Supplementary Figure 1: To test the role of mir-17~92 in orthologous genetic model of ADPKD, we generated Ksp/Cre;Pkd1 F/F (Pkd1-KO) and Ksp/Cre;Pkd1
|
|
|
- Kimberly Hardy
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Supplementary Figure 1: To test the role of mir-17~92 in orthologous genetic model of ADPKD, we generated Ksp/Cre;Pkd1 F/F (Pkd1-KO) and Ksp/Cre;Pkd1 F/F ;mir-17~92 F/F (Pkd1-miR-17~92KO) mice. (A) Q-PCR analysis revealed that compared to control kidneys (black), Pkd1 expression was equally reduced in both Pkd1-KO (red) and Pkd1-miR-17~92KO (green) kidneys, indicating that a similar level of Cre/loxP recombination was observed. (B) Q-PCR analysis revealed that, compared to control kidneys, mir-17 expression was increased in Pkd1-KO kidneys, whereas its expression was reduced in Pkd1-miR- 17~92KO mice. (C) Kidney-weight-to-body-weight (KW/BW) ratio and the expression of kidney injury markers (D) Kim1 and (E) Ngal was reduced in Pkd1-miR-17~92KO compared to Pkd1-KO kidneys. (F) The number of cyst epithelia undergoing apoptosis did not change in Pkd1-miR-17~92KO compared to Pkd1-KO kidneys. Error bars indicate SEM. * indicates P<0.05, ns indicates P>0.05. One-way ANOVA, Tukey s multiple comparisons test (A, B, D, E), Student s unpaired t-test (C, F) 1
2 Supplementary Figure 2: To test the role of mir-17~92 in an orthologous genetic model of ADPKD bearing mutations in Pkd2, we generated Pkhd1/Cre;Pkd2 F/F (Pkd2-KO) and Pkhd1/Cre;Pkd2;miR- 17~92 F/F (Pkd2-miR-17~92KO) mice. (A) Q-PCR analysis revealed that, compared to control kidneys (black), Pkd2 expression was equally reduced in both Pkd2-KO (orange) and Pkd2-miR-17~92KO (blue) kidneys, indicating that a similar level of Cre/loxP recombination was observed. (B) Western Blot analysis and quantification of Polycystin-2 (PC-2) expression in Pkd2-KO and Pkd2-miR-17~92KO kidneys is shown. mir-17 deletion did not affect PC-2 expression in Pkd2-miR-17~92KO kidneys. (C) Q- PCR analysis revealed that, compared to control kidneys, mir-17 expression was increased in Pkd2-KO kidneys, whereas its expression was reduced by ~60% in Pkd2-miR-17~92KO mice. (D) Cyst index and the expression of kidney injury markers (E) Kim1 and (F) Ngal was reduced in Pkd2-miR-17~92KO compared to Pkd2-KO kidneys. (G) The number of cyst epithelia undergoing apoptosis was higher in Pkd2-miR-17~92KO compared to Pkd2-KO kidneys. However, this difference was not statistically significant. Error bars indicate SEM. * indicates P<0.05, ns indicates P> One-way ANOVA, Tukey s multiple comparisons test (A, C, E, F), Student s unpaired t-test (B, D, G) 2
3 Supplementary Figure 3: To test the role of mir-17~92 in a long-lived ADPKD model, we generated Ksp/Cre;Pkd1 Flox/RC (Pkd1 F/RC SKO) and Ksp/Cre;Pkd1 Flox/RC ;mir-17~92 F/F (Pkd1 F/RC DKO) mice. This compound Pkd1-mutant mouse harbors a germline hypomorphic mutation on one allele and a Cre/loxP recombination-induced, renal tubule-specific, somatic null mutation on the other allele. (A) Q-PCR analysis revealed that Pkd1 expression was not different between control (black), Pkd1 F/RC SKO (red) and Pkd1 F/RC DKO (green) kidneys, suggesting that deleting one floxed allele does not affect the total Pkd1 mrna expression. (B) In contrast, Q-PCR analysis revealed that, compared to control kidneys, mir-17 expression was increased in Pkd1 F/RC SKO kidneys, whereas its expression was reduced by ~80% in Pkd1 F/RC DKO kidneys. (C) H&E staining of kidney sections from three-week-old and five-month-old Pkd1 F/RC SKO and Pkd1 F/RC DKO mice is shown. (D&E) Kidney-weight-to-body-weight (KW/BW) ratio, (F) blood urea nitrogen (BUN) level and the expression of (G) Kim1 and (H) Ngal was reduced in Pkd1 F/RC DKO compared to Pkd1 F/RC SKO mice. Thus, deletion of mir-17~92 markedly attenuates disease progression in Ksp/Cre;Pkd1 Flox/RC mice. Error bars indicate SEM. * indicates P<0.05, ns indicates P>0.05. One-way ANOVA, Tukey s multiple comparisons test (A, B, G, H), Student s unpaired t-test (D, E, F) 3
4 Supplementary Figure 4: To test the role of mir-17~92 in a slow cyst growth ADPKD model, we generated and characterized 6-month-old Pkd1 RC/RC ; Ksp/Cre (Pkd1 RC/RC ) and Pkd1 RC/RC ; Ksp/Cre;miR- 17~92 F/F mice (Pkd1 RC/RC DKO). Unlike the preceding three ADPKD models, Cre/loxP recombination is not required to induce Pkd1 mutation, and these mice develop significant renal fibrosis. Ksp/Cre was introduced into the cross to delete mir-17~92. (A) Q-PCR analysis revealed that, compared to control kidneys, mir-17 expression was increased in Pkd1 RC/RC kidneys, whereas its expression was reduced in Pkd1 RC/RC DKO compared to Pkd1 RC/RC mice. (B) Kidney-weight-to-body-weight ratio, (C) BUN and the expression of (D) Kim1 and (E) Ngal was decreased in Pkd1 RC/RC DKO compared to Pkd1 RC/RC mice. (F) Kidney sections were stained with an antibody against Fsp1 (fibroblast-specific protein 1). Fsp1 expression (green) was decreased in Pkd1 RC/RC DKO kidneys compared to Pkd1 RC/RC kidneys. (G-J) Q-PCR analysis showed that the expression of other fibrosis markers (Col4a6, Col1a1, Acta2, and Vimentin) was also decreased in Pkd1 RC/RC DKO kidneys compared to Pkd1 RC/RC kidneys. Collectively, these results indicate that mir-17~92 deletion attenuates disease progression in Pkd1 RC/RC mice. Error bars indicate SEM. * indicates P<0.05, ns indicates P>0.05. One-way ANOVA, Tukey s multiple comparisons test (A) Student s unpaired t-test (B-J). Scale Bar: 50 µm. 4
5 5
6 Supplementary Figure 5: (A) Genomic organization of the mir-17~92 and its paralogous clusters mir- 106a~363 and mir-106b~25 is shown. Collectively, these three mirna clusters encode mirnas that belong to either the mir-17 (blue), mir-19 (green), mir-18 (purple) or mir-25 (orange) mirna families. We have previously shown that our anti-mir-17 compound inhibits mirnas that are marked with an X in cultured cells. (B) The ability of this compound to inhibit mir-17 in vivo was measured using the mirna polysome shift assay (mipsa) 1. Normal mice were treated with a single subcutaneous dose of vehicle (PBS), anti-mir-17 (0.3, 3 or 30 mg per kg dose) or control oligonucleotide (30 mg per kg dose), and kidneys were harvested 7-days later (n=5-7 each group and dose). mir-17 fraction (normalized to let-7d) in high molecular weight (HMW) was measured by Q-PCR. mir-17 was displaced from HMW polysomes in kidneys of mice injected with anti-mir-17 in a dose-dependent manner. Similar mir-17 displacement was not observed in mice treated with vehicle or a control oligonucleotide. (C) Normal adult mice were injected with 300 mg per kg dose of anti-mir-17, vehicle or a control oligonucleotide known to produce liver toxicity (positive control). Measurement of the liver (ALT and AST) and kidney function (BUN) showed that anti-mir-17 does not produce acute liver or kidney toxicity. (D-F) The design of the delivery and therapeutic efficacy trials are shown. Error bars indicate SEM. * indicates P<0.05, ns indicates P>0.05. One-way ANOVA, Tukey s multiple comparisons test (B) Student s unpaired t-test (C) 6
7 Supplementary Figure 6: Primary cyst epithelial cultures derived from kidneys of ADPKD patients were transfected with anti-mir-17 (dose: 3 nm, 10 nm or 30 nm) or three different control oligonucleotides (dose: 30 nm, control oligo1, 2 and 3) or mock-transfected. These cells were then cultured to measure proliferation and in-vitro cyst formation. (A) Data for proliferation (n=5 for each treatment and dose) using primary cultures derived from ADPKD Donor1, 2, 3 and 5. (B) In-vitro cyst formation (n=3 for each treatment and dose) using primary cultures derived from ADPKD Donor 3. Anti-miR-17 reduced cell viability and cyst count in a dose-dependent manner. Error bars indicate SEM. *indicates P<0.05, **indicates ns indicates P<0.01, ***indicates ns indicates P<0.005, and ****indicates P< One-way ANOVA, Tukey s multiple comparisons test 7
8 Supplementary Figure 7: RNA-Seq analysis was performed to compare mrna expression profiles between kidneys of 21-day-old control, Pkd1 F/RC SKO and Pkd1 F/RC DKO mice (n=3). The differentially expressed genes (P<0.05, FDR<0.1) were further analyzed using the Ingenuity Pathway Analysis (IPA) software. Several mitochondrial pathways were differentially expressed. In particular, the oxidative phosphorylation pathway (shown above) was downregulated in Pkd1 F/RC SKO compared to control kidneys. In contrast, this pathway was upregulated in Pkd1 F/RC DKO compared to Pkd1 F/RC SKO kidneys. Green indicates downregulated genes, whereas red indicates upregulated genes. 8
9 Supplementary Figure 8: RNA-Seq analysis was performed to compare mrna expression profiles between kidneys of 21-day-old control, Pkd2-KO and Pkd2-miR-17~92KO mice (n=5). The differentially expressed genes (P<0.05, FDR<0.1) were further analyzed using the Ingenuity Pathway Analysis (IPA) software. Similar to the Pkd1-mutant mice, several mitochondrial pathways were differentially expressed. The oxidative phosphorylation pathway (shown above) was downregulated in Pkd2-KO compared to control kidneys. In contrast, this pathway was upregulated in Pkd2-miR-17~92KO compared to Pkd2-KO kidneys. Green indicates downregulated genes, whereas red indicates upregulated genes. 9
10 Supplementary Figure 9: RNA-Seq analysis was performed to compare mrna expression profiles between kidneys of 21-day-old control, Pkd1F/RCSKO and Pkd1F/RCDKO mice (n=3). The differentially expressed genes (P<0.05, FDR<0.1) were further analyzed using the Ingenuity Pathway Analysis (IPA) software to identify the upstream regulators that may be responsible for the gene expression changes observed after mir-17~92 deletion. PPARA-regulated gene network was predicted to be robustly activated after mir-17~92 deletion. Accordingly, a large number of direct PPARA targets (shown above) were upregulated in Pkd1F/RCDKO compared to Pkd1F/RCSKO kidneys. Green indicates downregulated genes, whereas red indicates upregulated genes. 10
11 Supplementary Figure 10: RNA-Seq analysis was performed to compare mrna expression profiles between kidneys of 21-day-old control, Pkd2-KO and Pkd2-miR-17~92KO mice (n=5). The differentially expressed genes (P<0.05, FDR<0.1) were further analyzed using the Ingenuity Pathway Analysis (IPA) software to identify the upstream regulators that may be responsible for the gene expression changes observed after mir-17~92 deletion in Pkd2-KO mice. Similar to Pkd1-mutant kidneys, PPARA-regulated gene network was predicted to be robustly activated after mir-17~92 deletion in Pkd2-KO kidneys. A number of direct PPARA targets (shown above) were upregulated in Pkd2-miR-17~92KO compared to Pkd2-KO kidneys. Green indicates downregulated genes, whereas red indicates upregulated genes. 11
12 Supplementary Figure 11: To test whether reduced Ppara gene dosage is sufficient to enhance proliferation and promote cyst formation, 6-week old Ppara -/-, Pkd1 RC/RC, and Pkd1 RC/RC ; Ppara-KO mice were characterized. Q-PCR analysis (A) Kim1 and (B) Ngal in the indicated mouse models is shown. Error bars indicate SEM. Multiplicity adjusted P values using Tukey s multiple comparison test are shown. 12
13 Supplementary Figure 12: Characterization of cultured cells transfected with (A) mir-17 mimics and (B) PPARA-expressing plasmid (pppara) is shown. To determine whether mir-17 affects OXPHOS, Seahorse XF 24 Analyzer was used to measure real-time mitochondrial oxygen consumption rate (OCR) of renal epithelial cells. (C) Real-time OCR tracings, (D) Basal OCR, (E) Oligomycin-treated OCR, and (F) ATP-dependent OCR of indicated cell lines is shown. ATP-dependent OCR was reduced in mimcd3 cells treated with mir-17 mimics compared to scramble mimics. Reexpression of Ppara prevented mir- 17-induced reductions in ATP-dependent OCR. (G&H) MTT assay was used to determine whether increased Ppara gene dosage inhibits mir-17-stimulated proliferation of renal epithelia. Treatment with mir-17 mimic increased proliferation of mimcd3 cells. (G) Transfection with a Ppara-expressing plasmid (pppara) reduced mir-17-stimulated proliferation whereas transfection with a control plasmid (pcmx) had no effect (n=3 biological replicates with three technical replicates). (H) Treatment with WY14643, a PPARA agonist, also reduced mir-17-stimulated proliferation whereas treatment with DMSO had no effect (n=3 biological replicates with three technical replicates). mir-17 mimic also increased proliferation of Pkd2 -/- kidney epithelia. Similar to mimcd3 cells, WY14643 reduced mir-17-stimulated proliferation of Pkd2 -/- cells whereas treatment with DMSO had no effect (n=3 biological replicates with three technical replicates). One-way ANOVA, Tukey s multiple comparisons test (D-H) Student s unpaired t-test (A, B) 13
14 Supplementary Figure 13: Song et al 2, have previously performed cdna microarrays (Human Genome U133 Plus 2.0 Array, Affymetrix) using RNA from three normal renal cortical samples, five minimally cystic ADPKD tissue samples and 13 ADPKD cysts of varying sizes (small, medium, and large). Analysis of this publically-available data ( revealed that PPARA (red arrow heads) and its targets are downregulated in human ADPKD cysts. 14
15 Supplementary Figure 14: The full, original Western blots are shown accompanied with indicated protein name (top left) and molecular weight (top right). 15
16 Supplementary Table 1:Differential expression of mirnas in ADPKD models Pkd1-KO vs. Control Pkd2-KO vs. Control mirna P10 AvgExp Fold-change P-value mmu-mir-29a E E mmu-mir-126-3p E E mmu-mir-200c E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-let-7g E E mmu-mir-20a/b E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-196b E E mmu-mir E E mmu-let-7i E E mmu-mir-199a-5p E E mmu-mir-29b E E mmu-mir-30e E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-126-5p E E mmu-mir-26b E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-199a-3p E E mmu-mir-30c E E mmu-mir-106a+mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-362-5p E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-340-5p E E mmu-mir-151-5p E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-200a E E mmu-mir-148b E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-345-5p E E mmu-mir p E E mmu-mir-196a E E mmu-mir-99a E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-532-5p E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-200b E E FDR P21 AvgExp Fold-change P-value FDR 16
17 mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-188-5p E E mmu-mir-135a E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-301a E E mmu-mir-10b E E mmu-mir-434-3p E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-376b E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-26a E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-376c E E mmu-mir-23a E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-335-5p E E mmu-mir-181c E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-23b E E mmu-let-7d E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-101a E E mmu-mir E E mmu-let-7a E E mmu-mir-615-3p E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-142-3p E E mmu-mir-125a-3p E E mmu-mir-148a E E mmu-mir-551b E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-15a E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-130b E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-338-3p E E mmu-mir E E mmu-let-7f E E mmu-mir-335-3p E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-139-5p E E mmu-mir-324-5p E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-450a-5p E E mmu-mir-331-3p E E mmu-mir-202-5p E E
18 mmu-mir-30b E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-434-5p E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir p E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-770-3p E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-669e E E mmu-mir-18a E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-290-5p E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-let-7b E E mmu-mir-30a E E mmu-mir-146a E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-743a E E mmu-mir-190b E E mmu-mir-342-3p E E mmu-mir-34a E E mmu-mir-466c-5p E E mmu-mir-574-3p E E mmu-mir-409-5p E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-574-5p E E mmu-mir-181a E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-501-5p E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-369-3p E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-450b-3p E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-296-5p E E
19 mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-133a E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-331-5p E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-19a E E mmu-mir-30d E E mmu-mir-380-3p E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-466d-3p E E mmu-mir-208b E E mmu-mir-129-5p E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-501-3p E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-466d-5p E E mmu-mir-487b E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-216a E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-876-5p E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-337-5p E E mmu-mir-342-5p E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-669h-5p E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-466l E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-743b-3p E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-301b E E mmu-mir-449a E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-666-3p E E
20 mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-290-3p E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-19b E E mmu-mir-130a E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-466a/b-3p E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-323-5p E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-106b E E mmu-mir-423-3p E E mmu-mir-532-3p E E mmu-mir-7b E E mmu-mir-582-5p E E mmu-mir-423-5p E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-133b E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-7a E E mmu-mir-202-3p E E mmu-mir-297c E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-181b/d E E mmu-mir-542-5p E E mmu-mir-875-5p E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-101b E E mmu-mir-193b E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-876-3p E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir p E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-125b-3p E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-29c E E
21 mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-92b E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-669a E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-467f E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-669o E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-340-3p E E mmu-mir-362-3p E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir p E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-27b E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-34b-3p E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-466g E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-542-3p E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-467c E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-466k E E mmu-mir p E E mmu-mir-125a-5p E E mmu-mir-467e E E mmu-mir-292-5p E E mmu-mir-669j E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-151-3p E E mmu-mir-99b E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-467h+mmu-mir-669d/l E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-669f E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-671-3p E E
22 mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-467g E E mmu-mir-323-3p E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-509-5p E E mmu-mir-467a E E mmu-mir p E E mmu-mir-146b E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-376a E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-129-3p E E mmu-mir-883b-3p E E mmu-mir-338-5p E E mmu-mir-770-5p E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-let-7c E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-142-5p E E mmu-mir-15b E E mmu-mir-125b-5p E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-27a E E mmu-mir-875-3p E E mmu-mir-369-5p E E mmu-mir-675-5p E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-1946a E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-34b-5p E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-883b-5p E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-883a-3p E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-764-3p E E mmu-mir-764-5p E E mmu-mir-669i E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-3470a/b E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-let-7e E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E
23 mmu-mir-654-3p E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-337-3p E E mmu-mir-467b E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-302d E E mmu-mir-743b-5p E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-292-3p E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-465b-5p E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-92a E E mmu-mir-450b-5p E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-135b E E mmu-mir-139-3p E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-188-3p E E mmu-mir p E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir p E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-18b E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir p E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-1946b E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-208a E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E
24 mmu-mir-216b E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-291a-3p E E mmu-mir-291a-5p E E mmu-mir-291b-3p E E mmu-mir-291b-5p E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-296-3p E E mmu-mir-297b-3p E E mmu-mir-297b-5p E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-302a E E mmu-mir-302b E E mmu-mir-302c E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-324-3p E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-339-3p E E mmu-mir-339-5p E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-345-3p E E mmu-mir-34c E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-380-5p E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-384-3p E E mmu-mir-384-5p E E mmu-mir-409-3p E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-449b E E mmu-mir-449c E E mmu-mir-450a-3p E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-465a-3p E E mmu-mir-465a-5p E E mmu-mir-465c-5p E E mmu-mir-466a/e-5p E E mmu-mir-466f-5p E E mmu-mir-466h E E mmu-mir-466i E E mmu-mir-466j E E mmu-mir-467d E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-509-3p E E
25 mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-540-3p E E mmu-mir-540-5p E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-582-3p E E mmu-mir-590-3p E E mmu-mir-590-5p E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-615-5p E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-654-5p E E mmu-mir-666-5p E E mmu-mir-669g E E mmu-mir-669m E E mmu-mir-671-5p E E mmu-mir-673-3p E E mmu-mir-673-5p E E mmu-mir-675-3p E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-693-3p E E mmu-mir-693-5p E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-878-3p E E mmu-mir-878-5p E E mmu-mir E E mmu-mir-883a-5p E E
26 Supplementary Table 2:Commonly Dysregulated mirnas in ADPKD models. UP mmu-mir-182 mmu-mir-183 mmu-mir-96 mmu-mir-21 mmu-mir-223 mmu-mir-199a-3p mmu-mir-199a-5p mmu-mir-200c mmu-mir-100 mmu-mir-350 mmu-let-7i mmu-mir-20a+mmu-mir-20b mmu-mir-28 mmu-mir-106a+mmu-mir-17 mmu-mir-532-5p mmu-mir-143 DOWN mmu-let-7g mmu-mir-99a mmu-mir-126-3p mmu-mir-151-5p mmu-mir-196a mmu-mir-26b mmu-mir-126-5p mmu-mir-30c mmu-mir-185 mmu-mir-30e mmu-mir-194 mmu-mir-378 mmu-mir
27 Supplementary Table 3: CT values of polysome shift assay (PSA) High Molecular Weight Fraction 3 High Molecular Weight Fraction 4 Kidney PSA Score mir-17 Let-7d mir-17 Let-7d Treatment Ct Mean Ct Mean dct ddct Ct Mean Ct Mean dct ddct Average ddct Fraction 3+4 PBS PBS PBS PBS PBS PBS PBS PBS anti-mir-17 (0.3mg/kg) anti-mir-17 (0.3mg/kg) anti-mir-17 (0.3mg/kg) anti-mir-17 (0.3mg/kg) anti-mir-17 (0.3mg/kg) anti-mir-17 (3mg/kg) anti-mir-17 (3mg/kg) anti-mir-17 (3mg/kg) anti-mir-17 (3mg/kg) anti-mir-17 (3mg/kg) anti-mir-17 (30mg/kg) anti-mir-17 (30mg/kg) anti-mir-17 (30mg/kg) anti-mir-17 (30mg/kg) anti-mir-17 (30mg/kg) Control (30mg/kg) Control (30mg/kg) Control (30mg/kg) Control (30mg/kg) Control (30mg/kg) Control (30mg/kg) Control (30mg/kg) Control (30mg/kg)
Supplementary Figure 1 Analysis of beige fat and cells and characteristics of exosome release, related to Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Analysis of beige fat and cells and characteristics of exosome release, related to Figure 1 (a) Fold-change in UCP-1 mrna abundance in white adipocytes upon β-adrenergic stimulation
Supplementary Figure 1 Analysis of beige fat and cells and characteristics of exosome release, related to Figure 1 (a) Fold-change in UCP-1 mrna abundance in white adipocytes upon β-adrenergic stimulation
FSC-W FSC-H CD4 CD62-L
 Supplementary Fig. 1 a SSC-A FSC-A FSC-W FSC-H SSC-W SSC-H CD4 CD62-L b SSC-A FSC-A FSC-W FSC-A FSC-A 7-AAD FSC-A CD4 IL-9 CD4 c SSC-A FSC-A FSC-W FSC-H SSC-W SSC-H 7-AAD KI67 Annexin-V 7-AAD d I L -5
Supplementary Fig. 1 a SSC-A FSC-A FSC-W FSC-H SSC-W SSC-H CD4 CD62-L b SSC-A FSC-A FSC-W FSC-A FSC-A 7-AAD FSC-A CD4 IL-9 CD4 c SSC-A FSC-A FSC-W FSC-H SSC-W SSC-H 7-AAD KI67 Annexin-V 7-AAD d I L -5
Nature Biotechnology: doi: /nbt Supplementary Figure 1. Generation of paraxial mesoderm from the H7 hesc line.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Generation of paraxial mesoderm from the H7 hesc line. H7 hescs were differentiated as shown in Figure 1a. (a) Flow cytometric analyses of the proportion of CD56+, PDGFRα+, and KDR+
Supplementary Figure 1 Generation of paraxial mesoderm from the H7 hesc line. H7 hescs were differentiated as shown in Figure 1a. (a) Flow cytometric analyses of the proportion of CD56+, PDGFRα+, and KDR+
Supplementary Figure 1. Markedly decreased numbers of marginal zone B cells in DOCK8 mutant mice Supplementary Figure 2.
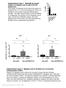 Supplementary Figure 1. Markedly decreased numbers of marginal zone B cells in DOCK8 mutant mice. Percentage of marginal zone B cells in the spleen of wild-type mice (+/+), mice homozygous for cpm or pri
Supplementary Figure 1. Markedly decreased numbers of marginal zone B cells in DOCK8 mutant mice. Percentage of marginal zone B cells in the spleen of wild-type mice (+/+), mice homozygous for cpm or pri
microrna pseudo-targets
 microrna pseudo-targets Natalia Pinzón Restrepo Institut de Génétique Humaine (CNRS), Montpellier, France August, 2012 microrna target identification mir: target: 2 7 5 N NNNNNNNNNNNNNN NNNNNN 3 the seed
microrna pseudo-targets Natalia Pinzón Restrepo Institut de Génétique Humaine (CNRS), Montpellier, France August, 2012 microrna target identification mir: target: 2 7 5 N NNNNNNNNNNNNNN NNNNNN 3 the seed
Supplemental material
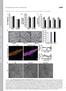 Supplemental material THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY Mourier et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201411100/dc1 Figure S1. Size and mitochondrial content in Mfn1 and Mfn2 knockout hearts. (A) Body
Supplemental material THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY Mourier et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201411100/dc1 Figure S1. Size and mitochondrial content in Mfn1 and Mfn2 knockout hearts. (A) Body
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1. HSP21 expression in 35S:HSP21 and hsp21 knockdown plants. (a) Since no T- DNA insertion line for HSP21 is available in the publicly available T-DNA collections,
Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1. HSP21 expression in 35S:HSP21 and hsp21 knockdown plants. (a) Since no T- DNA insertion line for HSP21 is available in the publicly available T-DNA collections,
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1. NAD + -related genes expression in mouse tissues and in cells overexpressing NRK1. mrna (a) and protein (b) levels of NRK1, NRK2 and other enzymes involved
Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1. NAD + -related genes expression in mouse tissues and in cells overexpressing NRK1. mrna (a) and protein (b) levels of NRK1, NRK2 and other enzymes involved
TRANSCRIPTOMICS. (or the analysis of the transcriptome) Mario Cáceres. Main objectives of genomics. Determine the entire DNA sequence of an organism
 TRANSCRIPTOMICS (or the analysis of the transcriptome) Mario Cáceres Main objectives of genomics Determine the entire DNA sequence of an organism Identify and annotate the complete set of genes encoded
TRANSCRIPTOMICS (or the analysis of the transcriptome) Mario Cáceres Main objectives of genomics Determine the entire DNA sequence of an organism Identify and annotate the complete set of genes encoded
Supplementary Figure 1.
 Supplementary Figure 1. Characterisation of IHG-1 overexpressing and knockdown cell lines. (A) Total cellular RNA was prepared from HeLa cells stably overexpressing IHG-1 or mts-ihg-1. IHG-1 mrna was quantified
Supplementary Figure 1. Characterisation of IHG-1 overexpressing and knockdown cell lines. (A) Total cellular RNA was prepared from HeLa cells stably overexpressing IHG-1 or mts-ihg-1. IHG-1 mrna was quantified
Illegitimate translation causes unexpected gene expression from on-target out-of-frame alleles
 Illegitimate translation causes unexpected gene expression from on-target out-of-frame alleles created by CRISPR-Cas9 Shigeru Makino, Ryutaro Fukumura, Yoichi Gondo* Mutagenesis and Genomics Team, RIKEN
Illegitimate translation causes unexpected gene expression from on-target out-of-frame alleles created by CRISPR-Cas9 Shigeru Makino, Ryutaro Fukumura, Yoichi Gondo* Mutagenesis and Genomics Team, RIKEN
Supplementary Figure 1. Nature Genetics: doi: /ng.3848
 Supplementary Figure 1 Phenotypes and epigenetic properties of Fab2L flies. A- Phenotypic classification based on eye pigment levels in Fab2L male (orange bars) and female (yellow bars) flies (n>150).
Supplementary Figure 1 Phenotypes and epigenetic properties of Fab2L flies. A- Phenotypic classification based on eye pigment levels in Fab2L male (orange bars) and female (yellow bars) flies (n>150).
Waithe et al Supplementary Figures
 Waithe et al Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 Expression and properties of WT and W391A mutant YFP- Ca V 2.2. A Immunoblot using Ca V 2.2 Ab for untransfected cells (UT, lane 1), YFP-Ca V 2.2
Waithe et al Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 Expression and properties of WT and W391A mutant YFP- Ca V 2.2. A Immunoblot using Ca V 2.2 Ab for untransfected cells (UT, lane 1), YFP-Ca V 2.2
robustness: revisting the significance of mirna-mediated regulation
 : revisting the significance of mirna-mediated regulation Hervé Seitz IGH (CNRS), Montpellier, France October 13, 2012 microrna target identification .. microrna target identification mir: target: 2 7
: revisting the significance of mirna-mediated regulation Hervé Seitz IGH (CNRS), Montpellier, France October 13, 2012 microrna target identification .. microrna target identification mir: target: 2 7
Mitochondrial Dynamics Is a Distinguishing Feature of Skeletal Muscle Fiber Types and Regulates Organellar Compartmentalization
 Cell Metabolism Supplemental Information Mitochondrial Dynamics Is a Distinguishing Feature of Skeletal Muscle Fiber Types and Regulates Organellar Compartmentalization Prashant Mishra, Grigor Varuzhanyan,
Cell Metabolism Supplemental Information Mitochondrial Dynamics Is a Distinguishing Feature of Skeletal Muscle Fiber Types and Regulates Organellar Compartmentalization Prashant Mishra, Grigor Varuzhanyan,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2362 Figure S1 CYLD and CASPASE 8 genes are co-regulated. Analysis of gene expression across 79 tissues was carried out as described previously [Ref: PMID: 18636086]. Briefly, microarray
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2362 Figure S1 CYLD and CASPASE 8 genes are co-regulated. Analysis of gene expression across 79 tissues was carried out as described previously [Ref: PMID: 18636086]. Briefly, microarray
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2819 Gαi3 / Actin / Acetylated Tubulin Gαi3 / Actin / Acetylated Tubulin a a Gαi3 a Actin Gαi3 WT Gαi3 WT Gαi3 WT b b Gαi3 b Actin Gαi3 KO Gαi3 KO Gαi3 KO # # Figure S1 Loss of protein
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2819 Gαi3 / Actin / Acetylated Tubulin Gαi3 / Actin / Acetylated Tubulin a a Gαi3 a Actin Gαi3 WT Gαi3 WT Gαi3 WT b b Gαi3 b Actin Gαi3 KO Gαi3 KO Gαi3 KO # # Figure S1 Loss of protein
Nature Methods: doi: /nmeth Supplementary Figure 1. In vitro screening of recombinant R-CaMP2 variants.
 Supplementary Figure 1 In vitro screening of recombinant R-CaMP2 variants. Baseline fluorescence compared to R-CaMP1.07 at nominally zero calcium plotted versus dynamic range ( F/F) for 150 recombinant
Supplementary Figure 1 In vitro screening of recombinant R-CaMP2 variants. Baseline fluorescence compared to R-CaMP1.07 at nominally zero calcium plotted versus dynamic range ( F/F) for 150 recombinant
DOWNLOAD OR READ : MITOCHONDRIAL FUNCTION AND DYSFUNCTION PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI
 DOWNLOAD OR READ : MITOCHONDRIAL FUNCTION AND DYSFUNCTION PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI Page 1 Page 2 mitochondrial function and dysfunction mitochondrial function and dysfunction pdf mitochondrial function and
DOWNLOAD OR READ : MITOCHONDRIAL FUNCTION AND DYSFUNCTION PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI Page 1 Page 2 mitochondrial function and dysfunction mitochondrial function and dysfunction pdf mitochondrial function and
Delivery. Delivery Processes. Delivery Processes: Distribution. Ultimate Toxicant
 Delivery Ultimate Toxicant The chemical species that reacts with the endogenous target. Toxicity depends on the concentration (dose) of the ultimate toxicant at the target site Delivery Processes Absorption
Delivery Ultimate Toxicant The chemical species that reacts with the endogenous target. Toxicity depends on the concentration (dose) of the ultimate toxicant at the target site Delivery Processes Absorption
Gene Ontology and Functional Enrichment. Genome 559: Introduction to Statistical and Computational Genomics Elhanan Borenstein
 Gene Ontology and Functional Enrichment Genome 559: Introduction to Statistical and Computational Genomics Elhanan Borenstein The parsimony principle: A quick review Find the tree that requires the fewest
Gene Ontology and Functional Enrichment Genome 559: Introduction to Statistical and Computational Genomics Elhanan Borenstein The parsimony principle: A quick review Find the tree that requires the fewest
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Discussion Rationale for using maternal ythdf2 -/- mutants as study subject To study the genetic basis of the embryonic developmental delay that we observed, we crossed fish with different
Supplementary Discussion Rationale for using maternal ythdf2 -/- mutants as study subject To study the genetic basis of the embryonic developmental delay that we observed, we crossed fish with different
TNFα 18hr. Control. CHX 18hr. TNFα+ CHX 18hr. TNFα: 18 18hr (KDa) PARP. Cleaved. Cleaved. Cleaved. Caspase3. Pellino3 shrna. Control shrna.
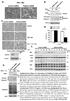 Survival ( %) a. TNFα 18hr b. Control sirna Pellino3 sirna TNFα: 18 18hr c. Control shrna Pellino3 shrna Caspase3 Actin Control d. Control shrna Pellino3 shrna *** 100 80 60 CHX 18hr 40 TNFα+ CHX 18hr
Survival ( %) a. TNFα 18hr b. Control sirna Pellino3 sirna TNFα: 18 18hr c. Control shrna Pellino3 shrna Caspase3 Actin Control d. Control shrna Pellino3 shrna *** 100 80 60 CHX 18hr 40 TNFα+ CHX 18hr
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn.2662
 Supplementary Figure 1 Atlastin phylogeny and homology. (a) Maximum likelihood phylogenetic tree based on 18 Atlastin-1 sequences using the program Quicktree. Numbers at internal nodes correspond to bootstrap
Supplementary Figure 1 Atlastin phylogeny and homology. (a) Maximum likelihood phylogenetic tree based on 18 Atlastin-1 sequences using the program Quicktree. Numbers at internal nodes correspond to bootstrap
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature11419 Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic representation of innate immune signaling pathways induced by intracellular Salmonella in cultured macrophages. a, During the infection Salmonella
doi:10.1038/nature11419 Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic representation of innate immune signaling pathways induced by intracellular Salmonella in cultured macrophages. a, During the infection Salmonella
The geneticist s questions
 The geneticist s questions a) What is consequence of reduced gene function? 1) gene knockout (deletion, RNAi) b) What is the consequence of increased gene function? 2) gene overexpression c) What does
The geneticist s questions a) What is consequence of reduced gene function? 1) gene knockout (deletion, RNAi) b) What is the consequence of increased gene function? 2) gene overexpression c) What does
Drosophila melanogaster and D. simulans, two fruit fly species that are nearly
 Comparative Genomics: Human versus chimpanzee 1. Introduction The chimpanzee is the closest living relative to humans. The two species are nearly identical in DNA sequence (>98% identity), yet vastly different
Comparative Genomics: Human versus chimpanzee 1. Introduction The chimpanzee is the closest living relative to humans. The two species are nearly identical in DNA sequence (>98% identity), yet vastly different
What are mitochondria?
 What are mitochondria? What are mitochondria? An intracellular organelle. There are 100 to 1000s of mitochondria/cell. Most mitochondria come from the mother. Mitochondria have their own DNA Mitochondria
What are mitochondria? What are mitochondria? An intracellular organelle. There are 100 to 1000s of mitochondria/cell. Most mitochondria come from the mother. Mitochondria have their own DNA Mitochondria
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/6/301/ra98/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Regulation of Epithelial Morphogenesis by the G Protein Coupled Receptor Mist and Its Ligand Fog Alyssa J. Manning,
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/6/301/ra98/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Regulation of Epithelial Morphogenesis by the G Protein Coupled Receptor Mist and Its Ligand Fog Alyssa J. Manning,
The role of FGF2 in craniofacial skeletogenesis
 The role of FGF2 in craniofacial skeletogenesis P. Ferretti, S. Sarkar, R. Moore, A. Petiot, C. J. Chan and A. Copp Summary E vidence that the major craniosynostosis syndromes are caused by mutations in
The role of FGF2 in craniofacial skeletogenesis P. Ferretti, S. Sarkar, R. Moore, A. Petiot, C. J. Chan and A. Copp Summary E vidence that the major craniosynostosis syndromes are caused by mutations in
GFP GAL bp 3964 bp
 Supplemental Data. Møller et al. (2009) Shoot Na + exclusion and increased salinity tolerance engineered by cell type-specific alteration of Na + transport in Arabidopsis Supplemental Figure 1. Salt-sensitive
Supplemental Data. Møller et al. (2009) Shoot Na + exclusion and increased salinity tolerance engineered by cell type-specific alteration of Na + transport in Arabidopsis Supplemental Figure 1. Salt-sensitive
Supplemental Information. The Mitochondrial Fission Receptor MiD51. Requires ADP as a Cofactor
 Structure, Volume 22 Supplemental Information The Mitochondrial Fission Receptor MiD51 Requires ADP as a Cofactor Oliver C. Losón, Raymond Liu, Michael E. Rome, Shuxia Meng, Jens T. Kaiser, Shu-ou Shan,
Structure, Volume 22 Supplemental Information The Mitochondrial Fission Receptor MiD51 Requires ADP as a Cofactor Oliver C. Losón, Raymond Liu, Michael E. Rome, Shuxia Meng, Jens T. Kaiser, Shu-ou Shan,
Supplementary Tables and Figures
 Supplementary Tables Supplementary Tables and Figures Supplementary Table 1: Tumor types and samples analyzed. Supplementary Table 2: Genes analyzed here. Supplementary Table 3: Statistically significant
Supplementary Tables Supplementary Tables and Figures Supplementary Table 1: Tumor types and samples analyzed. Supplementary Table 2: Genes analyzed here. Supplementary Table 3: Statistically significant
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/science.1243417/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Circadian Clock Cycle Drives Mitochondrial Oxidative Metabolism in Mice Clara Bien Peek, Alison H. Affinati, Kathryn
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/science.1243417/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Circadian Clock Cycle Drives Mitochondrial Oxidative Metabolism in Mice Clara Bien Peek, Alison H. Affinati, Kathryn
Introduction to Bioinformatics
 CSCI8980: Applied Machine Learning in Computational Biology Introduction to Bioinformatics Rui Kuang Department of Computer Science and Engineering University of Minnesota kuang@cs.umn.edu History of Bioinformatics
CSCI8980: Applied Machine Learning in Computational Biology Introduction to Bioinformatics Rui Kuang Department of Computer Science and Engineering University of Minnesota kuang@cs.umn.edu History of Bioinformatics
Genetically Modified Human Renal Proximal Tubule Epithelial Cells (RPTEC/TERT1) A New Model for Drug Toxicity Studies
 Genetically Modified Human Renal Proximal Tubule Epithelial Cells (RPTEC/TERT1) A New Model for Drug Toxicity Studies Chaozhong Zou, Ph.D. Senior Scientist, ATCC About ATCC Founded in 1925, ATCC is a non-profit
Genetically Modified Human Renal Proximal Tubule Epithelial Cells (RPTEC/TERT1) A New Model for Drug Toxicity Studies Chaozhong Zou, Ph.D. Senior Scientist, ATCC About ATCC Founded in 1925, ATCC is a non-profit
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Single-cell RNA sequencing reveals unique sets of neuropeptides, transcription factors and receptors in specific types of sympathetic neurons (a) Dissection of paravertebral SGs
Supplementary Figure 1 Single-cell RNA sequencing reveals unique sets of neuropeptides, transcription factors and receptors in specific types of sympathetic neurons (a) Dissection of paravertebral SGs
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Cao et al. 10.1073/pnas.1306220110 Gram - bacteria Hemolymph Cytoplasm PGRP-LC TAK1 signalosome Imd dfadd Dredd Dnr1 Ikk signalosome P Relish Nucleus AMP and effector genes Fig.
Supporting Information Cao et al. 10.1073/pnas.1306220110 Gram - bacteria Hemolymph Cytoplasm PGRP-LC TAK1 signalosome Imd dfadd Dredd Dnr1 Ikk signalosome P Relish Nucleus AMP and effector genes Fig.
Photoreceptor Regulation of Constans Protein in Photoperiodic Flowering
 Photoreceptor Regulation of Constans Protein in Photoperiodic Flowering by Valverde et. Al Published in Science 2004 Presented by Boyana Grigorova CBMG 688R Feb. 12, 2007 Circadian Rhythms: The Clock Within
Photoreceptor Regulation of Constans Protein in Photoperiodic Flowering by Valverde et. Al Published in Science 2004 Presented by Boyana Grigorova CBMG 688R Feb. 12, 2007 Circadian Rhythms: The Clock Within
Mole_Oce Lecture # 24: Introduction to genomics
 Mole_Oce Lecture # 24: Introduction to genomics DEFINITION: Genomics: the study of genomes or he study of genes and their function. Genomics (1980s):The systematic generation of information about genes
Mole_Oce Lecture # 24: Introduction to genomics DEFINITION: Genomics: the study of genomes or he study of genes and their function. Genomics (1980s):The systematic generation of information about genes
Supplementary Figure 1. AnnexinV FITC and Sytox orange staining in wild type, Nlrp3 /, ASC / and casp1/11 / TEC treated with TNF /CHX.
 Supplementary Figure 1. AnnexinV FITC and Sytox orange staining in wild type, Nlrp3 /, ASC / and casp1/11 / TEC treated with TNF /CHX. Phase contrast and widefield fluorescence microscopy (20x magnification).
Supplementary Figure 1. AnnexinV FITC and Sytox orange staining in wild type, Nlrp3 /, ASC / and casp1/11 / TEC treated with TNF /CHX. Phase contrast and widefield fluorescence microscopy (20x magnification).
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng Supplementary Figure 1. The phenotypes of PI , BR121, and Harosoy under short-day conditions.
 Supplementary Figure 1 The phenotypes of PI 159925, BR121, and Harosoy under short-day conditions. (a) Plant height. (b) Number of branches. (c) Average internode length. (d) Number of nodes. (e) Pods
Supplementary Figure 1 The phenotypes of PI 159925, BR121, and Harosoy under short-day conditions. (a) Plant height. (b) Number of branches. (c) Average internode length. (d) Number of nodes. (e) Pods
MIR-237 is Likely a Developmental Timing Gene that Regulates the L2-to-L3 Transition in C. Elegans
 Marquette University e-publications@marquette Master's Theses (2009 -) Dissertations, Theses, and Professional Projects MIR-237 is Likely a Developmental Timing Gene that Regulates the L2-to-L3 Transition
Marquette University e-publications@marquette Master's Theses (2009 -) Dissertations, Theses, and Professional Projects MIR-237 is Likely a Developmental Timing Gene that Regulates the L2-to-L3 Transition
AP Biology Gene Regulation and Development Review
 AP Biology Gene Regulation and Development Review 1. What does the regulatory gene code for? 2. Is the repressor by default active/inactive? 3. What changes the repressor activity? 4. What does repressor
AP Biology Gene Regulation and Development Review 1. What does the regulatory gene code for? 2. Is the repressor by default active/inactive? 3. What changes the repressor activity? 4. What does repressor
Analyzing Microgram Quantities of Isolated Mitochondria in the Agilent Seahorse XFe/XF24 Analyzer
 Analyzing Microgram Quantities of Isolated Mitochondria in the Agilent Seahorse XFe/XF24 Analyzer Application Note Introduction Enhanced appreciation of the role of altered mitochondrial function in tumorigenesis,
Analyzing Microgram Quantities of Isolated Mitochondria in the Agilent Seahorse XFe/XF24 Analyzer Application Note Introduction Enhanced appreciation of the role of altered mitochondrial function in tumorigenesis,
Geert Geeven. April 14, 2010
 iction of Gene Regulatory Interactions NDNS+ Workshop April 14, 2010 Today s talk - Outline Outline Biological Background Construction of Predictors The main aim of my project is to better understand the
iction of Gene Regulatory Interactions NDNS+ Workshop April 14, 2010 Today s talk - Outline Outline Biological Background Construction of Predictors The main aim of my project is to better understand the
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information MAP2/Hoechst Hyp.-AP ph 6.5 Hyp.-SD ph 7.2 Norm.-SD ph 7.2 Supplementary Figure 1. Mitochondrial elongation in cortical neurons by acidosis. Representative images of neuronal
Supplementary Information MAP2/Hoechst Hyp.-AP ph 6.5 Hyp.-SD ph 7.2 Norm.-SD ph 7.2 Supplementary Figure 1. Mitochondrial elongation in cortical neurons by acidosis. Representative images of neuronal
10-810: Advanced Algorithms and Models for Computational Biology. microrna and Whole Genome Comparison
 10-810: Advanced Algorithms and Models for Computational Biology microrna and Whole Genome Comparison Central Dogma: 90s Transcription factors DNA transcription mrna translation Proteins Central Dogma:
10-810: Advanced Algorithms and Models for Computational Biology microrna and Whole Genome Comparison Central Dogma: 90s Transcription factors DNA transcription mrna translation Proteins Central Dogma:
Cardiolipin Remodeling by ALCAT1 Regulates Dilated Cardiomyopathy Through Oxidative Stress and Mitophagy. Yuguang (Roger) Shi
 Cardiolipin Remodeling by ALCAT1 Regulates Dilated Cardiomyopathy Through xidative Stress and Mitophagy Yuguang (Roger) Shi yus11@psu.eud Cardiolipin Biosynthetic and Remodeling Pathways Phosphatidic Acid
Cardiolipin Remodeling by ALCAT1 Regulates Dilated Cardiomyopathy Through xidative Stress and Mitophagy Yuguang (Roger) Shi yus11@psu.eud Cardiolipin Biosynthetic and Remodeling Pathways Phosphatidic Acid
Supplementary Figure 1. Real time in vivo imaging of SG secretion. (a) SGs from Drosophila third instar larvae that express Sgs3-GFP (green) and
 Supplementary Figure 1. Real time in vivo imaging of SG secretion. (a) SGs from Drosophila third instar larvae that express Sgs3-GFP (green) and Lifeact-Ruby (red) were imaged in vivo to visualize secretion
Supplementary Figure 1. Real time in vivo imaging of SG secretion. (a) SGs from Drosophila third instar larvae that express Sgs3-GFP (green) and Lifeact-Ruby (red) were imaged in vivo to visualize secretion
Complete all warm up questions Focus on operon functioning we will be creating operon models on Monday
 Complete all warm up questions Focus on operon functioning we will be creating operon models on Monday 1. What is the Central Dogma? 2. How does prokaryotic DNA compare to eukaryotic DNA? 3. How is DNA
Complete all warm up questions Focus on operon functioning we will be creating operon models on Monday 1. What is the Central Dogma? 2. How does prokaryotic DNA compare to eukaryotic DNA? 3. How is DNA
Lesson Overview. Gene Regulation and Expression. Lesson Overview Gene Regulation and Expression
 13.4 Gene Regulation and Expression THINK ABOUT IT Think of a library filled with how-to books. Would you ever need to use all of those books at the same time? Of course not. Now picture a tiny bacterium
13.4 Gene Regulation and Expression THINK ABOUT IT Think of a library filled with how-to books. Would you ever need to use all of those books at the same time? Of course not. Now picture a tiny bacterium
The geneticist s questions. Deleting yeast genes. Functional genomics. From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
 From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Functional genomics..is a field of molecular biology that attempts to make use of the vast wealth of data produced by genomic projects (such as genome sequencing projects)
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Functional genomics..is a field of molecular biology that attempts to make use of the vast wealth of data produced by genomic projects (such as genome sequencing projects)
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng Supplementary Figure 1. ssp mutant phenotypes in a functional SP background.
 Supplementary Figure 1 ssp mutant phenotypes in a functional SP background. (a,b) Statistical comparisons of primary and sympodial shoot flowering times as determined by mean values for leaf number on
Supplementary Figure 1 ssp mutant phenotypes in a functional SP background. (a,b) Statistical comparisons of primary and sympodial shoot flowering times as determined by mean values for leaf number on
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/7/345/ra91/dc1 Supplementary Materials for TGF-β induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition proceeds through stepwise activation of multiple feedback loops Jingyu
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/7/345/ra91/dc1 Supplementary Materials for TGF-β induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition proceeds through stepwise activation of multiple feedback loops Jingyu
JMJ14-HA. Col. Col. jmj14-1. jmj14-1 JMJ14ΔFYR-HA. Methylene Blue. Methylene Blue
 Fig. S1 JMJ14 JMJ14 JMJ14ΔFYR Methylene Blue Col jmj14-1 JMJ14-HA Methylene Blue Col jmj14-1 JMJ14ΔFYR-HA Fig. S1. The expression level of JMJ14 and truncated JMJ14 with FYR (FYRN + FYRC) domain deletion
Fig. S1 JMJ14 JMJ14 JMJ14ΔFYR Methylene Blue Col jmj14-1 JMJ14-HA Methylene Blue Col jmj14-1 JMJ14ΔFYR-HA Fig. S1. The expression level of JMJ14 and truncated JMJ14 with FYR (FYRN + FYRC) domain deletion
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 GP2 Type I-piliated bacteria FAE M cell M cell pocket idc T cell mdc Generation of antigenspecific T cells Induction of antigen-specific mucosal immune response Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic diagram
GP2 Type I-piliated bacteria FAE M cell M cell pocket idc T cell mdc Generation of antigenspecific T cells Induction of antigen-specific mucosal immune response Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic diagram
Mitochondrie et muscle lisse. Vladimir Veksler
 Mitochondrie et muscle lisse Vladimir Veksler Main mitochonrial functions Energy production ATP consumption rate in smooth and striated muscle smooth muscle striated (cardiac) muscle at rest 30 µmol/min/g
Mitochondrie et muscle lisse Vladimir Veksler Main mitochonrial functions Energy production ATP consumption rate in smooth and striated muscle smooth muscle striated (cardiac) muscle at rest 30 µmol/min/g
This presentation contains forward-looking statements within the meaning of the "safe harbor" provisions of the Private Securities Litigation Reform
 This presentation contains forward-looking statements within the meaning of the "safe harbor" provisions of the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995, as amended. These forward-looking statements
This presentation contains forward-looking statements within the meaning of the "safe harbor" provisions of the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995, as amended. These forward-looking statements
Fig. S1. Proliferation and cell cycle exit are affected by the med mutation. (A,B) M-phase nuclei are visualized by a-ph3 labeling in wild-type (A)
 Fig. S1. Proliferation and cell cycle exit are affected by the med mutation. (A,B) M-phase nuclei are visualized by a-ph3 labeling in wild-type (A) and mutant (B) 4 dpf retinae. The central retina of the
Fig. S1. Proliferation and cell cycle exit are affected by the med mutation. (A,B) M-phase nuclei are visualized by a-ph3 labeling in wild-type (A) and mutant (B) 4 dpf retinae. The central retina of the
Organ-on-a-chip: practical applications & challenges. Remko van Vught
 Organ-on-a-chip: practical applications & challenges Remko van Vught 10-4-2018 A leap forward in physiological relevance The challenge of reductionism: Make things as simple as possible, but not simpler,
Organ-on-a-chip: practical applications & challenges Remko van Vught 10-4-2018 A leap forward in physiological relevance The challenge of reductionism: Make things as simple as possible, but not simpler,
*Equal contribution Contact: (TT) 1 Department of Biomedical Engineering, the Engineering Faculty, Tel Aviv
 Supplementary of Complementary Post Transcriptional Regulatory Information is Detected by PUNCH-P and Ribosome Profiling Hadas Zur*,1, Ranen Aviner*,2, Tamir Tuller 1,3 1 Department of Biomedical Engineering,
Supplementary of Complementary Post Transcriptional Regulatory Information is Detected by PUNCH-P and Ribosome Profiling Hadas Zur*,1, Ranen Aviner*,2, Tamir Tuller 1,3 1 Department of Biomedical Engineering,
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/6/281/ra51/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Rapgef2 Connects GPCR-Mediated camp Signals to ERK Activation in Neuronal and Endocrine Cells Andrew C. Emery, Maribeth
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/6/281/ra51/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Rapgef2 Connects GPCR-Mediated camp Signals to ERK Activation in Neuronal and Endocrine Cells Andrew C. Emery, Maribeth
Introduction. Gene expression is the combined process of :
 1 To know and explain: Regulation of Bacterial Gene Expression Constitutive ( house keeping) vs. Controllable genes OPERON structure and its role in gene regulation Regulation of Eukaryotic Gene Expression
1 To know and explain: Regulation of Bacterial Gene Expression Constitutive ( house keeping) vs. Controllable genes OPERON structure and its role in gene regulation Regulation of Eukaryotic Gene Expression
Scope & Outline. Joanna A. Korecka
 Scope & Outline Joanna A. Korecka 10 Scope Parkinson s disease (PD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder. According to the Parkinson s Disease Foundation, 7 to 10 million people suffer from PD worldwide.
Scope & Outline Joanna A. Korecka 10 Scope Parkinson s disease (PD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder. According to the Parkinson s Disease Foundation, 7 to 10 million people suffer from PD worldwide.
Arginase Assay Kit. Catalog Number KA assays Version: 05. Intended for research use only.
 Arginase Assay Kit Catalog Number KA1609 200 assays Version: 05 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3 Principle of the Assay...
Arginase Assay Kit Catalog Number KA1609 200 assays Version: 05 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3 Principle of the Assay...
Comparative analysis of RNA- Seq data with DESeq2
 Comparative analysis of RNA- Seq data with DESeq2 Simon Anders EMBL Heidelberg Two applications of RNA- Seq Discovery Eind new transcripts Eind transcript boundaries Eind splice junctions Comparison Given
Comparative analysis of RNA- Seq data with DESeq2 Simon Anders EMBL Heidelberg Two applications of RNA- Seq Discovery Eind new transcripts Eind transcript boundaries Eind splice junctions Comparison Given
Welcome to HST.508/Biophysics 170
 Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.58: Quantitative Genomics, Fall 5 Instructors: Leonid Mirny, Robert Berwick, Alvin Kho, Isaac Kohane Welcome to HST.58/Biophysics Our emphasis
Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.58: Quantitative Genomics, Fall 5 Instructors: Leonid Mirny, Robert Berwick, Alvin Kho, Isaac Kohane Welcome to HST.58/Biophysics Our emphasis
Written Exam 15 December Course name: Introduction to Systems Biology Course no
 Technical University of Denmark Written Exam 15 December 2008 Course name: Introduction to Systems Biology Course no. 27041 Aids allowed: Open book exam Provide your answers and calculations on separate
Technical University of Denmark Written Exam 15 December 2008 Course name: Introduction to Systems Biology Course no. 27041 Aids allowed: Open book exam Provide your answers and calculations on separate
Technology Platform 2018
 Technology Platform 2018 Forward Looking Statements This presentation contains forward-looking statements within the meaning of the "safe harbor" provisions of the Private Securities Litigation Reform
Technology Platform 2018 Forward Looking Statements This presentation contains forward-looking statements within the meaning of the "safe harbor" provisions of the Private Securities Litigation Reform
Supplementary Figure 1. Biochemical and sequence alignment analyses the
 Supplementary Figure 1. Biochemical and sequence alignment analyses the interaction of OPTN and TBK1. (a) Analytical gel filtration chromatography analysis of the interaction between TBK1 CTD and OPTN(1-119).
Supplementary Figure 1. Biochemical and sequence alignment analyses the interaction of OPTN and TBK1. (a) Analytical gel filtration chromatography analysis of the interaction between TBK1 CTD and OPTN(1-119).
GSBHSRSBRSRRk IZTI/^Q. LlML. I Iv^O IV I I I FROM GENES TO GENOMES ^^^H*" ^^^^J*^ ill! BQPIP. illt. goidbkc. itip31. li4»twlil FIFTH EDITION
 FIFTH EDITION IV I ^HHk ^ttm IZTI/^Q i I II MPHBBMWBBIHB '-llwmpbi^hbwm^^pfc ' GSBHSRSBRSRRk LlML I I \l 1MB ^HP'^^MMMP" jflp^^^^^^^^st I Iv^O FROM GENES TO GENOMES %^MiM^PM^^MWi99Mi$9i0^^ ^^^^^^^^^^^^^V^^^fii^^t^i^^^^^
FIFTH EDITION IV I ^HHk ^ttm IZTI/^Q i I II MPHBBMWBBIHB '-llwmpbi^hbwm^^pfc ' GSBHSRSBRSRRk LlML I I \l 1MB ^HP'^^MMMP" jflp^^^^^^^^st I Iv^O FROM GENES TO GENOMES %^MiM^PM^^MWi99Mi$9i0^^ ^^^^^^^^^^^^^V^^^fii^^t^i^^^^^
Principles of Genetics
 Principles of Genetics Snustad, D ISBN-13: 9780470903599 Table of Contents C H A P T E R 1 The Science of Genetics 1 An Invitation 2 Three Great Milestones in Genetics 2 DNA as the Genetic Material 6 Genetics
Principles of Genetics Snustad, D ISBN-13: 9780470903599 Table of Contents C H A P T E R 1 The Science of Genetics 1 An Invitation 2 Three Great Milestones in Genetics 2 DNA as the Genetic Material 6 Genetics
BMD645. Integration of Omics
 BMD645 Integration of Omics Shu-Jen Chen, Chang Gung University Dec. 11, 2009 1 Traditional Biology vs. Systems Biology Traditional biology : Single genes or proteins Systems biology: Simultaneously study
BMD645 Integration of Omics Shu-Jen Chen, Chang Gung University Dec. 11, 2009 1 Traditional Biology vs. Systems Biology Traditional biology : Single genes or proteins Systems biology: Simultaneously study
Supplementary material: Orbitofrontal and striatal circuits dynamically encode the shift. between goal-directed and habitual actions
 Supplementary material: Orbitofrontal and striatal circuits dynamically encode the shift between goal-directed and habitual actions Christina M. Gremel 1 & Rui M. Costa 1,2 1 Laboratory for Integrative
Supplementary material: Orbitofrontal and striatal circuits dynamically encode the shift between goal-directed and habitual actions Christina M. Gremel 1 & Rui M. Costa 1,2 1 Laboratory for Integrative
Role of Mitochondrial Remodeling in Programmed Cell Death in
 Developmental Cell, Vol. 12 Supplementary Data Role of Mitochondrial Remodeling in Programmed Cell Death in Drosophila melanogaster Gaurav Goyal, Brennan Fell, Apurva Sarin, Richard J. Youle, V. Sriram.
Developmental Cell, Vol. 12 Supplementary Data Role of Mitochondrial Remodeling in Programmed Cell Death in Drosophila melanogaster Gaurav Goyal, Brennan Fell, Apurva Sarin, Richard J. Youle, V. Sriram.
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/9/452/ra106/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Stem-piped light activates phytochrome B to trigger light responses in Arabidopsis thaliana roots Hyo-Jun Lee, Jun-Ho
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/9/452/ra106/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Stem-piped light activates phytochrome B to trigger light responses in Arabidopsis thaliana roots Hyo-Jun Lee, Jun-Ho
Heterosis and inbreeding depression of epigenetic Arabidopsis hybrids
 Heterosis and inbreeding depression of epigenetic Arabidopsis hybrids Plant growth conditions The soil was a 1:1 v/v mixture of loamy soil and organic compost. Initial soil water content was determined
Heterosis and inbreeding depression of epigenetic Arabidopsis hybrids Plant growth conditions The soil was a 1:1 v/v mixture of loamy soil and organic compost. Initial soil water content was determined
Live-cell imaging of alkyne-tagged small biomolecules by stimulated Raman scattering
 Live-cell imaging of alkyne-tagged small biomolecules by stimulated Raman scattering Lu Wei, Fanghao Hu, Yihui Shen, Zhixing Chen, Yong Yu, Chih-Chun Lin, Meng C. Wang, Wei Min * * To whom correspondence
Live-cell imaging of alkyne-tagged small biomolecules by stimulated Raman scattering Lu Wei, Fanghao Hu, Yihui Shen, Zhixing Chen, Yong Yu, Chih-Chun Lin, Meng C. Wang, Wei Min * * To whom correspondence
Utilizing Illumina high-throughput sequencing technology to gain insights into small RNA biogenesis and function
 Utilizing Illumina high-throughput sequencing technology to gain insights into small RNA biogenesis and function Brian D. Gregory Department of Biology Penn Genome Frontiers Institute University of Pennsylvania
Utilizing Illumina high-throughput sequencing technology to gain insights into small RNA biogenesis and function Brian D. Gregory Department of Biology Penn Genome Frontiers Institute University of Pennsylvania
Nature Structural and Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 SUMOylation of proteins changes drastically upon heat shock, MG-132 treatment and PR-619 treatment. (a) Schematic overview of all SUMOylation proteins identified to be differentially
Supplementary Figure 1 SUMOylation of proteins changes drastically upon heat shock, MG-132 treatment and PR-619 treatment. (a) Schematic overview of all SUMOylation proteins identified to be differentially
Hairpin Database: Why and How?
 Hairpin Database: Why and How? Clark Jeffries Research Professor Renaissance Computing Institute and School of Pharmacy University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, United States Why should a database
Hairpin Database: Why and How? Clark Jeffries Research Professor Renaissance Computing Institute and School of Pharmacy University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, United States Why should a database
Chapter 20. Initiation of transcription. Eukaryotic transcription initiation
 Chapter 20. Initiation of transcription Eukaryotic transcription initiation 2003. 5.22 Prokaryotic vs eukaryotic Bacteria = one RNA polymerase Eukaryotes have three RNA polymerases (I, II, and III) in
Chapter 20. Initiation of transcription Eukaryotic transcription initiation 2003. 5.22 Prokaryotic vs eukaryotic Bacteria = one RNA polymerase Eukaryotes have three RNA polymerases (I, II, and III) in
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Figure S1. Mitochondrial morphology in Fis1-null, Mff-null and Fis1/Mff-null MEF cells. (A) Western blotting of lysates from Fis1-null, Mff-null and Fis1/Mff-null cells. Lysates were
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Figure S1. Mitochondrial morphology in Fis1-null, Mff-null and Fis1/Mff-null MEF cells. (A) Western blotting of lysates from Fis1-null, Mff-null and Fis1/Mff-null cells. Lysates were
Hemophilia A gene therapy: AAV-mediated delivery of an enhanced F8 cassette to the liver produces supraphysiological levels of human FVIII in vivo
 Hemophilia A gene therapy: AAV-mediated delivery of an enhanced F8 cassette to the liver produces supraphysiological levels of human FVIII in vivo Brigit E. RILEY Director Discovery and Translational Research
Hemophilia A gene therapy: AAV-mediated delivery of an enhanced F8 cassette to the liver produces supraphysiological levels of human FVIII in vivo Brigit E. RILEY Director Discovery and Translational Research
Correlation between flowering time, circadian rhythm and gene expression in Capsella bursa-pastoris
 Correlation between flowering time, circadian rhythm and gene expression in Capsella bursa-pastoris Johanna Nyström Degree project in biology, Bachelor of science, 2013 Examensarbete i biologi 15 hp till
Correlation between flowering time, circadian rhythm and gene expression in Capsella bursa-pastoris Johanna Nyström Degree project in biology, Bachelor of science, 2013 Examensarbete i biologi 15 hp till
Time allowed: 2 hours Answer ALL questions in Section A, ALL PARTS of the question in Section B and ONE question from Section C.
 UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Biological Sciences Main Series UG Examination 2017-2018 GENETICS BIO-5009A Time allowed: 2 hours Answer ALL questions in Section A, ALL PARTS of the question in Section
UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Biological Sciences Main Series UG Examination 2017-2018 GENETICS BIO-5009A Time allowed: 2 hours Answer ALL questions in Section A, ALL PARTS of the question in Section
7.013 Problem Set
 7.013 Problem Set 5-2013 Question 1 During a summer hike you suddenly spot a huge grizzly bear. This emergency situation triggers a fight or flight response through a signaling pathway as shown below.
7.013 Problem Set 5-2013 Question 1 During a summer hike you suddenly spot a huge grizzly bear. This emergency situation triggers a fight or flight response through a signaling pathway as shown below.
7.06 Problem Set #4, Spring 2005
 7.06 Problem Set #4, Spring 2005 1. You re doing a mutant hunt in S. cerevisiae (budding yeast), looking for temperaturesensitive mutants that are defective in the cell cycle. You discover a mutant strain
7.06 Problem Set #4, Spring 2005 1. You re doing a mutant hunt in S. cerevisiae (budding yeast), looking for temperaturesensitive mutants that are defective in the cell cycle. You discover a mutant strain
Coding sequence array Office hours Wednesday 3-4pm 304A Stanley Hall
 Coding sequence array Office hours Wednesday 3-4pm 304A Stanley Hall Review session 5pm Thursday, Dec. 11 GPB100 Fig. 1.13 RNA-seq Expression effects of cancer AAAAA AAAAA AAAAA Solexa sequencing counts
Coding sequence array Office hours Wednesday 3-4pm 304A Stanley Hall Review session 5pm Thursday, Dec. 11 GPB100 Fig. 1.13 RNA-seq Expression effects of cancer AAAAA AAAAA AAAAA Solexa sequencing counts
RANK. Alternative names. Discovery. Structure. William J. Boyle* SUMMARY BACKGROUND
 RANK William J. Boyle* Department of Cell Biology, Amgen, Inc., One Amgen Center Drive, Thousand Oaks, CA 91320-1799, USA * corresponding author tel: 805-447-4304, fax: 805-447-1982, e-mail: bboyle@amgen.com
RANK William J. Boyle* Department of Cell Biology, Amgen, Inc., One Amgen Center Drive, Thousand Oaks, CA 91320-1799, USA * corresponding author tel: 805-447-4304, fax: 805-447-1982, e-mail: bboyle@amgen.com
CHAPTER : Prokaryotic Genetics
 CHAPTER 13.3 13.5: Prokaryotic Genetics 1. Most bacteria are not pathogenic. Identify several important roles they play in the ecosystem and human culture. 2. How do variations arise in bacteria considering
CHAPTER 13.3 13.5: Prokaryotic Genetics 1. Most bacteria are not pathogenic. Identify several important roles they play in the ecosystem and human culture. 2. How do variations arise in bacteria considering
S A T T A I T ST S I T CA C L A L DAT A A T
 Microarray Center STATISTICAL DATA ANALYSIS IN EXCEL Lecture 5 Linear Regression dr. Petr Nazarov 31-10-2011 petr.nazarov@crp-sante.lu Statistical data analysis in Excel. 5. Linear regression OUTLINE Lecture
Microarray Center STATISTICAL DATA ANALYSIS IN EXCEL Lecture 5 Linear Regression dr. Petr Nazarov 31-10-2011 petr.nazarov@crp-sante.lu Statistical data analysis in Excel. 5. Linear regression OUTLINE Lecture
Upstream Elements Regulating mir-241 and mir-48 Abstract Introduction
 Upstream Elements Regulating mir-241 and mir-48 Hanna Vollbrecht, Tamar Resnick, and Ann Rougvie University of Minnesota: Twin Cities Undergraduate Research Scholarship 2012-2013 Abstract Caenorhabditis
Upstream Elements Regulating mir-241 and mir-48 Hanna Vollbrecht, Tamar Resnick, and Ann Rougvie University of Minnesota: Twin Cities Undergraduate Research Scholarship 2012-2013 Abstract Caenorhabditis
Expression QTLs and Mapping of Complex Trait Loci. Paul Schliekelman Statistics Department University of Georgia
 Expression QTLs and Mapping of Complex Trait Loci Paul Schliekelman Statistics Department University of Georgia Definitions: Genes, Loci and Alleles A gene codes for a protein. Proteins due everything.
Expression QTLs and Mapping of Complex Trait Loci Paul Schliekelman Statistics Department University of Georgia Definitions: Genes, Loci and Alleles A gene codes for a protein. Proteins due everything.
Question Set # 4 Answer Key 7.22 Nov. 2002
 Question Set # 4 Answer Key 7.22 Nov. 2002 1) A variety of reagents and approaches are frequently used by developmental biologists to understand the tissue interactions and molecular signaling pathways
Question Set # 4 Answer Key 7.22 Nov. 2002 1) A variety of reagents and approaches are frequently used by developmental biologists to understand the tissue interactions and molecular signaling pathways
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Harvard Medical School Brigham and Women s Hospital VA Boston Healthcare System 2.79J/3.96J/BE.
 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Harvard Medical School Brigham and Women s Hospital VA Boston Healthcare System 2.79J/3.96J/BE.441/HST522J INTEGRINS I.V. Yannas, Ph.D. and M. Spector, Ph.D. Regulator
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Harvard Medical School Brigham and Women s Hospital VA Boston Healthcare System 2.79J/3.96J/BE.441/HST522J INTEGRINS I.V. Yannas, Ph.D. and M. Spector, Ph.D. Regulator
Enhanced zinc-finger-nuclease activity with improved obligate heterodimeric architectures
 Nature Methods Enhanced zinc-finger-nuclease activity with improved obligate heterodimeric architectures Yannick Doyon, Thuy D Vo, Matthew C Mendel, Shon G Greenberg, Jianbin Wang, Danny F Xia, Jeffrey
Nature Methods Enhanced zinc-finger-nuclease activity with improved obligate heterodimeric architectures Yannick Doyon, Thuy D Vo, Matthew C Mendel, Shon G Greenberg, Jianbin Wang, Danny F Xia, Jeffrey
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2647 Figure S1 Other Rab GTPases do not co-localize with the ER. a, Cos-7 cells cotransfected with an ER luminal marker (either KDEL-venus or mch-kdel) and mch-tagged human Rab5 (mch-rab5,
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2647 Figure S1 Other Rab GTPases do not co-localize with the ER. a, Cos-7 cells cotransfected with an ER luminal marker (either KDEL-venus or mch-kdel) and mch-tagged human Rab5 (mch-rab5,
GACE Biology Assessment Test I (026) Curriculum Crosswalk
 Subarea I. Cell Biology: Cell Structure and Function (50%) Objective 1: Understands the basic biochemistry and metabolism of living organisms A. Understands the chemical structures and properties of biologically
Subarea I. Cell Biology: Cell Structure and Function (50%) Objective 1: Understands the basic biochemistry and metabolism of living organisms A. Understands the chemical structures and properties of biologically
