhizobacteria Dietzia natronolimnaea modulates the expression of stress responsive genes providing protection of wheat from salinity stress Nidhi Bharti, Shiv
Supplementary Material Plant growth promoting rhizobacteria Dietzia natronolimnaea modulates the expression of stress responsive genes providing protection of wheat from salinity stress Nidhi Bharti, Shiv
Sampling Properties of DNA Sequence Data in Phylogenetic Analysis
 Sampling Properties of DNA Sequence Data in Phylogenetic Analysis Michael P. Cummings, Sarah P. Otto, 2 and John Wakeley3 Department of Integrative Biology, University of California at Berkeley We inferred
Sampling Properties of DNA Sequence Data in Phylogenetic Analysis Michael P. Cummings, Sarah P. Otto, 2 and John Wakeley3 Department of Integrative Biology, University of California at Berkeley We inferred
Biased amino acid composition in warm-blooded animals
 Biased amino acid composition in warm-blooded animals Guang-Zhong Wang and Martin J. Lercher Bioinformatics group, Heinrich-Heine-University, Düsseldorf, Germany Among eubacteria and archeabacteria, amino
Biased amino acid composition in warm-blooded animals Guang-Zhong Wang and Martin J. Lercher Bioinformatics group, Heinrich-Heine-University, Düsseldorf, Germany Among eubacteria and archeabacteria, amino
Letter to the Editor. Temperature Hypotheses. David P. Mindell, Alec Knight,? Christine Baer,$ and Christopher J. Huddlestons
 Letter to the Editor Slow Rates of Molecular Evolution Temperature Hypotheses in Birds and the Metabolic Rate and Body David P. Mindell, Alec Knight,? Christine Baer,$ and Christopher J. Huddlestons *Department
Letter to the Editor Slow Rates of Molecular Evolution Temperature Hypotheses in Birds and the Metabolic Rate and Body David P. Mindell, Alec Knight,? Christine Baer,$ and Christopher J. Huddlestons *Department
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
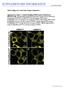 doi:10.1038/nature09606 Chen Li-Qing et al. A novel class of sugar transporters. Supplementary Figure 1. Confocal imaging of FRET sensor localization in HEK293T cells. The subcellular localization of the
doi:10.1038/nature09606 Chen Li-Qing et al. A novel class of sugar transporters. Supplementary Figure 1. Confocal imaging of FRET sensor localization in HEK293T cells. The subcellular localization of the
Genome-wide analysis of immunophilin FKBP genes and expression patterns in Zea mays
 Genome-wide analysis of immunophilin FKBP genes and expression patterns in Zea mays W.-W. Wang 1,2, Q. Ma 2, Y. Xiang 2, S.-W. Zhu 2 and B.-J. Cheng 2 1 School of Chemistry and Life Sciences, Suzhou University,
Genome-wide analysis of immunophilin FKBP genes and expression patterns in Zea mays W.-W. Wang 1,2, Q. Ma 2, Y. Xiang 2, S.-W. Zhu 2 and B.-J. Cheng 2 1 School of Chemistry and Life Sciences, Suzhou University,
The Workshop on Recent Progress in Theoretical and Computational Studies of 2D Materials Program
 The Workshop on Recent Progress in Theoretical and Computational Program December 26-27, 2015 Beijing, China December 26-27, 2015, Beijing, China The Workshop on Recent Progress in Theoretical and Computational
The Workshop on Recent Progress in Theoretical and Computational Program December 26-27, 2015 Beijing, China December 26-27, 2015, Beijing, China The Workshop on Recent Progress in Theoretical and Computational
Development of genotype independent cotton transformation protocol
 Development of genotype independent cotton transformation protocol Shyam Barampuram and Sergei Krasnyanski Department of Horticultural Science North Carolina State University What are our goals? Robust
Development of genotype independent cotton transformation protocol Shyam Barampuram and Sergei Krasnyanski Department of Horticultural Science North Carolina State University What are our goals? Robust
Systematic prediction of gene function in Arabidopsis thaliana using a probabilistic functional gene network
 Systematic prediction of gene function in Arabidopsis thaliana using a probabilistic functional gene network Sohyun Hwang 1, Seung Y Rhee 2, Edward M Marcotte 3,4 & Insuk Lee 1 protocol 1 Department of
Systematic prediction of gene function in Arabidopsis thaliana using a probabilistic functional gene network Sohyun Hwang 1, Seung Y Rhee 2, Edward M Marcotte 3,4 & Insuk Lee 1 protocol 1 Department of
Genome-Wide Computational Prediction and Analysis of Core Promoter Elements across Plant Monocots and Dicots
 Genome-Wide Computational Prediction and Analysis of Core Promoter Elements across Plant Monocots and Dicots Sunita Kumari 1, Doreen Ware 1,2 * 1 Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, New
Genome-Wide Computational Prediction and Analysis of Core Promoter Elements across Plant Monocots and Dicots Sunita Kumari 1, Doreen Ware 1,2 * 1 Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, New
The Journal of Animal & Plant Sciences, 28(5): 2018, Page: Sadia et al., ISSN:
 The Journal of Animal & Plant Sciences, 28(5): 2018, Page: 1532-1536 Sadia et al., ISSN: 1018-7081 Short Communication BIOINFORMATICS ANALYSIS OF CODON USAGE BIAS AND RNA SECONDARY STRUCTURES FOR SALT
The Journal of Animal & Plant Sciences, 28(5): 2018, Page: 1532-1536 Sadia et al., ISSN: 1018-7081 Short Communication BIOINFORMATICS ANALYSIS OF CODON USAGE BIAS AND RNA SECONDARY STRUCTURES FOR SALT
changes in gene expression, we developed and tested several models. Each model was
 Additional Files Additional File 1 File format: PDF Title: Experimental design and linear models Description: This additional file describes in detail the experimental design and linear models used to
Additional Files Additional File 1 File format: PDF Title: Experimental design and linear models Description: This additional file describes in detail the experimental design and linear models used to
Supplemental data. Vos et al. (2008). The plant TPX2 protein regulates pro-spindle assembly before nuclear envelope breakdown.
 Supplemental data. Vos et al. (2008). The plant TPX2 protein regulates pro-spindle assembly before nuclear envelope breakdown. SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE 1 ONLINE Xenopus laevis! Xenopus tropicalis! Danio rerio!
Supplemental data. Vos et al. (2008). The plant TPX2 protein regulates pro-spindle assembly before nuclear envelope breakdown. SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE 1 ONLINE Xenopus laevis! Xenopus tropicalis! Danio rerio!
York University School of Medicine, 550 First Avenue, MSB 599, New York, New York 10016, USA.
 SCF Fbxl3 Ubiquitin Ligase Targets Cryptochromes at Their Cofactor Pocket Weiman Xing 1,2, Luca Busino 3, Thomas R. Hinds 1, Samuel T. Marionni 4, Nabiha H. Saifee 1, Matthew F. Bush 4, Michele Pagano
SCF Fbxl3 Ubiquitin Ligase Targets Cryptochromes at Their Cofactor Pocket Weiman Xing 1,2, Luca Busino 3, Thomas R. Hinds 1, Samuel T. Marionni 4, Nabiha H. Saifee 1, Matthew F. Bush 4, Michele Pagano
