BIO 1130FF. Student Number: Seat Number. BIO 1130FF Final exam December 21, 2015 Multiple choice questions - Place your answers on the answer sheet
|
|
|
- Benedict Daniels
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 BIO 1130FF Final exam December 21, 2015 Multiple choice questions - Place your answers on the answer sheet Student Number: Seat Number BIO 1130FF An Introduction to Organismal biology Final examination - Worth 35% of your final grade December 21, 2015 Part A: Multiple choice questions - 29 points (1 point/question) Please read the following instructions and sign in the space provided below to acknowledge the instructions: a) Cellular phones, unauthorized electronic devices or course notes (unless an open-book exam) are not allowed during this exam. Phones and devices must be turned off and put away in your bag. Do not keep them in your possession, such as in your pockets. If caught with such a device or document, the following may occur: you will be asked to leave immediately the exam, academic fraud allegations will be filed which may result in you obtaining a 0 (zero) for the exam. b) Fill in the bubbles for your name and student number and BIO1130FF for the course code. Fill in the same information in text in the boxes above the bubbles. c) Use only a pencil to fill in the answer sheet. If you erase a question be sure to erase all of the pencil mark. Don t place any marks anywhere on the sheet other than where the bubbles are for personal information or your answers. d) Do not place any answers on the question sheet. e) This is not an open book exam. f) A calculator is not required for this exam. g) CAUTION to minimize paper waste this part of the exam has been printed back to back be sure you have all the pages NOTE: If you do not fill in the student number and course code as BIO1130FF it will be impossible to identify your answer sheet and you will receive a ZERO for this part of the exam Signature Page 1 of 5
2 BIO 1130FF Final exam December 21, 2015 Multiple choice questions - Place your answers on the answer sheet FF.1 A cnidarian skeleton is a. Bony b. Cartilagenous c. Made of spicules d. made of ossicles e. hydrostatic FF.2 Which of the following characteristics is not common to all animal species? a. heterotroph b. motility c. nervous system d. eukaryote FF.3 The shell of a mollusc is secreted by the a. radula. b. mantle. c. periostracum. d. foot. e. visceral mass. FF.4 Which type of plant tissue is specialized for conducting fluids? a. dermal tissue b. protoderm c. meristem d. vascular tissue FF.5 The first larval stage in the life history of a fluke is the a. Redia b. Miracidium c. Cercaria d. Sporocyst e. Oncomiracidium FF.6 A feature that appeared about the same time as jaws in vertebrates was. a. cranium b. movable paired fins c. amniote egg d. gill arches FF.7 The bodies of arthropods are supported mainly by a. an exoskeleton. b. only nonskeletal structures. c. joined exo- and endoskeletons. d. a hydrostatic skeleton. FF.8 The specialized male gametophyte of seed plants, such as gymnosperms, is called a(n) a. ovule. b. pollen grain. c. strobilus. d. sporopollenin. Page 2 of 5
3 BIO 1130FF Final exam December 21, 2015 Multiple choice questions - Place your answers on the answer sheet FF.9 Which of the following is found in some tetrapods but never in fish? a. asexual reproduction b. internal fertilization c. viviparity d. extensive parental care e. production of amniotic eggs FF.10 What accounts most directly for the extremely fast growth of a fungal mycelium? a. a dikaryotic condition that supplies greater amounts of proteins and nutrients b. a long tubular body shape c. rapid distribution of synthesized proteins by cytoplasmic streaming d. the readily available nutrients from their ingestive mode of nutrition FF.11 Which of the following characteristics distinguishes the life cycle of a pine from that of a fern? a. Microspores and megaspores are produced in pines. b. No antheridium is present in pines. c. Spores grow into gametophytes inside the sporangia in pines. d. all of the choices FF.12 The main benefit to a plant from a mycorrhizal association is a. enhanced water uptake. b. removal of excess carbohydrates. c. enhanced mineral ion uptake. d. enhanced flow of carbohydrates to the roots. FF.13 The evolution of which of the following features freed land plants from requiring water for reproduction? a. lignified stems b. fruits and roots c. seeds and pollen d. flowers and leaves FF.14 Which of the following do all fungi have in common? a. meiosis in basidia b. absorption of nutrients c. coenocytic hyphae d. symbioses with algae e. sexual life cycle FF.15 Small, photosynthetic protists found in aquatic habitats are collectively called a. chrysophytes. b. zooplankton. c. phagoplankton. d. phytoplankton. Page 3 of 5
4 BIO 1130FF Final exam December 21, 2015 Multiple choice questions - Place your answers on the answer sheet FF.16 Sperm in sponges is commonly formed from a. Pinacocytes b. Porocytes c. Choanocytes d. Sclerocytes e. None of the above FF.17 Which of the following is a correct element of alternation of generations? a. Two spores unite to form a zygote. b. The sporophyte is haploid and produces gametes. c. The gametophyte is diploid and produces gametes. d. The gametophyte is haploid and produces spores. e. The sporophyte is diploid and produces spores. FF.18 The original function of the water vascular system of echinoderms was probably a. Locomotion. b. feeding. c. excretion. d. respiration. e. circulation. FF.19 The first vertebrates to produce amniotic eggs were early members of the class a. Reptilia. b. Gnathostoma. c. Amphibia. d. Mammalia. e. Agnatha. FF.20 Which of the following occurs in the life cycle of both mosses and angiosperms? a. The sporophyte is the dominant generation. b. The gametophyte is the dominant generation. c. Spores develop into sporophytes. d. The sporophyte produces spores. FF.21 To nearest million years how long do most species exist before they go extinct a. 45 b. 20 c. 10 d. 0.5 e. 15 FF.22 The protostome animals are divided into lineages, or clades. How many clades are there? a. 1 b. 3 c. 2 d. 4 Page 4 of 5
5 BIO 1130FF Final exam December 21, 2015 Multiple choice questions - Place your answers on the answer sheet FF.23 When mesoderm cells in a developing animal embryo form near the lip of the blastopore and split open to form the coelom; the coelom is described as being this type. a. acoel b. pseudocoel c. schizocoel d. enterocoel e. blastocoel FF.24 Although not all the events in the evolution of plants may be listed, for those that are, what is the correct sequence of events for A: Seed, B: Lignification, C; Stomata, D: Chloroplast DNA inversion a. B, C, D, A b. C, D, B, A c. C, B, D, A d. B, D, C, A e. None of the above FF.25 The outer layer of the insect exoskeleton called the is made of a waxy lipoprotein, which makes it impermeable to water. a. procuticle b. mesocuticle c. epicuticle d. endocuticle e. Collagenous cuticle FF.26 Which of the following phyla is included in the Lophotrochozoa? a. Bryozoa b. Onychophora c. Nematoda d. Arthropoda FF.27. Among the Lophotrochozoa, segmentation evolved in. a. no group b. only Phylum Annelida c. Phylum Annelida and Phylum Mollusca d. all phyla FF.28. Which of the following characteristics is found only in the angiosperm life cycle? a. double fertilization b. megaspores c. ovule d. pollen tube FF.29. One advantage that angiosperms have is a unique triploid, a nutritive tissue produced during fertilization. a. pollen sac b. ovule c. endosperm d. ovary Page 5 of 5
6 BIO 1130 An Introduction to Organismal biology Final examination Worth 35% of your final grade Total points for both parts of the exam is 110 pts December 21, 2015 Part B: Written questions Please read the following instructions and sign in the space provided below to acknowledge the instructions: a) Cellular phones, unauthorized electronic devices or course notes (unless an open-book exam) are not allowed during this exam. Phones and devices must be turned off and put away in your bag. Do not keep them in your possession, such as in your pockets. If caught with such a device or document, the following may occur: you will be asked to leave immediately the exam, academic fraud allegations will be filed which may result in you obtaining a 0 (zero) for the exam b) Place your name and student number in the space provided below. Be sure only your student number, is on the top of each of the following pages the exam will be separated and if you name is not on a page your mark will be zero for that page. This part of the exam is worth 65 points. c) Answer all questions in the space provided on the exam. Do not transfer answers to the back of the page. c) You may use either pencil of ink for your answers. d) Answers as written paragraphs are preferred but point form is acceptable as long as the points are logically organized and not random statements or facts e) This is not an open book exam. f) A calculator is not required for the exam g) There are seven pages including this one in part B of the exam, be sure you have all seven pages Signature Name: Student number: Page 1 of 7
7 18 pts Part 1. Briefly explain what each of the following terms means or the biological contribution made by the person. Where possible include an example in your explanation from a group or an organism to which the term or name applies. Doushantuo fossils Indeterminate meristem Pseudocoelom Synapsid Page 2 of 7
8 Cell plate Ciliate micronucleus Anything written below this line will not be marked. Page 3 of 7
9 35 pts Part 2: Fill in the missing word, or provide the one word answer in the space provided at the end of the sentence. If the line is missing, add it. 2.1 The ancestral food for amphibians was this group of animals and their feeding strategy is this. 2.2 Chromosome compliment of hyphae before plasmogamy occurs. 2.3 Of the two main vascular tissues in vascular plants this moves water up the plant 2.4 Of the two types of muscles in worms important in the function of the hydrostatic skeleton, these stretch the muscles oriented in line with the anterior to posterior axis of the worm. 2.5 This geological period follows the Cambrian period. 2.6 These geological events are too small and infrequent to result in any change in greenhouses gasses to cause a mass extinction. 2.7 Thirty six cellulase molecules are organized into this structure in all plants. 2.8 The number of peripheral microtubular doublets in either a cilium or flagellum. 2.9 The main locomotory structures used by echinoderms Reptiles, birds and mammals are distinguished from fishes and amphibians in that their embryos develop in this fluid filled sac Together, bundles of the living cells that move sugar in a plant are referred to as this type of plant tissue In the life cycle of a gymnosperm pine, this type of spore is wind born This bacterial domain is the sister group to the Eukarya One of the main roles of Fungi is in this important part of the carbon cycle Bikonts are the ancestral cell to which of the multicellular eukaryote Kingdoms When plants first appeared on land the plant's fungal partner provided these essential nutrients to the plant and still do so today These genes control pattern in multicellular organisms Fungal hypae are wound together to form this filamentous stands. Page 4 of 7
10 2.19 The unique shape of a sharks tail, which has a dorsal lobe that is much larger than the ventral lobe Number of mass extinctions like the one at the end of the Ordovician that have happened One of the advantages of a nuclear envelope surrounding the nucleus is that replication and this stage in the central Dogma of Biology is restricted to the nucleus In cilia and flagella these molecular motors connect the outer microtubular components to each other The plant sap collected for making maple syrup is from this tissue Slits in this are one of the chordate characteristics This type of movement allowed the Cambrian fauna to tap into a rich unused food source of the marine sediments Like feathers, these help insulate mammals and are a diagnostic character of this vertebrate class The Cambrian period marks the start of this the final geological eon During the eight cell stage in the developing embryo, when the cells above the equatorial plane where cleavage occurs remain in place, and aligned perfectly with the cells underneath the cleavage pattern is this type Number of flagella on the moss sperm cell Unlike the primary cell wall the secondary cell is composed of cellulose and this compound A waterproof insect package of sperm is given this name Decreased dissolved oxygen in water makes the water Like the corals, these animals also built reefs in the Ordovician oceans This type of gliding was probably a precursor to movement in the first eukaryote cells The malaria parasite lives in these mosquito glands before being injected into the human host when the mosquito bites. Part three of the exam is on the next page Page 5 of 7
11 18 pts Part 3: Answer the following three questions in the space provided. Each answer is worth 6 points 3.1 Aquatic animals try to maintain neutral buoyancy so that all the energy used for locomotion is used for moving forward, not to counter the effects of gravity. What is neutral buoyancy and use one type of fish in your answer to explain how that fish attains neutral buoyancy. 3.2 Ancestral fungal cells lacked septa and, compared to plants and animals, developed a unique way to divide their cell. How does cell division occur in these early fungi fungus. Page 6 of 7
12 3.3 What is endocytosis and how is used to obtain nutrients by protists Anything written below this line will not be marked. Page 7 of 7
BIO 1130FF. Student Number: Seat Number. BIO 1130FF Final exam December 15, 2016 Multiple choice questions - Place your answers on the answer sheet
 Student Number: Seat Number BIO 1130FF An Introduction to Organismal biology Final examination - Worth 35% of your final grade December 15, 2016 Part A: Multiple choice questions - 29 points (1 point/question)
Student Number: Seat Number BIO 1130FF An Introduction to Organismal biology Final examination - Worth 35% of your final grade December 15, 2016 Part A: Multiple choice questions - 29 points (1 point/question)
December 7, c) Do not place any answers on the question sheet. d) This is not an open book exam. e) A calculator is not required for this exam
 BIO 1130FF Final exam December 7, 2013 Multiple choice questions - Place your answers on the answer sheet Student Number: Seat Number BIO 1130FF An Introduction to Organismal biology Final examination
BIO 1130FF Final exam December 7, 2013 Multiple choice questions - Place your answers on the answer sheet Student Number: Seat Number BIO 1130FF An Introduction to Organismal biology Final examination
Chapter 29 Plant Diversity I: How Plants Colonized Land
 Chapter 29: Plant Diversity I: How Plants Colonized Land Chapter 29 Plant Diversity I: How Plants Colonized Land Name Period Concept 29.1 Land plants evolved from green algae 1. Plants colonized land about
Chapter 29: Plant Diversity I: How Plants Colonized Land Chapter 29 Plant Diversity I: How Plants Colonized Land Name Period Concept 29.1 Land plants evolved from green algae 1. Plants colonized land about
Animal Diversity. Features shared by all animals. Animals are multicellular, heterotrophic eukaryotes with tissues that develop from embryonic layers
 Animal Diversity Animals are multicellular, heterotrophic eukaryotes with tissues that develop from embryonic layers Nutritional mode Ingest food and use enzymes in the body to digest Cell structure and
Animal Diversity Animals are multicellular, heterotrophic eukaryotes with tissues that develop from embryonic layers Nutritional mode Ingest food and use enzymes in the body to digest Cell structure and
8/23/2014. Introduction to Animal Diversity
 Introduction to Animal Diversity Chapter 32 Objectives List the characteristics that combine to define animals Summarize key events of the Paleozoic, Mesozoic, and Cenozoic eras Distinguish between the
Introduction to Animal Diversity Chapter 32 Objectives List the characteristics that combine to define animals Summarize key events of the Paleozoic, Mesozoic, and Cenozoic eras Distinguish between the
SG 9.2 notes Ideas about targets and terms: 9.2 In the past, all living things were classified in either the kingdom of animals or plants
 Ideas about targets and terms: 9.2 In the past, all living things were classified in either the kingdom of animals or plants Euglena are singled celled organisms in pond water They are green, so contain,
Ideas about targets and terms: 9.2 In the past, all living things were classified in either the kingdom of animals or plants Euglena are singled celled organisms in pond water They are green, so contain,
Kingdom Plantae. Biology : A Brief Survey of Plants. Jun 22 7:09 PM
 Kingdom Plantae Biology 2201 6.1 6.2 : A Brief Survey of Plants The study of plants is called botany. Plants are believed to have evolved from green algae. The main plant (land) characteristics are as
Kingdom Plantae Biology 2201 6.1 6.2 : A Brief Survey of Plants The study of plants is called botany. Plants are believed to have evolved from green algae. The main plant (land) characteristics are as
Chapter 32. Objectives. Table of Contents. Characteristics. Characteristics, continued. Section 1 The Nature of Animals
 Introduction to Animals Table of Contents Objectives Identify four important characteristics of animals. List two kinds of tissues found only in animals. Explain how the first animals may have evolved
Introduction to Animals Table of Contents Objectives Identify four important characteristics of animals. List two kinds of tissues found only in animals. Explain how the first animals may have evolved
Plant Diversity & Evolution (Outline)
 Plant Diversity & Evolution (Outline) Review the Life cycle of Fungi Characteristics of organisms in the Kingdom Plantae. Evolution of plants: Challenges and adaptations to living on land Highlights of
Plant Diversity & Evolution (Outline) Review the Life cycle of Fungi Characteristics of organisms in the Kingdom Plantae. Evolution of plants: Challenges and adaptations to living on land Highlights of
CHAPTERS 16 & 17: PROKARYOTES, FUNGI, AND PLANTS Honors Biology 2012 PROKARYOTES PROKARYOTES. Fig Lived alone on Earth for over 1 billion years
 CHAPTERS 6 & 7: PROKARYOTES, FUNGI, AND PLANTS Honors Biology 0 PROKARYOTES Lived alone on Earth for over billion years Most numerous and widespread organisms (total biomass of prokaryotes is ten times
CHAPTERS 6 & 7: PROKARYOTES, FUNGI, AND PLANTS Honors Biology 0 PROKARYOTES Lived alone on Earth for over billion years Most numerous and widespread organisms (total biomass of prokaryotes is ten times
What defines the zygote, the blastula, and the gastrula? Draw pictures.
 What makes a multicellular organism multicellular? a) Multiple cells b) Multiple cells that work together c) Specialized cells d) Multiple specialized cells that work together What defines the zygote,
What makes a multicellular organism multicellular? a) Multiple cells b) Multiple cells that work together c) Specialized cells d) Multiple specialized cells that work together What defines the zygote,
Biology 211 (1) Exam 3 Review! Chapter 31!
 Biology 211 (1) Exam 3 Review Chapter 31 Origin of Land Plants: 1. Fill in the correct amount of years ago the following events occurred. years ago there was a thin coating of cyanobacteri b. years ago
Biology 211 (1) Exam 3 Review Chapter 31 Origin of Land Plants: 1. Fill in the correct amount of years ago the following events occurred. years ago there was a thin coating of cyanobacteri b. years ago
An Introduction to Animal Diversity
 Chapter 32 An Introduction to Animal Diversity PowerPoint Lectures for Biology, Seventh Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero Overview: Welcome to Your Kingdom The animal kingdom
Chapter 32 An Introduction to Animal Diversity PowerPoint Lectures for Biology, Seventh Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero Overview: Welcome to Your Kingdom The animal kingdom
Bacteria, Protists, Fungi, Plants, Animals: Phylogeny and Diversity
 Bacteria, Protists, Fungi, Plants, Animals: Phylogeny and Diversity 1/8/2006 Phylogeny 2 1/8/2006 Phylogeny 3 Proteobacteria Chlamydias Spirochetes Cyanobacteria Gram positive bacteria Korarchaeotes Euryarchaeotes,
Bacteria, Protists, Fungi, Plants, Animals: Phylogeny and Diversity 1/8/2006 Phylogeny 2 1/8/2006 Phylogeny 3 Proteobacteria Chlamydias Spirochetes Cyanobacteria Gram positive bacteria Korarchaeotes Euryarchaeotes,
Resources. Visual Concepts. Chapter Presentation. Copyright by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
 Chapter Presentation Visual Concepts Transparencies Standardized Test Prep Introduction to Animals Table of Contents Section 2 Animal Body Systems Objectives Identify the features that animals have in
Chapter Presentation Visual Concepts Transparencies Standardized Test Prep Introduction to Animals Table of Contents Section 2 Animal Body Systems Objectives Identify the features that animals have in
Unit B: Diversity of Living Things
 Unit B: Diversity of Living Things Chapter 3: Multicellular Diversity - Considerable diversity exists among multicellular organisms, as well. Specific Expectations: In the chapter you will learn how to
Unit B: Diversity of Living Things Chapter 3: Multicellular Diversity - Considerable diversity exists among multicellular organisms, as well. Specific Expectations: In the chapter you will learn how to
Chapter 32 Introduction to Animal Diversity. Copyright 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
 Chapter 32 Introduction to Animal Diversity Welcome to Your Kingdom The animal kingdom extends far beyond humans and other animals we may encounter 1.3 million living species of animals have been identified
Chapter 32 Introduction to Animal Diversity Welcome to Your Kingdom The animal kingdom extends far beyond humans and other animals we may encounter 1.3 million living species of animals have been identified
Unit 2B- The Plants. Plants can be classified according to the presence or absence of vascular tissue.
 Unit 2B- The Plants Botany is the study of plants. All plants are said to have a common ancestor; (ie.) it is thought that plants have evolved from an ancient group of green algae. Plants and green algae
Unit 2B- The Plants Botany is the study of plants. All plants are said to have a common ancestor; (ie.) it is thought that plants have evolved from an ancient group of green algae. Plants and green algae
AP: CHAPTER 18: the Genetics of VIRUSES p What makes microbes good models to study molecular mechanisms? 4. What is a bacteriophage?
 AP: CHAPTER 18: the Genetics of VIRUSES p328-340 1. What makes microbes good models to study molecular mechanisms? Name Per 2. How were viruses first discovered? 3. What are the two basic components of
AP: CHAPTER 18: the Genetics of VIRUSES p328-340 1. What makes microbes good models to study molecular mechanisms? Name Per 2. How were viruses first discovered? 3. What are the two basic components of
Biology 211 (1) Exam 2 Worksheet!
 Biology 211 (1) Exam 2 Worksheet Chapter 33 Introduction to Animal Diversity Kingdom Animalia: 1. Approximately how many different animal species are alive on Earth currently. How many those species have
Biology 211 (1) Exam 2 Worksheet Chapter 33 Introduction to Animal Diversity Kingdom Animalia: 1. Approximately how many different animal species are alive on Earth currently. How many those species have
CHAPTER 29 PLANT DIVERSITY I: HOW PLANTS COLONIZED LAND. Section A: An Overview of Land Plant Evolution
 CHAPTER 29 PLANT DIVERSITY I: HOW PLANTS COLONIZED LAND Section A: An Overview of Land Plant Evolution 1. Evolutionary adaptations to terrestrial living characterize the four main groups of land plants
CHAPTER 29 PLANT DIVERSITY I: HOW PLANTS COLONIZED LAND Section A: An Overview of Land Plant Evolution 1. Evolutionary adaptations to terrestrial living characterize the four main groups of land plants
A Brief Survey of Life s Diversity 1
 Name A Brief Survey of Life s Diversity 1 AP WINTER BREAK ASSIGNMENT (CH 25-34). Complete the questions using the chapters of your textbook Campbell s Biology (8 th edition). CHAPTER 25: The History of
Name A Brief Survey of Life s Diversity 1 AP WINTER BREAK ASSIGNMENT (CH 25-34). Complete the questions using the chapters of your textbook Campbell s Biology (8 th edition). CHAPTER 25: The History of
KINGDOM ANIMALIA CHARACTERISTICS
 KINGDOM ANIMALIA CHARACTERISTICS EUKARYOTIC MULTICELLULAR HETEROTROPHIC (by ingestion) MOVE AT SOME POINT IN LIFE (not all - sponges are sessile) DIGEST FOOD TO GET NUTRIENTS LACK CELL WALLS CHARACTERISTICS
KINGDOM ANIMALIA CHARACTERISTICS EUKARYOTIC MULTICELLULAR HETEROTROPHIC (by ingestion) MOVE AT SOME POINT IN LIFE (not all - sponges are sessile) DIGEST FOOD TO GET NUTRIENTS LACK CELL WALLS CHARACTERISTICS
An Introduction to Animal Diversity
 Chapter 32 An Introduction to Animal Diversity PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions
Chapter 32 An Introduction to Animal Diversity PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions
UNIVERSITY OF BOLTON SCHOOL OF SPORT AND BIOMEDICAL SCIENCES BSC(HONS) BIOLOGY SEMESTER ONE EXAMINATION 2015/2016 DIVERSITY OF LIFE MODULE NO: BIO4003
 [LH4] UNIVERSITY OF BOLTON SCHOOL OF SPORT AND BIOMEDICAL SCIENCES BSC(HONS) BIOLOGY SEMESTER ONE EXAMINATION 2015/2016 DIVERSITY OF LIFE MODULE NO: BIO4003 Date: Friday 15 January 2016 Time: 10.00 am
[LH4] UNIVERSITY OF BOLTON SCHOOL OF SPORT AND BIOMEDICAL SCIENCES BSC(HONS) BIOLOGY SEMESTER ONE EXAMINATION 2015/2016 DIVERSITY OF LIFE MODULE NO: BIO4003 Date: Friday 15 January 2016 Time: 10.00 am
Kingdom Plantae. A Brief Survey of Plants
 Kingdom Plantae A Brief Survey of Plants The study of plants is called botany. Plants are believed to have evolved from green algae. The main plant (land) characteristics are as follows: 1. Common cellular
Kingdom Plantae A Brief Survey of Plants The study of plants is called botany. Plants are believed to have evolved from green algae. The main plant (land) characteristics are as follows: 1. Common cellular
Biology 11. The Kingdom Animalia
 Biology 11 The Kingdom Animalia Objectives By the end of the lesson you should be able to: Describe the 5 ways we classify animals Symmetry Germ layers Body plan Segmentation Animal Evolution Hank Video
Biology 11 The Kingdom Animalia Objectives By the end of the lesson you should be able to: Describe the 5 ways we classify animals Symmetry Germ layers Body plan Segmentation Animal Evolution Hank Video
What is a Plant? Plant Life Cycle. What did they evolve from? Original Habitat 1/15/2018. Plant Life Cycle Alternation of Generations
 What is a Plant? Multicellular Eukaryotic Autotrophic (photosynthesis) Has cell walls containing cellulose Lack mobility (sessile) Display Alternation of Generations in their life cycle Introduction to
What is a Plant? Multicellular Eukaryotic Autotrophic (photosynthesis) Has cell walls containing cellulose Lack mobility (sessile) Display Alternation of Generations in their life cycle Introduction to
Chapter 8-9 Intro to Animals. Image from:
 Chapter 8-9 Intro to Animals Image from: http://animaldiversity.ummz.umich.edu/index.html Zoology Definition: the scientific study of the behavior, structure, physiology, classification, and distribution
Chapter 8-9 Intro to Animals Image from: http://animaldiversity.ummz.umich.edu/index.html Zoology Definition: the scientific study of the behavior, structure, physiology, classification, and distribution
BIO 1130FF. Page 1 of 5. An introduction to Organismal biology Midterm examination Worth either 15% or 20% of your final grade
 BIO 1130FF An introduction to Organismal biology Midterm examination Worth either 15% or 20% of your final grade Saturday, November 9, 2013 Part A: Multiple choice questions 26 points (1 point/question)
BIO 1130FF An introduction to Organismal biology Midterm examination Worth either 15% or 20% of your final grade Saturday, November 9, 2013 Part A: Multiple choice questions 26 points (1 point/question)
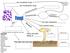
6 characteristics blastula
 Animals Characteristics The animal kingdom is divided into approximately 35 phyla with diverse species. However, all organisms in the animal kingdom share these 6 characteristics Eukaryotic Lack cell walls
Animals Characteristics The animal kingdom is divided into approximately 35 phyla with diverse species. However, all organisms in the animal kingdom share these 6 characteristics Eukaryotic Lack cell walls
copyright cmassengale Kingdoms and Classification
 1 Kingdoms and Classification 2 Domains Broadest, most inclusive taxon Three domains Archaea and Eubacteria are unicellular prokaryotes (no nucleus or membrane-bound organelles) Eukarya are more complex
1 Kingdoms and Classification 2 Domains Broadest, most inclusive taxon Three domains Archaea and Eubacteria are unicellular prokaryotes (no nucleus or membrane-bound organelles) Eukarya are more complex
Exam 2 BIO101, Fall 2010
 Exam 2 BIO101, Fall 2010 Name: Multiple Choice Questions. Circle the one best answer for each question. (3 points each) 1. All craniates are also classified as A. chordates. B. amniotes. C. vertebrates.
Exam 2 BIO101, Fall 2010 Name: Multiple Choice Questions. Circle the one best answer for each question. (3 points each) 1. All craniates are also classified as A. chordates. B. amniotes. C. vertebrates.
Introduction to Animals
 Introduction to Animals Characteristics of Animals multicellular Except for sponges, animal cells are arranged into tissues. Tissues are necessary to produce organs and organ systems. Tissues, organs,
Introduction to Animals Characteristics of Animals multicellular Except for sponges, animal cells are arranged into tissues. Tissues are necessary to produce organs and organ systems. Tissues, organs,
Today: Animal Body Plans. Animal Body Plans: The Gut. The Animal Kingdom- General Characteristics: Animal Body Plans: Symmetry
 Today: Exploring the Animal Kingdom Introduction to Ecology The Animal Kingdom- General Characteristics: Multicellular Heterotrophic (via ingestion) Eukaryotes Require Oxygen for aerobic respiration Reproduce
Today: Exploring the Animal Kingdom Introduction to Ecology The Animal Kingdom- General Characteristics: Multicellular Heterotrophic (via ingestion) Eukaryotes Require Oxygen for aerobic respiration Reproduce
Topic 2: Plants Ch. 16,28
 Topic 2: Plants Ch. 16,28 Characteristics of Plants p. 316 1. Multicellular eukaryotic organisms 2. Composed of tissues, organs and organ systems. 3. Cell walls made of cellulose. 4. Store energy as starch.
Topic 2: Plants Ch. 16,28 Characteristics of Plants p. 316 1. Multicellular eukaryotic organisms 2. Composed of tissues, organs and organ systems. 3. Cell walls made of cellulose. 4. Store energy as starch.
3/22/2011. Review. Review. Mitosis: division of cells that results in two identical daughter cells with same genetic information as the first cell
 Review Review Mitosis: division of cells that results in two identical daughter cells with same genetic information as the first cell Meiosis: division of cells that results in daughter cells with one-half
Review Review Mitosis: division of cells that results in two identical daughter cells with same genetic information as the first cell Meiosis: division of cells that results in daughter cells with one-half
1 Mosses and other bryophytes are like ferns in that both bryophytes and ferns exhibit each of the following traits EXCEPT
 Page 1 1 Mosses and other bryophytes are like ferns in that both bryophytes and ferns exhibit each of the following traits EXCEPT A haploid spores. B specialized cells and tissues. C vascular tissue for
Page 1 1 Mosses and other bryophytes are like ferns in that both bryophytes and ferns exhibit each of the following traits EXCEPT A haploid spores. B specialized cells and tissues. C vascular tissue for
What Is an Animal? Section 25.1 Typical Animal Characteristics. I. Characteristics of Animals. Biology II Mrs. Michaelsen
 What Is an Animal? Section 25.1 Typical Animal Characteristics Biology II Mrs. Michaelsen I. Characteristics of Animals A. All animals are eukaryotic, multicellular, have ways of moving to reproduce, obtain
What Is an Animal? Section 25.1 Typical Animal Characteristics Biology II Mrs. Michaelsen I. Characteristics of Animals A. All animals are eukaryotic, multicellular, have ways of moving to reproduce, obtain
An Introduction to Animal Diversity
 Chapter 32 An Introduction to Animal Diversity PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions
Chapter 32 An Introduction to Animal Diversity PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions
Chapter 32 Introduction to Animal Diversity
 Chapter 32 Introduction to Animal Diversity Review: Biology 101 There are 3 domains: They are Archaea Bacteria Protista! Eukarya Endosymbiosis (proposed by Lynn Margulis) is a relationship between two
Chapter 32 Introduction to Animal Diversity Review: Biology 101 There are 3 domains: They are Archaea Bacteria Protista! Eukarya Endosymbiosis (proposed by Lynn Margulis) is a relationship between two
Animal Diversity. Animals are multicellular, heterotrophic eukaryotes with tissues that develop from embryonic layers 9/20/2017
 Animal Diversity Chapter 32 Which of these organisms are animals? Animals are multicellular, heterotrophic eukaryotes with tissues that develop from embryonic layers Animals share the same: Nutritional
Animal Diversity Chapter 32 Which of these organisms are animals? Animals are multicellular, heterotrophic eukaryotes with tissues that develop from embryonic layers Animals share the same: Nutritional
Comparing Plants & Animals
 Section 6.1 Comparing Plants & Animals p. 164-168 Major Similarities: They are both multi-cellular, eukaryotes. Their sizes both range from microscopic to very large. Major Differences: How they obtain
Section 6.1 Comparing Plants & Animals p. 164-168 Major Similarities: They are both multi-cellular, eukaryotes. Their sizes both range from microscopic to very large. Major Differences: How they obtain
Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. FUNGI
 Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. FUNGI FUNGI Fungi are absorptive heterotrophic eukaryotes that digest their food externally and absorb the nutrients Most fungi consist of a mass of threadlike hyphae
Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. FUNGI FUNGI Fungi are absorptive heterotrophic eukaryotes that digest their food externally and absorb the nutrients Most fungi consist of a mass of threadlike hyphae
The Evolution of Animal Diversity. Dr. Stephen J. Salek Biology 130 Fayetteville State University
 The Evolution of Animal Diversity Dr. Stephen J. Salek Biology 130 Fayetteville State University Create your own animal? Start with a basic plant. Make the plant into a simple animal such as a worm. Consider:
The Evolution of Animal Diversity Dr. Stephen J. Salek Biology 130 Fayetteville State University Create your own animal? Start with a basic plant. Make the plant into a simple animal such as a worm. Consider:
Animals. What are they? Where did they come from? What are their evolutionary novelties? What characterizes their diversification?
 Animals What are they? Where did they come from? What are their evolutionary novelties? What characterizes their diversification? What synapomorphies unite Animals Multicellular Heterotrophs (Metazoans)?
Animals What are they? Where did they come from? What are their evolutionary novelties? What characterizes their diversification? What synapomorphies unite Animals Multicellular Heterotrophs (Metazoans)?
Behavioral and Structural Adaptations PPT Guided Notes
 A Essential Standard 2.1.2 Analyze how various organisms accomplish the following life functions through adaptations with particular environments and that these adaptations have evolved to ensure survival
A Essential Standard 2.1.2 Analyze how various organisms accomplish the following life functions through adaptations with particular environments and that these adaptations have evolved to ensure survival
Ch. 22: Plant Growth, Reproduction & Response
 Ch. 22: Plant Growth, Reproduction & Response generally reproduce sexually, though many can also reproduce asexually. Some have lost ability to reproduce sexually. All plant lifecycles involve alternation
Ch. 22: Plant Growth, Reproduction & Response generally reproduce sexually, though many can also reproduce asexually. Some have lost ability to reproduce sexually. All plant lifecycles involve alternation
Importance of Protists
 Protists Protists The kingdom Protista is a very diverse kingdom. Eukaryotes that are not classified as fungi, plants, or animals are classified as protists. However, even though they are officially in
Protists Protists The kingdom Protista is a very diverse kingdom. Eukaryotes that are not classified as fungi, plants, or animals are classified as protists. However, even though they are officially in
Due Friday, January 11, 2008
 Due Friday, January 11, 2008 Name AP Biology Winter Assignment Parade Through the Kingdoms A Brief Survey of Life s Diversity Complete the questions using Chapters 26 34 of your textbook: Biology (7th
Due Friday, January 11, 2008 Name AP Biology Winter Assignment Parade Through the Kingdoms A Brief Survey of Life s Diversity Complete the questions using Chapters 26 34 of your textbook: Biology (7th
Name: Date: Period: Forms a spore producing structure called an ascus Morals Truffles Yeast
 Name: Date: Period: Fungi and Plant Unit Review Worksheet Part I (KEY) Directions: Treat this like an assessment and answer as much as you can without ANY help. See how much you actually know by highlighting/starring
Name: Date: Period: Fungi and Plant Unit Review Worksheet Part I (KEY) Directions: Treat this like an assessment and answer as much as you can without ANY help. See how much you actually know by highlighting/starring
What Is an Animal? Animals come in many shapes, forms, and sizes. About 98 percent of all animals are invertebrates. The Kingdom Animalia
 What Is an Animal? What characteristics do all animals have? Animals come in many shapes, forms, and sizes. Scientists estimate that there are between 1 and 2 million species of animals! Some, like whales
What Is an Animal? What characteristics do all animals have? Animals come in many shapes, forms, and sizes. Scientists estimate that there are between 1 and 2 million species of animals! Some, like whales
Plants. and their classi.ication
 + Plants and their classi.ication +Why are plants important? n Photosynthesis Carbon dioxide + water + energy à sugar + oxygen 6CO 2 + 6H 2 O à C 6 H 12 O 6 + 6O 2 n Food (green tea, fruits, seeds, roots,
+ Plants and their classi.ication +Why are plants important? n Photosynthesis Carbon dioxide + water + energy à sugar + oxygen 6CO 2 + 6H 2 O à C 6 H 12 O 6 + 6O 2 n Food (green tea, fruits, seeds, roots,
Ms.Sastry, AP Biology Unit 4/Chp 26 to 34/Diversity 1 Chapter in class follow along lecture notes
 Ms.Sastry, AP Biology Unit 4/Chp 26 to 34/Diversity 1 Chapter 26 34 in class follow along lecture notes Chp 26 Origin of life: 1) When did earth form? 2) What is the order of evolution of life forms on
Ms.Sastry, AP Biology Unit 4/Chp 26 to 34/Diversity 1 Chapter 26 34 in class follow along lecture notes Chp 26 Origin of life: 1) When did earth form? 2) What is the order of evolution of life forms on
Saturday, November 12, Part B: Written questions
 BIO 1130 An Introduction to Organismal Biology Midterm examination Worth either 15% or 20% of your final grade Total points for both parts of the exam is 80 pts Saturday, November 12, 2016 Part B: Written
BIO 1130 An Introduction to Organismal Biology Midterm examination Worth either 15% or 20% of your final grade Total points for both parts of the exam is 80 pts Saturday, November 12, 2016 Part B: Written
Biosc 41 9/10 Announcements
 Biosc 41 9/10 Announcements v Genetics review: group problem sets Groups of 3-4 Correct answer presented to class = 2 pts extra credit Incorrect attempt = 1 pt extra credit v Lecture: Animal Body Plans
Biosc 41 9/10 Announcements v Genetics review: group problem sets Groups of 3-4 Correct answer presented to class = 2 pts extra credit Incorrect attempt = 1 pt extra credit v Lecture: Animal Body Plans
Resources. Visual Concepts. Chapter Presentation. Copyright by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
 Chapter Presentation Visual Concepts Transparencies Standardized Test Prep Introduction to the Kingdoms of Life Table of Contents Section 1 Introduction to Kingdoms and Domains Section 2 Advent of Multicellularity
Chapter Presentation Visual Concepts Transparencies Standardized Test Prep Introduction to the Kingdoms of Life Table of Contents Section 1 Introduction to Kingdoms and Domains Section 2 Advent of Multicellularity
A. Incorrect! Sponges are mostly marine animals. This is a feature of sponges.
 College Biology - Problem Drill 15: The Evolution of Animal Diversity Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which is not a feature of the phyla porifera- sponges? Question #01 (A) Most are marine animals. (B) They have
College Biology - Problem Drill 15: The Evolution of Animal Diversity Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which is not a feature of the phyla porifera- sponges? Question #01 (A) Most are marine animals. (B) They have
1. General Features of Animals
 Chapter 32: An Overview of Animal Diversity 1. General Features of Animals 2. The History of Animals 1. General Features of Animals General Characteristics of Animals animals are multicellular eukaryotic
Chapter 32: An Overview of Animal Diversity 1. General Features of Animals 2. The History of Animals 1. General Features of Animals General Characteristics of Animals animals are multicellular eukaryotic
Phanerozic - Paleozoic
 Phanerozoic Paleozoic era 1 Carboniferous and Permian 2 3 Page 1 4 5 Carboniferous terrestrial environment 6 Page 2 Carboniferous coal forests Club mosses Giant horse tails Tree ferns 7 Plant phylogeny
Phanerozoic Paleozoic era 1 Carboniferous and Permian 2 3 Page 1 4 5 Carboniferous terrestrial environment 6 Page 2 Carboniferous coal forests Club mosses Giant horse tails Tree ferns 7 Plant phylogeny
Phanerozic - Paleozoic
 Phanerozoic Paleozoic era Carboniferous and Permian 1 2 3 4 Carboniferous terrestrial environment 5 6 Page 1 Carboniferous coal forests Club mosses Giant horse tails Tree ferns Plant phylogeny Figure 24.9
Phanerozoic Paleozoic era Carboniferous and Permian 1 2 3 4 Carboniferous terrestrial environment 5 6 Page 1 Carboniferous coal forests Club mosses Giant horse tails Tree ferns Plant phylogeny Figure 24.9
Plants Review 1. List the 6 general characteristics of plants. 2. What did plants probably evolve from? 3. What are some advantages for life on land
 Plants Review 1. List the 6 general characteristics of plants. 2. What did plants probably evolve from? 3. What are some advantages for life on land for a plant? 4. What are the 3 main groups of plants?
Plants Review 1. List the 6 general characteristics of plants. 2. What did plants probably evolve from? 3. What are some advantages for life on land for a plant? 4. What are the 3 main groups of plants?
Protist Classification the Saga Continues
 Protist Classification the Saga Continues Learning Objectives Explain what a protist is. Describe how protists are related to other eukaryotes. What Are Protists? Photosynthetic Motile Unicellular Multicellular
Protist Classification the Saga Continues Learning Objectives Explain what a protist is. Describe how protists are related to other eukaryotes. What Are Protists? Photosynthetic Motile Unicellular Multicellular
22 1 Introduction to Plants Slide 2 of 33
 2 of 33 What Is a Plant? What is a plant? 3 of 33 What Is a Plant? What Is a Plant? Plants are multicellular eukaryotes that have cell walls made of cellulose. Plants develop from multicellular embryos
2 of 33 What Is a Plant? What is a plant? 3 of 33 What Is a Plant? What Is a Plant? Plants are multicellular eukaryotes that have cell walls made of cellulose. Plants develop from multicellular embryos
Biol/Env St 204 Quiz 2 Spring 2008
 Biol/Env St 204 Quiz 2 Spring 2008 Name: 40 points Short-Answer Section (20 points total) 1. In the reading Interview with a Fungus, why did Mr. Pilobolus conclude that fungi characterize mankind as expendable?
Biol/Env St 204 Quiz 2 Spring 2008 Name: 40 points Short-Answer Section (20 points total) 1. In the reading Interview with a Fungus, why did Mr. Pilobolus conclude that fungi characterize mankind as expendable?
BIO 1130FF. BIO 1130FF - Midterm Examination November 10, 2012 Multiple choice questions - Place your answers on the answer sheet.
 BIO 1130FF - Midterm Examination November 10, 2012 Multiple choice questions - Place your answers on the answer sheet BIO 1130FF An introduction to Organismal biology Midterm examination Worth either 15%
BIO 1130FF - Midterm Examination November 10, 2012 Multiple choice questions - Place your answers on the answer sheet BIO 1130FF An introduction to Organismal biology Midterm examination Worth either 15%
Introduction to Plants
 Introduction to Plants Name 5 reasons why we think plants are A OK 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 1. Plant Cells: Plants are multicellular eukaryotes that have cell walls made of cellulose. They develop from multicellular
Introduction to Plants Name 5 reasons why we think plants are A OK 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 1. Plant Cells: Plants are multicellular eukaryotes that have cell walls made of cellulose. They develop from multicellular
v Scientists have identified 1.3 million living species of animals v The definition of an animal
 Biosc 41 9/10 Announcements BIOSC 041 v Genetics review: group problem sets Groups of 3-4 Correct answer presented to class = 2 pts extra credit Incorrect attempt = 1 pt extra credit v Lecture: Animal
Biosc 41 9/10 Announcements BIOSC 041 v Genetics review: group problem sets Groups of 3-4 Correct answer presented to class = 2 pts extra credit Incorrect attempt = 1 pt extra credit v Lecture: Animal
LEARNING OBJECTIVES FOR BY 124 EXAM II. 1. List characteristics that distinguish fungi from organisms in other kingdoms.
 LEARNING OBJECTIVES FOR BY 124 EXAM II CHAPTER 31 1. List characteristics that distinguish fungi from organisms in other kingdoms. 2. Explain how fungi obtain their nutrients. 3. Describe the basic body
LEARNING OBJECTIVES FOR BY 124 EXAM II CHAPTER 31 1. List characteristics that distinguish fungi from organisms in other kingdoms. 2. Explain how fungi obtain their nutrients. 3. Describe the basic body
Kingdoms and Domains. Lisa Michalek
 Kingdoms and Domains Lisa Michalek The Kingdoms of Life Biologists have organized living things into large groups called Kingdoms. Biologists group organisms into six Kingdoms based on RNA and DNA sequencing
Kingdoms and Domains Lisa Michalek The Kingdoms of Life Biologists have organized living things into large groups called Kingdoms. Biologists group organisms into six Kingdoms based on RNA and DNA sequencing
Animal Origins and Evolution
 Animal Origins and Evolution Common Features of Animals multicellular heterotrophic motile Sexual reproduction, embryo Evolution of Animals All animals are multicellular and heterotrophic, which means
Animal Origins and Evolution Common Features of Animals multicellular heterotrophic motile Sexual reproduction, embryo Evolution of Animals All animals are multicellular and heterotrophic, which means
Outline. v Definition and major characteristics of animals v Dividing animals into groups based on: v Animal Phylogeny
 BIOSC 041 Overview of Animal Diversity: Animal Body Plans Reference: Chapter 32 Outline v Definition and major characteristics of animals v Dividing animals into groups based on: Body symmetry Tissues
BIOSC 041 Overview of Animal Diversity: Animal Body Plans Reference: Chapter 32 Outline v Definition and major characteristics of animals v Dividing animals into groups based on: Body symmetry Tissues
Chapter What is a Plant? Biology. Slide 1 of 33. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 Chapter 22.1 Biology What is a Plant? 1 of 33 Objectives 1. Describe the basic characteristics of life. 2. Describe what plants need to survive. 3. Describe the life cycle of plants. 4. Describe how the
Chapter 22.1 Biology What is a Plant? 1 of 33 Objectives 1. Describe the basic characteristics of life. 2. Describe what plants need to survive. 3. Describe the life cycle of plants. 4. Describe how the
Have cell walls Made of
 _ are unicellular fungi _ are multicellular fungi And can only Reproduce Using Can also reproduce Can spread using Because they do not make their own food Hyphae Mycelium Fruiting Body Heterotrophs Budding
_ are unicellular fungi _ are multicellular fungi And can only Reproduce Using Can also reproduce Can spread using Because they do not make their own food Hyphae Mycelium Fruiting Body Heterotrophs Budding
Characteristics of Animals
 Characteristics of Animals Multicellular Cellular Organization What is this? Heterotrophic Adaptations CHAPTER 9 Cellular Organization 4 Major Functions of Animals Obtain food and water Sustain metabolism
Characteristics of Animals Multicellular Cellular Organization What is this? Heterotrophic Adaptations CHAPTER 9 Cellular Organization 4 Major Functions of Animals Obtain food and water Sustain metabolism
a. capture sunlight and absorb CO 2
 BIO 274-01 Exam 1 Name Matching (10 pts) 1. Match each plant part with its function: root c a. capture sunlight and absorb CO 2 for photosynthesis leaves a b. provides support, conducts water and nutrients
BIO 274-01 Exam 1 Name Matching (10 pts) 1. Match each plant part with its function: root c a. capture sunlight and absorb CO 2 for photosynthesis leaves a b. provides support, conducts water and nutrients
The move from water to land. The move from water to land. Chapter 16- Evolution of Plants. Green algae are the ancestors to all plants
 Chapter 16- Evolution of Plants From Protists to Plants Moving right along! Green algae are the ancestors to all plants Who, ME? Wow I feel so important! Charophyceans 475 million years ago, shallow seas
Chapter 16- Evolution of Plants From Protists to Plants Moving right along! Green algae are the ancestors to all plants Who, ME? Wow I feel so important! Charophyceans 475 million years ago, shallow seas
BIOL1020U Mid-term Test 1. Name: Student Number: Tutorial section:
 BIOL1020U Mid-term Test 1 Name: Student Number: Tutorial section: Please read each question carefully and enter the best answer for each into both test booklet and Scantron. Be sure to indicate which test
BIOL1020U Mid-term Test 1 Name: Student Number: Tutorial section: Please read each question carefully and enter the best answer for each into both test booklet and Scantron. Be sure to indicate which test
Kingdom Animalia. Zoology the study of animals
 Kingdom Animalia Zoology the study of animals Summary Animals are multicellular and eukaryotic. consume and digest organic materials thereby being heterotrophs. Most are motile at some time in their lives.
Kingdom Animalia Zoology the study of animals Summary Animals are multicellular and eukaryotic. consume and digest organic materials thereby being heterotrophs. Most are motile at some time in their lives.
Slide 1. Slide 2. Slide Onto Land
 Slide 1 18.1 Onto Land 18.1.1 Describe the evolutionary relationship between green algae and land plants. 18.1.2 List the five significant events in the evolution of land plants. 18.1.3 Describe the alternation
Slide 1 18.1 Onto Land 18.1.1 Describe the evolutionary relationship between green algae and land plants. 18.1.2 List the five significant events in the evolution of land plants. 18.1.3 Describe the alternation
Intro to Animals. Chapter 32
 Intro to Animals Chapter 32 1) Multicellular Organization (Different cells have different functions) Specialization: adaptation of a cell for a particular function Remember: cells tissues organs organ
Intro to Animals Chapter 32 1) Multicellular Organization (Different cells have different functions) Specialization: adaptation of a cell for a particular function Remember: cells tissues organs organ
Invertebrate Diversity
 CHAPTER 23 Invertebrate Diversity Summary of Key Concepts Concept 23.1 Diverse animals share several key characteristics. (pp. 494 496) More than a million living species of animals are organized into
CHAPTER 23 Invertebrate Diversity Summary of Key Concepts Concept 23.1 Diverse animals share several key characteristics. (pp. 494 496) More than a million living species of animals are organized into
Announcements. Lab Quiz #1 on Monday: (30pts) conifers + cones, vegetative morphology. Study: Display case outside HCK 132 with labeled conifers
 Announcements Lab Quiz #1 on Monday: (30pts) conifers + cones, vegetative morphology Study: Display case outside HCK 132 with labeled conifers Movie: Sexual Encounters of the Floral Kind Intro to Keying/Greenhouse
Announcements Lab Quiz #1 on Monday: (30pts) conifers + cones, vegetative morphology Study: Display case outside HCK 132 with labeled conifers Movie: Sexual Encounters of the Floral Kind Intro to Keying/Greenhouse
Biology, 7e (Campbell) Chapter 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles
 Biology, 7e (Campbell) Chapter 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles Chapter Questions 1) What is a genome? A) the complete complement of an organism's genes B) a specific sequence of polypeptides within
Biology, 7e (Campbell) Chapter 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles Chapter Questions 1) What is a genome? A) the complete complement of an organism's genes B) a specific sequence of polypeptides within
Kingdom: Plantae. Domain Archaea. Domain Eukarya. Domain Bacteria. Common ancestor
 Kingdom: Plantae Domain Eukarya Domain Bacteria Domain Archaea Domain Eukarya Common ancestor The First Plants For more than 3 billion years, Earth s terrestrial surface was lifeless life evolved in the
Kingdom: Plantae Domain Eukarya Domain Bacteria Domain Archaea Domain Eukarya Common ancestor The First Plants For more than 3 billion years, Earth s terrestrial surface was lifeless life evolved in the
Biology Slide 1 of 28
 Biology 1 of 28 2 of 28 22-4 Seed Plants Seed plants are the most dominant group of photosynthetic organisms on land. 3 of 28 22-4 Seed Plants Seed plants are divided into two groups: Gymnosperms bear
Biology 1 of 28 2 of 28 22-4 Seed Plants Seed plants are the most dominant group of photosynthetic organisms on land. 3 of 28 22-4 Seed Plants Seed plants are divided into two groups: Gymnosperms bear
Features of the Animal
 Features of the Animal Kingdom Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Even though members of the animal kingdom are incredibly diverse, animals share common features that distinguish them from organisms in other kingdoms.
Features of the Animal Kingdom Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Even though members of the animal kingdom are incredibly diverse, animals share common features that distinguish them from organisms in other kingdoms.
Structures and Functions of Living Organisms
 Structures and Functions of Living Organisms 6.L.1 Understand the structures, processes and behaviors of plants that enable them to survive and reproduce. 6.L.1.1 Summarize the basic structures and functions
Structures and Functions of Living Organisms 6.L.1 Understand the structures, processes and behaviors of plants that enable them to survive and reproduce. 6.L.1.1 Summarize the basic structures and functions
Some History: In the life cycle of the kelp Laminaria. One way to separate algae from protozoa is that. Rocks of Cambrian Age (ca.
 One way to separate algae from protozoa is that a. Protozoa are photosynthetic, while algae are not. b. Algae are photosynthetic, while protozoa are not. c. Protozoa are prokaryotic, while algae are eukaryotic.
One way to separate algae from protozoa is that a. Protozoa are photosynthetic, while algae are not. b. Algae are photosynthetic, while protozoa are not. c. Protozoa are prokaryotic, while algae are eukaryotic.
Revision Based on Chapter 25 Grade 11
 Revision Based on Chapter 25 Grade 11 Biology Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A cell that contains a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles
Revision Based on Chapter 25 Grade 11 Biology Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A cell that contains a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles
Plants and Fungi. Bryophytes Bryophytes, most commonly mosses Sprawl as low mats over acres of land
 Plants and Fungi Terrestrial Adaptations of Plants Structural Adaptations A plant is a multicellular eukaryote and a photoautotroph, making organic molecules by photosynthesis In terrestrial habitats,
Plants and Fungi Terrestrial Adaptations of Plants Structural Adaptations A plant is a multicellular eukaryote and a photoautotroph, making organic molecules by photosynthesis In terrestrial habitats,
Characteristics and Classification of Living Organism (IGCSE Biology Syllabus )
 Characteristics and Classification of Living Organism (IGCSE Biology Syllabus 2016-2018) Characteristics of Living Organisms o Movement o Respiration o Sensitivity o Growth o Reproduction o Excretion o
Characteristics and Classification of Living Organism (IGCSE Biology Syllabus 2016-2018) Characteristics of Living Organisms o Movement o Respiration o Sensitivity o Growth o Reproduction o Excretion o
Plant Evolution & Diversity
 Plant Evolution & Diversity Ancestors of plants were probably charophytes (green algae) Chlorophyll a and b, beta carotene Similar thylakoid arrangements Identical cell walls Starch as a storage carbohydrate
Plant Evolution & Diversity Ancestors of plants were probably charophytes (green algae) Chlorophyll a and b, beta carotene Similar thylakoid arrangements Identical cell walls Starch as a storage carbohydrate
Classification of organisms. The grouping of objects or information based on similarities Taxonomy: branch of biology that classifies organisms
 Bell Work: Think about your CD, video game, DVD or book collection at home. How would you separate this collection into different groups? What would the groups be? Try to come up with 4 or 5. Classification
Bell Work: Think about your CD, video game, DVD or book collection at home. How would you separate this collection into different groups? What would the groups be? Try to come up with 4 or 5. Classification
Chapter 32, 10 th edition Q1.Which characteristic below is shared by plants, fungi, and animals? ( Concept 32.1)
 Chapter 32, 10 th edition Q1.Which characteristic below is shared by plants, fungi, and animals? ( Concept 32.1) A) They are multicellular eukaryotes. B) They are heterotrophs. C) Their cells are supported
Chapter 32, 10 th edition Q1.Which characteristic below is shared by plants, fungi, and animals? ( Concept 32.1) A) They are multicellular eukaryotes. B) They are heterotrophs. C) Their cells are supported
3. Diagram a cladogram showing the evolutionary relationships among the four main groups of living plants.
 OBJECTIVE SHEET PLANTS Phylum: Coniferophyta (gymnosperms the conifers) Phylum: Anthophyta (angiosperms the flowering plants) 1. Explain the alternation of generations in the two-phase life cycle of all
OBJECTIVE SHEET PLANTS Phylum: Coniferophyta (gymnosperms the conifers) Phylum: Anthophyta (angiosperms the flowering plants) 1. Explain the alternation of generations in the two-phase life cycle of all
Biology 11 Kingdom Plantae: Algae and Bryophyta
 Biology 11 Kingdom Plantae: Algae and Bryophyta Objectives By the end of the lesson you should be able to: State the 3 types of algae Why we believe land plants developed from algae Lifecycle of a bryophyte
Biology 11 Kingdom Plantae: Algae and Bryophyta Objectives By the end of the lesson you should be able to: State the 3 types of algae Why we believe land plants developed from algae Lifecycle of a bryophyte
Diversity of Plants How Plants Colonized the Land
 Chapter 29, 30. Diversity of Plants How Plants Colonized the Land 1 The first plants For more than 3 billion years, Earth s terrestrial surface was lifeless life evolved in the seas 1st photosynthetic
Chapter 29, 30. Diversity of Plants How Plants Colonized the Land 1 The first plants For more than 3 billion years, Earth s terrestrial surface was lifeless life evolved in the seas 1st photosynthetic
BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH.29 - PROTISTS.
 !! www.clutchprep.com Eukrayotic cells are large, have a nucleus, contain membrane-bound organelles, and use a cytoskeleton The nucleus is the synapomorphy that unifies eukaryotes Endosymbiotic theory
!! www.clutchprep.com Eukrayotic cells are large, have a nucleus, contain membrane-bound organelles, and use a cytoskeleton The nucleus is the synapomorphy that unifies eukaryotes Endosymbiotic theory
