Lipid Regulated Intramolecular Conformational Dynamics of SNARE-Protein Ykt6
|
|
|
- Elisabeth Dickerson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Supplementary Information for: Lipid Regulated Intramolecular Conformational Dynamics of SNARE-Protein Ykt6 Yawei Dai 1, 2, Markus Seeger 3, Jingwei Weng 4, Song Song 1, 2, Wenning Wang 4, Yan-Wen 1, 2, * Tan 1 Department of Physics, Fudan University, , Shanghai, P.R. China; 2 State Key Laboratory of Surface Physics, Fudan University, , Shanghai, P.R. China 3 Institute of Biophysics, Goethe-University Frankfurt Max-von-Laue-Str. 1, 60438, Frankfurt/Main, Germany 4 Shanghai Key Laboratory of Molecular Catalysis and Innovative Materials, Department of Chemistry and Institutes of Biomedical Sciences, Fudan University, 220 Handan Rd., , Shanghai, P.R. China; * Correspondence should be addressed to: ywtan@fudan.edu.cn.
2 Note 1: Design of rykt6δc FRET construct Single molecule FRET (smfret) is a direct and powerful technique for demonstrating the conformational changes between the longin domain and the SNARE core of rykt6 C. Nevertheless, for smfret measurements to perform well, the distances to be determined have to fall around the Förster radii R0 of a chosen FRET pair since smfret measurements are most sensitive there. The two labeling sites on the molecule, rykt6δc, has to be chosen such that the distances between them will optimally report any conformational changes between the longin domain and the SNARE core. There is a native Cysteine residue, C66, in the sequence of Ykt6 from Rattus norvegicus besides the CCAIM terminal. To minimize the perturbation of the original construct, we reserved this C66 in the longin domain as one of the FRET labeling sites. We then narrowed down our labeling site selection to the central part of the core domain. To choose the proper site, we fetched the longin domain sequences from Pfam and UniProt, ran multiple sequence alignment with ClustalWS, and calculated the conservation scores for each residue on rykt6. Residues with low conservation scores was chosen as potential labeling sites. We have chosen E175 as our labeling residue on rykt6δc. Since the only crystal structure of rykt6 available (PDB-ID: 3KYQ) is in the closed form bound with DPC, we used MD simulation result to predict an open structure. Full length of rykt6 C has 193 amino acids (Figure S1a), and the yielded distances between predicted label sites (C66 and E175C) are in the range of 20 Å and 62 Å for the closed and open conformations respectively. In this work we have chosen two different FRET pairs, Alexa 555/647 and Alexa 488/647, for smfret and FCCS experiments, respectively. The Förster radii R0 for these two pairs are 51 Å and 56 Å, which is suitable for reporting conformational changes between 20 Å and 62 Å. As a remark, previous work Hasegawa et al found that targeting function of Ykt6 is regulated by its longin domain (sequence: 1-137) and normal Ykt6 requires a soluble intermediate. In our earlier attempts, we found that the native cysteine C66 is a possible site related to the solubility of Ykt6. The final construct Ykt6/E175C keeps the soluble features as the wildtype one. Although the native C66 labeling site is not fully exposed to solution in the structure with PDB id 3KYQ, the construct rykt6 E175C can be readily doubly labeled which is observed in single-molecule experiment. (see Figure S2).
3 Note 2: Structure diversity analyzed by MD simulations at a longer distances range As the Cys66-Glu175 C distance falls within longer distance range, i.e nm, more prominent structural variability of the SNARE core was observed while the longin domain retains its structure. The conformations were divided into 49 clusters with a cutoff of 1.1 nm (Figure S7). The SNARE core becomes more stretched and less compact. The positions of the Glu175 Cα are obviously distributed in a larger space than that of the closed state, ranging around the αa helix, the βc-βd turn, the αd helix and the βd-βe turn (Figure S8(a), (b)). In spite of the more extended conformations in the open state, two clusters were still found with the longin-snare BSA of more than 12 nm2. The 1st cluster adopts a similar αg orientation as the 3rd and 5-8th clusters of the closed state with the helix lying parallel with αa (Figure S8(c)). The 2nd cluster shows an antiparallel orientation between the αg and αa helices, reminiscent of the 9th cluster of the closed state (Figure S8(d)). The N-terminus of αg helix is uncoiled in these two clusters, resulting in the longer distance between Glu175 and Cys66. We also inspect the centre structures with the smallest BSA (Figure S8(e-j)). In these structures, the αg helix is more than 0.9 nm away from the αa helix and has little contact with the longin domain. Nevertheless, the αg helix tends to pack with SNARE core itself in the last six clusters, placing its C-terminus in the vicinity of the αe helix. The backbone hydrogen bond interactions between βc and βf strands could be disrupted in the open state as in the last two clusters (Figure S8(i-j)). The disruption further reduces the BSA, providing extra conformational flexibility to the SNARE core. Though the open state is more disordered, the αg-αa packing is still observed, indicating the stability of the secondary structures.
4
5 Figure S1. Sequence, purification, and labeling strategy of our FRET construct rykt6 C. (a) Amino acid sequence of rykt6 C and the modified FRET-construct; The chosen labeling sites are C66 and E175C (highlighted in green and red). (b) SDS-PAGE gel showing the purified rykt6δc protein used in our studies. The red box points out the molecular weight of rykt6 C at 24.6 KDa. (c) Two structures predicts by our Molecular Dynamics (MD) simulations showing the structures of doubly labeled Ykt6 in open (left) and closed (right) states. Both structures are simulated based on PDB structure 3KYQ, which is closer to the closed form. Structures of dyes are simulated with assumed structures of Alexa 555 (green) and Alexa 647 (red). Figure S2. Single intensity vs. time trajectory of rykt6 C. The rykt6 C molecule is selected by the Co-localization method. The intensity vs. time trajectory of the chosen molecule is shown in Fig. S2. We impose a strict screening procedure to make sure each molecule taken into our data pool are labeled with one FRET pair (Alexa 555/647) as shown in Fig. S2. The blue curve stands for donor channel and the red curve stands for acceptor channel.
6 Figure S3. Correlations of double-labeled Poly-Proline (green: AC-d, red: AC-a, black: CC- da, blue: CC-ad). From Fig. S3(a) we found that all ACs (Autocorrelation) and CCs (Crosscorrelation) are obviously measurable. Regarding the correlation amplitude, the measurements confirms the expectations of a high amplitude of the AC-d (Autocorrelation Donor), a lower amplitude of acceptor and even lower amplitudes for the CCs. Furthermore the similarity of the CC shows the symmetry of the CCs. Fig. S3(b) shows that the normalized correlations owning the same correlation decay. This confirms that there is no time dependent difference between the four correlations. Since Poly- Proline15 can be seen as a rigid molecule without intramolecular conformational dynamics, these measurements are consistent with theoretical expectations. Regarding the yielded Poly-Proline fitting results shown in tab. S1, one can use the p-value marking the ratio of lateral to axial dimensions of the focal region for further measurements. The threshold of this parameter were set to 6.85 as the lower and 6.9 as the upper boundary conditions. Table S1: Fitting parameters of Poly-Proline
7 Figure S4. Normalized correlations of Rhodamine 6G with 1 nm and 5 nm (green: AC-d, red: AC-a). Rhodame 6G was used as a simple reference sample to calculate the dimension of the focal region. In Fig. S4, both correlation functions coincide with each other beyond 10 µs. From the fitting results one can calculate the dimensions of the focal region by using μ 2 = 4 D τ D with μ as the lateral dimension of the focus, D as the specific diffusion coefficient of the sample and τ D as the average transit time through the focus. This leads to the focal dimensions of 4.07µm x 0.59 µm. Table S2. Fitting results of Rhodamine 6G
8 Figure S5. DPC concentration ratio gradient of double-labeled Ykt6 (green: AC-d, red: AC-a, black: CC- da, blue: CC-ad). Left side of Fig. S5 shows the raw data of correlations of double-labeled Ykt6. The normalized correlation data on the right side of Fig. S5 shows, that with increasing amount of DPC the time shift between both AC and the CC decreases and nearly vanishes at a concentration ratio of Ykt6 1:2 DPC. This DPC concentration ratio gradient presents that 1:2 ratio is the saturate concentration forces Ykt6 into a stable state.
9 Figure S6. Cluster center structures of the snapshots with shorter Cys66-Glu175 distance in the metadynamics simulations using different cutoff values. The protein is represented by the cartoon mode and is coloured from red to blue. The Cα atoms of Glu175 in the cluster center structures are represented as green balls and the Cα atom of Cys66 is represented as magenta ball. Different cutoff values are used in the clustering analysis. Larger cutoff values lead to fewer clusters and when the cutoff equals 1.0 nm, a characteristic center structure is neglected as marked by the orange circle.
10 Figure S7. Cluster center structures of the snapshots with longer Cys66-Glu175 distance in the metadynamics simulations using different cutoff values. The protein is represented by the cartoon mode and is coloured from red to blue. The Cα atoms of Glu175 in the cluster center structures are represented as green balls and the Cα atom of Cys66 is represented as magenta ball. Different cutoff values are used in the clustering analysis. Larger cutoff values lead to fewer clusters and when the cutoff equals 1.0 nm, a characteristic center structure is neglected as marked by the orange circle.
11 Figure S8. Representative structures with longer Cys66-Glu175 Cα distance from the MD simulation. Front view (a) and top view (b) of the cluster centre structures of the snapshots with the Cys66-Glu175 distance ranging from 3.2 to 3.9 nm in the metadynamics simulations using a cutoff of 0.6 nm. The protein is represented by the cartoon mode and is coloured from red to blue. The Cα atoms of Glu175 in the cluster centre structures are represented as green balls and the Cα atom of Cys66 is represented as magenta ball. (c)-(d) The centre structures with the BSA between longin domain and SNARE core of more than 12 nm 2. (e)-(j) The six centre structures with the smallest BSA.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary materials Figure S1 Fusion protein of Sulfolobus solfataricus SRP54 and a signal peptide. a, Expression vector for the fusion protein. The signal peptide of yeast dipeptidyl aminopeptidase
Supplementary materials Figure S1 Fusion protein of Sulfolobus solfataricus SRP54 and a signal peptide. a, Expression vector for the fusion protein. The signal peptide of yeast dipeptidyl aminopeptidase
Protein Structure. W. M. Grogan, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES
 Protein Structure W. M. Grogan, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES 1. Describe the structure and characteristic properties of typical proteins. 2. List and describe the four levels of structure found in proteins. 3. Relate
Protein Structure W. M. Grogan, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES 1. Describe the structure and characteristic properties of typical proteins. 2. List and describe the four levels of structure found in proteins. 3. Relate
Supplementary figure 1 Application of tmfret in LeuT. (a) To assess the feasibility of using tmfret for distance-dependent measurements in LeuT, a
 Supplementary figure 1 Application of tmfret in LeuT. (a) To assess the feasibility of using tmfret for distance-dependent measurements in LeuT, a series of tmfret-pairs comprised of single cysteine mutants
Supplementary figure 1 Application of tmfret in LeuT. (a) To assess the feasibility of using tmfret for distance-dependent measurements in LeuT, a series of tmfret-pairs comprised of single cysteine mutants
Structure and evolution of the spliceosomal peptidyl-prolyl cistrans isomerase Cwc27
 Acta Cryst. (2014). D70, doi:10.1107/s1399004714021695 Supporting information Volume 70 (2014) Supporting information for article: Structure and evolution of the spliceosomal peptidyl-prolyl cistrans isomerase
Acta Cryst. (2014). D70, doi:10.1107/s1399004714021695 Supporting information Volume 70 (2014) Supporting information for article: Structure and evolution of the spliceosomal peptidyl-prolyl cistrans isomerase
Supplemental Materials and Methods
 Supplemental Materials and Methods Time-resolved FRET (trfret) to probe for changes in the Box A/A stem upon complex assembly U3 MINI was folded and the decay of Fl fluorescence was measured at 20 ºC (see
Supplemental Materials and Methods Time-resolved FRET (trfret) to probe for changes in the Box A/A stem upon complex assembly U3 MINI was folded and the decay of Fl fluorescence was measured at 20 ºC (see
Introduction to" Protein Structure
 Introduction to" Protein Structure Function, evolution & experimental methods Thomas Blicher, Center for Biological Sequence Analysis Learning Objectives Outline the basic levels of protein structure.
Introduction to" Protein Structure Function, evolution & experimental methods Thomas Blicher, Center for Biological Sequence Analysis Learning Objectives Outline the basic levels of protein structure.
Secondary Structure. Bioch/BIMS 503 Lecture 2. Structure and Function of Proteins. Further Reading. Φ, Ψ angles alone determine protein structure
 Bioch/BIMS 503 Lecture 2 Structure and Function of Proteins August 28, 2008 Robert Nakamoto rkn3c@virginia.edu 2-0279 Secondary Structure Φ Ψ angles determine protein structure Φ Ψ angles are restricted
Bioch/BIMS 503 Lecture 2 Structure and Function of Proteins August 28, 2008 Robert Nakamoto rkn3c@virginia.edu 2-0279 Secondary Structure Φ Ψ angles determine protein structure Φ Ψ angles are restricted
Nitrogenase MoFe protein from Clostridium pasteurianum at 1.08 Å resolution: comparison with the Azotobacter vinelandii MoFe protein
 Acta Cryst. (2015). D71, 274-282, doi:10.1107/s1399004714025243 Supporting information Volume 71 (2015) Supporting information for article: Nitrogenase MoFe protein from Clostridium pasteurianum at 1.08
Acta Cryst. (2015). D71, 274-282, doi:10.1107/s1399004714025243 Supporting information Volume 71 (2015) Supporting information for article: Nitrogenase MoFe protein from Clostridium pasteurianum at 1.08
Table S1. Overview of used PDZK1 constructs and their binding affinities to peptides. Related to figure 1.
 Table S1. Overview of used PDZK1 constructs and their binding affinities to peptides. Related to figure 1. PDZK1 constru cts Amino acids MW [kda] KD [μm] PEPT2-CT- FITC KD [μm] NHE3-CT- FITC KD [μm] PDZK1-CT-
Table S1. Overview of used PDZK1 constructs and their binding affinities to peptides. Related to figure 1. PDZK1 constru cts Amino acids MW [kda] KD [μm] PEPT2-CT- FITC KD [μm] NHE3-CT- FITC KD [μm] PDZK1-CT-
THE CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF THE SGT1-SKP1 COMPLEX: THE LINK BETWEEN
 THE CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF THE SGT1-SKP1 COMPLEX: THE LINK BETWEEN HSP90 AND BOTH SCF E3 UBIQUITIN LIGASES AND KINETOCHORES Oliver Willhoft, Richard Kerr, Dipali Patel, Wenjuan Zhang, Caezar Al-Jassar, Tina
THE CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF THE SGT1-SKP1 COMPLEX: THE LINK BETWEEN HSP90 AND BOTH SCF E3 UBIQUITIN LIGASES AND KINETOCHORES Oliver Willhoft, Richard Kerr, Dipali Patel, Wenjuan Zhang, Caezar Al-Jassar, Tina
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Fig. 1 Influences of crystal lattice contacts on Pol η structures. a. The dominant lattice contact between two hpol η molecules (silver and gold) in the type 1 crystals. b. A close-up view of the hydrophobic
Fig. 1 Influences of crystal lattice contacts on Pol η structures. a. The dominant lattice contact between two hpol η molecules (silver and gold) in the type 1 crystals. b. A close-up view of the hydrophobic
HOMOLOGY MODELING. The sequence alignment and template structure are then used to produce a structural model of the target.
 HOMOLOGY MODELING Homology modeling, also known as comparative modeling of protein refers to constructing an atomic-resolution model of the "target" protein from its amino acid sequence and an experimental
HOMOLOGY MODELING Homology modeling, also known as comparative modeling of protein refers to constructing an atomic-resolution model of the "target" protein from its amino acid sequence and an experimental
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature11054 Supplementary Fig. 1 Sequence alignment of Na v Rh with NaChBac, Na v Ab, and eukaryotic Na v and Ca v homologs. Secondary structural elements of Na v Rh are indicated above the
doi:10.1038/nature11054 Supplementary Fig. 1 Sequence alignment of Na v Rh with NaChBac, Na v Ab, and eukaryotic Na v and Ca v homologs. Secondary structural elements of Na v Rh are indicated above the
Structure and RNA-binding properties. of the Not1 Not2 Not5 module of the yeast Ccr4 Not complex
 Structure and RNA-binding properties of the Not1 Not2 Not5 module of the yeast Ccr4 Not complex Varun Bhaskar 1, Vladimir Roudko 2,3, Jerome Basquin 1, Kundan Sharma 4, Henning Urlaub 4, Bertrand Seraphin
Structure and RNA-binding properties of the Not1 Not2 Not5 module of the yeast Ccr4 Not complex Varun Bhaskar 1, Vladimir Roudko 2,3, Jerome Basquin 1, Kundan Sharma 4, Henning Urlaub 4, Bertrand Seraphin
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Dph2 SeMet (iron-free) # Dph2 (iron-free) Dph2-[4Fe-4S] Data collection Space group P2 1 2 1 2 1 P2 1 2 1 2 1 P2 1 2 1 2 1 Cell dimensions a, b, c (Å) 58.26, 82.08, 160.42 58.74, 81.87, 160.01 55.70, 80.53,
Dph2 SeMet (iron-free) # Dph2 (iron-free) Dph2-[4Fe-4S] Data collection Space group P2 1 2 1 2 1 P2 1 2 1 2 1 P2 1 2 1 2 1 Cell dimensions a, b, c (Å) 58.26, 82.08, 160.42 58.74, 81.87, 160.01 55.70, 80.53,
Lecture 26: Polymers: DNA Packing and Protein folding 26.1 Problem Set 4 due today. Reading for Lectures 22 24: PKT Chapter 8 [ ].
![Lecture 26: Polymers: DNA Packing and Protein folding 26.1 Problem Set 4 due today. Reading for Lectures 22 24: PKT Chapter 8 [ ]. Lecture 26: Polymers: DNA Packing and Protein folding 26.1 Problem Set 4 due today. Reading for Lectures 22 24: PKT Chapter 8 [ ].](/thumbs/84/90810734.jpg) Lecture 26: Polymers: DA Packing and Protein folding 26.1 Problem Set 4 due today. eading for Lectures 22 24: PKT hapter 8 DA Packing for Eukaryotes: The packing problem for the larger eukaryotic genomes
Lecture 26: Polymers: DA Packing and Protein folding 26.1 Problem Set 4 due today. eading for Lectures 22 24: PKT hapter 8 DA Packing for Eukaryotes: The packing problem for the larger eukaryotic genomes
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Ottmann et al. 10.1073/pnas.0907587106 Fig. S1. Primary structure alignment of SBT3 with C5 peptidase from Streptococcus pyogenes. The Matchmaker tool in UCSF Chimera (http:// www.cgl.ucsf.edu/chimera)
Supporting Information Ottmann et al. 10.1073/pnas.0907587106 Fig. S1. Primary structure alignment of SBT3 with C5 peptidase from Streptococcus pyogenes. The Matchmaker tool in UCSF Chimera (http:// www.cgl.ucsf.edu/chimera)
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11524 Supplementary discussion Functional analysis of the sugar porter family (SP) signature motifs. As seen in Fig. 5c, single point mutation of the conserved
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11524 Supplementary discussion Functional analysis of the sugar porter family (SP) signature motifs. As seen in Fig. 5c, single point mutation of the conserved
Protein Structure Basics
 Protein Structure Basics Presented by Alison Fraser, Christine Lee, Pradhuman Jhala, Corban Rivera Importance of Proteins Muscle structure depends on protein-protein interactions Transport across membranes
Protein Structure Basics Presented by Alison Fraser, Christine Lee, Pradhuman Jhala, Corban Rivera Importance of Proteins Muscle structure depends on protein-protein interactions Transport across membranes
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Results DNA binding property of the SRA domain was examined by an electrophoresis mobility shift assay (EMSA) using synthesized 12-bp oligonucleotide duplexes containing unmodified, hemi-methylated,
Supplementary Results DNA binding property of the SRA domain was examined by an electrophoresis mobility shift assay (EMSA) using synthesized 12-bp oligonucleotide duplexes containing unmodified, hemi-methylated,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Table 1: Data collection, phasing and refinement statistics ChbC/Ta 6 Br 12 Native ChbC Data collection Space group P4 3 2 1 2 P4 3 2 1 2 Cell dimensions a, c (Å) 132.75, 453.57 132.81, 452.95
Supplementary Table 1: Data collection, phasing and refinement statistics ChbC/Ta 6 Br 12 Native ChbC Data collection Space group P4 3 2 1 2 P4 3 2 1 2 Cell dimensions a, c (Å) 132.75, 453.57 132.81, 452.95
LS1a Fall 2014 Problem Set #2 Due Monday 10/6 at 6 pm in the drop boxes on the Science Center 2 nd Floor
 LS1a Fall 2014 Problem Set #2 Due Monday 10/6 at 6 pm in the drop boxes on the Science Center 2 nd Floor Note: Adequate space is given for each answer. Questions that require a brief explanation should
LS1a Fall 2014 Problem Set #2 Due Monday 10/6 at 6 pm in the drop boxes on the Science Center 2 nd Floor Note: Adequate space is given for each answer. Questions that require a brief explanation should
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Crystallization. a, Crystallization constructs of the ET B receptor are shown, with all of the modifications to the human wild-type the ET B receptor indicated. Residues interacting
Supplementary Figure 1 Crystallization. a, Crystallization constructs of the ET B receptor are shown, with all of the modifications to the human wild-type the ET B receptor indicated. Residues interacting
Design of a Novel Globular Protein Fold with Atomic-Level Accuracy
 Design of a Novel Globular Protein Fold with Atomic-Level Accuracy Brian Kuhlman, Gautam Dantas, Gregory C. Ireton, Gabriele Varani, Barry L. Stoddard, David Baker Presented by Kate Stafford 4 May 05 Protein
Design of a Novel Globular Protein Fold with Atomic-Level Accuracy Brian Kuhlman, Gautam Dantas, Gregory C. Ireton, Gabriele Varani, Barry L. Stoddard, David Baker Presented by Kate Stafford 4 May 05 Protein
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Table S1 Kinetic Analyses of the AMSH-LP mutants AMSH-LP K M (μm) k cat x 10-3 (s -1 ) WT 71.8 ± 6.3 860 ± 65.4 T353A 76.8 ± 11.7 46.3 ± 3.7 F355A 58.9 ± 10.4 5.33 ± 0.30 proximal S358A 75.1
Supplementary Table S1 Kinetic Analyses of the AMSH-LP mutants AMSH-LP K M (μm) k cat x 10-3 (s -1 ) WT 71.8 ± 6.3 860 ± 65.4 T353A 76.8 ± 11.7 46.3 ± 3.7 F355A 58.9 ± 10.4 5.33 ± 0.30 proximal S358A 75.1
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Table 1: Amplitudes of three current levels. Level 0 (pa) Level 1 (pa) Level 2 (pa) TrkA- TrkH WT 200 K 0.01 ± 0.01 9.5 ± 0.01 18.7 ± 0.03 200 Na * 0.001 ± 0.01 3.9 ± 0.01 12.5 ± 0.03 200
Supplementary Table 1: Amplitudes of three current levels. Level 0 (pa) Level 1 (pa) Level 2 (pa) TrkA- TrkH WT 200 K 0.01 ± 0.01 9.5 ± 0.01 18.7 ± 0.03 200 Na * 0.001 ± 0.01 3.9 ± 0.01 12.5 ± 0.03 200
Announcements. Primary (1 ) Structure. Lecture 7 & 8: PROTEIN ARCHITECTURE IV: Tertiary and Quaternary Structure
 Announcements TA Office Hours: Brian Eckenroth Monday 3-4 pm Thursday 11 am-12 pm Lecture 7 & 8: PROTEIN ARCHITECTURE IV: Tertiary and Quaternary Structure Margaret Daugherty Fall 2003 Homework II posted
Announcements TA Office Hours: Brian Eckenroth Monday 3-4 pm Thursday 11 am-12 pm Lecture 7 & 8: PROTEIN ARCHITECTURE IV: Tertiary and Quaternary Structure Margaret Daugherty Fall 2003 Homework II posted
The Structure and Functions of Proteins
 Wright State University CORE Scholar Computer Science and Engineering Faculty Publications Computer Science and Engineering 2003 The Structure and Functions of Proteins Dan E. Krane Wright State University
Wright State University CORE Scholar Computer Science and Engineering Faculty Publications Computer Science and Engineering 2003 The Structure and Functions of Proteins Dan E. Krane Wright State University
Introduction to Comparative Protein Modeling. Chapter 4 Part I
 Introduction to Comparative Protein Modeling Chapter 4 Part I 1 Information on Proteins Each modeling study depends on the quality of the known experimental data. Basis of the model Search in the literature
Introduction to Comparative Protein Modeling Chapter 4 Part I 1 Information on Proteins Each modeling study depends on the quality of the known experimental data. Basis of the model Search in the literature
BMB/Bi/Ch 173 Winter 2018
 BMB/Bi/Ch 173 Winter 2018 Homework Set 8.1 (100 Points) Assigned 2-27-18, due 3-6-18 by 10:30 a.m. TA: Rachael Kuintzle. Office hours: SFL 220, Friday 3/2 4:00-5:00pm and SFL 229, Monday 3/5 4:00-5:30pm.
BMB/Bi/Ch 173 Winter 2018 Homework Set 8.1 (100 Points) Assigned 2-27-18, due 3-6-18 by 10:30 a.m. TA: Rachael Kuintzle. Office hours: SFL 220, Friday 3/2 4:00-5:00pm and SFL 229, Monday 3/5 4:00-5:30pm.
Basics of protein structure
 Today: 1. Projects a. Requirements: i. Critical review of one paper ii. At least one computational result b. Noon, Dec. 3 rd written report and oral presentation are due; submit via email to bphys101@fas.harvard.edu
Today: 1. Projects a. Requirements: i. Critical review of one paper ii. At least one computational result b. Noon, Dec. 3 rd written report and oral presentation are due; submit via email to bphys101@fas.harvard.edu
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature11085 Supplementary Tables: Supplementary Table 1. Summary of crystallographic and structure refinement data Structure BRIL-NOP receptor Data collection Number of crystals 23 Space group
doi:10.1038/nature11085 Supplementary Tables: Supplementary Table 1. Summary of crystallographic and structure refinement data Structure BRIL-NOP receptor Data collection Number of crystals 23 Space group
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. doi: /nature07461
 Figure S1 Electrophysiology. a ph-activation of. Two-electrode voltage clamp recordings of Xenopus oocytes expressing in comparison to waterinjected oocytes. Currents were recorded at 40 mv. The ph of
Figure S1 Electrophysiology. a ph-activation of. Two-electrode voltage clamp recordings of Xenopus oocytes expressing in comparison to waterinjected oocytes. Currents were recorded at 40 mv. The ph of
Cryo-EM data collection, refinement and validation statistics
 1 Table S1 Cryo-EM data collection, refinement and validation statistics Data collection and processing CPSF-160 WDR33 (EMDB-7114) (PDB 6BM0) CPSF-160 WDR33 (EMDB-7113) (PDB 6BLY) CPSF-160 WDR33 CPSF-30
1 Table S1 Cryo-EM data collection, refinement and validation statistics Data collection and processing CPSF-160 WDR33 (EMDB-7114) (PDB 6BM0) CPSF-160 WDR33 (EMDB-7113) (PDB 6BLY) CPSF-160 WDR33 CPSF-30
Diphthamide biosynthesis requires a radical iron-sulfur enzyme. Pennsylvania State University, University Park, Pennsylvania 16802, USA
 Diphthamide biosynthesis requires a radical iron-sulfur enzyme Yang Zhang, 1,4 Xuling Zhu, 1,4 Andrew T. Torelli, 1 Michael Lee, 2 Boris Dzikovski, 1 Rachel Koralewski, 1 Eileen Wang, 1 Jack Freed, 1 Carsten
Diphthamide biosynthesis requires a radical iron-sulfur enzyme Yang Zhang, 1,4 Xuling Zhu, 1,4 Andrew T. Torelli, 1 Michael Lee, 2 Boris Dzikovski, 1 Rachel Koralewski, 1 Eileen Wang, 1 Jack Freed, 1 Carsten
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics. This journal is the Owner Societies 2016 Supporting Information Lipid molecules can induce an opening of membrane-facing
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics. This journal is the Owner Societies 2016 Supporting Information Lipid molecules can induce an opening of membrane-facing
DISCRETE TUTORIAL. Agustí Emperador. Institute for Research in Biomedicine, Barcelona APPLICATION OF DISCRETE TO FLEXIBLE PROTEIN-PROTEIN DOCKING:
 DISCRETE TUTORIAL Agustí Emperador Institute for Research in Biomedicine, Barcelona APPLICATION OF DISCRETE TO FLEXIBLE PROTEIN-PROTEIN DOCKING: STRUCTURAL REFINEMENT OF DOCKING CONFORMATIONS Emperador
DISCRETE TUTORIAL Agustí Emperador Institute for Research in Biomedicine, Barcelona APPLICATION OF DISCRETE TO FLEXIBLE PROTEIN-PROTEIN DOCKING: STRUCTURAL REFINEMENT OF DOCKING CONFORMATIONS Emperador
Section Week 3. Junaid Malek, M.D.
 Section Week 3 Junaid Malek, M.D. Biological Polymers DA 4 monomers (building blocks), limited structure (double-helix) RA 4 monomers, greater flexibility, multiple structures Proteins 20 Amino Acids,
Section Week 3 Junaid Malek, M.D. Biological Polymers DA 4 monomers (building blocks), limited structure (double-helix) RA 4 monomers, greater flexibility, multiple structures Proteins 20 Amino Acids,
Table 1. Crystallographic data collection, phasing and refinement statistics. Native Hg soaked Mn soaked 1 Mn soaked 2
 Table 1. Crystallographic data collection, phasing and refinement statistics Native Hg soaked Mn soaked 1 Mn soaked 2 Data collection Space group P2 1 2 1 2 1 P2 1 2 1 2 1 P2 1 2 1 2 1 P2 1 2 1 2 1 Cell
Table 1. Crystallographic data collection, phasing and refinement statistics Native Hg soaked Mn soaked 1 Mn soaked 2 Data collection Space group P2 1 2 1 2 1 P2 1 2 1 2 1 P2 1 2 1 2 1 P2 1 2 1 2 1 Cell
Protein Dynamics. The space-filling structures of myoglobin and hemoglobin show that there are no pathways for O 2 to reach the heme iron.
 Protein Dynamics The space-filling structures of myoglobin and hemoglobin show that there are no pathways for O 2 to reach the heme iron. Below is myoglobin hydrated with 350 water molecules. Only a small
Protein Dynamics The space-filling structures of myoglobin and hemoglobin show that there are no pathways for O 2 to reach the heme iron. Below is myoglobin hydrated with 350 water molecules. Only a small
NB-DNJ/GCase-pH 7.4 NB-DNJ+/GCase-pH 7.4 NB-DNJ+/GCase-pH 4.5
 SUPPLEMENTARY TABLES Suppl. Table 1. Protonation states at ph 7.4 and 4.5. Protonation states of titratable residues in GCase at ph 7.4 and 4.5. Histidine: HID, H at δ-nitrogen; HIE, H at ε-nitrogen; HIP,
SUPPLEMENTARY TABLES Suppl. Table 1. Protonation states at ph 7.4 and 4.5. Protonation states of titratable residues in GCase at ph 7.4 and 4.5. Histidine: HID, H at δ-nitrogen; HIE, H at ε-nitrogen; HIP,
Dana Alsulaibi. Jaleel G.Sweis. Mamoon Ahram
 15 Dana Alsulaibi Jaleel G.Sweis Mamoon Ahram Revision of last lectures: Proteins have four levels of structures. Primary,secondary, tertiary and quaternary. Primary structure is the order of amino acids
15 Dana Alsulaibi Jaleel G.Sweis Mamoon Ahram Revision of last lectures: Proteins have four levels of structures. Primary,secondary, tertiary and quaternary. Primary structure is the order of amino acids
Time-dependence of key H-bond/electrostatic interaction distances in the sirna5-hago2 complexes... Page S14
 Supporting Information Probing the Binding Interactions between Chemically Modified sirnas and Human Argonaute 2 Using Microsecond Molecular Dynamics Simulations S. Harikrishna* and P. I. Pradeepkumar*
Supporting Information Probing the Binding Interactions between Chemically Modified sirnas and Human Argonaute 2 Using Microsecond Molecular Dynamics Simulations S. Harikrishna* and P. I. Pradeepkumar*
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature17991 Supplementary Discussion Structural comparison with E. coli EmrE The DMT superfamily includes a wide variety of transporters with 4-10 TM segments 1. Since the subfamilies of the
doi:10.1038/nature17991 Supplementary Discussion Structural comparison with E. coli EmrE The DMT superfamily includes a wide variety of transporters with 4-10 TM segments 1. Since the subfamilies of the
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/5/243/ra68/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Superbinder SH2 Domains Act as Antagonists of Cell Signaling Tomonori Kaneko, Haiming Huang, Xuan Cao, Xing Li, Chengjun
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/5/243/ra68/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Superbinder SH2 Domains Act as Antagonists of Cell Signaling Tomonori Kaneko, Haiming Huang, Xuan Cao, Xing Li, Chengjun
Destruction of Amyloid Fibrils by Graphene through Penetration and Extraction of Peptides
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Destruction of Amyloid Fibrils by Graphene through Penetration and Extraction of Peptides Zaixing
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Destruction of Amyloid Fibrils by Graphene through Penetration and Extraction of Peptides Zaixing
I690/B680 Structural Bioinformatics Spring Protein Structure Determination by NMR Spectroscopy
 I690/B680 Structural Bioinformatics Spring 2006 Protein Structure Determination by NMR Spectroscopy Suggested Reading (1) Van Holde, Johnson, Ho. Principles of Physical Biochemistry, 2 nd Ed., Prentice
I690/B680 Structural Bioinformatics Spring 2006 Protein Structure Determination by NMR Spectroscopy Suggested Reading (1) Van Holde, Johnson, Ho. Principles of Physical Biochemistry, 2 nd Ed., Prentice
Model Mélange. Physical Models of Peptides and Proteins
 Model Mélange Physical Models of Peptides and Proteins In the Model Mélange activity, you will visit four different stations each featuring a variety of different physical models of peptides or proteins.
Model Mélange Physical Models of Peptides and Proteins In the Model Mélange activity, you will visit four different stations each featuring a variety of different physical models of peptides or proteins.
Get familiar with PDBsum and the PDB Extract atomic coordinates from protein data files Compute bond angles and dihedral angles
 CS483 Assignment #2 Due date: Mar. 1 at the start of class. Protein Geometry Bedbug spit? Just say NO! Purpose of this assignment Get familiar with PDBsum and the PDB Extract atomic coordinates from protein
CS483 Assignment #2 Due date: Mar. 1 at the start of class. Protein Geometry Bedbug spit? Just say NO! Purpose of this assignment Get familiar with PDBsum and the PDB Extract atomic coordinates from protein
Packing of Secondary Structures
 7.88 Lecture Notes - 4 7.24/7.88J/5.48J The Protein Folding and Human Disease Professor Gossard Retrieving, Viewing Protein Structures from the Protein Data Base Helix helix packing Packing of Secondary
7.88 Lecture Notes - 4 7.24/7.88J/5.48J The Protein Folding and Human Disease Professor Gossard Retrieving, Viewing Protein Structures from the Protein Data Base Helix helix packing Packing of Secondary
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature10955 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Electron-density maps and crystallographic dimer structures of the motor domain. (a f) Stereo views of the final electron-density maps
doi:10.1038/nature10955 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Electron-density maps and crystallographic dimer structures of the motor domain. (a f) Stereo views of the final electron-density maps
Examples of Protein Modeling. Protein Modeling. Primary Structure. Protein Structure Description. Protein Sequence Sources. Importing Sequences to MOE
 Examples of Protein Modeling Protein Modeling Visualization Examination of an experimental structure to gain insight about a research question Dynamics To examine the dynamics of protein structures To
Examples of Protein Modeling Protein Modeling Visualization Examination of an experimental structure to gain insight about a research question Dynamics To examine the dynamics of protein structures To
Secondary and sidechain structures
 Lecture 2 Secondary and sidechain structures James Chou BCMP201 Spring 2008 Images from Petsko & Ringe, Protein Structure and Function. Branden & Tooze, Introduction to Protein Structure. Richardson, J.
Lecture 2 Secondary and sidechain structures James Chou BCMP201 Spring 2008 Images from Petsko & Ringe, Protein Structure and Function. Branden & Tooze, Introduction to Protein Structure. Richardson, J.
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Resveratrol Serves as a Protein-Substrate Interaction Stabilizer in Human SIRT1 Activation Xuben Hou,, David Rooklin, Hao Fang *,,, Yingkai Zhang Department of Medicinal Chemistry
Supplementary Information Resveratrol Serves as a Protein-Substrate Interaction Stabilizer in Human SIRT1 Activation Xuben Hou,, David Rooklin, Hao Fang *,,, Yingkai Zhang Department of Medicinal Chemistry
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 www.nature.com/nature 1 Figure S1 Sequence alignment. a Structure based alignment of the plgic of E. chrysanthemi (ELIC), the acetylcholine binding protein from the snail Lymnea stagnalis (AchBP, PDB code
www.nature.com/nature 1 Figure S1 Sequence alignment. a Structure based alignment of the plgic of E. chrysanthemi (ELIC), the acetylcholine binding protein from the snail Lymnea stagnalis (AchBP, PDB code
A nano-positioning system for macromolecular structural analysis
 nature methods A nano-positioning system for macromolecular structural analysis Adam Muschielok, Joanna Andrecka, Anass Jawhari, Florian Brückner, Patrick Cramer & Jens Michaelis Supplementary figures
nature methods A nano-positioning system for macromolecular structural analysis Adam Muschielok, Joanna Andrecka, Anass Jawhari, Florian Brückner, Patrick Cramer & Jens Michaelis Supplementary figures
Orientational degeneracy in the presence of one alignment tensor.
 Orientational degeneracy in the presence of one alignment tensor. Rotation about the x, y and z axes can be performed in the aligned mode of the program to examine the four degenerate orientations of two
Orientational degeneracy in the presence of one alignment tensor. Rotation about the x, y and z axes can be performed in the aligned mode of the program to examine the four degenerate orientations of two
titin, has 35,213 amino acid residues (the human version of titin is smaller, with only 34,350 residues in the full length protein).
 Introduction to Protein Structure Proteins are large heteropolymers usually comprised of 50 2500 monomer units, although larger proteins are observed 8. The monomer units of proteins are amino acids. Proteins
Introduction to Protein Structure Proteins are large heteropolymers usually comprised of 50 2500 monomer units, although larger proteins are observed 8. The monomer units of proteins are amino acids. Proteins
Computational Protein Design
 11 Computational Protein Design This chapter introduces the automated protein design and experimental validation of a novel designed sequence, as described in Dahiyat and Mayo [1]. 11.1 Introduction Given
11 Computational Protein Design This chapter introduces the automated protein design and experimental validation of a novel designed sequence, as described in Dahiyat and Mayo [1]. 11.1 Introduction Given
Impact of the crystallization condition on importin-β conformation
 Supporting information Volume 72 (2016) Supporting information for article: Impact of the crystallization condition on importin-β conformation Marcel J. Tauchert, Clément Hémonnot, Piotr Neumann, Sarah
Supporting information Volume 72 (2016) Supporting information for article: Impact of the crystallization condition on importin-β conformation Marcel J. Tauchert, Clément Hémonnot, Piotr Neumann, Sarah
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Allosteric communication disrupted by small molecule binding to the Imidazole glycerol phosphate synthase protein-protein interface. Ivan Rivalta*,#, George P. Lisi #, Ning-Shiuan
Supporting Information Allosteric communication disrupted by small molecule binding to the Imidazole glycerol phosphate synthase protein-protein interface. Ivan Rivalta*,#, George P. Lisi #, Ning-Shiuan
Enhancing Specificity in the Janus Kinases: A Study on the Thienopyridine. JAK2 Selective Mechanism Combined Molecular Dynamics Simulation
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Molecular BioSystems. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information Enhancing Specificity in the Janus Kinases: A Study on the Thienopyridine
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Molecular BioSystems. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information Enhancing Specificity in the Janus Kinases: A Study on the Thienopyridine
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11539 Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic representation of plant (A) and mammalian (B) P 2B -ATPase domain organization. Actuator (A-), nucleotide binding (N-),
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11539 Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic representation of plant (A) and mammalian (B) P 2B -ATPase domain organization. Actuator (A-), nucleotide binding (N-),
Supplementary Figure 1. Aligned sequences of yeast IDH1 (top) and IDH2 (bottom) with isocitrate
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE LEGENDS Supplementary Figure 1. Aligned sequences of yeast IDH1 (top) and IDH2 (bottom) with isocitrate dehydrogenase from Escherichia coli [ICD, pdb 1PB1, Mesecar, A. D., and Koshland,
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE LEGENDS Supplementary Figure 1. Aligned sequences of yeast IDH1 (top) and IDH2 (bottom) with isocitrate dehydrogenase from Escherichia coli [ICD, pdb 1PB1, Mesecar, A. D., and Koshland,
PROTEIN STRUCTURE PREDICTION USING GAS PHASE MOLECULAR DYNAMICS SIMULATION: EOTAXIN-3 CYTOKINE AS A CASE STUDY
 International Conference Mathematical and Computational Biology 2011 International Journal of Modern Physics: Conference Series Vol. 9 (2012) 193 198 World Scientific Publishing Company DOI: 10.1142/S2010194512005259
International Conference Mathematical and Computational Biology 2011 International Journal of Modern Physics: Conference Series Vol. 9 (2012) 193 198 World Scientific Publishing Company DOI: 10.1142/S2010194512005259
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Mechanical unzipping and rezipping of a single SNARE complex reveals hysteresis as a force-generating mechanism Duyoung Min, Kipom Kim, Changbong Hyeon, Yong Hoon Cho, Yeon-Kyun
Supplementary Information Mechanical unzipping and rezipping of a single SNARE complex reveals hysteresis as a force-generating mechanism Duyoung Min, Kipom Kim, Changbong Hyeon, Yong Hoon Cho, Yeon-Kyun
Nature Structural and Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb.2938
 Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of designed leucine-rich-repeat proteins. (a) Water-mediate hydrogen-bond network is frequently visible in the convex region of LRR crystal structures. Examples
Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of designed leucine-rich-repeat proteins. (a) Water-mediate hydrogen-bond network is frequently visible in the convex region of LRR crystal structures. Examples
Supplementary Figure 1 Crystal contacts in COP apo structure (PDB code 3S0R)
 Supplementary Figure 1 Crystal contacts in COP apo structure (PDB code 3S0R) Shown in cyan and green are two adjacent tetramers from the crystallographic lattice of COP, forming the only unique inter-tetramer
Supplementary Figure 1 Crystal contacts in COP apo structure (PDB code 3S0R) Shown in cyan and green are two adjacent tetramers from the crystallographic lattice of COP, forming the only unique inter-tetramer
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Supplementary Figure 1 Protein sequence alignment of Vibrionaceae with either a 40-residue insertion or a 44-residue insertion. Identical residues are indicated by red background.
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Supplementary Figure 1 Protein sequence alignment of Vibrionaceae with either a 40-residue insertion or a 44-residue insertion. Identical residues are indicated by red background.
Supplementary figure 1. Comparison of unbound ogm-csf and ogm-csf as captured in the GIF:GM-CSF complex. Alignment of two copies of unbound ovine
 Supplementary figure 1. Comparison of unbound and as captured in the GIF:GM-CSF complex. Alignment of two copies of unbound ovine GM-CSF (slate) with bound GM-CSF in the GIF:GM-CSF complex (GIF: green,
Supplementary figure 1. Comparison of unbound and as captured in the GIF:GM-CSF complex. Alignment of two copies of unbound ovine GM-CSF (slate) with bound GM-CSF in the GIF:GM-CSF complex (GIF: green,
Supplemental Data SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURES
 Supplemental Data CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF THE MG.ADP-INHIBITED STATE OF THE YEAST F 1 C 10 ATP SYNTHASE Alain Dautant*, Jean Velours and Marie-France Giraud* From Université Bordeaux 2, CNRS; Institut de
Supplemental Data CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF THE MG.ADP-INHIBITED STATE OF THE YEAST F 1 C 10 ATP SYNTHASE Alain Dautant*, Jean Velours and Marie-France Giraud* From Université Bordeaux 2, CNRS; Institut de
Supplementary Information. The protease GtgE from Salmonella exclusively targets. inactive Rab GTPases
 Supplementary Information The protease GtgE from Salmonella exclusively targets inactive Rab GTPases Table of Contents Supplementary Figures... 2 Supplementary Figure 1... 2 Supplementary Figure 2... 3
Supplementary Information The protease GtgE from Salmonella exclusively targets inactive Rab GTPases Table of Contents Supplementary Figures... 2 Supplementary Figure 1... 2 Supplementary Figure 2... 3
Viewing and Analyzing Proteins, Ligands and their Complexes 2
 2 Viewing and Analyzing Proteins, Ligands and their Complexes 2 Overview Viewing the accessible surface Analyzing the properties of proteins containing thousands of atoms is best accomplished by representing
2 Viewing and Analyzing Proteins, Ligands and their Complexes 2 Overview Viewing the accessible surface Analyzing the properties of proteins containing thousands of atoms is best accomplished by representing
Prediction and refinement of NMR structures from sparse experimental data
 Prediction and refinement of NMR structures from sparse experimental data Jeff Skolnick Director Center for the Study of Systems Biology School of Biology Georgia Institute of Technology Overview of talk
Prediction and refinement of NMR structures from sparse experimental data Jeff Skolnick Director Center for the Study of Systems Biology School of Biology Georgia Institute of Technology Overview of talk
Biomolecules: lecture 10
 Biomolecules: lecture 10 - understanding in detail how protein 3D structures form - realize that protein molecules are not static wire models but instead dynamic, where in principle every atom moves (yet
Biomolecules: lecture 10 - understanding in detail how protein 3D structures form - realize that protein molecules are not static wire models but instead dynamic, where in principle every atom moves (yet
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information The direct role of selenocysteine in [NiFeSe] hydrogenase maturation and catalysis Marta C. Marques a, Cristina Tapia b, Oscar Gutiérrez-Sanz b, Ana Raquel Ramos a, Kimberly L.
Supplementary Information The direct role of selenocysteine in [NiFeSe] hydrogenase maturation and catalysis Marta C. Marques a, Cristina Tapia b, Oscar Gutiérrez-Sanz b, Ana Raquel Ramos a, Kimberly L.
THE TANGO ALGORITHM: SECONDARY STRUCTURE PROPENSITIES, STATISTICAL MECHANICS APPROXIMATION
 THE TANGO ALGORITHM: SECONDARY STRUCTURE PROPENSITIES, STATISTICAL MECHANICS APPROXIMATION AND CALIBRATION Calculation of turn and beta intrinsic propensities. A statistical analysis of a protein structure
THE TANGO ALGORITHM: SECONDARY STRUCTURE PROPENSITIES, STATISTICAL MECHANICS APPROXIMATION AND CALIBRATION Calculation of turn and beta intrinsic propensities. A statistical analysis of a protein structure
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Figure S1. Secondary structure of CAP (in the camp 2 -bound state) 10. α-helices are shown as cylinders and β- strands as arrows. Labeling of secondary structure is indicated. CDB, DBD and the hinge are
Figure S1. Secondary structure of CAP (in the camp 2 -bound state) 10. α-helices are shown as cylinders and β- strands as arrows. Labeling of secondary structure is indicated. CDB, DBD and the hinge are
Bulk behaviour. Alanine. FIG. 1. Chemical structure of the RKLPDA peptide. Numbers on the left mark alpha carbons.
 Bulk behaviour To characterise the conformational behaviour of the peptide, first we looked at the statistics of alpha carbons and the torsion angles. Then they were correlated with positions of positively
Bulk behaviour To characterise the conformational behaviour of the peptide, first we looked at the statistics of alpha carbons and the torsion angles. Then they were correlated with positions of positively
THE UNIVERSITY OF MANITOBA. PAPER NO: 409 LOCATION: Fr. Kennedy Gold Gym PAGE NO: 1 of 6 DEPARTMENT & COURSE NO: CHEM 4630 TIME: 3 HOURS
 PAPER NO: 409 LOCATION: Fr. Kennedy Gold Gym PAGE NO: 1 of 6 DEPARTMENT & COURSE NO: CHEM 4630 TIME: 3 HOURS EXAMINATION: Biochemistry of Proteins EXAMINER: J. O'Neil Section 1: You must answer all of
PAPER NO: 409 LOCATION: Fr. Kennedy Gold Gym PAGE NO: 1 of 6 DEPARTMENT & COURSE NO: CHEM 4630 TIME: 3 HOURS EXAMINATION: Biochemistry of Proteins EXAMINER: J. O'Neil Section 1: You must answer all of
1. What is an ångstrom unit, and why is it used to describe molecular structures?
 1. What is an ångstrom unit, and why is it used to describe molecular structures? The ångstrom unit is a unit of distance suitable for measuring atomic scale objects. 1 ångstrom (Å) = 1 10-10 m. The diameter
1. What is an ångstrom unit, and why is it used to describe molecular structures? The ångstrom unit is a unit of distance suitable for measuring atomic scale objects. 1 ångstrom (Å) = 1 10-10 m. The diameter
Structural insights into Aspergillus fumigatus lectin specificity - AFL binding sites are functionally non-equivalent
 Acta Cryst. (2015). D71, doi:10.1107/s1399004714026595 Supporting information Volume 71 (2015) Supporting information for article: Structural insights into Aspergillus fumigatus lectin specificity - AFL
Acta Cryst. (2015). D71, doi:10.1107/s1399004714026595 Supporting information Volume 71 (2015) Supporting information for article: Structural insights into Aspergillus fumigatus lectin specificity - AFL
Bacterial protease uses distinct thermodynamic signatures for substrate recognition
 Bacterial protease uses distinct thermodynamic signatures for substrate recognition Gustavo Arruda Bezerra, Yuko Ohara-Nemoto, Irina Cornaciu, Sofiya Fedosyuk, Guillaume Hoffmann, Adam Round, José A. Márquez,
Bacterial protease uses distinct thermodynamic signatures for substrate recognition Gustavo Arruda Bezerra, Yuko Ohara-Nemoto, Irina Cornaciu, Sofiya Fedosyuk, Guillaume Hoffmann, Adam Round, José A. Márquez,
Number sequence representation of protein structures based on the second derivative of a folded tetrahedron sequence
 Number sequence representation of protein structures based on the second derivative of a folded tetrahedron sequence Naoto Morikawa (nmorika@genocript.com) October 7, 2006. Abstract A protein is a sequence
Number sequence representation of protein structures based on the second derivative of a folded tetrahedron sequence Naoto Morikawa (nmorika@genocript.com) October 7, 2006. Abstract A protein is a sequence
Supplementary information
 Supplementary information The structural basis of modularity in ECF-type ABC transporters Guus B. Erkens 1,2, Ronnie P-A. Berntsson 1,2, Faizah Fulyani 1,2, Maria Majsnerowska 1,2, Andreja Vujičić-Žagar
Supplementary information The structural basis of modularity in ECF-type ABC transporters Guus B. Erkens 1,2, Ronnie P-A. Berntsson 1,2, Faizah Fulyani 1,2, Maria Majsnerowska 1,2, Andreja Vujičić-Žagar
Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic overview of ASTNs in neuronal migration. (a) Schematic of roles played by ASTNs 1 and 2. ASTN-1-mediated adhesions
 Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic overview of ASTNs in neuronal migration. (a) Schematic of roles played by ASTNs 1 and 2. ASTN-1-mediated adhesions undergo endocytosis into clathrin-coated vesicles dependent
Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic overview of ASTNs in neuronal migration. (a) Schematic of roles played by ASTNs 1 and 2. ASTN-1-mediated adhesions undergo endocytosis into clathrin-coated vesicles dependent
Supplementary Information. Structural basis for precursor protein-directed ribosomal peptide macrocyclization
 Supplementary Information Structural basis for precursor protein-directed ribosomal peptide macrocyclization Kunhua Li 1,3, Heather L. Condurso 1,3, Gengnan Li 1, Yousong Ding 2 and Steven D. Bruner 1*
Supplementary Information Structural basis for precursor protein-directed ribosomal peptide macrocyclization Kunhua Li 1,3, Heather L. Condurso 1,3, Gengnan Li 1, Yousong Ding 2 and Steven D. Bruner 1*
Nature Structural and Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1. Definition and assessment of ciap1 constructs.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Definition and assessment of ciap1 constructs. (a) ciap1 constructs used in this study are shown as primary structure schematics with domains colored as in the main text. Mutations
Supplementary Figure 1 Definition and assessment of ciap1 constructs. (a) ciap1 constructs used in this study are shown as primary structure schematics with domains colored as in the main text. Mutations
DEHYDROGENASES. Dog$ish (Squalus acanthius) Lactate Dehydrogenase (LDH)
 Prof. Alejandro Hochkoeppler Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences and Biotechnology University of Bologna E-mail: a.hochkoeppler@unibo.it Dog$ish (Squalus acanthius) Lactate Dehydrogenase (LDH) Homotetramer,
Prof. Alejandro Hochkoeppler Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences and Biotechnology University of Bologna E-mail: a.hochkoeppler@unibo.it Dog$ish (Squalus acanthius) Lactate Dehydrogenase (LDH) Homotetramer,
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Micelle-Triggered b-hairpin to a-helix Transition in a 14-Residue Peptide from a Choline-Binding Repeat of the Pneumococcal Autolysin LytA HØctor Zamora-Carreras, [a] Beatriz Maestro,
Supporting Information Micelle-Triggered b-hairpin to a-helix Transition in a 14-Residue Peptide from a Choline-Binding Repeat of the Pneumococcal Autolysin LytA HØctor Zamora-Carreras, [a] Beatriz Maestro,
Lecture 2 and 3: Review of forces (ctd.) and elementary statistical mechanics. Contributions to protein stability
 Lecture 2 and 3: Review of forces (ctd.) and elementary statistical mechanics. Contributions to protein stability Part I. Review of forces Covalent bonds Non-covalent Interactions: Van der Waals Interactions
Lecture 2 and 3: Review of forces (ctd.) and elementary statistical mechanics. Contributions to protein stability Part I. Review of forces Covalent bonds Non-covalent Interactions: Van der Waals Interactions
The protein folding problem consists of two parts:
 Energetics and kinetics of protein folding The protein folding problem consists of two parts: 1)Creating a stable, well-defined structure that is significantly more stable than all other possible structures.
Energetics and kinetics of protein folding The protein folding problem consists of two parts: 1)Creating a stable, well-defined structure that is significantly more stable than all other possible structures.
Principles of Physical Biochemistry
 Principles of Physical Biochemistry Kensal E. van Hold e W. Curtis Johnso n P. Shing Ho Preface x i PART 1 MACROMOLECULAR STRUCTURE AND DYNAMICS 1 1 Biological Macromolecules 2 1.1 General Principles
Principles of Physical Biochemistry Kensal E. van Hold e W. Curtis Johnso n P. Shing Ho Preface x i PART 1 MACROMOLECULAR STRUCTURE AND DYNAMICS 1 1 Biological Macromolecules 2 1.1 General Principles
Supplementary Materials for
 advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/4/1/eaau413/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Structure and dynamics conspire in the evolution of affinity between intrinsically disordered proteins Per Jemth*, Elin
advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/4/1/eaau413/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Structure and dynamics conspire in the evolution of affinity between intrinsically disordered proteins Per Jemth*, Elin
Physiochemical Properties of Residues
 Physiochemical Properties of Residues Various Sources C N Cα R Slide 1 Conformational Propensities Conformational Propensity is the frequency in which a residue adopts a given conformation (in a polypeptide)
Physiochemical Properties of Residues Various Sources C N Cα R Slide 1 Conformational Propensities Conformational Propensity is the frequency in which a residue adopts a given conformation (in a polypeptide)
4 Proteins: Structure, Function, Folding W. H. Freeman and Company
 4 Proteins: Structure, Function, Folding 2013 W. H. Freeman and Company CHAPTER 4 Proteins: Structure, Function, Folding Learning goals: Structure and properties of the peptide bond Structural hierarchy
4 Proteins: Structure, Function, Folding 2013 W. H. Freeman and Company CHAPTER 4 Proteins: Structure, Function, Folding Learning goals: Structure and properties of the peptide bond Structural hierarchy
What makes a good graphene-binding peptide? Adsorption of amino acids and peptides at aqueous graphene interfaces: Electronic Supplementary
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry B. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 21 What makes a good graphene-binding peptide? Adsorption of amino acids and
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry B. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 21 What makes a good graphene-binding peptide? Adsorption of amino acids and
Supplementary Figures:
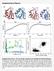 Supplementary Figures: Supplementary Figure 1: The two strings converge to two qualitatively different pathways. A) Models of active (red) and inactive (blue) states used as end points for the string calculations
Supplementary Figures: Supplementary Figure 1: The two strings converge to two qualitatively different pathways. A) Models of active (red) and inactive (blue) states used as end points for the string calculations
Dihedral Angles. Homayoun Valafar. Department of Computer Science and Engineering, USC 02/03/10 CSCE 769
 Dihedral Angles Homayoun Valafar Department of Computer Science and Engineering, USC The precise definition of a dihedral or torsion angle can be found in spatial geometry Angle between to planes Dihedral
Dihedral Angles Homayoun Valafar Department of Computer Science and Engineering, USC The precise definition of a dihedral or torsion angle can be found in spatial geometry Angle between to planes Dihedral
Problem Set 1
 2006 7.012 Problem Set 1 Due before 5 PM on FRIDAY, September 15, 2006. Turn answers in to the box outside of 68-120. PLEASE WRITE YOUR ANSWERS ON THIS PRINTOUT. 1. For each of the following parts, pick
2006 7.012 Problem Set 1 Due before 5 PM on FRIDAY, September 15, 2006. Turn answers in to the box outside of 68-120. PLEASE WRITE YOUR ANSWERS ON THIS PRINTOUT. 1. For each of the following parts, pick
