Genetic Basis of Variation in Bacteria
|
|
|
- Anastasia Logan
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Mechanisms of Infectious Disease Fall 2009 Genetics I Jonathan Dworkin, PhD Department of Microbiology jonathan.dworkin@columbia.edu Genetic Basis of Variation in Bacteria I. Organization of genetic material in bacteria a. chromosomes b. plasmids II. Genetic variation: Source a. point mutation b. DNA rearrangements III. Genetic variation: Transmission a. transformation b. transduction c. conjugation IV. Genetic variation: Implications for pathogenesis
2 Genetic Basis of Variation in Bacteria I. Organization of genetic material in bacteria a. chromosomes b. plasmids II. Genetic variation: Source a. point mutation b. DNA rearrangements III. Genetic variation: Transmission a. transformation b. transduction c. conjugation IV. Genetic variation: Implications for pathogenesis Genetic Basis of Variation in Bacteria I. Organization of genetic material in bacteria a. chromosomes b. plasmids II. Genetic variation: Source a. point mutations b. DNA rearrangements III. Genetic variation: Transmission a. transformation b. transduction c. conjugation IV. Genetic variation: Implications for pathogenesis
3 Genetic Basis of Variation in Bacteria I. Organization of genetic material in bacteria a. chromosomes b. plasmids II. Genetic variation: Source a. point mutations b. DNA rearrangements III. Genetic variation: Transmission a. transformation b. transduction c. conjugation IV. Genetic variation: Implications for pathogenesis Genetic Basis of Variation in Bacteria I. Organization of genetic material in bacteria a. chromosomes b. plasmids II. Genetic variation: Source a. point mutations b. DNA rearrangements III. Genetic variation: Transmission a. transformation b. transduction c. conjugation IV. Genetic variation: Implications for pathogenesis
4 Genetic basis of variation: Griffiths (1928) Genetic basis of variation: Griffiths (1928)
5 Genetic basis of variation: Avery et al. (1944) Genetic basis of variation: Hershey and Chase (1952)
6 Genetic Basis of Variation in Bacteria I. Organization of genetic material in bacteria a. chromosomes b. plasmids II. Genetic variation: Source a. point mutation b. DNA rearrangements III. Genetic variation: Transmission a. transformation b. transduction c. conjugation IV. Genetic variation: Implications for pathogenesis Organization of genetic material in bacteria: chromosomes Most bacteria contain a single chromosome (+ extrachromosomal elements) Some bacteria have been found also to contain 2-3 replicons which can be considered either megaplasmids or minichromosomes e.g. 3.0 Mb and 0.9 Mb replicons in Rhodobacter sphaeroides A few bacterial genera contain >1 chromosome e.g. 2.1 Mb and 1.2 Mb chromosomes in Brucella Some bacteria harbour large replicons essential for survival in a specific ecological niche but not under laboratory conditions e.g. 1.4 Mb and 1.7 Mb replicons in Rhizobium meliloti are required for plant symbiosis
7 Organization of genetic material in bacteria: chromosomes Organization of genetic material in bacteria: chromosomes Copyright 2004 by the National Academy of Sciences
8 Organization of genetic material in bacteria: plasmids Extrachromosomal Circular or linear 2 kb to hundreds of kb in size Non-essential May carry supplemental genetic information or may be cryptic Employ host functions for most of DNA metabolism Chromosome Plasmid Organization of genetic material in bacteria: plasmids Virulence Replication Maintenance Transfer Antibioticresistance
9 Organization of genetic material in bacteria: plasmids Transposon genes Replication and maintenance Antibiotic resistance Other Organization of genetic material in bacteria: plasmids Examples of naturally-occuring plasmids and relevant features Plasmid Host Plasmid size (kb) Relevant feature pt181 Staphylococcus aureus 4.4 Tetracycline resistance ColE1 Escherichia coli 6.6 Colicin production and immunity pgkl2 Kluyveromyces lactis b 13.5 Killer plasmid pamβ1 Enterococcus faecalis 26.0 Erythromycin resistance psk41 Staphylococcus aureus 46.4 Multidrug resistance pbm4000 Bacillus megaterium 53.0 rrna operon pi258 Staphylococcus aureus 28.0 Metal ion resistance pslt Salmonella enterica subsp. typhimurium 93.9 Virulence determinants pmt1 Yersinia pestis Virulence determinants padp-1 Pseudomonas sp Atrazine (herbicide) catabolism pww0 Pseudomonas putida Aromatic hydrocarbon degradation pbtoxis Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis Mosquito larval toxicity px01 Bacillus anthracis Exotoxin production psol1 Clostridium acetobutylicum Solvent production psymb Sinorhizobium meliloti Functions associated with plant symbiosis
10 Genetic Basis of Variation in Bacteria I. Organization of genetic material in bacteria a. chromosomes b. plasmids II. Genetic variation: Source a. point mutations b. DNA rearrangements III. Genetic variation: Transmission a. transformation b. transduction c. conjugation IV. Genetic variation: Implications for pathogenesis Sources of genetic variation: point mutations
11 Sources of genetic variation: point mutations Sources of genetic variation: point mutations
12 Sources of genetic variation: DNA rearrangements Insertion sequence (IS) elements: 1. Simplest type of transposable element found in bacterial chromosomes and plasmids. 2. Encode only genes for mobilization and insertion. 3. Range in size from 768 bp to 5 kb. 4. IS1 first identified in E. coli s glactose operon is 768 bp long and is present with 4-19 copies in the E. coli chromosome. 5. Ends of all known IS elements show inverted terminal repeats (ITRs). Sources of genetic variation: DNA rearrangements Integration of IS element in chromosomal DNA.
13 Sources of genetic variation: DNA rearrangements Sources of genetic variation: DNA rearrangements
14 Sources of genetic variation: frequency of occurrence Genetic Basis of Variation in Bacteria I. Organization of genetic material in bacteria a. chromosomes b. plasmids II. Genetic variation: Source a. point mutations b. DNA rearrangements III. Genetic variation: Transmission a. transformation b. transduction c. conjugation IV. Genetic variation: Implications for pathogenesis
15 Transmission of genetic variation Lengths of bars denote the amount of protein-coding DNA. For each bar, the native DNA is blue; foreign DNA identifiable as mobile elements, including transposons and bacteriophages, is yellow, and other foreign DNA is red. The percentage of foreign DNA is noted to the right of each bar. 'A' denotes an Archaeal genome.
16 Transmission of genetic variation: antibiotic resistance V. M. D'Costa et al. Science (2006) Fig. 1. Antibiotic resistance profiling of 480 soil-derived bacterial isolates Transmission of genetic variation: pathogenesis
17 Transmission of genetic variation: Luria-Delbruck test Transmission of genetic variation: Luria-Delbruck test
18 Transmission of genetic variation: Luria-Delbruck test Linear transmission of genetic variation
19 Horizontal transmission of genetic variation Transmission of genetic variation: mechanisms
20 Transmission of genetic variation: transformation Transmission of genetic variation: transformation Gene transfer resulting from the uptake of DNA from a donor. g p Factors affecting transformation DNA size and state Sensitive to nucleases Competence of the recipient (Bacillus, Haemophilus, Neisseria, Streptococcus) Competence factor Induced competence
21 Transmission of genetic variation: transformation Transmission of genetic variation: transformation
22 Transmission of genetic variation: transformation Transmission of genetic variation: mechanisms
23 Genetic Basis of Variation in Bacteria I. Organization of genetic material in bacteria a. chromosomes b. plasmids II. Genetic variation: Source a. point mutation b. DNA rearrangements III. Genetic variation: Transmission a. transformation b. transduction c. conjugation IV. Genetic variation: Implications for pathogenesis Genetic Basis of Variation in Bacteria I. Organization of genetic material in bacteria a. chromosomes b. plasmids II. Genetic variation: Source a. point mutations b. DNA rearrangements III. Genetic variation: Transmission a. transformation b. transduction c. conjugation IV. Genetic variation: Implications for pathogenesis
24 Genetic Basis of Variation in Bacteria I. Organization of genetic material in bacteria a. chromosomes b. plasmids II. Genetic variation: Source a. point mutations b. DNA rearrangements III. Genetic variation: Transmission a. transformation b. transduction c. conjugation IV. Genetic variation: Implications for pathogenesis
Gene expression in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, Plasmids: types, maintenance and functions. Mitesh Shrestha
 Gene expression in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, Plasmids: types, maintenance and functions. Mitesh Shrestha Plasmids 1. Extrachromosomal DNA, usually circular-parasite 2. Usually encode ancillary
Gene expression in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, Plasmids: types, maintenance and functions. Mitesh Shrestha Plasmids 1. Extrachromosomal DNA, usually circular-parasite 2. Usually encode ancillary
9/8/2017. Bacteria and Archaea. Three domain system: The present tree of life. Structural and functional adaptations contribute to prokaryotic success
 5 m 2 m 9/8/2017 Three domain system: The present tree of life Bacteria and Archaea Chapter 27 Structural and functional adaptations contribute to prokaryotic success Unicellular Small Variety of shapes
5 m 2 m 9/8/2017 Three domain system: The present tree of life Bacteria and Archaea Chapter 27 Structural and functional adaptations contribute to prokaryotic success Unicellular Small Variety of shapes
Bacterial Genetics & Operons
 Bacterial Genetics & Operons The Bacterial Genome Because bacteria have simple genomes, they are used most often in molecular genetics studies Most of what we know about bacterial genetics comes from the
Bacterial Genetics & Operons The Bacterial Genome Because bacteria have simple genomes, they are used most often in molecular genetics studies Most of what we know about bacterial genetics comes from the
The Evolution of Infectious Disease
 The Evolution of Infectious Disease Why are some bacteria pathogenic to humans while other (closely-related) bacteria are not? This question can be approached from two directions: 1.From the point of view
The Evolution of Infectious Disease Why are some bacteria pathogenic to humans while other (closely-related) bacteria are not? This question can be approached from two directions: 1.From the point of view
Biology 105/Summer Bacterial Genetics 8/12/ Bacterial Genomes p Gene Transfer Mechanisms in Bacteria p.
 READING: 14.2 Bacterial Genomes p. 481 14.3 Gene Transfer Mechanisms in Bacteria p. 486 Suggested Problems: 1, 7, 13, 14, 15, 20, 22 BACTERIAL GENETICS AND GENOMICS We still consider the E. coli genome
READING: 14.2 Bacterial Genomes p. 481 14.3 Gene Transfer Mechanisms in Bacteria p. 486 Suggested Problems: 1, 7, 13, 14, 15, 20, 22 BACTERIAL GENETICS AND GENOMICS We still consider the E. coli genome
Microbial Genetics, Mutation and Repair. 2. State the function of Rec A proteins in homologous genetic recombination.
 Answer the following questions 1. Define genetic recombination. Microbial Genetics, Mutation and Repair 2. State the function of Rec A proteins in homologous genetic recombination. 3. List 3 types of bacterial
Answer the following questions 1. Define genetic recombination. Microbial Genetics, Mutation and Repair 2. State the function of Rec A proteins in homologous genetic recombination. 3. List 3 types of bacterial
The two daughter cells are genetically identical to each other and the parent cell.
 Prokaryote Growth and Reproduction This micrograph shows a bacillus bacteria (probably E. coli) undergoing binary fission. This is a form of asexual reproduction. During prokaryotic binary fission, as
Prokaryote Growth and Reproduction This micrograph shows a bacillus bacteria (probably E. coli) undergoing binary fission. This is a form of asexual reproduction. During prokaryotic binary fission, as
Chapter 27: Bacteria and Archaea
 Name Period Overview 1. The chapter opens with amazing tales of life at the extreme edge. What are the masters of adaptation? Describe the one case you thought most dramatic. Concept 27.1 Structural and
Name Period Overview 1. The chapter opens with amazing tales of life at the extreme edge. What are the masters of adaptation? Describe the one case you thought most dramatic. Concept 27.1 Structural and
CHAPTER : Prokaryotic Genetics
 CHAPTER 13.3 13.5: Prokaryotic Genetics 1. Most bacteria are not pathogenic. Identify several important roles they play in the ecosystem and human culture. 2. How do variations arise in bacteria considering
CHAPTER 13.3 13.5: Prokaryotic Genetics 1. Most bacteria are not pathogenic. Identify several important roles they play in the ecosystem and human culture. 2. How do variations arise in bacteria considering
Genetic Variation: The genetic substrate for natural selection. Horizontal Gene Transfer. General Principles 10/2/17.
 Genetic Variation: The genetic substrate for natural selection What about organisms that do not have sexual reproduction? Horizontal Gene Transfer Dr. Carol E. Lee, University of Wisconsin In prokaryotes:
Genetic Variation: The genetic substrate for natural selection What about organisms that do not have sexual reproduction? Horizontal Gene Transfer Dr. Carol E. Lee, University of Wisconsin In prokaryotes:
Vital Statistics Derived from Complete Genome Sequencing (for E. coli MG1655)
 We still consider the E. coli genome as a fairly typical bacterial genome, and given the extensive information available about this organism and it's lifestyle, the E. coli genome is a useful point of
We still consider the E. coli genome as a fairly typical bacterial genome, and given the extensive information available about this organism and it's lifestyle, the E. coli genome is a useful point of
Bio 119 Bacterial Genomics 6/26/10
 BACTERIAL GENOMICS Reading in BOM-12: Sec. 11.1 Genetic Map of the E. coli Chromosome p. 279 Sec. 13.2 Prokaryotic Genomes: Sizes and ORF Contents p. 344 Sec. 13.3 Prokaryotic Genomes: Bioinformatic Analysis
BACTERIAL GENOMICS Reading in BOM-12: Sec. 11.1 Genetic Map of the E. coli Chromosome p. 279 Sec. 13.2 Prokaryotic Genomes: Sizes and ORF Contents p. 344 Sec. 13.3 Prokaryotic Genomes: Bioinformatic Analysis
By Eliza Bielak Bacterial Genomics and Epidemiology, DTU-Food Supervised by Henrik Hasman, PhD
 By Eliza Bielak Bacterial Genomics and Epidemiology, DTU-Food elibi@food.dtu.dk Supervised by Henrik Hasman, PhD 1. Introduction to plasmid biology 2. Plasmid encoded resistance to β- lactams (basic theories)
By Eliza Bielak Bacterial Genomics and Epidemiology, DTU-Food elibi@food.dtu.dk Supervised by Henrik Hasman, PhD 1. Introduction to plasmid biology 2. Plasmid encoded resistance to β- lactams (basic theories)
Horizontal transfer and pathogenicity
 Horizontal transfer and pathogenicity Victoria Moiseeva Genomics, Master on Advanced Genetics UAB, Barcelona, 2014 INDEX Horizontal Transfer Horizontal gene transfer mechanisms Detection methods of HGT
Horizontal transfer and pathogenicity Victoria Moiseeva Genomics, Master on Advanced Genetics UAB, Barcelona, 2014 INDEX Horizontal Transfer Horizontal gene transfer mechanisms Detection methods of HGT
Fitness constraints on horizontal gene transfer
 Fitness constraints on horizontal gene transfer Dan I Andersson University of Uppsala, Department of Medical Biochemistry and Microbiology, Uppsala, Sweden GMM 3, 30 Aug--2 Sep, Oslo, Norway Acknowledgements:
Fitness constraints on horizontal gene transfer Dan I Andersson University of Uppsala, Department of Medical Biochemistry and Microbiology, Uppsala, Sweden GMM 3, 30 Aug--2 Sep, Oslo, Norway Acknowledgements:
Ti plasmid derived plant vector systems: binary and co - integrative vectors transformation process; regeneration of the transformed lines
 Ti plasmid derived plant vector systems: binary and co - integrative vectors transformation process; regeneration of the transformed lines Mitesh Shrestha Constraints of Wild type Ti/Ri-plasmid Very large
Ti plasmid derived plant vector systems: binary and co - integrative vectors transformation process; regeneration of the transformed lines Mitesh Shrestha Constraints of Wild type Ti/Ri-plasmid Very large
AP Bio Module 16: Bacterial Genetics and Operons, Student Learning Guide
 Name: Period: Date: AP Bio Module 6: Bacterial Genetics and Operons, Student Learning Guide Getting started. Work in pairs (share a computer). Make sure that you log in for the first quiz so that you get
Name: Period: Date: AP Bio Module 6: Bacterial Genetics and Operons, Student Learning Guide Getting started. Work in pairs (share a computer). Make sure that you log in for the first quiz so that you get
C. elegans as an in vivo model to decipher microbial virulence. Centre d Immunologie de Marseille-Luminy
 C. elegans as an in vivo model to decipher microbial virulence Centre d Immunologie de Marseille-Luminy C. elegans : a model organism Mechanisms of apoptosis, RNA interference Neuronal function and development
C. elegans as an in vivo model to decipher microbial virulence Centre d Immunologie de Marseille-Luminy C. elegans : a model organism Mechanisms of apoptosis, RNA interference Neuronal function and development
A pathogen is an agent or microrganism that causes a disease in its host. Pathogens can be viruses, bacteria, fungi or protozoa.
 1 A pathogen is an agent or microrganism that causes a disease in its host. Pathogens can be viruses, bacteria, fungi or protozoa. Protozoa are single celled eukaryotic organisms. Some protozoa are pathogens.
1 A pathogen is an agent or microrganism that causes a disease in its host. Pathogens can be viruses, bacteria, fungi or protozoa. Protozoa are single celled eukaryotic organisms. Some protozoa are pathogens.
2. What was the Avery-MacLeod-McCarty experiment and why was it significant? 3. What was the Hershey-Chase experiment and why was it significant?
 Name Date Period AP Exam Review Part 6: Molecular Genetics I. DNA and RNA Basics A. History of finding out what DNA really is 1. What was Griffith s experiment and why was it significant? 1 2. What was
Name Date Period AP Exam Review Part 6: Molecular Genetics I. DNA and RNA Basics A. History of finding out what DNA really is 1. What was Griffith s experiment and why was it significant? 1 2. What was
HORIZONTAL TRANSFER IN EUKARYOTES KIMBERLEY MC GRAIL FERNÁNDEZ GENOMICS
 HORIZONTAL TRANSFER IN EUKARYOTES KIMBERLEY MC GRAIL FERNÁNDEZ GENOMICS OVERVIEW INTRODUCTION MECHANISMS OF HGT IDENTIFICATION TECHNIQUES EXAMPLES - Wolbachia pipientis - Fungus - Plants - Drosophila ananassae
HORIZONTAL TRANSFER IN EUKARYOTES KIMBERLEY MC GRAIL FERNÁNDEZ GENOMICS OVERVIEW INTRODUCTION MECHANISMS OF HGT IDENTIFICATION TECHNIQUES EXAMPLES - Wolbachia pipientis - Fungus - Plants - Drosophila ananassae
Essentiality in B. subtilis
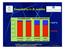 Essentiality in B. subtilis 100% 75% Essential genes Non-essential genes Lagging 50% 25% Leading 0% non-highly expressed highly expressed non-highly expressed highly expressed 1 http://www.pasteur.fr/recherche/unites/reg/
Essentiality in B. subtilis 100% 75% Essential genes Non-essential genes Lagging 50% 25% Leading 0% non-highly expressed highly expressed non-highly expressed highly expressed 1 http://www.pasteur.fr/recherche/unites/reg/
Obligate anaerobes - cannot grow in the presence of oxygen Facultative anaerobes - can grow with or without oxygen Aerobic - require oxygen
 PROKARYOTES *include bacteria and archaea *singular: bacterium / plural: bacteria PROPERTIES 1. Bacteria are classified into two kingdoms: Eubacteria (true bacteria) and Archaebacteria (Ancient Bacteria).
PROKARYOTES *include bacteria and archaea *singular: bacterium / plural: bacteria PROPERTIES 1. Bacteria are classified into two kingdoms: Eubacteria (true bacteria) and Archaebacteria (Ancient Bacteria).
MICROBIAL BIOCHEMISTRY BIOT 309. Dr. Leslye Johnson Sept. 30, 2012
 MICROBIAL BIOCHEMISTRY BIOT 309 Dr. Leslye Johnson Sept. 30, 2012 Phylogeny study of evoluhonary relatedness among groups of organisms (e.g. species, populahons), which is discovered through molecular
MICROBIAL BIOCHEMISTRY BIOT 309 Dr. Leslye Johnson Sept. 30, 2012 Phylogeny study of evoluhonary relatedness among groups of organisms (e.g. species, populahons), which is discovered through molecular
Chapter 19. Gene creatures, Part 1: viruses, viroids and plasmids. Prepared by Woojoo Choi
 Chapter 19. Gene creatures, Part 1: viruses, viroids and plasmids Prepared by Woojoo Choi Dead or alive? 1) In this chapter we will explore the twilight zone of biology and the gene creature who live there.
Chapter 19. Gene creatures, Part 1: viruses, viroids and plasmids Prepared by Woojoo Choi Dead or alive? 1) In this chapter we will explore the twilight zone of biology and the gene creature who live there.
DNA Technology, Bacteria, Virus and Meiosis Test REVIEW
 Be prepared to turn in a completed test review before your test. In addition to the questions below you should be able to make and analyze a plasmid map. Prokaryotic Gene Regulation 1. What is meant by
Be prepared to turn in a completed test review before your test. In addition to the questions below you should be able to make and analyze a plasmid map. Prokaryotic Gene Regulation 1. What is meant by
Assist. Prof. Martina Šeruga Musić acad. year 2016/17
 Assist. Prof. Martina Šeruga Musić acad. year 2016/17 PHYTOPATHOGENIC BACTERIA there are more than 100 species of known phytopathogenic bacteria genera Agrobacterium, Erwinia, Ralstonia, Pseudomonas, Xanthomonas,
Assist. Prof. Martina Šeruga Musić acad. year 2016/17 PHYTOPATHOGENIC BACTERIA there are more than 100 species of known phytopathogenic bacteria genera Agrobacterium, Erwinia, Ralstonia, Pseudomonas, Xanthomonas,
INTERPRETATION OF THE GRAM STAIN
 INTERPRETATION OF THE GRAM STAIN DISCLOSURE Relevant relationships with commercial entities none Potential for conflicts of interest within this presentation none Steps taken to review and mitigate potential
INTERPRETATION OF THE GRAM STAIN DISCLOSURE Relevant relationships with commercial entities none Potential for conflicts of interest within this presentation none Steps taken to review and mitigate potential
Shape, Arrangement, and Size. Cocci (s., coccus) bacillus (pl., bacilli) 9/21/2013
 Shape, Arrangement, and Size Cocci (s., coccus) are roughly spherical cells. The other common shape is that of a rod, sometimes called a bacillus (pl., bacilli). Spiral-shaped procaryotes can be either
Shape, Arrangement, and Size Cocci (s., coccus) are roughly spherical cells. The other common shape is that of a rod, sometimes called a bacillus (pl., bacilli). Spiral-shaped procaryotes can be either
Introduction to Molecular and Cell Biology
 Introduction to Molecular and Cell Biology Molecular biology seeks to understand the physical and chemical basis of life. and helps us answer the following? What is the molecular basis of disease? What
Introduction to Molecular and Cell Biology Molecular biology seeks to understand the physical and chemical basis of life. and helps us answer the following? What is the molecular basis of disease? What
Microbial Typing by Machine Learned DNA Melt Signatures
 Microbial Typing by Machine Learned DNA Melt Signatures Nadya Andini 1, Bo Wang 2, Pornpat Athamanolap 3, Justin Hardick 4, Billie J. Masek 5, Simone Thair 1, Annie Hu 1, Gideon Avornu 5, Stephen Peterson
Microbial Typing by Machine Learned DNA Melt Signatures Nadya Andini 1, Bo Wang 2, Pornpat Athamanolap 3, Justin Hardick 4, Billie J. Masek 5, Simone Thair 1, Annie Hu 1, Gideon Avornu 5, Stephen Peterson
2012 Univ Aguilera Lecture. Introduction to Molecular and Cell Biology
 2012 Univ. 1301 Aguilera Lecture Introduction to Molecular and Cell Biology Molecular biology seeks to understand the physical and chemical basis of life. and helps us answer the following? What is the
2012 Univ. 1301 Aguilera Lecture Introduction to Molecular and Cell Biology Molecular biology seeks to understand the physical and chemical basis of life. and helps us answer the following? What is the
Topology. 1 Introduction. 2 Chromosomes Topology & Counts. 3 Genome size. 4 Replichores and gene orientation. 5 Chirochores.
 Topology 1 Introduction 2 3 Genome size 4 Replichores and gene orientation 5 Chirochores 6 G+C content 7 Codon usage 27 marc.bailly-bechet@univ-lyon1.fr The big picture Eukaryota Bacteria Many linear chromosomes
Topology 1 Introduction 2 3 Genome size 4 Replichores and gene orientation 5 Chirochores 6 G+C content 7 Codon usage 27 marc.bailly-bechet@univ-lyon1.fr The big picture Eukaryota Bacteria Many linear chromosomes
Ecology of Infectious Disease
 Ecology of Infectious Disease What is the basis of community robustness (resistance to invasion)? How does robustness influence disease development? The Microbial Context: Microbial Interactions Affect
Ecology of Infectious Disease What is the basis of community robustness (resistance to invasion)? How does robustness influence disease development? The Microbial Context: Microbial Interactions Affect
Characteristics. Nucleoid Region single circular chromosome plasmids mesosome
 Prokaryotes Characteristics Nucleoid Region single circular chromosome plasmids mesosome No membranebound organelles Ribosomes (70S) Plasma membrane Cell wall peptidoglycan Capsule glycocalyx Flagella
Prokaryotes Characteristics Nucleoid Region single circular chromosome plasmids mesosome No membranebound organelles Ribosomes (70S) Plasma membrane Cell wall peptidoglycan Capsule glycocalyx Flagella
TER 26. Preview for 2/6/02 Dr. Kopeny. Bacteria and Archaea: The Prokaryotic Domains. Nitrogen cycle
 Preview for 2/6/02 Dr. Kopeny Bacteria and Archaea: The Prokaryotic Domains TER 26 Nitrogen cycle Mycobacterium tuberculosis Color-enhanced images shows rod-shaped bacterium responsible for tuberculosis
Preview for 2/6/02 Dr. Kopeny Bacteria and Archaea: The Prokaryotic Domains TER 26 Nitrogen cycle Mycobacterium tuberculosis Color-enhanced images shows rod-shaped bacterium responsible for tuberculosis
1. Which of the following species have strains that are capable of undergoing the process of conjugation?
 Biology 3340 Summer 2005 Second Examination Version A Name Be sure to put your name on the mark-sense sheet as well Directions: Write your name in the correct space on the mark-sense sheet and the exam
Biology 3340 Summer 2005 Second Examination Version A Name Be sure to put your name on the mark-sense sheet as well Directions: Write your name in the correct space on the mark-sense sheet and the exam
Special Topics on Genetics
 ARISTOTLE UNIVERSITY OF THESSALONIKI OPEN COURSES Section 9: Transposable elements Drosopoulou E License The offered educational material is subject to Creative Commons licensing. For educational material,
ARISTOTLE UNIVERSITY OF THESSALONIKI OPEN COURSES Section 9: Transposable elements Drosopoulou E License The offered educational material is subject to Creative Commons licensing. For educational material,
BACTERIA AND ARCHAEA 10/15/2012
 BACTERIA AND ARCHAEA Chapter 27 KEY CONCEPTS: Structural and functional adaptations contribute to prokaryotic success Rapid reproduction, mutation, and genetic recombination promote genetic diversity in
BACTERIA AND ARCHAEA Chapter 27 KEY CONCEPTS: Structural and functional adaptations contribute to prokaryotic success Rapid reproduction, mutation, and genetic recombination promote genetic diversity in
CRISPR-SeroSeq: A Developing Technique for Salmonella Subtyping
 Department of Biological Sciences Seminar Blog Seminar Date: 3/23/18 Speaker: Dr. Nikki Shariat, Gettysburg College Title: Probing Salmonella population diversity using CRISPRs CRISPR-SeroSeq: A Developing
Department of Biological Sciences Seminar Blog Seminar Date: 3/23/18 Speaker: Dr. Nikki Shariat, Gettysburg College Title: Probing Salmonella population diversity using CRISPRs CRISPR-SeroSeq: A Developing
Chapter 21 PROKARYOTES AND VIRUSES
 Chapter 21 PROKARYOTES AND VIRUSES Bozeman Video classification of life http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tyl_8gv 7RiE Impacts, Issues: West Nile Virus Takes Off Alexander the Great, 336 B.C., conquered a
Chapter 21 PROKARYOTES AND VIRUSES Bozeman Video classification of life http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tyl_8gv 7RiE Impacts, Issues: West Nile Virus Takes Off Alexander the Great, 336 B.C., conquered a
Figure Page 117 Microbiology: An Introduction, 10e (Tortora/ Funke/ Case)
 Chapter 11 The Prokaryotes: Domains Bacteria and Archaea Objective Questions 1) Which of the following are found primarily in the intestines of humans? A) Gram-negative aerobic rods and cocci B) Aerobic,
Chapter 11 The Prokaryotes: Domains Bacteria and Archaea Objective Questions 1) Which of the following are found primarily in the intestines of humans? A) Gram-negative aerobic rods and cocci B) Aerobic,
Overview of the major bacterial pathogens The major bacterial pathogens are presented in this table:
 Practical Microbiology 30/11/2018 University of Sulaimani college of Pharmacy Year2 Lab. 5: Overview of the major bacterial pathogens The major bacterial pathogens are presented in this table: Major Bacterial
Practical Microbiology 30/11/2018 University of Sulaimani college of Pharmacy Year2 Lab. 5: Overview of the major bacterial pathogens The major bacterial pathogens are presented in this table: Major Bacterial
(A) Exotoxin (B) Endotoxin (C) Cilia (D) Flagella (E) Capsule. A. Incorrect! Only gram-positive bacteria secrete exotoxin.
 College Biology - Problem Drill 13: Prokaryots and Protists Question No. 1 of 10 1. Gram-negative bacteria can cause disease in humans by release of what substance? Question #01 (A) Exotoxin (B) Endotoxin
College Biology - Problem Drill 13: Prokaryots and Protists Question No. 1 of 10 1. Gram-negative bacteria can cause disease in humans by release of what substance? Question #01 (A) Exotoxin (B) Endotoxin
Streptomyces Linear Plasmids: Their Discovery, Functions, Interactions with Other Replicons, and Evolutionary Significance
 Microbiol Monogr (7) F. Meinhardt R. Klassen: Microbial Linear Plasmids DOI 10.1007/7171_2007_097/Published online: 27 June 2007 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg 2007 Streptomyces Linear Plasmids: Their
Microbiol Monogr (7) F. Meinhardt R. Klassen: Microbial Linear Plasmids DOI 10.1007/7171_2007_097/Published online: 27 June 2007 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg 2007 Streptomyces Linear Plasmids: Their
ANTIMICROBIAL TESTING. E-Coli K-12 - E-Coli 0157:H7. Salmonella Enterica Servoar Typhimurium LT2 Enterococcus Faecalis
 ANTIMICROBIAL TESTING E-Coli K-12 - E-Coli 0157:H7 Salmonella Enterica Servoar Typhimurium LT2 Enterococcus Faecalis Staphylococcus Aureus (Staph Infection MRSA) Streptococcus Pyrogenes Anti Bacteria effect
ANTIMICROBIAL TESTING E-Coli K-12 - E-Coli 0157:H7 Salmonella Enterica Servoar Typhimurium LT2 Enterococcus Faecalis Staphylococcus Aureus (Staph Infection MRSA) Streptococcus Pyrogenes Anti Bacteria effect
The Role of the Horizontal Gene Pool and Lateral Gene Transfer in Enhancing Microbial Activities in Marine Sediments
 The Role of the Horizontal Gene Pool and Lateral Gene Transfer in Enhancing Microbial Activities in Marine Sediments Patricia A. Sobecky School of Biology Georgia Institute of Technology 310 Ferst Drive
The Role of the Horizontal Gene Pool and Lateral Gene Transfer in Enhancing Microbial Activities in Marine Sediments Patricia A. Sobecky School of Biology Georgia Institute of Technology 310 Ferst Drive
Kingdom Monera(Archaebacteria & Eubacteria)
 Kingdom Monera(Archaebacteria & All bacteria are prokaryotes Characteristics: 1. No nucleus Eubacteria) 2. No membrane bound organelles 3. Smaller & less ribosomes 4. Most are smaller than eukaryotes 5.
Kingdom Monera(Archaebacteria & All bacteria are prokaryotes Characteristics: 1. No nucleus Eubacteria) 2. No membrane bound organelles 3. Smaller & less ribosomes 4. Most are smaller than eukaryotes 5.
Introduction to Microbiology BIOL 220 Summer Session I, 1996 Exam # 1
 Name I. Multiple Choice (1 point each) Introduction to Microbiology BIOL 220 Summer Session I, 1996 Exam # 1 B 1. Which is possessed by eukaryotes but not by prokaryotes? A. Cell wall B. Distinct nucleus
Name I. Multiple Choice (1 point each) Introduction to Microbiology BIOL 220 Summer Session I, 1996 Exam # 1 B 1. Which is possessed by eukaryotes but not by prokaryotes? A. Cell wall B. Distinct nucleus
BACTERIAL PHYSIOLOGY SMALL GROUP. Monday, August 25, :00pm. Faculty: Adam Driks, Ph.D. Alan Wolfe, Ph.D.
 BACTERIAL PHYSIOLOGY SMALL GROUP Monday, August 25, 2014 1:00pm Faculty: Adam Driks, Ph.D. Alan Wolfe, Ph.D. Learning Goal To understand how bacterial physiology applies to the diagnosis and treatment
BACTERIAL PHYSIOLOGY SMALL GROUP Monday, August 25, 2014 1:00pm Faculty: Adam Driks, Ph.D. Alan Wolfe, Ph.D. Learning Goal To understand how bacterial physiology applies to the diagnosis and treatment
Plant transformation
 Plant transformation Objectives: 1. What is plant transformation? 2. What is Agrobacterium? How and why does it transform plant cells? 3. How is Agrobacterium used as a tool in molecular genetics? References:
Plant transformation Objectives: 1. What is plant transformation? 2. What is Agrobacterium? How and why does it transform plant cells? 3. How is Agrobacterium used as a tool in molecular genetics? References:
Mini-Tn7 Derivative Construction and Characterization. Mini-Tn7 derivatives for
 Supplemental Methods Mini-Tn7 Derivative Construction and Characterization. Mini-Tn7 derivatives for constitutive expression of fluorescent proteins in S. oneidensis were constructed as follows. The EcoRI-XbaI
Supplemental Methods Mini-Tn7 Derivative Construction and Characterization. Mini-Tn7 derivatives for constitutive expression of fluorescent proteins in S. oneidensis were constructed as follows. The EcoRI-XbaI
Biology 112 Practice Midterm Questions
 Biology 112 Practice Midterm Questions 1. Identify which statement is true or false I. Bacterial cell walls prevent osmotic lysis II. All bacterial cell walls contain an LPS layer III. In a Gram stain,
Biology 112 Practice Midterm Questions 1. Identify which statement is true or false I. Bacterial cell walls prevent osmotic lysis II. All bacterial cell walls contain an LPS layer III. In a Gram stain,
Structural biology of plasmid partition: uncovering the molecular mechanisms of DNA segregation
 Biochem. J. (2008) 412, 1 18 (Printed in Great Britain) doi:10.1042/bj20080359 1 REVIEW ARTICLE Structural biology of plasmid partition: uncovering the molecular mechanisms of DNA segregation Maria A.
Biochem. J. (2008) 412, 1 18 (Printed in Great Britain) doi:10.1042/bj20080359 1 REVIEW ARTICLE Structural biology of plasmid partition: uncovering the molecular mechanisms of DNA segregation Maria A.
The Minimal-Gene-Set -Kapil PHY498BIO, HW 3
 The Minimal-Gene-Set -Kapil Rajaraman(rajaramn@uiuc.edu) PHY498BIO, HW 3 The number of genes in organisms varies from around 480 (for parasitic bacterium Mycoplasma genitalium) to the order of 100,000
The Minimal-Gene-Set -Kapil Rajaraman(rajaramn@uiuc.edu) PHY498BIO, HW 3 The number of genes in organisms varies from around 480 (for parasitic bacterium Mycoplasma genitalium) to the order of 100,000
BACTERIA. CLS 212: Medical Microbiology Miss Zeina Alkudmani
 BACTERIA CLS 212: Medical Microbiology Miss Zeina Alkudmani Prokaryotes Prokaryotic cells possess simpler structures than eukaryotic cells, since they do not have a nucleus or a lot of cytoplasmic organelles.
BACTERIA CLS 212: Medical Microbiology Miss Zeina Alkudmani Prokaryotes Prokaryotic cells possess simpler structures than eukaryotic cells, since they do not have a nucleus or a lot of cytoplasmic organelles.
WHERE DOES THE VARIATION COME FROM IN THE FIRST PLACE?
 What factors contribute to phenotypic variation? The world s tallest man, Sultan Kosen (8 feet 1 inch) towers over the world s smallest, He Ping (2 feet 5 inches). WHERE DOES THE VARIATION COME FROM IN
What factors contribute to phenotypic variation? The world s tallest man, Sultan Kosen (8 feet 1 inch) towers over the world s smallest, He Ping (2 feet 5 inches). WHERE DOES THE VARIATION COME FROM IN
Microbes and you ON THE LATEST HUMAN MICROBIOME DISCOVERIES, COMPUTATIONAL QUESTIONS AND SOME SOLUTIONS. Elizabeth Tseng
 Microbes and you ON THE LATEST HUMAN MICROBIOME DISCOVERIES, COMPUTATIONAL QUESTIONS AND SOME SOLUTIONS Elizabeth Tseng Dept. of CSE, University of Washington Johanna Lampe Lab, Fred Hutchinson Cancer
Microbes and you ON THE LATEST HUMAN MICROBIOME DISCOVERIES, COMPUTATIONAL QUESTIONS AND SOME SOLUTIONS Elizabeth Tseng Dept. of CSE, University of Washington Johanna Lampe Lab, Fred Hutchinson Cancer
Microbiology Helmut Pospiech
 Microbiology http://researchmagazine.uga.edu/summer2002/bacteria.htm 05.04.2018 Helmut Pospiech The Species Concept in Microbiology No universally accepted concept of species for prokaryotes Current definition
Microbiology http://researchmagazine.uga.edu/summer2002/bacteria.htm 05.04.2018 Helmut Pospiech The Species Concept in Microbiology No universally accepted concept of species for prokaryotes Current definition
Intro to Prokaryotes Lecture 1 Spring 2014
 Intro to Prokaryotes Lecture 1 Spring 2014 Meet the Prokaryotes 1 Meet the Prokaryotes 2 Meet the Prokaryotes 3 Why study prokaryotes? Deep Time 4 Fig. 25.7 Fossilized stromatolite (above) and living stromatolite
Intro to Prokaryotes Lecture 1 Spring 2014 Meet the Prokaryotes 1 Meet the Prokaryotes 2 Meet the Prokaryotes 3 Why study prokaryotes? Deep Time 4 Fig. 25.7 Fossilized stromatolite (above) and living stromatolite
R. w. LACEY AND I. CHOPRA
 GENETIC STUDIES OF A MULTI-RESISTANT STRAIN OF STAPHYLOCOCCUS A UREUS R. w. LACEY AND I. CHOPRA Department of Bacteriology, The Medical School, University of Bristol, Bristol BS8 ITD A POLICY of limiting
GENETIC STUDIES OF A MULTI-RESISTANT STRAIN OF STAPHYLOCOCCUS A UREUS R. w. LACEY AND I. CHOPRA Department of Bacteriology, The Medical School, University of Bristol, Bristol BS8 ITD A POLICY of limiting
Warm-Up. Illustrate (via model, diagram, cartoon, et cetera) how viral replication introduces genetic variation in the viral population. (LO 3.
 Warm-Up Illustrate (via model, diagram, cartoon, et cetera) how viral replication introduces genetic variation in the viral population. (LO 3.30) Yesterday s Picture G C A T G C A T G C AG T A C C T A
Warm-Up Illustrate (via model, diagram, cartoon, et cetera) how viral replication introduces genetic variation in the viral population. (LO 3.30) Yesterday s Picture G C A T G C A T G C AG T A C C T A
the noisy gene Biology of the Universidad Autónoma de Madrid Jan 2008 Juan F. Poyatos Spanish National Biotechnology Centre (CNB)
 Biology of the the noisy gene Universidad Autónoma de Madrid Jan 2008 Juan F. Poyatos Spanish National Biotechnology Centre (CNB) day III: noisy bacteria - Regulation of noise (B. subtilis) - Intrinsic/Extrinsic
Biology of the the noisy gene Universidad Autónoma de Madrid Jan 2008 Juan F. Poyatos Spanish National Biotechnology Centre (CNB) day III: noisy bacteria - Regulation of noise (B. subtilis) - Intrinsic/Extrinsic
UNIVERSITY OF YORK. BA, BSc, and MSc Degree Examinations Department : BIOLOGY. Title of Exam: Molecular microbiology
 Examination Candidate Number: Desk Number: UNIVERSITY OF YORK BA, BSc, and MSc Degree Examinations 2017-8 Department : BIOLOGY Title of Exam: Molecular microbiology Time Allowed: 1 hour 30 minutes Marking
Examination Candidate Number: Desk Number: UNIVERSITY OF YORK BA, BSc, and MSc Degree Examinations 2017-8 Department : BIOLOGY Title of Exam: Molecular microbiology Time Allowed: 1 hour 30 minutes Marking
KINGDOM MONERA. Bacterial Cell Shape 8/22/2010. The Prokaryotes: Archaebacteria and Eubacteria
 KINGDOM MONERA The Prokaryotes: Archaebacteria and Eubacteria Bacteria are the most organisms living on the Earth. (i.e. 10mL of soil contains 1 x 10 10 bacteria. They are found in nearly every habitat
KINGDOM MONERA The Prokaryotes: Archaebacteria and Eubacteria Bacteria are the most organisms living on the Earth. (i.e. 10mL of soil contains 1 x 10 10 bacteria. They are found in nearly every habitat
Principles of Biotechnology Lectures of week 4 MICROBIOLOGY AND BIOTECHNOLOGY
 Principles of Biotechnology Lectures of week 4 MICROBIOLOGY AND BIOTECHNOLOGY INTRODUCTION TO MICROBIOLOGY What are microbes? Germs, microbe s s microorganisms are minute living things that individually
Principles of Biotechnology Lectures of week 4 MICROBIOLOGY AND BIOTECHNOLOGY INTRODUCTION TO MICROBIOLOGY What are microbes? Germs, microbe s s microorganisms are minute living things that individually
Domain Bacteria. BIO 220 Microbiology Jackson Community College
 Domain Bacteria BIO 220 Microbiology Jackson Community College John Ireland, Ph.D. 2006 Scientific Nomenclature Domain - Bacteria Phylum Important for gross characteristics Class Intermediate characteristics
Domain Bacteria BIO 220 Microbiology Jackson Community College John Ireland, Ph.D. 2006 Scientific Nomenclature Domain - Bacteria Phylum Important for gross characteristics Class Intermediate characteristics
Mouth animalcules (bacteria)
 Mouth animalcules (bacteria) 1684 http://en.citizendium.org/images/thumb/9/94/leeuwenhoek.jpg/300px-leeuwenhoek.jpg Prokaryotic Cell Shapes Coccus - cocci Bacillus - bacillus Spirillum - spirilli Vibrio
Mouth animalcules (bacteria) 1684 http://en.citizendium.org/images/thumb/9/94/leeuwenhoek.jpg/300px-leeuwenhoek.jpg Prokaryotic Cell Shapes Coccus - cocci Bacillus - bacillus Spirillum - spirilli Vibrio
MICROBIOLOGIA GENERALE. Structure and function of prokaryotic cells 3
 MICROBIOLOGIA GENERALE Structure and function of prokaryotic cells 3 Structure and function of prokaryotic cells: in the cytosol The bacterial chromosome is typically one large circular molecule of DNA
MICROBIOLOGIA GENERALE Structure and function of prokaryotic cells 3 Structure and function of prokaryotic cells: in the cytosol The bacterial chromosome is typically one large circular molecule of DNA
Comparative genomics: Overview & Tools + MUMmer algorithm
 Comparative genomics: Overview & Tools + MUMmer algorithm Urmila Kulkarni-Kale Bioinformatics Centre University of Pune, Pune 411 007. urmila@bioinfo.ernet.in Genome sequence: Fact file 1995: The first
Comparative genomics: Overview & Tools + MUMmer algorithm Urmila Kulkarni-Kale Bioinformatics Centre University of Pune, Pune 411 007. urmila@bioinfo.ernet.in Genome sequence: Fact file 1995: The first
Test Bank for Microbiology A Systems Approach 3rd edition by Cowan
 Test Bank for Microbiology A Systems Approach 3rd edition by Cowan Link download full: https://digitalcontentmarket.org/download/test-bank-formicrobiology-a-systems-approach-3rd-edition-by-cowan Chapter
Test Bank for Microbiology A Systems Approach 3rd edition by Cowan Link download full: https://digitalcontentmarket.org/download/test-bank-formicrobiology-a-systems-approach-3rd-edition-by-cowan Chapter
Microbiology Lecture 1
 Microbiology Lecture 1 Bacterial structure, Functions & Genetics TEAM 437 Red: important Green : doctor notes Black : original slides Grey: extra information Objectives 1. Define the cellular organization
Microbiology Lecture 1 Bacterial structure, Functions & Genetics TEAM 437 Red: important Green : doctor notes Black : original slides Grey: extra information Objectives 1. Define the cellular organization
What are viruses? Marine Viruses I & II. OCN 626 Marine Microplankton Ecology. Characteristics, Abundance, and Diversity
 OCN 626 Marine Microplankton Ecology Marine Viruses I & II Characteristics, Abundance, and Diversity What Are Viruses? What are they made of? How do they replicate? Are they alive? What are viruses? Infectious
OCN 626 Marine Microplankton Ecology Marine Viruses I & II Characteristics, Abundance, and Diversity What Are Viruses? What are they made of? How do they replicate? Are they alive? What are viruses? Infectious
Ladue Microbe Mission Test SCORE: / 90 Name: Date:
 Ladue Microbe Mission Test SCORE: / 90 Name: Date: You may not return to previous stations. However, you can move to another station early if you want to do so. I won t judge you for your grammar/writing
Ladue Microbe Mission Test SCORE: / 90 Name: Date: You may not return to previous stations. However, you can move to another station early if you want to do so. I won t judge you for your grammar/writing
Test Bank for Microbiology A Systems Approach 3rd edition by Cowan
 Test Bank for Microbiology A Systems Approach 3rd edition by Cowan Link download full: http://testbankair.com/download/test-bankfor-microbiology-a-systems-approach-3rd-by-cowan/ Chapter 1: The Main Themes
Test Bank for Microbiology A Systems Approach 3rd edition by Cowan Link download full: http://testbankair.com/download/test-bankfor-microbiology-a-systems-approach-3rd-by-cowan/ Chapter 1: The Main Themes
Outline. Genome Evolution. Genome. Genome Architecture. Constraints on Genome Evolution. New Evolutionary Synthesis 11/8/16
 Genome Evolution Outline 1. What: Patterns of Genome Evolution Carol Eunmi Lee Evolution 410 University of Wisconsin 2. Why? Evolution of Genome Complexity and the interaction between Natural Selection
Genome Evolution Outline 1. What: Patterns of Genome Evolution Carol Eunmi Lee Evolution 410 University of Wisconsin 2. Why? Evolution of Genome Complexity and the interaction between Natural Selection
SPECIES OF ARCHAEA ARE MORE CLOSELY RELATED TO EUKARYOTES THAN ARE SPECIES OF PROKARYOTES.
 THE TERMS RUN AND TUMBLE ARE GENERALLY ASSOCIATED WITH A) cell wall fluidity. B) cell membrane structures. C) taxic movements of the cell. D) clustering properties of certain rod-shaped bacteria. A MAJOR
THE TERMS RUN AND TUMBLE ARE GENERALLY ASSOCIATED WITH A) cell wall fluidity. B) cell membrane structures. C) taxic movements of the cell. D) clustering properties of certain rod-shaped bacteria. A MAJOR
Introduction to Digital Evolution Handout Answers
 Introduction to Digital Evolution Handout Answers Note to teacher: The questions in this handout and the suggested answers (in red, below) are meant to guide discussion, not be an assessment. It is recommended
Introduction to Digital Evolution Handout Answers Note to teacher: The questions in this handout and the suggested answers (in red, below) are meant to guide discussion, not be an assessment. It is recommended
The Complete Genome Sequence of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. chinensis strain CT-43
 JB Accepts, published online ahead of print on 6 May 2011 J. Bacteriol. doi:10.1128/jb.05085-11 Copyright 2011, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions. All Rights Reserved.
JB Accepts, published online ahead of print on 6 May 2011 J. Bacteriol. doi:10.1128/jb.05085-11 Copyright 2011, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions. All Rights Reserved.
Amelioration of Bacterial Genomes: Rates of Change and Exchange
 J Mol Evol (1997) 44:383 397 Springer-Verlag New York Inc. 1997 Amelioration of Bacterial Genomes: Rates of Change and Exchange Jeffrey G. Lawrence, 1, * Howard Ochman 2 1 Department of Biology, University
J Mol Evol (1997) 44:383 397 Springer-Verlag New York Inc. 1997 Amelioration of Bacterial Genomes: Rates of Change and Exchange Jeffrey G. Lawrence, 1, * Howard Ochman 2 1 Department of Biology, University
By signing below, you acknowledge that you have ensured that you are complying with the above statement.
 Instructions: This exam consists of 31 multiple choice questions on 8 pages, including this one. Please submit your answers on the scantron sheet provided and on this copy of the exam. This exam is closed
Instructions: This exam consists of 31 multiple choice questions on 8 pages, including this one. Please submit your answers on the scantron sheet provided and on this copy of the exam. This exam is closed
Kharkov National Medical University. Head of Microbiology, Virology and Immunology Department Minukhin Valeriy Vladimirivich
 Kharkov National Medical University Head of Microbiology, Virology and Immunology Department Minukhin Valeriy Vladimirivich Tkachenko Victoria 1, 5, 11, 14, 19, 21, 30 Kovalenko Natalia 2, 12, 25, 29 Siritsa
Kharkov National Medical University Head of Microbiology, Virology and Immunology Department Minukhin Valeriy Vladimirivich Tkachenko Victoria 1, 5, 11, 14, 19, 21, 30 Kovalenko Natalia 2, 12, 25, 29 Siritsa
Genômica comparativa. João Carlos Setubal IQ-USP outubro /5/2012 J. C. Setubal
 Genômica comparativa João Carlos Setubal IQ-USP outubro 2012 11/5/2012 J. C. Setubal 1 Comparative genomics There are currently (out/2012) 2,230 completed sequenced microbial genomes publicly available
Genômica comparativa João Carlos Setubal IQ-USP outubro 2012 11/5/2012 J. C. Setubal 1 Comparative genomics There are currently (out/2012) 2,230 completed sequenced microbial genomes publicly available
CHAPTER 13 PROKARYOTE GENES: E. COLI LAC OPERON
 PROKARYOTE GENES: E. COLI LAC OPERON CHAPTER 13 CHAPTER 13 PROKARYOTE GENES: E. COLI LAC OPERON Figure 1. Electron micrograph of growing E. coli. Some show the constriction at the location where daughter
PROKARYOTE GENES: E. COLI LAC OPERON CHAPTER 13 CHAPTER 13 PROKARYOTE GENES: E. COLI LAC OPERON Figure 1. Electron micrograph of growing E. coli. Some show the constriction at the location where daughter
Genome reduction in prokaryotic obligatory intracellular parasites of humans: a comparative analysis
 International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology (2004), 54, 1937 1941 DOI 10.1099/ijs.0.63090-0 Genome reduction in prokaryotic obligatory intracellular parasites of humans: a comparative
International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology (2004), 54, 1937 1941 DOI 10.1099/ijs.0.63090-0 Genome reduction in prokaryotic obligatory intracellular parasites of humans: a comparative
Bacteria are very small
 BACTERIA BACTERIA Bacteria are very small Bacteria are very small compared to cells with nuclei (Eukaryotic cells) This is a pore in human skin and the yellow spheres are bacteria CLASSIFICATION OF BACTERIA
BACTERIA BACTERIA Bacteria are very small Bacteria are very small compared to cells with nuclei (Eukaryotic cells) This is a pore in human skin and the yellow spheres are bacteria CLASSIFICATION OF BACTERIA
Unit 1: DNA & the Genome. 1.7: Evolution. 1.7 Evolution
 Unit 1: DNA & the Genome 1.7: Evolution 1.7 Evolution What you should already know from National 5 Mutations are random changes to genetic material and are the only source of new alleles. Mutation can
Unit 1: DNA & the Genome 1.7: Evolution 1.7 Evolution What you should already know from National 5 Mutations are random changes to genetic material and are the only source of new alleles. Mutation can
Prokaryotes & Viruses. Practice Questions. Slide 1 / 71. Slide 2 / 71. Slide 3 / 71. Slide 4 / 71. Slide 6 / 71. Slide 5 / 71
 Slide 1 / 71 Slide 2 / 71 New Jersey Center for Teaching and Learning Progressive Science Initiative This material is made freely available at www.njctl.org and is intended for the non-commercial use of
Slide 1 / 71 Slide 2 / 71 New Jersey Center for Teaching and Learning Progressive Science Initiative This material is made freely available at www.njctl.org and is intended for the non-commercial use of
Supplementary Information for Hurst et al.: Causes of trends of amino acid gain and loss
 Supplementary Information for Hurst et al.: Causes of trends of amino acid gain and loss Methods Identification of orthologues, alignment and evolutionary distances A preliminary set of orthologues was
Supplementary Information for Hurst et al.: Causes of trends of amino acid gain and loss Methods Identification of orthologues, alignment and evolutionary distances A preliminary set of orthologues was
The invention of the microscope has opened to us a world of extraordinary numbers. A singular drop of pond water reveals countless life forms
 Biology Chapter 19 Notes - Bacteria and Viruses The invention of the microscope has opened to us a world of extraordinary numbers. A singular drop of pond water reveals countless life forms I. Classifying
Biology Chapter 19 Notes - Bacteria and Viruses The invention of the microscope has opened to us a world of extraordinary numbers. A singular drop of pond water reveals countless life forms I. Classifying
Novel antibiotics from symbiotic peptides
 HU-NO Research conference and Knowledge exchange 15.02.2018 Novel antibiotics from symbiotic peptides Eva Kondorosi Biological Research Centre Hungarian Academy of Sciences Medicago truncatula-sinorhizobium
HU-NO Research conference and Knowledge exchange 15.02.2018 Novel antibiotics from symbiotic peptides Eva Kondorosi Biological Research Centre Hungarian Academy of Sciences Medicago truncatula-sinorhizobium
Campbell Biology Concepts & Connections 2015
 A Correlation of Concepts & Connections 2015 To the Science, , Science - Table of Contents From Molecules to Organisms: Structures and Processes... 3 Ecosystems: Interactions, Energy, and Dynamics... 5
A Correlation of Concepts & Connections 2015 To the Science, , Science - Table of Contents From Molecules to Organisms: Structures and Processes... 3 Ecosystems: Interactions, Energy, and Dynamics... 5
Miller & Levine Biology
 A Correlation of To the Science Biology A Correlation of, 2014 to the, Table of Contents From Molecules to Organisms: Structures and Processes... 3 Ecosystems: Interactions, Energy, and Dynamics... 4 Heredity:
A Correlation of To the Science Biology A Correlation of, 2014 to the, Table of Contents From Molecules to Organisms: Structures and Processes... 3 Ecosystems: Interactions, Energy, and Dynamics... 4 Heredity:
This is a repository copy of Plasmid-mediated horizontal gene transfer is a coevolutionary process.
 This is a repository copy of Plasmid-mediated horizontal gene transfer is a coevolutionary process. White Rose Research Online URL for this paper: http://eprints.whiterose.ac.uk// Version: Accepted Version
This is a repository copy of Plasmid-mediated horizontal gene transfer is a coevolutionary process. White Rose Research Online URL for this paper: http://eprints.whiterose.ac.uk// Version: Accepted Version
Studies with RP1 deletion plasmids: Incompatibility properties, plasmid curing and the spontaneous loss of resistance
 J. Biosci., Vol. 1, Number 3, September 1979, pp. 345 354. Printed in India. Studies with RP1 deletion plasmids: Incompatibility properties, plasmid curing and the spontaneous loss of resistance HABIBUL
J. Biosci., Vol. 1, Number 3, September 1979, pp. 345 354. Printed in India. Studies with RP1 deletion plasmids: Incompatibility properties, plasmid curing and the spontaneous loss of resistance HABIBUL
Rise and Fall of Mutator Bacteria
 Rise and Fall of Mutator Bacteria The Evolution of Mutation Rates in Bacteria Yoav Ram Hadany Evolutionary Theory Lab 29 May 2011 Bacteria Bacteria are unicellular, haploid and asexual Reproduce by binary
Rise and Fall of Mutator Bacteria The Evolution of Mutation Rates in Bacteria Yoav Ram Hadany Evolutionary Theory Lab 29 May 2011 Bacteria Bacteria are unicellular, haploid and asexual Reproduce by binary
μ gyra parc Escherichia coli Klebsiella pneumoniae Pseudomonas aeruginosa E. coli gyra E. coli parc gyra parc gyra Escherichia coli E. coli E.
 gyra parc Escherichia coli Klebsiella pneumoniae Pseudomonas aeruginosa E. coli μ E. coli gyra parc gyra parc gyra parc μ μ gyra parc Key words Escherichia coli gyra parc Escherichia coli E. coli gyra
gyra parc Escherichia coli Klebsiella pneumoniae Pseudomonas aeruginosa E. coli μ E. coli gyra parc gyra parc gyra parc μ μ gyra parc Key words Escherichia coli gyra parc Escherichia coli E. coli gyra
Overview: Masters of Adaptation. Prokaryotes thrive almost everywhere, including places too acidic, salty, cold, or hot for most other organisms
 Chapter 27 Bacteria and Archaea Overview: Masters of Adaptation Prokaryotes thrive almost everywhere, including places too acidic, salty, cold, or hot for most other organisms They have an astonishing
Chapter 27 Bacteria and Archaea Overview: Masters of Adaptation Prokaryotes thrive almost everywhere, including places too acidic, salty, cold, or hot for most other organisms They have an astonishing
Tetracycline Rationale for the EUCAST clinical breakpoints, version th November 2009
 Tetracycline Rationale for the EUCAST clinical breakpoints, version 1.0 20 th November 2009 Introduction The natural tetracyclines, including tetracycline, chlortetracycline, oxytetracycline and demethylchlortetracycline
Tetracycline Rationale for the EUCAST clinical breakpoints, version 1.0 20 th November 2009 Introduction The natural tetracyclines, including tetracycline, chlortetracycline, oxytetracycline and demethylchlortetracycline
CYTOPLASMIC INHERITANCE
 CYTOPLASMIC INHERITANCE Inheritance of most of the characters in eukaryotic organisms shows the following characteristic features. 1. The contributions by both male and female parents are equal so that
CYTOPLASMIC INHERITANCE Inheritance of most of the characters in eukaryotic organisms shows the following characteristic features. 1. The contributions by both male and female parents are equal so that
