Effect of Acetosyringone on Agrobacterium-mediated Transformation of Eustoma grandiflorum Leaf Disks
|
|
|
- Rosamund May
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 JARQ 51 (4), (2017) Improvement in Agrobacterium-mediated Transformation of Eustoma grandiflorum by Acetosyringone Effect of Acetosyringone on Agrobacterium-mediated Transformation of Eustoma grandiflorum Leaf Disks Yoshihiro NAKANO* Institute of Vegetable and Floriculture Science, National Agriculture and Food Research Organization (Tsukuba, Ibaraki , Japan). Abstract Eustoma grandiflorum is a popular ornamental flower worldwide. The production of transgenic Eustoma is expected to help in the study and modification of its traits, such as growth, flowering time, flower color, and flower shape. Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of leaf disks is a frequently used method of plant transformation. To improve the transformation efficiency of Eustoma, I focused on two steps: the inoculation of Agrobacterium into the leaf disks, and subsequent cocultivation. The effect of detergent in the inoculation buffer was tested. Given its marginal effect on the viability of the disks, Tween 20 was determined to be a better candidate for use in the buffer. Acetosyringone is known to improve transformation efficiency by up-regulating the virulence of Agrobacterium. In previous studies using Eustoma, the effect of this compound has only been tested during inoculation. However, I studied the effect of acetosyringone by adding it to the inoculation as well as the co-cultivation medium. When added to the co-cultivation medium, acetosyringone significantly increased the number of transformed calli harboring a marker transgene. More than 0.7 callus per leaf disk was obtained by adding acetosyringone, whereas less than 0.03 callus per disks were obtained in its absence. Thus, the mediated incorporation of a transgene into the Eustoma genome can be intensified by the addition of acetosyringone to the co-cultivation medium. Discipline: Horticulture Additional key words: Agrobacterium tumefaciens Introduction Eustoma grandiflorum, a member of the family Gentianaceae, has become a popular ornamental flower worldwide. However, there are some problems, such as heat-induced rosetting (Ohkawa et al. 1991), reduced rate of flowering under low temperature (Nakano et al. 2011), and flower bud necrosis under low light intensity (Ushio and Fukuta 2010), which reduce the productivity of Eustoma. To study the growth and flowering habits of Eustoma by introducing a gene of interest, it is important to develop an efficient transformation method. Transgenic breeding is employed in ornamental flower plants for altering the flower shape, color, and other properties. In a study aimed at improving the disease resistance in Eustoma by the stable integration of a candidate gene, Isuzugawa et al. (2002) evaluated the factors affecting the transformation of Eustoma. Thiruvengadam and Yang (2009) also reported a transformation method for altering the flowering time and flower shape in Eustoma. It is important to establish an efficient transformation technique that would aid further research and breeding studies on Eustoma. Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of plant leaf disks is widely used to study the biological function of genes and produce crops with novel traits. This transformation involves infecting leaf disks with Agrobacterium, the cells of which subsequently die along with the transformed calli being selected and regenerated into plants. For Eustoma, the growth environment and medium composition required for callus formation and plant regeneration have already been well standardized (Isuzugawa et al. 2002). Although transformation efficiency was not calculated in all previous studies, generally 2-3 transformants are obtained per 100 explants (Semeria et al. 1996; Ledger et al. 1997; Isuzugawa et al. 2002). In this study, we focused on the infection step, which entails the inoculation of Agrobacterium into the leaf disks and co-cultivation for enhanced infection efficiency. *Corresponding author: ynakano@affrc.go.jp Received 3 October 2016; accepted 27 February
2 Y. Nakano Materials and methods 1. Growth conditions of plants and bacteria Aseptically cultured Eustoma plants were used as the experimental material. Seeds of E. grandiflorum Tenryu White (Miyoshi, Tokyo, Japan) and Shihai (Fukkaen, Nagoya, Japan) were surface-sterilized by washing with 70% ethanol for 1 min and 5% sodium hypochlorite for 10 min. The seeds were subsequently washed three times with distilled water and inoculated on Murashige-Skoog (MS) medium containing 8 g L -1 of agar and 5 g L -1 of sucrose. The plants were grown in a clear box (W D H = cm) at 24 C for about 12 weeks, with transplantation to fresh medium every 3 weeks. The plants were provided continuous light (80 μmol m -1 s -1 ) using fluorescent tubes. Disks (5 mm in diameter) were punched out from the leaves by using a sterilized cork borer. Agrobacterium tumefaciens strain LBA4404 harboring the vector pbi121 (Clontech, California, USA) was cultured overnight at 28 C in LB medium supplemented with 50 mg L -1 of kanamycin and 50 mg L -1 of streptomycin. The bacterial cells were collected by centrifugation at 5,000 g for 5 min at 20 C, and then resuspended in inoculation medium as described below. 2. Effects of detergents on leaf disk viability Leaf disks were soaked in MS liquid medium supplemented with Triton X-100, Tween 20, or Silwet L-77, at concentrations of 0.01 or 0.1% for 15 min. The disks were blotted on filter paper and then grown on callus induction MS (CIM) medium consisting of 1 MS salts, 8 g L -1 of agar, 20 g L -1 of sucrose, 1.0 mg L -1 of 6-benzylaminopurine, and 1.0 mg L -1 of 1-naphthaleneacetic acid for 7 days. The disks whose cut surface stayed green were counted as viable. A total of 20 leaf disks was used for each treatment. 3. Effect of acetosyringone on transformation The A. tumefaciens pellet was resuspended in MS medium containing 0, 0.1, or 1.0 mm of acetosyringone (AS) to an optical density of 0.5 at 600 nm. The leaf disks were soaked in the bacterial suspension for 30 min and then blotted on filter paper for about 5 min. The disks were then placed on the co-cultivation medium (CIM medium supplemented with 0, 0.01, or 0.1 mm of AS). After co-cultivation at 25 C for 2 days in the dark, the disks were placed on CIM medium supplemented with 500 mg L -1 of carbenicillin for 2 days under continuous lighting to kill the Agrobacterium cells (Isuzugawa et al. 2002). To select the transformed cells using kanamycin resistance, the disks were transferred onto CIM medium supplemented with 100 mg L -1 of carbenicillin and kanamycin each, and then incubated for 4 weeks. 4. Histochemical β-glucuronidase staining β-glucuronidase (GUS) activity was tested according to Jefferson et al. (1987). The leaf disks were incubated in 50 mm sodium phosphate buffer, ph 7.0, containing 10% methanol, 10 mm of EDTA, 1 mm of potassium ferricyanide, 1 mm of potassium ferrocyanide, 0.2 mg ml -1 of 5-bromo-4-chloro-3-indolylβ-D-glucuronide cyclohexylammonium salt (X-Gluc), and 0.1% Triton X-100 at 30 C. Termination of staining and bleaching were performed by soaking the disks in 80% ethanol. 5. Genomic PCR Genomic PCR was performed by using KOD FX (TOYOBO, Osaka, Japan). Genomic DNA was extracted from the leaves (5 mm 5 mm) of wild-type and putatively transgenic plants by boiling, as per the manufacturer s instructions. A 903 bp fragment of the GUS gene (AAC53706) was amplified with a primer set (5 -CGATGCGGTCACTCATTACG-3 and 5 -CTGTAAGTGCGCTTGCTGAG-3 ). ACTIN gene was amplified as described previously (Nakano et al. 2011), as a positive control of DNA extraction. Results and discussion 1. Effects of detergents in inoculation buffer on leaf disk viability Given the water-repelling surface of the Eustoma leaf, the leaf disks stay afloat on the buffer during inoculation. The addition of a detergent to the inoculation buffer was considered to possibly improve infection efficiency, as reported in Arabidopsis thaliana (Kim et al. 2009). However, as some detergents are toxic to plant cells (Buchanan 1965), their effect on leaf disk viability was studied. Tween 20 and Triton X-100 are widely used detergents in transformation experiments (e.g. Kim et al. 2009). Silwet L-77 is used in Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis using the floral dip method (Clough and Bent 1998). Almost all the disks soaked in Tween 20 were viable after 7 days (Table 1). Conversely, not all disks were viable after soaking in Triton X-100 or Silwet L-77 at 0.01%. Nearly half of the disks turned brown after being dipped in a medium supplemented with 0.1% Triton X-100. Thus, Tween 20 could be used for inoculation without any negative effect. 352 JARQ 51 (4) 2017
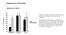
3 Improvement in Agrobacterium-mediated Transformation of Eustoma grandiflorum by Acetosyringone 2. Effect of acetosyringone on generation of transformed calli Next, I studied the effect of acetosyringone (AS) on infection efficiency. AS induces the vir gene in the Ti plasmid of Agrobacterium and enhances infection (Baker et al. 2005). AS is used for the transformation of monocots, such as Oryza sativa, which do not produce Table 1. Effect of detergents added to the inoculation buffer on leaf disk viability in Eustoma Tenryu White Detergent Concentration in inoculation buffer (%) Viability* (%) No detergent - 100a Tween a ± 2ab Triton X ± 9bc ± 8da Silwet L ± 8ab ± 6bc * A total of 20 leaf disks was used for each treatment. * Values are means ± SE (n = 3). * Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among the treatments (Tukey s test, P < 0.05). AS-like phenolic compounds (Hiei et al. 1994). In Eustoma transformation, AS is only used during the inoculation step (Isuzugawa et al. 2002; Thiruvengadam and Yang 2009). Here, I studied the effect of AS during inoculation and co-cultivation. After co-cultivation, transformed cells were selected on the medium supplemented with kanamycin. GUS activity derived from the vector pbi121 was detected by histochemical staining of the calli. No callus formation was observed on the cut surface of the leaf disks from non-transformed wild type plants (data not shown). Adding AS to the inoculation buffer did not affect the formation of kanamycin-resistant or GUS-stained calli (Table 2), as reported by Isuzugawa et al. (2002). In contrast, adding AS to the co-cultivation medium increased the number of kanamycin-resistant and X-Gluc-stained calli (Fig. 1 A and B; Table 2). In wheat, 0.1 mm of AS in the cocultivation medium resulted in a sevenfold increase of transformed calli (McCormac et al. 1998). The addition of AS into the co-cultivation medium seems effective in Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Eustoma, as well as monocots. Some calli were kanamycin-resistant, but were not stained by X-Gluc (Fig. 1A and B; Table 2). This was probably because the expression of GUS was insufficient for detection in these calli or AS induced the formation of non-transformed calli. Cultivar Table 2. Effect of acetosyringone on Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Eustoma AS concentration in inoculation buffer (mm) AS concentration in co-cultivation medium (mm) No. of kanamycinresistant calli/ No. of leaf disks* Replicate No. of X-Gluc stained calli/ No. of leaf disks* No. of X-Gluc stained calli/leaf disk** Replicate Tenryu White 0 0 0/44 0/45 1/47 0/44 0/45 1/47 < 0.01d /45 1/48 1/47 0/45 1/48 1/47 < 0.01d 1 0 3/43 0/45 1/48 3/43 0/45 1/ ± 0.02c /31 68/34 36/31 32/31 60/34 26/ ± 0.28b /46 128/30 62/32 92/46 82/30 58/ ± 0.28a Shihai 0 0 0/42 0/45 0/42 0/42 0/45 0/42 0c /45 0/48 0/47 0/45 0/48 0/47 0c 1 0 0/35 1/47 1/44 0/35 1/47 1/44 < 0.01b /38 36/33 24/31 34/38 26/33 16/ ± 0.11a /36 58/34 38/35 24/36 50/34 36/ ± 0.23a *Leaf disks contaminated with molds or bacteria were omitted. ** Values are means ± SE (n = 3). Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among the treatments (Tukey s test, P < 0.05). 353
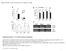
4 Y. Nakano A Co-cultivated with AS C without AS B D Wt Transgenic lines bp 500 bp GUS ACTIN Fig. 1. Effect of acetosyringone (AS) on Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Eustoma. A: Leaf disks were co-cultivated with Agrobacterium harboring the vector pbi121 on a medium supplemented with AS (upper row) or without it (lower row). After co-cultivation and eradication, the transformed cells were selected on CIM containing kanamycin for 28 days. B: GUS staining of the disks shown in A. The arrow indicates a kanamycin-resistant callus lacking GUS activity. C: Shoots were successfully re-differentiated from the transformed calli by using the shoot induction medium described by Isuzugawa et al. (2002). D: Genomic PCR of GUS gene. Wild-type (Wt) and six randomly selected putative transgenic plants were analyzed. The ACTIN gene was used as a positive control of DNA extraction. Table 3. Effects of detergents and acetosyringone on Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Eustoma cv. Tenryu White Tween 20 concentration in inoculation buffer (%) AS concentration in co-cultivation medium (mm) No. of X-Gluc stained calli/leaf disk* No. of kanamycin-resistant shoots/leaf disk** 0 0 0c 0c c 0c c 0c ± 0.05b 0.37 ± 0.03b ± 0.27a 0.58 ± 0.04a b0.87 ± 0.32ab 0.62 ± 0.07a AS concentration in the inoculation buffer was 0.1 mm. *Twenty leaf disks were grown on CIM containing kanamycin for 4 weeks. Values are means ± SE (n = 3). **Twenty leaf disks were grown on CIM for 1 week and on the shoot induction medium for 6 weeks in the presence of kanamycin. Values are means ± SE (n = 3). Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among the treatments (Tukey s test, P < 0.05). 354 JARQ 51 (4) 2017
5 Improvement in Agrobacterium-mediated Transformation of Eustoma grandiflorum by Acetosyringone 3. Efficient transformation of E. grandiflorum Finally, the combined effect of Tween 20 and AS was tested. Different combinations of the inoculation buffer containing 0, 0.01, or 0.1% Tween 20 and cocultivation medium containing 0 or 0.01 mm of AS were used. A total of 20 leaf disks was used for each treatment. The presence of AS in the co-cultivation medium strongly enhanced infection efficiency (Table 3). The addition of detergent in the inoculation buffer slightly improved the transformation efficiency in Arabidopsis (Kim et al. 2009). Tween 20 alone did not affect the transformation efficiency in Eustoma (Table 3). Tween 20 present in the inoculation buffer slightly increased the number of transformed calli only in combination with AS (Table 3). When the leaf disks were selected on the shoot regeneration medium described previously (Isuzugawa et al. 2002), transformed shoots could be successfully obtained (Fig. 1C; Table 3). Genomic PCR of six randomly selected shoots confirmed that GUS gene was successfully integrated into their genome (Fig. 1D). In conclusion, the incorporation of a gene of interest into the Eustoma genome by Agrobacterium-mediated transformation can be intensified by adding AS during co-cultivation. References Baker, C.J. et al. (2005) Involvement of acetosyringone in plant-pathogen recognition. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 328, Buchanan, G.A. (1965) Patterns of surfactant toxicity to plant tissues. In Retrospective theses and dissertations, Paper 3905, Iowa state University, Iowa, USA, Clough, S.J. & Bent, A.F. (1998) Floral dip: a simplified method for Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J., 16, Hiei, Y. et al. (1994) Efficient transformation of rice (Oryza sativa L.) mediated by Agrobacterium and sequence analysis of the boundaries of the T-DNA. Plant J., 6, Isuzugawa, K. et al. (2002) Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Lisianthus (Eustoma grandiflorum Griseb.). Bull. Yamagata Hortic. Exp. Stn., 14, 1-11 [In Japanese]. Jefferson, R.A. et al. (1987) GUS fusions: beta-glucuronidase as a sensitive and versatile gene fusion marker in higher plants. EMBO J., 6, Kim, M.J. et al. (2009) Optimization of conditions for transient Agrobacterium-mediated gene expression assays in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Rep., 28, Ledger, S.E. et al. (1997) Transformation of Lisianthus (Eustoma grandiflorum). Plant Cell Rep., 16, McCormac, A.C. et al. (1998) The use of visual marker genes as cell-specific reporters of Agrobacterium-mediated T-DNA delivery to wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) and barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Euphytica, 99, Nakano, Y. et al. (2011) Characterization of FLC, SOC1 and FT homologs in Eustoma grandiflorum: effects of vernalization and post-vernalization conditions on flowering and gene expression. Physiol. Plant., 141, Ohkawa, K. et al. (1991) Effects of air temperature and time on rosette formation in seedlings of Eustoma grandiflorum (Raf.) Shinn. Sci. Hortic., 48, Semeria, B. et al. (1996) Genetic transformation of Eustoma grandiflorum by Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult., 47, Thiruvengadam, M. & Yang, C.H. (2009) Ectopic expression of two MADS box genes from orchid (Oncidium Gower Ramsey) and lily (Lilium longiflorum) alters flower transition and formation in Eustoma grandiflorum. Plant Cell Rep., 28, Ushio, A. & Fukuta, N. (2010) Effects of nitrogen fertilization levels in nutrient solution applied before/after flower budding on blasting in winter-flowering of Eustoma grandiflorum (Raf.) Shinn. Hortic. Res., 9, [In Japanese]. 355
PEROXIDASE ACTIVITY IN EUSTOM GRANDIFLOR UM PLANTS TRANSFORMED BY AGROBACTERIUM RHIZOGENES
 PEROXIDASE ACTIVITY IN EUSTOM GRANDIFLOR UM PLANTS TRANSFORMED BY AGROBACTERIUM RHIZOGENES GABRIELA POPA', AURELIA BREZEANU~, C. PETRUTA CORNEA', J.P. BOE The effects of inoculation with wild type of Agrobacterium
PEROXIDASE ACTIVITY IN EUSTOM GRANDIFLOR UM PLANTS TRANSFORMED BY AGROBACTERIUM RHIZOGENES GABRIELA POPA', AURELIA BREZEANU~, C. PETRUTA CORNEA', J.P. BOE The effects of inoculation with wild type of Agrobacterium
Expression of Viral Resistance in Transformed Petunia Plants Regenerated in Vitro
 Expression of Viral Resistance in Transformed Petunia Plants Regenerated in Vitro Meira Ziv and Mirit Gandelman The RH Smith Institute of Plant Science The Hebrew University of Jerusalem, Rehovot, PO Box
Expression of Viral Resistance in Transformed Petunia Plants Regenerated in Vitro Meira Ziv and Mirit Gandelman The RH Smith Institute of Plant Science The Hebrew University of Jerusalem, Rehovot, PO Box
Plant transformation
 Plant transformation Objectives: 1. What is plant transformation? 2. What is Agrobacterium? How and why does it transform plant cells? 3. How is Agrobacterium used as a tool in molecular genetics? References:
Plant transformation Objectives: 1. What is plant transformation? 2. What is Agrobacterium? How and why does it transform plant cells? 3. How is Agrobacterium used as a tool in molecular genetics? References:
ScienceDirect. In planta Agrobacterium-Mediated Transformation of Rice
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Rice Science, 2017, 24(3): 181 186 In planta Agrobacterium-Mediated Transformation of Rice Kumrop RATANASUT, Weerawan ROD-IN, Kawee SUJIPULI (Department
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Rice Science, 2017, 24(3): 181 186 In planta Agrobacterium-Mediated Transformation of Rice Kumrop RATANASUT, Weerawan ROD-IN, Kawee SUJIPULI (Department
Development of a protocol for Agrobacterium mediated transformation of Brassica oleraceae L var botrytis cv Early kunwari
 204; (3): 34-38 ISSN 232-922 EJBB 204; (3): 34-38 Received 20-0-204 Accepted: **--204 Development of a protocol for Agrobacterium mediated transformation of Brassica oleraceae L var botrytis cv Early kunwari
204; (3): 34-38 ISSN 232-922 EJBB 204; (3): 34-38 Received 20-0-204 Accepted: **--204 Development of a protocol for Agrobacterium mediated transformation of Brassica oleraceae L var botrytis cv Early kunwari
Micropropagation of Lisianthus (Eustoma grandiflorum L.) from different explants to flowering onset
 583 Micropropagation of Lisianthus (Eustoma grandiflorum L.) from different explants to flowering onset Fatemeh Rezaee, Faezeh Ghanati* and Laleh Yusefzadeh Boroujeni Department of Plant Biology, Faculty
583 Micropropagation of Lisianthus (Eustoma grandiflorum L.) from different explants to flowering onset Fatemeh Rezaee, Faezeh Ghanati* and Laleh Yusefzadeh Boroujeni Department of Plant Biology, Faculty
AMADEPA Association Martiniquaise pour le Developpement des Plantes Alimentaires
 AMADEPA Association Martiniquaise pour le Developpement des Plantes Alimentaires 29eme CONGRES ANNUEL ANNUAL MEETING REUNION ANNUAL Agriculture Intensive dans les Iles de la Caraibe : enjeux, contraintes
AMADEPA Association Martiniquaise pour le Developpement des Plantes Alimentaires 29eme CONGRES ANNUEL ANNUAL MEETING REUNION ANNUAL Agriculture Intensive dans les Iles de la Caraibe : enjeux, contraintes
Last time: Obtaining information from a cloned gene
 Last time: Obtaining information from a cloned gene Objectives: 1. What is the biochemical role of the gene? 2. Where and when is the gene expressed (transcribed)? 3. Where and when is the protein made?
Last time: Obtaining information from a cloned gene Objectives: 1. What is the biochemical role of the gene? 2. Where and when is the gene expressed (transcribed)? 3. Where and when is the protein made?
An Efficient Agrobacterium-mediated Transformation Method for Sugarcane (Saccharum officinarum L.)
 An Efficient Agrobacterium-mediated Transformation Method for Sugarcane (Saccharum officinarum L.) 1 Efendi and 2 M. Matsuoka 1 Departmen of Agrotechnology, Faculty of Agriculture, Syiah Kuala University,
An Efficient Agrobacterium-mediated Transformation Method for Sugarcane (Saccharum officinarum L.) 1 Efendi and 2 M. Matsuoka 1 Departmen of Agrotechnology, Faculty of Agriculture, Syiah Kuala University,
** * * * Col-0 cau1 CAU1. Actin2 CAS. Actin2. Supplemental Figure 1. CAU1 affects calcium accumulation.
 Ca 2+ ug g -1 DW Ca 2+ ug g -1 DW Ca 2+ ug g -1 DW Supplemental Data. Fu et al. Plant Cell. (213). 1.115/tpc.113.113886 A 5 4 3 * Col- cau1 B 4 3 2 Col- cau1 ** * * ** C 2 1 25 2 15 1 5 Shoots Roots *
Ca 2+ ug g -1 DW Ca 2+ ug g -1 DW Ca 2+ ug g -1 DW Supplemental Data. Fu et al. Plant Cell. (213). 1.115/tpc.113.113886 A 5 4 3 * Col- cau1 B 4 3 2 Col- cau1 ** * * ** C 2 1 25 2 15 1 5 Shoots Roots *
INDUCTION OF IN VITRO FLOWERING OF INDONESIAN WILD ORCHID, Phalaenopsis amabilis (L.) Blume
 ISSN 2413-0877 Volume 2 (2015) 398-404 The 3rd International Conference on Biological Science 2013 (The 3rd ICBS-2013) INDUCTION OF IN VITRO FLOWERING OF INDONESIAN WILD ORCHID, Phalaenopsis amabilis (L.)
ISSN 2413-0877 Volume 2 (2015) 398-404 The 3rd International Conference on Biological Science 2013 (The 3rd ICBS-2013) INDUCTION OF IN VITRO FLOWERING OF INDONESIAN WILD ORCHID, Phalaenopsis amabilis (L.)
Cryotherapy: A New Method to Eliminate Pathogens from Sweetpotato Propagation Materials
 Cryotherapy: A New Method to Eliminate Pathogens from Sweetpotato Propagation Materials Margaret Worthington Graduate Group in Horticulture and Agronomy University of California, Davis April 14, 2009 http://www.judithbarathart.com
Cryotherapy: A New Method to Eliminate Pathogens from Sweetpotato Propagation Materials Margaret Worthington Graduate Group in Horticulture and Agronomy University of California, Davis April 14, 2009 http://www.judithbarathart.com
GENETIC ANALYSES OF ROOT SYSTEM DEVELOPMENT IN THE TOMATO CROP MODEL
 GENETIC ANALYSES OF ROOT SYSTEM DEVELOPMENT IN THE TOMATO CROP MODEL Kelsey Hoth 1 Dr. Maria Ivanchenko 2 Bioresourse Research 1, Department of Botany and Plant Physiology 2, Oregon State University, Corvallis,
GENETIC ANALYSES OF ROOT SYSTEM DEVELOPMENT IN THE TOMATO CROP MODEL Kelsey Hoth 1 Dr. Maria Ivanchenko 2 Bioresourse Research 1, Department of Botany and Plant Physiology 2, Oregon State University, Corvallis,
Supplementary Figure S1. Amino acid alignment of selected monocot FT-like and TFL-like sequences. Sequences were aligned using ClustalW and analyzed
 Supplementary Figure S1. Amino acid alignment of selected monocot FT-like and TFL-like sequences. Sequences were aligned using ClustalW and analyzed using the Geneious software. Accession numbers of the
Supplementary Figure S1. Amino acid alignment of selected monocot FT-like and TFL-like sequences. Sequences were aligned using ClustalW and analyzed using the Geneious software. Accession numbers of the
Supplemental Data. Perrella et al. (2013). Plant Cell /tpc
 Intensity Intensity Intensity Intensity Intensity Intensity 150 50 150 0 10 20 50 C 150 0 10 20 50 D 0 10 20 Distance (μm) 50 20 40 E 50 F 0 10 20 50 0 15 30 Distance (μm) Supplemental Figure 1: Co-localization
Intensity Intensity Intensity Intensity Intensity Intensity 150 50 150 0 10 20 50 C 150 0 10 20 50 D 0 10 20 Distance (μm) 50 20 40 E 50 F 0 10 20 50 0 15 30 Distance (μm) Supplemental Figure 1: Co-localization
Figure 1. Identification of UGT74E2 as an IBA glycosyltransferase. (A) Relative conversion rates of different plant hormones to their glucosylated
 Figure 1. Identification of UGT74E2 as an IBA glycosyltransferase. (A) Relative conversion rates of different plant hormones to their glucosylated form by recombinant UGT74E2. The naturally occurring auxin
Figure 1. Identification of UGT74E2 as an IBA glycosyltransferase. (A) Relative conversion rates of different plant hormones to their glucosylated form by recombinant UGT74E2. The naturally occurring auxin
Production of Haploid and Doubled Haploid Plants from Anther-derived Callus of Lilium formosanum
 Production of Haploid and Doubled Haploid Plants from Anther-derived Callus of Lilium formosanum D.-S. Han and Y. Niimi Faculty of Agriculture, Niigata University 2-8050 Ikarashi, Niigata 950-2181 Japan
Production of Haploid and Doubled Haploid Plants from Anther-derived Callus of Lilium formosanum D.-S. Han and Y. Niimi Faculty of Agriculture, Niigata University 2-8050 Ikarashi, Niigata 950-2181 Japan
Induction of Haploid Callus from Isolated Microspores of Peony in vitro
 Plant & Cell Physiol. 22(2): 337-34 (98) Short communication Induction of Haploid Callus from Isolated Microspores of Peony in vitro Kanji Ono and Shuichi Harashima Department of Biology, Faculty of Science,
Plant & Cell Physiol. 22(2): 337-34 (98) Short communication Induction of Haploid Callus from Isolated Microspores of Peony in vitro Kanji Ono and Shuichi Harashima Department of Biology, Faculty of Science,
Characterisation of abiotic stress inducible plant promoters and bacterial genes for osmotolerance using transgenic approach
 Characterisation of abiotic stress inducible plant promoters and bacterial genes for osmotolerance using transgenic approach ABSTRACT SUBMITTED TO JAMIA MILLIA ISLAMIA NEW DELHI IN PARTIAL FULFILMENT OF
Characterisation of abiotic stress inducible plant promoters and bacterial genes for osmotolerance using transgenic approach ABSTRACT SUBMITTED TO JAMIA MILLIA ISLAMIA NEW DELHI IN PARTIAL FULFILMENT OF
Supplemental Data. Chen and Thelen (2010). Plant Cell /tpc
 Supplemental Data. Chen and Thelen (2010). Plant Cell 10.1105/tpc.109.071837 1 C Total 5 kg 20 kg 100 kg Transmission Image 100 kg soluble pdtpi-gfp Plastid (PDH-alpha) Mito (PDH-alpha) GFP Image vector
Supplemental Data. Chen and Thelen (2010). Plant Cell 10.1105/tpc.109.071837 1 C Total 5 kg 20 kg 100 kg Transmission Image 100 kg soluble pdtpi-gfp Plastid (PDH-alpha) Mito (PDH-alpha) GFP Image vector
IN VITRO RHIZOGENESIS IN PAPAYA (CARICA PAPAYA L.)
 J. Plant Develop. 20(2013): 51 55 IN VITRO RHIZOGENESIS IN PAPAYA (CARICA PAPAYA L.) Jaime A. TEIXEIRA DA SILVA 1,2 Abstract: The seeds of two papaya (Carica papaya L.) cultivars ('Rainbow' and 'Sunrise
J. Plant Develop. 20(2013): 51 55 IN VITRO RHIZOGENESIS IN PAPAYA (CARICA PAPAYA L.) Jaime A. TEIXEIRA DA SILVA 1,2 Abstract: The seeds of two papaya (Carica papaya L.) cultivars ('Rainbow' and 'Sunrise
Effect of some root associative bacteria on germination of seeds, nitrogenase activity and dry matter production by rice plants
 Journal of crop and weed 2(2) : 47-51 (2006) Effect of some root associative bacteria on germination of seeds, nitrogenase activity and dry matter production by rice plants A. C. DAS AND S. C. KOLE Department
Journal of crop and weed 2(2) : 47-51 (2006) Effect of some root associative bacteria on germination of seeds, nitrogenase activity and dry matter production by rice plants A. C. DAS AND S. C. KOLE Department
Callus induction and plant regeneration on optimization of the culture conditions in Jow Haw rice (Oryza sativa L.)
 Journal of Agricultural Technology 2016 Vol. 12(2):241-248 Available online http://www.ijat-aatsea.com ISSN 1686-9141 Callus induction and plant regeneration on optimization of the culture conditions in
Journal of Agricultural Technology 2016 Vol. 12(2):241-248 Available online http://www.ijat-aatsea.com ISSN 1686-9141 Callus induction and plant regeneration on optimization of the culture conditions in
Somaclonal Variation
 Tissue-culture cycle involves: dedifferentiation in culture proliferation of cells (implies sev. cell generations removed from original differentiated cell) subsequent regeneration to plants no selection
Tissue-culture cycle involves: dedifferentiation in culture proliferation of cells (implies sev. cell generations removed from original differentiated cell) subsequent regeneration to plants no selection
Towards the Ultimate Solution: Genetic Resistance to HLB in Commercial Citrus. Greening Summit Florida Citrus Growers Institute 2008
 Towards the Ultimate Solution: Genetic Resistance to HLB in Commercial Citrus Greening Summit Florida Citrus Growers Institute 2008 Jude Grosser University of Florida, Citrus Research and Education Center,
Towards the Ultimate Solution: Genetic Resistance to HLB in Commercial Citrus Greening Summit Florida Citrus Growers Institute 2008 Jude Grosser University of Florida, Citrus Research and Education Center,
DEVELOPMENTAL GENETICS OF ARABIDOPSIS THALIANA
 DEVELOPMENTAL GENETICS OF ARABIDOPSIS THALIANA CHASE BALLARD LINDA EAN HECTOR LOPEZ DR. JOANNA WERNER-FRACZEK IN COLLABORATION WITH DR. PATRICIA SPRINGER S LAB AT UCR AND ROBERT KOBLE PURPOSE OF RESEARCH
DEVELOPMENTAL GENETICS OF ARABIDOPSIS THALIANA CHASE BALLARD LINDA EAN HECTOR LOPEZ DR. JOANNA WERNER-FRACZEK IN COLLABORATION WITH DR. PATRICIA SPRINGER S LAB AT UCR AND ROBERT KOBLE PURPOSE OF RESEARCH
Rapid, Efficient Production of Homozygous Transgenic Tobacco Plants with Agrobacterium tumefaciens: A Seed to Seed Protocol.
 1 Rapid, Efficient Production of Homozygous Transgenic Tobacco Plants with Agrobacterium tumefaciens: A Seed to Seed Protocol. Dane K. Fisher and Mark J. Guiltinan* Department of Horticulture, Intercollegiate
1 Rapid, Efficient Production of Homozygous Transgenic Tobacco Plants with Agrobacterium tumefaciens: A Seed to Seed Protocol. Dane K. Fisher and Mark J. Guiltinan* Department of Horticulture, Intercollegiate
Supplemental material
 Supplemental material Table 1- Segregation analysis of sgt1a sgt1b double mutant plants Parental genotype No. of lines Normal seeds Phenotype Abnormal seeds Ratio of abnormal seeds (%) WT 3 171 2 1.16
Supplemental material Table 1- Segregation analysis of sgt1a sgt1b double mutant plants Parental genotype No. of lines Normal seeds Phenotype Abnormal seeds Ratio of abnormal seeds (%) WT 3 171 2 1.16
Electronic Journal of Plant Breeding, 7(4): (December 2016) ISSN X
 Research Article Pflp gene transformation in pomegranate (Punica granatum L.) resistance to bacterial blight disease (Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. punicae) Akshata Hosamani *, Sukhada Mohandas, V. Manjula,
Research Article Pflp gene transformation in pomegranate (Punica granatum L.) resistance to bacterial blight disease (Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. punicae) Akshata Hosamani *, Sukhada Mohandas, V. Manjula,
1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate deaminase-producing Agrobacterium tumefaciens
 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate deaminase-producing Agrobacterium tumefaciens has higher ability for gene transfer into plant cells. Running title: ACC deaminase enhances Agrobacterium-mediated gene
1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate deaminase-producing Agrobacterium tumefaciens has higher ability for gene transfer into plant cells. Running title: ACC deaminase enhances Agrobacterium-mediated gene
Low Co-Cultivation Temperature at 20oC Improved Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated Transformation of Tobacco Leaf Disks
 Louisiana State University LSU Digital Commons LSU Master's Theses Graduate School 2010 Low Co-Cultivation Temperature at 20oC Improved Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated Transformation of Tobacco Leaf
Louisiana State University LSU Digital Commons LSU Master's Theses Graduate School 2010 Low Co-Cultivation Temperature at 20oC Improved Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated Transformation of Tobacco Leaf
Ti plasmid derived plant vector systems: binary and co - integrative vectors transformation process; regeneration of the transformed lines
 Ti plasmid derived plant vector systems: binary and co - integrative vectors transformation process; regeneration of the transformed lines Mitesh Shrestha Constraints of Wild type Ti/Ri-plasmid Very large
Ti plasmid derived plant vector systems: binary and co - integrative vectors transformation process; regeneration of the transformed lines Mitesh Shrestha Constraints of Wild type Ti/Ri-plasmid Very large
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/9/452/ra106/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Stem-piped light activates phytochrome B to trigger light responses in Arabidopsis thaliana roots Hyo-Jun Lee, Jun-Ho
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/9/452/ra106/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Stem-piped light activates phytochrome B to trigger light responses in Arabidopsis thaliana roots Hyo-Jun Lee, Jun-Ho
Agrobacterium mediated genetic transformation and regeneration in elite rice (Oryza sativa L.) cultivar BRRI dhan56
 Vol. 14(31), pp. 2415-2423, 5 August, 2015 DOI: 10.5897/AJB2015.14556 Article Number: 2C5FA1854554 ISSN 1684-5315 Copyright 2015 Author(s) retain the copyright of this article http://www.academicjournals.org/ajb
Vol. 14(31), pp. 2415-2423, 5 August, 2015 DOI: 10.5897/AJB2015.14556 Article Number: 2C5FA1854554 ISSN 1684-5315 Copyright 2015 Author(s) retain the copyright of this article http://www.academicjournals.org/ajb
Supplementary Material. stress responsive genes providing protection of wheat from salinity stress
 Supplementary Material Plant growth promoting rhizobacteria Dietzia natronolimnaea modulates the expression of stress responsive genes providing protection of wheat from salinity stress Nidhi Bharti, Shiv
Supplementary Material Plant growth promoting rhizobacteria Dietzia natronolimnaea modulates the expression of stress responsive genes providing protection of wheat from salinity stress Nidhi Bharti, Shiv
Transformation of Soybean (Glycine Max L.) Via GUS Labeled Agrobacterium Rhizogenes R1000
 International Journal of Science and Technology Volume 4 No. 6, June, 2015 Transformation of Soybean (Glycine Max L.) Via GUS Labeled Agrobacterium Rhizogenes R1000 Ghada SH. AL-Yozbaki ; Jamella H. Rasheed
International Journal of Science and Technology Volume 4 No. 6, June, 2015 Transformation of Soybean (Glycine Max L.) Via GUS Labeled Agrobacterium Rhizogenes R1000 Ghada SH. AL-Yozbaki ; Jamella H. Rasheed
Development of a haploid transformation system and overexpression of Phytochrome B gene in Brassica napus L.
 Development of a haploid transformation system and overexpression of Phytochrome B gene in Brassica napus L. Dissertation to obtain the Ph.D. degree in the faculty of Agricultural Sciences Georg-August-University
Development of a haploid transformation system and overexpression of Phytochrome B gene in Brassica napus L. Dissertation to obtain the Ph.D. degree in the faculty of Agricultural Sciences Georg-August-University
EVALUATION OF WILD JUGLANS SPECIES FOR CROWN GALL RESISTANCE
 EVALUATION OF WILD JUGLANS SPECIES FOR CROWN GALL RESISTANCE Ed Stover, Malendia Maccree, Malli Aradhya, Ali E. McClean, and Daniel A. Kluepfel INTRODUCTION Crown Gall disease of walnut is caused by the
EVALUATION OF WILD JUGLANS SPECIES FOR CROWN GALL RESISTANCE Ed Stover, Malendia Maccree, Malli Aradhya, Ali E. McClean, and Daniel A. Kluepfel INTRODUCTION Crown Gall disease of walnut is caused by the
CALLUS INDUCTION AND SOMATIC EMBRYOGENESIS FROM MAIZE MATURE EMBRYOS (ZEA MAYS L.)
 Journal of Cell and Tissue Research Vol. 13(1) 3565-3569 (2013) (Available online at www.tcrjournals.com) ISSN: 0973-0028; E-ISSN: 0974-0910 Original Article CALLUS INDUCTION AND SOMATIC EMBRYOGENESIS
Journal of Cell and Tissue Research Vol. 13(1) 3565-3569 (2013) (Available online at www.tcrjournals.com) ISSN: 0973-0028; E-ISSN: 0974-0910 Original Article CALLUS INDUCTION AND SOMATIC EMBRYOGENESIS
AGROBACTERIUM MEDIATED GENETIC TRANSFORMATION OF THE RESURRECTION PLANT HABERLEA RHODOPENSIS FRIV. Abstract. Introduction
 10 Bulgarian Journal of Agricultural Science, 19 (2) 2013, 10 14 Agricultural Academy AGROBACTERIUM MEDIATED GENETIC TRANSFORMATION OF THE RESURRECTION PLANT HABERLEA RHODOPENSIS FRIV. G. PETROVA* and
10 Bulgarian Journal of Agricultural Science, 19 (2) 2013, 10 14 Agricultural Academy AGROBACTERIUM MEDIATED GENETIC TRANSFORMATION OF THE RESURRECTION PLANT HABERLEA RHODOPENSIS FRIV. G. PETROVA* and
Looking for LOV: Location of LOV1 function in Nicotiana benthamiana cells
 Looking for LOV: Location of LOV1 function in Nicotiana benthamiana cells By: Patrick Rutledge 1 Dr. Jennifer Lorang 2,3, Dr. Marc Curtis 2,3, Dr. Thomas Wolpert 2,3 BioResource Research 1, Botany and
Looking for LOV: Location of LOV1 function in Nicotiana benthamiana cells By: Patrick Rutledge 1 Dr. Jennifer Lorang 2,3, Dr. Marc Curtis 2,3, Dr. Thomas Wolpert 2,3 BioResource Research 1, Botany and
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Supplementary figures % Occupancy 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 Wt tol-1(nr2033) Figure S1. Avoidance behavior to S. enterica was not observed in wild-type or tol-1(nr2033) mutant nematodes.
Supplementary Information Supplementary figures % Occupancy 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 Wt tol-1(nr2033) Figure S1. Avoidance behavior to S. enterica was not observed in wild-type or tol-1(nr2033) mutant nematodes.
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng Supplementary Figure 1. The phenotypes of PI , BR121, and Harosoy under short-day conditions.
 Supplementary Figure 1 The phenotypes of PI 159925, BR121, and Harosoy under short-day conditions. (a) Plant height. (b) Number of branches. (c) Average internode length. (d) Number of nodes. (e) Pods
Supplementary Figure 1 The phenotypes of PI 159925, BR121, and Harosoy under short-day conditions. (a) Plant height. (b) Number of branches. (c) Average internode length. (d) Number of nodes. (e) Pods
Development of genotype independent cotton transformation protocol
 Development of genotype independent cotton transformation protocol Shyam Barampuram and Sergei Krasnyanski Department of Horticultural Science North Carolina State University What are our goals? Robust
Development of genotype independent cotton transformation protocol Shyam Barampuram and Sergei Krasnyanski Department of Horticultural Science North Carolina State University What are our goals? Robust
Practical course 1. Microscopy
 Cellular and Molecular Biology Practicum 1 Practical course 1. Microscopy Name and surname Exercise 1. Prepare a part of plant tissue, for example a part of the leaf of Elodea canadensis by putting it
Cellular and Molecular Biology Practicum 1 Practical course 1. Microscopy Name and surname Exercise 1. Prepare a part of plant tissue, for example a part of the leaf of Elodea canadensis by putting it
THE DEVELOPMENT OF PLANT REGENERATION SYSTEMS FOR THE GENETIC IMPROVEMENT OF WALNUT. Walt Tu1ecke and Gale McGranahan
 THE DEVELOPMENT OF PLANT REGENERATION SYSTEMS FOR THE GENETIC IMPROVEMENT OF WALNUT Walt Tu1ecke and Gale McGranahan ABSTRACT The techniques and capability to regenerate asexual embryos from walnut cotyledon
THE DEVELOPMENT OF PLANT REGENERATION SYSTEMS FOR THE GENETIC IMPROVEMENT OF WALNUT Walt Tu1ecke and Gale McGranahan ABSTRACT The techniques and capability to regenerate asexual embryos from walnut cotyledon
ABSTRACT. Key words: hemp, microsporogenesis, androgenesis
 ABSTRACT Key words: hemp, microsporogenesis, androgenesis Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) has a growing economical importance, because of the various utilizations in alimentation, textiles, plastics, constructions
ABSTRACT Key words: hemp, microsporogenesis, androgenesis Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) has a growing economical importance, because of the various utilizations in alimentation, textiles, plastics, constructions
The Plant Cell, November. 2017, American Society of Plant Biologists. All rights reserved
 The Genetics of Floral Development Teaching Guide Overview The development of flowers in angiosperm plants provided a critical evolutionary advantage, allowing more options for pollen dispersal and seed
The Genetics of Floral Development Teaching Guide Overview The development of flowers in angiosperm plants provided a critical evolutionary advantage, allowing more options for pollen dispersal and seed
Agrobacterium tumefasciens, the Ti Plasmid, and Crown Gall Tumorigenesis
 Agrobacterium tumefasciens, the Ti Plasmid, and Crown Gall Tumorigenesis BOM-11: 10.9 Plasmids: General Principles (review) p. 274 10.11 Conjugation: Essential Features (review) p. 278 19.21 Agrobacterium
Agrobacterium tumefasciens, the Ti Plasmid, and Crown Gall Tumorigenesis BOM-11: 10.9 Plasmids: General Principles (review) p. 274 10.11 Conjugation: Essential Features (review) p. 278 19.21 Agrobacterium
Applying crown gall research-based knowledge to orchard management. E. Fichtner, UCCE Tulare County
 Applying crown gall research-based knowledge to orchard management E. Fichtner, UCCE Tulare County Paradox: Juglans hindsii x Juglans regia Crown Gall Common in walnut Paradox rootstock susceptible Less
Applying crown gall research-based knowledge to orchard management E. Fichtner, UCCE Tulare County Paradox: Juglans hindsii x Juglans regia Crown Gall Common in walnut Paradox rootstock susceptible Less
Agrobacterium rhizo genes-mediated Transformation and Regeneration of Vinca minor L.
 Original Papers Plant Tissue Culture Letters, 11(3), 191-198 (1994) Agrobacterium rhizo genes-mediated Transformation and Regeneration of Vinca minor L. Nobukazu TANAKA*, Misato TAKAO and Tekeshi MATSUMOTO
Original Papers Plant Tissue Culture Letters, 11(3), 191-198 (1994) Agrobacterium rhizo genes-mediated Transformation and Regeneration of Vinca minor L. Nobukazu TANAKA*, Misato TAKAO and Tekeshi MATSUMOTO
TrioMol Isolation Reagent
 TrioMol Isolation Reagent Technical Manual No. 0242 Version 06142007 I Description... 1 II Key Features... 1 III Storage..... 1 IV General Protocol Using Triomol Isolation Reagent 1 V Troubleshooting.
TrioMol Isolation Reagent Technical Manual No. 0242 Version 06142007 I Description... 1 II Key Features... 1 III Storage..... 1 IV General Protocol Using Triomol Isolation Reagent 1 V Troubleshooting.
TrioMol Isolation Reagent
 TrioMol Isolation Reagent Technical Manual No. 0242 Version 06142007 I Description... 1 II Key Features... 1 III Storage..... 1 IV General Protocol Using Triomol Isolation Reagent 1 V Troubleshooting.
TrioMol Isolation Reagent Technical Manual No. 0242 Version 06142007 I Description... 1 II Key Features... 1 III Storage..... 1 IV General Protocol Using Triomol Isolation Reagent 1 V Troubleshooting.
Chapter 1. Introduction
 Chapter 1 Introduction 1.1 Rice & Canola Rice (Oryza sativa) is one of the world s most important food crops, forming part of the staple diet of approximately half the world s population (Upadhyaya et
Chapter 1 Introduction 1.1 Rice & Canola Rice (Oryza sativa) is one of the world s most important food crops, forming part of the staple diet of approximately half the world s population (Upadhyaya et
Title Allantoin by Inosine in Nutrient So. Author(s) Toshihiro; Yokoi, Daisuke; Osaki, M
 Title Rice Root Growth with Increasing in Allantoin by Inosine in Nutrient So Author(s) Tokuhisa, Dai; Okazaki, Keiki; Shin Toshihiro; Yokoi, Daisuke; Osaki, M Citation The Proceedings of the Internationa
Title Rice Root Growth with Increasing in Allantoin by Inosine in Nutrient So Author(s) Tokuhisa, Dai; Okazaki, Keiki; Shin Toshihiro; Yokoi, Daisuke; Osaki, M Citation The Proceedings of the Internationa
Model plants and their Role in genetic manipulation. Mitesh Shrestha
 Model plants and their Role in genetic manipulation Mitesh Shrestha Definition of Model Organism Specific species or organism Extensively studied in research laboratories Advance our understanding of Cellular
Model plants and their Role in genetic manipulation Mitesh Shrestha Definition of Model Organism Specific species or organism Extensively studied in research laboratories Advance our understanding of Cellular
Plant Regeneration and Chromosome Doubling of Wild Gladiolus Species
 Plant Regeneration and Chromosome Doubling of Wild Gladiolus Species K. Suzuki, Y. Takatsu, T. Gonai and M. Kasumi Plant Biotechnology Institute Ibaraki Agricultural Center, Ibaraki Japan Keywords: gladiolus,
Plant Regeneration and Chromosome Doubling of Wild Gladiolus Species K. Suzuki, Y. Takatsu, T. Gonai and M. Kasumi Plant Biotechnology Institute Ibaraki Agricultural Center, Ibaraki Japan Keywords: gladiolus,
EFFECT OF BACTERIAL CULTURE DENSITY AND ACETOSYRINGONE CONCENTRATION ON AGROBACTERIUM MEDIATED TRANSFORMATION IN WHEAT
 Pak. J. Bot., 42(6): 4183-4189, 2010. EFFECT OF BACTERIAL CULTURE DENSITY AND ACETOSYRINGONE CONCENTRATION ON AGROBACTERIUM MEDIATED TRANSFORMATION IN WHEAT HAMID RASHID 1, ASMA AFZAL 2, M. HAROON KHAN
Pak. J. Bot., 42(6): 4183-4189, 2010. EFFECT OF BACTERIAL CULTURE DENSITY AND ACETOSYRINGONE CONCENTRATION ON AGROBACTERIUM MEDIATED TRANSFORMATION IN WHEAT HAMID RASHID 1, ASMA AFZAL 2, M. HAROON KHAN
Methods of isolation of Cucumis sativus and C. melo pollen grains and their utilization in in vitro pollination 1
 Methods of isolation of Cucumis sativus and C. melo pollen grains and their utilization in in vitro pollination 1 D. Skálová *, B. Navrátilová, and A. Lebeda * Palacký University, Faculty of Science, Department
Methods of isolation of Cucumis sativus and C. melo pollen grains and their utilization in in vitro pollination 1 D. Skálová *, B. Navrátilová, and A. Lebeda * Palacký University, Faculty of Science, Department
Transient expression of β-glucuronidase reporter gene in Agrobacterium-inoculated shoots of various teak clones
 African Journal of Biotechnology Vol. 8 (10), pp. 2143-2150, 18 May, 2009 Available online at http://www.academicjournals.org/ajb ISSN 1684 5315 2009 Academic Journals Full Length Research Paper Transient
African Journal of Biotechnology Vol. 8 (10), pp. 2143-2150, 18 May, 2009 Available online at http://www.academicjournals.org/ajb ISSN 1684 5315 2009 Academic Journals Full Length Research Paper Transient
Doubled haploid ramets via embryogenesis of haploid tissue cultures
 Doubled haploid ramets via embryogenesis of haploid tissue cultures Harry E. Iswandar 1, J. M. Dunwell 2, Brian P. Forster 3, Stephen P. C. Nelson 1,4 and Peter D. S. Caligari,3,4,5 ABSTRACT Tissue culture
Doubled haploid ramets via embryogenesis of haploid tissue cultures Harry E. Iswandar 1, J. M. Dunwell 2, Brian P. Forster 3, Stephen P. C. Nelson 1,4 and Peter D. S. Caligari,3,4,5 ABSTRACT Tissue culture
Identification of factors involved in Xylem Cell Differentiation Aarush Mohit Mittal 1, 2
 Identification of factors involved in Xylem Cell Differentiation Aarush Mohit Mittal 1, 2 1 Department of Biological Sciences and Bio-Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur, India 2 Department
Identification of factors involved in Xylem Cell Differentiation Aarush Mohit Mittal 1, 2 1 Department of Biological Sciences and Bio-Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur, India 2 Department
GFP GAL bp 3964 bp
 Supplemental Data. Møller et al. (2009) Shoot Na + exclusion and increased salinity tolerance engineered by cell type-specific alteration of Na + transport in Arabidopsis Supplemental Figure 1. Salt-sensitive
Supplemental Data. Møller et al. (2009) Shoot Na + exclusion and increased salinity tolerance engineered by cell type-specific alteration of Na + transport in Arabidopsis Supplemental Figure 1. Salt-sensitive
Development of genetic transformation protocol for selected elite clone of Populus deltoides
 Development of genetic transformation protocol for selected elite clone of Populus deltoides A Dissertation Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirement for the award of the degree of Master of
Development of genetic transformation protocol for selected elite clone of Populus deltoides A Dissertation Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirement for the award of the degree of Master of
Supplemental Data. Wang et al. (2014). Plant Cell /tpc
 Supplemental Figure1: Mock and NPA-treated tomato plants. (A) NPA treated tomato (cv. Moneymaker) developed a pin-like inflorescence (arrowhead). (B) Comparison of first and second leaves from mock and
Supplemental Figure1: Mock and NPA-treated tomato plants. (A) NPA treated tomato (cv. Moneymaker) developed a pin-like inflorescence (arrowhead). (B) Comparison of first and second leaves from mock and
In Vitro Polyploid Induction of Ophiopogon planiscapus. Dominic A. Gillooly, Darren H. Touchell and Thomas G. Ranney
 In Vitro Polyploid Induction of Ophiopogon planiscapus Dominic A. Gillooly, Darren H. Touchell and Thomas G. Ranney North Carolina State University, Departement of Horticultural Science Mountain Crop Improvement
In Vitro Polyploid Induction of Ophiopogon planiscapus Dominic A. Gillooly, Darren H. Touchell and Thomas G. Ranney North Carolina State University, Departement of Horticultural Science Mountain Crop Improvement
State Forest Research Institute, Post Box No. 159, Itanagar , India 1 Department of Botany, Rajiv Gandhi University, Itanagar , India
 Indian Journal of Biotechnology Vol 6, April 2007, pp. 256-261 Effects of different culture media on seed germination and subsequent in vitro development of protocorms of Hygrochilus parishii (Veith &
Indian Journal of Biotechnology Vol 6, April 2007, pp. 256-261 Effects of different culture media on seed germination and subsequent in vitro development of protocorms of Hygrochilus parishii (Veith &
AGROBACTERIUM. First described by Smith and Townsend (1907) Responsible for crown gall. Performed Koch's postulates
 AGROBACTERIUM First described by Smith and Townsend (1907) Responsible for crown gall Performed Koch's postulates The disease is worldwide in distribution Speciation was based on pathogenicity Agrobacterium
AGROBACTERIUM First described by Smith and Townsend (1907) Responsible for crown gall Performed Koch's postulates The disease is worldwide in distribution Speciation was based on pathogenicity Agrobacterium
By Jonathan I. Watkinson. Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University. Doctor of Philosophy Horticulture
 Characterization of two genes, trehalose-6-phosphate synthase/phosphatase and nucleotide binding protein, shown to be differentially regulated in roots of Cypripedium parviflorum var. pubescens grown with
Characterization of two genes, trehalose-6-phosphate synthase/phosphatase and nucleotide binding protein, shown to be differentially regulated in roots of Cypripedium parviflorum var. pubescens grown with
By the end of this lesson, you should be able to
 Allelopathy 1 Allelopathy By the end of this lesson, you should be able to define allelopathy explain the difference between allelopathy and competition identify the key interactions in allelopathy provide
Allelopathy 1 Allelopathy By the end of this lesson, you should be able to define allelopathy explain the difference between allelopathy and competition identify the key interactions in allelopathy provide
SMALL AUXIN UP RNA (SAUR) genes are the largest class of primary auxin (growth
 Abstract SMALL AUXIN UP RNA (SAUR) genes are the largest class of primary auxin (growth hormone) responsive genes in all land plants, many of which are expressed in actively growing plant tissues. This
Abstract SMALL AUXIN UP RNA (SAUR) genes are the largest class of primary auxin (growth hormone) responsive genes in all land plants, many of which are expressed in actively growing plant tissues. This
COMPARATIVE STUDY OF VIABILITY MEASUREMENT METHODS IN CROP PLANTS
 Acta Agronomica Hungarica, 61(3), pp. 219 226 (2013) DOI: 10.1556/AAgr.61.2013.3.5 COMPARATIVE STUDY OF VIABILITY MEASUREMENT METHODS IN CROP PLANTS O. K. GONDOR, T. JANDA and G. SZALAI AGRICULTURAL INSTITUTE,
Acta Agronomica Hungarica, 61(3), pp. 219 226 (2013) DOI: 10.1556/AAgr.61.2013.3.5 COMPARATIVE STUDY OF VIABILITY MEASUREMENT METHODS IN CROP PLANTS O. K. GONDOR, T. JANDA and G. SZALAI AGRICULTURAL INSTITUTE,
Management of Root Knot Disease in Rice Caused by Meloidogyne graminicola through Nematophagous Fungi
 Management of Root Knot Disease in Rice Caused by Meloidogyne graminicola through Nematophagous Fungi Sobita Simon H.O.D., Plant Protection Department Allahabad Agricultural Institute, D.U. Post Box No.
Management of Root Knot Disease in Rice Caused by Meloidogyne graminicola through Nematophagous Fungi Sobita Simon H.O.D., Plant Protection Department Allahabad Agricultural Institute, D.U. Post Box No.
Factors Affecting the Infection of Vesicular Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi in Transformed Root Culture
 Factors Affecting the Infection of Vesicular Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi in Transformed Root Culture Poonpilai Suwanaritl, Savitri Ascharakul2, Omsub Nopamornbodi3 and Malee Suwana-adth4 I Department
Factors Affecting the Infection of Vesicular Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi in Transformed Root Culture Poonpilai Suwanaritl, Savitri Ascharakul2, Omsub Nopamornbodi3 and Malee Suwana-adth4 I Department
Cryopreservation of Ornamental Plants
 Cryopreservation of Ornamental Plants Adela Halmagyi Institute of Biological Research, branch of NIRDBS, Republicii str. 48, 400015 Cluj-Napoca, Romania Cryopreservation benefits for ornamental plants
Cryopreservation of Ornamental Plants Adela Halmagyi Institute of Biological Research, branch of NIRDBS, Republicii str. 48, 400015 Cluj-Napoca, Romania Cryopreservation benefits for ornamental plants
INTRODUCING PLANT TISSUE CULTURE IN THE CLASSROOM CONCEPTS & HISTORICAL PERSPECTIVE
 INTRODUCING PLANT TISSUE CULTURE IN THE CLASSROOM CONCEPTS & HISTORICAL PERSPECTIVE Dr. Mike Kane University of Florida Applications of Plant Tissue Culture Concepts & Terminology Micropropagation: A Historical
INTRODUCING PLANT TISSUE CULTURE IN THE CLASSROOM CONCEPTS & HISTORICAL PERSPECTIVE Dr. Mike Kane University of Florida Applications of Plant Tissue Culture Concepts & Terminology Micropropagation: A Historical
EXPRESSION OF THE FIS2 PROMOTER IN ARABIDOPSIS THALIANA
 EXPRESSION OF THE FIS2 PROMOTER IN ARABIDOPSIS THALIANA Item Type text; Electronic Thesis Authors Bergstrand, Lauren Janel Publisher The University of Arizona. Rights Copyright is held by the author. Digital
EXPRESSION OF THE FIS2 PROMOTER IN ARABIDOPSIS THALIANA Item Type text; Electronic Thesis Authors Bergstrand, Lauren Janel Publisher The University of Arizona. Rights Copyright is held by the author. Digital
MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2012 series 9700 BIOLOGY
 CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Advanced Subsidiary Level and GCE Advanced Level MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2012 series 9700 BIOLOGY 9700/51 Paper 5 (Planning, Analysis and Evaluation),
CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Advanced Subsidiary Level and GCE Advanced Level MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2012 series 9700 BIOLOGY 9700/51 Paper 5 (Planning, Analysis and Evaluation),
Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of wild type (WT) and abci8 mutant in the paddy field.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of wild type (WT) and abci8 mutant in the paddy field. A, Phenotypes of 30-day old wild-type (WT) and abci8 mutant plants grown in a paddy field under normal sunny
Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of wild type (WT) and abci8 mutant in the paddy field. A, Phenotypes of 30-day old wild-type (WT) and abci8 mutant plants grown in a paddy field under normal sunny
Effect of diazotrophs on the mineralization of organic nitrogen in the rhizosphere soils of rice (Oryza sativa)
 Journal of Crop and Weed 3(1) : 47-51 (7) Effect of diazotrophs on the mineralization of organic nitrogen in the rhizosphere soils of rice (Oryza sativa) A. C. DAS AND D. SAHA Department of Agricultural
Journal of Crop and Weed 3(1) : 47-51 (7) Effect of diazotrophs on the mineralization of organic nitrogen in the rhizosphere soils of rice (Oryza sativa) A. C. DAS AND D. SAHA Department of Agricultural
Genetic Transformation of Wheat Mediated by Agrobacterium tumefaciens
 Plant Physiol. () : - Genetic Transformation of Wheat Mediated by Agrobacterium tumefaciens Ming Cheng*, Joyce E. Fry, Shengzhi Pang, Huaping Zhou, Catherine M. Hironaka, David R. Duncan, Timothy W. Conner,
Plant Physiol. () : - Genetic Transformation of Wheat Mediated by Agrobacterium tumefaciens Ming Cheng*, Joyce E. Fry, Shengzhi Pang, Huaping Zhou, Catherine M. Hironaka, David R. Duncan, Timothy W. Conner,
M.Sc. Botany (Previous ) DEGREE EXAMINATION, MAY First Year
 1 ( DBOT 01 ) M.Sc. Botany (Previous ) DEGREE EXAMINATION, MAY 2007. First Year Paper I BIOLOGY AND DIVERSITY OF ALGAE, BRYOPHYTES, PTERIDOPHYTES AND GYMNOSPERMS Answer ALL questions from Section B. 1.
1 ( DBOT 01 ) M.Sc. Botany (Previous ) DEGREE EXAMINATION, MAY 2007. First Year Paper I BIOLOGY AND DIVERSITY OF ALGAE, BRYOPHYTES, PTERIDOPHYTES AND GYMNOSPERMS Answer ALL questions from Section B. 1.
Other funding Sources Agency Name: MSU Agricultural Experiment Station /Project GREEEN Amount requested or awarded: 30,000
 FINAL PROJECT REPORT Project Title: Functional genomics of flowering in apple PI: Herb Aldwinckle Co-PI(2): Steve VanNocker Organization: Cornell University Organization: Michigan State University Telephone/email:
FINAL PROJECT REPORT Project Title: Functional genomics of flowering in apple PI: Herb Aldwinckle Co-PI(2): Steve VanNocker Organization: Cornell University Organization: Michigan State University Telephone/email:
RNAi Suppression of AGAMOUS-like Genes Causes Field Sterility in Populus
 RNAi Suppression of AGAMOUS-like Genes Causes Field Sterility in Populus Haiwei Lu and Steven H. Strauss Oregon State University Forest Tree Workshop PAG XXVI, San Diego, CA, 2018 The containment issue
RNAi Suppression of AGAMOUS-like Genes Causes Field Sterility in Populus Haiwei Lu and Steven H. Strauss Oregon State University Forest Tree Workshop PAG XXVI, San Diego, CA, 2018 The containment issue
Received 23 July 2014; received in revised form 25 October 2014; accepted 14 November 2014.
 Journal of Tropical Agriculture 52 (2) : 149-153, 2014 149 Short Communication Genetic transformation in Artemesia annua L. for hairy root induction and enhancement of secondary metabolites V.M. Shaneeja*,
Journal of Tropical Agriculture 52 (2) : 149-153, 2014 149 Short Communication Genetic transformation in Artemesia annua L. for hairy root induction and enhancement of secondary metabolites V.M. Shaneeja*,
POTASSIUM IN PLANT GROWTH AND YIELD. by Ismail Cakmak Sabanci University Istanbul, Turkey
 POTASSIUM IN PLANT GROWTH AND YIELD by Ismail Cakmak Sabanci University Istanbul, Turkey Low K High K High K Low K Low K High K Low K High K Control K Deficiency Cakmak et al., 1994, J. Experimental Bot.
POTASSIUM IN PLANT GROWTH AND YIELD by Ismail Cakmak Sabanci University Istanbul, Turkey Low K High K High K Low K Low K High K Low K High K Control K Deficiency Cakmak et al., 1994, J. Experimental Bot.
Heterosis and inbreeding depression of epigenetic Arabidopsis hybrids
 Heterosis and inbreeding depression of epigenetic Arabidopsis hybrids Plant growth conditions The soil was a 1:1 v/v mixture of loamy soil and organic compost. Initial soil water content was determined
Heterosis and inbreeding depression of epigenetic Arabidopsis hybrids Plant growth conditions The soil was a 1:1 v/v mixture of loamy soil and organic compost. Initial soil water content was determined
Using Crossbreeding and Hybrids
 Lesson C2 5 Using Crossbreeding and Hybrids Unit C. Plant and Soil Science Problem Area 2. Basic Principles of Plant Science Lesson 5. Using Crossbreeding and Hybrids New Mexico Content Standard: Pathway
Lesson C2 5 Using Crossbreeding and Hybrids Unit C. Plant and Soil Science Problem Area 2. Basic Principles of Plant Science Lesson 5. Using Crossbreeding and Hybrids New Mexico Content Standard: Pathway
Efficient plant regeneration via somatic embryogenesis from anthers of Datura stramonium L.
 Available online http://www.ijat-rmutto.com Journal of Agricultural Technology 2010 Vol. ISSN 6(4): 1686-9141 741-745 Efficient plant regeneration via somatic embryogenesis from anthers of Datura stramonium
Available online http://www.ijat-rmutto.com Journal of Agricultural Technology 2010 Vol. ISSN 6(4): 1686-9141 741-745 Efficient plant regeneration via somatic embryogenesis from anthers of Datura stramonium
Introduction. Phylogeny. Taxonomy
 jim_3-1-4.fm Page 91 Thursday, October 6, 2005 5:19 PM CHAPTER 3.1.4 eth sun Ge um i retcabor Ag The Genus Agrobacterium ANN G. MATTHYSSE Introduction The genus Agrobacterium is a group of Gramnegative
jim_3-1-4.fm Page 91 Thursday, October 6, 2005 5:19 PM CHAPTER 3.1.4 eth sun Ge um i retcabor Ag The Genus Agrobacterium ANN G. MATTHYSSE Introduction The genus Agrobacterium is a group of Gramnegative
The Relationship between SPAD Values and Leaf Blade Chlorophyll Content throughout the Rice Development Cycle
 JARQ 50 (4), 329-334 (2016) http://www.jircas.affrc.go.jp The Relationship between SPAD Values and Leaf Blade Chlorophyll Content throughout the Rice Development Cycle Yasuyuki WAKIYAMA* National Agriculture
JARQ 50 (4), 329-334 (2016) http://www.jircas.affrc.go.jp The Relationship between SPAD Values and Leaf Blade Chlorophyll Content throughout the Rice Development Cycle Yasuyuki WAKIYAMA* National Agriculture
Agrobacterium tumefaciens transformation genetic transformation of banana
 84 Agrobacterium tumefaciens transformation genetic transformation of banana EFFECTS OF VARIOUS VIRULENT STRAINS OF Agrobacterium tumefaciens ON GENETIC TRANSFORMATION OF BANANA (Musa sp.) CULTIVAR WILLIAMS
84 Agrobacterium tumefaciens transformation genetic transformation of banana EFFECTS OF VARIOUS VIRULENT STRAINS OF Agrobacterium tumefaciens ON GENETIC TRANSFORMATION OF BANANA (Musa sp.) CULTIVAR WILLIAMS
(17) CYCLANILIDE: MECHANISM OF ACTION AND USES AS A PLANT GROWTH REGULATOR IN COTTON
 (17) CYCLANILIDE: MECHANISM OF ACTION AND USES AS A PLANT GROWTH REGULATOR IN COTTON Jim Burton 1 and Marianne Pedersen Abstract. Cyclanilide [1-(2,4-dichlorophenylaminocarbonyl)-cyclopropane carboxylic
(17) CYCLANILIDE: MECHANISM OF ACTION AND USES AS A PLANT GROWTH REGULATOR IN COTTON Jim Burton 1 and Marianne Pedersen Abstract. Cyclanilide [1-(2,4-dichlorophenylaminocarbonyl)-cyclopropane carboxylic
Transitivity-dependent and transitivity-independent cell-to-cell movement of RNA
 Himber et al. Transitivity-dependent and transitivity-independent cell-to-cell movement of RNA silencing SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Supplemental material 1. Short-range movement of GFP silencing affects a nearly
Himber et al. Transitivity-dependent and transitivity-independent cell-to-cell movement of RNA silencing SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Supplemental material 1. Short-range movement of GFP silencing affects a nearly
The impact of Agrobacterium tumefaciens and other soil borne disease causing agents of economic importance in production of roses
 The impact of Agrobacterium tumefaciens and other soil borne disease causing agents of economic importance in production of roses Video conference on global competitiveness of the flower industry in the
The impact of Agrobacterium tumefaciens and other soil borne disease causing agents of economic importance in production of roses Video conference on global competitiveness of the flower industry in the
tumefaciens Attachment to Zea mays, Gladiolus sp.,
 JOURNAL OF BACTERIOLOGY, May 1988, p. 2395-2400 Vol. 170, No. 5 0021-9193/88/052395-06$02.00/0 Copyright 1988, American Society for Microbiology Scanning Electron Microscope Studies of Agrobacterium tumefaciens
JOURNAL OF BACTERIOLOGY, May 1988, p. 2395-2400 Vol. 170, No. 5 0021-9193/88/052395-06$02.00/0 Copyright 1988, American Society for Microbiology Scanning Electron Microscope Studies of Agrobacterium tumefaciens
North American Bramble Growers Research Foundation 2016 Report. Fire Blight: An Emerging Problem for Blackberry Growers in the Mid-South
 North American Bramble Growers Research Foundation 2016 Report Fire Blight: An Emerging Problem for Blackberry Growers in the Mid-South Principal Investigator: Burt Bluhm University of Arkansas Department
North American Bramble Growers Research Foundation 2016 Report Fire Blight: An Emerging Problem for Blackberry Growers in the Mid-South Principal Investigator: Burt Bluhm University of Arkansas Department
Segregation distortion in F 2 and doubled haploid populations of temperate japonica rice
 c Indian Academy of Sciences RESEARCH NOTE Segregation distortion in F 2 and doubled haploid populations of temperate japonica rice MASUMI YAMAGISHI 1,2,6, YOSHINOBU TAKEUCHI 3,7, ISAO TANAKA 4, IZUMI
c Indian Academy of Sciences RESEARCH NOTE Segregation distortion in F 2 and doubled haploid populations of temperate japonica rice MASUMI YAMAGISHI 1,2,6, YOSHINOBU TAKEUCHI 3,7, ISAO TANAKA 4, IZUMI
NORTHERN ILLINOIS UNIVERSITY. Screening of Chemical Libraries in Search of Inhibitors of Aflatoxin Biosynthesis. A Thesis Submitted to the
 NORTHERN ILLINOIS UNIVERSITY Screening of Chemical Libraries in Search of Inhibitors of Aflatoxin Biosynthesis A Thesis Submitted to the University Honors Program In Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements
NORTHERN ILLINOIS UNIVERSITY Screening of Chemical Libraries in Search of Inhibitors of Aflatoxin Biosynthesis A Thesis Submitted to the University Honors Program In Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements
The sucrose non-fermenting-1-related protein kinases SAPK1 and SAPK2 function collaboratively as positive regulators of salt stress tolerance in rice
 Lou et al. BMC Plant Biology (2018) 18:203 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-018-1408-0 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access The sucrose non-fermenting-1-related protein kinases SAPK1 and SAPK2 function collaboratively
Lou et al. BMC Plant Biology (2018) 18:203 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-018-1408-0 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access The sucrose non-fermenting-1-related protein kinases SAPK1 and SAPK2 function collaboratively
