M. oryzae Yashiromochi (Pita) Pi No.4 (Pita2) Fukunishiki (Piz) M. oryzae Ina168
|
|
|
- Philomena Henry
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Supplemental Data Yoshida et al., (2009) Association genetics reveals three novel avirulence genes from the rice blast fungal pathogen Magnaporthe oryzae. M. oryzae 70-15????????????? Sasanishiki (Pia) Kakehashi (Pii) Kanoto 51 (Pik) Tsuyuake (Pik-m) Fukunishiki (Piz) Yashiromochi (Pita) Pi No.4 (Pita2) Toride 1 (Piz-t) K60 (Pik-p) BL 1 (Pib) K59 (Pit) Moukoto (-) Shin-2 (-) R R R R R S R R S R R S S M. oryzae Ina168 Supplemental Figure 1. Ambiguous symptoms caused by isolate infected to various rice cultivars. Each isolate was sprayed onto the leaves of diagnostic rice cultivars differentially harboring eleven known resistance (R-) genes, Pia, Pii, Pik, Pik-m, Pik-p, Piz, Pita, Pita2, Piz-t, Pib, Pit cognate to the AVR genes (Kiyosawa, 1986) as well as susceptible cultivars Moukoto and Shin- 2, and compatible or incompatible interaction was observed among them. It is notable that in our experiments, the reaction between the isolate and these eleven rice R-genes could not be precisely defined since the disease symptoms caused by were not clear, and we could not assign each reaction as compatible or incompatible. In addition, inoculated Moukoto and Shin-2 also showed unclear symptoms. On the contrary, Ina168 induced typical susceptible spindleshaped lesions on Yahiromochi, K60, Moukoto and Shin-2 leaves, and typical resistance symptoms (few small brown spots) on the leaves of the other cultivars. Photos were taken 10 days after inoculation with conidia/ml (containing 0.01 % tween 20) of or conidia/ml (containing 0.01 % tween 20) of Ina168.
2 1000 Number of secreted protein genes AVR-Pita θ (x10-3 ) Supplemental Figure 2. Frequency distribution of nucleotide diversity among 1,032 loci of M. oryzae putative secreted protein genes. Nucleotide diversity (θ;watterson 1975) is given in x-axis and number of loci in the given θ range is shown in the y-axis. Out of 1,032 loci, 805 were monomorphic. of AVR-Pita (MG ) is
3 Supplemental Figure 3. Size distribution of predicted proteins of M. oryzae. Size 11,109 predicted proteins of Isolate (blue), 1,306 predicted secreted proteins of iso and 316 predicted secreted proteins in Ina168-unmapped regions (yellow).
4 a) pex22 ATCGCTTTGC CCTCATTGCA CACAACAACC TCCATTAAAA TACATACATA TTTCTATTCC 60 CTTTCCATAA CAGTATCCCT ACCCGCCAGC CCCATACACG AAAATTCTCA AAATGCATTT 120 TTCGACAATT TTCATCCCCT TTGCCTTAGC TGCTCTAAAA GTAAGCGCTG CGCCAGCTAG 180 ATTTTGCGTC TATTACGACG GCCACCTTCC CGCGACACGT GTCCTGCTTA TGTACGTTAG 240 AATCGGCACT ACAGCGACTA TTACGGCCCG TGGGCACGAA TTCGAAGTTG AAGCAAAAGA 300 CCAGAATTGC AAAGTTATTC TCACCAATGG CAAACAAGCA CCGGATTGGC TTGCTGCCGA 360 GCCTTACTAG GTTTAAAACG GAAGAGCAGC AGCTTGCTGG TTAAACTTCA AAATAAACGC 420 CAACTCAGTT ACTACTTACA ATACTATGAT TTCTGCCGAA AATTCCCTCT CCCCCTACCG 480 TACGTGTATA CCTGGGCTTT TACCAGGTTT ACTGTTTACG GGAGGAATCA AGTACCTAAA 540 TTTATTTTTT CCTTCAAAAT GATTACCAAA GTCGGAAACG CCCACAAGGC CTACACCACT 600 CGACGATGAA ACCAGGGTAG GCTTTTGTTA CCTGTGCAAT CATGGCAAAT TATCACTCTT 660 TAGCGAAAGT AAATACAAAC AAACGAGTTT CCAGG 695 Tag counts b) pex33 ATTTTTCATC TTAAAACTAA ACATTTAAAT TCAGCTTCAA ATATACCAAA ATCCCCTTTT 60 ATTCCTTCCA ATTTACCAAA ATGCAACTTT CCAAAATTAC TTTCGCTATT GCATTATATG 120 CAATCGGAAT CGCAGCACTT CCCACTCCGG CCAGCCTGAA TGGCAACACT GAGGTCGCAA 180 CCATCTCCGA CGTTAAACTT GAGGCCCGCA GCGACACCAC TTATCATAAA TGCTCCAAAT 240 GCGGTTATGG CAGCGATGAT TCCGACGCGT ATTTTAATCA TAAATGCAAC TAATCGCATA 300 CAAAGTAAGC TGGATTTTTC CAAACGAGCG GCGGACAGTT ATGGACTATT GCGGGAATTT 360 CAAGGATAGG AAAAGCCAAT TTGAAATATC CGGAATACTT TTTCCAAGCT TAACCATTAA 420 ATAACATGTC TTAAATCAAT CTACCTTTCG CGTTTAAA 458 Tag counts c) pex22 pex33 pex31 Supplemental Figure 4. pex22, pex33, pex31 transcripts are expressed during M. oryzae infection of rice leaf sheath as revealed by SuperSAGE and 3 -RACE RT-PCR. a) DNA sequence of the pex22 gene region. Pex22 ORF is indicated by red color. Location of the SuperSAGE tag Tag3294 is underlined. b) DNA sequence of the pex33 gene region. ORF is indicated by red color. Location of the SuperSAGE tag Tag1145 is underlined. c) 3 -RACE
5 pex22 Ina (+contig264) 1 2 Ina (+22p::pex22) 1 2 Ina Mg-Actin pex33 Mg-Actin Sasa2 (+contig389) Sasa2 (+22p::pex33) Sasa2 pex31 Sasa2 (+22p::pex31-D) Sasa2 (+pex31-dgenome) Sasa2 Mg-Actin Supplemental Figure 5. Confirmation of active transcription of pex transgenes by RT-PCR in M. oryzae transformants during infection.
6 a) O. sativa M. oryzae Sasanishiki Shin-2 (Pia + ) (Pia - ) TH TH (+contig264) b) O. sativa M. oryzae Kakehashi Shin-2 (Pii + ) (Pii - ) Ina Ina (+contig389) Ina (+22p::pex33) c) O. sativa M. oryzae Kanto51 (Pik + ) Tsuyuake (Pik-m + ) K60 (Pik-p + ) Shin-2 (Pik -, Pik-m -, Pik-p - ) Ina72 Ina72 (+pex31-d-genome) Ina72 (+22p::pex31-D) Supplemental Figure 6. Transformation of M. oryzae isolates with pex22, pex33 and pex31-d complements AVR-Pia, AVR-Pii and AVR-PIk/km/kp, respectively. Names of isolates and DNA fragments used for transformation are given in the left of each panel. (a) Transformation of TH with pex22 conferred the AVR-Pia phenotype. (b) Transformation of Ina with pex33 conferred the AVR-Pii phenotype. (c) Transformation of Ina72 with pex31 conferred the AVR-Pik/km/kp phenotypes.
7 a) O. sativa M. oryzae Sasa2 Hitomebore (Pii + ) Moukoto (Pii - ) WT +contig p::pex33 b) empty Relative Luciferase Activity pex22-ns pex33-ns 0 0 Akitakomachi (Pia +, Pii + ) Akitakomachi (Pia +, Pii + ) Supplemental Figure 7. Additional results of interactions between M. oryzae and rice. a) Results of interaction between M. oryzae and rice. The isolate Sasa2 is compatible with a rice cultivar Hitomebore harboring the R-gene Pii. Sasa2 transformed with contig389 (+contig389) as well as Sasa2 transformed with a fragment containing pex22 promoter fused with pex33 ORF (+22p::pex33) were incompatible with Hitomebore. Sasa2, [Sasa2(+contig389*)], [Sasa2 (+22p::pex33)] are all compatible with a rice cultivar Moukoto lacking Pii suggesting that the effect of transformation with contig389 and 22p::pex33 is Pii dependent. Photos were taken 10 days after inoculation with conidia/ml (containing 0.01 % tween 20) of each strain. b) Interaction
8 Ina168 GFSI1-7-2 Mb Supplemental Figure 8. Pulsed field gel electrophoresis images of chromosomes of Ina168 and GFSI1-7-2 isolates of M. oryzae. The typical 1.2 Mb supernumerary chromosome of GFSI1-7-2 is indicated by an arrowhead.
9 AVR-Pita Magnaporthe isolates?-? ????? ?? 1350 bp Magnaporthe iso?-? ????? bp 650 bp 600 bp 565 bp 530 bp 500 bp 495 bp 460 bp 400 bp 364 bp 350 bp 300 bp 255 bp 204 bp 200 bp 145 bp 100 bp IR DYE 700 IR DYE 8 Supplemental Figure 9. EcoTILLING result of AVR-Pita. The phenotypes of AVR-Pita (MG ) (top). The bands in red rectangles are significantly associated with the AVR-Pita phenotypes (Fisher s e
10 Supplemental Table isolates of M. oryzae used for EcoTILLING and phylogenetic analysis Code Code no. Isolate Host Race Country no. in Table Oryza sativa Guiana 2 GUY11 Oryza sativa Guiana Oryza sativa Guiana Br13 Oryza sativa 102 Brazil 5 15 Br18 Oryza sativa 176 Brazil 6 22 Br10 Oryza sativa 403 Brazil 7 Br15 Oryza sativa 507 Brazil 8 VHT6.1 Oryza sativa 002 Vietnam 9 VHG4.5 Oryza sativa 106 Vietnam 10 VTB6.1 Oryza sativa Vietnam 11 VHT3.3 Oryza sativa Vietnam 12 PO Oryza sativa Indonesia 13 PO Oryza sativa Indonesia 14 PO Oryza sativa Indonesia 15 PO Oryza sativa Indonesia 16 PO Oryza sativa Indonesia 17 TH3 Oryza sativa 135 Thailand 18 CHNOS Oryza sativa China 19 5 Shin85.86 Oryza sativa Japan 20 TH Oryza sativa Japan 21 Ken54-04 Oryza sativa Japan 22 Ken54-20 Oryza sativa Japan Oryza sativa 003 Japan 24 TH Oryza sativa Japan 25 Ina Oryza sativa Japan Ina Oryza sativa Japan Hoku1 Oryza sativa Japan Oryza sativa 007 Japan
11 Oryza sativa 007 Japan Oryza sativa Japan 31 Naga Oryza sativa 007 Japan TH87-20-BII Oryza sativa Japan 33 6 Ina72 Oryza sativa Japan Oryza sativa 033 Japan TH Oryza sativa Japan 36 7 TH Oryza sativa Japan Oryza sativa Japan Oryza sativa Japan Sasa2 Oryza sativa Japan 40 8 TH69-8 Oryza sativa Japan 41 1 Ina168 Oryza sativa Japan 42 Ken53-33 Oryza sativa Japan TH78-15 Oryza sativa Japan P-2b Oryza sativa Japan A Oryza sativa 433 Japan 46 P2 Oryza sativa 003 Japan
12 Supplemental Table 2. A list of M. oryzae putative secreted proteins possessing the [RK]CxxCxxxxxxxxxxxxH] motif >gi_ _ref_xp_ _ predicted protein [Magnaporthe grisea 70-15] MQISVSQLVTLAGLIMGASARLHSAAVCVQNRSYGSTGNGTPQGITYGSYVDYEIDSAATQCACNFYRNR HTGNNQWDSCPDCVFDGIQCLSNGWHLGGDEITYYCEKLCNSQGAQAN >gi_ _ref_xp_ _ hypothetical protein MG [Magnaporthe grisea 70-15] MQIFNIVQVLGLLAVGASALPTPANVGAVQPVEGSQLQARSSNFYSAGWTQYPSANSGYPSNSASTYYYK CNHCGKHTKEESQQKYHQENSHKGKESNYSEVQA >gi_ _ref_xp_ _ hypothetical protein MG [Magnaporthe grisea 70-15] MQIFKIVQVLGLLAVGTSALPAPANPAAVQPAQGGQLAVHGQPASCPPECRDVQGAKPGHLQARSRFYAT SDTGRPLANSGYPTHGYRDAYRCLYCGAVRDDVSAVQDHITYRHSNRGGDTSNYDTTTVRDDR >gi_ _ref_xp_ _ predicted protein [Magnaporthe grisea 70-15] MHTYKFIQIALLFASVALAIPTPPSPPNPPPVPQLPNSETKSNRLVSHSCEFCGVVKPSGPAYLEHYHQN HREEVWGKLATPSPPNPPPVPTQKVETHAPKTHGCEWCNKVEPSGPAYIKHYKENHEDQVWGKWAGQDAK ASP >gi_ _ref_xp_ _ predicted protein [Magnaporthe grisea 70-15] MHLSTVSQILALFTAVASSAPTSHAAVRARHVSPPEADLLHVVKRGDDTDFSDWQRYSLWNKRVEALSRN PELVSRYGYKCNSCGKGRMDENGMRRHIMFDHYSKDIPLEKSAHVNKYIEFRNKGG >gi_ _ref_xp_ _ predicted protein [Magnaporthe grisea 70-15] MKYSKVSFTLALIALGATAAPTDLHKLVARGEVEVCYDPRDPRVPPLQNDPNVEKWIDDKTGHHCFALMR GVQPDHPCKACQGHQADLYLDHIHCLAAGHVHANKGDSCEATRQARLDRYKTALKGFRVPYGTDISKLET GGKGVTFNVNDPSHKLFSGDRSLTQVVKDGNVEFVRPHGEKYRGQGEDLYATIQRQWYALKAAKILKAAR AAKAARTPDASDAGKLEPPAKLATQQRRLDESRSAE >gi_ _ref_xp_ _ predicted protein [Magnaporthe grisea 70-15] MQLHNVCSILALLAAGVFALPAPVNPSEIQARSAADKAKPKPQTERVWMDEPEAAQYLSDPRWKLVKKKY SCGYCDSSSSKVDKINKHRDEVHGTRQAQVDHTIYPGETRLTFERVSGYP >gi_ _ref_xp_ _ predicted protein [Magnaporthe grisea 70-15] MLPLFLVTSLFLTQFLAAAHTENFEIVKGLADKARVKLDLTGQQSYAIYEKFPAKVYNPLDYHMRLIVGH VECKDDNDCDFAANAFHMHAHGGSCERVLGSKTNQHSRNRPWKANHYYDKKEDIDKPLPQKNRYQWAGPT RTLSYDEIYALGDKWCGSCFHSRYNKVFNNCHHFVYSLYNKIKQK >gi_ _ref_xp_ _ predicted protein [Magnaporthe grisea 70-15] MRITRALAPLGLLPLPAAAAAVVGIPLQAIDTTATASSAMEPRQAGDGSGGSLKQCRDVSLVQSRPGLSL NDTVSATCHVGTAEYVNTLNLNECLGVDPATLELGWGRAGQLSSFCWGCELSELETGGPDGHLAVGRVVF SCVCYDYGQERATSVRLDDGGIESKDGVLACRNGKRATAIRMNPDAPVRTEPGRCNLGLGDMGYMDCIPK LYDGKIVPVGERNRYGSVFNDWRGD
13 Supplemental Table 3 A list of plasmids used for the genetic transformation of M. oryzae. Plasmid name Sources Description Construction methods M. oryzae isolates used for transformation pcb1004-pex22 pcb Kb fragment containing pex22 The 2.2 Kb fragment was amplified with the primers NotI-pex22-U1 (5 - ATAAGAATGCGGCCGCTTTCGTGACAGGC ACGTCGGG-3 ; NotI site is underlined) and XbaI-pex22-L1 (5 - GCTCTAGAACACGAGAATCAAAACCTGTA CAGACAGGTGGGTGGGC-3 ; XbaI site is underlined) using genomic DNA of Ina168 isolate as template, and inserted into pcb1004. TH and Ina isolates that do not have AVR- Pia locus. pcb1531-pex22p- EGFP pcb1531-pex22ppex22 pcb1531 EGFP fused to pex22 promoter The 1.4 Kb fragment containing pex22 gene promoter was amplified with the primers NotIpex22-U1 and XbaI-pex22p-L3 (5 - GCTCTAGAATTTTCGTGTATGGGGCTGGC GGGTAGGG-3 ; XbaI site is underlined) using pcb1004-pex22 as template, and inserted into pbagfp (Kimura et al., 2001). pcb1531 pex22 fused to pex22 promoter The pex22 ORF was amplified with the primers Xba1-pex22-U2 (5 - GCTCTAGACAAAATGCATTTTTCGACAATT TTC-3 ; XbaI site is underlined) and BamH1- pex22-l2 (5 - CGGGATCCTAGTAAGGCTCGGCAGCAAG CC-3 ; BamH1 site is underlined). EGFP in pcb1531-pex22p-egfp was replaced with pex22. pcb1531-pex33 pcb Kb fragment containing pex33 The 1.4 Kb fragment was amplified with the primers NotI-pex33-U1 (5 - ATAAGAATGCGGCCGCTTCGCTCTTTTGAT TAAATAC-3 ; NotI site is underlined) and XbaI-pex33-L1 (5 - GCTCTAGAAAACAGATTTGGAACTTTGGT GAAAACTAGAC-3 ; XbaI site is underlined) using genomic DNA of Ina168 isolate as template, and inserted into pcb1531. pcb1531-pex22ppex33 - Ina isolate that does not have AVR-Pia locus. Sasa2 and Ina isolates that do not have AVR-Pii locus. pcb1531 pex33 fused to pex22 promoter The pex33 ORF was amplified with the primers pbafp_kozak_pex33_xbai_f (5 - GCTCTAGACCAAAATGCAACTTTCCAAAAT TAC-3 ; XbaI site is underlined) and pbafp_pex33_bamhi_r (5 - CGGGATCCTTAGTTGCATTTATGATTAAAAT ACGC-3 ; BamHI site is underlined) using pcb1531-pex33 as template. EGFP in pcb1531-pex22p-egfp was replaced with pex33. Sasa2 and Ina isolates that do not have AVR-Pii locus. pcb1004-pex31-d pcb Kb fragment containing pex31- D pcb1531-pex22ppex31-d The 2.2 Kb fragment was amplified with the Sasa2, and Ina72 isolates that primers NotI-pex31-U1 (5 - do not have AVR-Pik, AVR-Pikm ATAAGAATGCGGCCGCAAAAGGAATAAGG and AVR-Pikp loci. CGGACCTCT-3 ; NotI site is underlined) and XbaI-pex31-L1 (5 - GCTCTAGATTAAAAGCCGGGCCTTTTTTTC CCCAA-3 ; XbaI site is underlined) using genomic DNA of Ina isolate as template, and inserted into pcb1004. pcb1531 pex31-d fused to pex22 promoter The pex31-d ORF was amplified with the Sasa2, and Ina72 isolates that primers Xba1_kozak_pex31_U1 (5 - do not have AVR-Pik, AVR-Pikm GCTCTAGAAAAGTCAATATGCGTGTTACCA and AVR-Pikp loci. CTTT-3 ; XbaI site is underlined) and pbafp_pex31_bamhi_r (5 - CGGATCCTCGTCAAACCTCCCTACG-3 ; BamHI site is underlined) using genomic DNA of Ina isolate as template. EGFP in pcb1531-pex22p-egfp was replaced with pex31-d. Kimura, A, Takano, Y, Furusawa, I, Okuno, T. (2001) Peroxisomal metabolic function is required for appressorium-mediated plant infection by Colletotrichum lagenarium. Plant Cell 13:
14 Supplemental Table 4. A list of transposons analyzed for the linkage with secreted protein genes Name Accession number DNA transposons Pot 2 Z Pot 3 U Occan AB LTR retrotransposons MAGGY L Pyret AB MGLR-3 AF Inago1 AB Inago2 AB Non-LTR retrotransposons MGL (MGR583) AF Mg-SINE MGU35313 Other retrotransposons Tf2 AY MINE-C EF MINE-B EF MINE-A EF MINE AJ
15 Supplemental Table 5. Primers used for plasmid construction and RT-PCR. Primer name Sequences (5' - 3') Description NotI-pex22-U1 ATAAGAATGCGGCCGCTTTCGTGACAGGCACGTCGGG Constructions of the plasmids pcb1004-pex22 and pcb1531-pex22p-egfp XbaI-pex22-L1 XbaI-pex22p-L3 Xba1-pex22-U2 BamH1-pex22-L2 GCTCTAGAACACGAGAATCAAAACCTGTACAGACAGGTGGGTGG GC GCTCTAGAATTTTCGTGTATGGGGCTGGCGGGTAGGG GCTCTAGACAAAATGCATTTTTCGACAATTTTC CGGGATCCTAGTAAGGCTCGGCAGCAAGCC Constructions of the plasmid pcb1004-pex22 Constructions of the plasmid pcb1531-pex22p-egfp Constructions of the plasmid pcb1531-pex22p-pex22 NotI-pex33-U1 XbaI-pex33-L1 ATAAGAATGCGGCCGCTTCGCTCTTTTGATTAAATAC GCTCTAGAAAACAGATTTGGAACTTTGGTGAAAACTAGAC Constructions of the plasmid pcb1531-pex33 pbafp_kozak_pex33_xb ai_f GCTCTAGACCAAAATGCAACTTTCCAAAATTAC pbafp_pex33_bamhi_r CGGGATCCTTAGTTGCATTTATGATTAAAATACGC Constructions of the plasmid pcb1531-pex22p-pex33 NotI-pex31-U1 XbaI-pex31-L1 ATAAGAATGCGGCCGCAAAAGGAATAAGGCGGACCTCT GCTCTAGATTAAAAGCCGGGCCTTTTTTTCCCCAA Constructions of the plasmid pcb1004-pex31-d Xba1_kozak_pex31_U1 GCTCTAGAAAAGTCAATATGCGTGTTACCACTTT pbafp_pex31_bamhi_r CGGATCCTCGTCAAACCTCCCTACG Constructions of the plasmid pcb1531-pex22p-pex31-d RTpex22-U1 RTpex22-L1 CCGCTCGAGCAAAATGGCGCCAGCTAGATTTTGCG CTAGTAAGGCTCGGCAGCAA RT-PCR for pex22 RTpex33-U1 RTpex33-L1 CTTCCCACTCCGGCCAGCCTGAATGGCA ATACTAGTTTAGTTGCATTTATGATTAA RT-PCR for pex33 RTpex31-U1 RTpex31-L1 CGACCTAAGTCGAGAGCGAGACCCTAAC TTAAAAGCCGGGCCTTTTTTTCCCCAA RT-PCR for pex31 RiceActin-U1 RiceActin-L1 CTGAAGAGCATCCTGTATTG GAACCTTTCTGCTCCGATGG RT-PCR for rice actin RAc7 MgActin-U1 MgActin-L1 TCGACGTCCGAAAGGATCTGT ACTCCTGCTTCGAGATCCACATC RT-PCR for Magnaprothe oryzae Actin
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng Supplementary Figure 1. The phenotypes of PI , BR121, and Harosoy under short-day conditions.
 Supplementary Figure 1 The phenotypes of PI 159925, BR121, and Harosoy under short-day conditions. (a) Plant height. (b) Number of branches. (c) Average internode length. (d) Number of nodes. (e) Pods
Supplementary Figure 1 The phenotypes of PI 159925, BR121, and Harosoy under short-day conditions. (a) Plant height. (b) Number of branches. (c) Average internode length. (d) Number of nodes. (e) Pods
Classical Selection, Balancing Selection, and Neutral Mutations
 Classical Selection, Balancing Selection, and Neutral Mutations Classical Selection Perspective of the Fate of Mutations All mutations are EITHER beneficial or deleterious o Beneficial mutations are selected
Classical Selection, Balancing Selection, and Neutral Mutations Classical Selection Perspective of the Fate of Mutations All mutations are EITHER beneficial or deleterious o Beneficial mutations are selected
Title: The Plant Disease Triangle - How Plants Defend Themselves, Part II Speaker: Dean Glawe. online.wsu.edu
 Title: The Plant Disease Triangle - How Plants Defend Themselves, Part II Speaker: Dean Glawe online.wsu.edu Plant Pathology 501 Lecture 5 The Plant Disease Triangle How Plants Defend Themselves, Part
Title: The Plant Disease Triangle - How Plants Defend Themselves, Part II Speaker: Dean Glawe online.wsu.edu Plant Pathology 501 Lecture 5 The Plant Disease Triangle How Plants Defend Themselves, Part
Exhaustive search. CS 466 Saurabh Sinha
 Exhaustive search CS 466 Saurabh Sinha Agenda Two different problems Restriction mapping Motif finding Common theme: exhaustive search of solution space Reading: Chapter 4. Restriction Mapping Restriction
Exhaustive search CS 466 Saurabh Sinha Agenda Two different problems Restriction mapping Motif finding Common theme: exhaustive search of solution space Reading: Chapter 4. Restriction Mapping Restriction
Regulatory Change in YABBY-like Transcription Factor Led to Evolution of Extreme Fruit Size during Tomato Domestication
 SUPPORTING ONLINE MATERIALS Regulatory Change in YABBY-like Transcription Factor Led to Evolution of Extreme Fruit Size during Tomato Domestication Bin Cong, Luz Barrero, & Steven Tanksley 1 SUPPORTING
SUPPORTING ONLINE MATERIALS Regulatory Change in YABBY-like Transcription Factor Led to Evolution of Extreme Fruit Size during Tomato Domestication Bin Cong, Luz Barrero, & Steven Tanksley 1 SUPPORTING
Looking for LOV: Location of LOV1 function in Nicotiana benthamiana cells
 Looking for LOV: Location of LOV1 function in Nicotiana benthamiana cells By: Patrick Rutledge 1 Dr. Jennifer Lorang 2,3, Dr. Marc Curtis 2,3, Dr. Thomas Wolpert 2,3 BioResource Research 1, Botany and
Looking for LOV: Location of LOV1 function in Nicotiana benthamiana cells By: Patrick Rutledge 1 Dr. Jennifer Lorang 2,3, Dr. Marc Curtis 2,3, Dr. Thomas Wolpert 2,3 BioResource Research 1, Botany and
Illegitimate translation causes unexpected gene expression from on-target out-of-frame alleles
 Illegitimate translation causes unexpected gene expression from on-target out-of-frame alleles created by CRISPR-Cas9 Shigeru Makino, Ryutaro Fukumura, Yoichi Gondo* Mutagenesis and Genomics Team, RIKEN
Illegitimate translation causes unexpected gene expression from on-target out-of-frame alleles created by CRISPR-Cas9 Shigeru Makino, Ryutaro Fukumura, Yoichi Gondo* Mutagenesis and Genomics Team, RIKEN
2. What was the Avery-MacLeod-McCarty experiment and why was it significant? 3. What was the Hershey-Chase experiment and why was it significant?
 Name Date Period AP Exam Review Part 6: Molecular Genetics I. DNA and RNA Basics A. History of finding out what DNA really is 1. What was Griffith s experiment and why was it significant? 1 2. What was
Name Date Period AP Exam Review Part 6: Molecular Genetics I. DNA and RNA Basics A. History of finding out what DNA really is 1. What was Griffith s experiment and why was it significant? 1 2. What was
Development 143: doi: /dev : Supplementary information
 Supplementary Materials and Methods Plant materials The mutants and transgenic plants used in the present study were as follows: E361 (from Alex Webb s laboratory); tmm-1, ptmm::tmm-gfp and flp-1 (from
Supplementary Materials and Methods Plant materials The mutants and transgenic plants used in the present study were as follows: E361 (from Alex Webb s laboratory); tmm-1, ptmm::tmm-gfp and flp-1 (from
Supplemental Data. Chen and Thelen (2010). Plant Cell /tpc
 Supplemental Data. Chen and Thelen (2010). Plant Cell 10.1105/tpc.109.071837 1 C Total 5 kg 20 kg 100 kg Transmission Image 100 kg soluble pdtpi-gfp Plastid (PDH-alpha) Mito (PDH-alpha) GFP Image vector
Supplemental Data. Chen and Thelen (2010). Plant Cell 10.1105/tpc.109.071837 1 C Total 5 kg 20 kg 100 kg Transmission Image 100 kg soluble pdtpi-gfp Plastid (PDH-alpha) Mito (PDH-alpha) GFP Image vector
Genetic diversity and population structure in rice. S. Kresovich 1,2 and T. Tai 3,5. Plant Breeding Dept, Cornell University, Ithaca, NY
 Genetic diversity and population structure in rice S. McCouch 1, A. Garris 1,2, J. Edwards 1, H. Lu 1,3 M Redus 4, J. Coburn 1, N. Rutger 4, S. Kresovich 1,2 and T. Tai 3,5 1 Plant Breeding Dept, Cornell
Genetic diversity and population structure in rice S. McCouch 1, A. Garris 1,2, J. Edwards 1, H. Lu 1,3 M Redus 4, J. Coburn 1, N. Rutger 4, S. Kresovich 1,2 and T. Tai 3,5 1 Plant Breeding Dept, Cornell
Non-host resistance to wheat stem rust in Brachypodium species
 Non-host resistance to wheat stem rust in Brachypodium species Dr. Melania Figueroa Assistant Professor Department of Plant Pathology and Stakman-Borlaug Center for Sustainable Plant Health University
Non-host resistance to wheat stem rust in Brachypodium species Dr. Melania Figueroa Assistant Professor Department of Plant Pathology and Stakman-Borlaug Center for Sustainable Plant Health University
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) Q1. What is meant by Satellite and Repetitive DNA? Ans: Satellite and repetitive DNA generally refers to DNA whose base sequence is repeated many times throughout the
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) Q1. What is meant by Satellite and Repetitive DNA? Ans: Satellite and repetitive DNA generally refers to DNA whose base sequence is repeated many times throughout the
PLNT2530 (2018) Unit 5 Genomes: Organization and Comparisons
 PLNT2530 (2018) Unit 5 Genomes: Organization and Comparisons Unless otherwise cited or referenced, all content of this presenataion is licensed under the Creative Commons License Attribution Share-Alike
PLNT2530 (2018) Unit 5 Genomes: Organization and Comparisons Unless otherwise cited or referenced, all content of this presenataion is licensed under the Creative Commons License Attribution Share-Alike
Mini-Tn7 Derivative Construction and Characterization. Mini-Tn7 derivatives for
 Supplemental Methods Mini-Tn7 Derivative Construction and Characterization. Mini-Tn7 derivatives for constitutive expression of fluorescent proteins in S. oneidensis were constructed as follows. The EcoRI-XbaI
Supplemental Methods Mini-Tn7 Derivative Construction and Characterization. Mini-Tn7 derivatives for constitutive expression of fluorescent proteins in S. oneidensis were constructed as follows. The EcoRI-XbaI
Optimization of the heme biosynthesis pathway for the production of. 5-aminolevulinic acid in Escherichia coli
 Supplementary Information Optimization of the heme biosynthesis pathway for the production of 5-aminolevulinic acid in Escherichia coli Junli Zhang 1,2,3, Zhen Kang 1,2,3, Jian Chen 2,3 & Guocheng Du 2,4
Supplementary Information Optimization of the heme biosynthesis pathway for the production of 5-aminolevulinic acid in Escherichia coli Junli Zhang 1,2,3, Zhen Kang 1,2,3, Jian Chen 2,3 & Guocheng Du 2,4
Transitivity-dependent and transitivity-independent cell-to-cell movement of RNA
 Himber et al. Transitivity-dependent and transitivity-independent cell-to-cell movement of RNA silencing SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Supplemental material 1. Short-range movement of GFP silencing affects a nearly
Himber et al. Transitivity-dependent and transitivity-independent cell-to-cell movement of RNA silencing SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Supplemental material 1. Short-range movement of GFP silencing affects a nearly
Supplementary Methods
 Supplementary Methods Microarray analysis Grains of 7 DAP of the wild-type and gif1 were harvested for RNA preparation. Microarray analysis was performed with the Affymetrix (Santa Clara, CA) GeneChip
Supplementary Methods Microarray analysis Grains of 7 DAP of the wild-type and gif1 were harvested for RNA preparation. Microarray analysis was performed with the Affymetrix (Santa Clara, CA) GeneChip
Effect of Acetosyringone on Agrobacterium-mediated Transformation of Eustoma grandiflorum Leaf Disks
 JARQ 51 (4), 351-355 (2017) https://www.jircas.go.jp Improvement in Agrobacterium-mediated Transformation of Eustoma grandiflorum by Acetosyringone Effect of Acetosyringone on Agrobacterium-mediated Transformation
JARQ 51 (4), 351-355 (2017) https://www.jircas.go.jp Improvement in Agrobacterium-mediated Transformation of Eustoma grandiflorum by Acetosyringone Effect of Acetosyringone on Agrobacterium-mediated Transformation
TE content correlates positively with genome size
 TE content correlates positively with genome size Mb 3000 Genomic DNA 2500 2000 1500 1000 TE DNA Protein-coding DNA 500 0 Feschotte & Pritham 2006 Transposable elements. Variation in gene numbers cannot
TE content correlates positively with genome size Mb 3000 Genomic DNA 2500 2000 1500 1000 TE DNA Protein-coding DNA 500 0 Feschotte & Pritham 2006 Transposable elements. Variation in gene numbers cannot
Genetic and physiological approach to elucidation of Cd absorption mechanism by rice plants
 Genetic and physiological approach to elucidation of Cd absorption mechanism by rice plants Satoru Ishikawa National Institute for Agro-Environmental Sciences, 3-1-3, Kannondai, Tsukuba, Ibaraki, 305-8604,
Genetic and physiological approach to elucidation of Cd absorption mechanism by rice plants Satoru Ishikawa National Institute for Agro-Environmental Sciences, 3-1-3, Kannondai, Tsukuba, Ibaraki, 305-8604,
RNA-seq to study rice defense responses upon parasitic nematode infections. Tina Kyndt
 RNA-seq to study rice defense responses upon parasitic nematode infections Tina Kyndt 1 Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Most important staple food for at least half of the human population Monocot model plant Paddy
RNA-seq to study rice defense responses upon parasitic nematode infections Tina Kyndt 1 Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Most important staple food for at least half of the human population Monocot model plant Paddy
Genetic Variation: The genetic substrate for natural selection. Horizontal Gene Transfer. General Principles 10/2/17.
 Genetic Variation: The genetic substrate for natural selection What about organisms that do not have sexual reproduction? Horizontal Gene Transfer Dr. Carol E. Lee, University of Wisconsin In prokaryotes:
Genetic Variation: The genetic substrate for natural selection What about organisms that do not have sexual reproduction? Horizontal Gene Transfer Dr. Carol E. Lee, University of Wisconsin In prokaryotes:
Supplementary Figure S1. Amino acid alignment of selected monocot FT-like and TFL-like sequences. Sequences were aligned using ClustalW and analyzed
 Supplementary Figure S1. Amino acid alignment of selected monocot FT-like and TFL-like sequences. Sequences were aligned using ClustalW and analyzed using the Geneious software. Accession numbers of the
Supplementary Figure S1. Amino acid alignment of selected monocot FT-like and TFL-like sequences. Sequences were aligned using ClustalW and analyzed using the Geneious software. Accession numbers of the
Supplemental Table 1. Primers used for cloning and PCR amplification in this study
 Supplemental Table 1. Primers used for cloning and PCR amplification in this study Target Gene Primer sequence NATA1 (At2g393) forward GGG GAC AAG TTT GTA CAA AAA AGC AGG CTT CAT GGC GCC TCC AAC CGC AGC
Supplemental Table 1. Primers used for cloning and PCR amplification in this study Target Gene Primer sequence NATA1 (At2g393) forward GGG GAC AAG TTT GTA CAA AAA AGC AGG CTT CAT GGC GCC TCC AAC CGC AGC
Genome sequence of Plasmopara viticola and insight into the pathogenic mechanism
 Genome sequence of Plasmopara viticola and insight into the pathogenic mechanism Ling Yin 1,3,, Yunhe An 1,2,, Junjie Qu 3,, Xinlong Li 1, Yali Zhang 1, Ian Dry 5, Huijun Wu 2*, Jiang Lu 1,4** 1 College
Genome sequence of Plasmopara viticola and insight into the pathogenic mechanism Ling Yin 1,3,, Yunhe An 1,2,, Junjie Qu 3,, Xinlong Li 1, Yali Zhang 1, Ian Dry 5, Huijun Wu 2*, Jiang Lu 1,4** 1 College
1/30/2015. Overview. Measuring host growth
 PLP 6404 Epidemiology of Plant Diseases Spring 2015 Lecture 8: Influence of Host Plant on Disease Development plant growth and Prof. Dr. Ariena van Bruggen Emerging Pathogens Institute and Plant Pathology
PLP 6404 Epidemiology of Plant Diseases Spring 2015 Lecture 8: Influence of Host Plant on Disease Development plant growth and Prof. Dr. Ariena van Bruggen Emerging Pathogens Institute and Plant Pathology
Introduction to Bioinformatics Integrated Science, 11/9/05
 1 Introduction to Bioinformatics Integrated Science, 11/9/05 Morris Levy Biological Sciences Research: Evolutionary Ecology, Plant- Fungal Pathogen Interactions Coordinator: BIOL 495S/CS490B/STAT490B Introduction
1 Introduction to Bioinformatics Integrated Science, 11/9/05 Morris Levy Biological Sciences Research: Evolutionary Ecology, Plant- Fungal Pathogen Interactions Coordinator: BIOL 495S/CS490B/STAT490B Introduction
Special Topics on Genetics
 ARISTOTLE UNIVERSITY OF THESSALONIKI OPEN COURSES Section 9: Transposable elements Drosopoulou E License The offered educational material is subject to Creative Commons licensing. For educational material,
ARISTOTLE UNIVERSITY OF THESSALONIKI OPEN COURSES Section 9: Transposable elements Drosopoulou E License The offered educational material is subject to Creative Commons licensing. For educational material,
,(CL806925),(CL ),(CL829057),(CL ),(CL862603) BAC45136 putative nucleotide-binding
 Additional Data File 13. List of 83 disease resistance-related genes that matched the unmapped BESs of On, Or, and Og. BESs that had internal stop codons within the aligned regions are presented in parentheses.
Additional Data File 13. List of 83 disease resistance-related genes that matched the unmapped BESs of On, Or, and Og. BESs that had internal stop codons within the aligned regions are presented in parentheses.
Principles of QTL Mapping. M.Imtiaz
 Principles of QTL Mapping M.Imtiaz Introduction Definitions of terminology Reasons for QTL mapping Principles of QTL mapping Requirements For QTL Mapping Demonstration with experimental data Merit of QTL
Principles of QTL Mapping M.Imtiaz Introduction Definitions of terminology Reasons for QTL mapping Principles of QTL mapping Requirements For QTL Mapping Demonstration with experimental data Merit of QTL
belonging to the Genus Pantoea
 Emerging diseases of maize and onion caused by bacteria belonging to the Genus Pantoea by Teresa Goszczynska Submitted in partial fulfilment of the requirements for the degree Philosophiae Doctoriae in
Emerging diseases of maize and onion caused by bacteria belonging to the Genus Pantoea by Teresa Goszczynska Submitted in partial fulfilment of the requirements for the degree Philosophiae Doctoriae in
Principles of Genetics
 Principles of Genetics Snustad, D ISBN-13: 9780470903599 Table of Contents C H A P T E R 1 The Science of Genetics 1 An Invitation 2 Three Great Milestones in Genetics 2 DNA as the Genetic Material 6 Genetics
Principles of Genetics Snustad, D ISBN-13: 9780470903599 Table of Contents C H A P T E R 1 The Science of Genetics 1 An Invitation 2 Three Great Milestones in Genetics 2 DNA as the Genetic Material 6 Genetics
 Supplemental Data. Tameling et al. (2010). Plant Cell 10.1105/tpc.110.077461 Supplemental Table 1. Primers used in plasmid construction Primer Code Sequence eo1 5 -GCCATGGCTCATGCAAGTGTGGCTTCTC-3 eo2 5
Supplemental Data. Tameling et al. (2010). Plant Cell 10.1105/tpc.110.077461 Supplemental Table 1. Primers used in plasmid construction Primer Code Sequence eo1 5 -GCCATGGCTCATGCAAGTGTGGCTTCTC-3 eo2 5
An Anatomical and Physiological Basis for Flood-Mediated Rice Blast Field Resistance
 PEST MANAGEMENT: DISEASES An Anatomical and Physiological Basis for Flood-Mediated Rice Blast Field Resistance M.P. Singh, P.A. Counce, and F.N. Lee ABSTRACT Rice blast, a production-limiting rice pathogen
PEST MANAGEMENT: DISEASES An Anatomical and Physiological Basis for Flood-Mediated Rice Blast Field Resistance M.P. Singh, P.A. Counce, and F.N. Lee ABSTRACT Rice blast, a production-limiting rice pathogen
Rapid speciation following recent host shift in the plant pathogenic fungus Rhynchosporium
 Rapid speciation following recent host shift in the plant pathogenic fungus Rhynchosporium Tiziana Vonlanthen, Laurin Müller 27.10.15 1 Second paper: Origin and Domestication of the Fungal Wheat Pathogen
Rapid speciation following recent host shift in the plant pathogenic fungus Rhynchosporium Tiziana Vonlanthen, Laurin Müller 27.10.15 1 Second paper: Origin and Domestication of the Fungal Wheat Pathogen
Coding sequence array Office hours Wednesday 3-4pm 304A Stanley Hall
 Coding sequence array Office hours Wednesday 3-4pm 304A Stanley Hall Review session 5pm Thursday, Dec. 11 GPB100 Fig. 1.13 RNA-seq Expression effects of cancer AAAAA AAAAA AAAAA Solexa sequencing counts
Coding sequence array Office hours Wednesday 3-4pm 304A Stanley Hall Review session 5pm Thursday, Dec. 11 GPB100 Fig. 1.13 RNA-seq Expression effects of cancer AAAAA AAAAA AAAAA Solexa sequencing counts
HORIZONTAL TRANSFER IN EUKARYOTES KIMBERLEY MC GRAIL FERNÁNDEZ GENOMICS
 HORIZONTAL TRANSFER IN EUKARYOTES KIMBERLEY MC GRAIL FERNÁNDEZ GENOMICS OVERVIEW INTRODUCTION MECHANISMS OF HGT IDENTIFICATION TECHNIQUES EXAMPLES - Wolbachia pipientis - Fungus - Plants - Drosophila ananassae
HORIZONTAL TRANSFER IN EUKARYOTES KIMBERLEY MC GRAIL FERNÁNDEZ GENOMICS OVERVIEW INTRODUCTION MECHANISMS OF HGT IDENTIFICATION TECHNIQUES EXAMPLES - Wolbachia pipientis - Fungus - Plants - Drosophila ananassae
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1. HSP21 expression in 35S:HSP21 and hsp21 knockdown plants. (a) Since no T- DNA insertion line for HSP21 is available in the publicly available T-DNA collections,
Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1. HSP21 expression in 35S:HSP21 and hsp21 knockdown plants. (a) Since no T- DNA insertion line for HSP21 is available in the publicly available T-DNA collections,
Supplemental Data. Wang et al. (2014). Plant Cell /tpc
 Supplemental Figure1: Mock and NPA-treated tomato plants. (A) NPA treated tomato (cv. Moneymaker) developed a pin-like inflorescence (arrowhead). (B) Comparison of first and second leaves from mock and
Supplemental Figure1: Mock and NPA-treated tomato plants. (A) NPA treated tomato (cv. Moneymaker) developed a pin-like inflorescence (arrowhead). (B) Comparison of first and second leaves from mock and
TIME-LINE OF INFECTION
 Review of Lecture 8: Getting inside the host is a critical step in disease development Fungal pathogens use contact and chemical tropisms to guide their way to a site where infection is possible Pathogens
Review of Lecture 8: Getting inside the host is a critical step in disease development Fungal pathogens use contact and chemical tropisms to guide their way to a site where infection is possible Pathogens
Gene expression in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, Plasmids: types, maintenance and functions. Mitesh Shrestha
 Gene expression in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, Plasmids: types, maintenance and functions. Mitesh Shrestha Plasmids 1. Extrachromosomal DNA, usually circular-parasite 2. Usually encode ancillary
Gene expression in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, Plasmids: types, maintenance and functions. Mitesh Shrestha Plasmids 1. Extrachromosomal DNA, usually circular-parasite 2. Usually encode ancillary
Bio 119 Bacterial Genomics 6/26/10
 BACTERIAL GENOMICS Reading in BOM-12: Sec. 11.1 Genetic Map of the E. coli Chromosome p. 279 Sec. 13.2 Prokaryotic Genomes: Sizes and ORF Contents p. 344 Sec. 13.3 Prokaryotic Genomes: Bioinformatic Analysis
BACTERIAL GENOMICS Reading in BOM-12: Sec. 11.1 Genetic Map of the E. coli Chromosome p. 279 Sec. 13.2 Prokaryotic Genomes: Sizes and ORF Contents p. 344 Sec. 13.3 Prokaryotic Genomes: Bioinformatic Analysis
Curriculum Links. AQA GCE Biology. AS level
 Curriculum Links AQA GCE Biology Unit 2 BIOL2 The variety of living organisms 3.2.1 Living organisms vary and this variation is influenced by genetic and environmental factors Causes of variation 3.2.2
Curriculum Links AQA GCE Biology Unit 2 BIOL2 The variety of living organisms 3.2.1 Living organisms vary and this variation is influenced by genetic and environmental factors Causes of variation 3.2.2
Bacterial Genetics & Operons
 Bacterial Genetics & Operons The Bacterial Genome Because bacteria have simple genomes, they are used most often in molecular genetics studies Most of what we know about bacterial genetics comes from the
Bacterial Genetics & Operons The Bacterial Genome Because bacteria have simple genomes, they are used most often in molecular genetics studies Most of what we know about bacterial genetics comes from the
Biological Roles of Cytokinins
 Direct Control of Shoot Meristem Activity by a Cytokinin-Activating Enzyme By Kurakawa et. Al. Published in Nature Presented by Boyana Grigorova Biological Roles of Cytokinins Cytokinins are positive regulators
Direct Control of Shoot Meristem Activity by a Cytokinin-Activating Enzyme By Kurakawa et. Al. Published in Nature Presented by Boyana Grigorova Biological Roles of Cytokinins Cytokinins are positive regulators
Eiji Yamamoto 1,2, Hiroyoshi Iwata 3, Takanari Tanabata 4, Ritsuko Mizobuchi 1, Jun-ichi Yonemaru 1,ToshioYamamoto 1* and Masahiro Yano 5,6
 Yamamoto et al. BMC Genetics 2014, 15:50 METHODOLOGY ARTICLE Open Access Effect of advanced intercrossing on genome structure and on the power to detect linked quantitative trait loci in a multi-parent
Yamamoto et al. BMC Genetics 2014, 15:50 METHODOLOGY ARTICLE Open Access Effect of advanced intercrossing on genome structure and on the power to detect linked quantitative trait loci in a multi-parent
Biology 112 Practice Midterm Questions
 Biology 112 Practice Midterm Questions 1. Identify which statement is true or false I. Bacterial cell walls prevent osmotic lysis II. All bacterial cell walls contain an LPS layer III. In a Gram stain,
Biology 112 Practice Midterm Questions 1. Identify which statement is true or false I. Bacterial cell walls prevent osmotic lysis II. All bacterial cell walls contain an LPS layer III. In a Gram stain,
CRISPR-SeroSeq: A Developing Technique for Salmonella Subtyping
 Department of Biological Sciences Seminar Blog Seminar Date: 3/23/18 Speaker: Dr. Nikki Shariat, Gettysburg College Title: Probing Salmonella population diversity using CRISPRs CRISPR-SeroSeq: A Developing
Department of Biological Sciences Seminar Blog Seminar Date: 3/23/18 Speaker: Dr. Nikki Shariat, Gettysburg College Title: Probing Salmonella population diversity using CRISPRs CRISPR-SeroSeq: A Developing
Supplementary Information for: The genome of the extremophile crucifer Thellungiella parvula
 Supplementary Information for: The genome of the extremophile crucifer Thellungiella parvula Maheshi Dassanayake 1,9, Dong-Ha Oh 1,9, Jeffrey S. Haas 1,2, Alvaro Hernandez 3, Hyewon Hong 1,4, Shahjahan
Supplementary Information for: The genome of the extremophile crucifer Thellungiella parvula Maheshi Dassanayake 1,9, Dong-Ha Oh 1,9, Jeffrey S. Haas 1,2, Alvaro Hernandez 3, Hyewon Hong 1,4, Shahjahan
Supplemental Data. Yang et al. (2012). Plant Cell /tpc
 Supplemental Figure 1. Mature flowers of P. heterotricha. (A) An inflorescence of P. heterotricha showing the front view of a zygomorphic flower characterized by two small dorsal petals and only two fertile
Supplemental Figure 1. Mature flowers of P. heterotricha. (A) An inflorescence of P. heterotricha showing the front view of a zygomorphic flower characterized by two small dorsal petals and only two fertile
Genetic Basis of Variation in Bacteria
 Mechanisms of Infectious Disease Fall 2009 Genetics I Jonathan Dworkin, PhD Department of Microbiology jonathan.dworkin@columbia.edu Genetic Basis of Variation in Bacteria I. Organization of genetic material
Mechanisms of Infectious Disease Fall 2009 Genetics I Jonathan Dworkin, PhD Department of Microbiology jonathan.dworkin@columbia.edu Genetic Basis of Variation in Bacteria I. Organization of genetic material
Characterization, expression patterns and functional analysis of the MAPK and MAPKK genes in watermelon (Citrullus lanatus)
 Song et al. BMC Plant Biology (2015) 15:298 DOI 10.1186/s12870-015-0681-4 RESEARCH ARTICLE Characterization, expression patterns and functional analysis of the MAPK and MAPKK genes in watermelon (Citrullus
Song et al. BMC Plant Biology (2015) 15:298 DOI 10.1186/s12870-015-0681-4 RESEARCH ARTICLE Characterization, expression patterns and functional analysis of the MAPK and MAPKK genes in watermelon (Citrullus
CHAPTER : Prokaryotic Genetics
 CHAPTER 13.3 13.5: Prokaryotic Genetics 1. Most bacteria are not pathogenic. Identify several important roles they play in the ecosystem and human culture. 2. How do variations arise in bacteria considering
CHAPTER 13.3 13.5: Prokaryotic Genetics 1. Most bacteria are not pathogenic. Identify several important roles they play in the ecosystem and human culture. 2. How do variations arise in bacteria considering
Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of wild type (WT) and abci8 mutant in the paddy field.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of wild type (WT) and abci8 mutant in the paddy field. A, Phenotypes of 30-day old wild-type (WT) and abci8 mutant plants grown in a paddy field under normal sunny
Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of wild type (WT) and abci8 mutant in the paddy field. A, Phenotypes of 30-day old wild-type (WT) and abci8 mutant plants grown in a paddy field under normal sunny
Duplication of an upstream silencer of FZP increases grain yield in rice
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Articles https://doi.org/10.1038/s41477-017-0042-4 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Duplication of an upstream silencer of FZP increases grain yield in rice
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Articles https://doi.org/10.1038/s41477-017-0042-4 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Duplication of an upstream silencer of FZP increases grain yield in rice
Supplementary Table 1. Primers used in this study.
 Supplementary Tale 1. Primers used in this study. Name Primer sequence (5'-3') Primers of PCR-ased molecular markers developed in this study M1 F M1 R M2 F M2 R M3 F M3 R M4 F M4 R M5 F M5 R M6 F M6 R
Supplementary Tale 1. Primers used in this study. Name Primer sequence (5'-3') Primers of PCR-ased molecular markers developed in this study M1 F M1 R M2 F M2 R M3 F M3 R M4 F M4 R M5 F M5 R M6 F M6 R
Analysis of Y-STR Profiles in Mixed DNA using Next Generation Sequencing
 Analysis of Y-STR Profiles in Mixed DNA using Next Generation Sequencing So Yeun Kwon, Hwan Young Lee, and Kyoung-Jin Shin Department of Forensic Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul,
Analysis of Y-STR Profiles in Mixed DNA using Next Generation Sequencing So Yeun Kwon, Hwan Young Lee, and Kyoung-Jin Shin Department of Forensic Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul,
Fitness constraints on horizontal gene transfer
 Fitness constraints on horizontal gene transfer Dan I Andersson University of Uppsala, Department of Medical Biochemistry and Microbiology, Uppsala, Sweden GMM 3, 30 Aug--2 Sep, Oslo, Norway Acknowledgements:
Fitness constraints on horizontal gene transfer Dan I Andersson University of Uppsala, Department of Medical Biochemistry and Microbiology, Uppsala, Sweden GMM 3, 30 Aug--2 Sep, Oslo, Norway Acknowledgements:
Plasmid Partition System of the P1par Family from the pwr100 Virulence Plasmid of Shigella flexneri
 JOURNAL OF BACTERIOLOGY, May 2005, p. 3369 3373 Vol. 187, No. 10 0021-9193/05/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/jb.187.10.3369 3373.2005 Plasmid Partition System of the P1par Family from the pwr100 Virulence Plasmid
JOURNAL OF BACTERIOLOGY, May 2005, p. 3369 3373 Vol. 187, No. 10 0021-9193/05/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/jb.187.10.3369 3373.2005 Plasmid Partition System of the P1par Family from the pwr100 Virulence Plasmid
Exam 1 PBG430/
 1 Exam 1 PBG430/530 2014 1. You read that the genome size of maize is 2,300 Mb and that in this species 2n = 20. This means that there are 2,300 Mb of DNA in a cell that is a. n (e.g. gamete) b. 2n (e.g.
1 Exam 1 PBG430/530 2014 1. You read that the genome size of maize is 2,300 Mb and that in this species 2n = 20. This means that there are 2,300 Mb of DNA in a cell that is a. n (e.g. gamete) b. 2n (e.g.
ydci GTC TGT TTG AAC GCG GGC GAC TGG GCG CGC AAT TAA CGG TGT GTA GGC TGG AGC TGC TTC
 Table S1. DNA primers used in this study. Name ydci P1ydcIkd3 Sequence GTC TGT TTG AAC GCG GGC GAC TGG GCG CGC AAT TAA CGG TGT GTA GGC TGG AGC TGC TTC Kd3ydcIp2 lacz fusion YdcIendP1 YdcItrgP2 GAC AGC
Table S1. DNA primers used in this study. Name ydci P1ydcIkd3 Sequence GTC TGT TTG AAC GCG GGC GAC TGG GCG CGC AAT TAA CGG TGT GTA GGC TGG AGC TGC TTC Kd3ydcIp2 lacz fusion YdcIendP1 YdcItrgP2 GAC AGC
Using Phylogenomics to Predict Novel Fungal Pathogenicity Genes
 Using Phylogenomics to Predict Novel Fungal Pathogenicity Genes David DeCaprio, Ying Li, Hung Nguyen (sequenced Ascomycetes genomes courtesy of the Broad Institute) Phylogenomics Combining whole genome
Using Phylogenomics to Predict Novel Fungal Pathogenicity Genes David DeCaprio, Ying Li, Hung Nguyen (sequenced Ascomycetes genomes courtesy of the Broad Institute) Phylogenomics Combining whole genome
Viroids are unique plant pathogens that are smaller than viruses and consist of a short single-stranded circular RNA without a protein coat (Diener,
 Citrus Viroids Viroids are unique plant pathogens that are smaller than viruses and consist of a short single-stranded circular RNA without a protein coat (Diener, 1971). These pathogens cause damage to
Citrus Viroids Viroids are unique plant pathogens that are smaller than viruses and consist of a short single-stranded circular RNA without a protein coat (Diener, 1971). These pathogens cause damage to
Supplemental material
 Supplemental material Table 1- Segregation analysis of sgt1a sgt1b double mutant plants Parental genotype No. of lines Normal seeds Phenotype Abnormal seeds Ratio of abnormal seeds (%) WT 3 171 2 1.16
Supplemental material Table 1- Segregation analysis of sgt1a sgt1b double mutant plants Parental genotype No. of lines Normal seeds Phenotype Abnormal seeds Ratio of abnormal seeds (%) WT 3 171 2 1.16
Valley Central School District 944 State Route 17K Montgomery, NY Telephone Number: (845) ext Fax Number: (845)
 Valley Central School District 944 State Route 17K Montgomery, NY 12549 Telephone Number: (845)457-2400 ext. 18121 Fax Number: (845)457-4254 Advance Placement Biology Presented to the Board of Education
Valley Central School District 944 State Route 17K Montgomery, NY 12549 Telephone Number: (845)457-2400 ext. 18121 Fax Number: (845)457-4254 Advance Placement Biology Presented to the Board of Education
MONOSOMIC ANALYSIS OF ADULT-PLANT RESISTANCE TO LEAF RUST IN THE BRAZILlAN WHEAT CULTIVAR 'TOROPI' 1. Abstract
 MONOSOMIC ANALYSIS OF ADULT-PLANT RESISTANCE TO LEAF RUST IN THE BRAZILlAN WHEAT CULTIVAR 'TOROPI' 1. Brammer, S.P.2, Worland, A. 3, Barcellos, A.L. 2, Fernandes, M.I.B. de M. 2 Abstract Favorable environment
MONOSOMIC ANALYSIS OF ADULT-PLANT RESISTANCE TO LEAF RUST IN THE BRAZILlAN WHEAT CULTIVAR 'TOROPI' 1. Brammer, S.P.2, Worland, A. 3, Barcellos, A.L. 2, Fernandes, M.I.B. de M. 2 Abstract Favorable environment
Agrobacterium tumefasciens, the Ti Plasmid, and Crown Gall Tumorigenesis
 Agrobacterium tumefasciens, the Ti Plasmid, and Crown Gall Tumorigenesis BOM-11: 10.9 Plasmids: General Principles (review) p. 274 10.11 Conjugation: Essential Features (review) p. 278 19.21 Agrobacterium
Agrobacterium tumefasciens, the Ti Plasmid, and Crown Gall Tumorigenesis BOM-11: 10.9 Plasmids: General Principles (review) p. 274 10.11 Conjugation: Essential Features (review) p. 278 19.21 Agrobacterium
Small RNA in rice genome
 Vol. 45 No. 5 SCIENCE IN CHINA (Series C) October 2002 Small RNA in rice genome WANG Kai ( 1, ZHU Xiaopeng ( 2, ZHONG Lan ( 1,3 & CHEN Runsheng ( 1,2 1. Beijing Genomics Institute/Center of Genomics and
Vol. 45 No. 5 SCIENCE IN CHINA (Series C) October 2002 Small RNA in rice genome WANG Kai ( 1, ZHU Xiaopeng ( 2, ZHONG Lan ( 1,3 & CHEN Runsheng ( 1,2 1. Beijing Genomics Institute/Center of Genomics and
Report of the Research Coordination Meeting Genetics of Root-Knot Nematode Resistance in Cotton Dallas, Texas, October 24, 2007
 Report of the Research Coordination Meeting Genetics of Root-Knot Nematode Resistance in Cotton Dallas, Texas, October 24, 2007 Participants: Frank Callahan, Peng Chee, Richard Davis, Mamadou Diop, Osman
Report of the Research Coordination Meeting Genetics of Root-Knot Nematode Resistance in Cotton Dallas, Texas, October 24, 2007 Participants: Frank Callahan, Peng Chee, Richard Davis, Mamadou Diop, Osman
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng Supplementary Figure 1. Icm/Dot secretion system region I in 41 Legionella species.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Icm/Dot secretion system region I in 41 Legionella species. Homologs of the effector-coding gene lega15 (orange) were found within Icm/Dot region I in 13 Legionella species. In four
Supplementary Figure 1 Icm/Dot secretion system region I in 41 Legionella species. Homologs of the effector-coding gene lega15 (orange) were found within Icm/Dot region I in 13 Legionella species. In four
Vital Statistics Derived from Complete Genome Sequencing (for E. coli MG1655)
 We still consider the E. coli genome as a fairly typical bacterial genome, and given the extensive information available about this organism and it's lifestyle, the E. coli genome is a useful point of
We still consider the E. coli genome as a fairly typical bacterial genome, and given the extensive information available about this organism and it's lifestyle, the E. coli genome is a useful point of
Transfer of Rust Resistance from Triticum aestivum L. Cultivar Chinese Spring to Cultivar WL 711
 Tropical Agricultural Research Vol. 16:71-78 (2004) Transfer of Rust Resistance from Triticum aestivum L. Cultivar Chinese Spring to Cultivar WL 711 S.P. Withanage and H. S. Dhaliwal 1 Rubber Research
Tropical Agricultural Research Vol. 16:71-78 (2004) Transfer of Rust Resistance from Triticum aestivum L. Cultivar Chinese Spring to Cultivar WL 711 S.P. Withanage and H. S. Dhaliwal 1 Rubber Research
Texas Biology Standards Review. Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company 26 A T
 2.B.6. 1 Which of the following statements best describes the structure of DN? wo strands of proteins are held together by sugar molecules, nitrogen bases, and phosphate groups. B wo strands composed of
2.B.6. 1 Which of the following statements best describes the structure of DN? wo strands of proteins are held together by sugar molecules, nitrogen bases, and phosphate groups. B wo strands composed of
Ti plasmid derived plant vector systems: binary and co - integrative vectors transformation process; regeneration of the transformed lines
 Ti plasmid derived plant vector systems: binary and co - integrative vectors transformation process; regeneration of the transformed lines Mitesh Shrestha Constraints of Wild type Ti/Ri-plasmid Very large
Ti plasmid derived plant vector systems: binary and co - integrative vectors transformation process; regeneration of the transformed lines Mitesh Shrestha Constraints of Wild type Ti/Ri-plasmid Very large
Jay Moore,, Graham King, James Lynn. Data integration for Brassica comparative genomics
 Jay Moore,, Graham King, James Lynn Data integration for Brassica comparative genomics How best to bring together diverse data about Brassica genome organisation? How best to make data accessible and useful
Jay Moore,, Graham King, James Lynn Data integration for Brassica comparative genomics How best to bring together diverse data about Brassica genome organisation? How best to make data accessible and useful
Fine Mapping and Candidate Gene Characterization of the Pepper Bacterial Spot Resistance Gene bs6
 Fine Mapping and Candidate Gene Characterization of the Pepper Bacterial Spot Resistance Gene bs6 Rebecca L. Wente, Jian Li, Samuel F. Hutton, Upinder Gill, Jeffrey B. Jones, Gerald V. Minsavage, Robert
Fine Mapping and Candidate Gene Characterization of the Pepper Bacterial Spot Resistance Gene bs6 Rebecca L. Wente, Jian Li, Samuel F. Hutton, Upinder Gill, Jeffrey B. Jones, Gerald V. Minsavage, Robert
Host-Pathogen Interaction. PN Sharma Department of Plant Pathology CSK HPKV, Palampur
 Host-Pathogen Interaction PN Sharma Department of Plant Pathology CSK HPKV, Palampur-176062 PATHOGEN DEFENCE IN PLANTS A BIOLOGICAL AND MOLECULAR VIEW Two types of plant resistance response to potential
Host-Pathogen Interaction PN Sharma Department of Plant Pathology CSK HPKV, Palampur-176062 PATHOGEN DEFENCE IN PLANTS A BIOLOGICAL AND MOLECULAR VIEW Two types of plant resistance response to potential
Last time: Obtaining information from a cloned gene
 Last time: Obtaining information from a cloned gene Objectives: 1. What is the biochemical role of the gene? 2. Where and when is the gene expressed (transcribed)? 3. Where and when is the protein made?
Last time: Obtaining information from a cloned gene Objectives: 1. What is the biochemical role of the gene? 2. Where and when is the gene expressed (transcribed)? 3. Where and when is the protein made?
Lipid transfer proteins confer resistance to trichothecenes
 Lipid transfer proteins confer resistance to trichothecenes John McLaughlin and Anwar Bin-Umer Tumer Laboratory National Fusarium Head Blight Forum December 6th, 2012 FY09-11: Identify trichothecene resistance
Lipid transfer proteins confer resistance to trichothecenes John McLaughlin and Anwar Bin-Umer Tumer Laboratory National Fusarium Head Blight Forum December 6th, 2012 FY09-11: Identify trichothecene resistance
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 reverse 3175 3175 F L C 318 318 3185 3185 319 319 3195 3195 315 8 1 315 3155 315 317 Supplementary Figure 3. Stability of expression of the GFP sensor constructs return to warm conditions. Semi-quantitative
reverse 3175 3175 F L C 318 318 3185 3185 319 319 3195 3195 315 8 1 315 3155 315 317 Supplementary Figure 3. Stability of expression of the GFP sensor constructs return to warm conditions. Semi-quantitative
Bi 1x Spring 2014: LacI Titration
 Bi 1x Spring 2014: LacI Titration 1 Overview In this experiment, you will measure the effect of various mutated LacI repressor ribosome binding sites in an E. coli cell by measuring the expression of a
Bi 1x Spring 2014: LacI Titration 1 Overview In this experiment, you will measure the effect of various mutated LacI repressor ribosome binding sites in an E. coli cell by measuring the expression of a
CHAPTER 23 THE EVOLUTIONS OF POPULATIONS. Section C: Genetic Variation, the Substrate for Natural Selection
 CHAPTER 23 THE EVOLUTIONS OF POPULATIONS Section C: Genetic Variation, the Substrate for Natural Selection 1. Genetic variation occurs within and between populations 2. Mutation and sexual recombination
CHAPTER 23 THE EVOLUTIONS OF POPULATIONS Section C: Genetic Variation, the Substrate for Natural Selection 1. Genetic variation occurs within and between populations 2. Mutation and sexual recombination
The Evolution of Infectious Disease
 The Evolution of Infectious Disease Why are some bacteria pathogenic to humans while other (closely-related) bacteria are not? This question can be approached from two directions: 1.From the point of view
The Evolution of Infectious Disease Why are some bacteria pathogenic to humans while other (closely-related) bacteria are not? This question can be approached from two directions: 1.From the point of view
. Supplementary Information
 . Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure S1. Mature embryo sac observations. Supplementary Figure S2. STT observations. Supplementary Figure S3. Comparison of the PTB1 cdna with that of the mutant.
. Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure S1. Mature embryo sac observations. Supplementary Figure S2. STT observations. Supplementary Figure S3. Comparison of the PTB1 cdna with that of the mutant.
2. Der Dissertation zugrunde liegende Publikationen und Manuskripte. 2.1 Fine scale mapping in the sex locus region of the honey bee (Apis mellifera)
 2. Der Dissertation zugrunde liegende Publikationen und Manuskripte 2.1 Fine scale mapping in the sex locus region of the honey bee (Apis mellifera) M. Hasselmann 1, M. K. Fondrk², R. E. Page Jr.² und
2. Der Dissertation zugrunde liegende Publikationen und Manuskripte 2.1 Fine scale mapping in the sex locus region of the honey bee (Apis mellifera) M. Hasselmann 1, M. K. Fondrk², R. E. Page Jr.² und
Biology I Level - 2nd Semester Final Review
 Biology I Level - 2nd Semester Final Review The 2 nd Semester Final encompasses all material that was discussed during second semester. It s important that you review ALL notes and worksheets from the
Biology I Level - 2nd Semester Final Review The 2 nd Semester Final encompasses all material that was discussed during second semester. It s important that you review ALL notes and worksheets from the
SUPPLEMENTARY DATA - 1 -
 - 1 - SUPPLEMENTARY DATA Construction of B. subtilis rnpb complementation plasmids For complementation, the B. subtilis rnpb wild-type gene (rnpbwt) under control of its native rnpb promoter and terminator
- 1 - SUPPLEMENTARY DATA Construction of B. subtilis rnpb complementation plasmids For complementation, the B. subtilis rnpb wild-type gene (rnpbwt) under control of its native rnpb promoter and terminator
Diagnostics and genetic variation of an invasive microsporidium (Nosema ceranae) in honey bees (Apis mellifera)
 Diagnostics and genetic variation of an invasive microsporidium (Nosema ceranae) in honey bees (Apis mellifera) Dr. M. M. Hamiduzzaman School of Environmental Sciences University of Guelph, Canada Importance
Diagnostics and genetic variation of an invasive microsporidium (Nosema ceranae) in honey bees (Apis mellifera) Dr. M. M. Hamiduzzaman School of Environmental Sciences University of Guelph, Canada Importance
Supplemental Data. Hou et al. (2016). Plant Cell /tpc
 Supplemental Data. Hou et al. (216). Plant Cell 1.115/tpc.16.295 A Distance to 1 st nt of start codon Distance to 1 st nt of stop codon B Normalized PARE abundance 8 14 nt 17 nt Frame1 Arabidopsis inflorescence
Supplemental Data. Hou et al. (216). Plant Cell 1.115/tpc.16.295 A Distance to 1 st nt of start codon Distance to 1 st nt of stop codon B Normalized PARE abundance 8 14 nt 17 nt Frame1 Arabidopsis inflorescence
PLANT resistance (R) genes have evolved to fight
 Copyright Ó 2009 by the Genetics Society of America DOI: 10.1534/genetics.109.108266 Evolutionary Dynamics of the Genomic Region Around the Blast Resistance Gene Pi-ta in AA Genome Oryza Species Seonghee
Copyright Ó 2009 by the Genetics Society of America DOI: 10.1534/genetics.109.108266 Evolutionary Dynamics of the Genomic Region Around the Blast Resistance Gene Pi-ta in AA Genome Oryza Species Seonghee
Introduction to Bioinformatics. Shifra Ben-Dor Irit Orr
 Introduction to Bioinformatics Shifra Ben-Dor Irit Orr Lecture Outline: Technical Course Items Introduction to Bioinformatics Introduction to Databases This week and next week What is bioinformatics? A
Introduction to Bioinformatics Shifra Ben-Dor Irit Orr Lecture Outline: Technical Course Items Introduction to Bioinformatics Introduction to Databases This week and next week What is bioinformatics? A
CGS 5991 (2 Credits) Bioinformatics Tools
 CAP 5991 (3 Credits) Introduction to Bioinformatics CGS 5991 (2 Credits) Bioinformatics Tools Giri Narasimhan 8/26/03 CAP/CGS 5991: Lecture 1 1 Course Schedules CAP 5991 (3 credit) will meet every Tue
CAP 5991 (3 Credits) Introduction to Bioinformatics CGS 5991 (2 Credits) Bioinformatics Tools Giri Narasimhan 8/26/03 CAP/CGS 5991: Lecture 1 1 Course Schedules CAP 5991 (3 credit) will meet every Tue
Genomes and Their Evolution
 Chapter 21 Genomes and Their Evolution PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from
Chapter 21 Genomes and Their Evolution PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from
Chapter 2: Extensions to Mendel: Complexities in Relating Genotype to Phenotype.
 Chapter 2: Extensions to Mendel: Complexities in Relating Genotype to Phenotype. please read pages 38-47; 49-55;57-63. Slide 1 of Chapter 2 1 Extension sot Mendelian Behavior of Genes Single gene inheritance
Chapter 2: Extensions to Mendel: Complexities in Relating Genotype to Phenotype. please read pages 38-47; 49-55;57-63. Slide 1 of Chapter 2 1 Extension sot Mendelian Behavior of Genes Single gene inheritance
Lab tomorrow: Bacterial Diseases. Bacteria
 Lab tomorrow: Bacterial Diseases Quiz: Koch s Postulates (p. 17-19), Botrytis Predisposition (p. 97)., And, intros for Bacteria (pp 67-69), Biocontrol of Crown Gall (p. 117), and Observation of Viral Movement
Lab tomorrow: Bacterial Diseases Quiz: Koch s Postulates (p. 17-19), Botrytis Predisposition (p. 97)., And, intros for Bacteria (pp 67-69), Biocontrol of Crown Gall (p. 117), and Observation of Viral Movement
The Developmental Transcriptome of the Mosquito Aedes aegypti, an invasive species and major arbovirus vector.
 The Developmental Transcriptome of the Mosquito Aedes aegypti, an invasive species and major arbovirus vector. Omar S. Akbari*, Igor Antoshechkin*, Henry Amrhein, Brian Williams, Race Diloreto, Jeremy
The Developmental Transcriptome of the Mosquito Aedes aegypti, an invasive species and major arbovirus vector. Omar S. Akbari*, Igor Antoshechkin*, Henry Amrhein, Brian Williams, Race Diloreto, Jeremy
A genomic insight into evolution and virulence of Corynebacterium diphtheriae
 A genomic insight into evolution and virulence of Corynebacterium diphtheriae Vartul Sangal, Ph.D. Northumbria University, Newcastle vartul.sangal@northumbria.ac.uk @VartulSangal Newcastle University 8
A genomic insight into evolution and virulence of Corynebacterium diphtheriae Vartul Sangal, Ph.D. Northumbria University, Newcastle vartul.sangal@northumbria.ac.uk @VartulSangal Newcastle University 8
GFP WxTP-GFP WxTP-GFP. stromules. DsRed WxTP-DsRed WxTP-DsRed. stromules
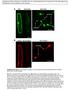 Supplemental Data. Kitajima et al. (2009). The rice -amylase glycoprotein is targeted from the Golgi apparatus through the secretory pathway to the plastids. A GFP WxTP-GFP WxTP-GFP stromules stromules
Supplemental Data. Kitajima et al. (2009). The rice -amylase glycoprotein is targeted from the Golgi apparatus through the secretory pathway to the plastids. A GFP WxTP-GFP WxTP-GFP stromules stromules
Horizontal transfer and pathogenicity
 Horizontal transfer and pathogenicity Victoria Moiseeva Genomics, Master on Advanced Genetics UAB, Barcelona, 2014 INDEX Horizontal Transfer Horizontal gene transfer mechanisms Detection methods of HGT
Horizontal transfer and pathogenicity Victoria Moiseeva Genomics, Master on Advanced Genetics UAB, Barcelona, 2014 INDEX Horizontal Transfer Horizontal gene transfer mechanisms Detection methods of HGT
