QUESTIONS TO MODULE "CYTOLOGY"
|
|
|
- Maude Simon
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 QUESTIONS TO MODULE "CYTOLOGY" 1. The structure of the Plasmolemma. 2. Characteristic of receptive and transport functions of the plasmolemma. 3. The structure of intercellular contacts: Simple contact, Zonular occludentes, Synapse. 4. The structure of intercellular contacts: Desmosome, Zonular adherents, Gap junctions. 5. Characteristic and structure of symplast and sincytium. 6. The structure and functions of Mitochondria. 7. The structure and functions of Lysosomes and Peroxisomes. 8. The structure and functions of Agranular Endoplasmic Reticulum. 9. The structure and functions of Granular Endoplasmic Reticulum and Ribosomes. 10. The structure and functions of Golgi Bodies. 11. The structure and functions of Microfilaments and Microtubules. 12. The structure and functions of Cytocentrum (centrosome). 13. The structure and functions of Cilia and Flagella. 14. Name of types Inclusions and their functions. 15. Reproduction of cells definition. 16. Cell cycle definition. 17. Stages of interphase, characteristic features. 18. Stages of mitosis. 19. Characteristic of polyploidy (endoreduplication). 20. Meiosis peculiarities. 21. Aging and death of cells. Necrosis and apoptosis.
2 QUESTIONS TO MODULE "EMBRIOLOGY" 1. Main features of Female sex cell. 2. Oocytes types. 3. Main features of the male sex cell. 4. Fertilazation, stages and biological significance. 5. Cleavage definition. Different modes of cleavage. Structure of blastula. 6. The cleavage peculiarities in the human. Chronology of the process. Structure of blastocyst. 7. Implantation site, significance and stages. 8. Vitelotrophic, histiotrophic and haematotrophic embryogenesis periods. 9. Gastrulation definition and attribute. Ways of gastrulation. 10. Human gastrulation early stage. Manners of germ layers and extraembryonal organs formation. 11. Gastrulation later stage. 12. Formation and functions of the primary streak. 13. Differentiation of mesoderm. 14. Amniotic tunic, its origin, structural components and functions. 15. The origin, structural components and functions of yolk sac. 16. Allantois origin, structure and functions. 17. Chorion formation and functions. 18. Structure and functions primary, secondary and tertiary villi of chorion. 19. Placenta definition. Structure of deciduous tunic. 20. Placenta definition. Structure of fetal part of placenta. 21. Structure and functions of placental barrier. 22. Structure and functions of umbilical cord.
3 MODUL OF THE TISSUES. 1. The formation of tissues (ontogenesis). 2. Structure and functional features of the epithelial tissues. 3. Structural - functional features of Simple epithelium (flat, cuboidal and columnar). 4. Structure of pseudostratified epithelium. 5. Structure of the stratified squamous nonkeratinized epithelium. 7. Structure of the stratified squamous keratinized epithelium. 8. Structure of the transitional epithelium. 9. Characteristic stages of secretion. 10. Characteristic ways of secretion. 11. Classification of glands. Characteristic of exocrine glands. 12. The common characteristic of blood. The blood functions. 13. The structure and functions of Erythrocytes. 14. The structural - functional features of Leucocytes. Leukocytic formula. 15. The structure and functions of Neutrophils. 16. The structure and functions of Eosinophils. 17. The structure and functions of Basophils. 18. The structure and functions of Monocytes. 19. The structure and functions of Lymphocytes. 20. The structure and functions of Thrombocytes. 21. The common characteristic of Loose Fibrous Connective tissue. 22. The structure and functions of Fibroblasts. 23. The structure and functions of Tissue Basophiles (Mast cells). 24. The structure and functions of Macrophages (Nistiocytes). 25. The structure and functions of Plasmatic cells. 26. The structure and functions of Adipose cells (Lipocytes). 27. The structure and functions of Pigmentocytes. 28. The structure and functions of Adventitial cells. 29. The structure of the intercellular substance of Connective tissue. 30. The structure and functions of collagenous fibers, elastic fibers, reticular fibers. 31. The common characteristic of Dense fibrous connective tissues. 32. The structure and functions of Tendons. 33. The structural - functional features of different types of Adipose tissue. 36. The common characteristic of Reticular tissue. 37. The common characteristic of Pigment tissue. 38. The common characteristic of Mucose tissue.
4 39. The structure of Cartilage Tissue. 40. The structure and functions of Chondroblasts. 41. The structure and functions of Chondrocytes. 42. Localization and structure of Hyaline cartilage. 43. Localization and structure of Elastic cartilage. 44. Localization and structure of Fibro cartilage. 45. Histogenesis of Cartilage Tissue. Growth and regeneration. 46. The structure of Bone (Osseous) Tissue. Classification of Osseous Tissue. 47. The structure and functions of Osteoblasts. 48. The structure and functions of Osteocytes. 49. The structure and functions of Osteoclasts. 50. Tubular bone structure. 51. Characteristic of direct osteogenesis (development from mesenchyma). 52. Characteristic of indirect osteogenesis. 53. Growth and regeneration. 54. The structure of Skeletal Muscle tissue. 55. The structure of Sarcomere. 56. The structure of Thick filament. 57. The structure of Thin filament. 58. The structure of Sarcoplasmic reticulum. 59. Mechanism of muscle contraction. 60. The structure of Smooth Muscle tissue. 61. Contraction of Smooth Muscle tissue. 62. The structure of Nervous tissue. The structure of Neurons. 63. Morphological and functional classification of Neurons. 64. The structure of Reflex arch. 65. The structure of Synapses. 66. The structure and functions of the Unmyelinated nerve fibers. 67. The structure and functions of the Myelinated nerve fibers. 69. The structure and functions of Macroglia. 70. The structure and functions of Microglia. 71. Common characteristic of Receptors. 72. The structure of free and non-free nerve endings.
5 QUESTIONS OF MODUL "Nervous system. Sense organs. Cardiovascular system. Organs of Hemopoiesis and Immune protection. Endocrine system." 1. Cytoarchitectonics of the hemisphere cortex of Brain. 2. The structure of the Ganglion layer of Cerebellum. 3. The structure of the Molecular layer of Cerebellum. 4. The structure of the Granular layer of Cerebellum. 5. The structure of the Cerebro-spinal ganglion. 6. The structure of the Spinal Cord. 7. The structure and functions of the Pyramidal cells. 8. The structure organization of the excitatory system of Cerebellum. 9. The structure organization of the inhibitory system of Cerebellum. 10. Classification of the Sense organs. 11. The structure and functions of the Rods. 12. The structure and functions of the Cones. 13. The structure of the Fibrous tunic of Eye. 14. The structure of the Vascular tunic of Eye. 15. The structure and functions of I V layers of Retina. 16. The structure and functions of VI - X layers of Retina. 17. The structure of the Internal Ear. 18. The structure of the Cochlear Duct. 19. The structure of the Spiral organ of Corti. 20. Arteries: classification, structure and functions. 21. Veins: classification, structure. The peculiarities of veins wall structure. 22. Capillaries: classification, structure. 23. Arteriovenular anastomoses: classification, structure. 24. The structure and functions of the Heart. 25. The structure and functions of the Red Bone Marrow. 26. The structure and functions of the Thymus. Hemato-Thymic barrier. 27. The structure and functions of the B-dependent zone of Lymph Nodes. 28. The structure and functions of the T-dependent zone of Lymph Nodes. 29. The structure and functions of the Spleen. 30. The structure and functions of the anterior portion of Hypothalamus. 31. The structure and functions of the middle and posterior portions of Hypothalamus. 32. The structure of the Hypophysis. 33. The functions of hormones of the Hypophisis. 34. The structure and functions of the Epiphysis. 35. Structure - functional organization of the Thyroid Gland. 36. Secretory cycle thyrocyti. 37. The structure and functions of the Parathyroid Gland. 38. Embryogenesis and structure of the Adrenal Glands. 39. The functions of hormones of the Adrenal Glands.
Organization of Vertebrate Body. Organization of Vertebrate Body
 The Animal Body and Principles of Regulation Chapter 43 There are four levels of organization: 1. Cells 2. Tissues 3. Organs 4. Organ systems Bodies of vertebrates are composed of different cell types
The Animal Body and Principles of Regulation Chapter 43 There are four levels of organization: 1. Cells 2. Tissues 3. Organs 4. Organ systems Bodies of vertebrates are composed of different cell types
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology. Chapter 3. Cells and Tissues. Slides Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L.
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 3 Cells and Tissues Slides 3.1 3.19 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook Cells and Tissues Carry out all chemical
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 3 Cells and Tissues Slides 3.1 3.19 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook Cells and Tissues Carry out all chemical
1. In regard to the characteristics of connective tissue, which of the following is TRUE?
 Anatomy and Physiology Fall 2017: Exam I Form A Name: 1. In regard to the characteristics of connective tissue, which of the following is TRUE? a. Once formed the ground substance found in areolar CT is
Anatomy and Physiology Fall 2017: Exam I Form A Name: 1. In regard to the characteristics of connective tissue, which of the following is TRUE? a. Once formed the ground substance found in areolar CT is
BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 19: Eukaryotic genes & Multicellular Organisms. Gene Families
 BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 19: Eukaryotic genes & Multicellular Organisms http://compbio.uchsc.edu/hunter/bio5099 Larry.Hunter@uchsc.edu Gene Families In metazoans,
BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 19: Eukaryotic genes & Multicellular Organisms http://compbio.uchsc.edu/hunter/bio5099 Larry.Hunter@uchsc.edu Gene Families In metazoans,
CYTOLOGY & HISTOLOGY THE STUDY OF CELLS AND TISSUES
 NAME: DATE: PARTNER: CYTOLOGY & HISTOLOGY THE STUDY OF CELLS AND TISSUES For ease of study, multicellular animals are often examined at various levels of structural organization. Starting from the most
NAME: DATE: PARTNER: CYTOLOGY & HISTOLOGY THE STUDY OF CELLS AND TISSUES For ease of study, multicellular animals are often examined at various levels of structural organization. Starting from the most
NATIONAL REVIEW COURSE. Cells, Tissues, and Membranes
 NATIONAL REVIEW COURSE Cells, Tissues, and Membranes I. Cell Types A. Prokaryote bacteria cells; a cell that does not have a nucleus in which to store its genetic material. B. Eukaryote plant or animal
NATIONAL REVIEW COURSE Cells, Tissues, and Membranes I. Cell Types A. Prokaryote bacteria cells; a cell that does not have a nucleus in which to store its genetic material. B. Eukaryote plant or animal
Netter's Histology Flash Cards Section 1 List Updated Edition
 Netter's Histology Flash Cards Section 1 List Updated Edition https://www.memrise.com/course/1578421/ Section 1 Cells and Tissues (74 cards) 1 The Cell (11 cards) Plate 1-1 The Cell 1-1.1 Centrioles 1-1.2
Netter's Histology Flash Cards Section 1 List Updated Edition https://www.memrise.com/course/1578421/ Section 1 Cells and Tissues (74 cards) 1 The Cell (11 cards) Plate 1-1 The Cell 1-1.1 Centrioles 1-1.2
Physiology. Organization of the Body. Assumptions in Physiology. Chapter 1. Physiology is the study of how living organisms function
 Introduction to Physiology and Homeostasis Chapter 1 Physiology Physiology is the study of how living organisms function On the street explanations are in terms of meeting a bodily need Physiologic explanations
Introduction to Physiology and Homeostasis Chapter 1 Physiology Physiology is the study of how living organisms function On the street explanations are in terms of meeting a bodily need Physiologic explanations
AVICENNA INTERNATIONAL COLLEGE
 AVICENNA INTERNATIONAL COLLEGE BIOLOGICAL SCIENCES ACADEMIC CALENDAR LECTURE SYLLABUS CELL & MOLECULAR BIOLOGY 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Characteristics of Living Organisms, Levels of Organization in Biology (Introduction
AVICENNA INTERNATIONAL COLLEGE BIOLOGICAL SCIENCES ACADEMIC CALENDAR LECTURE SYLLABUS CELL & MOLECULAR BIOLOGY 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Characteristics of Living Organisms, Levels of Organization in Biology (Introduction
Tissues: - A group of cells similar in structure and performing a particular function forms a tissue.
 Plant Tissues Class- IX Tissues: - A group of cells similar in structure and performing a particular function forms a tissue. PLANT TISSUES ANIMAL TISSUES 1. Most of the plant tissues are Most of the tissues
Plant Tissues Class- IX Tissues: - A group of cells similar in structure and performing a particular function forms a tissue. PLANT TISSUES ANIMAL TISSUES 1. Most of the plant tissues are Most of the tissues
Sioux Falls School District Anatomy and Physiology Holes Anatomy and Physiology Authors: Shier, Butler, and Lewis Glencoe/ McGraw hill
 Sioux Falls School District Anatomy and Physiology Holes Anatomy and Physiology Authors: Shier, Butler, and Lewis Glencoe/ McGraw hill Semester 1 Chapter 1: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology
Sioux Falls School District Anatomy and Physiology Holes Anatomy and Physiology Authors: Shier, Butler, and Lewis Glencoe/ McGraw hill Semester 1 Chapter 1: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology
3. Structure, Function, and Genetics of Plants and Animals
 3. Structure, Function, and Genetics of Plants and Animals 3.1 Structure of Plants 3.2 Plant Physiology and Reproduction 3.3 Structure and Function of Animal Tissues 3.4 Anatomy of Animal Systems, Part
3. Structure, Function, and Genetics of Plants and Animals 3.1 Structure of Plants 3.2 Plant Physiology and Reproduction 3.3 Structure and Function of Animal Tissues 3.4 Anatomy of Animal Systems, Part
INTRODUCTION Veterinary Physiology I Odd Semester 2015/2016. Division of Physiology Department of Anatomy, Physiology and Pharmacology FVM BAU
 INTRODUCTION Veterinary Physiology I Odd Semester 2015/2016 Division of Physiology Department of Anatomy, Physiology and Pharmacology FVM BAU 1 Main references: Cunningham, JG. 2002. Textbook of Veterinary
INTRODUCTION Veterinary Physiology I Odd Semester 2015/2016 Division of Physiology Department of Anatomy, Physiology and Pharmacology FVM BAU 1 Main references: Cunningham, JG. 2002. Textbook of Veterinary
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Revised 11/2010
 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Revised 11/2010 DESCRIPTION OF COURSE: Covers the basics of human anatomy and physiology including anatomical terminology, basic biochemistry, cells and tissues, and the integumentary,
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Revised 11/2010 DESCRIPTION OF COURSE: Covers the basics of human anatomy and physiology including anatomical terminology, basic biochemistry, cells and tissues, and the integumentary,
C5 Histology / MC3. What are the four primary tissue types? All tissue consist of cells and stuff between the cells.
 C5 Histology / MC3 What are the four primary tissue types? All tissue consist of cells and stuff between the cells. What is the stuff between the cells called? What are the components of this stuff? Why
C5 Histology / MC3 What are the four primary tissue types? All tissue consist of cells and stuff between the cells. What is the stuff between the cells called? What are the components of this stuff? Why
CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION. Copyright 2007 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. 1
 CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION Copyright 2007 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. 1 Anatomy and Physiology Four basic properties of life: Reception The ability of the organism to control its actions
CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION Copyright 2007 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. 1 Anatomy and Physiology Four basic properties of life: Reception The ability of the organism to control its actions
Active movement Cancer. Cell. Cell inclusion Cytoplasm Diffusion Organelle Osmosis Passive movement Plasma membrane. Cell
 CHAPTER ONE INTRODUCTION TO ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Learning Objective At the end of this chapter, the students should be able to: - Define Anatomy and Physiology - Explain Homeostasis - Describe levels
CHAPTER ONE INTRODUCTION TO ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Learning Objective At the end of this chapter, the students should be able to: - Define Anatomy and Physiology - Explain Homeostasis - Describe levels
Cells - Chapter 3. Transport into and out of cells. The Cell Theory. Hooke (1665) Leeuwenhoek ( ) Simple Cells Cell Tutorial
 Cells - Chapter 3 Cells Alive Intro Video Transport into and out of cells Organization/Review Simple Cells Cell Tutorial http://www.wisc-online.com/objects/framz.asp?objid=ap11604 Cell Death http://www.whfreeman.com/kuby/content/anm/kb04an01.htm
Cells - Chapter 3 Cells Alive Intro Video Transport into and out of cells Organization/Review Simple Cells Cell Tutorial http://www.wisc-online.com/objects/framz.asp?objid=ap11604 Cell Death http://www.whfreeman.com/kuby/content/anm/kb04an01.htm
Levels of Organization
 Levels of Organization MADE UP OF CELLS REPRO- DUCE 5 CHARACH- TERISTICS OF LIVING THINGS RESPOND TO CHANGES GROW AND DEVELOP USE ENERGY cells the basic units of structure and function of all living
Levels of Organization MADE UP OF CELLS REPRO- DUCE 5 CHARACH- TERISTICS OF LIVING THINGS RESPOND TO CHANGES GROW AND DEVELOP USE ENERGY cells the basic units of structure and function of all living
BIOL 225 Anatomy and Physiology I
 South Central College BIOL 225 Anatomy and Physiology I Course Outcome Summary Course Information Description Total Credits 4 Total Hours 80 Types of Instruction Instruction Type Anatomy and Physiology
South Central College BIOL 225 Anatomy and Physiology I Course Outcome Summary Course Information Description Total Credits 4 Total Hours 80 Types of Instruction Instruction Type Anatomy and Physiology
Chapter 3. Cells and Tissues. Mosby items and derived items 2010, 2006, 2002, 1997, 1992 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc.
 Chapter 3 Cells and Tissues Objectives Identify and discuss the basic structure and function of the three major components of a cell List and briefly discuss the functions of the primary cellular organelles
Chapter 3 Cells and Tissues Objectives Identify and discuss the basic structure and function of the three major components of a cell List and briefly discuss the functions of the primary cellular organelles
BIOLOGY TOPICS Jagiellonian University Medical College School of Medicine in English
 BIOLOGY TOPICS 2018 Jagiellonian University Medical College School of Medicine in English MOLECULAR BIOLOGY: DNA AND PROTEIN SYNTHESIS DNA Structure and Function A. DNA Structure and Function 1. Double-helix
BIOLOGY TOPICS 2018 Jagiellonian University Medical College School of Medicine in English MOLECULAR BIOLOGY: DNA AND PROTEIN SYNTHESIS DNA Structure and Function A. DNA Structure and Function 1. Double-helix
1. Which of the cellular components listed above are part of the endomembrane system and surrounded by a double membrane?
 Anatomy and Physiology 141 Fall 2014: Exam IA Name: Use the following list to answer Question 1. 1 Golgi apparatus 2 Nuclear membrane 3 Mitochondria 4 Rough ER 5 Smooth ER 1. Which of the cellular components
Anatomy and Physiology 141 Fall 2014: Exam IA Name: Use the following list to answer Question 1. 1 Golgi apparatus 2 Nuclear membrane 3 Mitochondria 4 Rough ER 5 Smooth ER 1. Which of the cellular components
Cell Structure and Cell Cycle
 E X E R C I S E 4 Cell Structure and Cell Cycle Materials model or diagram of a cell compound microscopes and lens paper prepared slides of human skeletal muscle cells, pseudostratified ciliated columnar
E X E R C I S E 4 Cell Structure and Cell Cycle Materials model or diagram of a cell compound microscopes and lens paper prepared slides of human skeletal muscle cells, pseudostratified ciliated columnar
East Penn School District Curriculum and Instruction
 East Penn School District Curriculum and Instruction Curriculum for: Human Anatomy/Physiology, College Preparatory Course(s): CP Human Anatomy/Physiology Grades: 10-12 Department: Science Length of Period
East Penn School District Curriculum and Instruction Curriculum for: Human Anatomy/Physiology, College Preparatory Course(s): CP Human Anatomy/Physiology Grades: 10-12 Department: Science Length of Period
Course Outcome Summary
 Course Information: Description: Instruction Level: 11-12 Total Credits: Prerequisites: Textbooks: Course Content: (SCANAT) Advanced Anatomy & Physiology A basic understanding of the human body is essential
Course Information: Description: Instruction Level: 11-12 Total Credits: Prerequisites: Textbooks: Course Content: (SCANAT) Advanced Anatomy & Physiology A basic understanding of the human body is essential
CUMBERLAND COUNTY SCHOOL DISTRICT BENCHMARK ASSESSMENT CURRICULUM PACING GUIDE Subject: Anatomy & Physiology Grade: 11-12
 Benchmark Assessment 1 Instructional Timeline: 8 weeks Topic(s): Introduction, Tissues, Integumentary System Describe the major components and functions of physiological systems, including skeletal, muscle,
Benchmark Assessment 1 Instructional Timeline: 8 weeks Topic(s): Introduction, Tissues, Integumentary System Describe the major components and functions of physiological systems, including skeletal, muscle,
University of Jordan School of Medicine MD Program Curriculum
 University of Jordan School of Medicine MD Program Curriculum Course Title: General Histology Course number: 0502111 Credit Hours: 2 credits Academic Year Level: 1st year, 2nd semester 2016/2017 Course
University of Jordan School of Medicine MD Program Curriculum Course Title: General Histology Course number: 0502111 Credit Hours: 2 credits Academic Year Level: 1st year, 2nd semester 2016/2017 Course
BIOL 225 Anatomy and Physiology I
 South Central College BIOL 225 Anatomy and Physiology I Course Information Description Anatomy and Physiology I is an introduction to the structure and function of the human body under normal and abnormal
South Central College BIOL 225 Anatomy and Physiology I Course Information Description Anatomy and Physiology I is an introduction to the structure and function of the human body under normal and abnormal
The University of Jordan. Accreditation & Quality Assurance Center. Histology 1 for dentistry. COURSE Syllabus
 The University of Jordan Accreditation & Quality Assurance Center COURSE Syllabus Histology 1 for dentistry 1 Course title Histology-1 2 Course number 0542226 Credit hours (theory, practical) 3 (2 theory,
The University of Jordan Accreditation & Quality Assurance Center COURSE Syllabus Histology 1 for dentistry 1 Course title Histology-1 2 Course number 0542226 Credit hours (theory, practical) 3 (2 theory,
Pacing: August June These benchmarks serve as common threads to be integrated throughout the units of study Teacher Notes:
 Anatomy and Honors and Non-Honors Curriculum Map al Focus Calendar 1 Body of Knowledge :Practice of Science Standard:SC.912.N.1.1 Essential Questions Pacing: August June These benchmarks serve as common
Anatomy and Honors and Non-Honors Curriculum Map al Focus Calendar 1 Body of Knowledge :Practice of Science Standard:SC.912.N.1.1 Essential Questions Pacing: August June These benchmarks serve as common
Year 7 - Cells Summary Notes
 Year 7 - Cells Summary Notes Life Processes All living things do all seven of the life processes. Things that are not living may do some but do not do all seven of the life processes. These are: Movement
Year 7 - Cells Summary Notes Life Processes All living things do all seven of the life processes. Things that are not living may do some but do not do all seven of the life processes. These are: Movement
Biology 13A Lab #3: Cells and Tissues
 Biology 13A Lab #3: Cells and Tissues Lab #3 Table of Contents: Expected Learning Outcomes.... 28 Introduction...... 28 Activity 1: Eukaryotic Cell Structure... 29 Activity 2: Perspectives on Tissue Preparations.
Biology 13A Lab #3: Cells and Tissues Lab #3 Table of Contents: Expected Learning Outcomes.... 28 Introduction...... 28 Activity 1: Eukaryotic Cell Structure... 29 Activity 2: Perspectives on Tissue Preparations.
Slide 1 / Arrange the following in order from least complex to most complex: organ, tissue, cell, organism, organ system.
 Slide 1 / 64 1 Arrange the following in order from least complex to most complex: organ, tissue, cell, organism, organ system. Slide 2 / 64 2 List the four major groups of tissues in animals. Slide 3 /
Slide 1 / 64 1 Arrange the following in order from least complex to most complex: organ, tissue, cell, organism, organ system. Slide 2 / 64 2 List the four major groups of tissues in animals. Slide 3 /
28.1. Levels of Organization. > Virginia standards
 28.1 Levels of Organization vocabulary determination differentiation tissue organ organ system > Virginia standards BIO.4 The student will investigate and understand life functions of Archaea, Bacteria
28.1 Levels of Organization vocabulary determination differentiation tissue organ organ system > Virginia standards BIO.4 The student will investigate and understand life functions of Archaea, Bacteria
Architectural Pattern of an animal. Chapter 9
 Architectural Pattern of an animal Chapter 9 What is an animal? Levels of organization and organismal complexity 5 major levels of complexity Unicellular Metazoan? Tissue Organ Organ systems Levels of
Architectural Pattern of an animal Chapter 9 What is an animal? Levels of organization and organismal complexity 5 major levels of complexity Unicellular Metazoan? Tissue Organ Organ systems Levels of
human cell Smallest living structure and constituent unit of human beings; the sizes and shapes of cells vary according to their function.
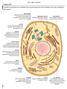 human cell CELL AND TISSUES Smallest living structure and constituent unit of human beings; the sizes and shapes of cells vary according to their function. Golgi apparatus Organelle composed of a series
human cell CELL AND TISSUES Smallest living structure and constituent unit of human beings; the sizes and shapes of cells vary according to their function. Golgi apparatus Organelle composed of a series
Academic Anatomy Pacing Guide
 Academic Anatomy Pacing Guide Course Description: This course provides the student with a general study of the structure of EOC VOCATS the human body and the detailed study of the functions of the body
Academic Anatomy Pacing Guide Course Description: This course provides the student with a general study of the structure of EOC VOCATS the human body and the detailed study of the functions of the body
Form and Function. Physical Laws and Form. Chapter 40: Basic Principles of Animal Form and Function. AP Biology Fig Figs & 40.
 Chapter 40: Basic Principles of Animal Form and Function AP Biology 2013 1 Form and Function Comparative studies show that form and function are closely related Natural selection can fit the form (anatomy)
Chapter 40: Basic Principles of Animal Form and Function AP Biology 2013 1 Form and Function Comparative studies show that form and function are closely related Natural selection can fit the form (anatomy)
HSC HUMAN BODY SYSTEMS Midterm Exam October 17, 2001 Department of Anatomy and Cell Biology and Department of Physiology Time: 50 minutes 1.
 HSC 208.6 - HUMAN BODY SYSTEMS Midterm Exam October 17, 2001 Department of Anatomy and Cell Biology and Department of Physiology Time: 50 minutes 1. An organ: A. is the smallest independent unit of life
HSC 208.6 - HUMAN BODY SYSTEMS Midterm Exam October 17, 2001 Department of Anatomy and Cell Biology and Department of Physiology Time: 50 minutes 1. An organ: A. is the smallest independent unit of life
Plant Tissues. Parenchyma Collenchyma Sclerenchyma
 BAL BHARATI PUBLIC SCHOOL, NOIDA CLASS-IX BIOLOGY TOPIC- TISSUES BY: UMESH VERMA Defination- A group of cells similar in structure and performing a particular function forms a tissue. Also this group od
BAL BHARATI PUBLIC SCHOOL, NOIDA CLASS-IX BIOLOGY TOPIC- TISSUES BY: UMESH VERMA Defination- A group of cells similar in structure and performing a particular function forms a tissue. Also this group od
STRUCTURE OF THE CELL
 STRUCTURE OF THE CELL The cell is the smallest standard unit of the organisms. - nucleus - vital functions (growth, metabolism, irritability, movement,reproduction) - independent existence in certain conditions
STRUCTURE OF THE CELL The cell is the smallest standard unit of the organisms. - nucleus - vital functions (growth, metabolism, irritability, movement,reproduction) - independent existence in certain conditions
Introduction to the Human Body. Cells. Body Functions. Tissues. Organs. Systems. Body Functions & Life Process
 complex functions for the body. Ten major systems compose the human body: Introduction to the Human Body Human beings are arguably the most complex organisms on this planet. Imagine billions of microscopic
complex functions for the body. Ten major systems compose the human body: Introduction to the Human Body Human beings are arguably the most complex organisms on this planet. Imagine billions of microscopic
GENERALIZED ANIMAL CELL
 Cells are the basic organizational units of life GENERALIZED ANIMAL CELL A typical animal cell has a plasma membrane surrounding the nucleus and the cytoplasm. Plasma membrance is a phospholipid bilayer
Cells are the basic organizational units of life GENERALIZED ANIMAL CELL A typical animal cell has a plasma membrane surrounding the nucleus and the cytoplasm. Plasma membrance is a phospholipid bilayer
DOWNLOAD OR READ : TISSUE STUDY GUIDE CHAPTER 4 PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI
 DOWNLOAD OR READ : TISSUE STUDY GUIDE CHAPTER 4 PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI Page 1 Page 2 tissue study guide chapter 4 tissue study guide chapter pdf tissue study guide chapter 4 STUDY GUIDE 7 1.Types of Muscle
DOWNLOAD OR READ : TISSUE STUDY GUIDE CHAPTER 4 PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI Page 1 Page 2 tissue study guide chapter 4 tissue study guide chapter pdf tissue study guide chapter 4 STUDY GUIDE 7 1.Types of Muscle
Levels of Organization. Monday, December 5, 16
 Levels of Organization The human body is structured into systems. Cells are the smallest unit of life. Calls similar in shape and function work together as tissues. Different types of tissues form organs
Levels of Organization The human body is structured into systems. Cells are the smallest unit of life. Calls similar in shape and function work together as tissues. Different types of tissues form organs
Essential Question Content Skills Assessment Standards. Anatomical terms. Homeostatic mechanisms. Characteristics of Life. Requirements for life
 Honors Anatomy & Physiology 2012 Michael Harshaw, Melissa Castone Essential Question Content Skills Assessment Standards Month Introduction September- 1.5 weeks How do Anatomy and Physiology relate to
Honors Anatomy & Physiology 2012 Michael Harshaw, Melissa Castone Essential Question Content Skills Assessment Standards Month Introduction September- 1.5 weeks How do Anatomy and Physiology relate to
Developmental Zoology. Ectodermal derivatives (ZOO ) Developmental Stages. Developmental Stages
 Developmental Zoology (ZOO 228.1.0) Ectodermal derivatives 1 Developmental Stages Ø Early Development Fertilization Cleavage Gastrulation Neurulation Ø Later Development Organogenesis Larval molts Metamorphosis
Developmental Zoology (ZOO 228.1.0) Ectodermal derivatives 1 Developmental Stages Ø Early Development Fertilization Cleavage Gastrulation Neurulation Ø Later Development Organogenesis Larval molts Metamorphosis
Exam 3 (Final Exam) December 20, 2007
 Biology 4361 Exam 3 (Final Exam) December 20, 2007 Name: ID: Multiple choice (1 point each. Indicate the best answer.) 1. During Drosophila gastrulation, mesoderm moves in through the a. primitives streak.
Biology 4361 Exam 3 (Final Exam) December 20, 2007 Name: ID: Multiple choice (1 point each. Indicate the best answer.) 1. During Drosophila gastrulation, mesoderm moves in through the a. primitives streak.
BIOL Anatomy and Physiology I ( version L )
 BIOL 2113 - Anatomy and Physiology I ( version 213L ) Course Title Course Development Learning Support Anatomy and Physiology I Standard No Course Description Introduces the anatomy and physiology of the
BIOL 2113 - Anatomy and Physiology I ( version 213L ) Course Title Course Development Learning Support Anatomy and Physiology I Standard No Course Description Introduces the anatomy and physiology of the
BIOL 1030 Introduction to Biology: Organismal Biology. Spring 2011 Section A. Steve Thompson:
 BIOL 1030 Introduction to Biology: Organismal Biology. Spring 2011 Section A Steve Thompson: stthompson@valdosta.edu http://www.bioinfo4u.net 1 And now on to something you all should be able to really
BIOL 1030 Introduction to Biology: Organismal Biology. Spring 2011 Section A Steve Thompson: stthompson@valdosta.edu http://www.bioinfo4u.net 1 And now on to something you all should be able to really
table of contents unit one: introduction to the study of the environment
 table of contents unit one: introduction to the study of the environment Chapter 1: Characteristics of Living Things 1 A. Biology and the Living Environment 1 B. What is Science 1 C. Scientific Inquiry
table of contents unit one: introduction to the study of the environment Chapter 1: Characteristics of Living Things 1 A. Biology and the Living Environment 1 B. What is Science 1 C. Scientific Inquiry
SCIENCE: ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY
 SCIENCE: ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY END-OF-COURSE EXAM GRADE 9-12 YEAR 17 18 ASSESSMENT BLUEPRINT Purpose Statement Anatomy and Physiology The Anatomy and Physiology End-of-Course (EOC) exam is intended to
SCIENCE: ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY END-OF-COURSE EXAM GRADE 9-12 YEAR 17 18 ASSESSMENT BLUEPRINT Purpose Statement Anatomy and Physiology The Anatomy and Physiology End-of-Course (EOC) exam is intended to
Intercellular Communication. Department of Physiology School of Medicine University of Sumatera Utara
 Intercellular Communication Department of Physiology School of Medicine University of Sumatera Utara Intercellular Communication and Signal Transduction The ability of cells to communicate with each other
Intercellular Communication Department of Physiology School of Medicine University of Sumatera Utara Intercellular Communication and Signal Transduction The ability of cells to communicate with each other
The Cell. C h a p t e r. PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas
 C h a p t e r 2 The Cell PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings Introduction
C h a p t e r 2 The Cell PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings Introduction
Broken Arrow Public Schools Physiology Objectives
 1 st six weeks 1 Define anatomy and physiology. 2 Compare and contrast levels of structural organization. 3 Identify necessary life functions and essential needs and how they are related to homeostasis.
1 st six weeks 1 Define anatomy and physiology. 2 Compare and contrast levels of structural organization. 3 Identify necessary life functions and essential needs and how they are related to homeostasis.
EASTERN ARIZONA COLLEGE Human Anatomy and Physiology I
 EASTERN ARIZONA COLLEGE Human Anatomy and Physiology I Course Design 2015-2016 Course Information Division Science Course Number BIO 201 (SUN# BIO 2201) Title Human Anatomy and Physiology I Credits 4 Developed
EASTERN ARIZONA COLLEGE Human Anatomy and Physiology I Course Design 2015-2016 Course Information Division Science Course Number BIO 201 (SUN# BIO 2201) Title Human Anatomy and Physiology I Credits 4 Developed
Cells to systems. 1) Chemical Level All matter is a combination of atoms: - Oxygen - Carbon - Nitrogen - Hydrogen Make up 96% of total body chemistry
 Cells to systems Organisation of the Human body: 1. Chemical level 2. Cellular level 3. Tissue level 4. Organ level 5. Body system level 6. Organism level 1) Chemical Level All matter is a combination
Cells to systems Organisation of the Human body: 1. Chemical level 2. Cellular level 3. Tissue level 4. Organ level 5. Body system level 6. Organism level 1) Chemical Level All matter is a combination
PROPERTY OF ELSEVIER SAMPLE CONTENT - NOT FINAL. The Nervous System and Muscle
 The Nervous System and Muscle SECTION 2 2-1 Nernst Potential 2-2 Resting Membrane Potential 2-3 Axonal Action Potential 2-4 Neurons 2-5 Axonal Conduction 2-6 Morphology of Synapses 2-7 Chemical Synaptic
The Nervous System and Muscle SECTION 2 2-1 Nernst Potential 2-2 Resting Membrane Potential 2-3 Axonal Action Potential 2-4 Neurons 2-5 Axonal Conduction 2-6 Morphology of Synapses 2-7 Chemical Synaptic
Bio 111 Study Guide Chapter 6 Tour of the Cell
 Bio 111 Study Guide Chapter 6 Tour of the Cell BEFORE CLASS: Reading: Read the whole chapter from p. 93-121, mostly skimming Concept 6.1 on microscopy. Figure 6.8 on pp. 100-101 is really helpful in showing
Bio 111 Study Guide Chapter 6 Tour of the Cell BEFORE CLASS: Reading: Read the whole chapter from p. 93-121, mostly skimming Concept 6.1 on microscopy. Figure 6.8 on pp. 100-101 is really helpful in showing
1. Know the hierarchy of organization: chemical, cellular, tissue, organ, organ system, organismal
 Anatomy and Physiology Anatomical Organization 1. Know the hierarchy of organization: chemical, cellular, tissue, organ, organ system, organismal 2. Be able to identify and describe the necessary life
Anatomy and Physiology Anatomical Organization 1. Know the hierarchy of organization: chemical, cellular, tissue, organ, organ system, organismal 2. Be able to identify and describe the necessary life
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology
 Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 3 Cells vary in size possess distinctive shapes measured in micrometers 2 A Composite Cell hypothetical cell major parts nucleus cytoplasm cell membrane 3
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 3 Cells vary in size possess distinctive shapes measured in micrometers 2 A Composite Cell hypothetical cell major parts nucleus cytoplasm cell membrane 3
4. Which of the following organelles digests waste using hydrolytic enzymes:
 Multichoice questions section. You must answer ALL questions. 1. A cell contains many organelles, each of which has a specific function. What is function of mitochondria? a) production of plasma membrane
Multichoice questions section. You must answer ALL questions. 1. A cell contains many organelles, each of which has a specific function. What is function of mitochondria? a) production of plasma membrane
Unit code: K/503/1682 QCF level: 4 Credit value: 15
 Unit 10: Anatomy and Physiology Unit code: K/503/1682 QCF level: 4 Credit value: 15 Aim This unit aims to develop learner understanding of physical support and movement in animals, body transport systems,
Unit 10: Anatomy and Physiology Unit code: K/503/1682 QCF level: 4 Credit value: 15 Aim This unit aims to develop learner understanding of physical support and movement in animals, body transport systems,
Chapter 6 General Anatomy and Physiology
 Chapter 6 General Anatomy and Physiology MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The study of the human body structures that can be seen with the naked eye is. a. anatomy c. biology b. physiology d. pathology Anatomy is the
Chapter 6 General Anatomy and Physiology MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The study of the human body structures that can be seen with the naked eye is. a. anatomy c. biology b. physiology d. pathology Anatomy is the
PHYSIOLOGY LECTURE. Dr. Mehmet Emin USLU, PhD
 PHYSIOLOGY LECTURE Dr. Mehmet Emin USLU, PhD Each physiological system is composed of discrete organs, such as the liver, heart, lungs, and kidneys. These organs are made up of assemblages of cells known
PHYSIOLOGY LECTURE Dr. Mehmet Emin USLU, PhD Each physiological system is composed of discrete organs, such as the liver, heart, lungs, and kidneys. These organs are made up of assemblages of cells known
Review sheet for exam III
 Review sheet for exam III WARNING: I have tried to be complete, but I may have missed something. You are responsible for all the material discussed in class. This is only a guide. NOTE: the extra material
Review sheet for exam III WARNING: I have tried to be complete, but I may have missed something. You are responsible for all the material discussed in class. This is only a guide. NOTE: the extra material
Cell Organelles. 2. Cells are the basic unit of organization in an organism Cells tissues organ organ system organism
 Cell Organelles What are some of the differences you see between these two cells? A. Cell Theory 1. All organisms are made up of one or more cells 2. Cells are the basic unit of organization in an organism
Cell Organelles What are some of the differences you see between these two cells? A. Cell Theory 1. All organisms are made up of one or more cells 2. Cells are the basic unit of organization in an organism
Chapter 6: Tissues. KEY CONCEPTS : [ *rating as per the significance of concept]
![Chapter 6: Tissues. KEY CONCEPTS : [ *rating as per the significance of concept] Chapter 6: Tissues. KEY CONCEPTS : [ *rating as per the significance of concept]](/thumbs/78/78538656.jpg) Chapter 6: Tissues KEY CONCEPTS : [ *rating as per the significance of concept] CONCEPTS RATING Meristems in plants ** Permanent tissues in plants **** Animal tissues ***** 1. Tissue is a group of cells
Chapter 6: Tissues KEY CONCEPTS : [ *rating as per the significance of concept] CONCEPTS RATING Meristems in plants ** Permanent tissues in plants **** Animal tissues ***** 1. Tissue is a group of cells
Muscle Cells skeletal muscle cardiac muscle smooth muscle
 Muscle Cells Muscle tissue, one of the four major tissue types, plays the vital role of providing movement and heat generation to the organs of the body. Within muscle tissue are three distinct groups
Muscle Cells Muscle tissue, one of the four major tissue types, plays the vital role of providing movement and heat generation to the organs of the body. Within muscle tissue are three distinct groups
Ministry of Public Health of Ukraine M. Gorky Donetsk National Medical University. SYLLABUS of histology, cytology and embryology
 1 Form Н-3.04 Ministry of Public Health of Ukraine M. Gorky Donetsk National Medical University "APPROVED The first Deputy Rector for Educational Procedure Professor A.N. Talalayenko. " " 2012 SYLLABUS
1 Form Н-3.04 Ministry of Public Health of Ukraine M. Gorky Donetsk National Medical University "APPROVED The first Deputy Rector for Educational Procedure Professor A.N. Talalayenko. " " 2012 SYLLABUS
4. Neural tube cells are specified by opposing dorsal-ventral gradients of a. Wnts and Nodal. b. FGF and Shh. c. BMPs and Wnts. d. BMPs and Shh.
 Biology 4361 Name: KEY Exam 4 ID#: August 1, 2008 Multiple choice (one point each; indicate the best answer) 1. Neural tube closure is accomplished by movement of the a. medial hinge point cells. b. medial
Biology 4361 Name: KEY Exam 4 ID#: August 1, 2008 Multiple choice (one point each; indicate the best answer) 1. Neural tube closure is accomplished by movement of the a. medial hinge point cells. b. medial
ORGANISATION IN THE LIVING THINGS
 2 ORGANISATION IN THE LIVING THINGS I. Multiple choice questions: Tick ( ) the correct choice. 1. A group of similar cells which perform a particular function is called (a) organism (b) tissue (c) organelle
2 ORGANISATION IN THE LIVING THINGS I. Multiple choice questions: Tick ( ) the correct choice. 1. A group of similar cells which perform a particular function is called (a) organism (b) tissue (c) organelle
CENTRAL TEXAS COLLEGE SYLLABUS FOR MDCA 1309 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY FOR MEDICAL ASSISTANTS Semester Hours Credit: 3 Instructor: Office Hours:
 1 CENTRAL TEXAS COLLEGE SYLLABUS FOR MDCA 1309 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY FOR MEDICAL ASSISTANTS Semester Hours Credit: 3 Instructor: I. INTRODUCTION Office Hours: A. Course Description: Emphasis on structure
1 CENTRAL TEXAS COLLEGE SYLLABUS FOR MDCA 1309 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY FOR MEDICAL ASSISTANTS Semester Hours Credit: 3 Instructor: I. INTRODUCTION Office Hours: A. Course Description: Emphasis on structure
Overview of Physiology & Homeostasis. Biological explanations Levels of organization Homeostasis
 Overview of Physiology & Homeostasis 1 Biological explanations Levels of organization Homeostasis 2 Biological Explanations Proximate Proximate causation: an explanation of an animal's behavior based on
Overview of Physiology & Homeostasis 1 Biological explanations Levels of organization Homeostasis 2 Biological Explanations Proximate Proximate causation: an explanation of an animal's behavior based on
BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH.32 - OVERVIEW OF ANIMALS.
 !! www.clutchprep.com Animals are multicellular, heterotrophic eukaryotes that feed by ingesting their food Most animals are diploid, and produce gametes produced directly by meiosis Animals lack cell
!! www.clutchprep.com Animals are multicellular, heterotrophic eukaryotes that feed by ingesting their food Most animals are diploid, and produce gametes produced directly by meiosis Animals lack cell
SHEET. Name: Class: Date: the sentence: write highest, lowest, higher, lower. level of organization is the organism; the
 1 1 Label the levels of organization Then complete the sentence: write highest, lowest, higher, lower The level of organization is the organism; the level of organization is the cell Tissues are a organs,
1 1 Label the levels of organization Then complete the sentence: write highest, lowest, higher, lower The level of organization is the organism; the level of organization is the cell Tissues are a organs,
SNC2D BIOLOGY 4/1/2013. TISSUES, ORGANS & SYSTEMS OF L Animal & Plant Tissues (P.42-45) Animal Tissues. Animal Tissues
 SNC2D BIOLOGY TISSUES, ORGANS & SYSTEMS OF L Animal & Plant Tissues (P.42-45) Animal Tissues As you already know, groups of cells that work together to perform a task are called tissues. For example, muscle
SNC2D BIOLOGY TISSUES, ORGANS & SYSTEMS OF L Animal & Plant Tissues (P.42-45) Animal Tissues As you already know, groups of cells that work together to perform a task are called tissues. For example, muscle
INTRODUCTION COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL
 I INTRODUCTION COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL 1 The Structural and Biochemical Hierarchy of a Cell and a Human There is no magician s mantle to compare with skin in its diverse roles of waterproof overcoat, sunshade,
I INTRODUCTION COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL 1 The Structural and Biochemical Hierarchy of a Cell and a Human There is no magician s mantle to compare with skin in its diverse roles of waterproof overcoat, sunshade,
( 4 c r e d i t s a n d 7 h o u r s ) Fall 2017 Summer 2018 FOR BIOLOGY 11 & 12. Navneet Kaur, Lecturer S Dr. Anna Rozenboym S
 KINGSBOROUGH COMMUNITY COLLEGE OF THE CITY UNIVERSITY OF NEW YORK BIOLOGY 11 Human Anatomy and Physiology ( 4 c r e d i t s a n d 7 h o u r s ) Fall 2017 Summer 2018 SYLLABUS AND COURSE INFORMATION COURSE
KINGSBOROUGH COMMUNITY COLLEGE OF THE CITY UNIVERSITY OF NEW YORK BIOLOGY 11 Human Anatomy and Physiology ( 4 c r e d i t s a n d 7 h o u r s ) Fall 2017 Summer 2018 SYLLABUS AND COURSE INFORMATION COURSE
Human biology Cells: The Basic Units of Life. Dr. Rawaa Salim Hameed
 Human biology Cells: The Basic Units of Life Dr. Rawaa Salim Hameed Reference Text book of human biology by John Kenneth Inglis 3 rd Ed (1985) Cells: The Basic Units of Life Cell theory Cell theory consists
Human biology Cells: The Basic Units of Life Dr. Rawaa Salim Hameed Reference Text book of human biology by John Kenneth Inglis 3 rd Ed (1985) Cells: The Basic Units of Life Cell theory Cell theory consists
Mitosis, development, regeneration and cell differentiation
 Mitosis, development, regeneration and cell differentiation Mitosis is a type of cell division by binary fission (splitting in two) which occurs in certain eukaryotic cells. Mitosis generates new body
Mitosis, development, regeneration and cell differentiation Mitosis is a type of cell division by binary fission (splitting in two) which occurs in certain eukaryotic cells. Mitosis generates new body
TISSUES. Tissue. TISSUE: A group of cells that are similar in structure and work together to achieve a particular function forms a tissue.
 Page 1 of 9 TISSUES In unicellular organisms all the life processes such as digestion, respiration, excretion, reproduction etc are performed by the single cell. But in multicellualr organisms different
Page 1 of 9 TISSUES In unicellular organisms all the life processes such as digestion, respiration, excretion, reproduction etc are performed by the single cell. But in multicellualr organisms different
Chapter 3 BIOLOGY AND BEHAVIOR
 Chapter 3 BIOLOGY AND BEHAVIOR Section 1: The Nervous System Section 2: The Brain: Our Control Center Section 3: The Endocrine System Section 4: Heredity: Our Genetic Background 1 Section 1: The Nervous
Chapter 3 BIOLOGY AND BEHAVIOR Section 1: The Nervous System Section 2: The Brain: Our Control Center Section 3: The Endocrine System Section 4: Heredity: Our Genetic Background 1 Section 1: The Nervous
7. CONTROL AND COORDINATION
 7. CONTROL AND COORDINATION Multicellular animals, except sponges, have specialized cells called neurons, for responding to stimuli. A neuron or nerve cell is the structural and functional unit of the
7. CONTROL AND COORDINATION Multicellular animals, except sponges, have specialized cells called neurons, for responding to stimuli. A neuron or nerve cell is the structural and functional unit of the
AUGUST 1995 BIOLOGY 12 PROVINCIAL EXAMINATION ANSWER KEY / SCORING GUIDE TOPICS
 AUGUST 995 BIOLOGY PROVINCIAL EXAMINATION ANSWER KEY / SCORING GUIDE TOPICS CORE:.. 3. 4. OPTIONS: (Choose two of six) 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 0. Section I: Section II: Section III: Section IV: Section V: Section
AUGUST 995 BIOLOGY PROVINCIAL EXAMINATION ANSWER KEY / SCORING GUIDE TOPICS CORE:.. 3. 4. OPTIONS: (Choose two of six) 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 0. Section I: Section II: Section III: Section IV: Section V: Section
ESSENTIAL LEARNING OUTCOMES:
 ESSENTIAL LEARNING OUTCOMES: Upon satisfactory completion of BIO 2331 - Anatomy and Physiology I, the student should be able to perform the following outcomes and supporting objectives: Outcome: A. Critical/Creative
ESSENTIAL LEARNING OUTCOMES: Upon satisfactory completion of BIO 2331 - Anatomy and Physiology I, the student should be able to perform the following outcomes and supporting objectives: Outcome: A. Critical/Creative
Cells. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Cells Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Microscopy Methods of histology: Treat the tissue with a preservative (e.g. formaldehyde). Dissect the region of interest. Embed
Cells Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Microscopy Methods of histology: Treat the tissue with a preservative (e.g. formaldehyde). Dissect the region of interest. Embed
Biology Final Exam Review
 Biology Final Exam Review Name: Date: Overview: This final exam review covers the basics from a whole year of basic biology studies. It is not a comprehensive review meaning that there may be questions
Biology Final Exam Review Name: Date: Overview: This final exam review covers the basics from a whole year of basic biology studies. It is not a comprehensive review meaning that there may be questions
Introduction. The study of animal form and function is integrated by the common set of problems that all animals must solve.
 Introduction The study of animal form and function is integrated by the common set of problems that all animals must solve. These include how to extract oxygen from the environment, how to nourish themselves,
Introduction The study of animal form and function is integrated by the common set of problems that all animals must solve. These include how to extract oxygen from the environment, how to nourish themselves,
HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY STRUCTURE 30
 HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY STRUCTURE 30 Description This second-year course in biology emphasizes the workings of the human body. The course is offered in the fall semester and meets six (6) periods per
HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY STRUCTURE 30 Description This second-year course in biology emphasizes the workings of the human body. The course is offered in the fall semester and meets six (6) periods per
Inferring disease-associated lncrnas using expression data and disease-associated protein coding genes
 Inferring disease-associated lncrnas using expression data and disease-associated protein coding genes Xiaoyong Pan Center for non-coding RNA in Technology and Health, Department of Clinical Veterinary
Inferring disease-associated lncrnas using expression data and disease-associated protein coding genes Xiaoyong Pan Center for non-coding RNA in Technology and Health, Department of Clinical Veterinary
Guided Reading Activities
 Name Period Chapter 4: A Tour of the Cell Guided Reading Activities Big Idea: Introduction to the Cell Answer the following questions as you read Modules 4.1 4.4: 1. A(n) uses a beam of light to illuminate
Name Period Chapter 4: A Tour of the Cell Guided Reading Activities Big Idea: Introduction to the Cell Answer the following questions as you read Modules 4.1 4.4: 1. A(n) uses a beam of light to illuminate
Anatomy and Physiology. Science Curriculum Framework
 Anatomy and Physiology Science Curriculum Framework Revised 005 Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy and Physiology should develop an understanding of the organization of the human body through studies of body
Anatomy and Physiology Science Curriculum Framework Revised 005 Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy and Physiology should develop an understanding of the organization of the human body through studies of body
Modesto Junior College Course Outline of Record ANAT 125
 Modesto Junior College Course Outline of Record ANAT 125 I. OVERVIEW The following information will appear in the 2010-2011 catalog ANAT 125 Human Anatomy 5 Units Prerequisite: Satisfactory completion
Modesto Junior College Course Outline of Record ANAT 125 I. OVERVIEW The following information will appear in the 2010-2011 catalog ANAT 125 Human Anatomy 5 Units Prerequisite: Satisfactory completion
Chapter 1: Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology
 Chapter 1: Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The anatomic term means toward the midline. a. anterior b. posterior c. medial d. cranial The term medial indicates an anatomic direction
Chapter 1: Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The anatomic term means toward the midline. a. anterior b. posterior c. medial d. cranial The term medial indicates an anatomic direction
Functions of the systems of the human body and their relation to homeostasis; includes disease prevention and cure, health, wellness, and nutrition.
 UNITED STATES INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF ARTS AND SCIENCES COURSE SYLLABUS NSC 2205: HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY CREDIT 3 UNITS A. COURSE DESCRIPTION Functions of the systems of the human body and their relation
UNITED STATES INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF ARTS AND SCIENCES COURSE SYLLABUS NSC 2205: HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY CREDIT 3 UNITS A. COURSE DESCRIPTION Functions of the systems of the human body and their relation
BIOLOGY AND GEOLOGY 3º DE E.S.O. Chapter 1: The organisation of the human body
 BIOLOGY AND GEOLOGY 3º DE E.S.O. Chapter 1: The organisation of the human body 1. INTRODUCTION: LEVELS OF ORGANISATION What is a cell? Definition of Cell A cell is the smallest unit that is capable of
BIOLOGY AND GEOLOGY 3º DE E.S.O. Chapter 1: The organisation of the human body 1. INTRODUCTION: LEVELS OF ORGANISATION What is a cell? Definition of Cell A cell is the smallest unit that is capable of
Developmental Biology Biology Ectodermal Organs. November 22, 2005
 Developmental Biology Biology 4361 Ectodermal Organs November 22, 2005 Germinal neuroepithelium external limiting membrane neural tube neuroepithelium (stem cells) Figure 13.3 Figure 13.4 Neuroepithelial
Developmental Biology Biology 4361 Ectodermal Organs November 22, 2005 Germinal neuroepithelium external limiting membrane neural tube neuroepithelium (stem cells) Figure 13.3 Figure 13.4 Neuroepithelial
JEFFERSON COLLEGE VERTEBRATE ANATOMY
 JEFFERSON COLLEGE COURSE SYLLABUS BIO207 VERTEBRATE ANATOMY 4 Credit Hours Prepared by: Mr. Jim McCain Revised Date: November 2005 by Dr. Ken Balak Division of Arts & Science Education Dr. Mindy Selsor,
JEFFERSON COLLEGE COURSE SYLLABUS BIO207 VERTEBRATE ANATOMY 4 Credit Hours Prepared by: Mr. Jim McCain Revised Date: November 2005 by Dr. Ken Balak Division of Arts & Science Education Dr. Mindy Selsor,
