Lecture 10: Sequential Networks: Timing and Retiming
|
|
|
- Aubrie Sullivan
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Lecture 10: Sequential Networks: Timing and Retiming CSE 140: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems Diba Mirza Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering University of California, San Diego 1
2 So far. Combinational Logic-level analysis
3 This lecture Combinational Our seemingly logically correct design can go wrong How can we design a circuit that works under real constraints?
4 Timing Constraints of flip flops The input to a flip-flop should be stable for a period of time around the rising edge of the clock D Q Q 4
5 Input Constraints: Set up and hold time D Q Q D t setup t hold I. Setup time: t setup t a Time before the clock edge that data must be stable (i.e. not change) II. Hold time: t hold Time after the clock edge that data must be stable Aperture time: t a Time around clock edge that data must be stable (t a = t setup + t hold ) 5
6 PIQ: Which of the following signals can cause a setup-time violation for this flip flop? Q(t) D(t) Q D A. The input signal D(t) Q B. The output signal Q(t) C. Both A and B D. None of the above 6
7 Output characteristics of flip flops D Q Q I. Minimum delay of Q II. Time after the clock edge for which Q is sure to not change Maximum delay of Q Time after the clock edge following which Q is sure to have stabilized 7
8 Output characteristics of flip flops D Q Q Q t ccq t pcq I. Min delay of flip flop, also called Contamination delay or min to Q delay: t ccq Time after clock edge that Q might be unstable (i.e., start changing) II. Max delay of flip flop, also called Propagation delay or maximum to Q delay: t pcq Time after clock edge that the output Q is guaranteed to be stable (i.e., to stop changing) 8
9 Fact 1: Once a flip flop has been built we are stuck with its timing characteristics: t setup, t hold, t ccq, t pcq D1 R1 Combinational R2 Now let s look at the timing characteristics of the combinational part 9
10 Combinational Logic Timing I. Min delay of a gate, also called Contamination delay: t cd Minimum time from when an input changes until the output starts to change II. Max delay of a gate, also called Propagation delay: t pd Maximum time from when an input changes until the output is guaranteed to reach its final value (i.e., stop changing) 10
11 Combinational Logic: Output timing constraints A B C D Y PI Q: Which path in the above circuit determines the contamination delay of the circuit (assuming the delay of all the gates is the same)? A. Green path B. Red path C. Both D. Neither 11
12 Combinational Logic: Output timing constraints A B C D Y PI Q: Which path in the above circuit determines the propagation delay of the circuit (assuming the delay of all the gates is the same)? A. Green path B. Red path C. Both D. Neither 12
13 Timing Issues If the input to a flip flop doesn t stabilize in time BEFORE the rising edge of the clock we have a setup time violation C L (a) R1 R2 T c (b) 13
14 Why would the input () not stabilize in time? changes because of Flip flop has maximum delay, stabilizes after this maximum delay from the clock edge The combinational circuit has a maximum delay, so even after has stabilized, takes a while to stabilize If doesn t stabilize on time we have a setup violation C L (a) R1 R2 T c (b) 14
15 Timing Issues If the input to a flip flop changes too quickly AFTER the rising edge of the clock we have a hold time violation C L (a) R1 R2 T c (b) 15
16 Why would the input () change too quickly? changes because of Flip flop has minimum delay, will start changing only after this minimum delay The combinational circuit has a minimum delay, after which the output of CL () will start reacting to a changing input. If starts changing too quickly we have a hold time violation C L R1 R2 (a) T c (b) 16
17 Why timing in Sequential Circuits can go wrong? Which of the following violations would occur if the min delay of R1 was 0 and the combinational circuit was just a wire? A. Hold time violation for R2 B. Setup violation for R2 C. Hold time violation for R1 D. Setup violation for R1 E. None of the above (a) R1 C L T c R2 (b) 17
18 Meeting the hold time constraint Input to a flip-flop comes from the output of another flip flop, through a combinational circuit The flipflop and combinational circuit have a min and max delay C L (a) R1 R2 To meet the hold time constraint: T c t hold < min delay(flipflop) + min delay(combinational) (b) 18
19 Why timing in Sequential Circuits can go wrong? Input to a flip-flop comes from the output of another flip flop, through a combinational circuit The flipflop and combinational circuit have a min and max delay (a) R1 C L T c R2 Which of the following violations would occur if the max delay of R1 was 0 and the max delay of the combinational circuit was equal to the clock period (b) A. Hold time violation for R2 B. Setup violation for R2 C. Hold time violation for R1 D. Setup violation for R1 E. None of the above 19
20 Meeting the setup time constraint Input to a flip-flop comes from the output of another flip flop, through a combinational circuit The flipflop and combinational circuit have a min and max delay C L (a) R1 R2 To meet the setup time constraint: T c T c max delay(flipflop) + max delay(combinational)+ t setup (b) 20
21 Formalizing the hold time constraint in Sequential Circuits C L To meet the hold time constraint: R1 R2 t hold < min delay(flipflop) + min delay(combinational) t hold < t ccq + t cd t ccq t cd t hold 21
22 Formalizing the setup time constraints in Sequential Circuits To meet the setup time constraint: R1 C L T c R2 T c max delay(flipflop) + max delay(combinational)+ t setup T c t pcq + t pd + t setup t pcq t pd t setup 22
23 Timing Analysis Timing Characteristics t ccq = 30 ps A B t pcq = 50 ps t setup = 60 ps t hold = 70 ps C D t pd (CL)= t cd (CL)= Setup time constraint: T c f c = 1/T c = X' Y' X Y t pd = 35 ps t cd = 25 ps Hold time constraint: t ccq + t cd (CL)> t hold? 23
24 Timing Analysis Timing Characteristics t ccq = 30 ps A B t pcq = 50 ps t setup = 60 ps t hold = 70 ps C X' X Y' D t pd = 3 x 35 ps = 105 ps t cd = 25 ps Setup time constraint: T c ( ) ps = 215 ps f c = 1/T c = 4.65 GHz Y t pd = 35 ps t cd = 25 ps Hold time constraint: t ccq + t cd > t hold? ( ) ps > 70 ps? No! 24
25 Fixing Hold Time Violation Add buffers to the short paths: A B Timing Characteristics t ccq = 30 ps t pcq = 50 ps t setup = 60 ps t hold = 70 ps C D t pd = X' Y' X Y t pd = 35 ps t cd = 25 ps t cd = Setup time constraint: Hold time constraint: T c t ccq + t cd > t hold? f c = 25
26 Fixing Hold Time Violation Add buffers to the short paths: A B Timing Characteristics t ccq = 30 ps t pcq = 50 ps t setup = 60 ps t hold = 70 ps C D X' X Y' Y t pd = 3 x 35 ps = 105 ps t cd = 2 x 25 ps = 50 ps Setup time constraint: T c ( ) ps = 215 ps f c = 1/T c = 4.65 GHz t pd = 35 ps t cd = 25 ps Hold time constraint: t ccq + t cd > t hold? ( ) ps > 70 ps? Yes! 26
27 Midterm review SR latch 27
28 SR latch timing diagrams 28
29 29 What do inputs A & B do?
30 FSM design example Design an overlapping finite string pattern recognizer output is 1 whenever the input sequences 101 and 011 are observed 30
31 Sequential circuit design Present Next state Output State W=0 W=1 Z
32 FSM Design Example Write the state table and implement the following state machine: 32
Timing Constraints in Sequential Designs. 63 Sources: TSR, Katz, Boriello & Vahid
 Timing Constraints in Sequential esigns 63 Sources: TSR, Katz, Boriello & Vahid Where we are now. What we covered last time: FSMs What we ll do next: Timing constraints Upcoming deadlines: ZyBook today:
Timing Constraints in Sequential esigns 63 Sources: TSR, Katz, Boriello & Vahid Where we are now. What we covered last time: FSMs What we ll do next: Timing constraints Upcoming deadlines: ZyBook today:
ALU, Latches and Flip-Flops
 CSE14: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems ALU, Latches and Flip-Flops Tajana Simunic Rosing Where we are. Last time: ALUs Plan for today: ALU example, latches and flip flops Exam #1 grades
CSE14: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems ALU, Latches and Flip-Flops Tajana Simunic Rosing Where we are. Last time: ALUs Plan for today: ALU example, latches and flip flops Exam #1 grades
CSE140: Design of Sequential Logic
 CSE4: Design of Sequential Logic Instructor: Mohsen Imani Flip Flops 2 Counter 3 Up counter 4 Up counter 5 FSM with JK-Flip Flop 6 State Table 7 State Table 8 Circuit Minimization 9 Circuit Timing Constraints
CSE4: Design of Sequential Logic Instructor: Mohsen Imani Flip Flops 2 Counter 3 Up counter 4 Up counter 5 FSM with JK-Flip Flop 6 State Table 7 State Table 8 Circuit Minimization 9 Circuit Timing Constraints
CPE100: Digital Logic Design I
 Chapter 3 Professor Brendan Morris, SEB 3216, brendan.morris@unlv.edu http://www.ee.unlv.edu/~b1morris/cpe1/ CPE1: Digital Logic Design I Section 14: Dr. Morris Sequential Logic Design Chapter 3 Chapter
Chapter 3 Professor Brendan Morris, SEB 3216, brendan.morris@unlv.edu http://www.ee.unlv.edu/~b1morris/cpe1/ CPE1: Digital Logic Design I Section 14: Dr. Morris Sequential Logic Design Chapter 3 Chapter
Chapter 3. Digital Design and Computer Architecture, 2 nd Edition. David Money Harris and Sarah L. Harris. Chapter 3 <1>
 Chapter 3 Digital Design and Computer Architecture, 2 nd Edition David Money Harris and Sarah L. Harris Chapter 3 Chapter 3 :: Topics Introduction Latches and Flip-Flops Synchronous Logic Design Finite
Chapter 3 Digital Design and Computer Architecture, 2 nd Edition David Money Harris and Sarah L. Harris Chapter 3 Chapter 3 :: Topics Introduction Latches and Flip-Flops Synchronous Logic Design Finite
CSE 140 Midterm 2 - Solutions Prof. Tajana Simunic Rosing Spring 2013
 CSE 140 Midterm 2 - Solutions Prof. Tajana Simunic Rosing Spring 2013 Do not start the exam until you are told. Write your name and PID at the top of every page. Do not separate the pages. Turn off and
CSE 140 Midterm 2 - Solutions Prof. Tajana Simunic Rosing Spring 2013 Do not start the exam until you are told. Write your name and PID at the top of every page. Do not separate the pages. Turn off and
Problem Set 9 Solutions
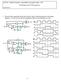 CSE 26 Digital Computers: Organization and Logical Design - 27 Jon Turner Problem Set 9 Solutions. For each of the sequential circuits shown below, draw in the missing parts of the timing diagrams. You
CSE 26 Digital Computers: Organization and Logical Design - 27 Jon Turner Problem Set 9 Solutions. For each of the sequential circuits shown below, draw in the missing parts of the timing diagrams. You
Chapter 3. Chapter 3 :: Topics. Introduction. Sequential Circuits
 Chapter 3 Chapter 3 :: Topics igital esign and Computer Architecture, 2 nd Edition avid Money Harris and Sarah L. Harris Introduction Latches and Flip Flops Synchronous Logic esign Finite State Machines
Chapter 3 Chapter 3 :: Topics igital esign and Computer Architecture, 2 nd Edition avid Money Harris and Sarah L. Harris Introduction Latches and Flip Flops Synchronous Logic esign Finite State Machines
Sequential Logic Worksheet
 Sequential Logic Worksheet Concept Inventory: Notes: D-latch & the Dynamic Discipline D-register Timing constraints for sequential circuits Set-up and hold times for sequential circuits 6.004 Worksheet
Sequential Logic Worksheet Concept Inventory: Notes: D-latch & the Dynamic Discipline D-register Timing constraints for sequential circuits Set-up and hold times for sequential circuits 6.004 Worksheet
Lecture 8: Sequential Networks and Finite State Machines
 Lecture 8: Sequential Networks and Finite State Machines CSE 140: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems Spring 2014 CK Cheng, Diba Mirza Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering University
Lecture 8: Sequential Networks and Finite State Machines CSE 140: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems Spring 2014 CK Cheng, Diba Mirza Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering University
Homework #4. CSE 140 Summer Session Instructor: Mohsen Imani. Only a subset of questions will be graded
 Homework #4 CSE 140 Summer Session 2 2017 Instructor: Mohsen Imani Only a subset of questions will be graded 1) For the circuit shown below, do the following: a. Write a logic equation for the output P
Homework #4 CSE 140 Summer Session 2 2017 Instructor: Mohsen Imani Only a subset of questions will be graded 1) For the circuit shown below, do the following: a. Write a logic equation for the output P
University of Toronto Faculty of Applied Science and Engineering Edward S. Rogers Sr. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
 University of Toronto Faculty of Applied Science and Engineering Edward S. Rogers Sr. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Final Examination ECE 241F - Digital Systems Examiners: S. Brown,
University of Toronto Faculty of Applied Science and Engineering Edward S. Rogers Sr. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Final Examination ECE 241F - Digital Systems Examiners: S. Brown,
CPE100: Digital Logic Design I
 Professor Brendan Morris, SEB 3216, brendan.morris@unlv.edu CPE100: Digital Logic Design I Final Review http://www.ee.unlv.edu/~b1morris/cpe100/ 2 Logistics Tuesday Dec 12 th 13:00-15:00 (1-3pm) 2 hour
Professor Brendan Morris, SEB 3216, brendan.morris@unlv.edu CPE100: Digital Logic Design I Final Review http://www.ee.unlv.edu/~b1morris/cpe100/ 2 Logistics Tuesday Dec 12 th 13:00-15:00 (1-3pm) 2 hour
CPE100: Digital Logic Design I
 Professor Brendan Morris, SEB 3216, brendan.morris@unlv.edu CPE100: Digital Logic Design I Midterm02 Review http://www.ee.unlv.edu/~b1morris/cpe100/ 2 Logistics Thursday Nov. 16 th In normal lecture (13:00-14:15)
Professor Brendan Morris, SEB 3216, brendan.morris@unlv.edu CPE100: Digital Logic Design I Midterm02 Review http://www.ee.unlv.edu/~b1morris/cpe100/ 2 Logistics Thursday Nov. 16 th In normal lecture (13:00-14:15)
Digital Circuits and Systems
 EE201: Digital Circuits and Systems 4 Sequential Circuits page 1 of 11 EE201: Digital Circuits and Systems Section 4 Sequential Circuits 4.1 Overview of Sequential Circuits: Definition The circuit whose
EE201: Digital Circuits and Systems 4 Sequential Circuits page 1 of 11 EE201: Digital Circuits and Systems Section 4 Sequential Circuits 4.1 Overview of Sequential Circuits: Definition The circuit whose
CSE 140: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems. Lecture 9: Sequential Networks: Implementation
 CSE 4: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems Lecture 9: Sequential Networks: Implementation CK Cheng Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering University of California, San Diego Implementation
CSE 4: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems Lecture 9: Sequential Networks: Implementation CK Cheng Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering University of California, San Diego Implementation
Review for Final Exam
 CSE140: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems Review for Final Exam Mohsen Imani CAPE Please submit your evaluations!!!! RTL design Use the RTL design process to design a system that has
CSE140: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems Review for Final Exam Mohsen Imani CAPE Please submit your evaluations!!!! RTL design Use the RTL design process to design a system that has
Lecture 7: Sequential Networks
 CSE 140: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems Lecture 7: Sequential Networks CK Cheng Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering University of California, San Diego 1 Part II: Sequential
CSE 140: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems Lecture 7: Sequential Networks CK Cheng Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering University of California, San Diego 1 Part II: Sequential
Sequential Circuits. Circuits with state. Silvina Hanono Wachman Computer Science & Artificial Intelligence Lab M.I.T. L06-1
 Sequential Circuits Circuits with state Silvina Hanono Wachman Computer Science & Artificial Intelligence Lab M.I.T. L06-1 Combinational circuits A 0 A 1 A n-1. Sel lg(n) O Mux A B Comparator Result: LT,
Sequential Circuits Circuits with state Silvina Hanono Wachman Computer Science & Artificial Intelligence Lab M.I.T. L06-1 Combinational circuits A 0 A 1 A n-1. Sel lg(n) O Mux A B Comparator Result: LT,
CSE 140 Midterm 3 version A Tajana Simunic Rosing Spring 2015
 CSE 140 Midterm 3 version A Tajana Simunic Rosing Spring 2015 Name of the person on your left : Name of the person on your right: 1. 20 points 2. 20 points 3. 20 points 4. 15 points 5. 15 points 6. 10
CSE 140 Midterm 3 version A Tajana Simunic Rosing Spring 2015 Name of the person on your left : Name of the person on your right: 1. 20 points 2. 20 points 3. 20 points 4. 15 points 5. 15 points 6. 10
ECEN 248: INTRODUCTION TO DIGITAL SYSTEMS DESIGN. Week 9 Dr. Srinivas Shakkottai Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering
 ECEN 248: INTRODUCTION TO DIGITAL SYSTEMS DESIGN Week 9 Dr. Srinivas Shakkottai Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering TIMING ANALYSIS Overview Circuits do not respond instantaneously to input changes
ECEN 248: INTRODUCTION TO DIGITAL SYSTEMS DESIGN Week 9 Dr. Srinivas Shakkottai Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering TIMING ANALYSIS Overview Circuits do not respond instantaneously to input changes
Lecture 14: State Tables, Diagrams, Latches, and Flip Flop
 EE210: Switching Systems Lecture 14: State Tables, Diagrams, Latches, and Flip Flop Prof. YingLi Tian Nov. 6, 2017 Department of Electrical Engineering The City College of New York The City University
EE210: Switching Systems Lecture 14: State Tables, Diagrams, Latches, and Flip Flop Prof. YingLi Tian Nov. 6, 2017 Department of Electrical Engineering The City College of New York The City University
10/12/2016. An FSM with No Inputs Moves from State to State. ECE 120: Introduction to Computing. Eventually, the States Form a Loop
 University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering An FSM with No Inputs Moves from State to State What happens if an FSM has no inputs? ECE 120: Introduction to Computing
University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering An FSM with No Inputs Moves from State to State What happens if an FSM has no inputs? ECE 120: Introduction to Computing
Jin-Fu Li Advanced Reliable Systems (ARES) Lab. Department of Electrical Engineering. Jungli, Taiwan
 Chapter 7 Sequential Circuits Jin-Fu Li Advanced Reliable Systems (ARES) Lab. epartment of Electrical Engineering National Central University it Jungli, Taiwan Outline Latches & Registers Sequencing Timing
Chapter 7 Sequential Circuits Jin-Fu Li Advanced Reliable Systems (ARES) Lab. epartment of Electrical Engineering National Central University it Jungli, Taiwan Outline Latches & Registers Sequencing Timing
Sequential Circuit Analysis
 Sequential Circuit Analysis Last time we started talking about latches and flip-flops, which are basic one-bit memory units. Today we ll talk about sequential circuit analysis and design. First, we ll
Sequential Circuit Analysis Last time we started talking about latches and flip-flops, which are basic one-bit memory units. Today we ll talk about sequential circuit analysis and design. First, we ll
Sequential Logic Circuits
 Chapter 4 Sequential Logic Circuits 4 1 The defining characteristic of a combinational circuit is that its output depends only on the current inputs applied to the circuit. The output of a sequential circuit,
Chapter 4 Sequential Logic Circuits 4 1 The defining characteristic of a combinational circuit is that its output depends only on the current inputs applied to the circuit. The output of a sequential circuit,
Synchronous Sequential Logic
 1 IT 201 DIGITAL SYSTEMS DESIGN MODULE4 NOTES Synchronous Sequential Logic Sequential Circuits - A sequential circuit consists of a combinational circuit and a feedback through the storage elements in
1 IT 201 DIGITAL SYSTEMS DESIGN MODULE4 NOTES Synchronous Sequential Logic Sequential Circuits - A sequential circuit consists of a combinational circuit and a feedback through the storage elements in
Week-5. Sequential Circuit Design. Acknowledgement: Most of the following slides are adapted from Prof. Kale's slides at UIUC, USA.
 Week-5 Sequential Circuit Design Acknowledgement: Most of the following slides are adapted from Prof. Kale's slides at UIUC, USA. Storing a value: SR = 00 What if S = 0 and R = 0? The equations on the
Week-5 Sequential Circuit Design Acknowledgement: Most of the following slides are adapted from Prof. Kale's slides at UIUC, USA. Storing a value: SR = 00 What if S = 0 and R = 0? The equations on the
Digital Logic Design - Chapter 4
 Digital Logic Design - Chapter 4 1. Analyze the latch circuit shown below by obtaining timing diagram for the circuit; include propagation delays. Y This circuit has two external input and one feedback
Digital Logic Design - Chapter 4 1. Analyze the latch circuit shown below by obtaining timing diagram for the circuit; include propagation delays. Y This circuit has two external input and one feedback
Lecture 7: Logic design. Combinational logic circuits
 /24/28 Lecture 7: Logic design Binary digital circuits: Two voltage levels: and (ground and supply voltage) Built from transistors used as on/off switches Analog circuits not very suitable for generic
/24/28 Lecture 7: Logic design Binary digital circuits: Two voltage levels: and (ground and supply voltage) Built from transistors used as on/off switches Analog circuits not very suitable for generic
Chapter 7 Sequential Logic
 Chapter 7 Sequential Logic SKEE2263 Digital Systems Mun im/ismahani/izam {munim@utm.my,e-izam@utm.my,ismahani@fke.utm.my} March 28, 2016 Table of Contents 1 Intro 2 Bistable Circuits 3 FF Characteristics
Chapter 7 Sequential Logic SKEE2263 Digital Systems Mun im/ismahani/izam {munim@utm.my,e-izam@utm.my,ismahani@fke.utm.my} March 28, 2016 Table of Contents 1 Intro 2 Bistable Circuits 3 FF Characteristics
Synchronous Sequential Circuit Design. Digital Computer Design
 Synchronous Sequential Circuit Design Digital Computer Design Races and Instability Combinational logic has no cyclic paths and no races If inputs are applied to combinational logic, the outputs will always
Synchronous Sequential Circuit Design Digital Computer Design Races and Instability Combinational logic has no cyclic paths and no races If inputs are applied to combinational logic, the outputs will always
CSE140: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems. Midterm Information. Instructor: Mohsen Imani. Sources: TSR, Katz, Boriello & Vahid
 CSE140: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems Midterm Information Instructor: Mohsen Imani Midterm Topics In general: everything that was covered in homework 1 and 2 and related lectures,
CSE140: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems Midterm Information Instructor: Mohsen Imani Midterm Topics In general: everything that was covered in homework 1 and 2 and related lectures,
Memory Elements I. CS31 Pascal Van Hentenryck. CS031 Lecture 6 Page 1
 Memory Elements I CS31 Pascal Van Hentenryck CS031 Lecture 6 Page 1 Memory Elements (I) Combinational devices are good for computing Boolean functions pocket calculator Computers also need to remember
Memory Elements I CS31 Pascal Van Hentenryck CS031 Lecture 6 Page 1 Memory Elements (I) Combinational devices are good for computing Boolean functions pocket calculator Computers also need to remember
CSE 140 Midterm 2 Tajana Simunic Rosing. Spring 2008
 CSE 14 Midterm 2 Tajana Simunic Rosing Spring 28 Do not start the exam until you are told to. Turn off any cell phones or pagers. Write your name and PID at the top of every page. Do not separate the pages.
CSE 14 Midterm 2 Tajana Simunic Rosing Spring 28 Do not start the exam until you are told to. Turn off any cell phones or pagers. Write your name and PID at the top of every page. Do not separate the pages.
3. Complete the following table of equivalent values. Use binary numbers with a sign bit and 7 bits for the value
 EGC22 Digital Logic Fundamental Additional Practice Problems. Complete the following table of equivalent values. Binary. Octal 35.77 33.23.875 29.99 27 9 64 Hexadecimal B.3 D.FD B.4C 2. Calculate the following
EGC22 Digital Logic Fundamental Additional Practice Problems. Complete the following table of equivalent values. Binary. Octal 35.77 33.23.875 29.99 27 9 64 Hexadecimal B.3 D.FD B.4C 2. Calculate the following
Chapter 4. Sequential Logic Circuits
 Chapter 4 Sequential Logic Circuits 1 2 Chapter 4 4 1 The defining characteristic of a combinational circuit is that its output depends only on the current inputs applied to the circuit. The output of
Chapter 4 Sequential Logic Circuits 1 2 Chapter 4 4 1 The defining characteristic of a combinational circuit is that its output depends only on the current inputs applied to the circuit. The output of
L4: Sequential Building Blocks (Flip-flops, Latches and Registers)
 L4: Sequential Building Blocks (Flip-flops, Latches and Registers) Acknowledgements:., Materials in this lecture are courtesy of the following people and used with permission. - Randy H. Katz (University
L4: Sequential Building Blocks (Flip-flops, Latches and Registers) Acknowledgements:., Materials in this lecture are courtesy of the following people and used with permission. - Randy H. Katz (University
P2 (10 points): Given the circuit below, answer the following questions:
 P1 (10 points): Given the function f(a, b, c, d) = m(3,4,5,10,14) + D(6,7): A: Fill in the timing diagram for f. B: Implement f using only 2-1 MUXes. Your circuit should not include more than four 2-1
P1 (10 points): Given the function f(a, b, c, d) = m(3,4,5,10,14) + D(6,7): A: Fill in the timing diagram for f. B: Implement f using only 2-1 MUXes. Your circuit should not include more than four 2-1
Sequential vs. Combinational
 Sequential Circuits Sequential vs. Combinational Combinational Logic: Output depends only on current input TV channel selector (-9) inputs system outputs Sequential Logic: Output depends not only on current
Sequential Circuits Sequential vs. Combinational Combinational Logic: Output depends only on current input TV channel selector (-9) inputs system outputs Sequential Logic: Output depends not only on current
UNIVERSITY OF BOLTON SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING BENG (HONS) ELECTRICAL & ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING EXAMINATION SEMESTER /2017
 UNIVERSITY OF BOLTON TW35 SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING BENG (HONS) ELECTRICAL & ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING EXAMINATION SEMESTER 2-2016/2017 INTERMEDIATE DIGITAL ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATIONS MODULE NO: EEE5002
UNIVERSITY OF BOLTON TW35 SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING BENG (HONS) ELECTRICAL & ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING EXAMINATION SEMESTER 2-2016/2017 INTERMEDIATE DIGITAL ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATIONS MODULE NO: EEE5002
Sequential Logic. Handouts: Lecture Slides Spring /27/01. L06 Sequential Logic 1
 Sequential Logic Handouts: Lecture Slides 6.4 - Spring 2 2/27/ L6 Sequential Logic Roadmap so far Fets & voltages Logic gates Combinational logic circuits Sequential Logic Voltage-based encoding V OL,
Sequential Logic Handouts: Lecture Slides 6.4 - Spring 2 2/27/ L6 Sequential Logic Roadmap so far Fets & voltages Logic gates Combinational logic circuits Sequential Logic Voltage-based encoding V OL,
CSE140: Digital Logic Design Registers and Counters
 CSE14: Digital Logic Design Registers and Counters Prof. Tajana Simunic Rosing 38 Where we are now. What we covered last time: ALUs, SR Latch Latches and FlipFlops (FFs) Registers What we ll do next FSMs
CSE14: Digital Logic Design Registers and Counters Prof. Tajana Simunic Rosing 38 Where we are now. What we covered last time: ALUs, SR Latch Latches and FlipFlops (FFs) Registers What we ll do next FSMs
Sequential Logic. Road Traveled So Far
 Comp 2 Spring 25 2/ Lecture page Sequential Logic These must be the slings and arrows of outrageous fortune ) Synchronous as an implementation of Sequential 2) Synchronous Timing Analysis 3) Single synchronous
Comp 2 Spring 25 2/ Lecture page Sequential Logic These must be the slings and arrows of outrageous fortune ) Synchronous as an implementation of Sequential 2) Synchronous Timing Analysis 3) Single synchronous
Chapter #6: Sequential Logic Design
 Chapter #6: equential Logic esign Contemporary Logic esign No. 6- Cross-Coupled NO Gates ust like cascaded inverters, with capability to force output to (reset) or (set) \ eset Hold et eset et ace \ Forbidden
Chapter #6: equential Logic esign Contemporary Logic esign No. 6- Cross-Coupled NO Gates ust like cascaded inverters, with capability to force output to (reset) or (set) \ eset Hold et eset et ace \ Forbidden
Example: vending machine
 Example: vending machine Release item after 15 cents are deposited Single coin slot for dimes, nickels o change Reset Coin Sensor Vending Machine FSM Open Release Mechanism Clock Spring 2005 CSE370 - guest
Example: vending machine Release item after 15 cents are deposited Single coin slot for dimes, nickels o change Reset Coin Sensor Vending Machine FSM Open Release Mechanism Clock Spring 2005 CSE370 - guest
Chapter 14 Sequential logic, Latches and Flip-Flops
 Chapter 14 Sequential logic, Latches and Flip-Flops Flops Lesson 4 JK Flip Flop Ch14L4-"Digital Principles and Design", Raj Kamal, Pearson Education, 2006 2 JK Flip-Flop ve edge triggered Output Q and
Chapter 14 Sequential logic, Latches and Flip-Flops Flops Lesson 4 JK Flip Flop Ch14L4-"Digital Principles and Design", Raj Kamal, Pearson Education, 2006 2 JK Flip-Flop ve edge triggered Output Q and
Lecture 12: Adders, Sequential Circuits
 Lecture 12: Adders, Sequential Circuits Today s topics: Carry-lookahead adder Clocks, latches, sequential circuits 1 Speed of Ripple Carry The carry propagates thru every 1-bit box: each 1-bit box sequentially
Lecture 12: Adders, Sequential Circuits Today s topics: Carry-lookahead adder Clocks, latches, sequential circuits 1 Speed of Ripple Carry The carry propagates thru every 1-bit box: each 1-bit box sequentially
Digital Logic and Design (Course Code: EE222) Lecture 19: Sequential Circuits Contd..
 Indian Institute of Technology Jodhpur, Year 2017-2018 Digital Logic and Design (Course Code: EE222) Lecture 19: Sequential Circuits Contd.. Course Instructor: Shree Prakash Tiwari Email: sptiwari@iitj.ac.in
Indian Institute of Technology Jodhpur, Year 2017-2018 Digital Logic and Design (Course Code: EE222) Lecture 19: Sequential Circuits Contd.. Course Instructor: Shree Prakash Tiwari Email: sptiwari@iitj.ac.in
CHAPTER 9: SEQUENTIAL CIRCUITS
 CHAPTER 9: ASYNCHRONOUS SEUENTIAL CIRCUITS Chapter Objectives 2 Sequential circuits that are not snchronized b a clock Asnchronous circuits Analsis of Asnchronous circuits Snthesis of Asnchronous circuits
CHAPTER 9: ASYNCHRONOUS SEUENTIAL CIRCUITS Chapter Objectives 2 Sequential circuits that are not snchronized b a clock Asnchronous circuits Analsis of Asnchronous circuits Snthesis of Asnchronous circuits
EXPERIMENT Traffic Light Controller
 11.1 Objectives EXPERIMENT 11 11. Traffic Light Controller Practice on the design of clocked sequential circuits. Applications of sequential circuits. 11.2 Overview In this lab you are going to develop
11.1 Objectives EXPERIMENT 11 11. Traffic Light Controller Practice on the design of clocked sequential circuits. Applications of sequential circuits. 11.2 Overview In this lab you are going to develop
Hardware testing and design for testability. EE 3610 Digital Systems
 EE 3610: Digital Systems 1 Hardware testing and design for testability Introduction A Digital System requires testing before and after it is manufactured 2 Level 1: behavioral modeling and test benches
EE 3610: Digital Systems 1 Hardware testing and design for testability Introduction A Digital System requires testing before and after it is manufactured 2 Level 1: behavioral modeling and test benches
COEN 312 DIGITAL SYSTEMS DESIGN - LECTURE NOTES Concordia University
 1 OEN 312 DIGIAL SYSEMS DESIGN - LEURE NOES oncordia University hapter 6: Registers and ounters NOE: For more examples and detailed description of the material in the lecture notes, please refer to the
1 OEN 312 DIGIAL SYSEMS DESIGN - LEURE NOES oncordia University hapter 6: Registers and ounters NOE: For more examples and detailed description of the material in the lecture notes, please refer to the
Chapter 3 Digital Logic Structures
 Chapter 3 Digital Logic Structures Original slides from Gregory Byrd, North Carolina State University Modified by C. Wilcox, M. Strout, Y. Malaiya Colorado State University Computing Layers Problems Algorithms
Chapter 3 Digital Logic Structures Original slides from Gregory Byrd, North Carolina State University Modified by C. Wilcox, M. Strout, Y. Malaiya Colorado State University Computing Layers Problems Algorithms
CMPEN 411. Spring Lecture 18: Static Sequential Circuits
 CMPEN 411 VLSI Digital Circuits Spring 2011 Lecture 18: Static Sequential Circuits [Adapted from Rabaey s Digital Integrated Circuits, Second Edition, 2003 J. Rabaey, A. Chandrakasan, B. Nikolic] Sp11
CMPEN 411 VLSI Digital Circuits Spring 2011 Lecture 18: Static Sequential Circuits [Adapted from Rabaey s Digital Integrated Circuits, Second Edition, 2003 J. Rabaey, A. Chandrakasan, B. Nikolic] Sp11
EECS Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems. FSMs 9/11/2007
 EECS 150 - Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems FSMs 9/11/2007 Sarah Bird Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California, Berkeley Slides borrowed from David Culler
EECS 150 - Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems FSMs 9/11/2007 Sarah Bird Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California, Berkeley Slides borrowed from David Culler
Lecture 13: Sequential Circuits, FSM
 Lecture 13: Sequential Circuits, FSM Today s topics: Sequential circuits Finite state machines 1 Clocks A microprocessor is composed of many different circuits that are operating simultaneously if each
Lecture 13: Sequential Circuits, FSM Today s topics: Sequential circuits Finite state machines 1 Clocks A microprocessor is composed of many different circuits that are operating simultaneously if each
ELE2120 Digital Circuits and Systems. Tutorial Note 9
 ELE2120 Digital Circuits and Systems Tutorial Note 9 Outline 1. Exercise(1) Sequential Circuit Analysis 2. Exercise (2) Sequential Circuit Analysis 3. Exercise (3) Sequential Circuit Analysis 4. Ref. Construction
ELE2120 Digital Circuits and Systems Tutorial Note 9 Outline 1. Exercise(1) Sequential Circuit Analysis 2. Exercise (2) Sequential Circuit Analysis 3. Exercise (3) Sequential Circuit Analysis 4. Ref. Construction
Lecture 9: Sequential Logic Circuits. Reading: CH 7
 Lecture 9: Sequential Logic Circuits Reading: CH 7 Sequential Logic FSM (Finite-state machine) Inputs Current State COMBINATIONAL LOGIC Registers Outputs = f(current, inputs) Next state 2 storage mechanisms
Lecture 9: Sequential Logic Circuits Reading: CH 7 Sequential Logic FSM (Finite-state machine) Inputs Current State COMBINATIONAL LOGIC Registers Outputs = f(current, inputs) Next state 2 storage mechanisms
Generalized FSM model: Moore and Mealy
 Lecture 18 Logistics HW7 is due on Monday (and topic included in midterm 2) Midterm 2 on Wednesday in lecture slot cover materials up to today s lecture Review session Tuesday 4:15pm in EEB125 Last lecture
Lecture 18 Logistics HW7 is due on Monday (and topic included in midterm 2) Midterm 2 on Wednesday in lecture slot cover materials up to today s lecture Review session Tuesday 4:15pm in EEB125 Last lecture
Ch 7. Finite State Machines. VII - Finite State Machines Contemporary Logic Design 1
 Ch 7. Finite State Machines VII - Finite State Machines Contemporary Logic esign 1 Finite State Machines Sequential circuits primitive sequential elements combinational logic Models for representing sequential
Ch 7. Finite State Machines VII - Finite State Machines Contemporary Logic esign 1 Finite State Machines Sequential circuits primitive sequential elements combinational logic Models for representing sequential
Lecture (08) Synchronous Sequential Logic
 Lecture (08) Synchronous Sequential Logic By: Dr. Ahmed ElShafee ١ Dr. Ahmed ElShafee, ACU : Spring 2018, CSE303 Logic design II Analysis of Clocked Sequential Circuits The behavior of a clocked sequential
Lecture (08) Synchronous Sequential Logic By: Dr. Ahmed ElShafee ١ Dr. Ahmed ElShafee, ACU : Spring 2018, CSE303 Logic design II Analysis of Clocked Sequential Circuits The behavior of a clocked sequential
L4: Sequential Building Blocks (Flip-flops, Latches and Registers)
 L4: Sequential Building Blocks (Flip-flops, Latches and Registers) Acknowledgements: Lecture material adapted from R. Katz, G. Borriello, Contemporary Logic esign (second edition), Prentice-Hall/Pearson
L4: Sequential Building Blocks (Flip-flops, Latches and Registers) Acknowledgements: Lecture material adapted from R. Katz, G. Borriello, Contemporary Logic esign (second edition), Prentice-Hall/Pearson
MODULE 5 Chapter 7. Clocked Storage Elements
 MODULE 5 Chapter 7 Clocked Storage Elements 3/9/2015 1 Outline Background Clocked Storage Elements Timing, terminology, classification Static CSEs Latches Registers Dynamic CSEs Latches Registers 3/9/2015
MODULE 5 Chapter 7 Clocked Storage Elements 3/9/2015 1 Outline Background Clocked Storage Elements Timing, terminology, classification Static CSEs Latches Registers Dynamic CSEs Latches Registers 3/9/2015
Sequential Circuit Design
 Sequential Circuit esign esign Procedure. Specification 2. Formulation Obtain a state diagram or state table 3. State Assignment Assign binary codes to the states 4. Flip-Flop Input Equation etermination
Sequential Circuit esign esign Procedure. Specification 2. Formulation Obtain a state diagram or state table 3. State Assignment Assign binary codes to the states 4. Flip-Flop Input Equation etermination
Lecture 10: Synchronous Sequential Circuits Design
 Lecture 0: Synchronous Sequential Circuits Design. General Form Input Combinational Flip-flops Combinational Output Circuit Circuit Clock.. Moore type has outputs dependent only on the state, e.g. ripple
Lecture 0: Synchronous Sequential Circuits Design. General Form Input Combinational Flip-flops Combinational Output Circuit Circuit Clock.. Moore type has outputs dependent only on the state, e.g. ripple
Fundamentals of Computer Systems
 Fundamentals of Computer Systems Sequential Logic Stephen A. Edwards Columbia University Summer 2017 State-Holding Elements Bistable Elements S Latch Latch Positive-Edge-Triggered Flip-Flop Flip-Flop with
Fundamentals of Computer Systems Sequential Logic Stephen A. Edwards Columbia University Summer 2017 State-Holding Elements Bistable Elements S Latch Latch Positive-Edge-Triggered Flip-Flop Flip-Flop with
5. Sequential Logic x Computation Structures Part 1 Digital Circuits. Copyright 2015 MIT EECS
 5. Sequential Logic 6.004x Computation Structures Part 1 igital Circuits Copyright 2015 MIT EECS 6.004 Computation Structures L5: Sequential Logic, Slide #1 Something We Can t Build (Yet) What if you were
5. Sequential Logic 6.004x Computation Structures Part 1 igital Circuits Copyright 2015 MIT EECS 6.004 Computation Structures L5: Sequential Logic, Slide #1 Something We Can t Build (Yet) What if you were
CPE/EE 422/522. Chapter 1 - Review of Logic Design Fundamentals. Dr. Rhonda Kay Gaede UAH. 1.1 Combinational Logic
 CPE/EE 422/522 Chapter - Review of Logic Design Fundamentals Dr. Rhonda Kay Gaede UAH UAH Chapter CPE/EE 422/522. Combinational Logic Combinational Logic has no control inputs. When the inputs to a combinational
CPE/EE 422/522 Chapter - Review of Logic Design Fundamentals Dr. Rhonda Kay Gaede UAH UAH Chapter CPE/EE 422/522. Combinational Logic Combinational Logic has no control inputs. When the inputs to a combinational
Topic 8: Sequential Circuits
 Topic 8: Sequential Circuits Readings : Patterson & Hennesy, Appendix B.4 - B.6 Goals Basic Principles behind Memory Elements Clocks Applications of sequential circuits Introduction to the concept of the
Topic 8: Sequential Circuits Readings : Patterson & Hennesy, Appendix B.4 - B.6 Goals Basic Principles behind Memory Elements Clocks Applications of sequential circuits Introduction to the concept of the
Boolean Algebra and Digital Logic 2009, University of Colombo School of Computing
 IT 204 Section 3.0 Boolean Algebra and Digital Logic Boolean Algebra 2 Logic Equations to Truth Tables X = A. B + A. B + AB A B X 0 0 0 0 3 Sum of Products The OR operation performed on the products of
IT 204 Section 3.0 Boolean Algebra and Digital Logic Boolean Algebra 2 Logic Equations to Truth Tables X = A. B + A. B + AB A B X 0 0 0 0 3 Sum of Products The OR operation performed on the products of
Lecture 3 Review on Digital Logic (Part 2)
 Lecture 3 Review on Digital Logic (Part 2) Xuan Silvia Zhang Washington University in St. Louis http://classes.engineering.wustl.edu/ese461/ ircuit Optimization Simplest implementation ost criterion literal
Lecture 3 Review on Digital Logic (Part 2) Xuan Silvia Zhang Washington University in St. Louis http://classes.engineering.wustl.edu/ese461/ ircuit Optimization Simplest implementation ost criterion literal
COE 202: Digital Logic Design Sequential Circuits Part 3. Dr. Ahmad Almulhem ahmadsm AT kfupm Phone: Office:
 COE 202: Digital Logic Design Sequential Circuits Part 3 Dr. Ahmad Almulhem Email: ahmadsm AT kfupm Phone: 860-7554 Office: 22-324 Objectives Important Design Concepts State Reduction and Assignment Design
COE 202: Digital Logic Design Sequential Circuits Part 3 Dr. Ahmad Almulhem Email: ahmadsm AT kfupm Phone: 860-7554 Office: 22-324 Objectives Important Design Concepts State Reduction and Assignment Design
Issues on Timing and Clocking
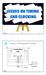 ECE152B TC 1 Issues on Timing and Clocking X Combinational Logic Z... clock clock clock period ECE152B TC 2 Latch and Flip-Flop L CK CK 1 L1 1 L2 2 CK CK CK ECE152B TC 3 Clocking X Combinational Logic...
ECE152B TC 1 Issues on Timing and Clocking X Combinational Logic Z... clock clock clock period ECE152B TC 2 Latch and Flip-Flop L CK CK 1 L1 1 L2 2 CK CK CK ECE152B TC 3 Clocking X Combinational Logic...
ECE380 Digital Logic. Synchronous sequential circuits
 ECE38 Digital Logic Synchronous Sequential Circuits: State Diagrams, State Tables Dr. D. J. Jackson Lecture 27- Synchronous sequential circuits Circuits here a clock signal is used to control operation
ECE38 Digital Logic Synchronous Sequential Circuits: State Diagrams, State Tables Dr. D. J. Jackson Lecture 27- Synchronous sequential circuits Circuits here a clock signal is used to control operation
Lecture 13: Sequential Circuits
 Lecture 13: Sequential Circuits Today s topics: Carry-lookahead adder Clocks and sequential circuits Finite state machines Reminder: Assignment 5 due on Thursday 10/12, mid-term exam Tuesday 10/24 1 Speed
Lecture 13: Sequential Circuits Today s topics: Carry-lookahead adder Clocks and sequential circuits Finite state machines Reminder: Assignment 5 due on Thursday 10/12, mid-term exam Tuesday 10/24 1 Speed
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, BERKELEY College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences
 UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, BERKELEY College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences Elad Alon Homework #9 EECS141 PROBLEM 1: TIMING Consider the simple state machine shown
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, BERKELEY College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences Elad Alon Homework #9 EECS141 PROBLEM 1: TIMING Consider the simple state machine shown
Different encodings generate different circuits
 FSM State Encoding Different encodings generate different circuits no easy way to find best encoding with fewest logic gates or shortest propagation delay. Binary encoding: K states need log 2 K bits i.e.,
FSM State Encoding Different encodings generate different circuits no easy way to find best encoding with fewest logic gates or shortest propagation delay. Binary encoding: K states need log 2 K bits i.e.,
CprE 281: Digital Logic
 CprE 281: Digital Logic Instructor: Alexander Stoytchev http://www.ece.iastate.edu/~alexs/classes/ Synchronous Sequential Circuits Basic Design Steps CprE 281: Digital Logic Iowa State University, Ames,
CprE 281: Digital Logic Instructor: Alexander Stoytchev http://www.ece.iastate.edu/~alexs/classes/ Synchronous Sequential Circuits Basic Design Steps CprE 281: Digital Logic Iowa State University, Ames,
ELEC Digital Logic Circuits Fall 2014 Sequential Circuits (Chapter 6) Finite State Machines (Ch. 7-10)
 ELEC 2200-002 Digital Logic Circuits Fall 2014 Sequential Circuits (Chapter 6) Finite State Machines (Ch. 7-10) Vishwani D. Agrawal James J. Danaher Professor Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
ELEC 2200-002 Digital Logic Circuits Fall 2014 Sequential Circuits (Chapter 6) Finite State Machines (Ch. 7-10) Vishwani D. Agrawal James J. Danaher Professor Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
The Design Procedure. Output Equation Determination - Derive output equations from the state table
 The Design Procedure Specification Formulation - Obtain a state diagram or state table State Assignment - Assign binary codes to the states Flip-Flop Input Equation Determination - Select flipflop types
The Design Procedure Specification Formulation - Obtain a state diagram or state table State Assignment - Assign binary codes to the states Flip-Flop Input Equation Determination - Select flipflop types
Sequential Logic. Rab Nawaz Khan Jadoon DCS. Lecturer COMSATS Lahore Pakistan. Department of Computer Science
 Sequential Logic Rab Nawaz Khan Jadoon DCS COMSATS Institute of Information Technology Lecturer COMSATS Lahore Pakistan Digital Logic and Computer Design Sequential Logic Combinational circuits with memory
Sequential Logic Rab Nawaz Khan Jadoon DCS COMSATS Institute of Information Technology Lecturer COMSATS Lahore Pakistan Digital Logic and Computer Design Sequential Logic Combinational circuits with memory
Boolean Logic Continued Prof. James L. Frankel Harvard University
 Boolean Logic Continued Prof. James L. Frankel Harvard University Version of 10:18 PM 5-Sep-2017 Copyright 2017, 2016 James L. Frankel. All rights reserved. D Latch D R S Clk D Clk R S X 0 ~S 0 = R 0 ~R
Boolean Logic Continued Prof. James L. Frankel Harvard University Version of 10:18 PM 5-Sep-2017 Copyright 2017, 2016 James L. Frankel. All rights reserved. D Latch D R S Clk D Clk R S X 0 ~S 0 = R 0 ~R
11.1 As mentioned in Experiment 10, sequential logic circuits are a type of logic circuit where the output of
 EE 2449 Experiment 11 Jack Levine and Nancy Warter-Perez CALIFORNIA STATE UNIVERSITY LOS ANGELES Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering EE-2449 Digital Logic Lab EXPERIMENT 11 SEQUENTIAL CIRCUITS
EE 2449 Experiment 11 Jack Levine and Nancy Warter-Perez CALIFORNIA STATE UNIVERSITY LOS ANGELES Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering EE-2449 Digital Logic Lab EXPERIMENT 11 SEQUENTIAL CIRCUITS
Example: A vending machine
 Lecture 22 Logistics HW8 due Monday (6/2), HW9 due Friday (6/6) Ant extra credit due 6/6 Take home extra credit final handed out 6/6 Final exam 6/9 8:30am Review? Last lecture Simplification Today State
Lecture 22 Logistics HW8 due Monday (6/2), HW9 due Friday (6/6) Ant extra credit due 6/6 Take home extra credit final handed out 6/6 Final exam 6/9 8:30am Review? Last lecture Simplification Today State
Sequential logic and design
 Principles Of Digital Design Sequential logic and design Analysis State-based (Moore) Input-based (Mealy) FSM definition Synthesis State minimization Encoding Optimization and timing Copyright 20-20by
Principles Of Digital Design Sequential logic and design Analysis State-based (Moore) Input-based (Mealy) FSM definition Synthesis State minimization Encoding Optimization and timing Copyright 20-20by
ECE 341. Lecture # 3
 ECE 341 Lecture # 3 Instructor: Zeshan Chishti zeshan@ece.pdx.edu October 7, 2013 Portland State University Lecture Topics Counters Finite State Machines Decoders Multiplexers Reference: Appendix A of
ECE 341 Lecture # 3 Instructor: Zeshan Chishti zeshan@ece.pdx.edu October 7, 2013 Portland State University Lecture Topics Counters Finite State Machines Decoders Multiplexers Reference: Appendix A of
Principles of Computer Architecture. Appendix B: Reduction of Digital Logic. Chapter Contents
 B-1 Principles of Computer Architecture Miles Murdocca and Vincent Heuring Appendix B: Reduction of Digital Logic B-2 Chapter Contents B.1 Reduction of Combinational Logic and Sequential Logic B.2 Reduction
B-1 Principles of Computer Architecture Miles Murdocca and Vincent Heuring Appendix B: Reduction of Digital Logic B-2 Chapter Contents B.1 Reduction of Combinational Logic and Sequential Logic B.2 Reduction
Lecture 13: Sequential Circuits, FSM
 Lecture 13: Sequential Circuits, FSM Today s topics: Sequential circuits Finite state machines Reminder: midterm on Tue 2/28 will cover Chapters 1-3, App A, B if you understand all slides, assignments,
Lecture 13: Sequential Circuits, FSM Today s topics: Sequential circuits Finite state machines Reminder: midterm on Tue 2/28 will cover Chapters 1-3, App A, B if you understand all slides, assignments,
ENEL Digital Circuits Final Examination
 Name: I#: Lecture Section: ENEL 353 - igital Circuits Final Examination Lecture sections : N. R. Bartley, MWF : :5, ENC 24 2: S. A. Norman, MWF : :5, ST 45 Wednesday, ecember 7, 24 Time: 7: PM : PM Locations:
Name: I#: Lecture Section: ENEL 353 - igital Circuits Final Examination Lecture sections : N. R. Bartley, MWF : :5, ENC 24 2: S. A. Norman, MWF : :5, ST 45 Wednesday, ecember 7, 24 Time: 7: PM : PM Locations:
Chapter 5 Synchronous Sequential Logic
 Chapter 5 Synchronous Sequential Logic Sequential circuit: A circuit that includes memory elements. In this case the output depends not only on the current input but also on the past inputs. Memory A synchronous
Chapter 5 Synchronous Sequential Logic Sequential circuit: A circuit that includes memory elements. In this case the output depends not only on the current input but also on the past inputs. Memory A synchronous
UNIVERSITY OF WISCONSIN MADISON
 CS/ECE 252: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER ENGINEERING UNIVERSITY OF WISCONSIN MADISON Prof. Gurindar Sohi TAs: Minsub Shin, Lisa Ossian, Sujith Surendran Midterm Examination 2 In Class (50 minutes) Friday,
CS/ECE 252: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER ENGINEERING UNIVERSITY OF WISCONSIN MADISON Prof. Gurindar Sohi TAs: Minsub Shin, Lisa Ossian, Sujith Surendran Midterm Examination 2 In Class (50 minutes) Friday,
Y. Tsiatouhas. VLSI Systems and Computer Architecture Lab
 CMOS INTEGRATE CIRCUIT ESIGN TECHNIUES University of Ioannina Memory Elements and other Circuits ept. of Computer Science and Engineering Y. Tsiatouhas CMOS Integrated Circuit esign Techniques Overview.
CMOS INTEGRATE CIRCUIT ESIGN TECHNIUES University of Ioannina Memory Elements and other Circuits ept. of Computer Science and Engineering Y. Tsiatouhas CMOS Integrated Circuit esign Techniques Overview.
Computers also need devices capable of Storing data and information Performing mathematical operations on such data
 Sequential Machines Introduction Logic devices examined so far Combinational Output function of input only Output valid as long as input true Change input change output Computers also need devices capable
Sequential Machines Introduction Logic devices examined so far Combinational Output function of input only Output valid as long as input true Change input change output Computers also need devices capable
ALU A functional unit
 ALU A functional unit that performs arithmetic operations such as ADD, SUB, MPY logical operations such as AND, OR, XOR, NOT on given data types: 8-,16-,32-, or 64-bit values A n-1 A n-2... A 1 A 0 B n-1
ALU A functional unit that performs arithmetic operations such as ADD, SUB, MPY logical operations such as AND, OR, XOR, NOT on given data types: 8-,16-,32-, or 64-bit values A n-1 A n-2... A 1 A 0 B n-1
Integrated Circuits & Systems
 Federal University of Santa Catarina Center for Technology Computer Science & Electronics Engineering Integrated Circuits & Systems INE 5442 Lecture 18 CMOS Sequential Circuits - 1 guntzel@inf.ufsc.br
Federal University of Santa Catarina Center for Technology Computer Science & Electronics Engineering Integrated Circuits & Systems INE 5442 Lecture 18 CMOS Sequential Circuits - 1 guntzel@inf.ufsc.br
COE 202: Digital Logic Design Sequential Circuits Part 3. Dr. Ahmad Almulhem ahmadsm AT kfupm Phone: Office:
 COE 202: Digital Logic Design Sequential Circuits Part 3 Dr. Ahmad Almulhem Email: ahmadsm AT kfupm Phone: 860-7554 Office: 22-324 Objectives State Reduction and Assignment Design of Synchronous Sequential
COE 202: Digital Logic Design Sequential Circuits Part 3 Dr. Ahmad Almulhem Email: ahmadsm AT kfupm Phone: 860-7554 Office: 22-324 Objectives State Reduction and Assignment Design of Synchronous Sequential
Finite State Machine. By : Ali Mustafa
 Finite State Machine By : Ali Mustafa So Far We have covered the memory elements issue and we are ready to implement the sequential circuits. We need to know how to Deal(analyze) with a sequential circuit?
Finite State Machine By : Ali Mustafa So Far We have covered the memory elements issue and we are ready to implement the sequential circuits. We need to know how to Deal(analyze) with a sequential circuit?
University of Toronto Faculty of Applied Science and Engineering Edward S. Rogers Sr. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
 University of Toronto Faculty of Applied Science and Engineering Edward S. Rogers Sr. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Final Examination ECE 241F - Digital Systems Examiners: J. Rose and
University of Toronto Faculty of Applied Science and Engineering Edward S. Rogers Sr. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Final Examination ECE 241F - Digital Systems Examiners: J. Rose and
Combinatorial Logic Design Multiplexers and ALUs CS 64: Computer Organization and Design Logic Lecture #13
 Combinatorial Logic Design Multiplexers and ALUs CS 64: Computer Organization and Design Logic Lecture #13 Ziad Matni Dept. of Computer Science, UCSB Administrative Re: Midterm Exam #2 Graded! 5/22/18
Combinatorial Logic Design Multiplexers and ALUs CS 64: Computer Organization and Design Logic Lecture #13 Ziad Matni Dept. of Computer Science, UCSB Administrative Re: Midterm Exam #2 Graded! 5/22/18
