CELL THEORY & CELL TYPES. Honors Biology, Arizona College Prep, Mrs. Glassmeyer Textbook Reference: 4.1, , The Living World 7 th edition
|
|
|
- Joshua Stewart
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CELL THEORY & CELL TYPES Honors Biology, Arizona College Prep, Mrs. Glassmeyer Textbook Reference: 4.1, , The Living World 7 th edition
2 Learning Goals: Unit Learning Goal: Student will be able to compare structure & analyze transport of materials into and out of prokaryotic & eukaryotic cells by accurately explaining the role of proteins & ATP. Presentation Learning Goals: 1. Student will be able to defend the importance of the development of the cell theory. 2. Student will be able to describe similarities and differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. 3. Student will be able to describe similarities and differences between plant & animal cells.
3 How was the Cell Theory Developed? Science stands on the shoulders of Giants. Many scientists and great thinkers enable those later to see even further than their predecessors did. Robert Hooke Anton van Leeuwenhoek Matthias Schleiden Theodor Schwann Rudolph Virchow
4 Who was Robert Hooke? A Englishman who decided used an early compound microscope. He viewed a crosssection of cork (nonliving plant tissue). He was the first person to use the term cellulae because what he was seeing looked like small rooms.
5 Who was Anton van Leeuwenhoek? Used a single-lens microscope to observe pond water and other things. In the small world he observed, living things seemed to be everywhere.
6 Who was Matthias Schleiden? German botanist, who in 1838, concluded that all plants were made up of cells
7 Who was Theodor Schwann? German biologist, who in 1839, stated that all animals were made of cells
8 Who was Rudolph Virchow? German physician, who in 1855, concluded that new cells could be produced only from the division of existing cells.
9 What are the tenets of Cell Theory? 1. All cells come from pre-existing cells. 2. Cells are the most basic unit of living organisms. (Cells are the basic units of life) 3. All living organisms are made up of one or more cells.
10 How to Remember Cell Theory? What significant information has been covered so far? Revisit your notes and discuss with your neighbor. Let s share some of the key information. Summarize this new knowledge using a strategy: Mneumonic Devices Non-linguistic representations (timelines) Write out a paragraph underlining key words
11 What are the two types of cells? Create a double bubble comparing/contrasting the two cell types.
12 Characteristics of prokaryotic cells Cell characteristics: No nucleus or membrane-bound organelles Has cell membrane, cell wall, ribosomes, DNA Age: more ancient than eukaryotic cells Size: tend to be smaller than eukaryotic cells Characteristics of organisms made up of prokaryotic cells: unicellular organisms Organisms are found in kingdoms Archae & Bacteria
13 Characteristics of eukaryotic cells Cell characteristics: Has nucleus & membrane-bound organelles Organelles serve as compartments for specific metabolic functions Age: younger than prokaryotic cells Size: tend to be larger than prokaryotic cells Characteristics of organisms made up of eukaryotic cells: Make up unicellular and multicellular organisms Organisms are found in kingdoms plantae, animalia, fungi, & protista
14 What are the two eukaryotic cells? Create a double bubble comparing/contrasting the two cells.
15 Characteristics of Animal Cells *Nucleus present *Membrane-bound organelles present Cell wall not present Chloroplasts not present Can have vacuoles but does not have a central vacuole Can have flagella *characteristics of eukaryotic cells
16 Characteristics of Plant Cells *Nucleus present *Membrane-bound organelles present Cell wall present made up of cellulose Central vacuole present Chloroplasts present *characteristics of eukaryotic cells
17 How did organelles come to be? The Endosymbiotic Theory concerns the mitochondria, plastids, (Chloroplasts) and possibly other organelles of eukaryotic cells. According to this theory, certain organelles originated as free-living bacteria that were taken inside another cells as endosymbionts. Mitochondria developed from proteobacteria and chloroplasts from cyanobacteria.
18 How are the Kingdoms related?
19 Reflection of Learning Goals What are the three parts of the cell theory? What are the structural similarities and differences between the two types of cells? What are the structural similarities and differences between the two types of eukaryotic cells? Presentation Learning Goals: 1. Student will be able to defend the importance of the development of the cell theory. 2. Student will be able to describe similarities and differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. 3. Student will be able to describe similarities and differences between plant & animal cells.
8.1 Life is cellular
 8.1 Life is cellular Early Microscopes In 1665, Englishman Robert Hooke used a microscope to look at a slice of cork. Cork was made of tiny, empty chambers that Hooke called cells. Anton van Leeuwenhoek
8.1 Life is cellular Early Microscopes In 1665, Englishman Robert Hooke used a microscope to look at a slice of cork. Cork was made of tiny, empty chambers that Hooke called cells. Anton van Leeuwenhoek
All living things are made of cells
 All about CELLS! 12F recognize that according to cell theory all organisms are composed of cells and cells carry on similar functions such as extracting energy from food to sustain life 12C recognize levels
All about CELLS! 12F recognize that according to cell theory all organisms are composed of cells and cells carry on similar functions such as extracting energy from food to sustain life 12C recognize levels
Cell Theory. The cell is the basic unit of structure and function for all living things, but no one knew they existed before the 17 th century!
 Cell Notes Cell Theory All living organisms are made of. cells The cell is the basic unit of structure and function for all living things, but no one knew they existed before the 17 th century! In 1665,
Cell Notes Cell Theory All living organisms are made of. cells The cell is the basic unit of structure and function for all living things, but no one knew they existed before the 17 th century! In 1665,
Biology Slide 1 of 31
 Biology 1 of 31 2 of 31 The Discovery of the Cell The Discovery of the Cell Because there were no instruments to make cells visible, the existence of cells was unknown for most of human history. This changed
Biology 1 of 31 2 of 31 The Discovery of the Cell The Discovery of the Cell Because there were no instruments to make cells visible, the existence of cells was unknown for most of human history. This changed
protein synthesis cell theory Centrioles specialization. unicellular ribosomes. mitochondria cell interdependence prokaryotes
 All cells must generate proteins. Cells make protein through a process called protein synthesis All living things are made of cells, Cells are the basic units of structure and function in all organisms,
All cells must generate proteins. Cells make protein through a process called protein synthesis All living things are made of cells, Cells are the basic units of structure and function in all organisms,
Name Hour. Section 7-1 Life Is Cellular (pages )
 Name Hour Section 7-1 Life Is Cellular (pages 169-173) Introduction (page 169) 1. What is the structure that makes up every living thing? The Discovery of the Cell (pages 169-170) 2. What was Anton van
Name Hour Section 7-1 Life Is Cellular (pages 169-173) Introduction (page 169) 1. What is the structure that makes up every living thing? The Discovery of the Cell (pages 169-170) 2. What was Anton van
What is a cell? (*Know the parts of the microscope!)
 Cells What is a cell? All living things have cells whether it is one or many! Therefore, a cell is the basic unit of all life. The invention of the microscope was pivotal to the study of cell biology.
Cells What is a cell? All living things have cells whether it is one or many! Therefore, a cell is the basic unit of all life. The invention of the microscope was pivotal to the study of cell biology.
The Discovery of the Cell
 The Discovery of the Cell The Discovery of the Cell Because there were no instruments to make cells visible, the existence of cells was unknown for most of human history. This changed with the invention
The Discovery of the Cell The Discovery of the Cell Because there were no instruments to make cells visible, the existence of cells was unknown for most of human history. This changed with the invention
Van Leeuwenhoek. 1 st crude microscope made by the Dutchman
 The Cell History of Cells In 1665, English scientist Robert Hooke used the first compound light microscope to see plant tissues He viewed several thin slices of cork He called the small chambers within
The Cell History of Cells In 1665, English scientist Robert Hooke used the first compound light microscope to see plant tissues He viewed several thin slices of cork He called the small chambers within
7.1 Life is Cellular. Robert Hooke: Anton van Leeuwenhoek: The smallest unit of any organism- the cell. Robert Hooke
 7.1 Life is Cellular Sunday, December 16, 2012 1:07 PM Vocabulary: Cell: basic unit of all forms of life Cell theory: fundamental concept of biology that states that all living things are composed of cells;
7.1 Life is Cellular Sunday, December 16, 2012 1:07 PM Vocabulary: Cell: basic unit of all forms of life Cell theory: fundamental concept of biology that states that all living things are composed of cells;
Cell Structure and Function. Chapter 4
 Cell Structure and Function Chapter 4 Chapter 4: Cell Structure Section 1: The History of Cell Biology Section 2: Introduction to Cells Section 3: Cell Organelles and Features Section 4: Unique Features
Cell Structure and Function Chapter 4 Chapter 4: Cell Structure Section 1: The History of Cell Biology Section 2: Introduction to Cells Section 3: Cell Organelles and Features Section 4: Unique Features
The Basic Unit of Life Copyright Amy Brown Science Stuff
 Cell Structure and Function The Basic Unit of Life Copyright Amy Brown Science Stuff The Discovery of the Cell Robert Hooke looked at thin slices of cork (plant cells) under the microscope. Named it a
Cell Structure and Function The Basic Unit of Life Copyright Amy Brown Science Stuff The Discovery of the Cell Robert Hooke looked at thin slices of cork (plant cells) under the microscope. Named it a
The Discovery of the Cell
 7-1 Life Is Cellular Review The cell is the basic unit of life! Life began with the first cell! All living things are composed of cells! Cells make up tissues, organs, organ systems and organisms! Understanding
7-1 Life Is Cellular Review The cell is the basic unit of life! Life began with the first cell! All living things are composed of cells! Cells make up tissues, organs, organ systems and organisms! Understanding
Cells Cytology = the study of cells. Nonliving Levels. Organization Levels of Life. Living Levels 11/14/13. More Living Levels
 Cells Cytology = the study of cells What Are the Main Characteristics of organisms? 1. Made of CELLS 2. Require ENERGY (food) 3. REPRODUCE (species) 4. Maintain HOMEOSTASIS 5. ORGANIZED 6. RESPOND to environment
Cells Cytology = the study of cells What Are the Main Characteristics of organisms? 1. Made of CELLS 2. Require ENERGY (food) 3. REPRODUCE (species) 4. Maintain HOMEOSTASIS 5. ORGANIZED 6. RESPOND to environment
STUDY GUIDE SECTION 4-1 The History of Cell Biology
 STUDY GUIDE SECTION 4-1 The History of Cell Biology Name Period Date Multiple Choice-Write the correct letter in the blank. 1. One early piece of evidence supporting the cell theory was the observation
STUDY GUIDE SECTION 4-1 The History of Cell Biology Name Period Date Multiple Choice-Write the correct letter in the blank. 1. One early piece of evidence supporting the cell theory was the observation
Cells. The basic units of a living system or organism
 Hairy T-cell Theory Definition: An idea that has been proposed, repeatedly tested, and found to be true-so far. A scientific hypothesis that survives experimental testing becomes a scientific theory Cells
Hairy T-cell Theory Definition: An idea that has been proposed, repeatedly tested, and found to be true-so far. A scientific hypothesis that survives experimental testing becomes a scientific theory Cells
It took more than years for scientists to develop that would allow them to really study.
 CELLS NOTES All living things are made of! THE DISCOVERY OF CELLS The Scientist Who? When? What was discovered? Robert Hooke Anton van Leeuwenhoek Looked through a very simple at a thin slice of and saw
CELLS NOTES All living things are made of! THE DISCOVERY OF CELLS The Scientist Who? When? What was discovered? Robert Hooke Anton van Leeuwenhoek Looked through a very simple at a thin slice of and saw
Discovery of the Cell
 Cell Structure Discovery of the Cell Who discovered cells? 1665 Robert Hooke used a compound microscope to examine a piece of cork (20X magnification) He saw little boxes in the cork and called them cells
Cell Structure Discovery of the Cell Who discovered cells? 1665 Robert Hooke used a compound microscope to examine a piece of cork (20X magnification) He saw little boxes in the cork and called them cells
Cell Biology. What is a cell? What is a cell?
 Cell Biology What is a cell? Cell = basic unit of life A cell is the smallest 'thing' that has all of the characteristics of life made of cells maintains homeostasis can reproduce uses energy grows is
Cell Biology What is a cell? Cell = basic unit of life A cell is the smallest 'thing' that has all of the characteristics of life made of cells maintains homeostasis can reproduce uses energy grows is
CHARACTERISTICS OF LIFE ORGANIZATION OF LIFE CELL THEORY TIMELINE
 CHARACTERISTICS OF LIFE 1. composed of cells either uni/multi 2. reproduce sexual and/or asexual 3. contain DNA in cells 4. grow and develop 5. use material/energy in metabolic reactions 6. respond to
CHARACTERISTICS OF LIFE 1. composed of cells either uni/multi 2. reproduce sexual and/or asexual 3. contain DNA in cells 4. grow and develop 5. use material/energy in metabolic reactions 6. respond to
Discovery of the Cell
 Cells Chapter 4 Discovery of the Cell 1665 Robert Hooke used a microscope to examine a piece of cork. He saw little boxes in the cork and called them cells. 1673 Anton van Leeuwenhoek was the first person
Cells Chapter 4 Discovery of the Cell 1665 Robert Hooke used a microscope to examine a piece of cork. He saw little boxes in the cork and called them cells. 1673 Anton van Leeuwenhoek was the first person
Biology Homework Chapter 5: The Cell Pages Answer the questions with complete thoughts!
 Name Biology Homework Chapter 5: The Cell Pages 115-133 Answer the questions with complete thoughts! Per. * Sections 5.1 through 5.3: Cells Are the Units of Life: Read pages 115 to 122 PART A: Define the
Name Biology Homework Chapter 5: The Cell Pages 115-133 Answer the questions with complete thoughts! Per. * Sections 5.1 through 5.3: Cells Are the Units of Life: Read pages 115 to 122 PART A: Define the
STEMscopedia: CELL STRUCTURES AND HOMEOSTASIS B1A
 Reflect B1A Have you wondered why you shiver in the cold? Or maybe why your stomach gets upset after eating something bad? These and many other reactions are ways your body is responding to a change in
Reflect B1A Have you wondered why you shiver in the cold? Or maybe why your stomach gets upset after eating something bad? These and many other reactions are ways your body is responding to a change in
LIFE SCIENCE CHAPTER 3 FLASHCARDS
 LIFE SCIENCE CHAPTER 3 FLASHCARDS Human beings are A. machines. B. organisms. C. systems. D. protists. One benefit of being a large organism is that you have A. larger cells. B. simpler functions. C. fewer
LIFE SCIENCE CHAPTER 3 FLASHCARDS Human beings are A. machines. B. organisms. C. systems. D. protists. One benefit of being a large organism is that you have A. larger cells. B. simpler functions. C. fewer
FLIP Student Assessment on Exploring Life Science Prentice Hall (1999)
 Chapter 3 CLOZE This activity is used to test your background knowledge for the Cells, Tissues, and Organ Systems chapter in our book. On a separate sheet of paper, please number 1-50. On that sheet of
Chapter 3 CLOZE This activity is used to test your background knowledge for the Cells, Tissues, and Organ Systems chapter in our book. On a separate sheet of paper, please number 1-50. On that sheet of
Chapter 3. Chapter 3. Bellringer. Objectives. Chapter 3. Chapter 3. Vocabulary. Objectives, continued
 Bellringer Why do you think cells weren t discovered until 1665? What invention do you think made their discovery possible? Do you think people can ever see cells with the naked eye? Explain your answer.
Bellringer Why do you think cells weren t discovered until 1665? What invention do you think made their discovery possible? Do you think people can ever see cells with the naked eye? Explain your answer.
Chapter 4 Cells: The Basic Units of Life The Big Idea All organisms are composed of one or more cells.
 Chapter 4 Cells: The Basic Units of Life The Big Idea All organisms are composed of one or more cells. Section 1 The Characteristics of Cells Key Concept Cells function similarly in all living organisms.
Chapter 4 Cells: The Basic Units of Life The Big Idea All organisms are composed of one or more cells. Section 1 The Characteristics of Cells Key Concept Cells function similarly in all living organisms.
Anaphase. Third phase of mitosis in which the chromosomes separate and move to opposite ends of the cell. Animal Cell
 Anaphase Third phase of mitosis in which the chromosomes separate and move to opposite ends of the cell. Animal Cell Antony Van Leevwenhoek 1643- Dutch microscope maker and merchant, observed and described
Anaphase Third phase of mitosis in which the chromosomes separate and move to opposite ends of the cell. Animal Cell Antony Van Leevwenhoek 1643- Dutch microscope maker and merchant, observed and described
Directed Reading A. Section: The Diversity of Cells. a(n). CELLS AND THE CELL THEORY. bacteria. of cells. cells. CELL SIZE.
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading A Section: The Diversity of Cells 1. The smallest unit that can perform all the processes necessary for life is a(n). CELLS AND THE CELL THEORY Match the correct description
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading A Section: The Diversity of Cells 1. The smallest unit that can perform all the processes necessary for life is a(n). CELLS AND THE CELL THEORY Match the correct description
Cellular basis of life History of cell Biology Year Name of the scientist Importance
 Cellular basis of life History of cell Biology Year Name of the scientist Importance 1590 Jansen 1650 Anton van Leeuwenhoek 1665 Robert Hooke 1831 Matthias Schleiden 1831 Theodore Schwann 1855 Rudolf Virchow
Cellular basis of life History of cell Biology Year Name of the scientist Importance 1590 Jansen 1650 Anton van Leeuwenhoek 1665 Robert Hooke 1831 Matthias Schleiden 1831 Theodore Schwann 1855 Rudolf Virchow
CELL THEORY, STRUCTURE & FUNCTION
 CELL THEORY, STRUCTURE & FUNCTION History of Cells Robert Hooke (1665) observed cork under a microscope Thought they looked like the rooms monks lived in called cells. History of Cells Antony Van Leeuwenhoek
CELL THEORY, STRUCTURE & FUNCTION History of Cells Robert Hooke (1665) observed cork under a microscope Thought they looked like the rooms monks lived in called cells. History of Cells Antony Van Leeuwenhoek
II. Eukaryotic Cell Structure A. Boundaries 1. plasma membrane a. serves as a boundary b/w the cell and its environment b. controls movement of
 I. History of the cell theory A. Anton van Leeuwenhoek (1600s) - dutch lens maker could see things with his lenses that were invisible to the naked eye - developed the simple microscope B. Robert Hooke
I. History of the cell theory A. Anton van Leeuwenhoek (1600s) - dutch lens maker could see things with his lenses that were invisible to the naked eye - developed the simple microscope B. Robert Hooke
Life is Cellular. At the cellular level, what is the difference between animal cells and bacterial cells? How do microscopes work?
 Life is Cellular At the cellular level, what is the difference between animal cells and bacterial cells? How do microscopes work? Objectives 8a) I can state the cell theory and distinguish between prokaryotes
Life is Cellular At the cellular level, what is the difference between animal cells and bacterial cells? How do microscopes work? Objectives 8a) I can state the cell theory and distinguish between prokaryotes
CHAPTER 7.1 OUTLINE SHEET
 CHAPTER 7.1 OUTLINE SHEET A. Development of Cell Theory 1. Identifying Cells a. Anton van Leeuwenhoek b. Robert Hooke 2. Development of Cell Theory a. Schleiden, Schwann, and Virchow 1. Schleiden 2. Schwann
CHAPTER 7.1 OUTLINE SHEET A. Development of Cell Theory 1. Identifying Cells a. Anton van Leeuwenhoek b. Robert Hooke 2. Development of Cell Theory a. Schleiden, Schwann, and Virchow 1. Schleiden 2. Schwann
Ask yourself. Chapter 3 Cell Structure and Function. Examples of Cells. A is cell the smallest unit that is capable of performing life functions.
 Chapter 3 Cell Structure and Function Ask yourself If you were a scientist living in the 1500s, what kind of questions would you ask yourself if you were the one to discover cells? Let me think. Cell Video
Chapter 3 Cell Structure and Function Ask yourself If you were a scientist living in the 1500s, what kind of questions would you ask yourself if you were the one to discover cells? Let me think. Cell Video
Name: Class: Date: ID: A
 Class: Date: Ch 7 Review Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Researchers use fluorescent labels and light microscopy to a. follow
Class: Date: Ch 7 Review Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Researchers use fluorescent labels and light microscopy to a. follow
Cell Structure and Function
 Chapter 5 Cell Structure and Function Can you name something that you know exists even though you can t see it with your eyes? A drop of pond water has tiny swimming organisms and small bits of plant material,
Chapter 5 Cell Structure and Function Can you name something that you know exists even though you can t see it with your eyes? A drop of pond water has tiny swimming organisms and small bits of plant material,
3.1 Cell Theory. KEY CONCEPT Cells are the Basic unit of life.
 KEY CONCEPT Cells are the Basic unit of life. Macrophages (large tan cells) take in and digest foreign material, such as invading bacteria (small red cells). They play an important role in your immune
KEY CONCEPT Cells are the Basic unit of life. Macrophages (large tan cells) take in and digest foreign material, such as invading bacteria (small red cells). They play an important role in your immune
Day 1. What You ll Learn. 1. Organisms are living things. 2. All organisms are made of one or more cells.
 What You ll Learn Day 1 1. Organisms are living things. 2. All organisms are made of one or more cells. 3. There are two main types of cells: Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic A cell is the basic unit and structure
What You ll Learn Day 1 1. Organisms are living things. 2. All organisms are made of one or more cells. 3. There are two main types of cells: Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic A cell is the basic unit and structure
Mission to Mars Day 4. Defining Life
 Mission to Mars Day 4 Defining Life Remember this quote? Mark Watney: If the oxygenator breaks down, I'll suffocate. If the water reclaimer breaks down, I'll die of thirst. If the hab breaches, I'll just
Mission to Mars Day 4 Defining Life Remember this quote? Mark Watney: If the oxygenator breaks down, I'll suffocate. If the water reclaimer breaks down, I'll die of thirst. If the hab breaches, I'll just
Cell Theory and Structure. Discoveries What are Cells? Cell Theory Cell Structures Organelles
 Cell Theory and Structure Discoveries What are Cells? Cell Theory Cell Structures Organelles Discoveries In 1665 Robert Hooke observed a thin slice of cork from an oak tree What he saw reminded him of
Cell Theory and Structure Discoveries What are Cells? Cell Theory Cell Structures Organelles Discoveries In 1665 Robert Hooke observed a thin slice of cork from an oak tree What he saw reminded him of
A D A E J (L) J(s) K L
 I A E A D G C B C F G E F H B J (L) H K L J(s) Animal Cells Less Support Needed Large, multicellular organisms made of animal cells often have support systems such as bones or exoskeletons Plant and Animal
I A E A D G C B C F G E F H B J (L) H K L J(s) Animal Cells Less Support Needed Large, multicellular organisms made of animal cells often have support systems such as bones or exoskeletons Plant and Animal
Science Interactive Notebook ZcienceClass.com
 Science Interactive Notebook ZcienceClass.com Mr. Zamarripa If found return to room 206 Week of 09/05/2016 52A Robert Hooke: The scientist that looked at cork cells that were dead and then "coined" the
Science Interactive Notebook ZcienceClass.com Mr. Zamarripa If found return to room 206 Week of 09/05/2016 52A Robert Hooke: The scientist that looked at cork cells that were dead and then "coined" the
The most widely used biological classification system has six kingdoms within three domains.
 Section 3: The most widely used biological classification system has six kingdoms within three domains. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Essential Questions What are the major characteristics
Section 3: The most widely used biological classification system has six kingdoms within three domains. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Essential Questions What are the major characteristics
BIOLOGY Cell Review Notes (source: SW Biology 11)
 BIOLOGY Cell Review Notes (source: SW Biology 11) CELL STRUCTURE, FUNCTION & PROCESS Both living and nonliving things are composed of molecules made from chemical elements such as carbon, hydrogen, oxygen,
BIOLOGY Cell Review Notes (source: SW Biology 11) CELL STRUCTURE, FUNCTION & PROCESS Both living and nonliving things are composed of molecules made from chemical elements such as carbon, hydrogen, oxygen,
Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 chapter 7 Test Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Who was one of the first people to identify and see cork cells? a. Anton van
chapter 7 Test Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Who was one of the first people to identify and see cork cells? a. Anton van
 http://koning.ecsu.ctstateu.edu/cell/cell.html 4A: Students will compare and contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells Robert Hooke (1665) Used a compound microscope to look at thin slices of cork (oak
http://koning.ecsu.ctstateu.edu/cell/cell.html 4A: Students will compare and contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells Robert Hooke (1665) Used a compound microscope to look at thin slices of cork (oak
Unit 1: Introduction to Biology
 Name: Unit 1: Introduction to Biology Students will be able to: 1.1 Plan and conduct an investigation: Define the question, develop a hypothesis, design an experiment and collect information, analyze and
Name: Unit 1: Introduction to Biology Students will be able to: 1.1 Plan and conduct an investigation: Define the question, develop a hypothesis, design an experiment and collect information, analyze and
Chapter 4. Table of Contents. Section 1 The History of Cell Biology. Section 2 Introduction to Cells. Section 3 Cell Organelles and Features
 Cell Structure and Function Table of Contents Section 1 The History of Cell Biology Section 2 Introduction to Cells Section 3 Cell Organelles and Features Section 4 Unique Features of Plant Cells Section
Cell Structure and Function Table of Contents Section 1 The History of Cell Biology Section 2 Introduction to Cells Section 3 Cell Organelles and Features Section 4 Unique Features of Plant Cells Section
Chapter 7: Cell Structure and Function 7.1: Life is Cellular
 Chapter 7: Cell Structure and Function 7.1: Life is Cellular Key Questions: 1) What is the cell theory? 2) How do microscopes work? 3) How are prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells different? THINK ABOUT IT
Chapter 7: Cell Structure and Function 7.1: Life is Cellular Key Questions: 1) What is the cell theory? 2) How do microscopes work? 3) How are prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells different? THINK ABOUT IT
What in the Cell is Going On?
 What in the Cell is Going On? Robert Hooke naturalist, philosopher, inventor, architect... (July 18, 1635 - March 3, 1703) In 1665 Robert Hooke publishes his book, Micrographia, which contains his drawings
What in the Cell is Going On? Robert Hooke naturalist, philosopher, inventor, architect... (July 18, 1635 - March 3, 1703) In 1665 Robert Hooke publishes his book, Micrographia, which contains his drawings
What is a cell? Recall your work yesterday. When classifying cells, what are the two groups scientists separate cells into?
 What is a cell? Recall your work yesterday. When classifying cells, what are the two groups scientists separate cells into? Light Microscopes and Total Power Magnification We can use microscopes to observe
What is a cell? Recall your work yesterday. When classifying cells, what are the two groups scientists separate cells into? Light Microscopes and Total Power Magnification We can use microscopes to observe
Cell Structure: What cells are made of. Can you pick out the cells from this picture?
 Cell Structure: What cells are made of Can you pick out the cells from this picture? Review of the cell theory Microscope was developed 1610. Anton van Leeuwenhoek saw living things in pond water. 1677
Cell Structure: What cells are made of Can you pick out the cells from this picture? Review of the cell theory Microscope was developed 1610. Anton van Leeuwenhoek saw living things in pond water. 1677
6.12A: You will understand that all organisms are composed of one or more cells.
 TEKS: 6.12A, B 6.12A: You will understand that all organisms are composed of one or more cells. Purpose: You will get to see and identify the smallest unit of life! As well as learn about who discovered
TEKS: 6.12A, B 6.12A: You will understand that all organisms are composed of one or more cells. Purpose: You will get to see and identify the smallest unit of life! As well as learn about who discovered
Happy Thursday 3/13/2014 D3: Please have your ID ON. K W L : What do you already KNOW about cells? (dig around in your brain
 Happy Thursday 3/13/2014 D3: Please have your ID ON Today, we begin the CELLS unit K W L : What do you already KNOW about cells? (dig around in your brain for those memories!) What do you WANT to know
Happy Thursday 3/13/2014 D3: Please have your ID ON Today, we begin the CELLS unit K W L : What do you already KNOW about cells? (dig around in your brain for those memories!) What do you WANT to know
Bio-CP Chapter 7 Cell Notes
 Bio-CP Chapter 7 Cell Notes I. Cell = Building block of all living organisms A. Robert Hooke (1665) observed cork under a crude microscope 1. He called the boxes cells because they looked like little rooms
Bio-CP Chapter 7 Cell Notes I. Cell = Building block of all living organisms A. Robert Hooke (1665) observed cork under a crude microscope 1. He called the boxes cells because they looked like little rooms
Cells. The Cell Theory. But what is a cell? Contributors to the Cell Theory:
 Cells "Long ago it became evident that the key to every biological problem must finally be sought in the cell; for every living organism is, or at some time, has been a cell." E.B. Wilson The Cell Theory
Cells "Long ago it became evident that the key to every biological problem must finally be sought in the cell; for every living organism is, or at some time, has been a cell." E.B. Wilson The Cell Theory
Biology I. Chapter 7
 Biology I Chapter 7 Interest Grabber NOTEBOOK #1 Are All Cells Alike? All living things are made up of cells. Some organisms are composed of only one cell. Other organisms are made up of many cells. 1.
Biology I Chapter 7 Interest Grabber NOTEBOOK #1 Are All Cells Alike? All living things are made up of cells. Some organisms are composed of only one cell. Other organisms are made up of many cells. 1.
Mid-Unit 1 Study Guide
 Mid- Study Guide Lessons 1, 3, & 4 1.1 Essential Questions: What are living things made of? What term describes the smallest unit that can perform all of the functions necessary for life? Eukaryotic cells
Mid- Study Guide Lessons 1, 3, & 4 1.1 Essential Questions: What are living things made of? What term describes the smallest unit that can perform all of the functions necessary for life? Eukaryotic cells
Cell Theory Essential Questions
 Cells Vocab words 1. Cell 2. Cell theory 3. Nucleus 4. Eukaryote 5. Prokaryote 6. Organelle 7. Cytoplasm 8. Nuclear envelope 9. Chromatin 10. Chromosome 11. Nucleolus 12. Ribosome 13. Endoplasmic reticulum
Cells Vocab words 1. Cell 2. Cell theory 3. Nucleus 4. Eukaryote 5. Prokaryote 6. Organelle 7. Cytoplasm 8. Nuclear envelope 9. Chromatin 10. Chromosome 11. Nucleolus 12. Ribosome 13. Endoplasmic reticulum
Chapter 7. Cell Structure & Function
 Chapter 7 Cell Structure & Function Scientists & Discoveries Early 1600 s (Holland): 1st microscope was constructed Anton van Leeuwenhoek (1600 s) used single lens as a microscope to study and very carefully
Chapter 7 Cell Structure & Function Scientists & Discoveries Early 1600 s (Holland): 1st microscope was constructed Anton van Leeuwenhoek (1600 s) used single lens as a microscope to study and very carefully
Cell structure and functions
 Cell structure and functions Cells: The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of life. All living organisms are made up of cells. Cells make tissues, tissues make organs, organs make organ systems
Cell structure and functions Cells: The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of life. All living organisms are made up of cells. Cells make tissues, tissues make organs, organs make organ systems
Learning Outcome B1 13/10/2012. Student Achievement Indicators. Taxonomy: Scientific Classification. Student Achievement Indicators
 Classification of Living Organisms Learning Outcome B1 Learning Outcome B1 Apply the Kingdom System of classification to study the diversity of organisms. Student Achievement Indicators Students who have
Classification of Living Organisms Learning Outcome B1 Learning Outcome B1 Apply the Kingdom System of classification to study the diversity of organisms. Student Achievement Indicators Students who have
Chapter: Life's Structure and Classification
 Table of Contents Chapter: Life's Structure and Classification Section 1: Living Things 1- What is an organism? Any living thing is called an organism. Organisms vary in size: 1)one-celled or unicellular
Table of Contents Chapter: Life's Structure and Classification Section 1: Living Things 1- What is an organism? Any living thing is called an organism. Organisms vary in size: 1)one-celled or unicellular
CELL THEORY & FUNCTION
 UNIT 1- THE CELL CELL THEORY & FUNCTION A Word From Bill Record your observations about the picture to the right. What do you think you are you looking at? Describe the structure with as much detail
UNIT 1- THE CELL CELL THEORY & FUNCTION A Word From Bill Record your observations about the picture to the right. What do you think you are you looking at? Describe the structure with as much detail
Table of Contents. Chapter Preview. 3.1 Discovering Cells. 3.2 Looking Inside Cells. 3.3 Chemical Compounds in Cells. 3.4 The Cell In Its Environment
 Table of Contents Chapter Preview 3.1 Discovering Cells 3.2 Looking Inside Cells 3.3 Chemical Compounds in Cells 3.4 The Cell In Its Environment Chapter 3 Preview Questions 1. In a microscope, an image
Table of Contents Chapter Preview 3.1 Discovering Cells 3.2 Looking Inside Cells 3.3 Chemical Compounds in Cells 3.4 The Cell In Its Environment Chapter 3 Preview Questions 1. In a microscope, an image
Living Things. Chapter 2
 Living Things Chapter 2 Section 1: What is Life? 6 Characteristics of Living Things: 1. cellular vs. cellular 2. Composed of 5 essential chemicals 1. 2. - main energy source 3. 4. (Fats) 5. - genetic material
Living Things Chapter 2 Section 1: What is Life? 6 Characteristics of Living Things: 1. cellular vs. cellular 2. Composed of 5 essential chemicals 1. 2. - main energy source 3. 4. (Fats) 5. - genetic material
Tor Olafsson. evolution.berkeley.edu 1
 The Eukaryotic cell is a complex dynamic compartmentalised structure that originated through endosymbiotic events. Discuss this describing the structures of the eukaryotic cell, together with their functions,
The Eukaryotic cell is a complex dynamic compartmentalised structure that originated through endosymbiotic events. Discuss this describing the structures of the eukaryotic cell, together with their functions,
Cell History and Microscopy Presentation Overview
 Cell History and Microscopy Presentation Overview This presentation provides background information on the discovery of cells and the cell theory. It introduces key scientists who were influential in these
Cell History and Microscopy Presentation Overview This presentation provides background information on the discovery of cells and the cell theory. It introduces key scientists who were influential in these
Biology Cell Test. Name: Class: Date: ID: A. Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Class: Date: Biology Cell Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1, Who. wasone of the first people to-identify and seecorkeells? -,- ; -...
Class: Date: Biology Cell Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1, Who. wasone of the first people to-identify and seecorkeells? -,- ; -...
Life is Cellular. Discovery of the Cell. Chapter 7 Cell Structure & Function. Exploring the Cell. Introduction. The Discovery of the Cell
 Chapter 7 Cell Structure & Function Life is Cellular Discovery of the Cell As is usually the case, it was the discovery of new technology that led to an important scientific advance Early microscopes led
Chapter 7 Cell Structure & Function Life is Cellular Discovery of the Cell As is usually the case, it was the discovery of new technology that led to an important scientific advance Early microscopes led
How do we know cells exist?
 How do we know cells exist? Click on box What we The know invention today and of accept the microscope to be true, even led biologists as students, to begin is VERY looking in different from to the what
How do we know cells exist? Click on box What we The know invention today and of accept the microscope to be true, even led biologists as students, to begin is VERY looking in different from to the what
Cells. basic structure of life
 Cells basic structure of life Cells are the smallest unit of life Cells (the smallest unit of life)- make up all living things, including your own body. Cells can differ in shape and sizes. The different
Cells basic structure of life Cells are the smallest unit of life Cells (the smallest unit of life)- make up all living things, including your own body. Cells can differ in shape and sizes. The different
Chapter Life Is Cellular
 Chapter 7 7-1 Life Is Cellular The Discovery of the Cell Anton van Leeuwenhoek used a single-lens microscope to observe tiny little organisms in pond water. The Discovery of the Cell In 1665, Robert Hooke
Chapter 7 7-1 Life Is Cellular The Discovery of the Cell Anton van Leeuwenhoek used a single-lens microscope to observe tiny little organisms in pond water. The Discovery of the Cell In 1665, Robert Hooke
Eubacteria Archaea Eukarya
 Taxonomy Eubacteria Archaea Eukarya, mostly heterotrophic, live in all sorts of environments Largest group of organisms on Earth Only a small amount cause disease Most have very important roles:, such
Taxonomy Eubacteria Archaea Eukarya, mostly heterotrophic, live in all sorts of environments Largest group of organisms on Earth Only a small amount cause disease Most have very important roles:, such
Biology Test 2 The Cell. For questions 1 15, choose ONLY ONE correct answer and fill in that choice on your Scantron form.
 Name Block Date Biology Test 2 The Cell For questions 1 15, choose ONLY ONE correct answer and fill in that choice on your Scantron form. 1. Which pair of structures best shows that plant cells have functions
Name Block Date Biology Test 2 The Cell For questions 1 15, choose ONLY ONE correct answer and fill in that choice on your Scantron form. 1. Which pair of structures best shows that plant cells have functions
PART A: MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
 PART A: MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS QUESTION 1. Which of the following correctly shows the sequence from smallest to largest? (e) Cell, nucleus, tissue, organ, system, organism Organism, system, organ, tissue,
PART A: MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS QUESTION 1. Which of the following correctly shows the sequence from smallest to largest? (e) Cell, nucleus, tissue, organ, system, organism Organism, system, organ, tissue,
Cell Theory & The Scientists Involved. By: Nicole, Sharon, Keelyn, Morgan & Katie
 http://personal.tmlp.com/jimr57/tour/cell/cell.htm Cell Theory & The Scientists Involved By: Nicole, Sharon, Keelyn, Morgan & Katie Anton Van Leeuwenhock Date: 1600 s Theory: saw living organisms in pond
http://personal.tmlp.com/jimr57/tour/cell/cell.htm Cell Theory & The Scientists Involved By: Nicole, Sharon, Keelyn, Morgan & Katie Anton Van Leeuwenhock Date: 1600 s Theory: saw living organisms in pond
11/18/2009. History. History. Small Living Things, What Surrounds Them, & How to Keep Them the Same
 Or Small Living Things, What Surrounds Them, & How to Keep Them the Same History 1663 Robert Hooke - Using a simple microscope, looked at cork, saw little boxes of cells Thought that they were sacks filled
Or Small Living Things, What Surrounds Them, & How to Keep Them the Same History 1663 Robert Hooke - Using a simple microscope, looked at cork, saw little boxes of cells Thought that they were sacks filled
Discovering Cell/ The Cell Theory. * Cells are the basic, smallest units of structure and function of living things.
 Discovering Cell/ The Cell Theory * Cells are the basic, smallest units of structure and function of living things. Since they are so small, before the invention of the microscope (around 1590), no one
Discovering Cell/ The Cell Theory * Cells are the basic, smallest units of structure and function of living things. Since they are so small, before the invention of the microscope (around 1590), no one
DAYSHEET 28: Intro to Microscopy
 UNIT 3: The Cell DAYSHEET 28: Intro to Microscopy Name Biology I Date: Bellringer: Carefully analyze the data table below. Use the data to create a line graph. Be sure to include all of the following labels
UNIT 3: The Cell DAYSHEET 28: Intro to Microscopy Name Biology I Date: Bellringer: Carefully analyze the data table below. Use the data to create a line graph. Be sure to include all of the following labels
What Are the Main Characteristics of organisms?
 What Are the Main Characteristics of organisms? 1. Made of CELLS 2. Require ENERGY (food) 3. REPRODUCE (species) 4. Maintain HOMEOSTASIS 5. ORGANIZED 6. RESPOND to environment 7. GROW and DEVELOP 8. EXCHANGE
What Are the Main Characteristics of organisms? 1. Made of CELLS 2. Require ENERGY (food) 3. REPRODUCE (species) 4. Maintain HOMEOSTASIS 5. ORGANIZED 6. RESPOND to environment 7. GROW and DEVELOP 8. EXCHANGE
Contents. Chapter 5 Elements and Compounds 129. Chapter 1 Living Cells 1. Chapter 6 Physical and Chemical Changes 161. Chapter 2 Organ Systems 25
 Contents Words to Watch iv Chapter 5 Elements and Compounds 129 1 1.1 Plant, animal and fungal cells 3 1.2 Structures within cells 7 1.3 Examining cells 9 1.4 Single-celled organisms 15 1.5 Cell division
Contents Words to Watch iv Chapter 5 Elements and Compounds 129 1 1.1 Plant, animal and fungal cells 3 1.2 Structures within cells 7 1.3 Examining cells 9 1.4 Single-celled organisms 15 1.5 Cell division
The Unity of Life. All living things are made up of small individual units called cells.
 The Unity of Life All living things are made up of small individual units called cells. Robert Hooke (1600 s) - examined slices of cork with a magnifying glass and observed box-like structures which he
The Unity of Life All living things are made up of small individual units called cells. Robert Hooke (1600 s) - examined slices of cork with a magnifying glass and observed box-like structures which he
If the statement is true, write true. If the statement is false, change the underlined word or words to make the statement true.
 1.1 Discovering Cells Understanding Main Ideas If the statement is true, write true. If the statement is false, change the underlined word or words to make the statement true. 1. Cells are the basic unit
1.1 Discovering Cells Understanding Main Ideas If the statement is true, write true. If the statement is false, change the underlined word or words to make the statement true. 1. Cells are the basic unit
Cell Structure, Function & Ultrastructure
 Cell Structure, Function & Ultrastructure Learning Objectives 2.1.2 Components of the cell as seen under the light microscope and their functions. Cell Structure and Function 1. Plant cells: cell wall,
Cell Structure, Function & Ultrastructure Learning Objectives 2.1.2 Components of the cell as seen under the light microscope and their functions. Cell Structure and Function 1. Plant cells: cell wall,
CELL HISTORY, STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION
 CELL HISTORY, STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION The cell is the smallest unit of life that can carry out life processes. Chapter 4 Robert Hooke 1665 -observed cork through a light microscope. Anton Van Leewenhoek
CELL HISTORY, STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION The cell is the smallest unit of life that can carry out life processes. Chapter 4 Robert Hooke 1665 -observed cork through a light microscope. Anton Van Leewenhoek
Free powerpoints at
 Free powerpoints at http://www.worldofteaching.com The Cell The basic unit of an organism Discovery made possible by the invention of the microscope 1600 s. Anton van Leeuwenhoek first described living
Free powerpoints at http://www.worldofteaching.com The Cell The basic unit of an organism Discovery made possible by the invention of the microscope 1600 s. Anton van Leeuwenhoek first described living
The diagram below represents levels of organization within a cell of a multicellular organism.
 STATION 1 1. Unlike prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells have the capacity to a. assemble into multicellular organisms b. establish symbiotic relationships with other organisms c. obtain energy from the
STATION 1 1. Unlike prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells have the capacity to a. assemble into multicellular organisms b. establish symbiotic relationships with other organisms c. obtain energy from the
Assessment Schedule 7B, 7E 7A, 7C, 7D
 Assessment Schedule 7B, 7E Wednesday, 03/20 -> Cell structure and func7on Test (25 T/F, comple7on, short answer ques7ons+ 1 essay ques7on) 7A, 7C, 7D Wednesday, 03/20 -> Cell structure and func7on Test
Assessment Schedule 7B, 7E Wednesday, 03/20 -> Cell structure and func7on Test (25 T/F, comple7on, short answer ques7ons+ 1 essay ques7on) 7A, 7C, 7D Wednesday, 03/20 -> Cell structure and func7on Test
Cell Structure and Function How do the structures and processes of a cell enable it to survive?
 Name Cell Structure and Function Date How do the structures and processes of a cell enable it to survive? Before You Read Before you read the chapter, think about what you know about the topic. Record
Name Cell Structure and Function Date How do the structures and processes of a cell enable it to survive? Before You Read Before you read the chapter, think about what you know about the topic. Record
CELL TYPE. Unit #4: Cell Structure & Func2on. Classifica(on, Endosymbiosis, Cell Type, Cell Organelles
 Unit #4: Cell Structure & Func2on Classifica(on, Endosymbiosis, Cell Type, Cell Organelles How are prokaryo(c cells and eukaryo(c cells similar? different? CELL TYPE Cell Theory Many scientists were involved
Unit #4: Cell Structure & Func2on Classifica(on, Endosymbiosis, Cell Type, Cell Organelles How are prokaryo(c cells and eukaryo(c cells similar? different? CELL TYPE Cell Theory Many scientists were involved
Introduction to Cells. Intro to Cells. Scientists who contributed to cell theory. Cell Theory. There are 2 types of cells: All Cells:
 Intro to Cells Key Concept: Cells are the basic unit of life. Introduction to Cells Cells are the basic units of organisms Cells can only be observed under microscope Basic types of cells: 1 Animal Cell
Intro to Cells Key Concept: Cells are the basic unit of life. Introduction to Cells Cells are the basic units of organisms Cells can only be observed under microscope Basic types of cells: 1 Animal Cell
7-1 Life Is Cellular. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 7-1 Life Is Cellular The Discovery of the Cell What is the cell theory? The Discovery of the Cell The cell theory states: All living things are composed of cells. Cells are the basic units of structure
7-1 Life Is Cellular The Discovery of the Cell What is the cell theory? The Discovery of the Cell The cell theory states: All living things are composed of cells. Cells are the basic units of structure
Cell Organelles. Wednesday, October 22, 14
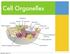 Cell Organelles Cell/Plasma Membrane ALL cells have a cell membrane It is the layer that surrounds the cell and controls what goes in and out Bacteria (Prokaryotic Cell) Cell/Plasma Membrane ALL cells
Cell Organelles Cell/Plasma Membrane ALL cells have a cell membrane It is the layer that surrounds the cell and controls what goes in and out Bacteria (Prokaryotic Cell) Cell/Plasma Membrane ALL cells
Biology Unit 3 A View of the Cell
 Biology Unit 3 A View of the Cell 3:1 Types of Microscopes MICROSCOPE: tool used to magnify small details SIMPLE MICROSCOPE: microscope using only one lens; magnifying glass COMPOUND MICROSCOPE: microscope
Biology Unit 3 A View of the Cell 3:1 Types of Microscopes MICROSCOPE: tool used to magnify small details SIMPLE MICROSCOPE: microscope using only one lens; magnifying glass COMPOUND MICROSCOPE: microscope
Unicellular Marine Organisms. Chapter 4
 Unicellular Marine Organisms Chapter 4 The Cellular Structure of Life: Review Cell wall: firm, fairly rigid structure located outside the plasma membrane of plants, fungi, most bacteria, and some protists;
Unicellular Marine Organisms Chapter 4 The Cellular Structure of Life: Review Cell wall: firm, fairly rigid structure located outside the plasma membrane of plants, fungi, most bacteria, and some protists;
CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION. Chapter 3 Day 1
 CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION Chapter 3 Day 1 REVIEW: CHARACTERISTICS OF LIVING THINGS 1. Made of CELLS 2. Require ENERGY (food) 3. REPRODUCE (species) 4. Maintain HOMEOSTASIS 5. ORGANIZED 6. RESPOND to
CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION Chapter 3 Day 1 REVIEW: CHARACTERISTICS OF LIVING THINGS 1. Made of CELLS 2. Require ENERGY (food) 3. REPRODUCE (species) 4. Maintain HOMEOSTASIS 5. ORGANIZED 6. RESPOND to
Lesson Overview. Homeostasis and Cells. Lesson Overview. 7.4 Homeostasis and Cells
 Lesson Overview 7.4 THINK ABOUT IT What s the smallest part of any living thing that still counts as being alive? Can we just keep dividing living things into smaller and smaller parts, or is there a point
Lesson Overview 7.4 THINK ABOUT IT What s the smallest part of any living thing that still counts as being alive? Can we just keep dividing living things into smaller and smaller parts, or is there a point
