downstream (0.8 kb) homologous sequences to the genomic locus of DIC. A DIC mutant strain (ro- 6
|
|
|
- Caitlin Brown
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
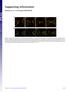
1 A B C D ts Figure S1 Generation of DIC- mcherry expressing N.crassa strain. A. N. crassa colony morphology. When a cot1 (top, left panel) strain is grown at permissive temperature (25 C), it exhibits straight hyphal growth morphology. At restrictive ts ts temperature (top, right panel; 37 C) cot1 strains exhibit compact colony growth. cot1 suppression mediated by ropy mutations lead to curly hyphal growth morphologies at permissive temperatures (bottom, left panel) and enlarged colony morphology at restrictive temperatures (bottom, right panel). B. A schematic representation of the targeting DNA consisting of mcherry coding sequence flanked by upstream (1.8kb) and 7bp Δ 1695 downstream (0.8 kb) homologous sequences to the genomic locus of DIC. A DIC mutant strain (ro- 6 ) exhibiting ropy 7bp Δ 1695 hyphal growth morphology was used for transformation. Homologous recombination of the targeting DNA into the ro- 6 locus resulted in the rescue of the ropy phenotype and restoration of wildtype hyphal growth morphology. 7bp Δ 1695 C. Comparison of colony morphologies between wildtype, DIC mutant ro- 6 and wildtype DIC- mcherry strains. Note that the wildtype DIC- mcherry strain exhibits growth morphology is indistinguishable from the wildtype strain. 7bp Δ 1695 D. Bar graph showing radial growth rates of wildtype, DIC mutant ro- 6, WT - DIC- mcherry strains. Data are shown as mean ± S.D. 2 SI S. Sivagurunathan et al.
2 Figure S2 Protein levels in representative DHC mutant strains. Western blot analysis of DHC expression/protein levels in 17 of the 34 mutant strains, including at least one representative from every class. The class of each strain is indicated in parentheses after the designated strain name. S. Sivagurunathan et al. 3 SI
3 Figure S3 An 8- second time series showing photobleaching of bright hyphal tip dynein fluorescence in a wildtype strain. Bars: 10 µm. 4 SI S. Sivagurunathan et al.
4 Figure S4 Colocalization of dynein and dynactin in wildtype and DHC mutant strains. A. Epifluorescence images of growing hyphae in strains expressing DIC- mcherry and EGFP- dynactin p150. Left panels: dynein; middle panels: dynactin, right panels: overlay. B. Epifluorescence images of growing hyphae in strains expressing DIC- mcherry in dynactin p150 null background. Bars: 10 µm in all panels. S. Sivagurunathan et al. 5 SI
5 A B Figure S5 A. Dynein purification scheme for N.crassa. B. Representative silver- stained gel image showing the final elution fraction from the StrepTrap column. The arrow points to the DHC band and the bar indicates the band corresponding to the tagged DIC. 6 SI S. Sivagurunathan et al.
6 Files S1- S9 Supporting Movies Representative live cell movies of FM 4-64 labeled vesicle trafficking in hyphal tips from each of the strains analyzed. Each movie was of 30 seconds duration and is sped up six- fold. Each movie is 86 µm x 65 µm in size. Files S1- S9 are available for download at as compressed.avi files. S. Sivagurunathan et al. 7 SI
7 Table S1 Summary of vesicle transport dynamics. Wildtype DHC Δ p150 Δ Nkin mut. Class 1 Class 2 Class 3 Class 4 Class 5 Motility index Mean movements/ µm hyphal length Overall movements n Mean velocity (µm/sec ± S.D.) 1.64 ± ± 0.62* 1.34 ± 0.49* 1.35 ± 0.52* 1.51 ± 0.59* 1.24 ± 0.41* 1.33 ± 0.45* 1.33 ± 0.41* 1.31 ± 0.48* Mean distance (µm ± S.D.) 4.26 ± ± 1.71* 3.19 ± 1.44* 3.49 ± 2.07* 4.48 ± ± 1.64* 2.85 ± 1.15* 3.17 ± 1.33* 3.96 ± 2.33 Inward movements Percent of total movements 48.7 % 47.1 % 48.9 % 48.8 % 41.7 % 52.7 % 53.8 % 41.5 % 47.1 % Mean velocity (µm/sec ± S.D.) 1.60 ± ± 0.53* 1.27 ± 0.51* 1.36 ± 0.53* 1.43 ± 0.54* 1.23 ± 0.45* 1.29 ± 0.48* 1.24 ± 0.40* 1.28 ± 0.53* Mean distance (µm ± S.D.) 4.16 ± ± 1.27* 2.78 ± 1.12* 3.23 ± 1.88* 3.90 ± ± 1.38* 2.69 ± 1.02* 2.66 ± 0.96* 3.77 ± 2.40 Outward movements Percent of total movements 51.3 % 52.9 % 51.1 % 51.2 % 58.3 % 47.3 % 46.2 % 58.5 % 52.9 % Mean velocity (µm/sec ± S.D.) 1.67 ± ± ± 0.47* 1.35 ± 0.51* 1.56 ± ± 0.36* 1.38 ± 0.42* 1.40 ± 0.41* 1.35 ± 0.44* Mean distance (µm ± S.D.) 4.36 ± ± 1.98* 3.59 ± 1.59* 3.75 ± 2.22* 4.89 ± ± 1.83* 3.05 ± 1.27* 3.53 ± 1.45* 4.13 ± 2.26 Vesicle accumulation Hyphal tip vesicle accumulation Hyphal body vesicle accumulation 60.0 % 92.3 % 27.3 % 100 % 72.7 % 86.7 % 90.0 % 78.6 % 100 % 13.3 % 7.7 % 90.9 % 0 % 9.1 % 6.7 % 20.0 % 21.4 % 0 % * = statistically significant difference from wild- type value as determined by students t- test (P < 0.05). 8 SI S. Sivagurunathan et al.
8 Table S2 Summary of dynein mislocalization phenotypes. Mislocalization phenotype Domain Mutation Class 1 (Distal - long linear tracks) AAA1 (Turn p- loop) AAA1 (H4) AAA2 (PS1 Insert) AAA2 (PS I Insert) AAA3 (β3/walker B) AAA5 (Strut C1) G1946R R2056H S2333R L2335P E2675Q aa Δ (RRSNLI) Class 2 (Apical - long linear tracks) Class 3 (Comet tails) Class 4 (Aggregates) Class 5 (Disperse) AAA1(Sensor 1 (β4)) AAA3 (β4 before sensor 1 ) MT Stalk (H8 - CC1) AAA6 (H1) Tail Tail Linker Subdomain 3 (H11 ) MT Stalk (H8 - CC1) MT- binding domain (H1) o)mtbd MT- Stalk (CC2) MT- binding domain (H7) MT- stalk ( H9 - CC2) N2050S C2722R aa Δ (SLEIQAALE) V4049D Y110S W1308G R1672S D3224P T3323P L3332P R3396G aa ins. C- terminus (H1) L4333* AAA1 (H3) MT- BS (H8 stalk CC1) AAA5 (Strut C1) AAA1 (H0) AAA1 (AAA1 H1 and B2) AAA1 (H4/ β4 R finger) AAA1 (H8) AAA3 (β4 before sensor 1) AAA5 (H0) AAA6 (H5) AAA6 (H7) AAA6 (between H8- H9) AAA6 (between h11 and h12) S2009W G3215D aa Δ (QLEKKLL) L1933P G1961R K2065E T2166P V2719D I3591P G4146A E4168K I4232N AAA6 (H12) W4311* AAA6 ( between H12- H13) D4296E; aa Δ (LVV) P4316S AAA- AAA domains of dynein, MT microtubule, H helix, β β strand, CC- coiled- coil, aa - amino acid, Δ - deletion, ins - insertion, * - nonsense mutation. S. Sivagurunathan et al. 9 SI
9 Table S3 Primary Neurospora crassa strains used in this study. Genotype Source Description mat a FGSC WT strain (FGSC # 4200) mat A FGSC WT strain (FGSC # 2489) mat a; kin- 1 FGSC Nkin mutant strain (FGSC # 9939) mat a; ro- 1::hygr This study DHC Δ mutant strain mat a; ro- 3::hygr FGSC Dynactin p150 Δ mutant strain (FGSC # 14726) rid(rip1) mat A his- 3 + ::Pccg- 1- Bml + - sgfp + mat A his- 3 + ::Pccg- 1- hh1 + - sgfp + FGSC FGSC Tubulin- GFP strain (FGSC # 9520) Histone h1- GFP strain (FGSC # 9518) mat a ro- 6 7bp Δ 1695 This study DIC mutant strain mat A ro- 6 + ::mcherry + This study WT DIC- mcherry strain mat A ro- 6 + ::mcherry + ; kin- 1 This study Nkin mutant - DIC- mcherry strain mat A ro- 6 + ::mcherry + ; Δ ro- 3 This study Dynactin p150 Δ mutant - DIC- mcherry strain mat A; ro- 3 + ::egfp + This study WT EGFP- Dynactin p150 strain mat A ro- 6 + ::hs + This study WT DIC- 6xHis- Strep- tag II strain 10 SI S. Sivagurunathan et al.
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Fleissner et al. 10.1073/pnas.0907039106 Fig. S1. (A) MAK-2-GFP localized to CATs tips is not bound by membrane. his-3::pccg1 mak-2-gfp; mak-2 strain labeled with membrane dye FM4
Supporting Information Fleissner et al. 10.1073/pnas.0907039106 Fig. S1. (A) MAK-2-GFP localized to CATs tips is not bound by membrane. his-3::pccg1 mak-2-gfp; mak-2 strain labeled with membrane dye FM4
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature10955 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Electron-density maps and crystallographic dimer structures of the motor domain. (a f) Stereo views of the final electron-density maps
doi:10.1038/nature10955 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Electron-density maps and crystallographic dimer structures of the motor domain. (a f) Stereo views of the final electron-density maps
7.06 Problem Set #4, Spring 2005
 7.06 Problem Set #4, Spring 2005 1. You re doing a mutant hunt in S. cerevisiae (budding yeast), looking for temperaturesensitive mutants that are defective in the cell cycle. You discover a mutant strain
7.06 Problem Set #4, Spring 2005 1. You re doing a mutant hunt in S. cerevisiae (budding yeast), looking for temperaturesensitive mutants that are defective in the cell cycle. You discover a mutant strain
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/6/301/ra98/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Regulation of Epithelial Morphogenesis by the G Protein Coupled Receptor Mist and Its Ligand Fog Alyssa J. Manning,
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/6/301/ra98/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Regulation of Epithelial Morphogenesis by the G Protein Coupled Receptor Mist and Its Ligand Fog Alyssa J. Manning,
Illegitimate translation causes unexpected gene expression from on-target out-of-frame alleles
 Illegitimate translation causes unexpected gene expression from on-target out-of-frame alleles created by CRISPR-Cas9 Shigeru Makino, Ryutaro Fukumura, Yoichi Gondo* Mutagenesis and Genomics Team, RIKEN
Illegitimate translation causes unexpected gene expression from on-target out-of-frame alleles created by CRISPR-Cas9 Shigeru Makino, Ryutaro Fukumura, Yoichi Gondo* Mutagenesis and Genomics Team, RIKEN
Heather Currinn, Benjamin Guscott, Zita Balklava, Alice Rothnie and Thomas Wassmer*
 Online Resources APP controls the formation of PI(3,5)P 2 vesicles through its binding of the PIKfyve complex. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences Heather Currinn, Benjamin Guscott, Zita Balklava, Alice
Online Resources APP controls the formation of PI(3,5)P 2 vesicles through its binding of the PIKfyve complex. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences Heather Currinn, Benjamin Guscott, Zita Balklava, Alice
Supplementary Figure 1. Biochemical and sequence alignment analyses the
 Supplementary Figure 1. Biochemical and sequence alignment analyses the interaction of OPTN and TBK1. (a) Analytical gel filtration chromatography analysis of the interaction between TBK1 CTD and OPTN(1-119).
Supplementary Figure 1. Biochemical and sequence alignment analyses the interaction of OPTN and TBK1. (a) Analytical gel filtration chromatography analysis of the interaction between TBK1 CTD and OPTN(1-119).
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2819 Gαi3 / Actin / Acetylated Tubulin Gαi3 / Actin / Acetylated Tubulin a a Gαi3 a Actin Gαi3 WT Gαi3 WT Gαi3 WT b b Gαi3 b Actin Gαi3 KO Gαi3 KO Gαi3 KO # # Figure S1 Loss of protein
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2819 Gαi3 / Actin / Acetylated Tubulin Gαi3 / Actin / Acetylated Tubulin a a Gαi3 a Actin Gαi3 WT Gαi3 WT Gαi3 WT b b Gαi3 b Actin Gαi3 KO Gαi3 KO Gαi3 KO # # Figure S1 Loss of protein
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2215 Figure S1 Number of egfp-vps4a bursts versus cellular expression levels. The total number of egfp-vps4a bursts, counted at the end of each movie (frame 2000, after 1h 28 min) are plotted
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2215 Figure S1 Number of egfp-vps4a bursts versus cellular expression levels. The total number of egfp-vps4a bursts, counted at the end of each movie (frame 2000, after 1h 28 min) are plotted
Supplementary Figure 1. SDS-PAGE analysis of GFP oligomer variants with different linkers. Oligomer mixtures were applied to a PAGE gel containing
 Supplementary Figure 1. SDS-PAGE analysis of GFP oligomer variants with different linkers. Oligomer mixtures were applied to a PAGE gel containing 0.1% SDS without boiling. The gel was analyzed by a fluorescent
Supplementary Figure 1. SDS-PAGE analysis of GFP oligomer variants with different linkers. Oligomer mixtures were applied to a PAGE gel containing 0.1% SDS without boiling. The gel was analyzed by a fluorescent
GFP GAL bp 3964 bp
 Supplemental Data. Møller et al. (2009) Shoot Na + exclusion and increased salinity tolerance engineered by cell type-specific alteration of Na + transport in Arabidopsis Supplemental Figure 1. Salt-sensitive
Supplemental Data. Møller et al. (2009) Shoot Na + exclusion and increased salinity tolerance engineered by cell type-specific alteration of Na + transport in Arabidopsis Supplemental Figure 1. Salt-sensitive
EST1 Homology Domain. 100 aa. hest1a / SMG6 PIN TPR TPR. Est1-like DBD? hest1b / SMG5. TPR-like TPR. a helical. hest1c / SMG7.
 hest1a / SMG6 EST1 Homology Domain 100 aa 853 695 761 780 1206 hest1 / SMG5 -like? -like 109 145 214 237 497 165 239 1016 114 207 212 381 583 hest1c / SMG7 a helical 1091 Sc 57 185 267 284 699 Figure S1:
hest1a / SMG6 EST1 Homology Domain 100 aa 853 695 761 780 1206 hest1 / SMG5 -like? -like 109 145 214 237 497 165 239 1016 114 207 212 381 583 hest1c / SMG7 a helical 1091 Sc 57 185 267 284 699 Figure S1:
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2647 Figure S1 Other Rab GTPases do not co-localize with the ER. a, Cos-7 cells cotransfected with an ER luminal marker (either KDEL-venus or mch-kdel) and mch-tagged human Rab5 (mch-rab5,
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2647 Figure S1 Other Rab GTPases do not co-localize with the ER. a, Cos-7 cells cotransfected with an ER luminal marker (either KDEL-venus or mch-kdel) and mch-tagged human Rab5 (mch-rab5,
NB-DNJ/GCase-pH 7.4 NB-DNJ+/GCase-pH 7.4 NB-DNJ+/GCase-pH 4.5
 SUPPLEMENTARY TABLES Suppl. Table 1. Protonation states at ph 7.4 and 4.5. Protonation states of titratable residues in GCase at ph 7.4 and 4.5. Histidine: HID, H at δ-nitrogen; HIE, H at ε-nitrogen; HIP,
SUPPLEMENTARY TABLES Suppl. Table 1. Protonation states at ph 7.4 and 4.5. Protonation states of titratable residues in GCase at ph 7.4 and 4.5. Histidine: HID, H at δ-nitrogen; HIE, H at ε-nitrogen; HIP,
Supplementary Figure 1. Phenotype of the HI strain.
 Supplementary Figure 1. Phenotype of the HI strain. (A) Phenotype of the HI and wild type plant after flowering (~1month). Wild type plant is tall with well elongated inflorescence. All four HI plants
Supplementary Figure 1. Phenotype of the HI strain. (A) Phenotype of the HI and wild type plant after flowering (~1month). Wild type plant is tall with well elongated inflorescence. All four HI plants
Supplemental Data. Perrella et al. (2013). Plant Cell /tpc
 Intensity Intensity Intensity Intensity Intensity Intensity 150 50 150 0 10 20 50 C 150 0 10 20 50 D 0 10 20 Distance (μm) 50 20 40 E 50 F 0 10 20 50 0 15 30 Distance (μm) Supplemental Figure 1: Co-localization
Intensity Intensity Intensity Intensity Intensity Intensity 150 50 150 0 10 20 50 C 150 0 10 20 50 D 0 10 20 Distance (μm) 50 20 40 E 50 F 0 10 20 50 0 15 30 Distance (μm) Supplemental Figure 1: Co-localization
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Purification of yeast CKM. (a) Silver-stained SDS-PAGE analysis of CKM purified through a TAP-tag engineered into the Cdk8 C-terminus. (b) Kinase activity
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Purification of yeast CKM. (a) Silver-stained SDS-PAGE analysis of CKM purified through a TAP-tag engineered into the Cdk8 C-terminus. (b) Kinase activity
Identification of TARP Phosphorylation Sites and Their Significance in the Brain
 Identification of TARP Phosphorylation Sites and Their Significance in the Brain Susumu Tomita @ SHM BE17 Department of Cellular and Molecular Physiology NIDA Neuroproteomics Center, December 13, 2008
Identification of TARP Phosphorylation Sites and Their Significance in the Brain Susumu Tomita @ SHM BE17 Department of Cellular and Molecular Physiology NIDA Neuroproteomics Center, December 13, 2008
Nature Biotechnology: doi: /nbt Supplementary Figure 1. Overexpression of YFP::GPR-1 in the germline.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Overexpression of YFP::GPR-1 in the germline. The pie-1 promoter and 3 utr were used to express yfp::gpr-1 in the germline. Expression levels from the yfp::gpr-1(cai 1.0)-expressing
Supplementary Figure 1 Overexpression of YFP::GPR-1 in the germline. The pie-1 promoter and 3 utr were used to express yfp::gpr-1 in the germline. Expression levels from the yfp::gpr-1(cai 1.0)-expressing
Three Myosins Contribute Uniquely to the Assembly and Constriction of the Fission Yeast Cytokinetic Contractile Ring
 Current Biology Supplemental Information Three Myosins Contribute Uniquely to the Assembly and Constriction of the Fission Yeast Cytokinetic Contractile Ring Caroline Laplante, Julien Berro, Erdem Karatekin,
Current Biology Supplemental Information Three Myosins Contribute Uniquely to the Assembly and Constriction of the Fission Yeast Cytokinetic Contractile Ring Caroline Laplante, Julien Berro, Erdem Karatekin,
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Figure S1. Mitochondrial morphology in Fis1-null, Mff-null and Fis1/Mff-null MEF cells. (A) Western blotting of lysates from Fis1-null, Mff-null and Fis1/Mff-null cells. Lysates were
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Figure S1. Mitochondrial morphology in Fis1-null, Mff-null and Fis1/Mff-null MEF cells. (A) Western blotting of lysates from Fis1-null, Mff-null and Fis1/Mff-null cells. Lysates were
Enhanced zinc-finger-nuclease activity with improved obligate heterodimeric architectures
 Nature Methods Enhanced zinc-finger-nuclease activity with improved obligate heterodimeric architectures Yannick Doyon, Thuy D Vo, Matthew C Mendel, Shon G Greenberg, Jianbin Wang, Danny F Xia, Jeffrey
Nature Methods Enhanced zinc-finger-nuclease activity with improved obligate heterodimeric architectures Yannick Doyon, Thuy D Vo, Matthew C Mendel, Shon G Greenberg, Jianbin Wang, Danny F Xia, Jeffrey
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Mullins et al. 10.1073/pnas.0906781106 SI Text Detection of Calcium Binding by 45 Ca 2 Overlay. The 45 CaCl 2 (1 mci, 37 MBq) was obtained from NEN. The general method of 45 Ca 2
Supporting Information Mullins et al. 10.1073/pnas.0906781106 SI Text Detection of Calcium Binding by 45 Ca 2 Overlay. The 45 CaCl 2 (1 mci, 37 MBq) was obtained from NEN. The general method of 45 Ca 2
A redundant function for the N-terminal tail of Ndc80 in kinetochore-microtubule interaction in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.
 Genetics: Published Articles Ahead of Print, published on July 30, 2012 as 10.1534/genetics.112.143818 A redundant function for the N-terminal tail of Ndc80 in kinetochore-microtubule interaction in Saccharomyces
Genetics: Published Articles Ahead of Print, published on July 30, 2012 as 10.1534/genetics.112.143818 A redundant function for the N-terminal tail of Ndc80 in kinetochore-microtubule interaction in Saccharomyces
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature12791 Supplementary Figure 1 (1/3) WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE 1 RESEARCH SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1 (2/3) 2 WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE SUPPLEMENTARY
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature12791 Supplementary Figure 1 (1/3) WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE 1 RESEARCH SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1 (2/3) 2 WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE SUPPLEMENTARY
Table S1. Overview of used PDZK1 constructs and their binding affinities to peptides. Related to figure 1.
 Table S1. Overview of used PDZK1 constructs and their binding affinities to peptides. Related to figure 1. PDZK1 constru cts Amino acids MW [kda] KD [μm] PEPT2-CT- FITC KD [μm] NHE3-CT- FITC KD [μm] PDZK1-CT-
Table S1. Overview of used PDZK1 constructs and their binding affinities to peptides. Related to figure 1. PDZK1 constru cts Amino acids MW [kda] KD [μm] PEPT2-CT- FITC KD [μm] NHE3-CT- FITC KD [μm] PDZK1-CT-
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1. HSP21 expression in 35S:HSP21 and hsp21 knockdown plants. (a) Since no T- DNA insertion line for HSP21 is available in the publicly available T-DNA collections,
Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1. HSP21 expression in 35S:HSP21 and hsp21 knockdown plants. (a) Since no T- DNA insertion line for HSP21 is available in the publicly available T-DNA collections,
Giblon and Lew The electrical phenotype of GFP-expressing Neurospora page 1 of 14
 Giblon and Lew The electrical phenotype of GFP-expressing Neurospora page 1 of 14 Aplestia: The effect of high levels of foreign gene expression on the electrical properties of Neurospora crassa 1. Rachel
Giblon and Lew The electrical phenotype of GFP-expressing Neurospora page 1 of 14 Aplestia: The effect of high levels of foreign gene expression on the electrical properties of Neurospora crassa 1. Rachel
Supplementary Information for. Single-cell dynamics of the chromosome replication and cell division cycles in mycobacteria
 Supplementary Information for Single-cell dynamics of the chromosome replication and cell division cycles in mycobacteria Isabella Santi 1 *, Neeraj Dhar 1, Djenet Bousbaine 1, Yuichi Wakamoto, John D.
Supplementary Information for Single-cell dynamics of the chromosome replication and cell division cycles in mycobacteria Isabella Santi 1 *, Neeraj Dhar 1, Djenet Bousbaine 1, Yuichi Wakamoto, John D.
Supplementary Figure 1. Markedly decreased numbers of marginal zone B cells in DOCK8 mutant mice Supplementary Figure 2.
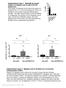 Supplementary Figure 1. Markedly decreased numbers of marginal zone B cells in DOCK8 mutant mice. Percentage of marginal zone B cells in the spleen of wild-type mice (+/+), mice homozygous for cpm or pri
Supplementary Figure 1. Markedly decreased numbers of marginal zone B cells in DOCK8 mutant mice. Percentage of marginal zone B cells in the spleen of wild-type mice (+/+), mice homozygous for cpm or pri
Supplemental Data. Wang et al. (2014). Plant Cell /tpc
 Supplemental Figure1: Mock and NPA-treated tomato plants. (A) NPA treated tomato (cv. Moneymaker) developed a pin-like inflorescence (arrowhead). (B) Comparison of first and second leaves from mock and
Supplemental Figure1: Mock and NPA-treated tomato plants. (A) NPA treated tomato (cv. Moneymaker) developed a pin-like inflorescence (arrowhead). (B) Comparison of first and second leaves from mock and
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature11589 Supplementary Figure 1 Ciona intestinalis and Petromyzon marinus neural crest expression domain comparison. Cartoon shows dorsal views of Ciona mid gastrula (left) and Petromyzon
doi:10.1038/nature11589 Supplementary Figure 1 Ciona intestinalis and Petromyzon marinus neural crest expression domain comparison. Cartoon shows dorsal views of Ciona mid gastrula (left) and Petromyzon
Supplementary Materials for
 www.advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/1/5/e1500358/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Transplantability of a circadian clock to a noncircadian organism Anna H. Chen, David Lubkowicz, Vivian Yeong,
www.advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/1/5/e1500358/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Transplantability of a circadian clock to a noncircadian organism Anna H. Chen, David Lubkowicz, Vivian Yeong,
Structure and RNA-binding properties. of the Not1 Not2 Not5 module of the yeast Ccr4 Not complex
 Structure and RNA-binding properties of the Not1 Not2 Not5 module of the yeast Ccr4 Not complex Varun Bhaskar 1, Vladimir Roudko 2,3, Jerome Basquin 1, Kundan Sharma 4, Henning Urlaub 4, Bertrand Seraphin
Structure and RNA-binding properties of the Not1 Not2 Not5 module of the yeast Ccr4 Not complex Varun Bhaskar 1, Vladimir Roudko 2,3, Jerome Basquin 1, Kundan Sharma 4, Henning Urlaub 4, Bertrand Seraphin
ydci GTC TGT TTG AAC GCG GGC GAC TGG GCG CGC AAT TAA CGG TGT GTA GGC TGG AGC TGC TTC
 Table S1. DNA primers used in this study. Name ydci P1ydcIkd3 Sequence GTC TGT TTG AAC GCG GGC GAC TGG GCG CGC AAT TAA CGG TGT GTA GGC TGG AGC TGC TTC Kd3ydcIp2 lacz fusion YdcIendP1 YdcItrgP2 GAC AGC
Table S1. DNA primers used in this study. Name ydci P1ydcIkd3 Sequence GTC TGT TTG AAC GCG GGC GAC TGG GCG CGC AAT TAA CGG TGT GTA GGC TGG AGC TGC TTC Kd3ydcIp2 lacz fusion YdcIendP1 YdcItrgP2 GAC AGC
Supplementary Figure 1. Real time in vivo imaging of SG secretion. (a) SGs from Drosophila third instar larvae that express Sgs3-GFP (green) and
 Supplementary Figure 1. Real time in vivo imaging of SG secretion. (a) SGs from Drosophila third instar larvae that express Sgs3-GFP (green) and Lifeact-Ruby (red) were imaged in vivo to visualize secretion
Supplementary Figure 1. Real time in vivo imaging of SG secretion. (a) SGs from Drosophila third instar larvae that express Sgs3-GFP (green) and Lifeact-Ruby (red) were imaged in vivo to visualize secretion
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb3267 Supplementary Figure 1 A group of genes required for formation or orientation of annular F-actin bundles and aecm ridges: RNAi phenotypes and their validation by standard mutations.
DOI: 10.1038/ncb3267 Supplementary Figure 1 A group of genes required for formation or orientation of annular F-actin bundles and aecm ridges: RNAi phenotypes and their validation by standard mutations.
CLIP-170 homolog and NUDE play overlapping roles in NUDF localization in. Aspergillus nidulans
 CLIP-170 homolog and NUDE play overlapping roles in NUDF localization in Aspergillus nidulans Vladimir P. Efimov *#, Jun Zhang #, Xin Xiang * Department of Pharmacology, UMDNJ - Robert Wood Johnson Medical
CLIP-170 homolog and NUDE play overlapping roles in NUDF localization in Aspergillus nidulans Vladimir P. Efimov *#, Jun Zhang #, Xin Xiang * Department of Pharmacology, UMDNJ - Robert Wood Johnson Medical
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature11419 Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic representation of innate immune signaling pathways induced by intracellular Salmonella in cultured macrophages. a, During the infection Salmonella
doi:10.1038/nature11419 Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic representation of innate immune signaling pathways induced by intracellular Salmonella in cultured macrophages. a, During the infection Salmonella
Heterozygous BMN lines
 Optical density at 80 hours 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 a YPD b YPD + 1µM nystatin c YPD + 2µM nystatin d YPD + 4µM nystatin 1 3 5 6 9 13 16 20 21 22 23 25 28 29 30
Optical density at 80 hours 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 a YPD b YPD + 1µM nystatin c YPD + 2µM nystatin d YPD + 4µM nystatin 1 3 5 6 9 13 16 20 21 22 23 25 28 29 30
Transitivity-dependent and transitivity-independent cell-to-cell movement of RNA
 Himber et al. Transitivity-dependent and transitivity-independent cell-to-cell movement of RNA silencing SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Supplemental material 1. Short-range movement of GFP silencing affects a nearly
Himber et al. Transitivity-dependent and transitivity-independent cell-to-cell movement of RNA silencing SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Supplemental material 1. Short-range movement of GFP silencing affects a nearly
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 GP2 Type I-piliated bacteria FAE M cell M cell pocket idc T cell mdc Generation of antigenspecific T cells Induction of antigen-specific mucosal immune response Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic diagram
GP2 Type I-piliated bacteria FAE M cell M cell pocket idc T cell mdc Generation of antigenspecific T cells Induction of antigen-specific mucosal immune response Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic diagram
Supporting Online Material for
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/1121356/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Polar PIN Localization Directs Auxin Flow in Plants Justyna Wiśniewska, Jian Xu, Daniela Seifertová, Philip B. Brewer, Kamil
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/1121356/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Polar PIN Localization Directs Auxin Flow in Plants Justyna Wiśniewska, Jian Xu, Daniela Seifertová, Philip B. Brewer, Kamil
The Functions of Myosin II and Myosin V Homologs in Tip Growth and Septation in Aspergillus nidulans
 The Functions of Myosin II and Myosin V Homologs in Tip Growth and Septation in Aspergillus nidulans Naimeh Taheri-Talesh 1, Yi Xiong 2, Berl R. Oakley 1,2 * 1 Department of Molecular Biosciences, University
The Functions of Myosin II and Myosin V Homologs in Tip Growth and Septation in Aspergillus nidulans Naimeh Taheri-Talesh 1, Yi Xiong 2, Berl R. Oakley 1,2 * 1 Department of Molecular Biosciences, University
Genetics 275 Notes Week 7
 Cytoplasmic Inheritance Genetics 275 Notes Week 7 Criteriafor recognition of cytoplasmic inheritance: 1. Reciprocal crosses give different results -mainly due to the fact that the female parent contributes
Cytoplasmic Inheritance Genetics 275 Notes Week 7 Criteriafor recognition of cytoplasmic inheritance: 1. Reciprocal crosses give different results -mainly due to the fact that the female parent contributes
Supplementary material
 Supplementary material Phosphorylation of the mitochondrial autophagy receptor Nix enhances its interaction with LC3 proteins Vladimir V. Rogov 1,*, Hironori Suzuki 2,3,*, Mija Marinković 4, Verena Lang
Supplementary material Phosphorylation of the mitochondrial autophagy receptor Nix enhances its interaction with LC3 proteins Vladimir V. Rogov 1,*, Hironori Suzuki 2,3,*, Mija Marinković 4, Verena Lang
Cytoplasmic Bulk Flow Propels Nuclei in Mature Hyphae of Neurospora crassa
 EUKARYOTIC CELL, Dec. 2009, p. 1880 1890 Vol. 8, No. 12 1535-9778/09/$12.00 doi:10.1128/ec.00062-09 Copyright 2009, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Cytoplasmic Bulk Flow Propels
EUKARYOTIC CELL, Dec. 2009, p. 1880 1890 Vol. 8, No. 12 1535-9778/09/$12.00 doi:10.1128/ec.00062-09 Copyright 2009, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Cytoplasmic Bulk Flow Propels
Serine-7 but not serine-5 phosphorylation primes RNA polymerase II CTD for P-TEFb recognition
 Supplementary Information to Serine-7 but not serine-5 phosphorylation primes RNA polymerase II CTD for P-TEFb recognition Nadine Czudnochowski 1,2, *, Christian A. Bösken 1, * & Matthias Geyer 1 1 Max-Planck-Institut
Supplementary Information to Serine-7 but not serine-5 phosphorylation primes RNA polymerase II CTD for P-TEFb recognition Nadine Czudnochowski 1,2, *, Christian A. Bösken 1, * & Matthias Geyer 1 1 Max-Planck-Institut
Localization of Wild Type and Mutant Class I Myosin Proteins in Aspergillus nidulans Using GFP-Fusion Proteins
 Cell Motility and the Cytoskeleton 45:163 172 (2000) Localization of Wild Type and Mutant Class I Myosin Proteins in Aspergillus nidulans Using GFP-Fusion Proteins Roxanne A. Yamashita, Nir Osherov, and
Cell Motility and the Cytoskeleton 45:163 172 (2000) Localization of Wild Type and Mutant Class I Myosin Proteins in Aspergillus nidulans Using GFP-Fusion Proteins Roxanne A. Yamashita, Nir Osherov, and
Apical hyphal growth. (1) the unidirectional flow of vesicles in the cytoplasm fusing with the plasma membrane at the apex,
 Apical hyphal growth The fungal cell wall is a dynamic structure that protects the cell from changes in osmotic pressure and other environmental stresses, while allowing the fungal cell to interact with
Apical hyphal growth The fungal cell wall is a dynamic structure that protects the cell from changes in osmotic pressure and other environmental stresses, while allowing the fungal cell to interact with
Supplementary figure 1 Application of tmfret in LeuT. (a) To assess the feasibility of using tmfret for distance-dependent measurements in LeuT, a
 Supplementary figure 1 Application of tmfret in LeuT. (a) To assess the feasibility of using tmfret for distance-dependent measurements in LeuT, a series of tmfret-pairs comprised of single cysteine mutants
Supplementary figure 1 Application of tmfret in LeuT. (a) To assess the feasibility of using tmfret for distance-dependent measurements in LeuT, a series of tmfret-pairs comprised of single cysteine mutants
Supplemental Data. Gao et al. (2012). Plant Cell /tpc
 Supplemental Figure 1. Plant EMP Proteins. (A) The Accession numbers of the 12 EMP members from Arabidopsis. (B) Phylogenetic analysis of EMP proteins from Arabidopsis, human and yeast using the Mac Vector
Supplemental Figure 1. Plant EMP Proteins. (A) The Accession numbers of the 12 EMP members from Arabidopsis. (B) Phylogenetic analysis of EMP proteins from Arabidopsis, human and yeast using the Mac Vector
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Breker et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201301120/dc1 Figure S1. Single-cell proteomics of stress responses. (a) Using
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Breker et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201301120/dc1 Figure S1. Single-cell proteomics of stress responses. (a) Using
Nuclear import of DNA: genetic modification of plants
 Nuclear import of DNA: genetic modification of plants gene delivery by Agrobacterium tumefaciens T. Tzfira & V. Citovsky. 2001. Trends in Cell Biol. 12: 121-129 VirE2 binds ssdna in vitro forms helical
Nuclear import of DNA: genetic modification of plants gene delivery by Agrobacterium tumefaciens T. Tzfira & V. Citovsky. 2001. Trends in Cell Biol. 12: 121-129 VirE2 binds ssdna in vitro forms helical
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/science.1244624/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Cytoneme-Mediated Contact-Dependent Transport of the Drosophila Decapentaplegic Signaling Protein Sougata Roy, Hai Huang,
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/science.1244624/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Cytoneme-Mediated Contact-Dependent Transport of the Drosophila Decapentaplegic Signaling Protein Sougata Roy, Hai Huang,
Osmotic Mutants of Neurospora crassa page 1 of 13
 Osmotic Mutants of Neurospora crassa page 1 of 13 Electrophysiological Response of the Scumbo (sc 5801 and sc R2386), Smco8, and Smco9 mutants of Neurospora crassa to Hyperosmotic Treatment 1. Shanar Nasserifar
Osmotic Mutants of Neurospora crassa page 1 of 13 Electrophysiological Response of the Scumbo (sc 5801 and sc R2386), Smco8, and Smco9 mutants of Neurospora crassa to Hyperosmotic Treatment 1. Shanar Nasserifar
Growth and Colony Patterning of Filamentous Fungi
 Letter Forma, 14, 315 320, 1999 Growth and Colony Patterning of Filamentous Fungi Shu MATSUURA School of High-Technology for Human Welfare, Tokai University, Numazu, Shizuoka 410-0395, Japan E-mail: shum@wing.
Letter Forma, 14, 315 320, 1999 Growth and Colony Patterning of Filamentous Fungi Shu MATSUURA School of High-Technology for Human Welfare, Tokai University, Numazu, Shizuoka 410-0395, Japan E-mail: shum@wing.
P. syringae and E. coli
 CHAPTER 6 A comparison of the recd mutant phenotypes of P. syringae and E. coli 6.1 INTRODUCTION The RecBCD complex is essential for recombination mediated repair of double strand breaks (DSBs) of DNA
CHAPTER 6 A comparison of the recd mutant phenotypes of P. syringae and E. coli 6.1 INTRODUCTION The RecBCD complex is essential for recombination mediated repair of double strand breaks (DSBs) of DNA
Supplementary Materials for
 advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/1/9/e1500511/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Contractility parameters of human -cardiac myosin with the hypertrophic cardiomyopathy mutation R403Q show loss of
advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/1/9/e1500511/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Contractility parameters of human -cardiac myosin with the hypertrophic cardiomyopathy mutation R403Q show loss of
Table S1. Sequence of primers used in RT-qPCR
 Table S1. Sequence of primers used in RT-qPCR Primer Name P16Ink4a-F P16Ink4a-R P15Ink4b-F P15Ink4b-R P19Arf-F P19Arf-R P53-F P53-R P21cip1-F P21cip1-R P27kip1-F P27kip1-R P18Ink4c-F P18Ink4c-R P19Ink4d-F
Table S1. Sequence of primers used in RT-qPCR Primer Name P16Ink4a-F P16Ink4a-R P15Ink4b-F P15Ink4b-R P19Arf-F P19Arf-R P53-F P53-R P21cip1-F P21cip1-R P27kip1-F P27kip1-R P18Ink4c-F P18Ink4c-R P19Ink4d-F
Supplemental Figure 1: Increased Fe deficiency gene expression in roots of nas4x-2
 Supplemental Figure 1: Increased Fe deficiency gene expression in roots of nas4x-2 IRT1, FRO2 and FIT expression levels in roots of the wild-type, nas4x- 1 and nas4x-2, showing that in both nas mutants
Supplemental Figure 1: Increased Fe deficiency gene expression in roots of nas4x-2 IRT1, FRO2 and FIT expression levels in roots of the wild-type, nas4x- 1 and nas4x-2, showing that in both nas mutants
4) Please cite Dagda et al J Biol Chem 284: , for any publications or presentations resulting from use or modification of the macro.
 Supplement Figure S1. Algorithmic quantification of mitochondrial morphology in SH- SY5Y cells treated with known fission/fusion mediators. Parental SH-SY5Y cells were transiently transfected with an empty
Supplement Figure S1. Algorithmic quantification of mitochondrial morphology in SH- SY5Y cells treated with known fission/fusion mediators. Parental SH-SY5Y cells were transiently transfected with an empty
Fig. S1. Expression pattern of moody-gal4 in third instar. Maximum projection illustrating a dissected moody-gal4>ngfp L3 larva stained for Repo
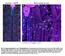 Fig. S1. Expression pattern of moody-gal4 in third instar. Maximum projection illustrating a dissected moody-gal4>ngfp L3 larva stained for Repo (magenta), Fas2 (blue) and GFP (green) in overview (A) and
Fig. S1. Expression pattern of moody-gal4 in third instar. Maximum projection illustrating a dissected moody-gal4>ngfp L3 larva stained for Repo (magenta), Fas2 (blue) and GFP (green) in overview (A) and
Kinesin-3 and dynein cooperate in long-range retrograde endosome motility along a nonuniform microtubule array
 MBoC ARTICLE Kinesin-3 and dynein cooperate in long-range retrograde endosome motility along a nonuniform microtubule array Martin Schuster a, Sreedhar Kilaru a, Gero Fink b, Jérôme Collemare c, *, Yvonne
MBoC ARTICLE Kinesin-3 and dynein cooperate in long-range retrograde endosome motility along a nonuniform microtubule array Martin Schuster a, Sreedhar Kilaru a, Gero Fink b, Jérôme Collemare c, *, Yvonne
Table S1. Aspergillus nidulans strains used in this study Strain Genotype Derivation
 Supplemental Material De Souza et al., 211 Table S1. Aspergillus nidulans strains used in this study Strain Genotype Derivation CDS295 pyrg89; pyroa4; pyrg Af ::son promotor::gfp-son nup98/nup96 ; chaa1
Supplemental Material De Souza et al., 211 Table S1. Aspergillus nidulans strains used in this study Strain Genotype Derivation CDS295 pyrg89; pyroa4; pyrg Af ::son promotor::gfp-son nup98/nup96 ; chaa1
Supplementary Figure 1. Nature Genetics: doi: /ng.3848
 Supplementary Figure 1 Phenotypes and epigenetic properties of Fab2L flies. A- Phenotypic classification based on eye pigment levels in Fab2L male (orange bars) and female (yellow bars) flies (n>150).
Supplementary Figure 1 Phenotypes and epigenetic properties of Fab2L flies. A- Phenotypic classification based on eye pigment levels in Fab2L male (orange bars) and female (yellow bars) flies (n>150).
Lipid transfer proteins confer resistance to trichothecenes
 Lipid transfer proteins confer resistance to trichothecenes John McLaughlin and Anwar Bin-Umer Tumer Laboratory National Fusarium Head Blight Forum December 6th, 2012 FY09-11: Identify trichothecene resistance
Lipid transfer proteins confer resistance to trichothecenes John McLaughlin and Anwar Bin-Umer Tumer Laboratory National Fusarium Head Blight Forum December 6th, 2012 FY09-11: Identify trichothecene resistance
Neurite formation & neuronal polarization. The cytoskeletal components of neurons have characteristic distributions and associations
 Mechanisms of neuronal migration & Neurite formation & neuronal polarization Paul Letourneau letou001@umn.edu Chapter 16; The Cytoskeleton; Molecular Biology of the Cell, Alberts et al. 1 The cytoskeletal
Mechanisms of neuronal migration & Neurite formation & neuronal polarization Paul Letourneau letou001@umn.edu Chapter 16; The Cytoskeleton; Molecular Biology of the Cell, Alberts et al. 1 The cytoskeletal
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI:.38/ncb97 P ( μm, hours) 1 2 4 P DMSO Figure S1 unningham et al. E 97 65 27 MFN1 GFP-Parkin Opa1 ctin GPDH HEK293 GFP-Parkin 19 115 97 65 27 Mitochondrial Fraction SH-SY5Y GFP-Parkin Mito DMSO Mito
DOI:.38/ncb97 P ( μm, hours) 1 2 4 P DMSO Figure S1 unningham et al. E 97 65 27 MFN1 GFP-Parkin Opa1 ctin GPDH HEK293 GFP-Parkin 19 115 97 65 27 Mitochondrial Fraction SH-SY5Y GFP-Parkin Mito DMSO Mito
Supplemental Information. The Mitochondrial Fission Receptor MiD51. Requires ADP as a Cofactor
 Structure, Volume 22 Supplemental Information The Mitochondrial Fission Receptor MiD51 Requires ADP as a Cofactor Oliver C. Losón, Raymond Liu, Michael E. Rome, Shuxia Meng, Jens T. Kaiser, Shu-ou Shan,
Structure, Volume 22 Supplemental Information The Mitochondrial Fission Receptor MiD51 Requires ADP as a Cofactor Oliver C. Losón, Raymond Liu, Michael E. Rome, Shuxia Meng, Jens T. Kaiser, Shu-ou Shan,
Using ADE Mutants to Study Respiration and Fermentation in Yeast Extensions to Basic Lab
 Using ADE Mutants to Study Respiration and Fermentation in Yeast Extensions to Basic Lab Introduction: David Form, Nashoba Regional High School And Jessica Forton, Melrose High School Bioinformatics Component
Using ADE Mutants to Study Respiration and Fermentation in Yeast Extensions to Basic Lab Introduction: David Form, Nashoba Regional High School And Jessica Forton, Melrose High School Bioinformatics Component
7.06 Problem Set
 7.06 Problem Set 5 -- 2006 1. In the first half of the course, we encountered many examples of proteins that entered the nucleus in response to the activation of a cell-signaling pathway. One example of
7.06 Problem Set 5 -- 2006 1. In the first half of the course, we encountered many examples of proteins that entered the nucleus in response to the activation of a cell-signaling pathway. One example of
Lecture 18 June 2 nd, Gene Expression Regulation Mutations
 Lecture 18 June 2 nd, 2016 Gene Expression Regulation Mutations From Gene to Protein Central Dogma Replication DNA RNA PROTEIN Transcription Translation RNA Viruses: genome is RNA Reverse Transcriptase
Lecture 18 June 2 nd, 2016 Gene Expression Regulation Mutations From Gene to Protein Central Dogma Replication DNA RNA PROTEIN Transcription Translation RNA Viruses: genome is RNA Reverse Transcriptase
Photoreceptor Regulation of Constans Protein in Photoperiodic Flowering
 Photoreceptor Regulation of Constans Protein in Photoperiodic Flowering by Valverde et. Al Published in Science 2004 Presented by Boyana Grigorova CBMG 688R Feb. 12, 2007 Circadian Rhythms: The Clock Within
Photoreceptor Regulation of Constans Protein in Photoperiodic Flowering by Valverde et. Al Published in Science 2004 Presented by Boyana Grigorova CBMG 688R Feb. 12, 2007 Circadian Rhythms: The Clock Within
The geneticist s questions
 The geneticist s questions a) What is consequence of reduced gene function? 1) gene knockout (deletion, RNAi) b) What is the consequence of increased gene function? 2) gene overexpression c) What does
The geneticist s questions a) What is consequence of reduced gene function? 1) gene knockout (deletion, RNAi) b) What is the consequence of increased gene function? 2) gene overexpression c) What does
Alleles held at equilibrium by balancing selection
 Alleles held at equilibrium by balancing selection Alleles held at equilibrium by balancing selection Neutral mutation Alleles held at equilibrium by balancing selection Lost by drift Neutral mutation
Alleles held at equilibrium by balancing selection Alleles held at equilibrium by balancing selection Neutral mutation Alleles held at equilibrium by balancing selection Lost by drift Neutral mutation
Cell Division. OpenStax College. 1 Genomic DNA
 OpenStax-CNX module: m44459 1 Cell Division OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you will be
OpenStax-CNX module: m44459 1 Cell Division OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you will be
JMJ14-HA. Col. Col. jmj14-1. jmj14-1 JMJ14ΔFYR-HA. Methylene Blue. Methylene Blue
 Fig. S1 JMJ14 JMJ14 JMJ14ΔFYR Methylene Blue Col jmj14-1 JMJ14-HA Methylene Blue Col jmj14-1 JMJ14ΔFYR-HA Fig. S1. The expression level of JMJ14 and truncated JMJ14 with FYR (FYRN + FYRC) domain deletion
Fig. S1 JMJ14 JMJ14 JMJ14ΔFYR Methylene Blue Col jmj14-1 JMJ14-HA Methylene Blue Col jmj14-1 JMJ14ΔFYR-HA Fig. S1. The expression level of JMJ14 and truncated JMJ14 with FYR (FYRN + FYRC) domain deletion
Comparing whole genomes
 BioNumerics Tutorial: Comparing whole genomes 1 Aim The Chromosome Comparison window in BioNumerics has been designed for large-scale comparison of sequences of unlimited length. In this tutorial you will
BioNumerics Tutorial: Comparing whole genomes 1 Aim The Chromosome Comparison window in BioNumerics has been designed for large-scale comparison of sequences of unlimited length. In this tutorial you will
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn.2717
 Supplementary Fig. 1. Dendrite length is not secondary to body length. Dendrite growth proceeds independently of the rate of body growth and decreases in rate in adults. n 20 on dendrite measurement, n
Supplementary Fig. 1. Dendrite length is not secondary to body length. Dendrite growth proceeds independently of the rate of body growth and decreases in rate in adults. n 20 on dendrite measurement, n
targets. clustering show that different complex pathway
 Supplementary Figure 1. CLICR allows clustering and activation of cytoplasmic protein targets. (a, b) Upon light activation, the Cry2 (red) and LRP6c (green) components co-cluster due to the heterodimeric
Supplementary Figure 1. CLICR allows clustering and activation of cytoplasmic protein targets. (a, b) Upon light activation, the Cry2 (red) and LRP6c (green) components co-cluster due to the heterodimeric
Transport of fungal RAB11 secretory vesicles involves myosin-5, dynein/dynactin/p25, and kinesin-1 and is independent of kinesin-3
 MBoC ARTICLE Transport of fungal RAB11 secretory vesicles involves myosin-5, dynein/dynactin/p25, and kinesin-1 and is independent of kinesin-3 Miguel A. Peñalva a, *, Jun Zhang b, Xin Xiang b, and Areti
MBoC ARTICLE Transport of fungal RAB11 secretory vesicles involves myosin-5, dynein/dynactin/p25, and kinesin-1 and is independent of kinesin-3 Miguel A. Peñalva a, *, Jun Zhang b, Xin Xiang b, and Areti
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Structural analysis of leader peptide binding enables leaderfree cyanobactin processing Jesko Koehnke 1,2, Greg Mann 1,2, Andrew F Bent 1,2, Hannes Ludewig 1, Sally Shirran 1,
Supplementary Information Structural analysis of leader peptide binding enables leaderfree cyanobactin processing Jesko Koehnke 1,2, Greg Mann 1,2, Andrew F Bent 1,2, Hannes Ludewig 1, Sally Shirran 1,
allosteric cis-acting DNA element coding strand dominant constitutive mutation coordinate regulation of genes denatured
 A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z AA BB CC DD EE FF GG HH II JJ KK LL MM NN OO PP QQ RR SS TT UU VV allosteric cis-acting DNA element coding strand codominant constitutive mutation coordinate
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z AA BB CC DD EE FF GG HH II JJ KK LL MM NN OO PP QQ RR SS TT UU VV allosteric cis-acting DNA element coding strand codominant constitutive mutation coordinate
cote cote-yfp spc This work cote cote-yfp spc This work cote cote-yfp spc This work cote cote-yfp spc This work cote cote-yfp spc This work
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Table S1. List of strains Strains Genotype Source B. subtilis PY79 Prototrophic derivative of B. subtilis 168 (60) RL1070 spovid::kan (12) HS176 cotz phs2 (cotz-gfp spc) (22)
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Table S1. List of strains Strains Genotype Source B. subtilis PY79 Prototrophic derivative of B. subtilis 168 (60) RL1070 spovid::kan (12) HS176 cotz phs2 (cotz-gfp spc) (22)
Molecular Motors. Structural and Mechanistic Overview! Kimberly Nguyen - December 6, 2013! MOLECULAR MOTORS - KIMBERLY NGUYEN
 Molecular Motors Structural and Mechanistic Overview!! Kimberly Nguyen - December 6, 2013!! 1 Molecular Motors: A Structure and Mechanism Overview! Introduction! Molecular motors are fundamental agents
Molecular Motors Structural and Mechanistic Overview!! Kimberly Nguyen - December 6, 2013!! 1 Molecular Motors: A Structure and Mechanism Overview! Introduction! Molecular motors are fundamental agents
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 med!1,2 Wild-type (N2) end!3 elt!2 5 1 15 Time (minutes) 5 1 15 Time (minutes) med!1,2 end!3 5 1 15 Time (minutes) elt!2 5 1 15 Time (minutes) Supplementary Figure 1: Number of med-1,2, end-3, end-1 and
med!1,2 Wild-type (N2) end!3 elt!2 5 1 15 Time (minutes) 5 1 15 Time (minutes) med!1,2 end!3 5 1 15 Time (minutes) elt!2 5 1 15 Time (minutes) Supplementary Figure 1: Number of med-1,2, end-3, end-1 and
A complementation test would be done by crossing the haploid strains and scoring the phenotype in the diploids.
 Problem set H answers 1. To study DNA repair mechanisms, geneticists isolated yeast mutants that were sensitive to various types of radiation; for example, mutants that were more sensitive to UV light.
Problem set H answers 1. To study DNA repair mechanisms, geneticists isolated yeast mutants that were sensitive to various types of radiation; for example, mutants that were more sensitive to UV light.
Penghui Li, Beibei Chen, Gaoyang Zhang, Longxiang Chen, Qiang Dong, Jiangqi Wen, Kirankumar S. Mysore and Jian Zhao
 New Phytologist Supporting Information Regulation of anthocyanin and proanthocyanidin biosynthesis by Medicago truncatula bhlh transcription factor MtTT8 Penghui Li, Beibei Chen, Gaoyang Zhang, Longxiang
New Phytologist Supporting Information Regulation of anthocyanin and proanthocyanidin biosynthesis by Medicago truncatula bhlh transcription factor MtTT8 Penghui Li, Beibei Chen, Gaoyang Zhang, Longxiang
Chapter 4 Evaluating a potential interaction between deltex and git in Drosophila: genetic interaction, gene overexpression and cell biology assays.
 Evaluating a potential interaction between deltex and git in Drosophila: genetic interaction, gene overexpression and cell biology assays. The data described in chapter 3 presented evidence that endogenous
Evaluating a potential interaction between deltex and git in Drosophila: genetic interaction, gene overexpression and cell biology assays. The data described in chapter 3 presented evidence that endogenous
Biology of Fungi. Fungal Structure and Function. Lecture: Structure/Function, Part A BIOL 4848/ Fall Overview of the Hypha
 Biology of Fungi Fungal Structure and Function Overview of the Hypha The hypha is a rigid tube containing cytoplasm Growth occurs at the tips of hyphae Behind the tip, the cell is aging Diagram of hyphal
Biology of Fungi Fungal Structure and Function Overview of the Hypha The hypha is a rigid tube containing cytoplasm Growth occurs at the tips of hyphae Behind the tip, the cell is aging Diagram of hyphal
Conformationally Variable Single Particles Heterogeneity in the real world
 Conformationally Variable Single Particles Heterogeneity in the real world Stan Burgess University of Leeds, UK Workshop on Advanced Topics in EM Structure Determination: Challenging Molecules November
Conformationally Variable Single Particles Heterogeneity in the real world Stan Burgess University of Leeds, UK Workshop on Advanced Topics in EM Structure Determination: Challenging Molecules November
According to the manufacture s direction (Pierce), RNA and DNA
 Supplementary method Electrophoretic Mobility-shift assay (EMSA) According to the manufacture s direction (Pierce), RNA and DNA oligonuleotides were firstly labeled by biotin. TAVb (1pM) was incubated
Supplementary method Electrophoretic Mobility-shift assay (EMSA) According to the manufacture s direction (Pierce), RNA and DNA oligonuleotides were firstly labeled by biotin. TAVb (1pM) was incubated
Chromosome Chr Duplica Duplic t a ion Pixley
 Chromosome Duplication Pixley Figure 4-6 Molecular Biology of the Cell ( Garland Science 2008) Figure 4-72 Molecular Biology of the Cell ( Garland Science 2008) Interphase During mitosis (cell division),
Chromosome Duplication Pixley Figure 4-6 Molecular Biology of the Cell ( Garland Science 2008) Figure 4-72 Molecular Biology of the Cell ( Garland Science 2008) Interphase During mitosis (cell division),
23-. Shoot and root development depend on ratio of IAA/CK
 Balance of Hormones regulate growth and development Environmental factors regulate hormone levels light- e.g. phototropism gravity- e.g. gravitropism temperature Mode of action of each hormone 1. Signal
Balance of Hormones regulate growth and development Environmental factors regulate hormone levels light- e.g. phototropism gravity- e.g. gravitropism temperature Mode of action of each hormone 1. Signal
7.06 Cell Biology EXAM #3 April 21, 2005
 7.06 Cell Biology EXAM #3 April 21, 2005 This is an open book exam, and you are allowed access to books, a calculator, and notes but not computers or any other types of electronic devices. Please write
7.06 Cell Biology EXAM #3 April 21, 2005 This is an open book exam, and you are allowed access to books, a calculator, and notes but not computers or any other types of electronic devices. Please write
Nature Genetics: doi:0.1038/ng.2768
 Supplementary Figure 1: Graphic representation of the duplicated region at Xq28 in each one of the 31 samples as revealed by acgh. Duplications are represented in red and triplications in blue. Top: Genomic
Supplementary Figure 1: Graphic representation of the duplicated region at Xq28 in each one of the 31 samples as revealed by acgh. Duplications are represented in red and triplications in blue. Top: Genomic
Supplementary Figure 1. CoMIC in 293T, HeLa, and HepG2 cells. (a) Mitochondrial morphology in 293T, HeLa and HepG2 cells. Cells were transfected with
 Supplementary Figure 1. CoMIC in 293T, HeLa, and HepG2 cells. (a) Mitochondrial morphology in 293T, HeLa and HepG2 cells. Cells were transfected with DsRed-mito. Right panels are time-course enlarged images
Supplementary Figure 1. CoMIC in 293T, HeLa, and HepG2 cells. (a) Mitochondrial morphology in 293T, HeLa and HepG2 cells. Cells were transfected with DsRed-mito. Right panels are time-course enlarged images
Lecture 10: Cyclins, cyclin kinases and cell division
 Chem*3560 Lecture 10: Cyclins, cyclin kinases and cell division The eukaryotic cell cycle Actively growing mammalian cells divide roughly every 24 hours, and follow a precise sequence of events know as
Chem*3560 Lecture 10: Cyclins, cyclin kinases and cell division The eukaryotic cell cycle Actively growing mammalian cells divide roughly every 24 hours, and follow a precise sequence of events know as
Waithe et al Supplementary Figures
 Waithe et al Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 Expression and properties of WT and W391A mutant YFP- Ca V 2.2. A Immunoblot using Ca V 2.2 Ab for untransfected cells (UT, lane 1), YFP-Ca V 2.2
Waithe et al Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 Expression and properties of WT and W391A mutant YFP- Ca V 2.2. A Immunoblot using Ca V 2.2 Ab for untransfected cells (UT, lane 1), YFP-Ca V 2.2
