Big Questions. Is polyploidy an evolutionary dead-end? If so, why are all plants the products of multiple polyploidization events?
|
|
|
- Raymond Poole
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Plant of the Day Cyperus esculentus - Cyperaceae Chufa (tigernut) 8,000 kg/ha, 720 kcal/sq m per month Top Crop for kcal productivity! One of the world s worst weeds
2 Big Questions Is polyploidy an evolutionary dead-end? If so, why are all plants the products of multiple polyploidization events? How do polyploid genomes diploidize (i.e., what are the rules)?
3 Paleopolyploidy Ancient whole genome duplication No different from neopolyploidy except that it happened a long time ago Track the historical contribution of polyploid speciation to evolution
4 Polyploidy = Evolutionary noise (1970) W. H. Wagner, Jr. polyploidy has contributed little to progressive evolution (1971) G. L. Stebbins
5 Diploidization
6 Diploidization Obscures evidence of paleopolyploidy Return to a diploid genetic system Restoration of full bivalent pairing Gene and chromosome loss Chromosomal rearrangements Proceeds at different rates in different lineages
7 Methods for Identifying Paleopolyploidy Fossils Synteny relationships of duplicated genes conserved gene order Age estimates of duplicate genes
8 Cell Size Increase Consequence of genome size increase 2 X increase in cell volume 2n 1.58 X increase in cell surface area 4n
9 Fossil Estimates Extant Platanus Miocene Platanus
10 Fossil Estimates Extant Platanus Miocene Platanus n > % angiosperms
11 Single copy Grape Poplar Grape Poplar Species tree Gene tree
12 Paleopolyploidy Grape Poplar Grape Poplar Poplar Species tree Gene tree
13 Paleopolyploidy Grape Poplar Grape Poplar Grape Poplar Species tree Gene tree
14 Paleopolyploidy Grape Poplar Grape Poplar Grape Poplar Species tree Gene tree How do we tell gene duplication from paleopolyploidy?
15 Synteny Analyses Grape Poplar What is the history of paleopolyploidy?
16 Synteny Analyses Grape Arabidopsis What is the history of paleopolyploidy?
17 Synteny Analyses Whole Genome Sequences
18 Duplicate Gene Age Distributions Find duplicate genes in the genome What is the sequence divergence between duplicates? This is a measure of when the duplication event occurred
19 Duplicate Gene Age Distributions No Paleopolyploidy % of Duplicate Pairs Gene duplicates lost over time Ks (~ Time)
20 Duplicate Gene Age Distributions Carthamus tinctorius % of Duplicate Pairs Ks (~ Time)
21 Previously Known Genome Duplications Barker et al., in prep
22 Newly Recognized Genome Duplications Barker et al., in prep
23 Newly Recognized Genome Duplications Li et al., 2015 Fig. 2. Phylogenetic placement of WGDs in seed plant and gymnosperm history. Ovals correspond to inferred locations of WGD events; black, seed plant WGD; gray, angiosperm WGD; purple, Welwitschia WGD; green, Pinaceae WGD; red, cupressophyte WGD. All botanical illustrations are in the public domain. Amborella image adopted from Amborella Genome Project, 2013 (46). Other botanical illustrations are in the public domain (59 75).
24 Newly Recognized Genome Duplications Infer 61 Independent Paleopolyploidizations 36 are newly observed All seed plants are ancient polyploids! Barker et al., in prep
25 Significant increases in diversification rates in flowering plants Half are associated with paleopolyploidy (p = 0.005)
26 What about neo-polyploidy? Application of BISSE: binary-state speciation and extinction (likelihood method developed by Maddison et al. 2007) Polyploidy: ê speciation, é extinction (I. Mayrose et al. 2011, Science) Frequency number of cases Extinction number of cases Speciation higher rate in diploids higher rate in diploids
27 Resolution Polyploidy is most often an evolutionary dead end, but the expanded genomic potential of those polyploids that do persist drives longer term evolutionary success.
28 Unanswered questions Do auto- and allopolyploids differ in their evolutionary success? What factors control the fate of duplicate genes? How long must a polyploid lineage persist before it transitions from a trajectory that favors extinction to one that favors diversification? What evolutionary genetic changes/processes underlie this transition?
Whole-genome duplications and paleopolyploidy
 Whole-genome duplications and paleopolyploidy Whole-genome duplications in protozoa Aury et al. (2006) analyzed the unicellular eukaryote Paramecium tetraurelia most of 40,000 genes arose through at least
Whole-genome duplications and paleopolyploidy Whole-genome duplications in protozoa Aury et al. (2006) analyzed the unicellular eukaryote Paramecium tetraurelia most of 40,000 genes arose through at least
Stage 1: Karyotype Stage 2: Gene content & order Step 3
 Supplementary Figure Method used for ancestral genome reconstruction. MRCA (Most Recent Common Ancestor), AMK (Ancestral Monocot Karyotype), AEK (Ancestral Eudicot Karyotype), AGK (Ancestral Grass Karyotype)
Supplementary Figure Method used for ancestral genome reconstruction. MRCA (Most Recent Common Ancestor), AMK (Ancestral Monocot Karyotype), AEK (Ancestral Eudicot Karyotype), AGK (Ancestral Grass Karyotype)
Case Study. Who s the daddy? TEACHER S GUIDE. James Clarkson. Dean Madden [Ed.] Polyploidy in plant evolution. Version 1.1. Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew
![Case Study. Who s the daddy? TEACHER S GUIDE. James Clarkson. Dean Madden [Ed.] Polyploidy in plant evolution. Version 1.1. Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew Case Study. Who s the daddy? TEACHER S GUIDE. James Clarkson. Dean Madden [Ed.] Polyploidy in plant evolution. Version 1.1. Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew](/thumbs/79/79405253.jpg) TEACHER S GUIDE Case Study Who s the daddy? Polyploidy in plant evolution James Clarkson Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew Dean Madden [Ed.] NCBE, University of Reading Version 1.1 Polypoidy in plant evolution
TEACHER S GUIDE Case Study Who s the daddy? Polyploidy in plant evolution James Clarkson Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew Dean Madden [Ed.] NCBE, University of Reading Version 1.1 Polypoidy in plant evolution
PLANT VARIATION AND EVOLUTION
 PLANT VARIATION AND EVOLUTION D. BRIGGS Department of Plant Sciences, University of Cambridge S. M. WALTERS Former Director of the University Botanic Garden, Cambridge 3rd EDITION CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY
PLANT VARIATION AND EVOLUTION D. BRIGGS Department of Plant Sciences, University of Cambridge S. M. WALTERS Former Director of the University Botanic Garden, Cambridge 3rd EDITION CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY
Unfortunately, there are many definitions Biological Species: species defined by Morphological Species (Morphospecies): characterizes species by
 1 2 3 4 5 6 Lecture 3: Chapter 27 -- Speciation Macroevolution Macroevolution and Speciation Microevolution Changes in the gene pool over successive generations; deals with alleles and genes Macroevolution
1 2 3 4 5 6 Lecture 3: Chapter 27 -- Speciation Macroevolution Macroevolution and Speciation Microevolution Changes in the gene pool over successive generations; deals with alleles and genes Macroevolution
How to detect paleoploidy?
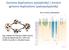 Genome duplications (polyploidy) / ancient genome duplications (paleopolyploidy) How to detect paleoploidy? e.g. a diploid cell undergoes failed meiosis, producing diploid gametes, which selffertilize
Genome duplications (polyploidy) / ancient genome duplications (paleopolyploidy) How to detect paleoploidy? e.g. a diploid cell undergoes failed meiosis, producing diploid gametes, which selffertilize
Speciation. Mechanisms of Speciation. Title goes here. Some Key Tenets of the Modern Synthesis
 Carol Eunmi Lee 11/9/17 Speciation Increasing genetic distance Fitness Mating between different species Mating between relatives Inbreeding Depression Hybrid Vigor Outbreeding Depression 2 Darwin s Origin
Carol Eunmi Lee 11/9/17 Speciation Increasing genetic distance Fitness Mating between different species Mating between relatives Inbreeding Depression Hybrid Vigor Outbreeding Depression 2 Darwin s Origin
Gene-Tree Reconciliation with MUL-Trees to Resolve Polyploidy Events
 Syst. Biol. 66(6):1007 1018, 2017 The Author(s) 2017. Published by Oxford University Press, on behalf of the Society of Systematic Biologists. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com
Syst. Biol. 66(6):1007 1018, 2017 The Author(s) 2017. Published by Oxford University Press, on behalf of the Society of Systematic Biologists. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com
8/23/2014. Phylogeny and the Tree of Life
 Phylogeny and the Tree of Life Chapter 26 Objectives Explain the following characteristics of the Linnaean system of classification: a. binomial nomenclature b. hierarchical classification List the major
Phylogeny and the Tree of Life Chapter 26 Objectives Explain the following characteristics of the Linnaean system of classification: a. binomial nomenclature b. hierarchical classification List the major
Chapter 26: Phylogeny and the Tree of Life Phylogenies Show Evolutionary Relationships
 Chapter 26: Phylogeny and the Tree of Life You Must Know The taxonomic categories and how they indicate relatedness. How systematics is used to develop phylogenetic trees. How to construct a phylogenetic
Chapter 26: Phylogeny and the Tree of Life You Must Know The taxonomic categories and how they indicate relatedness. How systematics is used to develop phylogenetic trees. How to construct a phylogenetic
The Origin of Species
 The Origin of Species Introduction A species can be defined as a group of organisms whose members can breed and produce fertile offspring, but who do not produce fertile offspring with members of other
The Origin of Species Introduction A species can be defined as a group of organisms whose members can breed and produce fertile offspring, but who do not produce fertile offspring with members of other
Computational analyses of ancient polyploidy
 Computational analyses of ancient polyploidy Kevin P. Byrne 1 and Guillaume Blanc 2* 1 Department of Genetics, Smurfit Institute, University of Dublin, Trinity College, Dublin 2, Ireland. 2 Laboratoire
Computational analyses of ancient polyploidy Kevin P. Byrne 1 and Guillaume Blanc 2* 1 Department of Genetics, Smurfit Institute, University of Dublin, Trinity College, Dublin 2, Ireland. 2 Laboratoire
Phylogenetic relationship among S. castellii, S. cerevisiae and C. glabrata.
 Supplementary Note S2 Phylogenetic relationship among S. castellii, S. cerevisiae and C. glabrata. Phylogenetic trees reconstructed by a variety of methods from either single-copy orthologous loci (Class
Supplementary Note S2 Phylogenetic relationship among S. castellii, S. cerevisiae and C. glabrata. Phylogenetic trees reconstructed by a variety of methods from either single-copy orthologous loci (Class
Speciation Plant Sciences, 2001Updated: June 1, 2012 Gale Document Number: GALE CV
 is the process of evolution by which new species arise. The key factor causing speciation is the appearance of genetic differences between two populations, which result from evolution by natural selection.
is the process of evolution by which new species arise. The key factor causing speciation is the appearance of genetic differences between two populations, which result from evolution by natural selection.
Macroevolution: Part III Sympatric Speciation
 Macroevolution: Part III Sympatric Speciation Types of Speciation: A Review Allopatric speciation is the evolution of geographically isolated populations into distinct species. There is no gene flow, which
Macroevolution: Part III Sympatric Speciation Types of Speciation: A Review Allopatric speciation is the evolution of geographically isolated populations into distinct species. There is no gene flow, which
- mutations can occur at different levels from single nucleotide positions in DNA to entire genomes.
 February 8, 2005 Bio 107/207 Winter 2005 Lecture 11 Mutation and transposable elements - the term mutation has an interesting history. - as far back as the 17th century, it was used to describe any drastic
February 8, 2005 Bio 107/207 Winter 2005 Lecture 11 Mutation and transposable elements - the term mutation has an interesting history. - as far back as the 17th century, it was used to describe any drastic
(Paleo)Polyploidy When Things Get Bigger
 (Paleo)Polyploidy When Things Get Bigger Hegarty and Hiscock 2008, Current Biology 18 Whole-genome duplications AUTOPOLYPLOIDY ALLOPOLYPLOIDY Examples of allopolyploid speciation Hegarty and Hiscock 2008,
(Paleo)Polyploidy When Things Get Bigger Hegarty and Hiscock 2008, Current Biology 18 Whole-genome duplications AUTOPOLYPLOIDY ALLOPOLYPLOIDY Examples of allopolyploid speciation Hegarty and Hiscock 2008,
Evolution by duplication: paleopolyploidy events in plants reconstructed by deciphering the evolutionary history of VOZ transcription factors
 Gao et al. BMC Plant Biology (2018) 18:256 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-018-1437-8 RESEARCH ARTICLE Evolution by duplication: paleopolyploidy events in plants reconstructed by deciphering the evolutionary
Gao et al. BMC Plant Biology (2018) 18:256 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-018-1437-8 RESEARCH ARTICLE Evolution by duplication: paleopolyploidy events in plants reconstructed by deciphering the evolutionary
Using phylogenetics to estimate species divergence times... Basics and basic issues for Bayesian inference of divergence times (plus some digression)
 Using phylogenetics to estimate species divergence times... More accurately... Basics and basic issues for Bayesian inference of divergence times (plus some digression) "A comparison of the structures
Using phylogenetics to estimate species divergence times... More accurately... Basics and basic issues for Bayesian inference of divergence times (plus some digression) "A comparison of the structures
Evolutionary model for the statistical divergence of paralogous and orthologous gene pairs generated by whole genome duplication and speciation
 Zhang et al. RESEARCH Evolutionary model for the statistical divergence of paralogous and orthologous gene pairs generated by whole genome duplication and speciation Yue Zhang, Chunfang Zheng and David
Zhang et al. RESEARCH Evolutionary model for the statistical divergence of paralogous and orthologous gene pairs generated by whole genome duplication and speciation Yue Zhang, Chunfang Zheng and David
Molecular evolution - Part 1. Pawan Dhar BII
 Molecular evolution - Part 1 Pawan Dhar BII Theodosius Dobzhansky Nothing in biology makes sense except in the light of evolution Age of life on earth: 3.85 billion years Formation of planet: 4.5 billion
Molecular evolution - Part 1 Pawan Dhar BII Theodosius Dobzhansky Nothing in biology makes sense except in the light of evolution Age of life on earth: 3.85 billion years Formation of planet: 4.5 billion
Comparative Genomics II
 Comparative Genomics II Advances in Bioinformatics and Genomics GEN 240B Jason Stajich May 19 Comparative Genomics II Slide 1/31 Outline Introduction Gene Families Pairwise Methods Phylogenetic Methods
Comparative Genomics II Advances in Bioinformatics and Genomics GEN 240B Jason Stajich May 19 Comparative Genomics II Slide 1/31 Outline Introduction Gene Families Pairwise Methods Phylogenetic Methods
Probabilistic Models of Chromosome Number Evolution and the Inference of Polyploidy
 Syst. Biol. 59(2):132 144, 2010 c The Author(s) 2009. Published by Oxford University Press, on behalf of the Society of Systematic Biologists. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oxfordjournals.org
Syst. Biol. 59(2):132 144, 2010 c The Author(s) 2009. Published by Oxford University Press, on behalf of the Society of Systematic Biologists. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oxfordjournals.org
Speciation. Mechanisms of Speciation. Title goes here. Some Key Tenets of the Modern Synthesis
 Carol Eunmi Lee 11/10/16 Speciation Increasing genetic distance Fitness Mating between different species Mating between relatives Inbreeding Depression Hybrid Vigor Outbreeding Depression 2 Darwin s Origin
Carol Eunmi Lee 11/10/16 Speciation Increasing genetic distance Fitness Mating between different species Mating between relatives Inbreeding Depression Hybrid Vigor Outbreeding Depression 2 Darwin s Origin
Evolutionary trends and mechanisms of chromosome number variation
 Evolutionary trends and mechanisms of chromosome number variation Chromosome number variation Chromosome numbers of plants vary enormously over a 360-fold range. n = 2 in five angiosperm species n = 630
Evolutionary trends and mechanisms of chromosome number variation Chromosome number variation Chromosome numbers of plants vary enormously over a 360-fold range. n = 2 in five angiosperm species n = 630
Lecture 14 Chapter 11 Biology 5865 Conservation Biology. Problems of Small Populations Population Viability Analysis
 Lecture 14 Chapter 11 Biology 5865 Conservation Biology Problems of Small Populations Population Viability Analysis Minimum Viable Population (MVP) Schaffer (1981) MVP- A minimum viable population for
Lecture 14 Chapter 11 Biology 5865 Conservation Biology Problems of Small Populations Population Viability Analysis Minimum Viable Population (MVP) Schaffer (1981) MVP- A minimum viable population for
Evaluate evidence provided by data from many scientific disciplines to support biological evolution. [LO 1.9, SP 5.3]
![Evaluate evidence provided by data from many scientific disciplines to support biological evolution. [LO 1.9, SP 5.3] Evaluate evidence provided by data from many scientific disciplines to support biological evolution. [LO 1.9, SP 5.3]](/thumbs/75/72965665.jpg) Learning Objectives Evaluate evidence provided by data from many scientific disciplines to support biological evolution. [LO 1.9, SP 5.3] Refine evidence based on data from many scientific disciplines
Learning Objectives Evaluate evidence provided by data from many scientific disciplines to support biological evolution. [LO 1.9, SP 5.3] Refine evidence based on data from many scientific disciplines
Lecture 7 Mutation and genetic variation
 Lecture 7 Mutation and genetic variation Thymidine dimer Natural selection at a single locus 2. Purifying selection a form of selection acting to eliminate harmful (deleterious) alleles from natural populations.
Lecture 7 Mutation and genetic variation Thymidine dimer Natural selection at a single locus 2. Purifying selection a form of selection acting to eliminate harmful (deleterious) alleles from natural populations.
EVOLUTION. Evolution - changes in allele frequency in populations over generations.
 EVOLUTION Evolution - changes in allele frequency in populations over generations. Sources of genetic variation: genetic recombination by sexual reproduction (produces new combinations of genes) mutation
EVOLUTION Evolution - changes in allele frequency in populations over generations. Sources of genetic variation: genetic recombination by sexual reproduction (produces new combinations of genes) mutation
C.DARWIN ( )
 C.DARWIN (1809-1882) LAMARCK Each evolutionary lineage has evolved, transforming itself, from a ancestor appeared by spontaneous generation DARWIN All organisms are historically interconnected. Their relationships
C.DARWIN (1809-1882) LAMARCK Each evolutionary lineage has evolved, transforming itself, from a ancestor appeared by spontaneous generation DARWIN All organisms are historically interconnected. Their relationships
Chapter 5. Evolution of Biodiversity
 Chapter 5. Evolution of Biodiversity I. Earth s tremendous diversity A. life comes in many forms B. Recall 1. we can think of biodiversity in three ways a) genetic diversity b) species diversity c) ecosystem
Chapter 5. Evolution of Biodiversity I. Earth s tremendous diversity A. life comes in many forms B. Recall 1. we can think of biodiversity in three ways a) genetic diversity b) species diversity c) ecosystem
Comparative genomics of gene families in relation with metabolic pathways for gene candidates highlighting
 Comparative genomics of gene families in relation with metabolic pathways for gene candidates highlighting Delphine Larivière & David Couvin Under the supervision of Dominique This, Jean-François Dufayard
Comparative genomics of gene families in relation with metabolic pathways for gene candidates highlighting Delphine Larivière & David Couvin Under the supervision of Dominique This, Jean-François Dufayard
Taming the Beast Workshop
 Workshop and Chi Zhang June 28, 2016 1 / 19 Species tree Species tree the phylogeny representing the relationships among a group of species Figure adapted from [Rogers and Gibbs, 2014] Gene tree the phylogeny
Workshop and Chi Zhang June 28, 2016 1 / 19 Species tree Species tree the phylogeny representing the relationships among a group of species Figure adapted from [Rogers and Gibbs, 2014] Gene tree the phylogeny
What is Evolution Systematics often divided into two areas: phylogenetics or pattern and biosystematics or process
 Speciation What is Evolution What is Evolution Systematics often divided into two areas: phylogenetics or pattern and biosystematics or process tree reticulation Genetic Variation within Species Evolution
Speciation What is Evolution What is Evolution Systematics often divided into two areas: phylogenetics or pattern and biosystematics or process tree reticulation Genetic Variation within Species Evolution
Warm-Up- Review Natural Selection and Reproduction for quiz today!!!! Notes on Evidence of Evolution Work on Vocabulary and Lab
 Date: Agenda Warm-Up- Review Natural Selection and Reproduction for quiz today!!!! Notes on Evidence of Evolution Work on Vocabulary and Lab Ask questions based on 5.1 and 5.2 Quiz on 5.1 and 5.2 How
Date: Agenda Warm-Up- Review Natural Selection and Reproduction for quiz today!!!! Notes on Evidence of Evolution Work on Vocabulary and Lab Ask questions based on 5.1 and 5.2 Quiz on 5.1 and 5.2 How
Processes of Evolution
 15 Processes of Evolution Forces of Evolution Concept 15.4 Selection Can Be Stabilizing, Directional, or Disruptive Natural selection can act on quantitative traits in three ways: Stabilizing selection
15 Processes of Evolution Forces of Evolution Concept 15.4 Selection Can Be Stabilizing, Directional, or Disruptive Natural selection can act on quantitative traits in three ways: Stabilizing selection
Plant evolution and speciation BY2204 EVOLUTION
 Plant evolution and speciation BY2204 EVOLUTION Trevor Hodkinson Plant Sciences Moderatorship Some evol. processes shared with other organisms (natural selection; allopatric speciation). Some more common
Plant evolution and speciation BY2204 EVOLUTION Trevor Hodkinson Plant Sciences Moderatorship Some evol. processes shared with other organisms (natural selection; allopatric speciation). Some more common
NOTES CH 24: The Origin of Species
 NOTES CH 24: The Origin of Species Species Hummingbirds of Costa Rica SPECIES: a group of individuals that mate with one another and produce fertile offspring; typically members of a species appear similar
NOTES CH 24: The Origin of Species Species Hummingbirds of Costa Rica SPECIES: a group of individuals that mate with one another and produce fertile offspring; typically members of a species appear similar
SPECIATION. REPRODUCTIVE BARRIERS PREZYGOTIC: Barriers that prevent fertilization. Habitat isolation Populations can t get together
 SPECIATION Origin of new species=speciation -Process by which one species splits into two or more species, accounts for both the unity and diversity of life SPECIES BIOLOGICAL CONCEPT Population or groups
SPECIATION Origin of new species=speciation -Process by which one species splits into two or more species, accounts for both the unity and diversity of life SPECIES BIOLOGICAL CONCEPT Population or groups
Thursday, March 21, 13. Evolution
 Evolution What is Evolution? Evolution involves inheritable changes in a population of organisms through time Fundamental to biology and paleontology Paleontology is the study of life history as revealed
Evolution What is Evolution? Evolution involves inheritable changes in a population of organisms through time Fundamental to biology and paleontology Paleontology is the study of life history as revealed
5/31/17. Week 10; Monday MEMORIAL DAY NO CLASS. Page 88
 Week 10; Monday MEMORIAL DAY NO CLASS Page 88 Week 10; Wednesday Announcements: Family ID final in lab Today Final exam next Tuesday at 8:30 am here Lecture: Species concepts & Speciation. What are species?
Week 10; Monday MEMORIAL DAY NO CLASS Page 88 Week 10; Wednesday Announcements: Family ID final in lab Today Final exam next Tuesday at 8:30 am here Lecture: Species concepts & Speciation. What are species?
The Origin of Species
 The Origin of Species What you need to know The difference between microevolution and macroevolution. The biological concept of species. Prezygotic and postzygotic barriers that maintain reproductive isolation
The Origin of Species What you need to know The difference between microevolution and macroevolution. The biological concept of species. Prezygotic and postzygotic barriers that maintain reproductive isolation
Examining the Fossil Record
 Examining the Fossil Record Objectives: analyze characteristics of fossils compare placement of fossils and determine relative ages develop a model evolutionary tree based on the morphology and age of
Examining the Fossil Record Objectives: analyze characteristics of fossils compare placement of fossils and determine relative ages develop a model evolutionary tree based on the morphology and age of
Gene Pool Genetic Drift Geographic Isolation Fitness Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium Natural Selection
 CONCEPT 1 EVOLUTION 1. Natural Selection a. Major mechanism of change over time Darwin s theory of evolution b. There is variation among phenotypes genetic mutations play a role in increasing variation
CONCEPT 1 EVOLUTION 1. Natural Selection a. Major mechanism of change over time Darwin s theory of evolution b. There is variation among phenotypes genetic mutations play a role in increasing variation
Chapter 5 Evolution of Biodiversity. Sunday, October 1, 17
 Chapter 5 Evolution of Biodiversity CHAPTER INTRO: The Dung of the Devil Read and Answer Questions Provided Module 14 The Biodiversity of Earth After reading this module you should be able to understand
Chapter 5 Evolution of Biodiversity CHAPTER INTRO: The Dung of the Devil Read and Answer Questions Provided Module 14 The Biodiversity of Earth After reading this module you should be able to understand
Speciation. What is Evolution. What is Evolution Systematics often divided into two areas: phylogenetics or pattern and biosystematics or process
 Speciation What is Evolution What is Evolution Systematics often divided into two areas: phylogenetics or pattern and biosystematics or process tree Genetic variation within species is the rule - human
Speciation What is Evolution What is Evolution Systematics often divided into two areas: phylogenetics or pattern and biosystematics or process tree Genetic variation within species is the rule - human
Yesterday s Picture UNIT 4D
 Warm-Up Flies without red pigment have a mutation in the white gene (w -- ); flies with the red pigment are considered wild-type (w + ). Explain how the allele frequency should change over the course of
Warm-Up Flies without red pigment have a mutation in the white gene (w -- ); flies with the red pigment are considered wild-type (w + ). Explain how the allele frequency should change over the course of
Reproduction- passing genetic information to the next generation
 166 166 Essential Question: How has biological evolution led to the diversity of life? B-5 Natural Selection Traits that make an organism more or less likely to survive in an environment and reproduce
166 166 Essential Question: How has biological evolution led to the diversity of life? B-5 Natural Selection Traits that make an organism more or less likely to survive in an environment and reproduce
Processes of Evolution
 Processes of Evolution Microevolution Processes of Microevolution How Species Arise Macroevolution Microevolution Population: localized group of individuals belonging to the same species with the potential
Processes of Evolution Microevolution Processes of Microevolution How Species Arise Macroevolution Microevolution Population: localized group of individuals belonging to the same species with the potential
Nested radiations and the pulse of angiosperm diversification: increased diversification rates often follow whole genome duplications
 Research Nested radiations and the pulse of angiosperm diversification: increased diversification rates often follow whole genome duplications David C. Tank 1,2, Jonathan M. Eastman 1,2, Matthew W. Pennell
Research Nested radiations and the pulse of angiosperm diversification: increased diversification rates often follow whole genome duplications David C. Tank 1,2, Jonathan M. Eastman 1,2, Matthew W. Pennell
UON, CAS, DBSC, General Biology II (BIOL102) Dr. Mustafa. A. Mansi. The Origin of Species
 The Origin of Species Galápagos Islands, landforms newly emerged from the sea, despite their geologic youth, are filled with plants and animals known no-where else in the world, Speciation: The origin
The Origin of Species Galápagos Islands, landforms newly emerged from the sea, despite their geologic youth, are filled with plants and animals known no-where else in the world, Speciation: The origin
Dating the origins of polyploidy events
 Research Dating the origins of polyploidy events Jeff J. Doyle and Ashley N. Egan L. H. Bailey Hortorium, Departmenf Plant Biology, 412 Mann Library Building, Cornell University, Ithaca, NY 14853, USA
Research Dating the origins of polyploidy events Jeff J. Doyle and Ashley N. Egan L. H. Bailey Hortorium, Departmenf Plant Biology, 412 Mann Library Building, Cornell University, Ithaca, NY 14853, USA
Q1) Explain how background selection and genetic hitchhiking could explain the positive correlation between genetic diversity and recombination rate.
 OEB 242 Exam Practice Problems Answer Key Q1) Explain how background selection and genetic hitchhiking could explain the positive correlation between genetic diversity and recombination rate. First, recall
OEB 242 Exam Practice Problems Answer Key Q1) Explain how background selection and genetic hitchhiking could explain the positive correlation between genetic diversity and recombination rate. First, recall
Enduring Understanding: Change in the genetic makeup of a population over time is evolution Pearson Education, Inc.
 Enduring Understanding: Change in the genetic makeup of a population over time is evolution. Objective: You will be able to identify the key concepts of evolution theory Do Now: Read the enduring understanding
Enduring Understanding: Change in the genetic makeup of a population over time is evolution. Objective: You will be able to identify the key concepts of evolution theory Do Now: Read the enduring understanding
Conceptually, we define species as evolutionary units :
 Bio 1M: Speciation 1 How are species defined? S24.1 (2ndEd S26.1) Conceptually, we define species as evolutionary units : Individuals within a species are evolving together Individuals of different species
Bio 1M: Speciation 1 How are species defined? S24.1 (2ndEd S26.1) Conceptually, we define species as evolutionary units : Individuals within a species are evolving together Individuals of different species
Chapter 27: Evolutionary Genetics
 Chapter 27: Evolutionary Genetics Student Learning Objectives Upon completion of this chapter you should be able to: 1. Understand what the term species means to biology. 2. Recognize the various patterns
Chapter 27: Evolutionary Genetics Student Learning Objectives Upon completion of this chapter you should be able to: 1. Understand what the term species means to biology. 2. Recognize the various patterns
Plant variation and evolution
 Plant variation and evolution D. BRIGGS S.M. WALTERS SECOND EDITION UNIVERSITATS- BIBLIOTHEK The right of the University of Cambridge all manner of books was granted by Henry VIII in 1534. The University
Plant variation and evolution D. BRIGGS S.M. WALTERS SECOND EDITION UNIVERSITATS- BIBLIOTHEK The right of the University of Cambridge all manner of books was granted by Henry VIII in 1534. The University
Patterns of evolution
 To branch or not to branch Patterns of evolution Chapter 3 Cladogenesis lineages branch into two or more lines Anagenesis evolutionary change in a lineage without branching Anagenesis and Cladogenesis
To branch or not to branch Patterns of evolution Chapter 3 Cladogenesis lineages branch into two or more lines Anagenesis evolutionary change in a lineage without branching Anagenesis and Cladogenesis
Ch. 24 The Origin of Species
 Ch. 24 The Origin of Species 2007-2008 So what is a species? Biological species concept defined by Ernst Mayr population whose members can interbreed & produce viable, fertile offspring reproductively
Ch. 24 The Origin of Species 2007-2008 So what is a species? Biological species concept defined by Ernst Mayr population whose members can interbreed & produce viable, fertile offspring reproductively
Plant of the Day Isoetes andicola
 Plant of the Day Isoetes andicola Endemic to central and southern Peru Found in scattered populations above 4000 m Restricted to the edges of bogs and lakes Leaves lack stomata and so CO 2 is obtained,
Plant of the Day Isoetes andicola Endemic to central and southern Peru Found in scattered populations above 4000 m Restricted to the edges of bogs and lakes Leaves lack stomata and so CO 2 is obtained,
The Origin of Species
 LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 24 The Origin of Species Lectures
LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 24 The Origin of Species Lectures
chromosome numbers and species numbers through time (polyploidy/aneuploidy/population structure/speciation/fossil record)
 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 73, No. 6, pp. 2086-2090, June 1976 Genetics Rates of evolution in seed plants: Net increase in diversity of chromosome numbers and species numbers through time (polyploidy/aneuploidy/population
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 73, No. 6, pp. 2086-2090, June 1976 Genetics Rates of evolution in seed plants: Net increase in diversity of chromosome numbers and species numbers through time (polyploidy/aneuploidy/population
Supplemental Data. Vanneste et al. (2015). Plant Cell /tpc
 Supplemental Figure 1: Representation of the structure of an orthogroup. Each orthogroup consists out of a paralogous pair representing the WGD (denoted by Equisetum 1 and Equisetum 2) supplemented with
Supplemental Figure 1: Representation of the structure of an orthogroup. Each orthogroup consists out of a paralogous pair representing the WGD (denoted by Equisetum 1 and Equisetum 2) supplemented with
PHYLOGENOMIC PLACEMENT OF ANCIENT POLYPLOIDY EVENTS WITHIN THE POALES AND AGAVOIDEAE (ASPARAGALES) MICHAEL RAMON MCKAIN
 PHYLOGENOMIC PLACEMENT OF ANCIENT POLYPLOIDY EVENTS WITHIN THE POALES AND AGAVOIDEAE (ASPARAGALES) by MICHAEL RAMON MCKAIN (Under the Direction of James H. Leebens-Mack) ABSTRACT Polyploidy has been an
PHYLOGENOMIC PLACEMENT OF ANCIENT POLYPLOIDY EVENTS WITHIN THE POALES AND AGAVOIDEAE (ASPARAGALES) by MICHAEL RAMON MCKAIN (Under the Direction of James H. Leebens-Mack) ABSTRACT Polyploidy has been an
The Origin of Species
 The Origin of Species A. Macroevolution: Up to this point we have discussed changes in alleles or microevolution, with evolution this is the evolution of new. is the origin of a new species. There are
The Origin of Species A. Macroevolution: Up to this point we have discussed changes in alleles or microevolution, with evolution this is the evolution of new. is the origin of a new species. There are
4/4/2017. Extrinsic Isolating Barriers. 1. Biological species concept: 2. Phylogenetic species concept:
 Chapter 13 The origin of species 13.1 What Is a Species? p. 414 Ways to identify species 1. Biological species concept: 1. There are many different concepts of species 2. Species are important taxonomic
Chapter 13 The origin of species 13.1 What Is a Species? p. 414 Ways to identify species 1. Biological species concept: 1. There are many different concepts of species 2. Species are important taxonomic
Amira A. AL-Hosary PhD of infectious diseases Department of Animal Medicine (Infectious Diseases) Faculty of Veterinary Medicine Assiut
 Amira A. AL-Hosary PhD of infectious diseases Department of Animal Medicine (Infectious Diseases) Faculty of Veterinary Medicine Assiut University-Egypt Phylogenetic analysis Phylogenetic Basics: Biological
Amira A. AL-Hosary PhD of infectious diseases Department of Animal Medicine (Infectious Diseases) Faculty of Veterinary Medicine Assiut University-Egypt Phylogenetic analysis Phylogenetic Basics: Biological
Mutation, Selection, Gene Flow, Genetic Drift, and Nonrandom Mating Results in Evolution
 Mutation, Selection, Gene Flow, Genetic Drift, and Nonrandom Mating Results in Evolution 15.2 Intro In biology, evolution refers specifically to changes in the genetic makeup of populations over time.
Mutation, Selection, Gene Flow, Genetic Drift, and Nonrandom Mating Results in Evolution 15.2 Intro In biology, evolution refers specifically to changes in the genetic makeup of populations over time.
Reproductive Morphology
 Week 3; Wednesday Announcements: 1 st lab quiz TODAY Reproductive Morphology Reproductive morphology - any portion of a plant that is involved with or a direct product of sexual reproduction Example: cones,
Week 3; Wednesday Announcements: 1 st lab quiz TODAY Reproductive Morphology Reproductive morphology - any portion of a plant that is involved with or a direct product of sexual reproduction Example: cones,
Outline of lectures 23-26
 Genome 453 J. Felsenstein Evolutionary Genetics Autumn, 2013 Chromosome Evolution Outline of lectures 23-26 1. Chromosomes can change by many kinds of rearrangement. These involve breakage of chromosomes
Genome 453 J. Felsenstein Evolutionary Genetics Autumn, 2013 Chromosome Evolution Outline of lectures 23-26 1. Chromosomes can change by many kinds of rearrangement. These involve breakage of chromosomes
Lecture 11 Friday, October 21, 2011
 Lecture 11 Friday, October 21, 2011 Phylogenetic tree (phylogeny) Darwin and classification: In the Origin, Darwin said that descent from a common ancestral species could explain why the Linnaean system
Lecture 11 Friday, October 21, 2011 Phylogenetic tree (phylogeny) Darwin and classification: In the Origin, Darwin said that descent from a common ancestral species could explain why the Linnaean system
Modes of Macroevolution
 Modes of Macroevolution Macroevolution is used to refer to any evolutionary change at or above the level of species. Darwin illustrated the combined action of descent with modification, the principle of
Modes of Macroevolution Macroevolution is used to refer to any evolutionary change at or above the level of species. Darwin illustrated the combined action of descent with modification, the principle of
Sporic life cycles involve 2 types of multicellular bodies:
 Chapter 3- Human Manipulation of Plants Sporic life cycles involve 2 types of multicellular bodies: -a diploid, spore-producing sporophyte -a haploid, gamete-producing gametophyte Sexual Reproduction in
Chapter 3- Human Manipulation of Plants Sporic life cycles involve 2 types of multicellular bodies: -a diploid, spore-producing sporophyte -a haploid, gamete-producing gametophyte Sexual Reproduction in
CHAPTERS 24-25: Evidence for Evolution and Phylogeny
 CHAPTERS 24-25: Evidence for Evolution and Phylogeny 1. For each of the following, indicate how it is used as evidence of evolution by natural selection or shown as an evolutionary trend: a. Paleontology
CHAPTERS 24-25: Evidence for Evolution and Phylogeny 1. For each of the following, indicate how it is used as evidence of evolution by natural selection or shown as an evolutionary trend: a. Paleontology
Phylogenetic analysis. Characters
 Typical steps: Phylogenetic analysis Selection of taxa. Selection of characters. Construction of data matrix: character coding. Estimating the best-fitting tree (model) from the data matrix: phylogenetic
Typical steps: Phylogenetic analysis Selection of taxa. Selection of characters. Construction of data matrix: character coding. Estimating the best-fitting tree (model) from the data matrix: phylogenetic
Evolution Problem Drill 10: Human Evolution
 Evolution Problem Drill 10: Human Evolution Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. Which of the following statements is true regarding the human phylogenetic relationship with the African great apes? Question
Evolution Problem Drill 10: Human Evolution Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. Which of the following statements is true regarding the human phylogenetic relationship with the African great apes? Question
MACROEVOLUTION Student Packet SUMMARY EVOLUTION IS A CHANGE IN THE GENETIC MAKEUP OF A POPULATION OVER TIME Macroevolution refers to large-scale
 MACROEVOLUTION Student Packet SUMMARY EVOLUTION IS A CHANGE IN THE GENETIC MAKEUP OF A POPULATION OVER TIME Macroevolution refers to large-scale evolutionary changes such as speciation events, origin of
MACROEVOLUTION Student Packet SUMMARY EVOLUTION IS A CHANGE IN THE GENETIC MAKEUP OF A POPULATION OVER TIME Macroevolution refers to large-scale evolutionary changes such as speciation events, origin of
Phylogenetic inference: from sequences to trees
 W ESTFÄLISCHE W ESTFÄLISCHE W ILHELMS -U NIVERSITÄT NIVERSITÄT WILHELMS-U ÜNSTER MM ÜNSTER VOLUTIONARY FUNCTIONAL UNCTIONAL GENOMICS ENOMICS EVOLUTIONARY Bioinformatics 1 Phylogenetic inference: from sequences
W ESTFÄLISCHE W ESTFÄLISCHE W ILHELMS -U NIVERSITÄT NIVERSITÄT WILHELMS-U ÜNSTER MM ÜNSTER VOLUTIONARY FUNCTIONAL UNCTIONAL GENOMICS ENOMICS EVOLUTIONARY Bioinformatics 1 Phylogenetic inference: from sequences
Major questions of evolutionary genetics. Experimental tools of evolutionary genetics. Theoretical population genetics.
 Evolutionary Genetics (for Encyclopedia of Biodiversity) Sergey Gavrilets Departments of Ecology and Evolutionary Biology and Mathematics, University of Tennessee, Knoxville, TN 37996-6 USA Evolutionary
Evolutionary Genetics (for Encyclopedia of Biodiversity) Sergey Gavrilets Departments of Ecology and Evolutionary Biology and Mathematics, University of Tennessee, Knoxville, TN 37996-6 USA Evolutionary
Phylogeny and systematics. Why are these disciplines important in evolutionary biology and how are they related to each other?
 Phylogeny and systematics Why are these disciplines important in evolutionary biology and how are they related to each other? Phylogeny and systematics Phylogeny: the evolutionary history of a species
Phylogeny and systematics Why are these disciplines important in evolutionary biology and how are they related to each other? Phylogeny and systematics Phylogeny: the evolutionary history of a species
The Origin of Species
 Chapter 24 The Origin of Species PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp
Chapter 24 The Origin of Species PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp
What examples can you think of?
 What examples can you think of? Geocentrism Alchemy Heliocentrism: Copernicus, Kepler, Newton, Galileo Nature of the chemical bond (Rutherford, Pauling ) Aristotelian view of the biosphere Woese/Pace (subject
What examples can you think of? Geocentrism Alchemy Heliocentrism: Copernicus, Kepler, Newton, Galileo Nature of the chemical bond (Rutherford, Pauling ) Aristotelian view of the biosphere Woese/Pace (subject
Speciation. Today s OUTLINE: Mechanisms of Speciation. Mechanisms of Speciation. Geographic Models of speciation. (1) Mechanisms of Speciation
 Speciation Today s OUTLINE: (1) Geographic Mechanisms of Speciation (What circumstances lead to the formation of new species?) (2) Species Concepts (How are Species Defined?) Mechanisms of Speciation Last
Speciation Today s OUTLINE: (1) Geographic Mechanisms of Speciation (What circumstances lead to the formation of new species?) (2) Species Concepts (How are Species Defined?) Mechanisms of Speciation Last
P OLYPLOIDY AND ANGIOSPERM DIVERSIFICATION 1
 American Journal of Botany 96(1): 336 348. 2009. P OLYPLOIDY AND ANGIOSPERM DIVERSIFICATION 1 Douglas E. Soltis,2,11 Victor A. Albert, 3 Jim Leebens-Mack,4 Charles D. Bell, 5 Andrew H. Paterson, 4,6 Chunfang
American Journal of Botany 96(1): 336 348. 2009. P OLYPLOIDY AND ANGIOSPERM DIVERSIFICATION 1 Douglas E. Soltis,2,11 Victor A. Albert, 3 Jim Leebens-Mack,4 Charles D. Bell, 5 Andrew H. Paterson, 4,6 Chunfang
Chapter 14 The Origin of Species
 Chapter 14 The Origin of Species PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Lecture by Joan
Chapter 14 The Origin of Species PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Lecture by Joan
Gametophyte. (n) (2n) Sporangium. Sporophyte. (2n) N N
 Tetrads of spores (n) Spores (n) Gametophyte (n) Archegonium with egg (n) Antheridium with sperm (n) fertilization Meiosis Zygote (2n) Spore mother cell (2n) Sporangium (2n) Sporophyte (2n) Embryo (2n)
Tetrads of spores (n) Spores (n) Gametophyte (n) Archegonium with egg (n) Antheridium with sperm (n) fertilization Meiosis Zygote (2n) Spore mother cell (2n) Sporangium (2n) Sporophyte (2n) Embryo (2n)
Review of molecular biology
 Review of molecular biology DNA is into RNA, which is into protein. What mrna sequence would be transcribed from the DNA template CTA? What sequence of trna would be attracted by the above mrna sequence?
Review of molecular biology DNA is into RNA, which is into protein. What mrna sequence would be transcribed from the DNA template CTA? What sequence of trna would be attracted by the above mrna sequence?
How should we organize the diversity of animal life?
 How should we organize the diversity of animal life? The difference between Taxonomy Linneaus, and Cladistics Darwin What are phylogenies? How do we read them? How do we estimate them? Classification (Taxonomy)
How should we organize the diversity of animal life? The difference between Taxonomy Linneaus, and Cladistics Darwin What are phylogenies? How do we read them? How do we estimate them? Classification (Taxonomy)
Bio 1B Lecture Outline (please print and bring along) Fall, 2007
 Bio 1B Lecture Outline (please print and bring along) Fall, 2007 B.D. Mishler, Dept. of Integrative Biology 2-6810, bmishler@berkeley.edu Evolution lecture #5 -- Molecular genetics and molecular evolution
Bio 1B Lecture Outline (please print and bring along) Fall, 2007 B.D. Mishler, Dept. of Integrative Biology 2-6810, bmishler@berkeley.edu Evolution lecture #5 -- Molecular genetics and molecular evolution
Review of Plant Cytogenetics
 Review of Plant Cytogenetics Updated 2/13/06 Reading: Richards, A.J. and R.K. Dawe. 1998. Plant centromeres: structure and control. Current Op. Plant Biol. 1: 130-135. R.K. Dawe. 2005. Centromere renewal
Review of Plant Cytogenetics Updated 2/13/06 Reading: Richards, A.J. and R.K. Dawe. 1998. Plant centromeres: structure and control. Current Op. Plant Biol. 1: 130-135. R.K. Dawe. 2005. Centromere renewal
Bio 2 Plant and Animal Biology
 Bio 2 Plant and Animal Biology Evolution Evolution as the explanation for life s unity and diversity Darwinian Revolution Two main Points Descent with Modification Natural Selection Biological Species
Bio 2 Plant and Animal Biology Evolution Evolution as the explanation for life s unity and diversity Darwinian Revolution Two main Points Descent with Modification Natural Selection Biological Species
The Origin of New Species
 The Origin of New Species Introduction If microevolution is small changes in gene frequencies What, then would macroevolution be? And how might that work???? The biological species concept emphasizes reproductive
The Origin of New Species Introduction If microevolution is small changes in gene frequencies What, then would macroevolution be? And how might that work???? The biological species concept emphasizes reproductive
Reconstruction of Ancestral Genome subject to Whole Genome Duplication, Speciation, Rearrangement and Loss
 Reconstruction of Ancestral Genome subject to Whole Genome Duplication, Speciation, Rearrangement and Loss Denis Bertrand, Yves Gagnon, Mathieu Blanchette 2, and Nadia El-Mabrouk DIRO, Université de Montréal,
Reconstruction of Ancestral Genome subject to Whole Genome Duplication, Speciation, Rearrangement and Loss Denis Bertrand, Yves Gagnon, Mathieu Blanchette 2, and Nadia El-Mabrouk DIRO, Université de Montréal,
Comparative genomics of Gossypium and Arabidopsis: Unraveling the consequences of both ancient and recent polyploidy
 Article Comparative genomics of Gossypium and Arabidopsis: Unraveling the consequences of both ancient and recent polyploidy Junkang Rong, 1 John E. Bowers, 1 Stefan R. Schulze, 1 Vijay N. Waghmare, 1
Article Comparative genomics of Gossypium and Arabidopsis: Unraveling the consequences of both ancient and recent polyploidy Junkang Rong, 1 John E. Bowers, 1 Stefan R. Schulze, 1 Vijay N. Waghmare, 1
THE OHIO JOURNAL OF SCIENCE
 THE OHIO JOURNAL OF SCIENCE VOL. LV NOVEMBER, 1955 No. 6 AN OUTLINE OF THE PROCESS OF ORGANIC EVOLUTION DONALD J. BORROR Department of Zoology and Entomology, The Ohio State University, Columbus, 10 THE
THE OHIO JOURNAL OF SCIENCE VOL. LV NOVEMBER, 1955 No. 6 AN OUTLINE OF THE PROCESS OF ORGANIC EVOLUTION DONALD J. BORROR Department of Zoology and Entomology, The Ohio State University, Columbus, 10 THE
EVOLUTION. - Selection, Survival, and Drift
 EVOLUTION - Selection, Survival, and Drift Evolution Darwin on the HMS Beagle Darwin s role on the ship was as a geologist and companion to the captain. His goal was to collect biological and geological
EVOLUTION - Selection, Survival, and Drift Evolution Darwin on the HMS Beagle Darwin s role on the ship was as a geologist and companion to the captain. His goal was to collect biological and geological
Major contributions of Darwin s work: Evolution Defined. 1. Evidence of change through time
 An overview of lines of evidence for evolution (or evolution in a nutshell) Major contributions of Darwin s work: Learning objectives: To assess types of evidence for evolution, including: 1. Evidence
An overview of lines of evidence for evolution (or evolution in a nutshell) Major contributions of Darwin s work: Learning objectives: To assess types of evidence for evolution, including: 1. Evidence
Plant Cell Advance Publication. Published on February 17, 2017, doi: /tpc
 Plant Cell Advance Publication. Published on February 17, 2017, doi:10.1105/tpc.16.00836 LETTER TO THE EDITOR Picking up the Ball at the K/Pg Boundary: The Distribution of Ancient Polyploidies in the Plant
Plant Cell Advance Publication. Published on February 17, 2017, doi:10.1105/tpc.16.00836 LETTER TO THE EDITOR Picking up the Ball at the K/Pg Boundary: The Distribution of Ancient Polyploidies in the Plant
The Tempo of Macroevolution: Patterns of Diversification and Extinction
 The Tempo of Macroevolution: Patterns of Diversification and Extinction During the semester we have been consider various aspects parameters associated with biodiversity. Current usage stems from 1980's
The Tempo of Macroevolution: Patterns of Diversification and Extinction During the semester we have been consider various aspects parameters associated with biodiversity. Current usage stems from 1980's
EVOLUTION OF COMPLEX LIFE FORMS
 0.002 0.6 1.0 1.9 2.8 Ancestral humans Diversification of mammals Invasion of the land Diversification of animals Origin of the major eukaryotic groups Eukaryotic cells abundant Atmospheric oxygen plentiful
0.002 0.6 1.0 1.9 2.8 Ancestral humans Diversification of mammals Invasion of the land Diversification of animals Origin of the major eukaryotic groups Eukaryotic cells abundant Atmospheric oxygen plentiful
