Biology. Slide 1 of 40. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
|
|
|
- Ursula Burns
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Biology 1 of 40
2 (p ) 2 of 40
3 Microorganisms = Microbes Microbiology is the study of living creatures too small to see with the unaided eye including : bacteria protozoa fungi algae viruses other miniature creatures. 3 of 40
4 Why study Microbiology? 1. Microbes are an essential component of an ecosystem - especially as saprophytes and their role in nutrient recycling. 2. We use them to produce pharmaceuticals, clean up hazardous waste and to make food products - like cheese, yoghurt, alcohol and breads. 3. Microbes can wreak havoc on all creatures by invading them and causing disturbance and infection. Understanding microbes is vital to life on earth 4 of 40
5 Examples of microbe uses Fungi: 1. Saccharmyces cerevisiae - yeast - used in bread, beer and wine-making. 2. Saccharmyces carisbergensis - yeast - used to make beer. 3. Saccharmyces rouxii - yeast - used to make soy sauce. 4. Penicillium roqueforti - fungi - used to make roquefort cheese. 5 of 40
6 Examples of microbe uses bacterium: 1. Lactococcus lactis - bacterium - producer of metabolites which kill other bacteria, especially spores from Clostridia botulinum which causes food poisoning. The bacterium is used in saugages when nitrate content is reduced. 2. Leuconostoc mesenteroides - bacterium used in the fermentation of sauerkraut. 3. Acetobacter and Gluconbacter - bacterium used in production of vinegar. 6 of 40
7 Bacteria - common word for prokaryote Unicellular organisms that lack a nucleus, they have a nucloid Typically range in size from 1 µm 5 µm. However, there are bacteria cells as large as 100 µm or 0.1 mm (Note: The typical eukaryotic cell ranges in size from 10 to 100 µm and viral particles are usually smaller than 1 µm). Prokaryotic cell- do not have cytoplasmic organelles found in eukaryotic cells except for ribosomes. 7 of 40
8 Cell Structure (p472) nucleoid region (no nucleus) -genetic material - ribonucleic acid (RNA) or deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) ribosomes cytoplasm cell membrane cell wall one or two layers thick pili if motile flagella Cell Structure Flagellum if photosynthetic photosynthetic pigments are found in the cell membrane Cell Wall Cell Membrane DNA Ribosomes Pili 8 of 40
9 Classifying Prokaryotes Classifying Prokaryotes All prokaryotes were once placed in the Kingdom Monera. Recently, biologists divided them into two different kingdoms: Eubacteria Archaebacteria 9 of 40
10 Classifying Prokaryotes Eubacteria ( true bacteria ) Eubacteria have a cell wall that protects the cell and determines its shape. The cell wall of eubacteria contain peptidoglycan. 10 of 40
11 Classifying Prokaryotes E. coli, a Typical Eubacterium Peptidoglycan Cell Wall Cell Membrane Ribosomes Flagellum DNA Pili 11 of 40
12 Classifying Prokaryotes Eubacteria include organisms that live in a variety of environments, including: in fresh and salt water on land in the human body 12 of 40
13 Classifying Prokaryotes Ex. of Eubacteria Cyanobacteria Blue green algae Photosynthetic Found throughout the world in different environments Fresh water, salt water, on land, hotsprings, in the Artic. 13 of 40
14 Classifying Prokaryotes Archaebacteria The cells walls of archaebacteria do not contain peptidoglycan. In addition, the DNA sequences of key archaebacterial genes are more like those of eukaryotes than those of eubacteria. 14 of 40
15 Classifying Prokaryotes Many archaebacteria live in extreme environments. Methanogens live in oxygen-free environments, such as thick mud and animal digestive tracts. Other archaebacteria live in salty environments or in hot springs where water temperatures approach the boiling point. 15 of 40
16 Identifying Prokaryotes Identifying Prokaryotes Prokaryotes are identified by characteristics such as: shape the chemical nature of their cell walls the way they move the way they obtain energy 16 of 40
17 Identifying Prokaryotes Shapes Rod-shaped prokaryotes are called bacilli. ex. E. Coli Bacilli 17 of 40
18 Identifying Prokaryotes Spherical prokaryotes are called cocci. Cocci ex. Streptococcus Pneumococcus 18 of 40
19 Identifying Prokaryotes Spiral and corkscrew-shaped prokaryotes are called spirilla. Spirilla 19 of 40
20 Cell Walls 19 1 Bacteria Identifying Prokaryotes Two different types of cell walls are found in eubacteria. Gram-positive bacteria have thick cell walls with large amounts of peptidoglycan. Gram-negative bacteria have thinner cell walls inside an outer lipid layer. 20 of 40
21 Cell Walls Identifying Prokaryotes A method called gram staining tells them apart. Does the bacterium take up the gram stain? Gram stain = crystal violet and saphrine. Either the violet or the red dye is taken up but not both. a. Gram +ve bacteria: look purple under the microscope. B have only one layer of cell wall. b. Gram ve bacteria: look red under the microscope. B has two layers of cell wall. 21 of 40
22 Identifying Prokaryotes Bacteria Movement Does the bacterium move? a. No movement b. Propelled by one or more flagella. c. Spiral or lash forward. 22 of 40
23 Identifying Prokaryotes Video Bacteria Shape and Move (3min) 23 of 40
24 Metabolic Diversity Metabolic Diversity (p ) How Do Bacteria Obtain Energy? Prokaryotes are divided into two main groups: 1. Heterotrophs get their energy by consuming organic molecules made by other organisms. 1.a) Photoheterotrophs These organisms are photosynthetic, using sunlight for energy, but they also need to take in organic compounds as a carbon source. 1.b) Chemoheterotrophs Most heterotrophic prokaryotes must take in organic molecules for both energy and a supply of carbon. 24 of 40
25 Metabolic Diversity Metabolic Diversity (p ) How Do Bacteria Obtain Energy? Prokaryotes are divided into two main groups: 2. Autotrophs make their own food from inorganic molecules. 2.a) Phototrophic autotrophs (ex. Cyanobacteria) Use light energy to convert carbon dioxide and water to carbon compounds and oxygen in a process similar to that used by green plants. These organisms are found where light is plentiful, such as near the surfaces of lakes, streams, and oceans. 25 of 40
26 Metabolic Diversity Metabolic Diversity (p ) How Do Bacteria Obtain Energy? Prokaryotes are divided into two main groups: 2. Autotrophs make their own food from inorganic molecules. 2.b) Chemitrophic autotrophs Like photoautotrophs, chemoautotrophs make organic carbon molecules from carbon dioxide. Unlike photoautotrophs, however, they do not require light as a source of energy. Instead, they use energy directly from chemical reactions involving ammonia, hydrogen sulfide, nitrites, sulfur, or iron. Some chemoautotrophs live deep in the darkness of the ocean. 26 of 40
27 Metabolic Diversity Releasing Energy Respiration in general: All organisms need a constant supply of energy to perform alltheir life activities. The energy (adenosine triphosphate) is supplied by the process of cellular respiration or fermentation. 1. Cellular Respiration (Aerobic Respiration) -requires oxygen and sugar. -end product: carbon dioxide and water. C H O + O C O + H O + ATP 2. Fermentation ( Anaerobic Respiration) -involves the formation of ATP in the absence of oxygen C H O C O + H O + ATP 27 of 40
28 Metabolic Diversity Bacterial Respiration Obligate aerobes require a constant supply of oxygen. Bacteria that live without oxygen because they may be killed by it are called obligate anaerobes. Bacteria that can survive with or without oxygen are known as facultative anaerobes. 28 of 40
29 Reproduction Growth and Reproduction Binary Fission (asexual reproduction) Binary fission is a type of asexual reproduction in which an organism replicates its DNA and divides in half, producing two identical daughter cells (clones). 29 of 40
30 Growth and Reproduction Bacterial cells divide every 20 minutes. Bacterial cells live in colonies. These colonies may be spherical in shape or rod-like in shape. Each cell in a colony is a clone of the original bacterium that started the colony. Genetic variation only arises through genetic mutation. 30 of 40
31 Growth and Reproduction Video Bacteria division (binary fission) (8sec) 31 of 40
32 Growth and Reproduction Conjugation (sexual reproduction) (p368) During conjugation, a hollow bridge forms between two bacterial cells, and genes move from one cell to the other. Each cell ends of with a different set of genetic material than before conjugation. 32 of 40
33 Growth and Reproduction Spore Formation (not a real form of reproduction!) In unfavorable growth conditions, many bacteria form spores. An endospore forms when a bacterium produces a thick internal wall that encloses its DNA and some of its cytoplasm. Spores can remain for months or even years while waiting for more favorable growth conditions. 33 of 40
34 Growth and Reproduction Unusual Lifestyles Cold tolerant bacteria - Psychrophiles Salt tolerant - Halophiles - can live in water with up to 20% salinity (our body fluids: 0.9% salinity) Hot temperature tolerant - thermoacidophiles - tolerate temperatures of up to 80 C and also tolerate low ph 1-4 (acidic). Found in geysers and hot springs. Spore formers - bacterium like Clostridium under extreme conditions will change form into an endospore - as an endospore - the bacterium can tolerate excessive heat/cold. They are resistant to extreme conditions b/c of the endospores thick cell wall. 34 of 40
35 Importance of Bacteria Importance of Bacteria (p ) Bacteria are vital to the living world. Some are producers that capture energy by photosynthesis. Nitrogen fixers change chemically nitrogen gas into ammonia or other nitrogen compounds, usable by plants. Many plants have symbiotic relationships with nitrogen-fixing bacteria in their roots. Others are decomposers that break down the nutrients in dead matter (saprophytes). Still other bacteria have human uses. 35 of 40
36 Importance of Bacteria Importance of Bacteria (p ) Bacteria are vital to the living world. Cattle can only digest grass b/c of the bacteria in their digestive tracts. Without these bacteria no vertebrate can digest grass or hay Many bacteria recycle and decompose dead material. Bacteria can be found in any habitats. All organisms on earth are dependent on nitrogen fixing bacteria. Sewage decomposition - bacteria are added to sewage to break it down. 36 of 40
37 Importance of Bacteria Human Uses of Bacteria Used in the production of foods/beverages. Used in industry-digest petroleum, waste management, mining, synthesizing drugs/chem Used in our bodies - required for digestion, absorption of nutrients. synthesis of drugs and chemicals via genetic engineering production of vitamins in human intestines 37 of 40 E. coli bacteria in digestive system, coloured SEM
38 Importance of Bacteria Only few Bacteria cause Harm Will be covered in Chapter of 40
39 19 1 Continue to: - or - Click to Launch: 39 of 40
40 19 1 Which characteristic distinguishes eubacteria from archaebacteria? a. Eubacteria lack peptidoglycan in their cell walls. b. Eubacteria contain peptidoglycan in their cell walls. c. Eubacteria lack a nucleus. d. Eubacteria do not possess mitochondria. 40 of 40
41 19 1 Rod-shaped prokaryotes are called a. bacilli. b. cocci. c. spirilla. d. streptococci. 41 of 40
42 19 1 Bacteria that must live without oxygen are called a. obligate aerobes. b. facultative anaerobes. c. obligate anaerobes. d. facultative aerobes. 42 of 40
43 19 1 Prokaryotes that make their own food molecules from carbon dioxide and water but live where there is no light are called a. photoautotrophs. b. photoheterotrophs. c. chemoautotrophs. d. chemoheterotrophs. 43 of 40
44 19 1 Bacteria that attack and digest the tissue of dead organisms are called a. decomposers. b. nitrogen fixers. c. chemoautotrophs. d. archaebacteria. 44 of 40
45 END OF SECTION
TRACING BACK TO THE BEGINNING
 BACTERIA! TRACING BACK TO THE BEGINNING PROKARYOTES KINGDOM EUBACTERIA KINGDOM ARCHAEBACTERIA CHARACTERISTICS: 1. NO NUCLEUS 2. NO MEMBRANE BOUND ORGANELLES 4. MOST ARE SMALLER THAN EUKARYOTES 5. ARE SINGLE-CELLED
BACTERIA! TRACING BACK TO THE BEGINNING PROKARYOTES KINGDOM EUBACTERIA KINGDOM ARCHAEBACTERIA CHARACTERISTICS: 1. NO NUCLEUS 2. NO MEMBRANE BOUND ORGANELLES 4. MOST ARE SMALLER THAN EUKARYOTES 5. ARE SINGLE-CELLED
Kingdom Bacteria Kingdom Archaea
 Section 5.1 Kingdom Bacteria Kingdom Archaea p. 132-139 Kingdom Bacteria General Characteristics: Cell Type: all are prokaryotic. Body Form: most are unicellular, some are colonial. Three main shapes are:
Section 5.1 Kingdom Bacteria Kingdom Archaea p. 132-139 Kingdom Bacteria General Characteristics: Cell Type: all are prokaryotic. Body Form: most are unicellular, some are colonial. Three main shapes are:
Kingdom Monera(Archaebacteria & Eubacteria)
 Kingdom Monera(Archaebacteria & All bacteria are prokaryotes Characteristics: 1. No nucleus Eubacteria) 2. No membrane bound organelles 3. Smaller & less ribosomes 4. Most are smaller than eukaryotes 5.
Kingdom Monera(Archaebacteria & All bacteria are prokaryotes Characteristics: 1. No nucleus Eubacteria) 2. No membrane bound organelles 3. Smaller & less ribosomes 4. Most are smaller than eukaryotes 5.
Classifying Prokaryotes: Eubacteria Plasma Membrane. Ribosomes. Plasmid (DNA) Capsule. Cytoplasm. Outer Membrane DNA. Flagellum.
 Bacteria The yellow band surrounding this hot spring is sulfur, a waste product of extremophilic prokaryotes, probably of the Domain Archaea, Kingdom Archaebacteria. Bacteria are prokaryotic cells (no
Bacteria The yellow band surrounding this hot spring is sulfur, a waste product of extremophilic prokaryotes, probably of the Domain Archaea, Kingdom Archaebacteria. Bacteria are prokaryotic cells (no
KINGDOM MONERA. Bacterial Cell Shape 8/22/2010. The Prokaryotes: Archaebacteria and Eubacteria
 KINGDOM MONERA The Prokaryotes: Archaebacteria and Eubacteria Bacteria are the most organisms living on the Earth. (i.e. 10mL of soil contains 1 x 10 10 bacteria. They are found in nearly every habitat
KINGDOM MONERA The Prokaryotes: Archaebacteria and Eubacteria Bacteria are the most organisms living on the Earth. (i.e. 10mL of soil contains 1 x 10 10 bacteria. They are found in nearly every habitat
Kingdom Monera Bacteria
 Kingdom Monera Bacteria Common bacteria Prokaryotes Strep throat Anthrax Chlamydia E. coli Meningitis Salmonella Micrococcus(intestinal) Streptococcus mutans Haemophilusinfluenzae Cellphonious bacterious
Kingdom Monera Bacteria Common bacteria Prokaryotes Strep throat Anthrax Chlamydia E. coli Meningitis Salmonella Micrococcus(intestinal) Streptococcus mutans Haemophilusinfluenzae Cellphonious bacterious
Chapter 19 Notes Kingdoms Archaebacteria andeubacteria
 Chapter 19 Notes Kingdoms Archaebacteria andeubacteria All bacteria are Prokaryotic. This means that they are organisms that are one-celled and do not contain a nucleus or other membrane bound organelles.
Chapter 19 Notes Kingdoms Archaebacteria andeubacteria All bacteria are Prokaryotic. This means that they are organisms that are one-celled and do not contain a nucleus or other membrane bound organelles.
Section 19 1 Bacteria (pages )
 Chapter 19 Bacteria and Viruses Section 19 1 Bacteria (pages 471 477) How do the two groups of prokaryotes differ? What factors are used to identify prokaryotes? What is the importance of bacteria? 13.
Chapter 19 Bacteria and Viruses Section 19 1 Bacteria (pages 471 477) How do the two groups of prokaryotes differ? What factors are used to identify prokaryotes? What is the importance of bacteria? 13.
The invention of the microscope has opened to us a world of extraordinary numbers. A singular drop of pond water reveals countless life forms
 Biology Chapter 19 Notes - Bacteria and Viruses The invention of the microscope has opened to us a world of extraordinary numbers. A singular drop of pond water reveals countless life forms I. Classifying
Biology Chapter 19 Notes - Bacteria and Viruses The invention of the microscope has opened to us a world of extraordinary numbers. A singular drop of pond water reveals countless life forms I. Classifying
20 Viruses and Prokaryotes Bacteria
 20 Viruses and Prokaryotes 20.2 - Bacteria Classifying Prokaryotes Prokaryote unicellular organisms that lacks a nucleus Most abundant and widespread organisms on Earth Divided into two groups Bacteria
20 Viruses and Prokaryotes 20.2 - Bacteria Classifying Prokaryotes Prokaryote unicellular organisms that lacks a nucleus Most abundant and widespread organisms on Earth Divided into two groups Bacteria
Current evidence indicates that eukaryotes evolved from prokaryotes between 1 and 1.5 billion years ago.
 Current evidence indicates that eukaryotes evolved from prokaryotes between 1 and 1.5 billion years ago. Two theories: 1. Infolding theory 2. Endosymbiotic theory The infolding of the prokaryotic plasma
Current evidence indicates that eukaryotes evolved from prokaryotes between 1 and 1.5 billion years ago. Two theories: 1. Infolding theory 2. Endosymbiotic theory The infolding of the prokaryotic plasma
Bacteria and Viruses. 1 Bacteria CHAPTER 18. MAINIDEA Bacteria are prokaryotic cells.
 CHAPTER 18 Bacteria and Viruses 1 Bacteria 7(F), 8(B), 8(C), 11(C), 12(A) Before You Read When you hear the word bacteria, what comes to mind? On the lines below, describe places you think bacteria might
CHAPTER 18 Bacteria and Viruses 1 Bacteria 7(F), 8(B), 8(C), 11(C), 12(A) Before You Read When you hear the word bacteria, what comes to mind? On the lines below, describe places you think bacteria might
19-1 Notes Bacteria. Named after the Greek word Little stick because many bacteria have a stick-like shape when viewed under a microscope
 19-1 Notes Bacteria Bacteria are found virtually everywhere! Named after the Greek word Little stick because many bacteria have a stick-like shape when viewed under a microscope We know that bacteria are
19-1 Notes Bacteria Bacteria are found virtually everywhere! Named after the Greek word Little stick because many bacteria have a stick-like shape when viewed under a microscope We know that bacteria are
Unit 5. Organisms C H A P T E R 1 5. Bacteria: Unicellular R E A D P
 Unit 5 Bacteria: Unicellular Organisms C H A P T E R 1 5 R E A D P. 2 9 3-305 Bacterial Cell Structure: Prokaryotic Single cellular no membrane bound organelles primitive Parts of Bacteria 1. Cell membrane
Unit 5 Bacteria: Unicellular Organisms C H A P T E R 1 5 R E A D P. 2 9 3-305 Bacterial Cell Structure: Prokaryotic Single cellular no membrane bound organelles primitive Parts of Bacteria 1. Cell membrane
The Prokaryotic World
 The Prokaryotic World A. An overview of prokaryotic life There is no doubt that prokaryotes are everywhere. By everywhere, I mean living in every geographic region, in extremes of environmental conditions,
The Prokaryotic World A. An overview of prokaryotic life There is no doubt that prokaryotes are everywhere. By everywhere, I mean living in every geographic region, in extremes of environmental conditions,
Notes - Microbiology Monera
 Notes - Microbiology Monera Part 1 Classification - Kingdom moneran is more commonly known as bacteria. This is the largest kingdom with inhabitants covering almost every square metre of the planet! -
Notes - Microbiology Monera Part 1 Classification - Kingdom moneran is more commonly known as bacteria. This is the largest kingdom with inhabitants covering almost every square metre of the planet! -
Vocabulary- Bacteria (34 words)
 Biology II BACTERIA Vocabulary- Bacteria (34 words) 1. Prokaryote 21. phototroph 2. Peptidoglycan 22. chemotroph 3. Methanogen 23. obligate anaerobe 4. Halophile 24. facultative anaerobe 5. Thermoacidophile
Biology II BACTERIA Vocabulary- Bacteria (34 words) 1. Prokaryote 21. phototroph 2. Peptidoglycan 22. chemotroph 3. Methanogen 23. obligate anaerobe 4. Halophile 24. facultative anaerobe 5. Thermoacidophile
Bacteria outline-- CHAPTER 19 Bacteria
 Bacteria outline-- CHAPTER 19 Bacteria Structure and Function Prokaryote & Eukaryote Evolution Cellular Evolution Current evidence indicates that eukaryotes evolved from prokaryotes between 1 and 1.5 billion
Bacteria outline-- CHAPTER 19 Bacteria Structure and Function Prokaryote & Eukaryote Evolution Cellular Evolution Current evidence indicates that eukaryotes evolved from prokaryotes between 1 and 1.5 billion
Kingdom Monera. These notes are to help you check your answers in your Bacteria unit handout package that you received in class.
 Kingdom Monera These notes are to help you check your answers in your Bacteria unit handout package that you received in class. Textbook reference pages Textbook Section 17-2 & 17-3 pages 360-375 Basic
Kingdom Monera These notes are to help you check your answers in your Bacteria unit handout package that you received in class. Textbook reference pages Textbook Section 17-2 & 17-3 pages 360-375 Basic
Outline. Viruses, Bacteria, and Archaea. Viruses Structure Classification Reproduction Prokaryotes Structure Reproduction Nutrition Bacteria Archaea
 Viruses, Bacteria, and Archaea Chapter 21 Viruses Structure Classification Reproduction Prokaryotes Structure Reproduction Nutrition Bacteria Archaea Outline The Viruses The Viruses Viruses are noncellular
Viruses, Bacteria, and Archaea Chapter 21 Viruses Structure Classification Reproduction Prokaryotes Structure Reproduction Nutrition Bacteria Archaea Outline The Viruses The Viruses Viruses are noncellular
Kingdom Monera - The Bacteria
 Chapter 8 The World of Microbes Kingdom Monera - The Bacteria Bio-significance- The down side: Disease of plants crop loss Disease of animals loss of livestock and herds Human disease cavities to The Plague
Chapter 8 The World of Microbes Kingdom Monera - The Bacteria Bio-significance- The down side: Disease of plants crop loss Disease of animals loss of livestock and herds Human disease cavities to The Plague
Lecture 2: Kingdoms Monera, Protoctista and Fungi
 KINGDOM MONERA Bacteria Lecture 2: Kingdoms Monera, Protoctista and Fungi Kingdom Monera Commonly called bacteria All monerans are unicellular All monerans are prokaryotes Prokaryotes: Single-celled organisms
KINGDOM MONERA Bacteria Lecture 2: Kingdoms Monera, Protoctista and Fungi Kingdom Monera Commonly called bacteria All monerans are unicellular All monerans are prokaryotes Prokaryotes: Single-celled organisms
9/8/2017. Bacteria and Archaea. Three domain system: The present tree of life. Structural and functional adaptations contribute to prokaryotic success
 5 m 2 m 9/8/2017 Three domain system: The present tree of life Bacteria and Archaea Chapter 27 Structural and functional adaptations contribute to prokaryotic success Unicellular Small Variety of shapes
5 m 2 m 9/8/2017 Three domain system: The present tree of life Bacteria and Archaea Chapter 27 Structural and functional adaptations contribute to prokaryotic success Unicellular Small Variety of shapes
PROPERTY OF: BIOLOGY UNIT 3 CHAPTER 19 NOTES THE HISTORY OF LIFE
 PROPERTY OF: BIOLOGY UNIT 3 CHAPTER 19 NOTES THE HISTORY OF LIFE Spontaneous Generation - theory that life arises from non-life (early-mid 1700 s) EX: rotting meat became covered with flies and maggots
PROPERTY OF: BIOLOGY UNIT 3 CHAPTER 19 NOTES THE HISTORY OF LIFE Spontaneous Generation - theory that life arises from non-life (early-mid 1700 s) EX: rotting meat became covered with flies and maggots
Archea and Bacteria- The PROKARYOTES
 ` Archea and Bacteria- The PROKARYOTES As late as 1977, all prokaryotes were put into one single kingdom called Monera. Taxonomists no longer accept that concept. Some prokaryotes are more closely related
` Archea and Bacteria- The PROKARYOTES As late as 1977, all prokaryotes were put into one single kingdom called Monera. Taxonomists no longer accept that concept. Some prokaryotes are more closely related
Cells & Bacteria Notes
 Cells & Bacteria Notes 4 Major Macromolecules Macromolecules are large molecules. The four groups of macromolecules are essential to the structure and function of a cell. Group Building Block Large Molecule
Cells & Bacteria Notes 4 Major Macromolecules Macromolecules are large molecules. The four groups of macromolecules are essential to the structure and function of a cell. Group Building Block Large Molecule
Archaebacteria and Eubacteria
 Archaebacteria and Eubacteria Bacteria are of immense importance because of their rapid growth, reproduction, and mutation rates, as well as, their ability to exist under adverse conditions. The oldest
Archaebacteria and Eubacteria Bacteria are of immense importance because of their rapid growth, reproduction, and mutation rates, as well as, their ability to exist under adverse conditions. The oldest
BACTERIA AND ARCHAEA 10/15/2012
 BACTERIA AND ARCHAEA Chapter 27 KEY CONCEPTS: Structural and functional adaptations contribute to prokaryotic success Rapid reproduction, mutation, and genetic recombination promote genetic diversity in
BACTERIA AND ARCHAEA Chapter 27 KEY CONCEPTS: Structural and functional adaptations contribute to prokaryotic success Rapid reproduction, mutation, and genetic recombination promote genetic diversity in
Ch. 19 Bacteria and Viruses Review: Prokaryote and Eukaryote
 Ch. 19 Bacteria and Viruses 19.1 Bacteria Review: Prokaryote and Eukaryote 2 Groups of Prokaryotes Prokaryote has no nucleus, bacteria Eukaryote has nucleus, plants, animals, fungi Archaebacteria Cell
Ch. 19 Bacteria and Viruses 19.1 Bacteria Review: Prokaryote and Eukaryote 2 Groups of Prokaryotes Prokaryote has no nucleus, bacteria Eukaryote has nucleus, plants, animals, fungi Archaebacteria Cell
Classification. Old 5 Kingdom system. New 3 Domain system. reflects a greater understanding of evolution & molecular evidence
 Classification Old 5 Kingdom system Monera, Protists, Plants, Fungi, Animals New 3 Domain system reflects a greater understanding of evolution & molecular evidence Prokaryote: Bacteria Prokaryote: Archaebacteria
Classification Old 5 Kingdom system Monera, Protists, Plants, Fungi, Animals New 3 Domain system reflects a greater understanding of evolution & molecular evidence Prokaryote: Bacteria Prokaryote: Archaebacteria
Section Title: Archaebacteria vs. Eubacteria
 Unit: 3.1 Name: Section Title: Archaebacteria vs. Eubacteria Latin Root Word: Review of Old Information: None New Information: Bacteria Notes Basic Bacteria Facts Classification of Bacteria: Kingdom Archaebacteria
Unit: 3.1 Name: Section Title: Archaebacteria vs. Eubacteria Latin Root Word: Review of Old Information: None New Information: Bacteria Notes Basic Bacteria Facts Classification of Bacteria: Kingdom Archaebacteria
There are 5 kingdoms: Animalia multicellular animals, heterotrophic (eat other things), evolved 700,000,000 years ago (1,000,000 2,000,000 species)
 Classification The modern system of naming gives each living thing 7 names. Each name is a little more specific than the one before it. The categories are (in order from least to most specific): Kingdom
Classification The modern system of naming gives each living thing 7 names. Each name is a little more specific than the one before it. The categories are (in order from least to most specific): Kingdom
Name Block Chapter 6, Section 3, Bacteria, pages Information taken from Prentice Hall Science Explorer, Life Science, 2004
 SOL LS.4 The student will investigate and understand how organisms can be classified. Key concepts include a) The distinguishing characteristics of domains of organisms b) The distinguishing characteristics
SOL LS.4 The student will investigate and understand how organisms can be classified. Key concepts include a) The distinguishing characteristics of domains of organisms b) The distinguishing characteristics
Prokaryotes Vs. Eukaryotes
 The Microbial World Prokaryotes Vs. Eukaryotes Mircrobes of the Ocean Primary Producers Are the organisms that produce bio-mass from inorganic compounds (autotrophs). -Photosynthetic autotrophs Phytoplankton
The Microbial World Prokaryotes Vs. Eukaryotes Mircrobes of the Ocean Primary Producers Are the organisms that produce bio-mass from inorganic compounds (autotrophs). -Photosynthetic autotrophs Phytoplankton
Directed Reading A. Section: Bacteria CHARACTERISTICS OF BACTERIA. bacteria? a. cocci b. spirilla c. flagella d. bacilli.
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading A Section: Bacteria 1 Which of the following is true of bacteria? a All bacteria are the same size b Most bacteria can be seen without a microscope c There are fewer bacteria
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading A Section: Bacteria 1 Which of the following is true of bacteria? a All bacteria are the same size b Most bacteria can be seen without a microscope c There are fewer bacteria
Unit 10: The simplest living beings
 Unit 10: The simplest living beings 1. Fungi 2. Protoctists 2.1. Protozoa 2.2. Algae 3. Bacteria 4. Viruses Think and answer? a. What type of organism can you see in the photograph? b. What type of cells
Unit 10: The simplest living beings 1. Fungi 2. Protoctists 2.1. Protozoa 2.2. Algae 3. Bacteria 4. Viruses Think and answer? a. What type of organism can you see in the photograph? b. What type of cells
Imagine living all your life as a member of the only family on
 19 1 Bacteria Imagine living all your life as a member of the only family on your street. Then, one morning, you open the front door and discover houses all around you. You see neighbors tending their
19 1 Bacteria Imagine living all your life as a member of the only family on your street. Then, one morning, you open the front door and discover houses all around you. You see neighbors tending their
Domains and Kingdoms. Images, from left to right: Cholera bacteria, Volvox colony, Strep bacteria
 Domains and Kingdoms Images, from left to right: Cholera bacteria, Volvox colony, Strep bacteria THE DOMAINS A domain is the broadest level in the classification of life. All living organisms belong to
Domains and Kingdoms Images, from left to right: Cholera bacteria, Volvox colony, Strep bacteria THE DOMAINS A domain is the broadest level in the classification of life. All living organisms belong to
Introduction to Bacteria
 Introduction to Bacteria USDA NIFSI Food Safety in the Classroom University of Tennessee, Knoxville 2006 A quick clip http://www2.beavercreek.k12.oh.us/vi deos/28824/chp937402_700k.asf Bacteria What are
Introduction to Bacteria USDA NIFSI Food Safety in the Classroom University of Tennessee, Knoxville 2006 A quick clip http://www2.beavercreek.k12.oh.us/vi deos/28824/chp937402_700k.asf Bacteria What are
Announcements KEY CONCEPTS
 What do these things have in common? Announcements Lab this week: bring textbook and photo atlas. Relevant reading BEFORE lab: Ch. 30 http://i.cnn.net/cnn/specials/2001/trade.center/images/anthrax.jpg
What do these things have in common? Announcements Lab this week: bring textbook and photo atlas. Relevant reading BEFORE lab: Ch. 30 http://i.cnn.net/cnn/specials/2001/trade.center/images/anthrax.jpg
SG 9.2 notes Ideas about targets and terms: 9.2 In the past, all living things were classified in either the kingdom of animals or plants
 Ideas about targets and terms: 9.2 In the past, all living things were classified in either the kingdom of animals or plants Euglena are singled celled organisms in pond water They are green, so contain,
Ideas about targets and terms: 9.2 In the past, all living things were classified in either the kingdom of animals or plants Euglena are singled celled organisms in pond water They are green, so contain,
Chapter 1. Basics of Microbiology
 Chapter 1 Basics of Microbiology Objectives How microorganisms are classified (taxonomy) What they look like (morphology) The major divisions among microorganisms based upon their function in the environment
Chapter 1 Basics of Microbiology Objectives How microorganisms are classified (taxonomy) What they look like (morphology) The major divisions among microorganisms based upon their function in the environment
Characteristics. Nucleoid Region single circular chromosome plasmids mesosome
 Prokaryotes Characteristics Nucleoid Region single circular chromosome plasmids mesosome No membranebound organelles Ribosomes (70S) Plasma membrane Cell wall peptidoglycan Capsule glycocalyx Flagella
Prokaryotes Characteristics Nucleoid Region single circular chromosome plasmids mesosome No membranebound organelles Ribosomes (70S) Plasma membrane Cell wall peptidoglycan Capsule glycocalyx Flagella
Unit 13.1: Prokaryotes
 Unit 13.1: Prokaryotes Can you guess what organisms are pictured here? Are they fat green worms on a red leaf? Here s a clue: There are more organisms like these than any other on Earth. Here s another
Unit 13.1: Prokaryotes Can you guess what organisms are pictured here? Are they fat green worms on a red leaf? Here s a clue: There are more organisms like these than any other on Earth. Here s another
Prokaryotes. Chapter 27. PowerPoint Lectures for Biology, Seventh Edition. Lectures by Chris Romero. Neil Campbell and Jane Reece
 Chapter 27 Prokaryotes PowerPoint Lectures for Biology, Seventh Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero Overview: They re (Almost) Everywhere! Most prokaryotes are microscopic But
Chapter 27 Prokaryotes PowerPoint Lectures for Biology, Seventh Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero Overview: They re (Almost) Everywhere! Most prokaryotes are microscopic But
Obligate anaerobes - cannot grow in the presence of oxygen Facultative anaerobes - can grow with or without oxygen Aerobic - require oxygen
 PROKARYOTES *include bacteria and archaea *singular: bacterium / plural: bacteria PROPERTIES 1. Bacteria are classified into two kingdoms: Eubacteria (true bacteria) and Archaebacteria (Ancient Bacteria).
PROKARYOTES *include bacteria and archaea *singular: bacterium / plural: bacteria PROPERTIES 1. Bacteria are classified into two kingdoms: Eubacteria (true bacteria) and Archaebacteria (Ancient Bacteria).
MAJOR EPISODES IN THE HISTORY OF LIFE
 MAJOR EPISODES IN THE HISTORY OF LIFE All the major phyla of animals evolved by the end of the Cambrian explosion, which began about 540 million years ago and lasted about 10 million years. Plants and
MAJOR EPISODES IN THE HISTORY OF LIFE All the major phyla of animals evolved by the end of the Cambrian explosion, which began about 540 million years ago and lasted about 10 million years. Plants and
Prokaryotes (Domains Bacteria & Archaea) KEY POINTS
 Prokaryotes (Domains Bacteria & Archaea) KEY POINTS 1. Decomposers: recycle organic and inorganic molecules in environment; makes them available to other organisms. 2. Essential components of symbioses.
Prokaryotes (Domains Bacteria & Archaea) KEY POINTS 1. Decomposers: recycle organic and inorganic molecules in environment; makes them available to other organisms. 2. Essential components of symbioses.
BACTERIA. CLS 212: Medical Microbiology Miss Zeina Alkudmani
 BACTERIA CLS 212: Medical Microbiology Miss Zeina Alkudmani Prokaryotes Prokaryotic cells possess simpler structures than eukaryotic cells, since they do not have a nucleus or a lot of cytoplasmic organelles.
BACTERIA CLS 212: Medical Microbiology Miss Zeina Alkudmani Prokaryotes Prokaryotic cells possess simpler structures than eukaryotic cells, since they do not have a nucleus or a lot of cytoplasmic organelles.
11/15/2011. Outline. Prokaryotes. Why care about the small stuff. Bacteria in our bodies. I. Categories of life. II.
 Chapter 27: Bacteria and Archaea Outline I. Categories of life A. Domains B. Eukaryote vs Prokaryote II. Domain Bacteria A. cell walls, structure B. Bacterial reproduction C. Nitrogen fixation D. Pathogenic
Chapter 27: Bacteria and Archaea Outline I. Categories of life A. Domains B. Eukaryote vs Prokaryote II. Domain Bacteria A. cell walls, structure B. Bacterial reproduction C. Nitrogen fixation D. Pathogenic
Chapter 21 PROKARYOTES AND VIRUSES
 Chapter 21 PROKARYOTES AND VIRUSES Bozeman Video classification of life http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tyl_8gv 7RiE Impacts, Issues: West Nile Virus Takes Off Alexander the Great, 336 B.C., conquered a
Chapter 21 PROKARYOTES AND VIRUSES Bozeman Video classification of life http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tyl_8gv 7RiE Impacts, Issues: West Nile Virus Takes Off Alexander the Great, 336 B.C., conquered a
Classification. Classifying Organisms. * Organisms are divided into 3 domains and 6 kingdoms based on the following characteristics
 Classification Classifying Organisms * Organisms are divided into 3 domains and 6 kingdoms based on the following characteristics Cell Type: Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Prokaryotic - No nucleus Eukaryotic
Classification Classifying Organisms * Organisms are divided into 3 domains and 6 kingdoms based on the following characteristics Cell Type: Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Prokaryotic - No nucleus Eukaryotic
Origins - Three Domain Classification PROKARYOTES
 Bacteria Origins - Three Domain Classification EU PROKARYOTES I. Origins of Bacteria Prokaryotes Eubacteria Archaebacteria A. Prokaryotes = 1. Kingdom Eubacteria 2. Kingdom Archaebacteria 3. Prokaryote
Bacteria Origins - Three Domain Classification EU PROKARYOTES I. Origins of Bacteria Prokaryotes Eubacteria Archaebacteria A. Prokaryotes = 1. Kingdom Eubacteria 2. Kingdom Archaebacteria 3. Prokaryote
Early History and Primitive Life. Unit 2: How do cells support life? Chapter: What are the origins of life? What are the simplest forms of life?
 Early History and Primitive Life Unit 2: How do cells support life? Chapter: What are the origins of life? What are the simplest forms of life? Chapter 17-2 EARTH S EARLY HISTORY Evidence for Early Life
Early History and Primitive Life Unit 2: How do cells support life? Chapter: What are the origins of life? What are the simplest forms of life? Chapter 17-2 EARTH S EARLY HISTORY Evidence for Early Life
1. spontaneous generation, Louis Pasteur, S-shaped flask experiment. 2. Miller-Urey experiment, early gases in Earth s atmosphere
 Honors Biology Unit 3 Chapter 15b TRACING EVOLUTIONARY HISTORY THE HISTORY OF LIFE 1. spontaneous generation, Louis Pasteur, S-shaped flask experiment 2. Miller-Urey experiment, early gases in Earth s
Honors Biology Unit 3 Chapter 15b TRACING EVOLUTIONARY HISTORY THE HISTORY OF LIFE 1. spontaneous generation, Louis Pasteur, S-shaped flask experiment 2. Miller-Urey experiment, early gases in Earth s
BACTERIA. Bacteria - small one celled monerans Bacteria like a warm, dark, and moist environment They are found almost everywhere: -on most objects
 Kingdom Monera 1 BACTERIA Bacteria - small one celled monerans Bacteria like a warm, dark, and moist environment They are found almost everywhere: -water -soil -skin -on most objects -air -food -inside
Kingdom Monera 1 BACTERIA Bacteria - small one celled monerans Bacteria like a warm, dark, and moist environment They are found almost everywhere: -water -soil -skin -on most objects -air -food -inside
4/17/2014. Prokaryotes have inhabited the Earth for billions of years
 Prokaryotes have inhabited the Earth for billions of years Fossil evidence shows that prokaryotes were abundant 3.5 bya, and they evolved alone for the following 2 billion years. Prokaryotes are ubiquitous,
Prokaryotes have inhabited the Earth for billions of years Fossil evidence shows that prokaryotes were abundant 3.5 bya, and they evolved alone for the following 2 billion years. Prokaryotes are ubiquitous,
Chapter 17B. Table of Contents. Section 1 Introduction to Kingdoms and Domains. Section 2 Advent of Multicellularity
 Introduction to the Kingdoms of Life Table of Contents Section 2 Advent of Multicellularity Section 3 Complex Multicellularity The Six Kingdoms of Life Living organisms are divided into six kingdoms and
Introduction to the Kingdoms of Life Table of Contents Section 2 Advent of Multicellularity Section 3 Complex Multicellularity The Six Kingdoms of Life Living organisms are divided into six kingdoms and
6 Kingdoms of Life. What is life? How are all living things organized?
 6 Kingdoms of Life What is life? How are all living things organized? Engage List reasons to support why this man is living. List reasons to support why this car is not living. Characteristics of Life
6 Kingdoms of Life What is life? How are all living things organized? Engage List reasons to support why this man is living. List reasons to support why this car is not living. Characteristics of Life
Eubacteria Archaea Eukarya
 Taxonomy Eubacteria Archaea Eukarya, mostly heterotrophic, live in all sorts of environments Largest group of organisms on Earth Only a small amount cause disease Most have very important roles:, such
Taxonomy Eubacteria Archaea Eukarya, mostly heterotrophic, live in all sorts of environments Largest group of organisms on Earth Only a small amount cause disease Most have very important roles:, such
1- Which of the following molecules stores hereditary information? A. ATP B. DNA C. protein D. carbohydrates
 Question 1: Multiple Choice (20 Marks) 1- Which of the following molecules stores hereditary information? A. ATP B. DNA C. protein D. carbohydrates 2- What is the name of the molecule in plants that stores
Question 1: Multiple Choice (20 Marks) 1- Which of the following molecules stores hereditary information? A. ATP B. DNA C. protein D. carbohydrates 2- What is the name of the molecule in plants that stores
Bacteria. The Three Types of Important Heterotrophic Bacteria
 Bacteria Kingdom Monera Prokaryote (their genetic material is not bound with a membrane) Classified according to shape - Spherical (cocci) - Spiral - Rod Shaped -TWO TYPES: Heterotrophic (organism that
Bacteria Kingdom Monera Prokaryote (their genetic material is not bound with a membrane) Classified according to shape - Spherical (cocci) - Spiral - Rod Shaped -TWO TYPES: Heterotrophic (organism that
Biological Kingdoms. An introduction to the six kingdoms of living things
 Biological Kingdoms An introduction to the six kingdoms of living things 3 Domains Archaea 6 Kingdoms Archaebacteria Bacteria Eubacteria Eukaryota Plantae Animalia Fungi Protista Domain Eukaryota Kingdom
Biological Kingdoms An introduction to the six kingdoms of living things 3 Domains Archaea 6 Kingdoms Archaebacteria Bacteria Eubacteria Eukaryota Plantae Animalia Fungi Protista Domain Eukaryota Kingdom
Some history. Now, we know that Robert Hooke was not looking at living cells, but the remains of dead cell walls.
 The Life of a Cell Some history In 1665, Robert Hooke examined the bark of an oak tree under an early microscope. He thought he was looking at something similar to the small rooms of dormitories and prisons;
The Life of a Cell Some history In 1665, Robert Hooke examined the bark of an oak tree under an early microscope. He thought he was looking at something similar to the small rooms of dormitories and prisons;
Ch. 4 Cells and Energy. Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration
 Ch. 4 Cells and Energy Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration 1 2 4.1 Chemical Energy and ATP Living organisms need energy Most comes indirectly from sun! Some change sunlight into organic compounds Others
Ch. 4 Cells and Energy Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration 1 2 4.1 Chemical Energy and ATP Living organisms need energy Most comes indirectly from sun! Some change sunlight into organic compounds Others
Prokaryotes Reading Bacteria Classification of Bacteria
 Prokaryotes Reading Did you ever wonder what happens to all the leaves that fall from the trees every autumn? Imagine if they just accumulated on the forest flour. In a few years, the leaves in the woods
Prokaryotes Reading Did you ever wonder what happens to all the leaves that fall from the trees every autumn? Imagine if they just accumulated on the forest flour. In a few years, the leaves in the woods
Classification by Aristotle and Theophrastus. Early Classification. Living Things
 Classification by Aristotle and Theophrastus Early Classification Living Things Plants Animals Classification by Aristotle and Theophrastus Aristotle's Classification Animals Air Dwellers Land Dwellers
Classification by Aristotle and Theophrastus Early Classification Living Things Plants Animals Classification by Aristotle and Theophrastus Aristotle's Classification Animals Air Dwellers Land Dwellers
B. Correct! Bacillus anthraces produces spores that can cause anthrax. D. Incorrect! Diphtheria is caused by Corynebacterium diphtheriae.
 Microbiology - Problem Drill 09 - The Prokaryotes No. 1 of 10 1. Bacillus anthraces is most closely associated with which of the following? (A) Botulism poisoning (B) Anthrax (C) Gangrene (D) Diphtheria
Microbiology - Problem Drill 09 - The Prokaryotes No. 1 of 10 1. Bacillus anthraces is most closely associated with which of the following? (A) Botulism poisoning (B) Anthrax (C) Gangrene (D) Diphtheria
1- What are rod-shaped bacteria called? A. cocci B. bacilli C. spirilla D. halophiles
 Question 1: Multiple Choice (20 Marks) 1- What are rod-shaped bacteria called? A. cocci B. bacilli C. spirilla D. halophiles 2- The eukaryotic nucleus houses all of the following except the A. RNA B. DNA
Question 1: Multiple Choice (20 Marks) 1- What are rod-shaped bacteria called? A. cocci B. bacilli C. spirilla D. halophiles 2- The eukaryotic nucleus houses all of the following except the A. RNA B. DNA
Part 2. The Basics of Biology:
 Part 2 The Basics of Biology: An Engineer s Perspective Chapter 2 An Overview of Biological Basics 21 2.1 Cells 2.2 Cell Construction 2.3 Cell Nutrient 2.1 Are all cells the same? Cells Basic unit of living
Part 2 The Basics of Biology: An Engineer s Perspective Chapter 2 An Overview of Biological Basics 21 2.1 Cells 2.2 Cell Construction 2.3 Cell Nutrient 2.1 Are all cells the same? Cells Basic unit of living
CHAPTER 3 : MONERA. Metabolic diversity. Metabolic diversity. Metabolic diversity 1/10/2016 BACTERIA
 BACTERIA CHAPTER 3 : MONERA Introduction The taxonomic Kingdom Monera consists of the bacteria. Bacteria are prokaryotes, and their cell structure is basically different from the cells of other living
BACTERIA CHAPTER 3 : MONERA Introduction The taxonomic Kingdom Monera consists of the bacteria. Bacteria are prokaryotes, and their cell structure is basically different from the cells of other living
CH 5 Mostly Microorganisms. Microorganisms covered in this chapter:
 Biology 2201 Name: CH 5 Mostly Microorganisms Microorganisms covered in this chapter: Kingdom Bacteria or Monera: Pg. 132-137 Bacteria are simple, prokaryotic organisms. They can be classified according
Biology 2201 Name: CH 5 Mostly Microorganisms Microorganisms covered in this chapter: Kingdom Bacteria or Monera: Pg. 132-137 Bacteria are simple, prokaryotic organisms. They can be classified according
INTRO TO MICROBIOLOGY
 INTRO TO MICROBIOLOGY Spring 2015 Peering through the microscope into a drop of seawater is like looking at stars with a telescope on a clear night. Dr. Gallardo, ocean researcher What will you be studying
INTRO TO MICROBIOLOGY Spring 2015 Peering through the microscope into a drop of seawater is like looking at stars with a telescope on a clear night. Dr. Gallardo, ocean researcher What will you be studying
Microbiology. Viruses
 Microbiology Microbiology: The branch of biology that deals with microorganisms and their effects on other living organisms. Typically we study bacteria & protists. Virology studies the impact of viruses
Microbiology Microbiology: The branch of biology that deals with microorganisms and their effects on other living organisms. Typically we study bacteria & protists. Virology studies the impact of viruses
Bacteria are very small
 BACTERIA BACTERIA Bacteria are very small Bacteria are very small compared to cells with nuclei This is a pore in human skin and the yellow spheres are bacteria BACTERIA LIVE ALMOST EVERYWHERE Hot springs
BACTERIA BACTERIA Bacteria are very small Bacteria are very small compared to cells with nuclei This is a pore in human skin and the yellow spheres are bacteria BACTERIA LIVE ALMOST EVERYWHERE Hot springs
Protists. Bacteria. Archea
 Protists Bacteria Archea Archaeans include inhabitants of some of the most extreme environments on the planet. Image of acid mine drain filled with Archaea. Archaea also thrive in mud and they are one
Protists Bacteria Archea Archaeans include inhabitants of some of the most extreme environments on the planet. Image of acid mine drain filled with Archaea. Archaea also thrive in mud and they are one
MORPHOLOGY: the study of form and structure
 MICROBIOLOGY CHAPTER 3 Bacteria Morphology 3:1 Bacteria Structure and Function MORPHOLOGY: the study of form and structure Structure of Bacteria 1. PROKARYOTIC no membrane bound nucleus nor other organelles
MICROBIOLOGY CHAPTER 3 Bacteria Morphology 3:1 Bacteria Structure and Function MORPHOLOGY: the study of form and structure Structure of Bacteria 1. PROKARYOTIC no membrane bound nucleus nor other organelles
Bacteria. Prepared by. Doua a Hamadi Gellan Ibrahim Rahma Younis Doua a Abdul-Hadi Doua a Amjad Hanin Laith Khamael Dawood
 Bacteria Prepared by Doua a Hamadi Gellan Ibrahim Rahma Younis Doua a Abdul-Hadi Doua a Amjad Hanin Laith Khamael Dawood History of Bacteriology Doua a Hamadi Bacteria were first observed by Antonie van
Bacteria Prepared by Doua a Hamadi Gellan Ibrahim Rahma Younis Doua a Abdul-Hadi Doua a Amjad Hanin Laith Khamael Dawood History of Bacteriology Doua a Hamadi Bacteria were first observed by Antonie van
Ch. 9 - Cellular Respiration/Fermentation Study Guide
 Ch. 9 - Cellular Respiration/Fermentation Study Guide A. Introduction 1. All living things need energy for metabolism. a. Plants produce glucose through photosynthesis; break down glucose during cellular
Ch. 9 - Cellular Respiration/Fermentation Study Guide A. Introduction 1. All living things need energy for metabolism. a. Plants produce glucose through photosynthesis; break down glucose during cellular
(A) Heterotrophs produce some organic nutrients, and must absorb inorganic nutrients from the environment.
 MCAT Biology - Problem Drill 09: Prokaryotes and Fungi Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem and answer choices carefully; (2) Work the problems on paper as needed; (3) Pick the correct
MCAT Biology - Problem Drill 09: Prokaryotes and Fungi Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem and answer choices carefully; (2) Work the problems on paper as needed; (3) Pick the correct
Introduction to Prokaryotes
 Introduction to Prokaryotes Say Thanks to the Authors Click http://www.ck12.org/saythanks (No sign in required) To access a customizable version of this book, as well as other interactive content, visit
Introduction to Prokaryotes Say Thanks to the Authors Click http://www.ck12.org/saythanks (No sign in required) To access a customizable version of this book, as well as other interactive content, visit
MICROBIOLOGY CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION TO MICROORGANISMS
 MICROBIOLOGY CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION TO MICROORGANISMS 1:1 What is Microbiology? MICROBIOLOGY: the study of living organisms that are individually too small to be seen with the unaided eye e.g. bacteria,
MICROBIOLOGY CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION TO MICROORGANISMS 1:1 What is Microbiology? MICROBIOLOGY: the study of living organisms that are individually too small to be seen with the unaided eye e.g. bacteria,
Bacteria are very small
 BACTERIA BACTERIA Bacteria are very small Bacteria are very small compared to cells with nuclei (Eukaryotic cells) This is a pore in human skin and the yellow spheres are bacteria CLASSIFICATION OF BACTERIA
BACTERIA BACTERIA Bacteria are very small Bacteria are very small compared to cells with nuclei (Eukaryotic cells) This is a pore in human skin and the yellow spheres are bacteria CLASSIFICATION OF BACTERIA
BIOLOGY. Bacteria and Archaea
 27 CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Bacteria and Archaea Outline I. Categories of life A. Domains B. Eukaryote vs Prokaryote II. Domain Bacteria A. cell walls,
27 CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Bacteria and Archaea Outline I. Categories of life A. Domains B. Eukaryote vs Prokaryote II. Domain Bacteria A. cell walls,
Outline 10: Origin of Life. Better Living Through Chemistry
 Outline 10: Origin of Life Better Living Through Chemistry What is Life? Internal chemical activity providing growth, repair, and generation of energy. The ability to reproduce. The capacity to respond
Outline 10: Origin of Life Better Living Through Chemistry What is Life? Internal chemical activity providing growth, repair, and generation of energy. The ability to reproduce. The capacity to respond
Have you had a cold, flu, or other infectious disease recently? Do you
 45 The World of Microbes r e a d i n g Have you had a cold, flu, or other infectious disease recently? Do you know what caused your illness? Microbes cause most infectious diseases. Microbes include the
45 The World of Microbes r e a d i n g Have you had a cold, flu, or other infectious disease recently? Do you know what caused your illness? Microbes cause most infectious diseases. Microbes include the
The Microbial World. Microorganisms of the Sea
 The Microbial World Microorganisms of the Sea Microorganisms Smallest, simplest marine organisms. Very important in evolutionary history of life on Earth. Important primary producers. Include prokaryotes
The Microbial World Microorganisms of the Sea Microorganisms Smallest, simplest marine organisms. Very important in evolutionary history of life on Earth. Important primary producers. Include prokaryotes
Study of Biology. copyright cmassengale
 Study of Biology 1 What is Biology? Biology is the study of all living things Living things are called organisms Organisms include bacteria, protists, fungi, plants, & animals 2 All Living Things Share
Study of Biology 1 What is Biology? Biology is the study of all living things Living things are called organisms Organisms include bacteria, protists, fungi, plants, & animals 2 All Living Things Share
(A) Exotoxin (B) Endotoxin (C) Cilia (D) Flagella (E) Capsule. A. Incorrect! Only gram-positive bacteria secrete exotoxin.
 College Biology - Problem Drill 13: Prokaryots and Protists Question No. 1 of 10 1. Gram-negative bacteria can cause disease in humans by release of what substance? Question #01 (A) Exotoxin (B) Endotoxin
College Biology - Problem Drill 13: Prokaryots and Protists Question No. 1 of 10 1. Gram-negative bacteria can cause disease in humans by release of what substance? Question #01 (A) Exotoxin (B) Endotoxin
 All Living Things Share Common Characteristics 1. Living Things are Composed of Cells: Single-cell organisms have everything they need to be self-sufficient. In multicellular organisms, some cells do only
All Living Things Share Common Characteristics 1. Living Things are Composed of Cells: Single-cell organisms have everything they need to be self-sufficient. In multicellular organisms, some cells do only
Characteristics of Life
 Characteristics of Life All living things share some basic characteristics: 1. Organization 2. Movement 3. Made up of cells 4. Reproduce 5. Grow and / or develop 6. Obtain and use energy 7. Respond to
Characteristics of Life All living things share some basic characteristics: 1. Organization 2. Movement 3. Made up of cells 4. Reproduce 5. Grow and / or develop 6. Obtain and use energy 7. Respond to
1A Review Questions. Matching 6. Class 7. Order 8. Binomial nomenclature 9. Phylum 10. Species
 1A Review Questions 1. What is taxonomy? a. Set of paired statements that are used to identify organisms b. Relationships between organisms c. A science involving naming and categorizing species based
1A Review Questions 1. What is taxonomy? a. Set of paired statements that are used to identify organisms b. Relationships between organisms c. A science involving naming and categorizing species based
How Cells Arose; Microbial Life
 How Cells Arose; Microbial Life No one knows for sure Earliest life thought to be like today s bacteria The earth formed 4.5 bya The first life originated around 2.5 bya at least 3 possibilities for origin
How Cells Arose; Microbial Life No one knows for sure Earliest life thought to be like today s bacteria The earth formed 4.5 bya The first life originated around 2.5 bya at least 3 possibilities for origin
The two daughter cells are genetically identical to each other and the parent cell.
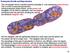 Prokaryote Growth and Reproduction This micrograph shows a bacillus bacteria (probably E. coli) undergoing binary fission. This is a form of asexual reproduction. During prokaryotic binary fission, as
Prokaryote Growth and Reproduction This micrograph shows a bacillus bacteria (probably E. coli) undergoing binary fission. This is a form of asexual reproduction. During prokaryotic binary fission, as
Cell organelles. Cell Wall
 Cell organelles Cell Wall Plant cells have an outermost structure called a cell wall. A cell wall is a rigid structure that gives support to a cell. Plants and algae have cell walls made of a complex sugar.
Cell organelles Cell Wall Plant cells have an outermost structure called a cell wall. A cell wall is a rigid structure that gives support to a cell. Plants and algae have cell walls made of a complex sugar.
Unit One: The Science of Biology
 Unit One: The Science of Biology 1 The process by which an organism reaches death In an organism, a condition in which there is reproduction, growth, development, metabolism, use of energy, excretion,
Unit One: The Science of Biology 1 The process by which an organism reaches death In an organism, a condition in which there is reproduction, growth, development, metabolism, use of energy, excretion,
Scientific names allow scientists to talk about particular species without confusion
 Unit 9 Test Review KEY a. Explain the history, purpose, and methods of taxonomy What is taxonomy? the science of naming and classifying organisms Who came up with it? Linnaeus Why do we use taxonomy? Scientific
Unit 9 Test Review KEY a. Explain the history, purpose, and methods of taxonomy What is taxonomy? the science of naming and classifying organisms Who came up with it? Linnaeus Why do we use taxonomy? Scientific
NOTES: 20.2 (& 20.3)
 NOTES: 20.2 (& 20.3) How are Bacteria Different from Viruses? Bacteria are different from viruses in that they: -are much bigger -have a different structure (made of cells) therefore are considered LIVING
NOTES: 20.2 (& 20.3) How are Bacteria Different from Viruses? Bacteria are different from viruses in that they: -are much bigger -have a different structure (made of cells) therefore are considered LIVING
MICROBE MISSION - SAMPLE TOURNAMENT #1 by Karen L. Lancour
 MICROBE MISSION - SAMPLE TOURNAMENT #1 by Karen L. Lancour STATION A: MICROSCOPY 1. A microscope has an 10 objective and oculars of 4X, 10X, 40X and 100X. What is the range of magnification for this microscope.
MICROBE MISSION - SAMPLE TOURNAMENT #1 by Karen L. Lancour STATION A: MICROSCOPY 1. A microscope has an 10 objective and oculars of 4X, 10X, 40X and 100X. What is the range of magnification for this microscope.
BIOLOGY 1021 UNIT 1: MULTICELLULAR STRUCTURE CHAPTER 15 P AND CHAPTER 16 P
 BIOLOGY 1021 UNIT 1: MULTICELLULAR STRUCTURE CHAPTER 15 P. 307-311 AND CHAPTER 16 P. 328-331 Be sure to know flow chart an understanding from atoms to multicellular organisms. Importance of carbon, hydrogen,
BIOLOGY 1021 UNIT 1: MULTICELLULAR STRUCTURE CHAPTER 15 P. 307-311 AND CHAPTER 16 P. 328-331 Be sure to know flow chart an understanding from atoms to multicellular organisms. Importance of carbon, hydrogen,
