THE INFLUENCE OF VARIOUS MOBILITY MODELS ON THE ITERATION PROCESS AND SOLUTION OF THE BASIC SEMICONDUCTOR EQUATIONS
|
|
|
- Joseph Randall
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 THE FLUECE OF VAROUS MOBLTY MODELS O THE TERATO PROCESS AD SOLUTO OF THE BASC SEMCODUCTOR EQUATOS 1) 1) 1) A.F.FRAZ, G.A.FRAZ, S.SELBERHERR P.MARKOWCH2) 1) Abteilung Physikalische Elektronik nstitut fur Allgemeine Elektrotechnik und Elektronik 2) nstitut fur Angeandte Mathematik TU Wien, Gui3hausstrai3e 27, A-14 ~Ji en, AUSTRA Abstract A comparison of various ays of modeling the carrier mobilities is presented. Using an already developed to-dimensional semiconductor simulation program e investigate non linear field- and carrier- dependend models. The impact on the discretization of the continuity equations and the calculation of the iteration matrix is discussed. We present simulation results of three different mobility models for a GaAs MESFET. The iteration process and the resulting electron densities are compared. Only ith constant mobility convergence is quadratical. The nonlinear models sho linear convergence behaviour. Considering the electron distributions the differences beteen the models become more evident. The results obtained by the constant mobility model must be completely rejected. A field-dependend model hich is appropriate for silicon devices gives better but not quantitatively reliable results. For accurate physically asserted calculations a negative differential mobility has to be used. 1. ntroduction The basic semiconductor equations contain several.types of physical parameters, eg. the carrier mobilities hich influence the continuity equations directly. Since the nonlinear PDE system is solved by iterative numerical methods the mobilities have to be calculated at each step. Therefore one is interested in simple parameter models to save computer time. But to obtain physically asserted results it is necessary to describe nonlinear field- and carrier- dependend mobility models. This paper investigates the influence of such complex models on the iteration process. An already developped to-dimensional semiconductor device simulation system SCDSS /1/ hich handles externally defined mobilities is applied using various mobility models. n section 2 e describe the discretization of the continuity equations ith respect to the mobilities. The effects of three different models are presented for a GaAs MESFET. Section 3 contains the device geometry and the parameters. We compare the convergence properties and the different physical results in section
2 2. Discretization of the continuity equations For the discretization of the continuity equations one has to calculate the current densities depending on the carrier mobilities. We have used the ell-knon Scharfetter - Gummel discretization in "Finite Boxes" formulation /1/, /2/, presuming constant densities beteen grid points. There the values of the mobilities must be calculated. They are implemented as external functions in order t'j change the models easily such that a high degree of flexibility is achieved. To compute even complex parameter models it is necessary to provide the grid point coordinates, the carrier concentrations, the doping concentration and the components of the electric field and of the current densities in x- and y- direction. For the implemented discretization scheme they must be calculated at the center of the line beteen to neighboured grid points hich is computationally rather time consuming. Since the solution of the nonlinear system of equations is obtained by a eton type method, the Jacobian contains the partial derivatives of the mobilities ith respect to the unknons, namely po~ential and carrier densities. We have investigated the influence of neglecting these partial derivatives. The results have shon no significant loss in the rate of convergence. This fact can save a large amount of computer time because the derivatives have to be calculated numerically. 3. Device geometry and parameter models We used the different mobility models for the computation of a GaAs MESFET. The geometry is shon in Fig. 1. The gate has been recessed into the active layer. The calculations have been done at an operating point of VG= OV and VD= 2V. We investigated three kinds of mobility models. Model 1 describes a typical mobility model for GaAs devices. Model 2 results from an average value of model 1. Model 3 is a mobility model commonly used in simulations of silicon devices. µ + vs.e3/e 4 µ = 56 cm 2 ;vs Mode 1 1 µ = l+(e/e )4 E = 3.5 kv /cm cm/s /4/ Model 2 : µ const = 2 cm2/vs Model 3 µ v (( µo.a +µmin (1-a )) B + ( ~ )S)l/S 1 Ep a l+(u.67.+o.33.n).73 Ep = max (,!.Jn ) ijnl µo µmin o vs 1429 cm2;vs 55.2 cm2;vs + - U + A 117 cm cm/s /3/ B -2 The resulting v(e) characteristics are plotted in Fig
3 4. Results We investigated the numerical behaviour and the physical impact of the different mobilities. Fig. 3 shos the series of iterations for the three mobility models. Only ith constant mobility (model 2) convergence is quadratical. f the part of the residual norm originating from Poisson's equation dominates the overall residual norm also model 1 and 3 converge quadratically. Otherise the convergence is only linear ith no significant differencies beteen the models 1 and 3. Fig. 3 represents the iterations on the initial grid ith 354 mesh points, hich is identical for all simulations. After automatic grid refinement according to the local discretization error hich of course depends on the parameter models the rate of convergence is alays quadratical. Small changes of drain- and gate- voltages sho no significant effect on the behaviour of the iterations. But if the device reaches pinch off voltage the continuity equations loose their dominance. Then quadratical convergence has been observed ith all three models. Considering the electron distributions (Fig. 4-6) the influence of the models on the qualitative results becomes more evident. n Fig. 4 the electron density using constant mobility is plotted. The electron channel is pinched off homogenously in a ide region under the gate. Using model 3 (Fig. 5) the channel is also pinched off and the typical silicon accumulation- and depletion- zone can be seen. n Fig. 6 (negative differential mobility model) a stationary dipole is formed by an excess electron density and a positive donor charge. The electron channel is also pinched off. The electric field reaches its maximum at the edge of the gate contact. 5. Conlusion We have investigated the influence of three different mobility models on the iteration process and the internal distributions. From the computational point of vie it ould be much easier to perform the simulations ith constant mobility, but from the physical point of vie those results are physically unreliable. Only complex mobility models hich include carrier-carrier-, surface- and impurity- ' scattering and field dependend velocity saturation yield correct results. Acknoledgement Helpful discussions ith Prof.Dr.H.W.Potzl ho also critically read the manuscript and Dr.A.SchUtz ere highly appreciated. We should also like to thank the nteruniversitare Rechenzentrum for the excellent computer access. Sponsored by the Fonds zur Forderung der issenschaftlichen Forschung, Projekt r. S22/11 and by the Research Lab. of Siemens AG Munich. References /1/ A.F.Franz, G.A.Franz, S.Selberherr, P.Markoich, C.Ringhofer, to be purlished in EEE Trans. Electron Devices, vol. ED-3, Sept
4 /2/ O.L.Scharfetter, H.K.Gummel, EEE Trans. Electron Devices, vol. E-16, pp /3/ S.Selberherr, Proc. ATO AS on Process and Device Simulation, /4/ P.Srnith, et al., Appl.Phys.Lett. vol. 37, pp.797, 198. = d= 1µm ts='ct= 2.5isn W 1.Bµm r=r 1 =r 2 = =Jµm.35isn d Fig. 1 lo * en :;:: "" LJ 16. Device geometry of the GaAs MESFET (2) DOPG: 5.E 16 ( 1J ~=5.1d6 s G D ~, ~.. s d.. ~ 9 'i Jetr >- - LJ _J > (3) Fig. 2 field dependent velocity characteristic of 3 different mobility models ELECTRC FELD rkv/cml 1 UG = V Fig. 3 teration process for VD 2V and VG OV UMBER OF TERATOS 3 12
5 7.Jtt,s ~ ~ ~1 4.E-4 4.4E-4 4.BOE-4 5.ZOE-4 5.6E-4 6.E-4 4.E-4 4.4E-4 4.BOE-4 5.ZDE-4 5.6E-4 6.DE-4 Fig. 4 Fig. 5 Electron density for constant mobility Electron density for silicon mobility L) L) L) ~ L) 4. OOE-4 4. 'toe-4 4. BOE-4 S. ZOE-4 S. 6E-4 6. ODE-4 Fig. 6 Electron density for negative differential mobility 121
NUMERICAL ANALYSIS OF BREAKDOWN PHENOMENA IN MOSFET's. A. SCHUTZ, S. SELBERHERR, and H.W. POTZL
 NUMERICAL ANALYSIS OF BREAKDOWN PHENOMENA IN MOSFET's A. SCHUTZ, S. SELBERHERR, and H.W. POTZL Institut ftir Physikalische Elektronik Technische Universitat Wien GuBhausstr. 27, 1040 VIENNA, AUSTRIA and
NUMERICAL ANALYSIS OF BREAKDOWN PHENOMENA IN MOSFET's A. SCHUTZ, S. SELBERHERR, and H.W. POTZL Institut ftir Physikalische Elektronik Technische Universitat Wien GuBhausstr. 27, 1040 VIENNA, AUSTRIA and
PROCESS AND DEVICE SIMULATION WITH ONE AND THE SAME PROGRAM. P.Pichler, W.Jlingling, S.Selberherr, E.Guerrero, H.Pbtzl
 PROCESS AND DEVICE SIMULATION WITH ONE AND THE SAME PROGRAM P.Pichler, W.Jlingling, S.Selberherr, E.Guerrero, H.Pbtzl Institut flir Allgemeine Elektrotechnik und Elektronik Abteilung flir Physikalische
PROCESS AND DEVICE SIMULATION WITH ONE AND THE SAME PROGRAM P.Pichler, W.Jlingling, S.Selberherr, E.Guerrero, H.Pbtzl Institut flir Allgemeine Elektrotechnik und Elektronik Abteilung flir Physikalische
Punch-Through in Resurf Devices
 Punch-Through in Resurf Devices G. Nanz, P. Dickinger, W. Kausel, S. Selberherr Institut for Allgemeine Elektrotechnik und Elektronik Technical University Vienna GuJ3hausstraJ3e 27-29, A-1040 Vienna, AUSTRIA
Punch-Through in Resurf Devices G. Nanz, P. Dickinger, W. Kausel, S. Selberherr Institut for Allgemeine Elektrotechnik und Elektronik Technical University Vienna GuJ3hausstraJ3e 27-29, A-1040 Vienna, AUSTRIA
Spring Semester 2012 Final Exam
 Spring Semester 2012 Final Exam Note: Show your work, underline results, and always show units. Official exam time: 2.0 hours; an extension of at least 1.0 hour will be granted to anyone. Materials parameters
Spring Semester 2012 Final Exam Note: Show your work, underline results, and always show units. Official exam time: 2.0 hours; an extension of at least 1.0 hour will be granted to anyone. Materials parameters
COMPUTATION OF WIRE AND JUNCTION CAPACITANCE IN VLSI STRUCTURES
 COMPUTATION OF WIRE AND JUNCTION CAPACITANCE IN VLSI STRUCTURES F. Straker, s. Selberherr Abteilung fur Physikalische Elektronik Institut flir allgemeine Elektrotechnik und Elektronik Technische Universitat
COMPUTATION OF WIRE AND JUNCTION CAPACITANCE IN VLSI STRUCTURES F. Straker, s. Selberherr Abteilung fur Physikalische Elektronik Institut flir allgemeine Elektrotechnik und Elektronik Technische Universitat
GaN based transistors
 GaN based transistors S FP FP dielectric G SiO 2 Al x Ga 1-x N barrier i-gan Buffer i-sic D Transistors "The Transistor was probably the most important invention of the 20th Century The American Institute
GaN based transistors S FP FP dielectric G SiO 2 Al x Ga 1-x N barrier i-gan Buffer i-sic D Transistors "The Transistor was probably the most important invention of the 20th Century The American Institute
MOSFET. Id-Vd curve. I DS Transfer curve V G. Lec. 8. Vd=1V. Saturation region. V Th
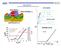 MOSFET Id-Vd curve Saturation region I DS Transfer curve Vd=1V V Th V G 1 0 < V GS < V T V GS > V T V Gs >V T & Small V D > 0 I DS WQ inv WC v WC i V V VDS V V G i T G n T L n I D g V D (g conductance
MOSFET Id-Vd curve Saturation region I DS Transfer curve Vd=1V V Th V G 1 0 < V GS < V T V GS > V T V Gs >V T & Small V D > 0 I DS WQ inv WC v WC i V V VDS V V G i T G n T L n I D g V D (g conductance
SIMULATION OF III-V DEVICES SEMI-INSULATING MATERIALS CENTRE NATIONAL D'ETUDES DES TELECOMMUNICATIONS LANNION - FRANCE
 494 SIMULATION OF III-V DEVICES SEMI-INSULATING MATERIALS S. MOTTET, J.E. VIALLET CENTRE NATIONAL D'ETUDES DES TELECOMMUNICATIONS 22300 LANNION - FRANCE ABSTRACT : Semi-insulating materials are commonly
494 SIMULATION OF III-V DEVICES SEMI-INSULATING MATERIALS S. MOTTET, J.E. VIALLET CENTRE NATIONAL D'ETUDES DES TELECOMMUNICATIONS 22300 LANNION - FRANCE ABSTRACT : Semi-insulating materials are commonly
Lecture 12: MOSFET Devices
 Lecture 12: MOSFET Devices Gu-Yeon Wei Division of Engineering and Applied Sciences Harvard University guyeon@eecs.harvard.edu Wei 1 Overview Reading S&S: Chapter 5.1~5.4 Supplemental Reading Background
Lecture 12: MOSFET Devices Gu-Yeon Wei Division of Engineering and Applied Sciences Harvard University guyeon@eecs.harvard.edu Wei 1 Overview Reading S&S: Chapter 5.1~5.4 Supplemental Reading Background
Arizona State University, Tempe, AZ 85287, USA 2 Department of Electrical Engineering. Arizona State University, Tempe, AZ 85287, USA ABSTRACT
 Accurate Three-Dimensional Simulation of Electron Mobility Including Electron-Electron and Electron-Dopant Interactions C. Heitzinger, 1 C. Ringhofer, 1 S. Ahmed, 2 D. Vasileska, 2 1 Department of Mathematics
Accurate Three-Dimensional Simulation of Electron Mobility Including Electron-Electron and Electron-Dopant Interactions C. Heitzinger, 1 C. Ringhofer, 1 S. Ahmed, 2 D. Vasileska, 2 1 Department of Mathematics
Investigation of the Thermal Noise of MOS Transistors under Analog and RF Operating Conditions
 Investigation of the Thermal Noise of MOS Transistors under Analog and RF Operating Conditions Ralf Brederlow 1, Georg Wenig 2, and Roland Thewes 1 1 Infineon Technologies, Corporate Research, 2 Technical
Investigation of the Thermal Noise of MOS Transistors under Analog and RF Operating Conditions Ralf Brederlow 1, Georg Wenig 2, and Roland Thewes 1 1 Infineon Technologies, Corporate Research, 2 Technical
A New Boundary Condition for Device Simulation Considering Outer Components. W.Kausel, G.Nanz, S.Selberherr, H.Poetzl
 625 SIMULATION OF SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES AND PROCESSES Vol. 3 Edited by G. Baccarani, M. Rudan - Bologna (Italy) September 26-28,1988 - Tecnoprinl A New Boundary Condition for Device Simulation Considering
625 SIMULATION OF SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES AND PROCESSES Vol. 3 Edited by G. Baccarani, M. Rudan - Bologna (Italy) September 26-28,1988 - Tecnoprinl A New Boundary Condition for Device Simulation Considering
Lecture 04 Review of MOSFET
 ECE 541/ME 541 Microelectronic Fabrication Techniques Lecture 04 Review of MOSFET Zheng Yang (ERF 3017, email: yangzhen@uic.edu) What is a Transistor? A Switch! An MOS Transistor V GS V T V GS S Ron D
ECE 541/ME 541 Microelectronic Fabrication Techniques Lecture 04 Review of MOSFET Zheng Yang (ERF 3017, email: yangzhen@uic.edu) What is a Transistor? A Switch! An MOS Transistor V GS V T V GS S Ron D
HW 5 posted due in two weeks Lab this week Midterm graded Project to be launched in week 7
 HW 5 posted due in two weeks Lab this week Midterm graded Project to be launched in week 7 2 What do digital IC designers need to know? 5 EE4 EECS4 6 3 0< V GS - V T < V DS Pinch-off 7 For (V GS V T )
HW 5 posted due in two weeks Lab this week Midterm graded Project to be launched in week 7 2 What do digital IC designers need to know? 5 EE4 EECS4 6 3 0< V GS - V T < V DS Pinch-off 7 For (V GS V T )
Overview of Modeling and Simulation TCAD - FLOOPS / FLOODS
 Overview of Modeling and Simulation TCAD - FLOOPS / FLOODS Modeling Overview Strain Effects Thermal Modeling TCAD Modeling Outline FLOOPS / FLOODS Introduction Progress on GaN Devices Prospects for Reliability
Overview of Modeling and Simulation TCAD - FLOOPS / FLOODS Modeling Overview Strain Effects Thermal Modeling TCAD Modeling Outline FLOOPS / FLOODS Introduction Progress on GaN Devices Prospects for Reliability
Typical example of the FET: MEtal Semiconductor FET (MESFET)
 Typical example of the FET: MEtal Semiconductor FET (MESFET) Conducting channel (RED) is made of highly doped material. The electron concentration in the channel n = the donor impurity concentration N
Typical example of the FET: MEtal Semiconductor FET (MESFET) Conducting channel (RED) is made of highly doped material. The electron concentration in the channel n = the donor impurity concentration N
ECE 342 Electronic Circuits. Lecture 6 MOS Transistors
 ECE 342 Electronic Circuits Lecture 6 MOS Transistors Jose E. Schutt-Aine Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Illinois jesa@illinois.edu 1 NMOS Transistor Typically L = 0.1 to 3 m, W = 0.2
ECE 342 Electronic Circuits Lecture 6 MOS Transistors Jose E. Schutt-Aine Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Illinois jesa@illinois.edu 1 NMOS Transistor Typically L = 0.1 to 3 m, W = 0.2
8. Schottky contacts / JFETs
 Technische Universität Graz Institute of Solid State Physics 8. Schottky contacts / JFETs Nov. 21, 2018 Technische Universität Graz Institute of Solid State Physics metal - semiconductor contacts Photoelectric
Technische Universität Graz Institute of Solid State Physics 8. Schottky contacts / JFETs Nov. 21, 2018 Technische Universität Graz Institute of Solid State Physics metal - semiconductor contacts Photoelectric
Semiconductor Physics Problems 2015
 Semiconductor Physics Problems 2015 Page and figure numbers refer to Semiconductor Devices Physics and Technology, 3rd edition, by SM Sze and M-K Lee 1. The purest semiconductor crystals it is possible
Semiconductor Physics Problems 2015 Page and figure numbers refer to Semiconductor Devices Physics and Technology, 3rd edition, by SM Sze and M-K Lee 1. The purest semiconductor crystals it is possible
Lecture 3: CMOS Transistor Theory
 Lecture 3: CMOS Transistor Theory Outline Introduction MOS Capacitor nmos I-V Characteristics pmos I-V Characteristics Gate and Diffusion Capacitance 2 Introduction So far, we have treated transistors
Lecture 3: CMOS Transistor Theory Outline Introduction MOS Capacitor nmos I-V Characteristics pmos I-V Characteristics Gate and Diffusion Capacitance 2 Introduction So far, we have treated transistors
MOSFET Physics: The Long Channel Approximation
 MOSFET Physics: The ong Channel Approximation A basic n-channel MOSFET (Figure 1) consists of two heavily-doped n-type regions, the Source and Drain, that comprise the main terminals of the device. The
MOSFET Physics: The ong Channel Approximation A basic n-channel MOSFET (Figure 1) consists of two heavily-doped n-type regions, the Source and Drain, that comprise the main terminals of the device. The
Schottky diodes. JFETs - MESFETs - MODFETs
 Technische Universität Graz Institute of Solid State Physics Schottky diodes JFETs - MESFETs - MODFETs Quasi Fermi level When the charge carriers are not in equilibrium the Fermi energy can be different
Technische Universität Graz Institute of Solid State Physics Schottky diodes JFETs - MESFETs - MODFETs Quasi Fermi level When the charge carriers are not in equilibrium the Fermi energy can be different
Chapter 5. Carrier Transport Phenomena
 Chapter 5 Carrier Transport Phenomena 1 We now study the effect of external fields (electric field, magnetic field) on semiconducting material 2 Objective Discuss drift and diffusion current densities
Chapter 5 Carrier Transport Phenomena 1 We now study the effect of external fields (electric field, magnetic field) on semiconducting material 2 Objective Discuss drift and diffusion current densities
MOS Capacitor MOSFET Devices. MOSFET s. INEL Solid State Electronics. Manuel Toledo Quiñones. ECE Dept. UPRM.
 INEL 6055 - Solid State Electronics ECE Dept. UPRM 20th March 2006 Definitions MOS Capacitor Isolated Metal, SiO 2, Si Threshold Voltage qφ m metal d vacuum level SiO qχ 2 E g /2 qφ F E C E i E F E v qφ
INEL 6055 - Solid State Electronics ECE Dept. UPRM 20th March 2006 Definitions MOS Capacitor Isolated Metal, SiO 2, Si Threshold Voltage qφ m metal d vacuum level SiO qχ 2 E g /2 qφ F E C E i E F E v qφ
Field effect = Induction of an electronic charge due to an electric field Example: Planar capacitor
 JFETs AND MESFETs Introduction Field effect = Induction of an electronic charge due to an electric field Example: Planar capacitor Why would an FET made of a planar capacitor with two metal plates, as
JFETs AND MESFETs Introduction Field effect = Induction of an electronic charge due to an electric field Example: Planar capacitor Why would an FET made of a planar capacitor with two metal plates, as
Fundamentals of the Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor
 Triode Working FET Fundamentals of the Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor The characteristics of energy bands as a function of applied voltage. Surface inversion. The expression for the
Triode Working FET Fundamentals of the Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor The characteristics of energy bands as a function of applied voltage. Surface inversion. The expression for the
ECE315 / ECE515 Lecture-2 Date:
 Lecture-2 Date: 04.08.2016 NMOS I/V Characteristics Discussion on I/V Characteristics MOSFET Second Order Effect NMOS I-V Characteristics ECE315 / ECE515 Gradual Channel Approximation: Cut-off Linear/Triode
Lecture-2 Date: 04.08.2016 NMOS I/V Characteristics Discussion on I/V Characteristics MOSFET Second Order Effect NMOS I-V Characteristics ECE315 / ECE515 Gradual Channel Approximation: Cut-off Linear/Triode
Lecture 2. Introduction to semiconductors Structures and characteristics in semiconductors
 Lecture 2 Introduction to semiconductors Structures and characteristics in semiconductors Semiconductor p-n junction Metal Oxide Silicon structure Semiconductor contact Literature Glen F. Knoll, Radiation
Lecture 2 Introduction to semiconductors Structures and characteristics in semiconductors Semiconductor p-n junction Metal Oxide Silicon structure Semiconductor contact Literature Glen F. Knoll, Radiation
Avalanche breakdown. Impact ionization causes an avalanche of current. Occurs at low doping
 Avalanche breakdown Impact ionization causes an avalanche of current Occurs at low doping Zener tunneling Electrons tunnel from valence band to conduction band Occurs at high doping Tunneling wave decays
Avalanche breakdown Impact ionization causes an avalanche of current Occurs at low doping Zener tunneling Electrons tunnel from valence band to conduction band Occurs at high doping Tunneling wave decays
Semiconductor Physics fall 2012 problems
 Semiconductor Physics fall 2012 problems 1. An n-type sample of silicon has a uniform density N D = 10 16 atoms cm -3 of arsenic, and a p-type silicon sample has N A = 10 15 atoms cm -3 of boron. For each
Semiconductor Physics fall 2012 problems 1. An n-type sample of silicon has a uniform density N D = 10 16 atoms cm -3 of arsenic, and a p-type silicon sample has N A = 10 15 atoms cm -3 of boron. For each
ECE 342 Electronic Circuits. 3. MOS Transistors
 ECE 342 Electronic Circuits 3. MOS Transistors Jose E. Schutt-Aine Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Illinois jschutt@emlab.uiuc.edu 1 NMOS Transistor Typically L = 0.1 to 3 m, W = 0.2 to
ECE 342 Electronic Circuits 3. MOS Transistors Jose E. Schutt-Aine Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Illinois jschutt@emlab.uiuc.edu 1 NMOS Transistor Typically L = 0.1 to 3 m, W = 0.2 to
Time-dependent Monte Carlo Simulation
 Computational Electronics Group University of Illinois Time-dependent Monte Carlo Simulation Umberto Ravaioli Beckman Institute and Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Illinois
Computational Electronics Group University of Illinois Time-dependent Monte Carlo Simulation Umberto Ravaioli Beckman Institute and Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Illinois
MOS Transistor I-V Characteristics and Parasitics
 ECEN454 Digital Integrated Circuit Design MOS Transistor I-V Characteristics and Parasitics ECEN 454 Facts about Transistors So far, we have treated transistors as ideal switches An ON transistor passes
ECEN454 Digital Integrated Circuit Design MOS Transistor I-V Characteristics and Parasitics ECEN 454 Facts about Transistors So far, we have treated transistors as ideal switches An ON transistor passes
Modeling and Computation of Gate Tunneling Current through Ultra Thin Gate Oxides in Double Gate MOSFETs with Ultra Thin Body Silicon Channel
 Modeling and Computation of Gate Tunneling Current through Ultra Thin Gate Oxides in Double Gate MOSFETs with Ultra Thin Body Silicon Channel Bhadrinarayana L V 17 th July 2008 Microelectronics Lab, Indian
Modeling and Computation of Gate Tunneling Current through Ultra Thin Gate Oxides in Double Gate MOSFETs with Ultra Thin Body Silicon Channel Bhadrinarayana L V 17 th July 2008 Microelectronics Lab, Indian
Reduction of Self-heating effect in LDMOS devices
 Reduction of Self-heating effect in LDMOS devices T.K.Maiti * and C. K. Maiti ** Department of Electronics and Electrical Communication Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur-721302, India
Reduction of Self-heating effect in LDMOS devices T.K.Maiti * and C. K. Maiti ** Department of Electronics and Electrical Communication Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur-721302, India
3D Simulation of SiC MESFET
 Lighting Up Semiconductor World 3D Simulation of SiC MESFET Crosslight Software, Inc., Vancouver, BC, Canada, (604)320-1704, www.crosslight.com Introduction Introduction to Simulation Flow 3D simulation
Lighting Up Semiconductor World 3D Simulation of SiC MESFET Crosslight Software, Inc., Vancouver, BC, Canada, (604)320-1704, www.crosslight.com Introduction Introduction to Simulation Flow 3D simulation
Technology Computer Aided Design (TCAD) Laboratory. Lecture 2, A simulation primer
 Technology Computer Aided Design (TCAD) Laboratory Lecture 2, A simulation primer [Source: Synopsys] Giovanni Betti Beneventi E-mail: gbbeneventi@arces.unibo.it ; giobettibeneventi@gmail.com Office: Engineering
Technology Computer Aided Design (TCAD) Laboratory Lecture 2, A simulation primer [Source: Synopsys] Giovanni Betti Beneventi E-mail: gbbeneventi@arces.unibo.it ; giobettibeneventi@gmail.com Office: Engineering
SELF-ADAPTIVE SPACE AND TIME GRIDS IN DEVICE SIMULATION
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL FOR NUMERICAL METHODS IN ENGINEERING, VOL. 31, 1357-1374 (1991) SELF-ADAPTIVE SPACE AND TIME GRIDS IN DEVICE SIMULATION G. NAN2 Institut fur Mikroelektronik, Technical University
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL FOR NUMERICAL METHODS IN ENGINEERING, VOL. 31, 1357-1374 (1991) SELF-ADAPTIVE SPACE AND TIME GRIDS IN DEVICE SIMULATION G. NAN2 Institut fur Mikroelektronik, Technical University
B. Both A and R are correct but R is not correct explanation of A. C. A is true, R is false. D. A is false, R is true
 1. Assertion (A): A demultiplexer can be used as a decode r. Reason (R): A demultiplexer can be built by using AND gates only. A. Both A and R are correct and R is correct explanation of A B. Both A and
1. Assertion (A): A demultiplexer can be used as a decode r. Reason (R): A demultiplexer can be built by using AND gates only. A. Both A and R are correct and R is correct explanation of A B. Both A and
Current mechanisms Exam January 27, 2012
 Current mechanisms Exam January 27, 2012 There are four mechanisms that typically cause currents to flow: thermionic emission, diffusion, drift, and tunneling. Explain briefly which kind of current mechanisms
Current mechanisms Exam January 27, 2012 There are four mechanisms that typically cause currents to flow: thermionic emission, diffusion, drift, and tunneling. Explain briefly which kind of current mechanisms
MOSFET: Introduction
 E&CE 437 Integrated VLSI Systems MOS Transistor 1 of 30 MOSFET: Introduction Metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistor (MOSFET) or MOS is widely used for implementing digital designs Its major
E&CE 437 Integrated VLSI Systems MOS Transistor 1 of 30 MOSFET: Introduction Metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistor (MOSFET) or MOS is widely used for implementing digital designs Its major
Lecture 2. Introduction to semiconductors Structures and characteristics in semiconductors. Fabrication of semiconductor sensor
 Lecture 2 Introduction to semiconductors Structures and characteristics in semiconductors Semiconductor p-n junction Metal Oxide Silicon structure Semiconductor contact Fabrication of semiconductor sensor
Lecture 2 Introduction to semiconductors Structures and characteristics in semiconductors Semiconductor p-n junction Metal Oxide Silicon structure Semiconductor contact Fabrication of semiconductor sensor
JFET Operating Characteristics: V GS = 0 V 14. JFET Operating Characteristics: V GS = 0 V 15
 J Operating Characteristics: V GS = 0 V 14 V GS = 0 and V DS increases from 0 to a more positive voltage: Gate and Source terminals: at the same potential Drain: at positive potential => reverse biased
J Operating Characteristics: V GS = 0 V 14 V GS = 0 and V DS increases from 0 to a more positive voltage: Gate and Source terminals: at the same potential Drain: at positive potential => reverse biased
ESE370: Circuit-Level Modeling, Design, and Optimization for Digital Systems. Today. Refinement. Last Time. No Field. Body Contact
 ESE370: Circuit-Level Modeling, Design, and Optimization for Digital Systems Day 10: September 6, 01 MOS Transistor Basics Today MOS Transistor Topology Threshold Operating Regions Resistive Saturation
ESE370: Circuit-Level Modeling, Design, and Optimization for Digital Systems Day 10: September 6, 01 MOS Transistor Basics Today MOS Transistor Topology Threshold Operating Regions Resistive Saturation
A Compact Analytical Modelling of the Electrical Characteristics of Submicron Channel MOSFETs
 ROMANIAN JOURNAL OF INFORMATION SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY Volume 11, Number 4, 2008, 383 395 A Compact Analytical Modelling of the Electrical Characteristics of Submicron Channel MOSFETs Andrei SEVCENCO,
ROMANIAN JOURNAL OF INFORMATION SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY Volume 11, Number 4, 2008, 383 395 A Compact Analytical Modelling of the Electrical Characteristics of Submicron Channel MOSFETs Andrei SEVCENCO,
Electronics Fets and Mosfets Prof D C Dube Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi
 Electronics Fets and Mosfets Prof D C Dube Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Module No. #05 Lecture No. #02 FETS and MOSFETS (contd.) In the previous lecture, we studied the working
Electronics Fets and Mosfets Prof D C Dube Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Module No. #05 Lecture No. #02 FETS and MOSFETS (contd.) In the previous lecture, we studied the working
à FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTORS
 Prof.M.G.Guvench à FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTORS ü FET: CONTENTS Principles of Operation Models: DC, S.S.A.C. and SPICE Applications: AC coupled S.S. Amplifiers ü FET: NAMES JFET Junction Field Effect Transistor
Prof.M.G.Guvench à FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTORS ü FET: CONTENTS Principles of Operation Models: DC, S.S.A.C. and SPICE Applications: AC coupled S.S. Amplifiers ü FET: NAMES JFET Junction Field Effect Transistor
Lecture 2. Introduction to semiconductors Structures and characteristics in semiconductors
 Lecture 2 Introduction to semiconductors Structures and characteristics in semiconductors Semiconductor p-n junction Metal Oxide Silicon structure Semiconductor contact Literature Glen F. Knoll, Radiation
Lecture 2 Introduction to semiconductors Structures and characteristics in semiconductors Semiconductor p-n junction Metal Oxide Silicon structure Semiconductor contact Literature Glen F. Knoll, Radiation
Section 12: Intro to Devices
 Section 12: Intro to Devices Extensive reading materials on reserve, including Robert F. Pierret, Semiconductor Device Fundamentals Bond Model of Electrons and Holes Si Si Si Si Si Si Si Si Si Silicon
Section 12: Intro to Devices Extensive reading materials on reserve, including Robert F. Pierret, Semiconductor Device Fundamentals Bond Model of Electrons and Holes Si Si Si Si Si Si Si Si Si Silicon
Integrated Circuits & Systems
 Federal University of Santa Catarina Center for Technology Computer Science & Electronics Engineering Integrated Circuits & Systems INE 5442 Lecture 10 MOSFET part 1 guntzel@inf.ufsc.br ual-well Trench-Isolated
Federal University of Santa Catarina Center for Technology Computer Science & Electronics Engineering Integrated Circuits & Systems INE 5442 Lecture 10 MOSFET part 1 guntzel@inf.ufsc.br ual-well Trench-Isolated
! PN Junction. ! MOS Transistor Topology. ! Threshold. ! Operating Regions. " Resistive. " Saturation. " Subthreshold (next class)
 ESE370: ircuitlevel Modeling, Design, and Optimization for Digital Systems Lec 7: September 20, 2017 MOS Transistor Operating Regions Part 1 Today! PN Junction! MOS Transistor Topology! Threshold! Operating
ESE370: ircuitlevel Modeling, Design, and Optimization for Digital Systems Lec 7: September 20, 2017 MOS Transistor Operating Regions Part 1 Today! PN Junction! MOS Transistor Topology! Threshold! Operating
Lecture 15: MOS Transistor models: Body effects, SPICE models. Context. In the last lecture, we discussed the modes of operation of a MOS FET:
 Lecture 15: MOS Transistor models: Body effects, SPICE models Context In the last lecture, we discussed the modes of operation of a MOS FET: oltage controlled resistor model I- curve (Square-Law Model)
Lecture 15: MOS Transistor models: Body effects, SPICE models Context In the last lecture, we discussed the modes of operation of a MOS FET: oltage controlled resistor model I- curve (Square-Law Model)
Electronic Circuits 1. Transistor Devices. Contents BJT and FET Characteristics Operations. Prof. C.K. Tse: Transistor devices
 Electronic Circuits 1 Transistor Devices Contents BJT and FET Characteristics Operations 1 What is a transistor? Three-terminal device whose voltage-current relationship is controlled by a third voltage
Electronic Circuits 1 Transistor Devices Contents BJT and FET Characteristics Operations 1 What is a transistor? Three-terminal device whose voltage-current relationship is controlled by a third voltage
Semiconductor Integrated Process Design (MS 635)
 Semiconductor Integrated Process Design (MS 635) Instructor: Prof. Keon Jae Lee - Office: 응용공학동 #4306, Tel: #3343 - Email: keonlee@kaist.ac.kr Lecture: (Tu, Th), 1:00-2:15 #2425 Office hour: Tues & Thur
Semiconductor Integrated Process Design (MS 635) Instructor: Prof. Keon Jae Lee - Office: 응용공학동 #4306, Tel: #3343 - Email: keonlee@kaist.ac.kr Lecture: (Tu, Th), 1:00-2:15 #2425 Office hour: Tues & Thur
Semiconductor Physics. Lecture 3
 Semiconductor Physics Lecture 3 Intrinsic carrier density Intrinsic carrier density Law of mass action Valid also if we add an impurity which either donates extra electrons or holes the number of carriers
Semiconductor Physics Lecture 3 Intrinsic carrier density Intrinsic carrier density Law of mass action Valid also if we add an impurity which either donates extra electrons or holes the number of carriers
Carriers Concentration, Current & Hall Effect in Semiconductors. Prof.P. Ravindran, Department of Physics, Central University of Tamil Nadu, India
 Carriers Concentration, Current & Hall Effect in Semiconductors 1 Prof.P. Ravindran, Department of Physics, Central University of Tamil Nadu, India http://folk.uio.no/ravi/semi2013 Conductivity Charge
Carriers Concentration, Current & Hall Effect in Semiconductors 1 Prof.P. Ravindran, Department of Physics, Central University of Tamil Nadu, India http://folk.uio.no/ravi/semi2013 Conductivity Charge
Chapter 4 Field-Effect Transistors
 Chapter 4 Field-Effect Transistors Microelectronic Circuit Design Richard C. Jaeger Travis N. Blalock 5/5/11 Chap 4-1 Chapter Goals Describe operation of MOSFETs. Define FET characteristics in operation
Chapter 4 Field-Effect Transistors Microelectronic Circuit Design Richard C. Jaeger Travis N. Blalock 5/5/11 Chap 4-1 Chapter Goals Describe operation of MOSFETs. Define FET characteristics in operation
PN Junction
 P Junction 2017-05-04 Definition Power Electronics = semiconductor switches are used Analogue amplifier = high power loss 250 200 u x 150 100 u Udc i 50 0 0 50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 i,u dc i,u u
P Junction 2017-05-04 Definition Power Electronics = semiconductor switches are used Analogue amplifier = high power loss 250 200 u x 150 100 u Udc i 50 0 0 50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 i,u dc i,u u
Semiconductor Physics fall 2012 problems
 Semiconductor Physics fall 2012 problems 1. An n-type sample of silicon has a uniform density N D = 10 16 atoms cm -3 of arsenic, and a p-type silicon sample has N A = 10 15 atoms cm -3 of boron. For each
Semiconductor Physics fall 2012 problems 1. An n-type sample of silicon has a uniform density N D = 10 16 atoms cm -3 of arsenic, and a p-type silicon sample has N A = 10 15 atoms cm -3 of boron. For each
Introduction to CMOS VLSI. Chapter 2: CMOS Transistor Theory. Harris, 2004 Updated by Li Chen, Outline
 Introduction to MOS VLSI Design hapter : MOS Transistor Theory copyright@david Harris, 004 Updated by Li hen, 010 Outline Introduction MOS apacitor nmos IV haracteristics pmos IV haracteristics Gate and
Introduction to MOS VLSI Design hapter : MOS Transistor Theory copyright@david Harris, 004 Updated by Li hen, 010 Outline Introduction MOS apacitor nmos IV haracteristics pmos IV haracteristics Gate and
Semi-insulating SiC substrates for high frequency devices
 Klausurtagung Silberbach, 19. - 21. Feb. 2002 Institut für Werkstoffwissenschaften - WW 6 Semi-insulating SiC substrates for high frequency devices Vortrag von Matthias Bickermann Semi-insulating SiC substrates
Klausurtagung Silberbach, 19. - 21. Feb. 2002 Institut für Werkstoffwissenschaften - WW 6 Semi-insulating SiC substrates for high frequency devices Vortrag von Matthias Bickermann Semi-insulating SiC substrates
Comparison of electron transport properties in submicrometer InAs, InP and GaAs n + -i-n + diode using ensemble Monte Carlo simulation
 Comparison of electron transport properties in submicrometer InAs, InP and GaAs n + -i-n + diode using ensemble Monte Carlo simulation A. Guen-Bouazza 1, C. Sayah 1, B. Bouazza 1, N. E. Chabane-Sari 1
Comparison of electron transport properties in submicrometer InAs, InP and GaAs n + -i-n + diode using ensemble Monte Carlo simulation A. Guen-Bouazza 1, C. Sayah 1, B. Bouazza 1, N. E. Chabane-Sari 1
CHAPTER 2 AN OVERVIEW OF TCAD SIMULATOR AND SIMULATION METHODOLOGY
 15 CHAPTER 2 AN OVERVIEW OF TCAD SIMULATOR AND SIMULATION METHODOLOGY In this chapter TCAD and the various modules available in the TCAD simulator have been discussed. The simulation methodologies to extract
15 CHAPTER 2 AN OVERVIEW OF TCAD SIMULATOR AND SIMULATION METHODOLOGY In this chapter TCAD and the various modules available in the TCAD simulator have been discussed. The simulation methodologies to extract
Long Channel MOS Transistors
 Long Channel MOS Transistors The theory developed for MOS capacitor (HO #2) can be directly extended to Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect transistors (MOSFET) by considering the following structure:
Long Channel MOS Transistors The theory developed for MOS capacitor (HO #2) can be directly extended to Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect transistors (MOSFET) by considering the following structure:
Computation of Integrated Circuit Interconnect Capacitances
 F. Straker, s. Selberherr Abteilung flir Physikalische Elektronik Institut f Ur allgemeine Elektrotechnik und Elektronik Technische Universitat WIEN GuBhausstraBe 27, 1040 WIEN, AUSTRIA Computation of
F. Straker, s. Selberherr Abteilung flir Physikalische Elektronik Institut f Ur allgemeine Elektrotechnik und Elektronik Technische Universitat WIEN GuBhausstraBe 27, 1040 WIEN, AUSTRIA Computation of
MOS Capacitors ECE 2204
 MOS apacitors EE 2204 Some lasses of Field Effect Transistors Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor MOSFET, which will be the type that we will study in this course. Metal-Semiconductor Field
MOS apacitors EE 2204 Some lasses of Field Effect Transistors Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor MOSFET, which will be the type that we will study in this course. Metal-Semiconductor Field
SECTION: Circle one: Alam Lundstrom. ECE 305 Exam 5 SOLUTIONS: Spring 2016 April 18, 2016 M. A. Alam and M.S. Lundstrom Purdue University
 NAME: PUID: SECTION: Circle one: Alam Lundstrom ECE 305 Exam 5 SOLUTIONS: April 18, 2016 M A Alam and MS Lundstrom Purdue University This is a closed book exam You may use a calculator and the formula
NAME: PUID: SECTION: Circle one: Alam Lundstrom ECE 305 Exam 5 SOLUTIONS: April 18, 2016 M A Alam and MS Lundstrom Purdue University This is a closed book exam You may use a calculator and the formula
Determination of properties in semiconductor materials by applying Matlab
 Determination of properties in semiconductor materials by applying Matlab Carlos Figueroa. 1, Raúl Riera A. 2 1 Departamento de Ingeniería Industrial. Universidad de Sonora A.P. 5-088, Hermosillo, Sonora.
Determination of properties in semiconductor materials by applying Matlab Carlos Figueroa. 1, Raúl Riera A. 2 1 Departamento de Ingeniería Industrial. Universidad de Sonora A.P. 5-088, Hermosillo, Sonora.
Intrinsic Small-Signal Equivalent Circuit of GaAs MESFET s
 Intrinsic Small-Signal Equivalent Circuit o GaAs MESFET s M KAMECHE *, M FEHAM M MELIANI, N BENAHMED, S DALI * National Centre o Space Techniques, Algeria Telecom Laboratory, University o Tlemcen, Algeria
Intrinsic Small-Signal Equivalent Circuit o GaAs MESFET s M KAMECHE *, M FEHAM M MELIANI, N BENAHMED, S DALI * National Centre o Space Techniques, Algeria Telecom Laboratory, University o Tlemcen, Algeria
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences. EECS 130 Professor Ali Javey Fall 2006
 UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences EECS 130 Professor Ali Javey Fall 2006 Midterm 2 Name: SID: Closed book. Two sheets of notes are
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences EECS 130 Professor Ali Javey Fall 2006 Midterm 2 Name: SID: Closed book. Two sheets of notes are
A Zero Field Monte Carlo Algorithm Accounting for the Pauli Exclusion Principle
 A Zero Field Monte Carlo Algorithm Accounting for the Pauli Exclusion Principle Sergey Smirnov, Hans Kosina, Mihail Nedjalkov, and Siegfried Selberherr Institute for Microelectronics, TU-Vienna, Gusshausstrasse
A Zero Field Monte Carlo Algorithm Accounting for the Pauli Exclusion Principle Sergey Smirnov, Hans Kosina, Mihail Nedjalkov, and Siegfried Selberherr Institute for Microelectronics, TU-Vienna, Gusshausstrasse
TRANSIENT SIMULATION OF MOSFETS. M. Razaz and S. F. Quigley Department of Electronic and Electrical Engineering, University of Birmingham, UK.
 30 TRANSIENT SIMULATION OF MOSFETS M. Razaz and S. F. Quigley Department of Electronic and Electrical Engineering, University of Birmingham, UK. SUMMARY Considerable research has been carried out in the
30 TRANSIENT SIMULATION OF MOSFETS M. Razaz and S. F. Quigley Department of Electronic and Electrical Engineering, University of Birmingham, UK. SUMMARY Considerable research has been carried out in the
Semiconductor Module
 Semiconductor Module Optics Seminar July 18, 2018 Yosuke Mizuyama, Ph.D. COMSOL, Inc. The COMSOL Product Suite Governing Equations Semiconductor Schrödinger Equation Semiconductor Optoelectronics, FD Semiconductor
Semiconductor Module Optics Seminar July 18, 2018 Yosuke Mizuyama, Ph.D. COMSOL, Inc. The COMSOL Product Suite Governing Equations Semiconductor Schrödinger Equation Semiconductor Optoelectronics, FD Semiconductor
1. Suppose preferences are represented by the Cobb-Douglas utility function, u(x1,x2) = Ax 1 a x 2
 Additional questions for chapter 7 1. Suppose preferences are represented by the Cobb-Douglas utility function ux1x2 = Ax 1 a x 2 1-a 0 < a < 1 &A > 0. Assuming an interior solution solve for the Marshallian
Additional questions for chapter 7 1. Suppose preferences are represented by the Cobb-Douglas utility function ux1x2 = Ax 1 a x 2 1-a 0 < a < 1 &A > 0. Assuming an interior solution solve for the Marshallian
CMPEN 411 VLSI Digital Circuits. Lecture 03: MOS Transistor
 CMPEN 411 VLSI Digital Circuits Lecture 03: MOS Transistor Kyusun Choi [Adapted from Rabaey s Digital Integrated Circuits, Second Edition, 2003 J. Rabaey, A. Chandrakasan, B. Nikolic] CMPEN 411 L03 S.1
CMPEN 411 VLSI Digital Circuits Lecture 03: MOS Transistor Kyusun Choi [Adapted from Rabaey s Digital Integrated Circuits, Second Edition, 2003 J. Rabaey, A. Chandrakasan, B. Nikolic] CMPEN 411 L03 S.1
Solid State Physics SEMICONDUCTORS - IV. Lecture 25. A.H. Harker. Physics and Astronomy UCL
 Solid State Physics SEMICONDUCTORS - IV Lecture 25 A.H. Harker Physics and Astronomy UCL 9.9 Carrier diffusion and recombination Suppose we have a p-type semiconductor, i.e. n h >> n e. (1) Create a local
Solid State Physics SEMICONDUCTORS - IV Lecture 25 A.H. Harker Physics and Astronomy UCL 9.9 Carrier diffusion and recombination Suppose we have a p-type semiconductor, i.e. n h >> n e. (1) Create a local
EE105 - Fall 2006 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits
 EE105 - Fall 2006 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits Prof. Jan M. Rabaey (jan@eecs) Lecture 7: MOS Transistor Some Administrative Issues Lab 2 this week Hw 2 due on We Hw 3 will be posted same day MIDTERM
EE105 - Fall 2006 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits Prof. Jan M. Rabaey (jan@eecs) Lecture 7: MOS Transistor Some Administrative Issues Lab 2 this week Hw 2 due on We Hw 3 will be posted same day MIDTERM
Metal-oxide-semiconductor field effect transistors (2 lectures)
 Metal-ide-semiconductor field effect transistors ( lectures) MOS physics (brief in book) Current-voltage characteristics - pinch-off / channel length modulation - weak inversion - velocity saturation -
Metal-ide-semiconductor field effect transistors ( lectures) MOS physics (brief in book) Current-voltage characteristics - pinch-off / channel length modulation - weak inversion - velocity saturation -
Section 12: Intro to Devices
 Section 12: Intro to Devices Extensive reading materials on reserve, including Robert F. Pierret, Semiconductor Device Fundamentals EE143 Ali Javey Bond Model of Electrons and Holes Si Si Si Si Si Si Si
Section 12: Intro to Devices Extensive reading materials on reserve, including Robert F. Pierret, Semiconductor Device Fundamentals EE143 Ali Javey Bond Model of Electrons and Holes Si Si Si Si Si Si Si
CMOS Digital Integrated Circuits Analysis and Design
 MOS igital ntegrated ircuits Analysis and esign hapter 4 Modeling of MOS ransistors Using SPE 1 ntroduction he SPE software that was distributed by U Berkeley beginning in the late 1970s had three built-in
MOS igital ntegrated ircuits Analysis and esign hapter 4 Modeling of MOS ransistors Using SPE 1 ntroduction he SPE software that was distributed by U Berkeley beginning in the late 1970s had three built-in
ECE 497 JS Lecture - 12 Device Technologies
 ECE 497 JS Lecture - 12 Device Technologies Spring 2004 Jose E. Schutt-Aine Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Illinois jose@emlab.uiuc.edu 1 NMOS Transistor 2 ρ Source channel charge density
ECE 497 JS Lecture - 12 Device Technologies Spring 2004 Jose E. Schutt-Aine Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Illinois jose@emlab.uiuc.edu 1 NMOS Transistor 2 ρ Source channel charge density
Complete Surface-Potential Modeling Approach Implemented in the HiSIM Compact Model Family for Any MOSFET Type
 Complete Surface-Potential Modeling Approach Implemented in the HiSIM Compact Model Family for Any MOSFET Type WCM in Boston 15. June, 2011 M. Miura-Mattausch, M. Miyake, H. Kikuchihara, U. Feldmann and
Complete Surface-Potential Modeling Approach Implemented in the HiSIM Compact Model Family for Any MOSFET Type WCM in Boston 15. June, 2011 M. Miura-Mattausch, M. Miyake, H. Kikuchihara, U. Feldmann and
JFET/MESFET. JFET: small gate current (reverse leakage of the gate-to-channel junction) More gate leakage than MOSFET, less than bipolar.
 JFET/MESFET JFET: small gate current (reverse leakage of the gate-to-channel junction) More gate leakage than MOSFET, less than bipolar. JFET has higher transconductance than the MOSFET. Used in low-noise,
JFET/MESFET JFET: small gate current (reverse leakage of the gate-to-channel junction) More gate leakage than MOSFET, less than bipolar. JFET has higher transconductance than the MOSFET. Used in low-noise,
PET467E-Analysis of Well Pressure Tests 2008 Spring/İTÜ HW No. 5 Solutions
 . Onur 13.03.2008 PET467E-Analysis of Well Pressure Tests 2008 Spring/İTÜ HW No. 5 Solutions Due date: 21.03.2008 Subject: Analysis of an dradon test ith ellbore storage and skin effects by using typecurve
. Onur 13.03.2008 PET467E-Analysis of Well Pressure Tests 2008 Spring/İTÜ HW No. 5 Solutions Due date: 21.03.2008 Subject: Analysis of an dradon test ith ellbore storage and skin effects by using typecurve
Transistors - a primer
 ransistors - a primer What is a transistor? Solid-state triode - three-terminal device, with voltage (or current) at third terminal used to control current between other two terminals. wo types: bipolar
ransistors - a primer What is a transistor? Solid-state triode - three-terminal device, with voltage (or current) at third terminal used to control current between other two terminals. wo types: bipolar
Final Examination EE 130 December 16, 1997 Time allotted: 180 minutes
 Final Examination EE 130 December 16, 1997 Time allotted: 180 minutes Problem 1: Semiconductor Fundamentals [30 points] A uniformly doped silicon sample of length 100µm and cross-sectional area 100µm 2
Final Examination EE 130 December 16, 1997 Time allotted: 180 minutes Problem 1: Semiconductor Fundamentals [30 points] A uniformly doped silicon sample of length 100µm and cross-sectional area 100µm 2
Defense Technical Information Center Compilation Part Notice
 UNCLASSIFIED Defense Technical Information Center Compilation Part Notice ADP013351 TITLE: The Effects of Plasma Induced Damage on the Channel Layers of Ion Implanted GaAs MESFETs during Reactive Ion Etching
UNCLASSIFIED Defense Technical Information Center Compilation Part Notice ADP013351 TITLE: The Effects of Plasma Induced Damage on the Channel Layers of Ion Implanted GaAs MESFETs during Reactive Ion Etching
Lecture 5: CMOS Transistor Theory
 Lecture 5: CMOS Transistor Theory Slides courtesy of Deming Chen Slides based on the initial set from David Harris CMOS VLSI Design Outline q q q q q q q Introduction MOS Capacitor nmos I-V Characteristics
Lecture 5: CMOS Transistor Theory Slides courtesy of Deming Chen Slides based on the initial set from David Harris CMOS VLSI Design Outline q q q q q q q Introduction MOS Capacitor nmos I-V Characteristics
META-STABILITY EFFECTS IN ORGANIC BASED TRANSISTORS
 META-STABILITY EFFECTS IN ORGANIC BASED TRANSISTORS H. L. Gomes 1*, P. Stallinga 1, F. Dinelli 2, M. Murgia 2, F. Biscarini 2, D. M. de Leeuw 3 1 University of Algarve, Faculty of Sciences and Technology
META-STABILITY EFFECTS IN ORGANIC BASED TRANSISTORS H. L. Gomes 1*, P. Stallinga 1, F. Dinelli 2, M. Murgia 2, F. Biscarini 2, D. M. de Leeuw 3 1 University of Algarve, Faculty of Sciences and Technology
ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals
 ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 4: January 24, 2017 MOS Transistor Theory, MOS Model Penn ESE 570 Spring 2017 Khanna Lecture Outline! Semiconductor Physics " Band gaps "
ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 4: January 24, 2017 MOS Transistor Theory, MOS Model Penn ESE 570 Spring 2017 Khanna Lecture Outline! Semiconductor Physics " Band gaps "
1 Name: Student number: DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS AND PHYSICAL OCEANOGRAPHY MEMORIAL UNIVERSITY OF NEWFOUNDLAND. Fall :00-11:00
 1 Name: DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS AND PHYSICAL OCEANOGRAPHY MEMORIAL UNIVERSITY OF NEWFOUNDLAND Final Exam Physics 3000 December 11, 2012 Fall 2012 9:00-11:00 INSTRUCTIONS: 1. Answer all seven (7) questions.
1 Name: DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS AND PHYSICAL OCEANOGRAPHY MEMORIAL UNIVERSITY OF NEWFOUNDLAND Final Exam Physics 3000 December 11, 2012 Fall 2012 9:00-11:00 INSTRUCTIONS: 1. Answer all seven (7) questions.
DRIFT-DIFFUSION SYSTEMS: VARIATIONAL PRINCIPLES AND FIXED POINT MAPS FOR STEADY STATE SEMICONDUCTOR MODELS
 DRIFT-DIFFUSION SYSTEMS: VARIATIONAL PRINCIPLES AND FIXED POINT MAPS FOR STEADY STATE SEMICONDUCTOR MODELS Joseph W. Jerome Department of Mathematics Northwestern University Evanston, IL 60208 Abstract
DRIFT-DIFFUSION SYSTEMS: VARIATIONAL PRINCIPLES AND FIXED POINT MAPS FOR STEADY STATE SEMICONDUCTOR MODELS Joseph W. Jerome Department of Mathematics Northwestern University Evanston, IL 60208 Abstract
JFETs - MESFETs - MODFETs
 Technische Universität raz Institute of Solid State Physics JFETs - MESFETs - MOFETs JFET n n-channel JFET S n-channel JFET x n 2 ( Vbi V) en S p-channel JFET 2 Pinch-off at h = x en n h Vp 2 V p = pinch-off
Technische Universität raz Institute of Solid State Physics JFETs - MESFETs - MOFETs JFET n n-channel JFET S n-channel JFET x n 2 ( Vbi V) en S p-channel JFET 2 Pinch-off at h = x en n h Vp 2 V p = pinch-off
EE105 - Fall 2005 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits
 EE105 - Fall 005 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits ecture 7 MOS Transistor Announcements Homework 3, due today Homework 4 due next week ab this week Reading: Chapter 4 1 ecture Material ast lecture
EE105 - Fall 005 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits ecture 7 MOS Transistor Announcements Homework 3, due today Homework 4 due next week ab this week Reading: Chapter 4 1 ecture Material ast lecture
Operation and Modeling of. The MOS Transistor. Second Edition. Yannis Tsividis Columbia University. New York Oxford OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS
 Operation and Modeling of The MOS Transistor Second Edition Yannis Tsividis Columbia University New York Oxford OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS CONTENTS Chapter 1 l.l 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 Chapter 2 2.1 2.2
Operation and Modeling of The MOS Transistor Second Edition Yannis Tsividis Columbia University New York Oxford OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS CONTENTS Chapter 1 l.l 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 Chapter 2 2.1 2.2
Lecture 11: J-FET and MOSFET
 ENE 311 Lecture 11: J-FET and MOSFET FETs vs. BJTs Similarities: Amplifiers Switching devices Impedance matching circuits Differences: FETs are voltage controlled devices. BJTs are current controlled devices.
ENE 311 Lecture 11: J-FET and MOSFET FETs vs. BJTs Similarities: Amplifiers Switching devices Impedance matching circuits Differences: FETs are voltage controlled devices. BJTs are current controlled devices.
On the approximation of real powers of sparse, infinite, bounded and Hermitian matrices
 On the approximation of real poers of sparse, infinite, bounded and Hermitian matrices Roman Werpachoski Center for Theoretical Physics, Al. Lotnikó 32/46 02-668 Warszaa, Poland Abstract We describe a
On the approximation of real poers of sparse, infinite, bounded and Hermitian matrices Roman Werpachoski Center for Theoretical Physics, Al. Lotnikó 32/46 02-668 Warszaa, Poland Abstract We describe a
Quantum and Non-local Transport Models in Crosslight Device Simulators. Copyright 2008 Crosslight Software Inc.
 Quantum and Non-local Transport Models in Crosslight Device Simulators Copyright 2008 Crosslight Software Inc. 1 Introduction Quantization effects Content Self-consistent charge-potential profile. Space
Quantum and Non-local Transport Models in Crosslight Device Simulators Copyright 2008 Crosslight Software Inc. 1 Introduction Quantization effects Content Self-consistent charge-potential profile. Space
Atomistic effect of delta doping layer in a 50 nm InP HEMT
 J Comput Electron (26) 5:131 135 DOI 1.7/s1825-6-8832-3 Atomistic effect of delta doping layer in a 5 nm InP HEMT N. Seoane A. J. García-Loureiro K. Kalna A. Asenov C Science + Business Media, LLC 26 Abstract
J Comput Electron (26) 5:131 135 DOI 1.7/s1825-6-8832-3 Atomistic effect of delta doping layer in a 5 nm InP HEMT N. Seoane A. J. García-Loureiro K. Kalna A. Asenov C Science + Business Media, LLC 26 Abstract
Early & Quick COSMIC-FFP Analysis using Analytic Hierarchy Process
 Early & Quick COSMIC-FFP Analysis using Analytic Hierarchy Process uca Santillo (luca.santillo@gmail.com) Abstract COSMIC-FFP is a rigorous measurement method that makes possible to measure the functional
Early & Quick COSMIC-FFP Analysis using Analytic Hierarchy Process uca Santillo (luca.santillo@gmail.com) Abstract COSMIC-FFP is a rigorous measurement method that makes possible to measure the functional
