Regulatory Change in YABBY-like Transcription Factor Led to Evolution of Extreme Fruit Size during Tomato Domestication
|
|
|
- Maximilian Lionel Henry
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SUPPORTING ONLINE MATERIALS Regulatory Change in YABBY-like Transcription Factor Led to Evolution of Extreme Fruit Size during Tomato Domestication Bin Cong, Luz Barrero, & Steven Tanksley 1
2 SUPPORTING ONLINE FIGURES Supplementary Figure 1 Intron: 1355bp bp Exon UTR Intron cdna length: 2,722bp ORF: 2,019bp Exons: 16 Introns:15 Amino acids: 672aa Supplementary Figure 1. Depicts exons and introns of TOUSLED-like protein kinase found in the BAC. 2
3 Supplementary Figure 2 A tsl actin SFB MFB LFB carpel M W M W M W M W B tsl actin C Wild species Mutant Wild type Fasciated allele allele TA56 SFB TA56 MFB TA56 LFB LA925 SFB LA925 MFB LA925 LFB 99T748-9 SFB 99T SFB 99T SFB 99T SFB 99T SFB 99T SFB tsl actin Supplementary Figure 2. Expression analysis of the tousled gene using RT-PCR analysis. (A) tousled mrna was strongly expressed in all developing flower stages and carpels dissected from anthesis flowers in wild type TA209 and mutant LA2371. (B) Similar experiments done in mutant line LA0767 and wild type TA496. tousled expressed equally in wild type flowers buds and in mutant. W in (A) and (B) means wild type; M means mutant. (C) tousled mrna expression was examined in F2 individuals derived from S. lycopersicum (LA0925, high locule number) and S. pennellii (LA0716, wild species with low locule number) and their parental lines LA0925 and LA0716, respectively. tousled strongly expressed in lines containing wild type fas locus on chromosome 11 and lines containing mutant fas locus on chromosome 11. Actin was used as internal control. SFB: small flower buds; MFB: medium flower buds; and LFB: large flower buds. 3
4 Supplementary Figure 3 Supplementary Figure 3. A representative transformation result with the fasciated gene. Left fruit from high-locule number genotype T1 plants transformed with the fasciated wild type allele; Right: fruit from non-transformed, high-locule number genotype T1 plants derived from the same hemizygous T0 individual. Note: The extremely large tomato fruit found in modern cultivars (including LA2371 which was used in the transformation experiments) is due, not only to the fasciated QTL, but also other QTLs that increase carpel/locule number (e.g. the locule-number QTL) 1,2. Transformation/ complementation experiments using the fasciated gene were thus not expected to reduce carpel/locule number to the extent found in fruit produced by primitive or wild tomato varieties (e.g. 2-4 carpels/locules). Rather, it was only expected to significantly decrease carpel/locule number as observed. 4
5 Supplementary Figure 4 Marker EcoRI EcoRV HaeIII ScaI HindIII Supplementary Figure 4. Southern blot showing a 6-8kb insertion in the first intron of the fasciated gene in mutant. Lane labeled with 1 indicating DNA extracted from wild type TA209; 2 indicating DNA from mutant LA2371. DNAs were digested with EcoRI, EcoRV, HaeIII, ScaI and HindIII. 5
6 Supplementary Figure 5 fasciated_1 fasciated 1 ATGTCATTCGATATGACTTTTTCTTCTTCACCTTCCTCAGAACGCGTTTGTTACTTGCAA 1 ATGTCATTCGATATGACTTTTTCTTCTTCACCTTCCTCAGAACGCGTTTGTTACTTGCAA fasciated_1 fasciated 61 TGTAATTTTTGCAACACCATTCTTGCGGTTAGTGTTCCATGCAGCAACATGTTAACCTTA 61 TGTAATTTTTGCAACACCATTCTTGCGGTTAGTGTTCCATGCAGCAACATGTTAACCTTA fasciated_1 121 GTGACAGTAAGATGTGGGCATTGTGCAAATATGCTTTCTGTTAATATTGGATCTTTAATT fasciated 121 GTGACAGTAAGATGTGGGCATTGTGCAAATATGCTTTCTGTTAATATTGGATCTTTAATT fasciated_1 181 CAAGCTCTACCCCTTCAAGATGTTCAAAAGCTGCAAAGGCAACAGTACACAAATGTTGAA fasciated 181 CAAGCTCTACCCCTTCAAGATGTTCAAAAGCTGCAAAGGCAACAGTACACAAATGTTGAA fasciated_1 241 AATAATTCTAGTAATTATAAAGCTTATGGTTCATCATCATCATCCTCTTCAAAGTTCAAC fasciated 241 AATAATTCTAGTAATTATAAAGCTTATGGTTCATCATCATCATCCTCTTCAAAGTTCAAC fasciated_1 301 AGATATTCTTCCATTGTTTCTCCTCAAATTGAACCTAAAATCCCTTCGATTCGTTCACCA fasciated 301 AGATATTCTTCCATTGTTTCTCCTCAAATTGAACCTAAAATCCCTTCGATTCGTCCACCA fasciated_1 361 GAGAAAAAGACAACGTGTTCCTTCTGCGTACAACCGATTCATCAAGGAAGAGATTCAAAG fasciated 361 GAGAAAA-GACAACGTGTTCCTTCTGCGTACAACCGATTCATCAAGGAAGAGATTCAAAG fasciated_1 421 GATCAAGGCCAGTAATCCTGATATTAGCCATCGTGAAGCTTTTAGCACTGCTGCCAAAAA fasciated 420 GATCAAGGCCAGTAATCCTGATATTAGCCATCGTGAAGCTTTTAGCACTGCTGCCAAAAA fasciated_1 481 TTGGGCACATTTTCCACATATTCACTTTGGACTCAAGCTGGAGGGCAACAAATAG fasciated 480 TTGGGCACATTTTCCACATATTCACTTTGGACTCAAGCTGGAGGGCAACAAATAG Supplementary Figure 5. Sequence comparison between a new allele of fasciated gene found in S.lycopersicum cv. cerasiforme with high-locule nubmer and cultivated wild type tomato showing a nucleotide substitution and followed by one nucleotide insertion which results a truncated protein in the new allele. 6
7 SUPPORTING ONLINE TABLES Supplementary Table 1. F3 progeny analysis of the selected recombinants in the fasciated region between makers T302 and clet24j2a on Chromosome 11 F2 family F3 family Markers b Parental pedigree ALN a F3 plant T302 T1948 TG105A F2 plant ALN(SD) P-value c 00T IL11-3 x LA TA (0.4) (0.2) 00T IL11-3 x LA TA (2.0) (1.6) 02T IL11-4 x LA TA (1.1) (0.1) 02T IL11-4 x LA TA (4.1) (1.1) 02T IL11-4 x LA TA (1.0) (0.7) 02T IL11-4 x LA TA (02) < (0.8) 02T IL11-4 x LA TA (4.1) (2.2) 02T IL11-4 x LA TA (1.6) (0.07) 02T IL11-4 x LA TA (0.4) (0.2) 02T IL11-4 x LA TA (1.4) (1.0) 02T IL11-4 x LA TA ( (1.7) 00T IL11-4 x LA TA (0.7) (2.0) 02T IL11-4 x LA TA (0.3) (0.0) 02T IL11-4 x LA TA (3.3) (5.5) 02T IL11-4 x LA TA (3.1) (1.2) 02T IL11-4 x LA TA (2.6) (0.2) 02T IL11-4 x LA TA (1.3) (0.5) T E19S 53K9T 89M2T clet24j2 7
8 02T IL11-4 x LA TA (1.3) (2.5) 02T IL11-4 x LA TA (2.2) (1.6) 02T IL11-4 x LA TA (3.9) (3.7) 02T IL11-4 x LA TA (1.7) (0.8) 02T IL11-4 x LA TA (1.0) (0.4) 02T IL11-4 x LA TA (3.4) (4.4) 02T IL11-4 x LA TA (0.15) < (0.06) 02T IL11-4 x LA TA (0.5) (1.3) 02T IL11-4 x LA TA (3.7) (2.2) 02T IL11-4 x LA TA (4.4) (0.6) 02T IL11-4 x LA TA (1.1) (1.2) 02T IL11-4 x LA TA (1.3) (1.0) 02T IL11-4 x LA TA (0.3) (1.4) a ALN- average locule number b Marker score: 1 homozygous for S.lycopersicum alleles; 3 homozygous for S.pennellii alleles c P-values of t-tests for comparisons within each F3 family 8
9 Supplementary Table 2. Summary of gene content for assembly 12D23 and 323E19 Start b End c Putative Function Accession/Species d E ID BAC Gene ID a Value 1 12D Glycosyl hydrolases ABI49503 Solanum demissum 0.0 family 17 protein 2 12D Ribosomal protein ABI49504 Solanum demissum 1e-43 L7/L12 C-terminal domain containing protein 3 12D hypothetical protein AAK91899 Solanum demissum D KPHMT1/PANB1 NP_ Arabidopsis thaliana 2e D Amidase family protein AAK91890 Solanum demissum D Hsp20/alpha crystallin AAK91897 Solanum demissum 9e-126 family protein 7 12D tubulin family protein AAK91898 Solanum demissum D hypothetical protein AAT40511 Solanum demissum D hypothetical protein AAT40514 Solanum demissum 7e D aldehyde oxidase AAG22607 s.lycopersicum D aldehyde oxidase AAG22607 s.lycopersicum D aldehyde oxidase AAG22605 s.lycopersicum D Putative retrotransposon AAT38724 Solanum demissum 2e-07 protein 14 12D aldehyde oxidase AAG22605 s.lycopersicum D ARR22 NP_ Arabidopsis thaliana 3e D NB-ARC domain AAT39932 Solanum demissum 7e-88 containing protein 17 12D beta-d-glucan BAA33065 Nicotiana tabacum 0.0 exohydrolase 18 12D Exoglucanase precursor NP_ Oryza sativa D hypothetical protein NP_ Oryza sativa 3e D pentatricopeptide, NP_ Oryza sativa 4e-143 putative 21 12D tousled-like kinase 2 NP_ Oryza sativa E pentatricopeptide, NP_ Oryza sativa 2e-145 putative E TSL (TOUSLED) NP_ Arabidopsis thaliana E zinc knuckle (CCHCtype) NP_ Arabidopsis thaliana 1e-66 family protein E UBP12 NP_ Arabidopsis thaliana E putative ubiquitin AAF23207 Arabidopsis thaliana 9e-146 carboxyl-terminal hydrolase E kinesin motor proteinrelated NP_ Arabidopsis thaliana E regulator of gene AAT65969 Solanum 2e-72 silencing lycopersicum E regulator of gene AAT65969 Solanum 1e-108 silencing lycopersicum E elongation factor Tu family protein NP_ Arabidopsis thaliana 0.0 9
10 29 323E hypothetical protein ABD32418 Medicago truncatula 9e E unknown ABK92625 Populus trichocarpa 1e E strictosidine synthase NP_ Arabidopsis thaliana 3e-171 family E YABBY2-like AAS10179 Antirrhinum majus 4e-42 transcription factor E protein kinase family NP_ Arabidopsis thaliana 2e E putative DNAJ protein CAC12824 Nicotiana tabacum E calmodulin binding NP_ Arabidopsis thaliana 2e E unknown protein NP_ Arabidopsis thaliana 3e E zinc finger NP_ Arabidopsis thaliana 7e E ubiquitin carrier protein 4 AAF03236 Glycine max 2e E unnamed protein product CAO64369 Vitis vinifera 1e-50 a The BACs were annotated by FGENESH at b,c indicating start and stop codon d Homologs blasted in NCBI with accession number and species 10
11 Supplementary Table 3A. Summary of transgenic complementation tests in T0 T0 Transgenic Material Number of Fruit ALN a ± s.d. P-value b 06T LA ± T LA ± T LA ± T LA ± T LA ± control LA ± a ALN average locule number b P-Values are results from one-tailed student s t-test between transgenic plants vs. nontransgenic plants Supplementary Table 3B. Summary of transgenic plants vs. non-transgenic plants segregated int1 from T0 complementation line (06T689-06) T1 Transgene a Number of fruit ALN ± s.d. P-value b 06T T ± T T ± T T ± T T ± T T ± T T ± T T ± T T ± T T ± T T ± T T ± T N ± T N ± T N ± T N ± T N ± T N ± 3.31 a Transgenic plants (T) and Non-transgenic plants (N) segregated in T1 family b P-Value is result from one-tailed student s t-test between transgenic plants vs. nontransgenic plants segregated from the same T0 line 11
12 Supplementary Table 4. Summary of indels among fasciated stocks and wild types Accessions Indel at about 330bp to 5' ATG 1 st intron insertion Locule Number RT- PCR Species 1 LA0014 7bp deletion 6-8kb fas S.lycopersicum 2 LA0020 7bp deletion 6-8kb fas S.lycopersicum 3 LA bp deletion 6-8kb fas S.lycopersicum 4 LA0767 7bp deletion 6-8kb fas No S.lycopersicum 5 LA0925 7bp deletion 6-8kb fas No S.lycopersicum 6 LA1113 7bp deletion 6-8kb fas No S.lycopersicum 7 LA1786 7bp deletion 6-8kb fas S.lycopersicum 8 LA2367 7bp deletion 6-8kb fas S.lycopersicum 9 LA2371 7bp deletion 6-8kb fas No S.lycopersicum 10 LA bp deletion 6-8kb fas S.lycopersicum 11 LA2595 7bp deletion 6-8kb fas S.lycopersicum 12 LA2799 7bp deletion 6-8kb fas S.lycopersicum 13 TA1486 7bp deletion 6-8kb fas S.lycopersicum 14 TA3757 7bp deletion 6-8kb fas S.lycopersicum 15 TA3762 7bp deletion 6-8kb fas S.lycopersicum 16 TA3765 7bp deletion 6-8kb fas S.lycopersicum 17 TA3766 7bp deletion 6-8kb fas S.lycopersicum 18 TA3767 7bp deletion 6-8kb fas S.lycopersicum 19 TA3768 7bp deletion 6-8kb fas S.lycopersicum 20 TA3769 7bp deletion 6-8kb fas S.lycopersicum 21 TA3770 7bp deletion 6-8kb fas S.lycopersicum 22 TA3771 7bp deletion 6-8kb fas S.lycopersicum 23 TA3772 7bp deletion 6-8kb fas No S.lycopersicum 24 TA3773 7bp deletion 6-8kb fas S.lycopersicum 25 TA3774 7bp deletion 6-8kb fas S.lycopersicum 26 TA209 No No Normal Yes S.lycopersicum 27 M82 No No Normal Yes S.lycopersicum 28 TA3752 7bp insertion No Normal S.lycopersicum 29 TA3753 7bp insertion No Normal S.lycopersicum 30 TA3754 7bp deletion No Normal Yes S.lycopersicum 31 TA3755 7bp insertion No Normal S.lycopersicum 32 TA3756 7bp insertion No Normal S.lycopersicum 33 TA3758 7bp insertion No Normal S.lycopersicum 34 TA3759 No No Normal S.lycopersicum 35 TA3760 7bp insertion No Normal S.lycopersicum 36 TA3761 7bp insertion No Normal S.lycopersicum 37 TA3763 7bp insertion No Normal S.lycopersicum 12
13 38 TA3764 7bp insertion No Normal S.lycopersicum 39 LA1654 No No 5-8 Yes cerasiforme 40 LA1654 No No 5-8 Yes cerasiforme 41 LA2121 7bp insertion No 5-8 Yes cerasiforme 42 LA2126 No No 5-8 Yes cerasiforme 43 LA2136 7bp insertion No 4-6 Yes cerasiforme 44 LA2095 7bp insertion No 4-6 weak cerasiforme 45 LA2845 No No 4-8 Yes cerasiforme 46 LA1247 No No Normal cerasiforme 47 LA1338 No No Normal Yes cerasiforme 48 LA1386 No No Normal cerasiforme 49 LA1423 No No Normal cerasiforme 50 LA1701 No No Normal cerasiforme 51 LA2135 No No Normal cerasiforme 52 LA2137 4bp deletion No Normal cerasiforme 53 LA2177 7bp insertion No Normal cerasiforme 54 LA2312 No No Normal cerasiforme 55 LA2844 7bp insertion No Normal cerasiforme 56 LA3623 7bp deletion No Normal Yes cerasiforme 57 LA3623 No No Normal Yes cerasiforme 58 LA3623 7bp deletion No Normal cerasiforme 59 LA1226 4bp deletion No Normal Yes cerasiforme 60 LA1228 4bp deletion No Normal cerasiforme 61 LA1231 Normal No Normal cerasiforme 62 LA1420 7bp insertion No Normal Yes cerasiforme 63 LA1429 No No Normal cerasiforme 64 LA1549 No No Normal Yes cerasiforme 64 LA2131 7bp insertion No 5-8 Yes cerasiforme 66 LA2308 No No Normal cerasiforme 67 LA2616 7bp insertion No Normal cerasiforme 68 LA1320 7bp deletion No Normal Yes cerasiforme 69 LA483 Normal S.cheesmanii 70 LA1589 No Normal pimpinellifolium 71 LA1708 No Normal S.peruvianum 72 LA1777 No Normal S.hirsutum 73 LA2133 No No Normal S.parviflorum 75 LA0716 No Normal Yes S.pennellii 13
14 Supplementary Table 5. Summary of tomato markers used for the fasciated region high-resolution map Marker a Forward Primer Reverse primer Marker Type Restrict Enzyme Source b T302 TGGCTCATCCTGA AGCTGATAGCGC AGTGTACATCCTTG CCATTGACT INDEL/ RFLP XbaI Clone cled-24- J21 323E19 T AGATAAGCGAAA GGGGTTTTACC TTATCACATCAGGA GTAATATCCTTC CAPs MspI BAC clone from Heinz 1706 T1948 TTCCCAATTTCAC CAATTTTTC ATCCAGAACCAGC ACATTTCTT CAPs/ RFLP DraI/ EcoRI, V Clone clet-45- E9 TG105A N/A N/A RFLP DraI Genomic clone T1949 AAAGATCACCCG GGAATTCCACGATG CAPs/ RsaI/ Clone cleg13c3 AAGTTCAAGA AAATGAAT RFLP HaeIII, DraI 323E19 S GAGCCACACAAC AGAGGATTC TGAAGAAAAATCA TTCTTGATGGT CAPs DpnII, ApoI BAC clone from Heinz K9 T CATGGTTCCCACG TATTAAATG AAATGATCTTTTTC CAATGTCAA SNPs N/A BAC clone from Heinz M2 T AGGGACTGACAA GTTTTGGTTTT TCCTAAAGGTTTAA TGAGAGTTATCCA CAPs RsaI BAC clone from Heinz 1706 clet24j2a CAACCATCCTAG CAATGAAATCT GAGGCATTCACTCT CTTCGATAC CAPs/ RFLP KpnI/ ScaI cdna clone a markers were developed from cdna, or BAC clones. If markers developed from BAC clones, with S indicating SP6 end; T indicating T7 end b detailed information may be found in 14
15 Supplementary Table 6. The primer pairs used to amplify wide type TA209 and mutant LA2371 and LA0767 Primer name Forward primer Reverse primer Corresponding region to 323E19 (bp) WPF1/R1 TGACCCATTGTTGCTTCTGA TGAAACGTAGTCCTCCGAAAA WPF2/F2 CTTTGGATCCAGATCCCGTA GAGGTGTGAACCGAAGTTAAAA WPF3/R3 TAAGTTTCGAGTTCACAAAGAATTG AATGCGAGAAATAAGTGATCAAAA prof/r GCTAACCGCATGTCAAACAC GCGTTCTGAGGAAGGTGAAG WPF4/R4 TGTGTTGGATGAATTGTGACC TGTTGGTTTTGGAGATATCTGGT prof2/r2 CTATCGCGTCATTGTTCTTCC TGGATCAAAGGGGAAGAGTG FP1/RP1 TTCCCCTTTGATCCATGTTC CAAAATTCATGACACAAAGGACA FP1/RP1a TTCCCCTTTGATCCATGTTC TGATCATACTCATCACACATGAGC FP2/RP2 CAGGAGCACCAAAAGTAAAGG TGGAACAAATCGAAAAGGAAA FP3/RP3 GTAAGATGTGGGCATTGTGC CCTGGTAGCCGGTTACACTT FP4/RP4 TGTTGTTTGCAACATGTCCTT TTTGGCAGCAGTGCTAAAAG FP5/RP5 CCTCTCTTGCCACCGAAAAT GGCCAAAAATAGACGCATGT FP6/RP6 TGCGTCTATTTTTGGCCATT CATCAAATGGGACAAAGGAGTAT EX4F/5R TCAAACTATGCAGCACCAGA GGACTTACATTTTTGGCAGCA EX6F/6R AGTGGGCACATTTTCCACAT AAATCTTCGACGAAAACAACA Supplementary Table 7. Primers used in the methods Primer name sequence BB25 GACTCGAGTCGACATCGA(dT) 17 BB26 GACTCGAGTCGACATCGA Actin (TOM52 F) CCAAAAGCCAATCGAGAGAA Actin (TOM52 R) GGTACCACCACTGAGGACGA 3 UTR F GCAACAAATAGCGAGGGAAA 3 UTR R CACAACTCTGAAAATAATATTAAGACGA 15
16 SUPPORTING ONLINE REFERENCES 1. Lippman, Z. & Tanksley, S.D. Dissecting the genetic pathway to extreme fruit size in tomato using a cross between the small-fruited wild species Lycopersicon pimpinellifolium and L. esculentum var. Giant Heirloom. Genetics 158, (2001). 2. Barrero, L.S. & Tanksley, S.D. Evaluating the genetic basis of multiple-locule fruit in a broad cross section of tomato cultivars. Theor Appl Genet 109, (2004). 16
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng Supplementary Figure 1. The phenotypes of PI , BR121, and Harosoy under short-day conditions.
 Supplementary Figure 1 The phenotypes of PI 159925, BR121, and Harosoy under short-day conditions. (a) Plant height. (b) Number of branches. (c) Average internode length. (d) Number of nodes. (e) Pods
Supplementary Figure 1 The phenotypes of PI 159925, BR121, and Harosoy under short-day conditions. (a) Plant height. (b) Number of branches. (c) Average internode length. (d) Number of nodes. (e) Pods
Supplemental Figure 1. Comparison of Tiller Bud Formation between the Wild Type and d27. (A) and (B) Longitudinal sections of shoot apex in wild-type
 A B 2 3 3 2 1 1 Supplemental Figure 1. Comparison of Tiller Bud Formation between the Wild Type and d27. (A) and (B) Longitudinal sections of shoot apex in wild-type (A) and d27 (B) seedlings at the four
A B 2 3 3 2 1 1 Supplemental Figure 1. Comparison of Tiller Bud Formation between the Wild Type and d27. (A) and (B) Longitudinal sections of shoot apex in wild-type (A) and d27 (B) seedlings at the four
allosteric cis-acting DNA element coding strand dominant constitutive mutation coordinate regulation of genes denatured
 A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z AA BB CC DD EE FF GG HH II JJ KK LL MM NN OO PP QQ RR SS TT UU VV allosteric cis-acting DNA element coding strand codominant constitutive mutation coordinate
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z AA BB CC DD EE FF GG HH II JJ KK LL MM NN OO PP QQ RR SS TT UU VV allosteric cis-acting DNA element coding strand codominant constitutive mutation coordinate
Illegitimate translation causes unexpected gene expression from on-target out-of-frame alleles
 Illegitimate translation causes unexpected gene expression from on-target out-of-frame alleles created by CRISPR-Cas9 Shigeru Makino, Ryutaro Fukumura, Yoichi Gondo* Mutagenesis and Genomics Team, RIKEN
Illegitimate translation causes unexpected gene expression from on-target out-of-frame alleles created by CRISPR-Cas9 Shigeru Makino, Ryutaro Fukumura, Yoichi Gondo* Mutagenesis and Genomics Team, RIKEN
Supplementary Methods
 Supplementary Methods Microarray analysis Grains of 7 DAP of the wild-type and gif1 were harvested for RNA preparation. Microarray analysis was performed with the Affymetrix (Santa Clara, CA) GeneChip
Supplementary Methods Microarray analysis Grains of 7 DAP of the wild-type and gif1 were harvested for RNA preparation. Microarray analysis was performed with the Affymetrix (Santa Clara, CA) GeneChip
Supplemental Data. Hou et al. (2016). Plant Cell /tpc
 Supplemental Data. Hou et al. (216). Plant Cell 1.115/tpc.16.295 A Distance to 1 st nt of start codon Distance to 1 st nt of stop codon B Normalized PARE abundance 8 14 nt 17 nt Frame1 Arabidopsis inflorescence
Supplemental Data. Hou et al. (216). Plant Cell 1.115/tpc.16.295 A Distance to 1 st nt of start codon Distance to 1 st nt of stop codon B Normalized PARE abundance 8 14 nt 17 nt Frame1 Arabidopsis inflorescence
Supplemental Table 1. Primers used for cloning and PCR amplification in this study
 Supplemental Table 1. Primers used for cloning and PCR amplification in this study Target Gene Primer sequence NATA1 (At2g393) forward GGG GAC AAG TTT GTA CAA AAA AGC AGG CTT CAT GGC GCC TCC AAC CGC AGC
Supplemental Table 1. Primers used for cloning and PCR amplification in this study Target Gene Primer sequence NATA1 (At2g393) forward GGG GAC AAG TTT GTA CAA AAA AGC AGG CTT CAT GGC GCC TCC AAC CGC AGC
Lecture 18 June 2 nd, Gene Expression Regulation Mutations
 Lecture 18 June 2 nd, 2016 Gene Expression Regulation Mutations From Gene to Protein Central Dogma Replication DNA RNA PROTEIN Transcription Translation RNA Viruses: genome is RNA Reverse Transcriptase
Lecture 18 June 2 nd, 2016 Gene Expression Regulation Mutations From Gene to Protein Central Dogma Replication DNA RNA PROTEIN Transcription Translation RNA Viruses: genome is RNA Reverse Transcriptase
Time allowed: 2 hours Answer ALL questions in Section A, ALL PARTS of the question in Section B and ONE question from Section C.
 UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Biological Sciences Main Series UG Examination 2017-2018 GENETICS BIO-5009A Time allowed: 2 hours Answer ALL questions in Section A, ALL PARTS of the question in Section
UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Biological Sciences Main Series UG Examination 2017-2018 GENETICS BIO-5009A Time allowed: 2 hours Answer ALL questions in Section A, ALL PARTS of the question in Section
J. MITCHELL MCGRATH, LESLIE G. HICKOK, and ERAN PICHERSKY
 P1. Syst. Evol. 189:203-210 (1994) --Plant Systematics and Evolution Springer-Verlag 1994 Printed in Austria Assessment of gene copy number in the homosporous ferns Ceratopteris thalictroides and C. richardii
P1. Syst. Evol. 189:203-210 (1994) --Plant Systematics and Evolution Springer-Verlag 1994 Printed in Austria Assessment of gene copy number in the homosporous ferns Ceratopteris thalictroides and C. richardii
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng Supplementary Figure 1. ssp mutant phenotypes in a functional SP background.
 Supplementary Figure 1 ssp mutant phenotypes in a functional SP background. (a,b) Statistical comparisons of primary and sympodial shoot flowering times as determined by mean values for leaf number on
Supplementary Figure 1 ssp mutant phenotypes in a functional SP background. (a,b) Statistical comparisons of primary and sympodial shoot flowering times as determined by mean values for leaf number on
Supplementary Information for: The genome of the extremophile crucifer Thellungiella parvula
 Supplementary Information for: The genome of the extremophile crucifer Thellungiella parvula Maheshi Dassanayake 1,9, Dong-Ha Oh 1,9, Jeffrey S. Haas 1,2, Alvaro Hernandez 3, Hyewon Hong 1,4, Shahjahan
Supplementary Information for: The genome of the extremophile crucifer Thellungiella parvula Maheshi Dassanayake 1,9, Dong-Ha Oh 1,9, Jeffrey S. Haas 1,2, Alvaro Hernandez 3, Hyewon Hong 1,4, Shahjahan
1. In most cases, genes code for and it is that
 Name Chapter 10 Reading Guide From DNA to Protein: Gene Expression Concept 10.1 Genetics Shows That Genes Code for Proteins 1. In most cases, genes code for and it is that determine. 2. Describe what Garrod
Name Chapter 10 Reading Guide From DNA to Protein: Gene Expression Concept 10.1 Genetics Shows That Genes Code for Proteins 1. In most cases, genes code for and it is that determine. 2. Describe what Garrod
. Supplementary Information
 . Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure S1. Mature embryo sac observations. Supplementary Figure S2. STT observations. Supplementary Figure S3. Comparison of the PTB1 cdna with that of the mutant.
. Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure S1. Mature embryo sac observations. Supplementary Figure S2. STT observations. Supplementary Figure S3. Comparison of the PTB1 cdna with that of the mutant.
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1. HSP21 expression in 35S:HSP21 and hsp21 knockdown plants. (a) Since no T- DNA insertion line for HSP21 is available in the publicly available T-DNA collections,
Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1. HSP21 expression in 35S:HSP21 and hsp21 knockdown plants. (a) Since no T- DNA insertion line for HSP21 is available in the publicly available T-DNA collections,
Supplemental Data. Yang et al. (2012). Plant Cell /tpc
 Supplemental Figure 1. Mature flowers of P. heterotricha. (A) An inflorescence of P. heterotricha showing the front view of a zygomorphic flower characterized by two small dorsal petals and only two fertile
Supplemental Figure 1. Mature flowers of P. heterotricha. (A) An inflorescence of P. heterotricha showing the front view of a zygomorphic flower characterized by two small dorsal petals and only two fertile
(Lys), resulting in translation of a polypeptide without the Lys amino acid. resulting in translation of a polypeptide without the Lys amino acid.
 1. A change that makes a polypeptide defective has been discovered in its amino acid sequence. The normal and defective amino acid sequences are shown below. Researchers are attempting to reproduce the
1. A change that makes a polypeptide defective has been discovered in its amino acid sequence. The normal and defective amino acid sequences are shown below. Researchers are attempting to reproduce the
Population transcriptomics uncovers the regulation of gene. expression variation in adaptation to changing environment
 Supplementary information Population transcriptomics uncovers the regulation of gene expression variation in adaptation to changing environment Qin Xu 1, Caiyun Zhu 2,4, Yangyang Fan 1,4, Zhihong Song
Supplementary information Population transcriptomics uncovers the regulation of gene expression variation in adaptation to changing environment Qin Xu 1, Caiyun Zhu 2,4, Yangyang Fan 1,4, Zhihong Song
Reading Assignments. A. Genes and the Synthesis of Polypeptides. Lecture Series 7 From DNA to Protein: Genotype to Phenotype
 Lecture Series 7 From DNA to Protein: Genotype to Phenotype Reading Assignments Read Chapter 7 From DNA to Protein A. Genes and the Synthesis of Polypeptides Genes are made up of DNA and are expressed
Lecture Series 7 From DNA to Protein: Genotype to Phenotype Reading Assignments Read Chapter 7 From DNA to Protein A. Genes and the Synthesis of Polypeptides Genes are made up of DNA and are expressed
Principles of Genetics
 Principles of Genetics Snustad, D ISBN-13: 9780470903599 Table of Contents C H A P T E R 1 The Science of Genetics 1 An Invitation 2 Three Great Milestones in Genetics 2 DNA as the Genetic Material 6 Genetics
Principles of Genetics Snustad, D ISBN-13: 9780470903599 Table of Contents C H A P T E R 1 The Science of Genetics 1 An Invitation 2 Three Great Milestones in Genetics 2 DNA as the Genetic Material 6 Genetics
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng Supplementary Figure 1. The FIN and FAB genes act separately from the meristem maturation pathway.
 Supplementary Figure 1 The FIN and FAB genes act separately from the meristem maturation pathway. (a) Representative inflorescence from the compound inflorescence (s, defective in the homolog of Arabidopsis
Supplementary Figure 1 The FIN and FAB genes act separately from the meristem maturation pathway. (a) Representative inflorescence from the compound inflorescence (s, defective in the homolog of Arabidopsis
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 reverse 3175 3175 F L C 318 318 3185 3185 319 319 3195 3195 315 8 1 315 3155 315 317 Supplementary Figure 3. Stability of expression of the GFP sensor constructs return to warm conditions. Semi-quantitative
reverse 3175 3175 F L C 318 318 3185 3185 319 319 3195 3195 315 8 1 315 3155 315 317 Supplementary Figure 3. Stability of expression of the GFP sensor constructs return to warm conditions. Semi-quantitative
Genetics 275 Notes Week 7
 Cytoplasmic Inheritance Genetics 275 Notes Week 7 Criteriafor recognition of cytoplasmic inheritance: 1. Reciprocal crosses give different results -mainly due to the fact that the female parent contributes
Cytoplasmic Inheritance Genetics 275 Notes Week 7 Criteriafor recognition of cytoplasmic inheritance: 1. Reciprocal crosses give different results -mainly due to the fact that the female parent contributes
Chapter 17. From Gene to Protein. Biology Kevin Dees
 Chapter 17 From Gene to Protein DNA The information molecule Sequences of bases is a code DNA organized in to chromosomes Chromosomes are organized into genes What do the genes actually say??? Reflecting
Chapter 17 From Gene to Protein DNA The information molecule Sequences of bases is a code DNA organized in to chromosomes Chromosomes are organized into genes What do the genes actually say??? Reflecting
SoyBase, the USDA-ARS Soybean Genetics and Genomics Database
 SoyBase, the USDA-ARS Soybean Genetics and Genomics Database David Grant Victoria Carollo Blake Steven B. Cannon Kevin Feeley Rex T. Nelson Nathan Weeks SoyBase Site Map and Navigation Video Tutorials:
SoyBase, the USDA-ARS Soybean Genetics and Genomics Database David Grant Victoria Carollo Blake Steven B. Cannon Kevin Feeley Rex T. Nelson Nathan Weeks SoyBase Site Map and Navigation Video Tutorials:
Genetic transformation of table grape via organogenesis and field evaluation of DefH9-iaaM transgenic plants
 Genetic transformation of table grape via organogenesis and field evaluation of DefH9-iaaM transgenic plants Mezzetti B., Silvestroni O., Costantini E. Dipartimento di Scienze Ambientali e delle Produzioni
Genetic transformation of table grape via organogenesis and field evaluation of DefH9-iaaM transgenic plants Mezzetti B., Silvestroni O., Costantini E. Dipartimento di Scienze Ambientali e delle Produzioni
Organization of Genes Differs in Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic DNA Chapter 10 p
 Organization of Genes Differs in Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic DNA Chapter 10 p.110-114 Arrangement of information in DNA----- requirements for RNA Common arrangement of protein-coding genes in prokaryotes=
Organization of Genes Differs in Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic DNA Chapter 10 p.110-114 Arrangement of information in DNA----- requirements for RNA Common arrangement of protein-coding genes in prokaryotes=
Genome-wide discovery of G-quadruplex forming sequences and their functional
 *Correspondence and requests for materials should be addressed to R.G. (rohini@nipgr.ac.in) Genome-wide discovery of G-quadruplex forming sequences and their functional relevance in plants Rohini Garg*,
*Correspondence and requests for materials should be addressed to R.G. (rohini@nipgr.ac.in) Genome-wide discovery of G-quadruplex forming sequences and their functional relevance in plants Rohini Garg*,
Full file at CHAPTER 2 Genetics
 CHAPTER 2 Genetics MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Chromosomes are a. small linear bodies. b. contained in cells. c. replicated during cell division. 2. A cross between true-breeding plants bearing yellow seeds produces
CHAPTER 2 Genetics MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Chromosomes are a. small linear bodies. b. contained in cells. c. replicated during cell division. 2. A cross between true-breeding plants bearing yellow seeds produces
Table S1 List of primers used for genotyping and qrt-pcr.
 Table S1 List of primers used for genotyping and qrt-pcr. genotyping! allele! ligomer*! 5'-sequence-3'! rice! d10-2! F! TTGGCTTTGCCTCGTTTC!!! R! AGCCTCCACTTGTACTGTG! Arabidopsis! max2-3, max2-4! F! ACTCTCTCCGACCTCCCTGACG!!!
Table S1 List of primers used for genotyping and qrt-pcr. genotyping! allele! ligomer*! 5'-sequence-3'! rice! d10-2! F! TTGGCTTTGCCTCGTTTC!!! R! AGCCTCCACTTGTACTGTG! Arabidopsis! max2-3, max2-4! F! ACTCTCTCCGACCTCCCTGACG!!!
Supplementary Figure 3
 Supplementary Figure 3 7.0 Col Kas-1 Line FTH1A 8.4 F3PII3 8.9 F26H11 ATQ1 T9I22 PLS8 F26B6-B 9.6 F27L4 9.81 F27D4 9.92 9.96 10.12 10.14 10.2 11.1 0.5 Mb T1D16 Col % RGR 83.3 101 227 93.5 75.9 132 90 375
Supplementary Figure 3 7.0 Col Kas-1 Line FTH1A 8.4 F3PII3 8.9 F26H11 ATQ1 T9I22 PLS8 F26B6-B 9.6 F27L4 9.81 F27D4 9.92 9.96 10.12 10.14 10.2 11.1 0.5 Mb T1D16 Col % RGR 83.3 101 227 93.5 75.9 132 90 375
GCD3033:Cell Biology. Transcription
 Transcription Transcription: DNA to RNA A) production of complementary strand of DNA B) RNA types C) transcription start/stop signals D) Initiation of eukaryotic gene expression E) transcription factors
Transcription Transcription: DNA to RNA A) production of complementary strand of DNA B) RNA types C) transcription start/stop signals D) Initiation of eukaryotic gene expression E) transcription factors
Potato Genome Analysis
 Potato Genome Analysis Xin Liu Deputy director BGI research 2016.1.21 WCRTC 2016 @ Nanning Reference genome construction???????????????????????????????????????? Sequencing HELL RIEND WELCOME BGI ZHEN LLOFRI
Potato Genome Analysis Xin Liu Deputy director BGI research 2016.1.21 WCRTC 2016 @ Nanning Reference genome construction???????????????????????????????????????? Sequencing HELL RIEND WELCOME BGI ZHEN LLOFRI
Supplemental Data. Perea-Resa et al. Plant Cell. (2012) /tpc
 Supplemental Data. Perea-Resa et al. Plant Cell. (22)..5/tpc.2.3697 Sm Sm2 Supplemental Figure. Sequence alignment of Arabidopsis LSM proteins. Alignment of the eleven Arabidopsis LSM proteins. Sm and
Supplemental Data. Perea-Resa et al. Plant Cell. (22)..5/tpc.2.3697 Sm Sm2 Supplemental Figure. Sequence alignment of Arabidopsis LSM proteins. Alignment of the eleven Arabidopsis LSM proteins. Sm and
Newly made RNA is called primary transcript and is modified in three ways before leaving the nucleus:
 m Eukaryotic mrna processing Newly made RNA is called primary transcript and is modified in three ways before leaving the nucleus: Cap structure a modified guanine base is added to the 5 end. Poly-A tail
m Eukaryotic mrna processing Newly made RNA is called primary transcript and is modified in three ways before leaving the nucleus: Cap structure a modified guanine base is added to the 5 end. Poly-A tail
Supplemental Data. Wang et al. (2014). Plant Cell /tpc
 Supplemental Figure1: Mock and NPA-treated tomato plants. (A) NPA treated tomato (cv. Moneymaker) developed a pin-like inflorescence (arrowhead). (B) Comparison of first and second leaves from mock and
Supplemental Figure1: Mock and NPA-treated tomato plants. (A) NPA treated tomato (cv. Moneymaker) developed a pin-like inflorescence (arrowhead). (B) Comparison of first and second leaves from mock and
RNAi Suppression of AGAMOUS-like Genes Causes Field Sterility in Populus
 RNAi Suppression of AGAMOUS-like Genes Causes Field Sterility in Populus Haiwei Lu and Steven H. Strauss Oregon State University Forest Tree Workshop PAG XXVI, San Diego, CA, 2018 The containment issue
RNAi Suppression of AGAMOUS-like Genes Causes Field Sterility in Populus Haiwei Lu and Steven H. Strauss Oregon State University Forest Tree Workshop PAG XXVI, San Diego, CA, 2018 The containment issue
The Eukaryotic Genome and Its Expression. The Eukaryotic Genome and Its Expression. A. The Eukaryotic Genome. Lecture Series 11
 The Eukaryotic Genome and Its Expression Lecture Series 11 The Eukaryotic Genome and Its Expression A. The Eukaryotic Genome B. Repetitive Sequences (rem: teleomeres) C. The Structures of Protein-Coding
The Eukaryotic Genome and Its Expression Lecture Series 11 The Eukaryotic Genome and Its Expression A. The Eukaryotic Genome B. Repetitive Sequences (rem: teleomeres) C. The Structures of Protein-Coding
Evolutionary analysis of the well characterized endo16 promoter reveals substantial variation within functional sites
 Evolutionary analysis of the well characterized endo16 promoter reveals substantial variation within functional sites Paper by: James P. Balhoff and Gregory A. Wray Presentation by: Stephanie Lucas Reviewed
Evolutionary analysis of the well characterized endo16 promoter reveals substantial variation within functional sites Paper by: James P. Balhoff and Gregory A. Wray Presentation by: Stephanie Lucas Reviewed
Multiple Choice Review- Eukaryotic Gene Expression
 Multiple Choice Review- Eukaryotic Gene Expression 1. Which of the following is the Central Dogma of cell biology? a. DNA Nucleic Acid Protein Amino Acid b. Prokaryote Bacteria - Eukaryote c. Atom Molecule
Multiple Choice Review- Eukaryotic Gene Expression 1. Which of the following is the Central Dogma of cell biology? a. DNA Nucleic Acid Protein Amino Acid b. Prokaryote Bacteria - Eukaryote c. Atom Molecule
Designer Genes C Test
 Northern Regional: January 19 th, 2019 Designer Genes C Test Name(s): Team Name: School Name: Team Number: Rank: Score: Directions: You will have 50 minutes to complete the test. You may not write on the
Northern Regional: January 19 th, 2019 Designer Genes C Test Name(s): Team Name: School Name: Team Number: Rank: Score: Directions: You will have 50 minutes to complete the test. You may not write on the
Genetic diversity and population structure in rice. S. Kresovich 1,2 and T. Tai 3,5. Plant Breeding Dept, Cornell University, Ithaca, NY
 Genetic diversity and population structure in rice S. McCouch 1, A. Garris 1,2, J. Edwards 1, H. Lu 1,3 M Redus 4, J. Coburn 1, N. Rutger 4, S. Kresovich 1,2 and T. Tai 3,5 1 Plant Breeding Dept, Cornell
Genetic diversity and population structure in rice S. McCouch 1, A. Garris 1,2, J. Edwards 1, H. Lu 1,3 M Redus 4, J. Coburn 1, N. Rutger 4, S. Kresovich 1,2 and T. Tai 3,5 1 Plant Breeding Dept, Cornell
Biology I Level - 2nd Semester Final Review
 Biology I Level - 2nd Semester Final Review The 2 nd Semester Final encompasses all material that was discussed during second semester. It s important that you review ALL notes and worksheets from the
Biology I Level - 2nd Semester Final Review The 2 nd Semester Final encompasses all material that was discussed during second semester. It s important that you review ALL notes and worksheets from the
Translation and Operons
 Translation and Operons You Should Be Able To 1. Describe the three stages translation. including the movement of trna molecules through the ribosome. 2. Compare and contrast the roles of three different
Translation and Operons You Should Be Able To 1. Describe the three stages translation. including the movement of trna molecules through the ribosome. 2. Compare and contrast the roles of three different
1. Draw, label and describe the structure of DNA and RNA including bonding mechanisms.
 Practicing Biology BIG IDEA 3.A 1. Draw, label and describe the structure of DNA and RNA including bonding mechanisms. 2. Using at least 2 well-known experiments, describe which features of DNA and RNA
Practicing Biology BIG IDEA 3.A 1. Draw, label and describe the structure of DNA and RNA including bonding mechanisms. 2. Using at least 2 well-known experiments, describe which features of DNA and RNA
Gene expression in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, Plasmids: types, maintenance and functions. Mitesh Shrestha
 Gene expression in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, Plasmids: types, maintenance and functions. Mitesh Shrestha Plasmids 1. Extrachromosomal DNA, usually circular-parasite 2. Usually encode ancillary
Gene expression in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, Plasmids: types, maintenance and functions. Mitesh Shrestha Plasmids 1. Extrachromosomal DNA, usually circular-parasite 2. Usually encode ancillary
Translation Part 2 of Protein Synthesis
 Translation Part 2 of Protein Synthesis IN: How is transcription like making a jello mold? (be specific) What process does this diagram represent? A. Mutation B. Replication C.Transcription D.Translation
Translation Part 2 of Protein Synthesis IN: How is transcription like making a jello mold? (be specific) What process does this diagram represent? A. Mutation B. Replication C.Transcription D.Translation
Supplemental Data. Chen and Thelen (2010). Plant Cell /tpc
 Supplemental Data. Chen and Thelen (2010). Plant Cell 10.1105/tpc.109.071837 1 C Total 5 kg 20 kg 100 kg Transmission Image 100 kg soluble pdtpi-gfp Plastid (PDH-alpha) Mito (PDH-alpha) GFP Image vector
Supplemental Data. Chen and Thelen (2010). Plant Cell 10.1105/tpc.109.071837 1 C Total 5 kg 20 kg 100 kg Transmission Image 100 kg soluble pdtpi-gfp Plastid (PDH-alpha) Mito (PDH-alpha) GFP Image vector
GSBHSRSBRSRRk IZTI/^Q. LlML. I Iv^O IV I I I FROM GENES TO GENOMES ^^^H*" ^^^^J*^ ill! BQPIP. illt. goidbkc. itip31. li4»twlil FIFTH EDITION
 FIFTH EDITION IV I ^HHk ^ttm IZTI/^Q i I II MPHBBMWBBIHB '-llwmpbi^hbwm^^pfc ' GSBHSRSBRSRRk LlML I I \l 1MB ^HP'^^MMMP" jflp^^^^^^^^st I Iv^O FROM GENES TO GENOMES %^MiM^PM^^MWi99Mi$9i0^^ ^^^^^^^^^^^^^V^^^fii^^t^i^^^^^
FIFTH EDITION IV I ^HHk ^ttm IZTI/^Q i I II MPHBBMWBBIHB '-llwmpbi^hbwm^^pfc ' GSBHSRSBRSRRk LlML I I \l 1MB ^HP'^^MMMP" jflp^^^^^^^^st I Iv^O FROM GENES TO GENOMES %^MiM^PM^^MWi99Mi$9i0^^ ^^^^^^^^^^^^^V^^^fii^^t^i^^^^^
Principles of QTL Mapping. M.Imtiaz
 Principles of QTL Mapping M.Imtiaz Introduction Definitions of terminology Reasons for QTL mapping Principles of QTL mapping Requirements For QTL Mapping Demonstration with experimental data Merit of QTL
Principles of QTL Mapping M.Imtiaz Introduction Definitions of terminology Reasons for QTL mapping Principles of QTL mapping Requirements For QTL Mapping Demonstration with experimental data Merit of QTL
Quiz answers. Allele. BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 17: The Quiz (and back to Eukaryotic DNA)
 BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 17: The Quiz (and back to Eukaryotic DNA) http://compbio.uchsc.edu/hunter/bio5099 Larry.Hunter@uchsc.edu Quiz answers Kinase: An enzyme
BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 17: The Quiz (and back to Eukaryotic DNA) http://compbio.uchsc.edu/hunter/bio5099 Larry.Hunter@uchsc.edu Quiz answers Kinase: An enzyme
Biological Roles of Cytokinins
 Direct Control of Shoot Meristem Activity by a Cytokinin-Activating Enzyme By Kurakawa et. Al. Published in Nature Presented by Boyana Grigorova Biological Roles of Cytokinins Cytokinins are positive regulators
Direct Control of Shoot Meristem Activity by a Cytokinin-Activating Enzyme By Kurakawa et. Al. Published in Nature Presented by Boyana Grigorova Biological Roles of Cytokinins Cytokinins are positive regulators
Supplementary Figure 1. Markedly decreased numbers of marginal zone B cells in DOCK8 mutant mice Supplementary Figure 2.
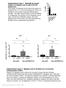 Supplementary Figure 1. Markedly decreased numbers of marginal zone B cells in DOCK8 mutant mice. Percentage of marginal zone B cells in the spleen of wild-type mice (+/+), mice homozygous for cpm or pri
Supplementary Figure 1. Markedly decreased numbers of marginal zone B cells in DOCK8 mutant mice. Percentage of marginal zone B cells in the spleen of wild-type mice (+/+), mice homozygous for cpm or pri
A dual sgrna approach for functional genomics in Arabidopsis thaliana
 A dual sgrna approach for functional genomics in Arabidopsis thaliana CRISPR AgBio Europe 2017 Laurens Pauwels #CRISPRAgBio @laurenspauwels Outline - Workflow for CRISPR/Cas9 in Arabidopsis thaliana -
A dual sgrna approach for functional genomics in Arabidopsis thaliana CRISPR AgBio Europe 2017 Laurens Pauwels #CRISPRAgBio @laurenspauwels Outline - Workflow for CRISPR/Cas9 in Arabidopsis thaliana -
Exam 1 PBG430/
 1 Exam 1 PBG430/530 2014 1. You read that the genome size of maize is 2,300 Mb and that in this species 2n = 20. This means that there are 2,300 Mb of DNA in a cell that is a. n (e.g. gamete) b. 2n (e.g.
1 Exam 1 PBG430/530 2014 1. You read that the genome size of maize is 2,300 Mb and that in this species 2n = 20. This means that there are 2,300 Mb of DNA in a cell that is a. n (e.g. gamete) b. 2n (e.g.
Sequence variation and functional analysis of a FRIGIDA orthologue (BnaA3.FRI) in Brassica napus
 Yi et al. BMC Plant Biology (2018) 18:32 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-018-1253-1 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Sequence variation and functional analysis of a FRIGIDA orthologue (BnaA3.FRI) in Brassica
Yi et al. BMC Plant Biology (2018) 18:32 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-018-1253-1 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Sequence variation and functional analysis of a FRIGIDA orthologue (BnaA3.FRI) in Brassica
Предсказание и анализ промотерных последовательностей. Татьяна Татаринова
 Предсказание и анализ промотерных последовательностей Татьяна Татаринова Eukaryotic Transcription 2 Initiation Promoter: the DNA sequence that initially binds the RNA polymerase The structure of promoter-polymerase
Предсказание и анализ промотерных последовательностей Татьяна Татаринова Eukaryotic Transcription 2 Initiation Promoter: the DNA sequence that initially binds the RNA polymerase The structure of promoter-polymerase
The Plant Cell, November. 2017, American Society of Plant Biologists. All rights reserved
 The Genetics of Floral Development Teaching Guide Overview The development of flowers in angiosperm plants provided a critical evolutionary advantage, allowing more options for pollen dispersal and seed
The Genetics of Floral Development Teaching Guide Overview The development of flowers in angiosperm plants provided a critical evolutionary advantage, allowing more options for pollen dispersal and seed
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature13082 Supplementary Table 1. Examination of nectar production in wild-type and atsweet9 flowers. No. of flowers with detectable nectar out of the total observed
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature13082 Supplementary Table 1. Examination of nectar production in wild-type and atsweet9 flowers. No. of flowers with detectable nectar out of the total observed
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS INTRO
 MR. POMERANTZ Page 1 of 6 Protein synthesis Intro. Use the text book to help properly answer the following questions 1. RNA differs from DNA in that RNA a. is single-stranded. c. contains the nitrogen
MR. POMERANTZ Page 1 of 6 Protein synthesis Intro. Use the text book to help properly answer the following questions 1. RNA differs from DNA in that RNA a. is single-stranded. c. contains the nitrogen
mrna Codon Table Mutant Dinosaur Name: Period:
 Mutant Dinosaur Name: Period: Intro Your dinosaur is born with a new genetic mutation. Your job is to map out the genes that are influenced by the mutation and to discover how the new dinosaurs interact
Mutant Dinosaur Name: Period: Intro Your dinosaur is born with a new genetic mutation. Your job is to map out the genes that are influenced by the mutation and to discover how the new dinosaurs interact
Cellular Neuroanatomy I The Prototypical Neuron: Soma. Reading: BCP Chapter 2
 Cellular Neuroanatomy I The Prototypical Neuron: Soma Reading: BCP Chapter 2 Functional Unit of the Nervous System The functional unit of the nervous system is the neuron. Neurons are cells specialized
Cellular Neuroanatomy I The Prototypical Neuron: Soma Reading: BCP Chapter 2 Functional Unit of the Nervous System The functional unit of the nervous system is the neuron. Neurons are cells specialized
Supplementary Figure 1. Phenotype of the HI strain.
 Supplementary Figure 1. Phenotype of the HI strain. (A) Phenotype of the HI and wild type plant after flowering (~1month). Wild type plant is tall with well elongated inflorescence. All four HI plants
Supplementary Figure 1. Phenotype of the HI strain. (A) Phenotype of the HI and wild type plant after flowering (~1month). Wild type plant is tall with well elongated inflorescence. All four HI plants
Supplementary Figure S1. Amino acid alignment of selected monocot FT-like and TFL-like sequences. Sequences were aligned using ClustalW and analyzed
 Supplementary Figure S1. Amino acid alignment of selected monocot FT-like and TFL-like sequences. Sequences were aligned using ClustalW and analyzed using the Geneious software. Accession numbers of the
Supplementary Figure S1. Amino acid alignment of selected monocot FT-like and TFL-like sequences. Sequences were aligned using ClustalW and analyzed using the Geneious software. Accession numbers of the
Controlling Gene Expression
 Controlling Gene Expression Control Mechanisms Gene regulation involves turning on or off specific genes as required by the cell Determine when to make more proteins and when to stop making more Housekeeping
Controlling Gene Expression Control Mechanisms Gene regulation involves turning on or off specific genes as required by the cell Determine when to make more proteins and when to stop making more Housekeeping
GFP GAL bp 3964 bp
 Supplemental Data. Møller et al. (2009) Shoot Na + exclusion and increased salinity tolerance engineered by cell type-specific alteration of Na + transport in Arabidopsis Supplemental Figure 1. Salt-sensitive
Supplemental Data. Møller et al. (2009) Shoot Na + exclusion and increased salinity tolerance engineered by cell type-specific alteration of Na + transport in Arabidopsis Supplemental Figure 1. Salt-sensitive
Lecture 13: PROTEIN SYNTHESIS II- TRANSLATION
 http://smtom.lecture.ub.ac.id/ Password: https://syukur16tom.wordpress.com/ Password: Lecture 13: PROTEIN SYNTHESIS II- TRANSLATION http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/organic/imgorg/translation2.gif
http://smtom.lecture.ub.ac.id/ Password: https://syukur16tom.wordpress.com/ Password: Lecture 13: PROTEIN SYNTHESIS II- TRANSLATION http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/organic/imgorg/translation2.gif
Chapter 2: Extensions to Mendel: Complexities in Relating Genotype to Phenotype.
 Chapter 2: Extensions to Mendel: Complexities in Relating Genotype to Phenotype. please read pages 38-47; 49-55;57-63. Slide 1 of Chapter 2 1 Extension sot Mendelian Behavior of Genes Single gene inheritance
Chapter 2: Extensions to Mendel: Complexities in Relating Genotype to Phenotype. please read pages 38-47; 49-55;57-63. Slide 1 of Chapter 2 1 Extension sot Mendelian Behavior of Genes Single gene inheritance
Systematic comparison of lncrnas with protein coding mrnas in population expression and their response to environmental change
 Xu et al. BMC Plant Biology (2017) 17:42 DOI 10.1186/s12870-017-0984-8 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Systematic comparison of lncrnas with protein coding mrnas in population expression and their response
Xu et al. BMC Plant Biology (2017) 17:42 DOI 10.1186/s12870-017-0984-8 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Systematic comparison of lncrnas with protein coding mrnas in population expression and their response
From gene to protein. Premedical biology
 From gene to protein Premedical biology Central dogma of Biology, Molecular Biology, Genetics transcription replication reverse transcription translation DNA RNA Protein RNA chemically similar to DNA,
From gene to protein Premedical biology Central dogma of Biology, Molecular Biology, Genetics transcription replication reverse transcription translation DNA RNA Protein RNA chemically similar to DNA,
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Rice APC/C TE controls tillering through mediating the degradation of MONOCULM 1 Qibing Lin 1*, Dan Wang 1*, Hui Dong 2*, Suhai Gu 1, Zhijun Cheng 1, Jie Gong 2, Ruizhen Qin 1,
Supplementary Information Rice APC/C TE controls tillering through mediating the degradation of MONOCULM 1 Qibing Lin 1*, Dan Wang 1*, Hui Dong 2*, Suhai Gu 1, Zhijun Cheng 1, Jie Gong 2, Ruizhen Qin 1,
Molecular Biology of the Cell
 Alberts Johnson Lewis Morgan Raff Roberts Walter Molecular Biology of the Cell Sixth Edition Chapter 6 (pp. 333-368) How Cells Read the Genome: From DNA to Protein Copyright Garland Science 2015 Genetic
Alberts Johnson Lewis Morgan Raff Roberts Walter Molecular Biology of the Cell Sixth Edition Chapter 6 (pp. 333-368) How Cells Read the Genome: From DNA to Protein Copyright Garland Science 2015 Genetic
GENETICS - CLUTCH CH.1 INTRODUCTION TO GENETICS.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: HISTORY OF GENETICS The earliest use of genetics was through of plants and animals (8000-1000 B.C.) Selective breeding (artificial selection) is the process of breeding organisms
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: HISTORY OF GENETICS The earliest use of genetics was through of plants and animals (8000-1000 B.C.) Selective breeding (artificial selection) is the process of breeding organisms
A complementation test would be done by crossing the haploid strains and scoring the phenotype in the diploids.
 Problem set H answers 1. To study DNA repair mechanisms, geneticists isolated yeast mutants that were sensitive to various types of radiation; for example, mutants that were more sensitive to UV light.
Problem set H answers 1. To study DNA repair mechanisms, geneticists isolated yeast mutants that were sensitive to various types of radiation; for example, mutants that were more sensitive to UV light.
Arabidopsis PPR40 connects abiotic stress responses to mitochondrial electron transport
 Ph.D. thesis Arabidopsis PPR40 connects abiotic stress responses to mitochondrial electron transport Zsigmond Laura Supervisor: Dr. Szabados László Arabidopsis Molecular Genetic Group Institute of Plant
Ph.D. thesis Arabidopsis PPR40 connects abiotic stress responses to mitochondrial electron transport Zsigmond Laura Supervisor: Dr. Szabados László Arabidopsis Molecular Genetic Group Institute of Plant
Plant transformation
 Plant transformation Objectives: 1. What is plant transformation? 2. What is Agrobacterium? How and why does it transform plant cells? 3. How is Agrobacterium used as a tool in molecular genetics? References:
Plant transformation Objectives: 1. What is plant transformation? 2. What is Agrobacterium? How and why does it transform plant cells? 3. How is Agrobacterium used as a tool in molecular genetics? References:
SELF-INCOMPATIBILITY (SI) is a widespread genetic
 NOTE The Role of a Pollen-Expressed Cullin1 Protein in Gametophytic Self-Incompatibility in Solanum Wentao Li and Roger T. Chetelat 1 C. M. Rick Tomato Genetics Resource Center, Department of Plant Sciences,
NOTE The Role of a Pollen-Expressed Cullin1 Protein in Gametophytic Self-Incompatibility in Solanum Wentao Li and Roger T. Chetelat 1 C. M. Rick Tomato Genetics Resource Center, Department of Plant Sciences,
7.06 Problem Set #4, Spring 2005
 7.06 Problem Set #4, Spring 2005 1. You re doing a mutant hunt in S. cerevisiae (budding yeast), looking for temperaturesensitive mutants that are defective in the cell cycle. You discover a mutant strain
7.06 Problem Set #4, Spring 2005 1. You re doing a mutant hunt in S. cerevisiae (budding yeast), looking for temperaturesensitive mutants that are defective in the cell cycle. You discover a mutant strain
Videos. Bozeman, transcription and translation: https://youtu.be/h3b9arupxzg Crashcourse: Transcription and Translation - https://youtu.
 Translation Translation Videos Bozeman, transcription and translation: https://youtu.be/h3b9arupxzg Crashcourse: Transcription and Translation - https://youtu.be/itsb2sqr-r0 Translation Translation The
Translation Translation Videos Bozeman, transcription and translation: https://youtu.be/h3b9arupxzg Crashcourse: Transcription and Translation - https://youtu.be/itsb2sqr-r0 Translation Translation The
Development 143: doi: /dev : Supplementary information
 Supplementary Materials and Methods Plant materials The mutants and transgenic plants used in the present study were as follows: E361 (from Alex Webb s laboratory); tmm-1, ptmm::tmm-gfp and flp-1 (from
Supplementary Materials and Methods Plant materials The mutants and transgenic plants used in the present study were as follows: E361 (from Alex Webb s laboratory); tmm-1, ptmm::tmm-gfp and flp-1 (from
Supplementary Table 1. Primers used in this study.
 Supplementary Tale 1. Primers used in this study. Name Primer sequence (5'-3') Primers of PCR-ased molecular markers developed in this study M1 F M1 R M2 F M2 R M3 F M3 R M4 F M4 R M5 F M5 R M6 F M6 R
Supplementary Tale 1. Primers used in this study. Name Primer sequence (5'-3') Primers of PCR-ased molecular markers developed in this study M1 F M1 R M2 F M2 R M3 F M3 R M4 F M4 R M5 F M5 R M6 F M6 R
Annotation of Plant Genomes using RNA-seq. Matteo Pellegrini (UCLA) In collaboration with Sabeeha Merchant (UCLA)
 Annotation of Plant Genomes using RNA-seq Matteo Pellegrini (UCLA) In collaboration with Sabeeha Merchant (UCLA) inuscu1-35bp 5 _ 0 _ 5 _ What is Annotation inuscu2-75bp luscu1-75bp 0 _ 5 _ Reconstruction
Annotation of Plant Genomes using RNA-seq Matteo Pellegrini (UCLA) In collaboration with Sabeeha Merchant (UCLA) inuscu1-35bp 5 _ 0 _ 5 _ What is Annotation inuscu2-75bp luscu1-75bp 0 _ 5 _ Reconstruction
Objectives. Announcements. Comparison of mitosis and meiosis
 Announcements Colloquium sessions for which you can get credit posted on web site: Feb 20, 27 Mar 6, 13, 20 Apr 17, 24 May 15. Review study CD that came with text for lab this week (especially mitosis
Announcements Colloquium sessions for which you can get credit posted on web site: Feb 20, 27 Mar 6, 13, 20 Apr 17, 24 May 15. Review study CD that came with text for lab this week (especially mitosis
Solutions to Problem Set 4
 Question 1 Solutions to 7.014 Problem Set 4 Because you have not read much scientific literature, you decide to study the genetics of garden peas. You have two pure breeding pea strains. One that is tall
Question 1 Solutions to 7.014 Problem Set 4 Because you have not read much scientific literature, you decide to study the genetics of garden peas. You have two pure breeding pea strains. One that is tall
Procedure to Create NCBI KOGS
 Procedure to Create NCBI KOGS full details in: Tatusov et al (2003) BMC Bioinformatics 4:41. 1. Detect and mask typical repetitive domains Reason: masking prevents spurious lumping of non-orthologs based
Procedure to Create NCBI KOGS full details in: Tatusov et al (2003) BMC Bioinformatics 4:41. 1. Detect and mask typical repetitive domains Reason: masking prevents spurious lumping of non-orthologs based
Biology. Biology. Slide 1 of 26. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 Biology Biology 1 of 26 Fruit fly chromosome 12-5 Gene Regulation Mouse chromosomes Fruit fly embryo Mouse embryo Adult fruit fly Adult mouse 2 of 26 Gene Regulation: An Example Gene Regulation: An Example
Biology Biology 1 of 26 Fruit fly chromosome 12-5 Gene Regulation Mouse chromosomes Fruit fly embryo Mouse embryo Adult fruit fly Adult mouse 2 of 26 Gene Regulation: An Example Gene Regulation: An Example
Cell Division: the process of copying and dividing entire cells The cell grows, prepares for division, and then divides to form new daughter cells.
 Mitosis & Meiosis SC.912.L.16.17 Compare and contrast mitosis and meiosis and relate to the processes of sexual and asexual reproduction and their consequences for genetic variation. 1. Students will describe
Mitosis & Meiosis SC.912.L.16.17 Compare and contrast mitosis and meiosis and relate to the processes of sexual and asexual reproduction and their consequences for genetic variation. 1. Students will describe
Heredity and Genetics WKSH
 Chapter 6, Section 3 Heredity and Genetics WKSH KEY CONCEPT Mendel s research showed that traits are inherited as discrete units. Vocabulary trait purebred law of segregation genetics cross MAIN IDEA:
Chapter 6, Section 3 Heredity and Genetics WKSH KEY CONCEPT Mendel s research showed that traits are inherited as discrete units. Vocabulary trait purebred law of segregation genetics cross MAIN IDEA:
Fitness constraints on horizontal gene transfer
 Fitness constraints on horizontal gene transfer Dan I Andersson University of Uppsala, Department of Medical Biochemistry and Microbiology, Uppsala, Sweden GMM 3, 30 Aug--2 Sep, Oslo, Norway Acknowledgements:
Fitness constraints on horizontal gene transfer Dan I Andersson University of Uppsala, Department of Medical Biochemistry and Microbiology, Uppsala, Sweden GMM 3, 30 Aug--2 Sep, Oslo, Norway Acknowledgements:
Heredity Composite. Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Heredity Composite Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. When a plant breeder crossed two red roses, 78% of the offspring had red flowers and
Heredity Composite Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. When a plant breeder crossed two red roses, 78% of the offspring had red flowers and
BIOLOGY FINAL EXAM REVIEW SHEET Chapters 10-15, 17-30
 Name Hour Due Date: BIOLOGY FINAL EXAM REVIEW SHEET Chapters 10-15, 17-30 The exam was prepared by the Biology teachers in the science departments of CVHS and DHS. 1. What is a Punnett Square? 2. Cross
Name Hour Due Date: BIOLOGY FINAL EXAM REVIEW SHEET Chapters 10-15, 17-30 The exam was prepared by the Biology teachers in the science departments of CVHS and DHS. 1. What is a Punnett Square? 2. Cross
Unit 3 - Molecular Biology & Genetics - Review Packet
 Name Date Hour Unit 3 - Molecular Biology & Genetics - Review Packet True / False Questions - Indicate True or False for the following statements. 1. Eye color, hair color and the shape of your ears can
Name Date Hour Unit 3 - Molecular Biology & Genetics - Review Packet True / False Questions - Indicate True or False for the following statements. 1. Eye color, hair color and the shape of your ears can
Noncanonical Translation Initiation of the Arabidopsis Flowering Time and Alternative Polyadenylation Regulator FCA C W
 The Plant Cell, Vol. 22: 3764 3777, November 2010, www.plantcell.org ã 2010 American Society of Plant Biologists Noncanonical Translation Initiation of the Arabidopsis Flowering Time and Alternative Polyadenylation
The Plant Cell, Vol. 22: 3764 3777, November 2010, www.plantcell.org ã 2010 American Society of Plant Biologists Noncanonical Translation Initiation of the Arabidopsis Flowering Time and Alternative Polyadenylation
BIS &003 Answers to Assigned Problems May 23, Week /18.6 How would you distinguish between an enhancer and a promoter?
 Week 9 Study Questions from the textbook: 6 th Edition: Chapter 19-19.6, 19.7, 19.15, 19.17 OR 7 th Edition: Chapter 18-18.6 18.7, 18.15, 18.17 19.6/18.6 How would you distinguish between an enhancer and
Week 9 Study Questions from the textbook: 6 th Edition: Chapter 19-19.6, 19.7, 19.15, 19.17 OR 7 th Edition: Chapter 18-18.6 18.7, 18.15, 18.17 19.6/18.6 How would you distinguish between an enhancer and
USDA-DOE Plant Feedstock Genomics for Bioenergy
 USDA-DOE Plant Feedstock Genomics for Bioenergy BERAC Thursday, June 7, 2012 Cathy Ronning, DOE-BER Ed Kaleikau, USDA-NIFA Plant Feedstock Genomics for Bioenergy Joint competitive grants program initiated
USDA-DOE Plant Feedstock Genomics for Bioenergy BERAC Thursday, June 7, 2012 Cathy Ronning, DOE-BER Ed Kaleikau, USDA-NIFA Plant Feedstock Genomics for Bioenergy Joint competitive grants program initiated
,(CL806925),(CL ),(CL829057),(CL ),(CL862603) BAC45136 putative nucleotide-binding
 Additional Data File 13. List of 83 disease resistance-related genes that matched the unmapped BESs of On, Or, and Og. BESs that had internal stop codons within the aligned regions are presented in parentheses.
Additional Data File 13. List of 83 disease resistance-related genes that matched the unmapped BESs of On, Or, and Og. BESs that had internal stop codons within the aligned regions are presented in parentheses.
Adaptation in the Human Genome. HapMap. The HapMap is a Resource for Population Genetic Studies. Single Nucleotide Polymorphism (SNP)
 Adaptation in the Human Genome A genome-wide scan for signatures of adaptive evolution using SNP data Single Nucleotide Polymorphism (SNP) A nucleotide difference at a given location in the genome Joanna
Adaptation in the Human Genome A genome-wide scan for signatures of adaptive evolution using SNP data Single Nucleotide Polymorphism (SNP) A nucleotide difference at a given location in the genome Joanna
Small RNA in rice genome
 Vol. 45 No. 5 SCIENCE IN CHINA (Series C) October 2002 Small RNA in rice genome WANG Kai ( 1, ZHU Xiaopeng ( 2, ZHONG Lan ( 1,3 & CHEN Runsheng ( 1,2 1. Beijing Genomics Institute/Center of Genomics and
Vol. 45 No. 5 SCIENCE IN CHINA (Series C) October 2002 Small RNA in rice genome WANG Kai ( 1, ZHU Xiaopeng ( 2, ZHONG Lan ( 1,3 & CHEN Runsheng ( 1,2 1. Beijing Genomics Institute/Center of Genomics and
Related Courses He who asks is a fool for five minutes, but he who does not ask remains a fool forever.
 CSE 527 Computational Biology http://www.cs.washington.edu/527 Lecture 1: Overview & Bio Review Autumn 2004 Larry Ruzzo Related Courses He who asks is a fool for five minutes, but he who does not ask remains
CSE 527 Computational Biology http://www.cs.washington.edu/527 Lecture 1: Overview & Bio Review Autumn 2004 Larry Ruzzo Related Courses He who asks is a fool for five minutes, but he who does not ask remains
From Gene to Protein
 From Gene to Protein Gene Expression Process by which DNA directs the synthesis of a protein 2 stages transcription translation All organisms One gene one protein 1. Transcription of DNA Gene Composed
From Gene to Protein Gene Expression Process by which DNA directs the synthesis of a protein 2 stages transcription translation All organisms One gene one protein 1. Transcription of DNA Gene Composed
