Electrostatic Single-walled Carbon Nanotube (CNT) Field Effect Transistor Device Modeling
|
|
|
- Claud Walton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Electrostatic Single-walled Carbon Nanotube (CNT) Field Effect Transistor Device Modeling Henok Abebe The Service USC Viterbi School of Engineering Information Sciences Institute Collaborator Ellis Cumberbatch CGU School of Mathematical Sciences, USA WCM 2011
2 Outline Carbon Nanotubes (CNTs). CNTFET. Channel charge density compact model. CNTFET surface potential modeling. Channel current model. Results. Future work p-type CNTFET measured I-V Vdata and dhysteresis effects 2
3 Carbon Nanotubes (CNTs) Graphene: High current carrying capability. High carrier mobility (~10 6 cm 2 /(V.s)). High carrier saturation velocity (~10 6 m/s). Nearest carbon-carbon distance is a=0.41nm. Excellent thermal conductivity (~10 3 W/(K.m)) Figure 1: Graphene sheet 3
4 Zig-Zag, Zag, Armchair and Chiral CNTs Figure 2: Illustration of the graphene lattice, T is is the CNT long axis, a 1 and a 2 are the lattice vectors, C h is the CNT circumference or GNR width vector with components n and m (chiral numbers). Zig-zag tubes are (n, 0), armchair tubes are (n, n) and chiral tubes are (n, m). The chirality is determined by how many times you have to move in the a 1 direction (n) and how many times you have to move in the a 2 direction (m) in order to return to an equivalent starting point. 4
5 Zig-Zag Zag CNTs (symmetric) Figure 3: Counting a (5,0) zig-zag nanotube. The red stars srepresent ese the same carbon atom; the stars would overlap if you were to roll the graphene sheet into a tube.. Figure 3: n m 5 (semiconductor) If n m 3i (metallic) 5
6 Armchair CNTs (symmetric) Figure 4: Counting a (3,3) 3) armchair nanotube. The red stars represent the same carbon atom; the stars would overlap if you were to roll the graphene sheet into a tube.. armchair tubes do not open any bandgap, and always remain metallic. 6
7 Chiral CNTs (asymmetric). Figure 5: Graphene (n,m) map. If n m 3 i (metallic) otherwise, it is a semiconductor 7
8 CNTFET Figure 6: Single-walled CNT field effect transistor. 8
9 Channel charge density compact model Surface charge density, Q cnt, in terms of the surface potential, ψ s, is Q ( V V ) C CNT gs fb s ins where C ins 2 ins tins ln( 1) R t, R t w / 2, w a 3 n 2 m 2 nm, and a=0.142nm 9
10 Integral representation of the charge density Q cnt q [ 1 kbt (1 e ) (1 e 1 ) ][ Eq s Eq s qvds 2 ( ) ( ) 2 2 k T ( E m m where is the coefficient of DOS for CNT. b E ) ] de The CNT charge density can be simplified using a first sub-band band energy approximation: Q CNT q 2 n e i q s k T b (1 e qv k T b ds ) 10
11 CNTFET surface potential modeling Q CNT q 2 n e i q s k T b (1 e qv k T b ds ) ( V gs V fb ) C s ins Surface potential as 2 qvds kbt q ni K T b s ( V gs, Vds ) Vgs V fb W (1 e ) e q 2kbTCins q( V gs k V b T fb ) where Lambert W(x) function is the solution W to x We And where 13.8d d t
12 Channel current model The channel current of a ballistic CNT-FET, which is the net flux of forward and backward traveling carriers, can be derived using the first sub-band b energy approximation: I ds ln(1 e 2 E 2 2qV E 4 q s g q s ds kb Tq 2k T 2 k T h b ) ln(1 e b g ) where s ( V s gs, V ds 0), E g 0.765(ev.nm) d t and h is Planck's constant. 12
13 Results Figure 7: CNT-FET channel surface potential versus relative gate voltage V gs -V fb for nanotube analytical diameters d t =0.8, 08 1 and d15 1.5nm, high-k hkdielectric ti thickness t ins =10nm with K=15 is used and V ds =0V. 13
14 Results (continued) Figure 8: CNT-FET channel charge versus relative gate voltage V gs -V fb for nanotube analytical diameters d t =0.8, 1.0 and 1.5nm, high-k dielectric thickness t ins =10nm with K=15 is used and V ds =0V. 14
15 Results (continued) Figure 9: CNT-FET gate capacitance per unit length versus relative gate voltage V gs -V fb for nanotube analytical diameters d t =0.8, 1.0 and 1.5nm, high-k dielectric thickness t ins =10nm with K=15 is used and V ds =0V. 15
16 Results (continued) Figure 10: CNT-FET channel current versus drain-source voltage V ds for nanotube analytical diameters d t =0.8, 1.0 and 1.5nm, high-k dielectric thickness t ins=10nm with K=15 is used. 16
17 Future work Figure 11: P type back gated CNTFET device with t ox =50nm 17
18 Future work (continued) Figure 12: Channel current versus back gate voltage for V ds =0.2, 0.4 and 1V 18
19 Future work (continued) Figure 13: Channel current versus drain/source voltage for V gs =-3, -4 and -5V 19
20 p-type CNTFET measured I-V data and hysteresis effects Figure 14: Gate voltage vs drain current for V ds =1V and t ox =50nm 20
NOVEL STRUCTURES FOR CARBON NANOTUBE FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTORS
 International Journal of Modern Physics B Vol. 23, No. 19 (2009) 3871 3880 c World Scientific Publishing Company NOVEL STRUCTURES FOR CARBON NANOTUBE FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTORS RAHIM FAEZ Electrical Engineering
International Journal of Modern Physics B Vol. 23, No. 19 (2009) 3871 3880 c World Scientific Publishing Company NOVEL STRUCTURES FOR CARBON NANOTUBE FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTORS RAHIM FAEZ Electrical Engineering
Metallic: 2n 1. +n 2. =3q Armchair structure always metallic = 2
 Properties of CNT d = 2.46 n 2 2 1 + n1n2 + n2 2π Metallic: 2n 1 +n 2 =3q Armchair structure always metallic a) Graphite Valence(π) and Conduction(π*) states touch at six points(fermi points) Carbon Nanotube:
Properties of CNT d = 2.46 n 2 2 1 + n1n2 + n2 2π Metallic: 2n 1 +n 2 =3q Armchair structure always metallic a) Graphite Valence(π) and Conduction(π*) states touch at six points(fermi points) Carbon Nanotube:
Lecture 6: 2D FET Electrostatics
 Lecture 6: 2D FET Electrostatics 2016-02-01 Lecture 6, High Speed Devices 2014 1 Lecture 6: III-V FET DC I - MESFETs Reading Guide: Liu: 323-337 (he mainly focuses on the single heterostructure FET) Jena:
Lecture 6: 2D FET Electrostatics 2016-02-01 Lecture 6, High Speed Devices 2014 1 Lecture 6: III-V FET DC I - MESFETs Reading Guide: Liu: 323-337 (he mainly focuses on the single heterostructure FET) Jena:
SECTION: Circle one: Alam Lundstrom. ECE 305 Exam 5 SOLUTIONS: Spring 2016 April 18, 2016 M. A. Alam and M.S. Lundstrom Purdue University
 NAME: PUID: SECTION: Circle one: Alam Lundstrom ECE 305 Exam 5 SOLUTIONS: April 18, 2016 M A Alam and MS Lundstrom Purdue University This is a closed book exam You may use a calculator and the formula
NAME: PUID: SECTION: Circle one: Alam Lundstrom ECE 305 Exam 5 SOLUTIONS: April 18, 2016 M A Alam and MS Lundstrom Purdue University This is a closed book exam You may use a calculator and the formula
Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective. Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic. The Devices. July 30, Devices.
 Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic The July 30, 2002 1 Goal of this chapter Present intuitive understanding of device operation Introduction
Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic The July 30, 2002 1 Goal of this chapter Present intuitive understanding of device operation Introduction
Computational Model of Edge Effects in Graphene Nanoribbon Transistors
 Nano Res (2008) 1: 395 402 DOI 10.1007/s12274-008-8039-y Research Article 00395 Computational Model of Edge Effects in Graphene Nanoribbon Transistors Pei Zhao 1, Mihir Choudhury 2, Kartik Mohanram 2,
Nano Res (2008) 1: 395 402 DOI 10.1007/s12274-008-8039-y Research Article 00395 Computational Model of Edge Effects in Graphene Nanoribbon Transistors Pei Zhao 1, Mihir Choudhury 2, Kartik Mohanram 2,
The Devices. Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective. Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic. July 30, 2002
 Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic The Devices July 30, 2002 Goal of this chapter Present intuitive understanding of device operation Introduction
Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic The Devices July 30, 2002 Goal of this chapter Present intuitive understanding of device operation Introduction
I-V characteristics model for Carbon Nanotube Field Effect Transistors
 International Journal of Engineering & Technology IJET-IJENS Vol:14 No:04 33 I-V characteristics model for Carbon Nanotube Field Effect Transistors Rebiha Marki, Chérifa Azizi and Mourad Zaabat. Abstract--
International Journal of Engineering & Technology IJET-IJENS Vol:14 No:04 33 I-V characteristics model for Carbon Nanotube Field Effect Transistors Rebiha Marki, Chérifa Azizi and Mourad Zaabat. Abstract--
Lecture 8: Ballistic FET I-V
 Lecture 8: Ballistic FET I-V 1 Lecture 1: Ballistic FETs Jena: 61-70 Diffusive Field Effect Transistor Source Gate L g >> l Drain Source V GS Gate Drain I D Mean free path much shorter than channel length
Lecture 8: Ballistic FET I-V 1 Lecture 1: Ballistic FETs Jena: 61-70 Diffusive Field Effect Transistor Source Gate L g >> l Drain Source V GS Gate Drain I D Mean free path much shorter than channel length
Device Models (PN Diode, MOSFET )
 Device Models (PN Diode, MOSFET ) Instructor: Steven P. Levitan steve@ece.pitt.edu TA: Gayatri Mehta, José Martínez Book: Digital Integrated Circuits: A Design Perspective; Jan Rabaey Lab Notes: Handed
Device Models (PN Diode, MOSFET ) Instructor: Steven P. Levitan steve@ece.pitt.edu TA: Gayatri Mehta, José Martínez Book: Digital Integrated Circuits: A Design Perspective; Jan Rabaey Lab Notes: Handed
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Flexible, high-performance carbon nanotube integrated circuits Dong-ming Sun, Marina Y. Timmermans, Ying Tian, Albert G. Nasibulin, Esko I. Kauppinen, Shigeru Kishimoto, Takashi
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Flexible, high-performance carbon nanotube integrated circuits Dong-ming Sun, Marina Y. Timmermans, Ying Tian, Albert G. Nasibulin, Esko I. Kauppinen, Shigeru Kishimoto, Takashi
6.012 Electronic Devices and Circuits
 Page 1 of 10 YOUR NAME Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Massachusetts Institute of Technology 6.012 Electronic Devices and Circuits Exam No. 2 Thursday, November 5, 2009 7:30 to
Page 1 of 10 YOUR NAME Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Massachusetts Institute of Technology 6.012 Electronic Devices and Circuits Exam No. 2 Thursday, November 5, 2009 7:30 to
Fig The electron mobility for a-si and poly-si TFT.
 Fig. 1-1-1 The electron mobility for a-si and poly-si TFT. Fig. 1-1-2 The aperture ratio for a-si and poly-si TFT. 33 Fig. 1-2-1 All kinds defect well. (a) is the Dirac well. (b) is the repulsive Columbic
Fig. 1-1-1 The electron mobility for a-si and poly-si TFT. Fig. 1-1-2 The aperture ratio for a-si and poly-si TFT. 33 Fig. 1-2-1 All kinds defect well. (a) is the Dirac well. (b) is the repulsive Columbic
CMOS Scaling. Two motivations to scale down. Faster transistors, both digital and analog. To pack more functionality per area. Lower the cost!
 Two motivations to scale down CMOS Scaling Faster transistors, both digital and analog To pack more functionality per area. Lower the cost! (which makes (some) physical sense) Scale all dimensions and
Two motivations to scale down CMOS Scaling Faster transistors, both digital and analog To pack more functionality per area. Lower the cost! (which makes (some) physical sense) Scale all dimensions and
The Devices. Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective. Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic. July 30, 2002
 igital Integrated Circuits A esign Perspective Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic The evices July 30, 2002 Goal of this chapter Present intuitive understanding of device operation Introduction
igital Integrated Circuits A esign Perspective Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic The evices July 30, 2002 Goal of this chapter Present intuitive understanding of device operation Introduction
RFIC2017 MO2B-2. A Simplified CMOS FET Model using Surface Potential Equations For Inter-modulation Simulations of Passive-Mixer-Like Circuits
 A Simplified CMOS FET Model using Surface Potential Equations For Inter-modulation Simulations of Passive-Mixer-Like Circuits M. Baraani Dastjerdi and H. Krishnaswamy CoSMIC Lab, Columbia University, New
A Simplified CMOS FET Model using Surface Potential Equations For Inter-modulation Simulations of Passive-Mixer-Like Circuits M. Baraani Dastjerdi and H. Krishnaswamy CoSMIC Lab, Columbia University, New
Carbon Nanotubes for Interconnect Applications Franz Kreupl, Andrew P. Graham, Maik Liebau, Georg S. Duesberg, Robert Seidel, Eugen Unger
 Carbon Nanotubes for Interconnect Applications Franz Kreupl, Andrew P. Graham, Maik Liebau, Georg S. Duesberg, Robert Seidel, Eugen Unger Infineon Technologies Corporate Research Munich, Germany Outline
Carbon Nanotubes for Interconnect Applications Franz Kreupl, Andrew P. Graham, Maik Liebau, Georg S. Duesberg, Robert Seidel, Eugen Unger Infineon Technologies Corporate Research Munich, Germany Outline
Lecture 04 Review of MOSFET
 ECE 541/ME 541 Microelectronic Fabrication Techniques Lecture 04 Review of MOSFET Zheng Yang (ERF 3017, email: yangzhen@uic.edu) What is a Transistor? A Switch! An MOS Transistor V GS V T V GS S Ron D
ECE 541/ME 541 Microelectronic Fabrication Techniques Lecture 04 Review of MOSFET Zheng Yang (ERF 3017, email: yangzhen@uic.edu) What is a Transistor? A Switch! An MOS Transistor V GS V T V GS S Ron D
Device Models (PN Diode, MOSFET )
 Device Models (PN Diode, MOSFET ) Instructor: Steven P. Levitan steve@ece.pitt.edu TA: Gayatri Mehta, José Martínez Book: Digital Integrated Circuits: A Design Perspective; Jan Rabaey Lab Notes: Handed
Device Models (PN Diode, MOSFET ) Instructor: Steven P. Levitan steve@ece.pitt.edu TA: Gayatri Mehta, José Martínez Book: Digital Integrated Circuits: A Design Perspective; Jan Rabaey Lab Notes: Handed
ECE 342 Electronic Circuits. 3. MOS Transistors
 ECE 342 Electronic Circuits 3. MOS Transistors Jose E. Schutt-Aine Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Illinois jschutt@emlab.uiuc.edu 1 NMOS Transistor Typically L = 0.1 to 3 m, W = 0.2 to
ECE 342 Electronic Circuits 3. MOS Transistors Jose E. Schutt-Aine Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Illinois jschutt@emlab.uiuc.edu 1 NMOS Transistor Typically L = 0.1 to 3 m, W = 0.2 to
The Critical Role of Quantum Capacitance in Compact Modeling of Nano-Scaled and Nanoelectronic Devices
 The Critical Role of Quantum Capacitance in Compact Modeling of Nano-Scaled and Nanoelectronic Devices Zhiping Yu and Jinyu Zhang Institute of Microelectronics Tsinghua University, Beijing, China yuzhip@tsinghua.edu.cn
The Critical Role of Quantum Capacitance in Compact Modeling of Nano-Scaled and Nanoelectronic Devices Zhiping Yu and Jinyu Zhang Institute of Microelectronics Tsinghua University, Beijing, China yuzhip@tsinghua.edu.cn
An Extended Hückel Theory based Atomistic Model for Graphene Nanoelectronics
 Journal of Computational Electronics X: YYY-ZZZ,? 6 Springer Science Business Media, Inc. Manufactured in The Netherlands An Extended Hückel Theory based Atomistic Model for Graphene Nanoelectronics HASSAN
Journal of Computational Electronics X: YYY-ZZZ,? 6 Springer Science Business Media, Inc. Manufactured in The Netherlands An Extended Hückel Theory based Atomistic Model for Graphene Nanoelectronics HASSAN
Simple Theory of the Ballistic Nanotransistor
 Simple Theory of the Ballistic Nanotransistor Mark Lundstrom Purdue University Network for Computational Nanoechnology outline I) Traditional MOS theory II) A bottom-up approach III) The ballistic nanotransistor
Simple Theory of the Ballistic Nanotransistor Mark Lundstrom Purdue University Network for Computational Nanoechnology outline I) Traditional MOS theory II) A bottom-up approach III) The ballistic nanotransistor
The Devices: MOS Transistors
 The Devices: MOS Transistors References: Semiconductor Device Fundamentals, R. F. Pierret, Addison-Wesley Digital Integrated Circuits: A Design Perspective, J. Rabaey et.al. Prentice Hall NMOS Transistor
The Devices: MOS Transistors References: Semiconductor Device Fundamentals, R. F. Pierret, Addison-Wesley Digital Integrated Circuits: A Design Perspective, J. Rabaey et.al. Prentice Hall NMOS Transistor
Evaluation of Electronic Characteristics of Double Gate Graphene Nanoribbon Field Effect Transistor for Wide Range of Temperatures
 Evaluation of Electronic Characteristics of Double Gate Graphene Nanoribbon Field Effect Transistor for Wide Range of Temperatures 1 Milad Abtin, 2 Ali Naderi 1 Department of electrical engineering, Masjed
Evaluation of Electronic Characteristics of Double Gate Graphene Nanoribbon Field Effect Transistor for Wide Range of Temperatures 1 Milad Abtin, 2 Ali Naderi 1 Department of electrical engineering, Masjed
Lecture 3: CMOS Transistor Theory
 Lecture 3: CMOS Transistor Theory Outline Introduction MOS Capacitor nmos I-V Characteristics pmos I-V Characteristics Gate and Diffusion Capacitance 2 Introduction So far, we have treated transistors
Lecture 3: CMOS Transistor Theory Outline Introduction MOS Capacitor nmos I-V Characteristics pmos I-V Characteristics Gate and Diffusion Capacitance 2 Introduction So far, we have treated transistors
Final exam. Introduction to Nanotechnology. Name: Student number:
 1 Final exam. Introduction to Nanotechnology Name: Student number: 1. (a) What is the definition for a cluster size-wise? (3%) (b) Calculate the energy separation near the Fermi surface of a metallic cluster
1 Final exam. Introduction to Nanotechnology Name: Student number: 1. (a) What is the definition for a cluster size-wise? (3%) (b) Calculate the energy separation near the Fermi surface of a metallic cluster
EECS130 Integrated Circuit Devices
 EECS130 Integrated Circuit Devices Professor Ali Javey 10/30/2007 MOSFETs Lecture 4 Reading: Chapter 17, 19 Announcements The next HW set is due on Thursday. Midterm 2 is next week!!!! Threshold and Subthreshold
EECS130 Integrated Circuit Devices Professor Ali Javey 10/30/2007 MOSFETs Lecture 4 Reading: Chapter 17, 19 Announcements The next HW set is due on Thursday. Midterm 2 is next week!!!! Threshold and Subthreshold
VLSI Design and Simulation
 VLSI Design and Simulation Performance Characterization Topics Performance Characterization Resistance Estimation Capacitance Estimation Inductance Estimation Performance Characterization Inverter Voltage
VLSI Design and Simulation Performance Characterization Topics Performance Characterization Resistance Estimation Capacitance Estimation Inductance Estimation Performance Characterization Inverter Voltage
Carbon Nanotube Electronics
 Carbon Nanotube Electronics Jeorg Appenzeller, Phaedon Avouris, Vincent Derycke, Stefan Heinz, Richard Martel, Marko Radosavljevic, Jerry Tersoff, Shalom Wind H.-S. Philip Wong hspwong@us.ibm.com IBM T.J.
Carbon Nanotube Electronics Jeorg Appenzeller, Phaedon Avouris, Vincent Derycke, Stefan Heinz, Richard Martel, Marko Radosavljevic, Jerry Tersoff, Shalom Wind H.-S. Philip Wong hspwong@us.ibm.com IBM T.J.
Diameter Optimization for Highest Degree of Ballisticity of Carbon Nanotube Field Effect Transistors I. Khan, O. Morshed and S. M.
 Diameter Optimization for Highest Degree of Ballisticity of Carbon Nanotube Field Effect Transistors I. Khan, O. Morshed and S. M. Mominuzzaman Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, Bangladesh
Diameter Optimization for Highest Degree of Ballisticity of Carbon Nanotube Field Effect Transistors I. Khan, O. Morshed and S. M. Mominuzzaman Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, Bangladesh
Understanding the effect of n-type and p-type doping in the channel of graphene nanoribbon transistor
 Bull. Mater. Sci., Vol. 39, No. 5, September 2016, pp. 1303 1309. DOI 10.1007/s12034-016-1277-9 c Indian Academy of Sciences. Understanding the effect of n-type and p-type doping in the channel of graphene
Bull. Mater. Sci., Vol. 39, No. 5, September 2016, pp. 1303 1309. DOI 10.1007/s12034-016-1277-9 c Indian Academy of Sciences. Understanding the effect of n-type and p-type doping in the channel of graphene
SEU RADIATION EFFECTS ON GAA-CNTFET BASED DIGITAL LOGIC CIRCUIT
 International Journal of Mechanical Engineering and Technology (IJMET) Volume 9, Issue 7, July 2018, pp. 345 353, Article ID: IJMET_09_07_039 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijmet/issues.asp?jtype=ijmet&vtype=9&itype=7
International Journal of Mechanical Engineering and Technology (IJMET) Volume 9, Issue 7, July 2018, pp. 345 353, Article ID: IJMET_09_07_039 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijmet/issues.asp?jtype=ijmet&vtype=9&itype=7
Quantized Electrical Conductance of Carbon nanotubes(cnts)
 Quantized Electrical Conductance of Carbon nanotubes(cnts) By Boxiao Chen PH 464: Applied Optics Instructor: Andres L arosa Abstract One of the main factors that impacts the efficiency of solar cells is
Quantized Electrical Conductance of Carbon nanotubes(cnts) By Boxiao Chen PH 464: Applied Optics Instructor: Andres L arosa Abstract One of the main factors that impacts the efficiency of solar cells is
CMPEN 411 VLSI Digital Circuits. Lecture 03: MOS Transistor
 CMPEN 411 VLSI Digital Circuits Lecture 03: MOS Transistor Kyusun Choi [Adapted from Rabaey s Digital Integrated Circuits, Second Edition, 2003 J. Rabaey, A. Chandrakasan, B. Nikolic] CMPEN 411 L03 S.1
CMPEN 411 VLSI Digital Circuits Lecture 03: MOS Transistor Kyusun Choi [Adapted from Rabaey s Digital Integrated Circuits, Second Edition, 2003 J. Rabaey, A. Chandrakasan, B. Nikolic] CMPEN 411 L03 S.1
Spring Semester 2012 Final Exam
 Spring Semester 2012 Final Exam Note: Show your work, underline results, and always show units. Official exam time: 2.0 hours; an extension of at least 1.0 hour will be granted to anyone. Materials parameters
Spring Semester 2012 Final Exam Note: Show your work, underline results, and always show units. Official exam time: 2.0 hours; an extension of at least 1.0 hour will be granted to anyone. Materials parameters
Designing a Carbon Nanotube Field-Effect Transistor with High Transition Frequency for Ultra-Wideband Application
 Engineering, 2017, 9, 22-35 http://www.scirp.org/journal/eng ISSN Online: 1947-394X ISSN Print: 1947-3931 Designing a Carbon Nanotube Field-Effect Transistor with High Transition Frequency for Ultra-Wideband
Engineering, 2017, 9, 22-35 http://www.scirp.org/journal/eng ISSN Online: 1947-394X ISSN Print: 1947-3931 Designing a Carbon Nanotube Field-Effect Transistor with High Transition Frequency for Ultra-Wideband
Investigation of the Thermal Noise of MOS Transistors under Analog and RF Operating Conditions
 Investigation of the Thermal Noise of MOS Transistors under Analog and RF Operating Conditions Ralf Brederlow 1, Georg Wenig 2, and Roland Thewes 1 1 Infineon Technologies, Corporate Research, 2 Technical
Investigation of the Thermal Noise of MOS Transistors under Analog and RF Operating Conditions Ralf Brederlow 1, Georg Wenig 2, and Roland Thewes 1 1 Infineon Technologies, Corporate Research, 2 Technical
Graphene and Carbon Nanotubes
 Graphene and Carbon Nanotubes 1 atom thick films of graphite atomic chicken wire Novoselov et al - Science 306, 666 (004) 100μm Geim s group at Manchester Novoselov et al - Nature 438, 197 (005) Kim-Stormer
Graphene and Carbon Nanotubes 1 atom thick films of graphite atomic chicken wire Novoselov et al - Science 306, 666 (004) 100μm Geim s group at Manchester Novoselov et al - Nature 438, 197 (005) Kim-Stormer
Electrostatics of Nanowire Transistors
 Electrostatics of Nanowire Transistors Jing Guo, Jing Wang, Eric Polizzi, Supriyo Datta and Mark Lundstrom School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Purdue University, West Lafayette, IN, 47907 ABSTRACTS
Electrostatics of Nanowire Transistors Jing Guo, Jing Wang, Eric Polizzi, Supriyo Datta and Mark Lundstrom School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Purdue University, West Lafayette, IN, 47907 ABSTRACTS
Graphene Devices, Interconnect and Circuits Challenges and Opportunities
 Graphene Devices, Interconnect and Circuits Challenges and Opportunities Mircea R. Stan, Dincer Unluer, Avik Ghosh, Frank Tseng Univ. of Virginia, ECE Dept., Charlottesville, VA 22904 {mircea,du7x,ag7rq,ft8e}@virginia.edu
Graphene Devices, Interconnect and Circuits Challenges and Opportunities Mircea R. Stan, Dincer Unluer, Avik Ghosh, Frank Tseng Univ. of Virginia, ECE Dept., Charlottesville, VA 22904 {mircea,du7x,ag7rq,ft8e}@virginia.edu
GRAPHENE NANORIBBONS Nahid Shayesteh,
 USC Department of Physics Graduate Seminar 1 GRAPHENE NANORIBBONS Nahid Shayesteh, Outlines 2 Carbon based material Discovery and innovation of graphen Graphene nanoribbons structure Application of Graphene
USC Department of Physics Graduate Seminar 1 GRAPHENE NANORIBBONS Nahid Shayesteh, Outlines 2 Carbon based material Discovery and innovation of graphen Graphene nanoribbons structure Application of Graphene
Device Performance Analysis of Graphene Nanoribbon Field-Effect Transistor with Rare- Earth Oxide (La 2 O 3 ) Based High-k Gate Dielectric
 Device Performance Analysis of Graphene Nanoribbon Field-Effect Transistor with Rare- Earth Oxide (La 2 O 3 ) Based High-k Gate Dielectric M. K. Bera 1, S. P. Pandey 2, A. K. Sharma 3, D. K. Tyagi 4, R.
Device Performance Analysis of Graphene Nanoribbon Field-Effect Transistor with Rare- Earth Oxide (La 2 O 3 ) Based High-k Gate Dielectric M. K. Bera 1, S. P. Pandey 2, A. K. Sharma 3, D. K. Tyagi 4, R.
Modeling and Simulation of Carbon Nanotubes based FET for Cervical Cancer Detection
 Modeling and Simulation of Carbon Nanotubes based FET for Cervical Cancer Detection Gopinath.P.G. 1, S. Aruna Mastani 2, V.R. Anitha 3 Research Scholar, Department of ECE, JNTUA, Anantapuramu, Andhra Pradesh,
Modeling and Simulation of Carbon Nanotubes based FET for Cervical Cancer Detection Gopinath.P.G. 1, S. Aruna Mastani 2, V.R. Anitha 3 Research Scholar, Department of ECE, JNTUA, Anantapuramu, Andhra Pradesh,
6.012 Electronic Devices and Circuits
 Page 1 of 12 YOUR NAME Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Massachusetts Institute of Technology 6.012 Electronic Devices and Circuits FINAL EXAMINATION Open book. Notes: 1. Unless
Page 1 of 12 YOUR NAME Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Massachusetts Institute of Technology 6.012 Electronic Devices and Circuits FINAL EXAMINATION Open book. Notes: 1. Unless
Application II: The Ballistic Field-E ect Transistor
 Chapter 1 Application II: The Ballistic Field-E ect Transistor 1.1 Introduction In this chapter, we apply the formalism we have developed for charge currents to understand the output characteristics of
Chapter 1 Application II: The Ballistic Field-E ect Transistor 1.1 Introduction In this chapter, we apply the formalism we have developed for charge currents to understand the output characteristics of
Modeling and Computation of Gate Tunneling Current through Ultra Thin Gate Oxides in Double Gate MOSFETs with Ultra Thin Body Silicon Channel
 Modeling and Computation of Gate Tunneling Current through Ultra Thin Gate Oxides in Double Gate MOSFETs with Ultra Thin Body Silicon Channel Bhadrinarayana L V 17 th July 2008 Microelectronics Lab, Indian
Modeling and Computation of Gate Tunneling Current through Ultra Thin Gate Oxides in Double Gate MOSFETs with Ultra Thin Body Silicon Channel Bhadrinarayana L V 17 th July 2008 Microelectronics Lab, Indian
1 Name: Student number: DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS AND PHYSICAL OCEANOGRAPHY MEMORIAL UNIVERSITY OF NEWFOUNDLAND. Fall :00-11:00
 1 Name: DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS AND PHYSICAL OCEANOGRAPHY MEMORIAL UNIVERSITY OF NEWFOUNDLAND Final Exam Physics 3000 December 11, 2012 Fall 2012 9:00-11:00 INSTRUCTIONS: 1. Answer all seven (7) questions.
1 Name: DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS AND PHYSICAL OCEANOGRAPHY MEMORIAL UNIVERSITY OF NEWFOUNDLAND Final Exam Physics 3000 December 11, 2012 Fall 2012 9:00-11:00 INSTRUCTIONS: 1. Answer all seven (7) questions.
ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals
 ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 4: January 23, 2018 MOS Transistor Theory, MOS Model Penn ESE 570 Spring 2018 Khanna Lecture Outline! CMOS Process Enhancements! Semiconductor
ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 4: January 23, 2018 MOS Transistor Theory, MOS Model Penn ESE 570 Spring 2018 Khanna Lecture Outline! CMOS Process Enhancements! Semiconductor
Physics of Nanoscale Transistors
 Physics of Nanoscale ransistors Mark Electrical and Computer Engineering University, West Lafayette, IN 1. Introduction 2. he Ballistic MOSFE 3. Scattering heory of the MOSFE 4. Beyond the Si MOSFE 5.
Physics of Nanoscale ransistors Mark Electrical and Computer Engineering University, West Lafayette, IN 1. Introduction 2. he Ballistic MOSFE 3. Scattering heory of the MOSFE 4. Beyond the Si MOSFE 5.
Appendix 1: List of symbols
 Appendix 1: List of symbols Symbol Description MKS Units a Acceleration m/s 2 a 0 Bohr radius m A Area m 2 A* Richardson constant m/s A C Collector area m 2 A E Emitter area m 2 b Bimolecular recombination
Appendix 1: List of symbols Symbol Description MKS Units a Acceleration m/s 2 a 0 Bohr radius m A Area m 2 A* Richardson constant m/s A C Collector area m 2 A E Emitter area m 2 b Bimolecular recombination
ᣂቇⴚ㗔 䇸䉮䊮䊏䊠䊷䊁䉞䉪䉴䈮䉋䉎 䊂䉱䉟䊮䋺ⶄว 㑐䈫㕖ᐔⴧ䉻䉟䊅䊚䉪䉴䇹 ᐔᚑ22ᐕᐲ ળ䇮2011ᐕ3 4ᣣ䇮 ੩ᄢቇᧄㇹ䉨䊞䊮䊌䉴 㗄 A02 ኒᐲ 㑐ᢙᴺℂ 䈮ၮ䈨䈒㕖ᐔⴧ 䊅䊉䉴䉬䊷䊦㔚 વዉ䉻䉟䊅䊚䉪䉴 ઍ ᄢᎿ ㆺ
 22201134 A02 GCOE Si device (further downsizing) Novel nanostructures (such as atomic chain) Nanoscale multi-terminal resistance measurement Carbon nanotube transistor Atomic switch Interplay:l Dynamics:
22201134 A02 GCOE Si device (further downsizing) Novel nanostructures (such as atomic chain) Nanoscale multi-terminal resistance measurement Carbon nanotube transistor Atomic switch Interplay:l Dynamics:
Lecture 4: CMOS Transistor Theory
 Introduction to CMOS VLSI Design Lecture 4: CMOS Transistor Theory David Harris, Harvey Mudd College Kartik Mohanram and Steven Levitan University of Pittsburgh Outline q Introduction q MOS Capacitor q
Introduction to CMOS VLSI Design Lecture 4: CMOS Transistor Theory David Harris, Harvey Mudd College Kartik Mohanram and Steven Levitan University of Pittsburgh Outline q Introduction q MOS Capacitor q
MOSFET. Id-Vd curve. I DS Transfer curve V G. Lec. 8. Vd=1V. Saturation region. V Th
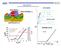 MOSFET Id-Vd curve Saturation region I DS Transfer curve Vd=1V V Th V G 1 0 < V GS < V T V GS > V T V Gs >V T & Small V D > 0 I DS WQ inv WC v WC i V V VDS V V G i T G n T L n I D g V D (g conductance
MOSFET Id-Vd curve Saturation region I DS Transfer curve Vd=1V V Th V G 1 0 < V GS < V T V GS > V T V Gs >V T & Small V D > 0 I DS WQ inv WC v WC i V V VDS V V G i T G n T L n I D g V D (g conductance
ELEC 3908, Physical Electronics, Lecture 23. The MOSFET Square Law Model
 ELEC 3908, Physical Electronics, Lecture 23 The MOSFET Square Law Model Lecture Outline As with the diode and bipolar, have looked at basic structure of the MOSFET and now turn to derivation of a current
ELEC 3908, Physical Electronics, Lecture 23 The MOSFET Square Law Model Lecture Outline As with the diode and bipolar, have looked at basic structure of the MOSFET and now turn to derivation of a current
ECE 546 Lecture 10 MOS Transistors
 ECE 546 Lecture 10 MOS Transistors Spring 2018 Jose E. Schutt-Aine Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Illinois jesa@illinois.edu NMOS Transistor NMOS Transistor N-Channel MOSFET Built on p-type
ECE 546 Lecture 10 MOS Transistors Spring 2018 Jose E. Schutt-Aine Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Illinois jesa@illinois.edu NMOS Transistor NMOS Transistor N-Channel MOSFET Built on p-type
Available online at ScienceDirect. Procedia Materials Science 11 (2015 )
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Materials Science 11 (2015 ) 287 292 5th International Biennial Conference on Ultrafine Grained and Nanostructured Materials, UFGNSM15 Tunneling
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Materials Science 11 (2015 ) 287 292 5th International Biennial Conference on Ultrafine Grained and Nanostructured Materials, UFGNSM15 Tunneling
ECE 305: Fall MOSFET Energy Bands
 ECE 305: Fall 2016 MOSFET Energy Bands Professor Peter Bermel Electrical and Computer Engineering Purdue University, West Lafayette, IN USA pbermel@purdue.edu Pierret, Semiconductor Device Fundamentals
ECE 305: Fall 2016 MOSFET Energy Bands Professor Peter Bermel Electrical and Computer Engineering Purdue University, West Lafayette, IN USA pbermel@purdue.edu Pierret, Semiconductor Device Fundamentals
Lecture 15: MOS Transistor models: Body effects, SPICE models. Context. In the last lecture, we discussed the modes of operation of a MOS FET:
 Lecture 15: MOS Transistor models: Body effects, SPICE models Context In the last lecture, we discussed the modes of operation of a MOS FET: oltage controlled resistor model I- curve (Square-Law Model)
Lecture 15: MOS Transistor models: Body effects, SPICE models Context In the last lecture, we discussed the modes of operation of a MOS FET: oltage controlled resistor model I- curve (Square-Law Model)
MOS Capacitor MOSFET Devices. MOSFET s. INEL Solid State Electronics. Manuel Toledo Quiñones. ECE Dept. UPRM.
 INEL 6055 - Solid State Electronics ECE Dept. UPRM 20th March 2006 Definitions MOS Capacitor Isolated Metal, SiO 2, Si Threshold Voltage qφ m metal d vacuum level SiO qχ 2 E g /2 qφ F E C E i E F E v qφ
INEL 6055 - Solid State Electronics ECE Dept. UPRM 20th March 2006 Definitions MOS Capacitor Isolated Metal, SiO 2, Si Threshold Voltage qφ m metal d vacuum level SiO qχ 2 E g /2 qφ F E C E i E F E v qφ
ECE 342 Electronic Circuits. Lecture 6 MOS Transistors
 ECE 342 Electronic Circuits Lecture 6 MOS Transistors Jose E. Schutt-Aine Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Illinois jesa@illinois.edu 1 NMOS Transistor Typically L = 0.1 to 3 m, W = 0.2
ECE 342 Electronic Circuits Lecture 6 MOS Transistors Jose E. Schutt-Aine Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Illinois jesa@illinois.edu 1 NMOS Transistor Typically L = 0.1 to 3 m, W = 0.2
Operation and Modeling of. The MOS Transistor. Second Edition. Yannis Tsividis Columbia University. New York Oxford OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS
 Operation and Modeling of The MOS Transistor Second Edition Yannis Tsividis Columbia University New York Oxford OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS CONTENTS Chapter 1 l.l 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 Chapter 2 2.1 2.2
Operation and Modeling of The MOS Transistor Second Edition Yannis Tsividis Columbia University New York Oxford OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS CONTENTS Chapter 1 l.l 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 Chapter 2 2.1 2.2
Chapter 6: Field-Effect Transistors
 Chapter 6: Field-Effect Transistors slamic University of Gaza Dr. Talal Skaik FETs vs. BJTs Similarities: Amplifiers Switching devices mpedance matching circuits Differences: FETs are voltage controlled
Chapter 6: Field-Effect Transistors slamic University of Gaza Dr. Talal Skaik FETs vs. BJTs Similarities: Amplifiers Switching devices mpedance matching circuits Differences: FETs are voltage controlled
Electrical Characteristics of MOS Devices
 Electrical Characteristics of MOS Devices The MOS Capacitor Voltage components Accumulation, Depletion, Inversion Modes Effect of channel bias and substrate bias Effect of gate oide charges Threshold-voltage
Electrical Characteristics of MOS Devices The MOS Capacitor Voltage components Accumulation, Depletion, Inversion Modes Effect of channel bias and substrate bias Effect of gate oide charges Threshold-voltage
Lecture 5: CMOS Transistor Theory
 Lecture 5: CMOS Transistor Theory Slides courtesy of Deming Chen Slides based on the initial set from David Harris CMOS VLSI Design Outline q q q q q q q Introduction MOS Capacitor nmos I-V Characteristics
Lecture 5: CMOS Transistor Theory Slides courtesy of Deming Chen Slides based on the initial set from David Harris CMOS VLSI Design Outline q q q q q q q Introduction MOS Capacitor nmos I-V Characteristics
HW 5 posted due in two weeks Lab this week Midterm graded Project to be launched in week 7
 HW 5 posted due in two weeks Lab this week Midterm graded Project to be launched in week 7 2 What do digital IC designers need to know? 5 EE4 EECS4 6 3 0< V GS - V T < V DS Pinch-off 7 For (V GS V T )
HW 5 posted due in two weeks Lab this week Midterm graded Project to be launched in week 7 2 What do digital IC designers need to know? 5 EE4 EECS4 6 3 0< V GS - V T < V DS Pinch-off 7 For (V GS V T )
P.Geetha, Dr.R.S.D.Wahida Banu.
 International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 5, Issue 5, MAY-2014 62 Performance Characterization of Capacitance Modeling for Carbon Nanotube MOSFET P.Geetha, Dr.R.S.D.Wahida Banu.
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 5, Issue 5, MAY-2014 62 Performance Characterization of Capacitance Modeling for Carbon Nanotube MOSFET P.Geetha, Dr.R.S.D.Wahida Banu.
Lecture 29 - The Long Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor (cont.) April 20, 2007
 6.720J/3.43J - Integrated Microelectronic Devices - Spring 2007 Lecture 29-1 Lecture 29 - The Long Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor (cont.) April 20, 2007 Contents: 1. Non-ideal and second-order
6.720J/3.43J - Integrated Microelectronic Devices - Spring 2007 Lecture 29-1 Lecture 29 - The Long Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor (cont.) April 20, 2007 Contents: 1. Non-ideal and second-order
MOS CAPACITOR AND MOSFET
 EE336 Semiconductor Devices 1 MOS CAPACITOR AND MOSFET Dr. Mohammed M. Farag Ideal MOS Capacitor Semiconductor Devices Physics and Technology Chapter 5 EE336 Semiconductor Devices 2 MOS Capacitor Structure
EE336 Semiconductor Devices 1 MOS CAPACITOR AND MOSFET Dr. Mohammed M. Farag Ideal MOS Capacitor Semiconductor Devices Physics and Technology Chapter 5 EE336 Semiconductor Devices 2 MOS Capacitor Structure
MOSFET Physics: The Long Channel Approximation
 MOSFET Physics: The ong Channel Approximation A basic n-channel MOSFET (Figure 1) consists of two heavily-doped n-type regions, the Source and Drain, that comprise the main terminals of the device. The
MOSFET Physics: The ong Channel Approximation A basic n-channel MOSFET (Figure 1) consists of two heavily-doped n-type regions, the Source and Drain, that comprise the main terminals of the device. The
Microsystems Technology Laboratories, MIT. Teledyne Scientific Company (TSC)
 Extraction of Virtual-Source Injection Velocity in sub-100 nm III-V HFETs 1,2) D.-H. Kim, 1) J. A. del Alamo, 1) D. A. Antoniadis and 2) B. Brar 1) Microsystems Technology Laboratories, MIT 2) Teledyne
Extraction of Virtual-Source Injection Velocity in sub-100 nm III-V HFETs 1,2) D.-H. Kim, 1) J. A. del Alamo, 1) D. A. Antoniadis and 2) B. Brar 1) Microsystems Technology Laboratories, MIT 2) Teledyne
The Gradual Channel Approximation for the MOSFET:
 6.01 - Electronic Devices and Circuits Fall 003 The Gradual Channel Approximation for the MOSFET: We are modeling the terminal characteristics of a MOSFET and thus want i D (v DS, v GS, v BS ), i B (v
6.01 - Electronic Devices and Circuits Fall 003 The Gradual Channel Approximation for the MOSFET: We are modeling the terminal characteristics of a MOSFET and thus want i D (v DS, v GS, v BS ), i B (v
Towards a Scalable EKV Compact Model Including Ballistic and Quasi-Ballistic Transport
 2011 Workshop on Compact Modeling Towards a Scalable EKV Compact Model Including Ballistic and Quasi-Ballistic Transport Christian Enz 1,2, A. Mangla 2 and J.-M. Sallese 2 1) Swiss Center for Electronics
2011 Workshop on Compact Modeling Towards a Scalable EKV Compact Model Including Ballistic and Quasi-Ballistic Transport Christian Enz 1,2, A. Mangla 2 and J.-M. Sallese 2 1) Swiss Center for Electronics
Research Article Analyses of Short Channel Effects of Single-Gate and Double-Gate Graphene Nanoribbon Field Effect Transistors
 Materials Volume 6, Article ID 84469, 8 pages http://dx.doi.org/.55/6/84469 Research Article Analyses of Short Channel Effects of Single-Gate and Double-Gate Graphene Nanoribbon Field Effect Transistors
Materials Volume 6, Article ID 84469, 8 pages http://dx.doi.org/.55/6/84469 Research Article Analyses of Short Channel Effects of Single-Gate and Double-Gate Graphene Nanoribbon Field Effect Transistors
Use of Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes for UV radiation detection
 Use of Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes for UV radiation detection Viviana Carillo 11th Topical Seminar on Innovative Particle and Radiation Detectors (IPRD08) 1-4 October 2008 Siena, Italy A new nanostructured
Use of Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes for UV radiation detection Viviana Carillo 11th Topical Seminar on Innovative Particle and Radiation Detectors (IPRD08) 1-4 October 2008 Siena, Italy A new nanostructured
doi: /
 doi: 10.1063/1.1840096 JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS 97, 034306 (2005) Characteristics of a carbon nanotube field-effect transistor analyzed as a ballistic nanowire field-effect transistor Kenji Natori, a)
doi: 10.1063/1.1840096 JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS 97, 034306 (2005) Characteristics of a carbon nanotube field-effect transistor analyzed as a ballistic nanowire field-effect transistor Kenji Natori, a)
! PN Junction. ! MOS Transistor Topology. ! Threshold. ! Operating Regions. " Resistive. " Saturation. " Subthreshold (next class)
 ESE370: ircuitlevel Modeling, Design, and Optimization for Digital Systems Lec 7: September 20, 2017 MOS Transistor Operating Regions Part 1 Today! PN Junction! MOS Transistor Topology! Threshold! Operating
ESE370: ircuitlevel Modeling, Design, and Optimization for Digital Systems Lec 7: September 20, 2017 MOS Transistor Operating Regions Part 1 Today! PN Junction! MOS Transistor Topology! Threshold! Operating
ECE 497 JS Lecture - 12 Device Technologies
 ECE 497 JS Lecture - 12 Device Technologies Spring 2004 Jose E. Schutt-Aine Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Illinois jose@emlab.uiuc.edu 1 NMOS Transistor 2 ρ Source channel charge density
ECE 497 JS Lecture - 12 Device Technologies Spring 2004 Jose E. Schutt-Aine Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Illinois jose@emlab.uiuc.edu 1 NMOS Transistor 2 ρ Source channel charge density
Part 4: Heterojunctions - MOS Devices. MOSFET Current Voltage Characteristics
 MOS Device Uses: Part 4: Heterojunctions - MOS Devices MOSCAP capacitor: storing charge, charge-coupled device (CCD), etc. MOSFET transistor: switch, current amplifier, dynamic random access memory (DRAM-volatile),
MOS Device Uses: Part 4: Heterojunctions - MOS Devices MOSCAP capacitor: storing charge, charge-coupled device (CCD), etc. MOSFET transistor: switch, current amplifier, dynamic random access memory (DRAM-volatile),
Semiconductor Physics Problems 2015
 Semiconductor Physics Problems 2015 Page and figure numbers refer to Semiconductor Devices Physics and Technology, 3rd edition, by SM Sze and M-K Lee 1. The purest semiconductor crystals it is possible
Semiconductor Physics Problems 2015 Page and figure numbers refer to Semiconductor Devices Physics and Technology, 3rd edition, by SM Sze and M-K Lee 1. The purest semiconductor crystals it is possible
ECE 305 Exam 5 SOLUTIONS: Spring 2015 April 17, 2015 Mark Lundstrom Purdue University
 NAME: PUID: : ECE 305 Exam 5 SOLUTIONS: April 17, 2015 Mark Lundstrom Purdue University This is a closed book exam. You may use a calculator and the formula sheet at the end of this exam. Following the
NAME: PUID: : ECE 305 Exam 5 SOLUTIONS: April 17, 2015 Mark Lundstrom Purdue University This is a closed book exam. You may use a calculator and the formula sheet at the end of this exam. Following the
Lecture 28 - The Long Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor (cont.) April 18, 2007
 6.720J/3.43J - Integrated Microelectronic Devices - Spring 2007 Lecture 28-1 Lecture 28 - The Long Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor (cont.) April 18, 2007 Contents: 1. Second-order and
6.720J/3.43J - Integrated Microelectronic Devices - Spring 2007 Lecture 28-1 Lecture 28 - The Long Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor (cont.) April 18, 2007 Contents: 1. Second-order and
MOSFET Model with Simple Extraction Procedures, Suitable for Sensitive Analog Simulations
 ROMANIAN JOURNAL OF INFORMATION SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY Volume 10, Number 2, 2007, 189 197 MOSFET Model with Simple Extraction Procedures, Suitable for Sensitive Analog Simulations S. EFTIMIE 1, ALEX. RUSU
ROMANIAN JOURNAL OF INFORMATION SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY Volume 10, Number 2, 2007, 189 197 MOSFET Model with Simple Extraction Procedures, Suitable for Sensitive Analog Simulations S. EFTIMIE 1, ALEX. RUSU
Electrical Characteristics of Multilayer MoS 2 FET s
 Electrical Characteristics of Multilayer MoS 2 FET s with MoS 2 /Graphene Hetero-Junction Contacts Joon Young Kwak,* Jeonghyun Hwang, Brian Calderon, Hussain Alsalman, Nini Munoz, Brian Schutter, and Michael
Electrical Characteristics of Multilayer MoS 2 FET s with MoS 2 /Graphene Hetero-Junction Contacts Joon Young Kwak,* Jeonghyun Hwang, Brian Calderon, Hussain Alsalman, Nini Munoz, Brian Schutter, and Michael
Available online at ScienceDirect. Procedia Materials Science 11 (2015 )
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Materials Science 11 (2015 ) 407 411 5th International Biennial Conference on Ultrafine Grained and Nanostructured Materials, FGNSM15 Simulation
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Materials Science 11 (2015 ) 407 411 5th International Biennial Conference on Ultrafine Grained and Nanostructured Materials, FGNSM15 Simulation
Projected Performance Advantage of Multilayer Graphene Nanoribbon as Transistor Channel Material
 Projected Performance Advantage of Multilayer Graphene Nanoribbon as Transistor Channel Material Yijian Ouyang 1, Hongjie Dai 2, and Jing Guo 1 1 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University
Projected Performance Advantage of Multilayer Graphene Nanoribbon as Transistor Channel Material Yijian Ouyang 1, Hongjie Dai 2, and Jing Guo 1 1 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University
Erik Lind
 High-Speed Devices, 2011 Erik Lind (Erik.Lind@ftf.lth.se) Course consists of: 30 h Lectures (H322, and Fys B check schedule) 8h Excercises 2x2h+4h Lab Excercises (2 Computer simulations, 4 RF measurment
High-Speed Devices, 2011 Erik Lind (Erik.Lind@ftf.lth.se) Course consists of: 30 h Lectures (H322, and Fys B check schedule) 8h Excercises 2x2h+4h Lab Excercises (2 Computer simulations, 4 RF measurment
Supporting information
 Supporting information Design, Modeling and Fabrication of CVD Grown MoS 2 Circuits with E-Mode FETs for Large-Area Electronics Lili Yu 1*, Dina El-Damak 1*, Ujwal Radhakrishna 1, Xi Ling 1, Ahmad Zubair
Supporting information Design, Modeling and Fabrication of CVD Grown MoS 2 Circuits with E-Mode FETs for Large-Area Electronics Lili Yu 1*, Dina El-Damak 1*, Ujwal Radhakrishna 1, Xi Ling 1, Ahmad Zubair
Lecture 9 MOSFET(II) MOSFET I V CHARACTERISTICS(contd.)
 Lecture 9 MOSFET(II) MOSFET I V CHARACTERISTICS(contd.) Outline 1. The saturation region 2. Backgate characteristics Reading Assignment: Howe and Sodini, Chapter 4, Section 4.4 6.012 Spring 2009 Lecture
Lecture 9 MOSFET(II) MOSFET I V CHARACTERISTICS(contd.) Outline 1. The saturation region 2. Backgate characteristics Reading Assignment: Howe and Sodini, Chapter 4, Section 4.4 6.012 Spring 2009 Lecture
ECE 340 Lecture 39 : MOS Capacitor II
 ECE 340 Lecture 39 : MOS Capacitor II Class Outline: Effects of Real Surfaces Threshold Voltage MOS Capacitance-Voltage Analysis Things you should know when you leave Key Questions What are the effects
ECE 340 Lecture 39 : MOS Capacitor II Class Outline: Effects of Real Surfaces Threshold Voltage MOS Capacitance-Voltage Analysis Things you should know when you leave Key Questions What are the effects
A Numerical Study of Scaling Issues for Schottky Barrier Carbon Nanotube Transistors
 A Numerical Study of Scaling Issues for Schottky Barrier Carbon Nanotube Transistors Jing Guo, Supriyo Datta and Mark Lundstrom School of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Purdue University, West Lafayette,
A Numerical Study of Scaling Issues for Schottky Barrier Carbon Nanotube Transistors Jing Guo, Supriyo Datta and Mark Lundstrom School of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Purdue University, West Lafayette,
Lecture 15 OUTLINE. MOSFET structure & operation (qualitative) Review of electrostatics The (N)MOS capacitor
 Lecture 15 OUTLINE MOSFET structure & operation (qualitative) Review of electrostatics The (N)MOS capacitor Electrostatics t ti Charge vs. voltage characteristic Reading: Chapter 6.1 6.2.1 EE105 Fall 2007
Lecture 15 OUTLINE MOSFET structure & operation (qualitative) Review of electrostatics The (N)MOS capacitor Electrostatics t ti Charge vs. voltage characteristic Reading: Chapter 6.1 6.2.1 EE105 Fall 2007
Random Telegraph Signal in Carbon Nanotube Device
 Random Telegraph Signal in Carbon Nanotube Device Tsz Wah Chan Feb 28, 2008 1 Introduction 1. Structure of Single-walled Carbon Nanotube (SWCNT) 2. Electronic properties of SWCNT 3. Sample preparation:
Random Telegraph Signal in Carbon Nanotube Device Tsz Wah Chan Feb 28, 2008 1 Introduction 1. Structure of Single-walled Carbon Nanotube (SWCNT) 2. Electronic properties of SWCNT 3. Sample preparation:
ELEC 3908, Physical Electronics, Lecture 26. MOSFET Small Signal Modelling
 ELEC 3908, Physical Electronics, Lecture 26 MOSFET Small Signal Modelling Lecture Outline MOSFET small signal behavior will be considered in the same way as for the diode and BJT Capacitances will be considered
ELEC 3908, Physical Electronics, Lecture 26 MOSFET Small Signal Modelling Lecture Outline MOSFET small signal behavior will be considered in the same way as for the diode and BJT Capacitances will be considered
! CMOS Process Enhancements. ! Semiconductor Physics. " Band gaps. " Field Effects. ! MOS Physics. " Cut-off. " Depletion.
 ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 4: January 3, 018 MOS Transistor Theory, MOS Model Lecture Outline! CMOS Process Enhancements! Semiconductor Physics " Band gaps " Field Effects!
ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 4: January 3, 018 MOS Transistor Theory, MOS Model Lecture Outline! CMOS Process Enhancements! Semiconductor Physics " Band gaps " Field Effects!
Projected Performance Advantage of Multilayer Graphene Nanoribbons as a Transistor Channel Material
 1Nano Res (2010) 3: 8 15 DOI 10.1007/s12274-010-1002-8 Research Article Projected Performance Advantage of Multilayer Graphene Nanoribbons as a Transistor Channel Material Yijian Ouyang 1 ( ), Hongjie
1Nano Res (2010) 3: 8 15 DOI 10.1007/s12274-010-1002-8 Research Article Projected Performance Advantage of Multilayer Graphene Nanoribbons as a Transistor Channel Material Yijian Ouyang 1 ( ), Hongjie
CARBON NANOTUBE ELECTRONICS: MODELING, PHYSICS, AND APPLICATIONS. A Thesis. Submitted to the Faculty. Purdue University. Jing Guo
 0 CARBON NANOTUBE ELECTRONICS: MODELING, PHYSICS, AND APPLICATIONS A Thesis Submitted to the Faculty of Purdue University by Jing Guo In Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of Doctor
0 CARBON NANOTUBE ELECTRONICS: MODELING, PHYSICS, AND APPLICATIONS A Thesis Submitted to the Faculty of Purdue University by Jing Guo In Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of Doctor
JFET/MESFET. JFET: small gate current (reverse leakage of the gate-to-channel junction) More gate leakage than MOSFET, less than bipolar.
 JFET/MESFET JFET: small gate current (reverse leakage of the gate-to-channel junction) More gate leakage than MOSFET, less than bipolar. JFET has higher transconductance than the MOSFET. Used in low-noise,
JFET/MESFET JFET: small gate current (reverse leakage of the gate-to-channel junction) More gate leakage than MOSFET, less than bipolar. JFET has higher transconductance than the MOSFET. Used in low-noise,
MOS Transistor Theory
 CHAPTER 3 MOS Transistor Theory Outline 2 1. Introduction 2. Ideal I-V Characteristics 3. Nonideal I-V Effects 4. C-V Characteristics 5. DC Transfer Characteristics 6. Switch-level RC Delay Models MOS
CHAPTER 3 MOS Transistor Theory Outline 2 1. Introduction 2. Ideal I-V Characteristics 3. Nonideal I-V Effects 4. C-V Characteristics 5. DC Transfer Characteristics 6. Switch-level RC Delay Models MOS
R. Ludwig and G. Bogdanov RF Circuit Design: Theory and Applications 2 nd edition. Figures for Chapter 6
 R. Ludwig and G. Bogdanov RF Circuit Design: Theory and Applications 2 nd edition Figures for Chapter 6 Free electron Conduction band Hole W g W C Forbidden Band or Bandgap W V Electron energy Hole Valence
R. Ludwig and G. Bogdanov RF Circuit Design: Theory and Applications 2 nd edition Figures for Chapter 6 Free electron Conduction band Hole W g W C Forbidden Band or Bandgap W V Electron energy Hole Valence
