Downloaded from
|
|
|
- Ethel Jasmin Turner
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 BAL BHARATI PUBLIC SCHOOL, PITAMPURA, DELHI GEOGRAPHY CLASS IX CHAPTER -3 DRAINAGE (summative assessment 1) Q.1. What is a River System? Ans. A river along with its tributaries is known as a River System or a Drainage system. Ex. Ganga River System, Indus River System etc. Q.2. Define the term drainage. Ans. The term drainage describes the river system of an area. Q.3. What is a drainage basin? Ans. The area drained by a single river system is called a drainage basin. Q.4. What do you understand by the term Water Divide? Ans. Any elevated area such as a mountain or an upland that separates two drainage basins is called a Water Divide. Ex. Ambala act as a water divide between Indus and Ganga River System. Q.5. Define the following: Ans. a. Drainage Pattern The pattern formed by a river in a drainage basin depending upon the slope of land, rock structure and also climatic condition is referred to as Drainage Pattern. b. Perennial Rivers Perennial rivers are those which have water throughout the year. These rivers receive water from rain as well as from melted snow of the mountains. Ex. Ganga, Indus, Brahamaputra. c. Seasonal Rivers
2 Seasonal rivers are those which are dependent upon rainfall for their flow. During the dry season, even the large rivers have reduced the flow of water. Ex. Peninsular Rivers like Mahanadi, Godavari, Narmada etc. Q.6. What are the two types of drainage systems found in India? Ans. Himalayan and Peninsular river systems. Q.7. Name the rivers that originate from Mansarovar Lake. Ans. River Indus, Satluj and Brahmaputra Q.8. Where the headwaters of Ganga meet at? Ans. Bhagirathi and Alaknanda meet at Dev Prayag in Uttarakhand. Q.9. Where river Ganga leaves behind the mountains and enter the plains? Ans. Haridwar Q.10. Which river flows in Tibet with the name Tsang Po? Ans. Brahamaputra Q.11. What is the source and mouth of the river? Ans. The place from where the river originates is called as the Source of the river. The place where the river meets its end is known as the Mouth of the river. Q.12.Apart from Narmada and Tapi, which are the other west flowing rivers? Ans. Sabarmati, Mahi, Periyar, Bharathpuzha. Q.13. Name the east flowing rivers of India apart from the major ones. Ans. Damodar, Brahmani, Subarn rekha, Baitarni. Q.14. Which peninsular rivers flow through a rift valley? Ans. Narmada and Tapi Q.15. Which rivers have the largest river basins in India and in Peninsular India? Ans. In India: Ganga In Peninsular India: Godavari Q.16. What are the characteristics of river Yamuna?
3 Ans. a. River Yamuna originates from the Yamunotri glacier of the Himalayas. b. It is the largest tributary of river Ganga. c. The river moves parallel to Ganga for a long distance and finally meets with Ganga at Allahabad. d. Many peninsular rivers join the Yamuna like Chambal, Betwa, Sind etc. Q.17. Explain the Indus Water Treaty. Ans. a. The Indus Water Treaty was sighned between India and Pakistan in b. According to the regulations of this treaty India can use only 20% of the total water carried by Indus system. c. This water is used for irrigation in the Punjab, Haryana and the southern and western parts of Rajasthan. Q.18. What are the features of Sundarban Delta? Ans. a. The delta formed by the rivers Ganga and Brahmaputra which is the largest delta of the world is known as Sundarban Delta. b. The delta derived its name from the Sundari trees which grows well in this marshland. c. It is the world s fast growing delta. d. It is also the home of Royal Bengal Tiger. Q.19. Differentiate between the following: Ans. A. Himalayan river system and Peninsular river system. HIMALAYAN RIVER SYSTEM 1. The Himalayan rivers originates from the Himalayas. 2. Most of the Himalayan rivers are perennial in nature, i.e., both rainfed and snowfed. 3. Himalayan rivers have longer course and carry more sediments in them. 4. These rivers are involved more in doing erosional and depositional activities and therefore, forms many land features like valleys, gorges, meanders, ox-bow lake, delta etc. PENINSULAR RIVER SYSTEM The Peninsular rivers have their source in the peninsula of the country. Most of the peninsular rivers are seasonal in nature i.e. only rainfed. Peninsular rivers have shorter course and carry less sediments in them. These rivers are involved less in the erosional and depositional activities. Most of the rivers form only deltas.
4 5. These rivers have got comparatively larger drainage basin. 6. Ex. Indus river system, Brahmaputra river system, Ganga river system. The drainage basin formed by these rivers is less. Ex. Mahanadi basin, Godavari basin, Tapi basin etc. B. Distributaries and Tributaries DISTRIBUTARIES 1. Distributaries are the small channels of rivers that separate themselves from the main river before into the sea. 2. Distributaries are formed in the lower course of the river. 3. Distributaries decreases the volume of water and the sediments from the main river. 4. Ex. Hoogli is a distributary of river Ganga. TRIBUTARIES Tributaries are rivers or streams that join the main river. Tributaries join the main river in the upper and middle course of the river. Tributaries increases the volume of water and sediments deposition of the main river. Ex. Yamuna is a tributary of Ganga. C. Delta and Estuary DELTA ESTUARY 1. A delta is formed by the river when it is When the river directly enter the sea it forms about to enter the sea by forming an estuary. various distributaries. 2. It is roughly triangular in shape. It is a funnel shaped land feature. 3. The delta region is highly fertile The region near estuary is not very fertile. because of the sediment deposition. 4. Agriculture can be practiced here. Estuary regions are good for fishing activites. 5. Ex. River Ganga, Indus, Godavari, Ex. Narmada and Tapi forms estuary. Mahanadi forms delta. D. East flowing rivers and West flowing rivers. EAST FLOWING RIVERS 1. These rivers originate from or near to the Western Ghats and flows towards east. 2. These peninsular rivers have longer courses and more sediments deposition. 3. Most of the east flowing rivers forms delta while into the Bay of Bengal. WEST FLOWING RIVERS These rivers originate from east and flows towards western India. These rivers have shorter courses and carry less sediment with them. Most of the rivers forms estuary while the Arabian sea.
5 4. Ex. Mahanadi, Godavari, Krishna, Kaveri. Ex. Narmada and Tapi Q.20. Why does the Brahmaputra in its Tibetan part have less silt, despite a longer course? Ans. In Tibet, the river carries a smaller volume of water and less silt as it is a cold and a dry area. When the river enters India, the volume of water increases by the tributaries added into it, high rainfall and melting snow. Therefore, Brahmaputra in its Tibetan part have less silt, despite a longer course. Q.21. Why river Godavari is often referred to as Dakshin Ganga? Ans. Since river Ganga and Godavari are carrying similar characteristics, therefore, river Godavari is often referred to as Dakshin Ganga. 1. As river Ganga is the largest river of India with the largest drainage basin, similarly Godavari is the largest river of peninsular India with the largest drainage basin. 2. River Godavari and Ganga have the similar religious sentiments of the people attached to it. Q.22. Explain the four drainage patterns. Ans. DENDRITIC PATTERN The dendritic pattern develops where the river channel follows the slope of the terrain. The stream along with its tributaries resembles the branches of a tree, thus the name dendritic. Ex. River Ganga along with its tributaries. TRELLIS PATTERN A river joined by its tributaries at approximately right angles, develop a trellis pattern. It is develop where hard and soft rocks are parallel to each-other. Ex. River Narmada along with its tributaries. RECTANGULAR PATTERN A rectangular pattern is developed on a strongly jointed rocky terrain. RADIAL PATTERN
6 The radial pattern develops when streams flow in different directions from a central peak or dome like structure. Ex. Rivers like Narmada and Tapi rising from the highlands of the peninsular plateau. Q.23. Study the information regarding the major river systems of India with the help of the following table: RIVER SOURCE MOUTH LENGTH TRIBUTARIES COURSE Indus river 2900km system Ganga river system Brahamaputra River System Near Mansarovar lake, in Tibet Headwaters- Bhagirathi from Gangotri glacier meets with Alaknanda at Dev Prayag in Uttarakhand to form river Ganga. East of Mansarovar lake in Tibet Forms a delta to the east of Karachi in Pakistan Meets with Brahmaput ra in Banglades h and forms the largest delta of the world known as Sundarban Delta (Bay of Bengal) Meets with Ganga in Banglades h and forms the largest delta of the world known as Over 2500km. Over 2900km *In Jammu and Kashmir Shyok, Hunza, Zaskar and Nubra. *Satluj, Beas, Ravi, Chenab and Jhelum meets Indus near Mithankot in Pakistan *Left bank tributaries: Ghaghara, Gandak and Kosi rising from Nepal Himalayas. *Right bank tributaries: **Yamuna is the largest tributary. **Son, a peninsular river is also a right bank tributary. **Sind, Chambal, Betwa are the tributaries of Yamuna and therefore, becomes a part of Ganga river system. Dibang, Lohit, Kenula, etc. From Tibet, river flows towards west and enters India through Ladakh district (J&K). In Kashmir valley, river flows through Baltistan and Gilgit and emerges at Attock mountain, Enters Pakistan and flows southwards towards Arabian sea. From Dev Prayag the river flows in the rugged mountainous region and enter the plains at Haridwar. Crossing the states like Uttarakhand, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar and West Bengal the river enters Bangladesh. At Farakka in West Bengal, The river divides itself into distributaries like Hoogli. From here, the river moves southward to form the delta towards Bay of Bengal. It flows eastward parallel to Himalayas in the Tibet. On reaching Namcha Barwa, it takes a U turn and enters India through a gorge in Arunachal Pradesh. The river
7 Narmada basin Tapi basin Mahanadi Basin Godavari Basin Krishna Basin Kaveri Basin From Amarkantak hills in Madhya Pradesh Rises in Satpura range, Betul district of Meghalaya. Rises in the highlands of Chattisgarh. Rises from slopes of the Western Ghats in Nasik district of Maharashtra. Rises from a spring near Mahabaleashwar in Maharashtra Rises in Brahmagri range of Western Ghats. Sundarban Delta (Bay of Bengal Forms an estuary while into the Arabian sea. Forms an estuary while into the Arabian sea. Forms a delta while into Bay of Bengal. Forms a delta while into Bay of Bengal Forms a delta while into Bay of Bengal Forms a delta while into Bay of Bengal to the south of Cuddalore. Shorter than Narmada About 860km 1500km (largest peninsular river) About 1400km About 760km All the tributaries of Narmada are very short and join the main stream at right angle. Purna, Wardha, Penganga, Wainganga etc. Tungabhadra, Bhima, Musi, Koyana etc. Amravati, Bhavani, Hemavati, Kabini. moves forward towards Assam and enters Bangladesh to form the delta with Ganga. The river flows towards the west in a rift valley. Near Jabalpur, the river flows through a deep gorge. Narmada basin covers parts of Madhya Pradesh and Gujarat. It also flows in a rift valley, parallel to Narmada. Its basin covers parts Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, and Gujarat. The drainage basin of river Mahanadi is shared by Maharashtra, Chattisgarh, Jharkhand and Orissa. Godavari has the largest drainage basin among the peninsular rivers. It cover Maharashtra (50%), Madhya Pradesh, Orissa, and Andhra Pradesh. The drainage basin of river Krishna is shared by Maharashtra, Karnataka, and Andhra Pradesh. Its basin drains parts of Karnataka, Kerela, and Tamil Nadu.
8 Q.24. Explain the different formations of lakes. Ans. A. Oxbow lake B. Lagoons An oxbow lake is formed when the meandering river across a flood plain forms cut offs. Spits and bars in the coastal areas formed by the depositional work of oceanic movement forms a lagoon. Ex. Chilika lake (largest lake in India), Pulikat lake, Kolleru lake C. Seasonal Lakes Lakes in the region of inland drainage are sometimes seasonal which depends upon the rainfall. Ex. Sambhar lake in Rajasthan which is a salt water lake. D. Glacial Lake These types of lakes are mostly found in Himalayan region. They are formed when glaciers dug out a basin which was later filled snow melt. Ex. Wular lake in Jammu & Kashmir which is the largest fresh water lake. E. Artificial Lakes Damming of rivers for the generation of hydel power has also led to the formation of lakes. Ex. Guru Gobind Sagar on Bhakra Nangal Project. Q.25. Why lakes are important for human beings? Ans. a. Regulate the flow of river Lakes help to regulate the flow of a river. During heavy rainfall, it prevents flooding and during the dry season, it helps to maintain an even flow of water. b. Generation of Hydel Power Damming of rivers is done in order to store the water for the generation of Hydro electricity. Ex. Hirakud dam on Mahanadi river. c. Promote Tourism Lakes are always an attraction for tourists for recreation. Lakes enhance the natural beauty of the adjoining area and hence, promote tourism. Ex. Wular lake, Dal Lake in Jammu & Kashmir.
9 d. Moderate Climate Lakes also help in moderating the climate of the adjoining area that supports ecosystem within the lake and also outside the lake. e. Source of rivers Many lakes are also the major source for many rivers. Ex. Indus, Satluj, Brahamaputra have their source in the Mansarovar lake. Q.26. What is the role of a river in building up of an economy? Ans. a. Cradle of Civilization River banks have attracted settlers from ancient times. All the major civilizations of the world were settled near to the river banks. Ex. Indus Valley Civilization, Nile Civilization etc. Even today, many important cities of the world are settled near to the river banks. b. Basic Natural Resource Rivers have been of fundamental importance throughout the human history. Water from the rivers is a basic natural resource, essential for various human activities. c. Deposition of Sediments The deposition of sediments done by the rivers makes the river banks highly good for cultivation, thus, promoting agriculture over there. d. Other uses Using rivers for irrigation, navigation, hydro-power generation is of special significance for a country. Q.27. What are the main causes of increasing river pollution? Ans. a. Industrial Effluents: A heavy load of untreated sewage and industrial effluents are emptied into the rivers. This affects the quality of water and also the self cleansing capacity of the river. b. Urbanization: Modern trends of living consume more water. Moreover, the sewage problems in cities have further added to the problem of water pollution. c. Domestic Use: The use of rivers and lakes done for domestic purposes like washing and bathing is adding to the problem of water pollution.
10
Social Science Class 9 th DRAINAGE Drainage System In India Himalayan River System Peninsular River System Lakes Role of Rivers in the Economy
 Social Science Class 9 th DRAINAGE Drainage System In India Himalayan River System Peninsular River System Lakes Role of Rivers in the Economy The term drainage describes the river system of an area. The
Social Science Class 9 th DRAINAGE Drainage System In India Himalayan River System Peninsular River System Lakes Role of Rivers in the Economy The term drainage describes the river system of an area. The
INDIAN SCHOOL MUSCAT SENIOR SECTION DEPARTMENT OF SOCIAL SCIENCE CLASS: IX - GEOGRAPHY CHAPTER:3 : DRAINAGE WORKSHEET NO. 09
 INDIAN SCHOOL MUSCAT SENIOR SECTION DEPARTMENT OF SOCIAL SCIENCE CLASS: IX - GEOGRAPHY CHAPTER: : DRAINAGE WORKSHEET NO. 09 Please write following question-answers in your note book: 2,4,, 8, 9, 12,18,
INDIAN SCHOOL MUSCAT SENIOR SECTION DEPARTMENT OF SOCIAL SCIENCE CLASS: IX - GEOGRAPHY CHAPTER: : DRAINAGE WORKSHEET NO. 09 Please write following question-answers in your note book: 2,4,, 8, 9, 12,18,
The term drainage describes the river
 3 DRAINAGE The term drainage describes the river system of an area. Look at the physical map. You will notice that small streams flowing from different directions come together to form the main river,
3 DRAINAGE The term drainage describes the river system of an area. Look at the physical map. You will notice that small streams flowing from different directions come together to form the main river,
ITL Public School GEOGRAPHY Ch -1: India -Size and Location Class IX
 ITL Public School GEOGRAPHY Ch -1: India -Size and Location Class IX INDIA KNOWN AS A SUB CONTINENT: India and the adjoining countries are considered to be a sub-continent as it comprises of all the characteristics
ITL Public School GEOGRAPHY Ch -1: India -Size and Location Class IX INDIA KNOWN AS A SUB CONTINENT: India and the adjoining countries are considered to be a sub-continent as it comprises of all the characteristics
ISSUED BY KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA - DOWNLOADED FROM CHAPTER -3 DRAINAGE SYSTEM
 CHAPTER -3 DRAINAGE SYSTEM The flow of water through well-defined channels is known as drainage The network of such channels is called a drainage system. The drainage pattern of an area is the outcome
CHAPTER -3 DRAINAGE SYSTEM The flow of water through well-defined channels is known as drainage The network of such channels is called a drainage system. The drainage pattern of an area is the outcome
SMART NOTES ON INDIAN GEOGRAPHY - 3
 ON INDIAN GEOGRAPHY - 3 Point. Precise. Powerful. www.thesmartnotes.org ON INDIAN GEOGRAPHY - 3 To our Hardworking and persistence aspirants. Success is going from failure to failure without losing enthusiasm.
ON INDIAN GEOGRAPHY - 3 Point. Precise. Powerful. www.thesmartnotes.org ON INDIAN GEOGRAPHY - 3 To our Hardworking and persistence aspirants. Success is going from failure to failure without losing enthusiasm.
TERM I UNIT II GEOGRAPHY CLASS IX Prepared by NARAYANAN MANNANDI. The Indian School Bahrain
 TERM I UNIT II GEOGRAPHY CLASS IX 2013-14 14 Prepared by NARAYANAN MANNANDI The Indian School Bahrain Ch 1 - INDIA SIZE AND LOCATION 1) Describe the size and location of India. Location:- i) India is a
TERM I UNIT II GEOGRAPHY CLASS IX 2013-14 14 Prepared by NARAYANAN MANNANDI The Indian School Bahrain Ch 1 - INDIA SIZE AND LOCATION 1) Describe the size and location of India. Location:- i) India is a
OUR COUNTRY INDIA LOCATIONAL SETTING
 7 India is a country of vast geographical expanse. In the north, it is bound by the lofty Himalayas. The Arabian Sea in the west, the Bay of Bengal in the east and the Indian Ocean in the south, wash the
7 India is a country of vast geographical expanse. In the north, it is bound by the lofty Himalayas. The Arabian Sea in the west, the Bay of Bengal in the east and the Indian Ocean in the south, wash the
N. K. Manglik Director
 N. K. Manglik Director Hydro-meteorological observations could be broadly defined as the scientific way for collection of flow data at a specific location along the river including selected meteorological
N. K. Manglik Director Hydro-meteorological observations could be broadly defined as the scientific way for collection of flow data at a specific location along the river including selected meteorological
Chapter 8 [Our World Continents and Oceans]
![Chapter 8 [Our World Continents and Oceans] Chapter 8 [Our World Continents and Oceans]](/thumbs/89/101173350.jpg) 1 (iv) so. std. Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) (for 2 nd Term) CLASS: IV SUBJECT: SOCIAL STUDIES Chapter 8 [Our World Continents and Oceans] 1. Earth is known as the planet. (a) red (b) blue (c) white
1 (iv) so. std. Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) (for 2 nd Term) CLASS: IV SUBJECT: SOCIAL STUDIES Chapter 8 [Our World Continents and Oceans] 1. Earth is known as the planet. (a) red (b) blue (c) white
Summative Assessment I
 Class: IV Time: 3 Hrs. Summative Assessment I Social Science Marks: 88 Handwriting: 2 Total: 90 1. All questions are compulsory. 2. Use crayons for colouring. General Instruction I. Multiple choice questions:
Class: IV Time: 3 Hrs. Summative Assessment I Social Science Marks: 88 Handwriting: 2 Total: 90 1. All questions are compulsory. 2. Use crayons for colouring. General Instruction I. Multiple choice questions:
INDIAN SCHOOL MUSCAT SENIOR SECTION DEPARTMENT OF SOCIAL SCIENCE CLASS: IX : GEOGRAPHY TOPIC/CHAPTER: CHAPTER: 2 PHYSICAL FEATURES
 INDIAN SCHOOL MUSCAT SENIOR SECTION DEPARTMENT OF SOCIAL SCIENCE CLASS: IX : GEOGRAPHY TOPIC/CHAPTER: CHAPTER: 2 PHYSICAL FEATURES WORKSHEET NO. 06 Summary:- Tectonic Plate Theory:- This theory is based
INDIAN SCHOOL MUSCAT SENIOR SECTION DEPARTMENT OF SOCIAL SCIENCE CLASS: IX : GEOGRAPHY TOPIC/CHAPTER: CHAPTER: 2 PHYSICAL FEATURES WORKSHEET NO. 06 Summary:- Tectonic Plate Theory:- This theory is based
India is a vast country with varied landforms. Our country has practically all major physical features of the earth i.e. mountains, plains, deserts,
 India is a vast country with varied landforms. Our country has practically all major physical features of the earth i.e. mountains, plains, deserts, plateaus and islands. India is a large landmass formed
India is a vast country with varied landforms. Our country has practically all major physical features of the earth i.e. mountains, plains, deserts, plateaus and islands. India is a large landmass formed
3. HYDROMETEROLOGY. 3.1 Introduction. 3.2 Hydro-meteorological Aspect. 3.3 Rain Gauge Stations
 3. HYDROMETEROLOGY 3.1 Introduction Hydrometeorology is a branch of meteorology and hydrology that studies the transfer of water and energy between the land surface and the lower atmosphere. Detailed hydrological
3. HYDROMETEROLOGY 3.1 Introduction Hydrometeorology is a branch of meteorology and hydrology that studies the transfer of water and energy between the land surface and the lower atmosphere. Detailed hydrological
CHAPTER 12 NATURAL DISASTERS
 CHAPTER 12 NATURAL DISASTERS In this chapter, you learn about the following: Natural calamities cyclones causes, effects and preventive measures Floods causes, affected areas, effects and control Land
CHAPTER 12 NATURAL DISASTERS In this chapter, you learn about the following: Natural calamities cyclones causes, effects and preventive measures Floods causes, affected areas, effects and control Land
BOARD OF SECONDARY EDUCATION (AP) SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT - I TENTH SOCIAL MODEL PAPER PAPER - I (ENGLISH VERSION) SECTION - I
 BOARD OF SECONDARY EDUCATION (AP) SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT - I TENTH SOCIAL MODEL PAPER PAPER - I (ENGLISH VERSION) Time: 2 hrs. 45 mins. PART - A& B Maximum Marks: 40 Time: 2 hrs. 15 mins. PART - A Marks:
BOARD OF SECONDARY EDUCATION (AP) SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT - I TENTH SOCIAL MODEL PAPER PAPER - I (ENGLISH VERSION) Time: 2 hrs. 45 mins. PART - A& B Maximum Marks: 40 Time: 2 hrs. 15 mins. PART - A Marks:
Year 6. Geography. Revision
 Year 6 Geography Revision November 2017 Rivers and World knowledge How the water cycle works and the meaning of the terms evaporation, condensation, precipitation, transpiration, surface run-off, groundwater
Year 6 Geography Revision November 2017 Rivers and World knowledge How the water cycle works and the meaning of the terms evaporation, condensation, precipitation, transpiration, surface run-off, groundwater
ALL INDIA WEATHER SUMMARY AND FORECAST BULLETIN
 Tuesday 08 May 2018 MID DAY Time of Issue: 1345 hours IST ALL INDIA WEATHER SUMMARY AND FORECAST BULLETIN Significant Weather Features Under the influence of the present Western Disturbance over Jammu
Tuesday 08 May 2018 MID DAY Time of Issue: 1345 hours IST ALL INDIA WEATHER SUMMARY AND FORECAST BULLETIN Significant Weather Features Under the influence of the present Western Disturbance over Jammu
Geography: Contemporary India - For Class IX Physical Features of India
 Geography: Contemporary India - For Class IX Physical Features of India (Q.1) Which are the two broad classification of peninsular plateau? (Q.2) What is a Doab? (Q.3) What is an Alluvial Plain. (Q.4)
Geography: Contemporary India - For Class IX Physical Features of India (Q.1) Which are the two broad classification of peninsular plateau? (Q.2) What is a Doab? (Q.3) What is an Alluvial Plain. (Q.4)
Board Question Paper : March 2015
 Board Question Paper : March 2015 BOARD QUESTION PAPER : MARCH 2015 Time: 2 Hours Total Marks: 40 Note: i. All questions are compulsory. ii. Figure to the right indicate full marks. iii. Solve Q. No.3
Board Question Paper : March 2015 BOARD QUESTION PAPER : MARCH 2015 Time: 2 Hours Total Marks: 40 Note: i. All questions are compulsory. ii. Figure to the right indicate full marks. iii. Solve Q. No.3
Surface Water and Stream Development
 Surface Water and Stream Development Surface Water The moment a raindrop falls to earth it begins its return to the sea. Once water reaches Earth s surface it may evaporate back into the atmosphere, soak
Surface Water and Stream Development Surface Water The moment a raindrop falls to earth it begins its return to the sea. Once water reaches Earth s surface it may evaporate back into the atmosphere, soak
UNIT 11 SOUTH ASIA SG 1 - PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY & THE ENVIRONMENT
 UNIT 11 SOUTH ASIA SG 1 - PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY & THE ENVIRONMENT I. PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY TAKE OUT YOUR PHYSICAL MAP OF SOUTH ASIA A. The Himalayan Mountains form the northern boundary of the region (color
UNIT 11 SOUTH ASIA SG 1 - PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY & THE ENVIRONMENT I. PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY TAKE OUT YOUR PHYSICAL MAP OF SOUTH ASIA A. The Himalayan Mountains form the northern boundary of the region (color
ALL INDIA WEATHER SUMMARY AND FORECAST BULLETIN
 Saturday 21 April 2018 MORNING Time of Issue: 0800 hours IST ALL INDIA WEATHER SUMMARY AND FORECAST BULLETIN Significant Weather Features Isolated thunder squalls and hailstorms are very likely over Sub
Saturday 21 April 2018 MORNING Time of Issue: 0800 hours IST ALL INDIA WEATHER SUMMARY AND FORECAST BULLETIN Significant Weather Features Isolated thunder squalls and hailstorms are very likely over Sub
Natural Vegetation and Wildlife
 Natural Vegetation and Wildlife Exercise Page 51 Question 1: Choose the right answer from the four alternatives given below. (i) To which one of the following types of vegetation does rubber belong? (a)
Natural Vegetation and Wildlife Exercise Page 51 Question 1: Choose the right answer from the four alternatives given below. (i) To which one of the following types of vegetation does rubber belong? (a)
NCERT Class 9th Social Science Geography Chapter 2: Physical Features of India
 NCERT Class 9th Social Science Geography Chapter 2: Physical Features of India Question 1. Choose the right answer from the four alternatives given below. (i) A landmass bounded by sea on three sides in
NCERT Class 9th Social Science Geography Chapter 2: Physical Features of India Question 1. Choose the right answer from the four alternatives given below. (i) A landmass bounded by sea on three sides in
Key Finding: Long Term Trend During 2014: Rain in Indian Tradition Measuring Rain
 Chapter 34 RAINFALL Key Finding: Long Term Trend Despite of theories suggesting increase in rainfall in Asian Region due to global warming, no significant trend has been observed at all India level (confirmed
Chapter 34 RAINFALL Key Finding: Long Term Trend Despite of theories suggesting increase in rainfall in Asian Region due to global warming, no significant trend has been observed at all India level (confirmed
ALL INDIA WEATHER SUMMARY AND FORECAST BULLETIN
 Sunday 22 April 2018 NIGHT Time of Issue: 2000 hours IST ALL INDIA WEATHER SUMMARY AND FORECAST BULLETIN Significant Weather Features The ongoing fairly widespread rainfall activity with isolated thunder
Sunday 22 April 2018 NIGHT Time of Issue: 2000 hours IST ALL INDIA WEATHER SUMMARY AND FORECAST BULLETIN Significant Weather Features The ongoing fairly widespread rainfall activity with isolated thunder
Chapter 11. Rivers: Shaping our landscape
 Chapter 11 Rivers: Shaping our landscape Learning outcomes In this presentation you will learn: Common terms associated with rivers About the three stages of a river About the processes of river erosion
Chapter 11 Rivers: Shaping our landscape Learning outcomes In this presentation you will learn: Common terms associated with rivers About the three stages of a river About the processes of river erosion
W E E K L Y MONSOON INSIGHT
 W E E K L Y MONSOON INSIGHT 08 th July 2016 Indian Monsoon Dynamics Recent Weather Development India received 35% surplus rainfall in the week ended 6 July with all regions recording above-normal rainfall
W E E K L Y MONSOON INSIGHT 08 th July 2016 Indian Monsoon Dynamics Recent Weather Development India received 35% surplus rainfall in the week ended 6 July with all regions recording above-normal rainfall
EXTERNAL LAND FORMING PROCESSES
 NAME SCHOOL INDEX NUMBER DATE EXTERNAL LAND FORMING PROCESSES WEATHERING 1 1998 Q 7 (a) (i) What is the difference between weathering and mass wasting (ii) List five processes involved in chemical weathering
NAME SCHOOL INDEX NUMBER DATE EXTERNAL LAND FORMING PROCESSES WEATHERING 1 1998 Q 7 (a) (i) What is the difference between weathering and mass wasting (ii) List five processes involved in chemical weathering
15. THE GLOBE AND THE MAP
 15. THE GLOBE AND THE MAP 1 DEFINE THE FOLLOWING 1. AXIS : The imaginary line which passes through the centre of the earth and joins the North Pole and South Pole is called the Axis. The earth rotates
15. THE GLOBE AND THE MAP 1 DEFINE THE FOLLOWING 1. AXIS : The imaginary line which passes through the centre of the earth and joins the North Pole and South Pole is called the Axis. The earth rotates
India - Relief Features
 India - Relief Features CHAPTER 1 In this chapter we shall study about relief features of India. In the subsequent chapters such as Climate in India; Rivers and Water Resources; The People etc we would
India - Relief Features CHAPTER 1 In this chapter we shall study about relief features of India. In the subsequent chapters such as Climate in India; Rivers and Water Resources; The People etc we would
CURRENT STATUS OF MONSOON Main Meteorological conditions of the last week (27August to 2 September)
 CURRENT STATUS OF MONSOON 2009 Main Meteorological conditions of the last week (27August to 2 September) Last week s low pressure area over Orissa and neighbourhood moved west-northwestwards across central
CURRENT STATUS OF MONSOON 2009 Main Meteorological conditions of the last week (27August to 2 September) Last week s low pressure area over Orissa and neighbourhood moved west-northwestwards across central
Earth Science Chapter 6 Section 2 Review
 Name: Class: Date: Earth Science Chapter 6 Section Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Most streams carry the largest part of their
Name: Class: Date: Earth Science Chapter 6 Section Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Most streams carry the largest part of their
Sec$on 1: Geography and Early China. How does China s geography affect the culture?
 Sec$on 1: Geography and Early China How does China s geography affect the culture? Con$nents of the World Label the continents. Where is China located? Where is China located? In your groups, begin filling
Sec$on 1: Geography and Early China How does China s geography affect the culture? Con$nents of the World Label the continents. Where is China located? Where is China located? In your groups, begin filling
Science EOG Review: Landforms
 Mathematician Science EOG Review: Landforms Vocabulary Definition Term canyon deep, large, V- shaped valley formed by a river over millions of years of erosion; sometimes called gorges (example: Linville
Mathematician Science EOG Review: Landforms Vocabulary Definition Term canyon deep, large, V- shaped valley formed by a river over millions of years of erosion; sometimes called gorges (example: Linville
2. PHYSICAL FEATURES OF INDIA
 2. PHYSICAL FEATURES OF INDIA Question 1: Choose the right answer from the four alternatives given below. (i) A landmass bound by sea on three sides is referred to as (a) Coast (c) Peninsula (b) Island
2. PHYSICAL FEATURES OF INDIA Question 1: Choose the right answer from the four alternatives given below. (i) A landmass bound by sea on three sides is referred to as (a) Coast (c) Peninsula (b) Island
ALL INDIA INSTALLED CAPACITY (IN MW) OF POWER STATIONS
 Region Northern Region Western Region Southern Region Eastern Region North Eastern Region Islands ALL INDIA Figures at decimal may not tally due to rounding off ALL INDIA INSTALLED CAPACITY (IN MW) OF
Region Northern Region Western Region Southern Region Eastern Region North Eastern Region Islands ALL INDIA Figures at decimal may not tally due to rounding off ALL INDIA INSTALLED CAPACITY (IN MW) OF
PHYSICAL FEATURES OF SOUTH ASIA
 PHYSICAL FEATURES OF SOUTH ASIA Formation India is a land of varied physical features. The physical features of India have evolved over several geological periods. According to the theory of Plate Tectonics
PHYSICAL FEATURES OF SOUTH ASIA Formation India is a land of varied physical features. The physical features of India have evolved over several geological periods. According to the theory of Plate Tectonics
By- Saurabh Pandey Junior research fellow(jrf) NET, MA, B.TECH 3 Years teaching experience UPSC Faculty
 Important Topics (Mapping) By- Saurabh Pandey Junior research fellow(jrf) NET, MA, B.TECH 3 Years teaching experience UPSC Faculty Topic 1 - PALESTINE AND ISRAEL west asia Q Which of the following countries
Important Topics (Mapping) By- Saurabh Pandey Junior research fellow(jrf) NET, MA, B.TECH 3 Years teaching experience UPSC Faculty Topic 1 - PALESTINE AND ISRAEL west asia Q Which of the following countries
Chapter 10. Running Water aka Rivers. BFRB Pages
 Chapter 10 Running Water aka Rivers BFRB Pages 101-116 Stream Erosion and Transportation Running water is all precipitation (rain, snow, etc) that falls on Earth and is pulled downhill by gravity. Running
Chapter 10 Running Water aka Rivers BFRB Pages 101-116 Stream Erosion and Transportation Running water is all precipitation (rain, snow, etc) that falls on Earth and is pulled downhill by gravity. Running
Part 1: Weather Forecast Severe Weather Warnings (Source: IMD, Date: 1 st September, 2008)
 Sphere India Unified Response Strategy Situation report (India Floods 2008) 01 st September 2008 Part 1: Weather Forecast Severe Weather Warnings (Source: IMD, Date: 1 st September, 2008) HEAVY RAINFALL
Sphere India Unified Response Strategy Situation report (India Floods 2008) 01 st September 2008 Part 1: Weather Forecast Severe Weather Warnings (Source: IMD, Date: 1 st September, 2008) HEAVY RAINFALL
South, Southeast, and East Asia. Physical Geography
 South, Southeast, and East Asia Physical Geography Mountains v Mountains are important in Asia because they influence: A. Population patterns B. Movement of people and goods C. Climate Mountains v The
South, Southeast, and East Asia Physical Geography Mountains v Mountains are important in Asia because they influence: A. Population patterns B. Movement of people and goods C. Climate Mountains v The
mountain rivers fixed channel boundaries (bedrock banks and bed) high transport capacity low storage input output
 mountain rivers fixed channel boundaries (bedrock banks and bed) high transport capacity low storage input output strong interaction between streams & hillslopes Sediment Budgets for Mountain Rivers Little
mountain rivers fixed channel boundaries (bedrock banks and bed) high transport capacity low storage input output strong interaction between streams & hillslopes Sediment Budgets for Mountain Rivers Little
Streams. Water. Hydrologic Cycle. Geol 104: Streams
 Streams Why study streams? Running water is the most important geologic agent in erosion, transportation and deposition of sediments. Water The unique physical and chemical properties of water make it
Streams Why study streams? Running water is the most important geologic agent in erosion, transportation and deposition of sediments. Water The unique physical and chemical properties of water make it
ALL INDIA INSTALLED CAPACITY (IN MW) OF POWER STATIONS
 Region Northern Region Western Region Southern Region Eastern Region North Eastern Region Islands ALL INDIA Figures at decimal may not tally due to rounding off ALL INDIA INSTALLED CAPACITY (IN MW) OF
Region Northern Region Western Region Southern Region Eastern Region North Eastern Region Islands ALL INDIA Figures at decimal may not tally due to rounding off ALL INDIA INSTALLED CAPACITY (IN MW) OF
Chapter 21 Southwest Asia: Harsh & Arid Lands
 Name Hour Chapter 21 Southwest Asia: Harsh & Arid Lands Essential Question: How has the physical geography of Asia influenced the development of these regions (i.e. history, population distribution, &
Name Hour Chapter 21 Southwest Asia: Harsh & Arid Lands Essential Question: How has the physical geography of Asia influenced the development of these regions (i.e. history, population distribution, &
BOARD ANSWER PAPER : MARCH 2014
 Geography and Economics BOARD ANSWER PAPER : MARCH 2014 GEOGRAPHY AND ECONOMICS Q.1. (A) Complete the following statements by choosing the appropriate alternatives from those given in the brackets and
Geography and Economics BOARD ANSWER PAPER : MARCH 2014 GEOGRAPHY AND ECONOMICS Q.1. (A) Complete the following statements by choosing the appropriate alternatives from those given in the brackets and
The City School PAF Chapter
 The City School PAF Chapter Geography Intervention workbook (1 st Term) Class 7 Topic: weather and climate Section A Q1. Fill in the blanks. [ /10] 1. The world can be divided into three broad climatic
The City School PAF Chapter Geography Intervention workbook (1 st Term) Class 7 Topic: weather and climate Section A Q1. Fill in the blanks. [ /10] 1. The world can be divided into three broad climatic
HYDROMET SERVICES FOR FLOOD FORECASTING. Dr. Surinder Kaur IMD, India, New Delhi
 HYDROMET SERVICES FOR FLOOD FORECASTING Dr. Surinder Kaur IMD, India, New Delhi Real Time Rainfall monitoring Hydromet Services Hyomet design Flood meteorological Services AWS=675 ARG=1289 Surface obs(dept)=
HYDROMET SERVICES FOR FLOOD FORECASTING Dr. Surinder Kaur IMD, India, New Delhi Real Time Rainfall monitoring Hydromet Services Hyomet design Flood meteorological Services AWS=675 ARG=1289 Surface obs(dept)=
Occurrence of heavy rainfall around the confluence line in monsoon disturbances and its importance in causing floods
 Occurrence of heavy rainfall around the confluence line in monsoon disturbances and its importance in causing floods GNAGESWARA RAO Department of Meteorology & Oceanography, Andhra University, Visakhapatnam
Occurrence of heavy rainfall around the confluence line in monsoon disturbances and its importance in causing floods GNAGESWARA RAO Department of Meteorology & Oceanography, Andhra University, Visakhapatnam
Erosion Surface Water. moving, transporting, and depositing sediment.
 + Erosion Surface Water moving, transporting, and depositing sediment. + Surface Water 2 Water from rainfall can hit Earth s surface and do a number of things: Slowly soak into the ground: Infiltration
+ Erosion Surface Water moving, transporting, and depositing sediment. + Surface Water 2 Water from rainfall can hit Earth s surface and do a number of things: Slowly soak into the ground: Infiltration
ALL INDIA INSTALLED CAPACITY (IN MW) OF POWER STATIONS
 Region Northern Region Western Region Southern Region Eastern Region North Eastern Region Islands ALL INDIA Figures at decimal may not tally due to rounding off ALL INDIA INSTALLED CAPACITY (IN MW) OF
Region Northern Region Western Region Southern Region Eastern Region North Eastern Region Islands ALL INDIA Figures at decimal may not tally due to rounding off ALL INDIA INSTALLED CAPACITY (IN MW) OF
Chapter 2. Wearing Down Landforms: Rivers and Ice. Physical Weathering
 Chapter 2 Wearing Down Landforms: Rivers and Ice Physical Weathering Weathering vs. Erosion Weathering is the breakdown of rock and minerals. Erosion is a two fold process that starts with 1) breakdown
Chapter 2 Wearing Down Landforms: Rivers and Ice Physical Weathering Weathering vs. Erosion Weathering is the breakdown of rock and minerals. Erosion is a two fold process that starts with 1) breakdown
ALL INDIA INSTALLED CAPACITY (IN MW) OF POWER STATIONS
 Region Northern Region Western Region Southern Region Eastern Region North Eastern Region Islands ALL INDIA Figures at decimal may not tally due to rounding off ALL INDIA INSTALLED CAPACITY (IN MW) OF
Region Northern Region Western Region Southern Region Eastern Region North Eastern Region Islands ALL INDIA Figures at decimal may not tally due to rounding off ALL INDIA INSTALLED CAPACITY (IN MW) OF
BOARD OF SECONDARY EDUCATION (AP) SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT - I TENTH CLASS SOCIAL STUDIES MODEL PAPER PAPER - I (ENGLISH VERSION)
 BOARD OF SECONDARY EDUCATION (AP) SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT - I TENTH CLASS SOCIAL STUDIES MODEL PAPER PAPER - I (ENGLISH VERSION) Time: 2 hrs. 45 mins. PART - A & B Maximum Marks: 40 INSTRUCTIONS: i) 15 minutes
BOARD OF SECONDARY EDUCATION (AP) SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT - I TENTH CLASS SOCIAL STUDIES MODEL PAPER PAPER - I (ENGLISH VERSION) Time: 2 hrs. 45 mins. PART - A & B Maximum Marks: 40 INSTRUCTIONS: i) 15 minutes
CHAPTER 5 ELECTRIC POWER SUPPLY AND SYSTEM LOSSES
 CHAPTER 5 ELECTRIC POWER SUPPLY AND SYSTEM LOSSES REVIEW: Central Electricity Authority General Review 2006 CHAPTER 5 ELECTRIC POWER SUPPLY AND SYSTEM LOSSES During the year 2004-05 gross electricity generation
CHAPTER 5 ELECTRIC POWER SUPPLY AND SYSTEM LOSSES REVIEW: Central Electricity Authority General Review 2006 CHAPTER 5 ELECTRIC POWER SUPPLY AND SYSTEM LOSSES During the year 2004-05 gross electricity generation
BOARD ANSWER PAPER : MARCH 2014
 Geography and Economics BOARD ANSWER PAPER : MARCH 2014 GEOGRAPHY AND ECONOMICS Q.1. (A) (B) Q.2. (A) Complete the following statements by choosing the appropriate alternatives from those given in the
Geography and Economics BOARD ANSWER PAPER : MARCH 2014 GEOGRAPHY AND ECONOMICS Q.1. (A) (B) Q.2. (A) Complete the following statements by choosing the appropriate alternatives from those given in the
DR.M.K.K ARYA MODEL SCHOOL
 DR.M.K.K ARYA MODEL SCHOOL Sub: Social science Syllabus Class-IV Session 2018-19 Prescribed book: Candid New Trends in Social Studies Syllabus to be completed in the month of April. Chapter 1.India Our
DR.M.K.K ARYA MODEL SCHOOL Sub: Social science Syllabus Class-IV Session 2018-19 Prescribed book: Candid New Trends in Social Studies Syllabus to be completed in the month of April. Chapter 1.India Our
The Impact of Geography in South and East Asia
 The Impact of Geography in South and East Asia Gobi desert, Mongolia Essential Question: How does the geography of SE Asia impact trade and the distribution of population throughout the region? (AKS #52a)
The Impact of Geography in South and East Asia Gobi desert, Mongolia Essential Question: How does the geography of SE Asia impact trade and the distribution of population throughout the region? (AKS #52a)
UNIT II CHAPTER -2 PHYSIOGRAPHY - INDIA
 UNIT II CHAPTER -2 PHYSIOGRAPHY - INDIA Structure and Relief; physiographic divisions Drainage systems: concept of water sheds the Himalayan and the Peninsular Can you map different phases in the movement
UNIT II CHAPTER -2 PHYSIOGRAPHY - INDIA Structure and Relief; physiographic divisions Drainage systems: concept of water sheds the Himalayan and the Peninsular Can you map different phases in the movement
STUDY GUIDE FOR CONTENT MASTERY. Surface Water Movement
 Surface Water SECTION 9.1 Surface Water Movement In your textbook, read about surface water and the way in which it moves sediment. Complete each statement. 1. An excessive amount of water flowing downslope
Surface Water SECTION 9.1 Surface Water Movement In your textbook, read about surface water and the way in which it moves sediment. Complete each statement. 1. An excessive amount of water flowing downslope
The Impact of Geography in South and East Asia
 The Impact of Geography in South and East Asia Gobi desert, Mongolia Essential Question: How does the geography of SE Asia impact trade and the distribution of population throughout the region? (AKS #52a)
The Impact of Geography in South and East Asia Gobi desert, Mongolia Essential Question: How does the geography of SE Asia impact trade and the distribution of population throughout the region? (AKS #52a)
Recent trend in spatiotemporal variation of rainfall over India an investigation into basin-scale rainfall fluctuations
 Regional Hydrological Impacts of Climatic Change Hydroclimatic Variability (Proceedings of symposium S6 held during the Seventh IAHS Scientific Assembly at Foz do Iguaçu, Brazil, April 2005). IAHS Publ.
Regional Hydrological Impacts of Climatic Change Hydroclimatic Variability (Proceedings of symposium S6 held during the Seventh IAHS Scientific Assembly at Foz do Iguaçu, Brazil, April 2005). IAHS Publ.
Long Range Forecast Update for 2014 Southwest Monsoon Rainfall
 Earth System Science Organization (ESSO) Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES) India Meteorological Department PRESS RELEASE New Delhi, 9 June 2014 Long Update for 2014 Southwest Monsoon Rainfall HIGHLIGHTS
Earth System Science Organization (ESSO) Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES) India Meteorological Department PRESS RELEASE New Delhi, 9 June 2014 Long Update for 2014 Southwest Monsoon Rainfall HIGHLIGHTS
ALL INDIA INSTALLED CAPACITY (IN MW) OF POWER STATIONS
 Region Northern Region Western Region Southern Region Eastern Region North Eastern Region Islands ALL INDIA Figures at decimal may not tally due to rounding off ALL INDIA INSTALLED CAPACITY (IN MW) OF
Region Northern Region Western Region Southern Region Eastern Region North Eastern Region Islands ALL INDIA Figures at decimal may not tally due to rounding off ALL INDIA INSTALLED CAPACITY (IN MW) OF
INDIAN GEOGRAPHY ADITYA IAS ACADEMY India Location & Size. Location
 ADITYA IAS ACADEMY www.adityaiasacademy.com INDIAN GEOGRAPHY 1. India Location & Size Location India lies entirely in the Northern Hemisphere. The mainland extends between - 8degree 4 N and 37degree 6
ADITYA IAS ACADEMY www.adityaiasacademy.com INDIAN GEOGRAPHY 1. India Location & Size Location India lies entirely in the Northern Hemisphere. The mainland extends between - 8degree 4 N and 37degree 6
Weathering, Erosion, Deposition, and Landscape Development
 Weathering, Erosion, Deposition, and Landscape Development I. Weathering - the breakdown of rocks into smaller particles, also called sediments, by natural processes. Weathering is further divided into
Weathering, Erosion, Deposition, and Landscape Development I. Weathering - the breakdown of rocks into smaller particles, also called sediments, by natural processes. Weathering is further divided into
SMART NOTES ON INDIAN GEOGRAPHY - 1
 ON INDIAN GEOGRAPHY - 1 Point. Precise. Powerful. www.thesmartnotes.org ON INDIAN GEOGRAPHY - 1 To our Hardworking and persistence aspirants. Success is going from failure to failure without losing enthusiasm.
ON INDIAN GEOGRAPHY - 1 Point. Precise. Powerful. www.thesmartnotes.org ON INDIAN GEOGRAPHY - 1 To our Hardworking and persistence aspirants. Success is going from failure to failure without losing enthusiasm.
Why study physical features? How does it help me during the course of studying Geography Elective?
 (b) Physical features Why study physical features? How does it help me during the course of studying Geography Elective? Physical factors influence the distribution of agricultural systems. Some factors
(b) Physical features Why study physical features? How does it help me during the course of studying Geography Elective? Physical factors influence the distribution of agricultural systems. Some factors
DISASTER PROFILE OF INDt\: REGIO.NALAND SEASONAL
 UNIT 4 DISASTER PROFILE OF INDt\: REGIO.NALAND SEASONAL Structure 4.0 4.1 4.2 Objectives Introduction Disasters in India: Regional Profile 4.2.1 Flood,. 4.2.2 Drought 4.3 4.4 4.5 4.6 4.7 4.2.3 Cyclone
UNIT 4 DISASTER PROFILE OF INDt\: REGIO.NALAND SEASONAL Structure 4.0 4.1 4.2 Objectives Introduction Disasters in India: Regional Profile 4.2.1 Flood,. 4.2.2 Drought 4.3 4.4 4.5 4.6 4.7 4.2.3 Cyclone
Streams. Stream Water Flow
 CHAPTER 14 OUTLINE Streams: Transport to the Oceans Does not contain complete lecture notes. To be used to help organize lecture notes and home/test studies. Streams Streams are the major geological agents
CHAPTER 14 OUTLINE Streams: Transport to the Oceans Does not contain complete lecture notes. To be used to help organize lecture notes and home/test studies. Streams Streams are the major geological agents
Contents. Foreword... (vii) Preface...(ix) About the Author...(xi) List of Tables...(xxi) List of Figures... (xxvii)
 (xiii) Contents Foreword... (vii) Preface...(ix) About the Author...(xi) List of Tables...(xxi) List of Figures... (xxvii) CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION TO WATER RESOURCES 1.1 Global Water Resources... 3 1.2
(xiii) Contents Foreword... (vii) Preface...(ix) About the Author...(xi) List of Tables...(xxi) List of Figures... (xxvii) CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION TO WATER RESOURCES 1.1 Global Water Resources... 3 1.2
SBOA. SCHOOLAND JUNIOR COLLEGE, CHENNAI 101 ASSIGNMENT (GEOGRAPHY & ECONOMICS)
 SBOA. SCHOOLAND JUNIOR COLLEGE, CHENNAI 101 STD: IX ASSIGNMENT (GEOGRAPHY & ECONOMICS) GEOGRAPHY 1. INDIA SIZE AND LOCATION 1. Name the group of islands lying in the Arabian Sea and Bay of Bengal. 2. Name
SBOA. SCHOOLAND JUNIOR COLLEGE, CHENNAI 101 STD: IX ASSIGNMENT (GEOGRAPHY & ECONOMICS) GEOGRAPHY 1. INDIA SIZE AND LOCATION 1. Name the group of islands lying in the Arabian Sea and Bay of Bengal. 2. Name
You have already learnt earlier that India
 2 PHYSICAL FEATURES OF INDIA You have already learnt earlier that India is a vast country with varied landforms. What kind of terrain do you live in? If you live in the plains you are familiar with the
2 PHYSICAL FEATURES OF INDIA You have already learnt earlier that India is a vast country with varied landforms. What kind of terrain do you live in? If you live in the plains you are familiar with the
ICSE Board Class X Geography Board Paper- 2014
 Time:2 hrs ICSE Board Class X Geography Board Paper- 2014 Total Marks: 80 General Instructions: 1. Answers to this paper must be written on the paper provided separately. 2. You will not be allowed to
Time:2 hrs ICSE Board Class X Geography Board Paper- 2014 Total Marks: 80 General Instructions: 1. Answers to this paper must be written on the paper provided separately. 2. You will not be allowed to
The Impact of Geography in South and East Asia
 The Impact of Geography in South and East Asia Gobi desert, Mongolia Essential Question: How does geography impact the distribution of population throughout South and East Asia? I CAN Explain how geography
The Impact of Geography in South and East Asia Gobi desert, Mongolia Essential Question: How does geography impact the distribution of population throughout South and East Asia? I CAN Explain how geography
Geography is the study of the earth, it s land, it s people and it s environments. When you study geography, you should be looking at five distinct
 I.N pg. 9 Geography is the study of the earth, it s land, it s people and it s environments. When you study geography, you should be looking at five distinct themes. LOCATION PLACE REGION MOVEMENT HUMANENVIRONMENTAL
I.N pg. 9 Geography is the study of the earth, it s land, it s people and it s environments. When you study geography, you should be looking at five distinct themes. LOCATION PLACE REGION MOVEMENT HUMANENVIRONMENTAL
What do you need for a Marathon?
 What do you need for a Marathon? Water and a snack? What about just a normal day? 1 flush = 3.5 gallons 1 flush = 3.5 gallons 10 minute shower = 20 gal 1 flush = 3.5 gallons 10 minute shower = 20 gal Jeans
What do you need for a Marathon? Water and a snack? What about just a normal day? 1 flush = 3.5 gallons 1 flush = 3.5 gallons 10 minute shower = 20 gal 1 flush = 3.5 gallons 10 minute shower = 20 gal Jeans
ON VARIABILITY OF HYDROLOGICAL WET SEASON, SEASONAL RAINFALL AND RAINWATER POTENTIAL OF THE RIVER BASINS OF INDIA ( )
 Journal of Hydrological Research and Development, Vol. 23, 8 ON VARIABILITY OF HYDROLOGICAL WET SEASON, SEASONAL RAINFALL AND RAINWATER POTENTIAL OF THE RIVER BASINS OF INDIA (1813-6) ASHWINI RANADE, NITYANAND
Journal of Hydrological Research and Development, Vol. 23, 8 ON VARIABILITY OF HYDROLOGICAL WET SEASON, SEASONAL RAINFALL AND RAINWATER POTENTIAL OF THE RIVER BASINS OF INDIA (1813-6) ASHWINI RANADE, NITYANAND
WHAT IS THE EARTH MADE OF? LITHOSPHERE AND HYDROSPHERE
 UNIT 8 WHAT IS THE EARTH MADE OF? LITHOSPHERE AND HYDROSPHERE TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 THE STRUCTURE OF THE EARTH... 2 2 THE FORMATION OF THE RELIEF: INTERNAL AND EXTERNAL FORCES.... 2 2.1 Internal forces:
UNIT 8 WHAT IS THE EARTH MADE OF? LITHOSPHERE AND HYDROSPHERE TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 THE STRUCTURE OF THE EARTH... 2 2 THE FORMATION OF THE RELIEF: INTERNAL AND EXTERNAL FORCES.... 2 2.1 Internal forces:
How Do Human Impacts and Geomorphological Responses Vary with Spatial Scale in the Streams and Rivers of the Illinois Basin?
 How Do Human Impacts and Geomorphological Responses Vary with Spatial Scale in the Streams and Rivers of the Illinois Basin? Bruce Rhoads Department of Geography University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
How Do Human Impacts and Geomorphological Responses Vary with Spatial Scale in the Streams and Rivers of the Illinois Basin? Bruce Rhoads Department of Geography University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
Geographical location and climatic condition of the
 Geographical location and climatic condition of the study sites North eastern region of India is comprised of eight states namely; Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland, Sikkim
Geographical location and climatic condition of the study sites North eastern region of India is comprised of eight states namely; Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland, Sikkim
CONTENTS. SmartPrep.in
 CONTENTS 1. INDIA - LOCATION... 1 Structure and Physiography...2 The Peninsular Block...2 The Himalayas and other Peninsular Mountains...2 Indo-Ganga-Brahmaputra Plain...2 Physiography...3 North and North
CONTENTS 1. INDIA - LOCATION... 1 Structure and Physiography...2 The Peninsular Block...2 The Himalayas and other Peninsular Mountains...2 Indo-Ganga-Brahmaputra Plain...2 Physiography...3 North and North
Fresh Water: Streams, Lakes Groundwater & Wetlands
 Fresh Water:, Lakes Groundwater & Wetlands Oct 27 Glaciers and Ice Ages Chp 13 Nov 3 Deserts and Wind and EXAM #3 Slope hydrologic cycle P = precip I = precip intercepted by veg ET = evapotranspiration
Fresh Water:, Lakes Groundwater & Wetlands Oct 27 Glaciers and Ice Ages Chp 13 Nov 3 Deserts and Wind and EXAM #3 Slope hydrologic cycle P = precip I = precip intercepted by veg ET = evapotranspiration
What are the different ways rocks can be weathered?
 Romano - 223 What are the different ways rocks can be weathered? Weathering - the breakdown of rocks and minerals at the Earth s surface 1. 2. PHYSICAL WEATHERING Rock is broken into smaller pieces with
Romano - 223 What are the different ways rocks can be weathered? Weathering - the breakdown of rocks and minerals at the Earth s surface 1. 2. PHYSICAL WEATHERING Rock is broken into smaller pieces with
Date of. Issued by (AICRPAM), & Earth System
 National Agromet Advisory Service Bulletin Based on Extended Range Weather Forecast (ERFS) Validity: 29 September 12 October 2017 Date of Issue: 29 September 2017 Issued by Indian Council of Agricultural
National Agromet Advisory Service Bulletin Based on Extended Range Weather Forecast (ERFS) Validity: 29 September 12 October 2017 Date of Issue: 29 September 2017 Issued by Indian Council of Agricultural
Figure 2.1: Constituent Area
 2 The Region 2.1 CONSTITUENT AREA The National Capital Region includes NCT-Delhi, nine districts of Haryana, six districts of Uttar Pradesh and one district of Rajasthan. Total area of the region is 34,144
2 The Region 2.1 CONSTITUENT AREA The National Capital Region includes NCT-Delhi, nine districts of Haryana, six districts of Uttar Pradesh and one district of Rajasthan. Total area of the region is 34,144
CANADA S LANDFORM REGIONS
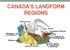 CANADA S LANDFORM REGIONS Canada s Regions Canada is divided into Eight major regions. A Region is an area that is defined on the basis of the presence or absence of certain characteristics: Age of rock
CANADA S LANDFORM REGIONS Canada s Regions Canada is divided into Eight major regions. A Region is an area that is defined on the basis of the presence or absence of certain characteristics: Age of rock
Erosion and Deposition
 Erosion and Deposition Erosion Sediment natural forces move rock/soil from one place to another. gravity, water, wind, glaciers, waves are causes material moved by erosion Deposition when erosion lays
Erosion and Deposition Erosion Sediment natural forces move rock/soil from one place to another. gravity, water, wind, glaciers, waves are causes material moved by erosion Deposition when erosion lays
[IASBABA S 60 DAYS PLAN-COMPILATION (GEOGRAPHY)
 2018 IASBABA.COM IASBABA IASBABA S 60 DAYS PLAN-COMPILATION (GEOGRAPHY) [ ] Born with the vision of Enabling a person located at the most remote destination a chance at cracking AIR 1 in IAS. Q.1) Consider
2018 IASBABA.COM IASBABA IASBABA S 60 DAYS PLAN-COMPILATION (GEOGRAPHY) [ ] Born with the vision of Enabling a person located at the most remote destination a chance at cracking AIR 1 in IAS. Q.1) Consider
ORIGINAL IN HINDI GOVERNMENT OF INDIA MINISTRY OF CONSUMER AFFAIRS, FOOD & PUBLIC DISTRIBUTION DEPARTMENT OF FOOD AND PUBLIC DISTRIBUTION
 ORIGINAL IN HINDI GOVERNMENT OF INDIA MINISTRY OF CONSUMER AFFAIRS, FOOD & PUBLIC DISTRIBUTION DEPARTMENT OF FOOD AND PUBLIC DISTRIBUTION LOK SABHA UNSTARRED QUESTION NO. 4122 TO BE ANSWERED ON 20 TH MARCH,
ORIGINAL IN HINDI GOVERNMENT OF INDIA MINISTRY OF CONSUMER AFFAIRS, FOOD & PUBLIC DISTRIBUTION DEPARTMENT OF FOOD AND PUBLIC DISTRIBUTION LOK SABHA UNSTARRED QUESTION NO. 4122 TO BE ANSWERED ON 20 TH MARCH,
Unit 1: Geography. For additional information, refer to this website: 1 G e o g r a p h y
 Unit 1: Geography For additional information, refer to this website: http://mryoungtms.weebly.com/ 1 G e o g r a p h y Continents and Oceans SOL USI. 2a Essential Understanding: Continents are large land
Unit 1: Geography For additional information, refer to this website: http://mryoungtms.weebly.com/ 1 G e o g r a p h y Continents and Oceans SOL USI. 2a Essential Understanding: Continents are large land
BOARD OF SECONDARY EDUCATION (TELANGANA) SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT - I TENTH CLASS SOCIAL STUDIES MODEL PAPER
 BOARD OF SECONDARY EDUCATION (TELANGANA) SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT - I TENTH CLASS SOCIAL STUDIES MODEL PAPER PAPER - I (ENGLISH VERSION) Time: 2 hrs. 45 mins. PART - A& B Maximum Marks: 40 INSTRUCTIONS: i)
BOARD OF SECONDARY EDUCATION (TELANGANA) SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT - I TENTH CLASS SOCIAL STUDIES MODEL PAPER PAPER - I (ENGLISH VERSION) Time: 2 hrs. 45 mins. PART - A& B Maximum Marks: 40 INSTRUCTIONS: i)
Chapter 3 Erosion and Deposition. The Big Question:
 Chapter 3 Erosion and Deposition The Big Question: 1 Design a way to represent and describe the 4 types of mass movement. You may use pictures, diagrams, list, web, chart, etc 2 Chapter 3: Erosion and
Chapter 3 Erosion and Deposition The Big Question: 1 Design a way to represent and describe the 4 types of mass movement. You may use pictures, diagrams, list, web, chart, etc 2 Chapter 3: Erosion and
1 LAND USE PLANNING IN INDIA - RETROSPECT AND PROSPECT
 1 LAND USE PLANNING IN INDIA - RETROSPECT AND PROSPECT T. Haque National Fellow, National Centre for Agricultural Economics and Policy Research, New Delhi Ever since independence, India's planners and
1 LAND USE PLANNING IN INDIA - RETROSPECT AND PROSPECT T. Haque National Fellow, National Centre for Agricultural Economics and Policy Research, New Delhi Ever since independence, India's planners and
Chapter 2 Planet Earth
 Chapter 2 Planet Earth Section Notes Earth and the Sun s Energy Water on Earth The Land Close-up The Water Cycle World Almanac Major Eruptions in the Ring of Fire Quick Facts Chapter 2 Visual Summary Video
Chapter 2 Planet Earth Section Notes Earth and the Sun s Energy Water on Earth The Land Close-up The Water Cycle World Almanac Major Eruptions in the Ring of Fire Quick Facts Chapter 2 Visual Summary Video
National Project on Organic Farming
 National Project on Organic Farming Department of Agriculture and Cooperation, Ministry of Agriculture Government of India Biofertilizers and Organic Fertilizers Statistics Year 2005-06 to 2009-10 Compiled
National Project on Organic Farming Department of Agriculture and Cooperation, Ministry of Agriculture Government of India Biofertilizers and Organic Fertilizers Statistics Year 2005-06 to 2009-10 Compiled
AFP Surveillance Bulletin - India Report for week 1, ending 5 January 2019
 Jan-18 Feb-18 Mar-18 Apr-18 May-18 Jun-18 Jul-18 Aug-18 Sep-18 Oct-18 Nov-18 Dec-18 Jan-19 Table 1: cases by month of paralysis onset, last 13 months State/UT's Total cases in cases as on week 1, cases
Jan-18 Feb-18 Mar-18 Apr-18 May-18 Jun-18 Jul-18 Aug-18 Sep-18 Oct-18 Nov-18 Dec-18 Jan-19 Table 1: cases by month of paralysis onset, last 13 months State/UT's Total cases in cases as on week 1, cases
Landforms in Canada. Canada is made up of three dis;nct types of landforms: Canadian Shield Highlands Lowlands
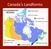 Canada s Landforms What is a Landform? A landform is any physical feature of the Earth s surface having a characteris;c, recognizable shape, produced by natural causes. Landforms include major features
Canada s Landforms What is a Landform? A landform is any physical feature of the Earth s surface having a characteris;c, recognizable shape, produced by natural causes. Landforms include major features
