Nature Biotechnology: doi: /nbt Supplementary Figure 1. The inflammatory response in the mammalian gut leads to tetrathionate generation.
|
|
|
- Randell Maxwell
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Supplementary Figure 1 The inflammatory response in the mammalian gut leads to tetrathionate generation. Cytokine signaling following an inflammatory insult leads to, among other responses, release of reactive oxygen species (ROS) into the gut lumen that inhibit microbial growth, and can oxidize thiosulfate, generated from hydrogen sulfide, to tetrathionate.
2
3 Supplementary Figure 2 PAS638 senses tetrathionate in a murine streptomycin-treated S. typhimurium colitis model a) Timecourse of PAS638 switching during infection of C57Bl/6 mice with wt and ΔttrR S. typhimurium (S.tm) (n= 6 for control and 7 for S. typhimurium infected groups). Switching was only apparent in colonies from mice co-infected with S.typhimurium ΔttrR and on days 4 and/or 5 post administration. b) Enumeration of PAS638 E. coli and c) S. typhimurium variant levels by selective plating showed relatively consistent levels across experimental groups. d) LCN-2 quantification demonstrated inflammation in both S. typhimurium ΔttrR and wt administered mice. Graphs show individual mouse values and mean. * p=0.02, ** p=0.001 *** p<0.0001, F(2,17) = 25.96, using one way ANOVA with Tukey s multiple comparisons test. e) Histology scoring of cecum, proximal and distal colon, showed inflammation in the presence of both S. typhimurium variants decreasingly apparent from the caecum to the distal colon. f) Scoring used a 0-4 point scale with example images of each score by histology provided. For cecal samples, only severity 3 and 4 were observed during S. typhimurium infection, characterized by accumulation of neutrophils (N) in epithelial tissues, edema (E), mucosal thickening and at times low-level presence of neutrophils in exudate at severity 3 and edema (E), extensive neutrophils present in exudate and/or epithelia (N), mucosal thickening and signs of crypt damage or regeneration (C) at severity 4. Proximal and distal colon showed signs of low-level inflammation (I) at severity 1, more extensive inflammation (I) and neutrophils in exudate (N) at severity 2. Severity 3 was noted in the proximal colon only and showed signs of ulceration (U), inflammatory cell migration (I), and neutrophils commonly present in exudate. Scale bars = 10μm.
4 Supplementary Figure 3 PAS638 senses tetrathionate in cybb /, IL10 /, and 129X1/SvJ mouse models. a) Weight of cybb-/- and C57Bl/6 control mice was measured following administration of PAS638 ± S. typhimurium (S.tm) ΔttrR. Graph shows percentage of pre-administration weight of individual mice (dotted) along with group averages (solid line). b) Elevated LCN-2 levels were apparent in S. typhimurium ΔttrR infected mice and cybb-/- uninfected controls. Graph shows maximum measurements from days 3-5 following bacterial administration. Means are marked. *p=0.01, **p=0.009, F(3,16) = 6.575, using one-way ANOVA analysis with Tukey s multiple comparison correction. For all other comparisons p>0.99. c) LCN-2 levels were elevated in IL10-/- compared to control mice in the week following PAS638 administration therefore PAS638 measurements were taken >1-week following administration. Values are averages of 2-3 measurements from individual mice, with mean shown. *p=0.02, **p=0.01, F(2,20) = 6.48 using one-way ANOVA test with Tukey s multiple comparison correction. >week 1 IL10-/- samples were not significantly increased over C57Bl/6 controls (p=0.9) d) A subset of IL10-/- mice administered PAS638 without streptomycin pre-treatment (n=10) showed elevated PAS638 switching. Graph shows maximum switching percentage from 4 measurements in the 12 days following administration. Mean is marked. e) When administered without streptomycin pre-treatment no indication of elevated LCN-2 levels was seen following
5 bacterial administration. Graph shows pre-administration levels (1 measurement) and average levels from 4 measurements in the 12 days following administration. Means are marked. n.s. = non-significant (p = 0.6) using a two-tailed Mann-Whitney test. f). PAS638 administered to 129X1/SvJ mice (n=5) without streptomycin pre-treatment colonized the gut successfully. Graph shows CFU values from individual mice (dotted lines) and average across the group (solid line). g) The absence of streptomycin pre-treatment did not affect PAS638 switching in these mice. Graph shows average switching from 4 measurements in the 12 days following bacterial administration. h) Histology scoring of small intestine, cecum, proximal and distal colon showed no signs of overt inflammation in X1/SvJ mice, including all that showed considerable switching by PAS638.
6 Supplementary Figure 4 Long-term stability of PAS638 during colonization of the mouse gut. a) Essentially all PAS638 colonies tested following 200 days colonized in the 129X1/SvJ mouse (corresponding to Fig3e-f) retained ex vivo function when grown in the presence of sodium tetrathionate under anaerobic conditions. PAS638 colonies isolated after 200 days colonization were administered to C57Bl/6 mice ± S. typhimurium (S.tm) ΔttrR. b) Histology scoring of cecum and colon using a 0-4 point scale documented in Supplementary Fig. 2f detected elevated signs of inflammation in S. typhimurium ΔttrR co-infected mice. c) S. typhimurium ΔttrR infected mice also lost weight following infection (graph shows single mouse values (dotted lines) as percentage of pre-administration weight along with group averages (solid lines)) and d) showed elevated LCN-2 values. Graph shows maximum values measured from d1-5 post bacterial administration. ****p< using separate two-tailed T-tests for the two individual experiments (t(8) = and t(8) = respectively). Means are shown.
7 Supplementary Figure 5 MS/MS fragmentation spectrum of tetrathionate Exemplary fragmentation spectrum (MS/MS) of tetrathionate (M = S 4O 6H 2) detected in a cecum sample (see Fig. 2c). Negative ion mode and collision induced dissociation (CID) with nitrogen gas at 10 ev was used. The parent ion was isolated as [M-H] at m/z = The corresponding chemical structures for the resulting fragments ([S 3O 3H]- and [SO 3H]-) are shown in the spectrum.
8 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL FOR: Synthetic biological circuits that demonstrate long-term genetic and functional stability in the mammalian gut Authors: David T Riglar 1, 2, Tobias W Giessen 1,2, Michael Baym 1,3, S Jordan Kerns 1, 2, Matthew J Niederhuber 1, 2, Roderick T Bronson 4, Jonathan W Kotula 1, 2, Georg K Gerber 5, Jeffrey C Way 2 & Pamela A Silver 1, 2 *. Affiliations: 1 Department of Systems Biology, Harvard Medical School, Boston Massachusetts, USA 2 Wyss Institute for Biologically Inspired Engineering, Harvard University, Boston Massachusetts, USA 3 Department of Biomedical Informatics, Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts, USA 4 Department of Microbiology and Immunology, Harvard Medical School, Boston Massachusetts, USA 5 Massachusetts Host-Microbiome Center, Department of Pathology, Brigham and Women s Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts, USA Current address: Emulate Inc., Boston, Massachusetts, USA Current address: SynLogic, Cambridge, Massachusetts, USA *Correspondence to: Pamela_Silver@hms.harvard.edu
9 Supplementary Table 1: Strains constructed for use in this study. Strain name Background Elements (template) PAS637 E. coli NGF1 LAM14 memory element and rpsl lys42arg Strep R (E. coli PAS132/133) 12 PAS638 E. coli NGF1 LAM14 memory element and rpsl lys42arg Strep R (E. coli PAS132/133) 12 ; ttrr/s- PttrBCA (S. typhimurium LT2) S. typhimurium wt (PAS639) S. typhimurium ΔttrR (PAS640) S. typhimurium 14028s S. typhimurium 14028s zhj- 1401::Tn10 ( S. typhimurium LT2 SA2700) (Salmonella Genetic Stock Database) zhj- 1401::Tn10 ( S. typhimurium LT2 SA2700) (Salmonella Genetic Stock Database); ΔttrR (S. typhimurium LT2 TT22470) 18 2
10 Supplementary Table 2: GnotoComplex 2.0 strains. The strains chosen are human commensals selected to recapitulate key physiologic functions and phylogenetic diversity in the host. Strain ID Akkermansia muciniphila DSM Anaerostipes hadrus DSM 3319 Bacteroides cellulosilyticus DSM Bacteroides fragilis ATCC Bacteroides ovatus ATCC 8483 Bacteroides vulgatus ATCC 8483 Bifidobacterium longum subsp. infantis ATCC Bilophila wadsworthia ATCC Blautia hansenii DSM Clostridium hiranonis DSM Clostridium ramosum DSM 1402 Clostridium scindens ATCC Coprococcus comes ATCC Dorea formicigenerans ATCC Eggerthella lenta DSM 2243 Enterococcus faecalis ATCC Escherichia coli MG1655 Klebsiella oxytoca ATCC Lactobacillus reuteri DSM Parabacteroides distasonis ATCC 8503 Prevotella melaninogenica ATCC Proteus mirabilis ATCC Roseburia hominis DSM Ruminococcus obeum ATCC Veillonella parvula ATCC
Bacteria Outline. 1. Overview. 2. Structural & Functional Features. 3. Taxonomy. 4. Communities
 Bacteria Outline 1. Overview 2. Structural & Functional Features 3. Taxonomy 4. Communities Bacteria - Taxonomy PHYLUM CLASS ORDER FAMILY GENUS SPECIES SUB-SPECIES & STRAINS Bacteria - Phyla Firmicutes
Bacteria Outline 1. Overview 2. Structural & Functional Features 3. Taxonomy 4. Communities Bacteria - Taxonomy PHYLUM CLASS ORDER FAMILY GENUS SPECIES SUB-SPECIES & STRAINS Bacteria - Phyla Firmicutes
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Sana et al. 10.1073/pnas.1608858113 Fig. S1. Representation of the SPI-6 type VI secretion system. (A) Representation of the SPI-6 genetic locus starting at STM0266 and ending at
Supporting Information Sana et al. 10.1073/pnas.1608858113 Fig. S1. Representation of the SPI-6 type VI secretion system. (A) Representation of the SPI-6 genetic locus starting at STM0266 and ending at
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature11711 Table(of(contents( Tableofcontents...1! 1.Methods...1! 1.1.Generationofareferencegenomeset...1! 1.2.MappingofIlluminareadstoreferencegenomes...2! 1.3.Detectingthepresenceofaspeciesinasample...3!
doi:10.1038/nature11711 Table(of(contents( Tableofcontents...1! 1.Methods...1! 1.1.Generationofareferencegenomeset...1! 1.2.MappingofIlluminareadstoreferencegenomes...2! 1.3.Detectingthepresenceofaspeciesinasample...3!
Analysis of the mouse gut microbiome using full-length. 16S rrna amplicon sequencing
 Analysis of the mouse gut microbiome using full-length 16S rrna amplicon sequencing Jongoh Shin 1,, Sooin Lee 1,, Min-Jeong Go 2, Sang Yup Lee 3, Sun Chang Kim 1,4, Chul-Ho Lee 2, and Byung-Kwan Cho 1,4,*
Analysis of the mouse gut microbiome using full-length 16S rrna amplicon sequencing Jongoh Shin 1,, Sooin Lee 1,, Min-Jeong Go 2, Sang Yup Lee 3, Sun Chang Kim 1,4, Chul-Ho Lee 2, and Byung-Kwan Cho 1,4,*
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature11419 Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic representation of innate immune signaling pathways induced by intracellular Salmonella in cultured macrophages. a, During the infection Salmonella
doi:10.1038/nature11419 Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic representation of innate immune signaling pathways induced by intracellular Salmonella in cultured macrophages. a, During the infection Salmonella
ANTIMICROBIAL TESTING. E-Coli K-12 - E-Coli 0157:H7. Salmonella Enterica Servoar Typhimurium LT2 Enterococcus Faecalis
 ANTIMICROBIAL TESTING E-Coli K-12 - E-Coli 0157:H7 Salmonella Enterica Servoar Typhimurium LT2 Enterococcus Faecalis Staphylococcus Aureus (Staph Infection MRSA) Streptococcus Pyrogenes Anti Bacteria effect
ANTIMICROBIAL TESTING E-Coli K-12 - E-Coli 0157:H7 Salmonella Enterica Servoar Typhimurium LT2 Enterococcus Faecalis Staphylococcus Aureus (Staph Infection MRSA) Streptococcus Pyrogenes Anti Bacteria effect
Granulocytes Impose a Tight Bottleneck upon the Gut Luminal Pathogen Population during Salmonella Typhimurium Colitis
 Granulocytes Impose a Tight Bottleneck upon the Gut Luminal Pathogen Population during Salmonella Typhimurium Colitis Lisa Maier 1,Médéric Diard 1, Mikael E. Sellin 1, Elsa-Sarah Chouffane 1, Kerstin Trautwein-Weidner
Granulocytes Impose a Tight Bottleneck upon the Gut Luminal Pathogen Population during Salmonella Typhimurium Colitis Lisa Maier 1,Médéric Diard 1, Mikael E. Sellin 1, Elsa-Sarah Chouffane 1, Kerstin Trautwein-Weidner
Istituto di Microbiologia. Università Cattolica del Sacro Cuore, Roma. Gut Microbiota assessment and the Meta-HIT program.
 Istituto di Microbiologia Università Cattolica del Sacro Cuore, Roma Gut Microbiota assessment and the Meta-HIT program Giovanni Delogu 1 Most of the bacteria species living in the gut cannot be cultivated
Istituto di Microbiologia Università Cattolica del Sacro Cuore, Roma Gut Microbiota assessment and the Meta-HIT program Giovanni Delogu 1 Most of the bacteria species living in the gut cannot be cultivated
THE EFFECT OF SMALL DOSES OF CALCIUM ACETYLACETONATE ON LARGE INTESTINAL MICROFLORA OF WHITE RATS AFTER ORAL ADMINISTRATION
 PHARMACIA, vol. 63, No. 3/2016 19 THE EFFECT OF SMALL DOSES OF CALCIUM ACETYLACETONATE ON LARGE INTESTINAL MICROFLORA OF WHITE RATS AFTER ORAL ADMINISTRATION H. P. Hamorak Abstract. Single introduction
PHARMACIA, vol. 63, No. 3/2016 19 THE EFFECT OF SMALL DOSES OF CALCIUM ACETYLACETONATE ON LARGE INTESTINAL MICROFLORA OF WHITE RATS AFTER ORAL ADMINISTRATION H. P. Hamorak Abstract. Single introduction
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 GP2 Type I-piliated bacteria FAE M cell M cell pocket idc T cell mdc Generation of antigenspecific T cells Induction of antigen-specific mucosal immune response Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic diagram
GP2 Type I-piliated bacteria FAE M cell M cell pocket idc T cell mdc Generation of antigenspecific T cells Induction of antigen-specific mucosal immune response Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic diagram
Time-course responses of ileal and fecal microbiota and metabolite profiles to. antibiotics in cannulated pigs
 Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology Time-course responses of ileal and fecal microbiota and metabolite profiles to antibiotics in cannulated pigs Kan Gao 1, Yu Pi 1, Yu Peng, Chun-Long Mu, Wei-Yun Zhu
Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology Time-course responses of ileal and fecal microbiota and metabolite profiles to antibiotics in cannulated pigs Kan Gao 1, Yu Pi 1, Yu Peng, Chun-Long Mu, Wei-Yun Zhu
Actinobacteria Relative abundance (%) Co-housed CD300f WT. CD300f KO. Colon length (cm) Day 9. Microscopic inflammation score
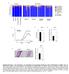 y groups y individuals 9 Actinobacteria Relative abundance (%) acteroidetes Cyanobacteria Deferribacteres Firmicutes Proteobacteria TM Tenericutes Unclassified CDf CDf Co-housed CDf Co-housed CDf CDf CDf
y groups y individuals 9 Actinobacteria Relative abundance (%) acteroidetes Cyanobacteria Deferribacteres Firmicutes Proteobacteria TM Tenericutes Unclassified CDf CDf Co-housed CDf Co-housed CDf CDf CDf
Pretreatment of Mice with Streptomycin Provides a Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium Colitis Model That Allows Analysis of Both Pathogen and Host
 Pretreatment of Mice with Streptomycin Provides a Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium Colitis Model That Allows Analysis of Both Pathogen and Host Authors Barthel, Manja; Hapfelmeier, Siegfried; Quintanilla-
Pretreatment of Mice with Streptomycin Provides a Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium Colitis Model That Allows Analysis of Both Pathogen and Host Authors Barthel, Manja; Hapfelmeier, Siegfried; Quintanilla-
Received 24 December 2008/Returned for modification 13 February 2009/Accepted 30 April 2009
 INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, July 2009, p. 2691 2702 Vol. 77, No. 7 0019-9567/09/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/iai.01570-08 Copyright 2009, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Perturbation of the
INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, July 2009, p. 2691 2702 Vol. 77, No. 7 0019-9567/09/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/iai.01570-08 Copyright 2009, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Perturbation of the
Copyright 2010 American Association for the Advancement of Science.
 Srikanth, C.V., Wall, D.M., Maldonado-Contreras, A., Shi, H.N., Zhou, D.G., Demma, Z., Mumy, K.L., and Mccormick, B.A. (2010) Salmonella Pathogenesis and Processing of Secreted Effectors by Caspase-3.
Srikanth, C.V., Wall, D.M., Maldonado-Contreras, A., Shi, H.N., Zhou, D.G., Demma, Z., Mumy, K.L., and Mccormick, B.A. (2010) Salmonella Pathogenesis and Processing of Secreted Effectors by Caspase-3.
Microbial Dynamics of the Broiler Intestinal Tract Margie Lee, Ph.D., D.V.M.
 Microbial Dynamics of the Broiler Intestinal Tract Margie Lee, Ph.D., D.V.M. Biography Ph.D., Medical Microbiology, The University of Georgia, 1990. M.S., Medical Microbiology, The University of Georgia,
Microbial Dynamics of the Broiler Intestinal Tract Margie Lee, Ph.D., D.V.M. Biography Ph.D., Medical Microbiology, The University of Georgia, 1990. M.S., Medical Microbiology, The University of Georgia,
-Supplementary Information- Changes of the human gut microbiome induced by a fermented milk product
 -Supplementary Information- Changes of the human gut microbiome induced by a fermented milk product Patrick Veiga a, Nicolas Pons b, Anurag Agrawal c, Raish Oozeer a, Denis Guyonnet a, Rémi Brazeilles
-Supplementary Information- Changes of the human gut microbiome induced by a fermented milk product Patrick Veiga a, Nicolas Pons b, Anurag Agrawal c, Raish Oozeer a, Denis Guyonnet a, Rémi Brazeilles
Supervised Learning to Predict Geographic Origin of Human Metagenomic Samples
 Supervised Learning to Predict Geographic Origin of Human Metagenomic Samples Christopher Malow cmalow@stanford.edu Abstract Metagenomic studies of human fecal samples have used whole genome shotgun sequencing
Supervised Learning to Predict Geographic Origin of Human Metagenomic Samples Christopher Malow cmalow@stanford.edu Abstract Metagenomic studies of human fecal samples have used whole genome shotgun sequencing
VPM 201: Veterinary Bacteriology and Mycology 6-7/10/2010. LABORATORY 5a - ENTEROBACTERIACEAE
 VPM 201: Veterinary Bacteriology and Mycology 6-7/10/2010 LABORATORY 5a - ENTEROBACTERIACEAE A large family of gram-negative bacilli. They grow readily on common culture media. Organisms are separated
VPM 201: Veterinary Bacteriology and Mycology 6-7/10/2010 LABORATORY 5a - ENTEROBACTERIACEAE A large family of gram-negative bacilli. They grow readily on common culture media. Organisms are separated
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Extended Discussion: Mathematical modelling of the planktonic population kinetics in the presence of high-avidity IgA In this section we present a mathematical model of the interactions between planktonic
Extended Discussion: Mathematical modelling of the planktonic population kinetics in the presence of high-avidity IgA In this section we present a mathematical model of the interactions between planktonic
Received 10 July 2003/Returned for modification 8 September 2003/Accepted 12 November 2003
 INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Feb. 2004, p. 795 809 Vol. 72, No. 2 0019-9567/04/$08.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/IAI.72.2.795 809.2004 Copyright 2004, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Role of the
INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Feb. 2004, p. 795 809 Vol. 72, No. 2 0019-9567/04/$08.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/IAI.72.2.795 809.2004 Copyright 2004, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Role of the
Koji NAGASHIMA 1 *, Jun MOCHIZUKI 2, Takayoshi HISADA 2, Shuji SUZUKI 2 and Kengo SHIMOMURA 2#
 Full Paper Bioscience Microflora Vol. 25 (3), 99 107, 2006 Phylogenetic Analysis of 16S Ribosomal RNA Gene Sequences from Human Fecal Microbiota and Improved Utility of Terminal Restriction Fragment Length
Full Paper Bioscience Microflora Vol. 25 (3), 99 107, 2006 Phylogenetic Analysis of 16S Ribosomal RNA Gene Sequences from Human Fecal Microbiota and Improved Utility of Terminal Restriction Fragment Length
Influences of Dietary and Environmental Stress on Microbial Populations in the Murine Gastrointestinal Tract
 INFECTION AND IMMUNrrY, Mar. 1974, p. 591-598 Copyright 0 1974 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 9, No. 3 Printed in U.S.A. Influences of Dietary and Environmental Stress on Microbial Populations
INFECTION AND IMMUNrrY, Mar. 1974, p. 591-598 Copyright 0 1974 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 9, No. 3 Printed in U.S.A. Influences of Dietary and Environmental Stress on Microbial Populations
Host Transmission of Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium Is Controlled by Virulence Factors and Indigenous Intestinal Microbiota
 INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Jan. 2008, p. 403 416 Vol. 76, No. 1 0019-9567/08/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/iai.01189-07 Copyright 2008, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Host Transmission of
INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Jan. 2008, p. 403 416 Vol. 76, No. 1 0019-9567/08/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/iai.01189-07 Copyright 2008, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Host Transmission of
Product Catalogue 2015 Clinical and Industrial Microbiology
 Acinetobacter baumannii ATCC BAA-747 * 89141 Actinomyces odontolyticus ATCC 17929 * 89114 Aeromonas hydrophila ATCC 7966 * 89119 Aggregatibacter aphrophilus ATCC 7901 * 89091 Aspergillus brasiliensis ATCC
Acinetobacter baumannii ATCC BAA-747 * 89141 Actinomyces odontolyticus ATCC 17929 * 89114 Aeromonas hydrophila ATCC 7966 * 89119 Aggregatibacter aphrophilus ATCC 7901 * 89091 Aspergillus brasiliensis ATCC
Commensal Bacteria Increase Invasion of Intestinal Epithelium by Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhi
 INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Nov. 2003, p. 6610 6614 Vol. 71, No. 11 0019-9567/03/$08.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/IAI.71.11.6610 6614.2003 Copyright 2003, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Commensal
INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Nov. 2003, p. 6610 6614 Vol. 71, No. 11 0019-9567/03/$08.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/IAI.71.11.6610 6614.2003 Copyright 2003, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Commensal
Human Microbiome Project
 Human Microbiome Project Definitions Microbiome: the collective genomes of the community of organisms that share our space Metagenome: culture independent study of genomes of many organisms in order to
Human Microbiome Project Definitions Microbiome: the collective genomes of the community of organisms that share our space Metagenome: culture independent study of genomes of many organisms in order to
μ gyra parc Escherichia coli Klebsiella pneumoniae Pseudomonas aeruginosa E. coli gyra E. coli parc gyra parc gyra Escherichia coli E. coli E.
 gyra parc Escherichia coli Klebsiella pneumoniae Pseudomonas aeruginosa E. coli μ E. coli gyra parc gyra parc gyra parc μ μ gyra parc Key words Escherichia coli gyra parc Escherichia coli E. coli gyra
gyra parc Escherichia coli Klebsiella pneumoniae Pseudomonas aeruginosa E. coli μ E. coli gyra parc gyra parc gyra parc μ μ gyra parc Key words Escherichia coli gyra parc Escherichia coli E. coli gyra
SULFIDE-INDOLE-MOTILITY (SIM) TEST
 Microbiology Laboratory (BIOL 3702L) Page 1 of 5 Principle and Purpose SULFIDE-INDOLE-MOTILITY (SIM) TEST Using Sulfide-Indole-Motility (SIM) media, various Gram-negative enteric bacilli can be distinguished
Microbiology Laboratory (BIOL 3702L) Page 1 of 5 Principle and Purpose SULFIDE-INDOLE-MOTILITY (SIM) TEST Using Sulfide-Indole-Motility (SIM) media, various Gram-negative enteric bacilli can be distinguished
Most common dose (mg) 1 g x 3 1 g x mg -1.0 g x 3 1 g x mg -1 g x mg -1 g x 3
 Meropenem Rationale for the EUCAST clinical breakpoints, version 1.5 1 st June 2009 Introduction Meropenem is a carbapenem, available only for parenteral use. Meropenem is relevant for therapy of septicaemia,
Meropenem Rationale for the EUCAST clinical breakpoints, version 1.5 1 st June 2009 Introduction Meropenem is a carbapenem, available only for parenteral use. Meropenem is relevant for therapy of septicaemia,
doi: /nature18849 Appreciation of the important role of the microbiota in human
 2016MacmilanPublishersLimited.Alrightsreserved.Interactions between the microbiota and pathogenic bacteria in the gut Andreas J. Bäumler 1 & Vanessa Sperandio 2,3 The microbiome has an important role in
2016MacmilanPublishersLimited.Alrightsreserved.Interactions between the microbiota and pathogenic bacteria in the gut Andreas J. Bäumler 1 & Vanessa Sperandio 2,3 The microbiome has an important role in
INTERPRETATION OF THE GRAM STAIN
 INTERPRETATION OF THE GRAM STAIN DISCLOSURE Relevant relationships with commercial entities none Potential for conflicts of interest within this presentation none Steps taken to review and mitigate potential
INTERPRETATION OF THE GRAM STAIN DISCLOSURE Relevant relationships with commercial entities none Potential for conflicts of interest within this presentation none Steps taken to review and mitigate potential
by author ESCMID Online Lecture Library Differentation of anaerobic bacteria according to the Wadsworth method Arrangement (non-) selective media
 Differentation of anaerobic bacteria according to the Wadsworth method Peptostreptococcus Anaerococcus Peptoniphilus Parvimonas Finegoldia Classification Clostridium-Eubacterium Actinomyces Propionibacterium
Differentation of anaerobic bacteria according to the Wadsworth method Peptostreptococcus Anaerococcus Peptoniphilus Parvimonas Finegoldia Classification Clostridium-Eubacterium Actinomyces Propionibacterium
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION ARTICLE NUMBER: 16161 DOI: 10.1038/NMICROBIOL.2016.161 A reference gene catalogue of the pig gut microbiome Liang Xiao 1, Jordi Estellé 2, Pia Kiilerich 3, Yuliaxis Ramayo-Caldas
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION ARTICLE NUMBER: 16161 DOI: 10.1038/NMICROBIOL.2016.161 A reference gene catalogue of the pig gut microbiome Liang Xiao 1, Jordi Estellé 2, Pia Kiilerich 3, Yuliaxis Ramayo-Caldas
3M Food Safety Technical Bulletin
 3M Petrifilm Aqua Enterobacteriaceae Count Plates Performance Summary 3M Petrifi lm Aqua Enterobacteriaceae (AQEB) Count Plates are sample ready media plates used in the microbial testing of bottled water.
3M Petrifilm Aqua Enterobacteriaceae Count Plates Performance Summary 3M Petrifi lm Aqua Enterobacteriaceae (AQEB) Count Plates are sample ready media plates used in the microbial testing of bottled water.
EZ-COMP EZ-COMP For Training and Proficiency Testing Product Details
 EZ-COMP For Training and Proficiency Testing Mixed microorganism populations Identified by codes rather than descriptions Refrigerated storage Traceable to reference culture Product warranty Product Details
EZ-COMP For Training and Proficiency Testing Mixed microorganism populations Identified by codes rather than descriptions Refrigerated storage Traceable to reference culture Product warranty Product Details
Retail Catalog 39th Edition Supplemental Information Individual Microorganisms Price Microorganism Description
 LYFO DISK KWIK-STIK Vial 6 Pk Pk Individual Microorganisms Price Microorganism Description ode BSL omment 049L 049K 049P 0645L 0645K 0645P Aggregatibacter aphrophilus AT 4997 D formerly Haemophilus paraphrophilus
LYFO DISK KWIK-STIK Vial 6 Pk Pk Individual Microorganisms Price Microorganism Description ode BSL omment 049L 049K 049P 0645L 0645K 0645P Aggregatibacter aphrophilus AT 4997 D formerly Haemophilus paraphrophilus
Bile Chrysoidin Glycerol Agar with MUG
 INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE READY-TO-USE PLATED MEDIA PA-257430.04 Rev.: Mar 2013 Bile Chrysoidin Glycerol Agar with MUG INTENDED USE Partially selective medium for the isolation and differentiation of Enterobacteriaceae
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE READY-TO-USE PLATED MEDIA PA-257430.04 Rev.: Mar 2013 Bile Chrysoidin Glycerol Agar with MUG INTENDED USE Partially selective medium for the isolation and differentiation of Enterobacteriaceae
FOR RUMINANTS. kemin.com/guthealth
 FOR RUMINANTS kemin.com/guthealth What is CLOSTAT? CLOSTAT contains a proprietary, patented strain of Bacillus subtilis PB6. PB6 is a unique, naturally occurring, spore-forming microorganism. Kemin has
FOR RUMINANTS kemin.com/guthealth What is CLOSTAT? CLOSTAT contains a proprietary, patented strain of Bacillus subtilis PB6. PB6 is a unique, naturally occurring, spore-forming microorganism. Kemin has
Microbial Taxonomy. Classification of living organisms into groups. A group or level of classification
 Lec 2 Oral Microbiology Dr. Chatin Purpose Microbial Taxonomy Classification Systems provide an easy way grouping of diverse and huge numbers of microbes To provide an overview of how physicians think
Lec 2 Oral Microbiology Dr. Chatin Purpose Microbial Taxonomy Classification Systems provide an easy way grouping of diverse and huge numbers of microbes To provide an overview of how physicians think
Product Catalogue 2016 Clinical and Industrial Microbiology
 Acinetobacter baumannii ATCC BAA-747 * 89141 Acinetobacter baumannii ATCC 19606 * 89174 Actinomyces odontolyticus ATCC 17929 * 89114 Aeromonas hydrophila ATCC 7966 * 89119 Aeromonas hydrophila ATCC 35654
Acinetobacter baumannii ATCC BAA-747 * 89141 Acinetobacter baumannii ATCC 19606 * 89174 Actinomyces odontolyticus ATCC 17929 * 89114 Aeromonas hydrophila ATCC 7966 * 89119 Aeromonas hydrophila ATCC 35654
Antibiotic-Induced Perturbations of the Intestinal Microbiota Alter Host Susceptibility to Enteric Infection
 INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Oct. 2008, p. 4726 4736 Vol. 76, No. 10 0019-9567/08/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/iai.00319-08 Copyright 2008, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Antibiotic-Induced
INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Oct. 2008, p. 4726 4736 Vol. 76, No. 10 0019-9567/08/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/iai.00319-08 Copyright 2008, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Antibiotic-Induced
Enteric Salmonellosis Disrupts the Microbial Ecology of the Murine Gastrointestinal Tract
 INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Mar. 2008, p. 907 915 Vol. 76, No. 3 0019-9567/08/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/iai.01432-07 Copyright 2008, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Enteric Salmonellosis
INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Mar. 2008, p. 907 915 Vol. 76, No. 3 0019-9567/08/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/iai.01432-07 Copyright 2008, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Enteric Salmonellosis
Novel fluorescent reporters for studying host-pathogen interactions
 The Essentials of Life Science Research Globally Delivered Novel fluorescent reporters for studying host-pathogen interactions Mariette Barbier, Ph.D.¹, ², Dev Mittar, Ph.D.² ¹University of Virginia, Charlottesville,
The Essentials of Life Science Research Globally Delivered Novel fluorescent reporters for studying host-pathogen interactions Mariette Barbier, Ph.D.¹, ², Dev Mittar, Ph.D.² ¹University of Virginia, Charlottesville,
A mathematical and computational model of necrotizing enterocolitis
 A mathematical and computational model of necrotizing enterocolitis Ivan Yotov Department of Mathematics, University of Pittsburgh McGowan Institute Scientific Retreat March 10-12, 2008 Acknowledgment:
A mathematical and computational model of necrotizing enterocolitis Ivan Yotov Department of Mathematics, University of Pittsburgh McGowan Institute Scientific Retreat March 10-12, 2008 Acknowledgment:
Supplementary Figure 1: To test the role of mir-17~92 in orthologous genetic model of ADPKD, we generated Ksp/Cre;Pkd1 F/F (Pkd1-KO) and Ksp/Cre;Pkd1
 Supplementary Figure 1: To test the role of mir-17~92 in orthologous genetic model of ADPKD, we generated Ksp/Cre;Pkd1 F/F (Pkd1-KO) and Ksp/Cre;Pkd1 F/F ;mir-17~92 F/F (Pkd1-miR-17~92KO) mice. (A) Q-PCR
Supplementary Figure 1: To test the role of mir-17~92 in orthologous genetic model of ADPKD, we generated Ksp/Cre;Pkd1 F/F (Pkd1-KO) and Ksp/Cre;Pkd1 F/F ;mir-17~92 F/F (Pkd1-miR-17~92KO) mice. (A) Q-PCR
Game plan Lecture Lab Prelabs
 Game plan Lecture Binary fission Growth curves Physical requirements for growth Chemical requirements for growth Lab Lab Exam Prelabs Growth Curve Bring books and APO-3 for next class Microbial growth
Game plan Lecture Binary fission Growth curves Physical requirements for growth Chemical requirements for growth Lab Lab Exam Prelabs Growth Curve Bring books and APO-3 for next class Microbial growth
ENTEROBACTER AEROGENES UNKNOWN BACTERIA FLOW CHART UNKNOWN LAB REPORT, MICROBIOLOGY ENTEROBACTER AEROGENES
 ENTEROBACTER AEROGENES UNKNOWN BACTERIA PDF UNKNOWN LAB REPORT, MICROBIOLOGY ENTEROBACTER AEROGENES IDENTIFICATION OF AN UNKNOWN BACTERIAL SPECIES OF 1 / 5 2 / 5 3 / 5 enterobacter aerogenes unknown bacteria
ENTEROBACTER AEROGENES UNKNOWN BACTERIA PDF UNKNOWN LAB REPORT, MICROBIOLOGY ENTEROBACTER AEROGENES IDENTIFICATION OF AN UNKNOWN BACTERIAL SPECIES OF 1 / 5 2 / 5 3 / 5 enterobacter aerogenes unknown bacteria
Original Article Effect of DSS on Bacterial Growth in Gastrointestinal Tract
 Original Article Effect of DSS on Bacterial Growth in Gastrointestinal Tract (IBD / DSS colitis / bacterial growth / S. typhimurium SL7207 / E. coli Nissle 1917) J. HLINKOVÁ 1, H. SVOBODOVÁ 1, T. BRACHTLOVÁ
Original Article Effect of DSS on Bacterial Growth in Gastrointestinal Tract (IBD / DSS colitis / bacterial growth / S. typhimurium SL7207 / E. coli Nissle 1917) J. HLINKOVÁ 1, H. SVOBODOVÁ 1, T. BRACHTLOVÁ
Toll-Like Receptor 5-Deficient Mice Have Dysregulated Intestinal Gene Expression and Nonspecific Resistance to Salmonella-Induced Typhoid-Like Disease
 INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Mar. 2008, p. 1276 1281 Vol. 76, No. 3 0019-9567/08/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/iai.01491-07 Copyright 2008, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Toll-Like Receptor
INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Mar. 2008, p. 1276 1281 Vol. 76, No. 3 0019-9567/08/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/iai.01491-07 Copyright 2008, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Toll-Like Receptor
Supplementary Methods
 Supplementary Methods MMPBSA Free energy calculation Molecular Mechanics/Poisson Boltzmann Surface Area (MM/PBSA) has been widely used to calculate binding free energy for protein-ligand systems (1-7).
Supplementary Methods MMPBSA Free energy calculation Molecular Mechanics/Poisson Boltzmann Surface Area (MM/PBSA) has been widely used to calculate binding free energy for protein-ligand systems (1-7).
Article (peer-reviewed)
 Title Author(s) The composition of human milk and infant faecal microbiota over the first three months of life: a pilot study Murphy, Kiera; Curley, David; O'Callaghan, Tom F.; O'Shea, Carol Anne; Dempsey,
Title Author(s) The composition of human milk and infant faecal microbiota over the first three months of life: a pilot study Murphy, Kiera; Curley, David; O'Callaghan, Tom F.; O'Shea, Carol Anne; Dempsey,
Line. Chickens. Health. Program. Nutrition. Program. SILO patented 1-Monoglycerides from C1 to C7 for treating animals. Patent n.
 Chickens Line N Health Program H Nutrition Program SILO patented 1-Monoglycerides from C1 to C7 for treating animals Patent n. EP 2 410 871 B1 USAGE SILOhealth is a synergistic combination of short, medium
Chickens Line N Health Program H Nutrition Program SILO patented 1-Monoglycerides from C1 to C7 for treating animals Patent n. EP 2 410 871 B1 USAGE SILOhealth is a synergistic combination of short, medium
Most common dose (mg) 1g x 1 1g x 1 1g x 1 1g x 1 1g x 1 1g x 1. Maximum dose schedule (mg) 1g x 1 1g x 1 1g x 1 1g x 1 1g x 1 1g x 1
 Ertapenem Rationale for the EUCAST clinical breakpoints, version 1.3 1 st June 2009 Introduction Ertapenem is a carbapenem, available only for parenteral use. Ertapenem is relevant for therapy of septicaemia,
Ertapenem Rationale for the EUCAST clinical breakpoints, version 1.3 1 st June 2009 Introduction Ertapenem is a carbapenem, available only for parenteral use. Ertapenem is relevant for therapy of septicaemia,
The effect of salinomycin on Salmonella, Campylobacter and the intestinal microflora in experimentally infected broiler chickens
 The effect of salinomycin on Salmonella, Campylobacter and the intestinal microflora in experimentally infected broiler chickens C. H. JOHANSEN, L. BJERRUM, M. LUND and K. PEDERSEN* Danish Institute for
The effect of salinomycin on Salmonella, Campylobacter and the intestinal microflora in experimentally infected broiler chickens C. H. JOHANSEN, L. BJERRUM, M. LUND and K. PEDERSEN* Danish Institute for
Tetracycline Rationale for the EUCAST clinical breakpoints, version th November 2009
 Tetracycline Rationale for the EUCAST clinical breakpoints, version 1.0 20 th November 2009 Introduction The natural tetracyclines, including tetracycline, chlortetracycline, oxytetracycline and demethylchlortetracycline
Tetracycline Rationale for the EUCAST clinical breakpoints, version 1.0 20 th November 2009 Introduction The natural tetracyclines, including tetracycline, chlortetracycline, oxytetracycline and demethylchlortetracycline
Evaluation of the efficiency of Mxxxx as a barrier against microrganisms crossing
 Evaluation of the efficiency of as a barrier against microrganisms crossing A) composition of filter The filter of has the following characteristics: 1. An outer layer, which is composed by a medical,
Evaluation of the efficiency of as a barrier against microrganisms crossing A) composition of filter The filter of has the following characteristics: 1. An outer layer, which is composed by a medical,
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Comparison of trap formation by fresh and autoclaved dung samples. The fresh or autoclaved dung was diluted with water and placed on a water agar plate within
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Comparison of trap formation by fresh and autoclaved dung samples. The fresh or autoclaved dung was diluted with water and placed on a water agar plate within
GI Microbiota. Human Intestinal Symbiotes. Neurological Disorders. Diabetes. Autoimmune. Heart Disease. Cancer. Inflammation.
 GI Microbiota Human Intestinal Symbiotes Neurological Disorders Diabetes Autoimmune Heart Disease 100s Species Millions Genes Trillions Cells Cancer Inflammation Chemical Toxicity Mammalian Xenobiotic
GI Microbiota Human Intestinal Symbiotes Neurological Disorders Diabetes Autoimmune Heart Disease 100s Species Millions Genes Trillions Cells Cancer Inflammation Chemical Toxicity Mammalian Xenobiotic
Helicobacter pylori is a Gram-negative bacterium that
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Prior Helicobacter pylori Infection Ameliorates Salmonella Typhimurium-Induced Colitis: Mucosal Crosstalk Between Stomach and Distal Intestine* Peter D.R. Higgins, MD, PhD, MSc, Laura
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Prior Helicobacter pylori Infection Ameliorates Salmonella Typhimurium-Induced Colitis: Mucosal Crosstalk Between Stomach and Distal Intestine* Peter D.R. Higgins, MD, PhD, MSc, Laura
DEPARTMENT OF MICROBIOLOGY. Microbiology Programme: Bachelor of Science (Honours) Microbiology
 DEPARTMENT OF MICROBIOLOGY Microbiology Programme: Bachelor of Science (Honours) Microbiology Philosophy Microbiology is simply a natural science that deals with the study of microbes: their structure,
DEPARTMENT OF MICROBIOLOGY Microbiology Programme: Bachelor of Science (Honours) Microbiology Philosophy Microbiology is simply a natural science that deals with the study of microbes: their structure,
Working with Food Microbiome Data
 Working with Food Microbiome Data Relative abundance of microbes After processing the sequencing data, we obtain the relative abundance of all microbes found in each sample. The microbes are identified
Working with Food Microbiome Data Relative abundance of microbes After processing the sequencing data, we obtain the relative abundance of all microbes found in each sample. The microbes are identified
Flagella and Chemotaxis Are Required for Efficient Induction of Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium Colitis in Streptomycin-Pretreated Mice
 INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, July 2004, p. 4138 4150 Vol. 72, No. 7 0019-9567/04/$08.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/IAI.72.7.4138 4150.2004 Copyright 2004, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Flagella
INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, July 2004, p. 4138 4150 Vol. 72, No. 7 0019-9567/04/$08.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/IAI.72.7.4138 4150.2004 Copyright 2004, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Flagella
C. elegans as an in vivo model to decipher microbial virulence. Centre d Immunologie de Marseille-Luminy
 C. elegans as an in vivo model to decipher microbial virulence Centre d Immunologie de Marseille-Luminy C. elegans : a model organism Mechanisms of apoptosis, RNA interference Neuronal function and development
C. elegans as an in vivo model to decipher microbial virulence Centre d Immunologie de Marseille-Luminy C. elegans : a model organism Mechanisms of apoptosis, RNA interference Neuronal function and development
MICROBIOLOGY REVIEWS. Introduction REVIEW ARTICLE. B arbel Stecher 1,2, *, David Berry 3, * & Alexander Loy 3. Abstract
 REVIEW ARTICLE Colonization resistance and microbial ecophysiology: using gnotobiotic mouse models and single-cell technology to explore the intestinal jungle B arbel Stecher 1,2, *, David Berry 3, * &
REVIEW ARTICLE Colonization resistance and microbial ecophysiology: using gnotobiotic mouse models and single-cell technology to explore the intestinal jungle B arbel Stecher 1,2, *, David Berry 3, * &
3M Food Safety Technical Bulletin
 3M Petrifilm Aqua Heterotrophic Count Plate Performance Summary 3M Petrifilm Aqua Heterotrophic Count (AQHC) Plates are sample ready media plates used in the microbial testing of bottled water. Each plate
3M Petrifilm Aqua Heterotrophic Count Plate Performance Summary 3M Petrifilm Aqua Heterotrophic Count (AQHC) Plates are sample ready media plates used in the microbial testing of bottled water. Each plate
Intestinal epithelial specific MyD88 signaling impacts host susceptibility. to infectious colitis by promoting protective goblet cell and
 IAI Accepts, published online ahead of print on 23 June 2014 Infect. Immun. doi:10.1128/iai.02045-14 Copyright 2014, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13
IAI Accepts, published online ahead of print on 23 June 2014 Infect. Immun. doi:10.1128/iai.02045-14 Copyright 2014, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13
Our product offering. The ATCC Licensed Derivative Program
 Our product offering Currently MECCONTI offers three different product lines of lyophilized micro-organisms: MicroSwabs: A MicroSwab consists of a lyophilized pellet of a single micro-organism strain inside
Our product offering Currently MECCONTI offers three different product lines of lyophilized micro-organisms: MicroSwabs: A MicroSwab consists of a lyophilized pellet of a single micro-organism strain inside
Life in an unusual intracellular niche a bacterial symbiont infecting the nucleus of amoebae
 Life in an unusual intracellular niche a bacterial symbiont infecting the nucleus of amoebae Frederik Schulz, Ilias Lagkouvardos, Florian Wascher, Karin Aistleitner, Rok Kostanjšek, Matthias Horn Supplementary
Life in an unusual intracellular niche a bacterial symbiont infecting the nucleus of amoebae Frederik Schulz, Ilias Lagkouvardos, Florian Wascher, Karin Aistleitner, Rok Kostanjšek, Matthias Horn Supplementary
About OMICS Group Conferences
 About OMICS Group OMICS Group International is an amalgamation of Open Access publications and worldwide international science conferences and events. Established in the year 2007 with the sole aim of
About OMICS Group OMICS Group International is an amalgamation of Open Access publications and worldwide international science conferences and events. Established in the year 2007 with the sole aim of
LETTERS. Self-destructive cooperation mediated by phenotypic noise
 Vol 454 21 August 2008 doi:10.1038/nature07067 Self-destructive cooperation mediated by phenotypic noise LETTERS Martin Ackermann 1, Bärbel Stecher 2, Nikki E. Freed 1, Pascal Songhet 2, Wolf-Dietrich
Vol 454 21 August 2008 doi:10.1038/nature07067 Self-destructive cooperation mediated by phenotypic noise LETTERS Martin Ackermann 1, Bärbel Stecher 2, Nikki E. Freed 1, Pascal Songhet 2, Wolf-Dietrich
Chronic Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium-Induced Colitis and Cholangitis in Streptomycin-Pretreated Nramp1 / Mice
 INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Sept. 2006, p. 5047 5057 Vol. 74, No. 9 0019-9567/06/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/iai.00072-06 Copyright 2006, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Chronic Salmonella
INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Sept. 2006, p. 5047 5057 Vol. 74, No. 9 0019-9567/06/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/iai.00072-06 Copyright 2006, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Chronic Salmonella
ELECTRONIC SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION for
 ELECTRONIC SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION for Complex Function by Design Using Spatially Pre-Structured Synthetic Microbial Communities: Degradation of Pentachlorophenol in the Presence of Hg(II) Supporting
ELECTRONIC SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION for Complex Function by Design Using Spatially Pre-Structured Synthetic Microbial Communities: Degradation of Pentachlorophenol in the Presence of Hg(II) Supporting
Fitness constraints on horizontal gene transfer
 Fitness constraints on horizontal gene transfer Dan I Andersson University of Uppsala, Department of Medical Biochemistry and Microbiology, Uppsala, Sweden GMM 3, 30 Aug--2 Sep, Oslo, Norway Acknowledgements:
Fitness constraints on horizontal gene transfer Dan I Andersson University of Uppsala, Department of Medical Biochemistry and Microbiology, Uppsala, Sweden GMM 3, 30 Aug--2 Sep, Oslo, Norway Acknowledgements:
Considerations with Antibiotic Therapy PART
 Considerations with Antibiotic Therapy PART 1 The Wonderful World of Microbiology 1 Despite the promises of the household-products industry, almost every surface is covered in microorganisms almost all
Considerations with Antibiotic Therapy PART 1 The Wonderful World of Microbiology 1 Despite the promises of the household-products industry, almost every surface is covered in microorganisms almost all
Escherichia coli F-18 To Colonize the Streptomycin-
 INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Sept. 1990, p. 2957-2961 0019-9567/90/092957-05$02.00/0 Copyright 1990, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 58, No. 9 Neither Motility nor Chemotaxis Plays a Role in the Ability
INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Sept. 1990, p. 2957-2961 0019-9567/90/092957-05$02.00/0 Copyright 1990, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 58, No. 9 Neither Motility nor Chemotaxis Plays a Role in the Ability
Salmonella typhimurium in Mice
 INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Apr. 1985, p. 169-174 0019-9567/85/040169-06$02.00/0 Copyright 1985, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 48, No. 1 Effect of Streptomycin Administration on Colonization Resistance
INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Apr. 1985, p. 169-174 0019-9567/85/040169-06$02.00/0 Copyright 1985, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 48, No. 1 Effect of Streptomycin Administration on Colonization Resistance
Supporting Information
 1 Supporting Information 2 3 4 5 Automated High-Throughput Identification and Characterisation of Clinically Important Bacteria and Fungi using Rapid Evaporative Ionisation Mass Spectrometry (REIMS) 6
1 Supporting Information 2 3 4 5 Automated High-Throughput Identification and Characterisation of Clinically Important Bacteria and Fungi using Rapid Evaporative Ionisation Mass Spectrometry (REIMS) 6
MICROBIAL BIOCHEMISTRY BIOT 309. Dr. Leslye Johnson Sept. 30, 2012
 MICROBIAL BIOCHEMISTRY BIOT 309 Dr. Leslye Johnson Sept. 30, 2012 Phylogeny study of evoluhonary relatedness among groups of organisms (e.g. species, populahons), which is discovered through molecular
MICROBIAL BIOCHEMISTRY BIOT 309 Dr. Leslye Johnson Sept. 30, 2012 Phylogeny study of evoluhonary relatedness among groups of organisms (e.g. species, populahons), which is discovered through molecular
Comparison of 61 E. coli genomes
 Comparison of 61 E. coli genomes Center for Biological Sequence Analysis Department of Systems Biology Dave Ussery! DTU course 27105 - Comparative Genomics Oksana s 61 E. coli genomes paper! Monday, 23
Comparison of 61 E. coli genomes Center for Biological Sequence Analysis Department of Systems Biology Dave Ussery! DTU course 27105 - Comparative Genomics Oksana s 61 E. coli genomes paper! Monday, 23
NUT-TTC/EMB Code 5541
 NUT-TTC/EMB Code 5541 COMING SOON! BioPaddles Colony Identification App Nutrient-TTC Agar (NUT-TTC) Eosin Methylene Blue Agar (EMB) USE: Isolation and differentiation of Gram (-) enteric bacilli. Coliform
NUT-TTC/EMB Code 5541 COMING SOON! BioPaddles Colony Identification App Nutrient-TTC Agar (NUT-TTC) Eosin Methylene Blue Agar (EMB) USE: Isolation and differentiation of Gram (-) enteric bacilli. Coliform
On the Use of the Bross Formula for Prioritizing Covariates in the High-Dimensional Propensity Score Algorithm
 On the Use of the Bross Formula for Prioritizing Covariates in the High-Dimensional Propensity Score Algorithm Richard Wyss 1, Bruce Fireman 2, Jeremy A. Rassen 3, Sebastian Schneeweiss 1 Author Affiliations:
On the Use of the Bross Formula for Prioritizing Covariates in the High-Dimensional Propensity Score Algorithm Richard Wyss 1, Bruce Fireman 2, Jeremy A. Rassen 3, Sebastian Schneeweiss 1 Author Affiliations:
The biogeography of polymicrobial infection
 MICROBIAL BIOFILMS The biogeography of polymicrobial infection Apollo Stacy 1, Luke McNally 2, Sophie E. Darch 1, Sam P. Brown 3 and Marvin Whiteley 1 Abstract Microbial communities are spatially organized
MICROBIAL BIOFILMS The biogeography of polymicrobial infection Apollo Stacy 1, Luke McNally 2, Sophie E. Darch 1, Sam P. Brown 3 and Marvin Whiteley 1 Abstract Microbial communities are spatially organized
Microbial Typing by Machine Learned DNA Melt Signatures
 Microbial Typing by Machine Learned DNA Melt Signatures Nadya Andini 1, Bo Wang 2, Pornpat Athamanolap 3, Justin Hardick 4, Billie J. Masek 5, Simone Thair 1, Annie Hu 1, Gideon Avornu 5, Stephen Peterson
Microbial Typing by Machine Learned DNA Melt Signatures Nadya Andini 1, Bo Wang 2, Pornpat Athamanolap 3, Justin Hardick 4, Billie J. Masek 5, Simone Thair 1, Annie Hu 1, Gideon Avornu 5, Stephen Peterson
Microbiota: Its Evolution and Essence. Hsin-Jung Joyce Wu "Microbiota and man: the story about us
 Microbiota: Its Evolution and Essence Overview q Define microbiota q Learn the tool q Ecological and evolutionary forces in shaping gut microbiota q Gut microbiota versus free-living microbe communities
Microbiota: Its Evolution and Essence Overview q Define microbiota q Learn the tool q Ecological and evolutionary forces in shaping gut microbiota q Gut microbiota versus free-living microbe communities
The Intestinal Microbiota Plays a Role in Salmonella- Induced Colitis Independent of Pathogen Colonization
 The Intestinal Microbiota Plays a Role in Salmonella- Induced Colitis Independent of Pathogen Colonization Rosana B. R. Ferreira 1, Navkiran Gill 1, Benjamin P. Willing 1, L. Caetano M. Antunes 1, Shannon
The Intestinal Microbiota Plays a Role in Salmonella- Induced Colitis Independent of Pathogen Colonization Rosana B. R. Ferreira 1, Navkiran Gill 1, Benjamin P. Willing 1, L. Caetano M. Antunes 1, Shannon
Chapter X. Pathogenic Escherichia coli Kyle S. Enger, MPH
 Chapter X. Pathogenic Escherichia coli Kyle S. Enger, MPH X.1 Overview Escherichia coli usually exists as a commensal bacterium in the mammalian large intestine, benefiting itself as well as the host.
Chapter X. Pathogenic Escherichia coli Kyle S. Enger, MPH X.1 Overview Escherichia coli usually exists as a commensal bacterium in the mammalian large intestine, benefiting itself as well as the host.
The invention of the microscope has opened to us a world of extraordinary numbers. A singular drop of pond water reveals countless life forms
 Biology Chapter 19 Notes - Bacteria and Viruses The invention of the microscope has opened to us a world of extraordinary numbers. A singular drop of pond water reveals countless life forms I. Classifying
Biology Chapter 19 Notes - Bacteria and Viruses The invention of the microscope has opened to us a world of extraordinary numbers. A singular drop of pond water reveals countless life forms I. Classifying
ARTICLES. AL Fr antz 1, EW Ro g i er 1, CR Web er 2, L Shen 2, DA C ohen 1, L A Fenton 1, MEC Bruno 1 and CS Kae tz el 1. nature publishing group
 nature publishing group ARTICLES Targeted deletion of MyD88 in intestinal epithelial cells results in compromised antibacterial immunity associated with downregulation of polymeric immunoglobulin receptor,
nature publishing group ARTICLES Targeted deletion of MyD88 in intestinal epithelial cells results in compromised antibacterial immunity associated with downregulation of polymeric immunoglobulin receptor,
Toronto General Hospital ANTIBIOGRAM Emergency Department January 1, December 31, 2016
 IV (meningitis) IV (non-meningitis) (meningitis) (non-meningitis) Blood Isolates % Susceptible 644 18 36 70 78 74 59 69 75 262 100 19 64 75 100 92 54 72 78 76 68 89 86 99 Escherichia coli 153 58 30 67
IV (meningitis) IV (non-meningitis) (meningitis) (non-meningitis) Blood Isolates % Susceptible 644 18 36 70 78 74 59 69 75 262 100 19 64 75 100 92 54 72 78 76 68 89 86 99 Escherichia coli 153 58 30 67
Mesenteric Lymph Nodes Confine Dendritic Cell-Mediated Dissemination of Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium and Limit Systemic Disease in Mice
 INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Aug. 2009, p. 3170 3180 Vol. 77, No. 8 0019-9567/09/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/iai.00272-09 Copyright 2009, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Mesenteric Lymph Nodes
INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Aug. 2009, p. 3170 3180 Vol. 77, No. 8 0019-9567/09/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/iai.00272-09 Copyright 2009, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Mesenteric Lymph Nodes
Effects of Moisture Content on Long-Term Survival and Regrowth of Bacteria in Wastewater Sludge
 APPLED AND ENVIRONMENTAL MICROBIOLOGY, May 1981, p. 1117-1122 0099-2240/81/051117-06$02.00/0 Vol. 41, No. 5 Effects of Moisture Content on Long-Term Survival and Regrowth of Bacteria in Wastewater Sludge
APPLED AND ENVIRONMENTAL MICROBIOLOGY, May 1981, p. 1117-1122 0099-2240/81/051117-06$02.00/0 Vol. 41, No. 5 Effects of Moisture Content on Long-Term Survival and Regrowth of Bacteria in Wastewater Sludge
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature10534 Supplementary Fig. 1. Diagrammatic representation of the N-end rule pathway of targeted proteolysis (after Graciet and Wellmer 2010 9 ). Tertiary, secondary
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature10534 Supplementary Fig. 1. Diagrammatic representation of the N-end rule pathway of targeted proteolysis (after Graciet and Wellmer 2010 9 ). Tertiary, secondary
Statistical methods for the analysis of microbiome compositional data in HIV studies
 1/ 56 Statistical methods for the analysis of microbiome compositional data in HIV studies Javier Rivera Pinto November 30, 2018 Outline 1 Introduction 2 Compositional data and microbiome analysis 3 Kernel
1/ 56 Statistical methods for the analysis of microbiome compositional data in HIV studies Javier Rivera Pinto November 30, 2018 Outline 1 Introduction 2 Compositional data and microbiome analysis 3 Kernel
Identifying genomic and metabolic features that can underlie early successional and opportunistic lifestyles of human gut symbionts
 Research Identifying genomic and metabolic features that can underlie early successional and opportunistic lifestyles of human gut symbionts Catherine Lozupone, 1 Karoline Faust, 2,3 Jeroen Raes, 2,3 Jeremiah
Research Identifying genomic and metabolic features that can underlie early successional and opportunistic lifestyles of human gut symbionts Catherine Lozupone, 1 Karoline Faust, 2,3 Jeroen Raes, 2,3 Jeremiah
Kingdom Monera Bacteria
 Kingdom Monera Bacteria Common bacteria Prokaryotes Strep throat Anthrax Chlamydia E. coli Meningitis Salmonella Micrococcus(intestinal) Streptococcus mutans Haemophilusinfluenzae Cellphonious bacterious
Kingdom Monera Bacteria Common bacteria Prokaryotes Strep throat Anthrax Chlamydia E. coli Meningitis Salmonella Micrococcus(intestinal) Streptococcus mutans Haemophilusinfluenzae Cellphonious bacterious
Mestrado em Microbiologia Aplicada. FRM Fisiologia e Regulação Microbiana. IFRM Introdução à Fisiologia e Regulação Microbiana. Ano Lectivo 2017/2018
 Mestrado em Microbiologia Aplicada FRM Fisiologia e Regulação Microbiana IFRM Introdução à Fisiologia e Regulação Microbiana Ano Lectivo 2017/2018 Program FRM /IFRM- Fisiologia e Regulação Microbiana 1.
Mestrado em Microbiologia Aplicada FRM Fisiologia e Regulação Microbiana IFRM Introdução à Fisiologia e Regulação Microbiana Ano Lectivo 2017/2018 Program FRM /IFRM- Fisiologia e Regulação Microbiana 1.
Company Profile SALTOSE. New Bio-Culture & Enzyme Combination
 Company Profile Company name Head office PIC-BIO,Inc. Registered office; Gosaku Bld., 1-29-2 Nishigotanda, Shinagawa-ku, Tokyo, 141-0031, Japan TEL: +81-3-3490-8220 FAX: +81-3-3490-1859 Warehouse; 7399,
Company Profile Company name Head office PIC-BIO,Inc. Registered office; Gosaku Bld., 1-29-2 Nishigotanda, Shinagawa-ku, Tokyo, 141-0031, Japan TEL: +81-3-3490-8220 FAX: +81-3-3490-1859 Warehouse; 7399,
Virulence of Broad- and Narrow-Host-Range Salmonella enterica Serovars in the Streptomycin-Pretreated Mouse Model
 INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Jan. 2006, p. 632 644 Vol. 74, No. 1 0019-9567/06/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/iai.74.1.632 644.2006 Copyright 2006, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Virulence of
INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Jan. 2006, p. 632 644 Vol. 74, No. 1 0019-9567/06/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/iai.74.1.632 644.2006 Copyright 2006, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Virulence of
CLASSIFICATION OF MICROORGANISMS
 CLASSIFICATION OF MICROORGANISMS DISCLOSURE Relevant relationships with commercial entities none Potential for conflicts of interest within this presentation none Steps taken to review and mitigate potential
CLASSIFICATION OF MICROORGANISMS DISCLOSURE Relevant relationships with commercial entities none Potential for conflicts of interest within this presentation none Steps taken to review and mitigate potential
