Bioinformatics tools to analyze complex genomes. Yves Van de Peer Ghent University/VIB
|
|
|
- Catherine O’Connor’
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Bioinformatics tools to analyze complex genomes Yves Van de Peer Ghent University/VIB
2
3
4 Detecting colinearity and large-scale gene duplications A Speciation/Duplicatio n S1 S Gene loss, insertions, rearrangements, translocation, etc Time 2 S1 S retained orthologs (anchor points)
5 Detecting colinearity and large-scale gene duplications S1 S segment S X X Gene Homology Matrix: Conserved gene content and order Collinear regions appear as diagonals segment S2 4 X X 11
6 Detecting colinearity and large-scale gene duplications In an actual genome this becomes complex Good statistical model to find biologically relevant regions Real clusters A noise cluster
7 The Arabidopsis genome duplication The Arabidopsis Genome Initiative (2000)
8 Transitive homology B A C Segments B and C are homologous because both are homologous to the segment A However, segments B and C share only 1 gene because of differential gene loss
9 Detecting homology in the twilight zone : genomic profiles C Not Not significant A B Not significant C Not significant Building genomic profiles A B
10 Searching for diagonals revisited A B C significant homology!
11 Genomic profiles: increasing the multiplication level Simillion et al. (2004) Genome Res. 14,
12 i-adhore 3.0 MCSCan: Tang et al., 2008 Cyntenator: Rödelsperger et al., 2010 Fostier et al., 2011
13 i-adhore 3.0 is extremely efficient in analyzing large datasets
14
15 Gene loss and colinearity/synteny WGDs add to the complexity of plant genomes (both in numbers of genes and genome structure) Van de Peer et al. (2009) Trends Plant Science
16 Linking WGDs with great or decisive moments in evolution
17 Darwin s abominable mystery WGD?
18 Another way of unveiling WGDs: K S age distributions Continuous mode of gene duplication Number of duplicates Genome duplication events Ks or Time Corresponds with age older Maere et al. (2005) PNAS Vanneste et al. (2013) Mol. Biol. Evol.
19 Many plants have undergone a recent genome duplication Shi et al., (2010) Annals Bot. Cui et al., Genome Research (2006) Blanc and Wolfe, Plant Cell, (2004) K s frequency distribution (%) 16% 14% 12% 10% 8% 6% 4% 2% Ginger-Ginger Musa-Ginger Musa-Musa Musa-Rice Lescot et al. (2008) BMC Genomics (2008) 0% K s
20 The Solanum lineage has experienced two consecutive genome triplications: one that is ancient and shared with rosids, and a more recent one. These triplications set the stage for the neofunctionalization of genes controlling fruit characteristics, such as colour and fleshiness.
21 A whole-genome duplication (WGD) approximately 58 Myr ago had a major role in shaping the M. truncatula genome and thereby contributed to the evolution of endosymbiotic nitrogen fixation.
22 An intriguing aspect of the apple's biology concerns its characteristic fruit, the pome, which is found only in the Pyreae tribe. This indicates that the pome probably evolved after a relatively recent Pyreae-specific GWD, a polyploidization step that we hypothesize has contributed to the apple's developmental and metabolic specificity.
23 Calibrating the molecular clock.
24 Many plants have undergone a recent genome duplication Cui et al., Genome Research (2006) Organism Molecular clock rates (K S ) Arabidopsis thaliana (8), 65 mya (11) Populus trichocarpa 13 mya (3) Vitis vinifera No recent duplication Medicago truncatula > 50 mya (29); 58 mya (10) Lotus japonicus b > 50 mya (29) Glycine max 44 mya (10) Gossypium hirsutum mya (8) Carica papaya No recent duplication Solanum tuberosum b mya (10) Solanum lycopersicum mya (10) Eschscholzia californica Unknown Musa spp, 61 mya (13) Oryza sativa mya (10); 70 mya (6) Sorghum bicolor b mya (10); 70 mya (6) Acorus americanus Unknown Physcomitrella patens Unknown
25 Absolute dating through the construction of phylogenetic trees Ath 1 Ath 2 duplication speciation Ath 1 Ath 2 poplar rice moss Time (mya)
26 Absolute dating through the construction of phylogenetic trees
27 Duplications are clustered in time The Cretaceous Tertiary (KT) extinction event is known as the most recent large-scale mass extinction of animal and plant species in a geologically short period of time, approximately 65 mya. Fawcett et al. (2009) PNAS Vanneste et al. (2014) Genome Research (accepted, pending revisions)
28 Jurassic Cretaceous Tertiary mya Monocots 100 Eudicots 125 Asterids 150 Eurosids II 175 Eurosids I Cucumis melo Cucumis sativus Citrullus lanatus Malus domestica Pyrus bretschneideri Prunus persica Prunus mume Fragaria vesca Glycine max Cajanus cajan Medicago truncatula Cicer arietinum Lotus japonicus Ricinus communis Manihot esculenta Jatropha curcas Linum usitatissimum Populus trichocarpa Brassica rapa Thelungiella parvula Arabidopsis thaliana Arabidopsis lyrata Carica papaya Theobroma cacao Gossypium raimonddi Eucalyptus grandis Vitis vinifera Solanum lycopersicum Solanum tubersomum Lactuca sativa Nelumbo nucifera Aquilegia formosa x pubescens Brachypodium distachyon Hordeum vulgare Oryza sativa Zea mays Sorghum bicolor Setaria italica Musa acuminata Phoenix dactylifera Phaeodactylum equestris Nuphar advena Physcomitrella patens
29 65 mya: the Cretaceous Tertiary (KT) extinction event Hiroshima:15 kiloton Tsar Bomba: 57 megaton K-T impactor: 2 million times Tsar Bomba
30 65 mya: the Cretaceous Tertiary (KT) extinction event These catastrophic events have: caused huge wildfires reduced sunlight and prolonged darkness caused temperatures to drop caused acid rain As a result, there was: hindered photosynthesis reduced germination of seeds abrupt extinction or local disappearance of terrestrial vegetation Paleobotanical studies of fossil pollen, spores and leaves from North American localities have shown that 18-30% of plant genera and families and up to 60% of plant species disappeared at the KT boundary.
31 Polyploids: evolutionary dead ends or hopeful monsters? Although polyploids occur frequently in the wild under natural conditions Under normal circumstances Not many survive, not many get established, not many proliferate Many polyploids have reduced fertility, reduced fitness,
32 Polyploids: evolutionary dead ends or hopeful monsters? Stress Environmental fluctuations Extinction Hybridization Unreduced gametes NEUTRAL Polyploid formation ADAPTIVE Transgressive segregation Phenotypic variability/plasticity Environment Rapid adaptive changes facilitated by the plastic genomic background Polyploid establishment Fawcett et al. (2009) PNAS Van de Peer et al. (2009) Nat Rev Genet Vanneste et al. (2014) Genome Research (accepted, pending revisions)
33 Acknowledgements
Supplementary Figure 1. Number of CC- and TIR- type NBS- LRR genes and presence of mir482/2118 on sequenced plant genomes.
 Number of CC- NBS and CC- NBS- LRR R- genes Number of TIR- NBS and TIR- NBS- LRR R- genes 0 50 100 150 200 250 0 50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 450 mir482 and mir2118 Cajanus cajan Glycine max Hevea brasiliensis
Number of CC- NBS and CC- NBS- LRR R- genes Number of TIR- NBS and TIR- NBS- LRR R- genes 0 50 100 150 200 250 0 50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 450 mir482 and mir2118 Cajanus cajan Glycine max Hevea brasiliensis
Supplementary Figure 3
 Supplementary Figure 3 7.0 Col Kas-1 Line FTH1A 8.4 F3PII3 8.9 F26H11 ATQ1 T9I22 PLS8 F26B6-B 9.6 F27L4 9.81 F27D4 9.92 9.96 10.12 10.14 10.2 11.1 0.5 Mb T1D16 Col % RGR 83.3 101 227 93.5 75.9 132 90 375
Supplementary Figure 3 7.0 Col Kas-1 Line FTH1A 8.4 F3PII3 8.9 F26H11 ATQ1 T9I22 PLS8 F26B6-B 9.6 F27L4 9.81 F27D4 9.92 9.96 10.12 10.14 10.2 11.1 0.5 Mb T1D16 Col % RGR 83.3 101 227 93.5 75.9 132 90 375
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature13082 Supplementary Table 1. Examination of nectar production in wild-type and atsweet9 flowers. No. of flowers with detectable nectar out of the total observed
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature13082 Supplementary Table 1. Examination of nectar production in wild-type and atsweet9 flowers. No. of flowers with detectable nectar out of the total observed
Evaluation of Genome Sequencing Quality in Selected Plant Species Using Expressed Sequence Tags
 Evaluation of Genome Sequencing Quality in Selected Plant Species Using Expressed Sequence Tags Lingfei Shangguan 1, Jian Han 1, Emrul Kayesh 1, Xin Sun 1, Changqing Zhang 2, Tariq Pervaiz 1, Xicheng Wen
Evaluation of Genome Sequencing Quality in Selected Plant Species Using Expressed Sequence Tags Lingfei Shangguan 1, Jian Han 1, Emrul Kayesh 1, Xin Sun 1, Changqing Zhang 2, Tariq Pervaiz 1, Xicheng Wen
Cao, J, K Schneeberger, S Ossowski, et al Whole genome sequencing of multiple Arabidopsis thaliana populations. Nat Genet 43:
 Figure S1. Syntenic map of SAE1B duplication. We have used the nucleotide sequences of Arabidopsis thaliana Col-0 gene tandem duplicates AT5G50580 and AT5G506800 as queries in independent BLASTN searches
Figure S1. Syntenic map of SAE1B duplication. We have used the nucleotide sequences of Arabidopsis thaliana Col-0 gene tandem duplicates AT5G50580 and AT5G506800 as queries in independent BLASTN searches
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Fawcett et al. 10.1073/pnas.0900906106 SI Text Estimating the Age of Gene Duplication Events: The Use of K S Values. One of the most common methods used to study and visualize gene
Supporting Information Fawcett et al. 10.1073/pnas.0900906106 SI Text Estimating the Age of Gene Duplication Events: The Use of K S Values. One of the most common methods used to study and visualize gene
Plant Genome Sequencing
 Plant Genome Sequencing Traditional Sanger Sequencing Genome Sequencing Approach 1. Create sequencing libraries of different insert sizes 2kb o Bulk of sequencing is performed on these libraries 10kb o
Plant Genome Sequencing Traditional Sanger Sequencing Genome Sequencing Approach 1. Create sequencing libraries of different insert sizes 2kb o Bulk of sequencing is performed on these libraries 10kb o
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:1.138/nature11394 Supplementary Note Our study is based on two different tracriptome indices. Both combine tracriptional information with an important evolutionary parameter. For the tracriptome age
doi:1.138/nature11394 Supplementary Note Our study is based on two different tracriptome indices. Both combine tracriptional information with an important evolutionary parameter. For the tracriptome age
Stage 1: Karyotype Stage 2: Gene content & order Step 3
 Supplementary Figure Method used for ancestral genome reconstruction. MRCA (Most Recent Common Ancestor), AMK (Ancestral Monocot Karyotype), AEK (Ancestral Eudicot Karyotype), AGK (Ancestral Grass Karyotype)
Supplementary Figure Method used for ancestral genome reconstruction. MRCA (Most Recent Common Ancestor), AMK (Ancestral Monocot Karyotype), AEK (Ancestral Eudicot Karyotype), AGK (Ancestral Grass Karyotype)
Supplementary Material
 Supplementary Material Supplementary Table S1. Genomes available in build 47 Supplementary Table S2. Counts of putative contiguous gene split models in 39 plant reference genomes in build 47 Supplementary
Supplementary Material Supplementary Table S1. Genomes available in build 47 Supplementary Table S2. Counts of putative contiguous gene split models in 39 plant reference genomes in build 47 Supplementary
Potato Genome Analysis
 Potato Genome Analysis Xin Liu Deputy director BGI research 2016.1.21 WCRTC 2016 @ Nanning Reference genome construction???????????????????????????????????????? Sequencing HELL RIEND WELCOME BGI ZHEN LLOFRI
Potato Genome Analysis Xin Liu Deputy director BGI research 2016.1.21 WCRTC 2016 @ Nanning Reference genome construction???????????????????????????????????????? Sequencing HELL RIEND WELCOME BGI ZHEN LLOFRI
Whole-genome duplications and paleopolyploidy
 Whole-genome duplications and paleopolyploidy Whole-genome duplications in protozoa Aury et al. (2006) analyzed the unicellular eukaryote Paramecium tetraurelia most of 40,000 genes arose through at least
Whole-genome duplications and paleopolyploidy Whole-genome duplications in protozoa Aury et al. (2006) analyzed the unicellular eukaryote Paramecium tetraurelia most of 40,000 genes arose through at least
Evolution by duplication: paleopolyploidy events in plants reconstructed by deciphering the evolutionary history of VOZ transcription factors
 Gao et al. BMC Plant Biology (2018) 18:256 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-018-1437-8 RESEARCH ARTICLE Evolution by duplication: paleopolyploidy events in plants reconstructed by deciphering the evolutionary
Gao et al. BMC Plant Biology (2018) 18:256 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-018-1437-8 RESEARCH ARTICLE Evolution by duplication: paleopolyploidy events in plants reconstructed by deciphering the evolutionary
Analysis of 41 plant genomes supports a wave of successful genome duplications in association with the Cretaceous Paleogene boundary
 Research Analysis of 41 plant genomes supports a wave of successful genome duplications in association with the Cretaceous Paleogene boundary Kevin Vanneste, 1,2 Guy Baele, 3 Steven Maere, 1,2 and Yves
Research Analysis of 41 plant genomes supports a wave of successful genome duplications in association with the Cretaceous Paleogene boundary Kevin Vanneste, 1,2 Guy Baele, 3 Steven Maere, 1,2 and Yves
Supplementary Information for: The genome of the extremophile crucifer Thellungiella parvula
 Supplementary Information for: The genome of the extremophile crucifer Thellungiella parvula Maheshi Dassanayake 1,9, Dong-Ha Oh 1,9, Jeffrey S. Haas 1,2, Alvaro Hernandez 3, Hyewon Hong 1,4, Shahjahan
Supplementary Information for: The genome of the extremophile crucifer Thellungiella parvula Maheshi Dassanayake 1,9, Dong-Ha Oh 1,9, Jeffrey S. Haas 1,2, Alvaro Hernandez 3, Hyewon Hong 1,4, Shahjahan
Eud! Mag! Chl! Cer! Mon! outgroup! g 88. Eud! Cer! <50. Chl! Mag! Mon! outgroup! Eud! Mon! Cer! Mag! Chl! outgroup!
 a
a
Genome-wide discovery of G-quadruplex forming sequences and their functional
 *Correspondence and requests for materials should be addressed to R.G. (rohini@nipgr.ac.in) Genome-wide discovery of G-quadruplex forming sequences and their functional relevance in plants Rohini Garg*,
*Correspondence and requests for materials should be addressed to R.G. (rohini@nipgr.ac.in) Genome-wide discovery of G-quadruplex forming sequences and their functional relevance in plants Rohini Garg*,
Genome-wide Identification of Lineage Specific Genes in Arabidopsis, Oryza and Populus
 Genome-wide Identification of Lineage Specific Genes in Arabidopsis, Oryza and Populus Xiaohan Yang Sara Jawdy Timothy Tschaplinski Gerald Tuskan Environmental Sciences Division Oak Ridge National Laboratory
Genome-wide Identification of Lineage Specific Genes in Arabidopsis, Oryza and Populus Xiaohan Yang Sara Jawdy Timothy Tschaplinski Gerald Tuskan Environmental Sciences Division Oak Ridge National Laboratory
Miloš Duchoslav and Lukáš Fischer *
 Duchoslav and Fischer BMC Plant Biology (2015) 15:133 DOI 10.1186/s12870-015-0523-4 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Parallel subfunctionalisation of PsbO protein isoforms in angiosperms revealed by phylogenetic
Duchoslav and Fischer BMC Plant Biology (2015) 15:133 DOI 10.1186/s12870-015-0523-4 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Parallel subfunctionalisation of PsbO protein isoforms in angiosperms revealed by phylogenetic
Jill M Duarte 1, P Kerr Wall 1,5, Patrick P Edger 2, Lena L Landherr 1, Hong Ma 1,4, J Chris Pires 2, Jim Leebens-Mack 3, Claude W depamphilis 1*
 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Identification of shared single copy nuclear genes in Arabidopsis, Populus, Vitis and Oryza and their phylogenetic utility across various taxonomic levels Jill M Duarte 1,
RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Identification of shared single copy nuclear genes in Arabidopsis, Populus, Vitis and Oryza and their phylogenetic utility across various taxonomic levels Jill M Duarte 1,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:1.138/nature111 cytosol Model: PILS function in cellular auxin homeostasis ER nucleus IAA degradation? sequestration? conjugation? storage? signalling? PILS IAA ER cytosol Supplemental Figure 1 Model
doi:1.138/nature111 cytosol Model: PILS function in cellular auxin homeostasis ER nucleus IAA degradation? sequestration? conjugation? storage? signalling? PILS IAA ER cytosol Supplemental Figure 1 Model
Supplemental Figure 1. Comparison of Tiller Bud Formation between the Wild Type and d27. (A) and (B) Longitudinal sections of shoot apex in wild-type
 A B 2 3 3 2 1 1 Supplemental Figure 1. Comparison of Tiller Bud Formation between the Wild Type and d27. (A) and (B) Longitudinal sections of shoot apex in wild-type (A) and d27 (B) seedlings at the four
A B 2 3 3 2 1 1 Supplemental Figure 1. Comparison of Tiller Bud Formation between the Wild Type and d27. (A) and (B) Longitudinal sections of shoot apex in wild-type (A) and d27 (B) seedlings at the four
AtTIL-P91V. AtTIL-P92V. AtTIL-P95V. AtTIL-P98V YFP-HPR
 Online Resource 1. Primers used to generate constructs AtTIL-P91V, AtTIL-P92V, AtTIL-P95V and AtTIL-P98V and YFP(HPR) using overlapping PCR. pentr/d- TOPO-AtTIL was used as template to generate the constructs
Online Resource 1. Primers used to generate constructs AtTIL-P91V, AtTIL-P92V, AtTIL-P95V and AtTIL-P98V and YFP(HPR) using overlapping PCR. pentr/d- TOPO-AtTIL was used as template to generate the constructs
Supplemental Data. Vanneste et al. (2015). Plant Cell /tpc
 Supplemental Figure 1: Representation of the structure of an orthogroup. Each orthogroup consists out of a paralogous pair representing the WGD (denoted by Equisetum 1 and Equisetum 2) supplemented with
Supplemental Figure 1: Representation of the structure of an orthogroup. Each orthogroup consists out of a paralogous pair representing the WGD (denoted by Equisetum 1 and Equisetum 2) supplemented with
Paleo-evolutionary plasticity of plant disease resistance genes
 Zhang et al. BMC Genomics 2014, 15:187 RESEARCH ARTICLE Paleo-evolutionary plasticity of plant disease resistance genes Rongzhi Zhang 1,2, Florent Murat 1, Caroline Pont 1, Thierry Langin 1 and Jerome
Zhang et al. BMC Genomics 2014, 15:187 RESEARCH ARTICLE Paleo-evolutionary plasticity of plant disease resistance genes Rongzhi Zhang 1,2, Florent Murat 1, Caroline Pont 1, Thierry Langin 1 and Jerome
Big Questions. Is polyploidy an evolutionary dead-end? If so, why are all plants the products of multiple polyploidization events?
 Plant of the Day Cyperus esculentus - Cyperaceae Chufa (tigernut) 8,000 kg/ha, 720 kcal/sq m per month Top Crop for kcal productivity! One of the world s worst weeds Big Questions Is polyploidy an evolutionary
Plant of the Day Cyperus esculentus - Cyperaceae Chufa (tigernut) 8,000 kg/ha, 720 kcal/sq m per month Top Crop for kcal productivity! One of the world s worst weeds Big Questions Is polyploidy an evolutionary
Browsing Genomic Information with Ensembl Plants
 Browsing Genomic Information with Ensembl Plants Etienne de Villiers, PhD (Adapted from slides by Bert Overduin EMBL-EBI) Outline of workshop Brief introduction to Ensembl Plants History Content Tutorial
Browsing Genomic Information with Ensembl Plants Etienne de Villiers, PhD (Adapted from slides by Bert Overduin EMBL-EBI) Outline of workshop Brief introduction to Ensembl Plants History Content Tutorial
Impact of recurrent gene duplication on adaptation of plant genomes
 Fischer et al. BMC Plant Biology 2014, 14:151 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Impact of recurrent gene duplication on adaptation of plant genomes Iris Fischer 1,2*, Jacques Dainat 3,6, Vincent Ranwez 3, Sylvain
Fischer et al. BMC Plant Biology 2014, 14:151 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Impact of recurrent gene duplication on adaptation of plant genomes Iris Fischer 1,2*, Jacques Dainat 3,6, Vincent Ranwez 3, Sylvain
Supplemental Figure 1. Comparisons of GC3 distribution computed with raw EST data, bi-beta fits and complete genome sequences for 6 species.
 Supplemental Figure 1. Comparisons of GC3 distribution computed with raw EST data, bi-beta fits and complete genome sequences for 6 species. Filled distributions: GC3 computed with raw EST data. Dashed
Supplemental Figure 1. Comparisons of GC3 distribution computed with raw EST data, bi-beta fits and complete genome sequences for 6 species. Filled distributions: GC3 computed with raw EST data. Dashed
Fractionation resistance of duplicate genes following whole genome duplication in plants as a function of gene ontology category and expression level
 Fractionation resistance of duplicate genes following whole genome duplication in plants as a function of gene ontology category and expression level Eric Chun-Hung Chen Thesis submitted to the Faculty
Fractionation resistance of duplicate genes following whole genome duplication in plants as a function of gene ontology category and expression level Eric Chun-Hung Chen Thesis submitted to the Faculty
USDA-DOE Plant Feedstock Genomics for Bioenergy
 USDA-DOE Plant Feedstock Genomics for Bioenergy BERAC Thursday, June 7, 2012 Cathy Ronning, DOE-BER Ed Kaleikau, USDA-NIFA Plant Feedstock Genomics for Bioenergy Joint competitive grants program initiated
USDA-DOE Plant Feedstock Genomics for Bioenergy BERAC Thursday, June 7, 2012 Cathy Ronning, DOE-BER Ed Kaleikau, USDA-NIFA Plant Feedstock Genomics for Bioenergy Joint competitive grants program initiated
In 1996, when the research plant community decided to determine
 The hidden duplication past of Arabidopsis thaliana Cedric Simillion, Klaas Vandepoele, Marc C. E. Van Montagu, Marc Zabeau, and Yves Van de Peer* Department of Plant Systems Biology, Flanders Interuniversity
The hidden duplication past of Arabidopsis thaliana Cedric Simillion, Klaas Vandepoele, Marc C. E. Van Montagu, Marc Zabeau, and Yves Van de Peer* Department of Plant Systems Biology, Flanders Interuniversity
(Paleo)Polyploidy When Things Get Bigger
 (Paleo)Polyploidy When Things Get Bigger Hegarty and Hiscock 2008, Current Biology 18 Whole-genome duplications AUTOPOLYPLOIDY ALLOPOLYPLOIDY Examples of allopolyploid speciation Hegarty and Hiscock 2008,
(Paleo)Polyploidy When Things Get Bigger Hegarty and Hiscock 2008, Current Biology 18 Whole-genome duplications AUTOPOLYPLOIDY ALLOPOLYPLOIDY Examples of allopolyploid speciation Hegarty and Hiscock 2008,
PaleoGenomics & Evolution (group PaleoEVO). UMR1095 INRA UBP Génétique, Diversité & Ecophysiologie des Céréales
 TranscriptomePartitioning Following Polyploidization Events in Grasses Journée Transcriptome URGV 1 Mai 13 Plant and Animal Genomes SPECIES COMMON NAME CHROMOSOMES GENOME (MB) ANNOTATED GENES SYNTENY DUPLICATION
TranscriptomePartitioning Following Polyploidization Events in Grasses Journée Transcriptome URGV 1 Mai 13 Plant and Animal Genomes SPECIES COMMON NAME CHROMOSOMES GENOME (MB) ANNOTATED GENES SYNTENY DUPLICATION
Identification of new members of the MAPK gene family in plants shows diverse conserved domains and novel activation loop variants
 Mohanta et al. BMC Genomics (2015) 16:58 DOI 10.1186/s12864-015-1244-7 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Identification of new members of the MAPK gene family in plants shows diverse conserved domains and novel
Mohanta et al. BMC Genomics (2015) 16:58 DOI 10.1186/s12864-015-1244-7 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Identification of new members of the MAPK gene family in plants shows diverse conserved domains and novel
Supplemental Data. Yang et al. (2012). Plant Cell /tpc
 Supplemental Figure 1. Mature flowers of P. heterotricha. (A) An inflorescence of P. heterotricha showing the front view of a zygomorphic flower characterized by two small dorsal petals and only two fertile
Supplemental Figure 1. Mature flowers of P. heterotricha. (A) An inflorescence of P. heterotricha showing the front view of a zygomorphic flower characterized by two small dorsal petals and only two fertile
The Origin of Species
 The Origin of Species Introduction A species can be defined as a group of organisms whose members can breed and produce fertile offspring, but who do not produce fertile offspring with members of other
The Origin of Species Introduction A species can be defined as a group of organisms whose members can breed and produce fertile offspring, but who do not produce fertile offspring with members of other
How to detect paleoploidy?
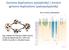 Genome duplications (polyploidy) / ancient genome duplications (paleopolyploidy) How to detect paleoploidy? e.g. a diploid cell undergoes failed meiosis, producing diploid gametes, which selffertilize
Genome duplications (polyploidy) / ancient genome duplications (paleopolyploidy) How to detect paleoploidy? e.g. a diploid cell undergoes failed meiosis, producing diploid gametes, which selffertilize
Chapter 1-Plants in Our World
 Chapter 1-Plants in Our World Formation of earth-4.5-4.6 billion years ago Evidence of life from organic material-3.8 billion years ago Many cyanobacteria are photosynthetic, but these microscopic organisms
Chapter 1-Plants in Our World Formation of earth-4.5-4.6 billion years ago Evidence of life from organic material-3.8 billion years ago Many cyanobacteria are photosynthetic, but these microscopic organisms
Phylogenetic Comparison of F-Box (FBX) Gene Superfamily within the Plant Kingdom Reveals Divergent Evolutionary Histories Indicative of Genomic Drift
 Phylogenetic Comparison of F-Box (FBX) Gene Superfamily within the Plant Kingdom Reveals Divergent Evolutionary Histories Indicative of Genomic Drift Zhihua Hua 1, Cheng Zou 2, Shin-Han Shiu 2, Richard
Phylogenetic Comparison of F-Box (FBX) Gene Superfamily within the Plant Kingdom Reveals Divergent Evolutionary Histories Indicative of Genomic Drift Zhihua Hua 1, Cheng Zou 2, Shin-Han Shiu 2, Richard
Lineage specific conserved noncoding sequences in plants
 Lineage specific conserved noncoding sequences in plants Nilmini Hettiarachchi Department of Genetics, SOKENDAI National Institute of Genetics, Mishima, Japan 20 th June 2014 Conserved Noncoding Sequences
Lineage specific conserved noncoding sequences in plants Nilmini Hettiarachchi Department of Genetics, SOKENDAI National Institute of Genetics, Mishima, Japan 20 th June 2014 Conserved Noncoding Sequences
gi (NCBI databse: ES frame +2 (NCBI: databse
 Figure legend for supplemental tables (S1-S6). The predicted and annotated amino acid sequences for the different LEA proteins found in the available databases (378) were analyzed using MEME software (Bailey
Figure legend for supplemental tables (S1-S6). The predicted and annotated amino acid sequences for the different LEA proteins found in the available databases (378) were analyzed using MEME software (Bailey
PLAZA: A Comparative Genomics Resource to Study Gene and Genome Evolution in Plants W
 The Plant Cell, Vol. 21: 3718 3731, December 2009, www.plantcell.org ã 2009 American Society of Plant Biologists Special Series on Large-Scale Biology PLAZA: A Comparative Genomics Resource to Study Gene
The Plant Cell, Vol. 21: 3718 3731, December 2009, www.plantcell.org ã 2009 American Society of Plant Biologists Special Series on Large-Scale Biology PLAZA: A Comparative Genomics Resource to Study Gene
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL SUPPLEMENTARY TABLES
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL SUPPLEMENTARY TABLES Supplementary Table 1. Genomes available in Gramene build 38 Supplementary Table 2. Ontology associations in Gramene build 38 Supplementary Table 3. Synteny
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL SUPPLEMENTARY TABLES Supplementary Table 1. Genomes available in Gramene build 38 Supplementary Table 2. Ontology associations in Gramene build 38 Supplementary Table 3. Synteny
Chapter 26: Phylogeny and the Tree of Life Phylogenies Show Evolutionary Relationships
 Chapter 26: Phylogeny and the Tree of Life You Must Know The taxonomic categories and how they indicate relatedness. How systematics is used to develop phylogenetic trees. How to construct a phylogenetic
Chapter 26: Phylogeny and the Tree of Life You Must Know The taxonomic categories and how they indicate relatedness. How systematics is used to develop phylogenetic trees. How to construct a phylogenetic
Revision Based on Chapter 19 Grade 11
 Revision Based on Chapter 19 Grade 11 Biology Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Most fossils are found in rusty water. volcanic rock. sedimentary
Revision Based on Chapter 19 Grade 11 Biology Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Most fossils are found in rusty water. volcanic rock. sedimentary
A greedy, graph-based algorithm for the alignment of multiple homologous gene lists
 A greedy, graph-based algorithm for the alignment of multiple homologous gene lists Jan Fostier, Sebastian Proost, Bart Dhoedt, Yvan Saeys, Piet Demeester, Yves Van de Peer, and Klaas Vandepoele Bioinformatics
A greedy, graph-based algorithm for the alignment of multiple homologous gene lists Jan Fostier, Sebastian Proost, Bart Dhoedt, Yvan Saeys, Piet Demeester, Yves Van de Peer, and Klaas Vandepoele Bioinformatics
P OLYPLOIDY AND ANGIOSPERM DIVERSIFICATION 1
 American Journal of Botany 96(1): 336 348. 2009. P OLYPLOIDY AND ANGIOSPERM DIVERSIFICATION 1 Douglas E. Soltis,2,11 Victor A. Albert, 3 Jim Leebens-Mack,4 Charles D. Bell, 5 Andrew H. Paterson, 4,6 Chunfang
American Journal of Botany 96(1): 336 348. 2009. P OLYPLOIDY AND ANGIOSPERM DIVERSIFICATION 1 Douglas E. Soltis,2,11 Victor A. Albert, 3 Jim Leebens-Mack,4 Charles D. Bell, 5 Andrew H. Paterson, 4,6 Chunfang
South Green Bioinformatics activities at CIRAD
 South Green Bioinformatics activities at CIRAD Data Integration Team of the research unit DAP Manuel Ruiz, CIP, Lima, 23rd january The Joint Research Unit DAP (Développement et Amélioration des Plantes
South Green Bioinformatics activities at CIRAD Data Integration Team of the research unit DAP Manuel Ruiz, CIP, Lima, 23rd january The Joint Research Unit DAP (Développement et Amélioration des Plantes
Charles Darwin ( ) Sailed around the world
 Charles Darwin (1809-1882) Sailed around the world 1831-1836 How did tortoises and birds differ among the islands of the Galapagos? Each island had its own type of tortoises and birds that were clearly
Charles Darwin (1809-1882) Sailed around the world 1831-1836 How did tortoises and birds differ among the islands of the Galapagos? Each island had its own type of tortoises and birds that were clearly
Host_microbe_PPI - R package to analyse intra-species and interspecies protein-protein interactions in the model plant Arabidopsis thaliana
 Host_microbe_PPI - R package to analyse intra-species and interspecies protein-protein interactions in the model plant Arabidopsis thaliana Thomas Nussbaumer 1,2 1 Institute of Network Biology (INET),
Host_microbe_PPI - R package to analyse intra-species and interspecies protein-protein interactions in the model plant Arabidopsis thaliana Thomas Nussbaumer 1,2 1 Institute of Network Biology (INET),
Accepted Article. Received Date : 19-Oct Accepted Date : 25-Jan-2017
 Received Date : 19-Oct-2016 Accepted Date : 25-Jan-2017 Article type : Original Article Phylogenomic analysis of gene co-expression networks reveals the evolution of functional modules Colin Ruprecht 1,
Received Date : 19-Oct-2016 Accepted Date : 25-Jan-2017 Article type : Original Article Phylogenomic analysis of gene co-expression networks reveals the evolution of functional modules Colin Ruprecht 1,
Concerted divergence after gene duplication in Polycomb Repressor. complexes
 Plant Physiology Preview. Published on April 28, 2017, as DOI:10.1104/pp.16.01983 1 Short title: Concerted divergence of duplicated genes 2 3 4 Concerted divergence after gene duplication in Polycomb Repressor
Plant Physiology Preview. Published on April 28, 2017, as DOI:10.1104/pp.16.01983 1 Short title: Concerted divergence of duplicated genes 2 3 4 Concerted divergence after gene duplication in Polycomb Repressor
PLANT VARIATION AND EVOLUTION
 PLANT VARIATION AND EVOLUTION D. BRIGGS Department of Plant Sciences, University of Cambridge S. M. WALTERS Former Director of the University Botanic Garden, Cambridge 3rd EDITION CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY
PLANT VARIATION AND EVOLUTION D. BRIGGS Department of Plant Sciences, University of Cambridge S. M. WALTERS Former Director of the University Botanic Garden, Cambridge 3rd EDITION CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY
Evolution Problem Drill 09: The Tree of Life
 Evolution Problem Drill 09: The Tree of Life Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. The age of the Earth is estimated to be about 4.0 to 4.5 billion years old. All of the following methods may be used to estimate
Evolution Problem Drill 09: The Tree of Life Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. The age of the Earth is estimated to be about 4.0 to 4.5 billion years old. All of the following methods may be used to estimate
The Origin of Species
 The Origin of Species What you need to know The difference between microevolution and macroevolution. The biological concept of species. Prezygotic and postzygotic barriers that maintain reproductive isolation
The Origin of Species What you need to know The difference between microevolution and macroevolution. The biological concept of species. Prezygotic and postzygotic barriers that maintain reproductive isolation
Scientific Names of Common Plants/Trees Scientific Names - Fruits and Vegetables
 OUR OWN HIGH SCHOOL, Al WARQA A, DUBAI BIOLOGY Grade 11 Unit 1 Diversity in the living world Name : Chapter The Living World Class and Section: Topic Binomial Nomenclature Date: s of Common Plants/Trees
OUR OWN HIGH SCHOOL, Al WARQA A, DUBAI BIOLOGY Grade 11 Unit 1 Diversity in the living world Name : Chapter The Living World Class and Section: Topic Binomial Nomenclature Date: s of Common Plants/Trees
Using phylogenetics to estimate species divergence times... Basics and basic issues for Bayesian inference of divergence times (plus some digression)
 Using phylogenetics to estimate species divergence times... More accurately... Basics and basic issues for Bayesian inference of divergence times (plus some digression) "A comparison of the structures
Using phylogenetics to estimate species divergence times... More accurately... Basics and basic issues for Bayesian inference of divergence times (plus some digression) "A comparison of the structures
Neofunctionalization within the Omp85 protein superfamily during
 Neofunctionalization within the Omp protein superfamily during chloroplast evolution Mats Töpel, Qihua Ling and Paul Jarvis, * Department of Plant and Environmental Sciences; Göteborg University; Göteborg,
Neofunctionalization within the Omp protein superfamily during chloroplast evolution Mats Töpel, Qihua Ling and Paul Jarvis, * Department of Plant and Environmental Sciences; Göteborg University; Göteborg,
Bio 1B Lecture Outline (please print and bring along) Fall, 2007
 Bio 1B Lecture Outline (please print and bring along) Fall, 2007 B.D. Mishler, Dept. of Integrative Biology 2-6810, bmishler@berkeley.edu Evolution lecture #5 -- Molecular genetics and molecular evolution
Bio 1B Lecture Outline (please print and bring along) Fall, 2007 B.D. Mishler, Dept. of Integrative Biology 2-6810, bmishler@berkeley.edu Evolution lecture #5 -- Molecular genetics and molecular evolution
Gene order in Rosid phylogeny, inferred from pairwise syntenies among extant genomes
 Gene order in Rosid phylogeny, inferred from pairwise syntenies among extant genomes Chunfang Zheng 1,2 and David Sanko 2 1 Département d informatique et de recherche opérationnelle, Université de Montréal
Gene order in Rosid phylogeny, inferred from pairwise syntenies among extant genomes Chunfang Zheng 1,2 and David Sanko 2 1 Département d informatique et de recherche opérationnelle, Université de Montréal
Phylogeny and systematics. Why are these disciplines important in evolutionary biology and how are they related to each other?
 Phylogeny and systematics Why are these disciplines important in evolutionary biology and how are they related to each other? Phylogeny and systematics Phylogeny: the evolutionary history of a species
Phylogeny and systematics Why are these disciplines important in evolutionary biology and how are they related to each other? Phylogeny and systematics Phylogeny: the evolutionary history of a species
Plant of the Day Isoetes andicola
 Plant of the Day Isoetes andicola Endemic to central and southern Peru Found in scattered populations above 4000 m Restricted to the edges of bogs and lakes Leaves lack stomata and so CO 2 is obtained,
Plant of the Day Isoetes andicola Endemic to central and southern Peru Found in scattered populations above 4000 m Restricted to the edges of bogs and lakes Leaves lack stomata and so CO 2 is obtained,
Changes in Twelve Homoeologous Genomic Regions in Soybean following Three Rounds of Polyploidy W
 The Plant Cell, Vol. 23: 3129 3136, September 2011, www.plantcell.org ã 2011 American Society of Plant Biologists. All rights reserved. RESEARCH ARTICLES Changes in Twelve Homoeologous Genomic Regions
The Plant Cell, Vol. 23: 3129 3136, September 2011, www.plantcell.org ã 2011 American Society of Plant Biologists. All rights reserved. RESEARCH ARTICLES Changes in Twelve Homoeologous Genomic Regions
Supplemental Table 1. Primers used for cloning and PCR amplification in this study
 Supplemental Table 1. Primers used for cloning and PCR amplification in this study Target Gene Primer sequence NATA1 (At2g393) forward GGG GAC AAG TTT GTA CAA AAA AGC AGG CTT CAT GGC GCC TCC AAC CGC AGC
Supplemental Table 1. Primers used for cloning and PCR amplification in this study Target Gene Primer sequence NATA1 (At2g393) forward GGG GAC AAG TTT GTA CAA AAA AGC AGG CTT CAT GGC GCC TCC AAC CGC AGC
Guided Notes: Evolution. is the change in traits through generations over! Occurs in, NOT individual organisms
 Guided Notes: Evolution The Theory of Evolution is the change in traits through generations over! Occurs in, NOT individual organisms How Have Organisms Changed? At the time life emerged, the Earth was
Guided Notes: Evolution The Theory of Evolution is the change in traits through generations over! Occurs in, NOT individual organisms How Have Organisms Changed? At the time life emerged, the Earth was
Slovene Plant Gene Bank (SPGB) and Genetic Resources Programme
 Slovene Plant Gene Bank (SPGB) and Genetic Resources Programme Second Meeting of the ECPGR Working Group on Leafy Vegetables 8 9 October, Ljubljana, Slovenia Vladimir MEGLIČ, Jelka ŠUŠTAR VOZLIČ Slovene
Slovene Plant Gene Bank (SPGB) and Genetic Resources Programme Second Meeting of the ECPGR Working Group on Leafy Vegetables 8 9 October, Ljubljana, Slovenia Vladimir MEGLIČ, Jelka ŠUŠTAR VOZLIČ Slovene
EVOLUTION. Evolution - changes in allele frequency in populations over generations.
 EVOLUTION Evolution - changes in allele frequency in populations over generations. Sources of genetic variation: genetic recombination by sexual reproduction (produces new combinations of genes) mutation
EVOLUTION Evolution - changes in allele frequency in populations over generations. Sources of genetic variation: genetic recombination by sexual reproduction (produces new combinations of genes) mutation
Case Study. Who s the daddy? TEACHER S GUIDE. James Clarkson. Dean Madden [Ed.] Polyploidy in plant evolution. Version 1.1. Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew
![Case Study. Who s the daddy? TEACHER S GUIDE. James Clarkson. Dean Madden [Ed.] Polyploidy in plant evolution. Version 1.1. Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew Case Study. Who s the daddy? TEACHER S GUIDE. James Clarkson. Dean Madden [Ed.] Polyploidy in plant evolution. Version 1.1. Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew](/thumbs/79/79405253.jpg) TEACHER S GUIDE Case Study Who s the daddy? Polyploidy in plant evolution James Clarkson Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew Dean Madden [Ed.] NCBE, University of Reading Version 1.1 Polypoidy in plant evolution
TEACHER S GUIDE Case Study Who s the daddy? Polyploidy in plant evolution James Clarkson Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew Dean Madden [Ed.] NCBE, University of Reading Version 1.1 Polypoidy in plant evolution
FOSSILS. Evidence of change over time
 FOSSILS Evidence of change over time Fossils What is a fossil? Preserved remains or evidence of an ancient organism. What do fossils tell us? Fossils tell us what an organism was like (structure) and what
FOSSILS Evidence of change over time Fossils What is a fossil? Preserved remains or evidence of an ancient organism. What do fossils tell us? Fossils tell us what an organism was like (structure) and what
Fossils Biology 2 Thursday, January 31, 2013
 Fossils Biology 2 Evolution Change in the genetic composition of a group of organisms over time. Causes: Natural Selection Artificial Selection Genetic Engineering Genetic Drift Hybridization Mutation
Fossils Biology 2 Evolution Change in the genetic composition of a group of organisms over time. Causes: Natural Selection Artificial Selection Genetic Engineering Genetic Drift Hybridization Mutation
Agave Genomics in Support
 Agave Genomics in Support of CAM Engineering cambiodesign.org Xiaohan Yang Biosciences Division Oak Ridge National Laboratory C4-CAM Conference August 09, 2013 Acknowledgements Oak Ridge National Laboratory
Agave Genomics in Support of CAM Engineering cambiodesign.org Xiaohan Yang Biosciences Division Oak Ridge National Laboratory C4-CAM Conference August 09, 2013 Acknowledgements Oak Ridge National Laboratory
Chapter 27: Evolutionary Genetics
 Chapter 27: Evolutionary Genetics Student Learning Objectives Upon completion of this chapter you should be able to: 1. Understand what the term species means to biology. 2. Recognize the various patterns
Chapter 27: Evolutionary Genetics Student Learning Objectives Upon completion of this chapter you should be able to: 1. Understand what the term species means to biology. 2. Recognize the various patterns
Topic 2: Plants Ch. 16,28
 Topic 2: Plants Ch. 16,28 Characteristics of Plants p. 316 1. Multicellular eukaryotic organisms 2. Composed of tissues, organs and organ systems. 3. Cell walls made of cellulose. 4. Store energy as starch.
Topic 2: Plants Ch. 16,28 Characteristics of Plants p. 316 1. Multicellular eukaryotic organisms 2. Composed of tissues, organs and organ systems. 3. Cell walls made of cellulose. 4. Store energy as starch.
673 Comparative Genomics of Angiosperm MADS Box Genes Yale University, New Haven, CT. 674 The evolution of plant architecture in Brassicaceae
 673 Comparative Genomics of Angiosperm MADS Box Genes Vivian F. Irish Yale University, New Haven, CT. MADS box genes encode key transcriptional regulators that have been implicated in the control of various
673 Comparative Genomics of Angiosperm MADS Box Genes Vivian F. Irish Yale University, New Haven, CT. MADS box genes encode key transcriptional regulators that have been implicated in the control of various
Gene and genome duplications: the impact of dosage-sensitivity on the fate of nuclear genes
 Chromosome Research (2009) 17:699 717 DOI 10.1007/s10577-009-9055-9 Gene and genome duplications: the impact of dosage-sensitivity on the fate of nuclear genes Patrick P. Edger & J. Chris Pires # Springer
Chromosome Research (2009) 17:699 717 DOI 10.1007/s10577-009-9055-9 Gene and genome duplications: the impact of dosage-sensitivity on the fate of nuclear genes Patrick P. Edger & J. Chris Pires # Springer
Genome Evolution Greg Lang, Department of Biological Sciences
 Genome Evolution Greg Lang, Department of Biological Sciences BioS 010: Bioscience in the 21st Century Mechanisms of genome evolution Gene Duplication Genome Rearrangement Whole Genome Duplication Gene
Genome Evolution Greg Lang, Department of Biological Sciences BioS 010: Bioscience in the 21st Century Mechanisms of genome evolution Gene Duplication Genome Rearrangement Whole Genome Duplication Gene
Section 17 1 The Fossil Record (pages )
 Name Class Date Chapter 17 The History of Life Section 17 1 The Fossil Record (pages 417 422) This section explains how fossils form and how they can be interpreted. It also describes the geologic time
Name Class Date Chapter 17 The History of Life Section 17 1 The Fossil Record (pages 417 422) This section explains how fossils form and how they can be interpreted. It also describes the geologic time
8/23/2014. Phylogeny and the Tree of Life
 Phylogeny and the Tree of Life Chapter 26 Objectives Explain the following characteristics of the Linnaean system of classification: a. binomial nomenclature b. hierarchical classification List the major
Phylogeny and the Tree of Life Chapter 26 Objectives Explain the following characteristics of the Linnaean system of classification: a. binomial nomenclature b. hierarchical classification List the major
Unsaved Test, Version: 1 1
 Name: Key Concepts Select the term or terms that best complete the statement. A. algae and bacteria B. Cretaceous Extinction C. fossil record D. mass extinction E. multicellular organism F. Permian Extinction
Name: Key Concepts Select the term or terms that best complete the statement. A. algae and bacteria B. Cretaceous Extinction C. fossil record D. mass extinction E. multicellular organism F. Permian Extinction
Ch. 16 Evolution of Populations
 Ch. 16 Evolution of Populations Gene pool the combined genetic information of all the members of a population. There are typically 2 or more alleles for a certain trait. (dominant or recessive) Allele
Ch. 16 Evolution of Populations Gene pool the combined genetic information of all the members of a population. There are typically 2 or more alleles for a certain trait. (dominant or recessive) Allele
Chapter 22: Descent with Modification 1. BRIEFLY summarize the main points that Darwin made in The Origin of Species.
 AP Biology Chapter Packet 7- Evolution Name Chapter 22: Descent with Modification 1. BRIEFLY summarize the main points that Darwin made in The Origin of Species. 2. Define the following terms: a. Natural
AP Biology Chapter Packet 7- Evolution Name Chapter 22: Descent with Modification 1. BRIEFLY summarize the main points that Darwin made in The Origin of Species. 2. Define the following terms: a. Natural
Natural Selection. Factors for Natural Selection: 1. Variation 2. Heritability 3. Overproduction (Overpopulation) 4. Reproductive Advantage
 Natural Selection Variation: Heritability: Overproduction: Reproductive Advantage Driven by Environment Factors for Natural Selection: 1. Variation 2. Heritability 3. Overproduction (Overpopulation) 4.
Natural Selection Variation: Heritability: Overproduction: Reproductive Advantage Driven by Environment Factors for Natural Selection: 1. Variation 2. Heritability 3. Overproduction (Overpopulation) 4.
MACROEVOLUTION Student Packet SUMMARY EVOLUTION IS A CHANGE IN THE GENETIC MAKEUP OF A POPULATION OVER TIME Macroevolution refers to large-scale
 MACROEVOLUTION Student Packet SUMMARY EVOLUTION IS A CHANGE IN THE GENETIC MAKEUP OF A POPULATION OVER TIME Macroevolution refers to large-scale evolutionary changes such as speciation events, origin of
MACROEVOLUTION Student Packet SUMMARY EVOLUTION IS A CHANGE IN THE GENETIC MAKEUP OF A POPULATION OVER TIME Macroevolution refers to large-scale evolutionary changes such as speciation events, origin of
Integrative Biology 200A "PRINCIPLES OF PHYLOGENETICS" Spring 2012 University of California, Berkeley
 Integrative Biology 200A "PRINCIPLES OF PHYLOGENETICS" Spring 2012 University of California, Berkeley B.D. Mishler Feb. 7, 2012. Morphological data IV -- ontogeny & structure of plants The last frontier
Integrative Biology 200A "PRINCIPLES OF PHYLOGENETICS" Spring 2012 University of California, Berkeley B.D. Mishler Feb. 7, 2012. Morphological data IV -- ontogeny & structure of plants The last frontier
UoN, CAS, DBSC BIOL102 lecture notes by: Dr. Mustafa A. Mansi. The Phylogenetic Systematics (Phylogeny and Systematics)
 - Phylogeny? - Systematics? The Phylogenetic Systematics (Phylogeny and Systematics) - Phylogenetic systematics? Connection between phylogeny and classification. - Phylogenetic systematics informs the
- Phylogeny? - Systematics? The Phylogenetic Systematics (Phylogeny and Systematics) - Phylogenetic systematics? Connection between phylogeny and classification. - Phylogenetic systematics informs the
Chapter 14 The Origin of Species
 Chapter 14 The Origin of Species PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Lecture by Joan
Chapter 14 The Origin of Species PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Lecture by Joan
Cryopreservation of syn seeds
 COST Action FA1104 Sustainable production of high-quality cherries for the European market Long Term Preservation of Woody Species by Cryo Techniques, March 2015, Firenze Cryopreservation of syn seeds
COST Action FA1104 Sustainable production of high-quality cherries for the European market Long Term Preservation of Woody Species by Cryo Techniques, March 2015, Firenze Cryopreservation of syn seeds
Evolution as Fact and Theory. What is a Scientific Theory? Examples of Scientific Theories:
 Evolution as Fact and Theory What is a Scientific Theory? A well-substantiated explanation of some aspect of the natural world; an organized system of accepted knowledge that applies in a variety of circumstances
Evolution as Fact and Theory What is a Scientific Theory? A well-substantiated explanation of some aspect of the natural world; an organized system of accepted knowledge that applies in a variety of circumstances
Evolution as Fact and Theory
 Evolution as Fact and Theory What is a Scientific Theory? A well-substantiated explanation of some aspect of the natural world; an organized system of accepted knowledge that applies in a variety of circumstances
Evolution as Fact and Theory What is a Scientific Theory? A well-substantiated explanation of some aspect of the natural world; an organized system of accepted knowledge that applies in a variety of circumstances
Unit 7: Evolution Guided Reading Questions (80 pts total)
 AP Biology Biology, Campbell and Reece, 10th Edition Adapted from chapter reading guides originally created by Lynn Miriello Name: Unit 7: Evolution Guided Reading Questions (80 pts total) Chapter 22 Descent
AP Biology Biology, Campbell and Reece, 10th Edition Adapted from chapter reading guides originally created by Lynn Miriello Name: Unit 7: Evolution Guided Reading Questions (80 pts total) Chapter 22 Descent
Unit 9: Evolution Guided Reading Questions (80 pts total)
 Name: AP Biology Biology, Campbell and Reece, 7th Edition Adapted from chapter reading guides originally created by Lynn Miriello Unit 9: Evolution Guided Reading Questions (80 pts total) Chapter 22 Descent
Name: AP Biology Biology, Campbell and Reece, 7th Edition Adapted from chapter reading guides originally created by Lynn Miriello Unit 9: Evolution Guided Reading Questions (80 pts total) Chapter 22 Descent
Biology. Slide 1 of 25. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 Biology 1 of 25 Macroevolution refers to large-scale evolutionary patterns and processes that occur over long periods of time. 2 of 25 Macroevolution Six important topics in macroevolution are: extinction
Biology 1 of 25 Macroevolution refers to large-scale evolutionary patterns and processes that occur over long periods of time. 2 of 25 Macroevolution Six important topics in macroevolution are: extinction
Evolutionary model for the statistical divergence of paralogous and orthologous gene pairs generated by whole genome duplication and speciation
 Zhang et al. RESEARCH Evolutionary model for the statistical divergence of paralogous and orthologous gene pairs generated by whole genome duplication and speciation Yue Zhang, Chunfang Zheng and David
Zhang et al. RESEARCH Evolutionary model for the statistical divergence of paralogous and orthologous gene pairs generated by whole genome duplication and speciation Yue Zhang, Chunfang Zheng and David
Genome-Wide Identification of NBS-Encoding Resistance Genes in Sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.)
 Article Genome-Wide Identification of NBS-Encoding Resistance Genes in Sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.) Surendra Neupane, Ethan J. Andersen, Achal Neupane and Madhav P. Nepal * Department of Biology and
Article Genome-Wide Identification of NBS-Encoding Resistance Genes in Sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.) Surendra Neupane, Ethan J. Andersen, Achal Neupane and Madhav P. Nepal * Department of Biology and
Identification and Characterization of Shared Duplications between Rice and Wheat Provide New Insight into Grass Genome Evolution W
 The Plant Cell, Vol. 20: 11 24, January 2008, www.plantcell.org ª 2008 American Society of Plant Biologists RESEARCH ARTICLES Identification and Characterization of Shared Duplications between Rice and
The Plant Cell, Vol. 20: 11 24, January 2008, www.plantcell.org ª 2008 American Society of Plant Biologists RESEARCH ARTICLES Identification and Characterization of Shared Duplications between Rice and
Supplemental Data. Perea-Resa et al. Plant Cell. (2012) /tpc
 Supplemental Data. Perea-Resa et al. Plant Cell. (22)..5/tpc.2.3697 Sm Sm2 Supplemental Figure. Sequence alignment of Arabidopsis LSM proteins. Alignment of the eleven Arabidopsis LSM proteins. Sm and
Supplemental Data. Perea-Resa et al. Plant Cell. (22)..5/tpc.2.3697 Sm Sm2 Supplemental Figure. Sequence alignment of Arabidopsis LSM proteins. Alignment of the eleven Arabidopsis LSM proteins. Sm and
Ancient polyploidization predating divergence of the cereals, and its consequences for comparative genomics
 Ancient polyploidization predating divergence of the cereals, and its consequences for comparative genomics A. H. Paterson*, J. E. Bowers, and B. A. Chapman Plant Genome Mapping Laboratory, University
Ancient polyploidization predating divergence of the cereals, and its consequences for comparative genomics A. H. Paterson*, J. E. Bowers, and B. A. Chapman Plant Genome Mapping Laboratory, University
Origins of Life and Extinction
 Origins of Life and Extinction What is evolution? What is evolution? The change in the genetic makeup of a population over time Evolution accounts for the diversity of life on Earth Natural selection is
Origins of Life and Extinction What is evolution? What is evolution? The change in the genetic makeup of a population over time Evolution accounts for the diversity of life on Earth Natural selection is
Quantitative Genetics & Evolutionary Genetics
 Quantitative Genetics & Evolutionary Genetics (CHAPTER 24 & 26- Brooker Text) May 14, 2007 BIO 184 Dr. Tom Peavy Quantitative genetics (the study of traits that can be described numerically) is important
Quantitative Genetics & Evolutionary Genetics (CHAPTER 24 & 26- Brooker Text) May 14, 2007 BIO 184 Dr. Tom Peavy Quantitative genetics (the study of traits that can be described numerically) is important
