Using ADE Mutants to Study Respiration and Fermentation in Yeast Extensions to Basic Lab
|
|
|
- Suzan Norris
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Using ADE Mutants to Study Respiration and Fermentation in Yeast Extensions to Basic Lab Introduction: David Form, Nashoba Regional High School And Jessica Forton, Melrose High School Bioinformatics Component We have experimentally determined the energy-yielding and color phenotypes of two adenine-requiring mutants in the presence of glucose, glycerol and excess adenine. We will now use bioinformatics to compare the two mutations and their position in the biochemical chain of reactions that produces adenine in yeast. Specifically, we will compare each of the genes and their enzyme products according to: 1. n which of the 16 yeast chromosomes each gene is located. 2. The name and function of each enzyme. 3. The size of each enzyme 4. The 3-D structure of each enzyme. Each student will be asked to research one of the genetic mutants associated with the ade biochemical pathway. Student groups will be formed so that you can compile the information in order to determine the position of each enzyme mutant in the biochemical pathway that leads to the production of adenine. Procedure: 1. Go to the Saccharomyces Genome yeastgenome.org. 2. Under Sequence, go Gene/Sequence Resources. 3. Under 1. Enter a Name enter Ade* and click on Submit Form. 4. You will see a list of each gene in the Ade pathway. 5. Select the gene in which you are interested. 6. Under Biology/Literature, we will be exploring Locus info, Protein Info and 3-D structure. 7. Under Locus Info, you will be able to determine: i. The chromosome on which this gene is located. ii. iii. The name of the enzyme. The function of the enzyme. 8. Under Protein info, you will be able to find the size of the protein in amino acids and the molecular weight of the protein. 9. Under 3-D structure, you will find the PDB code for the first homolog (variant) of this protein. This code will allow you to view the 3-D structure of the enzyme, using jmol.
2 10. Use the information gathered from SGD to fill in the information for your assigned gene/enzyme on Tables 1 and When you are done, to to FirstGlance in 12. Insert the PDB code for your enzyme in the box. 13. A new window will open up with a 3-D model of your enzyme. 14. Click on spin and background to stop the model from spinning and to make the background black. 15. bserve your model in cartoon (ribbon) and contact (space-fill) views. Feel free to play around with the other views and features of this program! Data Table 1 Mutant Symbol Name of enzyme Enzyme Function Ade1 Ade2 Ade3 Ade4
3 Ade5/7 Ade6 Ade5/7 Ade8 Data Table 2 Mutant Symbol Chromosome # Protein length (# of a.a) M.W. of protein PDB id # Ade1 Ade2 Ade3 Ade4 Ade5/7 Ade6 Ade5/7 Ade8 Critical Thinking Questions
4 1. Summarize all of the ways in which you have demonstrated that the various enzymes of the adenine-producing pathway in yeast are separate, distinct proteins, with different structures, specificities and encoded by different genes. 2. Did you find evidence that a single enzyme can catalyze more than one reaction? How do you think that this is possible? 3. Mutations in the ade1 and ade2 genes result in yeast that develop a pink phenotype under certain conditions. What are these conditions? 4. Why do these (Ade1 and Ade2) mutations yield a pink phenotype, while mutations in the other ade genes will not yield a pink phenotype?
5 Ade1 Mutant Symbol Data Table 1 (Teacher s Version) Name of enzyme N-succinyl-5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide ribotide (SAICAR) synthetase Enzyme Function required for 'de novo' purine nucleotide biosynthesis; red pigment accumulates in mutant cells deprived of adenine Ade2 Phosphoribosylaminoimidazole carboxylase catalyzes a step in the 'de novo' purine nucleotide biosynthetic pathway; red pigment accumulates in mutant cells deprived of adenine Ade3 C1-tetrahydrofolate synthase involved in single carbon metabolism and required for biosynthesis of purines, thymidylate, methionine, and histidine; null mutation causes auxotrophy for adenine and histidine Ade4 Phosphoribosylpyrophosphate amidotransferase (PRPPAT; amidophosphoribosyltransferase), catalyzes first step of the 'de novo' purine nucleotide biosynthetic pathway Ade5,7 aminoimidazole ribotide synthetase and Bifunctional enzyme of the 'de
6 glycinamide ribotide synthetase novo' purine nucleotide biosynthetic pathway Ade6 Formylglycinamidine-ribonucleotide (FGAM)- synthetase catalyzes a step in the 'de novo' purine nucleotide biosynthetic pathway Ade5,7 aminoimidazole ribotide synthetase and glycinamide ribotide synthetase Bifunctional enzyme of the 'de novo' purine nucleotide biosynthetic pathway Ade8 Phosphoribosyl-glycinamide transformylase catalyzes a step in the 'de novo' purine nucleotide biosynthetic pathway Data Table 2 (Teacher s Version) Mutant Symbol Chromosome # Protein length M.W. of protein PDB id # (# of a.a) Ade ,603 2CNQ Ade2 XV ,339 3K5H Ade3 VII ,204 3PZX Ade4 XIII ,719 1ECF Ade5,7 VII ,067 2QK4 Ade6 VII 1, ,904 1T3T Ade5,7 VII ,067 2QK4
7 Ade8 IV ,540 3TQR
8 Using ADE Mutants to Study Respiration and Fermentation in Yeast David Form, Nashoba Regional High School And Jessica Forton, Melrose High School Extensions to Basic Lab Genetic Analysis of Ade1 and Ade2 Mutants: Demonstrating Genetic Dominance and Complementarity with Living Punnet Squares Introduction: The wild type, as well as the ade1 and ade2 mutant strains of yeast, are haploid. So, the wild type have one copy of the version of ade1 and ade2 that produce functional enzymes. The ade1 mutants have a gene that produces a functional copy of the ade 2 enzyme, but a mutant copy of the ade1 gene, which does not produce a functional enzyme. In contrast, the ade2 yeast contain a single copy of a normal ade1 gene and a mutant version of the ade2 gene. They produce a functional ade1 enzyme, but a non-functional ade2 enzyme. When we mate these yeast, they will produce diploid offspring that contain two copies of each ade gene, one from each parent. The dominant allele will determine the phenotype (white or red) of the diploid offspring. By mating individuals who have mutations on different genes that affect the same process, we will produce offspring with a normal, or wild-type phenotype. This is because the offspring have one copy of the normal allele for both genes. This is known as genetic complementation. In this experiment, we will cross the ade 1 and ade2 mutants with the wild type to determine if these mutations are dominant or recessive. We will cross the ade1 and ade2 mutants to determine if the ade1 and ade2 alleles are on separate genes. Procedure: 1. Prepare streak plates of the following yeast cultures: i. Ade1 alpha strain ii. iii. iv. Ade1 a strain Ade2 alpha strain Ade2 a strain v. Wild type alpha strain vi. Wild type a strain 2. Pour YED agar into sets of four Petri dishes. Pairs of students will work on ne of the four dishes: i. Draw a Punnett square on the bottom of each dish as follows:
9 1 WT alpha Ade1 alpha Ade1 a 2 WT alpha Ade2 alpha Ade2 a 3 WT alpha Ade1 alpha Ade2 a
10 4 WT alpha Ade2 alpha Ade1 a 3. For each plate: i. bserve and record the phenotypes (color) of each parental haploid yeast strain. ii. iii. iv. n the agar, over each circle, you will mix two strains of haploid yeast, represented by the closest box to the side and above the circle. For example, in plate 1 in the circle on the upper left, you will mix the strains WT alpha and. To mix the strains, use a sterile Q-tip, or inoculating loop, to pick a single colony of yeast and spread it evenly over the area of the circle. Use a second sterile Q-tip to pick a colony of the second yeast strain and spread it evenly over the area of the same circle. v. The yeast need to be well mixed, so that they can mate and form diploid offspring. It is also important to use a small amount of yeast, as you want to observe the phenotypes of the offspring, and not the parental strains. vi. Incubate the plates for 2-3 days and record the phenotypes of the offspring.
11 Data Use colored pencils to record the phenotypes (pink or white) of each cross in the four circle in each Punnett square. Write the genotypes of the diploid offspring above each circle. 1 WT alpha Ade1 alpha Ade1 a 2 WT alpha Ade2 alpha Ade2 a 3 WT alpha Ade1 alpha
12 Ade2 a 4 WT alpha Ade2 alpha Ade1 a Data Table Strain Ploidy Phenotype Genotype WT alpha haploid white WT Ade1 alpha haploid Ade1 a WT/WT diploid pink Ade1 WT/Ade1 WT/Ade2 Ade1/Ade1 Ade2/Ade2 Ade1/Ade2
13 Critical Thinking Exercises: 1. When combined with the wild type allele, is the Ade1 mutation dominant or recessive? How do you know? 2. When combined with the wild type allele, is the Ade2 mutation dominant or recessive? How do you know? 3. From the data discussed in q. 1 and 2, what color did you expect for the Ade1/Ade2 diploid hybrids? Explain your choice. 4. Do the Ade1/Ade1, Ade2/Ade2 and the Ade1/Ade2 diploid yeast have at least one good copy of the Ade1 and Ade2 enzymes? 5. Explain why the Ade1/Ade2 diploid yeast differed from the Ade1/Ade1 and Ade2/Ade2 diploid yeast in phenotype. 6. Why are the Ade1 and Ade2 mutations called complementary mutations? What does this have to do with the position of these enzymes in the biochemical pathway for the production of adenine?
14 TEACHER S VERSIN Data Use colored pencils to record the phenotypes (pink or white) of each cross in the four circle in each Punnett square. Write the genotypes of the diploid offspring above each circle. 1 WT alpha o white Ade1 alpha o red white Ade1 a red 2 WT alpha o white Ade2 alpha o o Ade2 a o 3 WT alpha o white Ade1 alpha o red
15 white Ade2 a red 4 white WT alpha o white white Ade2 alpha o red white Ade1 a red white white Data Table Strain Ploidy Phenotype Genotype WT alpha haploid white WT haploid white WT Ade1 alpha haploid pink Ade1 Ade1 a haploid pink Ade1 WT/WT diploid white WT/WT WT/Ade1 diploid white WT/Ade1 WT/Ade2 diploid white WT/Ade2 Ade1/Ade1 diploid pink Ade1/Ade1 Ade2/Ade2 diploid pink Ade2/Ade2
16 Ade1/Ade2 diploid white Ade1/Ade2
Verification of the Principles of Genetics by Manipulating Saccharomyces Cerevisiae and Observing Meiotic Products ABSTRACT
 November 27, 2002 Bio251 Dr. Calhoon Verification of the Principles of Genetics by Manipulating Saccharomyces Cerevisiae and Observing Meiotic Products ABSTRACT The experiment was conducted to verify the
November 27, 2002 Bio251 Dr. Calhoon Verification of the Principles of Genetics by Manipulating Saccharomyces Cerevisiae and Observing Meiotic Products ABSTRACT The experiment was conducted to verify the
Genetics 275 Notes Week 7
 Cytoplasmic Inheritance Genetics 275 Notes Week 7 Criteriafor recognition of cytoplasmic inheritance: 1. Reciprocal crosses give different results -mainly due to the fact that the female parent contributes
Cytoplasmic Inheritance Genetics 275 Notes Week 7 Criteriafor recognition of cytoplasmic inheritance: 1. Reciprocal crosses give different results -mainly due to the fact that the female parent contributes
7.06 Problem Set #4, Spring 2005
 7.06 Problem Set #4, Spring 2005 1. You re doing a mutant hunt in S. cerevisiae (budding yeast), looking for temperaturesensitive mutants that are defective in the cell cycle. You discover a mutant strain
7.06 Problem Set #4, Spring 2005 1. You re doing a mutant hunt in S. cerevisiae (budding yeast), looking for temperaturesensitive mutants that are defective in the cell cycle. You discover a mutant strain
The phenotype of this worm is wild type. When both genes are mutant: The phenotype of this worm is double mutant Dpy and Unc phenotype.
 Series 2: Cross Diagrams - Complementation There are two alleles for each trait in a diploid organism In C. elegans gene symbols are ALWAYS italicized. To represent two different genes on the same chromosome:
Series 2: Cross Diagrams - Complementation There are two alleles for each trait in a diploid organism In C. elegans gene symbols are ALWAYS italicized. To represent two different genes on the same chromosome:
1. Contains the sugar ribose instead of deoxyribose. 2. Single-stranded instead of double stranded. 3. Contains uracil in place of thymine.
 Protein Synthesis & Mutations RNA 1. Contains the sugar ribose instead of deoxyribose. 2. Single-stranded instead of double stranded. 3. Contains uracil in place of thymine. RNA Contains: 1. Adenine 2.
Protein Synthesis & Mutations RNA 1. Contains the sugar ribose instead of deoxyribose. 2. Single-stranded instead of double stranded. 3. Contains uracil in place of thymine. RNA Contains: 1. Adenine 2.
Chromosome Chr Duplica Duplic t a ion Pixley
 Chromosome Duplication Pixley Figure 4-6 Molecular Biology of the Cell ( Garland Science 2008) Figure 4-72 Molecular Biology of the Cell ( Garland Science 2008) Interphase During mitosis (cell division),
Chromosome Duplication Pixley Figure 4-6 Molecular Biology of the Cell ( Garland Science 2008) Figure 4-72 Molecular Biology of the Cell ( Garland Science 2008) Interphase During mitosis (cell division),
 www.lessonplansinc.com Topic: Dinosaur Evolution Project Summary: Students pretend to evolve two dinosaurs using genetics and watch how the dinosaurs adapt to an environmental change. This is a very comprehensive
www.lessonplansinc.com Topic: Dinosaur Evolution Project Summary: Students pretend to evolve two dinosaurs using genetics and watch how the dinosaurs adapt to an environmental change. This is a very comprehensive
 www.lessonplansinc.com Topic: Dinosaur Evolution Project Summary: Students pretend to evolve two dinosaurs using genetics and watch how the dinosaurs adapt to an environmental change. This is a very comprehensive
www.lessonplansinc.com Topic: Dinosaur Evolution Project Summary: Students pretend to evolve two dinosaurs using genetics and watch how the dinosaurs adapt to an environmental change. This is a very comprehensive
Heredity and Genetics WKSH
 Chapter 6, Section 3 Heredity and Genetics WKSH KEY CONCEPT Mendel s research showed that traits are inherited as discrete units. Vocabulary trait purebred law of segregation genetics cross MAIN IDEA:
Chapter 6, Section 3 Heredity and Genetics WKSH KEY CONCEPT Mendel s research showed that traits are inherited as discrete units. Vocabulary trait purebred law of segregation genetics cross MAIN IDEA:
Unit 3 - Molecular Biology & Genetics - Review Packet
 Name Date Hour Unit 3 - Molecular Biology & Genetics - Review Packet True / False Questions - Indicate True or False for the following statements. 1. Eye color, hair color and the shape of your ears can
Name Date Hour Unit 3 - Molecular Biology & Genetics - Review Packet True / False Questions - Indicate True or False for the following statements. 1. Eye color, hair color and the shape of your ears can
genome a specific characteristic that varies from one individual to another gene the passing of traits from one generation to the next
 genetics the study of heredity heredity sequence of DNA that codes for a protein and thus determines a trait genome a specific characteristic that varies from one individual to another gene trait the passing
genetics the study of heredity heredity sequence of DNA that codes for a protein and thus determines a trait genome a specific characteristic that varies from one individual to another gene trait the passing
m1 m2 m3 m4 m5 m6 m7 m8 wt m m m m m m m m8 - + wt +
 otherwise, you couldn't grow them!) You perform pairwise infections with each of your mutant bacteriophage strains and get the following results: (+) = pair of phages lysed host cells, (-) = pair of phages
otherwise, you couldn't grow them!) You perform pairwise infections with each of your mutant bacteriophage strains and get the following results: (+) = pair of phages lysed host cells, (-) = pair of phages
Jeopardy. Evolution Q $100 Q $100 Q $100 Q $100 Q $100 Q $200 Q $200 Q $200 Q $200 Q $200 Q $300 Q $300 Q $300 Q $300 Q $300
 Jeopardy Mutations Crosses & Punnett Sqs. Meiosis & Variability Evolution Photo, Cell Resp, Energy, Matter Q $100 Q $200 Q $300 Q $400 Q $500 Q $100 Q $100 Q $100 Q $100 Q $200 Q $200 Q $200 Q $200 Q $300
Jeopardy Mutations Crosses & Punnett Sqs. Meiosis & Variability Evolution Photo, Cell Resp, Energy, Matter Q $100 Q $200 Q $300 Q $400 Q $500 Q $100 Q $100 Q $100 Q $100 Q $200 Q $200 Q $200 Q $200 Q $300
Ch 11.Introduction to Genetics.Biology.Landis
 Nom Section 11 1 The Work of Gregor Mendel (pages 263 266) This section describes how Gregor Mendel studied the inheritance of traits in garden peas and what his conclusions were. Introduction (page 263)
Nom Section 11 1 The Work of Gregor Mendel (pages 263 266) This section describes how Gregor Mendel studied the inheritance of traits in garden peas and what his conclusions were. Introduction (page 263)
Meiosis and Tetrad Analysis Lab
 Meiosis and Tetrad Analysis Lab Objectives: - Explain how meiosis and crossing over result in the different arrangements of ascospores within asci. - Learn how to calculate the map distance between a gene
Meiosis and Tetrad Analysis Lab Objectives: - Explain how meiosis and crossing over result in the different arrangements of ascospores within asci. - Learn how to calculate the map distance between a gene
Name Class Date. KEY CONCEPT Gametes have half the number of chromosomes that body cells have.
 Section 1: Chromosomes and Meiosis KEY CONCEPT Gametes have half the number of chromosomes that body cells have. VOCABULARY somatic cell autosome fertilization gamete sex chromosome diploid homologous
Section 1: Chromosomes and Meiosis KEY CONCEPT Gametes have half the number of chromosomes that body cells have. VOCABULARY somatic cell autosome fertilization gamete sex chromosome diploid homologous
Cell Division: the process of copying and dividing entire cells The cell grows, prepares for division, and then divides to form new daughter cells.
 Mitosis & Meiosis SC.912.L.16.17 Compare and contrast mitosis and meiosis and relate to the processes of sexual and asexual reproduction and their consequences for genetic variation. 1. Students will describe
Mitosis & Meiosis SC.912.L.16.17 Compare and contrast mitosis and meiosis and relate to the processes of sexual and asexual reproduction and their consequences for genetic variation. 1. Students will describe
Labs 7 and 8: Mitosis, Meiosis, Gametes and Genetics
 Biology 107 General Biology Labs 7 and 8: Mitosis, Meiosis, Gametes and Genetics In Biology 107, our discussion of the cell has focused on the structure and function of subcellular organelles. The next
Biology 107 General Biology Labs 7 and 8: Mitosis, Meiosis, Gametes and Genetics In Biology 107, our discussion of the cell has focused on the structure and function of subcellular organelles. The next
1. Ch 6. #17 In sweet peas, the synthesis of purple anthocyanin pigment in the petals is controlled by two genes, B and D.
 Day 11 Tutorial Answers for BIOL 234 section 921 summer 2014 students ONLY J. Klenz L. McDonnell Not for sale or duplication. Learning Goals: Given the functions of two or more gene products that control
Day 11 Tutorial Answers for BIOL 234 section 921 summer 2014 students ONLY J. Klenz L. McDonnell Not for sale or duplication. Learning Goals: Given the functions of two or more gene products that control
Chem Lecture 10 Lipid, Amino Acid, and Nucleotide Metabolism Part III: Nucleotide Metabolism
 Chem 352 - Lecture 10 Lipid, Amino Acid, and Nucleotide Metabolism Part III: Nucleotide Metabolism Lipid Metabolism Chem 352, Lecture 10, Part I: Lipid Metabolism 2 Lipid Metabolism Question: Draw a general
Chem 352 - Lecture 10 Lipid, Amino Acid, and Nucleotide Metabolism Part III: Nucleotide Metabolism Lipid Metabolism Chem 352, Lecture 10, Part I: Lipid Metabolism 2 Lipid Metabolism Question: Draw a general
Objective 3.01 (DNA, RNA and Protein Synthesis)
 Objective 3.01 (DNA, RNA and Protein Synthesis) DNA Structure o Discovered by Watson and Crick o Double-stranded o Shape is a double helix (twisted ladder) o Made of chains of nucleotides: o Has four types
Objective 3.01 (DNA, RNA and Protein Synthesis) DNA Structure o Discovered by Watson and Crick o Double-stranded o Shape is a double helix (twisted ladder) o Made of chains of nucleotides: o Has four types
Introduction to Genetics
 Introduction to Genetics We ve all heard of it, but What is genetics? Genetics: the study of gene structure and action and the patterns of inheritance of traits from parent to offspring. Ancient ideas
Introduction to Genetics We ve all heard of it, but What is genetics? Genetics: the study of gene structure and action and the patterns of inheritance of traits from parent to offspring. Ancient ideas
I. GREGOR MENDEL - father of heredity
 GENETICS: Mendel Background: Students know that Meiosis produces 4 haploid sex cells that are not identical, allowing for genetic variation. Essential Question: What are two characteristics about Mendel's
GENETICS: Mendel Background: Students know that Meiosis produces 4 haploid sex cells that are not identical, allowing for genetic variation. Essential Question: What are two characteristics about Mendel's
mrna Codon Table Mutant Dinosaur Name: Period:
 Mutant Dinosaur Name: Period: Intro Your dinosaur is born with a new genetic mutation. Your job is to map out the genes that are influenced by the mutation and to discover how the new dinosaurs interact
Mutant Dinosaur Name: Period: Intro Your dinosaur is born with a new genetic mutation. Your job is to map out the genes that are influenced by the mutation and to discover how the new dinosaurs interact
Investigation 7: Cell Division Part B: Meiosis and Crossing Over
 Background Investigation 7: Cell Division Part B: Meiosis and Crossing Over Ascomycota are a diverse group of fungi including the familiar single-celled baker s yeast, the complex morel mushroom, and the
Background Investigation 7: Cell Division Part B: Meiosis and Crossing Over Ascomycota are a diverse group of fungi including the familiar single-celled baker s yeast, the complex morel mushroom, and the
Meiosis and Fertilization Understanding How Genes Are Inherited 1
 Meiosis and Fertilization Understanding How Genes Are Inherited 1 Introduction In this activity, you will learn how you inherited two copies of each gene, one from your mother and one from your father.
Meiosis and Fertilization Understanding How Genes Are Inherited 1 Introduction In this activity, you will learn how you inherited two copies of each gene, one from your mother and one from your father.
Topic 10. Meiosis I. The Process of Meiosis
 Topic 10. Meiosis I. The Process of Meiosis Meiosis is a process of two sequenced nuclear divisions neither of which is identical to mitosis. Meiosis always begins with a nucleus with two sets of chromosomes
Topic 10. Meiosis I. The Process of Meiosis Meiosis is a process of two sequenced nuclear divisions neither of which is identical to mitosis. Meiosis always begins with a nucleus with two sets of chromosomes
Full file at CHAPTER 2 Genetics
 CHAPTER 2 Genetics MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Chromosomes are a. small linear bodies. b. contained in cells. c. replicated during cell division. 2. A cross between true-breeding plants bearing yellow seeds produces
CHAPTER 2 Genetics MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Chromosomes are a. small linear bodies. b. contained in cells. c. replicated during cell division. 2. A cross between true-breeding plants bearing yellow seeds produces
GENETICS - CLUTCH CH.1 INTRODUCTION TO GENETICS.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: HISTORY OF GENETICS The earliest use of genetics was through of plants and animals (8000-1000 B.C.) Selective breeding (artificial selection) is the process of breeding organisms
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: HISTORY OF GENETICS The earliest use of genetics was through of plants and animals (8000-1000 B.C.) Selective breeding (artificial selection) is the process of breeding organisms
Life Cycles, Meiosis and Genetic Variability24/02/2015 2:26 PM
 Life Cycles, Meiosis and Genetic Variability iclicker: 1. A chromosome just before mitosis contains two double stranded DNA molecules. 2. This replicated chromosome contains DNA from only one of your parents
Life Cycles, Meiosis and Genetic Variability iclicker: 1. A chromosome just before mitosis contains two double stranded DNA molecules. 2. This replicated chromosome contains DNA from only one of your parents
What is a sex cell? How are sex cells made? How does meiosis help explain Mendel s results?
 CHAPTER 6 3 Meiosis SECTION Heredity BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is a sex cell? How are sex cells made? How does meiosis help explain
CHAPTER 6 3 Meiosis SECTION Heredity BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is a sex cell? How are sex cells made? How does meiosis help explain
Meiosis and Fertilization Understanding How Genes Are Inherited 1
 Meiosis and Fertilization Understanding How Genes Are Inherited 1 Almost all the cells in your body were produced by mitosis. The only exceptions are the gametes sperm or eggs which are produced by a different
Meiosis and Fertilization Understanding How Genes Are Inherited 1 Almost all the cells in your body were produced by mitosis. The only exceptions are the gametes sperm or eggs which are produced by a different
2. Look at the table below. How many of these asci contain a spore arrangement that resulted from crossing over?
 INS 2007-08 Pre-lab III Questions 1. The cell cycle in a certain cell type has the duration of 16 hours. The nuclei of 660 cells showed 13 cells in anaphase. What is the approximate duration of anaphase
INS 2007-08 Pre-lab III Questions 1. The cell cycle in a certain cell type has the duration of 16 hours. The nuclei of 660 cells showed 13 cells in anaphase. What is the approximate duration of anaphase
Add Up and Cross Over
 Add Up and Cross Over Sordaria Genetics Simulation Introduction SCIENTIFIC BIO FAX! Crossing over occurs during meiosis I. During crossing over, homologous pairs of chromosomes exchange sections of DNA
Add Up and Cross Over Sordaria Genetics Simulation Introduction SCIENTIFIC BIO FAX! Crossing over occurs during meiosis I. During crossing over, homologous pairs of chromosomes exchange sections of DNA
progeny. Observe the phenotypes of the F1 progeny flies resulting from this reciprocal cross.
 Name Fruit Fly Exercise 8 Goal In this exercise, you will use the StarGenetics, a software tool that simulates mating experiments, to perform your own simulated genetic crosses to analyze the mode of inheritance
Name Fruit Fly Exercise 8 Goal In this exercise, you will use the StarGenetics, a software tool that simulates mating experiments, to perform your own simulated genetic crosses to analyze the mode of inheritance
BIOLOGY 321. Answers to text questions th edition: Chapter 2
 BIOLOGY 321 SPRING 2013 10 TH EDITION OF GRIFFITHS ANSWERS TO ASSIGNMENT SET #1 I have made every effort to prevent errors from creeping into these answer sheets. But, if you spot a mistake, please send
BIOLOGY 321 SPRING 2013 10 TH EDITION OF GRIFFITHS ANSWERS TO ASSIGNMENT SET #1 I have made every effort to prevent errors from creeping into these answer sheets. But, if you spot a mistake, please send
UNIT 8 BIOLOGY: Meiosis and Heredity Page 148
 UNIT 8 BIOLOGY: Meiosis and Heredity Page 148 CP: CHAPTER 6, Sections 1-6; CHAPTER 7, Sections 1-4; HN: CHAPTER 11, Section 1-5 Standard B-4: The student will demonstrate an understanding of the molecular
UNIT 8 BIOLOGY: Meiosis and Heredity Page 148 CP: CHAPTER 6, Sections 1-6; CHAPTER 7, Sections 1-4; HN: CHAPTER 11, Section 1-5 Standard B-4: The student will demonstrate an understanding of the molecular
Introduction to Genetics
 Chapter 11 Introduction to Genetics Section 11 1 The Work of Gregor Mendel (pages 263 266) This section describes how Gregor Mendel studied the inheritance of traits in garden peas and what his conclusions
Chapter 11 Introduction to Genetics Section 11 1 The Work of Gregor Mendel (pages 263 266) This section describes how Gregor Mendel studied the inheritance of traits in garden peas and what his conclusions
Chromosome duplication and distribution during cell division
 CELL DIVISION AND HEREDITY Student Packet SUMMARY IN EUKARYOTES, HERITABLE INFORMATION IS PASSED TO THE NEXT GENERATION VIA PROCESSES THAT INCLUDE THE CELL CYCLE, MITOSIS /MEIOSIS AND FERTILIZATION Mitosis
CELL DIVISION AND HEREDITY Student Packet SUMMARY IN EUKARYOTES, HERITABLE INFORMATION IS PASSED TO THE NEXT GENERATION VIA PROCESSES THAT INCLUDE THE CELL CYCLE, MITOSIS /MEIOSIS AND FERTILIZATION Mitosis
Biology I Level - 2nd Semester Final Review
 Biology I Level - 2nd Semester Final Review The 2 nd Semester Final encompasses all material that was discussed during second semester. It s important that you review ALL notes and worksheets from the
Biology I Level - 2nd Semester Final Review The 2 nd Semester Final encompasses all material that was discussed during second semester. It s important that you review ALL notes and worksheets from the
Family resemblance can be striking!
 Family resemblance can be striking! 1 Chapter 14. Mendel & Genetics 2 Gregor Mendel! Modern genetics began in mid-1800s in an abbey garden, where a monk named Gregor Mendel documented inheritance in peas
Family resemblance can be striking! 1 Chapter 14. Mendel & Genetics 2 Gregor Mendel! Modern genetics began in mid-1800s in an abbey garden, where a monk named Gregor Mendel documented inheritance in peas
Microevolution Changing Allele Frequencies
 Microevolution Changing Allele Frequencies Evolution Evolution is defined as a change in the inherited characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. Microevolution involves the
Microevolution Changing Allele Frequencies Evolution Evolution is defined as a change in the inherited characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. Microevolution involves the
Alleles Notes. 3. In the above table, circle each symbol that represents part of a DNA molecule. Underline each word that is the name of a protein.
 Alleles Notes Different versions of the same gene are called alleles. Different alleles give the instructions for making different versions of a protein. This table shows examples for two human genes.
Alleles Notes Different versions of the same gene are called alleles. Different alleles give the instructions for making different versions of a protein. This table shows examples for two human genes.
Meiosis and Mendel. Chapter 6
 Meiosis and Mendel Chapter 6 6.1 CHROMOSOMES AND MEIOSIS Key Concept Gametes have half the number of chromosomes that body cells have. Body Cells vs. Gametes You have body cells and gametes body cells
Meiosis and Mendel Chapter 6 6.1 CHROMOSOMES AND MEIOSIS Key Concept Gametes have half the number of chromosomes that body cells have. Body Cells vs. Gametes You have body cells and gametes body cells
Section 11 1 The Work of Gregor Mendel
 Chapter 11 Introduction to Genetics Section 11 1 The Work of Gregor Mendel (pages 263 266) What is the principle of dominance? What happens during segregation? Gregor Mendel s Peas (pages 263 264) 1. The
Chapter 11 Introduction to Genetics Section 11 1 The Work of Gregor Mendel (pages 263 266) What is the principle of dominance? What happens during segregation? Gregor Mendel s Peas (pages 263 264) 1. The
Table of Contents. Chapter Preview. 5.1 Mendel s Work. 5.2 Probability and Heredity. 5.3 The Cell and Inheritance. 5.4 Genes, DNA, and Proteins
 Table of Contents Chapter Preview 5.1 Mendel s Work 5.2 Probability and Heredity 5.3 The Cell and Inheritance 5.4 Genes, DNA, and Proteins Chapter 5 Preview Questions 1. What carries the instructions that
Table of Contents Chapter Preview 5.1 Mendel s Work 5.2 Probability and Heredity 5.3 The Cell and Inheritance 5.4 Genes, DNA, and Proteins Chapter 5 Preview Questions 1. What carries the instructions that
The Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance
 The Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance Mitosis and meiosis were first described in the late 800s. The chromosome theory of inheritance states: Mendelian genes have specific loci (positions) on chromosomes.
The Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance Mitosis and meiosis were first described in the late 800s. The chromosome theory of inheritance states: Mendelian genes have specific loci (positions) on chromosomes.
The phenotype of this worm is wild type. When both genes are mutant: The phenotype of this worm is double mutant Dpy and Unc phenotype.
 Series 1: Cross Diagrams There are two alleles for each trait in a diploid organism In C. elegans gene symbols are ALWAYS italicized. To represent two different genes on the same chromosome: When both
Series 1: Cross Diagrams There are two alleles for each trait in a diploid organism In C. elegans gene symbols are ALWAYS italicized. To represent two different genes on the same chromosome: When both
Name Class Date. Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Prentice Hall. 33
 Chapter 11 Introduction to Genetics Chapter Vocabulary Review Matching On the lines provided, write the letter of the definition of each term. 1. genetics a. likelihood that something will happen 2. trait
Chapter 11 Introduction to Genetics Chapter Vocabulary Review Matching On the lines provided, write the letter of the definition of each term. 1. genetics a. likelihood that something will happen 2. trait
Related Courses He who asks is a fool for five minutes, but he who does not ask remains a fool forever.
 CSE 527 Computational Biology http://www.cs.washington.edu/527 Lecture 1: Overview & Bio Review Autumn 2004 Larry Ruzzo Related Courses He who asks is a fool for five minutes, but he who does not ask remains
CSE 527 Computational Biology http://www.cs.washington.edu/527 Lecture 1: Overview & Bio Review Autumn 2004 Larry Ruzzo Related Courses He who asks is a fool for five minutes, but he who does not ask remains
Heterozygous BMN lines
 Optical density at 80 hours 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 a YPD b YPD + 1µM nystatin c YPD + 2µM nystatin d YPD + 4µM nystatin 1 3 5 6 9 13 16 20 21 22 23 25 28 29 30
Optical density at 80 hours 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 a YPD b YPD + 1µM nystatin c YPD + 2µM nystatin d YPD + 4µM nystatin 1 3 5 6 9 13 16 20 21 22 23 25 28 29 30
allosteric cis-acting DNA element coding strand dominant constitutive mutation coordinate regulation of genes denatured
 A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z AA BB CC DD EE FF GG HH II JJ KK LL MM NN OO PP QQ RR SS TT UU VV allosteric cis-acting DNA element coding strand codominant constitutive mutation coordinate
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z AA BB CC DD EE FF GG HH II JJ KK LL MM NN OO PP QQ RR SS TT UU VV allosteric cis-acting DNA element coding strand codominant constitutive mutation coordinate
Lesson 4: Understanding Genetics
 Lesson 4: Understanding Genetics 1 Terms Alleles Chromosome Co dominance Crossover Deoxyribonucleic acid DNA Dominant Genetic code Genome Genotype Heredity Heritability Heritability estimate Heterozygous
Lesson 4: Understanding Genetics 1 Terms Alleles Chromosome Co dominance Crossover Deoxyribonucleic acid DNA Dominant Genetic code Genome Genotype Heredity Heritability Heritability estimate Heterozygous
UNIT IV - FOUNDATIONS OF GENETIC ENGINEERING. Cell Reproduction and Genetics. Study Questions. 1. What is mitosis? 2. What is meiosis?
 UNIT IV - FOUNDATIONS OF GENETIC ENGINEERING Lesson 2: Cell Reproduction and Genetics Competency/Objective: Explain how cells reproduce. Study Questions References 1. What is mitosis? 2. What is meiosis?
UNIT IV - FOUNDATIONS OF GENETIC ENGINEERING Lesson 2: Cell Reproduction and Genetics Competency/Objective: Explain how cells reproduce. Study Questions References 1. What is mitosis? 2. What is meiosis?
2. Yeast two-hybrid system
 2. Yeast two-hybrid system I. Process workflow a. Mating of haploid two-hybrid strains on YPD plates b. Replica-plating of diploids on selective plates c. Two-hydrid experiment plating on selective plates
2. Yeast two-hybrid system I. Process workflow a. Mating of haploid two-hybrid strains on YPD plates b. Replica-plating of diploids on selective plates c. Two-hydrid experiment plating on selective plates
Genetics_2011.notebook. May 13, Aim: What is heredity? Homework. Rd pp p.270 # 2,3,4. Feb 8 11:46 PM. Mar 25 1:15 PM.
 Aim: What is heredity? LE1 3/25/11 Do Now: 1.Make a T Chart comparing and contrasting mitosis & meiosis. 2. Have your lab out to be collected Homework for Tuesday 3/29 Read pp. 267 270 p.270 # 1,3 Vocabulary:
Aim: What is heredity? LE1 3/25/11 Do Now: 1.Make a T Chart comparing and contrasting mitosis & meiosis. 2. Have your lab out to be collected Homework for Tuesday 3/29 Read pp. 267 270 p.270 # 1,3 Vocabulary:
Guided Reading Chapter 1: The Science of Heredity
 Name Number Date Guided Reading Chapter 1: The Science of Heredity Section 1-1: Mendel s Work 1. Gregor Mendel experimented with hundreds of pea plants to understand the process of _. Match the term with
Name Number Date Guided Reading Chapter 1: The Science of Heredity Section 1-1: Mendel s Work 1. Gregor Mendel experimented with hundreds of pea plants to understand the process of _. Match the term with
Biology Fall Final Review 2005/2006 Mrs. Nuño
 Biology Fall Final Review 2005/2006 Mrs. Nuño Unit 1: The Nature of Science (Chapter 1) 7 characteristics of life. 7 major themes of biology, including the definitions of science terms describing those
Biology Fall Final Review 2005/2006 Mrs. Nuño Unit 1: The Nature of Science (Chapter 1) 7 characteristics of life. 7 major themes of biology, including the definitions of science terms describing those
Introduction to Genetics
 Introduction to Genetics We ve all heard of it, but What is genetics? Genetics: the study of gene structure and action and the patterns of inheritance of traits from parent to offspring. Ancient ideas
Introduction to Genetics We ve all heard of it, but What is genetics? Genetics: the study of gene structure and action and the patterns of inheritance of traits from parent to offspring. Ancient ideas
When one gene is wild type and the other mutant:
 Series 2: Cross Diagrams Linkage Analysis There are two alleles for each trait in a diploid organism In C. elegans gene symbols are ALWAYS italicized. To represent two different genes on the same chromosome:
Series 2: Cross Diagrams Linkage Analysis There are two alleles for each trait in a diploid organism In C. elegans gene symbols are ALWAYS italicized. To represent two different genes on the same chromosome:
Rebops. Your Rebop Traits Alternative forms. Procedure (work in pairs):
 Rebops The power of sexual reproduction to create diversity can be demonstrated through the breeding of Rebops. You are going to explore genetics by creating Rebop babies. Rebops are creatures that have
Rebops The power of sexual reproduction to create diversity can be demonstrated through the breeding of Rebops. You are going to explore genetics by creating Rebop babies. Rebops are creatures that have
GENETICS UNIT VOCABULARY CHART. Word Definition Word Part Visual/Mnemonic Related Words 1. adenine Nitrogen base, pairs with thymine in DNA and uracil
 Word Definition Word Part Visual/Mnemonic Related Words 1. adenine Nitrogen base, pairs with thymine in DNA and uracil in RNA 2. allele One or more alternate forms of a gene Example: P = Dominant (purple);
Word Definition Word Part Visual/Mnemonic Related Words 1. adenine Nitrogen base, pairs with thymine in DNA and uracil in RNA 2. allele One or more alternate forms of a gene Example: P = Dominant (purple);
BIOINFORMATICS LAB AP BIOLOGY
 BIOINFORMATICS LAB AP BIOLOGY Bioinformatics is the science of collecting and analyzing complex biological data. Bioinformatics combines computer science, statistics and biology to allow scientists to
BIOINFORMATICS LAB AP BIOLOGY Bioinformatics is the science of collecting and analyzing complex biological data. Bioinformatics combines computer science, statistics and biology to allow scientists to
Meiosis and Fertilization Understanding How Genes Are Inherited 1
 Meiosis and Fertilization Understanding How Genes Are Inherited 1 Introduction In this activity, you will learn how you inherited two copies of each gene, one from your mother and one from your father.
Meiosis and Fertilization Understanding How Genes Are Inherited 1 Introduction In this activity, you will learn how you inherited two copies of each gene, one from your mother and one from your father.
Cells and Their Processes. 1. What element do organic compounds have that inorganic compounds do not?
 Name: Date: Cells and Their Processes 1. What element do organic compounds have that inorganic compounds do not? 2. List the four types of organic compounds, describe the function of each AND list a food
Name: Date: Cells and Their Processes 1. What element do organic compounds have that inorganic compounds do not? 2. List the four types of organic compounds, describe the function of each AND list a food
Biology 322 Fall 2009 Wasp Genetics: Genetic Heterogeneity and Complementation Revisted
 Biology 322 Fall 2009 Wasp Genetics: Genetic Heterogeneity and Complementation Revisted Required Reading: Deaf by Design Nature 431: 894-896 October 21, 2004 http://fire.biol.wwu.edu/trent/trent/naturedeafdesign.pdf
Biology 322 Fall 2009 Wasp Genetics: Genetic Heterogeneity and Complementation Revisted Required Reading: Deaf by Design Nature 431: 894-896 October 21, 2004 http://fire.biol.wwu.edu/trent/trent/naturedeafdesign.pdf
Chapter 11 Meiosis and Genetics
 Chapter 11 Meiosis and Genetics Chapter 11 Meiosis and Genetics Grade:«grade» Subject:Biology Date:«date» 1 What are homologous chromosomes? A two tetrads, both from mom or both from dad B a matching pair
Chapter 11 Meiosis and Genetics Chapter 11 Meiosis and Genetics Grade:«grade» Subject:Biology Date:«date» 1 What are homologous chromosomes? A two tetrads, both from mom or both from dad B a matching pair
Solutions to Problem Set 4
 Question 1 Solutions to 7.014 Problem Set 4 Because you have not read much scientific literature, you decide to study the genetics of garden peas. You have two pure breeding pea strains. One that is tall
Question 1 Solutions to 7.014 Problem Set 4 Because you have not read much scientific literature, you decide to study the genetics of garden peas. You have two pure breeding pea strains. One that is tall
Cover Requirements: Name of Unit Colored picture representing something in the unit
 Name: Period: Cover Requirements: Name of Unit Colored picture representing something in the unit Biology B1 1 Target # Biology Unit B1 (Genetics & Meiosis) Learning Targets Genetics & Meiosis I can explain
Name: Period: Cover Requirements: Name of Unit Colored picture representing something in the unit Biology B1 1 Target # Biology Unit B1 (Genetics & Meiosis) Learning Targets Genetics & Meiosis I can explain
Add Up and Cross Over Sordaria Genetics Simulation
 Introduction Add Up and Cross Over Sordaria Genetics Simulation Publication No. Crossing over occurs during metaphase I of meiosis. During crossing over, homologous pairs of chromosomes exchange sections
Introduction Add Up and Cross Over Sordaria Genetics Simulation Publication No. Crossing over occurs during metaphase I of meiosis. During crossing over, homologous pairs of chromosomes exchange sections
Name: Period: EOC Review Part F Outline
 Name: Period: EOC Review Part F Outline Mitosis and Meiosis SC.912.L.16.17 Compare and contrast mitosis and meiosis and relate to the processes of sexual and asexual reproduction and their consequences
Name: Period: EOC Review Part F Outline Mitosis and Meiosis SC.912.L.16.17 Compare and contrast mitosis and meiosis and relate to the processes of sexual and asexual reproduction and their consequences
INS Biology Lab 5 Pre-Lab Name:
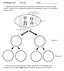 INS Biology Lab 5 Pre-Lab Name: 1. Diagram one possible fate of the chromosomes (assuming no crossover) during meiosis, starting with a hypothetical diploid cell containing two pairs of homologous chromosomes:
INS Biology Lab 5 Pre-Lab Name: 1. Diagram one possible fate of the chromosomes (assuming no crossover) during meiosis, starting with a hypothetical diploid cell containing two pairs of homologous chromosomes:
Part 2- Biology Paper 2 Inheritance and Variation Knowledge Questions
 Part 2- Biology Paper 2 Inheritance and Variation Knowledge Questions AQA TRILOGY Biology (8464) from 2016 Topic T4.6 Inheritance, variation and evolution Topic Student Checklist R A G Describe features
Part 2- Biology Paper 2 Inheritance and Variation Knowledge Questions AQA TRILOGY Biology (8464) from 2016 Topic T4.6 Inheritance, variation and evolution Topic Student Checklist R A G Describe features
Problems for 3505 (2011)
 Problems for 505 (2011) 1. In the simplex of genotype distributions x + y + z = 1, for two alleles, the Hardy- Weinberg distributions x = p 2, y = 2pq, z = q 2 (p + q = 1) are characterized by y 2 = 4xz.
Problems for 505 (2011) 1. In the simplex of genotype distributions x + y + z = 1, for two alleles, the Hardy- Weinberg distributions x = p 2, y = 2pq, z = q 2 (p + q = 1) are characterized by y 2 = 4xz.
2015 FALL FINAL REVIEW
 2015 FALL FINAL REVIEW Biomolecules & Enzymes Illustrate table and fill in parts missing 9A I can compare and contrast the structure and function of biomolecules. 9C I know the role of enzymes and how
2015 FALL FINAL REVIEW Biomolecules & Enzymes Illustrate table and fill in parts missing 9A I can compare and contrast the structure and function of biomolecules. 9C I know the role of enzymes and how
that does not happen during mitosis?
 Review! What is a somatic cell?! What is a sex cell?! What is a haploid cell?! What is a diploid cell?! Why is cell division important?! What are the different types of cell division?! What are these useful
Review! What is a somatic cell?! What is a sex cell?! What is a haploid cell?! What is a diploid cell?! Why is cell division important?! What are the different types of cell division?! What are these useful
Genetics Review Sheet Learning Target 11: Explain where and how an organism inherits its genetic information and this influences their
 Genetics Review Sheet Learning Target 11: Explain where and how an organism inherits its genetic information and this influences their characteristics. 1. Define the following terms: Name Block a. Heredity
Genetics Review Sheet Learning Target 11: Explain where and how an organism inherits its genetic information and this influences their characteristics. 1. Define the following terms: Name Block a. Heredity
Mitosis and Genetics Study Guide Answer Key
 Mitosis and Genetics Study Guide Answer Key 1. Which of the following is true of Interphase? a. It is part of Meiosis b. It occurs before Meiosis c. The cell does normal cell activities during interphase
Mitosis and Genetics Study Guide Answer Key 1. Which of the following is true of Interphase? a. It is part of Meiosis b. It occurs before Meiosis c. The cell does normal cell activities during interphase
Chapter 11 INTRODUCTION TO GENETICS
 Chapter 11 INTRODUCTION TO GENETICS 11-1 The Work of Gregor Mendel I. Gregor Mendel A. Studied pea plants 1. Reproduce sexually (have two sex cells = gametes) 2. Uniting of male and female gametes = Fertilization
Chapter 11 INTRODUCTION TO GENETICS 11-1 The Work of Gregor Mendel I. Gregor Mendel A. Studied pea plants 1. Reproduce sexually (have two sex cells = gametes) 2. Uniting of male and female gametes = Fertilization
Parts 2. Modeling chromosome segregation
 Genome 371, Autumn 2018 Quiz Section 2 Meiosis Goals: To increase your familiarity with the molecular control of meiosis, outcomes of meiosis, and the important role of crossing over in generating genetic
Genome 371, Autumn 2018 Quiz Section 2 Meiosis Goals: To increase your familiarity with the molecular control of meiosis, outcomes of meiosis, and the important role of crossing over in generating genetic
Introduction to population genetics & evolution
 Introduction to population genetics & evolution Course Organization Exam dates: Feb 19 March 1st Has everybody registered? Did you get the email with the exam schedule Summer seminar: Hot topics in Bioinformatics
Introduction to population genetics & evolution Course Organization Exam dates: Feb 19 March 1st Has everybody registered? Did you get the email with the exam schedule Summer seminar: Hot topics in Bioinformatics
Pre-Lab: Aipotu: Evolution
 Name: Pre-Lab: Aipotu: Evolution 1) On page Aipotu:Evolution-5, the Lab Manual described a color trait with two alleles, red (R) and white (r). On page Aipotu: Evolution -8, the Lab Manual describes a
Name: Pre-Lab: Aipotu: Evolution 1) On page Aipotu:Evolution-5, the Lab Manual described a color trait with two alleles, red (R) and white (r). On page Aipotu: Evolution -8, the Lab Manual describes a
Introduction to Genetics. Why do biological relatives resemble one another?
 Introduction to Genetics Why do biological relatives resemble one another? Heritage Hair color, eye color, height, and lots of other traits are passed down through families. How does that happen? REPRODUCTION
Introduction to Genetics Why do biological relatives resemble one another? Heritage Hair color, eye color, height, and lots of other traits are passed down through families. How does that happen? REPRODUCTION
KEY: Chapter 9 Genetics of Animal Breeding.
 KEY: Chapter 9 Genetics of Animal Breeding. Answer each question using the reading assigned to you. You can access this information by clicking on the following URL: https://drive.google.com/a/meeker.k12.co.us/file/d/0b1yf08xgyhnad08xugxsnfvba28/edit?usp=sh
KEY: Chapter 9 Genetics of Animal Breeding. Answer each question using the reading assigned to you. You can access this information by clicking on the following URL: https://drive.google.com/a/meeker.k12.co.us/file/d/0b1yf08xgyhnad08xugxsnfvba28/edit?usp=sh
DNA Structure and Function
 DNA Structure and Function Nucleotide Structure 1. 5-C sugar RNA ribose DNA deoxyribose 2. Nitrogenous Base N attaches to 1 C of sugar Double or single ring Four Bases Adenine, Guanine, Thymine, Cytosine
DNA Structure and Function Nucleotide Structure 1. 5-C sugar RNA ribose DNA deoxyribose 2. Nitrogenous Base N attaches to 1 C of sugar Double or single ring Four Bases Adenine, Guanine, Thymine, Cytosine
Parts 2. Modeling chromosome segregation
 Genome 371, Autumn 2017 Quiz Section 2 Meiosis Goals: To increase your familiarity with the molecular control of meiosis, outcomes of meiosis, and the important role of crossing over in generating genetic
Genome 371, Autumn 2017 Quiz Section 2 Meiosis Goals: To increase your familiarity with the molecular control of meiosis, outcomes of meiosis, and the important role of crossing over in generating genetic
Cell Shape coccus bacillus spirillum vibrio
 wrong 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 right 56 55 54 53 52 51 50 49 48 47 46 45 44 43 42 41 40 39 38 score 100 98.2 96.4 94.6 92.9 91.1 89.3 87.5 85.7 83.9 82.1 80.4 78.6 76.8 75 73.2 71.4
wrong 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 right 56 55 54 53 52 51 50 49 48 47 46 45 44 43 42 41 40 39 38 score 100 98.2 96.4 94.6 92.9 91.1 89.3 87.5 85.7 83.9 82.1 80.4 78.6 76.8 75 73.2 71.4
A complementation test would be done by crossing the haploid strains and scoring the phenotype in the diploids.
 Problem set H answers 1. To study DNA repair mechanisms, geneticists isolated yeast mutants that were sensitive to various types of radiation; for example, mutants that were more sensitive to UV light.
Problem set H answers 1. To study DNA repair mechanisms, geneticists isolated yeast mutants that were sensitive to various types of radiation; for example, mutants that were more sensitive to UV light.
F1 Parent Cell R R. Name Period. Concept 15.1 Mendelian inheritance has its physical basis in the behavior of chromosomes
 Name Period Concept 15.1 Mendelian inheritance has its physical basis in the behavior of chromosomes 1. What is the chromosome theory of inheritance? 2. Explain the law of segregation. Use two different
Name Period Concept 15.1 Mendelian inheritance has its physical basis in the behavior of chromosomes 1. What is the chromosome theory of inheritance? 2. Explain the law of segregation. Use two different
Meiosis and Fertilization Understanding How Genes Are Inherited 1
 Meiosis and Fertilization Understanding How Genes Are Inherited 1 Almost all the cells in your body were produced by mitosis. The only exceptions are the gametes sperm or eggs which are produced by a different
Meiosis and Fertilization Understanding How Genes Are Inherited 1 Almost all the cells in your body were produced by mitosis. The only exceptions are the gametes sperm or eggs which are produced by a different
Curriculum Map. Biology, Quarter 1 Big Ideas: From Molecules to Organisms: Structures and Processes (BIO1.LS1)
 1 Biology, Quarter 1 Big Ideas: From Molecules to Organisms: Structures and Processes (BIO1.LS1) Focus Standards BIO1.LS1.2 Evaluate comparative models of various cell types with a focus on organic molecules
1 Biology, Quarter 1 Big Ideas: From Molecules to Organisms: Structures and Processes (BIO1.LS1) Focus Standards BIO1.LS1.2 Evaluate comparative models of various cell types with a focus on organic molecules
Chromosomes. Which chromosomes in a nucleus are similar? Which are identical? Which are completely different?
 Chromosomes The big questions: Which chromosomes in a nucleus are similar? Which are identical? Which are completely different? How do chromosomes align during mitosis? How do chromosomes align during
Chromosomes The big questions: Which chromosomes in a nucleus are similar? Which are identical? Which are completely different? How do chromosomes align during mitosis? How do chromosomes align during
Guided Notes Unit 6: Classical Genetics
 Name: Date: Block: Chapter 6: Meiosis and Mendel I. Concept 6.1: Chromosomes and Meiosis Guided Notes Unit 6: Classical Genetics a. Meiosis: i. (In animals, meiosis occurs in the sex organs the testes
Name: Date: Block: Chapter 6: Meiosis and Mendel I. Concept 6.1: Chromosomes and Meiosis Guided Notes Unit 6: Classical Genetics a. Meiosis: i. (In animals, meiosis occurs in the sex organs the testes
Teachers Guide. Overview
 Teachers Guide Overview BioLogica is multilevel courseware for genetics. All the levels are linked so that changes in one level are reflected in all the other levels. The BioLogica activities guide learners
Teachers Guide Overview BioLogica is multilevel courseware for genetics. All the levels are linked so that changes in one level are reflected in all the other levels. The BioLogica activities guide learners
Picture from "Mendel's experiments: Figure 3," by Robert Bear et al
 Plant Genetics Learning Objectives: Understand the basics o genetics Understand how genetics is used in Plant Science today Learn the basics o extracting DNA Learn how to make crosses between plants and
Plant Genetics Learning Objectives: Understand the basics o genetics Understand how genetics is used in Plant Science today Learn the basics o extracting DNA Learn how to make crosses between plants and
Biology Review Second Quarter Mr. Pagani. 2 nd 9 Weeks. Review of major concepts of Biology. Plant structure & Function
 2 nd 9 Weeks Review of major concepts of Biology Plant structure & Function 1. Label each part of the plant diagram above. 2. What is the function of each part? (1) (2) (3) (4) (5) (6) 3. What is a plant?)
2 nd 9 Weeks Review of major concepts of Biology Plant structure & Function 1. Label each part of the plant diagram above. 2. What is the function of each part? (1) (2) (3) (4) (5) (6) 3. What is a plant?)
Objectives. Announcements. Comparison of mitosis and meiosis
 Announcements Colloquium sessions for which you can get credit posted on web site: Feb 20, 27 Mar 6, 13, 20 Apr 17, 24 May 15. Review study CD that came with text for lab this week (especially mitosis
Announcements Colloquium sessions for which you can get credit posted on web site: Feb 20, 27 Mar 6, 13, 20 Apr 17, 24 May 15. Review study CD that came with text for lab this week (especially mitosis
Do all living things grow, move, and breathe? All living things are made of what?
 All living things are made of what? Do all living things grow, move, and breathe? All living things respond to external conditions. This is called what? Which of the 7 traits of life is defined as the
All living things are made of what? Do all living things grow, move, and breathe? All living things respond to external conditions. This is called what? Which of the 7 traits of life is defined as the
BIOLOGY STANDARDS BASED RUBRIC
 BIOLOGY STANDARDS BASED RUBRIC STUDENTS WILL UNDERSTAND THAT THE FUNDAMENTAL PROCESSES OF ALL LIVING THINGS DEPEND ON A VARIETY OF SPECIALIZED CELL STRUCTURES AND CHEMICAL PROCESSES. First Semester Benchmarks:
BIOLOGY STANDARDS BASED RUBRIC STUDENTS WILL UNDERSTAND THAT THE FUNDAMENTAL PROCESSES OF ALL LIVING THINGS DEPEND ON A VARIETY OF SPECIALIZED CELL STRUCTURES AND CHEMICAL PROCESSES. First Semester Benchmarks:
Name: Per: Task: To create a model that explains how bi-racial parents can have black and white twins
 Name: Per: Genetics Test Review Task: To create a model that explains how bi-racial parents can have black and white twins Part 1: DNA to Protein to Trait LT15 (Protein and Traits) - Proteins express inherited
Name: Per: Genetics Test Review Task: To create a model that explains how bi-racial parents can have black and white twins Part 1: DNA to Protein to Trait LT15 (Protein and Traits) - Proteins express inherited
