1. Prokaryotic Nutritional & Metabolic Adaptations
|
|
|
- Donald Hawkins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 27B: Bacteria and Archaea 1. Prokaryotic Nutritional & Metabolic Adaptations 2. Survey of Prokaryotic Groups A. Domain Bacteria Gram-negative groups B. Domain Bacteria Gram-positive groups C. Domain Archaea 1. Prokaryotic Nutritional & Metabolic Adaptations Important Metabolic Terms Oxygen tolerance/usage: aerobic requires or can use oxygen (O 2 ) anaerobic does not require or cannot tolerate O 2 Energy usage: phototroph uses light as an energy source all photosynthetic organisms chemotroph acquires energy from organic or inorganic molecules organotrophs get energy from organic molecules lithotrophs get energy from inorganic molecules 1
2 Facultative vs Obligate (or Strict): more Important Terms Carbon Source: autotroph uses CO 2 as a carbon source e.g., photoautotrophs or chemoautotrophs heterotroph requires organic carbon source e.g., chemoheterotroph gets energy & carbon from organic molecules facultative able to, but not requiring e.g., facultative anaerobes can survive with or without O 2 obligate absolutely requires e.g., obligate anaerobes cannot survive in O 2 Nitrogen Fixation Plants require the element nitrogen in the form of ammonium (NH 4+ ) or nitrate (NO 3- ) ions, however they CAN T fix atmospheric nitrogen (N 2 ) into these forms. Certain soil CAN fix nitrogen (i.e., nitrogen fixers ), thus plants depend on these microbes for useable forms of nitrogen. ATMOSPHERE N 2 N 2 Soil Nitrogen-fixing ammonium & nitrate ions taken up by roots H + Amino acids, etc. NH 4 + Ammonifying Organic material NH 3 NH 4 + (ammonium) Nitrifying NO 3 (nitrate) Root 2A. Survey of Prokaryotic Groups Domain Bacteria Gram-negative groups Archaea Bacteria 2
3 2.5 µm 2/15/2015 UNIVERSAL ANCESTOR Eukaryotes Korarchaeotes Euryarchaeotes Crenarchaeotes Nanoarchaeotes Proteo Chlamydias Cyano Gram-positive Domain Domain Archaea Domain Bacteria Gram-negative Groups Proteo The phylum Proteo contains most of the Gram-negative heterotrophs and is divided into 5 classes: Alphaproteo Betaproteo Gammaproteo Deltaproteo Epsilonproteo Alpha Beta Gamma Delta Epsilon Proteo Alpha subgroup Rhizobium (arrows) inside a root cell of a legume (TEM) Alphaproteo scientists hypothesize that mitochondria evolved from aerobic alpha proteo through endosymbiosis Genera of note: Agrobacterium Rickettsia Rhizobium nitrogen fixation in soil cause tumors in plants, used in genetic engineering cause of typhus, rickets, Rocky Mountain spotted fever 3
4 300 µm 200 µm 2/15/2015 Betaproteo Genus of ecological importance: Nitrosomonas enrich soils through nitrification (ammonium NH 4+ to nitrite NO 2 ) Pathogenic genera: Neisseria gonorrhea (N. gonorrheae) N. gonorrhoeae Bordetella whooping cough (B. pertussis) Gammaproteo largest & most diverse class of Proteo Thiomargarita and other genera important in the sulfur cycle Gamma subgroup Thiomargarita namibiensis containing sulfur wastes (LM) V. cholerae Vibrio cause of cholera (V. cholerae) Escherichia normal gut flora (E. coli) Salmonella typhoid fever, foodborne salmonellosis Deltaproteo Myxo the slime-secreting myxo, which produces drought resistant myxospores Bdellovibrio unusual and interesting l predator Delta subgroup Fruiting bodies of Chondromyces crocatus, a myxobacterium (SEM) 4
5 2.5 µm 5 µm 2 µm 2/15/2015 Epsilonproteo Most members of this group have are helical or vibrioid morphology. Pathogenic genera: Helicobacter H. pylori peptic ulcers Epsilon subgroup Helicobacter pylori (colorized TEM) Campylobacter various species cause blood poisoning, intestinal illness (e.g., C. jejuni) Other Gram-negative Groups Treponema Chlamydias T. pallidum cause of syphilis Borrelia B. burgdorferi Lyme disease Chlamydia (arrows) inside an animal cell (colorized TEM) Leptospira, a spirochete (colorized TEM) Chlamydiae small intracellular pathogens with cell walls lacking peptidoglycan Chlamydia trachomatis most common STD Cyano Gram-negative, oxygenic photoautotrophs produce vast amounts of oxygen gas via photosynthesis fix nitrogen (N 2 NH 4+ ) Anabaena carries out nitrogen fixation in non-photosynthetic heterocysts Oscillatora another genus of cyano Vegetative cell Sheath Heterocyst Akinete Anabaena Oscillatora 5
6 2B. Survey of Prokaryotic Groups Domain Bacteria Gram-positive groups Archaea Bacteria UNIVERSAL ANCESTOR Eukaryotes Korarchaeotes Euryarchaeotes Crenarchaeotes Nanoarchaeotes Proteo Chlamydias Cyano Gram-positive Domain Domain Archaea Domain Bacteria Gram-positive Groups Gram-Positive Phyla Most known Gram-positive are found in 2 main phyla: Firmicutes low G + C content (less than 50%) many common pathogens Actino high G + C content (greater than 50%) characterized by branching filaments 6
7 5 µm 2 µm 2/15/2015 Firmicutes Pathogenic genera: Streptococcus cause of strep throat (S. pyogenes) Streptococcus Staphylococcus includes Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) *Bacillus cause of anthrax (B. anthracis) Clostridium *Clostridium cause of tetanus (C. tetani) cause of botulism (C. botulinum) *produce endospores other Firmicutes Lactobacillus species used in fermented food products (e.g., yogurt, buttermilk, pickles) part of normal, healthy microbiota in human mouth, digestive tract, vagina Mycoplasma very small (less than 1 mm) no cell wall (are Gram-neg.) obligate intracellular pathogens Hundreds of mycoplasmas covering a human fibroblast cell (colorized SEM) Streptomyces Actino important soil, recycle nutrients source of many antibiotics (e.g., erythromycin, tetracycline) Streptomyces, the source of many antibiotics (SEM) Pathogenic genera: Corynebacterium cause of diphtheria (C. diphtheriae) Mycobacterium cause of tuberculosis (M. tuberculosis) cause of leprosy (M. leprae) 7
8 2C. Survey of Prokaryotic Groups Domain Archaea Archaea Bacteria UNIVERSAL ANCESTOR Eukaryotes Korarchaeotes Euryarchaeotes Crenarchaeotes Nanoarchaeotes Proteo Chlamydias Cyano Gram-positive Domain Domain Archaea Domain Bacteria The Domain Archaea The Domain Archaea Highly diverse group of prokaryotes first classified in 1977 by Carl Woese and George Fox: have metabolic processes, rrna sequences and other features more closely resembling eukaryotes e.g., initiate translation with methionine (as do eukaryotes) rather than N-formyl methionine as do the Bacteria cell walls made of material other than peptidoglycan have unusual membrane lipids many species inhabit extreme environments 8
9 Comparison of the 3 Domains ***Archaea have more in common with eukaryotes than.*** The Two Major Groups of Archaea Crenarchaeota includes most of the thermophiles Geogemma Euryarchaeotes (can survive at 130 o C!) Pyrodictium (found in acidic hot springs) includes the methanogens, halophiles, and a few thermophiles Methanosarcina **NO known archaeon causes disease in humans or animals!** 9
Overview: Masters of Adaptation. Prokaryotes thrive almost everywhere, including places too acidic, salty, cold, or hot for most other organisms
 Chapter 27 Bacteria and Archaea Overview: Masters of Adaptation Prokaryotes thrive almost everywhere, including places too acidic, salty, cold, or hot for most other organisms They have an astonishing
Chapter 27 Bacteria and Archaea Overview: Masters of Adaptation Prokaryotes thrive almost everywhere, including places too acidic, salty, cold, or hot for most other organisms They have an astonishing
9/8/2017. Bacteria and Archaea. Three domain system: The present tree of life. Structural and functional adaptations contribute to prokaryotic success
 5 m 2 m 9/8/2017 Three domain system: The present tree of life Bacteria and Archaea Chapter 27 Structural and functional adaptations contribute to prokaryotic success Unicellular Small Variety of shapes
5 m 2 m 9/8/2017 Three domain system: The present tree of life Bacteria and Archaea Chapter 27 Structural and functional adaptations contribute to prokaryotic success Unicellular Small Variety of shapes
Figure Page 117 Microbiology: An Introduction, 10e (Tortora/ Funke/ Case)
 Chapter 11 The Prokaryotes: Domains Bacteria and Archaea Objective Questions 1) Which of the following are found primarily in the intestines of humans? A) Gram-negative aerobic rods and cocci B) Aerobic,
Chapter 11 The Prokaryotes: Domains Bacteria and Archaea Objective Questions 1) Which of the following are found primarily in the intestines of humans? A) Gram-negative aerobic rods and cocci B) Aerobic,
Characteristics. Nucleoid Region single circular chromosome plasmids mesosome
 Prokaryotes Characteristics Nucleoid Region single circular chromosome plasmids mesosome No membranebound organelles Ribosomes (70S) Plasma membrane Cell wall peptidoglycan Capsule glycocalyx Flagella
Prokaryotes Characteristics Nucleoid Region single circular chromosome plasmids mesosome No membranebound organelles Ribosomes (70S) Plasma membrane Cell wall peptidoglycan Capsule glycocalyx Flagella
Ch 27: The Prokaryotes Bacteria & Archaea Older: (Eu)bacteria & Archae(bacteria)
 Ch 27: The Prokaryotes Bacteria & Archaea Older: (Eu)bacteria & Archae(bacteria) (don t study Concept 27.2) Some phyla Remember: Bacterial cell structure and shapes 1 Usually very small but some are unusually
Ch 27: The Prokaryotes Bacteria & Archaea Older: (Eu)bacteria & Archae(bacteria) (don t study Concept 27.2) Some phyla Remember: Bacterial cell structure and shapes 1 Usually very small but some are unusually
Obligate anaerobes - cannot grow in the presence of oxygen Facultative anaerobes - can grow with or without oxygen Aerobic - require oxygen
 PROKARYOTES *include bacteria and archaea *singular: bacterium / plural: bacteria PROPERTIES 1. Bacteria are classified into two kingdoms: Eubacteria (true bacteria) and Archaebacteria (Ancient Bacteria).
PROKARYOTES *include bacteria and archaea *singular: bacterium / plural: bacteria PROPERTIES 1. Bacteria are classified into two kingdoms: Eubacteria (true bacteria) and Archaebacteria (Ancient Bacteria).
Classification. Old 5 Kingdom system. New 3 Domain system. reflects a greater understanding of evolution & molecular evidence
 Classification Old 5 Kingdom system Monera, Protists, Plants, Fungi, Animals New 3 Domain system reflects a greater understanding of evolution & molecular evidence Prokaryote: Bacteria Prokaryote: Archaebacteria
Classification Old 5 Kingdom system Monera, Protists, Plants, Fungi, Animals New 3 Domain system reflects a greater understanding of evolution & molecular evidence Prokaryote: Bacteria Prokaryote: Archaebacteria
LECTURE PRESENTATIONS
 LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 27 Bacteria and Archaea Lectures
LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 27 Bacteria and Archaea Lectures
Prokaryotes. Chapter 27. PowerPoint Lectures for Biology, Seventh Edition. Lectures by Chris Romero. Neil Campbell and Jane Reece
 Chapter 27 Prokaryotes PowerPoint Lectures for Biology, Seventh Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero Overview: They re (Almost) Everywhere! Most prokaryotes are microscopic But
Chapter 27 Prokaryotes PowerPoint Lectures for Biology, Seventh Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero Overview: They re (Almost) Everywhere! Most prokaryotes are microscopic But
4/17/2014. Prokaryotes have inhabited the Earth for billions of years
 Prokaryotes have inhabited the Earth for billions of years Fossil evidence shows that prokaryotes were abundant 3.5 bya, and they evolved alone for the following 2 billion years. Prokaryotes are ubiquitous,
Prokaryotes have inhabited the Earth for billions of years Fossil evidence shows that prokaryotes were abundant 3.5 bya, and they evolved alone for the following 2 billion years. Prokaryotes are ubiquitous,
Vocabulary- Bacteria (34 words)
 Biology II BACTERIA Vocabulary- Bacteria (34 words) 1. Prokaryote 21. phototroph 2. Peptidoglycan 22. chemotroph 3. Methanogen 23. obligate anaerobe 4. Halophile 24. facultative anaerobe 5. Thermoacidophile
Biology II BACTERIA Vocabulary- Bacteria (34 words) 1. Prokaryote 21. phototroph 2. Peptidoglycan 22. chemotroph 3. Methanogen 23. obligate anaerobe 4. Halophile 24. facultative anaerobe 5. Thermoacidophile
Bacteria & Archaea. Ms.Tanyaratana Dumkua Biology Department, MahidolWittayanusorn school
 Bacteria & Archaea Ms.Tanyaratana Dumkua Biology Department, MahidolWittayanusorn school What is the bacteria? http://www.unc.edu/depts/tcf/mycoplasma.gif http://gsbs.utmb.edu/microbook/images/fig37_1.jpg
Bacteria & Archaea Ms.Tanyaratana Dumkua Biology Department, MahidolWittayanusorn school What is the bacteria? http://www.unc.edu/depts/tcf/mycoplasma.gif http://gsbs.utmb.edu/microbook/images/fig37_1.jpg
Section Title: Archaebacteria vs. Eubacteria
 Unit: 3.1 Name: Section Title: Archaebacteria vs. Eubacteria Latin Root Word: Review of Old Information: None New Information: Bacteria Notes Basic Bacteria Facts Classification of Bacteria: Kingdom Archaebacteria
Unit: 3.1 Name: Section Title: Archaebacteria vs. Eubacteria Latin Root Word: Review of Old Information: None New Information: Bacteria Notes Basic Bacteria Facts Classification of Bacteria: Kingdom Archaebacteria
Chapter 19 Notes Kingdoms Archaebacteria andeubacteria
 Chapter 19 Notes Kingdoms Archaebacteria andeubacteria All bacteria are Prokaryotic. This means that they are organisms that are one-celled and do not contain a nucleus or other membrane bound organelles.
Chapter 19 Notes Kingdoms Archaebacteria andeubacteria All bacteria are Prokaryotic. This means that they are organisms that are one-celled and do not contain a nucleus or other membrane bound organelles.
Bacteria and Viruses. 1 Bacteria CHAPTER 18. MAINIDEA Bacteria are prokaryotic cells.
 CHAPTER 18 Bacteria and Viruses 1 Bacteria 7(F), 8(B), 8(C), 11(C), 12(A) Before You Read When you hear the word bacteria, what comes to mind? On the lines below, describe places you think bacteria might
CHAPTER 18 Bacteria and Viruses 1 Bacteria 7(F), 8(B), 8(C), 11(C), 12(A) Before You Read When you hear the word bacteria, what comes to mind? On the lines below, describe places you think bacteria might
The Prokaryotes: Domains Bacteria and Archaea
 PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Bradley W. Christian, McLennan Community College C H A P T E R 11 The Prokaryotes: Domains Bacteria and Archaea Table 11.1 Classification of Selected Prokaryotes*
PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Bradley W. Christian, McLennan Community College C H A P T E R 11 The Prokaryotes: Domains Bacteria and Archaea Table 11.1 Classification of Selected Prokaryotes*
B. Correct! Bacillus anthraces produces spores that can cause anthrax. D. Incorrect! Diphtheria is caused by Corynebacterium diphtheriae.
 Microbiology - Problem Drill 09 - The Prokaryotes No. 1 of 10 1. Bacillus anthraces is most closely associated with which of the following? (A) Botulism poisoning (B) Anthrax (C) Gangrene (D) Diphtheria
Microbiology - Problem Drill 09 - The Prokaryotes No. 1 of 10 1. Bacillus anthraces is most closely associated with which of the following? (A) Botulism poisoning (B) Anthrax (C) Gangrene (D) Diphtheria
Top Ten Reasons that Biology 211 Students Think itʼs BORING to Learn About Organisms that You Canʼt Even SEE Without a Microscope
 Announcements There are NO assignments for points in this class on Mastering Biology - this is intended as a study resource for you Powerpoint files are in the Learning Modules on WebCT Exam over Unit
Announcements There are NO assignments for points in this class on Mastering Biology - this is intended as a study resource for you Powerpoint files are in the Learning Modules on WebCT Exam over Unit
KINGDOM MONERA. Bacterial Cell Shape 8/22/2010. The Prokaryotes: Archaebacteria and Eubacteria
 KINGDOM MONERA The Prokaryotes: Archaebacteria and Eubacteria Bacteria are the most organisms living on the Earth. (i.e. 10mL of soil contains 1 x 10 10 bacteria. They are found in nearly every habitat
KINGDOM MONERA The Prokaryotes: Archaebacteria and Eubacteria Bacteria are the most organisms living on the Earth. (i.e. 10mL of soil contains 1 x 10 10 bacteria. They are found in nearly every habitat
Bacteria outline-- CHAPTER 19 Bacteria
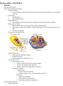 Bacteria outline-- CHAPTER 19 Bacteria Structure and Function Prokaryote & Eukaryote Evolution Cellular Evolution Current evidence indicates that eukaryotes evolved from prokaryotes between 1 and 1.5 billion
Bacteria outline-- CHAPTER 19 Bacteria Structure and Function Prokaryote & Eukaryote Evolution Cellular Evolution Current evidence indicates that eukaryotes evolved from prokaryotes between 1 and 1.5 billion
Archea and Bacteria- The PROKARYOTES
 ` Archea and Bacteria- The PROKARYOTES As late as 1977, all prokaryotes were put into one single kingdom called Monera. Taxonomists no longer accept that concept. Some prokaryotes are more closely related
` Archea and Bacteria- The PROKARYOTES As late as 1977, all prokaryotes were put into one single kingdom called Monera. Taxonomists no longer accept that concept. Some prokaryotes are more closely related
Kingdom Monera(Archaebacteria & Eubacteria)
 Kingdom Monera(Archaebacteria & All bacteria are prokaryotes Characteristics: 1. No nucleus Eubacteria) 2. No membrane bound organelles 3. Smaller & less ribosomes 4. Most are smaller than eukaryotes 5.
Kingdom Monera(Archaebacteria & All bacteria are prokaryotes Characteristics: 1. No nucleus Eubacteria) 2. No membrane bound organelles 3. Smaller & less ribosomes 4. Most are smaller than eukaryotes 5.
Classifying Prokaryotes: Eubacteria Plasma Membrane. Ribosomes. Plasmid (DNA) Capsule. Cytoplasm. Outer Membrane DNA. Flagellum.
 Bacteria The yellow band surrounding this hot spring is sulfur, a waste product of extremophilic prokaryotes, probably of the Domain Archaea, Kingdom Archaebacteria. Bacteria are prokaryotic cells (no
Bacteria The yellow band surrounding this hot spring is sulfur, a waste product of extremophilic prokaryotes, probably of the Domain Archaea, Kingdom Archaebacteria. Bacteria are prokaryotic cells (no
Characterizing and Classifying Prokaryotes
 PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Mindy Miller-Kittrell, North Carolina State University C H A P T E R 11 Characterizing and Classifying Prokaryotes General Characteristics of Prokaryotic Organisms
PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Mindy Miller-Kittrell, North Carolina State University C H A P T E R 11 Characterizing and Classifying Prokaryotes General Characteristics of Prokaryotic Organisms
11/15/2011. Outline. Prokaryotes. Why care about the small stuff. Bacteria in our bodies. I. Categories of life. II.
 Chapter 27: Bacteria and Archaea Outline I. Categories of life A. Domains B. Eukaryote vs Prokaryote II. Domain Bacteria A. cell walls, structure B. Bacterial reproduction C. Nitrogen fixation D. Pathogenic
Chapter 27: Bacteria and Archaea Outline I. Categories of life A. Domains B. Eukaryote vs Prokaryote II. Domain Bacteria A. cell walls, structure B. Bacterial reproduction C. Nitrogen fixation D. Pathogenic
TRACING BACK TO THE BEGINNING
 BACTERIA! TRACING BACK TO THE BEGINNING PROKARYOTES KINGDOM EUBACTERIA KINGDOM ARCHAEBACTERIA CHARACTERISTICS: 1. NO NUCLEUS 2. NO MEMBRANE BOUND ORGANELLES 4. MOST ARE SMALLER THAN EUKARYOTES 5. ARE SINGLE-CELLED
BACTERIA! TRACING BACK TO THE BEGINNING PROKARYOTES KINGDOM EUBACTERIA KINGDOM ARCHAEBACTERIA CHARACTERISTICS: 1. NO NUCLEUS 2. NO MEMBRANE BOUND ORGANELLES 4. MOST ARE SMALLER THAN EUKARYOTES 5. ARE SINGLE-CELLED
Current evidence indicates that eukaryotes evolved from prokaryotes between 1 and 1.5 billion years ago.
 Current evidence indicates that eukaryotes evolved from prokaryotes between 1 and 1.5 billion years ago. Two theories: 1. Infolding theory 2. Endosymbiotic theory The infolding of the prokaryotic plasma
Current evidence indicates that eukaryotes evolved from prokaryotes between 1 and 1.5 billion years ago. Two theories: 1. Infolding theory 2. Endosymbiotic theory The infolding of the prokaryotic plasma
The invention of the microscope has opened to us a world of extraordinary numbers. A singular drop of pond water reveals countless life forms
 Biology Chapter 19 Notes - Bacteria and Viruses The invention of the microscope has opened to us a world of extraordinary numbers. A singular drop of pond water reveals countless life forms I. Classifying
Biology Chapter 19 Notes - Bacteria and Viruses The invention of the microscope has opened to us a world of extraordinary numbers. A singular drop of pond water reveals countless life forms I. Classifying
Characterizing and Classifying Prokaryotes
 PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Mindy Miller-Kittrell, North Carolina State University C H A P T E R 11 Characterizing and Classifying Prokaryotes Bacteria as Plastic Recyclers http://www.cnn.com/2016/03/11/world/b
PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Mindy Miller-Kittrell, North Carolina State University C H A P T E R 11 Characterizing and Classifying Prokaryotes Bacteria as Plastic Recyclers http://www.cnn.com/2016/03/11/world/b
016/03/11/world/bact eria-discoveryplastic/index.html
 PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Mindy Miller-Kittrell, North Carolina State University C H A P T E R 11 Characterizing and Classifying Prokaryotes http://www.cnn.com/2 016/03/11/world/bact
PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Mindy Miller-Kittrell, North Carolina State University C H A P T E R 11 Characterizing and Classifying Prokaryotes http://www.cnn.com/2 016/03/11/world/bact
2/25/2013. Chapter 11 The Prokaryotes: Domains Bacteria and Archaea The Prokaryotes
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Chapter 11 The Prokaryotes: Domains Bacteria and Archaea The Prokaryotes Domain Bacteria Proteobacteria From the mythical Greek god Proteus, who could assume many shapes Gram-negative
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Chapter 11 The Prokaryotes: Domains Bacteria and Archaea The Prokaryotes Domain Bacteria Proteobacteria From the mythical Greek god Proteus, who could assume many shapes Gram-negative
Kingdom Bacteria Kingdom Archaea
 Section 5.1 Kingdom Bacteria Kingdom Archaea p. 132-139 Kingdom Bacteria General Characteristics: Cell Type: all are prokaryotic. Body Form: most are unicellular, some are colonial. Three main shapes are:
Section 5.1 Kingdom Bacteria Kingdom Archaea p. 132-139 Kingdom Bacteria General Characteristics: Cell Type: all are prokaryotic. Body Form: most are unicellular, some are colonial. Three main shapes are:
Prokaryotes (Domains Bacteria & Archaea) KEY POINTS
 Prokaryotes (Domains Bacteria & Archaea) KEY POINTS 1. Decomposers: recycle organic and inorganic molecules in environment; makes them available to other organisms. 2. Essential components of symbioses.
Prokaryotes (Domains Bacteria & Archaea) KEY POINTS 1. Decomposers: recycle organic and inorganic molecules in environment; makes them available to other organisms. 2. Essential components of symbioses.
The Prokaryotic World
 The Prokaryotic World A. An overview of prokaryotic life There is no doubt that prokaryotes are everywhere. By everywhere, I mean living in every geographic region, in extremes of environmental conditions,
The Prokaryotic World A. An overview of prokaryotic life There is no doubt that prokaryotes are everywhere. By everywhere, I mean living in every geographic region, in extremes of environmental conditions,
Chapter 28 - Bacteria and Archaea
 Chapter 28 - Bacteria and Archaea Learning Objectives: Students should be able to... Defend the statement that bacteria and archaea are the most important, diverse, and abundant organisms on the planet.
Chapter 28 - Bacteria and Archaea Learning Objectives: Students should be able to... Defend the statement that bacteria and archaea are the most important, diverse, and abundant organisms on the planet.
Characterizing and Classifying Prokaryotes
 CSLO2. Provide examples of the impact of microorganisms on agriculture, environment, ecosystem, energy, and human health, including biofilms. CSLO5. Describe evidence for the evolution of cells, organelles
CSLO2. Provide examples of the impact of microorganisms on agriculture, environment, ecosystem, energy, and human health, including biofilms. CSLO5. Describe evidence for the evolution of cells, organelles
Major Events in the History of Earth
 Major Events in the History of Earth Cenozoic Humans Land plants Animals Origin of solar system and Earth Multicellular eukaryotes 1 Proterozoic eon 2 Archaean eon 3 4 Single-celled eukaryotes Atmospheric
Major Events in the History of Earth Cenozoic Humans Land plants Animals Origin of solar system and Earth Multicellular eukaryotes 1 Proterozoic eon 2 Archaean eon 3 4 Single-celled eukaryotes Atmospheric
Kingdom Monera Bacteria
 Kingdom Monera Bacteria Common bacteria Prokaryotes Strep throat Anthrax Chlamydia E. coli Meningitis Salmonella Micrococcus(intestinal) Streptococcus mutans Haemophilusinfluenzae Cellphonious bacterious
Kingdom Monera Bacteria Common bacteria Prokaryotes Strep throat Anthrax Chlamydia E. coli Meningitis Salmonella Micrococcus(intestinal) Streptococcus mutans Haemophilusinfluenzae Cellphonious bacterious
Notes - Microbiology Monera
 Notes - Microbiology Monera Part 1 Classification - Kingdom moneran is more commonly known as bacteria. This is the largest kingdom with inhabitants covering almost every square metre of the planet! -
Notes - Microbiology Monera Part 1 Classification - Kingdom moneran is more commonly known as bacteria. This is the largest kingdom with inhabitants covering almost every square metre of the planet! -
Prokaryotes Vs. Eukaryotes
 The Microbial World Prokaryotes Vs. Eukaryotes Mircrobes of the Ocean Primary Producers Are the organisms that produce bio-mass from inorganic compounds (autotrophs). -Photosynthetic autotrophs Phytoplankton
The Microbial World Prokaryotes Vs. Eukaryotes Mircrobes of the Ocean Primary Producers Are the organisms that produce bio-mass from inorganic compounds (autotrophs). -Photosynthetic autotrophs Phytoplankton
BIOLOGY. Bacteria and Archaea
 27 CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Bacteria and Archaea Outline I. Categories of life A. Domains B. Eukaryote vs Prokaryote II. Domain Bacteria A. cell walls,
27 CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Bacteria and Archaea Outline I. Categories of life A. Domains B. Eukaryote vs Prokaryote II. Domain Bacteria A. cell walls,
Kingdom Monera. These notes are to help you check your answers in your Bacteria unit handout package that you received in class.
 Kingdom Monera These notes are to help you check your answers in your Bacteria unit handout package that you received in class. Textbook reference pages Textbook Section 17-2 & 17-3 pages 360-375 Basic
Kingdom Monera These notes are to help you check your answers in your Bacteria unit handout package that you received in class. Textbook reference pages Textbook Section 17-2 & 17-3 pages 360-375 Basic
Bacteria and Archaea
 27 Bacteria and Archaea KEY CONC EPTS 27.1 Structural and functional adaptations contribute to prokaryotic success 27.2 Rapid reproduction, mutation, and genetic recombination promote genetic diversity
27 Bacteria and Archaea KEY CONC EPTS 27.1 Structural and functional adaptations contribute to prokaryotic success 27.2 Rapid reproduction, mutation, and genetic recombination promote genetic diversity
Domain Bacteria. BIO 220 Microbiology Jackson Community College
 Domain Bacteria BIO 220 Microbiology Jackson Community College John Ireland, Ph.D. 2006 Scientific Nomenclature Domain - Bacteria Phylum Important for gross characteristics Class Intermediate characteristics
Domain Bacteria BIO 220 Microbiology Jackson Community College John Ireland, Ph.D. 2006 Scientific Nomenclature Domain - Bacteria Phylum Important for gross characteristics Class Intermediate characteristics
Microbial Taxonomy. Classification of living organisms into groups. A group or level of classification
 Lec 2 Oral Microbiology Dr. Chatin Purpose Microbial Taxonomy Classification Systems provide an easy way grouping of diverse and huge numbers of microbes To provide an overview of how physicians think
Lec 2 Oral Microbiology Dr. Chatin Purpose Microbial Taxonomy Classification Systems provide an easy way grouping of diverse and huge numbers of microbes To provide an overview of how physicians think
NOTES: 20.2 (& 20.3)
 NOTES: 20.2 (& 20.3) How are Bacteria Different from Viruses? Bacteria are different from viruses in that they: -are much bigger -have a different structure (made of cells) therefore are considered LIVING
NOTES: 20.2 (& 20.3) How are Bacteria Different from Viruses? Bacteria are different from viruses in that they: -are much bigger -have a different structure (made of cells) therefore are considered LIVING
Announcements KEY CONCEPTS
 What do these things have in common? Announcements Lab this week: bring textbook and photo atlas. Relevant reading BEFORE lab: Ch. 30 http://i.cnn.net/cnn/specials/2001/trade.center/images/anthrax.jpg
What do these things have in common? Announcements Lab this week: bring textbook and photo atlas. Relevant reading BEFORE lab: Ch. 30 http://i.cnn.net/cnn/specials/2001/trade.center/images/anthrax.jpg
Bacteria are very small
 BACTERIA BACTERIA Bacteria are very small Bacteria are very small compared to cells with nuclei (Eukaryotic cells) This is a pore in human skin and the yellow spheres are bacteria CLASSIFICATION OF BACTERIA
BACTERIA BACTERIA Bacteria are very small Bacteria are very small compared to cells with nuclei (Eukaryotic cells) This is a pore in human skin and the yellow spheres are bacteria CLASSIFICATION OF BACTERIA
TER 26. Preview for 2/6/02 Dr. Kopeny. Bacteria and Archaea: The Prokaryotic Domains. Nitrogen cycle
 Preview for 2/6/02 Dr. Kopeny Bacteria and Archaea: The Prokaryotic Domains TER 26 Nitrogen cycle Mycobacterium tuberculosis Color-enhanced images shows rod-shaped bacterium responsible for tuberculosis
Preview for 2/6/02 Dr. Kopeny Bacteria and Archaea: The Prokaryotic Domains TER 26 Nitrogen cycle Mycobacterium tuberculosis Color-enhanced images shows rod-shaped bacterium responsible for tuberculosis
Chapter 21 PROKARYOTES AND VIRUSES
 Chapter 21 PROKARYOTES AND VIRUSES Bozeman Video classification of life http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tyl_8gv 7RiE Impacts, Issues: West Nile Virus Takes Off Alexander the Great, 336 B.C., conquered a
Chapter 21 PROKARYOTES AND VIRUSES Bozeman Video classification of life http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tyl_8gv 7RiE Impacts, Issues: West Nile Virus Takes Off Alexander the Great, 336 B.C., conquered a
EASTERN ARIZONA COLLEGE Microbiology
 EASTERN ARIZONA COLLEGE Microbiology Course Design 2015-2016 Course Information Division Science Course Number BIO 205 (SUN# BIO 2205) Title Microbiology Credits 4 Developed by Ed Butler/Revised by Willis
EASTERN ARIZONA COLLEGE Microbiology Course Design 2015-2016 Course Information Division Science Course Number BIO 205 (SUN# BIO 2205) Title Microbiology Credits 4 Developed by Ed Butler/Revised by Willis
Biology. Slide 1 of 40. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 Biology 1 of 40 (p471-477) 2 of 40 Microorganisms = Microbes Microbiology is the study of living creatures too small to see with the unaided eye including : bacteria protozoa fungi algae viruses other
Biology 1 of 40 (p471-477) 2 of 40 Microorganisms = Microbes Microbiology is the study of living creatures too small to see with the unaided eye including : bacteria protozoa fungi algae viruses other
Outline. Viruses, Bacteria, and Archaea. Viruses Structure Classification Reproduction Prokaryotes Structure Reproduction Nutrition Bacteria Archaea
 Viruses, Bacteria, and Archaea Chapter 21 Viruses Structure Classification Reproduction Prokaryotes Structure Reproduction Nutrition Bacteria Archaea Outline The Viruses The Viruses Viruses are noncellular
Viruses, Bacteria, and Archaea Chapter 21 Viruses Structure Classification Reproduction Prokaryotes Structure Reproduction Nutrition Bacteria Archaea Outline The Viruses The Viruses Viruses are noncellular
Chapter 26 (8 th edition) Lectures 3 & 4. Prokaryotes. Dr Angelika Stollewerk
 Chapter 26 (8 th edition) Lectures 3 & 4 Prokaryotes Dr Angelika Stollewerk Prokaryotes Aims: To overview the diversity of the three domains of life To consider where prokaryotes are found To consider
Chapter 26 (8 th edition) Lectures 3 & 4 Prokaryotes Dr Angelika Stollewerk Prokaryotes Aims: To overview the diversity of the three domains of life To consider where prokaryotes are found To consider
Bacteria are very small
 BACTERIA BACTERIA Bacteria are very small Bacteria are very small compared to cells with nuclei This is a pore in human skin and the yellow spheres are bacteria BACTERIA LIVE ALMOST EVERYWHERE Hot springs
BACTERIA BACTERIA Bacteria are very small Bacteria are very small compared to cells with nuclei This is a pore in human skin and the yellow spheres are bacteria BACTERIA LIVE ALMOST EVERYWHERE Hot springs
LECTURE 13. THE BACTERIA (cont.) Photosynthetic Bacteria, phylogenetically widespread. And many Proteobacteria. Photosynthetic Bacteria
 Photosynthetic Bacteria, phylogenetically widespread LECTURE 13 THE BACTERIA (cont.) And many Proteobacteria Photosynthetic Bacteria > Green Sulfur > Green Nonsulfur > Purple Sulfur > Purple Nonsulfur
Photosynthetic Bacteria, phylogenetically widespread LECTURE 13 THE BACTERIA (cont.) And many Proteobacteria Photosynthetic Bacteria > Green Sulfur > Green Nonsulfur > Purple Sulfur > Purple Nonsulfur
19-1 Notes Bacteria. Named after the Greek word Little stick because many bacteria have a stick-like shape when viewed under a microscope
 19-1 Notes Bacteria Bacteria are found virtually everywhere! Named after the Greek word Little stick because many bacteria have a stick-like shape when viewed under a microscope We know that bacteria are
19-1 Notes Bacteria Bacteria are found virtually everywhere! Named after the Greek word Little stick because many bacteria have a stick-like shape when viewed under a microscope We know that bacteria are
Introduction to Bacteria
 Introduction to Bacteria USDA NIFSI Food Safety in the Classroom University of Tennessee, Knoxville 2006 A quick clip http://www2.beavercreek.k12.oh.us/vi deos/28824/chp937402_700k.asf Bacteria What are
Introduction to Bacteria USDA NIFSI Food Safety in the Classroom University of Tennessee, Knoxville 2006 A quick clip http://www2.beavercreek.k12.oh.us/vi deos/28824/chp937402_700k.asf Bacteria What are
MAJOR EPISODES IN THE HISTORY OF LIFE
 MAJOR EPISODES IN THE HISTORY OF LIFE All the major phyla of animals evolved by the end of the Cambrian explosion, which began about 540 million years ago and lasted about 10 million years. Plants and
MAJOR EPISODES IN THE HISTORY OF LIFE All the major phyla of animals evolved by the end of the Cambrian explosion, which began about 540 million years ago and lasted about 10 million years. Plants and
9/24/2013. Bacteria and Archaea. Masters of Adaptation. Archaea. Three domain system: The present tree of life
 200 m 2. 300 m 2 m 1 m Bacteria and Archaea Three domain system: The present tree of life Chapter 27 Masters of Adaptation Structural and functional adaptations contribute to prokaryotic success Unicellular
200 m 2. 300 m 2 m 1 m Bacteria and Archaea Three domain system: The present tree of life Chapter 27 Masters of Adaptation Structural and functional adaptations contribute to prokaryotic success Unicellular
Class announcements. Prokaryotic cell structure. Prokaryotic Diversity II - Coming attractions 2/10/11. Prokaryotic cell structure
 Class announcements 1. Today no clickers; Friday probably clickers 2. Discuss phylogenetic tree homework in your study group, but write up the HW on your own 3. Friday phylogenetic tree HW due 4. Friday
Class announcements 1. Today no clickers; Friday probably clickers 2. Discuss phylogenetic tree homework in your study group, but write up the HW on your own 3. Friday phylogenetic tree HW due 4. Friday
BACTERIA AND ARCHAEA 10/15/2012
 BACTERIA AND ARCHAEA Chapter 27 KEY CONCEPTS: Structural and functional adaptations contribute to prokaryotic success Rapid reproduction, mutation, and genetic recombination promote genetic diversity in
BACTERIA AND ARCHAEA Chapter 27 KEY CONCEPTS: Structural and functional adaptations contribute to prokaryotic success Rapid reproduction, mutation, and genetic recombination promote genetic diversity in
1/21/2017. Lecture 5: Chapters 26 & 27 Diversity of Prokaryotes & Protists
 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Lecture 5: Chapters 26 & 27 Diversity of Prokaryotes & Protists Prokaryotes Two domains Bacteria Archaea While these are different domains, we will first consider the groups together as they
2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Lecture 5: Chapters 26 & 27 Diversity of Prokaryotes & Protists Prokaryotes Two domains Bacteria Archaea While these are different domains, we will first consider the groups together as they
Lecture 2: Kingdoms Monera, Protoctista and Fungi
 KINGDOM MONERA Bacteria Lecture 2: Kingdoms Monera, Protoctista and Fungi Kingdom Monera Commonly called bacteria All monerans are unicellular All monerans are prokaryotes Prokaryotes: Single-celled organisms
KINGDOM MONERA Bacteria Lecture 2: Kingdoms Monera, Protoctista and Fungi Kingdom Monera Commonly called bacteria All monerans are unicellular All monerans are prokaryotes Prokaryotes: Single-celled organisms
Taxonomy. Ancestral Life Form. Monera Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia
 Taxonomy The term taxonomy alone is enough to cause glazing over of students eyes in traditional Biology courses. The significance of taxonomy cannot be overlooked as it is the basis for categorizing organisms.
Taxonomy The term taxonomy alone is enough to cause glazing over of students eyes in traditional Biology courses. The significance of taxonomy cannot be overlooked as it is the basis for categorizing organisms.
vast metabolic diversity, mostly unique; - many sources of energy & matter
 Bacteria are the most ancient life forms - signs from ~3,500 m.y.a. Bacteria can tolerate great physical extremes from ocean deeps to the stratosphere to inside rocks & earth's crust essentials = only
Bacteria are the most ancient life forms - signs from ~3,500 m.y.a. Bacteria can tolerate great physical extremes from ocean deeps to the stratosphere to inside rocks & earth's crust essentials = only
Microbiology Helmut Pospiech
 Microbiology http://researchmagazine.uga.edu/summer2002/bacteria.htm 05.04.2018 Helmut Pospiech The Species Concept in Microbiology No universally accepted concept of species for prokaryotes Current definition
Microbiology http://researchmagazine.uga.edu/summer2002/bacteria.htm 05.04.2018 Helmut Pospiech The Species Concept in Microbiology No universally accepted concept of species for prokaryotes Current definition
Overview of the major bacterial pathogens The major bacterial pathogens are presented in this table:
 Practical Microbiology 30/11/2018 University of Sulaimani college of Pharmacy Year2 Lab. 5: Overview of the major bacterial pathogens The major bacterial pathogens are presented in this table: Major Bacterial
Practical Microbiology 30/11/2018 University of Sulaimani college of Pharmacy Year2 Lab. 5: Overview of the major bacterial pathogens The major bacterial pathogens are presented in this table: Major Bacterial
CLASSIFICATION OF BACTERIA
 CLASSIFICATION OF BACTERIA DISCLOSURE Relevant relationships with commercial entities none Potential for conflicts of interest within this presentation none Steps taken to review and mitigate potential
CLASSIFICATION OF BACTERIA DISCLOSURE Relevant relationships with commercial entities none Potential for conflicts of interest within this presentation none Steps taken to review and mitigate potential
What is Microbiology?
 Microbiology What is Microbiology? Microbiology is the Science that studies Microorganisms. Microorganisms, roughly, are those living things that are too small to be seen with the naked eye. Microorganisms
Microbiology What is Microbiology? Microbiology is the Science that studies Microorganisms. Microorganisms, roughly, are those living things that are too small to be seen with the naked eye. Microorganisms
Bacillus anthracis. Causes Anthrax Especially deadly when inhaled
 Eubacteria Bacteria are the most abundant organisms on earth. An estimated 5 X 1030individuals. One bacterium can give rise to 10 million in 24 hours. Both aerobic (with oxygen) and anaerobic (without
Eubacteria Bacteria are the most abundant organisms on earth. An estimated 5 X 1030individuals. One bacterium can give rise to 10 million in 24 hours. Both aerobic (with oxygen) and anaerobic (without
Bacteria and Archaea
 Chapter 27 Bacteria and Archaea Lecture Outline Overview: Masters of Adaptation Parts of Utah s Great Salt Lake has a salt concentration of 32%, nearly 10 times saltier than seawater. Despite its harsh
Chapter 27 Bacteria and Archaea Lecture Outline Overview: Masters of Adaptation Parts of Utah s Great Salt Lake has a salt concentration of 32%, nearly 10 times saltier than seawater. Despite its harsh
Classification of Life
 Classification of Life Aristotle 2 divisions: Plant and Animal Linnaeus (1735-1759) New division Vermes New category Chaos (where microbes were placed) Classification of Life Ernst Haeckel (1866) 3 Kingdom
Classification of Life Aristotle 2 divisions: Plant and Animal Linnaeus (1735-1759) New division Vermes New category Chaos (where microbes were placed) Classification of Life Ernst Haeckel (1866) 3 Kingdom
Objects of the Medical Microbiology revision a) Pathogenic microbes (causing diseases of human beings or animals) b) Normal microflora (microbes commo
 Institute for Microbiology, Medical Faculty of Masaryk University and St. Anna Faculty Hospital in Brno Miroslav Votava MORPHOLOGY AND STRUCTURE OF BACTERIAL CELL The 2nd lecture for 2nd-year students
Institute for Microbiology, Medical Faculty of Masaryk University and St. Anna Faculty Hospital in Brno Miroslav Votava MORPHOLOGY AND STRUCTURE OF BACTERIAL CELL The 2nd lecture for 2nd-year students
Bacteria Outline. 1. Overview. 2. Structural & Functional Features. 3. Taxonomy. 4. Communities
 Bacteria Outline 1. Overview 2. Structural & Functional Features 3. Taxonomy 4. Communities Bacteria - Taxonomy PHYLUM CLASS ORDER FAMILY GENUS SPECIES SUB-SPECIES & STRAINS Bacteria - Phyla Firmicutes
Bacteria Outline 1. Overview 2. Structural & Functional Features 3. Taxonomy 4. Communities Bacteria - Taxonomy PHYLUM CLASS ORDER FAMILY GENUS SPECIES SUB-SPECIES & STRAINS Bacteria - Phyla Firmicutes
Intro to Prokaryotes Lecture 1 Spring 2014
 Intro to Prokaryotes Lecture 1 Spring 2014 Meet the Prokaryotes 1 Meet the Prokaryotes 2 Meet the Prokaryotes 3 Why study prokaryotes? Deep Time 4 Fig. 25.7 Fossilized stromatolite (above) and living stromatolite
Intro to Prokaryotes Lecture 1 Spring 2014 Meet the Prokaryotes 1 Meet the Prokaryotes 2 Meet the Prokaryotes 3 Why study prokaryotes? Deep Time 4 Fig. 25.7 Fossilized stromatolite (above) and living stromatolite
Kharkov National Medical University. Head of Microbiology, Virology and Immunology Department Minukhin Valeriy Vladimirivich
 Kharkov National Medical University Head of Microbiology, Virology and Immunology Department Minukhin Valeriy Vladimirivich Tkachenko Victoria 1, 5, 11, 14, 19, 21, 30 Kovalenko Natalia 2, 12, 25, 29 Siritsa
Kharkov National Medical University Head of Microbiology, Virology and Immunology Department Minukhin Valeriy Vladimirivich Tkachenko Victoria 1, 5, 11, 14, 19, 21, 30 Kovalenko Natalia 2, 12, 25, 29 Siritsa
Unit 13.1: Prokaryotes
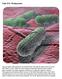 Unit 13.1: Prokaryotes Can you guess what organisms are pictured here? Are they fat green worms on a red leaf? Here s a clue: There are more organisms like these than any other on Earth. Here s another
Unit 13.1: Prokaryotes Can you guess what organisms are pictured here? Are they fat green worms on a red leaf? Here s a clue: There are more organisms like these than any other on Earth. Here s another
There are 5 kingdoms: Animalia multicellular animals, heterotrophic (eat other things), evolved 700,000,000 years ago (1,000,000 2,000,000 species)
 Classification The modern system of naming gives each living thing 7 names. Each name is a little more specific than the one before it. The categories are (in order from least to most specific): Kingdom
Classification The modern system of naming gives each living thing 7 names. Each name is a little more specific than the one before it. The categories are (in order from least to most specific): Kingdom
Domains and Kingdoms. Images, from left to right: Cholera bacteria, Volvox colony, Strep bacteria
 Domains and Kingdoms Images, from left to right: Cholera bacteria, Volvox colony, Strep bacteria THE DOMAINS A domain is the broadest level in the classification of life. All living organisms belong to
Domains and Kingdoms Images, from left to right: Cholera bacteria, Volvox colony, Strep bacteria THE DOMAINS A domain is the broadest level in the classification of life. All living organisms belong to
INTERPRETATION OF THE GRAM STAIN
 INTERPRETATION OF THE GRAM STAIN DISCLOSURE Relevant relationships with commercial entities none Potential for conflicts of interest within this presentation none Steps taken to review and mitigate potential
INTERPRETATION OF THE GRAM STAIN DISCLOSURE Relevant relationships with commercial entities none Potential for conflicts of interest within this presentation none Steps taken to review and mitigate potential
Bacteria and Archaea
 Chapter 27 Bacteria and Archaea Lecture Outline Overview: Masters of Adaptation California s Owens Lake has a salt concentration of 32%, nine times saltier than seawater. Despite its harsh conditions,
Chapter 27 Bacteria and Archaea Lecture Outline Overview: Masters of Adaptation California s Owens Lake has a salt concentration of 32%, nine times saltier than seawater. Despite its harsh conditions,
Chapter 27: Bacteria and Archaea
 Name Period Overview 1. The chapter opens with amazing tales of life at the extreme edge. What are the masters of adaptation? Describe the one case you thought most dramatic. Concept 27.1 Structural and
Name Period Overview 1. The chapter opens with amazing tales of life at the extreme edge. What are the masters of adaptation? Describe the one case you thought most dramatic. Concept 27.1 Structural and
20 Viruses and Prokaryotes Bacteria
 20 Viruses and Prokaryotes 20.2 - Bacteria Classifying Prokaryotes Prokaryote unicellular organisms that lacks a nucleus Most abundant and widespread organisms on Earth Divided into two groups Bacteria
20 Viruses and Prokaryotes 20.2 - Bacteria Classifying Prokaryotes Prokaryote unicellular organisms that lacks a nucleus Most abundant and widespread organisms on Earth Divided into two groups Bacteria
MICROBIAL GROUPS CE 421/521
 MICROBIAL GROUPS CE 421/521 Chapter 10 in Vaccari et.al. www.ibuf.coartuja.csic.es www.environmentaleverage.com www.astrosurf.com www.lbl.gov www.library.thinkquest.org www.ecosys.uni-erlangen.de erlangen.de
MICROBIAL GROUPS CE 421/521 Chapter 10 in Vaccari et.al. www.ibuf.coartuja.csic.es www.environmentaleverage.com www.astrosurf.com www.lbl.gov www.library.thinkquest.org www.ecosys.uni-erlangen.de erlangen.de
Chapter 1. Basics of Microbiology
 Chapter 1 Basics of Microbiology Objectives How microorganisms are classified (taxonomy) What they look like (morphology) The major divisions among microorganisms based upon their function in the environment
Chapter 1 Basics of Microbiology Objectives How microorganisms are classified (taxonomy) What they look like (morphology) The major divisions among microorganisms based upon their function in the environment
Game plan Lecture Lab Prelabs
 Game plan Lecture Binary fission Growth curves Physical requirements for growth Chemical requirements for growth Lab Lab Exam Prelabs Growth Curve Bring books and APO-3 for next class Microbial growth
Game plan Lecture Binary fission Growth curves Physical requirements for growth Chemical requirements for growth Lab Lab Exam Prelabs Growth Curve Bring books and APO-3 for next class Microbial growth
MICROBIAL BIOCHEMISTRY BIOT 309. Dr. Leslye Johnson Sept. 30, 2012
 MICROBIAL BIOCHEMISTRY BIOT 309 Dr. Leslye Johnson Sept. 30, 2012 Phylogeny study of evoluhonary relatedness among groups of organisms (e.g. species, populahons), which is discovered through molecular
MICROBIAL BIOCHEMISTRY BIOT 309 Dr. Leslye Johnson Sept. 30, 2012 Phylogeny study of evoluhonary relatedness among groups of organisms (e.g. species, populahons), which is discovered through molecular
Kingdom Monera - The Bacteria
 Chapter 8 The World of Microbes Kingdom Monera - The Bacteria Bio-significance- The down side: Disease of plants crop loss Disease of animals loss of livestock and herds Human disease cavities to The Plague
Chapter 8 The World of Microbes Kingdom Monera - The Bacteria Bio-significance- The down side: Disease of plants crop loss Disease of animals loss of livestock and herds Human disease cavities to The Plague
Cells & Bacteria Notes
 Cells & Bacteria Notes 4 Major Macromolecules Macromolecules are large molecules. The four groups of macromolecules are essential to the structure and function of a cell. Group Building Block Large Molecule
Cells & Bacteria Notes 4 Major Macromolecules Macromolecules are large molecules. The four groups of macromolecules are essential to the structure and function of a cell. Group Building Block Large Molecule
Classification. Classifying Organisms. * Organisms are divided into 3 domains and 6 kingdoms based on the following characteristics
 Classification Classifying Organisms * Organisms are divided into 3 domains and 6 kingdoms based on the following characteristics Cell Type: Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Prokaryotic - No nucleus Eukaryotic
Classification Classifying Organisms * Organisms are divided into 3 domains and 6 kingdoms based on the following characteristics Cell Type: Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Prokaryotic - No nucleus Eukaryotic
Hierarchies can be represented as trees:
 Diversity of Life Classification - an organized scheme for grouping organisms - a tool for communication - Hierarchical - a series of successive and inclusive rankings Domain - the highest rank - contains
Diversity of Life Classification - an organized scheme for grouping organisms - a tool for communication - Hierarchical - a series of successive and inclusive rankings Domain - the highest rank - contains
BIO 101 INTRODUCTORY BIOLOGY PROF. ANI NKANG DEPT. OF BIOLOGICAL SCIENCES ARTHUR JARVIS UNIVERSITY
 BIO 101 INTRODUCTORY BIOLOGY PROF. ANI NKANG DEPT. OF BIOLOGICAL SCIENCES ARTHUR JARVIS UNIVERSITY What does it mean to say that something is alive? An organism is a life form- a living entity made up
BIO 101 INTRODUCTORY BIOLOGY PROF. ANI NKANG DEPT. OF BIOLOGICAL SCIENCES ARTHUR JARVIS UNIVERSITY What does it mean to say that something is alive? An organism is a life form- a living entity made up
The Tree of Life. Metabolic Pathways. Calculation Of Energy Yields
 The Tree of Life Metabolic Pathways Calculation Of Energy Yields OCN 401 - Biogeochemical Systems 8/27/09 Earth s History (continental crust) 170 Oldest oceanic crust Ga = billions of years ago The Traditional
The Tree of Life Metabolic Pathways Calculation Of Energy Yields OCN 401 - Biogeochemical Systems 8/27/09 Earth s History (continental crust) 170 Oldest oceanic crust Ga = billions of years ago The Traditional
Mouth animalcules (bacteria)
 Mouth animalcules (bacteria) 1684 http://en.citizendium.org/images/thumb/9/94/leeuwenhoek.jpg/300px-leeuwenhoek.jpg Prokaryotic Cell Shapes Coccus - cocci Bacillus - bacillus Spirillum - spirilli Vibrio
Mouth animalcules (bacteria) 1684 http://en.citizendium.org/images/thumb/9/94/leeuwenhoek.jpg/300px-leeuwenhoek.jpg Prokaryotic Cell Shapes Coccus - cocci Bacillus - bacillus Spirillum - spirilli Vibrio
Archaebacteria and Eubacteria
 Archaebacteria and Eubacteria Bacteria are of immense importance because of their rapid growth, reproduction, and mutation rates, as well as, their ability to exist under adverse conditions. The oldest
Archaebacteria and Eubacteria Bacteria are of immense importance because of their rapid growth, reproduction, and mutation rates, as well as, their ability to exist under adverse conditions. The oldest
Molecular Biosciences 305: The Diversity of Prokaryotic Organisms Lecture 25 [Consetta Helmick] Slide # 1. Slide Title: WSU Online Title Slide
![Molecular Biosciences 305: The Diversity of Prokaryotic Organisms Lecture 25 [Consetta Helmick] Slide # 1. Slide Title: WSU Online Title Slide Molecular Biosciences 305: The Diversity of Prokaryotic Organisms Lecture 25 [Consetta Helmick] Slide # 1. Slide Title: WSU Online Title Slide](/thumbs/83/87494309.jpg) Molecular Biosciences 305: The Diversity of Prokaryotic Organisms Lecture 25 [Consetta Helmick] Slide # 1 Slide Title: WSU Online Title Slide Title: The Diversity of Prokaryotic Organisms Instructor: Consetta
Molecular Biosciences 305: The Diversity of Prokaryotic Organisms Lecture 25 [Consetta Helmick] Slide # 1 Slide Title: WSU Online Title Slide Title: The Diversity of Prokaryotic Organisms Instructor: Consetta
Chapter 17B. Table of Contents. Section 1 Introduction to Kingdoms and Domains. Section 2 Advent of Multicellularity
 Introduction to the Kingdoms of Life Table of Contents Section 2 Advent of Multicellularity Section 3 Complex Multicellularity The Six Kingdoms of Life Living organisms are divided into six kingdoms and
Introduction to the Kingdoms of Life Table of Contents Section 2 Advent of Multicellularity Section 3 Complex Multicellularity The Six Kingdoms of Life Living organisms are divided into six kingdoms and
Microbe Mission C Test
 Microbe Mission C Test Science Olympiad North Regional Tournament at the University of Florida Rank: Points: Name(s): Team Name: School Name: Team Number: Page 2 Part 1: Microscopes Names the following
Microbe Mission C Test Science Olympiad North Regional Tournament at the University of Florida Rank: Points: Name(s): Team Name: School Name: Team Number: Page 2 Part 1: Microscopes Names the following
Early History and Primitive Life. Unit 2: How do cells support life? Chapter: What are the origins of life? What are the simplest forms of life?
 Early History and Primitive Life Unit 2: How do cells support life? Chapter: What are the origins of life? What are the simplest forms of life? Chapter 17-2 EARTH S EARLY HISTORY Evidence for Early Life
Early History and Primitive Life Unit 2: How do cells support life? Chapter: What are the origins of life? What are the simplest forms of life? Chapter 17-2 EARTH S EARLY HISTORY Evidence for Early Life
