PHYSICAL FEATURES OF SOUTH ASIA
|
|
|
- Deirdre Dawson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 PHYSICAL FEATURES OF SOUTH ASIA Formation India is a land of varied physical features. The physical features of India have evolved over several geological periods. According to the theory of Plate Tectonics the earth s crust is formed from seven major and some minor plates. When the plates move, they cause disturbances in the continental crust leading to folding, faulting and volcanic activity. These plates are classified into: Convergent boundary, Divergent boundary and Transform boundary
2 Convergent boundary is formed when two plates converge or move towards each other. Divergent boundary is formed when two plates move away from each other. Transform boundary is formed when two plates move towards each other, but finally end up sliding past each other. Peninsular India is a part of an ancient super continent: Gondwanaland. Gondwanaland originally consisted of a number of landmasses including South America, Africa, Australia, and Antarctica all joined together. Convectional currents split up the crust of Gondwanaland into smaller parts, of which the Indian plate was one.
3 The Indian plate drifted north till it collided with the Eurasian plate. The collision caused the sedimentary rocks in the Tethys Sea to be lifted upwards. This is how the Himalayas were formed. The oldest physical feature is the Peninsular Plateau. It is composed of igneous and metamorphic rocks, and has hills and wide valleys. The Himalayas The Himalayas are geologically young fold mountains covering the northern border of India. The Himalayan range is the highest and the most rugged mountain range in the world. The Himalayas are formed from three parallel ranges of mountains: The Himadri,
4 The Himachal and The Shiwaliks. The Himadri also called the Great or Inner Himalayas, is the northern most range of the Himalayas. This range is in a single, unbroken line and has the highest peaks like Mount Everest and Mount Godwin Austin. Several glaciers, such as the Gangotri and the Siachen, originate from this range. The Zoji La pass is situated in the Great Himalayan range and serves as the only link between Ladakh and Kashmir. The next range the Himachal, is located south of the Greater Himalayas. The height of mountains in this range is between 3700 and 4500 metres hence is also referred to as the Lesser Himalayas! In other words,
5 the Himachal is made up of altered rocks. The Pir Panjal is the longest range in the Lesser Himalayas. The Dhaula Dhar and the Mahabharat are other ranges famous for their beauty. The Himalayas are also divided into regions from east to west. The area between the Indus and the Sutlej is traditionally known as the Punjab Himalaya. Nanga Parbat is the highest peak in Punjab Himalaya. The Kumaon Himalayas is the name used regionally for the portion of the Himalayas between the Sutlej and the Kali rivers. Nanda Devi is the highest peak in this region. The area that lies between the Kali and the Tista rivers is known as the Nepal Himalayas. The Assam Himalayas refer to
6 the region between the Tista and the Dihang rivers. The division of the Himalayas on the east is called the Purvanchal or the Eastern Hills and Mountains. The Brahamputra forms the eastern most boundary of the Purvanchal region. The Purvanchal range is made up of the Patkai hills, the Naga hills, the Manipur hills and the Mizo hills. The Northern Plain The Northern Plain is located in the southern part of the Himalayan range. The plain is formed from the flood plains of three big river systems: The Indus, The Ganga and The Brahmaputra
7 The Northern Plain is also called the Indo- Gangetic plain. The soil cover in this plain is rich and fertile, and water is found in plenty, combined with a favourable climate for growing several major crops, the Northern Plain is one of the world s most intensively farmed areas and hence very densely populated. The rivers coming from the northern mountain carry a huge load of eroded soil and debris. As a river flows down towards the plains, due to the gentler slopes, its velocity decreases, and the material carried by it gets deposited on the way creating riverine islands. The Northern Plain can be divided into three main parts: The Indus and its tributaries the Jhelum, the Chenab, the Ravi, the Beas
8 and the Sutlej - originate in the Himalaya. This part of the Northern Plain is also called the Punjab Plain. The Ganga Plain lies between the Ghaggar and the Teesta rivers. The Brahmaputra Plain lies in the state of Assam. The states that fall under the Northern Plain are: Punjab, Haryana, Delhi, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, parts of Jharkhand and West Bengal, and Assam. The Northern Plain is divided into four regions: Bhabar, Terai, Bhangar and Khadar
9 The Bhabar region is a narrow belt of level surface in the Northern Plain, lying parallel to the slope of the Shiwaliks. All rivers and streams that disappear in the Bhabar belt resurface in the Terai region. The Terai region consists of wet, swampy and marshy land. Bhangar, is the largest part of the northern plain and is formed of older alluvium. This region lies above the flood plains of the rivers. The newer, younger deposits of the flood plains form the fourth region of the Northern Plain called Khadar. The land is fertile, and used extensively for agriculture.
10 The Peninsular Plateau Plateaus are also called tablelands like the Peninsular Plateau which is a tableland. This tableland was formed when Gondwanaland broke and the pieces drifted apart. It is composed of old crystalline, igneous and metamorphic rocks. The Peninsular Plateau consists of both broad and shallow valleys, and rounded hills. The Peninsular Plateau has two broad divisions: The Central Highlands and The Deccan Plateau The Central Highlands refer to the portion of the Peninsular Plateau that lies to the north of the Narmada river and covers a majority of the Malwa Plateau.
11 The Vindhya Range forms the boundary of the Central Highlands on the south while the Aravalis form the north-western boundary of these highlands. The Peninsular Plateau gradually merges into the sandy and rocky desert of Rajasthan and the rivers are the Chambal, the Sind, the Betwa and the Ken. Bundelkhand is the local name for the eastward extensions of the Peninsular Plateau. The other eastward extension is Baghelkhand. The Chhota Nagpur Plateau is the eastern extension of the Central Highlands. The Damodar is an important river that drains this region. The Deccan Plateau is a triangular landmass lying to the south of the Narmada. It has the Mahadev hills, the
12 Kaimur hills and the Maikal range on the eastern side. In the north-east is an extension of the Plateau, called the Meghalaya and Karbi-Anglong Plateau. A fault demarcates the Meghalaya and Karbi-Anglong Plateau from the Chhota Nagpur Plateau. There are three prominent hill ranges on the north-eastern side of the plateau i.e. the Garo range, the Khasi ranges, and the Jaintia hills. The Deccan Plateau in the south is bordered by Western Ghats on the west, and the Eastern Ghats on the east. The Western Ghats are tall, lie parallel to the western coast, are continuous and can be crossed through passes only.
13 The Eastern Ghats stretch from the Mahanadi Valley to the Nilgiris in the south. The Eastern Ghats are discontinuous and irregular. They are interspersed with several rivers that drain into the Bay of Bengal which are the Godavari, the Mahanadi, the Krishna, and the Kaveri. Orographic rainfall in the Western Ghats is caused when a range of mountains intercepts rain-bearing monsoon winds. The Western Ghats intercept the westerly monsoon winds, forcing these winds to deposit most of their rain in the windward side, which is the western side. Therefore, the area of the Deccan Plateau to the east of the Ghats receives very little rainfall. The Western Ghats are known in different regions by different names like the Konkan coast in Maharashtra while as the Malabar
14 Coast in Kerela. One of the distinct features of the Peninsular Plateau is the black soil area, known as the Deccan Trap. The Deccan Trap is of volcanic origin. On the western and north-western margins of the plateau are the Aravali hills, one of the oldest ranges in the world. The Aravali hills extend from Gujarat to Delhi in a south-west to north-east direction. Peninsular Rivers The Western Ghats make up an important water divide in peninsular India. The major rivers in peninsular India are the Mahanadi, the Godavari, the Krishna and the Kaveri, which flow eastwards and drain into the Bay of Bengal.
15 The two major rivers that flow westward and drain into the Arabian Sea are the Narmada and the Tapi. The tributaries of Narmada river are the Sher, the Shakkar, the Dudhi and the Tawa. The Godavari is the longest and the largest peninsular river. It starts from Trimbak located in Nashik district of Maharashtra. The tributaries that strengthen the Godavari are the Purna, the Wardha and the Pranhita. The major tributaries are the Wainganga, the Manjira and the Penganga. The biggest tributary of the Mahanadi is the Shivnath river. The Krishna river is the second longest peninsular river. The main tributaries of Krishna river are the Tungbhadra, the Koyana, the Ghatprabha, the Musi and the Bhima.
16 The major tributaries of the Kaveri are the Amravati, the Bhavani, the Hemavati and the Kabini. The Sivanasamudram falls made by the Kaveri are the second highest waterfall in India. The Indian Desert, the Coastal Plains and the Islands The Great Indian Desert is a rolling sandy plain covered by sand dunes and most of these are crescent-shaped sand dunes, called Barchans of longitudinal dunes. Seif dunes are thought to develop from barchans if the direction of the wind changes. The rainfall in this region is quite low-below 150 millimetres per year. During the rainy season, some streams but as these do not have enough water to reach the sea they disappear slowly into the sand
17 again. The only exception is the river Luni, which is a large river. Beyond the Western Ghats and the Eastern Ghats, the plateau is bordered by narrow coastal strips. The western strip runs along the Arabian Sea, while the eastern strip is along the Bay of Bengal. The western coastal area is divided into three sections: Konkan The Kannad Plain and The Malabar Coast. The eastern coast runs along the Bay of Bengal, displays wide and level stretches and has different local names. In the northern parts, people refer to this coastal area as the Northern Circars while people in the south call it the Coromandel Coast.
18 Large rivers like the Mahanadi, the Godavari, the Krishna and the Kaveri form a wide delta on the eastern coast. The lake Cilika on the eastern coast is said to be the largest salt water lake in India. It is located in Orissa, to the south of the Mahanadi delta. Off the mainland, the country consists of two groups of islands or archipelagos: The Lakshadweep Islands group, and The Andaman and Nicobar Islands. The Lakshadweep Islands overall consists of small coral islands. Coral polyps are microscopic marine organisms, which have short life spans. Coral reefs are built of a combination of a hard rock-like secretion from the coral polyps and their skeletons.
19 There are three main kinds of reefs: Barrier reef, Fringing reef and Atolls. A barrier reef is one that is separated from a mainland or island shore by a deep lagoon like The Great Barrier Reef of Australia. An atoll is a circular barrier reef. There is no central island, and the reef extends all the way around the lagoon, forming the shape of a horseshoe. A fringe reef is one that is directly attached to a shore. Before 1973, the Lakshadweep Islands were known as Laccadive, Minicoy and Amindive. The Andaman and Nicobar Islands is a long chain of islands extending from north to south, located in the Bay of Bengal. The entire group of islands is
20 divided into two broad categories: the northern islands are called the Andaman, and the southern islands constitute the Nicobar. The Andaman and Nicobar Islands house India s only active volcano located on the Barren Island. Pakistan: Features and Climate Location Though Pakistan and India share a some common history their physical features are quiet different from each other. Five of the fourteen highest peaks in the world are located in Pakistan. Pakistan is located on India's north-western boarder, Iran to its west, Afghanistan to its north west and the Arabian sea to its south.
21 Physical features Because of its location along the coalition point between Indian and Asian tectonic plates, most of the country has high and rugged mountains. Earth quakes occur when the tech tonic plates move towards each other. Due to this cause nearly 18 earth quakes occurred in Pakistan till now. Moutains Sulaiman Range and Kirthr Range are there in the western region of Pakistan. In the north western region the two important mountain passes are Khyber and Bolan. Thse passes have Historical importance as foreign traders and invaders enter to Indian subcontinent through these passes.
22 Rivers Though Pakistan was a mountainious country it was fertile because of Indus river and its tributaries Jhelum, Chenab, Ravi, Sutlej and Beas. Due to these rivers this region is known as Gift of the Indus. Agriculture The fertile soil in this region supports agriculture. Agriculture is the chief occupation of this country. Wheat and paddy are the important crops grown in the wet areas and Maize is grown in dry areas. Sugar cane and cotton are important cash crops of Pakistan.
23 Industries Most of the industries are based on agriculture as Pakistan was basically an agricultural country. Pakistan has Industries like Cotton textile, sugar, cement, paper and chemical. Mineral resources Pakistan also has some minerals like coal and petroleum, which contribute to the development of the country's economy. Economic Centers Some of the economic centers of Pakistan are Islamabad, the Capital city of Pakistan. Karchi, an important port. Peshawar, gateway to the Khyber pass. Quetta, situated along the Bolan pass.
24 Hyderabd, Lahore and Rawalpindi are other important cities. Climate Generally Pakistan experiences hot summers and very cold winters. The country receives abundant rainfall from South west monsoon in summer and from the north west cyclonic winds in the winter. Bangladesh Bangladesh is located to the east of India. The Tropic of Cancer divides it into two equal halves. It is bordered by Myanmar in the southeast and Bay of Bengal in the south. It shares its eastern, western and
25 northern boundaries with India. Rivers Bangladesh has many tributaries of the rivers Ganga and Brahmaputra and lowlying wet lands known as marshy areas.much of Bangladesh is less than ten meters above sea level. Eighty percent of rests on the flooded plains of the River Ganga. Floods As the country is located on the Ganga Brahmaputra delta Bangladesh is troubled by disastrous floods almost every year. each year about 26,000 square kilometres of the country is flooded either from monsoon rain or from snow-fed rivers. These conditions have caused huge
26 damages in Bangladesh in the past. Ganga and Brahmaputra delta Most of the country is composed of fertile alluvium sediments, deposited by the rivers that overflow their banks during the monsoons and cover most of the country. The rivers Ganga and Brahmaputra together form the world s largest delta. This delta region has many tributaries of rivers and also has the lowlying wet lands known as marshy areas. Rain fall The marshy lowlands of Bangladesh get flooded during the monsoon months as they receive heavy rains caused by the southwest monsoon winds. When the monsoon retreats, it brings with it periodic
27 cyclones that cause a lot of destruction. Climate The temperatures in Bangladesh are generally very high in the summers and gradually decrease during the winters. The Sylhet and Chittagong hills, which are covered with monsoon forests. Teak is one of the predominant trees grown in this region. Forests The Sundarbans forest located to the south of the country. The name Sundarbans have been derived from the Sundari trees that grow abundantly here. The forest is also well known for its tigers. While tigers inhabit the Sundarbans, snakes are common in the marshy
28 lowlands of Bangladesh. Agriculture Agriculture is the major occupation of the people in Bangladesh due to this most of the industries in Bangladesh are agrobased. The other industries that contribute to the economy are paper, sugar, tea, glass and match box industries. The marshy lowlands support the cultivation of jute. The jute industry here is well known all over the world. Paddy, cotton and tobacco are also grown in Bangladesh. Tea is cultivated on the slopes of the hills.
29 Mineral Resources Mineral resources such as limestone, natural gas, salt and petroleum are found here in small quantities. Mineral resources also contribute to the country s economy. Cities Bangladesh has some of the fast growing cities in the world. They are Dhaka, the capital city, Chittagong, a major port, and Khulna, another important city.these cities and the other regions of Bangladesh are highly populated.
30 Population Bangladesh has made considerable economic progress. Though is it the most densely populated country in the world and troubled of the floods, cyclones, famines and other natural disasters that have struck the country. Nepal Nepal, also known as the Himalayan Kingdom due to it's dominance in the Himalayas in world. Nepal is also called as located to the north of India. India on its east, west and south made Nepal a land locked nation with no coastal line. Mountains of Nepal In the northern part of Nepal the great Himalayan range, which is also called the Himadri streched. Some of the well
31 known peaks in the world Mt.Makalu, Mt. Kanchenjunga, Mt. Daulagiri and Mt. Annpurna are located here. The Himalayan Kingdom of Nepal is home to the worlds' highest peak, Mt. Everest. Terai region of Nepal In the Southern part of Himalyas there is a low lying region, which is known as terai. Most of the rivers of the Nepal flows through this region. The rivers like Karnali, Kali gandaki, Sapta kosi.these rivers are originated from the mountains and fed by the melting glaciers. Valleys of Nepal Valleys are located between the steep moutains of Nepal. Kathmandu and Pokhara are the two main valleys of that
32 kind. Kathmandu is the capital city of Nepal. Climate of Nepal In northern parts of Nepal the temperature is extremely low because this region is coverd in snow due to its high altitude. In the terai region of Nepal the temperatiute is high in summers. The rain fall is heavy in the east and decreases towards the west. Forests of Nepal Forest cover of Nepal is different from valleys to mountains. The lower slopes have evergreen forests while the higher slopes have deciduous forests. At the highest areas evergreen, decidduous and cofirerrous trees are found. At much higher levels only the coniferrous forests are
33 found. Wildlife of Nepal Rhinoceros, Tigers, Leopards, Bear and Deer are found in the thik forests of nepal. At much higher altitude Musk deer, Snow leapard, Yaks and Red pandas are found. Agriculture As this country is mountanious only 1/5th of land is used for cultivation. The main occuaption of Nepal is agriculture.paddy, Wheat, Jute, Vegetables and Fruits are grown in the Teria region. Corn, Milets and Pulses are cultivated in the lower slopes of the Himalayas.
34 Mineral resources Mica, Copper, Iron ore and Lignite are the minerals found here which also contributre to the Nepals economy. Due to its moutanious terrain much of the country hasn't been utilised for mining. Industries The economy of Nepal is also dependent on its small scale industries like cigarette, bricks, terxtiles, foot wear, liquor, cement etc. Along with these marble polishing is also a popular occupation of Nepal.
2. PHYSICAL FEATURES OF INDIA
 2. PHYSICAL FEATURES OF INDIA Question 1: Choose the right answer from the four alternatives given below. (i) A landmass bound by sea on three sides is referred to as (a) Coast (c) Peninsula (b) Island
2. PHYSICAL FEATURES OF INDIA Question 1: Choose the right answer from the four alternatives given below. (i) A landmass bound by sea on three sides is referred to as (a) Coast (c) Peninsula (b) Island
NCERT Class 9th Social Science Geography Chapter 2: Physical Features of India
 NCERT Class 9th Social Science Geography Chapter 2: Physical Features of India Question 1. Choose the right answer from the four alternatives given below. (i) A landmass bounded by sea on three sides in
NCERT Class 9th Social Science Geography Chapter 2: Physical Features of India Question 1. Choose the right answer from the four alternatives given below. (i) A landmass bounded by sea on three sides in
India is a vast country with varied landforms. Our country has practically all major physical features of the earth i.e. mountains, plains, deserts,
 India is a vast country with varied landforms. Our country has practically all major physical features of the earth i.e. mountains, plains, deserts, plateaus and islands. India is a large landmass formed
India is a vast country with varied landforms. Our country has practically all major physical features of the earth i.e. mountains, plains, deserts, plateaus and islands. India is a large landmass formed
INDIAN SCHOOL MUSCAT SENIOR SECTION DEPARTMENT OF SOCIAL SCIENCE CLASS: IX : GEOGRAPHY TOPIC/CHAPTER: CHAPTER: 2 PHYSICAL FEATURES
 INDIAN SCHOOL MUSCAT SENIOR SECTION DEPARTMENT OF SOCIAL SCIENCE CLASS: IX : GEOGRAPHY TOPIC/CHAPTER: CHAPTER: 2 PHYSICAL FEATURES WORKSHEET NO. 06 Summary:- Tectonic Plate Theory:- This theory is based
INDIAN SCHOOL MUSCAT SENIOR SECTION DEPARTMENT OF SOCIAL SCIENCE CLASS: IX : GEOGRAPHY TOPIC/CHAPTER: CHAPTER: 2 PHYSICAL FEATURES WORKSHEET NO. 06 Summary:- Tectonic Plate Theory:- This theory is based
Geography: Contemporary India - For Class IX Physical Features of India
 Geography: Contemporary India - For Class IX Physical Features of India (Q.1) Which are the two broad classification of peninsular plateau? (Q.2) What is a Doab? (Q.3) What is an Alluvial Plain. (Q.4)
Geography: Contemporary India - For Class IX Physical Features of India (Q.1) Which are the two broad classification of peninsular plateau? (Q.2) What is a Doab? (Q.3) What is an Alluvial Plain. (Q.4)
OUR COUNTRY INDIA LOCATIONAL SETTING
 7 India is a country of vast geographical expanse. In the north, it is bound by the lofty Himalayas. The Arabian Sea in the west, the Bay of Bengal in the east and the Indian Ocean in the south, wash the
7 India is a country of vast geographical expanse. In the north, it is bound by the lofty Himalayas. The Arabian Sea in the west, the Bay of Bengal in the east and the Indian Ocean in the south, wash the
You have already learnt earlier that India
 2 PHYSICAL FEATURES OF INDIA You have already learnt earlier that India is a vast country with varied landforms. What kind of terrain do you live in? If you live in the plains you are familiar with the
2 PHYSICAL FEATURES OF INDIA You have already learnt earlier that India is a vast country with varied landforms. What kind of terrain do you live in? If you live in the plains you are familiar with the
SMART NOTES ON INDIAN GEOGRAPHY - 3
 ON INDIAN GEOGRAPHY - 3 Point. Precise. Powerful. www.thesmartnotes.org ON INDIAN GEOGRAPHY - 3 To our Hardworking and persistence aspirants. Success is going from failure to failure without losing enthusiasm.
ON INDIAN GEOGRAPHY - 3 Point. Precise. Powerful. www.thesmartnotes.org ON INDIAN GEOGRAPHY - 3 To our Hardworking and persistence aspirants. Success is going from failure to failure without losing enthusiasm.
Summative Assessment I
 Class: IV Time: 3 Hrs. Summative Assessment I Social Science Marks: 88 Handwriting: 2 Total: 90 1. All questions are compulsory. 2. Use crayons for colouring. General Instruction I. Multiple choice questions:
Class: IV Time: 3 Hrs. Summative Assessment I Social Science Marks: 88 Handwriting: 2 Total: 90 1. All questions are compulsory. 2. Use crayons for colouring. General Instruction I. Multiple choice questions:
ITL Public School GEOGRAPHY Ch -1: India -Size and Location Class IX
 ITL Public School GEOGRAPHY Ch -1: India -Size and Location Class IX INDIA KNOWN AS A SUB CONTINENT: India and the adjoining countries are considered to be a sub-continent as it comprises of all the characteristics
ITL Public School GEOGRAPHY Ch -1: India -Size and Location Class IX INDIA KNOWN AS A SUB CONTINENT: India and the adjoining countries are considered to be a sub-continent as it comprises of all the characteristics
Natural Vegetation and Wildlife
 Natural Vegetation and Wildlife Exercise Page 51 Question 1: Choose the right answer from the four alternatives given below. (i) To which one of the following types of vegetation does rubber belong? (a)
Natural Vegetation and Wildlife Exercise Page 51 Question 1: Choose the right answer from the four alternatives given below. (i) To which one of the following types of vegetation does rubber belong? (a)
TERM I UNIT II GEOGRAPHY CLASS IX Prepared by NARAYANAN MANNANDI. The Indian School Bahrain
 TERM I UNIT II GEOGRAPHY CLASS IX 2013-14 14 Prepared by NARAYANAN MANNANDI The Indian School Bahrain Ch 1 - INDIA SIZE AND LOCATION 1) Describe the size and location of India. Location:- i) India is a
TERM I UNIT II GEOGRAPHY CLASS IX 2013-14 14 Prepared by NARAYANAN MANNANDI The Indian School Bahrain Ch 1 - INDIA SIZE AND LOCATION 1) Describe the size and location of India. Location:- i) India is a
Chapter 6, Part Colonizers arriving in North America found extremely landscapes. It looked different to region showing great.
 Social Studies 9 Unit 1 Worksheet Chapter 6, Part 1. 1. Colonizers arriving in North America found extremely landscapes. It looked different to region showing great. 2. The Earth is years old and is composed
Social Studies 9 Unit 1 Worksheet Chapter 6, Part 1. 1. Colonizers arriving in North America found extremely landscapes. It looked different to region showing great. 2. The Earth is years old and is composed
Social Science Class 9 th DRAINAGE Drainage System In India Himalayan River System Peninsular River System Lakes Role of Rivers in the Economy
 Social Science Class 9 th DRAINAGE Drainage System In India Himalayan River System Peninsular River System Lakes Role of Rivers in the Economy The term drainage describes the river system of an area. The
Social Science Class 9 th DRAINAGE Drainage System In India Himalayan River System Peninsular River System Lakes Role of Rivers in the Economy The term drainage describes the river system of an area. The
SMART NOTES ON INDIAN GEOGRAPHY - 1
 ON INDIAN GEOGRAPHY - 1 Point. Precise. Powerful. www.thesmartnotes.org ON INDIAN GEOGRAPHY - 1 To our Hardworking and persistence aspirants. Success is going from failure to failure without losing enthusiasm.
ON INDIAN GEOGRAPHY - 1 Point. Precise. Powerful. www.thesmartnotes.org ON INDIAN GEOGRAPHY - 1 To our Hardworking and persistence aspirants. Success is going from failure to failure without losing enthusiasm.
Chapter 21 Southwest Asia: Harsh & Arid Lands
 Name Hour Chapter 21 Southwest Asia: Harsh & Arid Lands Essential Question: How has the physical geography of Asia influenced the development of these regions (i.e. history, population distribution, &
Name Hour Chapter 21 Southwest Asia: Harsh & Arid Lands Essential Question: How has the physical geography of Asia influenced the development of these regions (i.e. history, population distribution, &
India - Relief Features
 India - Relief Features CHAPTER 1 In this chapter we shall study about relief features of India. In the subsequent chapters such as Climate in India; Rivers and Water Resources; The People etc we would
India - Relief Features CHAPTER 1 In this chapter we shall study about relief features of India. In the subsequent chapters such as Climate in India; Rivers and Water Resources; The People etc we would
Chapter 8 [Our World Continents and Oceans]
![Chapter 8 [Our World Continents and Oceans] Chapter 8 [Our World Continents and Oceans]](/thumbs/89/101173350.jpg) 1 (iv) so. std. Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) (for 2 nd Term) CLASS: IV SUBJECT: SOCIAL STUDIES Chapter 8 [Our World Continents and Oceans] 1. Earth is known as the planet. (a) red (b) blue (c) white
1 (iv) so. std. Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) (for 2 nd Term) CLASS: IV SUBJECT: SOCIAL STUDIES Chapter 8 [Our World Continents and Oceans] 1. Earth is known as the planet. (a) red (b) blue (c) white
Board Question Paper : March 2015
 Board Question Paper : March 2015 BOARD QUESTION PAPER : MARCH 2015 Time: 2 Hours Total Marks: 40 Note: i. All questions are compulsory. ii. Figure to the right indicate full marks. iii. Solve Q. No.3
Board Question Paper : March 2015 BOARD QUESTION PAPER : MARCH 2015 Time: 2 Hours Total Marks: 40 Note: i. All questions are compulsory. ii. Figure to the right indicate full marks. iii. Solve Q. No.3
South, Southeast, and East Asia. Physical Geography
 South, Southeast, and East Asia Physical Geography Mountains v Mountains are important in Asia because they influence: A. Population patterns B. Movement of people and goods C. Climate Mountains v The
South, Southeast, and East Asia Physical Geography Mountains v Mountains are important in Asia because they influence: A. Population patterns B. Movement of people and goods C. Climate Mountains v The
Downloaded from
 BAL BHARATI PUBLIC SCHOOL, PITAMPURA, DELHI GEOGRAPHY CLASS IX CHAPTER -3 DRAINAGE (summative assessment 1) Q.1. What is a River System? Ans. A river along with its tributaries is known as a River System
BAL BHARATI PUBLIC SCHOOL, PITAMPURA, DELHI GEOGRAPHY CLASS IX CHAPTER -3 DRAINAGE (summative assessment 1) Q.1. What is a River System? Ans. A river along with its tributaries is known as a River System
15. THE GLOBE AND THE MAP
 15. THE GLOBE AND THE MAP 1 DEFINE THE FOLLOWING 1. AXIS : The imaginary line which passes through the centre of the earth and joins the North Pole and South Pole is called the Axis. The earth rotates
15. THE GLOBE AND THE MAP 1 DEFINE THE FOLLOWING 1. AXIS : The imaginary line which passes through the centre of the earth and joins the North Pole and South Pole is called the Axis. The earth rotates
UNIT 11 SOUTH ASIA SG 1 - PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY & THE ENVIRONMENT
 UNIT 11 SOUTH ASIA SG 1 - PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY & THE ENVIRONMENT I. PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY TAKE OUT YOUR PHYSICAL MAP OF SOUTH ASIA A. The Himalayan Mountains form the northern boundary of the region (color
UNIT 11 SOUTH ASIA SG 1 - PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY & THE ENVIRONMENT I. PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY TAKE OUT YOUR PHYSICAL MAP OF SOUTH ASIA A. The Himalayan Mountains form the northern boundary of the region (color
3. HYDROMETEROLOGY. 3.1 Introduction. 3.2 Hydro-meteorological Aspect. 3.3 Rain Gauge Stations
 3. HYDROMETEROLOGY 3.1 Introduction Hydrometeorology is a branch of meteorology and hydrology that studies the transfer of water and energy between the land surface and the lower atmosphere. Detailed hydrological
3. HYDROMETEROLOGY 3.1 Introduction Hydrometeorology is a branch of meteorology and hydrology that studies the transfer of water and energy between the land surface and the lower atmosphere. Detailed hydrological
Mount Everest and the Gobi Desert
 Mount Everest and the Gobi Desert 1 Mount Everest is part of the mountain chain known as the Himalaya. Adventurers from all over the world come to try to climb it. Mount Everest is the highest mountain
Mount Everest and the Gobi Desert 1 Mount Everest is part of the mountain chain known as the Himalaya. Adventurers from all over the world come to try to climb it. Mount Everest is the highest mountain
Landforms in Canada. Canada is made up of three dis;nct types of landforms: Canadian Shield Highlands Lowlands
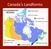 Canada s Landforms What is a Landform? A landform is any physical feature of the Earth s surface having a characteris;c, recognizable shape, produced by natural causes. Landforms include major features
Canada s Landforms What is a Landform? A landform is any physical feature of the Earth s surface having a characteris;c, recognizable shape, produced by natural causes. Landforms include major features
INDIAN SCHOOL MUSCAT SENIOR SECTION DEPARTMENT OF SOCIAL SCIENCE CLASS: IX - GEOGRAPHY CHAPTER:3 : DRAINAGE WORKSHEET NO. 09
 INDIAN SCHOOL MUSCAT SENIOR SECTION DEPARTMENT OF SOCIAL SCIENCE CLASS: IX - GEOGRAPHY CHAPTER: : DRAINAGE WORKSHEET NO. 09 Please write following question-answers in your note book: 2,4,, 8, 9, 12,18,
INDIAN SCHOOL MUSCAT SENIOR SECTION DEPARTMENT OF SOCIAL SCIENCE CLASS: IX - GEOGRAPHY CHAPTER: : DRAINAGE WORKSHEET NO. 09 Please write following question-answers in your note book: 2,4,, 8, 9, 12,18,
Chapter 1 Section 2. Land, Water, and Climate
 Chapter 1 Section 2 Land, Water, and Climate Vocabulary 1. Landforms- natural features of the Earth s land surface 2. Elevation- height above sea level 3. Relief- changes in height 4. Core- most inner
Chapter 1 Section 2 Land, Water, and Climate Vocabulary 1. Landforms- natural features of the Earth s land surface 2. Elevation- height above sea level 3. Relief- changes in height 4. Core- most inner
discussion of North America s physical features, including its landforms and bodies of
 Chapter 7 Natural Environments of North America Chapter 7 focuses on the natural environments of North America. The chapter opens with a discussion of North America s physical features, including its landforms
Chapter 7 Natural Environments of North America Chapter 7 focuses on the natural environments of North America. The chapter opens with a discussion of North America s physical features, including its landforms
DR.M.K.K ARYA MODEL SCHOOL
 DR.M.K.K ARYA MODEL SCHOOL Sub: Social science Syllabus Class-IV Session 2018-19 Prescribed book: Candid New Trends in Social Studies Syllabus to be completed in the month of April. Chapter 1.India Our
DR.M.K.K ARYA MODEL SCHOOL Sub: Social science Syllabus Class-IV Session 2018-19 Prescribed book: Candid New Trends in Social Studies Syllabus to be completed in the month of April. Chapter 1.India Our
EQ: Discuss main geographic landforms of the U.S. & Canada and examine varied landforms in relation to their lifestyles.
 EQ: Discuss main geographic landforms of the U.S. & Canada and examine varied landforms in relation to their lifestyles. Places & Terms for Discussion Appalachian Mountains Great Plains Canadian Shield
EQ: Discuss main geographic landforms of the U.S. & Canada and examine varied landforms in relation to their lifestyles. Places & Terms for Discussion Appalachian Mountains Great Plains Canadian Shield
Geographical location and climatic condition of the
 Geographical location and climatic condition of the study sites North eastern region of India is comprised of eight states namely; Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland, Sikkim
Geographical location and climatic condition of the study sites North eastern region of India is comprised of eight states namely; Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland, Sikkim
What landforms make up Australia?!
 What landforms make up Australia? The tectonic forces of folding, faulting and volcanic activity have created many of Australia's major landforms. Other forces that work on the surface of Australia, and
What landforms make up Australia? The tectonic forces of folding, faulting and volcanic activity have created many of Australia's major landforms. Other forces that work on the surface of Australia, and
(version 3) I. HumAN -Environment Interaction
 (version 3) I. HumAN -Environment Interaction A. Landforms 1. Earth s topography is made up of many different types of landforms. 2. While the planet is covered primarily with water, the four major types
(version 3) I. HumAN -Environment Interaction A. Landforms 1. Earth s topography is made up of many different types of landforms. 2. While the planet is covered primarily with water, the four major types
Unit 2. United States Physical Geography
 Unit 2 United States Physical Geography Physical Geography U.S. extends from the Atlantic to Pacific U.S. is the 3rd largest country U.S. has fertile soils, vast forests, and variety of minerals All major
Unit 2 United States Physical Geography Physical Geography U.S. extends from the Atlantic to Pacific U.S. is the 3rd largest country U.S. has fertile soils, vast forests, and variety of minerals All major
By- Saurabh Pandey Junior research fellow(jrf) NET, MA, B.TECH 3 Years teaching experience UPSC Faculty
 Important Topics (Mapping) By- Saurabh Pandey Junior research fellow(jrf) NET, MA, B.TECH 3 Years teaching experience UPSC Faculty Topic 1 - PALESTINE AND ISRAEL west asia Q Which of the following countries
Important Topics (Mapping) By- Saurabh Pandey Junior research fellow(jrf) NET, MA, B.TECH 3 Years teaching experience UPSC Faculty Topic 1 - PALESTINE AND ISRAEL west asia Q Which of the following countries
Unit 1: Geography. For additional information, refer to this website: 1 G e o g r a p h y
 Unit 1: Geography For additional information, refer to this website: http://mryoungtms.weebly.com/ 1 G e o g r a p h y Continents and Oceans SOL USI. 2a Essential Understanding: Continents are large land
Unit 1: Geography For additional information, refer to this website: http://mryoungtms.weebly.com/ 1 G e o g r a p h y Continents and Oceans SOL USI. 2a Essential Understanding: Continents are large land
water erosion lithosphere Describe the process of erosion and deposition. chemical weathering Dissolving limestone is an example of.
 At one time, there was one large island off the coast of Mississippi and now it is two separate islands. What caused the island to be split into two? water erosion The crust and the top part of the upper
At one time, there was one large island off the coast of Mississippi and now it is two separate islands. What caused the island to be split into two? water erosion The crust and the top part of the upper
Tropical Moist Rainforest
 Tropical or Lowlatitude Climates: Controlled by equatorial tropical air masses Tropical Moist Rainforest Rainfall is heavy in all months - more than 250 cm. (100 in.). Common temperatures of 27 C (80 F)
Tropical or Lowlatitude Climates: Controlled by equatorial tropical air masses Tropical Moist Rainforest Rainfall is heavy in all months - more than 250 cm. (100 in.). Common temperatures of 27 C (80 F)
Grade 9 Social Studies Canadian Identity. Chapter 2 Review Canada s Physical Landscape
 Grade 9 Social Studies Canadian Identity Chapter 2 Review Canada s Physical Landscape Name: Unit 1: Empowerment Terms (notes or textbook) 1. Core 2. Crust 3. Mantle 4. Magma 5. Continental drift 6. Plate
Grade 9 Social Studies Canadian Identity Chapter 2 Review Canada s Physical Landscape Name: Unit 1: Empowerment Terms (notes or textbook) 1. Core 2. Crust 3. Mantle 4. Magma 5. Continental drift 6. Plate
Chapter 2 Planet Earth
 Chapter 2 Planet Earth Section Notes Earth and the Sun s Energy Water on Earth The Land Close-up The Water Cycle World Almanac Major Eruptions in the Ring of Fire Quick Facts Chapter 2 Visual Summary Video
Chapter 2 Planet Earth Section Notes Earth and the Sun s Energy Water on Earth The Land Close-up The Water Cycle World Almanac Major Eruptions in the Ring of Fire Quick Facts Chapter 2 Visual Summary Video
Earth s Geological Cycle
 Earth s Geological Cycle What Are the Earth s Major Geological Processes? Main Processes: 1. Plate Tectonics 2. Rock Cycle 3. Soil Formation LITHOSPHERE The Earth s Structure Earth s Interior Core (Nickel
Earth s Geological Cycle What Are the Earth s Major Geological Processes? Main Processes: 1. Plate Tectonics 2. Rock Cycle 3. Soil Formation LITHOSPHERE The Earth s Structure Earth s Interior Core (Nickel
The peak and southern face of Mount Everest, the tallest mountain on the planet. Photo: Wikimedia Commons.
 Landforms: Mountains By Encyclopaedia Britannica, adapted by Newsela staff on 10.10.17 Word Count 563 Level 800L The peak and southern face of Mount Everest, the tallest mountain on the planet. Photo:
Landforms: Mountains By Encyclopaedia Britannica, adapted by Newsela staff on 10.10.17 Word Count 563 Level 800L The peak and southern face of Mount Everest, the tallest mountain on the planet. Photo:
Geography and Economics
 Written as per the revised syllabus prescribed by the Maharashtra State Board of Secondary and Higher Secondary Education, Pune. Social Sciences Part II Geography and Economics Std. X Salient Features
Written as per the revised syllabus prescribed by the Maharashtra State Board of Secondary and Higher Secondary Education, Pune. Social Sciences Part II Geography and Economics Std. X Salient Features
Geography Class XI Fundamentals of Physical Geography Section A Total Periods : 140 Total Marks : 70. Periods Topic Subject Matter Geographical Skills
 Geography Class XI Fundamentals of Physical Geography Section A Total Periods : 140 Total Marks : 70 Sr. No. 01 Periods Topic Subject Matter Geographical Skills Nature and Scope Definition, nature, i)
Geography Class XI Fundamentals of Physical Geography Section A Total Periods : 140 Total Marks : 70 Sr. No. 01 Periods Topic Subject Matter Geographical Skills Nature and Scope Definition, nature, i)
BOARD OF SECONDARY EDUCATION (AP) SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT - I TENTH SOCIAL MODEL PAPER PAPER - I (ENGLISH VERSION) SECTION - I
 BOARD OF SECONDARY EDUCATION (AP) SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT - I TENTH SOCIAL MODEL PAPER PAPER - I (ENGLISH VERSION) Time: 2 hrs. 45 mins. PART - A& B Maximum Marks: 40 Time: 2 hrs. 15 mins. PART - A Marks:
BOARD OF SECONDARY EDUCATION (AP) SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT - I TENTH SOCIAL MODEL PAPER PAPER - I (ENGLISH VERSION) Time: 2 hrs. 45 mins. PART - A& B Maximum Marks: 40 Time: 2 hrs. 15 mins. PART - A Marks:
Lab 7: Sedimentary Structures
 Name: Lab 7: Sedimentary Structures Sedimentary rocks account for a negligibly small fraction of Earth s mass, yet they are commonly encountered because the processes that form them are ubiquitous in the
Name: Lab 7: Sedimentary Structures Sedimentary rocks account for a negligibly small fraction of Earth s mass, yet they are commonly encountered because the processes that form them are ubiquitous in the
UNIT 2 WARM UP. List the OCEANS. Bonus: Name the Largest LAKE on Earth
 UNIT 2 WARM UP List the OCEANS Bonus: Name the Largest LAKE on Earth Land Forms Land Mountain Hill Cliff Butte Mesa Plateau Cave Volcano Desert Plains Prairie Steppe Marsh Swamp Tundra Glacier Continent
UNIT 2 WARM UP List the OCEANS Bonus: Name the Largest LAKE on Earth Land Forms Land Mountain Hill Cliff Butte Mesa Plateau Cave Volcano Desert Plains Prairie Steppe Marsh Swamp Tundra Glacier Continent
Our Environment Class 7 Questions on Give Reasons for quick revision for Competitive Exams
 Questions on Give reasons at the end of each Chapter Chapter 1 1. Man modifies his environment Man has tried to make life more comfortable for his own species on a continuous basis. For this he has learnt
Questions on Give reasons at the end of each Chapter Chapter 1 1. Man modifies his environment Man has tried to make life more comfortable for his own species on a continuous basis. For this he has learnt
Downloaded from
 I II III IV V VI Define the following terms:- a) Orbitb) Meteoroids c) Celestial bodies GEOGRAPHY ASSIGNMENTS The Earth In The Solar System d) Satellite e) Comets Give one word answers:- a) Blue planet
I II III IV V VI Define the following terms:- a) Orbitb) Meteoroids c) Celestial bodies GEOGRAPHY ASSIGNMENTS The Earth In The Solar System d) Satellite e) Comets Give one word answers:- a) Blue planet
BOARD OF SECONDARY EDUCATION (AP) SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT - I TENTH CLASS SOCIAL STUDIES MODEL PAPER PAPER - I (ENGLISH VERSION)
 BOARD OF SECONDARY EDUCATION (AP) SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT - I TENTH CLASS SOCIAL STUDIES MODEL PAPER PAPER - I (ENGLISH VERSION) Time: 2 hrs. 45 mins. PART - A & B Maximum Marks: 40 INSTRUCTIONS: i) 15 minutes
BOARD OF SECONDARY EDUCATION (AP) SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT - I TENTH CLASS SOCIAL STUDIES MODEL PAPER PAPER - I (ENGLISH VERSION) Time: 2 hrs. 45 mins. PART - A & B Maximum Marks: 40 INSTRUCTIONS: i) 15 minutes
The United States & Canada. A Regional Study of Anglo America
 A Regional Study of Anglo America Landform Regions of the United States & Canada world leaders in agricultural and industrial production because of... VAST LANDS stretch from the Atlantic Ocean on the
A Regional Study of Anglo America Landform Regions of the United States & Canada world leaders in agricultural and industrial production because of... VAST LANDS stretch from the Atlantic Ocean on the
Chapter-3 GEOGRAPHICAL LOCATION, CLIMATE AND SOIL CHARACTERISTICS OF THE STUDY SITE
 Chapter-3 GEOGRAPHICAL LOCATION, CLIMATE AND SOIL CHARACTERISTICS OF THE STUDY SITE Chapter-3 GEOGRAPHICAL LOCATION, CLIMATE AND SOIL CHARACTERISTICS OF THE STUDY SITE Assam, the eastern most state of
Chapter-3 GEOGRAPHICAL LOCATION, CLIMATE AND SOIL CHARACTERISTICS OF THE STUDY SITE Chapter-3 GEOGRAPHICAL LOCATION, CLIMATE AND SOIL CHARACTERISTICS OF THE STUDY SITE Assam, the eastern most state of
ICSE Board Class X Geography Board Paper- 2014
 Time:2 hrs ICSE Board Class X Geography Board Paper- 2014 Total Marks: 80 General Instructions: 1. Answers to this paper must be written on the paper provided separately. 2. You will not be allowed to
Time:2 hrs ICSE Board Class X Geography Board Paper- 2014 Total Marks: 80 General Instructions: 1. Answers to this paper must be written on the paper provided separately. 2. You will not be allowed to
Terrain Units PALEOGEOGRAPHY: LANDFORM CREATION. Present Geology of NYS. Detailed Geologic Map of NYS
 NYS TOPOGRAPHY Why so? PALEOGEOGRAPHY: LANDFORM CREATION Prof. Anthony Grande AFG 014 Present Geology of NYS Detailed Geologic Map of NYS Generalized Geology Detailed Geology Hot links to the fold out
NYS TOPOGRAPHY Why so? PALEOGEOGRAPHY: LANDFORM CREATION Prof. Anthony Grande AFG 014 Present Geology of NYS Detailed Geologic Map of NYS Generalized Geology Detailed Geology Hot links to the fold out
The Impact of Geography in South and East Asia
 The Impact of Geography in South and East Asia Gobi desert, Mongolia Essential Question: How does geography impact the distribution of population throughout South and East Asia? I CAN Explain how geography
The Impact of Geography in South and East Asia Gobi desert, Mongolia Essential Question: How does geography impact the distribution of population throughout South and East Asia? I CAN Explain how geography
The Impact of Geography in South and East Asia
 The Impact of Geography in South and East Asia Gobi desert, Mongolia Essential Question: How does the geography of SE Asia impact trade and the distribution of population throughout the region? (AKS #52a)
The Impact of Geography in South and East Asia Gobi desert, Mongolia Essential Question: How does the geography of SE Asia impact trade and the distribution of population throughout the region? (AKS #52a)
The Impact of Geography in South and East Asia
 The Impact of Geography in South and East Asia Gobi desert, Mongolia Essential Question: How does the geography of SE Asia impact trade and the distribution of population throughout the region? (AKS #52a)
The Impact of Geography in South and East Asia Gobi desert, Mongolia Essential Question: How does the geography of SE Asia impact trade and the distribution of population throughout the region? (AKS #52a)
The structure of the Earth and how its motion creates the seasons. The landforms of the earth and the forces that shape the land.
 The structure of the Earth and how its motion creates the seasons. The landforms of the earth and the forces that shape the land. The role of wind and water in creating climate. The different climate and
The structure of the Earth and how its motion creates the seasons. The landforms of the earth and the forces that shape the land. The role of wind and water in creating climate. The different climate and
Chapter 2 Earth s Interlocking Systems pg The Earth and Its Forces pg
 Chapter 2 Earth s Interlocking Systems pg. 24 55 2 1 The Earth and Its Forces pg. 27 33 Connecting to Your World and Internal Forces Shaping the Earth The Earth is unique in the solar system because it
Chapter 2 Earth s Interlocking Systems pg. 24 55 2 1 The Earth and Its Forces pg. 27 33 Connecting to Your World and Internal Forces Shaping the Earth The Earth is unique in the solar system because it
CANADA S LANDFORM REGIONS
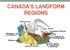 CANADA S LANDFORM REGIONS Canada s Regions Canada is divided into Eight major regions. A Region is an area that is defined on the basis of the presence or absence of certain characteristics: Age of rock
CANADA S LANDFORM REGIONS Canada s Regions Canada is divided into Eight major regions. A Region is an area that is defined on the basis of the presence or absence of certain characteristics: Age of rock
Module 10: Resources and Virginia Geology Topic 4 Content: Virginia Geology Notes
 Virginia is composed of a very diverse landscape that extends from the beaches and barrier islands all of the way to the highly elevated Appalachian Plateau. Geologists have discovered ancient shallow
Virginia is composed of a very diverse landscape that extends from the beaches and barrier islands all of the way to the highly elevated Appalachian Plateau. Geologists have discovered ancient shallow
The Sea Floor. Chapter 2
 The Sea Floor Chapter 2 Geography of the Ocean Basins World ocean is the predominant feature on the Earth in total area Northern Hemisphere = 61% of the total area is ocean. Southern Hemisphere = about
The Sea Floor Chapter 2 Geography of the Ocean Basins World ocean is the predominant feature on the Earth in total area Northern Hemisphere = 61% of the total area is ocean. Southern Hemisphere = about
WHAT IS THE EARTH MADE OF? LITHOSPHERE AND HYDROSPHERE
 UNIT 8 WHAT IS THE EARTH MADE OF? LITHOSPHERE AND HYDROSPHERE TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 THE STRUCTURE OF THE EARTH... 2 2 THE FORMATION OF THE RELIEF: INTERNAL AND EXTERNAL FORCES.... 2 2.1 Internal forces:
UNIT 8 WHAT IS THE EARTH MADE OF? LITHOSPHERE AND HYDROSPHERE TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 THE STRUCTURE OF THE EARTH... 2 2 THE FORMATION OF THE RELIEF: INTERNAL AND EXTERNAL FORCES.... 2 2.1 Internal forces:
ARE YOU READY TO THINK? Look at the first slide THINK PAIR SHARE!
 ARE YOU READY TO THINK? Look at the first slide THINK PAIR SHARE! WHAT PROMINENT FEATURE CAN YOU IDENTIFY IN THIS PICTURE? What do you think the different colors represent? Who might find such a picture
ARE YOU READY TO THINK? Look at the first slide THINK PAIR SHARE! WHAT PROMINENT FEATURE CAN YOU IDENTIFY IN THIS PICTURE? What do you think the different colors represent? Who might find such a picture
THE EARTH S RELIEF SOCIAL SCIENCES 1º ESO
 THE EARTH S RELIEF SOCIAL SCIENCES 1º ESO 1. THE STRUCTURE OF THE EARTH The Earth is divided into layers: The crust is the surface layer. It is a thin, solid layer made of rock. The Earth s crust has a
THE EARTH S RELIEF SOCIAL SCIENCES 1º ESO 1. THE STRUCTURE OF THE EARTH The Earth is divided into layers: The crust is the surface layer. It is a thin, solid layer made of rock. The Earth s crust has a
Continental Drift. & Plate Tectonics
 Continental Drift & Plate Tectonics Alfred Wegener, a German scientist, proposed the hypothesis of CONTINENTAL DRIFT, in 1912. Hypothesis stated: All Earth s continents were once a single landmass (Pangaea)
Continental Drift & Plate Tectonics Alfred Wegener, a German scientist, proposed the hypothesis of CONTINENTAL DRIFT, in 1912. Hypothesis stated: All Earth s continents were once a single landmass (Pangaea)
Plate Tectonics CHAPTER 17
 Plate Tectonics CHAPTER 17 Layers of the Earth A. Crust- solid, 5-70 km thick Moho Two Types of Crust: Oceanic- ocean floor, more dense then because of more iron Continental-dry land (mostly silicates
Plate Tectonics CHAPTER 17 Layers of the Earth A. Crust- solid, 5-70 km thick Moho Two Types of Crust: Oceanic- ocean floor, more dense then because of more iron Continental-dry land (mostly silicates
6.E E Rock Cycle/Weathering/Soil
 Name: Date: 1. A lake is surrounded by hills covered with trees and shrubs. Which statement correctly describes how a change to the plants in this area will affect this environment? A. Adding plants to
Name: Date: 1. A lake is surrounded by hills covered with trees and shrubs. Which statement correctly describes how a change to the plants in this area will affect this environment? A. Adding plants to
Social Studies. Chapter 2 Canada s Physical Landscape
 Social Studies Chapter 2 Canada s Physical Landscape Introduction Canada s geography its landforms and climate - has a great impact on Canadians sense of identity. Planet Earth The earth is divided into
Social Studies Chapter 2 Canada s Physical Landscape Introduction Canada s geography its landforms and climate - has a great impact on Canadians sense of identity. Planet Earth The earth is divided into
Report on Disaster statistics of Nepal
 Report on Disaster statistics of Nepal Submitted by Altaf Rehman Submitted to Dr. Naveed Ahmed University of engineering and technology Peshawar Assignment 1 Section A Registration id 14PWCIV456 Page 1
Report on Disaster statistics of Nepal Submitted by Altaf Rehman Submitted to Dr. Naveed Ahmed University of engineering and technology Peshawar Assignment 1 Section A Registration id 14PWCIV456 Page 1
Exploring the Geography of West Asia
 Unit 3 - Lesson 1 Content Expectations 7 G1.1.1: Explain and use a variety of maps, globes, and web based geography technology to study the world, including global, interregional, regional, and local scales.
Unit 3 - Lesson 1 Content Expectations 7 G1.1.1: Explain and use a variety of maps, globes, and web based geography technology to study the world, including global, interregional, regional, and local scales.
deep within the planet. They are also shaped by conditions on the planet s surface. In
 Chapter 4 Landforms, Water, and Natural Resources Earth is home to many different types of landforms. These landforms are shaped by forces deep within the planet. They are also shaped by conditions on
Chapter 4 Landforms, Water, and Natural Resources Earth is home to many different types of landforms. These landforms are shaped by forces deep within the planet. They are also shaped by conditions on
CHAPTER 12 NATURAL DISASTERS
 CHAPTER 12 NATURAL DISASTERS In this chapter, you learn about the following: Natural calamities cyclones causes, effects and preventive measures Floods causes, affected areas, effects and control Land
CHAPTER 12 NATURAL DISASTERS In this chapter, you learn about the following: Natural calamities cyclones causes, effects and preventive measures Floods causes, affected areas, effects and control Land
Lesson- 6 WEATHER AND CLIMATE
 Lesson- 6 WEATHER AND CLIMATE New Words 1. Heat Zones:- the division of the earth according to the climate. 2. Frigid:- the zone that is the coldest 3. Temperate:- the zone that is neither too hot nor
Lesson- 6 WEATHER AND CLIMATE New Words 1. Heat Zones:- the division of the earth according to the climate. 2. Frigid:- the zone that is the coldest 3. Temperate:- the zone that is neither too hot nor
Landscape evolution. An Anthropic landscape is the landscape modified by humans for their activities and life
 Landforms Landscape evolution A Natural landscape is the original landscape that exists before it is acted upon by human culture. An Anthropic landscape is the landscape modified by humans for their activities
Landforms Landscape evolution A Natural landscape is the original landscape that exists before it is acted upon by human culture. An Anthropic landscape is the landscape modified by humans for their activities
Explain the impact of location, climate, natural resources, and population distribution on Europe. a. Compare how the location, climate, and natural
 SS6G10 Explain the impact of location, climate, natural resources, and population distribution on Europe. a. Compare how the location, climate, and natural resources of Germany, the United Kingdom and
SS6G10 Explain the impact of location, climate, natural resources, and population distribution on Europe. a. Compare how the location, climate, and natural resources of Germany, the United Kingdom and
Pangaea to the Present Lesson #2
 Pangaea to the Present Lesson #2 The Earth is a dynamic or constantly changing planet. The thin, fragile plates slide very slowly on the mantle's upper layer. This sliding of the plates is caused by the
Pangaea to the Present Lesson #2 The Earth is a dynamic or constantly changing planet. The thin, fragile plates slide very slowly on the mantle's upper layer. This sliding of the plates is caused by the
Figure 2.1: Constituent Area
 2 The Region 2.1 CONSTITUENT AREA The National Capital Region includes NCT-Delhi, nine districts of Haryana, six districts of Uttar Pradesh and one district of Rajasthan. Total area of the region is 34,144
2 The Region 2.1 CONSTITUENT AREA The National Capital Region includes NCT-Delhi, nine districts of Haryana, six districts of Uttar Pradesh and one district of Rajasthan. Total area of the region is 34,144
PHYSICAL FEATURES OF EUROPE. Europe Unit
 PHYSICAL FEATURES OF EUROPE Europe Unit PENINSULA OF PENINSULAS Europe is a large peninsula that consists of many smaller peninsulas Most places in Europe are no more than 300 miles from an ocean or sea
PHYSICAL FEATURES OF EUROPE Europe Unit PENINSULA OF PENINSULAS Europe is a large peninsula that consists of many smaller peninsulas Most places in Europe are no more than 300 miles from an ocean or sea
The term drainage describes the river
 3 DRAINAGE The term drainage describes the river system of an area. Look at the physical map. You will notice that small streams flowing from different directions come together to form the main river,
3 DRAINAGE The term drainage describes the river system of an area. Look at the physical map. You will notice that small streams flowing from different directions come together to form the main river,
Chapter 27. Bhutan, Maldives, Nepal, & Sri Lanka
 Chapter 27 Bhutan, Maldives, Nepal, & Sri Lanka Physical Geography of Bhutan, Maldives, Nepal & Sri Lanka Landforms Their locations on the fringe of South Asia means their physical and human geography
Chapter 27 Bhutan, Maldives, Nepal, & Sri Lanka Physical Geography of Bhutan, Maldives, Nepal & Sri Lanka Landforms Their locations on the fringe of South Asia means their physical and human geography
LANDFORM REGIONS IN CANADA. Classroom Notes and Descriptions
 LANDFORM REGIONS IN CANADA Classroom Notes and Descriptions Landform Regions in Canada There are eight distinct landforms in Canada: Western Cordillera Region Interior Plains Canadian Shield Hudson Bay
LANDFORM REGIONS IN CANADA Classroom Notes and Descriptions Landform Regions in Canada There are eight distinct landforms in Canada: Western Cordillera Region Interior Plains Canadian Shield Hudson Bay
Chapter 1: The Geography of the Western Hemisphere
 Chapter 1: The Geography of the Western Hemisphere Chapter 1, Lesson 1: The Changing Earth Objectives: - You will be able to identify the major natural events that cause the earth to change. - You will
Chapter 1: The Geography of the Western Hemisphere Chapter 1, Lesson 1: The Changing Earth Objectives: - You will be able to identify the major natural events that cause the earth to change. - You will
Unit 4 - Water. Earth s Interior. Earth s Interior. Continental Drift. Continental Drift. Continental Drift. Crust. Mantle. Core.
 Unit 4 - Water How did the oceans form? What special adaptations do saltwater organisms have? Where does our water come from? How do humans affect the Earth s water? Crust Rigid outer shell of Earth Oceanic
Unit 4 - Water How did the oceans form? What special adaptations do saltwater organisms have? Where does our water come from? How do humans affect the Earth s water? Crust Rigid outer shell of Earth Oceanic
Geosphere Final Exam Study Guide
 Geosphere Final Exam Study Guide Chapter 1 Intro to Earth Systems 1. Name and describe Earth s 4 major spheres Geosphere-- nonliving, mostly solid rock divided into crust, mantle, and core Atmosphere a
Geosphere Final Exam Study Guide Chapter 1 Intro to Earth Systems 1. Name and describe Earth s 4 major spheres Geosphere-- nonliving, mostly solid rock divided into crust, mantle, and core Atmosphere a
Physical Geography of East Asia
 Physical Geography of East Asia Satellite View of China Landforms of China China s Geography China Miles 0 250 500 1,000 1,500 2,000 United States 3 rd largest country in the world. Comparable to the US
Physical Geography of East Asia Satellite View of China Landforms of China China s Geography China Miles 0 250 500 1,000 1,500 2,000 United States 3 rd largest country in the world. Comparable to the US
Directed Reading. Section: How Mountains Form MOUNTAIN RANGES AND SYSTEMS. Skills Worksheet
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: How Mountains Form 1. How high is Mount Everest? a. about 1980 km above sea level b. more than 8 km below sea level c. more than 8 km above sea level d. more
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: How Mountains Form 1. How high is Mount Everest? a. about 1980 km above sea level b. more than 8 km below sea level c. more than 8 km above sea level d. more
ISSUED BY KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA - DOWNLOADED FROM
 UNIT II CHAPTER -2 PHYSIOGRAPHY - INDIA PHYSIOGRAPHY Structure and Relief; physiographic divisions Drainage systems: concept of water sheds the Himalayan and the Peninsular Can you map different phases
UNIT II CHAPTER -2 PHYSIOGRAPHY - INDIA PHYSIOGRAPHY Structure and Relief; physiographic divisions Drainage systems: concept of water sheds the Himalayan and the Peninsular Can you map different phases
Earth Science S5E1b (EarthScienceS5E1b)
 Name: Date: 1. The flattest part of the ocean floor is the A. trench. B. abyssal plain. C. continental shelf. D. mid-ocean rift valley. 2. Which causes some parts of the ocean to be saltier than other
Name: Date: 1. The flattest part of the ocean floor is the A. trench. B. abyssal plain. C. continental shelf. D. mid-ocean rift valley. 2. Which causes some parts of the ocean to be saltier than other
Unit 1: Geography GeoTrekkers in the Western Hemisphere. Illustrated Glossary
 Unit 1: Geography GeoTrekkers in the Western Hemisphere Illustrated Glossary adapt to change in order to fit new condi/ons archipelago a group or chain of islands clustered together in a sea or ocean bodies
Unit 1: Geography GeoTrekkers in the Western Hemisphere Illustrated Glossary adapt to change in order to fit new condi/ons archipelago a group or chain of islands clustered together in a sea or ocean bodies
UNIT 3 GEOLOGY VOCABULARY FLASHCARDS THESE KEY VOCABULARY WORDS AND PHRASES APPEAR ON THE UNIT 3 CBA
 UNIT 3 GEOLOGY VOCABULARY FLASHCARDS THESE KEY VOCABULARY WORDS AND PHRASES APPEAR ON THE UNIT 3 CBA A map that shows Earth s Topographic Map surface topography, which is Earth s shape and features Contour
UNIT 3 GEOLOGY VOCABULARY FLASHCARDS THESE KEY VOCABULARY WORDS AND PHRASES APPEAR ON THE UNIT 3 CBA A map that shows Earth s Topographic Map surface topography, which is Earth s shape and features Contour
Geography Definitions/Sentences
 Geography Definitions/Sentences 1. BEACH 1. The shore of a body of water, especially when sandy or pebbly. 2. The sand or pebbles on a shore. The zone above the water line at a shore of a body of water,
Geography Definitions/Sentences 1. BEACH 1. The shore of a body of water, especially when sandy or pebbly. 2. The sand or pebbles on a shore. The zone above the water line at a shore of a body of water,
CLASS XI. Smart Skills Sanskriti School. Smart Skills Sanskriti School. Smart Skills Sanskriti School. Class XI / Geography / 1
 Principal s Message The second edition of Smartskills has been prepared with the belief that knowledge must continually be renewed with focus and effort. Our aim, as before is to help students understand,
Principal s Message The second edition of Smartskills has been prepared with the belief that knowledge must continually be renewed with focus and effort. Our aim, as before is to help students understand,
Chapter 27. Bhutan, Maldives, Nepal, & Sri Lanka
 Chapter 27 Bhutan, Maldives, Nepal, & Sri Lanka Physical Geography of Bhutan, Maldives, Nepal & Sri Lanka Landforms Their locations on the fringe of South Asia means their physical and human geography
Chapter 27 Bhutan, Maldives, Nepal, & Sri Lanka Physical Geography of Bhutan, Maldives, Nepal & Sri Lanka Landforms Their locations on the fringe of South Asia means their physical and human geography
GLOBAL CLIMATES FOCUS
 which you will learn more about in Chapter 6. Refer to the climate map and chart on pages 28-29 as you read the rest of this chapter. FOCUS GLOBAL CLIMATES What are the major influences on climate? Where
which you will learn more about in Chapter 6. Refer to the climate map and chart on pages 28-29 as you read the rest of this chapter. FOCUS GLOBAL CLIMATES What are the major influences on climate? Where
Fossil Clues Teacher s Notes
 Fossils are the remains of living things which have been changed into rock. The father of modern geology, James Hutton, said that we can interpret the nature of creatures from the past and the environment
Fossils are the remains of living things which have been changed into rock. The father of modern geology, James Hutton, said that we can interpret the nature of creatures from the past and the environment
Name. 4. The diagram below shows a soil profile formed in an area of granite bedrock. Four different soil horizons, A, B, C, and D, are shown.
 Name 1. In the cross section of the hill shown below, which rock units are probably most resistant to weathering? 4. The diagram below shows a soil profile formed in an area of granite bedrock. Four different
Name 1. In the cross section of the hill shown below, which rock units are probably most resistant to weathering? 4. The diagram below shows a soil profile formed in an area of granite bedrock. Four different
Directed Reading. Section: Continental Drift. years ago? WEGENER S HYPOTHESIS
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Continental Drift 1. Who obtained new information about the continents and their coastlines 400 years ago? 2. What did people notice when they studied new world
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Continental Drift 1. Who obtained new information about the continents and their coastlines 400 years ago? 2. What did people notice when they studied new world
PLATE TECTONICS. SECTION 17.1 Drifting Continents
 Date Period Name PLATE TECTONICS SECTION.1 Drifting Continents In your textbook, read about continental drift. Circle the letter of the choice that best completes each statement. 1. Early mapmakers thought
Date Period Name PLATE TECTONICS SECTION.1 Drifting Continents In your textbook, read about continental drift. Circle the letter of the choice that best completes each statement. 1. Early mapmakers thought
