C. elegans as an in vivo model to decipher microbial virulence. Centre d Immunologie de Marseille-Luminy
|
|
|
- Frank Atkinson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 C. elegans as an in vivo model to decipher microbial virulence Centre d Immunologie de Marseille-Luminy
2 C. elegans : a model organism Mechanisms of apoptosis, RNA interference Neuronal function and development Intracellular signaling pathways Stress, pathogenesis (Huntington, muscular dystrophy ) Host-pathogen interactions
3
4
5 Why C. elegans? Small size 1mm Thousands of animals on a Petri dish Transparent Reporter gene expression Study bacterial infection in vivo Rapid generation time From egg to gravid adult in 2 days 300 eggs laid in 3 days Clonal All the worms in a population can be genetically identical 0.1 mm image taken from Devgen nl
6 Why C. elegans to study host-pathogen interactions? Some Pathogens have a broad range of hosts. Some of their virulence factors might be used whatever the host is. Universal virulence factors. Science (1995) Ausubel Lab Using C. elegans as a host can allow the identification of these virulence factors.
7 Known pathogens of C. elegans Gram-positive bacteria: Bacillus thuringiensis Enterococcus faecalis Listeria monocytogenes Microbacterium nematophilum Staphylococcus aureus Streptococcus pneumoniae Gram-negative bacteria: Fungi: Arthrobotrys sp. Candida albicans Cryptococcus neoformans Drechmeria coniospora Duddingtonia flagrans Paecilomyces lilacinus Acinetobacter baumannii Aeromonas hydrophila Agrobacterium tumefaciens Burkholderia cepacia B. thailandensis B. pseudomallei Erwinia christamthemi E. carotovora carotovora Escherichia coli (EPEPC & EHEC) Pseudomonas aeruginosa P. fluorescens Salmonella typhimurium Shewanella frigidimarina S. massalia Serratia marcescens Vibrio cholerae Yersinia spp. VIRUSES VSV, FHV
8 Assays to test for infectivity or toxicity Is the microorganism intoxicating or infecting C. elegans?
9 Survival of C. elegans on different bacteria E. coli OP50 E. coli 1106 Bacillus megaterium Time (days Couillault & Ewbank (2002) Infect & Immun.
10 Infection of C. elegans by different bacteria 100 Worms alive (%) E. coli OP50 Photorhabdus luminescens Hb Xenorhabdus nematophila A24 Aeromonas hydrophila AH6 Aeromonas hydrophila AH10 Shewanella massalia Shewanella frigidimarina Time (days) Toxicity or infectivity? Couillault & Ewbank, Infect & Immun. (2002)
11 Infectivity or toxicity? % worms alive E. coli OP50 Aeromonas hydrophila AH6 Agrobacterium tumefaciens Photorhabdus luminescens Hb Xenorhabdus nematophila A24 Erwinia carotovora Time (days) Couillault & Ewbank (2002) Infect & Immun.
12 Infectivity or toxicity? + Filters Survival?
13 Infectivity or toxicity? P. aeruginosa PA01 Darby et al., (1999) PNAS Toxin secreted in the media P. aeruginosa PA14 Mahajan-Miklos et al., Cell (1999) Tan et al., PNAS (1999) Infection S. marcescens Db11 Kurz et al., (2003) Embo J
14 In vivo observation of the infection
15 E. coli does not enter the intestine Short contact with fluorescent E. coli Intact bacteria Autofluorescent gut granules Kurz et al. (2003) Embo J
16 S. marcescens enters the intestinal lumen Short contact with fluorescent S. marcescens Kurz et al. (2003) Embo J
17 Intestinal colonization E. coli S. marcescens Kurz et al. (2003) Embo J
18 Assays to decipher microbial virulence Use of nematodes to identify microbial virulence genes required for infection in mammals
19 C. elegans to identify universal virulence factors Unbiaised forward genetic screens for attenuated bacterial mutants
20 Screening protocol Bank of bacterial Mutants (transposon) Synchronized worms n individual clones 96, 24 or 6 well plates Infection Identification of less virulent bacterial clones
21 PA14 Universal virulence factors 2000 mutants screened in C. elegans 8 mutants Decreased virulence in: Arabidopsis 6 7 Wax moth 6 Mahajan-Miklos et al. (2000) Mol. Microbiol.
22 Serratia marcescens Universal virulence factors 2000 mutants screened in C. elegans 23 mutants Decreased virulence in: Drosophila 10 Human cells 3 1/3 Kurz et al. (2003) Embo J
23 Assays to rapidly detect infectivity or toxicity
24 Use of the worm as a biosensor for microbial pathogenicity Already done by several groups to assess soil pollution Identification of genes induced under a specific treatment Construction of transgenic nematodes with fluorescent reporters No heavy metals Heavy metals
25 Antifungal innate immunity
26 D. coniospora kills worms 100 % worms alive Time (Hours)
27 Antimicrobial peptide genes are induced 100 Microarrays % worms alive Time (Hours) Antimicrobial peptide genes nlps Couillault et al. 2004
28 A reporter gene to detect an immune response Pathogen transgenic strain pcol-12 RFP constitutive pnlp-29 GFP inducible Non-infected Infected
29 Why C. elegans to assess potential toxicity in humans? Cost, speed reproducibility In vivo assays with a multicellular organism Natural infection Tools available to decipher molecular mechanisms Ethical issues
30 Drawbacks and conclusions Many cases where infectivity in nematodes means infectivity in mammals (Serratia, Pseudomonas, Salmonella, ) But, cases with nematode-specific infectivity Drechmeria, Microbacterium, Mammalian-specific pathogens will be missed So, infectivity in nematodes is not a good sign for mammals, but a lack of infectivity doesn t mean it s innocuous for vertebrates
31 Equipe FRM Jonathan Ewbank s lab C. Couillault J. Belougne S. Cypowyj L. Kurz K.Z. Lee I. Engelmann N. Pujol B. Squiban K. Ziegler O. Zugasti Tohey Matsuyama Cori Bargmann Niigata New York Elizabeth Pradel Centre d Immunologie de Marseille-Luminy
C. elegans as an. Centre d Immunologie de Marseille-Luminy
 C. elegans as an alternative ti model host Centre d Immunologie de Marseille-Luminy http://www.wormatlas.org/ http://www.wormatlas.org/ Why C. elegans? Small size Transparent Rapid generation time evgen
C. elegans as an alternative ti model host Centre d Immunologie de Marseille-Luminy http://www.wormatlas.org/ http://www.wormatlas.org/ Why C. elegans? Small size Transparent Rapid generation time evgen
The art of serendipity: killing of Caenorhabditis elegans by human pathogens as a model of bacterial and fungal pathogenesis
 Review The art of serendipity: killing of Caenorhabditis elegans by human pathogens as a model of bacterial and fungal pathogenesis Eleftherios Mylonakis, Frederick M Ausubel, Robin Jian Tang and Stephen
Review The art of serendipity: killing of Caenorhabditis elegans by human pathogens as a model of bacterial and fungal pathogenesis Eleftherios Mylonakis, Frederick M Ausubel, Robin Jian Tang and Stephen
Supplementary Information
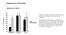 Supplementary Information Supplementary figures % Occupancy 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 Wt tol-1(nr2033) Figure S1. Avoidance behavior to S. enterica was not observed in wild-type or tol-1(nr2033) mutant nematodes.
Supplementary Information Supplementary figures % Occupancy 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 Wt tol-1(nr2033) Figure S1. Avoidance behavior to S. enterica was not observed in wild-type or tol-1(nr2033) mutant nematodes.
Novel antibiotics from symbiotic peptides
 HU-NO Research conference and Knowledge exchange 15.02.2018 Novel antibiotics from symbiotic peptides Eva Kondorosi Biological Research Centre Hungarian Academy of Sciences Medicago truncatula-sinorhizobium
HU-NO Research conference and Knowledge exchange 15.02.2018 Novel antibiotics from symbiotic peptides Eva Kondorosi Biological Research Centre Hungarian Academy of Sciences Medicago truncatula-sinorhizobium
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,900 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,900 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
Caenorhabditis elegans as a model for innate immunity to pathogens
 Blackwell Science, LtdOxford, UKCMICellular Microbiology1462-5814Blackwell Publishing Ltd, 200576741751Review ArticleC. elegans as an innate immunity modelm. J. Gravato-Nobre and J. Hodgkin Cellular Microbiology
Blackwell Science, LtdOxford, UKCMICellular Microbiology1462-5814Blackwell Publishing Ltd, 200576741751Review ArticleC. elegans as an innate immunity modelm. J. Gravato-Nobre and J. Hodgkin Cellular Microbiology
Caenorhabditis elegans: a model organism for investigating immunity. Elizabeth K. Marsh and Robin C. May*
 AEM Accepts, published online ahead of print on 27 January 2012 Appl. Environ. Microbiol. doi:10.1128/aem.07486-11 Copyright 2012, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 2 MINIREVIEWS
AEM Accepts, published online ahead of print on 27 January 2012 Appl. Environ. Microbiol. doi:10.1128/aem.07486-11 Copyright 2012, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 2 MINIREVIEWS
Genetic Basis of Variation in Bacteria
 Mechanisms of Infectious Disease Fall 2009 Genetics I Jonathan Dworkin, PhD Department of Microbiology jonathan.dworkin@columbia.edu Genetic Basis of Variation in Bacteria I. Organization of genetic material
Mechanisms of Infectious Disease Fall 2009 Genetics I Jonathan Dworkin, PhD Department of Microbiology jonathan.dworkin@columbia.edu Genetic Basis of Variation in Bacteria I. Organization of genetic material
MICROBIAL BIOCHEMISTRY BIOT 309. Dr. Leslye Johnson Sept. 30, 2012
 MICROBIAL BIOCHEMISTRY BIOT 309 Dr. Leslye Johnson Sept. 30, 2012 Phylogeny study of evoluhonary relatedness among groups of organisms (e.g. species, populahons), which is discovered through molecular
MICROBIAL BIOCHEMISTRY BIOT 309 Dr. Leslye Johnson Sept. 30, 2012 Phylogeny study of evoluhonary relatedness among groups of organisms (e.g. species, populahons), which is discovered through molecular
CAENORHABDITIS ELEGANS AS A MODEL TO ELUCIDATE HOST- PATHOGEN INTERACTIONS FOR HUMAN BACTERIAL PATHOGENS
 From the Department of Microbiology, Tumor and Cell Biology Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden CAENORHABDITIS ELEGANS AS A MODEL TO ELUCIDATE HOST- PATHOGEN INTERACTIONS FOR HUMAN BACTERIAL PATHOGENS
From the Department of Microbiology, Tumor and Cell Biology Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden CAENORHABDITIS ELEGANS AS A MODEL TO ELUCIDATE HOST- PATHOGEN INTERACTIONS FOR HUMAN BACTERIAL PATHOGENS
3M Food Safety Technical Bulletin
 3M Petrifilm Aqua Heterotrophic Count Plate Performance Summary 3M Petrifilm Aqua Heterotrophic Count (AQHC) Plates are sample ready media plates used in the microbial testing of bottled water. Each plate
3M Petrifilm Aqua Heterotrophic Count Plate Performance Summary 3M Petrifilm Aqua Heterotrophic Count (AQHC) Plates are sample ready media plates used in the microbial testing of bottled water. Each plate
Tackling both sides of the host pathogen equation with Caenorhabditis elegans
 Microbes and Infection 4 (2002) 247 256 Review www.elsevier.com/locate/micinf Tackling both sides of the host pathogen equation with Caenorhabditis elegans Jonathan J. Ewbank * Centre d immunologie de
Microbes and Infection 4 (2002) 247 256 Review www.elsevier.com/locate/micinf Tackling both sides of the host pathogen equation with Caenorhabditis elegans Jonathan J. Ewbank * Centre d immunologie de
Infection of Caenorhabditis elegans by Salmonella typhi Ty2
 Electronic Journal of Biotechnology ISSN: 0717-3458 Vol.6 No.2, Issue of August 15, 2003 2003 by -- Chile Received January 23, 2003 / Accepted July 15, 2003 SHORT COMMUNICATION Javier Santander Laboratorio
Electronic Journal of Biotechnology ISSN: 0717-3458 Vol.6 No.2, Issue of August 15, 2003 2003 by -- Chile Received January 23, 2003 / Accepted July 15, 2003 SHORT COMMUNICATION Javier Santander Laboratorio
Product Catalogue 2015 Clinical and Industrial Microbiology
 Acinetobacter baumannii ATCC BAA-747 * 89141 Actinomyces odontolyticus ATCC 17929 * 89114 Aeromonas hydrophila ATCC 7966 * 89119 Aggregatibacter aphrophilus ATCC 7901 * 89091 Aspergillus brasiliensis ATCC
Acinetobacter baumannii ATCC BAA-747 * 89141 Actinomyces odontolyticus ATCC 17929 * 89114 Aeromonas hydrophila ATCC 7966 * 89119 Aggregatibacter aphrophilus ATCC 7901 * 89091 Aspergillus brasiliensis ATCC
Gram negative bacilli
 Gram negative bacilli 1-Enterobacteriaceae Gram negative bacilli-rods Enterobacteriaceae Are everywhere Part of normal flora of humans and most animals They are cause of -30-35% septisemia -more than 70%
Gram negative bacilli 1-Enterobacteriaceae Gram negative bacilli-rods Enterobacteriaceae Are everywhere Part of normal flora of humans and most animals They are cause of -30-35% septisemia -more than 70%
Infection of Caenorhabditis elegans by Salmonella typhi Ty2
 Electronic Journal of Biotechnology ISSN: 0717-3458 Vol.6 No.2, Issue of August 15, 2003 2003 by -- Chile Received January 23, 2003 / Accepted July 15, 2003 SHORT COMMUNICATION Infection of Caenorhabditis
Electronic Journal of Biotechnology ISSN: 0717-3458 Vol.6 No.2, Issue of August 15, 2003 2003 by -- Chile Received January 23, 2003 / Accepted July 15, 2003 SHORT COMMUNICATION Infection of Caenorhabditis
In vitro the effect of intestinal normal flora on some pathogenic bacteria.
 In vitro the effect of intestinal normal flora on some pathogenic bacteria. Abstract: Dr.abbass shaker Ali adel Leena abd Al-Redha The effect of two types of intestinal bacterial normal floral ( and klebsiella)
In vitro the effect of intestinal normal flora on some pathogenic bacteria. Abstract: Dr.abbass shaker Ali adel Leena abd Al-Redha The effect of two types of intestinal bacterial normal floral ( and klebsiella)
Anti-Fungal Innate Immunity in C. elegans Is Enhanced by Evolutionary Diversification of Antimicrobial Peptides
 Is Enhanced by Evolutionary Diversification of Antimicrobial Peptides Nathalie Pujol 1,2,3., Olivier Zugasti 1,2,3., Daniel Wong 1,2,3., Carole Couillault 1,2,3,C.Léopold Kurz 1,2,3, Hinrich Schulenburg
Is Enhanced by Evolutionary Diversification of Antimicrobial Peptides Nathalie Pujol 1,2,3., Olivier Zugasti 1,2,3., Daniel Wong 1,2,3., Carole Couillault 1,2,3,C.Léopold Kurz 1,2,3, Hinrich Schulenburg
EZ-COMP EZ-COMP For Training and Proficiency Testing Product Details
 EZ-COMP For Training and Proficiency Testing Mixed microorganism populations Identified by codes rather than descriptions Refrigerated storage Traceable to reference culture Product warranty Product Details
EZ-COMP For Training and Proficiency Testing Mixed microorganism populations Identified by codes rather than descriptions Refrigerated storage Traceable to reference culture Product warranty Product Details
Ecology of Infectious Disease
 Ecology of Infectious Disease What is the basis of community robustness (resistance to invasion)? How does robustness influence disease development? The Microbial Context: Microbial Interactions Affect
Ecology of Infectious Disease What is the basis of community robustness (resistance to invasion)? How does robustness influence disease development? The Microbial Context: Microbial Interactions Affect
Product Catalogue 2016 Clinical and Industrial Microbiology
 Acinetobacter baumannii ATCC BAA-747 * 89141 Acinetobacter baumannii ATCC 19606 * 89174 Actinomyces odontolyticus ATCC 17929 * 89114 Aeromonas hydrophila ATCC 7966 * 89119 Aeromonas hydrophila ATCC 35654
Acinetobacter baumannii ATCC BAA-747 * 89141 Acinetobacter baumannii ATCC 19606 * 89174 Actinomyces odontolyticus ATCC 17929 * 89114 Aeromonas hydrophila ATCC 7966 * 89119 Aeromonas hydrophila ATCC 35654
Quorum sensing in plantassociated. S. Brook Peterson Parsek Lab UW Microbiology
 Quorum sensing in plantassociated bacteria S. Brook Peterson Parsek Lab UW Microbiology Outline What is quorum sensing? QS in plant associated bacteria What traits are regulated by QS? What benefits does
Quorum sensing in plantassociated bacteria S. Brook Peterson Parsek Lab UW Microbiology Outline What is quorum sensing? QS in plant associated bacteria What traits are regulated by QS? What benefits does
THE INTERACTION BETWEEN CAENORHABDITIS ELEGANS AND THE BACTERIAL PATHOGEN STENOTROPHOMONAS MALTOPHILIA CORIN VASHOUN WHITE
 THE INTERACTION BETWEEN CAENORHABDITIS ELEGANS AND THE BACTERIAL PATHOGEN STENOTROPHOMONAS MALTOPHILIA by CORIN VASHOUN WHITE B.S., Spelman College, 2010 AN ABSTRACT OF A DISSERTATION submitted in partial
THE INTERACTION BETWEEN CAENORHABDITIS ELEGANS AND THE BACTERIAL PATHOGEN STENOTROPHOMONAS MALTOPHILIA by CORIN VASHOUN WHITE B.S., Spelman College, 2010 AN ABSTRACT OF A DISSERTATION submitted in partial
Antimicrobial peptides
 Název: Školitel: Antimicrobial peptides Zbyněk Heger Datum: 2. 8. 2013 Reg.č.projektu: CZ.1.07/2.4.00/31.0023 Název projektu: Partnerská síť centra excelentního bionanotechnologického výzkumu 2 Content
Název: Školitel: Antimicrobial peptides Zbyněk Heger Datum: 2. 8. 2013 Reg.č.projektu: CZ.1.07/2.4.00/31.0023 Název projektu: Partnerská síť centra excelentního bionanotechnologického výzkumu 2 Content
CLASSIFICATION OF MICROORGANISMS
 CLASSIFICATION OF MICROORGANISMS DISCLOSURE Relevant relationships with commercial entities none Potential for conflicts of interest within this presentation none Steps taken to review and mitigate potential
CLASSIFICATION OF MICROORGANISMS DISCLOSURE Relevant relationships with commercial entities none Potential for conflicts of interest within this presentation none Steps taken to review and mitigate potential
The Evolution of Infectious Disease
 The Evolution of Infectious Disease Why are some bacteria pathogenic to humans while other (closely-related) bacteria are not? This question can be approached from two directions: 1.From the point of view
The Evolution of Infectious Disease Why are some bacteria pathogenic to humans while other (closely-related) bacteria are not? This question can be approached from two directions: 1.From the point of view
ENTEROBACTER AEROGENES UNKNOWN BACTERIA FLOW CHART UNKNOWN LAB REPORT, MICROBIOLOGY ENTEROBACTER AEROGENES
 ENTEROBACTER AEROGENES UNKNOWN BACTERIA PDF UNKNOWN LAB REPORT, MICROBIOLOGY ENTEROBACTER AEROGENES IDENTIFICATION OF AN UNKNOWN BACTERIAL SPECIES OF 1 / 5 2 / 5 3 / 5 enterobacter aerogenes unknown bacteria
ENTEROBACTER AEROGENES UNKNOWN BACTERIA PDF UNKNOWN LAB REPORT, MICROBIOLOGY ENTEROBACTER AEROGENES IDENTIFICATION OF AN UNKNOWN BACTERIAL SPECIES OF 1 / 5 2 / 5 3 / 5 enterobacter aerogenes unknown bacteria
Bile Chrysoidin Glycerol Agar with MUG
 INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE READY-TO-USE PLATED MEDIA PA-257430.04 Rev.: Mar 2013 Bile Chrysoidin Glycerol Agar with MUG INTENDED USE Partially selective medium for the isolation and differentiation of Enterobacteriaceae
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE READY-TO-USE PLATED MEDIA PA-257430.04 Rev.: Mar 2013 Bile Chrysoidin Glycerol Agar with MUG INTENDED USE Partially selective medium for the isolation and differentiation of Enterobacteriaceae
Host-pathogen interactions in the innate immune response of the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans
 Host-pathogen interactions in the innate immune response of the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans by Elizabeth Kate Marsh A thesis submitted to University of Birmingham for the degree of DOCTOR OF PHILOSOPHY
Host-pathogen interactions in the innate immune response of the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans by Elizabeth Kate Marsh A thesis submitted to University of Birmingham for the degree of DOCTOR OF PHILOSOPHY
Microbial pollutants in stagnant water in an informal settlement in the Western Cape, South Africa
 Microbial pollutants in stagnant water in an informal settlement in the Western Cape, South Africa Qenehelo A. Leuta, James P. Odendaal and Arnelia N. Paulse Department of Environmental and Occupational
Microbial pollutants in stagnant water in an informal settlement in the Western Cape, South Africa Qenehelo A. Leuta, James P. Odendaal and Arnelia N. Paulse Department of Environmental and Occupational
ID Membranes for Microbial Rapid Identification
 ID Membranes for Microbial Rapid Identification Chromogenic Reaction by Specific Substrates on Membranes Classical plates are still used today as first steps in modern microbiology. Smart, inexpensive
ID Membranes for Microbial Rapid Identification Chromogenic Reaction by Specific Substrates on Membranes Classical plates are still used today as first steps in modern microbiology. Smart, inexpensive
Considerations with Antibiotic Therapy PART
 Considerations with Antibiotic Therapy PART 1 The Wonderful World of Microbiology 1 Despite the promises of the household-products industry, almost every surface is covered in microorganisms almost all
Considerations with Antibiotic Therapy PART 1 The Wonderful World of Microbiology 1 Despite the promises of the household-products industry, almost every surface is covered in microorganisms almost all
Sample Date: March 30, 2018 Date Received: March 31, 2018 Date of Report: April 9, 2018 (877) Fax: (877)
 U.S. Micro-Solutions, Inc. * 075 South Main Street, Suite 04 * Greensburg, PA 560 Phone: (877) 876-4276 Fax: (724) 853-4049 AIHA-LAP, LLC EMLAP #03009 075 South Main Street, Suite 04 Greensburg, PA 560
U.S. Micro-Solutions, Inc. * 075 South Main Street, Suite 04 * Greensburg, PA 560 Phone: (877) 876-4276 Fax: (724) 853-4049 AIHA-LAP, LLC EMLAP #03009 075 South Main Street, Suite 04 Greensburg, PA 560
BIOL 3702L: MICROBIOLOGY LABORATORY SCHEDULE, SUMMER 2015
 BIOL 3702L: MICROBIOLOGY LABORATORY SCHEDULE, SUMMER 2015 Week of May 18 th Introduction to the Microbiology Laboratory: Become familiar with the laboratory and its safety features Review safety rules
BIOL 3702L: MICROBIOLOGY LABORATORY SCHEDULE, SUMMER 2015 Week of May 18 th Introduction to the Microbiology Laboratory: Become familiar with the laboratory and its safety features Review safety rules
The Scope of Food Microbiology p. 1 Micro-organisms and Food p. 2 Food Spoilage/Preservation p. 2 Food Safety p. 4 Fermentation p.
 The Scope of Food Microbiology p. 1 Micro-organisms and Food p. 2 Food Spoilage/Preservation p. 2 Food Safety p. 4 Fermentation p. 4 Microbiological Quality Assurance p. 4 Micro-organisms and Food Materials
The Scope of Food Microbiology p. 1 Micro-organisms and Food p. 2 Food Spoilage/Preservation p. 2 Food Safety p. 4 Fermentation p. 4 Microbiological Quality Assurance p. 4 Micro-organisms and Food Materials
Indicator Organisms SCI5508
 Indicator Organisms SCI5508 Indicator Organisms REFLECTS microbiological quality organisms and/or their metabolic products whose presence in given foods at certain levels may be used to assess existing
Indicator Organisms SCI5508 Indicator Organisms REFLECTS microbiological quality organisms and/or their metabolic products whose presence in given foods at certain levels may be used to assess existing
3M Food Safety Technical Bulletin
 3M Petrifilm Aqua Enterobacteriaceae Count Plates Performance Summary 3M Petrifi lm Aqua Enterobacteriaceae (AQEB) Count Plates are sample ready media plates used in the microbial testing of bottled water.
3M Petrifilm Aqua Enterobacteriaceae Count Plates Performance Summary 3M Petrifi lm Aqua Enterobacteriaceae (AQEB) Count Plates are sample ready media plates used in the microbial testing of bottled water.
Interaction of Candida albicans with an Intestinal Pathogen, Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium
 EUKARYOTIC CELL, May 2009, p. 732 737 Vol. 8, No. 5 1535-9778/09/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/ec.00016-09 Copyright 2009, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Interaction of Candida albicans
EUKARYOTIC CELL, May 2009, p. 732 737 Vol. 8, No. 5 1535-9778/09/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/ec.00016-09 Copyright 2009, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Interaction of Candida albicans
INTERPRETATION OF THE GRAM STAIN
 INTERPRETATION OF THE GRAM STAIN DISCLOSURE Relevant relationships with commercial entities none Potential for conflicts of interest within this presentation none Steps taken to review and mitigate potential
INTERPRETATION OF THE GRAM STAIN DISCLOSURE Relevant relationships with commercial entities none Potential for conflicts of interest within this presentation none Steps taken to review and mitigate potential
A pathogen is an agent or microrganism that causes a disease in its host. Pathogens can be viruses, bacteria, fungi or protozoa.
 1 A pathogen is an agent or microrganism that causes a disease in its host. Pathogens can be viruses, bacteria, fungi or protozoa. Protozoa are single celled eukaryotic organisms. Some protozoa are pathogens.
1 A pathogen is an agent or microrganism that causes a disease in its host. Pathogens can be viruses, bacteria, fungi or protozoa. Protozoa are single celled eukaryotic organisms. Some protozoa are pathogens.
Overview of the major bacterial pathogens The major bacterial pathogens are presented in this table:
 Practical Microbiology 30/11/2018 University of Sulaimani college of Pharmacy Year2 Lab. 5: Overview of the major bacterial pathogens The major bacterial pathogens are presented in this table: Major Bacterial
Practical Microbiology 30/11/2018 University of Sulaimani college of Pharmacy Year2 Lab. 5: Overview of the major bacterial pathogens The major bacterial pathogens are presented in this table: Major Bacterial
Laboratory Exercise # 7: Aseptic Technique
 Laboratory Exercise # 7: Aseptic Technique Purpose: The purpose of this laboratory exercise is to acquaint the student with the procedures of aseptic transfer of microbiological cultures. ntroduction:
Laboratory Exercise # 7: Aseptic Technique Purpose: The purpose of this laboratory exercise is to acquaint the student with the procedures of aseptic transfer of microbiological cultures. ntroduction:
Evaluation of the efficiency of Mxxxx as a barrier against microrganisms crossing
 Evaluation of the efficiency of as a barrier against microrganisms crossing A) composition of filter The filter of has the following characteristics: 1. An outer layer, which is composed by a medical,
Evaluation of the efficiency of as a barrier against microrganisms crossing A) composition of filter The filter of has the following characteristics: 1. An outer layer, which is composed by a medical,
_ + Discriminates aerobic organisms that produce catalase to degrade hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen
 Lab 11 Goals and Objectives: Catalase Test Exercise 39: Oxidation and Fermentation Tests (Catalase) Exercise 67: Staphylococci Identification (MSA & Coagulase) Exercise 68: Streptococci & Enterococci Identification
Lab 11 Goals and Objectives: Catalase Test Exercise 39: Oxidation and Fermentation Tests (Catalase) Exercise 67: Staphylococci Identification (MSA & Coagulase) Exercise 68: Streptococci & Enterococci Identification
μ gyra parc Escherichia coli Klebsiella pneumoniae Pseudomonas aeruginosa E. coli gyra E. coli parc gyra parc gyra Escherichia coli E. coli E.
 gyra parc Escherichia coli Klebsiella pneumoniae Pseudomonas aeruginosa E. coli μ E. coli gyra parc gyra parc gyra parc μ μ gyra parc Key words Escherichia coli gyra parc Escherichia coli E. coli gyra
gyra parc Escherichia coli Klebsiella pneumoniae Pseudomonas aeruginosa E. coli μ E. coli gyra parc gyra parc gyra parc μ μ gyra parc Key words Escherichia coli gyra parc Escherichia coli E. coli gyra
Know Your Microbes Introduction to food microbiology Factors affecting microbial growth Temperature Time
 Know Your Microbes Know Your Microbes Introduction to food microbiology Factors affecting microbial growth Temperature Time ph Water activity (Aw) Nutrient availability Atmosphere Hurdle technology Foodborne
Know Your Microbes Know Your Microbes Introduction to food microbiology Factors affecting microbial growth Temperature Time ph Water activity (Aw) Nutrient availability Atmosphere Hurdle technology Foodborne
Tetracycline Rationale for the EUCAST clinical breakpoints, version th November 2009
 Tetracycline Rationale for the EUCAST clinical breakpoints, version 1.0 20 th November 2009 Introduction The natural tetracyclines, including tetracycline, chlortetracycline, oxytetracycline and demethylchlortetracycline
Tetracycline Rationale for the EUCAST clinical breakpoints, version 1.0 20 th November 2009 Introduction The natural tetracyclines, including tetracycline, chlortetracycline, oxytetracycline and demethylchlortetracycline
Occurrence and enumeration of predator bacteria, Bdellovibrio, and their prey in plant rhizosphere and soil
 Symposium no. 11 Paper no. 1763 Presentation: poster Occurrence and enumeration of predator bacteria, Bdellovibrio, and their prey in plant rhizosphere and soil MARKELOVA Natalya Y., KERZHENTSEV Anatoliy
Symposium no. 11 Paper no. 1763 Presentation: poster Occurrence and enumeration of predator bacteria, Bdellovibrio, and their prey in plant rhizosphere and soil MARKELOVA Natalya Y., KERZHENTSEV Anatoliy
Most common dose (mg) 1g x 1 1g x 1 1g x 1 1g x 1 1g x 1 1g x 1. Maximum dose schedule (mg) 1g x 1 1g x 1 1g x 1 1g x 1 1g x 1 1g x 1
 Ertapenem Rationale for the EUCAST clinical breakpoints, version 1.3 1 st June 2009 Introduction Ertapenem is a carbapenem, available only for parenteral use. Ertapenem is relevant for therapy of septicaemia,
Ertapenem Rationale for the EUCAST clinical breakpoints, version 1.3 1 st June 2009 Introduction Ertapenem is a carbapenem, available only for parenteral use. Ertapenem is relevant for therapy of septicaemia,
Two-Component Regulatory System
 Two-Component Regulatory System Two Component Regulatory Systems A two-component regulatory system is a signal transduction system that uses the transfer of phosphoryl groups to control gene transcription
Two-Component Regulatory System Two Component Regulatory Systems A two-component regulatory system is a signal transduction system that uses the transfer of phosphoryl groups to control gene transcription
Bacteria Outline. 1. Overview. 2. Structural & Functional Features. 3. Taxonomy. 4. Communities
 Bacteria Outline 1. Overview 2. Structural & Functional Features 3. Taxonomy 4. Communities Bacteria - Taxonomy PHYLUM CLASS ORDER FAMILY GENUS SPECIES SUB-SPECIES & STRAINS Bacteria - Phyla Firmicutes
Bacteria Outline 1. Overview 2. Structural & Functional Features 3. Taxonomy 4. Communities Bacteria - Taxonomy PHYLUM CLASS ORDER FAMILY GENUS SPECIES SUB-SPECIES & STRAINS Bacteria - Phyla Firmicutes
KINGDOM MONERA. Bacterial Cell Shape 8/22/2010. The Prokaryotes: Archaebacteria and Eubacteria
 KINGDOM MONERA The Prokaryotes: Archaebacteria and Eubacteria Bacteria are the most organisms living on the Earth. (i.e. 10mL of soil contains 1 x 10 10 bacteria. They are found in nearly every habitat
KINGDOM MONERA The Prokaryotes: Archaebacteria and Eubacteria Bacteria are the most organisms living on the Earth. (i.e. 10mL of soil contains 1 x 10 10 bacteria. They are found in nearly every habitat
Microbial Typing by Machine Learned DNA Melt Signatures
 Microbial Typing by Machine Learned DNA Melt Signatures Nadya Andini 1, Bo Wang 2, Pornpat Athamanolap 3, Justin Hardick 4, Billie J. Masek 5, Simone Thair 1, Annie Hu 1, Gideon Avornu 5, Stephen Peterson
Microbial Typing by Machine Learned DNA Melt Signatures Nadya Andini 1, Bo Wang 2, Pornpat Athamanolap 3, Justin Hardick 4, Billie J. Masek 5, Simone Thair 1, Annie Hu 1, Gideon Avornu 5, Stephen Peterson
Interaction of a Free-Living Soil Nematode, Caenorhabditis elegans, with Surrogates of Foodborne Pathogenic Bacteria
 1543 Journal of Food Protection, Vol. 66, No. 9, 2003, Pages 1543 1549 Copyright q, International Association for Food Protection Interaction of a Free-Living Soil Nematode, Caenorhabditis elegans, with
1543 Journal of Food Protection, Vol. 66, No. 9, 2003, Pages 1543 1549 Copyright q, International Association for Food Protection Interaction of a Free-Living Soil Nematode, Caenorhabditis elegans, with
The Prokaryotes: Domains Bacteria and Archaea
 PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Bradley W. Christian, McLennan Community College C H A P T E R 11 The Prokaryotes: Domains Bacteria and Archaea Table 11.1 Classification of Selected Prokaryotes*
PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Bradley W. Christian, McLennan Community College C H A P T E R 11 The Prokaryotes: Domains Bacteria and Archaea Table 11.1 Classification of Selected Prokaryotes*
Report. B. subtilis GS67 Protects C. elegans from Gram-Positive Pathogens via Fengycin-Mediated Microbial Antagonism
 Current Biology 24, 2720 2727, November 17, 2014 ª2014 Elsevier Ltd All rights reserved http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2014.09.055 B. subtilis GS67 Protects C. elegans from Gram-Positive Pathogens via
Current Biology 24, 2720 2727, November 17, 2014 ª2014 Elsevier Ltd All rights reserved http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2014.09.055 B. subtilis GS67 Protects C. elegans from Gram-Positive Pathogens via
INTRODUCTION MATERIALS & METHODS
 Evaluation of Three Bacterial Transport Systems, The New Copan M40 Transystem, Remel Bactiswab And Medical Wire & Equipment Transwab, for Maintenance of Aerobic Fastidious and Non-Fastidious Organisms
Evaluation of Three Bacterial Transport Systems, The New Copan M40 Transystem, Remel Bactiswab And Medical Wire & Equipment Transwab, for Maintenance of Aerobic Fastidious and Non-Fastidious Organisms
Dr. habil. Anna Salek. Mikrobiologist Biotechnologist Research Associate
 Dr. habil. Anna Salek Mikrobiologist Biotechnologist Research Associate BIOTECHNOLOGY of Food Science Cell Biology of Microorganisms Physiology of Microorganisms Biochemistry of Microorganisms Molecularbiology
Dr. habil. Anna Salek Mikrobiologist Biotechnologist Research Associate BIOTECHNOLOGY of Food Science Cell Biology of Microorganisms Physiology of Microorganisms Biochemistry of Microorganisms Molecularbiology
Figure Page 117 Microbiology: An Introduction, 10e (Tortora/ Funke/ Case)
 Chapter 11 The Prokaryotes: Domains Bacteria and Archaea Objective Questions 1) Which of the following are found primarily in the intestines of humans? A) Gram-negative aerobic rods and cocci B) Aerobic,
Chapter 11 The Prokaryotes: Domains Bacteria and Archaea Objective Questions 1) Which of the following are found primarily in the intestines of humans? A) Gram-negative aerobic rods and cocci B) Aerobic,
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Comparison of trap formation by fresh and autoclaved dung samples. The fresh or autoclaved dung was diluted with water and placed on a water agar plate within
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Comparison of trap formation by fresh and autoclaved dung samples. The fresh or autoclaved dung was diluted with water and placed on a water agar plate within
Ch 10. Classification of Microorganisms
 Ch 10 Classification of Microorganisms Student Learning Outcomes Define taxonomy, taxon, and phylogeny. List the characteristics of the Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukarya domains. Differentiate among eukaryotic,
Ch 10 Classification of Microorganisms Student Learning Outcomes Define taxonomy, taxon, and phylogeny. List the characteristics of the Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukarya domains. Differentiate among eukaryotic,
Domain Bacteria. BIO 220 Microbiology Jackson Community College
 Domain Bacteria BIO 220 Microbiology Jackson Community College John Ireland, Ph.D. 2006 Scientific Nomenclature Domain - Bacteria Phylum Important for gross characteristics Class Intermediate characteristics
Domain Bacteria BIO 220 Microbiology Jackson Community College John Ireland, Ph.D. 2006 Scientific Nomenclature Domain - Bacteria Phylum Important for gross characteristics Class Intermediate characteristics
Outline. Collective behavior in bacteria. Know your horsemen. Importance. Cooperation and disease. Medical applications?
 Collective behavior in bacteria Will Driscoll April 30 th, 2008 Outline Importance Our macrobial bias Quorum sensing Biofilms Physiology Development Prokaryotic stab at multicellularity? Discussion But
Collective behavior in bacteria Will Driscoll April 30 th, 2008 Outline Importance Our macrobial bias Quorum sensing Biofilms Physiology Development Prokaryotic stab at multicellularity? Discussion But
In vitro Antibacterial Activity of Bougainvillea spectabilis Leaves Extracts
 Advances in Biological Research 2 (1-2): 01-05, 2008 ISSN 1992-0067 IDOSI Publications, 2008 In vitro Antibacterial Activity of Bougainvillea spectabilis Leaves Extracts A. Umamaheswari, R. Shreevidya
Advances in Biological Research 2 (1-2): 01-05, 2008 ISSN 1992-0067 IDOSI Publications, 2008 In vitro Antibacterial Activity of Bougainvillea spectabilis Leaves Extracts A. Umamaheswari, R. Shreevidya
FOR RUMINANTS. kemin.com/guthealth
 FOR RUMINANTS kemin.com/guthealth What is CLOSTAT? CLOSTAT contains a proprietary, patented strain of Bacillus subtilis PB6. PB6 is a unique, naturally occurring, spore-forming microorganism. Kemin has
FOR RUMINANTS kemin.com/guthealth What is CLOSTAT? CLOSTAT contains a proprietary, patented strain of Bacillus subtilis PB6. PB6 is a unique, naturally occurring, spore-forming microorganism. Kemin has
Microbe Mission C Test
 Microbe Mission C Test Science Olympiad North Regional Tournament at the University of Florida Rank: Points: Name(s): Team Name: School Name: Team Number: Page 2 Part 1: Microscopes Names the following
Microbe Mission C Test Science Olympiad North Regional Tournament at the University of Florida Rank: Points: Name(s): Team Name: School Name: Team Number: Page 2 Part 1: Microscopes Names the following
Dial Complete Foaming Antimicrobial Hand Soap
 Dial Complete Foaming Antimicrobial Hand Soap The Dial Corporation Healthcare Division Table of Contents I. Background II. Dial Complete s Key Benefits Superior Germ Kill Superior Mildness Cost Effectiveness
Dial Complete Foaming Antimicrobial Hand Soap The Dial Corporation Healthcare Division Table of Contents I. Background II. Dial Complete s Key Benefits Superior Germ Kill Superior Mildness Cost Effectiveness
Development and Evaluation of Visual Biosensors for Rapid Detection of Salmonella spp. and Listeria monocytogenes
 Development and Evaluation of Visual Biosensors for Rapid Detection of Salmonella spp. and Listeria monocytogenes Lawrence D. Goodridge Department of Animal Sciences Colorado State University Lawrence.Goodridge@colostate.edu
Development and Evaluation of Visual Biosensors for Rapid Detection of Salmonella spp. and Listeria monocytogenes Lawrence D. Goodridge Department of Animal Sciences Colorado State University Lawrence.Goodridge@colostate.edu
ANTIMICROBIAL TESTING. E-Coli K-12 - E-Coli 0157:H7. Salmonella Enterica Servoar Typhimurium LT2 Enterococcus Faecalis
 ANTIMICROBIAL TESTING E-Coli K-12 - E-Coli 0157:H7 Salmonella Enterica Servoar Typhimurium LT2 Enterococcus Faecalis Staphylococcus Aureus (Staph Infection MRSA) Streptococcus Pyrogenes Anti Bacteria effect
ANTIMICROBIAL TESTING E-Coli K-12 - E-Coli 0157:H7 Salmonella Enterica Servoar Typhimurium LT2 Enterococcus Faecalis Staphylococcus Aureus (Staph Infection MRSA) Streptococcus Pyrogenes Anti Bacteria effect
Michael Jon TeKippe. Department of Molecular Genetics and Microbiology Duke University. Date: Approved: Alejandro Aballay, Ph.D.
 Immunity in Caenorhabditis elegans: A Tale of Two Transcription Factors by Michael Jon TeKippe Department of Molecular Genetics and Microbiology Duke University Date: Approved: Alejandro Aballay, Ph.D.,
Immunity in Caenorhabditis elegans: A Tale of Two Transcription Factors by Michael Jon TeKippe Department of Molecular Genetics and Microbiology Duke University Date: Approved: Alejandro Aballay, Ph.D.,
Microbiological Testing Summary
 BACTERICIDAL ACTIVITY EN 1276 - Chemical disinfectants and antiseptics - Quantitative suspension test for the evaluation of bactericidal activity of chemical disinfectants and antiseptics used in food,
BACTERICIDAL ACTIVITY EN 1276 - Chemical disinfectants and antiseptics - Quantitative suspension test for the evaluation of bactericidal activity of chemical disinfectants and antiseptics used in food,
Enlargement of WHO Repository Transfusion Relevant Bacteria Reference Strains - Report on experimental preparatory work and study design
 WP-TTID Chair: Silvano Wendel, Brazil Subgroup on Bacteria Chair: Thomas Montag, Germany Co-Chair: Erica Wood, Australia Enlargement of WHO Repository Transfusion Relevant Bacteria Reference Strains -
WP-TTID Chair: Silvano Wendel, Brazil Subgroup on Bacteria Chair: Thomas Montag, Germany Co-Chair: Erica Wood, Australia Enlargement of WHO Repository Transfusion Relevant Bacteria Reference Strains -
Our product offering. The ATCC Licensed Derivative Program
 Our product offering Currently MECCONTI offers three different product lines of lyophilized micro-organisms: MicroSwabs: A MicroSwab consists of a lyophilized pellet of a single micro-organism strain inside
Our product offering Currently MECCONTI offers three different product lines of lyophilized micro-organisms: MicroSwabs: A MicroSwab consists of a lyophilized pellet of a single micro-organism strain inside
Retail Catalog 39th Edition Supplemental Information Individual Microorganisms Price Microorganism Description
 LYFO DISK KWIK-STIK Vial 6 Pk Pk Individual Microorganisms Price Microorganism Description ode BSL omment 049L 049K 049P 0645L 0645K 0645P Aggregatibacter aphrophilus AT 4997 D formerly Haemophilus paraphrophilus
LYFO DISK KWIK-STIK Vial 6 Pk Pk Individual Microorganisms Price Microorganism Description ode BSL omment 049L 049K 049P 0645L 0645K 0645P Aggregatibacter aphrophilus AT 4997 D formerly Haemophilus paraphrophilus
Gentamicin Rationale for the EUCAST clinical breakpoints, version th February, 2009
 Gentamicin Rationale for the EUCAST clinical breakpoints, version 1.2 16 th February, 2009 Introduction The aminoglycosides are a group of naturally occurring or semi-synthetic compounds with bactericidal
Gentamicin Rationale for the EUCAST clinical breakpoints, version 1.2 16 th February, 2009 Introduction The aminoglycosides are a group of naturally occurring or semi-synthetic compounds with bactericidal
Course Syllabus, First Half to Midterm Biology 524 Strategies of Host-Microbe Interactions Fall Semester, 2020 M,W
 Course Syllabus, First Half to Midterm Biology 524 Strategies of Host-Microbe Interactions Fall Semester, 2020 M,W 2.00-3.15 Coker 119 Jeff Dangl email: dangl@email.unc.edu office hours by appointment,
Course Syllabus, First Half to Midterm Biology 524 Strategies of Host-Microbe Interactions Fall Semester, 2020 M,W 2.00-3.15 Coker 119 Jeff Dangl email: dangl@email.unc.edu office hours by appointment,
Interactions between symbiotic microbes, their mammalian host, and invading pathogens
 Interactions between symbiotic microbes, their mammalian host, and invading pathogens Vanessa Sperandio UT Southwestern Medical Center Depts. Microbiology and Biochemistry To have a quorum you need chemicals
Interactions between symbiotic microbes, their mammalian host, and invading pathogens Vanessa Sperandio UT Southwestern Medical Center Depts. Microbiology and Biochemistry To have a quorum you need chemicals
DEPARTMENT OF ANIMAL HEALTH TECHNOLOGY COURSE OUTLINE - FALL 2014 LAB PROCEDURES AND MICROBIOLOGY AH 174 E- MAIL:
 DEPARTMENT OF ANIMAL HEALTH TECHNOLOGY COURSE OUTLINE - FALL 2014 LAB PROCEDURES AND MICROBIOLOGY AH 174 INSTRUCTOR: Dr. Chris Mizzi Kristy Mergeart, RAHT PHONE: 780-835-6617 780-835-6779 OFFICE: AS 133
DEPARTMENT OF ANIMAL HEALTH TECHNOLOGY COURSE OUTLINE - FALL 2014 LAB PROCEDURES AND MICROBIOLOGY AH 174 INSTRUCTOR: Dr. Chris Mizzi Kristy Mergeart, RAHT PHONE: 780-835-6617 780-835-6779 OFFICE: AS 133
Update on the ISBT TTID study on establishment of bacterial reference strains for RBC
 Update on the ISBT TTID study on establishment of bacterial reference strains for RBC Dr. Marcel Prax Paul-Ehrlich-Institut Federal Institute for Vaccines and Biomedicines Division Microbial Safety Germany
Update on the ISBT TTID study on establishment of bacterial reference strains for RBC Dr. Marcel Prax Paul-Ehrlich-Institut Federal Institute for Vaccines and Biomedicines Division Microbial Safety Germany
Test Bank for Microbiology A Systems Approach 3rd edition by Cowan
 Test Bank for Microbiology A Systems Approach 3rd edition by Cowan Link download full: https://digitalcontentmarket.org/download/test-bank-formicrobiology-a-systems-approach-3rd-edition-by-cowan Chapter
Test Bank for Microbiology A Systems Approach 3rd edition by Cowan Link download full: https://digitalcontentmarket.org/download/test-bank-formicrobiology-a-systems-approach-3rd-edition-by-cowan Chapter
Phylogenetic Diversity of Coliform Isolates in USA. Phylogenetic Classification
 Phylogenetic Diversity of Coliform Isolates in USA Ya Zhang and Wen Tso Liu University of Illinois at Urbana Champaign Mark LeChevallier American Water Inc. Nov 2011 Phylogenetic Classification group organisms
Phylogenetic Diversity of Coliform Isolates in USA Ya Zhang and Wen Tso Liu University of Illinois at Urbana Champaign Mark LeChevallier American Water Inc. Nov 2011 Phylogenetic Classification group organisms
Class announcements. Prokaryotic cell structure. Prokaryotic Diversity II - Coming attractions 2/10/11. Prokaryotic cell structure
 Class announcements 1. Today no clickers; Friday probably clickers 2. Discuss phylogenetic tree homework in your study group, but write up the HW on your own 3. Friday phylogenetic tree HW due 4. Friday
Class announcements 1. Today no clickers; Friday probably clickers 2. Discuss phylogenetic tree homework in your study group, but write up the HW on your own 3. Friday phylogenetic tree HW due 4. Friday
Test Bank for Microbiology A Systems Approach 3rd edition by Cowan
 Test Bank for Microbiology A Systems Approach 3rd edition by Cowan Link download full: http://testbankair.com/download/test-bankfor-microbiology-a-systems-approach-3rd-by-cowan/ Chapter 1: The Main Themes
Test Bank for Microbiology A Systems Approach 3rd edition by Cowan Link download full: http://testbankair.com/download/test-bankfor-microbiology-a-systems-approach-3rd-by-cowan/ Chapter 1: The Main Themes
Lidia Sas Paszt The Rhizosphere Laboratory, Research Institute of Horticulture, Skierniewice, Poland,
 Lidia Sas Paszt lidia.sas@inhort.pl The Rhizosphere Laboratory, Research Institute of Horticulture, Skierniewice, Poland, www.inhort.pl - Research on the role of roots & rhizosphere in growth & yelding
Lidia Sas Paszt lidia.sas@inhort.pl The Rhizosphere Laboratory, Research Institute of Horticulture, Skierniewice, Poland, www.inhort.pl - Research on the role of roots & rhizosphere in growth & yelding
Obligate anaerobes - cannot grow in the presence of oxygen Facultative anaerobes - can grow with or without oxygen Aerobic - require oxygen
 PROKARYOTES *include bacteria and archaea *singular: bacterium / plural: bacteria PROPERTIES 1. Bacteria are classified into two kingdoms: Eubacteria (true bacteria) and Archaebacteria (Ancient Bacteria).
PROKARYOTES *include bacteria and archaea *singular: bacterium / plural: bacteria PROPERTIES 1. Bacteria are classified into two kingdoms: Eubacteria (true bacteria) and Archaebacteria (Ancient Bacteria).
Antibiotic Resistance in Enterobacteriaceae
 Antibiotic Resistance in Enterobacteriaceae Prof. P. Nordmann 16 es JNI, Nancy, du 10 au 12 juin 2015 1 16 es JNI, Nancy, du 10 au 12 juin 2015 16 es JNI, Nancy, du 10 au 12 juin 2015 16 es JNI, Nancy,
Antibiotic Resistance in Enterobacteriaceae Prof. P. Nordmann 16 es JNI, Nancy, du 10 au 12 juin 2015 1 16 es JNI, Nancy, du 10 au 12 juin 2015 16 es JNI, Nancy, du 10 au 12 juin 2015 16 es JNI, Nancy,
Microbial Genetics, Mutation and Repair. 2. State the function of Rec A proteins in homologous genetic recombination.
 Answer the following questions 1. Define genetic recombination. Microbial Genetics, Mutation and Repair 2. State the function of Rec A proteins in homologous genetic recombination. 3. List 3 types of bacterial
Answer the following questions 1. Define genetic recombination. Microbial Genetics, Mutation and Repair 2. State the function of Rec A proteins in homologous genetic recombination. 3. List 3 types of bacterial
Yersinia enterocolitica Infection and tcaa-dependent Killing of Caenorhabditis elegans
 APPLIED AND ENVIRONMENTAL MICROBIOLOGY, Sept. 2010, p. 6277 6285 Vol. 76, No. 18 0099-2240/10/$12.00 doi:10.1128/aem.01274-10 Copyright 2010, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Yersinia
APPLIED AND ENVIRONMENTAL MICROBIOLOGY, Sept. 2010, p. 6277 6285 Vol. 76, No. 18 0099-2240/10/$12.00 doi:10.1128/aem.01274-10 Copyright 2010, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Yersinia
Universiteit van Pretoria University of Pretoria. Mikrobiologie 251 Toets Maart 2012 Microbiology 251 Test March Examiners: Dr L Moleleki
 Universiteit van Pretoria University of Pretoria Mikrobiologie 251 Toets Maart 2012 Microbiology 251 Test March 2012 Tyd: 1 uur Time: 1 hour Eksaminatore: Dr L Moleleki Examiners: Dr L Moleleki Beantwoord
Universiteit van Pretoria University of Pretoria Mikrobiologie 251 Toets Maart 2012 Microbiology 251 Test March 2012 Tyd: 1 uur Time: 1 hour Eksaminatore: Dr L Moleleki Examiners: Dr L Moleleki Beantwoord
Product List. - Kits & Reagents
 Product List - Kits & Reagents Bacterial Pathogens Viral Pathogens Beverage Spoilage Organisms Yeast and Mold GMOs Allergens Animal Identification Veterinary Environmental Pharma DNA/RNA Extraction Additional
Product List - Kits & Reagents Bacterial Pathogens Viral Pathogens Beverage Spoilage Organisms Yeast and Mold GMOs Allergens Animal Identification Veterinary Environmental Pharma DNA/RNA Extraction Additional
Optical forward scattering for colony identification and differentiation of bacterial species
 Optical forward scattering for colony identification and differentiation of bacterial species Arun K. Bhunia, E. D. Hirleman and J.P. Robinson Center for Food Safety and Engineering, Purdue University
Optical forward scattering for colony identification and differentiation of bacterial species Arun K. Bhunia, E. D. Hirleman and J.P. Robinson Center for Food Safety and Engineering, Purdue University
HACCP: INTRODUCTION AND HAZARD ANALYSIS
 Food Hygiene HACCP: INTRODUCTION AND HAZARD ANALYSIS State: December 15, 2004 WPF 5/0 Important milestones in the development of food safety systems Time Activity Distant past Use of prohibition principle
Food Hygiene HACCP: INTRODUCTION AND HAZARD ANALYSIS State: December 15, 2004 WPF 5/0 Important milestones in the development of food safety systems Time Activity Distant past Use of prohibition principle
NUT-TTC/EMB Code 5541
 NUT-TTC/EMB Code 5541 COMING SOON! BioPaddles Colony Identification App Nutrient-TTC Agar (NUT-TTC) Eosin Methylene Blue Agar (EMB) USE: Isolation and differentiation of Gram (-) enteric bacilli. Coliform
NUT-TTC/EMB Code 5541 COMING SOON! BioPaddles Colony Identification App Nutrient-TTC Agar (NUT-TTC) Eosin Methylene Blue Agar (EMB) USE: Isolation and differentiation of Gram (-) enteric bacilli. Coliform
Research Article Evaluation of Verigene Blood Culture Test Systems for Rapid Identification of Positive Blood Cultures
 BioMed Volume 2016, Article ID 1081536, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/1081536 Research Article Evaluation of Verigene Blood Culture Test Systems for Rapid Identification of Positive Blood Cultures
BioMed Volume 2016, Article ID 1081536, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/1081536 Research Article Evaluation of Verigene Blood Culture Test Systems for Rapid Identification of Positive Blood Cultures
Most common dose (mg) 1 g x 3 1 g x mg -1.0 g x 3 1 g x mg -1 g x mg -1 g x 3
 Meropenem Rationale for the EUCAST clinical breakpoints, version 1.5 1 st June 2009 Introduction Meropenem is a carbapenem, available only for parenteral use. Meropenem is relevant for therapy of septicaemia,
Meropenem Rationale for the EUCAST clinical breakpoints, version 1.5 1 st June 2009 Introduction Meropenem is a carbapenem, available only for parenteral use. Meropenem is relevant for therapy of septicaemia,
CATALOGUE OF TEST, CONTROL OR BIOASSAY STRAINS FROM BCCM CULTURE COLLECTIONS
 CATALOGUE OF TEST, CONTROL OR BIOASSAY STRAINS FROM BCCM CULTURE COLLECTIONS LIST OF STRAINS INVOLVED IN NORMS AND STANDARDISED MICROBIOLOGICAL METHODS The Belgian Co-ordinated Collections of Micro-organisms
CATALOGUE OF TEST, CONTROL OR BIOASSAY STRAINS FROM BCCM CULTURE COLLECTIONS LIST OF STRAINS INVOLVED IN NORMS AND STANDARDISED MICROBIOLOGICAL METHODS The Belgian Co-ordinated Collections of Micro-organisms
SSI ENTERIC PRODUCT INFORMATION. Detects all Enterobacteria. Direct identification. Rapid diagnosis. Cost saving
 SSI ENTERIC M E D I U M Detects all Enterobacteria Direct identification Rapid diagnosis Cost saving SSI Diagnostica 2 Herredsvejen 3400 Hillerød Denmark PRODUCT INFORMATION Tel: +45 4829 9100 Fax: +45
SSI ENTERIC M E D I U M Detects all Enterobacteria Direct identification Rapid diagnosis Cost saving SSI Diagnostica 2 Herredsvejen 3400 Hillerød Denmark PRODUCT INFORMATION Tel: +45 4829 9100 Fax: +45
EASTERN ARIZONA COLLEGE Microbiology
 EASTERN ARIZONA COLLEGE Microbiology Course Design 2015-2016 Course Information Division Science Course Number BIO 205 (SUN# BIO 2205) Title Microbiology Credits 4 Developed by Ed Butler/Revised by Willis
EASTERN ARIZONA COLLEGE Microbiology Course Design 2015-2016 Course Information Division Science Course Number BIO 205 (SUN# BIO 2205) Title Microbiology Credits 4 Developed by Ed Butler/Revised by Willis
A New Model System for the Study of the Animal Innate Immune Response to Fungal Infections 1
 ISSN 0096-3925, Moscow University Biological Sciences Bulletin, 2014, Vol. 69, No. 2, pp. 45 50. Allerton Press, Inc., 2014. Original Russian Text J. Plotnikova, O.V. Kamzolkina, F.M. Ausubel, 2014, published
ISSN 0096-3925, Moscow University Biological Sciences Bulletin, 2014, Vol. 69, No. 2, pp. 45 50. Allerton Press, Inc., 2014. Original Russian Text J. Plotnikova, O.V. Kamzolkina, F.M. Ausubel, 2014, published
Cytolytic pore-forming toxins (PFTs) comprise 25% of all
 Mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways defend against bacterial pore-forming toxins Danielle L. Huffman*, Laurence Abrami, Roman Sasik, Jacques Corbeil, F. Gisou van der Goot, and Raffi V. Aroian*,
Mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways defend against bacterial pore-forming toxins Danielle L. Huffman*, Laurence Abrami, Roman Sasik, Jacques Corbeil, F. Gisou van der Goot, and Raffi V. Aroian*,
