Supplementary Information
|
|
|
- Ernest Palmer
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
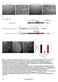
1 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1: MEIOC is a novel evolutionarily conserved protein Alignments of some representative MEIOC amino acid sequences encoded by orthologs were processed with the Multalin software ( 1. Represented species are as follows: worm, Caenorhabditis elegans; tunicate, Ciona intestinalis; wasp, Nasonia vitripennis; annelid, Capitella teleta; oyster, Crassostrea gigas; urchin, Strongylocentrotus purpuratus; zebrafish, Danio rerio; frog, Xenopus tropicalis; platypus, Ornithorhynchus anatinus; lizard, Anolis carolinensis; marsupial, Sarcophilus harrisii; mouse, Mus musculus; rat, Rattus norvegicus; human, Homo sapiens; and chick, Gallus gallus. PAM: percent accepted mutation.
2 Supplementary Figure 2: Meioc is expressed specifically in gonads and meiotic cells a. b Meioc mrna expression was measured by RT-qPCR in the various indicated adult (a) and fetal (b) mouse organs. Embryos were collected at 13.5 dpc. Mean±SEM; mice analyzed n=3; *** p<0.001 (Multiple comparisons ANOVA). c. Vasa/Ddx4, Fst and Meioc expression was measured by RT-qPCR in the purified germ cell fraction (GFP+) and somatic cell fraction (GFP-) from Oct4-Gfp 13.5 dpc ovaries. Vasa/Ddx4 and Fst are specific markers for the germ and somatic populations, respectively. Mean ± SEM, n=4. d. MEIOC and STRA8 mrna expression was measured in whole human fetal ovaries harvested at the indicated developmental stages. wpf, weeks post-fertilization. MEIOC expression in human fetal ovaries at the time of MPI reinforces the correlation observed in mouse gonads.
3 Supplementary Figure 3: Validation of anti-meioc sera and antibodies In this study we used 2 purified (commercial) antibodies and 2 home-made sera against the MEIOC protein. All provided similar results but serum n 2 was the most efficient for immunofluorescence staining. a. Anti- MEIOC antibody recognized specifically the recombinant protein. HEK293 transfected with tagged-meioc- IRES-eGFP (FLAG_MEIOC) expression vector or empty vector (PCIG). Western blot analysis allowed detection of a band at the expected molecular weight (109 kda). Immunofluorescence with anti-meioc (red) and anti-flag (blue) antibodies evidenced a co-localization only in the GFP-positive cells (green). b. 16 dpp testis sections were stained with SYCP3 meiotic marker (red) and with anti-meioc or preimmune serum (green) and with DAPI (blue). Bar, 40µm. c,d. Immunofluorescence for MEIOC (anti-meioc serum n 2, green), SYCP3 (red) and DAPI (blue) in (c) fetal (15.5 dpc on upper pictures) Meioc +/+ and -/- ovaries (bar, 40 µm) and (d) 16 dpp Meioc +/+ and Meioc -/- testis sections (bar, 10 µm). Magnifications of meiotic germ cells in c were captured from 15.5 dpc (Lepto, Zygo, Pachy and Lepto-like) and 18.5 dpc (Diplo and Zygo-like) Meioc +/+ and -/- ovaries. Lepto, leptotene; Zygo, zygotene; Pachy, pachytene; Diplo, diplotene.
4 Supplementary Figure 4: Meioc invalidation in mice a. Schematic representation of MEIOC gene invalidation with insertion of a promoter-less lacz reporter and neomycin selection marker (Neo) between exons 2 and 3 and insertions of two Frt sites and three LoxP sites. This produces a knock-out straight allele due to interruption of the Meioc gene (-). Crossings with mice expressing the Flippase and Vasacre mice enabled production of a floxed allele (Flox) and an exon 3-deleted allele (Δ). b. Meioc and LacZ mrna expression was investigated by RT-qPCR in Meioc +/+, Meioc +/- and Meioc -/- adult testes. Mean ± SEM, n=3. c. Western blot of Meioc +/+, Meioc +/- and Meioc -/- adult testis protein extracts hybridized with anti-meioc and β-actin. d. Histological sections of adult Meioc +/+ and Meioc / epididymides. Bar, 40 µm. e. γ-h2ax immunohistochemistry in adult testes exhibiting meiosis prophase I spermatocyte arrest in Meioc-deficient testes. Bar, 40 µm. f. The testis/body (mg/g) ratio was calculated for Meioc +/+ (white columns), Meioc +/- (grey columns) and Meioc -/- (black columns) mice at 8, 10 and 16 dpp and at adulthood. Mean ± SEM, n=3-26; ***p<0.001 (Student s t-test). g. Analysis of the percentage of tubules with more than ten cells positive for the apoptotic marker TUNEL was performed on histological Meioc +/+ (white columns) and Meioc -/- (black columns) at 10 and 16 days post-partum (dpp) and at adulthood. Mean ± SEM, n=3 mice analyzed; *p<0.05 (Student s t-test). h. Representative histological sections of 8 dpp Meioc +/+ and Meioc -/- ovaries showing the absence of germ cells in the sections from mutant gonads while oocytes formed follicles in the wild type gonads. Bar, 20 µm. i. Representative histological sections showing meiosis prophase I stages in Meioc +/+ and Meioc -/ dpc ovaries. PL, preleptotene; L, leptotene; Z, zygotene; P, pachytene; D, Diplotene; e, early; m, mid; l, late. Bar, 10 µm.
5 Supplementary Figure 5: Cohesins and CREST localization in Meioc deficient spermatocytes a, b. SYCP3 (red) and (a) REC8 (green) or (b) SMC3 (green) detection in zygotene Meioc +/+ and zygotenelike Meioc -/- spermatocytes chromosome spreads. Lepto, leptotene; Zygo, zygotene; Pachy, pachytene. c. SYCP3 (red) and CREST (green) were detected in the chromosome spreads of various meiosis prophase I wild type and Meioc -/- spermatocytes.
6 Supplementary Figure 6: Recombination defects in Meioc deficient spermatocytes a-c. Left panels: SYCP3 (red) and RPA2 (a), DMC1 (b) or RAD51 (c) (green, DSB markers) were detected in the chromosome spreads of various meiosis prophase I wild type and Meioc / spermatocytes. Right panels: Quantification of RPA2, DMC1 and RAD51 foci in wild type spermatocytes at leptotene (n=9; n=10; n=15), zygotene (n=13; n=16; n=18) and pachytene (n=13; n=20; n=21) stages (white symbols) and in mutant spermatocytes at leptotene (n=10; n=17; n=18) and zygotene-like stages (n=31; n=32; n=30) (black symbols). Three mice were analyzed for each genotype. Median numbers of foci are marked by horizontal lines. ns, not significant; *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p< (Student s t-test).
7 Supplementary Figure 7: Abnormal metaphase phenotype in Meioc-deficient mice a. 16 dpp Meioc +/+ and Meioc -/- testes sections were stained for SYCP3 (red), ph3 (green) and DAPI (blue) revealing abundant abnormal metaphases in Meioc -/- seminiferous tubules. Bar, 40 µm. b. 16 dpp Meioc -/- testes sections were stained for TUNEL. Only few abnormal metaphases are stained with TUNEL apoptotic marker. Bar, 5 µm. c. BrdU treated 16 dpp Meioc -/- testes sections were stained for SYCP3 (red), BrdU (green) and DAPI (blue). BrdU was injected to 15 dpp Meioc-/- mouse 36 hours before harvesting gonads. Upper panel, the presence of BrdU in the abnormal metaphases, preleptotene and leptotene cells suggests that these cells completed premeiotic S phase, bar, 40µm. Lower panel, arrow heads indicate abnormal metaphases and arrows indicate leptotene cells associated in the same tubule. Bar, 5µm. d. Meioc +/+ and Meioc -/- testes sections were stained for SYCP3 (red), ph3 (green) and DAPI (blue). Unlike mitotic metaphases, abnormal metaphases in Meioc mutants display SYCP3 staining. The abnormal metaphase chromosomes are spherically arranged in rosette configuration instead of being aligned at the cell equator. Bars, 5 µm.
8 Supplementary Figure 8: Meiosis prophase I genes are down-regulated in Meioc-/- gonads a. Microarray analysis was performed in meiosis initiating male (8 dpp) and female (14.5 dpc) wild type and Meioc mutant gonads. Bar charts representing the significantly affected cell cycle functions in meiosis-initiating male and female wild type and Meioc mutant gonads. chr, chromosomes; BCCL, bone cancer cell lines; PCCL, pancreatic cancer cell lines; TCL, tumor cell lines. b. Heatmap representing the 42 differentially expressed genes in both female and male gonads (Significantly differentially regulated by at least 1.5-fold in mutant fetal ovaries and 1.2-fold in mutant testes (p<0.05, ANOVA); Pearson s dissimilarity, mean linkage). Genes were sorted into 6 categories according to the functions identified with GO-term analysis ( and expression profiles (GEOProfile). Ov, ovaries; T, testes. In total, 182 genes were up- or down-regulated by at least 1.5-fold in mutant fetal ovaries, and 114 genes were up- or down-regulated by at least 1.2-fold in mutant testes. c. Heatmap representing the differential expression of meiotic genes in both female and male gonads (Pearson s dissimilarity, mean linkage). Ov, ovaries; T, testes. Most of those genes are down-regulated in Meioc -/- gonads. Note the exception of Stra8 and Rec8 pre-meiotic genes that are not down-regulated in Meioc mutants. d. RT-qPCR measurements of MPI transcripts in whole Meioc +/+ and Meioc -/- 20 days post-partum testes. Mean ± SEM, n=3-4; *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001 (Student s t-test). e. Western blot analysis of STRA8 and SPATA22 in adult mouse testis protein extracts. β-actin/actb was used as a control.
9 Supplementary Figure 9: Meiotic transcripts stability and splicing in Meioc -/- gonads a. Meiob -/- and Meioc -/- testes were treated with actinomycin D to inhibit transcription. The relative expression of Gapdh (as a control for meiotic gene Rad21L presented in Figure 8e) after 12 and 24 hours of actinomycin D treatment compared with mrna expression levels without drug treatment. Linear regressions were calculated, and slope coefficients representing degradation rates were compared between Meiob and Meioc mutant gonads. Data represent Gapdh expression following exposure to actinomycin D. b. Alternative splicing was assessed by performing RT-PCR on full length meiotic transcripts in Meioc +/+ and Meioc -/- postnatal testes. Although transcript abundancy was strongly reduced in mutants, no alternate splicing was detected in gel.
10 Supplementary Figure 10: Meiob transcript splicing in Meioc-/- gonad Purified Meiob RT-PCR products were sequenced (SUPREMErunTM, GATC, Germany) confirming proper transcript splicing in Meioc-/- testes. Sequences from wild type testes (++Meiob) and Meioc-/- testes (--Meiob) were aligned with Meiob-201 reference cdna sequence (MeiobcDNA) from Ensembl Genome Browser ( Alignments were performed with Multalin software (
11 Supplementary Figure 11: Spata22 transcript splicing in Meioc -/- gonad Purified Spata22 RT-PCR products were sequenced (SUPREMErun TM, GATC, Germany) confirming proper transcript splicing in Meioc -/- testes. Sequences from wild type testes (++Spata22) and Meioc -/- testes (-- Spata22) were aligned with Spata reference cdna sequence (Spata22cDNA) from Ensembl Genome Browser ( Alignments were performed with Multalin software ( 1.
12 Supplementary Figure 12: Rad21L transcript splicing in Meioc -/- gonad Purified Rad21L RT-PCR products were sequenced (SUPREMErun TM, GATC, Germany) confirming proper transcript splicing in Meioc -/- testes. Sequences from wild type testes (++Rad21L) and Meioc -/- testes (-- Rad21L) were aligned with Rad21L-001 reference cdna sequence (Rad21LcDNA) from Ensembl Genome Browser ( Alignments were performed with Multalin software ( 1.
13 Supplementary Figure 13: Ythdc2 expression in gonads and Meioc mutants RT-qPCR measurement of Ythdc2 in whole Meioc +/+ and Meioc -/ dpc ovaries and 8 dpp testes and in whole Meioc -/- adult testes compared with Meiob -/- adult testes as a reference. Right, data were normalized on β-actin ubiquitous marker. Left, data were normalized on Ddx4/Vasa germ cells specific marker to correct for potential difference in germ cell populations. Mean ± SEM, n=3.
14 Supplementary Figure 14: YTHDC2 binds meiotic mrna a. Western blot analysis of co-ip of YTHDC2 in post-natal Meioc +/+ and Meioc -/- testes reveals that YTHDC2 is immunoprecipitated at a relative low level in absence of MEIOC. b. RT-qPCR analysis of mrna bound after IP assays using anti-ythdc2 antibody (YTH) or IgG in Meioc -/- testicular protein extracts. Statistical analysis compares mrna fold enrichment/input levels with that of Gapdh. Mean ± SEM; n=6. *p<0.05 (Student s t-test). c. RIP was performed in HEK- 293 cells overexpressing Meioc cdna and MEIOB cdna or PCIG empty vector and MEIOB, which was selected as the YTHDC2 target. The MEIOB expression plasmid and a Meioc containing vector or the empty vector were transfected. Bound MEIOB and ACTB mrna were analyzed using RT-qPCR and fold enrichments of mrna in the RIP samples relative to inputs were calculated. n=3. d. MEIOC increases MEIOB mrna levels when over-expressed in HEK-293 cells. MEIOB expression plasmid was co-transfected in HEK293 cells with the empty (PCIG) plasmid or with the Meioc plasmid (as in b) and MEIOB expression was measured by RT-qPCR. n=3. Mean ± SEM; **p<0.001 (Student s t-test).
15 Supplementary Figure 15: Uncropped images of fluorescent immunoblots shown in the indicated Figures Uncropped images of fluorescent blots displayed in (a) Fig 1c and Supplementary Fig 4 ; (b) Fig 9a. Green and dotted boxes indicate the lanes shown in the indicated Figures. Cy3 or Cy5 mentions indicate fluorescent dye (or equivalent one) that were used and visualized on the scans. MW: Molecular weight. Numbers on the right of the scans indicate the molecular weight (in kda) corresponding to the bands of the marker.
16 Supplementary Figure 16: Uncropped images of fluorescent immunoblots shown in Fig 9b Uncropped images of fluorescent blots displayed in Fig 9b. Green boxes indicate the lanes shown in the Figure. Cy3 or Cy5 mentions indicate fluorescent dye (or equivalent one) that were used and visualized on the scans. Numbers on the right of the scans indicate the molecular weight (in kda) corresponding to the bands of the marker.
17 Supplementary Figure 17: Uncropped images of fluorescent immunoblots shown in the indicated Figures Uncropped images of fluorescent blots displayed in (a) Fig 9e ; (b) Supplementary Fig. 3a ; (c) Supplementary Fig. 10a. Green boxes indicate the lanes shown in the Figures. Cy3 or Cy5 mentions indicate fluorescent dye (or equivalent one) that were used and visualized on the scans. Numbers on the right of the scans indicate the molecular weight (in kda) corresponding to the bands of the marker.
18 Supplementary Table 1: MEIOC homologs Species Organism Gene Protein accession (NCBI / UniProt) ANNELID Capitella telela R7UFS9 CHICK Gallus gallus XP_ FROG Xenopus (Silurana) tropicalis XP_ HUMAN Homo sapiens C17ORF104 NP_ LIZARD Anolis carolinensis XP_ MARSUPIAL Sarcophilus harrisii XP_ MOUSE Mus musculus Gm1564 NP_ OYSTER Crassostrea gigas K1RFZ3 PLATYPUS Ornithorhynchus anatinus XP_ RAT Rattus norvegicus NP_ TUNICATE Ciona intestinalis XP_ URCHIN Strongylocentrotus purpuratus XP_ WASP Nasonia vitripennis XP_ WORM Caenorhabditis elegans Y39A1A.9 NP_ ZEBRAFISH Danio rerio XP_ Table specifying protein accessions for MEIOC homologs detected in the represented organisms.
19 Supplementary Table 2: MEIOC partners identification Protein UniProt ID Accession Enrichment Fold Peptides Function RNA/nucleotid binding proteins ; RNA processing and translation regulation YTHDC YTDC2_MOUSE RNA processing YBX YBOX2_MOUSE 18 6 Translation regulator activity HSPA HSP72_MOUSE Protein refolding PIWIL PIWL2_MOUSE 10 6 Translation regulation HNRNPL HNRPL_MOUSE 9 4 mrna processing EIF4G IF4G3_MOUSE 8 4 Translation regulation LARP LARP7_MOUSE 8 5 RNA processing PRPF PRP8_MOUSE 8 7 mrna splicing BOLL BOLL_MOUSE 6 2 Translation regulation RBMY1A RBY1A_MOUSE 6 3 mrna splicing SPATA SPAT5_MOUSE 6 4 mitochondrion VIR homolog VIR_MOUSE 6 4 mrna splicing IGF2BP IF2B1_MOUSE 5 3 Translation regulation XRN XRN1_MOUSE 5 4 RNA processing RNA/nucleotid binding proteins ; Microtubule organization KIF3C KIF3C_MOUSE 15 2 microtubule-based movement MARK MARK1_MOUSE microtubule cytoskeleton organization TUBA1B TBA1B_MOUSE 8 8 cytoskeleton KIF KIF22_MOUSE 7 6 microtubule-based movement SEPT SEP10_MOUSE 5 5 cytoskeleton Ribonucleoproteins; Translation regulation and protein transport RPL RL31_MOUSE 8 3 ribosome RPLP RLA1_MOUSE 8 2 ribosome UBAP2L UBP2L_MOUSE 7 2 ribosome RPL RL15_MOUSE 5 2 ribosome RPL RL19_MOUSE 5 2 ribosome RRBP RRBP1_MOUSE 5 4 endoplasmic reticulum Proteins in anti-meioc IP samples with at least a 5-fold enrichment in wild type 16 dpp testes compared with Meioc -/- samples, as detected by mass spectrometry. Proteins were classified according to their fold enrichment and with GO-terms ( The number of specific peptides identified by spectrometry is provided. Bold indicates proteins also enriched in IP samples performed in HEK-293 cells overexpressing Flag-tagged MEIOC compared with HEK-293 cells overexpressing the corresponding empty vector.
20 Supplementary Table 3: List of the antibodies used in the study Antibodies Company Ref Host sp Mono/Poly Application Concentration MEIOC Sigma-Aldrich HPA Rabbit P WB ; IF ; IP 1/400 ; 1/200 ; 8µg β-actin Sigma-Aldrich AS41 Mouse M WB 1/2500 MEIOC Toth s Lab Guinnea-Pig P IF ; IP 1/1000 ; 1/10 FLAG Sigma-Aldrich F1404 Mouse M IF ; WB 1/1000 ; 1/500 STRA8 Abcam Ab49602 Rabbit P IF & IHC ; WB 1/1000 ; 1/400 SYCP3 Abcam Ab97672 Mouse M IF 1/500 P63 Santa-Cruz Sc-8431 Rabbit P IHC 1/200 γh2ax Millipore Mouse M IHC ; IF 1/500 DDX4 Abcam Ab13840 Rabbit P IHC 1/200 DDX4 Abcam Ab27591 Mouse M IHC 1/500 POU5F1 Santa-Cruz Sc-5279 Mouse M IHC 1/50 SYCP3 Novus NB Rabbit P IF 1/400 SYCP1 Abcam Ab15090 Rabbit P IF 1/200 DMC1 Santa-Cruz Sc Rabbit P IF 1/200 KASH5 Burke s Lab Rabbit P IF 1/500 ph3 Cell Signalling Mouse M IF 1/500 α-tubuli N Abcam Ab80779 Mouse M IF 1/500 CREST Immunovision HCT-0100 Human P IF 1/200 SMC3 Chemicon Ab3914 Rabbit P IF 1/100 REC8 Eijpe et al (RαN) 2 Rabbit P IF 1/200 RPA2 Cell signaling Rat M IF 1/200 RAD51 Calbiochem PC130 Rabbit P IF 1/200 YTHDC2 Santa-Cruz Sc Goat P IF ; WB ; IP 1/200 ; 1/400 ; 8µg SPATA22 Proteintech AP Europe Rabbit P WB 1/500 Cy5 anti-rabbit GE Healthcare Goat P WB 1/2500 Cy3-anti-Mouse GE Healthcare Goat P WB 1/2500 Alexa647anti- Life A21447 Goat technologies Donkey P WB 1/2500 Alexa488 anti- Life A11073 GuinneaPig technologies Goat P IF 1/500 Alexa594 antimouse technologies Life A21203 Donkey P IF 1/ anti- SAB Sigma-Aldrich GuinneaPig Donkey P IF 1/500 Alexa594 antirabbit technologies Life A21207 Donkey P IF 1/500 Alexa488 anti- Life A11006 Rat technologies Goat P IF 1/500 Alexa488 antirabbit technologies Life A21206 Donkey P IF 1/500 Alexa488 antimouse technologies Life A21202 Donkey P IF 1/500 Alexa350 antimouse technologies Life A10035 Goat P IF 1/500 Alexa488 anti- Life A11055 Goat technologies Donkey P IF 1/500 Alexa594 anti- Life A11058 Goat technologies Doneky P IF 1/500 Alexa488 anti- Life A11013 Human technologies Goat P IF 1/500
21 Supplementary Table 4: List of all RT-qPCR and PCR primers used in the study gene Species Application Forward Reverse Meioc Mouse RT-qPCR 5'-TTAATTGTGGATGAACTTCGAGAACA-3' 5'-GCCCAGTAAAGTCACAACTCTGG β-actin Mouse RT-qPCR 5'-GCCCTGAGGCTCTTTTCCAG-3' 5'-TGCCACAGGATTCCATACCC-3' Ddx4 Mouse RT-qPCR 5'-GAAGAAATCCAGAGGTTGGC-3' 5'-GAAGGATCGTCTGCTGAACA-3' Fst Mouse RT-qPCR 5'-CCAGGCAGGTCCACTTGTGT-3' 5'-AGTCACTCCATCATTTCCACAAAG-3' Meiob Mouse RT-qPCR 5'-ACTACATCCGCTCGCTGTCC-3' 5'-TTATCACACACTCAGCAACCCTG-3' Gapdh Mouse RT-qPCR 5'-CCAGTATGACTCCACTCACG-3' 5'-GACTCCACGACATACTCAGC-3' Rad21L Mouse RT-qPCR 5'-GGTGAAAATTGCACTCCGAAC-3' 5'-CGAACAACCCCCAAAAGAAG-3' Spata22 Mouse RT-qPCR 5'-TTCTGACAGTTACGGTTCCCCTT-3' 5'-GCTTCCCACGCCCAATCT-3' Spo11 Mouse RT-qPCR 5'-GCCCAGGAGGAGTCTGCAC-3' 5'-CCAGCAATCAATCCCTTGGA-3' 18S Mouse RT-qPCR 5'-GAATTCCCAGTAAGTGCGGG-3' 5'-GGGCAGGGACTTAATCAACG-3' Sycp3 Mouse RT-qPCR 5'-AAAGAAATGGCTATGTTGCAAAAA-3' 5'-TTGCCACTCCTTGCTGCTGA-3' LacZ Mouse RT-qPCR 5'-ATCCTCTGCATGGTCAGGTC-3' 5'-CGTGGCCTGATTCATTCC-3' RARβ Mouse RT-qPCR 5'-TTTAATCTGTGGAGACCGCCA-3' 5'-TTGTCTACTTTTGTTGGTTCCTCAAG-3' Stra8 Mouse RT-qPCR 5'-GCCTGGAGACCTTTGACGA-3' 5'-GGCTTTTGGAAGCAGCCTTT-3' Sdha Mouse RT-qPCR 5'-CCATGACTCTTGAGATCCGTGA-3' 5'-GATCTTTCTCAGGGCCACAGC-3' Ythdc2 Mouse RT-qPCR 5'-ATTGATGGCAGGTGATAGCACAT-3' 5'-GAATCGATCCCTTTCATGCACT -3' Rad21L * Mouse RT-qPCR 5'-TAATCCCCCTGATGATGGCA-3' 5'-TCTCATCATGTTCAAAGGTTCCC-3' Meiob * Mouse RT-qPCR 5'-ATTTACTGTGAGGGAAAACCCCA-3' 5'-CTCTCCTGAGCAAAGGCTGC-3' Spata22 * Mouse RT-qPCR 5'-CCCCCCTTTGCCTGTAAGAA-3' 5'-AAATGCTGCTAGGAGTGTGTGTG-3' Spo11 * Mouse RT-qPCR 5'-GAGACAAACAGAAGCGAGGAGG-3' 5'-GGATGGTGGGATTGCAGATG-3' MEIOC Human RT-qPCR 5'-ATCGGCAAAGGCAAGGAGT-3' 5'-GCGTGTTTTCCGAGTAGCCA-3' MEIOB Human RT-qPCR 5'-CAGAGTCGTCTTTTGCGATAGC-3' 5'-TCGTGGCATCCAGCTCTGT-3' β-actin Human RT-qPCR 5'-GACCCAGATCATGTTTGAGA-3' 5'-TACGGCCAGAGGCGTACAGG-3' STRA8 Human RT-qPCR 5'-CTGGACAAAAGTGAGGTTCCG-3' 5'-GGCAAGCACTGAACTGGAGC-3' Meioc Mouse Genotyping 5'-TACCTGCATGCTTTATGTACACCA-3' 5'-TTACAAATAGGCTGCAATTCCTCA-3' LacZ Mouse Genotyping 5'-ATCCTCTGCATGGTCAGGTC-3' 5'-CGTGGCCTGATTCATTCC-3' Rad21L Mouse PCR 5'-ATGGCTTGCAGCTCACTGG-3' 5'-GGAACACTCTGGCTCAGCTCA-3' Spata22 Mouse PCR 5'-CTGCTGAAGGAGGCGAGGT-3' 5'-GCAAAAGCTCCTGCTCATACTGT-3' Meiob Mouse PCR 5'-CTAGCGGGCCCGGAAGTAT-3' 5'-TCGTAAGAGTTAAATGTCTATATT-3' * Pre mrna primers
22 Supplementary Table 5: List of all primers used for sequencing of the full length purified PCR amplicons of Meiob, Spata22 and Rad21L in Meioc +/+ and Meioc -/- 20 dpp testes Primers list for sequencing cdna Meiob Primer number 3'-5' sequence P7 AGGATACATTCACAAAGTG P8 ACAGTTGCTGCCATGCAG P9 AGCTTACAGGAGAGTATGG P11 TCGTAAGAGTTAAATGTCTATATT P21 TGTCCTTTCTTTGGATCAG P22 TAGCTGTTCCACTGTATAG P23 TTATCACACAGAGCAAGG cdna Spata22 Primer number 3'-5' sequence P4 TGCTGAAGGAGGCGAGG P5 TACTGTGTAATTCCCTTTG P6 AATCCAGAGGTGGCTCC P16 ACAGGCAAACAGCCTGC P17 ATAAGAAGCAGAAGCTGG P19 TTCAGCTGTCACATCTGG P27 TACAATTGCAGATGCTGAG cdna Rad21L Primer number 3'-5' sequence P2 TCTGGCTCAGCTCAATAG P3 TACTGACTCCTTCAGTGTC P13 AATGCAGTCCTTTAGTCTG P14 TAGTGTTGTAAGCTGCTTC P24 ATATGCTTCTGTCAACTGC P26 AAGAATATCCTGCTCAGAG Supplementary references 1 Corpet, F. Multiple sequence alignment with hierarchical clustering. Nucleic acids research 16, (1988). 2 Eijpe, M., Offenberg, H., Jessberger, R., Revenkova, E. & Heyting, C. Meiotic cohesin REC8 marks the axial elements of rat synaptonemal complexes before cohesins SMC1beta and SMC3. The Journal of cell biology 160, (2003).
Supplementary Figure 1. Nature Genetics: doi: /ng.3848
 Supplementary Figure 1 Phenotypes and epigenetic properties of Fab2L flies. A- Phenotypic classification based on eye pigment levels in Fab2L male (orange bars) and female (yellow bars) flies (n>150).
Supplementary Figure 1 Phenotypes and epigenetic properties of Fab2L flies. A- Phenotypic classification based on eye pigment levels in Fab2L male (orange bars) and female (yellow bars) flies (n>150).
Fig. S1. Proliferation and cell cycle exit are affected by the med mutation. (A,B) M-phase nuclei are visualized by a-ph3 labeling in wild-type (A)
 Fig. S1. Proliferation and cell cycle exit are affected by the med mutation. (A,B) M-phase nuclei are visualized by a-ph3 labeling in wild-type (A) and mutant (B) 4 dpf retinae. The central retina of the
Fig. S1. Proliferation and cell cycle exit are affected by the med mutation. (A,B) M-phase nuclei are visualized by a-ph3 labeling in wild-type (A) and mutant (B) 4 dpf retinae. The central retina of the
Camello, a novel family of Histone Acetyltransferases that acetylate histone H4 and is essential for zebrafish development
 Supplementary Information: Camello, a novel family of Histone Acetyltransferases that acetylate histone H4 and is essential for zebrafish development Krishanpal Karmodiya 1, Krishanpal Anamika 1,2, Vijaykumar
Supplementary Information: Camello, a novel family of Histone Acetyltransferases that acetylate histone H4 and is essential for zebrafish development Krishanpal Karmodiya 1, Krishanpal Anamika 1,2, Vijaykumar
Illegitimate translation causes unexpected gene expression from on-target out-of-frame alleles
 Illegitimate translation causes unexpected gene expression from on-target out-of-frame alleles created by CRISPR-Cas9 Shigeru Makino, Ryutaro Fukumura, Yoichi Gondo* Mutagenesis and Genomics Team, RIKEN
Illegitimate translation causes unexpected gene expression from on-target out-of-frame alleles created by CRISPR-Cas9 Shigeru Makino, Ryutaro Fukumura, Yoichi Gondo* Mutagenesis and Genomics Team, RIKEN
Supplementary Figure 1: To test the role of mir-17~92 in orthologous genetic model of ADPKD, we generated Ksp/Cre;Pkd1 F/F (Pkd1-KO) and Ksp/Cre;Pkd1
 Supplementary Figure 1: To test the role of mir-17~92 in orthologous genetic model of ADPKD, we generated Ksp/Cre;Pkd1 F/F (Pkd1-KO) and Ksp/Cre;Pkd1 F/F ;mir-17~92 F/F (Pkd1-miR-17~92KO) mice. (A) Q-PCR
Supplementary Figure 1: To test the role of mir-17~92 in orthologous genetic model of ADPKD, we generated Ksp/Cre;Pkd1 F/F (Pkd1-KO) and Ksp/Cre;Pkd1 F/F ;mir-17~92 F/F (Pkd1-miR-17~92KO) mice. (A) Q-PCR
FSC-W FSC-H CD4 CD62-L
 Supplementary Fig. 1 a SSC-A FSC-A FSC-W FSC-H SSC-W SSC-H CD4 CD62-L b SSC-A FSC-A FSC-W FSC-A FSC-A 7-AAD FSC-A CD4 IL-9 CD4 c SSC-A FSC-A FSC-W FSC-H SSC-W SSC-H 7-AAD KI67 Annexin-V 7-AAD d I L -5
Supplementary Fig. 1 a SSC-A FSC-A FSC-W FSC-H SSC-W SSC-H CD4 CD62-L b SSC-A FSC-A FSC-W FSC-A FSC-A 7-AAD FSC-A CD4 IL-9 CD4 c SSC-A FSC-A FSC-W FSC-H SSC-W SSC-H 7-AAD KI67 Annexin-V 7-AAD d I L -5
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Discussion Rationale for using maternal ythdf2 -/- mutants as study subject To study the genetic basis of the embryonic developmental delay that we observed, we crossed fish with different
Supplementary Discussion Rationale for using maternal ythdf2 -/- mutants as study subject To study the genetic basis of the embryonic developmental delay that we observed, we crossed fish with different
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Cao et al. 10.1073/pnas.1306220110 Gram - bacteria Hemolymph Cytoplasm PGRP-LC TAK1 signalosome Imd dfadd Dredd Dnr1 Ikk signalosome P Relish Nucleus AMP and effector genes Fig.
Supporting Information Cao et al. 10.1073/pnas.1306220110 Gram - bacteria Hemolymph Cytoplasm PGRP-LC TAK1 signalosome Imd dfadd Dredd Dnr1 Ikk signalosome P Relish Nucleus AMP and effector genes Fig.
TNFα 18hr. Control. CHX 18hr. TNFα+ CHX 18hr. TNFα: 18 18hr (KDa) PARP. Cleaved. Cleaved. Cleaved. Caspase3. Pellino3 shrna. Control shrna.
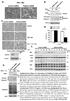 Survival ( %) a. TNFα 18hr b. Control sirna Pellino3 sirna TNFα: 18 18hr c. Control shrna Pellino3 shrna Caspase3 Actin Control d. Control shrna Pellino3 shrna *** 100 80 60 CHX 18hr 40 TNFα+ CHX 18hr
Survival ( %) a. TNFα 18hr b. Control sirna Pellino3 sirna TNFα: 18 18hr c. Control shrna Pellino3 shrna Caspase3 Actin Control d. Control shrna Pellino3 shrna *** 100 80 60 CHX 18hr 40 TNFα+ CHX 18hr
7.06 Problem Set #4, Spring 2005
 7.06 Problem Set #4, Spring 2005 1. You re doing a mutant hunt in S. cerevisiae (budding yeast), looking for temperaturesensitive mutants that are defective in the cell cycle. You discover a mutant strain
7.06 Problem Set #4, Spring 2005 1. You re doing a mutant hunt in S. cerevisiae (budding yeast), looking for temperaturesensitive mutants that are defective in the cell cycle. You discover a mutant strain
Table S1. Sequence of primers used in RT-qPCR
 Table S1. Sequence of primers used in RT-qPCR Primer Name P16Ink4a-F P16Ink4a-R P15Ink4b-F P15Ink4b-R P19Arf-F P19Arf-R P53-F P53-R P21cip1-F P21cip1-R P27kip1-F P27kip1-R P18Ink4c-F P18Ink4c-R P19Ink4d-F
Table S1. Sequence of primers used in RT-qPCR Primer Name P16Ink4a-F P16Ink4a-R P15Ink4b-F P15Ink4b-R P19Arf-F P19Arf-R P53-F P53-R P21cip1-F P21cip1-R P27kip1-F P27kip1-R P18Ink4c-F P18Ink4c-R P19Ink4d-F
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1. HSP21 expression in 35S:HSP21 and hsp21 knockdown plants. (a) Since no T- DNA insertion line for HSP21 is available in the publicly available T-DNA collections,
Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1. HSP21 expression in 35S:HSP21 and hsp21 knockdown plants. (a) Since no T- DNA insertion line for HSP21 is available in the publicly available T-DNA collections,
Mouse HORMAD1 and HORMAD2, Two Conserved Meiotic Chromosomal Proteins, Are Depleted from Synapsed Chromosome Axes with the Help of TRIP13 AAA-ATPase
 Mouse HORMAD1 and HORMAD2, Two Conserved Meiotic Chromosomal Proteins, Are Depleted from Synapsed Chromosome Axes with the Help of TRIP13 AAA-ATPase Lukasz Wojtasz 1., Katrin Daniel 1., Ignasi Roig 2,
Mouse HORMAD1 and HORMAD2, Two Conserved Meiotic Chromosomal Proteins, Are Depleted from Synapsed Chromosome Axes with the Help of TRIP13 AAA-ATPase Lukasz Wojtasz 1., Katrin Daniel 1., Ignasi Roig 2,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 reverse 3175 3175 F L C 318 318 3185 3185 319 319 3195 3195 315 8 1 315 3155 315 317 Supplementary Figure 3. Stability of expression of the GFP sensor constructs return to warm conditions. Semi-quantitative
reverse 3175 3175 F L C 318 318 3185 3185 319 319 3195 3195 315 8 1 315 3155 315 317 Supplementary Figure 3. Stability of expression of the GFP sensor constructs return to warm conditions. Semi-quantitative
Waithe et al Supplementary Figures
 Waithe et al Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 Expression and properties of WT and W391A mutant YFP- Ca V 2.2. A Immunoblot using Ca V 2.2 Ab for untransfected cells (UT, lane 1), YFP-Ca V 2.2
Waithe et al Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 Expression and properties of WT and W391A mutant YFP- Ca V 2.2. A Immunoblot using Ca V 2.2 Ab for untransfected cells (UT, lane 1), YFP-Ca V 2.2
A new role for the mitotic RAD21/SCC1 cohesin in meiotic chromosome cohesion and segregation in the mouse
 scientificreport A new role for the mitotic RAD21/SCC1 cohesin in meiotic chromosome cohesion and segregation in the mouse Huiling Xu 1, Matthew Beasley 1 *, Sandra Verschoor 1 *, Amy Inselman 2, Mary
scientificreport A new role for the mitotic RAD21/SCC1 cohesin in meiotic chromosome cohesion and segregation in the mouse Huiling Xu 1, Matthew Beasley 1 *, Sandra Verschoor 1 *, Amy Inselman 2, Mary
Unit 5: Cell Division and Development Guided Reading Questions (45 pts total)
 Name: AP Biology Biology, Campbell and Reece, 7th Edition Adapted from chapter reading guides originally created by Lynn Miriello Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Unit 5: Cell Division and Development Guided
Name: AP Biology Biology, Campbell and Reece, 7th Edition Adapted from chapter reading guides originally created by Lynn Miriello Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Unit 5: Cell Division and Development Guided
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn.2662
 Supplementary Figure 1 Atlastin phylogeny and homology. (a) Maximum likelihood phylogenetic tree based on 18 Atlastin-1 sequences using the program Quicktree. Numbers at internal nodes correspond to bootstrap
Supplementary Figure 1 Atlastin phylogeny and homology. (a) Maximum likelihood phylogenetic tree based on 18 Atlastin-1 sequences using the program Quicktree. Numbers at internal nodes correspond to bootstrap
Comparing Genomes! Homologies and Families! Sequence Alignments!
 Comparing Genomes! Homologies and Families! Sequence Alignments! Allows us to achieve a greater understanding of vertebrate evolution! Tells us what is common and what is unique between different species
Comparing Genomes! Homologies and Families! Sequence Alignments! Allows us to achieve a greater understanding of vertebrate evolution! Tells us what is common and what is unique between different species
Supplementary Figure 1. Markedly decreased numbers of marginal zone B cells in DOCK8 mutant mice Supplementary Figure 2.
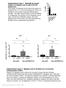 Supplementary Figure 1. Markedly decreased numbers of marginal zone B cells in DOCK8 mutant mice. Percentage of marginal zone B cells in the spleen of wild-type mice (+/+), mice homozygous for cpm or pri
Supplementary Figure 1. Markedly decreased numbers of marginal zone B cells in DOCK8 mutant mice. Percentage of marginal zone B cells in the spleen of wild-type mice (+/+), mice homozygous for cpm or pri
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/6/301/ra98/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Regulation of Epithelial Morphogenesis by the G Protein Coupled Receptor Mist and Its Ligand Fog Alyssa J. Manning,
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/6/301/ra98/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Regulation of Epithelial Morphogenesis by the G Protein Coupled Receptor Mist and Its Ligand Fog Alyssa J. Manning,
Quiz Section 4 Molecular analysis of inheritance: An amphibian puzzle
 Genome 371, Autumn 2018 Quiz Section 4 Molecular analysis of inheritance: An amphibian puzzle Goals: To illustrate how molecular tools can be used to track inheritance. In this particular example, we will
Genome 371, Autumn 2018 Quiz Section 4 Molecular analysis of inheritance: An amphibian puzzle Goals: To illustrate how molecular tools can be used to track inheritance. In this particular example, we will
Chapter 13 Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction
 Biology 110 Sec. 11 J. Greg Doheny Chapter 13 Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction Quiz Questions: 1. What word do you use to describe a chromosome or gene allele that we inherit from our Mother? From our Father?
Biology 110 Sec. 11 J. Greg Doheny Chapter 13 Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction Quiz Questions: 1. What word do you use to describe a chromosome or gene allele that we inherit from our Mother? From our Father?
Supplemental Figure 1.
 Supplemental Material: Annu. Rev. Genet. 2015. 49:213 42 doi: 10.1146/annurev-genet-120213-092023 A Uniform System for the Annotation of Vertebrate microrna Genes and the Evolution of the Human micrornaome
Supplemental Material: Annu. Rev. Genet. 2015. 49:213 42 doi: 10.1146/annurev-genet-120213-092023 A Uniform System for the Annotation of Vertebrate microrna Genes and the Evolution of the Human micrornaome
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng Supplementary Figure 1. The phenotypes of PI , BR121, and Harosoy under short-day conditions.
 Supplementary Figure 1 The phenotypes of PI 159925, BR121, and Harosoy under short-day conditions. (a) Plant height. (b) Number of branches. (c) Average internode length. (d) Number of nodes. (e) Pods
Supplementary Figure 1 The phenotypes of PI 159925, BR121, and Harosoy under short-day conditions. (a) Plant height. (b) Number of branches. (c) Average internode length. (d) Number of nodes. (e) Pods
The CSN/COP9 Signalosome Regulates Synaptonemal Complex Assembly during Meiotic Prophase I of Caenorhabditis elegans
 The CSN/COP9 Signalosome Regulates Synaptonemal Complex Assembly during Meiotic Prophase I of Caenorhabditis elegans Heather Brockway 1, Nathan Balukoff 2, Martha Dean 2, Benjamin Alleva 2, Sarit Smolikove
The CSN/COP9 Signalosome Regulates Synaptonemal Complex Assembly during Meiotic Prophase I of Caenorhabditis elegans Heather Brockway 1, Nathan Balukoff 2, Martha Dean 2, Benjamin Alleva 2, Sarit Smolikove
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2647 Figure S1 Other Rab GTPases do not co-localize with the ER. a, Cos-7 cells cotransfected with an ER luminal marker (either KDEL-venus or mch-kdel) and mch-tagged human Rab5 (mch-rab5,
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2647 Figure S1 Other Rab GTPases do not co-localize with the ER. a, Cos-7 cells cotransfected with an ER luminal marker (either KDEL-venus or mch-kdel) and mch-tagged human Rab5 (mch-rab5,
4) Please cite Dagda et al J Biol Chem 284: , for any publications or presentations resulting from use or modification of the macro.
 Supplement Figure S1. Algorithmic quantification of mitochondrial morphology in SH- SY5Y cells treated with known fission/fusion mediators. Parental SH-SY5Y cells were transiently transfected with an empty
Supplement Figure S1. Algorithmic quantification of mitochondrial morphology in SH- SY5Y cells treated with known fission/fusion mediators. Parental SH-SY5Y cells were transiently transfected with an empty
Overview of Genetic Organization and Scale
 CHAPTER ONE Overview of Genetic Organization and Scale The genetic material is a molecule called deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). Each chromosome contains a single long strand of DNA that encodes the information
CHAPTER ONE Overview of Genetic Organization and Scale The genetic material is a molecule called deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). Each chromosome contains a single long strand of DNA that encodes the information
2. Which of the following are NOT prokaryotes? A) eubacteria B) archaea C) viruses D) ancient bacteria
 1. Which of the following statements is FALSE? A) Errors in chromosome separation are rarely a problem for an organism. B) Errors in chromosome separation can result in a miscarriage. C) Errors in chromosome
1. Which of the following statements is FALSE? A) Errors in chromosome separation are rarely a problem for an organism. B) Errors in chromosome separation can result in a miscarriage. C) Errors in chromosome
A diploid somatic cell from a rat has a total of 42 chromosomes (2n = 42). As in humans, sex chromosomes determine sex: XX in females and XY in males.
 Multiple Choice Use the following information for questions 1-3. A diploid somatic cell from a rat has a total of 42 chromosomes (2n = 42). As in humans, sex chromosomes determine sex: XX in females and
Multiple Choice Use the following information for questions 1-3. A diploid somatic cell from a rat has a total of 42 chromosomes (2n = 42). As in humans, sex chromosomes determine sex: XX in females and
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2819 Gαi3 / Actin / Acetylated Tubulin Gαi3 / Actin / Acetylated Tubulin a a Gαi3 a Actin Gαi3 WT Gαi3 WT Gαi3 WT b b Gαi3 b Actin Gαi3 KO Gαi3 KO Gαi3 KO # # Figure S1 Loss of protein
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2819 Gαi3 / Actin / Acetylated Tubulin Gαi3 / Actin / Acetylated Tubulin a a Gαi3 a Actin Gαi3 WT Gαi3 WT Gαi3 WT b b Gαi3 b Actin Gαi3 KO Gαi3 KO Gαi3 KO # # Figure S1 Loss of protein
Biased amino acid composition in warm-blooded animals
 Biased amino acid composition in warm-blooded animals Guang-Zhong Wang and Martin J. Lercher Bioinformatics group, Heinrich-Heine-University, Düsseldorf, Germany Among eubacteria and archeabacteria, amino
Biased amino acid composition in warm-blooded animals Guang-Zhong Wang and Martin J. Lercher Bioinformatics group, Heinrich-Heine-University, Düsseldorf, Germany Among eubacteria and archeabacteria, amino
LAB-1 Targets PP1 and Restricts Aurora B Kinase upon Entrance into Meiosis to Promote Sister Chromatid Cohesion
 LAB-1 Targets PP1 and Restricts Aurora B Kinase upon Entrance into Meiosis to Promote Sister Chromatid Cohesion The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access
LAB-1 Targets PP1 and Restricts Aurora B Kinase upon Entrance into Meiosis to Promote Sister Chromatid Cohesion The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access
Supplementary Figure 1 Analysis of beige fat and cells and characteristics of exosome release, related to Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Analysis of beige fat and cells and characteristics of exosome release, related to Figure 1 (a) Fold-change in UCP-1 mrna abundance in white adipocytes upon β-adrenergic stimulation
Supplementary Figure 1 Analysis of beige fat and cells and characteristics of exosome release, related to Figure 1 (a) Fold-change in UCP-1 mrna abundance in white adipocytes upon β-adrenergic stimulation
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2362 Figure S1 CYLD and CASPASE 8 genes are co-regulated. Analysis of gene expression across 79 tissues was carried out as described previously [Ref: PMID: 18636086]. Briefly, microarray
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2362 Figure S1 CYLD and CASPASE 8 genes are co-regulated. Analysis of gene expression across 79 tissues was carried out as described previously [Ref: PMID: 18636086]. Briefly, microarray
Supplementary Figure 1. Phenotype of the HI strain.
 Supplementary Figure 1. Phenotype of the HI strain. (A) Phenotype of the HI and wild type plant after flowering (~1month). Wild type plant is tall with well elongated inflorescence. All four HI plants
Supplementary Figure 1. Phenotype of the HI strain. (A) Phenotype of the HI and wild type plant after flowering (~1month). Wild type plant is tall with well elongated inflorescence. All four HI plants
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 med!1,2 Wild-type (N2) end!3 elt!2 5 1 15 Time (minutes) 5 1 15 Time (minutes) med!1,2 end!3 5 1 15 Time (minutes) elt!2 5 1 15 Time (minutes) Supplementary Figure 1: Number of med-1,2, end-3, end-1 and
med!1,2 Wild-type (N2) end!3 elt!2 5 1 15 Time (minutes) 5 1 15 Time (minutes) med!1,2 end!3 5 1 15 Time (minutes) elt!2 5 1 15 Time (minutes) Supplementary Figure 1: Number of med-1,2, end-3, end-1 and
Supplemental material
 Supplemental material THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY Mourier et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201411100/dc1 Figure S1. Size and mitochondrial content in Mfn1 and Mfn2 knockout hearts. (A) Body
Supplemental material THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY Mourier et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201411100/dc1 Figure S1. Size and mitochondrial content in Mfn1 and Mfn2 knockout hearts. (A) Body
16 The Cell Cycle. Chapter Outline The Eukaryotic Cell Cycle Regulators of Cell Cycle Progression The Events of M Phase Meiosis and Fertilization
 The Cell Cycle 16 The Cell Cycle Chapter Outline The Eukaryotic Cell Cycle Regulators of Cell Cycle Progression The Events of M Phase Meiosis and Fertilization Introduction Self-reproduction is perhaps
The Cell Cycle 16 The Cell Cycle Chapter Outline The Eukaryotic Cell Cycle Regulators of Cell Cycle Progression The Events of M Phase Meiosis and Fertilization Introduction Self-reproduction is perhaps
doi: /nature09429
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature09429 C. e xnd-1 MSSEPIVANLDN------------------SMTTEPAPAAFPPISPMSFAFMNEEERAAVKFP--- C. b xnd-1 MN--DLAKN---------------------LLKHSQTTDSAPPISPLSFAFMTDEEKAAFKFPASE
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature09429 C. e xnd-1 MSSEPIVANLDN------------------SMTTEPAPAAFPPISPMSFAFMNEEERAAVKFP--- C. b xnd-1 MN--DLAKN---------------------LLKHSQTTDSAPPISPLSFAFMTDEEKAAFKFPASE
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature12791 Supplementary Figure 1 (1/3) WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE 1 RESEARCH SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1 (2/3) 2 WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE SUPPLEMENTARY
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature12791 Supplementary Figure 1 (1/3) WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE 1 RESEARCH SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1 (2/3) 2 WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE SUPPLEMENTARY
Supplemental Materials Molecular Biology of the Cell
 Supplemental Materials Molecular iology of the Cell Figure S1 Krüger et al. Arabidopsis Plasmodium H. sapiens* 1) Xenopus* 1) Drosophila C.elegans S.cerevisae S.pombe L.major T.cruzi T.brucei DCP5 CITH
Supplemental Materials Molecular iology of the Cell Figure S1 Krüger et al. Arabidopsis Plasmodium H. sapiens* 1) Xenopus* 1) Drosophila C.elegans S.cerevisae S.pombe L.major T.cruzi T.brucei DCP5 CITH
Cellular Neuroanatomy I The Prototypical Neuron: Soma. Reading: BCP Chapter 2
 Cellular Neuroanatomy I The Prototypical Neuron: Soma Reading: BCP Chapter 2 Functional Unit of the Nervous System The functional unit of the nervous system is the neuron. Neurons are cells specialized
Cellular Neuroanatomy I The Prototypical Neuron: Soma Reading: BCP Chapter 2 Functional Unit of the Nervous System The functional unit of the nervous system is the neuron. Neurons are cells specialized
JCB. Meiotic condensin is required for proper chromosome compaction, SC assembly, and resolution of recombination-dependent chromosome linkages
 JCB Published Online: 8 December, 2003 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.200308027 Downloaded from jcb.rupress.org on May 12, 2018 Article Meiotic condensin is required for proper chromosome compaction,
JCB Published Online: 8 December, 2003 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.200308027 Downloaded from jcb.rupress.org on May 12, 2018 Article Meiotic condensin is required for proper chromosome compaction,
Genetics Essentials Concepts and Connections 3rd Edition by Benjamin A Pierce Test Bank
 Genetics Essentials Concepts and Connections 3rd Edition by Benjamin A Pierce Test Bank Which of the following statements is FALSE? A) Errors in chromosome separation are rarely a problem for an organism.
Genetics Essentials Concepts and Connections 3rd Edition by Benjamin A Pierce Test Bank Which of the following statements is FALSE? A) Errors in chromosome separation are rarely a problem for an organism.
Supplemental Data. Perrella et al. (2013). Plant Cell /tpc
 Intensity Intensity Intensity Intensity Intensity Intensity 150 50 150 0 10 20 50 C 150 0 10 20 50 D 0 10 20 Distance (μm) 50 20 40 E 50 F 0 10 20 50 0 15 30 Distance (μm) Supplemental Figure 1: Co-localization
Intensity Intensity Intensity Intensity Intensity Intensity 150 50 150 0 10 20 50 C 150 0 10 20 50 D 0 10 20 Distance (μm) 50 20 40 E 50 F 0 10 20 50 0 15 30 Distance (μm) Supplemental Figure 1: Co-localization
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature11589 Supplementary Figure 1 Ciona intestinalis and Petromyzon marinus neural crest expression domain comparison. Cartoon shows dorsal views of Ciona mid gastrula (left) and Petromyzon
doi:10.1038/nature11589 Supplementary Figure 1 Ciona intestinalis and Petromyzon marinus neural crest expression domain comparison. Cartoon shows dorsal views of Ciona mid gastrula (left) and Petromyzon
Objectives. Announcements. Comparison of mitosis and meiosis
 Announcements Colloquium sessions for which you can get credit posted on web site: Feb 20, 27 Mar 6, 13, 20 Apr 17, 24 May 15. Review study CD that came with text for lab this week (especially mitosis
Announcements Colloquium sessions for which you can get credit posted on web site: Feb 20, 27 Mar 6, 13, 20 Apr 17, 24 May 15. Review study CD that came with text for lab this week (especially mitosis
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb3267 Supplementary Figure 1 A group of genes required for formation or orientation of annular F-actin bundles and aecm ridges: RNAi phenotypes and their validation by standard mutations.
DOI: 10.1038/ncb3267 Supplementary Figure 1 A group of genes required for formation or orientation of annular F-actin bundles and aecm ridges: RNAi phenotypes and their validation by standard mutations.
Chromosome Chr Duplica Duplic t a ion Pixley
 Chromosome Duplication Pixley Figure 4-6 Molecular Biology of the Cell ( Garland Science 2008) Figure 4-72 Molecular Biology of the Cell ( Garland Science 2008) Interphase During mitosis (cell division),
Chromosome Duplication Pixley Figure 4-6 Molecular Biology of the Cell ( Garland Science 2008) Figure 4-72 Molecular Biology of the Cell ( Garland Science 2008) Interphase During mitosis (cell division),
Genomics and bioinformatics summary. Finding genes -- computer searches
 Genomics and bioinformatics summary 1. Gene finding: computer searches, cdnas, ESTs, 2. Microarrays 3. Use BLAST to find homologous sequences 4. Multiple sequence alignments (MSAs) 5. Trees quantify sequence
Genomics and bioinformatics summary 1. Gene finding: computer searches, cdnas, ESTs, 2. Microarrays 3. Use BLAST to find homologous sequences 4. Multiple sequence alignments (MSAs) 5. Trees quantify sequence
Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis. Chapter 11
 Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis Chapter 11 1 Sexual life cycle Made up of meiosis and fertilization Diploid cells Somatic cells of adults have 2 sets of chromosomes Haploid cells Gametes (egg and sperm)
Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis Chapter 11 1 Sexual life cycle Made up of meiosis and fertilization Diploid cells Somatic cells of adults have 2 sets of chromosomes Haploid cells Gametes (egg and sperm)
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Single-cell RNA sequencing reveals unique sets of neuropeptides, transcription factors and receptors in specific types of sympathetic neurons (a) Dissection of paravertebral SGs
Supplementary Figure 1 Single-cell RNA sequencing reveals unique sets of neuropeptides, transcription factors and receptors in specific types of sympathetic neurons (a) Dissection of paravertebral SGs
Supplementary Figure 1. Biochemical and sequence alignment analyses the
 Supplementary Figure 1. Biochemical and sequence alignment analyses the interaction of OPTN and TBK1. (a) Analytical gel filtration chromatography analysis of the interaction between TBK1 CTD and OPTN(1-119).
Supplementary Figure 1. Biochemical and sequence alignment analyses the interaction of OPTN and TBK1. (a) Analytical gel filtration chromatography analysis of the interaction between TBK1 CTD and OPTN(1-119).
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature11419 Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic representation of innate immune signaling pathways induced by intracellular Salmonella in cultured macrophages. a, During the infection Salmonella
doi:10.1038/nature11419 Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic representation of innate immune signaling pathways induced by intracellular Salmonella in cultured macrophages. a, During the infection Salmonella
The Gametic Cell Cycle
 The Gametic Cell Cycle Diploid Parents MEIOSIS Haploid Gametes FERTILIZATION The Somatic Cell Cycle Diploid Zygote MITOSIS Diploid organism Activities of meiosis that differ from mitosis? Life cycle of
The Gametic Cell Cycle Diploid Parents MEIOSIS Haploid Gametes FERTILIZATION The Somatic Cell Cycle Diploid Zygote MITOSIS Diploid organism Activities of meiosis that differ from mitosis? Life cycle of
What happens to the replicated chromosomes? depends on the goal of the division
 Segregating the replicated chromosomes What happens to the replicated chromosomes? depends on the goal of the division - to make more vegetative cells: mitosis daughter cells chromosome set should be identical
Segregating the replicated chromosomes What happens to the replicated chromosomes? depends on the goal of the division - to make more vegetative cells: mitosis daughter cells chromosome set should be identical
Complex elaboration: making sense of meiotic cohesin dynamics
 MINIREVIEW Complex elaboration: making sense of meiotic cohesin dynamics Susannah Rankin Program in Cell Cycle and Cancer Biology, Oklahoma Medical Research Foundation, OK, USA Keywords cell cycle; cohesin
MINIREVIEW Complex elaboration: making sense of meiotic cohesin dynamics Susannah Rankin Program in Cell Cycle and Cancer Biology, Oklahoma Medical Research Foundation, OK, USA Keywords cell cycle; cohesin
Caenorhabditis elegans
 Caenorhabditis elegans Why C. elegans? Sea urchins have told us much about embryogenesis. They are suited well for study in the lab; however, they do not tell us much about the genetics involved in embryogenesis.
Caenorhabditis elegans Why C. elegans? Sea urchins have told us much about embryogenesis. They are suited well for study in the lab; however, they do not tell us much about the genetics involved in embryogenesis.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2215 Figure S1 Number of egfp-vps4a bursts versus cellular expression levels. The total number of egfp-vps4a bursts, counted at the end of each movie (frame 2000, after 1h 28 min) are plotted
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2215 Figure S1 Number of egfp-vps4a bursts versus cellular expression levels. The total number of egfp-vps4a bursts, counted at the end of each movie (frame 2000, after 1h 28 min) are plotted
Biological Roles of Cytokinins
 Direct Control of Shoot Meristem Activity by a Cytokinin-Activating Enzyme By Kurakawa et. Al. Published in Nature Presented by Boyana Grigorova Biological Roles of Cytokinins Cytokinins are positive regulators
Direct Control of Shoot Meristem Activity by a Cytokinin-Activating Enzyme By Kurakawa et. Al. Published in Nature Presented by Boyana Grigorova Biological Roles of Cytokinins Cytokinins are positive regulators
GATA family of transcription factors of vertebrates: phylogenetics and chromosomal synteny
 Phylogenetics and chromosomal synteny of the GATAs 1273 GATA family of transcription factors of vertebrates: phylogenetics and chromosomal synteny CHUNJIANG HE, HANHUA CHENG* and RONGJIA ZHOU* Department
Phylogenetics and chromosomal synteny of the GATAs 1273 GATA family of transcription factors of vertebrates: phylogenetics and chromosomal synteny CHUNJIANG HE, HANHUA CHENG* and RONGJIA ZHOU* Department
Biology I Level - 2nd Semester Final Review
 Biology I Level - 2nd Semester Final Review The 2 nd Semester Final encompasses all material that was discussed during second semester. It s important that you review ALL notes and worksheets from the
Biology I Level - 2nd Semester Final Review The 2 nd Semester Final encompasses all material that was discussed during second semester. It s important that you review ALL notes and worksheets from the
CPEB proteins control two key steps in spermatogenesis in C. elegans
 CPEB proteins control two key steps in spermatogenesis in C. elegans Cameron Luitjens, 1 Maria Gallegos, 1,4,6 Brian Kraemer, 2,5,6 Judith Kimble, 2,3 and Marvin Wickens 2,7 1 Program in Cell and Molecular
CPEB proteins control two key steps in spermatogenesis in C. elegans Cameron Luitjens, 1 Maria Gallegos, 1,4,6 Brian Kraemer, 2,5,6 Judith Kimble, 2,3 and Marvin Wickens 2,7 1 Program in Cell and Molecular
Supplementary Information. Recognition of the pre-mirna structure by Drosophila Dicer-1
 Supplementary Information Recognition of the pre-mirna structure by Drosophila Dicer-1 Akihisa Tsutsumi 1,2, Tomoko Kawamata 1, Natsuko Izumi 1 Hervé Seitz 3,4 and Yukihide Tomari 1,2 Nature Structural
Supplementary Information Recognition of the pre-mirna structure by Drosophila Dicer-1 Akihisa Tsutsumi 1,2, Tomoko Kawamata 1, Natsuko Izumi 1 Hervé Seitz 3,4 and Yukihide Tomari 1,2 Nature Structural
Eukaryotic vs. Prokaryotic genes
 BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 18: Eukaryotic genes http://compbio.uchsc.edu/hunter/bio5099 Larry.Hunter@uchsc.edu Eukaryotic vs. Prokaryotic genes Like in prokaryotes,
BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 18: Eukaryotic genes http://compbio.uchsc.edu/hunter/bio5099 Larry.Hunter@uchsc.edu Eukaryotic vs. Prokaryotic genes Like in prokaryotes,
When one gene is wild type and the other mutant:
 Series 2: Cross Diagrams Linkage Analysis There are two alleles for each trait in a diploid organism In C. elegans gene symbols are ALWAYS italicized. To represent two different genes on the same chromosome:
Series 2: Cross Diagrams Linkage Analysis There are two alleles for each trait in a diploid organism In C. elegans gene symbols are ALWAYS italicized. To represent two different genes on the same chromosome:
downstream (0.8 kb) homologous sequences to the genomic locus of DIC. A DIC mutant strain (ro- 6
 A B C D ts Figure S1 Generation of DIC- mcherry expressing N.crassa strain. A. N. crassa colony morphology. When a cot1 (top, left panel) strain is grown at permissive temperature (25 C), it exhibits straight
A B C D ts Figure S1 Generation of DIC- mcherry expressing N.crassa strain. A. N. crassa colony morphology. When a cot1 (top, left panel) strain is grown at permissive temperature (25 C), it exhibits straight
GENETICS UNIT VOCABULARY CHART. Word Definition Word Part Visual/Mnemonic Related Words 1. adenine Nitrogen base, pairs with thymine in DNA and uracil
 Word Definition Word Part Visual/Mnemonic Related Words 1. adenine Nitrogen base, pairs with thymine in DNA and uracil in RNA 2. allele One or more alternate forms of a gene Example: P = Dominant (purple);
Word Definition Word Part Visual/Mnemonic Related Words 1. adenine Nitrogen base, pairs with thymine in DNA and uracil in RNA 2. allele One or more alternate forms of a gene Example: P = Dominant (purple);
Supplemental Data. Chen and Thelen (2010). Plant Cell /tpc
 Supplemental Data. Chen and Thelen (2010). Plant Cell 10.1105/tpc.109.071837 1 C Total 5 kg 20 kg 100 kg Transmission Image 100 kg soluble pdtpi-gfp Plastid (PDH-alpha) Mito (PDH-alpha) GFP Image vector
Supplemental Data. Chen and Thelen (2010). Plant Cell 10.1105/tpc.109.071837 1 C Total 5 kg 20 kg 100 kg Transmission Image 100 kg soluble pdtpi-gfp Plastid (PDH-alpha) Mito (PDH-alpha) GFP Image vector
Supplementary Figure 1: Mechanism of Lbx2 action on the Wnt/ -catenin signalling pathway. (a) The Wnt/ -catenin signalling pathway and its
 Supplementary Figure 1: Mechanism of Lbx2 action on the Wnt/ -catenin signalling pathway. (a) The Wnt/ -catenin signalling pathway and its transcriptional activity in wild-type embryo. A gradient of canonical
Supplementary Figure 1: Mechanism of Lbx2 action on the Wnt/ -catenin signalling pathway. (a) The Wnt/ -catenin signalling pathway and its transcriptional activity in wild-type embryo. A gradient of canonical
The phenotype of this worm is wild type. When both genes are mutant: The phenotype of this worm is double mutant Dpy and Unc phenotype.
 Series 2: Cross Diagrams - Complementation There are two alleles for each trait in a diploid organism In C. elegans gene symbols are ALWAYS italicized. To represent two different genes on the same chromosome:
Series 2: Cross Diagrams - Complementation There are two alleles for each trait in a diploid organism In C. elegans gene symbols are ALWAYS italicized. To represent two different genes on the same chromosome:
Chapter 3: Structure and Function of the Cell
 Chapter 3: Structure and Function of the Cell I. Functions of the Cell A. List and describe the main functions of the cell: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. II. How We See Cells A. Light microscopes allow us to B. Electron
Chapter 3: Structure and Function of the Cell I. Functions of the Cell A. List and describe the main functions of the cell: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. II. How We See Cells A. Light microscopes allow us to B. Electron
Supplemental Information. The Mitochondrial Fission Receptor MiD51. Requires ADP as a Cofactor
 Structure, Volume 22 Supplemental Information The Mitochondrial Fission Receptor MiD51 Requires ADP as a Cofactor Oliver C. Losón, Raymond Liu, Michael E. Rome, Shuxia Meng, Jens T. Kaiser, Shu-ou Shan,
Structure, Volume 22 Supplemental Information The Mitochondrial Fission Receptor MiD51 Requires ADP as a Cofactor Oliver C. Losón, Raymond Liu, Michael E. Rome, Shuxia Meng, Jens T. Kaiser, Shu-ou Shan,
Optimization of Immunoblot Protocol for Use with a Yeast Strain Containing the CDC7 Gene Tagged with myc
 OPTIMIZATION OF IMMUNOBLOT PROTOCOL 121 Optimization of Immunoblot Protocol for Use with a Yeast Strain Containing the CDC7 Gene Tagged with myc Jacqueline Bjornton and John Wheeler Faculty Sponsor: Anne
OPTIMIZATION OF IMMUNOBLOT PROTOCOL 121 Optimization of Immunoblot Protocol for Use with a Yeast Strain Containing the CDC7 Gene Tagged with myc Jacqueline Bjornton and John Wheeler Faculty Sponsor: Anne
CAPE Biology Unit 1 Scheme of Work
 CAPE Biology Unit 1 Scheme of Work 2011-2012 Term 1 DATE SYLLABUS OBJECTIVES TEXT PAGES ASSIGNMENTS COMMENTS Orientation Introduction to CAPE Biology syllabus content and structure of the exam Week 05-09
CAPE Biology Unit 1 Scheme of Work 2011-2012 Term 1 DATE SYLLABUS OBJECTIVES TEXT PAGES ASSIGNMENTS COMMENTS Orientation Introduction to CAPE Biology syllabus content and structure of the exam Week 05-09
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Figure S1. Mitochondrial morphology in Fis1-null, Mff-null and Fis1/Mff-null MEF cells. (A) Western blotting of lysates from Fis1-null, Mff-null and Fis1/Mff-null cells. Lysates were
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Figure S1. Mitochondrial morphology in Fis1-null, Mff-null and Fis1/Mff-null MEF cells. (A) Western blotting of lysates from Fis1-null, Mff-null and Fis1/Mff-null cells. Lysates were
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Normal diploid somatic (body) cells of the mosquito Culex pipiens contain six chromosomes.
Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Normal diploid somatic (body) cells of the mosquito Culex pipiens contain six chromosomes.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS Mef2 primary screen. RNAi hairpins from the VDRC collection were crossed to Mef2-GAL4 at 27 C. After 2 weeks lethality rate and stage was scored, and if possible 20-30 males containing
SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS Mef2 primary screen. RNAi hairpins from the VDRC collection were crossed to Mef2-GAL4 at 27 C. After 2 weeks lethality rate and stage was scored, and if possible 20-30 males containing
Lesson 1. Cell cycle Chromosomes Mitosis phases
 Lesson 1 Cell cycle Chromosomes Mitosis phases Organism Diploid chromosome # (2n) in body cells Haploid chromosome # (n) in gametes Human *(memorize) 46 23 Goat 60 30 Guinea pig 64 32 Bat 44 22 Squirrel
Lesson 1 Cell cycle Chromosomes Mitosis phases Organism Diploid chromosome # (2n) in body cells Haploid chromosome # (n) in gametes Human *(memorize) 46 23 Goat 60 30 Guinea pig 64 32 Bat 44 22 Squirrel
MCB142/ICB163 Overview. Instructors:
 MCB142/ICB163 Overview Instructors: Professor Sharon Amacher Professor Abby Dernburg Professor Monty Slatkin GSIs: Kristin Camfield Nat Hallihan Hana Lee Christine Preston Richard Price Kate Smallenburg
MCB142/ICB163 Overview Instructors: Professor Sharon Amacher Professor Abby Dernburg Professor Monty Slatkin GSIs: Kristin Camfield Nat Hallihan Hana Lee Christine Preston Richard Price Kate Smallenburg
Germline stem cell differentiation entails regional control of cell fate. regulator GLD-1 in Caenorhabditis elegans
 Genetics: Early Online, published on January 12, 216 as 1.1534/genetics.115.185678 Germline stem cell differentiation entails regional control of cell fate regulator GLD-1 in Caenorhabditis elegans John
Genetics: Early Online, published on January 12, 216 as 1.1534/genetics.115.185678 Germline stem cell differentiation entails regional control of cell fate regulator GLD-1 in Caenorhabditis elegans John
Genetic recombination
 Genetic recombination Genetic recombination Obtaining of new gene combinations by rearrangements in genetic material: Between two DNA molecules Between two different chromosomes Between two sets of chromosomes
Genetic recombination Genetic recombination Obtaining of new gene combinations by rearrangements in genetic material: Between two DNA molecules Between two different chromosomes Between two sets of chromosomes
Designer Genes C Test
 Northern Regional: January 19 th, 2019 Designer Genes C Test Name(s): Team Name: School Name: Team Number: Rank: Score: Directions: You will have 50 minutes to complete the test. You may not write on the
Northern Regional: January 19 th, 2019 Designer Genes C Test Name(s): Team Name: School Name: Team Number: Rank: Score: Directions: You will have 50 minutes to complete the test. You may not write on the
Computational Biology: Basics & Interesting Problems
 Computational Biology: Basics & Interesting Problems Summary Sources of information Biological concepts: structure & terminology Sequencing Gene finding Protein structure prediction Sources of information
Computational Biology: Basics & Interesting Problems Summary Sources of information Biological concepts: structure & terminology Sequencing Gene finding Protein structure prediction Sources of information
Developmental Role and Regulation of cortex, a Meiosis-Specific Anaphase-Promoting Complex/Cyclosome Activator
 Developmental Role and Regulation of cortex, a Meiosis-Specific Anaphase-Promoting Complex/Cyclosome Activator Jillian A. Pesin 1,2, Terry L. Orr-Weaver 1,2* 1 Department of Biology, Massachusetts Institute
Developmental Role and Regulation of cortex, a Meiosis-Specific Anaphase-Promoting Complex/Cyclosome Activator Jillian A. Pesin 1,2, Terry L. Orr-Weaver 1,2* 1 Department of Biology, Massachusetts Institute
Supplementary Figure 1.
 Supplementary Figure 1. Characterisation of IHG-1 overexpressing and knockdown cell lines. (A) Total cellular RNA was prepared from HeLa cells stably overexpressing IHG-1 or mts-ihg-1. IHG-1 mrna was quantified
Supplementary Figure 1. Characterisation of IHG-1 overexpressing and knockdown cell lines. (A) Total cellular RNA was prepared from HeLa cells stably overexpressing IHG-1 or mts-ihg-1. IHG-1 mrna was quantified
Induction of cap-independent BiP (hsp-3) and Bcl-2 (ced-9) translation in response to eif4g (IFG-1) depletion in C. elegans
 Research Paper Translation 2, e28935; April; 2014 Landes Bioscience Research Paper Induction of cap-independent BiP (hsp-3) and Bcl-2 (ced-9) translation in response to eif4g (IFG-1) depletion in C. elegans
Research Paper Translation 2, e28935; April; 2014 Landes Bioscience Research Paper Induction of cap-independent BiP (hsp-3) and Bcl-2 (ced-9) translation in response to eif4g (IFG-1) depletion in C. elegans
BIOINFORMATICS LAB AP BIOLOGY
 BIOINFORMATICS LAB AP BIOLOGY Bioinformatics is the science of collecting and analyzing complex biological data. Bioinformatics combines computer science, statistics and biology to allow scientists to
BIOINFORMATICS LAB AP BIOLOGY Bioinformatics is the science of collecting and analyzing complex biological data. Bioinformatics combines computer science, statistics and biology to allow scientists to
Honors Biology Reading Guide Chapter 11
 Honors Biology Reading Guide Chapter 11 v Promoter a specific nucleotide sequence in DNA located near the start of a gene that is the binding site for RNA polymerase and the place where transcription begins
Honors Biology Reading Guide Chapter 11 v Promoter a specific nucleotide sequence in DNA located near the start of a gene that is the binding site for RNA polymerase and the place where transcription begins
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI:.38/ncb97 P ( μm, hours) 1 2 4 P DMSO Figure S1 unningham et al. E 97 65 27 MFN1 GFP-Parkin Opa1 ctin GPDH HEK293 GFP-Parkin 19 115 97 65 27 Mitochondrial Fraction SH-SY5Y GFP-Parkin Mito DMSO Mito
DOI:.38/ncb97 P ( μm, hours) 1 2 4 P DMSO Figure S1 unningham et al. E 97 65 27 MFN1 GFP-Parkin Opa1 ctin GPDH HEK293 GFP-Parkin 19 115 97 65 27 Mitochondrial Fraction SH-SY5Y GFP-Parkin Mito DMSO Mito
QQ 10/5/18 Copy the following into notebook:
 Chapter 13- Meiosis QQ 10/5/18 Copy the following into notebook: Similarities: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Differences: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Figure 13.1 Living organisms are distinguished by their ability to reproduce their
Chapter 13- Meiosis QQ 10/5/18 Copy the following into notebook: Similarities: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Differences: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Figure 13.1 Living organisms are distinguished by their ability to reproduce their
Figure 1. Identification of UGT74E2 as an IBA glycosyltransferase. (A) Relative conversion rates of different plant hormones to their glucosylated
 Figure 1. Identification of UGT74E2 as an IBA glycosyltransferase. (A) Relative conversion rates of different plant hormones to their glucosylated form by recombinant UGT74E2. The naturally occurring auxin
Figure 1. Identification of UGT74E2 as an IBA glycosyltransferase. (A) Relative conversion rates of different plant hormones to their glucosylated form by recombinant UGT74E2. The naturally occurring auxin
G C T G U A. template strand
 A 5 w 3 3 c 5 mrna RNA polymerase T G C A G C C T G U A coding or sense st AUG?? template strand The triplet code 3 bases = 1 amino acid Punctuation: sta rt: sto p: AUGA CUU CAGUAAC AU U AA C C AUG = methionine,
A 5 w 3 3 c 5 mrna RNA polymerase T G C A G C C T G U A coding or sense st AUG?? template strand The triplet code 3 bases = 1 amino acid Punctuation: sta rt: sto p: AUGA CUU CAGUAAC AU U AA C C AUG = methionine,
Tiffany Samaroo MB&B 452a December 8, Take Home Final. Topic 1
 Tiffany Samaroo MB&B 452a December 8, 2003 Take Home Final Topic 1 Prior to 1970, protein and DNA sequence alignment was limited to visual comparison. This was a very tedious process; even proteins with
Tiffany Samaroo MB&B 452a December 8, 2003 Take Home Final Topic 1 Prior to 1970, protein and DNA sequence alignment was limited to visual comparison. This was a very tedious process; even proteins with
UNIT 5. Protein Synthesis 11/22/16
 UNIT 5 Protein Synthesis IV. Transcription (8.4) A. RNA carries DNA s instruction 1. Francis Crick defined the central dogma of molecular biology a. Replication copies DNA b. Transcription converts DNA
UNIT 5 Protein Synthesis IV. Transcription (8.4) A. RNA carries DNA s instruction 1. Francis Crick defined the central dogma of molecular biology a. Replication copies DNA b. Transcription converts DNA
MEIOSIS, THE BASIS OF SEXUAL REPRODUCTION
 MEIOSIS, THE BASIS OF SEXUAL REPRODUCTION Why do kids look different from the parents? How are they similar to their parents? Why aren t brothers or sisters more alike? Meiosis A process where the number
MEIOSIS, THE BASIS OF SEXUAL REPRODUCTION Why do kids look different from the parents? How are they similar to their parents? Why aren t brothers or sisters more alike? Meiosis A process where the number
High density of REC8 constrains sister chromatid axes and prevents illegitimate synaptonemal complex formation
 Article High density of REC8 constrains sister chromatid axes and prevents illegitimate synaptonemal complex formation Ana Agostinho 1,*, Otto Manneberg 2, Robin van Schendel 3, Abrahan Hernández-Hernández
Article High density of REC8 constrains sister chromatid axes and prevents illegitimate synaptonemal complex formation Ana Agostinho 1,*, Otto Manneberg 2, Robin van Schendel 3, Abrahan Hernández-Hernández
JMJ14-HA. Col. Col. jmj14-1. jmj14-1 JMJ14ΔFYR-HA. Methylene Blue. Methylene Blue
 Fig. S1 JMJ14 JMJ14 JMJ14ΔFYR Methylene Blue Col jmj14-1 JMJ14-HA Methylene Blue Col jmj14-1 JMJ14ΔFYR-HA Fig. S1. The expression level of JMJ14 and truncated JMJ14 with FYR (FYRN + FYRC) domain deletion
Fig. S1 JMJ14 JMJ14 JMJ14ΔFYR Methylene Blue Col jmj14-1 JMJ14-HA Methylene Blue Col jmj14-1 JMJ14ΔFYR-HA Fig. S1. The expression level of JMJ14 and truncated JMJ14 with FYR (FYRN + FYRC) domain deletion
