Bacteria Outline. 1. Overview. 2. Structural & Functional Features. 3. Taxonomy. 4. Communities
|
|
|
- Brenda Jennings
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Bacteria Outline 1. Overview 2. Structural & Functional Features 3. Taxonomy 4. Communities
2 Bacteria - Taxonomy PHYLUM CLASS ORDER FAMILY GENUS SPECIES SUB-SPECIES & STRAINS
3 Bacteria - Phyla Firmicutes Bacteroidetes 90% Proteobacteria Actinobacteria Tenericutes Verrucomicrobia Fusobacteria Cyanobacteria etc.
4 Do we really need to learn taxonomy? Yes. (if you want to interpret functional labs and understand the microbiome in depth)
5 Taxonomy + Function Important for Interpreting functional microbiome test results (stool tests, organic acid tests, etc.) Understanding probiotics and interaction with microbiome Understanding importance / relevance of scientific and clinical microbiome research Be patient! Mastering technical terminology takes time and familiarity.
6
7
8 1. Lactobacillus acidophilus 2. Bifidobacterium bifidum PHYLUM CLASS ORDER FAMILY GENUS SPECIES STRAIN Firmicutes Bacilli Lactobacillales Lactobacillaceae Lactobacillus L. acidophilus DDS-1 Actinobacteria Actinobacteria Bifidobacteriales Bifidobacteriaceae Bifidobacterium B. bifidum ATCC 29521
9 Firmicutes Mostly gram-positive ( strong skin ) Tend to be associated closely with intestinal mucosa (vs. lumenal) Mostly coccus and bacillus forms Many can produce endospores Common groups: Lactobacillus (commensal and probiotic) Bacillus (commensal and probiotic) Clostridia (commensal)
10 Gram-negative & anaerobic Tend to be located lumenally (vs. mucosal) Rod-shaped Do not form endospores Common groups: Bacteroides Prevotella Bacteroidetes
11 Gram-negative Proteobacteria Facultative & obligate anaerobes Very diverse forms ( protean = capable of assuming many forms) Includes a variety of well-known pathogens / pathobionts Escherichia coli, Salmonella, Helicobacter pylori, Yersinia pestis (plague)
12 Actinobacteria Gram-positive Long rods & filaments Example: Bifidobacteria Verrucomicrobia Other Phyla Verruca = wart Anaerobic, gram-negative Example: Akkermansia muciniphila
13 A few notable groups and species (commensals, pathobionts, and pathogens)
14 Firmicutes > Clostridia Clostridia Abundant (10-40% of total gut bacteria) and complex group Very important group; some perform many beneficial functions Strictly anaerobic, gram-positive Colonizes near the epithelial barrier in the colon
15 Clostridia Major butyrate producers (feed colon epithelial cells) Also produce secondary bile acids from primary bile acids Form endospores Includes some pathogens: C. difficile, C. tetani, C. botulinum, etc.
16
17
18
19 Clostridia Examples COMMENSALS Faecalibacterium prausnitzii Roseburia intestinalis Eubacterium rectale Coprococcus eutactus Clostridium scindens Butyrivibrio crossotus PATHOGENS Clostridium difficile (diarrhea, severe colitis) Clostridium tetani (tetanus) Clostridium botulinum (botulism, botox) Clostridium perfringens (food poisoning, gangrene)
20
21
22 Akkermansia Muciniphila Phylum: Verrucomicrobia Relatively abundant: up to 3.0% of gut bacterial population on average Strictly anaerobic, gram-negative Colonizes the mucus layer; produces propionate and acetate from mucus SCFAs modulate gene expression via epigenetics Improves epithelial barrier function
23
24 Pathobionts & Pathogens INTERNAL (Long-term) Commensals (Symbionts) Dysbiosis & Pathobionts EXTERNAL (Transient) Beneficial Microbes Pathogens & Parasites
25 Bacteroidetes Bacteroides fragilis Proteobacteria Pathobiont Examples Helicobacter pylori: Can cause ulcers and stomach cancer but may reduce esophageal cancer risk Bilophila wadsworthia: normal commensal but may contribute to colitis with high-fat diet Klebsiella: normal commensal but can cause infections (sometimes serious)
26 Bacteroides fragilis Obligate anaerobe, gram-negative Polysaccharide A: stimulates anti-inflammatory response (induces Treg cells) BUT, it can be a pathobiont Can produce a capsule (virulence factor) Common opportunistic pathogen in internal abdominal infections (leaky gut) Underscores importance of barrier integrity for both commensals and pathogens
27 Proteobacteria Salmonella enterica (typhimurium) Escherichia coli (pathogenic strains) Vibrio cholerae Pathogenic Bacteria Campylobacter jejuni Klebsiella pneumoniae Firmicutes > Bacilli > Lactobaciallales Enterococcus faecalis Enterococcus faecium
28 Taxonomy: Take-Homes Taxonomy important for working with microbiome Commensals: some groups and species play a special positive role Immune function, intestinal barrier, motility, many others Keeping pathobionts and pathogens in check Pathobionts & pathogens Can cause disease Depends on context, including the health of the individual, the overall health of the microbiome, and environmental factors
29 Bacteria Outline 1. Overview 2. Structural & Functional Features 3. Taxonomy 4. Communities
30 Adaptibility & Resilience Flexibility in using different substrates (depending on genes within each bacteria) Ability to tolerate variable physiological factors (oxygen, ph, bile, etc.) Rapid evolution of DNA Horizontal gene transfer (via plasmids) Replication rate, formation of endospores Community interactions, biofilms
31 Microbiome Communities Complex ecological communities of microbes Composition depends on local factors (physiological conditions, available substrates, other microbes, etc.) Highly interdependent, complex functional relationships (with each other & with us) Cooperate and compete Relatively stable & resilient
32 Physiological Factors Location Digestive tract region & microenvironment / niche Mucus layer vs. lumen Available substrates ph Oxygen Transit time / flow rate Barriers & immune factors Attachment sites Others: Redox status, bile salts, etc.
33 Substrates (Nutrients) Sources & types (diet, secretions, microbe metabolites) Availability Competition with other microbes Digestion / absorption by GI tract Concentration, flow rate, etc. Position in community food chain
34 Cross-Feeding & Competition A Resistant starch Butyrate SPECIES 2 SPECIES 1 C B Acetate SPECIES 3 SPECIES 4
35 Direct Competition Substrates (nutrients / metabolites) Space / attachment sites (mucus / epithelial later) Antimicrobial factors: organic acids, bacteriocins, lactocillin, etc. Indirect Suppress immune response to themselves Enhance immune response to competitors Others, including possibly affecting eating behavior
36 Cross-feeding / food web (mutualism) Metabolites produced by one species can be used as a substrate for another Coordination via quorum sensing Molecules used to coordinate activities Depends on density Sharing DNA e.g. - antibiotic resistance genes Biofilms Cooperation
37 Biofilms Bacteria + EPS (extracellular polymeric substance polysaccharides, proteins & nucleic acids) Normal part of many communities, but can contribute to pathogenicity (resistance to treatments) More stable, protected microenvironment Enables greater synergy & cooperation within community Contains extracellular enzymes external shared digestion
38 Colonization Resistance Capacity of microbiome communities to resist new colonization by pathogens and other transients (e.g., probiotics, foodborne microbes) Key to preventing GI infections: First line of defense Main factors contributing: Lack of niches (competition - space, available substrates) Hostile environment (ph, antimicrobial factors, immune factors) Biofilms Coordination (quorum sensing)
39 Stability & Resilience Above factors contribute to stability & resilience Stability: resistance to change, ability to maintain homeostasis Resilience: capacity to return to homeostasis after disturbance Diverse ecosystems are generally more stable & resilient Microbiome stability, resilience, & functional capacity contribute to human health & resilience Less prone to disruption of our homeostasis & health Contributes to tolerance of a wider range of foods and conditions Makes it challenging to change the microbiome BUT less diverse (less stable) microbiomes may be easier to change
40 Bacteria Outline 1. Overview 2. Structural & Functional Features 3. Taxonomy 4. Communities
41 Module 1 Overview 1. Microbiome overview: getting a sense of the microbiome, research, what we know 2. Bacteria: features, functions, communities & taxonomy 3. Other microbes: archaea, fungi, viruses, parasites (protozoa & helminths)
42
The Prokaryotes: Domains Bacteria and Archaea
 PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Bradley W. Christian, McLennan Community College C H A P T E R 11 The Prokaryotes: Domains Bacteria and Archaea Table 11.1 Classification of Selected Prokaryotes*
PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Bradley W. Christian, McLennan Community College C H A P T E R 11 The Prokaryotes: Domains Bacteria and Archaea Table 11.1 Classification of Selected Prokaryotes*
Microbiota: Its Evolution and Essence. Hsin-Jung Joyce Wu "Microbiota and man: the story about us
 Microbiota: Its Evolution and Essence Overview q Define microbiota q Learn the tool q Ecological and evolutionary forces in shaping gut microbiota q Gut microbiota versus free-living microbe communities
Microbiota: Its Evolution and Essence Overview q Define microbiota q Learn the tool q Ecological and evolutionary forces in shaping gut microbiota q Gut microbiota versus free-living microbe communities
B. Correct! Bacillus anthraces produces spores that can cause anthrax. D. Incorrect! Diphtheria is caused by Corynebacterium diphtheriae.
 Microbiology - Problem Drill 09 - The Prokaryotes No. 1 of 10 1. Bacillus anthraces is most closely associated with which of the following? (A) Botulism poisoning (B) Anthrax (C) Gangrene (D) Diphtheria
Microbiology - Problem Drill 09 - The Prokaryotes No. 1 of 10 1. Bacillus anthraces is most closely associated with which of the following? (A) Botulism poisoning (B) Anthrax (C) Gangrene (D) Diphtheria
Human Microbiome Project
 Human Microbiome Project Definitions Microbiome: the collective genomes of the community of organisms that share our space Metagenome: culture independent study of genomes of many organisms in order to
Human Microbiome Project Definitions Microbiome: the collective genomes of the community of organisms that share our space Metagenome: culture independent study of genomes of many organisms in order to
Characteristics. Nucleoid Region single circular chromosome plasmids mesosome
 Prokaryotes Characteristics Nucleoid Region single circular chromosome plasmids mesosome No membranebound organelles Ribosomes (70S) Plasma membrane Cell wall peptidoglycan Capsule glycocalyx Flagella
Prokaryotes Characteristics Nucleoid Region single circular chromosome plasmids mesosome No membranebound organelles Ribosomes (70S) Plasma membrane Cell wall peptidoglycan Capsule glycocalyx Flagella
9/8/2017. Bacteria and Archaea. Three domain system: The present tree of life. Structural and functional adaptations contribute to prokaryotic success
 5 m 2 m 9/8/2017 Three domain system: The present tree of life Bacteria and Archaea Chapter 27 Structural and functional adaptations contribute to prokaryotic success Unicellular Small Variety of shapes
5 m 2 m 9/8/2017 Three domain system: The present tree of life Bacteria and Archaea Chapter 27 Structural and functional adaptations contribute to prokaryotic success Unicellular Small Variety of shapes
Obligate anaerobes - cannot grow in the presence of oxygen Facultative anaerobes - can grow with or without oxygen Aerobic - require oxygen
 PROKARYOTES *include bacteria and archaea *singular: bacterium / plural: bacteria PROPERTIES 1. Bacteria are classified into two kingdoms: Eubacteria (true bacteria) and Archaebacteria (Ancient Bacteria).
PROKARYOTES *include bacteria and archaea *singular: bacterium / plural: bacteria PROPERTIES 1. Bacteria are classified into two kingdoms: Eubacteria (true bacteria) and Archaebacteria (Ancient Bacteria).
Microbial Dynamics of the Broiler Intestinal Tract Margie Lee, Ph.D., D.V.M.
 Microbial Dynamics of the Broiler Intestinal Tract Margie Lee, Ph.D., D.V.M. Biography Ph.D., Medical Microbiology, The University of Georgia, 1990. M.S., Medical Microbiology, The University of Georgia,
Microbial Dynamics of the Broiler Intestinal Tract Margie Lee, Ph.D., D.V.M. Biography Ph.D., Medical Microbiology, The University of Georgia, 1990. M.S., Medical Microbiology, The University of Georgia,
Ch 27: The Prokaryotes Bacteria & Archaea Older: (Eu)bacteria & Archae(bacteria)
 Ch 27: The Prokaryotes Bacteria & Archaea Older: (Eu)bacteria & Archae(bacteria) (don t study Concept 27.2) Some phyla Remember: Bacterial cell structure and shapes 1 Usually very small but some are unusually
Ch 27: The Prokaryotes Bacteria & Archaea Older: (Eu)bacteria & Archae(bacteria) (don t study Concept 27.2) Some phyla Remember: Bacterial cell structure and shapes 1 Usually very small but some are unusually
Game plan Lecture Lab Prelabs
 Game plan Lecture Binary fission Growth curves Physical requirements for growth Chemical requirements for growth Lab Lab Exam Prelabs Growth Curve Bring books and APO-3 for next class Microbial growth
Game plan Lecture Binary fission Growth curves Physical requirements for growth Chemical requirements for growth Lab Lab Exam Prelabs Growth Curve Bring books and APO-3 for next class Microbial growth
Kingdom Monera(Archaebacteria & Eubacteria)
 Kingdom Monera(Archaebacteria & All bacteria are prokaryotes Characteristics: 1. No nucleus Eubacteria) 2. No membrane bound organelles 3. Smaller & less ribosomes 4. Most are smaller than eukaryotes 5.
Kingdom Monera(Archaebacteria & All bacteria are prokaryotes Characteristics: 1. No nucleus Eubacteria) 2. No membrane bound organelles 3. Smaller & less ribosomes 4. Most are smaller than eukaryotes 5.
LECTURE 13. THE BACTERIA (cont.) Photosynthetic Bacteria, phylogenetically widespread. And many Proteobacteria. Photosynthetic Bacteria
 Photosynthetic Bacteria, phylogenetically widespread LECTURE 13 THE BACTERIA (cont.) And many Proteobacteria Photosynthetic Bacteria > Green Sulfur > Green Nonsulfur > Purple Sulfur > Purple Nonsulfur
Photosynthetic Bacteria, phylogenetically widespread LECTURE 13 THE BACTERIA (cont.) And many Proteobacteria Photosynthetic Bacteria > Green Sulfur > Green Nonsulfur > Purple Sulfur > Purple Nonsulfur
KINGDOM MONERA. Bacterial Cell Shape 8/22/2010. The Prokaryotes: Archaebacteria and Eubacteria
 KINGDOM MONERA The Prokaryotes: Archaebacteria and Eubacteria Bacteria are the most organisms living on the Earth. (i.e. 10mL of soil contains 1 x 10 10 bacteria. They are found in nearly every habitat
KINGDOM MONERA The Prokaryotes: Archaebacteria and Eubacteria Bacteria are the most organisms living on the Earth. (i.e. 10mL of soil contains 1 x 10 10 bacteria. They are found in nearly every habitat
Vocabulary- Bacteria (34 words)
 Biology II BACTERIA Vocabulary- Bacteria (34 words) 1. Prokaryote 21. phototroph 2. Peptidoglycan 22. chemotroph 3. Methanogen 23. obligate anaerobe 4. Halophile 24. facultative anaerobe 5. Thermoacidophile
Biology II BACTERIA Vocabulary- Bacteria (34 words) 1. Prokaryote 21. phototroph 2. Peptidoglycan 22. chemotroph 3. Methanogen 23. obligate anaerobe 4. Halophile 24. facultative anaerobe 5. Thermoacidophile
Nature Biotechnology: doi: /nbt Supplementary Figure 1. The inflammatory response in the mammalian gut leads to tetrathionate generation.
 Supplementary Figure 1 The inflammatory response in the mammalian gut leads to tetrathionate generation. Cytokine signaling following an inflammatory insult leads to, among other responses, release of
Supplementary Figure 1 The inflammatory response in the mammalian gut leads to tetrathionate generation. Cytokine signaling following an inflammatory insult leads to, among other responses, release of
Bacteria and Viruses. 1 Bacteria CHAPTER 18. MAINIDEA Bacteria are prokaryotic cells.
 CHAPTER 18 Bacteria and Viruses 1 Bacteria 7(F), 8(B), 8(C), 11(C), 12(A) Before You Read When you hear the word bacteria, what comes to mind? On the lines below, describe places you think bacteria might
CHAPTER 18 Bacteria and Viruses 1 Bacteria 7(F), 8(B), 8(C), 11(C), 12(A) Before You Read When you hear the word bacteria, what comes to mind? On the lines below, describe places you think bacteria might
Microbial Taxonomy. Classification of living organisms into groups. A group or level of classification
 Lec 2 Oral Microbiology Dr. Chatin Purpose Microbial Taxonomy Classification Systems provide an easy way grouping of diverse and huge numbers of microbes To provide an overview of how physicians think
Lec 2 Oral Microbiology Dr. Chatin Purpose Microbial Taxonomy Classification Systems provide an easy way grouping of diverse and huge numbers of microbes To provide an overview of how physicians think
INTERPRETATION OF THE GRAM STAIN
 INTERPRETATION OF THE GRAM STAIN DISCLOSURE Relevant relationships with commercial entities none Potential for conflicts of interest within this presentation none Steps taken to review and mitigate potential
INTERPRETATION OF THE GRAM STAIN DISCLOSURE Relevant relationships with commercial entities none Potential for conflicts of interest within this presentation none Steps taken to review and mitigate potential
Domain Bacteria. BIO 220 Microbiology Jackson Community College
 Domain Bacteria BIO 220 Microbiology Jackson Community College John Ireland, Ph.D. 2006 Scientific Nomenclature Domain - Bacteria Phylum Important for gross characteristics Class Intermediate characteristics
Domain Bacteria BIO 220 Microbiology Jackson Community College John Ireland, Ph.D. 2006 Scientific Nomenclature Domain - Bacteria Phylum Important for gross characteristics Class Intermediate characteristics
Figure Page 117 Microbiology: An Introduction, 10e (Tortora/ Funke/ Case)
 Chapter 11 The Prokaryotes: Domains Bacteria and Archaea Objective Questions 1) Which of the following are found primarily in the intestines of humans? A) Gram-negative aerobic rods and cocci B) Aerobic,
Chapter 11 The Prokaryotes: Domains Bacteria and Archaea Objective Questions 1) Which of the following are found primarily in the intestines of humans? A) Gram-negative aerobic rods and cocci B) Aerobic,
Chapter 27: Bacteria and Archaea
 Name Period Overview 1. The chapter opens with amazing tales of life at the extreme edge. What are the masters of adaptation? Describe the one case you thought most dramatic. Concept 27.1 Structural and
Name Period Overview 1. The chapter opens with amazing tales of life at the extreme edge. What are the masters of adaptation? Describe the one case you thought most dramatic. Concept 27.1 Structural and
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION ARTICLE NUMBER: 16161 DOI: 10.1038/NMICROBIOL.2016.161 A reference gene catalogue of the pig gut microbiome Liang Xiao 1, Jordi Estellé 2, Pia Kiilerich 3, Yuliaxis Ramayo-Caldas
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION ARTICLE NUMBER: 16161 DOI: 10.1038/NMICROBIOL.2016.161 A reference gene catalogue of the pig gut microbiome Liang Xiao 1, Jordi Estellé 2, Pia Kiilerich 3, Yuliaxis Ramayo-Caldas
1. Prokaryotic Nutritional & Metabolic Adaptations
 Chapter 27B: Bacteria and Archaea 1. Prokaryotic Nutritional & Metabolic Adaptations 2. Survey of Prokaryotic Groups A. Domain Bacteria Gram-negative groups B. Domain Bacteria Gram-positive groups C. Domain
Chapter 27B: Bacteria and Archaea 1. Prokaryotic Nutritional & Metabolic Adaptations 2. Survey of Prokaryotic Groups A. Domain Bacteria Gram-negative groups B. Domain Bacteria Gram-positive groups C. Domain
Section Title: Archaebacteria vs. Eubacteria
 Unit: 3.1 Name: Section Title: Archaebacteria vs. Eubacteria Latin Root Word: Review of Old Information: None New Information: Bacteria Notes Basic Bacteria Facts Classification of Bacteria: Kingdom Archaebacteria
Unit: 3.1 Name: Section Title: Archaebacteria vs. Eubacteria Latin Root Word: Review of Old Information: None New Information: Bacteria Notes Basic Bacteria Facts Classification of Bacteria: Kingdom Archaebacteria
Kingdom Monera. These notes are to help you check your answers in your Bacteria unit handout package that you received in class.
 Kingdom Monera These notes are to help you check your answers in your Bacteria unit handout package that you received in class. Textbook reference pages Textbook Section 17-2 & 17-3 pages 360-375 Basic
Kingdom Monera These notes are to help you check your answers in your Bacteria unit handout package that you received in class. Textbook reference pages Textbook Section 17-2 & 17-3 pages 360-375 Basic
Bacteria are very small
 BACTERIA BACTERIA Bacteria are very small Bacteria are very small compared to cells with nuclei This is a pore in human skin and the yellow spheres are bacteria BACTERIA LIVE ALMOST EVERYWHERE Hot springs
BACTERIA BACTERIA Bacteria are very small Bacteria are very small compared to cells with nuclei This is a pore in human skin and the yellow spheres are bacteria BACTERIA LIVE ALMOST EVERYWHERE Hot springs
LESSON 1.3 WORKBOOK. Bacterial structures. Workbook Lesson 1.3
 Colonize the ability of bacteria to adapt to permanently inhabit our bodies. Capsule an external layer made of sugars that surrounds some bacteria. Cell wall an external layer surrounding the plasma membrane
Colonize the ability of bacteria to adapt to permanently inhabit our bodies. Capsule an external layer made of sugars that surrounds some bacteria. Cell wall an external layer surrounding the plasma membrane
Introduction to Microbiology. CLS 212: Medical Microbiology Miss Zeina Alkudmani
 Introduction to Microbiology CLS 212: Medical Microbiology Miss Zeina Alkudmani Microbiology Micro- means very small (that needs a microscope to see). Microbiology is the study of very small living organisms.
Introduction to Microbiology CLS 212: Medical Microbiology Miss Zeina Alkudmani Microbiology Micro- means very small (that needs a microscope to see). Microbiology is the study of very small living organisms.
In vitro the effect of intestinal normal flora on some pathogenic bacteria.
 In vitro the effect of intestinal normal flora on some pathogenic bacteria. Abstract: Dr.abbass shaker Ali adel Leena abd Al-Redha The effect of two types of intestinal bacterial normal floral ( and klebsiella)
In vitro the effect of intestinal normal flora on some pathogenic bacteria. Abstract: Dr.abbass shaker Ali adel Leena abd Al-Redha The effect of two types of intestinal bacterial normal floral ( and klebsiella)
Kingdom Monera Bacteria
 Kingdom Monera Bacteria Common bacteria Prokaryotes Strep throat Anthrax Chlamydia E. coli Meningitis Salmonella Micrococcus(intestinal) Streptococcus mutans Haemophilusinfluenzae Cellphonious bacterious
Kingdom Monera Bacteria Common bacteria Prokaryotes Strep throat Anthrax Chlamydia E. coli Meningitis Salmonella Micrococcus(intestinal) Streptococcus mutans Haemophilusinfluenzae Cellphonious bacterious
EASTERN ARIZONA COLLEGE Microbiology
 EASTERN ARIZONA COLLEGE Microbiology Course Design 2015-2016 Course Information Division Science Course Number BIO 205 (SUN# BIO 2205) Title Microbiology Credits 4 Developed by Ed Butler/Revised by Willis
EASTERN ARIZONA COLLEGE Microbiology Course Design 2015-2016 Course Information Division Science Course Number BIO 205 (SUN# BIO 2205) Title Microbiology Credits 4 Developed by Ed Butler/Revised by Willis
Risk Assessment of Staphylococcus aureus and Clostridium perfringens in ready to eat Egg Products
 Risk Assessment of Staphylococcus aureus and Clostridium perfringens in ready to eat Egg Products Introduction Egg products refer to products made by adding other types of food or food additives to eggs
Risk Assessment of Staphylococcus aureus and Clostridium perfringens in ready to eat Egg Products Introduction Egg products refer to products made by adding other types of food or food additives to eggs
Ch 3. Bacteria and Archaea
 Ch 3 Bacteria and Archaea SLOs for Culturing of Microorganisms Compare and contrast the overall cell structure of prokaryotes and eukaryotes. List structures all bacteria possess. Describe three basic
Ch 3 Bacteria and Archaea SLOs for Culturing of Microorganisms Compare and contrast the overall cell structure of prokaryotes and eukaryotes. List structures all bacteria possess. Describe three basic
Kharkov National Medical University. Head of Microbiology, Virology and Immunology Department Minukhin Valeriy Vladimirivich
 Kharkov National Medical University Head of Microbiology, Virology and Immunology Department Minukhin Valeriy Vladimirivich Tkachenko Victoria 1, 5, 11, 14, 19, 21, 30 Kovalenko Natalia 2, 12, 25, 29 Siritsa
Kharkov National Medical University Head of Microbiology, Virology and Immunology Department Minukhin Valeriy Vladimirivich Tkachenko Victoria 1, 5, 11, 14, 19, 21, 30 Kovalenko Natalia 2, 12, 25, 29 Siritsa
VPM 201: Veterinary Bacteriology and Mycology 6-7/10/2010. LABORATORY 5a - ENTEROBACTERIACEAE
 VPM 201: Veterinary Bacteriology and Mycology 6-7/10/2010 LABORATORY 5a - ENTEROBACTERIACEAE A large family of gram-negative bacilli. They grow readily on common culture media. Organisms are separated
VPM 201: Veterinary Bacteriology and Mycology 6-7/10/2010 LABORATORY 5a - ENTEROBACTERIACEAE A large family of gram-negative bacilli. They grow readily on common culture media. Organisms are separated
19-1 Notes Bacteria. Named after the Greek word Little stick because many bacteria have a stick-like shape when viewed under a microscope
 19-1 Notes Bacteria Bacteria are found virtually everywhere! Named after the Greek word Little stick because many bacteria have a stick-like shape when viewed under a microscope We know that bacteria are
19-1 Notes Bacteria Bacteria are found virtually everywhere! Named after the Greek word Little stick because many bacteria have a stick-like shape when viewed under a microscope We know that bacteria are
Bacteria are very small
 BACTERIA BACTERIA Bacteria are very small Bacteria are very small compared to cells with nuclei (Eukaryotic cells) This is a pore in human skin and the yellow spheres are bacteria CLASSIFICATION OF BACTERIA
BACTERIA BACTERIA Bacteria are very small Bacteria are very small compared to cells with nuclei (Eukaryotic cells) This is a pore in human skin and the yellow spheres are bacteria CLASSIFICATION OF BACTERIA
Objective 1: The student will demonstrate an understanding of the nature of science.
 August 2003 Objective 1: The student will demonstrate an understanding of the nature of science. Biology (1) and Integrated Physics and Chemistry (1) Scientific Processes. The student, for at least 40%
August 2003 Objective 1: The student will demonstrate an understanding of the nature of science. Biology (1) and Integrated Physics and Chemistry (1) Scientific Processes. The student, for at least 40%
FOR RUMINANTS. kemin.com/guthealth
 FOR RUMINANTS kemin.com/guthealth What is CLOSTAT? CLOSTAT contains a proprietary, patented strain of Bacillus subtilis PB6. PB6 is a unique, naturally occurring, spore-forming microorganism. Kemin has
FOR RUMINANTS kemin.com/guthealth What is CLOSTAT? CLOSTAT contains a proprietary, patented strain of Bacillus subtilis PB6. PB6 is a unique, naturally occurring, spore-forming microorganism. Kemin has
BACTERIA AND ARCHAEA 10/15/2012
 BACTERIA AND ARCHAEA Chapter 27 KEY CONCEPTS: Structural and functional adaptations contribute to prokaryotic success Rapid reproduction, mutation, and genetic recombination promote genetic diversity in
BACTERIA AND ARCHAEA Chapter 27 KEY CONCEPTS: Structural and functional adaptations contribute to prokaryotic success Rapid reproduction, mutation, and genetic recombination promote genetic diversity in
Istituto di Microbiologia. Università Cattolica del Sacro Cuore, Roma. Gut Microbiota assessment and the Meta-HIT program.
 Istituto di Microbiologia Università Cattolica del Sacro Cuore, Roma Gut Microbiota assessment and the Meta-HIT program Giovanni Delogu 1 Most of the bacteria species living in the gut cannot be cultivated
Istituto di Microbiologia Università Cattolica del Sacro Cuore, Roma Gut Microbiota assessment and the Meta-HIT program Giovanni Delogu 1 Most of the bacteria species living in the gut cannot be cultivated
Classifying Prokaryotes: Eubacteria Plasma Membrane. Ribosomes. Plasmid (DNA) Capsule. Cytoplasm. Outer Membrane DNA. Flagellum.
 Bacteria The yellow band surrounding this hot spring is sulfur, a waste product of extremophilic prokaryotes, probably of the Domain Archaea, Kingdom Archaebacteria. Bacteria are prokaryotic cells (no
Bacteria The yellow band surrounding this hot spring is sulfur, a waste product of extremophilic prokaryotes, probably of the Domain Archaea, Kingdom Archaebacteria. Bacteria are prokaryotic cells (no
Know Your Microbes Introduction to food microbiology Factors affecting microbial growth Temperature Time
 Know Your Microbes Know Your Microbes Introduction to food microbiology Factors affecting microbial growth Temperature Time ph Water activity (Aw) Nutrient availability Atmosphere Hurdle technology Foodborne
Know Your Microbes Know Your Microbes Introduction to food microbiology Factors affecting microbial growth Temperature Time ph Water activity (Aw) Nutrient availability Atmosphere Hurdle technology Foodborne
MICROBIAL BIOCHEMISTRY BIOT 309. Dr. Leslye Johnson Sept. 30, 2012
 MICROBIAL BIOCHEMISTRY BIOT 309 Dr. Leslye Johnson Sept. 30, 2012 Phylogeny study of evoluhonary relatedness among groups of organisms (e.g. species, populahons), which is discovered through molecular
MICROBIAL BIOCHEMISTRY BIOT 309 Dr. Leslye Johnson Sept. 30, 2012 Phylogeny study of evoluhonary relatedness among groups of organisms (e.g. species, populahons), which is discovered through molecular
Classification. Old 5 Kingdom system. New 3 Domain system. reflects a greater understanding of evolution & molecular evidence
 Classification Old 5 Kingdom system Monera, Protists, Plants, Fungi, Animals New 3 Domain system reflects a greater understanding of evolution & molecular evidence Prokaryote: Bacteria Prokaryote: Archaebacteria
Classification Old 5 Kingdom system Monera, Protists, Plants, Fungi, Animals New 3 Domain system reflects a greater understanding of evolution & molecular evidence Prokaryote: Bacteria Prokaryote: Archaebacteria
Overview of the major bacterial pathogens The major bacterial pathogens are presented in this table:
 Practical Microbiology 30/11/2018 University of Sulaimani college of Pharmacy Year2 Lab. 5: Overview of the major bacterial pathogens The major bacterial pathogens are presented in this table: Major Bacterial
Practical Microbiology 30/11/2018 University of Sulaimani college of Pharmacy Year2 Lab. 5: Overview of the major bacterial pathogens The major bacterial pathogens are presented in this table: Major Bacterial
The Prokaryotic World
 The Prokaryotic World A. An overview of prokaryotic life There is no doubt that prokaryotes are everywhere. By everywhere, I mean living in every geographic region, in extremes of environmental conditions,
The Prokaryotic World A. An overview of prokaryotic life There is no doubt that prokaryotes are everywhere. By everywhere, I mean living in every geographic region, in extremes of environmental conditions,
THE EFFECT OF SMALL DOSES OF CALCIUM ACETYLACETONATE ON LARGE INTESTINAL MICROFLORA OF WHITE RATS AFTER ORAL ADMINISTRATION
 PHARMACIA, vol. 63, No. 3/2016 19 THE EFFECT OF SMALL DOSES OF CALCIUM ACETYLACETONATE ON LARGE INTESTINAL MICROFLORA OF WHITE RATS AFTER ORAL ADMINISTRATION H. P. Hamorak Abstract. Single introduction
PHARMACIA, vol. 63, No. 3/2016 19 THE EFFECT OF SMALL DOSES OF CALCIUM ACETYLACETONATE ON LARGE INTESTINAL MICROFLORA OF WHITE RATS AFTER ORAL ADMINISTRATION H. P. Hamorak Abstract. Single introduction
Chapter 21 PROKARYOTES AND VIRUSES
 Chapter 21 PROKARYOTES AND VIRUSES Bozeman Video classification of life http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tyl_8gv 7RiE Impacts, Issues: West Nile Virus Takes Off Alexander the Great, 336 B.C., conquered a
Chapter 21 PROKARYOTES AND VIRUSES Bozeman Video classification of life http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tyl_8gv 7RiE Impacts, Issues: West Nile Virus Takes Off Alexander the Great, 336 B.C., conquered a
The invention of the microscope has opened to us a world of extraordinary numbers. A singular drop of pond water reveals countless life forms
 Biology Chapter 19 Notes - Bacteria and Viruses The invention of the microscope has opened to us a world of extraordinary numbers. A singular drop of pond water reveals countless life forms I. Classifying
Biology Chapter 19 Notes - Bacteria and Viruses The invention of the microscope has opened to us a world of extraordinary numbers. A singular drop of pond water reveals countless life forms I. Classifying
Considerations with Antibiotic Therapy PART
 Considerations with Antibiotic Therapy PART 1 The Wonderful World of Microbiology 1 Despite the promises of the household-products industry, almost every surface is covered in microorganisms almost all
Considerations with Antibiotic Therapy PART 1 The Wonderful World of Microbiology 1 Despite the promises of the household-products industry, almost every surface is covered in microorganisms almost all
Outline. Collective behavior in bacteria. Know your horsemen. Importance. Cooperation and disease. Medical applications?
 Collective behavior in bacteria Will Driscoll April 30 th, 2008 Outline Importance Our macrobial bias Quorum sensing Biofilms Physiology Development Prokaryotic stab at multicellularity? Discussion But
Collective behavior in bacteria Will Driscoll April 30 th, 2008 Outline Importance Our macrobial bias Quorum sensing Biofilms Physiology Development Prokaryotic stab at multicellularity? Discussion But
Dr. habil. Anna Salek. Mikrobiologist Biotechnologist Research Associate
 Dr. habil. Anna Salek Mikrobiologist Biotechnologist Research Associate BIOTECHNOLOGY of Food Science Cell Biology of Microorganisms Physiology of Microorganisms Biochemistry of Microorganisms Molecularbiology
Dr. habil. Anna Salek Mikrobiologist Biotechnologist Research Associate BIOTECHNOLOGY of Food Science Cell Biology of Microorganisms Physiology of Microorganisms Biochemistry of Microorganisms Molecularbiology
Prokaryotes. Chapter 27. PowerPoint Lectures for Biology, Seventh Edition. Lectures by Chris Romero. Neil Campbell and Jane Reece
 Chapter 27 Prokaryotes PowerPoint Lectures for Biology, Seventh Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero Overview: They re (Almost) Everywhere! Most prokaryotes are microscopic But
Chapter 27 Prokaryotes PowerPoint Lectures for Biology, Seventh Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero Overview: They re (Almost) Everywhere! Most prokaryotes are microscopic But
Seminar 2 : Good Bugs
 Seminar 2 : Good Bugs Part 2 Viruses What is a virus? Microscopic particles that infect other organisms and can only replicate within a host cell Contain either contain DNA or RNA surrounded by a protective
Seminar 2 : Good Bugs Part 2 Viruses What is a virus? Microscopic particles that infect other organisms and can only replicate within a host cell Contain either contain DNA or RNA surrounded by a protective
20 Viruses and Prokaryotes Bacteria
 20 Viruses and Prokaryotes 20.2 - Bacteria Classifying Prokaryotes Prokaryote unicellular organisms that lacks a nucleus Most abundant and widespread organisms on Earth Divided into two groups Bacteria
20 Viruses and Prokaryotes 20.2 - Bacteria Classifying Prokaryotes Prokaryote unicellular organisms that lacks a nucleus Most abundant and widespread organisms on Earth Divided into two groups Bacteria
Characterizing and Classifying Prokaryotes
 CSLO2. Provide examples of the impact of microorganisms on agriculture, environment, ecosystem, energy, and human health, including biofilms. CSLO5. Describe evidence for the evolution of cells, organelles
CSLO2. Provide examples of the impact of microorganisms on agriculture, environment, ecosystem, energy, and human health, including biofilms. CSLO5. Describe evidence for the evolution of cells, organelles
Electric polarization properties of single bacteria measured with electrostatic force microscopy
 Electric polarization properties of single bacteria measured with electrostatic force microscopy Theoretical and practical studies of Dielectric constant of single bacteria and smaller elements Daniel
Electric polarization properties of single bacteria measured with electrostatic force microscopy Theoretical and practical studies of Dielectric constant of single bacteria and smaller elements Daniel
Kingdom Bacteria Kingdom Archaea
 Section 5.1 Kingdom Bacteria Kingdom Archaea p. 132-139 Kingdom Bacteria General Characteristics: Cell Type: all are prokaryotic. Body Form: most are unicellular, some are colonial. Three main shapes are:
Section 5.1 Kingdom Bacteria Kingdom Archaea p. 132-139 Kingdom Bacteria General Characteristics: Cell Type: all are prokaryotic. Body Form: most are unicellular, some are colonial. Three main shapes are:
culprits and strategies OEST 740
 Biofilm Predation: culprits and strategies OEST 740 031708 Outline Introduction Bacteria Predators Protist Predators Viral - parasitic Conclusion/Summary Predation All +/- interactions in which one organism
Biofilm Predation: culprits and strategies OEST 740 031708 Outline Introduction Bacteria Predators Protist Predators Viral - parasitic Conclusion/Summary Predation All +/- interactions in which one organism
Introduction to microbiology
 Sulaimani University College of Pharmacy Microbiology Introduction to microbiology Dr. Abdullah Ahmed Hama PhD. Molecular Medical Parasitology abdullah.hama@spu.edu.iq 1 Definition Microbiology: is the
Sulaimani University College of Pharmacy Microbiology Introduction to microbiology Dr. Abdullah Ahmed Hama PhD. Molecular Medical Parasitology abdullah.hama@spu.edu.iq 1 Definition Microbiology: is the
A pathogen is an agent or microrganism that causes a disease in its host. Pathogens can be viruses, bacteria, fungi or protozoa.
 1 A pathogen is an agent or microrganism that causes a disease in its host. Pathogens can be viruses, bacteria, fungi or protozoa. Protozoa are single celled eukaryotic organisms. Some protozoa are pathogens.
1 A pathogen is an agent or microrganism that causes a disease in its host. Pathogens can be viruses, bacteria, fungi or protozoa. Protozoa are single celled eukaryotic organisms. Some protozoa are pathogens.
BACTERIAL PHYSIOLOGY SMALL GROUP. Monday, August 25, :00pm. Faculty: Adam Driks, Ph.D. Alan Wolfe, Ph.D.
 BACTERIAL PHYSIOLOGY SMALL GROUP Monday, August 25, 2014 1:00pm Faculty: Adam Driks, Ph.D. Alan Wolfe, Ph.D. Learning Goal To understand how bacterial physiology applies to the diagnosis and treatment
BACTERIAL PHYSIOLOGY SMALL GROUP Monday, August 25, 2014 1:00pm Faculty: Adam Driks, Ph.D. Alan Wolfe, Ph.D. Learning Goal To understand how bacterial physiology applies to the diagnosis and treatment
BIO 101 INTRODUCTORY BIOLOGY PROF. ANI NKANG DEPT. OF BIOLOGICAL SCIENCES ARTHUR JARVIS UNIVERSITY
 BIO 101 INTRODUCTORY BIOLOGY PROF. ANI NKANG DEPT. OF BIOLOGICAL SCIENCES ARTHUR JARVIS UNIVERSITY What does it mean to say that something is alive? An organism is a life form- a living entity made up
BIO 101 INTRODUCTORY BIOLOGY PROF. ANI NKANG DEPT. OF BIOLOGICAL SCIENCES ARTHUR JARVIS UNIVERSITY What does it mean to say that something is alive? An organism is a life form- a living entity made up
Bacteria outline-- CHAPTER 19 Bacteria
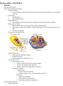 Bacteria outline-- CHAPTER 19 Bacteria Structure and Function Prokaryote & Eukaryote Evolution Cellular Evolution Current evidence indicates that eukaryotes evolved from prokaryotes between 1 and 1.5 billion
Bacteria outline-- CHAPTER 19 Bacteria Structure and Function Prokaryote & Eukaryote Evolution Cellular Evolution Current evidence indicates that eukaryotes evolved from prokaryotes between 1 and 1.5 billion
Cells & Bacteria Notes
 Cells & Bacteria Notes 4 Major Macromolecules Macromolecules are large molecules. The four groups of macromolecules are essential to the structure and function of a cell. Group Building Block Large Molecule
Cells & Bacteria Notes 4 Major Macromolecules Macromolecules are large molecules. The four groups of macromolecules are essential to the structure and function of a cell. Group Building Block Large Molecule
Overview: Masters of Adaptation. Prokaryotes thrive almost everywhere, including places too acidic, salty, cold, or hot for most other organisms
 Chapter 27 Bacteria and Archaea Overview: Masters of Adaptation Prokaryotes thrive almost everywhere, including places too acidic, salty, cold, or hot for most other organisms They have an astonishing
Chapter 27 Bacteria and Archaea Overview: Masters of Adaptation Prokaryotes thrive almost everywhere, including places too acidic, salty, cold, or hot for most other organisms They have an astonishing
- A virus is a short piece of DNA or RNA, sometimes with some associated enzymes.
 Viruses, bacteria, protists & fungi (just the basics!) I. Viruses: - parasites postponed until we discuss them in class. - A virus is a short piece of DNA or RNA, sometimes with some associated enzymes.
Viruses, bacteria, protists & fungi (just the basics!) I. Viruses: - parasites postponed until we discuss them in class. - A virus is a short piece of DNA or RNA, sometimes with some associated enzymes.
Current evidence indicates that eukaryotes evolved from prokaryotes between 1 and 1.5 billion years ago.
 Current evidence indicates that eukaryotes evolved from prokaryotes between 1 and 1.5 billion years ago. Two theories: 1. Infolding theory 2. Endosymbiotic theory The infolding of the prokaryotic plasma
Current evidence indicates that eukaryotes evolved from prokaryotes between 1 and 1.5 billion years ago. Two theories: 1. Infolding theory 2. Endosymbiotic theory The infolding of the prokaryotic plasma
Bacterial Morphology and Structure م.م رنا مشعل
 Bacterial Morphology and Structure م.م رنا مشعل SIZE OF BACTERIA Unit for measurement : Micron or micrometer, μm: 1μm=10-3 mm Size: Varies with kinds of bacteria, and also related to their age and external
Bacterial Morphology and Structure م.م رنا مشعل SIZE OF BACTERIA Unit for measurement : Micron or micrometer, μm: 1μm=10-3 mm Size: Varies with kinds of bacteria, and also related to their age and external
Microbial Genetics, Mutation and Repair. 2. State the function of Rec A proteins in homologous genetic recombination.
 Answer the following questions 1. Define genetic recombination. Microbial Genetics, Mutation and Repair 2. State the function of Rec A proteins in homologous genetic recombination. 3. List 3 types of bacterial
Answer the following questions 1. Define genetic recombination. Microbial Genetics, Mutation and Repair 2. State the function of Rec A proteins in homologous genetic recombination. 3. List 3 types of bacterial
Introductory Microbiology Dr. Hala Al Daghistani
 Introductory Microbiology Dr. Hala Al Daghistani Why Study Microbes? Microbiology is the branch of biological sciences concerned with the study of the microbes. 1. Microbes and Man in Sickness and Health
Introductory Microbiology Dr. Hala Al Daghistani Why Study Microbes? Microbiology is the branch of biological sciences concerned with the study of the microbes. 1. Microbes and Man in Sickness and Health
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature11711 Table(of(contents( Tableofcontents...1! 1.Methods...1! 1.1.Generationofareferencegenomeset...1! 1.2.MappingofIlluminareadstoreferencegenomes...2! 1.3.Detectingthepresenceofaspeciesinasample...3!
doi:10.1038/nature11711 Table(of(contents( Tableofcontents...1! 1.Methods...1! 1.1.Generationofareferencegenomeset...1! 1.2.MappingofIlluminareadstoreferencegenomes...2! 1.3.Detectingthepresenceofaspeciesinasample...3!
Archea and Bacteria- The PROKARYOTES
 ` Archea and Bacteria- The PROKARYOTES As late as 1977, all prokaryotes were put into one single kingdom called Monera. Taxonomists no longer accept that concept. Some prokaryotes are more closely related
` Archea and Bacteria- The PROKARYOTES As late as 1977, all prokaryotes were put into one single kingdom called Monera. Taxonomists no longer accept that concept. Some prokaryotes are more closely related
Tetracycline Rationale for the EUCAST clinical breakpoints, version th November 2009
 Tetracycline Rationale for the EUCAST clinical breakpoints, version 1.0 20 th November 2009 Introduction The natural tetracyclines, including tetracycline, chlortetracycline, oxytetracycline and demethylchlortetracycline
Tetracycline Rationale for the EUCAST clinical breakpoints, version 1.0 20 th November 2009 Introduction The natural tetracyclines, including tetracycline, chlortetracycline, oxytetracycline and demethylchlortetracycline
BACTERIA. CLS 212: Medical Microbiology Miss Zeina Alkudmani
 BACTERIA CLS 212: Medical Microbiology Miss Zeina Alkudmani Prokaryotes Prokaryotic cells possess simpler structures than eukaryotic cells, since they do not have a nucleus or a lot of cytoplasmic organelles.
BACTERIA CLS 212: Medical Microbiology Miss Zeina Alkudmani Prokaryotes Prokaryotic cells possess simpler structures than eukaryotic cells, since they do not have a nucleus or a lot of cytoplasmic organelles.
MODULE #2: Kingdom Monera Prokaryota(pro kehreeaht' uh)
 MODULE #2: Kingdom Monera Prokaryota(pro kehreeaht' uh) The general namebacteria(singular is bacterium) can essentially be applied to all of the organisms inkingdommonera. Pathogen An organism that causes
MODULE #2: Kingdom Monera Prokaryota(pro kehreeaht' uh) The general namebacteria(singular is bacterium) can essentially be applied to all of the organisms inkingdommonera. Pathogen An organism that causes
MORPHOLOGY: the study of form and structure
 MICROBIOLOGY CHAPTER 3 Bacteria Morphology 3:1 Bacteria Structure and Function MORPHOLOGY: the study of form and structure Structure of Bacteria 1. PROKARYOTIC no membrane bound nucleus nor other organelles
MICROBIOLOGY CHAPTER 3 Bacteria Morphology 3:1 Bacteria Structure and Function MORPHOLOGY: the study of form and structure Structure of Bacteria 1. PROKARYOTIC no membrane bound nucleus nor other organelles
Microbiology Helmut Pospiech
 Microbiology http://researchmagazine.uga.edu/summer2002/bacteria.htm 05.04.2018 Helmut Pospiech The Species Concept in Microbiology No universally accepted concept of species for prokaryotes Current definition
Microbiology http://researchmagazine.uga.edu/summer2002/bacteria.htm 05.04.2018 Helmut Pospiech The Species Concept in Microbiology No universally accepted concept of species for prokaryotes Current definition
Outline. Viruses, Bacteria, and Archaea. Viruses Structure Classification Reproduction Prokaryotes Structure Reproduction Nutrition Bacteria Archaea
 Viruses, Bacteria, and Archaea Chapter 21 Viruses Structure Classification Reproduction Prokaryotes Structure Reproduction Nutrition Bacteria Archaea Outline The Viruses The Viruses Viruses are noncellular
Viruses, Bacteria, and Archaea Chapter 21 Viruses Structure Classification Reproduction Prokaryotes Structure Reproduction Nutrition Bacteria Archaea Outline The Viruses The Viruses Viruses are noncellular
Part 2. The Basics of Biology:
 Part 2 The Basics of Biology: An Engineer s Perspective Chapter 2 An Overview of Biological Basics 21 2.1 Cells 2.2 Cell Construction 2.3 Cell Nutrient 2.1 Are all cells the same? Cells Basic unit of living
Part 2 The Basics of Biology: An Engineer s Perspective Chapter 2 An Overview of Biological Basics 21 2.1 Cells 2.2 Cell Construction 2.3 Cell Nutrient 2.1 Are all cells the same? Cells Basic unit of living
4/17/2014. Prokaryotes have inhabited the Earth for billions of years
 Prokaryotes have inhabited the Earth for billions of years Fossil evidence shows that prokaryotes were abundant 3.5 bya, and they evolved alone for the following 2 billion years. Prokaryotes are ubiquitous,
Prokaryotes have inhabited the Earth for billions of years Fossil evidence shows that prokaryotes were abundant 3.5 bya, and they evolved alone for the following 2 billion years. Prokaryotes are ubiquitous,
16S Metagenomics Report
 Sample: BL-09 Report Date: 05/11/2017 18:40:20 Sample Information Sample ID: Sample Name: Run Folder: Taxonomy File: BL_09 BL_09 D:\Illumina\MiSeqAnalysis\170509_M01675_0059_000000000-AW8GB gg_13_5_species_32bp.dat
Sample: BL-09 Report Date: 05/11/2017 18:40:20 Sample Information Sample ID: Sample Name: Run Folder: Taxonomy File: BL_09 BL_09 D:\Illumina\MiSeqAnalysis\170509_M01675_0059_000000000-AW8GB gg_13_5_species_32bp.dat
Kingdom Monera - The Bacteria
 Chapter 8 The World of Microbes Kingdom Monera - The Bacteria Bio-significance- The down side: Disease of plants crop loss Disease of animals loss of livestock and herds Human disease cavities to The Plague
Chapter 8 The World of Microbes Kingdom Monera - The Bacteria Bio-significance- The down side: Disease of plants crop loss Disease of animals loss of livestock and herds Human disease cavities to The Plague
Scientific names allow scientists to talk about particular species without confusion
 Unit 9 Test Review KEY a. Explain the history, purpose, and methods of taxonomy What is taxonomy? the science of naming and classifying organisms Who came up with it? Linnaeus Why do we use taxonomy? Scientific
Unit 9 Test Review KEY a. Explain the history, purpose, and methods of taxonomy What is taxonomy? the science of naming and classifying organisms Who came up with it? Linnaeus Why do we use taxonomy? Scientific
Microbe Mission C Test
 Microbe Mission C Test Science Olympiad North Regional Tournament at the University of Florida Rank: Points: Name(s): Team Name: School Name: Team Number: Page 2 Part 1: Microscopes Names the following
Microbe Mission C Test Science Olympiad North Regional Tournament at the University of Florida Rank: Points: Name(s): Team Name: School Name: Team Number: Page 2 Part 1: Microscopes Names the following
Major Events in the History of Earth
 Major Events in the History of Earth Cenozoic Humans Land plants Animals Origin of solar system and Earth Multicellular eukaryotes 1 Proterozoic eon 2 Archaean eon 3 4 Single-celled eukaryotes Atmospheric
Major Events in the History of Earth Cenozoic Humans Land plants Animals Origin of solar system and Earth Multicellular eukaryotes 1 Proterozoic eon 2 Archaean eon 3 4 Single-celled eukaryotes Atmospheric
Chapter 28 - Bacteria and Archaea
 Chapter 28 - Bacteria and Archaea Learning Objectives: Students should be able to... Defend the statement that bacteria and archaea are the most important, diverse, and abundant organisms on the planet.
Chapter 28 - Bacteria and Archaea Learning Objectives: Students should be able to... Defend the statement that bacteria and archaea are the most important, diverse, and abundant organisms on the planet.
Full file at
 Chapter # and Question type Short answer #1. Question How did Louis Pasteur help disprove spontaneous generation? Answer Pasteur demonstrated that swan necked flasks containing sterile growth medium would
Chapter # and Question type Short answer #1. Question How did Louis Pasteur help disprove spontaneous generation? Answer Pasteur demonstrated that swan necked flasks containing sterile growth medium would
Intro to Prokaryotes Lecture 1 Spring 2014
 Intro to Prokaryotes Lecture 1 Spring 2014 Meet the Prokaryotes 1 Meet the Prokaryotes 2 Meet the Prokaryotes 3 Why study prokaryotes? Deep Time 4 Fig. 25.7 Fossilized stromatolite (above) and living stromatolite
Intro to Prokaryotes Lecture 1 Spring 2014 Meet the Prokaryotes 1 Meet the Prokaryotes 2 Meet the Prokaryotes 3 Why study prokaryotes? Deep Time 4 Fig. 25.7 Fossilized stromatolite (above) and living stromatolite
1. Which of the following species have strains that are capable of undergoing the process of conjugation?
 Biology 3340 Summer 2005 Second Examination Version A Name Be sure to put your name on the mark-sense sheet as well Directions: Write your name in the correct space on the mark-sense sheet and the exam
Biology 3340 Summer 2005 Second Examination Version A Name Be sure to put your name on the mark-sense sheet as well Directions: Write your name in the correct space on the mark-sense sheet and the exam
STAAR Biology Assessment
 STAAR Biology Assessment Reporting Category 1: Cell Structure and Function The student will demonstrate an understanding of biomolecules as building blocks of cells, and that cells are the basic unit of
STAAR Biology Assessment Reporting Category 1: Cell Structure and Function The student will demonstrate an understanding of biomolecules as building blocks of cells, and that cells are the basic unit of
Gram negative bacilli
 Gram negative bacilli 1-Enterobacteriaceae Gram negative bacilli-rods Enterobacteriaceae Are everywhere Part of normal flora of humans and most animals They are cause of -30-35% septisemia -more than 70%
Gram negative bacilli 1-Enterobacteriaceae Gram negative bacilli-rods Enterobacteriaceae Are everywhere Part of normal flora of humans and most animals They are cause of -30-35% septisemia -more than 70%
Chapter 26 (8 th edition) Lectures 3 & 4. Prokaryotes. Dr Angelika Stollewerk
 Chapter 26 (8 th edition) Lectures 3 & 4 Prokaryotes Dr Angelika Stollewerk Prokaryotes Aims: To overview the diversity of the three domains of life To consider where prokaryotes are found To consider
Chapter 26 (8 th edition) Lectures 3 & 4 Prokaryotes Dr Angelika Stollewerk Prokaryotes Aims: To overview the diversity of the three domains of life To consider where prokaryotes are found To consider
Microbiota: the human body is a home for bacteria
 Microbiota: the human body is a home for bacteria Digestive system and bacteria As well as allowing us to conduct our everyday lives, our body is home to a huge number of organisms, which all together
Microbiota: the human body is a home for bacteria Digestive system and bacteria As well as allowing us to conduct our everyday lives, our body is home to a huge number of organisms, which all together
-Supplementary Information- Changes of the human gut microbiome induced by a fermented milk product
 -Supplementary Information- Changes of the human gut microbiome induced by a fermented milk product Patrick Veiga a, Nicolas Pons b, Anurag Agrawal c, Raish Oozeer a, Denis Guyonnet a, Rémi Brazeilles
-Supplementary Information- Changes of the human gut microbiome induced by a fermented milk product Patrick Veiga a, Nicolas Pons b, Anurag Agrawal c, Raish Oozeer a, Denis Guyonnet a, Rémi Brazeilles
Microbial Diversity and Assessment (II) Spring, 2007 Guangyi Wang, Ph.D. POST103B
 Microbial Diversity and Assessment (II) Spring, 007 Guangyi Wang, Ph.D. POST03B guangyi@hawaii.edu http://www.soest.hawaii.edu/marinefungi/ocn403webpage.htm General introduction and overview Taxonomy [Greek
Microbial Diversity and Assessment (II) Spring, 007 Guangyi Wang, Ph.D. POST03B guangyi@hawaii.edu http://www.soest.hawaii.edu/marinefungi/ocn403webpage.htm General introduction and overview Taxonomy [Greek
DOC - LIST OF GRAM POSITIVE AND GRAM NEGATIVE BACTERIA DOWNLOAD
 24 December, 2017 DOC - LIST OF GRAM POSITIVE AND GRAM NEGATIVE BACTERIA DOWNLOAD Document Filetype: PDF 232.18 KB 0 DOC - LIST OF GRAM POSITIVE AND GRAM NEGATIVE BACTERIA DOWNLOAD The following article
24 December, 2017 DOC - LIST OF GRAM POSITIVE AND GRAM NEGATIVE BACTERIA DOWNLOAD Document Filetype: PDF 232.18 KB 0 DOC - LIST OF GRAM POSITIVE AND GRAM NEGATIVE BACTERIA DOWNLOAD The following article
Shape, Arrangement, and Size. Cocci (s., coccus) bacillus (pl., bacilli) 9/21/2013
 Shape, Arrangement, and Size Cocci (s., coccus) are roughly spherical cells. The other common shape is that of a rod, sometimes called a bacillus (pl., bacilli). Spiral-shaped procaryotes can be either
Shape, Arrangement, and Size Cocci (s., coccus) are roughly spherical cells. The other common shape is that of a rod, sometimes called a bacillus (pl., bacilli). Spiral-shaped procaryotes can be either
2/25/2013. Chapter 11 The Prokaryotes: Domains Bacteria and Archaea The Prokaryotes
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Chapter 11 The Prokaryotes: Domains Bacteria and Archaea The Prokaryotes Domain Bacteria Proteobacteria From the mythical Greek god Proteus, who could assume many shapes Gram-negative
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Chapter 11 The Prokaryotes: Domains Bacteria and Archaea The Prokaryotes Domain Bacteria Proteobacteria From the mythical Greek god Proteus, who could assume many shapes Gram-negative
