Phase Noise in LC Oscillators: From Basic Concepts to Advanced Topologies. Carlo Samori. Politecnico di Milano Milano, Italy
|
|
|
- Antony Bates
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Phase Nise in LC Oscillatrs: Frm Basic Cncepts t Advanced Tplgies Carl Samri carl.samri@plimi.it Plitecnic di Milan Milan, Italy Carl Samri
2 Outline Basics f LC Vltage-Cntrlled Oscillatrs (VCOs) Phase Nise thery and mdels (simplified) Practical issues and trade-ffs Advanced LC scillatr s tplgies Carl Samri
3 LC Tank L C V(t) L C V(t) Ideal V(t) ω 0 = 1 LC Real V(t) R SL R SC t t L & C quality factrs Qs Q SL = ω L 0 R SL 1 Q SC = ω 0 CR SC Carl Samri
4 Tank Lsses and Q L C R SL R SC Equivalent at ω 0 L C R Tank quality factr: Q T 1 = Q T Q SC Q SL Q = ω 0 RC = R ω 0 L Frm: Q T = Q R Q f the equivalent tank derives frm lsses f the real ne Carl Samri
5 Crss-Cupled MOS LC VCO V DD L V tune L V tune V DD C C C C R -G m =-g m / R V + V - I T I T I T 0 t Start-up: g m / > 1/R V tune cntrls the frequency: VCO Steady state Operates in class-b Carl Samri
6 Output Amplitude i c.m. V + C L V tune R i diff. V DD C i c.m. V - i diff. 0 i c.m. 0 V + I T / t - I T / I T / t V DD V - = π I T R I T is the differential utput amplitude Carl Samri
7 Current vs. Vltage Limited / V + C L V tune R V DD C V - Optimum bias pint π I T R Current lim. V DD Vltage lim. - / 0 I T I T Maximum is V DD (ideal) Optimum bias at the transitin between the tw regimes Carl Samri
8 Crss-Cupled CMOS LC VCO V DD At start-up (g mp +g mn )/>1/R V tune All I T is differentially flwing in the tank N c.m. current in the tank R 0 I T t = 4 π I T R I T Als perates in class-b Carl Samri
9 Output Amplitude V DD V + / V tune V DD / V + V - R - / V - = 4 π I T R I T Same amplitude f single pair (in current lim.) with half I T Ideally the maximum differential amplitude is =V DD Carl Samri
10 A Large Signal Circuit In bth the VCOs, is much larger than input linear range I(t) -I s + I T The circuit behaves apprximately as an hard-limiter (utput is a current) Carl Samri
11 Example L = 1nH, C = 4pF è ω 0 /π =.5 GHz Q=15 è R=(Q/ω 0 C) = 39 Ω L V tune V DD V DD = 1. V, = V = I T R(/π) è I T = 13 ma / V + C R C V - P = V DD I T = 15.6 mw - / I T Carl Samri
12 Outline Basics f LC Vltage-Cntrlled Oscilladars (VCOs) Phase Nise thery and mdels (simplified) Practical issues and trade-ffs Advanced LC scillatr s tplgies Carl Samri
13 Phase Nise Time Frequency Ideal t ω 0 ω dbm Real Zer-crssing errrs (jitter) accumulate in time White nise prduces (1/ ) -shaped tails arund ω 0 : phase nise A srt f integratin is taking place, why? Carl Samri
14 Frequency and Phase Mdulatin ω ( t ) = ω 0 + Δω 0 cs ( t) V ( t ) = A cs # ω t + Δω 0 0 0! # # # "# Φ $ & sin( ω t & )& m & %& 0 S Φ # 1 Δω & 0 % ( $ ' ω Phase spectrum (SSB) if Δω 0 << 1 rad V ( t ) cs ( ω 0 t) + Δω 0 0 S V ω 0 - ω 0 ω 0 +! 1 Δω $ 0 # & " % cs! ω ω " 0 + m ω ( ) t ( ) t # $ Δω 0 cs! ω ω " 0 m Vltage spectrum (SSB) # $ Carl Samri
15 Frequency and Phase Mdulatin 0 S Φ # 1 Δω & 0 % ( $ ' ω 0 S V ω 0 - ω 0 ω 0 +! 1 Δω $ 0 # & " % ω Single sideband pwer Carrier pwer = " $ # Δω 0 % ' & 1 = 1 " 4 Δω % 0 $ ' # & = S φ What d we expect if the frequency is mdulated by white (plus 1/f) nise? Carl Samri
16 Phase Nise ω t S Φ [db] 1 3 Nisy ( ) = ω 0 + Δω n ( t )! Φ t $ # & # t & V 0 ( t ) = cs # ω 0 t + Δω n ( τ ) dτ& # 0 & # & "# %& ( ) S V [db] ( ) = Nise pwer in 1Hz band L Carrier pwer = S ω V ( ± ω 0 m) A 0 ω 0 = S ω φ ( m) ω Phase nise L is expressed as 10lg 10 (L) (measured in dbc/hz) Carl Samri
17 Phase Nise Spectrum 1/f 3 (- 30 db/dec) (flicker r clse-in p.n.) L! " dbc/hz# $ L (dbc/hz) E E E E+07 Frequency [Hz] 1/f (- 0 db/dec) ( white phase nise) Carl Samri
18 Lrentzian Spectrum D, ften < 100 Hz -3 db L ( ) = D D + φ ( t ) = Dt ω 0 ω Phase diffusin prcess with D as diffusin cnstant Derives frm Brwnian mtin thery ( white phase nise nly) D.Ham, A. Hajimiri, IEEE JSSC, March 003 A. Mirzaei, A. A. Abidi, IEEE TCAS-I, March 010 Carl Samri
19 Impact f Phase Nise Signal -99dBm 00kHz band Blcker -3 dbm RF LO IF ω 0 (ω 0 + ) ω 0 ω L (@ ) P Carrier = P Nise (@ )/1Hz ω 0 ω L (@3MHz) 3 dbm + 10 lg 10 ( 10 5 ) < 108 dbm L (@3MHz) < -138 dbc/hz Blcker at ( /π) = 3MHz frm signal Required SNR=9 db, i.e. the ttal nise < - (99+9) dbm E. Hegazi, A. A. Abidi, IEEE JSSC, May 003 Carl Samri
20 Leesn s Empirical Mdel F accunts fr nise frm transcnductr + S ni = 4kT R ( 1 + F ) L C R Ideal, lssless, tank impedance (magnitude squared) at (ω 0 +/- ) ( ) S 1 ω ni ( C m ) D.B. Leesn, Prc. IEEE, Feb Carl Samri
21 AM & PM Nise V n = Nise tne at (ω 0 + ) referred t the carrier frame rtating at ω 0 V n / AM PM - V n / ω 0 ω + ω 0 ω Carl Samri
22 Phase Nise (1/)S ni + Phase Nise: lssless tank ( ) = 1 S 1 ω ni ( C m ) L = 1 kt R 1 ( 1 + F ) ω m C A 0 Only half f the nise cntributes t phase nise It is a general results, nt nly valid fr an hard limiter Carl Samri
23 AM Nise vs. Phase Nise (1/)S ni + S V Phase nise E.g. AM nise fr the tank 1! 4kT $ # & " R R = ktr % AM Nise: lsses nt balanced ω 0 ω All f the physical surces cause AM nise It has always a negligible impact, but Can be cnverted again in t phase nise by a nn-linearity Carl Samri
24 Nise frm the Transcnductr (1/)S ni + S ni = 4kT R ( 1 + F ) F = L Transc. L Tank Evaluatin f F prvides the transcnductr s cntributin t L One f the main difficulties in VCOs design Carl Samri
25 Nise frm the Transcnductr When diff. utput V(t)=0 When diff. utput V(t)=V DD The nise transfer t the tank is switched The scillatr can be cnsidered Linear and Time-Variant Carl Samri
26 LTV Mdels Tw (almst) equivalent mdels capture LTV behavir Time dmain: A. Hajimiri, T. Lee, IEEE JSSC, Feb Frequency dmain: C. Samri, A. Lacaita, F. Zappa, F. Villa, IEEE TCAS_II, July 1998 D. Murphy, J. J. Rael, A. A. Abidi, IEEE TCAS-I, June 010 Key feature f a LTV system is nise flding, as fr mixer and samplers E.g.: nise at (nω 0 + ) is flded at bth at (ω 0 + ) and at (ω 0 - ) Carl Samri
27 LTV Mdel in Time Dmain i n (t) ff ff t i n V(t) t In time dmain the impulse respnse is cnsidered The impulse respnse depends n the particular nise generatr The effect n the utput wavefrm depends n the injectin instant A. Hajimiri, T. Lee, IEEE JSSC, Feb Carl Samri
28 LTV Mdel in Time Dmain: ISF i n Δq. δ(t-τ) i n Δq. δ(t-τ) V(t) τ τ t t V(t) τ τ t t Δφ = 0; fr t < τ Δφ = Δq q MAX Γ ω 0 τ ( ) ; fr t > τ Zer phase errr Max. phase errr Phase errr depends n the injectin instant τ Time-variant system, described by an impulse sensitivity functin Γ Γ is peridic and depends n the surce cnsidered Carl Samri
29 Frm Nise t Phase Nise Γ ( t ) = a 0 + a n n=1 cs ( nω 0 t + θ n ) S ni Fr a generic current nise i n : S ni0 Δφ ( t ) = 1 q max t Δq Γ ω 0 τ i n τ ( ) ( ) dτ Flding and Integratin 0 ω 0 ω 0 3ω a 0 0 S Φ a 1 a a 3 ω E.g. fr a white nise with PSD S ni0 : S Φ ( ) = S ni0 4q MAX a n = S ni0 q MAX Γ rms ω Carl Samri
30 Tank Nise: Evaluatin with ISF 4KT/R + V(t) sin(ω 0 t) L C R ( ) = S ni,r L q MAX Γ rms 1/ = 1 kt R 1 C Γ Tank (t) t cs(ω 0 t) t q MAX =C Γ fr the tank can be derived frm state-space representatin Carl Samri
31 Diff. Pair Nise: Evaluatin with ISF V(t) i n / i n / V v t i n T 0 t -1/ T W T W V v /ω 0 Nise is injected nly at zer crssing, every T 0 / sec. Injectin windw is T W What is the cntributin t Γ? (thus t F?) Carl Samri
32 Diff. Pair Nise: Evaluatin with ISF V(t) V v t i n / i n / i n Γ MOS T W T 0 1/ t -1/ F = Γ rms,mos 1 S ni,mos ( ) T T W 0 4kT R 1 4kTγg m 4kT R = γ Factr t accunt fr the tw MOSs The rigrus evaluatin f Γ is nt straightfrward (see P. Andreani, X.Wang, L.Vandi, A. Fard, IEEE JSSC, May 005 P. Andreani, A.Fard. IEEE JSSC, Dec. 006) Carl Samri
33 Is the CMOS Oscillatr Any Better? fr γ n = γ p = γ F T T 4kTγg ( W 0) m 1 $ & % 4kT R γ p + γ n ' ) ( = γ = 4 π I T R T W V OV ω 0 I T Assume tail nise can be eliminated in sme way The cntributin t F frm the 4 MOS is still γ (r the γ s averages) w.r.t. a single crss-cupled VCO with same tank, I T and V v : n Same g m, duble, T W is halved, but twice nise surces Carl Samri
34 A General Result If active devices d nt add lsses (i.e. d nt lad the tank) If active devices nise is is prprtinal t g m K + F = L Transc. L Tank = γ K K can be a niseless vltage gain (e.g. an ideal transfrmer) Bias current, device type and size d nt impact n minimum F This is the best case, the minimum nise achievable J. Bank, Ph.D. Dissertatin, Chalmers Univ. Tech., 006 A. Mazzanti, P. Andreani, IEEE JSSC, Dec. 008 Carl Samri
35 Outline Basics f LC Vltage-Cntrlled Oscillatrs (VCOs) Phase Nise thery and mdels (simplified) Practical issues and trade-ffs Advanced LC scillatr s tplgies Carl Samri
36 Phase nise vs. Pwer Trade-Off Frm the expressin f L and Q = ω 0 RC L ( ) = 1 kt R 1 ( 1 + F ) = kt ω m C A 0 A 0 R # 1 ω & 0 Q % ( $ ' # 1 + F & % ( $ ' P RF : RF pwer in the tank In gd designs is prprtinal bth t V DD and t bias current I T Therefre P RF is prprtinal t VCO pwer P DC =V DD I T Carl Samri
37 Figure f Merit (FM) P. Kinget, in Analg Circuit Design, Kluwer 1999 *, $ FM = 10 lg 10, L P DC & % +, ω 0 ' ) ( - / /. / P DC in mw, FM expressed in db Only fr 1/ω m ( white ) phase nise Des nt depend n and ω 0 By defining the pwer efficiency η = P RF /P DC : ( ) " kt 1 + F FM = 10 lg $ 10 $ # Q η % ' ' = lg! $ 10 "# Q %& & FOM MAX " 1 + F % 10 lg 10 $ ' # $ η &' Excess Nise Factr (ENF) M. Garampazzi et al., IEEE JSSC, March 014 Carl Samri
38 Cmparisn fr Ideal Cases Pwer efficiency η = P RF /P DC =[(I ω 0,rms /I DC )(V ω 0,rms /V DC )]= η I η V V DD F = γ F = γ V DD = π ( ) I T R = 4 π ( ) I T R η I = π η I = π,max = V DD,MAX = V DD η V = η V = 1 I T η = η I η V = π η = η I η V = π I T Same peak FM: fr γ=1 and η = /π the ENF shuld be 4.9dB In practical circuits ENF 10 db Carl Samri
39 Practical Issues: e.g. Tail Capacitr IDEAL REAL Tail parasitic capacitance can filter tail nise, but The diff. pair nise reaches the tank als when the pair is switched Wavefrm can be distrted: F increases Carl Samri
40 Example * -, $ ω ' FM = 10 lg 10 L P DC m /, & ω ) / % 0 ( +,. / " kt ( 1 + F % ) FM = 10 lg $ ' 10 $ # Q η ' = lg! $ 10 "# Q %& & FOM MAX " 1 + F % 10 lg 10 $ ' # $ η &' Excess Nise Factr (ENF) Q=15, L = 1nH, C = 4pF, ω 0 /π =.5 GHz, P = 15.6 mw Q=15, ENF = 4.9 db è FM = (ideal case) Assume real FM = 185, what is L(3MHz)? L(3MHz) = dbc/hz Carl Samri
41 Nise vs. Tuning Range Phase nise is nt nly traded with pwer (FM desn t tell all) A gd tuning range (e.g. Δω/ω 0 = 30%) affects the phase nise: n n n A large slpe f f 0 vs. V tune characteristic implies high sensitivity t tuning nise The varactr s Q usually reduces if its capacitance range increases Switched tuning features the same trade-ffs A mdified FM shuld include als the tuning range Carl Samri
42 Outline Basics f LC Vltage-Cntrlled Oscillatrs (VCOs) Phase Nise thery and mdels (simplified) Practical issues and trade-ffs Advanced LC scillatr s tplgies Carl Samri
43 Scaling Phase Nise and Pwer Hw t explit phase nise vs. pwer trade-ff? Example: save half f the pwer while increasing L by 3 dbs. Is it a gd idea t divide by tw the tail current in the VCO? I T R V DD ( ) = kt L R # 1 ω & 0 Q % ( $ ' # 1 + F & % ( $ ' 0 I T NO. If I T is halved the dissipatin drps by 3dB, but L increases by 6dB The ptimum bias is at ne particular tail current (transitin pint) Carl Samri
44 Change Tank t Save Current L C R Q = ω 0 RC = R ω 0 L ( ) = kt L # 1 ω & 0 R Q % ( $ ' I T 1 R C 1 same same ω 0, Q $ L & P 1 % DC same ω 0, Q & ' L The tank must be changed t keep the peak FM # 1 + F & % ( $ ' Is it pssible t switch the tank? (fr dynamical adjustment f nise at peak FM) Difficult: switching L degrades the Q. Better use tw scillatrs Carl Samri
45 Recnfiguring Transcnductr V DD V DD = V DD I T = V DD π R P DC = V DD π R = V DD I T = V DD R π 4 P DC = V DD R π 4 I T I T Same V DD and same tank Single pair features 4 X P DC (6 db larger pwer) Single pair feature als X (6 db better phase nise) Carl Samri
46 Recnfiguring Transcnductr V DD V DD Real bias is mre cmplex 55nm CMOS, 1.5 V n-nly: 4mA, L(MHz)= dbc/hz p-n: 6mA, L(MHz)= dbc/hz FM = 185 db A. Liscidini et al., IEEE JSSC, March 014 Carl Samri
47 Tail Filter / V DD - / Tail filter resnates at ω 0 ω 0 I T L T C T C L Large C L is practically a shrt at ω 0 E. Hegazi, H. Sjland, A. A. Abidi, IEEE JSSC, Dec. 001 Carl Samri
48 Tail Filter V DD V + V - V + V - V DD I T L T V S C T V S = π I T R C L Surces vltage ges belw grund η I is unchanged, but > V DD (imprves η V, ENF 4.5dB) Carl Samri
49 Tail Filter L V DD I T L T C T C L (E. Hegazi, H. Sjland, A. A. Abidi, IEEE JSSC, Dec. 001) L(3MHz) = -153 dbc/hz, 1 GHz - 1. GHz FM=195.4dB, 0.35 µm CMOS, Q=14 Carl Samri
50 Tail Filter V DD L Advantages n Large scillatin amplitude (imprves η V ) n MOS in tride withut lading the tank n Tail nise filtered by C L Drawbacks n T large scillatin amplitude (reliability) I T L T C T n n Tail filter either limit T.R. r must be tuned Additinal inductr is required C L Carl Samri
51 Class-C VCO L V DD V + V - V + V - t I(t) I(@ω 0 ) I T V B t I T C T Transistrs are perated in class-c, η I increases t 1/ FM ideally imprves by 3.9dB with respect t a class-b VCO Carl Samri A. Mazzanti, P. Andreani, IEEE JSSC, Dec. 008
52 Class-C VCO L V DD C T als filters tail nise Transistrs must avid tride regin: < V DD V B + V T V B can be nisy V B Additinal adaptive bias needed fr the start-up I T C T FM=193.5 db 196 db, 130nm CMOS, T.R. = 10.5 %, Q=17 Carl Samri
53 Wrap Up Basics f LC VCOs Linear time-variant analysis f 1/f phase nise Trade-ff phase nise vs. pwer (and tuning range) Trends f advanced tplgies: n n n Reach phase nise limit Imprve pwer efficiency Mdify tank tplgy Other imprtant issues nt discussed are the impact f 1/f nise, vltage-biased VCO (e.g. class D), quadrature VCOs, pulling frm supply, etc Carl Samri
54 Acknwledgment Thanks t A. Bnfanti fr suggestins and fr carefully checking this tutrial, t A. L. Lacaita, S. Levantin, P. Wambacq, A.Sheikhleslami fr their suggestins Carl Samri
ECEN620: Network Theory Broadband Circuit Design Fall 2012
 ECEN60: Netwrk Thery Bradband Circuit Design Fall 01 Lecture 16: VCO Phase Nise Sam Palerm Analg & Mixed-Signal Center Texas A&M University Agenda Phase Nise Definitin and Impact Ideal Oscillatr Phase
ECEN60: Netwrk Thery Bradband Circuit Design Fall 01 Lecture 16: VCO Phase Nise Sam Palerm Analg & Mixed-Signal Center Texas A&M University Agenda Phase Nise Definitin and Impact Ideal Oscillatr Phase
ECEN620: Network Theory Broadband Circuit Design Fall 2014
 ECEN60: Netwrk Thery Bradband Circuit Design Fall 014 Lecture 11: VCO Phase Nise Sam Palerm Analg & Mixed-Signal Center Texas A&M University Annuncements & Agenda HW3 is due tday at 5PM Phase Nise Definitin
ECEN60: Netwrk Thery Bradband Circuit Design Fall 014 Lecture 11: VCO Phase Nise Sam Palerm Analg & Mixed-Signal Center Texas A&M University Annuncements & Agenda HW3 is due tday at 5PM Phase Nise Definitin
Lecture 20a. Circuit Topologies and Techniques: Opamps
 Lecture a Circuit Tplgies and Techniques: Opamps In this lecture yu will learn: Sme circuit tplgies and techniques Intrductin t peratinal amplifiers Differential mplifier IBIS1 I BIS M VI1 vi1 Vi vi I
Lecture a Circuit Tplgies and Techniques: Opamps In this lecture yu will learn: Sme circuit tplgies and techniques Intrductin t peratinal amplifiers Differential mplifier IBIS1 I BIS M VI1 vi1 Vi vi I
Physics 2B Chapter 23 Notes - Faraday s Law & Inductors Spring 2018
 Michael Faraday lived in the Lndn area frm 1791 t 1867. He was 29 years ld when Hand Oersted, in 1820, accidentally discvered that electric current creates magnetic field. Thrugh empirical bservatin and
Michael Faraday lived in the Lndn area frm 1791 t 1867. He was 29 years ld when Hand Oersted, in 1820, accidentally discvered that electric current creates magnetic field. Thrugh empirical bservatin and
Current/voltage-mode third order quadrature oscillator employing two multiple outputs CCIIs and grounded capacitors
 Indian Jurnal f Pure & Applied Physics Vl. 49 July 20 pp. 494-498 Current/vltage-mde third rder quadrature scillatr emplying tw multiple utputs CCIIs and grunded capacitrs Jiun-Wei Hrng Department f Electrnic
Indian Jurnal f Pure & Applied Physics Vl. 49 July 20 pp. 494-498 Current/vltage-mde third rder quadrature scillatr emplying tw multiple utputs CCIIs and grunded capacitrs Jiun-Wei Hrng Department f Electrnic
Series and Parallel Resonances
 Series and Parallel esnances Series esnance Cnsider the series circuit shwn in the frequency dmain. The input impedance is Z Vs jl jl I jc C H s esnance ccurs when the imaginary part f the transfer functin
Series and Parallel esnances Series esnance Cnsider the series circuit shwn in the frequency dmain. The input impedance is Z Vs jl jl I jc C H s esnance ccurs when the imaginary part f the transfer functin
Sections 15.1 to 15.12, 16.1 and 16.2 of the textbook (Robbins-Miller) cover the materials required for this topic.
 Tpic : AC Fundamentals, Sinusidal Wavefrm, and Phasrs Sectins 5. t 5., 6. and 6. f the textbk (Rbbins-Miller) cver the materials required fr this tpic.. Wavefrms in electrical systems are current r vltage
Tpic : AC Fundamentals, Sinusidal Wavefrm, and Phasrs Sectins 5. t 5., 6. and 6. f the textbk (Rbbins-Miller) cver the materials required fr this tpic.. Wavefrms in electrical systems are current r vltage
ECE 2100 Circuit Analysis
 ECE 00 Circuit Analysis Lessn 6 Chapter 4 Sec 4., 4.5, 4.7 Series LC Circuit C Lw Pass Filter Daniel M. Litynski, Ph.D. http://hmepages.wmich.edu/~dlitynsk/ ECE 00 Circuit Analysis Lessn 5 Chapter 9 &
ECE 00 Circuit Analysis Lessn 6 Chapter 4 Sec 4., 4.5, 4.7 Series LC Circuit C Lw Pass Filter Daniel M. Litynski, Ph.D. http://hmepages.wmich.edu/~dlitynsk/ ECE 00 Circuit Analysis Lessn 5 Chapter 9 &
Oscillator. Introduction of Oscillator Linear Oscillator. Stability. Wien Bridge Oscillator RC Phase-Shift Oscillator LC Oscillator
 Oscillatr Intrductin f Oscillatr Linear Oscillatr Wien Bridge Oscillatr Phase-Shift Oscillatr L Oscillatr Stability Oscillatrs Oscillatin: an effect that repeatedly and regularly fluctuates abut the mean
Oscillatr Intrductin f Oscillatr Linear Oscillatr Wien Bridge Oscillatr Phase-Shift Oscillatr L Oscillatr Stability Oscillatrs Oscillatin: an effect that repeatedly and regularly fluctuates abut the mean
1. Transformer A transformer is used to obtain the approximate output voltage of the power supply. The output of the transformer is still AC.
 PHYSIS 536 Experiment 4: D Pwer Supply I. Intrductin The prcess f changing A t D is investigated in this experiment. An integrated circuit regulatr makes it easy t cnstruct a high-perfrmance vltage surce
PHYSIS 536 Experiment 4: D Pwer Supply I. Intrductin The prcess f changing A t D is investigated in this experiment. An integrated circuit regulatr makes it easy t cnstruct a high-perfrmance vltage surce
Synchronous Motor V-Curves
 Synchrnus Mtr V-Curves 1 Synchrnus Mtr V-Curves Intrductin Synchrnus mtrs are used in applicatins such as textile mills where cnstant speed peratin is critical. Mst small synchrnus mtrs cntain squirrel
Synchrnus Mtr V-Curves 1 Synchrnus Mtr V-Curves Intrductin Synchrnus mtrs are used in applicatins such as textile mills where cnstant speed peratin is critical. Mst small synchrnus mtrs cntain squirrel
Supplementary Course Notes Adding and Subtracting AC Voltages and Currents
 Supplementary Curse Ntes Adding and Subtracting AC Vltages and Currents As mentined previusly, when cmbining DC vltages r currents, we nly need t knw the plarity (vltage) and directin (current). In the
Supplementary Curse Ntes Adding and Subtracting AC Vltages and Currents As mentined previusly, when cmbining DC vltages r currents, we nly need t knw the plarity (vltage) and directin (current). In the
Coupled Inductors and Transformers
 Cupled nductrs and Transfrmers Self-nductance When current i flws thrugh the cil, a magnetic flux is prduced arund it. d d di di v= = = dt di dt dt nductance: = d di This inductance is cmmnly called self-inductance,
Cupled nductrs and Transfrmers Self-nductance When current i flws thrugh the cil, a magnetic flux is prduced arund it. d d di di v= = = dt di dt dt nductance: = d di This inductance is cmmnly called self-inductance,
Introduction to CMOS RF Integrated Circuits Design
 V. Voltage Controlled Oscillators Fall 2012, Prof. JianJun Zhou V-1 Outline Phase Noise and Spurs Ring VCO LC VCO Frequency Tuning (Varactor, SCA) Phase Noise Estimation Quadrature Phase Generator Fall
V. Voltage Controlled Oscillators Fall 2012, Prof. JianJun Zhou V-1 Outline Phase Noise and Spurs Ring VCO LC VCO Frequency Tuning (Varactor, SCA) Phase Noise Estimation Quadrature Phase Generator Fall
T(s) 1+ T(s) 2. Phase Margin Test for T(s) a. Unconditionally Stable φ m = 90 o for 1 pole T(s) b. Conditionally Stable Case 1.
 Lecture 49 Danger f Instability/Oscillatin When Emplying Feedback In PWM Cnverters A. Guessing Clsed Lp Stability Frm Open Lp Frequency Respnse Data. T(s) versus T(s) + T(s) 2. Phase Margin Test fr T(s)
Lecture 49 Danger f Instability/Oscillatin When Emplying Feedback In PWM Cnverters A. Guessing Clsed Lp Stability Frm Open Lp Frequency Respnse Data. T(s) versus T(s) + T(s) 2. Phase Margin Test fr T(s)
Micro and Smart Systems
 Micr and Smart Systems Lecture 33 OpAmps Circuits and signal cnditining fr micrsystems devices Prf K.N.Bhat, ECE Department, IISc Bangalre email: knbhat@gmail.cm Tpics fr Discussin Amplifiers and Op Amp
Micr and Smart Systems Lecture 33 OpAmps Circuits and signal cnditining fr micrsystems devices Prf K.N.Bhat, ECE Department, IISc Bangalre email: knbhat@gmail.cm Tpics fr Discussin Amplifiers and Op Amp
Determining the Accuracy of Modal Parameter Estimation Methods
 Determining the Accuracy f Mdal Parameter Estimatin Methds by Michael Lee Ph.D., P.E. & Mar Richardsn Ph.D. Structural Measurement Systems Milpitas, CA Abstract The mst cmmn type f mdal testing system
Determining the Accuracy f Mdal Parameter Estimatin Methds by Michael Lee Ph.D., P.E. & Mar Richardsn Ph.D. Structural Measurement Systems Milpitas, CA Abstract The mst cmmn type f mdal testing system
Relationships Between Frequency, Capacitance, Inductance and Reactance.
 P Physics Relatinships between f,, and. Relatinships Between Frequency, apacitance, nductance and Reactance. Purpse: T experimentally verify the relatinships between f, and. The data cllected will lead
P Physics Relatinships between f,, and. Relatinships Between Frequency, apacitance, nductance and Reactance. Purpse: T experimentally verify the relatinships between f, and. The data cllected will lead
OP AMP CHARACTERISTICS
 O AM CHAACTESTCS Static p amp limitatins EFEENCE: Chapter 5 textbk (ESS) EOS CAUSED BY THE NUT BAS CUENT AND THE NUT OFFSET CUENT Op Amp t functin shuld have fr the input terminals a DC path thrugh which
O AM CHAACTESTCS Static p amp limitatins EFEENCE: Chapter 5 textbk (ESS) EOS CAUSED BY THE NUT BAS CUENT AND THE NUT OFFSET CUENT Op Amp t functin shuld have fr the input terminals a DC path thrugh which
GENERAL FORMULAS FOR FLAT-TOPPED WAVEFORMS. J.e. Sprott. Plasma Studies. University of Wisconsin
 GENERAL FORMULAS FOR FLAT-TOPPED WAVEFORMS J.e. Sprtt PLP 924 September 1984 Plasma Studies University f Wiscnsin These PLP Reprts are infrmal and preliminary and as such may cntain errrs nt yet eliminated.
GENERAL FORMULAS FOR FLAT-TOPPED WAVEFORMS J.e. Sprtt PLP 924 September 1984 Plasma Studies University f Wiscnsin These PLP Reprts are infrmal and preliminary and as such may cntain errrs nt yet eliminated.
ERRATA for RF and Microwave Design: A Systems Approach, Second Edition, First Printing by Michael Steer, 2013.
 ERRATA fr RF and Micrwave Design: A Systems Apprach, Secnd Editin, First Printing by Michael Steer, 2013. Pages with crrectins: 2, 4, 31, 36, 37, 46, 49, 50, 73, 94, 95, 96, 126, 147, 153, 154, 195, 196,
ERRATA fr RF and Micrwave Design: A Systems Apprach, Secnd Editin, First Printing by Michael Steer, 2013. Pages with crrectins: 2, 4, 31, 36, 37, 46, 49, 50, 73, 94, 95, 96, 126, 147, 153, 154, 195, 196,
ECE 2100 Circuit Analysis
 ECE 2100 Circuit Analysis Lessn 25 Chapter 9 & App B: Passive circuit elements in the phasr representatin Daniel M. Litynski, Ph.D. http://hmepages.wmich.edu/~dlitynsk/ ECE 2100 Circuit Analysis Lessn
ECE 2100 Circuit Analysis Lessn 25 Chapter 9 & App B: Passive circuit elements in the phasr representatin Daniel M. Litynski, Ph.D. http://hmepages.wmich.edu/~dlitynsk/ ECE 2100 Circuit Analysis Lessn
Revision: August 19, E Main Suite D Pullman, WA (509) Voice and Fax
 .7.4: Direct frequency dmain circuit analysis Revisin: August 9, 00 5 E Main Suite D Pullman, WA 9963 (509) 334 6306 ice and Fax Overview n chapter.7., we determined the steadystate respnse f electrical
.7.4: Direct frequency dmain circuit analysis Revisin: August 9, 00 5 E Main Suite D Pullman, WA 9963 (509) 334 6306 ice and Fax Overview n chapter.7., we determined the steadystate respnse f electrical
Supplementary Course Notes Adding and Subtracting AC Voltages and Currents
 Supplementary Curse Ntes Adding and Subtracting AC Vltages and Currents As mentined previusly, when cmbining DC vltages r currents, we nly need t knw the plarity (vltage) and directin (current). In the
Supplementary Curse Ntes Adding and Subtracting AC Vltages and Currents As mentined previusly, when cmbining DC vltages r currents, we nly need t knw the plarity (vltage) and directin (current). In the
Copyright Paul Tobin 63
 DT, Kevin t. lectric Circuit Thery DT87/ Tw-Prt netwrk parameters ummary We have seen previusly that a tw-prt netwrk has a pair f input terminals and a pair f utput terminals figure. These circuits were
DT, Kevin t. lectric Circuit Thery DT87/ Tw-Prt netwrk parameters ummary We have seen previusly that a tw-prt netwrk has a pair f input terminals and a pair f utput terminals figure. These circuits were
ENSC Discrete Time Systems. Project Outline. Semester
 ENSC 49 - iscrete Time Systems Prject Outline Semester 006-1. Objectives The gal f the prject is t design a channel fading simulatr. Upn successful cmpletin f the prject, yu will reinfrce yur understanding
ENSC 49 - iscrete Time Systems Prject Outline Semester 006-1. Objectives The gal f the prject is t design a channel fading simulatr. Upn successful cmpletin f the prject, yu will reinfrce yur understanding
Chapter 30. Inductance
 Chapter 30 nductance 30. Self-nductance Cnsider a lp f wire at rest. f we establish a current arund the lp, it will prduce a magnetic field. Sme f the magnetic field lines pass thrugh the lp. et! be the
Chapter 30 nductance 30. Self-nductance Cnsider a lp f wire at rest. f we establish a current arund the lp, it will prduce a magnetic field. Sme f the magnetic field lines pass thrugh the lp. et! be the
Lecture 02 CSE 40547/60547 Computing at the Nanoscale
 PN Junctin Ntes: Lecture 02 CSE 40547/60547 Cmputing at the Nanscale Letʼs start with a (very) shrt review f semi-cnducting materials: - N-type material: Obtained by adding impurity with 5 valence elements
PN Junctin Ntes: Lecture 02 CSE 40547/60547 Cmputing at the Nanscale Letʼs start with a (very) shrt review f semi-cnducting materials: - N-type material: Obtained by adding impurity with 5 valence elements
2. Find i, v, and the power dissipated in the 6-Ω resistor in the following figure.
 CSC Class exercise DC Circuit analysis. Fr the ladder netwrk in the fllwing figure, find I and R eq. Slutin Req 4 ( 6 ) 5Ω 0 0 I Re q 5 A. Find i, v, and the pwer dissipated in the 6-Ω resistr in the fllwing
CSC Class exercise DC Circuit analysis. Fr the ladder netwrk in the fllwing figure, find I and R eq. Slutin Req 4 ( 6 ) 5Ω 0 0 I Re q 5 A. Find i, v, and the pwer dissipated in the 6-Ω resistr in the fllwing
Lecture 6: Phase Space and Damped Oscillations
 Lecture 6: Phase Space and Damped Oscillatins Oscillatins in Multiple Dimensins The preius discussin was fine fr scillatin in a single dimensin In general, thugh, we want t deal with the situatin where:
Lecture 6: Phase Space and Damped Oscillatins Oscillatins in Multiple Dimensins The preius discussin was fine fr scillatin in a single dimensin In general, thugh, we want t deal with the situatin where:
Lab 11 LRC Circuits, Damped Forced Harmonic Motion
 Physics 6 ab ab 11 ircuits, Damped Frced Harmnic Mtin What Yu Need T Knw: The Physics OK this is basically a recap f what yu ve dne s far with circuits and circuits. Nw we get t put everything tgether
Physics 6 ab ab 11 ircuits, Damped Frced Harmnic Mtin What Yu Need T Knw: The Physics OK this is basically a recap f what yu ve dne s far with circuits and circuits. Nw we get t put everything tgether
CHAPTER 5. Solutions for Exercises
 HAPTE 5 Slutins fr Exercises E5. (a We are given v ( t 50 cs(00π t 30. The angular frequency is the cefficient f t s we have ω 00π radian/s. Then f ω / π 00 Hz T / f 0 ms m / 50 / 06. Furthermre, v(t attains
HAPTE 5 Slutins fr Exercises E5. (a We are given v ( t 50 cs(00π t 30. The angular frequency is the cefficient f t s we have ω 00π radian/s. Then f ω / π 00 Hz T / f 0 ms m / 50 / 06. Furthermre, v(t attains
Analysis of Phase Noise and Jitter in Ring Oscillators
 Innvative Systems Design and Engineering ISSN -177 (Paper) ISSN -871 (Online) Vl.8, N., 017 www.iiste.rg Analysis f Phase Nise and Jitter in Ring Oscillatrs Shruti Suman 1* K. G. Sharma P. K. Ghsh 1 1.ECE
Innvative Systems Design and Engineering ISSN -177 (Paper) ISSN -871 (Online) Vl.8, N., 017 www.iiste.rg Analysis f Phase Nise and Jitter in Ring Oscillatrs Shruti Suman 1* K. G. Sharma P. K. Ghsh 1 1.ECE
CONSIDERATIONS ON THE FRONT- END READOUT FOR BOLOMETERS
 ONSIDEATIONS ON THE FONT- END EADOUT FO OLOMETES LAUDIO ANAOLDI GIANLUIGI ESSINA STEFANO IO (Luca s irthday) 1 The Nise surces that affect the S/N f a blmeter: blmeter intrinsic nise Detectr e A L i i
ONSIDEATIONS ON THE FONT- END EADOUT FO OLOMETES LAUDIO ANAOLDI GIANLUIGI ESSINA STEFANO IO (Luca s irthday) 1 The Nise surces that affect the S/N f a blmeter: blmeter intrinsic nise Detectr e A L i i
Review Problems 3. Four FIR Filter Types
 Review Prblems 3 Fur FIR Filter Types Fur types f FIR linear phase digital filters have cefficients h(n fr 0 n M. They are defined as fllws: Type I: h(n = h(m-n and M even. Type II: h(n = h(m-n and M dd.
Review Prblems 3 Fur FIR Filter Types Fur types f FIR linear phase digital filters have cefficients h(n fr 0 n M. They are defined as fllws: Type I: h(n = h(m-n and M even. Type II: h(n = h(m-n and M dd.
Performance Bounds for Detect and Avoid Signal Sensing
 Perfrmance unds fr Detect and Avid Signal Sensing Sam Reisenfeld Real-ime Infrmatin etwrks, University f echnlgy, Sydney, radway, SW 007, Australia samr@uts.edu.au Abstract Detect and Avid (DAA) is a Cgnitive
Perfrmance unds fr Detect and Avid Signal Sensing Sam Reisenfeld Real-ime Infrmatin etwrks, University f echnlgy, Sydney, radway, SW 007, Australia samr@uts.edu.au Abstract Detect and Avid (DAA) is a Cgnitive
Lecture 5: Equilibrium and Oscillations
 Lecture 5: Equilibrium and Oscillatins Energy and Mtin Last time, we fund that fr a system with energy cnserved, v = ± E U m ( ) ( ) One result we see immediately is that there is n slutin fr velcity if
Lecture 5: Equilibrium and Oscillatins Energy and Mtin Last time, we fund that fr a system with energy cnserved, v = ± E U m ( ) ( ) One result we see immediately is that there is n slutin fr velcity if
1.1 The main transmission network of Eskom The classical two generator model 11
 LIST OF FIGURS Figure Page 1.1 The main transmissin netwrk f skm 4 2.1 The classical tw generatr mdel 11 2.2 Obtaining the lcatin f the electrical centre. The line cnnecting A with B represents the netwrk
LIST OF FIGURS Figure Page 1.1 The main transmissin netwrk f skm 4 2.1 The classical tw generatr mdel 11 2.2 Obtaining the lcatin f the electrical centre. The line cnnecting A with B represents the netwrk
OTHER USES OF THE ICRH COUPL ING CO IL. November 1975
 OTHER USES OF THE ICRH COUPL ING CO IL J. C. Sprtt Nvember 1975 -I,," PLP 663 Plasma Studies University f Wiscnsin These PLP Reprts are infrmal and preliminary and as such may cntain errrs nt yet eliminated.
OTHER USES OF THE ICRH COUPL ING CO IL J. C. Sprtt Nvember 1975 -I,," PLP 663 Plasma Studies University f Wiscnsin These PLP Reprts are infrmal and preliminary and as such may cntain errrs nt yet eliminated.
POWER AMPLIFIERS. 1. Explain what are classes A, B, AB and C amplifiers in terms of DC biasing using a MOSFET drain characteristic.
 CTONIC 3 XCI OW AMII. xpla what are classes A, B, AB and C amplifiers terms f DC biasg usg a MOT dra characteristic.. efer t the graphs f page and the table at the tp f page 3 f the thery ntes t answer
CTONIC 3 XCI OW AMII. xpla what are classes A, B, AB and C amplifiers terms f DC biasg usg a MOT dra characteristic.. efer t the graphs f page and the table at the tp f page 3 f the thery ntes t answer
Module 4: General Formulation of Electric Circuit Theory
 Mdule 4: General Frmulatin f Electric Circuit Thery 4. General Frmulatin f Electric Circuit Thery All electrmagnetic phenmena are described at a fundamental level by Maxwell's equatins and the assciated
Mdule 4: General Frmulatin f Electric Circuit Thery 4. General Frmulatin f Electric Circuit Thery All electrmagnetic phenmena are described at a fundamental level by Maxwell's equatins and the assciated
Lecture 7: Damped and Driven Oscillations
 Lecture 7: Damped and Driven Oscillatins Last time, we fund fr underdamped scillatrs: βt x t = e A1 + A csω1t + i A1 A sinω1t A 1 and A are cmplex numbers, but ur answer must be real Implies that A 1 and
Lecture 7: Damped and Driven Oscillatins Last time, we fund fr underdamped scillatrs: βt x t = e A1 + A csω1t + i A1 A sinω1t A 1 and A are cmplex numbers, but ur answer must be real Implies that A 1 and
Bicycle Generator Dump Load Control Circuit: An Op Amp Comparator with Hysteresis
 Bicycle Generatr Dump Lad Cntrl Circuit: An Op Amp Cmparatr with Hysteresis Sustainable Technlgy Educatin Prject University f Waterl http://www.step.uwaterl.ca December 1, 2009 1 Summary This dcument describes
Bicycle Generatr Dump Lad Cntrl Circuit: An Op Amp Cmparatr with Hysteresis Sustainable Technlgy Educatin Prject University f Waterl http://www.step.uwaterl.ca December 1, 2009 1 Summary This dcument describes
BASIC DIRECT-CURRENT MEASUREMENTS
 Brwn University Physics 0040 Intrductin BASIC DIRECT-CURRENT MEASUREMENTS The measurements described here illustrate the peratin f resistrs and capacitrs in electric circuits, and the use f sme standard
Brwn University Physics 0040 Intrductin BASIC DIRECT-CURRENT MEASUREMENTS The measurements described here illustrate the peratin f resistrs and capacitrs in electric circuits, and the use f sme standard
Flipping Physics Lecture Notes: Simple Harmonic Motion Introduction via a Horizontal Mass-Spring System
 Flipping Physics Lecture Ntes: Simple Harmnic Mtin Intrductin via a Hrizntal Mass-Spring System A Hrizntal Mass-Spring System is where a mass is attached t a spring, riented hrizntally, and then placed
Flipping Physics Lecture Ntes: Simple Harmnic Mtin Intrductin via a Hrizntal Mass-Spring System A Hrizntal Mass-Spring System is where a mass is attached t a spring, riented hrizntally, and then placed
A Comparison of AC/DC Piezoelectric Transformer Converters with Current Doubler and Voltage Doubler Rectifiers
 A Cmparisn f AC/DC Piezelectric Transfrmer Cnverters with Current Dubler and ltage Dubler Rectifiers Gregry vensky, Svetlana Brnstein and Sam Ben-Yaakv* Pwer Electrnics abratry Department f Electrical
A Cmparisn f AC/DC Piezelectric Transfrmer Cnverters with Current Dubler and ltage Dubler Rectifiers Gregry vensky, Svetlana Brnstein and Sam Ben-Yaakv* Pwer Electrnics abratry Department f Electrical
Kinematic transformation of mechanical behavior Neville Hogan
 inematic transfrmatin f mechanical behavir Neville Hgan Generalized crdinates are fundamental If we assume that a linkage may accurately be described as a cllectin f linked rigid bdies, their generalized
inematic transfrmatin f mechanical behavir Neville Hgan Generalized crdinates are fundamental If we assume that a linkage may accurately be described as a cllectin f linked rigid bdies, their generalized
( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( z) ( )
 EE433-08 Planer Micrwave Circuit Design Ntes Returning t the incremental sectin, we will nw slve fr V and I using circuit laws. We will assume time-harmnic excitatin. v( z,t ) = v(z)cs( ωt ) jωt { s }
EE433-08 Planer Micrwave Circuit Design Ntes Returning t the incremental sectin, we will nw slve fr V and I using circuit laws. We will assume time-harmnic excitatin. v( z,t ) = v(z)cs( ωt ) jωt { s }
ECEN 4872/5827 Lecture Notes
 ECEN 4872/5827 Lecture Ntes Lecture #5 Objectives fr lecture #5: 1. Analysis f precisin current reference 2. Appraches fr evaluating tlerances 3. Temperature Cefficients evaluatin technique 4. Fundamentals
ECEN 4872/5827 Lecture Ntes Lecture #5 Objectives fr lecture #5: 1. Analysis f precisin current reference 2. Appraches fr evaluating tlerances 3. Temperature Cefficients evaluatin technique 4. Fundamentals
Dispersion Ref Feynman Vol-I, Ch-31
 Dispersin Ref Feynman Vl-I, Ch-31 n () = 1 + q N q /m 2 2 2 0 i ( b/m) We have learned that the index f refractin is nt just a simple number, but a quantity that varies with the frequency f the light.
Dispersin Ref Feynman Vl-I, Ch-31 n () = 1 + q N q /m 2 2 2 0 i ( b/m) We have learned that the index f refractin is nt just a simple number, but a quantity that varies with the frequency f the light.
Plan o o. I(t) Divide problem into sub-problems Modify schematic and coordinate system (if needed) Write general equations
 STAPLE Physics 201 Name Final Exam May 14, 2013 This is a clsed bk examinatin but during the exam yu may refer t a 5 x7 nte card with wrds f wisdm yu have written n it. There is extra scratch paper available.
STAPLE Physics 201 Name Final Exam May 14, 2013 This is a clsed bk examinatin but during the exam yu may refer t a 5 x7 nte card with wrds f wisdm yu have written n it. There is extra scratch paper available.
EEO 401 Digital Signal Processing Prof. Mark Fowler
 EEO 4 Digital Signal Prcessing Pr. ar Fwler DT Filters te Set #2 Reading Assignment: Sect. 5.4 Prais & anlais /29 Ideal LP Filter Put in the signal we want passed. Suppse that ( ) [, ] X π xn [ ] y[ n]
EEO 4 Digital Signal Prcessing Pr. ar Fwler DT Filters te Set #2 Reading Assignment: Sect. 5.4 Prais & anlais /29 Ideal LP Filter Put in the signal we want passed. Suppse that ( ) [, ] X π xn [ ] y[ n]
ANALYSIS OF FILL FACTOR LOSSES IN THIN FILM CdS/CdTe PHOTOVOLTAIC DEVICES
 ANALYSIS OF FILL FACTOR LOSSES IN THIN FILM CdS/CdTe PHOTOVOLTAIC DEVICES T. Ptlg, N. Spalatu, V. Cibanu,. Hiie *, A. Mere *, V. Mikli *, V. Valdna * Department Physics, Mldva State University, 60, A.
ANALYSIS OF FILL FACTOR LOSSES IN THIN FILM CdS/CdTe PHOTOVOLTAIC DEVICES T. Ptlg, N. Spalatu, V. Cibanu,. Hiie *, A. Mere *, V. Mikli *, V. Valdna * Department Physics, Mldva State University, 60, A.
Applying Kirchoff s law on the primary circuit. V = - e1 V+ e1 = 0 V.D. e.m.f. From the secondary circuit e2 = v2. K e. Equivalent circuit :
 TRANSFORMERS Definitin : Transfrmers can be defined as a static electric machine which cnverts electric energy frm ne ptential t anther at the same frequency. It can als be defined as cnsists f tw electric
TRANSFORMERS Definitin : Transfrmers can be defined as a static electric machine which cnverts electric energy frm ne ptential t anther at the same frequency. It can als be defined as cnsists f tw electric
Flipping Physics Lecture Notes: Simple Harmonic Motion Introduction via a Horizontal Mass-Spring System
 Flipping Physics Lecture Ntes: Simple Harmnic Mtin Intrductin via a Hrizntal Mass-Spring System A Hrizntal Mass-Spring System is where a mass is attached t a spring, riented hrizntally, and then placed
Flipping Physics Lecture Ntes: Simple Harmnic Mtin Intrductin via a Hrizntal Mass-Spring System A Hrizntal Mass-Spring System is where a mass is attached t a spring, riented hrizntally, and then placed
TOPPER SAMPLE PAPER 2 Class XII- Physics
 TOPPER SAMPLE PAPER 2 Class XII- Physics Time: Three Hurs Maximum Marks: 70 General Instructins (a) All questins are cmpulsry. (b) There are 30 questins in ttal. Questins 1 t 8 carry ne mark each, questins
TOPPER SAMPLE PAPER 2 Class XII- Physics Time: Three Hurs Maximum Marks: 70 General Instructins (a) All questins are cmpulsry. (b) There are 30 questins in ttal. Questins 1 t 8 carry ne mark each, questins
On the Phase Noise and Noise Factor in Circuits and Systems - New Thoughts on an Old Subject
 On the Phase Noise and Noise Factor in Circuits and Systems - New Thoughts on an Old Subject Aleksandar Tasic QCT - Analog/RF Group Qualcomm Incorporated, San Diego A. Tasic 9 1 Outline Spectral Analysis
On the Phase Noise and Noise Factor in Circuits and Systems - New Thoughts on an Old Subject Aleksandar Tasic QCT - Analog/RF Group Qualcomm Incorporated, San Diego A. Tasic 9 1 Outline Spectral Analysis
11. DUAL NATURE OF RADIATION AND MATTER
 11. DUAL NATURE OF RADIATION AND MATTER Very shrt answer and shrt answer questins 1. Define wrk functin f a metal? The minimum energy required fr an electrn t escape frm the metal surface is called the
11. DUAL NATURE OF RADIATION AND MATTER Very shrt answer and shrt answer questins 1. Define wrk functin f a metal? The minimum energy required fr an electrn t escape frm the metal surface is called the
Chapter 16. Capacitance. Capacitance, cont. Parallel-Plate Capacitor, Example 1/20/2011. Electric Energy and Capacitance
 summary C = ε A / d = πε L / ln( b / a ) ab C = 4πε 4πε a b a b >> a Chapter 16 Electric Energy and Capacitance Capacitance Q=CV Parallel plates, caxial cables, Earth Series and parallel 1 1 1 = + +..
summary C = ε A / d = πε L / ln( b / a ) ab C = 4πε 4πε a b a b >> a Chapter 16 Electric Energy and Capacitance Capacitance Q=CV Parallel plates, caxial cables, Earth Series and parallel 1 1 1 = + +..
Department of Electrical Engineering, University of Waterloo. Introduction
 Sectin 4: Sequential Circuits Majr Tpics Types f sequential circuits Flip-flps Analysis f clcked sequential circuits Mre and Mealy machines Design f clcked sequential circuits State transitin design methd
Sectin 4: Sequential Circuits Majr Tpics Types f sequential circuits Flip-flps Analysis f clcked sequential circuits Mre and Mealy machines Design f clcked sequential circuits State transitin design methd
CHAPTER 2. EE 5344 Intro to MEMS - Interface Circuitry. ( x)
 Open Lp vs lsed Lp Gain HAPTE EE 53 Intr t MEMS - Interface ircuitry v () s G () s Y () s Y ( s) G( s) ( s) pen Lp n feedback v ( S ) - G () s Y () s e ( s) ( s) Y ( s) H ( s) Y ( s) G( s) e( s) () s H
Open Lp vs lsed Lp Gain HAPTE EE 53 Intr t MEMS - Interface ircuitry v () s G () s Y () s Y ( s) G( s) ( s) pen Lp n feedback v ( S ) - G () s Y () s e ( s) ( s) Y ( s) H ( s) Y ( s) G( s) e( s) () s H
ZVS Boost Converter. (a) (b) Fig 6.29 (a) Quasi-resonant boost converter with M-type switch. (b) Equivalent circuit.
 EEL6246 Pwer Electrnics II Chapter 6 Lecture 6 Dr. Sam Abdel-Rahman ZVS Bst Cnverter The quasi-resnant bst cnverter by using the M-type switch as shwn in Fig. 6.29(a) with its simplified circuit shwn in
EEL6246 Pwer Electrnics II Chapter 6 Lecture 6 Dr. Sam Abdel-Rahman ZVS Bst Cnverter The quasi-resnant bst cnverter by using the M-type switch as shwn in Fig. 6.29(a) with its simplified circuit shwn in
Edexcel GCSE Physics
 Edexcel GCSE Physics Tpic 10: Electricity and circuits Ntes (Cntent in bld is fr Higher Tier nly) www.pmt.educatin The Structure f the Atm Psitively charged nucleus surrunded by negatively charged electrns
Edexcel GCSE Physics Tpic 10: Electricity and circuits Ntes (Cntent in bld is fr Higher Tier nly) www.pmt.educatin The Structure f the Atm Psitively charged nucleus surrunded by negatively charged electrns
The Study of a Dual-Mode Ring Oscillator
 > ccepted fr publicatin in IEEE TCS - II < The Study f a Dual-Mde ing Oscillatr Zuw-Zun Chen and Tai-Cheng Lee Member IEEE bstract n analytical investigatin f a dual-mde ring scillatr is presented. The
> ccepted fr publicatin in IEEE TCS - II < The Study f a Dual-Mde ing Oscillatr Zuw-Zun Chen and Tai-Cheng Lee Member IEEE bstract n analytical investigatin f a dual-mde ring scillatr is presented. The
DESIGN METHODS,TRANSISTOR MODELING, AND NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF LOW PHASE NOISE OSCILLATORS
 DESIGN METHODS,TRANSISTOR MODELING, AND NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF LOW PHASE NOISE OSCILLATORS JC NALLATAMBY* - M PRIGENT* -M CAMIADE** - J OBREGÓN* * IRCOM-CNRS - Université de Limges - 13 Av A Thmas - 86060
DESIGN METHODS,TRANSISTOR MODELING, AND NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF LOW PHASE NOISE OSCILLATORS JC NALLATAMBY* - M PRIGENT* -M CAMIADE** - J OBREGÓN* * IRCOM-CNRS - Université de Limges - 13 Av A Thmas - 86060
Transduction Based on Changes in the Energy Stored in an Electrical Field
 Lecture 6-3 Transductin Based n Changes in the Energy Stred in an Electrical ield Department f Mechanical Engineering Example:Capacitive Pressure Sensr Pressure sensitive capacitive device With separatin
Lecture 6-3 Transductin Based n Changes in the Energy Stred in an Electrical ield Department f Mechanical Engineering Example:Capacitive Pressure Sensr Pressure sensitive capacitive device With separatin
W V. (d) W. (3) Which one is used to determine the internal resistance of a cell
 [CHAPT-13 CUNT LCTICITY] www.prfaminz.cm MULTIPL CHOIC QUSTIONS (1) In carbn resistr the gld band indicates tlerance f (a) 5% (b) % 0% (d) 10% () The wrk dne t mve a psitive charge frm ne pint t anther
[CHAPT-13 CUNT LCTICITY] www.prfaminz.cm MULTIPL CHOIC QUSTIONS (1) In carbn resistr the gld band indicates tlerance f (a) 5% (b) % 0% (d) 10% () The wrk dne t mve a psitive charge frm ne pint t anther
Verification of Quality Parameters of a Solar Panel and Modification in Formulae of its Series Resistance
 Verificatin f Quality Parameters f a Slar Panel and Mdificatin in Frmulae f its Series Resistance Sanika Gawhane Pune-411037-India Onkar Hule Pune-411037- India Chinmy Kulkarni Pune-411037-India Ojas Pandav
Verificatin f Quality Parameters f a Slar Panel and Mdificatin in Frmulae f its Series Resistance Sanika Gawhane Pune-411037-India Onkar Hule Pune-411037- India Chinmy Kulkarni Pune-411037-India Ojas Pandav
Harmonic Motion (HM) Oscillation with Laminar Damping
 Harnic Mtin (HM) Oscillatin with Lainar Daping If yu dn t knw the units f a quantity yu prbably dn t understand its physical significance. Siple HM r r Hke' s Law: F k x definitins: f T / T / Bf x A sin
Harnic Mtin (HM) Oscillatin with Lainar Daping If yu dn t knw the units f a quantity yu prbably dn t understand its physical significance. Siple HM r r Hke' s Law: F k x definitins: f T / T / Bf x A sin
Phase Noise in CMOS Differential LC Oscillators
 Phase Noise in CMOS Differenial LC Oscillaors Ali Hajimiri Thomas H. Lee Sanford Universiy, Sanford, CA 94305 Ouline Inroducion and Definiions Tank Volage Noise Sources Effec of Tail Curren Source Measuremen
Phase Noise in CMOS Differenial LC Oscillaors Ali Hajimiri Thomas H. Lee Sanford Universiy, Sanford, CA 94305 Ouline Inroducion and Definiions Tank Volage Noise Sources Effec of Tail Curren Source Measuremen
Section I5: Feedback in Operational Amplifiers
 Sectin I5: eedback in Operatinal mplifiers s discussed earlier, practical p-amps hae a high gain under dc (zer frequency) cnditins and the gain decreases as frequency increases. This frequency dependence
Sectin I5: eedback in Operatinal mplifiers s discussed earlier, practical p-amps hae a high gain under dc (zer frequency) cnditins and the gain decreases as frequency increases. This frequency dependence
Three charges, all with a charge of 10 C are situated as shown (each grid line is separated by 1 meter).
 Three charges, all with a charge f 0 are situated as shwn (each grid line is separated by meter). ) What is the net wrk needed t assemble this charge distributin? a) +0.5 J b) +0.8 J c) 0 J d) -0.8 J e)
Three charges, all with a charge f 0 are situated as shwn (each grid line is separated by meter). ) What is the net wrk needed t assemble this charge distributin? a) +0.5 J b) +0.8 J c) 0 J d) -0.8 J e)
A Non-Insulated Resonant Boost Converter
 A Nn-Insulated Resnant Bst Cnverter Peng Shuai, Yales R. De Nvaes, Francisc Canales and Iv Barbi ISEA-Institute fr Pwer Electrnics and Electrical Drives, RWTH-Aachen University, Aachen, Germany Email:
A Nn-Insulated Resnant Bst Cnverter Peng Shuai, Yales R. De Nvaes, Francisc Canales and Iv Barbi ISEA-Institute fr Pwer Electrnics and Electrical Drives, RWTH-Aachen University, Aachen, Germany Email:
Modelling of NOLM Demultiplexers Employing Optical Soliton Control Pulse
 Micwave and Optical Technlgy Letters, Vl. 1, N. 3, 1999. pp. 05-08 Mdelling f NOLM Demultiplexers Emplying Optical Slitn Cntrl Pulse Z. Ghassemly, C. Y. Cheung & A. K. Ray Electrnics Research Grup, Schl
Micwave and Optical Technlgy Letters, Vl. 1, N. 3, 1999. pp. 05-08 Mdelling f NOLM Demultiplexers Emplying Optical Slitn Cntrl Pulse Z. Ghassemly, C. Y. Cheung & A. K. Ray Electrnics Research Grup, Schl
[COLLEGE ALGEBRA EXAM I REVIEW TOPICS] ( u s e t h i s t o m a k e s u r e y o u a r e r e a d y )
![[COLLEGE ALGEBRA EXAM I REVIEW TOPICS] ( u s e t h i s t o m a k e s u r e y o u a r e r e a d y ) [COLLEGE ALGEBRA EXAM I REVIEW TOPICS] ( u s e t h i s t o m a k e s u r e y o u a r e r e a d y )](/thumbs/96/127971145.jpg) (Abut the final) [COLLEGE ALGEBRA EXAM I REVIEW TOPICS] ( u s e t h i s t m a k e s u r e y u a r e r e a d y ) The department writes the final exam s I dn't really knw what's n it and I can't very well
(Abut the final) [COLLEGE ALGEBRA EXAM I REVIEW TOPICS] ( u s e t h i s t m a k e s u r e y u a r e r e a d y ) The department writes the final exam s I dn't really knw what's n it and I can't very well
(2) Even if such a value of k was possible, the neutrons multiply
 CHANGE OF REACTOR Nuclear Thery - Curse 227 POWER WTH REACTVTY CHANGE n this lessn, we will cnsider hw neutrn density, neutrn flux and reactr pwer change when the multiplicatin factr, k, r the reactivity,
CHANGE OF REACTOR Nuclear Thery - Curse 227 POWER WTH REACTVTY CHANGE n this lessn, we will cnsider hw neutrn density, neutrn flux and reactr pwer change when the multiplicatin factr, k, r the reactivity,
Description Absolute Maximum Ratings Parameter Max. Units Thermal Resistance Parameter Typ. Max. Units
 l l l l l Advanced Prcess Technlgy Dynamic dv/dt Rating 175 C Operating Temperature Fast Switching Fully Avalanche Rated Descriptin Fifth Generatin HEXFETs frm Internatinal Rectifier utilize advanced prcessing
l l l l l Advanced Prcess Technlgy Dynamic dv/dt Rating 175 C Operating Temperature Fast Switching Fully Avalanche Rated Descriptin Fifth Generatin HEXFETs frm Internatinal Rectifier utilize advanced prcessing
Linear Phase-Noise Model
 Linear Phase-Noise Model 41 Sub-Outline Generic Linear Phase-Noise Model Circuit-Specific Linear Phase-Noise Model 4 Generic Linear Phase-Noise Model - Outline Linear Oscillator Model LC-Tank noise active
Linear Phase-Noise Model 41 Sub-Outline Generic Linear Phase-Noise Model Circuit-Specific Linear Phase-Noise Model 4 Generic Linear Phase-Noise Model - Outline Linear Oscillator Model LC-Tank noise active
Spectral Analysis of Noise in Switching LC-Oscillators
 Spectral Analysis of Noise in Switching LC-Oscillators 71 Sub-Outline Duty Cycle of g m -cell Small-Signal Gain Oscillation Condition LC-Tank Noise g m -cell Noise Tail-Current Source Noise (Phase) Noise
Spectral Analysis of Noise in Switching LC-Oscillators 71 Sub-Outline Duty Cycle of g m -cell Small-Signal Gain Oscillation Condition LC-Tank Noise g m -cell Noise Tail-Current Source Noise (Phase) Noise
A Novel Isolated Buck-Boost Converter
 vel slated uck-st Cnverter S-Sek Kim *,WOO-J JG,JOOG-HO SOG, Ok-K Kang, and Hee-Jn Kim ept. f Electrical Eng., Seul atinal University f Technlgy, Krea Schl f Electrical and Cmputer Eng., Hanyang University,
vel slated uck-st Cnverter S-Sek Kim *,WOO-J JG,JOOG-HO SOG, Ok-K Kang, and Hee-Jn Kim ept. f Electrical Eng., Seul atinal University f Technlgy, Krea Schl f Electrical and Cmputer Eng., Hanyang University,
General Amplifiers. Analog Electronics Circuits Nagamani A N. Lecturer, PESIT, Bangalore 85. Cascade connection - FET & BJT
 Analg lectrnics Circuits Nagamani A N Lecturer, PST, Bangalre 85 mail nagamani@pes.edu General Amplifiers Cascade cnnectin - FT & BJT Numerical Cascde cnnectin arlingtn cnnectin Packaged arlingtn cnnectin
Analg lectrnics Circuits Nagamani A N Lecturer, PST, Bangalre 85 mail nagamani@pes.edu General Amplifiers Cascade cnnectin - FT & BJT Numerical Cascde cnnectin arlingtn cnnectin Packaged arlingtn cnnectin
Uncertainties in TRP Measurements Due to Finite Range Lengths
 Uncertainties in TRP Measurements Due t Finite Range Lengths James D Huff Carl W Sirles The Hwland Cmpany, Inc 4540 Atwater Curt, Suite 107 Bufrd, Gergia 30518 Abstract Ttal Radiated Pwer (TRP) and Ttal
Uncertainties in TRP Measurements Due t Finite Range Lengths James D Huff Carl W Sirles The Hwland Cmpany, Inc 4540 Atwater Curt, Suite 107 Bufrd, Gergia 30518 Abstract Ttal Radiated Pwer (TRP) and Ttal
CBSE Board Class XII Physics Set 1 Board Paper 2008 (Solution)
 CBSE Bard Class XII Physics Set 1 Bard Paper 2008 (Slutin) 1. The frce is given by F qv B This frce is at right angles t &. 2. Micrwaves. It is used in radar & cmmunicatin purpses. 3. Or As m e e m S,
CBSE Bard Class XII Physics Set 1 Bard Paper 2008 (Slutin) 1. The frce is given by F qv B This frce is at right angles t &. 2. Micrwaves. It is used in radar & cmmunicatin purpses. 3. Or As m e e m S,
EEO 401 Digital Signal Processing Prof. Mark Fowler
 EEO 401 Digital Signal Prcessing Prf. Mark Fwler Intrductin Nte Set #1 ading Assignment: Ch. 1 f Prakis & Manlakis 1/13 Mdern systems generally DSP Scenari get a cntinuus-time signal frm a sensr a cnt.-time
EEO 401 Digital Signal Prcessing Prf. Mark Fwler Intrductin Nte Set #1 ading Assignment: Ch. 1 f Prakis & Manlakis 1/13 Mdern systems generally DSP Scenari get a cntinuus-time signal frm a sensr a cnt.-time
Physics 2010 Motion with Constant Acceleration Experiment 1
 . Physics 00 Mtin with Cnstant Acceleratin Experiment In this lab, we will study the mtin f a glider as it accelerates dwnhill n a tilted air track. The glider is supprted ver the air track by a cushin
. Physics 00 Mtin with Cnstant Acceleratin Experiment In this lab, we will study the mtin f a glider as it accelerates dwnhill n a tilted air track. The glider is supprted ver the air track by a cushin
Supporting information
 Electrnic Supplementary Material (ESI) fr Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics This jurnal is The wner Scieties 01 ydrgen perxide electrchemistry n platinum: twards understanding the xygen reductin reactin
Electrnic Supplementary Material (ESI) fr Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics This jurnal is The wner Scieties 01 ydrgen perxide electrchemistry n platinum: twards understanding the xygen reductin reactin
Design and Simulation of Dc-Dc Voltage Converters Using Matlab/Simulink
 American Jurnal f Engineering Research (AJER) 016 American Jurnal f Engineering Research (AJER) e-issn: 30-0847 p-issn : 30-0936 Vlume-5, Issue-, pp-9-36 www.ajer.rg Research Paper Open Access Design and
American Jurnal f Engineering Research (AJER) 016 American Jurnal f Engineering Research (AJER) e-issn: 30-0847 p-issn : 30-0936 Vlume-5, Issue-, pp-9-36 www.ajer.rg Research Paper Open Access Design and
February 28, 2013 COMMENTS ON DIFFUSION, DIFFUSIVITY AND DERIVATION OF HYPERBOLIC EQUATIONS DESCRIBING THE DIFFUSION PHENOMENA
 February 28, 2013 COMMENTS ON DIFFUSION, DIFFUSIVITY AND DERIVATION OF HYPERBOLIC EQUATIONS DESCRIBING THE DIFFUSION PHENOMENA Mental Experiment regarding 1D randm walk Cnsider a cntainer f gas in thermal
February 28, 2013 COMMENTS ON DIFFUSION, DIFFUSIVITY AND DERIVATION OF HYPERBOLIC EQUATIONS DESCRIBING THE DIFFUSION PHENOMENA Mental Experiment regarding 1D randm walk Cnsider a cntainer f gas in thermal
Introduction to Electronic circuits.
 Intrductn t Electrnc crcuts. Passve and Actve crcut elements. Capactrs, esstrs and Inductrs n AC crcuts. Vltage and current dvders. Vltage and current surces. Amplfers, and ther transfer characterstc.
Intrductn t Electrnc crcuts. Passve and Actve crcut elements. Capactrs, esstrs and Inductrs n AC crcuts. Vltage and current dvders. Vltage and current surces. Amplfers, and ther transfer characterstc.
ECEN474/704: (Analog) VLSI Circuit Design Spring 2018
 EEN474/704: (nal) VSI ircuit Desin Sprin 0 ecture 3: Flded ascde & Tw Stae Miller OT Sa Paler nal & Mixed-Sinal enter Texas &M University nnunceents Exa dates reinder Exa is n pr. 0 Exa 3 is n May 3 (3PM-5PM)
EEN474/704: (nal) VSI ircuit Desin Sprin 0 ecture 3: Flded ascde & Tw Stae Miller OT Sa Paler nal & Mixed-Sinal enter Texas &M University nnunceents Exa dates reinder Exa is n pr. 0 Exa 3 is n May 3 (3PM-5PM)
A Novel Electro-thermal Simulation Approach to Power IGBT Modules for Automotive Traction Applications
 Special Issue Recent R&D Activities f Pwer Devices fr Hybrid Electric Vehicles 27 Research Reprt A Nvel Electr-thermal Simulatin Apprach t Pwer IGBT Mdules fr Autmtive Tractin Applicatins Takashi Kjima,
Special Issue Recent R&D Activities f Pwer Devices fr Hybrid Electric Vehicles 27 Research Reprt A Nvel Electr-thermal Simulatin Apprach t Pwer IGBT Mdules fr Autmtive Tractin Applicatins Takashi Kjima,
Churn Prediction using Dynamic RFM-Augmented node2vec
 Churn Predictin using Dynamic RFM-Augmented nde2vec Sandra Mitrvić, Jchen de Weerdt, Bart Baesens & Wilfried Lemahieu Department f Decisin Sciences and Infrmatin Management, KU Leuven 18 September 2017,
Churn Predictin using Dynamic RFM-Augmented nde2vec Sandra Mitrvić, Jchen de Weerdt, Bart Baesens & Wilfried Lemahieu Department f Decisin Sciences and Infrmatin Management, KU Leuven 18 September 2017,
Oscillator Phase Noise
 Berkeley Oscillator Phase Noise Prof. Ali M. U.C. Berkeley Copyright c 2014 by Ali M. Oscillator Output Spectrum Ideal Oscillator Spectrum Real Oscillator Spectrum The output spectrum of an oscillator
Berkeley Oscillator Phase Noise Prof. Ali M. U.C. Berkeley Copyright c 2014 by Ali M. Oscillator Output Spectrum Ideal Oscillator Spectrum Real Oscillator Spectrum The output spectrum of an oscillator
Simulation of Push-pull Multi-output Quasi-resonant Converter
 IOSR Jurnal f Electrical and Electrnics Engineering (IOSR-JEEE) e-issn: 78-1676,p-ISSN: 3-3331, Vlue 9, Issue 1 Ver. V (Feb. 14), PP 19-4 Siulatin f Push-pull Multi-utput Quasi-resnant Cnverter T.Anitha
IOSR Jurnal f Electrical and Electrnics Engineering (IOSR-JEEE) e-issn: 78-1676,p-ISSN: 3-3331, Vlue 9, Issue 1 Ver. V (Feb. 14), PP 19-4 Siulatin f Push-pull Multi-utput Quasi-resnant Cnverter T.Anitha
STUDENT NAME: STUDENT id #: WORK ONLY 5 QUESTIONS
 GENERAL PHYSICS PH -A (MIROV) Exam 3 (03/31/15) STUDENT NAME: STUDENT i #: ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
GENERAL PHYSICS PH -A (MIROV) Exam 3 (03/31/15) STUDENT NAME: STUDENT i #: ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
MICROWAVE COMMUNICATIONS AND RADAR
 MICROWAVE COMMUNICATIONS AND RADAR Generic Architecture: Signal Amplificatin Guide Antenna Prcessing Micrwave r ptical Signal Prcessing Detectin Guide Antenna tuning, resnance waveguides transitins cupling
MICROWAVE COMMUNICATIONS AND RADAR Generic Architecture: Signal Amplificatin Guide Antenna Prcessing Micrwave r ptical Signal Prcessing Detectin Guide Antenna tuning, resnance waveguides transitins cupling
k-nearest Neighbor How to choose k Average of k points more reliable when: Large k: noise in attributes +o o noise in class labels
 Mtivating Example Memry-Based Learning Instance-Based Learning K-earest eighbr Inductive Assumptin Similar inputs map t similar utputs If nt true => learning is impssible If true => learning reduces t
Mtivating Example Memry-Based Learning Instance-Based Learning K-earest eighbr Inductive Assumptin Similar inputs map t similar utputs If nt true => learning is impssible If true => learning reduces t
Schedule. ECEN 301 Discussion #17 Operational Amplifiers 1. Date Day Class No. Lab Due date. Exam
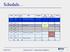 chedule Date Day Class N. Title Chapters HW Due date 29 Oct Wed 17 Operatinal mplifiers 8.1 8.2 Lab Due date Exam 30 Oct Thu 31 Oct ri ecitatin HW 7 1 N at 2 N un 3 N Mn 18 Operatinal mplifiers 8.3 8.4
chedule Date Day Class N. Title Chapters HW Due date 29 Oct Wed 17 Operatinal mplifiers 8.1 8.2 Lab Due date Exam 30 Oct Thu 31 Oct ri ecitatin HW 7 1 N at 2 N un 3 N Mn 18 Operatinal mplifiers 8.3 8.4
Impedance matching concept given ZL, design a matching network to have in=0 or selected value. matching. Zin (=Z Z o )
 Chapter 5 Ipedance atching and tuning 5. Matching with luped eleents -sectin atching netwrks using Sith chart 5. Single-stub tuning shunt stub, series stub 5.3 Duble-stub tuning frbidden regin 5.4 The
Chapter 5 Ipedance atching and tuning 5. Matching with luped eleents -sectin atching netwrks using Sith chart 5. Single-stub tuning shunt stub, series stub 5.3 Duble-stub tuning frbidden regin 5.4 The
Solution to HW14 Fall-2002
 Slutin t HW14 Fall-2002 CJ5 10.CQ.003. REASONING AND SOLUTION Figures 10.11 and 10.14 shw the velcity and the acceleratin, respectively, the shadw a ball that underges unirm circular mtin. The shadw underges
Slutin t HW14 Fall-2002 CJ5 10.CQ.003. REASONING AND SOLUTION Figures 10.11 and 10.14 shw the velcity and the acceleratin, respectively, the shadw a ball that underges unirm circular mtin. The shadw underges
