B I O L O G Y CLASS XI. dher%` Book Code : 8999 ISBN :
|
|
|
- Rosalyn Lynch
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1
2 thofokku B I O L O G Y CLASS XI Book Code : 8999 ISBN : dher%`
3 thofokku B I O L O G Y CLASS XI Strictly according to the latest syllabus prescribed by Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE), Delhi and State Boards of Jharkhand, Uttarakhand, Rajasthan and Other States & Navodaya, Kendriya Vidyalayas etc. following CBSE curriculum based on NCERT guidelines MkW-vks-ih-lDlsuk ih&,p-mh-],q-,-tsm-],q-,-vkbz-],q-,-bz-ch-],q-vkbz-,q-,l-vkbz-],q-,-,q-,l-(fqyhihul) iwoz izksisglj,oa v/;{k]izkf.kfokkufohkx eqyrkuheyeksnh(ikslv&xzstq,v)dkwyst]eksnhuxj [ iwoz la;kstd]cksmz vkwqlvmht]fjlpz fmxzhdesvh] pks-pj.kflagfo'ofo ky;]esjb] rfkhkwriwoz Lis'kyQkWjsufoftfVaxizksisGlj]tkiku es?kcaly
4 Syllabus Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE), Delhi BIOLOGY XI One Paper Three Hours Max. Marks : 70 Marks Unit Title Marks 1. Diversity of Living Organisms Structural Organisation in Plants and Animals Cell : Structure and Function Plant Physiology Human Physiology 18 Total 70 Unit I : Diversity of Living Organisms : (25 Periods) What is living? Biodiversity; Need for classification; Three domains of life; Taxonomy & Systematics; Concept of species and taxonomical hierarchy; Binomial nomenclature; Tools for study of Taxonomy Museums, Zorogical Parks, Herbaria, Botanical gardens. Five kingdom classification; Salient features and classification of Monera; Protista and Fungi into major groups; Lichens; Viruses and Viroids. Salient features and classification of plants into major groups-algae, Bryophyta, Pteridophyta, Gymnospermae and Angiospermae (three to five salient and distinguising features and at least two examples of each category); Angiosperms-classification up to class, characteristic features and examples. Salient features and classification of animals-non chordate up to phyla level and chordates up to classes level (three of five salient features and at least two examples). Unit II : Structural Organisation in Plants and Animals : (25 Periods) Morphology and modifications; Tissues; Anatomy and functions of different parts of flowering plants: Root, stem, leaf, inflorescence-cymose and racemose, flower, fruit and seed (To be dealt along with the relevant practical of the Practical Syllabus.) Animal tissues; Morphology, anatomy and functions of different systems (digestive, circulatory, respiratory, nervous and reproductive) of an insect (cockroach). (a brief account only) Unit III : Cell : Structure and Function : (40 Periods) Cells theory and cell as the basic unit of life; Structure of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells; Plant cell and animal cell; Cell envelope, cell membrane, cell wall; Cell organelles-structure and function; Endomembrane systemendoplasmic reticulum, Golgi bodies, lysosomes, vacuoles; mitochondria, ribosomes, plastids, microbodies; Cytoskeleton, cilia, flagella, centrioles (ultra structure and function); Nucleus-nuclear membrane, chromatin, nucleolus. Chemical constituents of living cells; Biomolecules-structure and function of proteins, carbodydrates, lipids, nucleic acids, Enzymes-types, properties, enzymes action. Cell division : Cell cycle, mitosis, meiosis and their significance. Unit IV : Plant Physiology : (45 Periods) Transport in plants; Movement of water, gases and nutrients; Cell to cell transport-diffusion, facilitated diffusion, active transport; Plant-water relations-imbibition, water potential, osmosis, plasmolysis; Long distance transport of water-absorption, apoplast, symplast, transpiration pull, root pressure and guttation; Transpiration-Opening and closing of stomata; Uptake and translocation of mineral nutrients-transport of food, phloem transport, Mass flow hypothesis; Diffusion of gases.
5 (ii) Mineral nutrition : Essential minerals, macro and micronutrients and their role; Deficiency symptoms; Mineral toxicity; elementary idea of Hydroponics as a method to study mineral nutrition; Nitrogen metabolism-nitrogen cycle, biological nitrogen fixation. Photosynthesis : Photosynthesis as a means of Autotrophic nutrition; pigments involved in Photosynthesis (Elementary idea); Photochemical and biosynthetic phases of photosynthesis; Cyclic and non cyclic photophosphorylation; Chemiosmotic hypothesis; Photorespiration; C3 and C4 pathways; factors affecting photosynthesis. Respiration : Exchange of gases; Cellular respiration - glycolysis, fermentation (anaerobic), TCA cycle and electron transport system (aerobic); Energy relations-number of ATP molecules generated; Amphibolic pathways; Respiratroy quotient. Plant growth and development : Seed germination; Phase of plant growth and plant growth rate; Conditions of growth; Differentiation, dedifferentiation and redifferentiation; sequence of developmental process in a plant cell; Growth regulators-auxin, gibberellin, cytokinin, ethylene, ABA; Seed dormancy; Vernalisation: Photoperiodism. Unit V : Human Physiology : (45 Periods) Digestion and absorption: Alimentary canal and digestive glands, Role of digestive enzymes and gastrointestinal hormones; Peristalsis, digestion, absorption and assimilation of proteins, carbohydrates and fats; Calorific value of proteins, carbohydrates and fats; Egestion; Nutritional and digestive disorders-pem, indigestion, constipation, vomiting, jaundice, diarrhoea. Breathing and Respiration: Respiratory organs in animals (recall only); Respiratory system in humans; Mechanism of breathing and its regulation in humans-exchange of gases, transport of gases and regulation of respiration, Respiratory volume. Disorders related to respiration-asthama, Emphysema, Occupational respiratory disorders. Body fluids and circulation: Composition of blood, blood groups, coagulation of blood; Composition of lymph and its function; Human circulatory system- Structure of human heart and blood vessels; Cardiac cycle, cardiac output, ECG; Double circulation; Regulation of cardiac activity; Disorders of circulatory system-hypertension, Coronary artery disease, Angina pectoris, Heart failure. Excretory products and their elimination: Modes of excretion-ammonotelism, ureotelism, uricotelism; Human excretory system-structure and function; Urine formation, Osmoregulation; Regulation of kidney function-renin-angiotensin, Atrial Natriuretic Factor, ADH and Diabetes insipidus; Role of other organs in excretion; Disorders-Uraemia, Renal failure, Renal calculi, Nephritis; Dialysis and artificial kidney. Locomotion and Movement: Types of movement-ciliary, flagellar, muscular; Skeletal muscle-contractile proteins and muscle contraction; Skeletal system and its functions Joints; Disorders of muscular and skeletal system-myasthenia gravis, Tetany, Muscular dystrophy, Arthritis, Osteoporosis, Gout. Neural control and coordination: Neuron and nerves; Nervous system in humans-central nervous system & peripheral nervous system and visceral nervous system; Generation and conduction of nerve impulse; Reflex action; Sensory perception; Sense organs; Elementary structure and function of eye and ear. Chemical coordination and regulation: Endocrine glands and hormones; Human endocrine system-hypothalamus, Pituitary, Pineal, Thyroid, Parathyroid, Adrenal, Pancreas, Gonads; Mechanism of hormone action (Elementary Idea); Role of hormones as messengers and regulators, Hypo-and hyperactivity and related disorders Dwarfism, Acromegaly, Cretinism, goite, exophthalmic goiter, diabetes, Addision's disease). Note : Diseases related to all the human physiology systems (to be taught in brief).
6 (iii) One Paper Three Hours Max. Marks : 70 Marks Unit Title Marks 1. Diversity in Living World Structural Organization in animals and plants Cell : Structure and Function Plant Physiology Human Physiology 18 Total 70 Unit-I : Diversity in Living World : (25 Periods) Diversity of living organisms. Classification of the living organisms (five kingdom classification, major groups and principles of classification within each kingdom). Systematics and binomial system of nomenclature. Salient features of animal (non chordates up to phylum level, and chordates up to class level) and plant (major groups : Angiosperms up to subclass) classification. Botanical gardens, herbaria, zoological parks and museums. Unit-II : Structural Organisation in Animals and Plants : (30 Periods) Tissues in animals and plants Morphology, anatomy and functions of different parts of flowering plants : Root, stem, leaf, inflorensence, flower, fruit and seed. Morphology, anatomy and functions of different systems of an annelid (earthworm), an insect (cockroach) and an amphibian (frog.) Unit-III : Cell : Structure and Function : (40 Periods) Cell : Cell wall, cell membrane and cell organelles (plastids, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi bodies/dictyosomes, ribosomes, lysosomes, vacuoles, centrioles) and nuclear organisation. Mitosis, meiosis, cell cycle. Basic chemical constituents of living bodies. Structure and functions of carbohydrates, proteins, lipids and nucleic acids. Enzymes : Types, properties and function. Unit-IV : Plant Physiology : (40 Periods) Movement of water, food, nutrients and gases. Plants and Water : Mineral nutrition Respiration Photosynthesis Plant growth and development Unit-V : Human Physiology : (45 Periods) Digestion and absorption Breathing and respiration Body fluids and circulation Excretory products and elimination Locomotion and movement control and coordination. l
7 v/;k; fo"k;&lwph ì"bla[;k 1. lthotxr~ 1 14 [The Living World] thofokku]lthod;kgs\]thotxresa fofo/krk]ofxzdh]thoksa dkukedj.k]ofxzdhlaoxz]ofxzdhlgk;rk lk/ku]ofxzdhdqath]lej.kh;fcunq],u-lh-bz-vkj-vh-dkwuzj]izfr;ksxhijh{kifjf'k"v]vo/kj.krediz'u,oa muosgmÿkj]vh;kliz'u]mpplrjh;cqfºdks'kyiz'u&mÿkj@laosgrlfgra 2. thotxr~ dkoxhzdj.k [Classification of Living Beings] oxhzdj.kds ykhk]oxhzdj.kds izdkj]tho/kfj;ksa dhf}&txr~ oxhzdj.kiz.kyh]tho/kfj;ksa dkik ptxr~ oxhzdj.k]ik ptho&txr~ oxhzdj.kds vk/kjh;y{k.k]eksusjktxr~]izksfvlvktxr~]txr~%dod]dod&lw=ksa ds leqpp;%fo'ks"kdodjpuk, ]'ksd]fo"k.kq]lej.kh;fcunq],u-lh-bz-vkj-vh-dkwuzj]izfr;ksxhijh{kifjf'k"v] 3. oulifrtxr~ [Plant Kingdom] 'ksoky]czk;ksqkbvk]vsfjmksqkbvk]chthikni]iknithou&pÿrfkih<+h,dkurj.k]lej.kh;fcunq],u-lh-bzvkj-vh-dkwuzj]izfr;ksxhijh{kifjf'k"v]vo/kj.krediz'u,oa muosgmÿkj]vh;kliz'u]mpplrjh;cqfº dks'kyiz'u&mÿkj@laosgrlfgra 4. izkf.ktxr~ [Animal Kingdom] turqvksa ds izeq[kvfhky{k.k]turq lajpukiz.kyh]'kjhjdhlefefr]nsgxqgk;klhykse]nsg[k.mh&hkou]'kjhjdk vk/kj,oa lqj{k]turq fofo/krk]vd'ks#fd;ksa dkoxhzdj.k]dkwmszv~l(ì"boa'kh)turqvksa dkoxhzdj.k]oxz 1 :,EQhfc;k]oxZ 2 : jsivhfy;kvfkzr~ ljhlì]oxz 3 : i{khvfkzr~,oht]oxz 4 : esesfy;kvfkoklruh]lej.kh; fcunq],u-lh-bz-vkj-vh-dkwuzj]izfr;ksxhijh{kifjf'k"v]vo/kj.krediz'u,oa muosgmÿkj]vh;kliz'u]mpp Lrjh;cqfºdkS'kyiz'u&mŸkj@laosGrlfgrA 5. iq"ihikniksa dhvkdkfjdh [Morphology of Flowering Plants] ewy]ruk]lrehkoewyesa vurj]i.kz]iq"iÿe]iq"i]qy]qyksa ds izdkj]cht]qyksa ochtksa dkizdh.kzu]lej.kh; fcunq],u-lh-bz-vkj-vh-dkwuzj]izfr;ksxhijh{kifjf'k"v]vo/kj.krediz'u,oa muosgmÿkj]vh;kliz'u]mpp Lrjh;cqfºdkS'kyiz'u&mŸkj@laosGrlfgrA 6. iq"ihikniksa dh'kjhfjdh [Anatomy of Flowering Plants] rd]i. fohkt;ksrdh rd]ii. LFk;h rd_lk/kj.k rd]tfvy rd]fof'k"v rd] rdru=]vf/kpez rdru=]hkj.k rdru=]laogu rdru=]ewyksa dhvkurfjdlajpuk]lrehkdhvkurfjdlajpuk]f}chti=h
8 v/;k; (ii) ì"b&la[;k LrEHk]f}chti=hruksa esa f}rh;dòfº]f}chti=hewyksa esa f}rh;dòfº]laogu,/kdkfuekz.kvksjfÿ;k'khyrk]?kodkhkjuk]foyxu%ir>m+ ;ki.kz ikru]ifÿk;k %vkurfjdlajpuk]f}ì"bh;kf}ì"b/kjhiÿkh]lej.kh;fcunq],u-lh-bz-vkj-vh-dkwuzj]izfr;ksxhijh{kifjf'k"v]vo/kj.krediz'u,oa muosgmÿkj]vh;kliz'u]mpplrjh; 7. izkf.k;ksa esa lajpukredlaxbu [Structural Organization in Animals] rd] rdksa ds izdkjµ1. midyk]2. la;ksth rd]3. is'kh; rd]4. rfu=dk rd]vd'ks#dhizkf.k;ksa dk thou&bfrgkl%1. dsapqvk]2. fryfpv~vk]3. esa<d]lej.kh;fcunq],u-lh-bz-vkj-vh-dkwuzj]izfr;ksxhijh{k ifjf'k"v] 8. dksf'kdk%lajpukred,oa dk;kzredbdkbz [Cell : Structural and Functional Unit] dksf'kdkvksa dkvkdkj,oa vkœfr]dksf'kdkls lecfu/krizeq[k[kstsa]dksf'kdkflºkur]izksosgfj;ksfvd,oa ;wosgfj;ksfvdksf'kdk, dksf'kdkfhkfÿk]dksf'kdkf>yyh]dksf'kdh;vo;oksa dhlajpuk,oa dk;z]thoêo;]dsuêd] Lej.kh;fcUnq],u-lh-bZ-vkj-Vh-dkWuZj]izfr;ksxhijh{kifjf'k"V]vo/kj.kRediz'u,oa muosgmÿkj]vh;kl iz'u]mpplrjh;cqfºdks'kyiz'u&mÿkj@laosgrlfgra 9. tsov.kq [Biomolecules] dksf'kdh;dq.m]ljy(y?kq)tsov.kq,oa ògn~ tsov.kq]dkckszgkbm sm%lsdsjkbm~l]olk,,oa fyfim~l]vehuks vey]u;wfdyvksvkbm]izksvhul]fodj%tso&mrizsjd]lej.kh;fcunq],u-lh-bz-vkj-vh-dkwuzj]izfr;ksxhijh{k ifjf'k"v] 10. dksf'kdkpÿ,oa dksf'kdkfohktu [Cell Cycle and Cell Division] ekbvksflvfkoklw=hfohktu]fe;ksflvfkokvºzlw=hfohktu]eks;ksflvfkokvºzlw=hfohktu]lej.kh; fcunq],u-lh-bz-vkj-vh-dkwuzj]izfr;ksxhijh{kifjf'k"v]vo/kj.krediz'u,oa muosgmÿkj]vh;kliz'u]mpp Lrjh;cqfºdkS'kyiz'u&mŸkj@laosGrlfgrA 11. iks/ksa esa ifjogu [Transportation in Plants] ikni&tylecu/k]folj.k]ijklj.k]thoêo;dqapu]vur%pw"k.k;kvur%'ks"k.k]jlkjksg.k]ok"iksrltzu]lej.kh; fcunq],u-lh-bz-vkj-vh-dkwuzj]izfr;ksxhijh{kifjf'k"v]vo/kj.krediz'u,oa muosgmÿkj]vh;kliz'u]mpp Lrjh;cqfºdkS'kyiz'u&mŸkj@laosGrlfgrA 12. iks/ksa esa [kfutiks"k.k [Mineral Nutrition in Plants] [kfutrroksa dhvko';drk][kfutrroksa ds lkeku;dk;z]vfuok;z rroksa ds dk;z][kfutyo.ksa dkvo'ks"k.k% lfÿ;ofuf"ÿ;]iks/ksa esa ukbv kstuiks"k.k]xzfufkfuekz.k]tsfodukbv kstuflfkjhdj.kdhfof/k]vehuks veydk la'ys"k.k][k inkfks± dklfkukurj.k]lej.kh;fcunq],u-lh-bz-vkj-vh-dkwuzj]izfr;ksxhijh{kifjf'k"v]
9 v/;k; (iii) ì"b&la[;k 13. mppikniksa esa izdk'k&la'ys"k.k [Photosynthesis in Higher Plants] izdk'k&la'ys"khfÿ;kfof/k]izdk'k'olu]izdk'k'olu,oa vizdkf'kd'olu]izdk'k&la'ys"k.kdks izhkfor djus okys dkjd]iz;ksxkredk;z]lej.kh;fcunq],u-lh-bz-vkj-vh-dkwuzj]izfr;ksxhijh{kifjf'k"v] 14. ikniksa esa 'olu [Respiration in Plants],-Vh-ih-(,sMhuksfluV kbqklqsv)]'oluvksjnguesa vurj]'oluds izdkj]'oludhfÿ;kfof/k]bysdv kwu ifjoguds in]ikb#fodveydkvok;oh;vkwdlhdj.k]fd.ou]fd.ouovukwdlh'oludhrqyuk]'olu xq.kad]'oludks izhkfordjus okys dkjd]'olufÿ;kls lecfu/kriz;ksx]lej.kh;fcunq],u-lh-bz-vkj-vhdkwuzj]izfr;ksxhijh{kifjf'k"v]vo/kj.krediz'u,oa muosgmÿkj]vh;kliz'u]mpplrjh;cqfºdks'ky 15. ikniòfº,oa ifjo/kzu [Growth and Development in Plants] òfºdhizkolfk, ]òfºekiu]òfºfu;u=d;kiknigkwekszul]gkwekszulds izdkj]iks/ksa esa iq"iu]nhfirdkfyrk] olurhdj.k]izdk'k&lajpukfodkl]lej.kh;fcunq],u-lh-bz-vkj-vh-dkwuzj]izfr;ksxhijh{kifjf'k"v]vh;kl 16. ikpu,oa vo'ks"k.k [Digestion and Absorption] iks"kdrro]ekuoikpuru=]euq";dhikpufÿ;k]hkstudkvo'ks"k.k]lokaxhdj.k]lurqfyrhkstu]lqiks"k.k] dqiks"k.krfkviks"k.k]vfriks"k.kds ifj.ke]lej.kh;fcunq],u-lh-bz-vkj-vh-dkwuzj]izfr;ksxhijh{kifjf'k"v] 'oluvksjxslksa dkfofue; [Respiration and Gaseous Exchange] 'olu]œf=e'olu]'oluru=ds fodkj]lej.kh;fcunq],u-lh-bz-vkj-vh-dkwuzj]izfr;ksxhijh{kifjf'k"v] 18. 'kjhjêodkifjlapj.k [Circulation of Body Fluid] rdhifjhk"k]ifjoguru=ds lkeku;y{k.k]ifjoguru=ds izdkj](a) jdr(#f/kj)]jdrk.kq]ekuoesa jdr lewg](b) n;](c) jdrokfgfu;k ]/keuhvksjf'kjkesa vurj] n;dh/km+dudkfu;u=.k] n;pÿ]/keuhru=] f'kjkru=]dqnlkeku; n;jksx]lej.kh;fcunq],u-lh-bz-vkj-vh-dkwuzj]izfr;ksxhijh{kifjf'k"v] 19. mrlthz mrikn,oa mudkfu"dklu [Excretory Products and their Excretion] mrltzu]izeq[kmrlthz mrikn]vd'ks#fd;ksa esa mrltzuvax]ekuomrltzuru=]òdd;kxqnsz ds dk;z]mrltzudh fÿ;kfof/k,oa ew=fuekz.k]òddesa ew=fuekz.k,oa mldkmrltzu]mrltzuesa vu;vaxksa dhhkwfedk]ekuoesa mrltzu
10 v/;k; (iv) ì"b&la[;k lecu/khfoœfr;k ]òddksa }kjkijklj.kfu;u=.k]lej.kh;fcunq],u-lh-bz-vkj-vh-dkwuzj]izfr;ksxhijh{k ifjf'k"v] 20. xfr,oa izpyu [Locomotion and Movement] izpyudkegro]vd'ks#fd;ksa esa izpyu]ekuodadky]fofhkuud'ks#dkvksa dhfo'ks"krk,oa jpukdkv/;u] d'ks#dn.mds dk;z]tksm+ vales[kykrfkgk;dhvflfk;k ]Jksf.k&es[kykrFkiSjdhvfLFk;k ;klaf/k;k ] ek lisf'k;k ]ykyrfk'osris'khrarq]lej.kh;fcunq],u-lh-bz-vkj-vh-dkwuzj]izfr;ksxhijh{kifjf'k"v] 21. raf=dh;fu;u=.k,oa leuo; [Nervous Control and Co-ordination] raf=dkra=ds Hkx]U;wjkWudkfÿ;kRedlaxBu]U;wjkWUlds izdkj]dsuêh;raf=dkra=]lok;ÿkraf=dkra=]ifj/kh; raf=dkra=]izfrorhz fÿ;k]izfrorhz pki]raf=dkvkosxdhizœfr]vurjkraf=dh;mìhiulapj.k]la;qxeuij vkosxdklapkj.k]laosnhvax@laosnkax]lej.kh;fcunq],u-lh-bz-vkj-vh-dkwuzj]izfr;ksxhijh{kifjf'k"v] 22. jklk;fudleuo;rfk,dhdj.k [Chemical Co-ordinations and Controlling] xzaffk;ksa ds izdkj]gkwekszul]euq";dhvur%úkohxzaffk;k ](A) ih;w"kxzfufkvfkzr~ fiv~;wvjhckwmh] (B) Fk;jkWbMxzfUFk](C) isjkfk;jkwbmxzfufk](d) vf/kòddvfkzr~,m huyxzfufk](e) FkbelxzfUFk]Lej.kh; fcunq],u-lh-bz-vkj-vh-dkwuzj]izfr;ksxhijh{kifjf'k"v]vo/kj.krediz'u,oa muosgmÿkj]vh;kliz'u]mpp Lrjh;cqfºdkS'kyiz'u&mŸkj@laosGrlfgrA ijh{kiz'u&i= [Examinations Paper] (i)
11 Biology Class XIth 30% OFF Publisher : Sbpd Publications ISBN : Author : Dr.O P Saxena,Megha Bansal Type the URL : Get this ebook
BIRLA VIDYAMANDIR, NAINITAL Syllabus for Annual Examination 2017 Class 11 ENGLISH MATHEMATICS
 1. Notice writing 2. Letter to editor writing 3. Article writing 4. Childhood 5. Father To Son 6. The Ailing Planet 7. Discovering Tut: The Saga Continues 8. Albert Einstein At School 9. Birth 10. The
1. Notice writing 2. Letter to editor writing 3. Article writing 4. Childhood 5. Father To Son 6. The Ailing Planet 7. Discovering Tut: The Saga Continues 8. Albert Einstein At School 9. Birth 10. The
MONTHLY SYLLABUS SESSION CLASS-XI SUBJECT : BIOLOGY FIRST-TERM APRIL 2017 TO SEPTEMBER
 MONTHLY SYLLABUS SESSION-2017-18 CLASS-XI SUBJECT : BIOLOGY FIRST-TERM APRIL 2017 TO SEPTEMBER - 2017 MONTH July 2017 CONTENTS Orientation and Recapitulation :-Discussion on importance of Biology, scope
MONTHLY SYLLABUS SESSION-2017-18 CLASS-XI SUBJECT : BIOLOGY FIRST-TERM APRIL 2017 TO SEPTEMBER - 2017 MONTH July 2017 CONTENTS Orientation and Recapitulation :-Discussion on importance of Biology, scope
CBSE SOLVED PAPER 2018 BIOLOGY CLASS 11 OSWAAL BOOKS LEARNING MADE SIMPLE. Strictly as per the Latest NCERT Edition FOR MARCH 2019 EXAM
 Strictly as per the Latest NCERT Edition 2018-19 OSWAAL BOOKS LEARNING MADE SIMPLE CBSE FOR MARCH 2019 EXAM SOLVED PAPER 2018 BIOLOGY CLASS 11 Strictly based on the latest CBSE curriculum ISSUED ON 15
Strictly as per the Latest NCERT Edition 2018-19 OSWAAL BOOKS LEARNING MADE SIMPLE CBSE FOR MARCH 2019 EXAM SOLVED PAPER 2018 BIOLOGY CLASS 11 Strictly based on the latest CBSE curriculum ISSUED ON 15
Std. XI: Biology (Upgraded syllabus) Section I - Botany.
 Unit 1 Diversity in Living World: Chapter 1- Diversity in organisms 1. Diversity in living organisms-brief idea. Std. XI: Biology (Upgraded syllabus) Section I - Botany. 2. Systematic and binomial system
Unit 1 Diversity in Living World: Chapter 1- Diversity in organisms 1. Diversity in living organisms-brief idea. Std. XI: Biology (Upgraded syllabus) Section I - Botany. 2. Systematic and binomial system
Biology syllabus for NEET Exam: Topics covered in respective. Unit number. Unit. name
 Biology syllabus for NEET Exam: number I II III name Diversity in Living World Structural Organisation in Animals and Plants Cell Structure and Function Topics covered in respective subjects Class XI syllabus
Biology syllabus for NEET Exam: number I II III name Diversity in Living World Structural Organisation in Animals and Plants Cell Structure and Function Topics covered in respective subjects Class XI syllabus
NEET Syllabus for Biology
 NEET Syllabus for Biology Class 11th NEET Syllabus 2019 If you want to crack the NEET 2019 Exam in the first attempt, then it is very important to cover the complete syllabus of NEET. There are many topics
NEET Syllabus for Biology Class 11th NEET Syllabus 2019 If you want to crack the NEET 2019 Exam in the first attempt, then it is very important to cover the complete syllabus of NEET. There are many topics
Entrance Examination Syllabus for 5-Year Integrated M.Sc. course in Molecular Biology
 Entrance Examination Syllabus for 5-Year Integrated M.Sc. course in Molecular Biology Duration of Entrance Examination: 1 Hr Pattern: 50 multiple choice questions of I mark each Biology -30, Chemistry-10,
Entrance Examination Syllabus for 5-Year Integrated M.Sc. course in Molecular Biology Duration of Entrance Examination: 1 Hr Pattern: 50 multiple choice questions of I mark each Biology -30, Chemistry-10,
9. BIOLOGY (Code No. 044)
 9. BIOLOGY (Code No. 044) The present syllabus provides the students with new concepts along with an extended exposure to contemporary areas of the subject. The syllabus also aims at emphasizing on the
9. BIOLOGY (Code No. 044) The present syllabus provides the students with new concepts along with an extended exposure to contemporary areas of the subject. The syllabus also aims at emphasizing on the
HPCET-2016 Syllabus for B.Tech./B.Pharmacy/B. Pharmacy (Ayurveda)
 HPCET-2016 Syllabus for B.Tech./B.Pharmacy/B. Pharmacy (Ayurveda) Syllabus for HPCET-2016 of B.Tech, B.Pharma(Ayur. & Allo.) Page 1 Syllabus for HPCET-2016 of B.Tech, B.Pharma(Ayur. & Allo.) Page 2 Syllabus
HPCET-2016 Syllabus for B.Tech./B.Pharmacy/B. Pharmacy (Ayurveda) Syllabus for HPCET-2016 of B.Tech, B.Pharma(Ayur. & Allo.) Page 1 Syllabus for HPCET-2016 of B.Tech, B.Pharma(Ayur. & Allo.) Page 2 Syllabus
GAT-UGTP-2018 Page 1 of 7 Page 1 of 7
 BOTANY UNIT 1 Diversity in living world: 1. What is living? Biodiversity, Need for classification. Three domains of life. Taxonomy & systematic concepts of species and taxonomical hierarchy. Binomial nomenclature
BOTANY UNIT 1 Diversity in living world: 1. What is living? Biodiversity, Need for classification. Three domains of life. Taxonomy & systematic concepts of species and taxonomical hierarchy. Binomial nomenclature
Marks -40 Theory Classes Section- First Botany Systematic and binomial system of nomenclature - meaning of the terms taxonomy, systematics,
 Sr..No. 1. 1.1 Agril. Polytechnic Syllabus First Year Subject :- (C) Biology I (Theory) Reference Book :- Biology Std XI Publisher :- Secretary, Maharashtra State Board of Secondary & Higher Secondary
Sr..No. 1. 1.1 Agril. Polytechnic Syllabus First Year Subject :- (C) Biology I (Theory) Reference Book :- Biology Std XI Publisher :- Secretary, Maharashtra State Board of Secondary & Higher Secondary
BITSAT EXAMINATION SYLLABUS PART IV MATHEMATICS OR BIOLOGY
 BITSAT EXAMINATION SYLLABUS PART IV MATHEMATICS OR BIOLOGY 1. Algebra 1.1 Complex numbers, addition, multiplication, conjugation, polar representation, properties of modulus and principal argument, triangle
BITSAT EXAMINATION SYLLABUS PART IV MATHEMATICS OR BIOLOGY 1. Algebra 1.1 Complex numbers, addition, multiplication, conjugation, polar representation, properties of modulus and principal argument, triangle
Stewards Pooi Kei College Secondary 3 Biology Teaching Schedule ( )
 Stewards Pooi Kei College Secondary Biology Teaching Schedule (009-010) Subject Teachers: KSit (Form coordinator), WChiang, SLee /10-day Cycle: Cycles 1 (1/9 11/9) Teaching Topics/Content Ch. 1 Introducing
Stewards Pooi Kei College Secondary Biology Teaching Schedule (009-010) Subject Teachers: KSit (Form coordinator), WChiang, SLee /10-day Cycle: Cycles 1 (1/9 11/9) Teaching Topics/Content Ch. 1 Introducing
PREFACE O-LEVEL TOPICAL SCIENCE (BIOLOGY)
 PREFACE O-LEVEL TOPICAL SCIENCE (BIOLOGY) provides a thorough revision for students taking the GCE O-Level Science (Biology) Examination. Past examination questions have been carefully classified into
PREFACE O-LEVEL TOPICAL SCIENCE (BIOLOGY) provides a thorough revision for students taking the GCE O-Level Science (Biology) Examination. Past examination questions have been carefully classified into
Gymnázium, Brno, Slovanské nám. 7, SHEME OF WORK - Biology SCHEME OF WORK.
 SCHEME OF WORK http://agb.gymnaslo.cz Subject: Biology Year: first grade, 1.X School year:../ List of topics # Topics Time period 1. Introduction to Biology 09 2. Origin and History of life 10 3. Cell
SCHEME OF WORK http://agb.gymnaslo.cz Subject: Biology Year: first grade, 1.X School year:../ List of topics # Topics Time period 1. Introduction to Biology 09 2. Origin and History of life 10 3. Cell
AVICENNA INTERNATIONAL COLLEGE
 AVICENNA INTERNATIONAL COLLEGE BIOLOGICAL SCIENCES ACADEMIC CALENDAR LECTURE SYLLABUS CELL & MOLECULAR BIOLOGY 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Characteristics of Living Organisms, Levels of Organization in Biology (Introduction
AVICENNA INTERNATIONAL COLLEGE BIOLOGICAL SCIENCES ACADEMIC CALENDAR LECTURE SYLLABUS CELL & MOLECULAR BIOLOGY 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Characteristics of Living Organisms, Levels of Organization in Biology (Introduction
BIOLOGY Grades Summer Units: 10 high school credits UC Requirement Category: d. General Description:
 Summer 2015 Units: 10 high school credits UC Requirement Category: d General Description: BIOLOGY Grades 9-12 Summer session biology will be an intense, fast paced course. Students will gain an understanding
Summer 2015 Units: 10 high school credits UC Requirement Category: d General Description: BIOLOGY Grades 9-12 Summer session biology will be an intense, fast paced course. Students will gain an understanding
Schedule & Syllabus of ONLINE TEST SERIES [Academic Session : ] NEET-UG Nurture Online Test Series : Target NEET-UG 2019
![Schedule & Syllabus of ONLINE TEST SERIES [Academic Session : ] NEET-UG Nurture Online Test Series : Target NEET-UG 2019 Schedule & Syllabus of ONLINE TEST SERIES [Academic Session : ] NEET-UG Nurture Online Test Series : Target NEET-UG 2019](/thumbs/75/71655621.jpg) Basic Mathematics used in Physics- ALGEBRA : Quadratic Equation ( Roots of quadratic equation, Solution by Factorization and by Shridharacharya Formula, Properties of roots (real, equal, imaginary etc),
Basic Mathematics used in Physics- ALGEBRA : Quadratic Equation ( Roots of quadratic equation, Solution by Factorization and by Shridharacharya Formula, Properties of roots (real, equal, imaginary etc),
The diagram below represents levels of organization within a cell of a multicellular organism.
 STATION 1 1. Unlike prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells have the capacity to a. assemble into multicellular organisms b. establish symbiotic relationships with other organisms c. obtain energy from the
STATION 1 1. Unlike prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells have the capacity to a. assemble into multicellular organisms b. establish symbiotic relationships with other organisms c. obtain energy from the
Biology Fall Semester Exam Review. Unit 1: Scientific method, characteristics of life What are the characteristics of life (pg. 6)
 Biology Fall Semester Exam Review Unit 1: Scientific method, characteristics of life What are the characteristics of life (pg. 6) Define the following terms: biology observation hypothesis dependent variable
Biology Fall Semester Exam Review Unit 1: Scientific method, characteristics of life What are the characteristics of life (pg. 6) Define the following terms: biology observation hypothesis dependent variable
Massachusetts Tests for Educator Licensure (MTEL )
 Massachusetts Tests for Educator Licensure (MTEL ) FIELD 13: BIOLOGY TEST OBJECTIVES Subarea Multiple-Choice Range of Objectives Approximate Test Weighting I. Nature of Science 01 04 10% II. Chemistry
Massachusetts Tests for Educator Licensure (MTEL ) FIELD 13: BIOLOGY TEST OBJECTIVES Subarea Multiple-Choice Range of Objectives Approximate Test Weighting I. Nature of Science 01 04 10% II. Chemistry
PREFACE. N-LEVEL TOPICAL SCIENCE (BIOLOGY) provides a thorough revision for students taking the GCE N-Level Science (Biology) Examination.
 PREFACE N-LEVEL TOPICAL SCIENCE (BIOLOGY) provides a thorough revision for students taking the GCE N-Level Science (Biology) Examination. This book contains: Useful Notes Students are able to revise their
PREFACE N-LEVEL TOPICAL SCIENCE (BIOLOGY) provides a thorough revision for students taking the GCE N-Level Science (Biology) Examination. This book contains: Useful Notes Students are able to revise their
DIRECTORATE OF SCHOOL EDUCATION, GOVERNMENT OF TAMILNADU, CHENNAI BOTANY SYLLABUS
 Unit - I Taxonomy of Angiosperms 1.1 to 1.3. Analyses the Systems of Classification of plants Recalls uses of Herbaria develops skill in preparing Herbarium Sheets in a Scientific manner. Recalls Economic
Unit - I Taxonomy of Angiosperms 1.1 to 1.3. Analyses the Systems of Classification of plants Recalls uses of Herbaria develops skill in preparing Herbarium Sheets in a Scientific manner. Recalls Economic
The Cell Notes 1 of 11
 The Cell The basic unit of structure and function in living things The smallest units in living things The smallest units in living things that show the characteristics of life Organisms can be made of
The Cell The basic unit of structure and function in living things The smallest units in living things The smallest units in living things that show the characteristics of life Organisms can be made of
BIOLOGY. PAPER 1 (THEORY) (Maximum Marks: 70) (Time allowed: Three hours)
 BIOLOGY PAPER 1 (THEY) (Maximum Marks: 70) (Time allowed: Three hours) (Candidates are allowed additional 15 minutes for only reading the paper. They must NOT start writing during this time) ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
BIOLOGY PAPER 1 (THEY) (Maximum Marks: 70) (Time allowed: Three hours) (Candidates are allowed additional 15 minutes for only reading the paper. They must NOT start writing during this time) ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
02/02/ Living things are organized. Analyze the functional inter-relationship of cell structures. Learning Outcome B1
 Analyze the functional inter-relationship of cell structures Learning Outcome B1 Describe the following cell structures and their functions: Cell membrane Cell wall Chloroplast Cytoskeleton Cytoplasm Golgi
Analyze the functional inter-relationship of cell structures Learning Outcome B1 Describe the following cell structures and their functions: Cell membrane Cell wall Chloroplast Cytoskeleton Cytoplasm Golgi
UGZY-01 Animal Diversity-I
 UGZY-01 Animal Diversity-I Block-I I Diversity of Animal Life-I (Organisation) Five Kingdom Classification The Protozoans The Metazoa- Origin and Evolution Diverstiy of Animal Life-II (Classification)
UGZY-01 Animal Diversity-I Block-I I Diversity of Animal Life-I (Organisation) Five Kingdom Classification The Protozoans The Metazoa- Origin and Evolution Diverstiy of Animal Life-II (Classification)
AIR-1. Pre-Medical (NEET(UG), AIIMS) NURTURE Test Series Syllabus VIPUL GARG. Result : AIPMT-2015 PHYSICS
 PHYSICS Test No. Topic Covered 01 BASIC MATHEMATICS USED IN PHYSICS ALGEBRA : Quadratic Equation ( Roots of quadratic equation, Solution by Factorization and by Shridharacharya Formula, Properties of roots
PHYSICS Test No. Topic Covered 01 BASIC MATHEMATICS USED IN PHYSICS ALGEBRA : Quadratic Equation ( Roots of quadratic equation, Solution by Factorization and by Shridharacharya Formula, Properties of roots
Curriculum Catalog
 2017-2018 Curriculum Catalog 2017 Glynlyon, Inc. Table of Contents BIOLOGY COURSE OVERVIEW...1 UNIT 1: TAXONOMY: KEY TO ORGANIZATION... 1 UNIT 2: CHEMISTRY OF LIFE... 2 UNIT 3: CELLS... 2 UNIT 4: CELL
2017-2018 Curriculum Catalog 2017 Glynlyon, Inc. Table of Contents BIOLOGY COURSE OVERVIEW...1 UNIT 1: TAXONOMY: KEY TO ORGANIZATION... 1 UNIT 2: CHEMISTRY OF LIFE... 2 UNIT 3: CELLS... 2 UNIT 4: CELL
Curriculum Catalog. Biology. Released Glynlyon, Inc
 Curriculum Catalog Biology 2012 Glynlyon, Inc Released 4-1-12 Table of Contents Course Overview... 1 UNIT 1: TAXONOMY: KEY TO ORGANIZATION... 2 UNIT 2: CHEMISTRY OF LIFE... 2 UNIT 3: CELLS... 2 UNIT 4:
Curriculum Catalog Biology 2012 Glynlyon, Inc Released 4-1-12 Table of Contents Course Overview... 1 UNIT 1: TAXONOMY: KEY TO ORGANIZATION... 2 UNIT 2: CHEMISTRY OF LIFE... 2 UNIT 3: CELLS... 2 UNIT 4:
What in the Cell is Going On?
 What in the Cell is Going On? Robert Hooke naturalist, philosopher, inventor, architect... (July 18, 1635 - March 3, 1703) In 1665 Robert Hooke publishes his book, Micrographia, which contains his drawings
What in the Cell is Going On? Robert Hooke naturalist, philosopher, inventor, architect... (July 18, 1635 - March 3, 1703) In 1665 Robert Hooke publishes his book, Micrographia, which contains his drawings
Module A Unit 1 Basic Biological Principles. Mr. Mitcheltree
 Module A Unit 1 Basic Biological Principles Mr. Mitcheltree Biochemistry Cytology Genetics Evolution Taxonomy Microbiology Mycology Botany Zoology Ecology Branches of Biology Characteristics of Life Made
Module A Unit 1 Basic Biological Principles Mr. Mitcheltree Biochemistry Cytology Genetics Evolution Taxonomy Microbiology Mycology Botany Zoology Ecology Branches of Biology Characteristics of Life Made
TEST SUMMARY AND FRAMEWORK TEST SUMMARY
 Washington Educator Skills Tests Endorsements (WEST E) TEST SUMMARY AND FRAMEWORK TEST SUMMARY BIOLOGY Copyright 2014 by the Washington Professional Educator Standards Board 1 Washington Educator Skills
Washington Educator Skills Tests Endorsements (WEST E) TEST SUMMARY AND FRAMEWORK TEST SUMMARY BIOLOGY Copyright 2014 by the Washington Professional Educator Standards Board 1 Washington Educator Skills
AIR-2. Pre-Medical (NEET (UG), AIIMS) NURTURE Test Series Syllabus. NEET (UG) Result Archit Gupta (Classroom) PHYSICS
 PHYSICS Test No. Topic Covered 01 BASIC MATHEMATICS USED IN PHYSICS ALGEBRA : Quadratic Equation ( Roots of quadratic equation, Solution by Factorization and by Shridharacharya Formula, Properties of roots
PHYSICS Test No. Topic Covered 01 BASIC MATHEMATICS USED IN PHYSICS ALGEBRA : Quadratic Equation ( Roots of quadratic equation, Solution by Factorization and by Shridharacharya Formula, Properties of roots
13. The diagram below shows two different kinds of substances, A and B, entering a cell.
 Name 1. In the binomial system of nomenclature, which two classification groups provide the scientific name of an organism? A) kingdom and phylum B) phylum and species C) kingdom and genus D) genus and
Name 1. In the binomial system of nomenclature, which two classification groups provide the scientific name of an organism? A) kingdom and phylum B) phylum and species C) kingdom and genus D) genus and
Course Name: Biology Level: A Points: 5 Teacher Name: Claire E. Boudreau
 Course Name: Biology Level: A Points: 5 Teacher Name: Claire E. Boudreau Texts/Instructional Materials: Biology : Concepts and Connections 5 th edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor and Simon Pearson Syllabus:
Course Name: Biology Level: A Points: 5 Teacher Name: Claire E. Boudreau Texts/Instructional Materials: Biology : Concepts and Connections 5 th edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor and Simon Pearson Syllabus:
Department Curriculum and Assessment Outline
 Department: Science Year Group: 10 Teaching, learning and assessment during the course: Combined Science 1 2 B1 Key concepts in Biology B2 Cells and control What are the structure and function of cells.
Department: Science Year Group: 10 Teaching, learning and assessment during the course: Combined Science 1 2 B1 Key concepts in Biology B2 Cells and control What are the structure and function of cells.
MAHARASHTRA BOARD CURRICULUM. Standard XI Biology Content list
 An ISO 9001-2008 Certified Organization MAHARASHTRA BOARD CURRICULUM Standard XI Content list Designmate (I) PVT LTD Horizon, Swati Society Road, Darpan Circle, Ahmedabad 380014 www.des ig nm ate.com Follow
An ISO 9001-2008 Certified Organization MAHARASHTRA BOARD CURRICULUM Standard XI Content list Designmate (I) PVT LTD Horizon, Swati Society Road, Darpan Circle, Ahmedabad 380014 www.des ig nm ate.com Follow
CELL PRACTICE TEST
 Name: Date: 1. As a human red blood cell matures, it loses its nucleus. As a result of this loss, a mature red blood cell lacks the ability to (1) take in material from the blood (2) release hormones to
Name: Date: 1. As a human red blood cell matures, it loses its nucleus. As a result of this loss, a mature red blood cell lacks the ability to (1) take in material from the blood (2) release hormones to
Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the diagram below which represents a typical green plant cell and on your knowledge of biology.
 Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the diagram below which represents a typical green plant cell and on your knowledge of biology. 5. Which letter corresponds to that of the endoplasmic reticulum?
Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the diagram below which represents a typical green plant cell and on your knowledge of biology. 5. Which letter corresponds to that of the endoplasmic reticulum?
Human biology Cells: The Basic Units of Life. Dr. Rawaa Salim Hameed
 Human biology Cells: The Basic Units of Life Dr. Rawaa Salim Hameed Reference Text book of human biology by John Kenneth Inglis 3 rd Ed (1985) Cells: The Basic Units of Life Cell theory Cell theory consists
Human biology Cells: The Basic Units of Life Dr. Rawaa Salim Hameed Reference Text book of human biology by John Kenneth Inglis 3 rd Ed (1985) Cells: The Basic Units of Life Cell theory Cell theory consists
Cell Theory Essential Questions
 Cells Vocab words 1. Cell 2. Cell theory 3. Nucleus 4. Eukaryote 5. Prokaryote 6. Organelle 7. Cytoplasm 8. Nuclear envelope 9. Chromatin 10. Chromosome 11. Nucleolus 12. Ribosome 13. Endoplasmic reticulum
Cells Vocab words 1. Cell 2. Cell theory 3. Nucleus 4. Eukaryote 5. Prokaryote 6. Organelle 7. Cytoplasm 8. Nuclear envelope 9. Chromatin 10. Chromosome 11. Nucleolus 12. Ribosome 13. Endoplasmic reticulum
Assignment Question Paper I
 M.sc Previous (Botany) Subject : I- Cell and Molecular Biology of Plants Maximum Marks : 30 Q-1 Discuss the role of plasmodesmeta in movements of molecular and macro molecules. Q-2 Given an ultra structure
M.sc Previous (Botany) Subject : I- Cell and Molecular Biology of Plants Maximum Marks : 30 Q-1 Discuss the role of plasmodesmeta in movements of molecular and macro molecules. Q-2 Given an ultra structure
The Science Department Academic Year Year 10 Biology Curriculum Overview
 The Science Department Academic Year 2012-2013 Year 10 Biology Curriculum Overview Subject: Biology Term 1 Year Level: 10 Week Starting date Unit Learning Outcomes In this unit we will. Curriculum links
The Science Department Academic Year 2012-2013 Year 10 Biology Curriculum Overview Subject: Biology Term 1 Year Level: 10 Week Starting date Unit Learning Outcomes In this unit we will. Curriculum links
VENPER ACADEMY CRASH COURSE SCHEDULE
 VENPER ACADEMY CRASH COURSE SCHEDULE (April 8th to May 5th 08) Lecture Date Day Physics Hrs. Chemistry Hrs. Botany Hrs. Zoology Hrs. Lecture 8-Apr-8 Sunday Lecture 9 Apr 8 Monday Lecture 0 Apr 7 Tuesday
VENPER ACADEMY CRASH COURSE SCHEDULE (April 8th to May 5th 08) Lecture Date Day Physics Hrs. Chemistry Hrs. Botany Hrs. Zoology Hrs. Lecture 8-Apr-8 Sunday Lecture 9 Apr 8 Monday Lecture 0 Apr 7 Tuesday
1. Looking at the data above, what was the questions that was being tested?
 UCS BIOLOGY STUDY GUIDE FOR 1 ST SEMESTER MIDTERM EXAM 2017-2018 CHAPTER 1 Use the data table and graph below to answer the 7 questions that follow. 1. Looking at the data above, what was the questions
UCS BIOLOGY STUDY GUIDE FOR 1 ST SEMESTER MIDTERM EXAM 2017-2018 CHAPTER 1 Use the data table and graph below to answer the 7 questions that follow. 1. Looking at the data above, what was the questions
Cells & Cell Organelles. Doing Life s Work
 Cells & Cell Organelles Doing Life s Work Types of cells bacteria cells Prokaryote Eukaryotes animal cells plant cells Cell size comparison Animal cell Bacterial cell most bacteria 1-10 microns eukaryotic
Cells & Cell Organelles Doing Life s Work Types of cells bacteria cells Prokaryote Eukaryotes animal cells plant cells Cell size comparison Animal cell Bacterial cell most bacteria 1-10 microns eukaryotic
THE CELL THEORY (R+R+R+E+G+N+T+S) 3).
 CELL BIOLOGY All living things are made up of small individual units called cells. Cells are the smallest functioning living unit. Cells can not normally be seen with the naked eye. To usually observe
CELL BIOLOGY All living things are made up of small individual units called cells. Cells are the smallest functioning living unit. Cells can not normally be seen with the naked eye. To usually observe
Cell Structure Vocab. Plasma membrane. Vacuole. Cell wall. Nuclear envelope. Chloroplast. Nucleus. Cytoskeleton. Nucleolus. Cytoplasm.
 The Cell Cell Structure Vocab Plasma membrane Nuclear envelope Nucleus Nucleolus Cytoplasm Mitochondria Endoplasmic reticulum Golgi apparatus Lysosome Vacuole Cell wall Chloroplast Cytoskeleton Centriole
The Cell Cell Structure Vocab Plasma membrane Nuclear envelope Nucleus Nucleolus Cytoplasm Mitochondria Endoplasmic reticulum Golgi apparatus Lysosome Vacuole Cell wall Chloroplast Cytoskeleton Centriole
Biology. Mrs. Michaelsen. Types of cells. Cells & Cell Organelles. Cell size comparison. The Cell. Doing Life s Work. Hooke first viewed cork 1600 s
 Types of cells bacteria cells Prokaryote - no organelles Cells & Cell Organelles Doing Life s Work Eukaryotes - organelles animal cells plant cells Cell size comparison Animal cell Bacterial cell most
Types of cells bacteria cells Prokaryote - no organelles Cells & Cell Organelles Doing Life s Work Eukaryotes - organelles animal cells plant cells Cell size comparison Animal cell Bacterial cell most
1. The Chemistry of Life Chapter 3 Central Concept: Chemical elements form organic molecules that interact to perform the basic functions of life.
 Biology High School Standards Review Worksheet 1. The Chemistry of Life Chapter 3 Central Concept: Chemical elements form organic molecules that interact to perform the basic functions of life. 1.1 Recognize
Biology High School Standards Review Worksheet 1. The Chemistry of Life Chapter 3 Central Concept: Chemical elements form organic molecules that interact to perform the basic functions of life. 1.1 Recognize
BIOLOGY AND GEOLOGY 3º DE E.S.O. Chapter 1: The organisation of the human body
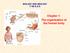 BIOLOGY AND GEOLOGY 3º DE E.S.O. Chapter 1: The organisation of the human body 1. INTRODUCTION: LEVELS OF ORGANISATION What is a cell? Definition of Cell A cell is the smallest unit that is capable of
BIOLOGY AND GEOLOGY 3º DE E.S.O. Chapter 1: The organisation of the human body 1. INTRODUCTION: LEVELS OF ORGANISATION What is a cell? Definition of Cell A cell is the smallest unit that is capable of
Grading Scheme 2 nd, Semester Tests 30% Quizzes 15% Labs 10% Assignments 10% Exam 30% Participation 5%
 San Pedro High School San Pedro Town Belize District Telefax: 226-2045 Email Address: esantizo@sphs.edu.bz 4 th Form BIOLOGY YEARLY CURRICULUM Text: BIOLOGY FOR CXC Credit Hours: 5 Teacher: Mr. Erick Santizo
San Pedro High School San Pedro Town Belize District Telefax: 226-2045 Email Address: esantizo@sphs.edu.bz 4 th Form BIOLOGY YEARLY CURRICULUM Text: BIOLOGY FOR CXC Credit Hours: 5 Teacher: Mr. Erick Santizo
Chemistry of Life Cells & Bioprocesses CRT Review
 Chemistry of Life Cells & Bioprocesses CRT Review Chapter 2: The Chemistry of Life macromolecules - The four types of macromolecules are carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids, and proteins Types of Macromolecules
Chemistry of Life Cells & Bioprocesses CRT Review Chapter 2: The Chemistry of Life macromolecules - The four types of macromolecules are carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids, and proteins Types of Macromolecules
Cell (Learning Objectives)
 Cell (Learning Objectives) 1. Understand & describe the basic components necessary for a functional cell. 2. Review the order of appearance of cells on earth and explain the endosymbiotic theory. 3. Compare
Cell (Learning Objectives) 1. Understand & describe the basic components necessary for a functional cell. 2. Review the order of appearance of cells on earth and explain the endosymbiotic theory. 3. Compare
Introduction to Biology with Lab
 Introduction to Biology with Lab Course Text/Materials Mader, Sylvia S. Inquiry into Life, 12th edition, McGraw-Hill, 2008, ISBN: 9780073309330 [find and buy the text: Straighterline.com/textbooks] Custom
Introduction to Biology with Lab Course Text/Materials Mader, Sylvia S. Inquiry into Life, 12th edition, McGraw-Hill, 2008, ISBN: 9780073309330 [find and buy the text: Straighterline.com/textbooks] Custom
CELL PART Expanded Definition Cell Structure Illustration Function Summary Location ALL CELLS DNA Common in Animals Uncommon in Plants Lysosome
 CELL PART Expanded Definition Cell Structure Illustration Function Summary Location is the material that contains the Carry genetic ALL CELLS information that determines material inherited characteristics.
CELL PART Expanded Definition Cell Structure Illustration Function Summary Location is the material that contains the Carry genetic ALL CELLS information that determines material inherited characteristics.
Unit 2: Characteristics of Living Things Lesson 18: From Cell To Organism
 Name Unit 2: Characteristics of Living Things Lesson 18: From Cell To Organism Date Objective: Students will be able to compare organisms unique cells and cellular organization. Essential Questions: 1.
Name Unit 2: Characteristics of Living Things Lesson 18: From Cell To Organism Date Objective: Students will be able to compare organisms unique cells and cellular organization. Essential Questions: 1.
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Revised 11/2010
 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Revised 11/2010 DESCRIPTION OF COURSE: Covers the basics of human anatomy and physiology including anatomical terminology, basic biochemistry, cells and tissues, and the integumentary,
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Revised 11/2010 DESCRIPTION OF COURSE: Covers the basics of human anatomy and physiology including anatomical terminology, basic biochemistry, cells and tissues, and the integumentary,
The Cell. The basic unit of all living things
 The Cell The basic unit of all living things 1 Robert Hooke was the first to name the cell (1665) 2 The Cell Theory The cell is the unit of Structure of all living things. The cell is the unit of Function
The Cell The basic unit of all living things 1 Robert Hooke was the first to name the cell (1665) 2 The Cell Theory The cell is the unit of Structure of all living things. The cell is the unit of Function
Biology (Miller/Levine) 2010 Correlated to: Massachusetts Learning Standards for Biology (High School)
 I. CONTENT STANDARDS 1. The Chemistry of Life Central Concept: Chemical elements form organic molecules that interact to perform the basic functions of life. 1.1 Recognize that biological organisms are
I. CONTENT STANDARDS 1. The Chemistry of Life Central Concept: Chemical elements form organic molecules that interact to perform the basic functions of life. 1.1 Recognize that biological organisms are
Cell Types. Prokaryotes
 Cell Types Prokaryotes before nucleus no membrane-bound nucleus only organelle present is the ribosome all other reactions occur in the cytoplasm not very efficient Ex.: bacteria 1 Cell Types Eukaryotes
Cell Types Prokaryotes before nucleus no membrane-bound nucleus only organelle present is the ribosome all other reactions occur in the cytoplasm not very efficient Ex.: bacteria 1 Cell Types Eukaryotes
Chetek-Weyerhaeuser Middle School
 Chetek-Weyerhaeuser Middle School Science 7 Units and s Science 7A Unit 1 Nature of Science Scientific Explanations (12 days) s 1. I can make an informed decision using a scientific decision-making model
Chetek-Weyerhaeuser Middle School Science 7 Units and s Science 7A Unit 1 Nature of Science Scientific Explanations (12 days) s 1. I can make an informed decision using a scientific decision-making model
BIOLOGY (Code No. 044)
 BIOLOGY (Code No. 044) The present syllabus provides the students with new concepts along with an extended exposure to contemporary areas of the subject. The syllabus also aims at emphasizing on the underlying
BIOLOGY (Code No. 044) The present syllabus provides the students with new concepts along with an extended exposure to contemporary areas of the subject. The syllabus also aims at emphasizing on the underlying
Honors Biology Midterm Review
 Honors Biology Midterm Review 1. CHARACTERISTICS OF LIFE Match each item in the boxes with a characteristic a. Reproduction (DNA) 1-passing DNA on to 1, 5 offspring b. Homeostasis 2-trait that helps 7,
Honors Biology Midterm Review 1. CHARACTERISTICS OF LIFE Match each item in the boxes with a characteristic a. Reproduction (DNA) 1-passing DNA on to 1, 5 offspring b. Homeostasis 2-trait that helps 7,
CELL BIOLOGY. Which of the following cell structures does not have membranes? A. Ribosomes B. Mitochondria C. Chloroplasts D.
 1 CELL BIOLOGY PROKARYOTIC and EUKARYOTIC SP/1. SP/2. SP/4. Plant and animal cells both have A. ribosomes, cell walls and mitochondria. B. Golgi apparatus, chromosomes and mitochondria. C. Golgi apparatus,
1 CELL BIOLOGY PROKARYOTIC and EUKARYOTIC SP/1. SP/2. SP/4. Plant and animal cells both have A. ribosomes, cell walls and mitochondria. B. Golgi apparatus, chromosomes and mitochondria. C. Golgi apparatus,
Class IX: Biology Chapter 5: The fundamental unit of life. Chapter Notes. 1) In 1665, Robert Hooke first discovered and named the cells.
 Class IX: Biology Chapter 5: The fundamental unit of life. Key learnings: Chapter Notes 1) In 1665, Robert Hooke first discovered and named the cells. 2) Cell is the structural and functional unit of all
Class IX: Biology Chapter 5: The fundamental unit of life. Key learnings: Chapter Notes 1) In 1665, Robert Hooke first discovered and named the cells. 2) Cell is the structural and functional unit of all
7. Which letter in the diagram below indicates the structure that is most closely associated with excretion?
 1. Which sequence of terms is in the correct order from simplest to most complex? 1) cells tissues organs organ systems 2) tissues organisms cells organ systems 3) cells tissues organ systems organs 4)
1. Which sequence of terms is in the correct order from simplest to most complex? 1) cells tissues organs organ systems 2) tissues organisms cells organ systems 3) cells tissues organ systems organs 4)
NAME: PERIOD: DATE: A View of the Cell. Use Chapter 8 of your book to complete the chart of eukaryotic cell components.
 NAME: PERIOD: DATE: A View of the Cell Use Chapter 8 of your book to complete the chart of eukaryotic cell components. Cell Part Cell Wall Centriole Chloroplast Cilia Cytoplasm Cytoskeleton Endoplasmic
NAME: PERIOD: DATE: A View of the Cell Use Chapter 8 of your book to complete the chart of eukaryotic cell components. Cell Part Cell Wall Centriole Chloroplast Cilia Cytoplasm Cytoskeleton Endoplasmic
Principles of Cellular Biology
 Principles of Cellular Biology آشنایی با مبانی اولیه سلول Biologists are interested in objects ranging in size from small molecules to the tallest trees: Cell Basic building blocks of life Understanding
Principles of Cellular Biology آشنایی با مبانی اولیه سلول Biologists are interested in objects ranging in size from small molecules to the tallest trees: Cell Basic building blocks of life Understanding
9. BIOLOGY (Code No. 044)
 9. BIOLOGY (Code No. 044) The present syllabus provides the students with new concepts along with an extended exposure to contemporary areas of the subject. The syllabus also aims at emphasizing on the
9. BIOLOGY (Code No. 044) The present syllabus provides the students with new concepts along with an extended exposure to contemporary areas of the subject. The syllabus also aims at emphasizing on the
Components of a functional cell. Boundary-membrane Cytoplasm: Cytosol (soluble components) & particulates DNA-information Ribosomes-protein synthesis
 Cell (Outline) - Components of a functional cell - Major Events in the History of Earth: abiotic and biotic phases; anaerobic and aerobic atmosphere - Prokaryotic cells impact on the biosphere - Origin
Cell (Outline) - Components of a functional cell - Major Events in the History of Earth: abiotic and biotic phases; anaerobic and aerobic atmosphere - Prokaryotic cells impact on the biosphere - Origin
2012 Curriculum Catalog
 2012 Curriculum Catalog Biology 2012 Glynlyon, Inc. Released 7.14.12 Welcome to Alpha Omega Publications! We are excited that you are including Ignitia as part of your program of instruction, and we look
2012 Curriculum Catalog Biology 2012 Glynlyon, Inc. Released 7.14.12 Welcome to Alpha Omega Publications! We are excited that you are including Ignitia as part of your program of instruction, and we look
UNIT 3 CP BIOLOGY: Cell Structure
 UNIT 3 CP BIOLOGY: Cell Structure Page CP: CHAPTER 3, Sections 1-3; HN: CHAPTER 7, Sections 1-2 Standard B-2: The student will demonstrate an understanding of the structure and function of cells and their
UNIT 3 CP BIOLOGY: Cell Structure Page CP: CHAPTER 3, Sections 1-3; HN: CHAPTER 7, Sections 1-2 Standard B-2: The student will demonstrate an understanding of the structure and function of cells and their
SYLLABUS FOR WRITTEN EXAMINATION (BIOLOGY)
 SYLLABUS FOR WRITTEN EXAMINATION (BIOLOGY) Diversity of living world Taxonomic aids, keys, specimen management ; Systematic and binomial system of nomenclature; Classification of living organisms( five
SYLLABUS FOR WRITTEN EXAMINATION (BIOLOGY) Diversity of living world Taxonomic aids, keys, specimen management ; Systematic and binomial system of nomenclature; Classification of living organisms( five
Jordan University of Science & Technology. Faculty of Arts and Sciences. Department of Applied Biological Sciences
 Jordan University of Science & Technology Faculty of Arts and Sciences Department of Applied Biological Sciences Course Title Title & Instructor General Biology Course Number BIO 104 Instructor Office
Jordan University of Science & Technology Faculty of Arts and Sciences Department of Applied Biological Sciences Course Title Title & Instructor General Biology Course Number BIO 104 Instructor Office
2. Cellular and Molecular Biology
 2. Cellular and Molecular Biology 2.1 Cell Structure 2.2 Transport Across Cell Membranes 2.3 Cellular Metabolism 2.4 DNA Replication 2.5 Cell Division 2.6 Biosynthesis 2.1 Cell Structure What is a cell?
2. Cellular and Molecular Biology 2.1 Cell Structure 2.2 Transport Across Cell Membranes 2.3 Cellular Metabolism 2.4 DNA Replication 2.5 Cell Division 2.6 Biosynthesis 2.1 Cell Structure What is a cell?
7 Characteristics of Life
 7 Characteristics of Life 1. Interdependence 2. Metabolism 3. Homeostasis 4. Cellular Structure and Function 5. Reproduction 6. Heredity 7. Evolution The Cell Theory All living things are composed of one
7 Characteristics of Life 1. Interdependence 2. Metabolism 3. Homeostasis 4. Cellular Structure and Function 5. Reproduction 6. Heredity 7. Evolution The Cell Theory All living things are composed of one
Name: Class: Date: ID: A
 Class: Date: Ch 7 Review Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Researchers use fluorescent labels and light microscopy to a. follow
Class: Date: Ch 7 Review Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Researchers use fluorescent labels and light microscopy to a. follow
Honors Biology summer assignment. Review the notes and study them. There will be a test on this information the 1 st week of class
 Honors Biology summer assignment Review the notes and study them. There will be a test on this information the 1 st week of class Biomolecules Molecules that make up living things. There are 4 molecules
Honors Biology summer assignment Review the notes and study them. There will be a test on this information the 1 st week of class Biomolecules Molecules that make up living things. There are 4 molecules
Chapter 4. Table of Contents. Section 1 The History of Cell Biology. Section 2 Introduction to Cells. Section 3 Cell Organelles and Features
 Cell Structure and Function Table of Contents Section 1 The History of Cell Biology Section 2 Introduction to Cells Section 3 Cell Organelles and Features Section 4 Unique Features of Plant Cells Section
Cell Structure and Function Table of Contents Section 1 The History of Cell Biology Section 2 Introduction to Cells Section 3 Cell Organelles and Features Section 4 Unique Features of Plant Cells Section
I. Molecules & Cells. A. Unit One: The Nature of Science. B. Unit Two: The Chemistry of Life. C. Unit Three: The Biology of the Cell.
 I. Molecules & Cells A. Unit One: The Nature of Science a. How is the scientific method used to solve problems? b. What is the importance of controls? c. How does Darwin s theory of evolution illustrate
I. Molecules & Cells A. Unit One: The Nature of Science a. How is the scientific method used to solve problems? b. What is the importance of controls? c. How does Darwin s theory of evolution illustrate
The Unity of Life. All living things are made up of small individual units called cells.
 The Unity of Life All living things are made up of small individual units called cells. Robert Hooke (1600 s) - examined slices of cork with a magnifying glass and observed box-like structures which he
The Unity of Life All living things are made up of small individual units called cells. Robert Hooke (1600 s) - examined slices of cork with a magnifying glass and observed box-like structures which he
table of contents unit one: introduction to the study of the environment
 table of contents unit one: introduction to the study of the environment Chapter 1: Characteristics of Living Things 1 A. Biology and the Living Environment 1 B. What is Science 1 C. Scientific Inquiry
table of contents unit one: introduction to the study of the environment Chapter 1: Characteristics of Living Things 1 A. Biology and the Living Environment 1 B. What is Science 1 C. Scientific Inquiry
Sioux Falls School District Anatomy and Physiology Holes Anatomy and Physiology Authors: Shier, Butler, and Lewis Glencoe/ McGraw hill
 Sioux Falls School District Anatomy and Physiology Holes Anatomy and Physiology Authors: Shier, Butler, and Lewis Glencoe/ McGraw hill Semester 1 Chapter 1: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology
Sioux Falls School District Anatomy and Physiology Holes Anatomy and Physiology Authors: Shier, Butler, and Lewis Glencoe/ McGraw hill Semester 1 Chapter 1: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology
Basic Structure of a Cell
 Basic Structure of a Cell Introduction to Cells Cells are the basic units of organisms Cells can only be observed under microscope Basic types of cells: Animal Cell Plant Cell Bacterial Cell 1 2 Number
Basic Structure of a Cell Introduction to Cells Cells are the basic units of organisms Cells can only be observed under microscope Basic types of cells: Animal Cell Plant Cell Bacterial Cell 1 2 Number
Chapter 7 Learning Targets Cell Structure & Function
 Name: Chapter 7 Learning Targets Cell Structure & Function a. Define the word cell: 1. I know the history of the cell: b. Who discovered the cell? What did he observe? 2. I can list the three parts of
Name: Chapter 7 Learning Targets Cell Structure & Function a. Define the word cell: 1. I know the history of the cell: b. Who discovered the cell? What did he observe? 2. I can list the three parts of
CONTENTS. Physics Chemistry Motion Work, Energy and Power Gravitation Properties of Fluid 22-23
 CONTENTS Physics...5-58 1. Motion 7-13 2. Work, Energy and Power 14-16 3. Gravitation 17-21 4. Properties of Fluid 22-23 5. Heat 24-27 6. Wave 28-30 7. Sound 31-35 8. Light 36-46 9. Electricity and Magnetism
CONTENTS Physics...5-58 1. Motion 7-13 2. Work, Energy and Power 14-16 3. Gravitation 17-21 4. Properties of Fluid 22-23 5. Heat 24-27 6. Wave 28-30 7. Sound 31-35 8. Light 36-46 9. Electricity and Magnetism
TWGHs Chen Zao Men College S3 Biology Teaching Schedule ( )
 TWGHs Chen Zao Men College S3 Biology Teaching Schedule (2015-2016) Date Period Topics Practical / Activities 2/9 4/9 1 Laboratory safety Note taking skills 7/9 20/10 11 Ch 1 Molecules of life Chemicals
TWGHs Chen Zao Men College S3 Biology Teaching Schedule (2015-2016) Date Period Topics Practical / Activities 2/9 4/9 1 Laboratory safety Note taking skills 7/9 20/10 11 Ch 1 Molecules of life Chemicals
Biology I Midterm 2018 Study Guide
 Biology I Midterm 2018 Study Guide These questions are designed to get you thinking about all the concepts we have discussed from Chapters 1-11. However, you will be responsible for knowing ALL the information
Biology I Midterm 2018 Study Guide These questions are designed to get you thinking about all the concepts we have discussed from Chapters 1-11. However, you will be responsible for knowing ALL the information
Broken Arrow Public Schools Physiology Objectives
 1 st six weeks 1 Define anatomy and physiology. 2 Compare and contrast levels of structural organization. 3 Identify necessary life functions and essential needs and how they are related to homeostasis.
1 st six weeks 1 Define anatomy and physiology. 2 Compare and contrast levels of structural organization. 3 Identify necessary life functions and essential needs and how they are related to homeostasis.
Biology B. There are no objectives for this lesson.
 Biology B Course Summary This is the second of two courses that comprise Biology. This course is designed to prepare the student to confidently enter and complete college-level biology courses. The Glencoe
Biology B Course Summary This is the second of two courses that comprise Biology. This course is designed to prepare the student to confidently enter and complete college-level biology courses. The Glencoe
Foundation Year Programme
 Foundation Year Programme Entrance Tests BIOLOGY SPECIFICATION Standard ATS sample material 2 3 Biology 1. Living organisms 1.1. Characteristics of living organisms a. List and define the main characteristics
Foundation Year Programme Entrance Tests BIOLOGY SPECIFICATION Standard ATS sample material 2 3 Biology 1. Living organisms 1.1. Characteristics of living organisms a. List and define the main characteristics
3.2 Cell Organelles. KEY CONCEPT Eukaryotic cells share many similarities.
 KEY CONCEPT Eukaryotic cells share many similarities. ! Cells have an internal structure. ! Cells have an internal structure. The cytoskeleton has many functions. ! Cells have an internal structure. The
KEY CONCEPT Eukaryotic cells share many similarities. ! Cells have an internal structure. ! Cells have an internal structure. The cytoskeleton has many functions. ! Cells have an internal structure. The
NCERT solution for Fundamental Unit of Life
 1 NCERT solution for Fundamental Unit of Life Question 1 Who discovered cells and how? An English Botanist, Robert Hooke discovered cells. In 1665, he used self-designed microscope to observe cells in
1 NCERT solution for Fundamental Unit of Life Question 1 Who discovered cells and how? An English Botanist, Robert Hooke discovered cells. In 1665, he used self-designed microscope to observe cells in
JEFFERSON COLLEGE VERTEBRATE ANATOMY
 JEFFERSON COLLEGE COURSE SYLLABUS BIO207 VERTEBRATE ANATOMY 4 Credit Hours Prepared by: Mr. Jim McCain Revised Date: November 2005 by Dr. Ken Balak Division of Arts & Science Education Dr. Mindy Selsor,
JEFFERSON COLLEGE COURSE SYLLABUS BIO207 VERTEBRATE ANATOMY 4 Credit Hours Prepared by: Mr. Jim McCain Revised Date: November 2005 by Dr. Ken Balak Division of Arts & Science Education Dr. Mindy Selsor,
BIOLOGY Cell Review Notes (source: SW Biology 11)
 BIOLOGY Cell Review Notes (source: SW Biology 11) CELL STRUCTURE, FUNCTION & PROCESS Both living and nonliving things are composed of molecules made from chemical elements such as carbon, hydrogen, oxygen,
BIOLOGY Cell Review Notes (source: SW Biology 11) CELL STRUCTURE, FUNCTION & PROCESS Both living and nonliving things are composed of molecules made from chemical elements such as carbon, hydrogen, oxygen,
Science Grade 5 AZ. Course Overview
 Course Overview Experimentation is integral to science in Grade 5. Students spend the first five weeks of school learning the scientific method through a discovery model. They complete discovery activities
Course Overview Experimentation is integral to science in Grade 5. Students spend the first five weeks of school learning the scientific method through a discovery model. They complete discovery activities
Which row in the chart correctly identifies the functions of structures A, B, and C? A) 1 B) 2 C) 3 D) 4
 1. What is a similarity between all bacteria and plants? A) They both have a nucleus B) They are both composed of cells C) They both have chloroplasts D) They both lack a cell wall 2. Which statement is
1. What is a similarity between all bacteria and plants? A) They both have a nucleus B) They are both composed of cells C) They both have chloroplasts D) They both lack a cell wall 2. Which statement is
5. The cells in the liver that detoxify poison substances contain lots of a. smooth ER b. rough ER c. Golgi apparatus d. lysosomes e.
 Chapter 7 practice 1. What scientist originally came up with the term "cell"? a. von Leeuwenhoek d. Watson b. Hooke e. Virchow c. van der Waals 2. When you wish to look at the coat of a virus on the surface
Chapter 7 practice 1. What scientist originally came up with the term "cell"? a. von Leeuwenhoek d. Watson b. Hooke e. Virchow c. van der Waals 2. When you wish to look at the coat of a virus on the surface
