Netter's Histology Flash Cards Section 1 List Updated Edition
|
|
|
- Damian Mason
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Netter's Histology Flash Cards Section 1 List Updated Edition Section 1 Cells and Tissues (74 cards) 1 The Cell (11 cards) Plate 1-1 The Cell Centrioles Microvillus Rough endoplasmic reticulum Smooth endoplasmic reticulum Mitochondrion Nucleus Golgi complex Plate 1-2 Cell Junctions Plasma (cell) membrane Gap (communicating) junction Connexin monomer Hydrophilic channel (pore) Connexon (hexamer) Plate 1-3 Nucleus Heterochromatin Nuclear envelope Euchromatin Plate 1-4 Nucleus Nuclear envelope Nuclear pore (complex) Perinuclear space Nucleus (with heterochromatin) Cytoplasm (Cytosol) Rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) Plate 1-5 Mitochondria Rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) Cristae Mitochondrial matrix Outer mitochondrial membrane Plate 1-6 Ribosomes Cisterna of rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) Ribosome Polyribosome Plate 1-7 Golgi Complex Trans-surface of Golgi complex Saccule of medial compartment Cis-surface of Golgi complex Golgi vesicles Plate 1-8 Cytoplasm Nucleus Golgi complex Mitochondria Glycogen Peroxisome Plate 1-9 Inclusions Glycogen rosettes Rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) Mitochondria Plate 1-10 Cytoplasmic Vesicles Caveolae Cytoplasmic vesicle Plasma membrane Netter's Histology Flash Cards Section 1 List /9
2 Basement membrane Plate 1-11 Cytoskeleton Microtubules Mitochondrion 2 Epithelium and Exocrine Glands (11 cards) Plate 2-1 Classification of Epithelia Simple squamous Simple cuboidal Simple columnar Pseudostratified columnar Stratified squamous nonkeratinized Stratified squamous keratinized Stratified cuboidal Stratified columnar Transitional (Urothelium) Plate 2-2 Simple Squamous Epithelium Mesothelium Connective tissue Lumen of venule Endothelial cell (endothelium) Mitochondrion Basal lamina Plate 2-3 Simple Columnar and Pseudostratified Epithelia Simple columnar epithelium Nucleus of columnar epithelial cell Lumen of venule Ciliated border Pseudostratified ciliated columnar (respiratory) epithelium Goblet cell Basement membrane Plate 2-4 Simple Columnar Epithelium Nucleus of columnar epithelial cell Microvillus Glycocalyx Tight junction Intermediate junction Desmosome Lysosome Mitochondrion Plate 2-5 Stratified Squamous Keratinized Epithelium Basal cell Dermis (collagen) Nucleus of keratinocyte Keratin Plate 2-6 Stratified Epithelium Stratified cuboidal epithelium (duct of mucous gland) Connective tissue (stroma) Stratified columnar epithelium (of male urethra) Capillary Basement membrane Plate 2-7 Transitional Epithelium Umbrella cell Nucleus of basal cell Lamina propria (loose connective tissue) Apical plasma membrane Junctional complex (tight junction) Nucleus Nucleolus Plate 2-8 Classification of Exocrine Glands Simple tubular Netter's Histology Flash Cards Section 1 List 2/9
3 2-8.2 Simple acinar Simple tubulo-acinar Compound tubular Compound acinar Compound tubulo-acinar (-alveolar) Plate 2-9 Serous Cells Golgi complex Nucleus Mitochondrion Secretory vesicle Lumen of serous acinus Plate 2-10 Mucous Cells Mucous acinus Serous acinus Secretory vesicle or mucous droplet Nucleus Rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) Plate 2-11 Mammary Gland Myoepithelial cell Duct Lumen of alveolus Apical plasma membrane Lipid droplet Intercellular (tight) junction Rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) Nucleus euchromatin Mitochondrion 3 Connective Tissue (10 cards) Plate 3-1 Loose Connective Tissue Pericyte Collagen fibers Erythrocyte in capillary Monocyte Lymphocyte Adipocyte Mast cell Eosinophil Plasma cell Fibroblast Plate 3-2 Dense Connective Tissue Collagen bundle Nucleus of fibroblast Capillary Tendon (dense regular connective tissue) Plate 3-3 Fibroblasts Heterochromatin (of fibroblast) Euchromatin (of fibroblast) Cell processes (of fibroblasts) Collagen Plate 3-4 Collagen Plasma membrane of fibroblast Collagen fibril Mitochondrion Cisterna of rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) Ribosome Plate 3-5 Elastic Connective Tissue Internal elastic lamina (of arteriole) Microfibrils and elastin Plate 3-6 Reticular Connective Tissue Reticular fibers Netter's Histology Flash Cards Section 1 List 3/9
4 3-6.2 Macrophage Plate 3-7 Mast Cells Nucleus of endothelial cell Lumen of venule Erythrocyte Nucleolus Collagen Granule Mast cell nucleus Plate 3-8 Plasma Cells Juxtanuclear halo (Golgi complex) Plasma cell nucleus Mitochondrion Rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) Production of antibodies Plate 3-9 Macrophages Phagocytosis Primary lysosome Tertiary (residual) lysosome Secondary lysosome Kupffer cell of liver Plate 3-10 Adipose Tissue Adipocyte Arteriole Connective tissue Venule Nucleus of adipocyte Lipid droplet 4 Muscle Tissue (10 cards) Plate 4-1 Skeletal Muscle Capillary Mitochondria Nucleus Perimysium (collagen) Nerve fascicle Skeletal muscle fiber Plate 4-2 Skeletal Muscle Myofibril T-tubule Sarcoplasmic reticulum Z band Nucleus Sarcolemma I band A band Mitochondria Plate 4-3 Sarcomere I band Z band H zone M band A band Thin filament Thick filament Plate 4-4 Satellite Cells Nucleus of skeletal muscle fiber Satellite cell Euchromatin External lamina Mitochondrion Netter's Histology Flash Cards Section 1 List 4/9
5 4-4.6 Ribosomes Myofibril Plate 4-5 Neuromuscular Junction Myofibril Synaptic vesicles Schwann cell Myelin sheath Axoplasm Synaptic cleft Postsynaptic membrane (junctional fold) Mitochondrion in presynaptic nerve terminal Plate 4-6 Cardiac Muscle Capillary (endothelial cell) Collagen Fibroblast Sarcolemma Intercalated disc Mitochondrion Z band Myofibril Cardiac muscle cell Plate 4-7 Cardiac Muscle Intercalated disc Erythrocyte in capillary Nucleus of cardiac muscle cell Lipofuscin A band Z band Mitochondrion Plate 4-8 Cardiac Conduction System Blood vessel (capillary) Myocardium (cardiac muscle fibers) Endocardium Purkinje fibers Ventricular lumen (cardiac chamber) Plate 4-9 Smooth muscle Caveolae Mitochondrion Dense body Nucleus Myosin (thick filament) Actin (thin filament) Centriole Plate 4-10 Smooth muscle Mitochondrion of Schwann cell Unmyelinated axon Axonal varicosity Schwann cell Mitochondrion of smooth muscle cell Nucleus of smooth muscle cell 5 Nervous Tissue (12) Plate 5-1 Meninges Dura mater Subarachnoid space Arachnoid mater Lumen of cerebral artery Pia mater Nervous tissue Plate 5-2 Cerebrum Gray matter Netter's Histology Flash Cards Section 1 List 5/9
6 5-2.2 Blood vessel White matter Medulla oblongata Cerebellum Plate 5-3 Cerebellum Corpus callosum Pituitary gland White matter Granular cell layer Molecular layer Plate 5-4 Neuron Ependyma Astrocyte Dendrite of neuron Nucleus euchromatin Endothelium of capillary Axon Oligodendrocyte Plate 5-5 Neuron Dendrite Axon Axon hillock Mitochondria Golgi complex Rough endoplasmic reticulum Nucleolus Plate 5-6 Synapse in the CNS Axon Synaptic vesicles Presynaptic terminal Postsynaptic terminal Outer membrane of mitochondrion Crista of mitochondrion Plate 5-7 Blood-brain Barrier Astrocyte foot process Mitochondrion Tight junction between endothelial cells Nucleus (euchromatin) of endothelial cell Nucleus of astrocyte Erythrocyte in lumen of capillary Plate 5-8 Choroid Plexus Lateral ventricle Third ventricle Fourth ventricle Ependyma (modified); simple cuboidal epithelium Capillary (fenestrated) Loose connective tissue Cerebrospinal fluid Plate 5-9 Spinal Cord Ventral (anterior) horn Pia mater Nucleolus of motor neuron Axon White matter Dorsal (posterior) horn Plate 5-10 Peripheral Nerve Schwann cell Mitochondrion Perineurial cell Collagen fibrils of endoneurium Netter's Histology Flash Cards Section 1 List 6/9
7 Myelin sheath Neurofilaments Plate 5-11 Peripheral Nerve Unmyelinated nerve fiber Schwann cell Synaptic vesicles Basal lamina of Schwann cell Collagen fibrils Plate 5-12 Peripheral Ganglia Satellite cell Lipofuscin in perikaryon Nerve fiber (axon) Nucleus of neuron Nissl substance 6 Cartilage and Bone (10 cards) Plate 6-1 Articular Hyaline Cartilage Articular surface Chondrocyte Spongy bone Subchondral bone Calcified cartilage zone Plate 6-2 Hyaline Cartilage Perichondrium Blood vessel (capillary) in perichondrium Territorial matrix Chondrocyte Isogenous nest Interterritorial matrix Plate 6-3 Fibrocartilage Spongy bone of vertebra Nucleus pulposis Annulus fibrosis Compact bone of vertebra Plate 6-4 Elastic Cartilage Chondrocyte Matrix Perichondrium Plate 6-5 Chondrocyte Nucleus Plasma membrane of chondrocyte Matrix Rough endoplasmic reticulum Mitochondrion Plate 6-6 Growth Plate Reserve zone Proliferative zone Zone of maturation and hypertrophy Zone of provisional calcification Zone of ossification (primary spongiosa) Zone of ossification (secondary spongiosa) Plate 6-7 Spongy Bone Osteoclast Osteocyte Osteoblasts Blood vessel Woven bone (trabecula) Lamellar bone (trabecula) Fat cell adipocyte Plate 6-8 Cells of Bone Trabeculae of spongy bone Netter's Histology Flash Cards Section 1 List 7/9
8 6-8.2 Osteoclast Bony matrix Osteoid (newly synthesized bone) Osteoblasts Plate 6-9 Compact Bone Periosteum Capillary in Haversian canal Concentric lamella Osteocyte Trabecula Plate 6-10 Synovium Meniscus Synovial cavity Synovial villus of synovium Articular cartilage Subintimal layer loose connective tissue 7 Blood and Bone Marrow (10 cards) Plate 7-1 Formed Elements of Blood Eosinophil Neutrophil Erythrocyte Lymphocyte Platelets Monocyte Basophil Plate 7-2 Erythrocytes and Platelets Hemoglobin days Blood coagulation (clotting) Megakaryocyte Endothelial cell Dense granules of platelet Plate 7-3 Neutrophil Chromatin strand (interconnecting lobes of nucleus) Lobe of nucleus Specific granules Barr body (present in females only) Golgi complex Plate 7-4 Eosinophil Lobe of nucleus Chromatin strand Specific granules Golgi complex Heterochromatin Euchromatin Rough endoplasmic reticulum Plate 7-5 Basophil Specific granules Golgi complex Nucleus Rough endoplasmic reticulum Plate 7-6 Lymphocyte Erythrocyte Nucleus Microvilli Mitochondria Plate 7-7 Monocyte Nucleus (horseshoe shaped) Pseudopod Endothelial cell Netter's Histology Flash Cards Section 1 List 8/9
9 7-7.4 Rough endoplasmic reticulum Membrane ruffles Plate 7-8 Bone Marrow Bone marrow smear Trephine needle biopsy section Venous sinusoid filled with erythrocytes Hematopoietic tissue Megakaryocytes Fat cells (adipocytes) Bone trabecula Plate 7-9 Megakaryocyte Nuclei Dense granules Demarcation channels between forming platelets Platelets Plate 7-10 Erythropoeisis and Granulopoeisis Proerythroblast Polychromatophilic erythroblast Normoblast (orthochromatic erythroblast) Metamyelocytes Promyelocytes Netter's Histology Flash Cards Section 1 List 9/9
QUESTIONS TO MODULE "CYTOLOGY"
 QUESTIONS TO MODULE "CYTOLOGY" 1. The structure of the Plasmolemma. 2. Characteristic of receptive and transport functions of the plasmolemma. 3. The structure of intercellular contacts: Simple contact,
QUESTIONS TO MODULE "CYTOLOGY" 1. The structure of the Plasmolemma. 2. Characteristic of receptive and transport functions of the plasmolemma. 3. The structure of intercellular contacts: Simple contact,
Organization of Vertebrate Body. Organization of Vertebrate Body
 The Animal Body and Principles of Regulation Chapter 43 There are four levels of organization: 1. Cells 2. Tissues 3. Organs 4. Organ systems Bodies of vertebrates are composed of different cell types
The Animal Body and Principles of Regulation Chapter 43 There are four levels of organization: 1. Cells 2. Tissues 3. Organs 4. Organ systems Bodies of vertebrates are composed of different cell types
1. In regard to the characteristics of connective tissue, which of the following is TRUE?
 Anatomy and Physiology Fall 2017: Exam I Form A Name: 1. In regard to the characteristics of connective tissue, which of the following is TRUE? a. Once formed the ground substance found in areolar CT is
Anatomy and Physiology Fall 2017: Exam I Form A Name: 1. In regard to the characteristics of connective tissue, which of the following is TRUE? a. Once formed the ground substance found in areolar CT is
CYTOLOGY & HISTOLOGY THE STUDY OF CELLS AND TISSUES
 NAME: DATE: PARTNER: CYTOLOGY & HISTOLOGY THE STUDY OF CELLS AND TISSUES For ease of study, multicellular animals are often examined at various levels of structural organization. Starting from the most
NAME: DATE: PARTNER: CYTOLOGY & HISTOLOGY THE STUDY OF CELLS AND TISSUES For ease of study, multicellular animals are often examined at various levels of structural organization. Starting from the most
Cells. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Cells Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Microscopy Methods of histology: Treat the tissue with a preservative (e.g. formaldehyde). Dissect the region of interest. Embed
Cells Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Microscopy Methods of histology: Treat the tissue with a preservative (e.g. formaldehyde). Dissect the region of interest. Embed
NATIONAL REVIEW COURSE. Cells, Tissues, and Membranes
 NATIONAL REVIEW COURSE Cells, Tissues, and Membranes I. Cell Types A. Prokaryote bacteria cells; a cell that does not have a nucleus in which to store its genetic material. B. Eukaryote plant or animal
NATIONAL REVIEW COURSE Cells, Tissues, and Membranes I. Cell Types A. Prokaryote bacteria cells; a cell that does not have a nucleus in which to store its genetic material. B. Eukaryote plant or animal
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology. Chapter 3. Cells and Tissues. Slides Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L.
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 3 Cells and Tissues Slides 3.1 3.19 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook Cells and Tissues Carry out all chemical
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 3 Cells and Tissues Slides 3.1 3.19 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook Cells and Tissues Carry out all chemical
NOTE: LOOK ON MY WEBSITE FOR THE MUSCLE LABELING POWER POINT/PDF Part I. Identify the parts of the neuron that are labeled below.
 Anatomy & Physiology Nervous System Part I 2/26/16 NOTE: LOOK ON MY WEBSITE FOR THE MUSCLE LABELING POWER POINT/PDF Part I. Identify the parts of the neuron that are labeled below. 1. 2. 3. 5. 4. 6. Part
Anatomy & Physiology Nervous System Part I 2/26/16 NOTE: LOOK ON MY WEBSITE FOR THE MUSCLE LABELING POWER POINT/PDF Part I. Identify the parts of the neuron that are labeled below. 1. 2. 3. 5. 4. 6. Part
The University of Jordan. Accreditation & Quality Assurance Center. Histology 1 for dentistry. COURSE Syllabus
 The University of Jordan Accreditation & Quality Assurance Center COURSE Syllabus Histology 1 for dentistry 1 Course title Histology-1 2 Course number 0542226 Credit hours (theory, practical) 3 (2 theory,
The University of Jordan Accreditation & Quality Assurance Center COURSE Syllabus Histology 1 for dentistry 1 Course title Histology-1 2 Course number 0542226 Credit hours (theory, practical) 3 (2 theory,
Tissues: - A group of cells similar in structure and performing a particular function forms a tissue.
 Plant Tissues Class- IX Tissues: - A group of cells similar in structure and performing a particular function forms a tissue. PLANT TISSUES ANIMAL TISSUES 1. Most of the plant tissues are Most of the tissues
Plant Tissues Class- IX Tissues: - A group of cells similar in structure and performing a particular function forms a tissue. PLANT TISSUES ANIMAL TISSUES 1. Most of the plant tissues are Most of the tissues
Neural Tissue. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres. Lone Star College North Harris Pearson Education, Inc.
 12 Neural Tissue PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the Nervous System The Nervous System Includes all neural tissue in the body
12 Neural Tissue PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the Nervous System The Nervous System Includes all neural tissue in the body
Cells - Chapter 3. Transport into and out of cells. The Cell Theory. Hooke (1665) Leeuwenhoek ( ) Simple Cells Cell Tutorial
 Cells - Chapter 3 Cells Alive Intro Video Transport into and out of cells Organization/Review Simple Cells Cell Tutorial http://www.wisc-online.com/objects/framz.asp?objid=ap11604 Cell Death http://www.whfreeman.com/kuby/content/anm/kb04an01.htm
Cells - Chapter 3 Cells Alive Intro Video Transport into and out of cells Organization/Review Simple Cells Cell Tutorial http://www.wisc-online.com/objects/framz.asp?objid=ap11604 Cell Death http://www.whfreeman.com/kuby/content/anm/kb04an01.htm
Cell Structure and Cell Cycle
 E X E R C I S E 4 Cell Structure and Cell Cycle Materials model or diagram of a cell compound microscopes and lens paper prepared slides of human skeletal muscle cells, pseudostratified ciliated columnar
E X E R C I S E 4 Cell Structure and Cell Cycle Materials model or diagram of a cell compound microscopes and lens paper prepared slides of human skeletal muscle cells, pseudostratified ciliated columnar
Chapter 6: A Tour of the Cell
 Chapter 6: A Tour of the Cell 1. The study of cells has been limited by their small size, and so they were not seen and described until 1665, when Robert Hooke first looked at dead cells from an oak tree.
Chapter 6: A Tour of the Cell 1. The study of cells has been limited by their small size, and so they were not seen and described until 1665, when Robert Hooke first looked at dead cells from an oak tree.
East Penn School District Curriculum and Instruction
 East Penn School District Curriculum and Instruction Curriculum for: Human Anatomy/Physiology, College Preparatory Course(s): CP Human Anatomy/Physiology Grades: 10-12 Department: Science Length of Period
East Penn School District Curriculum and Instruction Curriculum for: Human Anatomy/Physiology, College Preparatory Course(s): CP Human Anatomy/Physiology Grades: 10-12 Department: Science Length of Period
Biology 13A Lab #3: Cells and Tissues
 Biology 13A Lab #3: Cells and Tissues Lab #3 Table of Contents: Expected Learning Outcomes.... 28 Introduction...... 28 Activity 1: Eukaryotic Cell Structure... 29 Activity 2: Perspectives on Tissue Preparations.
Biology 13A Lab #3: Cells and Tissues Lab #3 Table of Contents: Expected Learning Outcomes.... 28 Introduction...... 28 Activity 1: Eukaryotic Cell Structure... 29 Activity 2: Perspectives on Tissue Preparations.
GENERALIZED ANIMAL CELL
 Cells are the basic organizational units of life GENERALIZED ANIMAL CELL A typical animal cell has a plasma membrane surrounding the nucleus and the cytoplasm. Plasma membrance is a phospholipid bilayer
Cells are the basic organizational units of life GENERALIZED ANIMAL CELL A typical animal cell has a plasma membrane surrounding the nucleus and the cytoplasm. Plasma membrance is a phospholipid bilayer
A. The Cell: The Basic Unit of Life. B. Prokaryotic Cells. D. Organelles that Process Information. E. Organelles that Process Energy
 The Organization of Cells A. The Cell: The Basic Unit of Life Lecture Series 4 The Organization of Cells B. Prokaryotic Cells C. Eukaryotic Cells D. Organelles that Process Information E. Organelles that
The Organization of Cells A. The Cell: The Basic Unit of Life Lecture Series 4 The Organization of Cells B. Prokaryotic Cells C. Eukaryotic Cells D. Organelles that Process Information E. Organelles that
Prelab Exercise 1. Cell structure
 Prelab Exercise 1 CELLS, EPITHELIA, GLANDS AND CONNECTIVE TISSUE Prelab guide: this will function as a review of material that will be important to your performance of the lab. The first lab will examine
Prelab Exercise 1 CELLS, EPITHELIA, GLANDS AND CONNECTIVE TISSUE Prelab guide: this will function as a review of material that will be important to your performance of the lab. The first lab will examine
PROPERTY OF ELSEVIER SAMPLE CONTENT - NOT FINAL. The Nervous System and Muscle
 The Nervous System and Muscle SECTION 2 2-1 Nernst Potential 2-2 Resting Membrane Potential 2-3 Axonal Action Potential 2-4 Neurons 2-5 Axonal Conduction 2-6 Morphology of Synapses 2-7 Chemical Synaptic
The Nervous System and Muscle SECTION 2 2-1 Nernst Potential 2-2 Resting Membrane Potential 2-3 Axonal Action Potential 2-4 Neurons 2-5 Axonal Conduction 2-6 Morphology of Synapses 2-7 Chemical Synaptic
Course Outcome Summary
 Course Information: Description: Instruction Level: 11-12 Total Credits: Prerequisites: Textbooks: Course Content: (SCANAT) Advanced Anatomy & Physiology A basic understanding of the human body is essential
Course Information: Description: Instruction Level: 11-12 Total Credits: Prerequisites: Textbooks: Course Content: (SCANAT) Advanced Anatomy & Physiology A basic understanding of the human body is essential
BIOL 225 Anatomy and Physiology I
 South Central College BIOL 225 Anatomy and Physiology I Course Outcome Summary Course Information Description Total Credits 4 Total Hours 80 Types of Instruction Instruction Type Anatomy and Physiology
South Central College BIOL 225 Anatomy and Physiology I Course Outcome Summary Course Information Description Total Credits 4 Total Hours 80 Types of Instruction Instruction Type Anatomy and Physiology
Chapter 3. Cells and Tissues. Mosby items and derived items 2010, 2006, 2002, 1997, 1992 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc.
 Chapter 3 Cells and Tissues Objectives Identify and discuss the basic structure and function of the three major components of a cell List and briefly discuss the functions of the primary cellular organelles
Chapter 3 Cells and Tissues Objectives Identify and discuss the basic structure and function of the three major components of a cell List and briefly discuss the functions of the primary cellular organelles
STRUCTURE OF THE CELL
 STRUCTURE OF THE CELL The cell is the smallest standard unit of the organisms. - nucleus - vital functions (growth, metabolism, irritability, movement,reproduction) - independent existence in certain conditions
STRUCTURE OF THE CELL The cell is the smallest standard unit of the organisms. - nucleus - vital functions (growth, metabolism, irritability, movement,reproduction) - independent existence in certain conditions
Composition of the Nervous System
 Composition of the Nervous System Brain -100 billion neurons and 1000-10000 synapses per neuron -20% of body s oxygen (94% used by grey matter) -15-25% of total blood supply -Composed of 10-12% lipids
Composition of the Nervous System Brain -100 billion neurons and 1000-10000 synapses per neuron -20% of body s oxygen (94% used by grey matter) -15-25% of total blood supply -Composed of 10-12% lipids
Zimmerman AP Biology CBHS South Name Chapter 7&8 Guided Reading Assignment 1) What is resolving power and why is it important in biology?
 Zimmerman AP Biology CBHS South Name Chapter 7&8 Guided Reading Assignment 1) What is resolving power and why is it important in biology? 2) How does an electron microscope work and what is the difference
Zimmerman AP Biology CBHS South Name Chapter 7&8 Guided Reading Assignment 1) What is resolving power and why is it important in biology? 2) How does an electron microscope work and what is the difference
A. The Cell: The Basic Unit of Life. B. Prokaryotic Cells. C. Eukaryotic Cells. D. Organelles that Process Information
 The Organization of Cells A. The Cell: The Basic Unit of Life Lecture Series 4 The Organization of Cells B. Prokaryotic Cells C. Eukaryotic Cells D. Organelles that Process Information E. Organelles that
The Organization of Cells A. The Cell: The Basic Unit of Life Lecture Series 4 The Organization of Cells B. Prokaryotic Cells C. Eukaryotic Cells D. Organelles that Process Information E. Organelles that
Neurochemistry 1. Nervous system is made of neurons & glia, as well as other cells. Santiago Ramon y Cajal Nobel Prize 1906
 Neurochemistry 1 Nervous system is made of neurons & glia, as well as other cells. Santiago Ramon y Cajal Nobel Prize 1906 How Many Neurons Do We Have? The human brain contains ~86 billion neurons and
Neurochemistry 1 Nervous system is made of neurons & glia, as well as other cells. Santiago Ramon y Cajal Nobel Prize 1906 How Many Neurons Do We Have? The human brain contains ~86 billion neurons and
Cells of the nervous system
 Cells of the nervous system There are approximately 100 billion neurons in the human brain There are about 100 times as many glial cells in the human brain Similar origin, different functions Other cells
Cells of the nervous system There are approximately 100 billion neurons in the human brain There are about 100 times as many glial cells in the human brain Similar origin, different functions Other cells
human cell Smallest living structure and constituent unit of human beings; the sizes and shapes of cells vary according to their function.
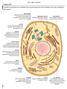 human cell CELL AND TISSUES Smallest living structure and constituent unit of human beings; the sizes and shapes of cells vary according to their function. Golgi apparatus Organelle composed of a series
human cell CELL AND TISSUES Smallest living structure and constituent unit of human beings; the sizes and shapes of cells vary according to their function. Golgi apparatus Organelle composed of a series
THE FUNDAMENTAL UNIT OF LIFE Robert Hooke (1665)observed honeycomb like dead cells in a thin slice of cork under microscope. He coined the term cell,
 THE FUNDAMENTAL UNIT OF LIFE Robert Hooke (1665)observed honeycomb like dead cells in a thin slice of cork under microscope. He coined the term cell, which means a small room or compartment. Anton Von
THE FUNDAMENTAL UNIT OF LIFE Robert Hooke (1665)observed honeycomb like dead cells in a thin slice of cork under microscope. He coined the term cell, which means a small room or compartment. Anton Von
4. Which of the following organelles digests waste using hydrolytic enzymes:
 Multichoice questions section. You must answer ALL questions. 1. A cell contains many organelles, each of which has a specific function. What is function of mitochondria? a) production of plasma membrane
Multichoice questions section. You must answer ALL questions. 1. A cell contains many organelles, each of which has a specific function. What is function of mitochondria? a) production of plasma membrane
Active movement Cancer. Cell. Cell inclusion Cytoplasm Diffusion Organelle Osmosis Passive movement Plasma membrane. Cell
 CHAPTER ONE INTRODUCTION TO ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Learning Objective At the end of this chapter, the students should be able to: - Define Anatomy and Physiology - Explain Homeostasis - Describe levels
CHAPTER ONE INTRODUCTION TO ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Learning Objective At the end of this chapter, the students should be able to: - Define Anatomy and Physiology - Explain Homeostasis - Describe levels
University of Jordan School of Medicine MD Program Curriculum
 University of Jordan School of Medicine MD Program Curriculum Course Title: General Histology Course number: 0502111 Credit Hours: 2 credits Academic Year Level: 1st year, 2nd semester 2016/2017 Course
University of Jordan School of Medicine MD Program Curriculum Course Title: General Histology Course number: 0502111 Credit Hours: 2 credits Academic Year Level: 1st year, 2nd semester 2016/2017 Course
Chapter 6 A Tour of the Cell
 Chapter 6 A Tour of the Cell The cell is the basic unit of life Although cells differ substantially from one another, they all share certain characteristics that reflect a common ancestry and remind us
Chapter 6 A Tour of the Cell The cell is the basic unit of life Although cells differ substantially from one another, they all share certain characteristics that reflect a common ancestry and remind us
Chapter 6: A Tour of the Cell
 AP Biology Reading Guide Fred and Theresa Holtzclaw Chapter 6: A Tour of the Cell Name Period Chapter 6: A Tour of the Cell Concept 6.1 To study cells, biologists use microscopes and the tools of biochemistry
AP Biology Reading Guide Fred and Theresa Holtzclaw Chapter 6: A Tour of the Cell Name Period Chapter 6: A Tour of the Cell Concept 6.1 To study cells, biologists use microscopes and the tools of biochemistry
According to the diagram, which of the following is NOT true?
 Instructions: Review Chapter 44 on muscular-skeletal systems and locomotion, and then complete the following Blackboard activity. This activity will introduce topics that will be covered in the next few
Instructions: Review Chapter 44 on muscular-skeletal systems and locomotion, and then complete the following Blackboard activity. This activity will introduce topics that will be covered in the next few
Our patient for the day...
 Muscles Ch.12 Our patient for the day... Name: Eddy Age: Newborn Whole-body muscle contractions No relaxation Severe difficulty breathing due to inadequate relaxation of breathing muscles Diagnosed with
Muscles Ch.12 Our patient for the day... Name: Eddy Age: Newborn Whole-body muscle contractions No relaxation Severe difficulty breathing due to inadequate relaxation of breathing muscles Diagnosed with
4.1 Cells are the Fundamental Units of Life. Cell Structure. Cells. Fundamental units of life Cell theory. Except possibly viruses.
 Cells 4.1 Cells are the Fundamental Units of Life Fundamental units of life Cell theory All living things are composed of one or more cells. The cell is the most basic unit of life. All cells come from
Cells 4.1 Cells are the Fundamental Units of Life Fundamental units of life Cell theory All living things are composed of one or more cells. The cell is the most basic unit of life. All cells come from
Bossier Parish Community College Master Syllabus. Course Prefix and Number: BLGY 230 Credits Hours: 3
 Bossier Parish Community College Master Syllabus Course Prefix and Number: BLGY 230 Credits Hours: 3 Course Title: Human Anatomy and Physiology I Course Prerequisites: Reading competency Textbook: OpenStax
Bossier Parish Community College Master Syllabus Course Prefix and Number: BLGY 230 Credits Hours: 3 Course Title: Human Anatomy and Physiology I Course Prerequisites: Reading competency Textbook: OpenStax
PHYSIOLOGY CHAPTER 9 MUSCLE TISSUE Fall 2016
 PHYSIOLOGY CHAPTER 9 MUSCLE TISSUE Fall 2016 2 Chapter 9 Muscles and Muscle Tissue Overview of Muscle Tissue types of muscle: are all prefixes for muscle Contractility all muscles cells can Smooth & skeletal
PHYSIOLOGY CHAPTER 9 MUSCLE TISSUE Fall 2016 2 Chapter 9 Muscles and Muscle Tissue Overview of Muscle Tissue types of muscle: are all prefixes for muscle Contractility all muscles cells can Smooth & skeletal
HSC HUMAN BODY SYSTEMS Midterm Exam October 17, 2001 Department of Anatomy and Cell Biology and Department of Physiology Time: 50 minutes 1.
 HSC 208.6 - HUMAN BODY SYSTEMS Midterm Exam October 17, 2001 Department of Anatomy and Cell Biology and Department of Physiology Time: 50 minutes 1. An organ: A. is the smallest independent unit of life
HSC 208.6 - HUMAN BODY SYSTEMS Midterm Exam October 17, 2001 Department of Anatomy and Cell Biology and Department of Physiology Time: 50 minutes 1. An organ: A. is the smallest independent unit of life
Cell Is the basic structural, functional, and biological unit of all known living organisms. Cells are the smallest unit of life and are often called
 The Cell Cell Is the basic structural, functional, and biological unit of all known living organisms. Cells are the smallest unit of life and are often called the "building blocks of life". The study of
The Cell Cell Is the basic structural, functional, and biological unit of all known living organisms. Cells are the smallest unit of life and are often called the "building blocks of life". The study of
UNIT 6 THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM
 UNIT 6 THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM I. Functions of Muscular System A. Produces Movement Internal vs. External «locomotion & manipulation «circulate blood & maintain blood pressure «move fluids, food, baby B. Maintaining
UNIT 6 THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM I. Functions of Muscular System A. Produces Movement Internal vs. External «locomotion & manipulation «circulate blood & maintain blood pressure «move fluids, food, baby B. Maintaining
Intro and Homeostasis
 Intro and Homeostasis Physiology - how the body works. Homeostasis - staying the same. Functional Types of Neurons Sensory (afferent - coming in) neurons: Detects the changes in the body. Informations
Intro and Homeostasis Physiology - how the body works. Homeostasis - staying the same. Functional Types of Neurons Sensory (afferent - coming in) neurons: Detects the changes in the body. Informations
Outline. Cell Structure and Function. Cell Theory Cell Size Prokaryotic Cells Eukaryotic Cells Organelles. Chapter 4
 Cell Structure and Function Chapter 4 Cell Theory Cell Size Prokaryotic Cells Eukaryotic Cells Organelles! Nucleus Outline! Endomembrane System! Cytoskeleton! Centrioles, Cilia, and Flagella 1 2 Cell Theory
Cell Structure and Function Chapter 4 Cell Theory Cell Size Prokaryotic Cells Eukaryotic Cells Organelles! Nucleus Outline! Endomembrane System! Cytoskeleton! Centrioles, Cilia, and Flagella 1 2 Cell Theory
INTRODUCTION COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL
 I INTRODUCTION COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL 1 The Structural and Biochemical Hierarchy of a Cell and a Human There is no magician s mantle to compare with skin in its diverse roles of waterproof overcoat, sunshade,
I INTRODUCTION COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL 1 The Structural and Biochemical Hierarchy of a Cell and a Human There is no magician s mantle to compare with skin in its diverse roles of waterproof overcoat, sunshade,
Cell Theory. Cell Structure. Chapter 4. Cell is basic unit of life. Cells discovered in 1665 by Robert Hooke
 Cell Structure Chapter 4 Cell is basic unit of life Cell Theory Cells discovered in 1665 by Robert Hooke Early cell studies conducted by - Mathias Schleiden (1838) - Theodor Schwann (1839) Schleiden &
Cell Structure Chapter 4 Cell is basic unit of life Cell Theory Cells discovered in 1665 by Robert Hooke Early cell studies conducted by - Mathias Schleiden (1838) - Theodor Schwann (1839) Schleiden &
O.k., Now Starts the Good Stuff (Part II) Eukaryotic Cell Structure and Function
 O.k., Now Starts the Good Stuff (Part II) Eukaryotic Cell Structure and Function Eukaryotic Cells These cells have membrane-bound structures called organelles. Cell processes occur in these organelles.
O.k., Now Starts the Good Stuff (Part II) Eukaryotic Cell Structure and Function Eukaryotic Cells These cells have membrane-bound structures called organelles. Cell processes occur in these organelles.
SHEET. Name: Class: Date: the sentence: write highest, lowest, higher, lower. level of organization is the organism; the
 1 1 Label the levels of organization Then complete the sentence: write highest, lowest, higher, lower The level of organization is the organism; the level of organization is the cell Tissues are a organs,
1 1 Label the levels of organization Then complete the sentence: write highest, lowest, higher, lower The level of organization is the organism; the level of organization is the cell Tissues are a organs,
Nervous System Organization
 The Nervous System Nervous System Organization Receptors respond to stimuli Sensory receptors detect the stimulus Motor effectors respond to stimulus Nervous system divisions Central nervous system Command
The Nervous System Nervous System Organization Receptors respond to stimuli Sensory receptors detect the stimulus Motor effectors respond to stimulus Nervous system divisions Central nervous system Command
Bio 111 Study Guide Chapter 6 Tour of the Cell
 Bio 111 Study Guide Chapter 6 Tour of the Cell BEFORE CLASS: Reading: Read the whole chapter from p. 93-121, mostly skimming Concept 6.1 on microscopy. Figure 6.8 on pp. 100-101 is really helpful in showing
Bio 111 Study Guide Chapter 6 Tour of the Cell BEFORE CLASS: Reading: Read the whole chapter from p. 93-121, mostly skimming Concept 6.1 on microscopy. Figure 6.8 on pp. 100-101 is really helpful in showing
Lecture Series 3 The Organization of Cells
 Lecture Series 3 The Organization of Cells Reading Assignments Read Chapter 15 Endomembrane System Read Chapter 17 Cytoskeleton A. The Cell: The Basic Unit of Life Cell Theory: All cells come from preexisting
Lecture Series 3 The Organization of Cells Reading Assignments Read Chapter 15 Endomembrane System Read Chapter 17 Cytoskeleton A. The Cell: The Basic Unit of Life Cell Theory: All cells come from preexisting
Reading Assignments. A. The Cell: The Basic Unit of Life. Lecture Series 3 The Organization of Cells
 Lecture Series 3 The Organization of Cells Reading Assignments Read Chapter 15 Endomembrane System Read Chapter 17 Cytoskeleton A. The Cell: The Basic Unit of Life Cell Theory: All cells come from preexisting
Lecture Series 3 The Organization of Cells Reading Assignments Read Chapter 15 Endomembrane System Read Chapter 17 Cytoskeleton A. The Cell: The Basic Unit of Life Cell Theory: All cells come from preexisting
Dendrites - receives information from other neuron cells - input receivers.
 The Nerve Tissue Neuron - the nerve cell Dendrites - receives information from other neuron cells - input receivers. Cell body - includes usual parts of the organelles of a cell (nucleus, mitochondria)
The Nerve Tissue Neuron - the nerve cell Dendrites - receives information from other neuron cells - input receivers. Cell body - includes usual parts of the organelles of a cell (nucleus, mitochondria)
Dr. Dina A. A. Hassan Associate Professor, Pharmacology
 Cytology Dr. Dina A. A. Hassan Associate Professor, Pharmacology Email: da.hassan@psau.edu.sa Cells All living things are made up of cells Basic building blocks of life It is the smallest functional and
Cytology Dr. Dina A. A. Hassan Associate Professor, Pharmacology Email: da.hassan@psau.edu.sa Cells All living things are made up of cells Basic building blocks of life It is the smallest functional and
Components of a functional cell. Boundary-membrane Cytoplasm: Cytosol (soluble components) & particulates DNA-information Ribosomes-protein synthesis
 Cell (Outline) - Components of a functional cell - Major Events in the History of Earth: abiotic and biotic phases; anaerobic and aerobic atmosphere - Prokaryotic cells impact on the biosphere - Origin
Cell (Outline) - Components of a functional cell - Major Events in the History of Earth: abiotic and biotic phases; anaerobic and aerobic atmosphere - Prokaryotic cells impact on the biosphere - Origin
Unit 2: Cells Guided Reading Questions (55 pts total)
 Name: AP Biology Biology, Campbell and Reece, 7th Edition Adapted from chapter reading guides originally created by Lynn Miriello Chapter 6 A Tour of the Cell Unit 2: Cells Guided Reading Questions (55
Name: AP Biology Biology, Campbell and Reece, 7th Edition Adapted from chapter reading guides originally created by Lynn Miriello Chapter 6 A Tour of the Cell Unit 2: Cells Guided Reading Questions (55
CUMBERLAND COUNTY SCHOOL DISTRICT BENCHMARK ASSESSMENT CURRICULUM PACING GUIDE Subject: Anatomy & Physiology Grade: 11-12
 Benchmark Assessment 1 Instructional Timeline: 8 weeks Topic(s): Introduction, Tissues, Integumentary System Describe the major components and functions of physiological systems, including skeletal, muscle,
Benchmark Assessment 1 Instructional Timeline: 8 weeks Topic(s): Introduction, Tissues, Integumentary System Describe the major components and functions of physiological systems, including skeletal, muscle,
Name: Class: Date: Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Class: Date: Anatomy Final Exam Review: This review is an overview, and does not represent a complete copy of the final exam, nor is it an exhaustive listing of topics from this year. Directions: Complete
Class: Date: Anatomy Final Exam Review: This review is an overview, and does not represent a complete copy of the final exam, nor is it an exhaustive listing of topics from this year. Directions: Complete
Nervous System Organization
 The Nervous System Chapter 44 Nervous System Organization All animals must be able to respond to environmental stimuli -Sensory receptors = Detect stimulus -Motor effectors = Respond to it -The nervous
The Nervous System Chapter 44 Nervous System Organization All animals must be able to respond to environmental stimuli -Sensory receptors = Detect stimulus -Motor effectors = Respond to it -The nervous
Cells: The Working Units of Life
 4 Cells: The Working Units of Life Chapter 4 Cells: The Working Units of Life Key Concepts 4.1 Cells Provide Compartments for Biochemical Reactions 4.2 Prokaryotic Cells Do Not Have a Nucleus 4.3 Eukaryotic
4 Cells: The Working Units of Life Chapter 4 Cells: The Working Units of Life Key Concepts 4.1 Cells Provide Compartments for Biochemical Reactions 4.2 Prokaryotic Cells Do Not Have a Nucleus 4.3 Eukaryotic
TABLE OF CONTENTS. Foundations of Chemistry Cells and their Membranes Homeostasis and Inheritance Bones and Joints
 TABLE OF CONTENTS Week 1 Week 2 Week 3 Week 4 Week 5 Week 6 Week 7 Week 8 Week 9 Week 10 Week 11 Foundations of Chemistry Cells and their Membranes Homeostasis and Inheritance Bones and Joints Nerve Cells
TABLE OF CONTENTS Week 1 Week 2 Week 3 Week 4 Week 5 Week 6 Week 7 Week 8 Week 9 Week 10 Week 11 Foundations of Chemistry Cells and their Membranes Homeostasis and Inheritance Bones and Joints Nerve Cells
Human biology Cells: The Basic Units of Life. Dr. Rawaa Salim Hameed
 Human biology Cells: The Basic Units of Life Dr. Rawaa Salim Hameed Reference Text book of human biology by John Kenneth Inglis 3 rd Ed (1985) Cells: The Basic Units of Life Cell theory Cell theory consists
Human biology Cells: The Basic Units of Life Dr. Rawaa Salim Hameed Reference Text book of human biology by John Kenneth Inglis 3 rd Ed (1985) Cells: The Basic Units of Life Cell theory Cell theory consists
Chapter 4 A Tour of the Cell*
 Chapter 4 A Tour of the Cell* *Lecture notes are to be used as a study guide only and do not represent the comprehensive information you will need to know for the exams. The Fundamental Units of Life Cells
Chapter 4 A Tour of the Cell* *Lecture notes are to be used as a study guide only and do not represent the comprehensive information you will need to know for the exams. The Fundamental Units of Life Cells
SCIENCE: ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY
 SCIENCE: ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY END-OF-COURSE EXAM GRADE 9-12 YEAR 17 18 ASSESSMENT BLUEPRINT Purpose Statement Anatomy and Physiology The Anatomy and Physiology End-of-Course (EOC) exam is intended to
SCIENCE: ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY END-OF-COURSE EXAM GRADE 9-12 YEAR 17 18 ASSESSMENT BLUEPRINT Purpose Statement Anatomy and Physiology The Anatomy and Physiology End-of-Course (EOC) exam is intended to
Chapter 4 Active Reading Guide A Tour of the Cell
 Name: AP Biology Mr. Croft Chapter 4 Active Reading Guide A Tour of the Cell Section 1 1. The study of cells has been limited by their small size, and so they were not seen and described until 1665, when
Name: AP Biology Mr. Croft Chapter 4 Active Reading Guide A Tour of the Cell Section 1 1. The study of cells has been limited by their small size, and so they were not seen and described until 1665, when
Muscle tissue. Types. Functions. Cardiac, Smooth, and Skeletal
 Types Cardiac, Smooth, and Skeletal Functions movements posture and body position Support soft tissues Guard openings body temperature nutrient reserves Muscle tissue Special Characteristics of Muscle
Types Cardiac, Smooth, and Skeletal Functions movements posture and body position Support soft tissues Guard openings body temperature nutrient reserves Muscle tissue Special Characteristics of Muscle
General A&P Cell Labs - Cellular Anatomy & Division (Mitosis) Pre-Lab Guide
 1 General A&P Cell Labs - Cellular Anatomy & Division (Mitosis) Pre-Lab AWalk-About@ Guide Have someone in your group read the following out loud, while the others read along: In this "Walk About", we
1 General A&P Cell Labs - Cellular Anatomy & Division (Mitosis) Pre-Lab AWalk-About@ Guide Have someone in your group read the following out loud, while the others read along: In this "Walk About", we
BIOL 225 Anatomy and Physiology I
 South Central College BIOL 225 Anatomy and Physiology I Course Information Description Anatomy and Physiology I is an introduction to the structure and function of the human body under normal and abnormal
South Central College BIOL 225 Anatomy and Physiology I Course Information Description Anatomy and Physiology I is an introduction to the structure and function of the human body under normal and abnormal
AVICENNA INTERNATIONAL COLLEGE
 AVICENNA INTERNATIONAL COLLEGE BIOLOGICAL SCIENCES ACADEMIC CALENDAR LECTURE SYLLABUS CELL & MOLECULAR BIOLOGY 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Characteristics of Living Organisms, Levels of Organization in Biology (Introduction
AVICENNA INTERNATIONAL COLLEGE BIOLOGICAL SCIENCES ACADEMIC CALENDAR LECTURE SYLLABUS CELL & MOLECULAR BIOLOGY 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Characteristics of Living Organisms, Levels of Organization in Biology (Introduction
Introduction to the Human Body. Cells. Body Functions. Tissues. Organs. Systems. Body Functions & Life Process
 complex functions for the body. Ten major systems compose the human body: Introduction to the Human Body Human beings are arguably the most complex organisms on this planet. Imagine billions of microscopic
complex functions for the body. Ten major systems compose the human body: Introduction to the Human Body Human beings are arguably the most complex organisms on this planet. Imagine billions of microscopic
1. Which of the cellular components listed above are part of the endomembrane system and surrounded by a double membrane?
 Anatomy and Physiology 141 Fall 2014: Exam IA Name: Use the following list to answer Question 1. 1 Golgi apparatus 2 Nuclear membrane 3 Mitochondria 4 Rough ER 5 Smooth ER 1. Which of the cellular components
Anatomy and Physiology 141 Fall 2014: Exam IA Name: Use the following list to answer Question 1. 1 Golgi apparatus 2 Nuclear membrane 3 Mitochondria 4 Rough ER 5 Smooth ER 1. Which of the cellular components
Amneh Auben. Abdulrahman Jabr. Diala Abu-Hassan
 21 Amneh Auben Abdulrahman Jabr Diala Abu-Hassan Matrix polysaccharides Extracellular matrix (ECM): It s a collection of components that fills the spaces outside the cell or between the cells. ---------
21 Amneh Auben Abdulrahman Jabr Diala Abu-Hassan Matrix polysaccharides Extracellular matrix (ECM): It s a collection of components that fills the spaces outside the cell or between the cells. ---------
The Cell. C h a p t e r. PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas
 C h a p t e r 2 The Cell PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings Introduction
C h a p t e r 2 The Cell PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings Introduction
Concept 6.1 To study cells, biologists use microscopes and the tools of biochemistry
 Name Period Chapter 6: A Tour of the Cell Concept 6.1 To study cells, biologists use microscopes and the tools of biochemistry 1. The study of cells has been limited by their small size, and so they were
Name Period Chapter 6: A Tour of the Cell Concept 6.1 To study cells, biologists use microscopes and the tools of biochemistry 1. The study of cells has been limited by their small size, and so they were
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which body fluid compartment contains high levels of K +, large anions, and proteins?
Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which body fluid compartment contains high levels of K +, large anions, and proteins?
Cell (Learning Objectives)
 Cell (Learning Objectives) 1. Understand & describe the basic components necessary for a functional cell. 2. Review the order of appearance of cells on earth and explain the endosymbiotic theory. 3. Compare
Cell (Learning Objectives) 1. Understand & describe the basic components necessary for a functional cell. 2. Review the order of appearance of cells on earth and explain the endosymbiotic theory. 3. Compare
BIO 210: Anatomy and Physiology Text: Fundamentals of Anatomy and Physiology 9ed. Chapter 12 NEURAL TISSUE
 NAME COURSE BIO 210: Anatomy and Physiology Text: Fundamentals of Anatomy and Physiology 9ed. Chapter 12 NEURAL TISSUE Like a telephone switchboard, the nervous system directs a countless number of incoming
NAME COURSE BIO 210: Anatomy and Physiology Text: Fundamentals of Anatomy and Physiology 9ed. Chapter 12 NEURAL TISSUE Like a telephone switchboard, the nervous system directs a countless number of incoming
BIOL Anatomy and Physiology I ( version L )
 BIOL 2113 - Anatomy and Physiology I ( version 213L ) Course Title Course Development Learning Support Anatomy and Physiology I Standard No Course Description Introduces the anatomy and physiology of the
BIOL 2113 - Anatomy and Physiology I ( version 213L ) Course Title Course Development Learning Support Anatomy and Physiology I Standard No Course Description Introduces the anatomy and physiology of the
Cell Structure. Chapter 4. Cell Theory. Cells were discovered in 1665 by Robert Hooke.
 Cell Structure Chapter 4 Cell Theory Cells were discovered in 1665 by Robert Hooke. Early studies of cells were conducted by - Mathias Schleiden (1838) - Theodor Schwann (1839) Schleiden and Schwann proposed
Cell Structure Chapter 4 Cell Theory Cells were discovered in 1665 by Robert Hooke. Early studies of cells were conducted by - Mathias Schleiden (1838) - Theodor Schwann (1839) Schleiden and Schwann proposed
Muscles and Muscle Tissue: Part A
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College CHAPTER 9 Muscles and Muscle Tissue: Part A Warm Up 12/12/16 Describe the major differences between cardiac, skeletal and smooth
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College CHAPTER 9 Muscles and Muscle Tissue: Part A Warm Up 12/12/16 Describe the major differences between cardiac, skeletal and smooth
EASTERN ARIZONA COLLEGE Human Anatomy and Physiology I
 EASTERN ARIZONA COLLEGE Human Anatomy and Physiology I Course Design 2015-2016 Course Information Division Science Course Number BIO 201 (SUN# BIO 2201) Title Human Anatomy and Physiology I Credits 4 Developed
EASTERN ARIZONA COLLEGE Human Anatomy and Physiology I Course Design 2015-2016 Course Information Division Science Course Number BIO 201 (SUN# BIO 2201) Title Human Anatomy and Physiology I Credits 4 Developed
Unit 2: Cells Guided Reading Questions (60 pts total)
 Name: AP Biology Biology, Campbell and Reece, 7th Edition Adapted from chapter reading guides originally created by Lynn Miriello Chapter 6 A Tour of the Cell Unit 2: Cells Guided Reading Questions (60
Name: AP Biology Biology, Campbell and Reece, 7th Edition Adapted from chapter reading guides originally created by Lynn Miriello Chapter 6 A Tour of the Cell Unit 2: Cells Guided Reading Questions (60
Lecture Series 3 The Organization of Cells
 Lecture Series 3 The Organization of Cells Reading Assignments Read Chapter 15 Endomembrane System Read Chapter 17 Cytoskeleton A. The Cell: The Basic Unit of Life Cell Theory: All cells come from preexisting
Lecture Series 3 The Organization of Cells Reading Assignments Read Chapter 15 Endomembrane System Read Chapter 17 Cytoskeleton A. The Cell: The Basic Unit of Life Cell Theory: All cells come from preexisting
Neurons and Nervous Systems
 34 Neurons and Nervous Systems Concept 34.1 Nervous Systems Consist of Neurons and Glia Nervous systems have two categories of cells: Neurons, or nerve cells, are excitable they generate and transmit electrical
34 Neurons and Nervous Systems Concept 34.1 Nervous Systems Consist of Neurons and Glia Nervous systems have two categories of cells: Neurons, or nerve cells, are excitable they generate and transmit electrical
Chapter 4: Cells: The Working Units of Life
 Name Period Chapter 4: Cells: The Working Units of Life 1. What are the three critical components of the cell theory? 2. What are the two important conceptual implications of the cell theory? 3. Which
Name Period Chapter 4: Cells: The Working Units of Life 1. What are the three critical components of the cell theory? 2. What are the two important conceptual implications of the cell theory? 3. Which
Biology: Life on Earth
 Teresa Audesirk Gerald Audesirk Bruce E. Byers Biology: Life on Earth Eighth Edition Lecture for Chapter 4 Cell Structure and Function Copyright 2008 Pearson Prentice Hall, Inc. Chapter 4 Outline 4.1 What
Teresa Audesirk Gerald Audesirk Bruce E. Byers Biology: Life on Earth Eighth Edition Lecture for Chapter 4 Cell Structure and Function Copyright 2008 Pearson Prentice Hall, Inc. Chapter 4 Outline 4.1 What
C5 Histology / MC3. What are the four primary tissue types? All tissue consist of cells and stuff between the cells.
 C5 Histology / MC3 What are the four primary tissue types? All tissue consist of cells and stuff between the cells. What is the stuff between the cells called? What are the components of this stuff? Why
C5 Histology / MC3 What are the four primary tissue types? All tissue consist of cells and stuff between the cells. What is the stuff between the cells called? What are the components of this stuff? Why
CHAPTER 3. Cell Structure and Genetic Control. Chapter 3 Outline
 CHAPTER 3 Cell Structure and Genetic Control Chapter 3 Outline Plasma Membrane Cytoplasm and Its Organelles Cell Nucleus and Gene Expression Protein Synthesis and Secretion DNA Synthesis and Cell Division
CHAPTER 3 Cell Structure and Genetic Control Chapter 3 Outline Plasma Membrane Cytoplasm and Its Organelles Cell Nucleus and Gene Expression Protein Synthesis and Secretion DNA Synthesis and Cell Division
A cell is chemical system that is able to maintain its structure and reproduce. Cells are the fundamental unit of life. All living things are cells
 Cell Biology A cell is chemical system that is able to maintain its structure and reproduce. Cells are the fundamental unit of life. All living things are cells or composed of cells. 1 The interior contents
Cell Biology A cell is chemical system that is able to maintain its structure and reproduce. Cells are the fundamental unit of life. All living things are cells or composed of cells. 1 The interior contents
1. Know the hierarchy of organization: chemical, cellular, tissue, organ, organ system, organismal
 Anatomy and Physiology Anatomical Organization 1. Know the hierarchy of organization: chemical, cellular, tissue, organ, organ system, organismal 2. Be able to identify and describe the necessary life
Anatomy and Physiology Anatomical Organization 1. Know the hierarchy of organization: chemical, cellular, tissue, organ, organ system, organismal 2. Be able to identify and describe the necessary life
Cell Structure. Chapter 4
 Cell Structure Chapter 4 Cell Theory Cells were discovered in 1665 by Robert Hooke. Early studies of cells were conducted by - Mathias Schleiden (1838) - Theodor Schwann (1839) Schleiden and Schwann proposed
Cell Structure Chapter 4 Cell Theory Cells were discovered in 1665 by Robert Hooke. Early studies of cells were conducted by - Mathias Schleiden (1838) - Theodor Schwann (1839) Schleiden and Schwann proposed
122-Biology Guide-5thPass 12/06/14. Topic 1 An overview of the topic
 Topic 1 http://bioichiban.blogspot.com Cellular Functions 1.1 The eukaryotic cell* An overview of the topic Key idea 1: Cell Organelles Key idea 2: Plasma Membrane Key idea 3: Transport Across Membrane
Topic 1 http://bioichiban.blogspot.com Cellular Functions 1.1 The eukaryotic cell* An overview of the topic Key idea 1: Cell Organelles Key idea 2: Plasma Membrane Key idea 3: Transport Across Membrane
Architectural Pattern of an animal. Chapter 9
 Architectural Pattern of an animal Chapter 9 What is an animal? Levels of organization and organismal complexity 5 major levels of complexity Unicellular Metazoan? Tissue Organ Organ systems Levels of
Architectural Pattern of an animal Chapter 9 What is an animal? Levels of organization and organismal complexity 5 major levels of complexity Unicellular Metazoan? Tissue Organ Organ systems Levels of
Zimmerman AP Biology CBHS South Name Chapter 7&8 Guided Reading Assignment 1) What is resolving power and why is it important in biology?
 Zimmerman AP Biology CBHS South Name Chapter 7&8 Guided Reading Assignment 1) What is resolving power and why is it important in biology? 2) How does an electron microscope work and what is the difference
Zimmerman AP Biology CBHS South Name Chapter 7&8 Guided Reading Assignment 1) What is resolving power and why is it important in biology? 2) How does an electron microscope work and what is the difference
Nervous system. 3 Basic functions of the nervous system !!!! !!! 1-Sensory. 2-Integration. 3-Motor
 Nervous system 3 Basic functions of the nervous system 1-Sensory 2-Integration 3-Motor I. Central Nervous System (CNS) Brain Spinal Cord I. Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) 2) Afferent towards afferent
Nervous system 3 Basic functions of the nervous system 1-Sensory 2-Integration 3-Motor I. Central Nervous System (CNS) Brain Spinal Cord I. Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) 2) Afferent towards afferent
Overview: The Fundamental Units of Life Concept 6.1: Biologists use microscopes and the tools of biochemistry to study cells Microscopy
 Overview: The Fundamental Units of Life All organisms are made of cells The cell is the simplest collection of matter that can be alive Cell structure is correlated to cellular function All cells are related
Overview: The Fundamental Units of Life All organisms are made of cells The cell is the simplest collection of matter that can be alive Cell structure is correlated to cellular function All cells are related
History of Cell Theory. Organization of Life
 History of Cell Theory Robert Hooke first observed cells while examining cork under the microscope (mid- 1600 s) Anton van Leeuwenhoek first observed microscopic organisms in pond water, as well as blood
History of Cell Theory Robert Hooke first observed cells while examining cork under the microscope (mid- 1600 s) Anton van Leeuwenhoek first observed microscopic organisms in pond water, as well as blood
BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 19: Eukaryotic genes & Multicellular Organisms. Gene Families
 BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 19: Eukaryotic genes & Multicellular Organisms http://compbio.uchsc.edu/hunter/bio5099 Larry.Hunter@uchsc.edu Gene Families In metazoans,
BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 19: Eukaryotic genes & Multicellular Organisms http://compbio.uchsc.edu/hunter/bio5099 Larry.Hunter@uchsc.edu Gene Families In metazoans,
