Supplemental Figures. Supplemental Data. Sugliani et al. Plant Cell (2016) /tpc Clades RSH1. Rsh1[HS] RSH2 RSH3. Rsh4[HS] HYD TGS ACT
|
|
|
- Silas Watts
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Supplemental Figures Clades RSH1 TP - HYD TGS ACT Rsh1[HS] RSH2 TP HYD SYN TGS Rsh2[HS] RSH3 TP HYD SYN TGS CRSH TP - SYN EFh Rsh4[HS] Supplemental Figure 1. Arabidopsis RSH domain structure. Schematic representation of the domain structure of the Arabidopsis RSH enzymes, adapted from Atkinson et al., 211. Membership of RSH gene clades is indicated to the right using the nomenclature of Atkinson et al., 211. TP, chloroplast target peptide; HYD, ppgpp hydrolase domain; SYN, ppgpp synthase domain; TGS, TGS regulatory domain; ACT, ACT regulatory domain; EFh, calcium binding EF hand. RSH1 has a serine substitution in the ppgpp synthase domain that abolishes ppgpp synthase activity and the hydrolase domain of CRSH is degraded and may not be functional (Mizusawa et al., 28, Atkinson et al., 211). 1
2 A rela spot Vector RSH3 RSH3-GFP RSH3 B rela Vector RSH2 RSH2-GFP RSH2 Supplemental Figure 2. Complementation of ppgpp deficient E. coli mutants by the expression of RSH2 and RSH3 GFP fusion proteins. (A) Expression of the mature form of RSH3 or an RSH3 GFP fusion complemented the growth of a ppgpp null ( rela spot) mutant on minimal media without amino acids. Mutation of the ppgpp synthase active site abolished complementation (RSH3). Bacteria containing the active RSH2 expression constructs could not be recovered in the ppgpp null mutant, as previously described (Mizusawa et al., 28). Therefore RSH2 was tested in a ppgpp deficient rela mutant ( rela) on SMG medium (B). Expression of the mature form of RSH2 and an RSH2 GFP fusion complemented rela, and mutation of the ppgpp synthase active site abolished complementation (RSH2). In both cases the same GFP fusions were used as those in the OX:RSH2-GFP and OX:RSH3-GFP plant lines. 2
3 A OX:RSH2 GFP B OX:RSH2 GFP F C OX:RSH3 GFP D OX:RSH3 GFP.1 OX:RSH2 GFP OX:RSH3 GFP.8 αgfp PR RBCL seed area, mm RBCS OX:RSH2 GFP.1 OX:RSH3 GFP.1 OX:RSH3 GFP.2 Supplemental Figure 3. Phenotypes of different RSH2-GFP and RSH3-GFP overexpression lines. Wildtype seedlings and different RSH2-GFP (OX:RSH2 GFP ) and RSH3-GFP (OX:RSH3 GFP ) overexpression lines were grown in plates for 12 DAS and (A) photographed and (B) imaged for chlorophyll fluorescence. F false color scale bar, 5-35 arbitrary units. (C) Immunoblots on equal quantities of total protein extracted from the same seedlings showed that the RSH-GFP fusion protein could be detected in the lines that were small and pale, had a high F, and a low PSII maximum quantum yield QY. Proteins were also revealed by Ponceau Red (PR). (D) Lines overexpressing RSH2-GFP and RSH3-GFP produced smaller seeds than wild type plants ( P<.1, Kruskal-Wallis test with post hoc Dunn test, n=254-14). Error bars, SEM 3
4 SYN Seedling area, cm SYN Days post induction Supplemental Figure 4. Growth of SYN and ΔSYN following induction. 12 DAS seedlings were induced by submersion in 3 µm dexamethasone for 3 minutes and then photographed each day post induction for four days. Seedling area was determined in ImageJ. P<.5, two-way Student test, n=3 plants. Error bars, SEM. 4
5 Transcript abundance in total RNA 1 OX:RSH GFP 16S 23S RPS14 RPS18 TRNR TRNY RPOA RPOB PSAB PSAC PSBA PSBD PETB NDHF ATPB RBCL CLPP1 YCF1 YCF2 ACCD Translation PEP PSI PSII Supplemental Figure 5. qrt PCR analysis of plants overexpressing RSH3-GFP. qrt PCR for chloroplast transcripts in wildtype (dark green) and OX:RSH3-GFP.1 (OX:RSH3 GFP ) seedlings (light green) 12 DAS. Data are presented as means ± SEM for three independent biological replicates and are normalized to 18S, APT1, PP2A and ULP7 reference transcripts. Transcripts produced principally or partially by NEP are indicated in purple. P<.5, two-way Student test. 5
6 A Time, hrs Puro Loading control Supplemental Figure 6. Proof of concept for puromycin labeling in plants. Puromycin is incorporated into cytosolic and chloroplastic proteins in a time dependent manner, and incorporation is inhibited by translation inhibitors. (A) Immunoblots of total Arabidopsis seedling proteins using a monoclonal anti-puromycin antibody (αpuro). 12-day old Arabidopsis seedlings were labeled with 5 µg/ml puromycin for the indicated time intervals before extraction of proteins, and equal quantities of protein were separated by SDS PAGE. Note the absence of a background signal in the unlabeled sample ( hrs). (B) Immunoblots of equal quantities of chloroplast total protein from 12 day old seedlings labelled with puromycin for 1 hr. Incorporation of puromycin is inhibited by the pretreatment with the cytosolic translation inhibitor cycloheximide (CHX, 1 µg/ml) and is further inhibited by the chloroplast translation inhibitor lincomycin (L, 1 mm). Note that although cycloheximide blocks cytosolic translation, it also introduces a significant background signal that is caused by the puromycylation of cycloheximide arrested nascent peptide chains (David et al., 212). This background is visible in the sample from seedlings treated with cycloheximide and lincomycin. Loading and transfer controls are RBCL stained with Ponceau red. 6
7 A B RSH1 At4g226 RSH2 At3g145 RSH3 At1g5413 CRSH At4g1747 SAIL_391_E11 rsh1-1 SAIL _35_B12 rsh2-1 SAIL_99_G5 rsh3-1 SAIL_1295_C4 crsh1-1 crsh-ami C 1.2 Relative expression QM Relative expression.8.4 QMai QMaii RSH1 RSH2 RSH3 CRSH CRSH Supplemental Figure 7. Insertion sites and gene expression in the RSH mutants. (A) The insertion sites of the Arabidopsis TDNA insertion mutants used in this study. Insertions for RSH1, RSH2 and RSH3 are upstream of the conserved ppgpp synthase and hydrolase domains. The region of the CRSH transcript targeted by the amirna in crsh-ami is indicated. qrt PCR analysis of RSH gene expression in seedlings 12 DAS using primers downstream of the insertion sites in (B) the rsh1-1 rsh2-1 rsh3-1 crsh1-1 quadruple mutant (QM) and (C) the rsh1-1 rsh2-1 rsh3-1 crsh-ami quadruple mutants (QMai and QMaii). QMai and QMaii have independent TDNA insertions for crsh-ami. Primers for qrt PCR and mutant genotyping are listed in Supplemental Data Set 1. qrt PCR data are presented as means ± SEM for three independent biological replicates and transcript abundance was normalized to 18S and PP2A reference genes. 7
8 4 ppgpp, pmol/g fresh weight QMaii OX:RSH1GFP.1 Supplemental Figure 8. ppgpp levels in QMaii and RSH1-GFP overexpressing plants were determined using a large scale extraction. ppgpp was extracted from seedlings grown on plates for 12 DAS and quantified by UPLC-MS, P<.1, two-way Student t-test versus. Data are presented as means ± SEM for four independent biological replicates. 8
9 A Transcript abudance 2 1 rsh1-1 DM-23 QMaii B 16S TRNR RBCL OX:RSH3 GFP rsh1-1 QMaii OX:RSH1 GFP C D Chloroplast area / cell area 1% 75% 5% 25% Rosette area, cm % OX:RSH3 GFP OX:RSH1 GFP rsh1-1 DM-23 QM QMai QMaii Supplementantal Figure 9. Phenotypes of RSH mutants during vegetative growth. (A) qrt PCR for chloroplast transcripts in wildtype and mutant plants 12 DAS. Data are presented as means ± SEM for five independent biological replicates and transcript abundance was normalized to 18S, APT1, PP2A and ULP7 reference transcripts. Statistical analysis was performed using ANOVA with post hoc Dunnett tests versus the wildtype control. (B) Images of representative protoplasts from fully expanded leaves of plants grown on soil at 35 DAS (scale bar, 2 µm). Analysis of these protoplast populations is presented in Figure 6B. (C) Chloroplast plan area per cell area was analyzed in intact mesophyll cells 28 DAS as described previously (Pyke and Leech, 1991). Data were analyzed by the Kruskal-Wallis test with the Dunn test post hoc, 44 cells were analyzed for, 5 for OX:RSH1-GFP.1 and 2 for OX:RSH3-GFP.1 (D) The average rosette area for selected mutants after 24 days growth on soil under long day conditions. Data were analyzed by ANOVA with post hoc Dunnett tests versus the wildtype controls, n=16 plants. OX:RSH3 GFP, OX:RSH3-GFP.1; OX:RSH1 GFP, OX:RSH1-GFP.1; P<.1; error bars, SEM. 9
10 rsh1-1 QMai QMaii Supplemental Figure 1. RSH mutants show visible growth phenotypes under short day conditions. After flowering under short day conditions rsh1-1 plants rapidly become pale and show large numbers of senescent leaves compared to plants. In contrast, QMai and QMaii plants have small rosettes and darker leaves. The plants shown are 95 days old. 1
11 2 Absolute Expression RSH1 RSH2 RSH3 CRSH Imbibed Seed, 24h Root Hypocotyl Cotyledon Leaf 1+2 Vegetative Rosette Cauline Leaf Senescing Leaf Flower Stage 15, Pedicels Flower Stage 15, Sepals Flower Stage 15, Petals Flower Stage 15, Stamens Flower Stage 15, Carpels Seed Stage 4 w/o Siliques Seed Stage 7 w/o Siliques Seed Stage 1 w/o Siliques Dry Seed Supplemental Figure 11. RSH2 and RSH3 are strongly expressed during senescence and late plant development. Microarray expression profiles of Arabidopsis RSH genes (displayed from left to right: RSH1, RSH2, RSH3 and CRSH) in different plant organs and at different stages of development. Data are presented as means ± SEM for three biological replicates. Data are from Schmid et al. (25) and were retrieved from Genevestigator (Zimmermann et al., 24). 11
12 A 1. B 1. Chl mg/g fresh weight.5 Chl mg/g fresh weight rsh1-1 DM-23 QM QMai QMaii OX:RSH1 GFP Supplemental Figure 12. Additional dark-induced senescence phenotypes. (A) CRSH may also contribute to the progression of dark-induced senescence. Chlorophyll levels in the leaves of wildtype and selected mutant lines following senescence induction. Prior to senescence induction plants used were grown under long day conditions for 3 days, and had just initiated flowering. This later developmental timepoint results in a faster progression of senescence than in Figure 7A. Chlorophyll loss was significantly greater in the wildtype than in DM-23, QM, QMai and QMaii (P<.1, n=3 plants). In addition the stay green phenotype of QMaii was significantly stronger than that of DM-23 suggesting that CRSH may also contribute during senescence despite its low level of expression, P<.5. Data were analyzed by ANOVA. (B) Plants overexpressing RSH1-GFP show a stay-green phenotype. Chlorophyll content in 27 day old and OX:RSH1-GFP.1 (OX:RSH1 GFP ) plants under normal growth conditions (dark green) or after senescence induction in the dark for three days (light green), P =.1 versus OX:RSH1-GFP.1 after 3 days in the dark, n=3 plants, two-way Student t-test; error bars, SEM. 12
13 Supplemental Figure 13. Natural senescence is affected in RSH mutants. Leaves were recovered from the base of the rosette of 95 day old plants grown under short day conditions and arranged in order of age from the oldest on the left. Gaps were left for missing leaves. Natural senescence is visible in the wild type, and appears enhanced in rsh1-1 and reduced in DM-23. QMaii leaves display an unusual senescence phenotype where they crumple and dry out while remaining green. 13
14 rsh1-1 DM-23 QM QMai QMaii Seed weight, ug Supplemental Figure 14. RSH mutants have altered seed weight suggesting defects in nutrient remobilization or seed development. 3-5 seeds per plant were counted and weighed for seven or more biological replicates. Data were analyzed by ANOVA with post hoc Dunnett tests versus the wildtype controls, P<.1; error bars, SEM. 14
15 A KDa M OX:RSH3 GFP OX:RSH1 GFP B KDa M DM23 T1 DM23 + ProRSH3:RSH3 L RBCL D RBCL RBCS D RBCL RBCS D RBCL RBCS Supplemental Figure 15. RuBisCO degradation is regulated by ppgpp during darkinduced senescence. (A) Equal quantities of total protein from, OX:RSH3-GFP.1 (OX:RSH3 GFP ) and OX:RSH1-GFP.1 (OX:RSH1 GFP ) plants were separated by SDS-PAGE and visualized by Coomassie Brilliant Blue after extraction from the leaves of selected lines after 4 days (D4) and 6 days (D6) of darkness. Plants had grown for 21 DAS at the start of treatment. Non-treated leaves were used as a control on day 4 (L4). Extractions from the leaves of three independent plants are shown for each line. (B) The leaves of, DM-23 and independent first generation (T1) DM-23 lines transformed with the genomic RSH3 (ProRSH3:RSH3) were analyzed as above after 6 days (D6) of darkness. Below each lane pixel densities for RBCL are shown, normalized to the wild type control on the same gel. 15
16 References ATKINSON, G. C., TENSON, T. & HAURYLIUK, V The RelA/SpoT homolog (RSH) superfamily: distribution and functional evolution of ppgpp synthetases and hydrolases across the tree of life. PLoS One, 6, e DAVID, A., DOLAN, B. P., HICKMAN, H. D., KNOWLTON, J. J., CLAVARINO, G., PIERRE, P., BENNINK, J. R. & YEWDELL, J. W Nuclear translation visualized by ribosome-bound nascent chain puromycylation. J Cell Biol, 197, MIZUSAWA, K., MASUDA, S. & OHTA, H. 28. Expression profiling of four RelA/SpoT-like proteins, homologues of bacterial stringent factors, in Arabidopsis thaliana. Planta, 228, PYKE, K. A. & LEECH, R. M Rapid Image Analysis Screening Procedure for Identifying Chloroplast Number Mutants in Mesophyll Cells of Arabidopsis thaliana (L.) Heynh. Plant Physiol, 96, SCHMID, M., DAVISON, T. S., HENZ, S. R., PAPE, U. J., DEMAR, M., VINGRON, M., SCHOLKOPF, B., WEIGEL, D. & LOHMANN, J. U. 25. A gene expression map of Arabidopsis thaliana development. Nat Genet, 37, ZIMMERMANN, P., HIRSCH-HOFFMANN, M., HENNIG, L. & GRUISSEM, W. 24. GENEVESTIGATOR. Arabidopsis microarray database and analysis toolbox. Plant Physiol., 136,
Figure 1. Identification of UGT74E2 as an IBA glycosyltransferase. (A) Relative conversion rates of different plant hormones to their glucosylated
 Figure 1. Identification of UGT74E2 as an IBA glycosyltransferase. (A) Relative conversion rates of different plant hormones to their glucosylated form by recombinant UGT74E2. The naturally occurring auxin
Figure 1. Identification of UGT74E2 as an IBA glycosyltransferase. (A) Relative conversion rates of different plant hormones to their glucosylated form by recombinant UGT74E2. The naturally occurring auxin
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1. HSP21 expression in 35S:HSP21 and hsp21 knockdown plants. (a) Since no T- DNA insertion line for HSP21 is available in the publicly available T-DNA collections,
Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1. HSP21 expression in 35S:HSP21 and hsp21 knockdown plants. (a) Since no T- DNA insertion line for HSP21 is available in the publicly available T-DNA collections,
Supplemental Data. Perrella et al. (2013). Plant Cell /tpc
 Intensity Intensity Intensity Intensity Intensity Intensity 150 50 150 0 10 20 50 C 150 0 10 20 50 D 0 10 20 Distance (μm) 50 20 40 E 50 F 0 10 20 50 0 15 30 Distance (μm) Supplemental Figure 1: Co-localization
Intensity Intensity Intensity Intensity Intensity Intensity 150 50 150 0 10 20 50 C 150 0 10 20 50 D 0 10 20 Distance (μm) 50 20 40 E 50 F 0 10 20 50 0 15 30 Distance (μm) Supplemental Figure 1: Co-localization
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng Supplementary Figure 1. The phenotypes of PI , BR121, and Harosoy under short-day conditions.
 Supplementary Figure 1 The phenotypes of PI 159925, BR121, and Harosoy under short-day conditions. (a) Plant height. (b) Number of branches. (c) Average internode length. (d) Number of nodes. (e) Pods
Supplementary Figure 1 The phenotypes of PI 159925, BR121, and Harosoy under short-day conditions. (a) Plant height. (b) Number of branches. (c) Average internode length. (d) Number of nodes. (e) Pods
Supplemental Data. Chen and Thelen (2010). Plant Cell /tpc
 Supplemental Data. Chen and Thelen (2010). Plant Cell 10.1105/tpc.109.071837 1 C Total 5 kg 20 kg 100 kg Transmission Image 100 kg soluble pdtpi-gfp Plastid (PDH-alpha) Mito (PDH-alpha) GFP Image vector
Supplemental Data. Chen and Thelen (2010). Plant Cell 10.1105/tpc.109.071837 1 C Total 5 kg 20 kg 100 kg Transmission Image 100 kg soluble pdtpi-gfp Plastid (PDH-alpha) Mito (PDH-alpha) GFP Image vector
** * * * Col-0 cau1 CAU1. Actin2 CAS. Actin2. Supplemental Figure 1. CAU1 affects calcium accumulation.
 Ca 2+ ug g -1 DW Ca 2+ ug g -1 DW Ca 2+ ug g -1 DW Supplemental Data. Fu et al. Plant Cell. (213). 1.115/tpc.113.113886 A 5 4 3 * Col- cau1 B 4 3 2 Col- cau1 ** * * ** C 2 1 25 2 15 1 5 Shoots Roots *
Ca 2+ ug g -1 DW Ca 2+ ug g -1 DW Ca 2+ ug g -1 DW Supplemental Data. Fu et al. Plant Cell. (213). 1.115/tpc.113.113886 A 5 4 3 * Col- cau1 B 4 3 2 Col- cau1 ** * * ** C 2 1 25 2 15 1 5 Shoots Roots *
Lipid transfer proteins confer resistance to trichothecenes
 Lipid transfer proteins confer resistance to trichothecenes John McLaughlin and Anwar Bin-Umer Tumer Laboratory National Fusarium Head Blight Forum December 6th, 2012 FY09-11: Identify trichothecene resistance
Lipid transfer proteins confer resistance to trichothecenes John McLaughlin and Anwar Bin-Umer Tumer Laboratory National Fusarium Head Blight Forum December 6th, 2012 FY09-11: Identify trichothecene resistance
Figure 18.1 Blue-light stimulated phototropism Blue light Inhibits seedling hypocotyl elongation
 Blue Light and Photomorphogenesis Q: Figure 18.3 Blue light responses - phototropsim of growing Corn Coleoptile 1. How do we know plants respond to blue light? 2. What are the functions of multiple BL
Blue Light and Photomorphogenesis Q: Figure 18.3 Blue light responses - phototropsim of growing Corn Coleoptile 1. How do we know plants respond to blue light? 2. What are the functions of multiple BL
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature12791 Supplementary Figure 1 (1/3) WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE 1 RESEARCH SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1 (2/3) 2 WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE SUPPLEMENTARY
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature12791 Supplementary Figure 1 (1/3) WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE 1 RESEARCH SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1 (2/3) 2 WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE SUPPLEMENTARY
Supplemental Data. Perea-Resa et al. Plant Cell. (2012) /tpc
 Supplemental Data. Perea-Resa et al. Plant Cell. (22)..5/tpc.2.3697 Sm Sm2 Supplemental Figure. Sequence alignment of Arabidopsis LSM proteins. Alignment of the eleven Arabidopsis LSM proteins. Sm and
Supplemental Data. Perea-Resa et al. Plant Cell. (22)..5/tpc.2.3697 Sm Sm2 Supplemental Figure. Sequence alignment of Arabidopsis LSM proteins. Alignment of the eleven Arabidopsis LSM proteins. Sm and
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/9/452/ra106/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Stem-piped light activates phytochrome B to trigger light responses in Arabidopsis thaliana roots Hyo-Jun Lee, Jun-Ho
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/9/452/ra106/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Stem-piped light activates phytochrome B to trigger light responses in Arabidopsis thaliana roots Hyo-Jun Lee, Jun-Ho
Regulation of Phosphate Homeostasis by microrna in Plants
 Regulation of Phosphate Homeostasis by microrna in Plants Tzyy-Jen Chiou 1 *, Kyaw Aung 1,2, Shu-I Lin 1,3, Chia-Chune Wu 1, Su-Fen Chiang 1, and Chun-Lin Su 1 Abstract Upon phosphate (Pi) starvation,
Regulation of Phosphate Homeostasis by microrna in Plants Tzyy-Jen Chiou 1 *, Kyaw Aung 1,2, Shu-I Lin 1,3, Chia-Chune Wu 1, Su-Fen Chiang 1, and Chun-Lin Su 1 Abstract Upon phosphate (Pi) starvation,
Maria V. Yamburenko, Yan O. Zubo, Radomíra Vanková, Victor V. Kusnetsov, Olga N. Kulaeva, Thomas Börner
 ABA represses the transcription of chloroplast genes Maria V. Yamburenko, Yan O. Zubo, Radomíra Vanková, Victor V. Kusnetsov, Olga N. Kulaeva, Thomas Börner Supplementary data Supplementary tables Table
ABA represses the transcription of chloroplast genes Maria V. Yamburenko, Yan O. Zubo, Radomíra Vanková, Victor V. Kusnetsov, Olga N. Kulaeva, Thomas Börner Supplementary data Supplementary tables Table
GFP GAL bp 3964 bp
 Supplemental Data. Møller et al. (2009) Shoot Na + exclusion and increased salinity tolerance engineered by cell type-specific alteration of Na + transport in Arabidopsis Supplemental Figure 1. Salt-sensitive
Supplemental Data. Møller et al. (2009) Shoot Na + exclusion and increased salinity tolerance engineered by cell type-specific alteration of Na + transport in Arabidopsis Supplemental Figure 1. Salt-sensitive
Heterosis and inbreeding depression of epigenetic Arabidopsis hybrids
 Heterosis and inbreeding depression of epigenetic Arabidopsis hybrids Plant growth conditions The soil was a 1:1 v/v mixture of loamy soil and organic compost. Initial soil water content was determined
Heterosis and inbreeding depression of epigenetic Arabidopsis hybrids Plant growth conditions The soil was a 1:1 v/v mixture of loamy soil and organic compost. Initial soil water content was determined
Supplemental Figure 1: Increased Fe deficiency gene expression in roots of nas4x-2
 Supplemental Figure 1: Increased Fe deficiency gene expression in roots of nas4x-2 IRT1, FRO2 and FIT expression levels in roots of the wild-type, nas4x- 1 and nas4x-2, showing that in both nas mutants
Supplemental Figure 1: Increased Fe deficiency gene expression in roots of nas4x-2 IRT1, FRO2 and FIT expression levels in roots of the wild-type, nas4x- 1 and nas4x-2, showing that in both nas mutants
EXPRESSION OF THE FIS2 PROMOTER IN ARABIDOPSIS THALIANA
 EXPRESSION OF THE FIS2 PROMOTER IN ARABIDOPSIS THALIANA Item Type text; Electronic Thesis Authors Bergstrand, Lauren Janel Publisher The University of Arizona. Rights Copyright is held by the author. Digital
EXPRESSION OF THE FIS2 PROMOTER IN ARABIDOPSIS THALIANA Item Type text; Electronic Thesis Authors Bergstrand, Lauren Janel Publisher The University of Arizona. Rights Copyright is held by the author. Digital
Supplemental Data. Wang et al. (2014). Plant Cell /tpc
 Supplemental Figure1: Mock and NPA-treated tomato plants. (A) NPA treated tomato (cv. Moneymaker) developed a pin-like inflorescence (arrowhead). (B) Comparison of first and second leaves from mock and
Supplemental Figure1: Mock and NPA-treated tomato plants. (A) NPA treated tomato (cv. Moneymaker) developed a pin-like inflorescence (arrowhead). (B) Comparison of first and second leaves from mock and
23-. Shoot and root development depend on ratio of IAA/CK
 Balance of Hormones regulate growth and development Environmental factors regulate hormone levels light- e.g. phototropism gravity- e.g. gravitropism temperature Mode of action of each hormone 1. Signal
Balance of Hormones regulate growth and development Environmental factors regulate hormone levels light- e.g. phototropism gravity- e.g. gravitropism temperature Mode of action of each hormone 1. Signal
Supplemental Data. Hou et al. (2016). Plant Cell /tpc
 Supplemental Data. Hou et al. (216). Plant Cell 1.115/tpc.16.295 A Distance to 1 st nt of start codon Distance to 1 st nt of stop codon B Normalized PARE abundance 8 14 nt 17 nt Frame1 Arabidopsis inflorescence
Supplemental Data. Hou et al. (216). Plant Cell 1.115/tpc.16.295 A Distance to 1 st nt of start codon Distance to 1 st nt of stop codon B Normalized PARE abundance 8 14 nt 17 nt Frame1 Arabidopsis inflorescence
Supplemental Data. Yamamoto et al. (2016). Plant Cell /tpc WT + HCO 3. slac1-4/δnc #5 + HCO 3 WT + ABA. slac1-4/δnc #5 + ABA
 I (pa) I (pa) A WT + HCO 3 B 2 V (mv) 15 1 5 5 2 slac14/δnc #5 + HCO 3 4 6 WT (n = 6) 8 WT + HCO 3 (n = 7) slac14/δnc #5 (n = 6) slac14/δnc #5 + HCO 3 (n = 1) C WT + ABA D 2 V (mv) 15 1 5 5 2 slac14/δnc
I (pa) I (pa) A WT + HCO 3 B 2 V (mv) 15 1 5 5 2 slac14/δnc #5 + HCO 3 4 6 WT (n = 6) 8 WT + HCO 3 (n = 7) slac14/δnc #5 (n = 6) slac14/δnc #5 + HCO 3 (n = 1) C WT + ABA D 2 V (mv) 15 1 5 5 2 slac14/δnc
Ethylene is critical to the maintenance of primary root growth and Fe. homeostasis under Fe stress in Arabidopsis
 Ethylene is critical to the maintenance of primary root growth and Fe homeostasis under Fe stress in Arabidopsis Guangjie Li, Weifeng Xu, Herbert J. Kronzucker, Weiming Shi * Supplementary Data Supplementary
Ethylene is critical to the maintenance of primary root growth and Fe homeostasis under Fe stress in Arabidopsis Guangjie Li, Weifeng Xu, Herbert J. Kronzucker, Weiming Shi * Supplementary Data Supplementary
Genome-wide Identification of Lineage Specific Genes in Arabidopsis, Oryza and Populus
 Genome-wide Identification of Lineage Specific Genes in Arabidopsis, Oryza and Populus Xiaohan Yang Sara Jawdy Timothy Tschaplinski Gerald Tuskan Environmental Sciences Division Oak Ridge National Laboratory
Genome-wide Identification of Lineage Specific Genes in Arabidopsis, Oryza and Populus Xiaohan Yang Sara Jawdy Timothy Tschaplinski Gerald Tuskan Environmental Sciences Division Oak Ridge National Laboratory
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 reverse 3175 3175 F L C 318 318 3185 3185 319 319 3195 3195 315 8 1 315 3155 315 317 Supplementary Figure 3. Stability of expression of the GFP sensor constructs return to warm conditions. Semi-quantitative
reverse 3175 3175 F L C 318 318 3185 3185 319 319 3195 3195 315 8 1 315 3155 315 317 Supplementary Figure 3. Stability of expression of the GFP sensor constructs return to warm conditions. Semi-quantitative
Supp- Figure 2 Confocal micrograph of N. benthamiana tissues transiently expressing 35S:YFP-PDCB1. PDCB1 was targeted to plasmodesmata (twin punctate
 Supplemental Data. Simpson et al. (009). n rabidopsis GPI-anchor plasmodesmal neck protein with callosebinding activity and potential to regulate cell-to-cell trafficking. 5 0 stack Supp- Figure Confocal
Supplemental Data. Simpson et al. (009). n rabidopsis GPI-anchor plasmodesmal neck protein with callosebinding activity and potential to regulate cell-to-cell trafficking. 5 0 stack Supp- Figure Confocal
. Supplementary Information
 . Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure S1. Mature embryo sac observations. Supplementary Figure S2. STT observations. Supplementary Figure S3. Comparison of the PTB1 cdna with that of the mutant.
. Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure S1. Mature embryo sac observations. Supplementary Figure S2. STT observations. Supplementary Figure S3. Comparison of the PTB1 cdna with that of the mutant.
Supplementary Figure S1. Amino acid alignment of selected monocot FT-like and TFL-like sequences. Sequences were aligned using ClustalW and analyzed
 Supplementary Figure S1. Amino acid alignment of selected monocot FT-like and TFL-like sequences. Sequences were aligned using ClustalW and analyzed using the Geneious software. Accession numbers of the
Supplementary Figure S1. Amino acid alignment of selected monocot FT-like and TFL-like sequences. Sequences were aligned using ClustalW and analyzed using the Geneious software. Accession numbers of the
Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of wild type (WT) and abci8 mutant in the paddy field.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of wild type (WT) and abci8 mutant in the paddy field. A, Phenotypes of 30-day old wild-type (WT) and abci8 mutant plants grown in a paddy field under normal sunny
Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of wild type (WT) and abci8 mutant in the paddy field. A, Phenotypes of 30-day old wild-type (WT) and abci8 mutant plants grown in a paddy field under normal sunny
Supplementary Figure 1. Phenotype of the HI strain.
 Supplementary Figure 1. Phenotype of the HI strain. (A) Phenotype of the HI and wild type plant after flowering (~1month). Wild type plant is tall with well elongated inflorescence. All four HI plants
Supplementary Figure 1. Phenotype of the HI strain. (A) Phenotype of the HI and wild type plant after flowering (~1month). Wild type plant is tall with well elongated inflorescence. All four HI plants
Supplemental Data. Fernández-Calvo et al. Plant Cell. (2011) /tpc
 Supplemental Data. Fernández-Calvo et al. Plant Cell. (2011). 10.1105/tpc.110.080788 Supplemental Figure S1. Phylogenetic tree of MYC2-related proteins from Arabidopsis and other plants. Phenogram representation
Supplemental Data. Fernández-Calvo et al. Plant Cell. (2011). 10.1105/tpc.110.080788 Supplemental Figure S1. Phylogenetic tree of MYC2-related proteins from Arabidopsis and other plants. Phenogram representation
Genetic Characterization and Functional Analysis of the GID1 Gibberellin Receptors in Arabidopsis W
 The Plant Cell, Vol. 18, 3399 3414, December 2006, www.plantcell.org ª 2006 American Society of Plant Biologists Genetic Characterization and Functional Analysis of the GID1 Gibberellin Receptors in Arabidopsis
The Plant Cell, Vol. 18, 3399 3414, December 2006, www.plantcell.org ª 2006 American Society of Plant Biologists Genetic Characterization and Functional Analysis of the GID1 Gibberellin Receptors in Arabidopsis
A MicroRNA as a Translational Repressor of APETALA2 in Arabidopsis Flower Development
 A MicroRNA as a Translational Repressor of APETALA2 in Arabidopsis Flower Development Xuemei Chen Waksman Institute, Rutgers University, Piscataway, NJ 08854, USA. E-mail: xuemei@waksman.rutgers.edu Plant
A MicroRNA as a Translational Repressor of APETALA2 in Arabidopsis Flower Development Xuemei Chen Waksman Institute, Rutgers University, Piscataway, NJ 08854, USA. E-mail: xuemei@waksman.rutgers.edu Plant
Supporting Online Material
 1 Stomatal Patterning and Differentiation by Synergistic Interactions of Receptor Kinases Elena D. Shpak, Jessica Messmer McAbee, Lynn Jo Pillitteri, and Keiko U. Torii Supporting Online Material Material
1 Stomatal Patterning and Differentiation by Synergistic Interactions of Receptor Kinases Elena D. Shpak, Jessica Messmer McAbee, Lynn Jo Pillitteri, and Keiko U. Torii Supporting Online Material Material
The Plant Cell, November. 2017, American Society of Plant Biologists. All rights reserved
 The Genetics of Floral Development Teaching Guide Overview The development of flowers in angiosperm plants provided a critical evolutionary advantage, allowing more options for pollen dispersal and seed
The Genetics of Floral Development Teaching Guide Overview The development of flowers in angiosperm plants provided a critical evolutionary advantage, allowing more options for pollen dispersal and seed
Photoreceptor Regulation of Constans Protein in Photoperiodic Flowering
 Photoreceptor Regulation of Constans Protein in Photoperiodic Flowering by Valverde et. Al Published in Science 2004 Presented by Boyana Grigorova CBMG 688R Feb. 12, 2007 Circadian Rhythms: The Clock Within
Photoreceptor Regulation of Constans Protein in Photoperiodic Flowering by Valverde et. Al Published in Science 2004 Presented by Boyana Grigorova CBMG 688R Feb. 12, 2007 Circadian Rhythms: The Clock Within
Illegitimate translation causes unexpected gene expression from on-target out-of-frame alleles
 Illegitimate translation causes unexpected gene expression from on-target out-of-frame alleles created by CRISPR-Cas9 Shigeru Makino, Ryutaro Fukumura, Yoichi Gondo* Mutagenesis and Genomics Team, RIKEN
Illegitimate translation causes unexpected gene expression from on-target out-of-frame alleles created by CRISPR-Cas9 Shigeru Makino, Ryutaro Fukumura, Yoichi Gondo* Mutagenesis and Genomics Team, RIKEN
7.06 Problem Set #4, Spring 2005
 7.06 Problem Set #4, Spring 2005 1. You re doing a mutant hunt in S. cerevisiae (budding yeast), looking for temperaturesensitive mutants that are defective in the cell cycle. You discover a mutant strain
7.06 Problem Set #4, Spring 2005 1. You re doing a mutant hunt in S. cerevisiae (budding yeast), looking for temperaturesensitive mutants that are defective in the cell cycle. You discover a mutant strain
Supplemental Data. Yang et al. (2012). Plant Cell /tpc
 Supplemental Figure 1. Mature flowers of P. heterotricha. (A) An inflorescence of P. heterotricha showing the front view of a zygomorphic flower characterized by two small dorsal petals and only two fertile
Supplemental Figure 1. Mature flowers of P. heterotricha. (A) An inflorescence of P. heterotricha showing the front view of a zygomorphic flower characterized by two small dorsal petals and only two fertile
** LCA LCN PCA
 % of wild type value % of wild type value a 12 1 8 2 b 12 1 8 2 LCA LCN PCA Col- sod3-1 Supplementary Figure 1 sod3-1 influences cell proliferation. (a) Fifth leaf cell area (LCA) and leaf cell number
% of wild type value % of wild type value a 12 1 8 2 b 12 1 8 2 LCA LCN PCA Col- sod3-1 Supplementary Figure 1 sod3-1 influences cell proliferation. (a) Fifth leaf cell area (LCA) and leaf cell number
Supplemental material
 Supplemental material Table 1- Segregation analysis of sgt1a sgt1b double mutant plants Parental genotype No. of lines Normal seeds Phenotype Abnormal seeds Ratio of abnormal seeds (%) WT 3 171 2 1.16
Supplemental material Table 1- Segregation analysis of sgt1a sgt1b double mutant plants Parental genotype No. of lines Normal seeds Phenotype Abnormal seeds Ratio of abnormal seeds (%) WT 3 171 2 1.16
GENETIC ANALYSES OF ROOT SYSTEM DEVELOPMENT IN THE TOMATO CROP MODEL
 GENETIC ANALYSES OF ROOT SYSTEM DEVELOPMENT IN THE TOMATO CROP MODEL Kelsey Hoth 1 Dr. Maria Ivanchenko 2 Bioresourse Research 1, Department of Botany and Plant Physiology 2, Oregon State University, Corvallis,
GENETIC ANALYSES OF ROOT SYSTEM DEVELOPMENT IN THE TOMATO CROP MODEL Kelsey Hoth 1 Dr. Maria Ivanchenko 2 Bioresourse Research 1, Department of Botany and Plant Physiology 2, Oregon State University, Corvallis,
Analysis of regulatory function of circadian clock. on photoreceptor gene expression
 Thesis of Ph.D. dissertation Analysis of regulatory function of circadian clock on photoreceptor gene expression Tóth Réka Supervisor: Dr. Ferenc Nagy Biological Research Center of the Hungarian Academy
Thesis of Ph.D. dissertation Analysis of regulatory function of circadian clock on photoreceptor gene expression Tóth Réka Supervisor: Dr. Ferenc Nagy Biological Research Center of the Hungarian Academy
THE ROLE OF THE PHYTOCHROME B PHOTORECEPTOR IN THE REGULATION OF PHOTOPERIODIC FLOWERING. AnitaHajdu. Thesis of the Ph.D.
 THE ROLE OF THE PHYTOCHROME B PHOTORECEPTOR IN THE REGULATION OF PHOTOPERIODIC FLOWERING AnitaHajdu Thesis of the Ph.D. dissertation Supervisor: Dr. LászlóKozma-Bognár - senior research associate Doctoral
THE ROLE OF THE PHYTOCHROME B PHOTORECEPTOR IN THE REGULATION OF PHOTOPERIODIC FLOWERING AnitaHajdu Thesis of the Ph.D. dissertation Supervisor: Dr. LászlóKozma-Bognár - senior research associate Doctoral
DNA or RNA metabolism (1%) Signal transduction (2%) Development (2%) Other cellular processes (17%)
 Fig. 35-24 Other metabolism (18%) DNA or RNA metabolism (1%) Signal transduction (2%) Development (2%) Unknown (24%) Energy pathways (3%) Cell division and organization (3%) Transport (4%) Transcription
Fig. 35-24 Other metabolism (18%) DNA or RNA metabolism (1%) Signal transduction (2%) Development (2%) Unknown (24%) Energy pathways (3%) Cell division and organization (3%) Transport (4%) Transcription
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature10534 Supplementary Fig. 1. Diagrammatic representation of the N-end rule pathway of targeted proteolysis (after Graciet and Wellmer 2010 9 ). Tertiary, secondary
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature10534 Supplementary Fig. 1. Diagrammatic representation of the N-end rule pathway of targeted proteolysis (after Graciet and Wellmer 2010 9 ). Tertiary, secondary
Biological Roles of Cytokinins
 Direct Control of Shoot Meristem Activity by a Cytokinin-Activating Enzyme By Kurakawa et. Al. Published in Nature Presented by Boyana Grigorova Biological Roles of Cytokinins Cytokinins are positive regulators
Direct Control of Shoot Meristem Activity by a Cytokinin-Activating Enzyme By Kurakawa et. Al. Published in Nature Presented by Boyana Grigorova Biological Roles of Cytokinins Cytokinins are positive regulators
CHAPTER 13 PROKARYOTE GENES: E. COLI LAC OPERON
 PROKARYOTE GENES: E. COLI LAC OPERON CHAPTER 13 CHAPTER 13 PROKARYOTE GENES: E. COLI LAC OPERON Figure 1. Electron micrograph of growing E. coli. Some show the constriction at the location where daughter
PROKARYOTE GENES: E. COLI LAC OPERON CHAPTER 13 CHAPTER 13 PROKARYOTE GENES: E. COLI LAC OPERON Figure 1. Electron micrograph of growing E. coli. Some show the constriction at the location where daughter
Supplemental Information. Full transcription of the chloroplast genome in photosynthetic
 Supplemental Information Full transcription of the chloroplast genome in photosynthetic eukaryotes Chao Shi 1,3*, Shuo Wang 2*, En-Hua Xia 1,3*, Jian-Jun Jiang 2, Fan-Chun Zeng 2, and 1, 2 ** Li-Zhi Gao
Supplemental Information Full transcription of the chloroplast genome in photosynthetic eukaryotes Chao Shi 1,3*, Shuo Wang 2*, En-Hua Xia 1,3*, Jian-Jun Jiang 2, Fan-Chun Zeng 2, and 1, 2 ** Li-Zhi Gao
By Jonathan I. Watkinson. Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University. Doctor of Philosophy Horticulture
 Characterization of two genes, trehalose-6-phosphate synthase/phosphatase and nucleotide binding protein, shown to be differentially regulated in roots of Cypripedium parviflorum var. pubescens grown with
Characterization of two genes, trehalose-6-phosphate synthase/phosphatase and nucleotide binding protein, shown to be differentially regulated in roots of Cypripedium parviflorum var. pubescens grown with
Electromagenetic spectrum
 Light Controls of Plant Development 1 Electromagenetic spectrum 2 Light It is vital for photosynthesis and is also necessary to direct plant growth and development. It acts as a signal to initiate and
Light Controls of Plant Development 1 Electromagenetic spectrum 2 Light It is vital for photosynthesis and is also necessary to direct plant growth and development. It acts as a signal to initiate and
Questions for Biology IIB (SS 2006) Wilhelm Gruissem
 Questions for Biology IIB (SS 2006) Plant biology Wilhelm Gruissem The questions for my part of Biology IIB, Plant Biology, are provided for self-study and as material for the exam. Please note that the
Questions for Biology IIB (SS 2006) Plant biology Wilhelm Gruissem The questions for my part of Biology IIB, Plant Biology, are provided for self-study and as material for the exam. Please note that the
Arabidopsis COMPASS-Like Complexes Mediate Histone H3 Lysine-4 Trimethylation to Control Floral Transition and Plant Development
 Arabidopsis COMPASS-Like Complexes Mediate Histone H3 Lysine-4 Trimethylation to Control Floral Transition and Plant Development Danhua Jiang 1,2, Nicholas C. Kong 1,2, Xiaofeng Gu 2, Zicong Li 1, Yuehui
Arabidopsis COMPASS-Like Complexes Mediate Histone H3 Lysine-4 Trimethylation to Control Floral Transition and Plant Development Danhua Jiang 1,2, Nicholas C. Kong 1,2, Xiaofeng Gu 2, Zicong Li 1, Yuehui
The geneticist s questions. Deleting yeast genes. Functional genomics. From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
 From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Functional genomics..is a field of molecular biology that attempts to make use of the vast wealth of data produced by genomic projects (such as genome sequencing projects)
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Functional genomics..is a field of molecular biology that attempts to make use of the vast wealth of data produced by genomic projects (such as genome sequencing projects)
Genetic and molecular basis of chlorophyll retention in soybean seed
 Genetic and molecular basis of chlorophyll retention in soybean seed Henk Hilhorst, Wageningen University, Edvaldo A Amaral da Silva Universidade Estadual Paulista (FCA) Collaborators in Brazil: José França-Neto
Genetic and molecular basis of chlorophyll retention in soybean seed Henk Hilhorst, Wageningen University, Edvaldo A Amaral da Silva Universidade Estadual Paulista (FCA) Collaborators in Brazil: José França-Neto
Development 143: doi: /dev : Supplementary information
 Supplementary Materials and Methods Plant materials The mutants and transgenic plants used in the present study were as follows: E361 (from Alex Webb s laboratory); tmm-1, ptmm::tmm-gfp and flp-1 (from
Supplementary Materials and Methods Plant materials The mutants and transgenic plants used in the present study were as follows: E361 (from Alex Webb s laboratory); tmm-1, ptmm::tmm-gfp and flp-1 (from
Table S1 List of primers used for genotyping and qrt-pcr.
 Table S1 List of primers used for genotyping and qrt-pcr. genotyping! allele! ligomer*! 5'-sequence-3'! rice! d10-2! F! TTGGCTTTGCCTCGTTTC!!! R! AGCCTCCACTTGTACTGTG! Arabidopsis! max2-3, max2-4! F! ACTCTCTCCGACCTCCCTGACG!!!
Table S1 List of primers used for genotyping and qrt-pcr. genotyping! allele! ligomer*! 5'-sequence-3'! rice! d10-2! F! TTGGCTTTGCCTCGTTTC!!! R! AGCCTCCACTTGTACTGTG! Arabidopsis! max2-3, max2-4! F! ACTCTCTCCGACCTCCCTGACG!!!
NATURAL VARIATION IN THE CYTOKININ METABOLIC NETWORK IN ARABIDOPSIS THALIANA
 NATURAL VARIATION IN THE CYTOKININ METABOLIC NETWORK IN ARABIDOPSIS THALIANA PŘÍRODNÍ VARIACE METABOLISMU CYTOKININŮ U ARABIDOPSIS THALIANA Samsonová Z. 1, 2, 3, Kuklová A. 1, 2, Mazura P. 1, 2, Rotková
NATURAL VARIATION IN THE CYTOKININ METABOLIC NETWORK IN ARABIDOPSIS THALIANA PŘÍRODNÍ VARIACE METABOLISMU CYTOKININŮ U ARABIDOPSIS THALIANA Samsonová Z. 1, 2, 3, Kuklová A. 1, 2, Mazura P. 1, 2, Rotková
Plant Growth and Development
 Plant Growth and Development Concept 26.1 Plants Develop in Response to the Environment Factors involved in regulating plant growth and development: 1. Environmental cues (e.g., day length) 2. Receptors
Plant Growth and Development Concept 26.1 Plants Develop in Response to the Environment Factors involved in regulating plant growth and development: 1. Environmental cues (e.g., day length) 2. Receptors
Introduction. Gene expression is the combined process of :
 1 To know and explain: Regulation of Bacterial Gene Expression Constitutive ( house keeping) vs. Controllable genes OPERON structure and its role in gene regulation Regulation of Eukaryotic Gene Expression
1 To know and explain: Regulation of Bacterial Gene Expression Constitutive ( house keeping) vs. Controllable genes OPERON structure and its role in gene regulation Regulation of Eukaryotic Gene Expression
Lecture 10: Cyclins, cyclin kinases and cell division
 Chem*3560 Lecture 10: Cyclins, cyclin kinases and cell division The eukaryotic cell cycle Actively growing mammalian cells divide roughly every 24 hours, and follow a precise sequence of events know as
Chem*3560 Lecture 10: Cyclins, cyclin kinases and cell division The eukaryotic cell cycle Actively growing mammalian cells divide roughly every 24 hours, and follow a precise sequence of events know as
Other funding Sources Agency Name: MSU Agricultural Experiment Station /Project GREEEN Amount requested or awarded: 30,000
 FINAL PROJECT REPORT Project Title: Functional genomics of flowering in apple PI: Herb Aldwinckle Co-PI(2): Steve VanNocker Organization: Cornell University Organization: Michigan State University Telephone/email:
FINAL PROJECT REPORT Project Title: Functional genomics of flowering in apple PI: Herb Aldwinckle Co-PI(2): Steve VanNocker Organization: Cornell University Organization: Michigan State University Telephone/email:
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng Supplementary Figure 1. ssp mutant phenotypes in a functional SP background.
 Supplementary Figure 1 ssp mutant phenotypes in a functional SP background. (a,b) Statistical comparisons of primary and sympodial shoot flowering times as determined by mean values for leaf number on
Supplementary Figure 1 ssp mutant phenotypes in a functional SP background. (a,b) Statistical comparisons of primary and sympodial shoot flowering times as determined by mean values for leaf number on
Supplementary Figure 1. Markedly decreased numbers of marginal zone B cells in DOCK8 mutant mice Supplementary Figure 2.
 Supplementary Figure 1. Markedly decreased numbers of marginal zone B cells in DOCK8 mutant mice. Percentage of marginal zone B cells in the spleen of wild-type mice (+/+), mice homozygous for cpm or pri
Supplementary Figure 1. Markedly decreased numbers of marginal zone B cells in DOCK8 mutant mice. Percentage of marginal zone B cells in the spleen of wild-type mice (+/+), mice homozygous for cpm or pri
FSC-W FSC-H CD4 CD62-L
 Supplementary Fig. 1 a SSC-A FSC-A FSC-W FSC-H SSC-W SSC-H CD4 CD62-L b SSC-A FSC-A FSC-W FSC-A FSC-A 7-AAD FSC-A CD4 IL-9 CD4 c SSC-A FSC-A FSC-W FSC-H SSC-W SSC-H 7-AAD KI67 Annexin-V 7-AAD d I L -5
Supplementary Fig. 1 a SSC-A FSC-A FSC-W FSC-H SSC-W SSC-H CD4 CD62-L b SSC-A FSC-A FSC-W FSC-A FSC-A 7-AAD FSC-A CD4 IL-9 CD4 c SSC-A FSC-A FSC-W FSC-H SSC-W SSC-H 7-AAD KI67 Annexin-V 7-AAD d I L -5
Supplementary Table 1. Primers used in this study.
 Supplementary Tale 1. Primers used in this study. Name Primer sequence (5'-3') Primers of PCR-ased molecular markers developed in this study M1 F M1 R M2 F M2 R M3 F M3 R M4 F M4 R M5 F M5 R M6 F M6 R
Supplementary Tale 1. Primers used in this study. Name Primer sequence (5'-3') Primers of PCR-ased molecular markers developed in this study M1 F M1 R M2 F M2 R M3 F M3 R M4 F M4 R M5 F M5 R M6 F M6 R
the noisy gene Biology of the Universidad Autónoma de Madrid Jan 2008 Juan F. Poyatos Spanish National Biotechnology Centre (CNB)
 Biology of the the noisy gene Universidad Autónoma de Madrid Jan 2008 Juan F. Poyatos Spanish National Biotechnology Centre (CNB) day III: noisy bacteria - Regulation of noise (B. subtilis) - Intrinsic/Extrinsic
Biology of the the noisy gene Universidad Autónoma de Madrid Jan 2008 Juan F. Poyatos Spanish National Biotechnology Centre (CNB) day III: noisy bacteria - Regulation of noise (B. subtilis) - Intrinsic/Extrinsic
Biology 112 Practice Midterm Questions
 Biology 112 Practice Midterm Questions 1. Identify which statement is true or false I. Bacterial cell walls prevent osmotic lysis II. All bacterial cell walls contain an LPS layer III. In a Gram stain,
Biology 112 Practice Midterm Questions 1. Identify which statement is true or false I. Bacterial cell walls prevent osmotic lysis II. All bacterial cell walls contain an LPS layer III. In a Gram stain,
Last time: Obtaining information from a cloned gene
 Last time: Obtaining information from a cloned gene Objectives: 1. What is the biochemical role of the gene? 2. Where and when is the gene expressed (transcribed)? 3. Where and when is the protein made?
Last time: Obtaining information from a cloned gene Objectives: 1. What is the biochemical role of the gene? 2. Where and when is the gene expressed (transcribed)? 3. Where and when is the protein made?
Epigenetics and Flowering Any potentially stable and heritable change in gene expression that occurs without a change in DNA sequence
 Epigenetics and Flowering Any potentially stable and heritable change in gene expression that occurs without a change in DNA sequence www.plantcell.org/cgi/doi/10.1105/tpc.110.tt0110 Epigenetics Usually
Epigenetics and Flowering Any potentially stable and heritable change in gene expression that occurs without a change in DNA sequence www.plantcell.org/cgi/doi/10.1105/tpc.110.tt0110 Epigenetics Usually
Chloroplastic protein IOJAP is important for coldacclimation
 University of Tennessee, Knoxville Trace: Tennessee Research and Creative Exchange University of Tennessee Honors Thesis Projects University of Tennessee Honors Program 5-216 Chloroplastic protein IOJAP
University of Tennessee, Knoxville Trace: Tennessee Research and Creative Exchange University of Tennessee Honors Thesis Projects University of Tennessee Honors Program 5-216 Chloroplastic protein IOJAP
Growth and development of Arabidopsis thaliana under single-wavelength red
 1 Supplementary Information 2 3 4 Growth and development of Arabidopsis thaliana under single-wavelength red and blue laser light 5 6 7 8 Authors Amanda Ooi 1 *, Aloysius Wong 1 *, Tien Khee Ng 2, Claudius
1 Supplementary Information 2 3 4 Growth and development of Arabidopsis thaliana under single-wavelength red and blue laser light 5 6 7 8 Authors Amanda Ooi 1 *, Aloysius Wong 1 *, Tien Khee Ng 2, Claudius
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplemental Methods Isolation and mapping of SPCH An EMS-mutagenized population of tmm-1 (Col);E1728 (an enhancer trap GFP marking guard cells) was created. M2 seeds were collected from M1 s planted in
Supplemental Methods Isolation and mapping of SPCH An EMS-mutagenized population of tmm-1 (Col);E1728 (an enhancer trap GFP marking guard cells) was created. M2 seeds were collected from M1 s planted in
Liu, Yang (2012) The characterization of a novel abscission-related gene in Arabidopsis thaliana. PhD thesis, University of Nottingham.
 Liu, Yang (2012) The characterization of a novel abscission-related gene in Arabidopsis thaliana. PhD thesis, University of Nottingham. Access from the University of Nottingham repository: http://eprints.nottingham.ac.uk/12529/3/thesis_part_2_final.pdf
Liu, Yang (2012) The characterization of a novel abscission-related gene in Arabidopsis thaliana. PhD thesis, University of Nottingham. Access from the University of Nottingham repository: http://eprints.nottingham.ac.uk/12529/3/thesis_part_2_final.pdf
DEVELOPMENTAL GENETICS OF ARABIDOPSIS THALIANA
 DEVELOPMENTAL GENETICS OF ARABIDOPSIS THALIANA CHASE BALLARD LINDA EAN HECTOR LOPEZ DR. JOANNA WERNER-FRACZEK IN COLLABORATION WITH DR. PATRICIA SPRINGER S LAB AT UCR AND ROBERT KOBLE PURPOSE OF RESEARCH
DEVELOPMENTAL GENETICS OF ARABIDOPSIS THALIANA CHASE BALLARD LINDA EAN HECTOR LOPEZ DR. JOANNA WERNER-FRACZEK IN COLLABORATION WITH DR. PATRICIA SPRINGER S LAB AT UCR AND ROBERT KOBLE PURPOSE OF RESEARCH
Leucine-rich repeat receptor-like kinases (LRR-RLKs), HAESA, ERECTA-family
 Leucine-rich repeat receptor-like kinases (LRR-RLKs), HAESA, ERECTA-family GENES & DEVELOPMENT (2000) 14: 108 117 INTRODUCTION Flower Diagram INTRODUCTION Abscission In plant, the process by which a plant
Leucine-rich repeat receptor-like kinases (LRR-RLKs), HAESA, ERECTA-family GENES & DEVELOPMENT (2000) 14: 108 117 INTRODUCTION Flower Diagram INTRODUCTION Abscission In plant, the process by which a plant
AUXIN RESPONSE FACTOR1 and AUXIN RESPONSE FACTOR2. thaliana. regulate senescence and floral organ abscission in Arabidopsis.
 Research article 4563 AUXIN RESPONSE FACTOR1 and AUXIN RESPONSE FACTOR2 regulate senescence and floral organ abscission in Arabidopsis thaliana Christine M. Ellis 1, Punita Nagpal 1, Jeffery C. Young 3,
Research article 4563 AUXIN RESPONSE FACTOR1 and AUXIN RESPONSE FACTOR2 regulate senescence and floral organ abscission in Arabidopsis thaliana Christine M. Ellis 1, Punita Nagpal 1, Jeffery C. Young 3,
Supplemental material
 Supplemental material THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY Mourier et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201411100/dc1 Figure S1. Size and mitochondrial content in Mfn1 and Mfn2 knockout hearts. (A) Body
Supplemental material THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY Mourier et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201411100/dc1 Figure S1. Size and mitochondrial content in Mfn1 and Mfn2 knockout hearts. (A) Body
3.B.1 Gene Regulation. Gene regulation results in differential gene expression, leading to cell specialization.
 3.B.1 Gene Regulation Gene regulation results in differential gene expression, leading to cell specialization. We will focus on gene regulation in prokaryotes first. Gene regulation accounts for some of
3.B.1 Gene Regulation Gene regulation results in differential gene expression, leading to cell specialization. We will focus on gene regulation in prokaryotes first. Gene regulation accounts for some of
7.06 Problem Set
 7.06 Problem Set 5 -- 2006 1. In the first half of the course, we encountered many examples of proteins that entered the nucleus in response to the activation of a cell-signaling pathway. One example of
7.06 Problem Set 5 -- 2006 1. In the first half of the course, we encountered many examples of proteins that entered the nucleus in response to the activation of a cell-signaling pathway. One example of
m1 m2 m3 m4 m5 m6 m7 m8 wt m m m m m m m m8 - + wt +
 otherwise, you couldn't grow them!) You perform pairwise infections with each of your mutant bacteriophage strains and get the following results: (+) = pair of phages lysed host cells, (-) = pair of phages
otherwise, you couldn't grow them!) You perform pairwise infections with each of your mutant bacteriophage strains and get the following results: (+) = pair of phages lysed host cells, (-) = pair of phages
Ph.D. thesis. Study of proline accumulation and transcriptional regulation of genes involved in this process in Arabidopsis thaliana
 Ph.D. thesis Study of proline accumulation and transcriptional regulation of genes involved in this process in Arabidopsis thaliana Written by: Edit Ábrahám Temesváriné Supervisors: Dr. László Szabados
Ph.D. thesis Study of proline accumulation and transcriptional regulation of genes involved in this process in Arabidopsis thaliana Written by: Edit Ábrahám Temesváriné Supervisors: Dr. László Szabados
PYR1 PYL1 PYL2 PYL3 PYL4 PYL5 PYL6 PYL7 PYL8 PYL9 PYL10 PYL11/12
 Supplemental Data. Gonzalez-Guzman et al. Plant Cell. (212). 1.115/tpc.112.98574 Supplemental Figure 1. Gene expression levels of the PYR/PYL/RCAR ABA receptors in the Arabidopsis transcriptome genomic
Supplemental Data. Gonzalez-Guzman et al. Plant Cell. (212). 1.115/tpc.112.98574 Supplemental Figure 1. Gene expression levels of the PYR/PYL/RCAR ABA receptors in the Arabidopsis transcriptome genomic
4) Please cite Dagda et al J Biol Chem 284: , for any publications or presentations resulting from use or modification of the macro.
 Supplement Figure S1. Algorithmic quantification of mitochondrial morphology in SH- SY5Y cells treated with known fission/fusion mediators. Parental SH-SY5Y cells were transiently transfected with an empty
Supplement Figure S1. Algorithmic quantification of mitochondrial morphology in SH- SY5Y cells treated with known fission/fusion mediators. Parental SH-SY5Y cells were transiently transfected with an empty
University of Groningen
 University of Groningen Photosynthetic Quantum Yield Dynamics Hogewoning, Sander W.; Wientjes, Emilie; Douwstra, Peter; Trouwborst, Govert; van Ieperen, Wim; Croce, Roberta; Harbinson, Jeremy Published
University of Groningen Photosynthetic Quantum Yield Dynamics Hogewoning, Sander W.; Wientjes, Emilie; Douwstra, Peter; Trouwborst, Govert; van Ieperen, Wim; Croce, Roberta; Harbinson, Jeremy Published
(Lys), resulting in translation of a polypeptide without the Lys amino acid. resulting in translation of a polypeptide without the Lys amino acid.
 1. A change that makes a polypeptide defective has been discovered in its amino acid sequence. The normal and defective amino acid sequences are shown below. Researchers are attempting to reproduce the
1. A change that makes a polypeptide defective has been discovered in its amino acid sequence. The normal and defective amino acid sequences are shown below. Researchers are attempting to reproduce the
Arabidopsis PPR40 connects abiotic stress responses to mitochondrial electron transport
 Ph.D. thesis Arabidopsis PPR40 connects abiotic stress responses to mitochondrial electron transport Zsigmond Laura Supervisor: Dr. Szabados László Arabidopsis Molecular Genetic Group Institute of Plant
Ph.D. thesis Arabidopsis PPR40 connects abiotic stress responses to mitochondrial electron transport Zsigmond Laura Supervisor: Dr. Szabados László Arabidopsis Molecular Genetic Group Institute of Plant
Quantification of Protein Half-Lives in the Budding Yeast Proteome
 Supporting Methods Quantification of Protein Half-Lives in the Budding Yeast Proteome 1 Cell Growth and Cycloheximide Treatment Three parallel cultures (17 ml) of each TAP-tagged strain were grown in separate
Supporting Methods Quantification of Protein Half-Lives in the Budding Yeast Proteome 1 Cell Growth and Cycloheximide Treatment Three parallel cultures (17 ml) of each TAP-tagged strain were grown in separate
Functional analysis of complexes with mixed primary and secondary cellulose synthases
 Short Communication Plant Signaling & Behavior 8:3, e23179; March 2013; 2013 Landes Bioscience Short Communication Functional analysis of complexes with mixed primary and secondary cellulose synthases
Short Communication Plant Signaling & Behavior 8:3, e23179; March 2013; 2013 Landes Bioscience Short Communication Functional analysis of complexes with mixed primary and secondary cellulose synthases
Penghui Li, Beibei Chen, Gaoyang Zhang, Longxiang Chen, Qiang Dong, Jiangqi Wen, Kirankumar S. Mysore and Jian Zhao
 New Phytologist Supporting Information Regulation of anthocyanin and proanthocyanidin biosynthesis by Medicago truncatula bhlh transcription factor MtTT8 Penghui Li, Beibei Chen, Gaoyang Zhang, Longxiang
New Phytologist Supporting Information Regulation of anthocyanin and proanthocyanidin biosynthesis by Medicago truncatula bhlh transcription factor MtTT8 Penghui Li, Beibei Chen, Gaoyang Zhang, Longxiang
Multiple Choice Review- Eukaryotic Gene Expression
 Multiple Choice Review- Eukaryotic Gene Expression 1. Which of the following is the Central Dogma of cell biology? a. DNA Nucleic Acid Protein Amino Acid b. Prokaryote Bacteria - Eukaryote c. Atom Molecule
Multiple Choice Review- Eukaryotic Gene Expression 1. Which of the following is the Central Dogma of cell biology? a. DNA Nucleic Acid Protein Amino Acid b. Prokaryote Bacteria - Eukaryote c. Atom Molecule
The Role of Inorganic Carbon Transport and Accumulation in the CO 2 -Concentrating Mechanism and CO 2 Assimilation in Chlamydomonas
 The Role of Inorganic Carbon Transport and Accumulation in the CO 2 -Concentrating Mechanism and CO 2 Assimilation in Chlamydomonas Is there a Role for the CCM in Increasing Biological CO 2 Capture? Generalized
The Role of Inorganic Carbon Transport and Accumulation in the CO 2 -Concentrating Mechanism and CO 2 Assimilation in Chlamydomonas Is there a Role for the CCM in Increasing Biological CO 2 Capture? Generalized
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Cao et al. 10.1073/pnas.1306220110 Gram - bacteria Hemolymph Cytoplasm PGRP-LC TAK1 signalosome Imd dfadd Dredd Dnr1 Ikk signalosome P Relish Nucleus AMP and effector genes Fig.
Supporting Information Cao et al. 10.1073/pnas.1306220110 Gram - bacteria Hemolymph Cytoplasm PGRP-LC TAK1 signalosome Imd dfadd Dredd Dnr1 Ikk signalosome P Relish Nucleus AMP and effector genes Fig.
Supporting Online Material for
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/1121356/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Polar PIN Localization Directs Auxin Flow in Plants Justyna Wiśniewska, Jian Xu, Daniela Seifertová, Philip B. Brewer, Kamil
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/1121356/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Polar PIN Localization Directs Auxin Flow in Plants Justyna Wiśniewska, Jian Xu, Daniela Seifertová, Philip B. Brewer, Kamil
Translation and Operons
 Translation and Operons You Should Be Able To 1. Describe the three stages translation. including the movement of trna molecules through the ribosome. 2. Compare and contrast the roles of three different
Translation and Operons You Should Be Able To 1. Describe the three stages translation. including the movement of trna molecules through the ribosome. 2. Compare and contrast the roles of three different
Model plants and their Role in genetic manipulation. Mitesh Shrestha
 Model plants and their Role in genetic manipulation Mitesh Shrestha Definition of Model Organism Specific species or organism Extensively studied in research laboratories Advance our understanding of Cellular
Model plants and their Role in genetic manipulation Mitesh Shrestha Definition of Model Organism Specific species or organism Extensively studied in research laboratories Advance our understanding of Cellular
downstream (0.8 kb) homologous sequences to the genomic locus of DIC. A DIC mutant strain (ro- 6
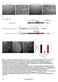 A B C D ts Figure S1 Generation of DIC- mcherry expressing N.crassa strain. A. N. crassa colony morphology. When a cot1 (top, left panel) strain is grown at permissive temperature (25 C), it exhibits straight
A B C D ts Figure S1 Generation of DIC- mcherry expressing N.crassa strain. A. N. crassa colony morphology. When a cot1 (top, left panel) strain is grown at permissive temperature (25 C), it exhibits straight
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature11419 Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic representation of innate immune signaling pathways induced by intracellular Salmonella in cultured macrophages. a, During the infection Salmonella
doi:10.1038/nature11419 Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic representation of innate immune signaling pathways induced by intracellular Salmonella in cultured macrophages. a, During the infection Salmonella
7.06 Cell Biology EXAM #3 April 21, 2005
 7.06 Cell Biology EXAM #3 April 21, 2005 This is an open book exam, and you are allowed access to books, a calculator, and notes but not computers or any other types of electronic devices. Please write
7.06 Cell Biology EXAM #3 April 21, 2005 This is an open book exam, and you are allowed access to books, a calculator, and notes but not computers or any other types of electronic devices. Please write
CONTROL OF PLANT GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT BI-2232 RIZKITA R E
 CONTROL OF PLANT GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT BI-2232 RIZKITA R E The development of a plant the series of progressive changes that take place throughout its life is regulated in complex ways. Factors take part
CONTROL OF PLANT GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT BI-2232 RIZKITA R E The development of a plant the series of progressive changes that take place throughout its life is regulated in complex ways. Factors take part
Control of Retrograde Signaling by Rapid Turnover of GENOMES UNCOUPLED 1
 Plant Physiology Preview. Published on January 24, 2018, as DOI:10.1104/pp.18.00009 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 Short title: Post-translational regulation
Plant Physiology Preview. Published on January 24, 2018, as DOI:10.1104/pp.18.00009 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 Short title: Post-translational regulation
