Biology 2. Lecture Material. For. Macroevolution. Systematics
|
|
|
- Evangeline Baldwin
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Biology 2 Macroevolution & Systematics 1 Biology 2 Lecture Material For Macroevolution & Systematics
2 Biology 2 Macroevolution & Systematics 2 Microevolution: Biological Species: Two Patterns of Evolutionary Change Allopatric Speciation: Evidence of: Favorable Conditions:
3 Biology 2 Macroevolution & Systematics 3 Sympatric Speciation: Autopolyploidy: Allopolyploidy: Hybrid Zones: Reinforcement: Fusion: Stability: Adaptive Radiation: The emergence of numerous species from a common ancestor introduced into an environment, presenting a diversity of new opportunities and problems
4 Biology 2 Macroevolution & Systematics 4 Macroevolution: Gradualism: Three Types: : new traits become established in a population by increasing their frequency from a small fraction of the population to the majority : New traits, even those that are strikingly different from ancestral ones are produced in small increments : On a geological time scale, there are intermediate forms connecting the phenotypes of ancestors and descendents Punctuated Equilibrium:
5 Biology 2 Macroevolution & Systematics 5 Macroevolution through many Speciation Events Evolutionary Novelties Evolution of Genes that control development Changes in Spatial Pattern Changes in Rate and Timing Origin of Evolutionary Novelty Exaptation (preadaptation): Evolution of Genes that control development: (Julian Huxley) 1. Gradual evolution can be explained by small genetic changes that produce variation which is acted upon by natural selection 2. The evolution at higher taxonomic levels and of greater magnitude can be explained by long periods of time Evo-devo
6 Biology 2 Macroevolution & Systematics 6 Changes in Spatial Patterns: Homeotic Genes: Hox Genes: Homeobox:
7 Biology 2 Macroevolution & Systematics 7 Changes in Rate and Timing: Allometric Growth: Heterochrony: Paedeomorphosis: Paedeogenesis:
8 Biology 2 Macroevolution & Systematics 8 Evolutionary Trends: Species Selection (Steven Stanley): Size: Toe Reduction: Tooth shape/size: Fossil Records Sedimentary Rocks: Hard Parts: Minerals: Organic Material Casts: Trace Fossils: Entire Organisms:
9 Biology 2 Macroevolution & Systematics 9 Fossil Record Limitations Absolute Dating HALF-LIFE Use the concept of half-life to answer the following questions about the ages of fossils. 1. The half-life of carbon-14 is 5730 years. A fossil that is 22,920 years old would have what amount of the normal portion of C-14 to C-12? 2. The half-life of potassium-40 is 1.3 billion years. If a rock specimen contained 12 milligrams of potassium- 40 when it was formed and now contained 3 milligrams of potassium-40, How old is the rock? Relative Dating
10 Biology 2 Macroevolution & Systematics 10 ERA PERIOD EPOCH AGE EVENTS Now
11 Biology 2 Macroevolution & Systematics 11 Plate Tectonics and Continental Drift Plate Tectonics: Continental Drift: Pangaea: Laurasia: Gondwana: Mass Extinctions:
12 Biology 2 Macroevolution & Systematics 12 SYSTEMATICS: Comparing the genes or genomes of two species is the most direct measure of inheritance from shared ancestors. Comparisons can be made by using three methods: DNA-DNA hybridization, restriction maps, and DNA sequencing. Use the information to determine where species A through F belong in the phylogenetic tree. The information below is comparing the number of differences between an amino acid sequence from a blood protein found in rodents. (Assumption: The larger the number, the longer they have been separated from their common ancestor) A B C D E F A B C D E F
13 Biology 2 Macroevolution & Systematics 13 PHYLOGENETIC GROUPINGS: Monophyletic: Paraphyletic: Polyphyletic: Use the diagram below to identify whether the grouping is monophyletic, paraphyletic or polyphyletic. A B C D E F G H 1. A and B 2. A, B and C 3. D, E, and F 4. E, F, G and H 5. F, G, and H 6. E, F, and G
14 Biology 2 Macroevolution & Systematics 14 SIMILARITIES Homology: Analogy: Molecular Homeoplasy: ONTOGENY RECAPITULATES PHYLOGENY (Ernst Haekel)
15 Biology 2 Macroevolution & Systematics 15 SYSTEMATICS: Classical Evolutionary (Linnaean) Systematics: Cladistics: Assumptions: Synapomorphies: Shared ancestral characters Plesiomorphies: Primitive characters Apomorphies: Shared derived characters
16 Biology 2 Macroevolution & Systematics 16 Phylograms: Ultrametric Trees: Parsimony: Maximum Likelyhood:
17 Biology 2 Macroevolution & Systematics 17
18 Biology 2 Macroevolution & Systematics 18 Cladistic taxonomy and classical evolutionary taxonomy are different methods of interpreting phylogenetic data and classifying organisms. Read each statement below and check whether it relates to the cladistic approach, the classical approach, or both. Cladistic Classical 1. Method of classifying organisms and reconstructing phylogeny 2. Concerned only with the order of branching lineages 3. Produces cladograms 4. Concerned with branching and degree of divergence 5. Differentiates between primitive and derived characters 6. Puts lizards and crocodiles in one class, birds in another 7. Becoming more popular with researchers 8. Says birds are closer to crocodiles than to other reptiles 9. Uses anatomy and molecular biology to determine relationship 10. Places humans in the same family as some other apes 11. Places humans in their own family, separate from apes 12. The approach used 15 years ago 13. Considered to be more objective approach 14. Involves subjective judgements about divergence Place the new species into their proper position on the classical evolutionary phylogenetic tree You are the first zoologist to penetrate the Timbasi Swamp and explore the Okongo Forest. You identify 7 new species of guenon monkeys. You collect blood sample and compare the new species blood proteins and facial markings to decide where on the current phylogenetic tree these new species belong. Match each of the new monkey species with one of the letters inserted into the revised phylogenetic tree. 1. Ann s: More closely related to Diana than any other species 2. Flat-topped: As close to Mona as Mona is to Campbell s 3. Gladstone s: Closer to redtail and moustached than any other new species 4. Bearded: Related to Diana but not as closely as Ann s 5. Liebaert s: A ground-dweller not closely related to any of the others 6. Perkins s: Related to Mona and Campbell s but it branched off earlier 7. Striped: Equally related to blue and redtail, but closer to ancestor
19 Biology 2 Macroevolution & Systematics 19 Cladogram Place the taxa (outgroup, A, B, C, and D) on the cladogram based on the presence or absence of the characters 1-4 as shown in this table. Indicate before each branch point, which shared derived character evolved in the ancestor of the clade. Primate Phylogeny Examine the three primate phylogenies shown. Do the three phylogenies show the same relationships and the same order of branching? Do they give different impressions of whether there was a goal of primate evolution or what the highest primate is? Explain.
20 Biology 2 Macroevolution & Systematics 20 Cladistic Analysis of a DNA Sequence The study group below is an example of three species of chameleons, two from Madagascar and one for Equatorial Guinea. The outgroup is a lizard that is a distant relative of chameleons. The question is are the two Madagascan species (genus: Brookesia) really more closely related to each other over one being more closely related to the Equatorial Guinea species (Chamaeleo). The information below is from a piece of mitochondrial DNA sequence which encodes an amino acid of a protein called NADH dehydrogenase subuit 2. Uromastyx B. theili B. brygooi C. feae AAACCTTAAAAGACACCACAACCATATGAACAACAACACCAACAATCAGCACACTAC AAACACTACAAAATATAACAACTGCATGAACAACATCAACCACAGCAAACATTTTAC AAACACTACAAGACATAACAACAGCATGAACTACTTCAACAACAGCAAATATTACAC AAACCCTACGAGACGCAACAACAATATGATCCACTTCCCCCACAACAAACACAATTT Possible Cladograms B. theili 1. B. brygooi Number of changes C. feae 2. B. brygooi C. feae Number of changes B. theili 3. B. theili C. feae Number of changes B. brygooi
21 Biology 2 Macroevolution & Systematics 21 ERA PERIOD EPOCH AGE EVENTS Now
22 Biology 2 Macroevolution & Systematics 22 ERA PERIOD EPOCH AGE EVENTS Now
23 Biology 2 Macroevolution & Systematics 23 ERA PERIOD EPOCH AGE EVENTS Now
Biology 2. Lecture Material. For. Exam 1
 Biology 2 Macroevolution & Systematics 1 Biology 2 Lecture Material For Exam 1 Eukaryotes Halophiles Archaea Thermophiles Univeral Ancestor Methanogens Proteobacteria Chlamydia Bacteria Spirochetes Cyanobacteria
Biology 2 Macroevolution & Systematics 1 Biology 2 Lecture Material For Exam 1 Eukaryotes Halophiles Archaea Thermophiles Univeral Ancestor Methanogens Proteobacteria Chlamydia Bacteria Spirochetes Cyanobacteria
Bio 2 Plant and Animal Biology
 Bio 2 Plant and Animal Biology Evolution Evolution as the explanation for life s unity and diversity Darwinian Revolution Two main Points Descent with Modification Natural Selection Biological Species
Bio 2 Plant and Animal Biology Evolution Evolution as the explanation for life s unity and diversity Darwinian Revolution Two main Points Descent with Modification Natural Selection Biological Species
Name 14 The Origin of Species Test Date Study Guide You must know: The difference between microevolution and macroevolution. The biological concept
 Name _ 14 The Origin of Species Test Date Study Guide You must know: The difference between microevolution and macroevolution. The biological concept of species Prezygotic and postzygotic barriers that
Name _ 14 The Origin of Species Test Date Study Guide You must know: The difference between microevolution and macroevolution. The biological concept of species Prezygotic and postzygotic barriers that
Phylogeny and systematics. Why are these disciplines important in evolutionary biology and how are they related to each other?
 Phylogeny and systematics Why are these disciplines important in evolutionary biology and how are they related to each other? Phylogeny and systematics Phylogeny: the evolutionary history of a species
Phylogeny and systematics Why are these disciplines important in evolutionary biology and how are they related to each other? Phylogeny and systematics Phylogeny: the evolutionary history of a species
8/23/2014. Phylogeny and the Tree of Life
 Phylogeny and the Tree of Life Chapter 26 Objectives Explain the following characteristics of the Linnaean system of classification: a. binomial nomenclature b. hierarchical classification List the major
Phylogeny and the Tree of Life Chapter 26 Objectives Explain the following characteristics of the Linnaean system of classification: a. binomial nomenclature b. hierarchical classification List the major
Unit 9: Evolution Guided Reading Questions (80 pts total)
 Name: AP Biology Biology, Campbell and Reece, 7th Edition Adapted from chapter reading guides originally created by Lynn Miriello Unit 9: Evolution Guided Reading Questions (80 pts total) Chapter 22 Descent
Name: AP Biology Biology, Campbell and Reece, 7th Edition Adapted from chapter reading guides originally created by Lynn Miriello Unit 9: Evolution Guided Reading Questions (80 pts total) Chapter 22 Descent
Chapter 22: Descent with Modification 1. BRIEFLY summarize the main points that Darwin made in The Origin of Species.
 AP Biology Chapter Packet 7- Evolution Name Chapter 22: Descent with Modification 1. BRIEFLY summarize the main points that Darwin made in The Origin of Species. 2. Define the following terms: a. Natural
AP Biology Chapter Packet 7- Evolution Name Chapter 22: Descent with Modification 1. BRIEFLY summarize the main points that Darwin made in The Origin of Species. 2. Define the following terms: a. Natural
Unit 7: Evolution Guided Reading Questions (80 pts total)
 AP Biology Biology, Campbell and Reece, 10th Edition Adapted from chapter reading guides originally created by Lynn Miriello Name: Unit 7: Evolution Guided Reading Questions (80 pts total) Chapter 22 Descent
AP Biology Biology, Campbell and Reece, 10th Edition Adapted from chapter reading guides originally created by Lynn Miriello Name: Unit 7: Evolution Guided Reading Questions (80 pts total) Chapter 22 Descent
SPECIATION. REPRODUCTIVE BARRIERS PREZYGOTIC: Barriers that prevent fertilization. Habitat isolation Populations can t get together
 SPECIATION Origin of new species=speciation -Process by which one species splits into two or more species, accounts for both the unity and diversity of life SPECIES BIOLOGICAL CONCEPT Population or groups
SPECIATION Origin of new species=speciation -Process by which one species splits into two or more species, accounts for both the unity and diversity of life SPECIES BIOLOGICAL CONCEPT Population or groups
Chapter 26: Phylogeny and the Tree of Life Phylogenies Show Evolutionary Relationships
 Chapter 26: Phylogeny and the Tree of Life You Must Know The taxonomic categories and how they indicate relatedness. How systematics is used to develop phylogenetic trees. How to construct a phylogenetic
Chapter 26: Phylogeny and the Tree of Life You Must Know The taxonomic categories and how they indicate relatedness. How systematics is used to develop phylogenetic trees. How to construct a phylogenetic
UoN, CAS, DBSC BIOL102 lecture notes by: Dr. Mustafa A. Mansi. The Phylogenetic Systematics (Phylogeny and Systematics)
 - Phylogeny? - Systematics? The Phylogenetic Systematics (Phylogeny and Systematics) - Phylogenetic systematics? Connection between phylogeny and classification. - Phylogenetic systematics informs the
- Phylogeny? - Systematics? The Phylogenetic Systematics (Phylogeny and Systematics) - Phylogenetic systematics? Connection between phylogeny and classification. - Phylogenetic systematics informs the
Phylogeny 9/8/2014. Evolutionary Relationships. Data Supporting Phylogeny. Chapter 26
 Phylogeny Chapter 26 Taxonomy Taxonomy: ordered division of organisms into categories based on a set of characteristics used to assess similarities and differences Carolus Linnaeus developed binomial nomenclature,
Phylogeny Chapter 26 Taxonomy Taxonomy: ordered division of organisms into categories based on a set of characteristics used to assess similarities and differences Carolus Linnaeus developed binomial nomenclature,
Lecture 11 Friday, October 21, 2011
 Lecture 11 Friday, October 21, 2011 Phylogenetic tree (phylogeny) Darwin and classification: In the Origin, Darwin said that descent from a common ancestral species could explain why the Linnaean system
Lecture 11 Friday, October 21, 2011 Phylogenetic tree (phylogeny) Darwin and classification: In the Origin, Darwin said that descent from a common ancestral species could explain why the Linnaean system
Reproduction- passing genetic information to the next generation
 166 166 Essential Question: How has biological evolution led to the diversity of life? B-5 Natural Selection Traits that make an organism more or less likely to survive in an environment and reproduce
166 166 Essential Question: How has biological evolution led to the diversity of life? B-5 Natural Selection Traits that make an organism more or less likely to survive in an environment and reproduce
Chapter 19: Taxonomy, Systematics, and Phylogeny
 Chapter 19: Taxonomy, Systematics, and Phylogeny AP Curriculum Alignment Chapter 19 expands on the topics of phylogenies and cladograms, which are important to Big Idea 1. In order for students to understand
Chapter 19: Taxonomy, Systematics, and Phylogeny AP Curriculum Alignment Chapter 19 expands on the topics of phylogenies and cladograms, which are important to Big Idea 1. In order for students to understand
CHAPTER 26 PHYLOGENY AND THE TREE OF LIFE Connecting Classification to Phylogeny
 CHAPTER 26 PHYLOGENY AND THE TREE OF LIFE Connecting Classification to Phylogeny To trace phylogeny or the evolutionary history of life, biologists use evidence from paleontology, molecular data, comparative
CHAPTER 26 PHYLOGENY AND THE TREE OF LIFE Connecting Classification to Phylogeny To trace phylogeny or the evolutionary history of life, biologists use evidence from paleontology, molecular data, comparative
Reconstructing the history of lineages
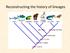 Reconstructing the history of lineages Class outline Systematics Phylogenetic systematics Phylogenetic trees and maps Class outline Definitions Systematics Phylogenetic systematics/cladistics Systematics
Reconstructing the history of lineages Class outline Systematics Phylogenetic systematics Phylogenetic trees and maps Class outline Definitions Systematics Phylogenetic systematics/cladistics Systematics
ESS 345 Ichthyology. Systematic Ichthyology Part II Not in Book
 ESS 345 Ichthyology Systematic Ichthyology Part II Not in Book Thought for today: Now, here, you see, it takes all the running you can do, to keep in the same place. If you want to get somewhere else,
ESS 345 Ichthyology Systematic Ichthyology Part II Not in Book Thought for today: Now, here, you see, it takes all the running you can do, to keep in the same place. If you want to get somewhere else,
Chapter 27: Evolutionary Genetics
 Chapter 27: Evolutionary Genetics Student Learning Objectives Upon completion of this chapter you should be able to: 1. Understand what the term species means to biology. 2. Recognize the various patterns
Chapter 27: Evolutionary Genetics Student Learning Objectives Upon completion of this chapter you should be able to: 1. Understand what the term species means to biology. 2. Recognize the various patterns
Ch. 25/26 Warm-Up. 2. List 3 pieces of evidence to support the endosymbiont theory.
 Ch. 25/26 Warm-Up 1. Answer the following using the diagram below: A B C 3 4 2 D 1 a. a common ancestor for D & F b. most closely related species c. least related species d. new species C arises at this
Ch. 25/26 Warm-Up 1. Answer the following using the diagram below: A B C 3 4 2 D 1 a. a common ancestor for D & F b. most closely related species c. least related species d. new species C arises at this
How should we organize the diversity of animal life?
 How should we organize the diversity of animal life? The difference between Taxonomy Linneaus, and Cladistics Darwin What are phylogenies? How do we read them? How do we estimate them? Classification (Taxonomy)
How should we organize the diversity of animal life? The difference between Taxonomy Linneaus, and Cladistics Darwin What are phylogenies? How do we read them? How do we estimate them? Classification (Taxonomy)
Classification and Phylogeny
 Classification and Phylogeny The diversity of life is great. To communicate about it, there must be a scheme for organization. There are many species that would be difficult to organize without a scheme
Classification and Phylogeny The diversity of life is great. To communicate about it, there must be a scheme for organization. There are many species that would be difficult to organize without a scheme
Classification and Phylogeny
 Classification and Phylogeny The diversity it of life is great. To communicate about it, there must be a scheme for organization. There are many species that would be difficult to organize without a scheme
Classification and Phylogeny The diversity it of life is great. To communicate about it, there must be a scheme for organization. There are many species that would be difficult to organize without a scheme
AP: CHAPTER 24: THE ORIGIN OF SPECIES 1. Define the term species.
 AP Biology Chapter 24 Guided Reading Assignment Ms. Hall Name AP: CHAPTER 24: THE ORIGIN OF SPECIES 1. Define the term species. 2. How do the patterns of speciation differ? a. anagenesis b. cladogenesis
AP Biology Chapter 24 Guided Reading Assignment Ms. Hall Name AP: CHAPTER 24: THE ORIGIN OF SPECIES 1. Define the term species. 2. How do the patterns of speciation differ? a. anagenesis b. cladogenesis
Chapters Objectives
 Chapter 22 Darwinian View of Life Objectives Chapters 22-26 Objectives The Historical Context for Evolutionary Theory 1 Explain the mechanism for evolutionary change proposed by Charles Darwin in On the
Chapter 22 Darwinian View of Life Objectives Chapters 22-26 Objectives The Historical Context for Evolutionary Theory 1 Explain the mechanism for evolutionary change proposed by Charles Darwin in On the
What is Phylogenetics
 What is Phylogenetics Phylogenetics is the area of research concerned with finding the genetic connections and relationships between species. The basic idea is to compare specific characters (features)
What is Phylogenetics Phylogenetics is the area of research concerned with finding the genetic connections and relationships between species. The basic idea is to compare specific characters (features)
GENETICS - CLUTCH CH.22 EVOLUTIONARY GENETICS.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: OVERVIEW OF EVOLUTION Evolution is a process through which variation in individuals makes it more likely for them to survive and reproduce There are principles to the theory
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: OVERVIEW OF EVOLUTION Evolution is a process through which variation in individuals makes it more likely for them to survive and reproduce There are principles to the theory
Chapter 26 Phylogeny and the Tree of Life
 Chapter 26 Phylogeny and the Tree of Life Chapter focus Shifting from the process of how evolution works to the pattern evolution produces over time. Phylogeny Phylon = tribe, geny = genesis or origin
Chapter 26 Phylogeny and the Tree of Life Chapter focus Shifting from the process of how evolution works to the pattern evolution produces over time. Phylogeny Phylon = tribe, geny = genesis or origin
Phylogenies & Classifying species (AKA Cladistics & Taxonomy) What are phylogenies & cladograms? How do we read them? How do we estimate them?
 Phylogenies & Classifying species (AKA Cladistics & Taxonomy) What are phylogenies & cladograms? How do we read them? How do we estimate them? Carolus Linneaus:Systema Naturae (1735) Swedish botanist &
Phylogenies & Classifying species (AKA Cladistics & Taxonomy) What are phylogenies & cladograms? How do we read them? How do we estimate them? Carolus Linneaus:Systema Naturae (1735) Swedish botanist &
Chapter 19 Organizing Information About Species: Taxonomy and Cladistics
 Chapter 19 Organizing Information About Species: Taxonomy and Cladistics An unexpected family tree. What are the evolutionary relationships among a human, a mushroom, and a tulip? Molecular systematics
Chapter 19 Organizing Information About Species: Taxonomy and Cladistics An unexpected family tree. What are the evolutionary relationships among a human, a mushroom, and a tulip? Molecular systematics
SCIENTIFIC EVIDENCE TO SUPPORT THE THEORY OF EVOLUTION. Using Anatomy, Embryology, Biochemistry, and Paleontology
 SCIENTIFIC EVIDENCE TO SUPPORT THE THEORY OF EVOLUTION Using Anatomy, Embryology, Biochemistry, and Paleontology Scientific Fields Different fields of science have contributed evidence for the theory of
SCIENTIFIC EVIDENCE TO SUPPORT THE THEORY OF EVOLUTION Using Anatomy, Embryology, Biochemistry, and Paleontology Scientific Fields Different fields of science have contributed evidence for the theory of
CHAPTERS 24-25: Evidence for Evolution and Phylogeny
 CHAPTERS 24-25: Evidence for Evolution and Phylogeny 1. For each of the following, indicate how it is used as evidence of evolution by natural selection or shown as an evolutionary trend: a. Paleontology
CHAPTERS 24-25: Evidence for Evolution and Phylogeny 1. For each of the following, indicate how it is used as evidence of evolution by natural selection or shown as an evolutionary trend: a. Paleontology
Biology 211 (2) Week 1 KEY!
 Biology 211 (2) Week 1 KEY Chapter 1 KEY FIGURES: 1.2, 1.3, 1.4, 1.5, 1.6, 1.7 VOCABULARY: Adaptation: a trait that increases the fitness Cells: a developed, system bound with a thin outer layer made of
Biology 211 (2) Week 1 KEY Chapter 1 KEY FIGURES: 1.2, 1.3, 1.4, 1.5, 1.6, 1.7 VOCABULARY: Adaptation: a trait that increases the fitness Cells: a developed, system bound with a thin outer layer made of
Macroevolution Part I: Phylogenies
 Macroevolution Part I: Phylogenies Taxonomy Classification originated with Carolus Linnaeus in the 18 th century. Based on structural (outward and inward) similarities Hierarchal scheme, the largest most
Macroevolution Part I: Phylogenies Taxonomy Classification originated with Carolus Linnaeus in the 18 th century. Based on structural (outward and inward) similarities Hierarchal scheme, the largest most
Classification, Phylogeny yand Evolutionary History
 Classification, Phylogeny yand Evolutionary History The diversity of life is great. To communicate about it, there must be a scheme for organization. There are many species that would be difficult to organize
Classification, Phylogeny yand Evolutionary History The diversity of life is great. To communicate about it, there must be a scheme for organization. There are many species that would be difficult to organize
PHYLOGENY AND SYSTEMATICS
 AP BIOLOGY EVOLUTION/HEREDITY UNIT Unit 1 Part 11 Chapter 26 Activity #15 NAME DATE PERIOD PHYLOGENY AND SYSTEMATICS PHYLOGENY Evolutionary history of species or group of related species SYSTEMATICS Study
AP BIOLOGY EVOLUTION/HEREDITY UNIT Unit 1 Part 11 Chapter 26 Activity #15 NAME DATE PERIOD PHYLOGENY AND SYSTEMATICS PHYLOGENY Evolutionary history of species or group of related species SYSTEMATICS Study
Cladistics and Bioinformatics Questions 2013
 AP Biology Name Cladistics and Bioinformatics Questions 2013 1. The following table shows the percentage similarity in sequences of nucleotides from a homologous gene derived from five different species
AP Biology Name Cladistics and Bioinformatics Questions 2013 1. The following table shows the percentage similarity in sequences of nucleotides from a homologous gene derived from five different species
Phylogeny and Systematics
 Chapter 25 Phylogeny and Systematics PowerPoint Lectures for Biology, Seventh Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero Modified by Maria Morlin racing phylogeny Phylogeny: he evolutionary
Chapter 25 Phylogeny and Systematics PowerPoint Lectures for Biology, Seventh Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero Modified by Maria Morlin racing phylogeny Phylogeny: he evolutionary
B. Phylogeny and Systematics:
 Tracing Phylogeny A. Fossils: Some fossils form as is weathered and eroded from the land and carried by rivers to seas and where the particles settle to the bottom. Deposits pile up and the older sediments
Tracing Phylogeny A. Fossils: Some fossils form as is weathered and eroded from the land and carried by rivers to seas and where the particles settle to the bottom. Deposits pile up and the older sediments
Historical Biogeography. Historical Biogeography. Systematics
 Historical Biogeography I. Definitions II. Fossils: problems with fossil record why fossils are important III. Phylogeny IV. Phenetics VI. Phylogenetic Classification Disjunctions debunked: Examples VII.
Historical Biogeography I. Definitions II. Fossils: problems with fossil record why fossils are important III. Phylogeny IV. Phenetics VI. Phylogenetic Classification Disjunctions debunked: Examples VII.
The Origin of Species
 The Origin of Species Introduction A species can be defined as a group of organisms whose members can breed and produce fertile offspring, but who do not produce fertile offspring with members of other
The Origin of Species Introduction A species can be defined as a group of organisms whose members can breed and produce fertile offspring, but who do not produce fertile offspring with members of other
Lecture V Phylogeny and Systematics Dr. Kopeny
 Delivered 1/30 and 2/1 Lecture V Phylogeny and Systematics Dr. Kopeny Lecture V How to Determine Evolutionary Relationships: Concepts in Phylogeny and Systematics Textbook Reading: pp 425-433, 435-437
Delivered 1/30 and 2/1 Lecture V Phylogeny and Systematics Dr. Kopeny Lecture V How to Determine Evolutionary Relationships: Concepts in Phylogeny and Systematics Textbook Reading: pp 425-433, 435-437
Name. Ecology & Evolutionary Biology 2245/2245W Exam 2 1 March 2014
 Name 1 Ecology & Evolutionary Biology 2245/2245W Exam 2 1 March 2014 1. Use the following matrix of nucleotide sequence data and the corresponding tree to answer questions a. through h. below. (16 points)
Name 1 Ecology & Evolutionary Biology 2245/2245W Exam 2 1 March 2014 1. Use the following matrix of nucleotide sequence data and the corresponding tree to answer questions a. through h. below. (16 points)
Anatomy of a tree. clade is group of organisms with a shared ancestor. a monophyletic group shares a single common ancestor = tapirs-rhinos-horses
 Anatomy of a tree outgroup: an early branching relative of the interest groups sister taxa: taxa derived from the same recent ancestor polytomy: >2 taxa emerge from a node Anatomy of a tree clade is group
Anatomy of a tree outgroup: an early branching relative of the interest groups sister taxa: taxa derived from the same recent ancestor polytomy: >2 taxa emerge from a node Anatomy of a tree clade is group
5/31/17. Week 10; Monday MEMORIAL DAY NO CLASS. Page 88
 Week 10; Monday MEMORIAL DAY NO CLASS Page 88 Week 10; Wednesday Announcements: Family ID final in lab Today Final exam next Tuesday at 8:30 am here Lecture: Species concepts & Speciation. What are species?
Week 10; Monday MEMORIAL DAY NO CLASS Page 88 Week 10; Wednesday Announcements: Family ID final in lab Today Final exam next Tuesday at 8:30 am here Lecture: Species concepts & Speciation. What are species?
1. T/F: Genetic variation leads to evolution. 2. What is genetic equilibrium? 3. What is speciation? How does it occur?
 1. T/F: Genetic variation leads to evolution. 2. What is genetic equilibrium? 3. What is speciation? How does it occur? Warm UP Notes on Environmental Factor Concept Map Brief 6 questions and Concept Map
1. T/F: Genetic variation leads to evolution. 2. What is genetic equilibrium? 3. What is speciation? How does it occur? Warm UP Notes on Environmental Factor Concept Map Brief 6 questions and Concept Map
Fig. 26.7a. Biodiversity. 1. Course Outline Outcomes Instructors Text Grading. 2. Course Syllabus. Fig. 26.7b Table
 Fig. 26.7a Biodiversity 1. Course Outline Outcomes Instructors Text Grading 2. Course Syllabus Fig. 26.7b Table 26.2-1 1 Table 26.2-2 Outline: Systematics and the Phylogenetic Revolution I. Naming and
Fig. 26.7a Biodiversity 1. Course Outline Outcomes Instructors Text Grading 2. Course Syllabus Fig. 26.7b Table 26.2-1 1 Table 26.2-2 Outline: Systematics and the Phylogenetic Revolution I. Naming and
Chapter 26 Phylogeny and the Tree of Life
 Chapter 26 Phylogeny and the Tree of Life Biologists estimate that there are about 5 to 100 million species of organisms living on Earth today. Evidence from morphological, biochemical, and gene sequence
Chapter 26 Phylogeny and the Tree of Life Biologists estimate that there are about 5 to 100 million species of organisms living on Earth today. Evidence from morphological, biochemical, and gene sequence
The practice of naming and classifying organisms is called taxonomy.
 Chapter 18 Key Idea: Biologists use taxonomic systems to organize their knowledge of organisms. These systems attempt to provide consistent ways to name and categorize organisms. The practice of naming
Chapter 18 Key Idea: Biologists use taxonomic systems to organize their knowledge of organisms. These systems attempt to provide consistent ways to name and categorize organisms. The practice of naming
Phylogeny and the Tree of Life
 LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 26 Phylogeny and the Tree of Life
LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 26 Phylogeny and the Tree of Life
Chapters 25 and 26. Searching for Homology. Phylogeny
 Chapters 25 and 26 The Origin of Life as we know it. Phylogeny traces evolutionary history of taxa Systematics- analyzes relationships (modern and past) of organisms Figure 25.1 A gallery of fossils The
Chapters 25 and 26 The Origin of Life as we know it. Phylogeny traces evolutionary history of taxa Systematics- analyzes relationships (modern and past) of organisms Figure 25.1 A gallery of fossils The
How Biological Diversity Evolves
 CHAPTER 14 How Biological Diversity Evolves PowerPoint Lectures for Essential Biology, Third Edition Neil Campbell, Jane Reece, and Eric Simon Essential Biology with Physiology, Second Edition Neil Campbell,
CHAPTER 14 How Biological Diversity Evolves PowerPoint Lectures for Essential Biology, Third Edition Neil Campbell, Jane Reece, and Eric Simon Essential Biology with Physiology, Second Edition Neil Campbell,
Phylogeny and the Tree of Life
 Chapter 26 Phylogeny and the Tree of Life PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from
Chapter 26 Phylogeny and the Tree of Life PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from
Speciation. Today s OUTLINE: Mechanisms of Speciation. Mechanisms of Speciation. Geographic Models of speciation. (1) Mechanisms of Speciation
 Speciation Today s OUTLINE: (1) Geographic Mechanisms of Speciation (What circumstances lead to the formation of new species?) (2) Species Concepts (How are Species Defined?) Mechanisms of Speciation Last
Speciation Today s OUTLINE: (1) Geographic Mechanisms of Speciation (What circumstances lead to the formation of new species?) (2) Species Concepts (How are Species Defined?) Mechanisms of Speciation Last
A Summary of the Theory of Evolution
 A Summary of the Theory of Evolution Raúl Esperante Geoscience Research Institute Loma Linda, California What is Evolution? What does the term evolution mean? The word has three meanings that are relevant
A Summary of the Theory of Evolution Raúl Esperante Geoscience Research Institute Loma Linda, California What is Evolution? What does the term evolution mean? The word has three meanings that are relevant
Biology 1B Evolution Lecture 2 (February 26, 2010) Natural Selection, Phylogenies
 1 Natural Selection (Darwin-Wallace): There are three conditions for natural selection: 1. Variation: Individuals within a population have different characteristics/traits (or phenotypes). 2. Inheritance:
1 Natural Selection (Darwin-Wallace): There are three conditions for natural selection: 1. Variation: Individuals within a population have different characteristics/traits (or phenotypes). 2. Inheritance:
Outline. Classification of Living Things
 Outline Classification of Living Things Chapter 20 Mader: Biology 8th Ed. Taxonomy Binomial System Species Identification Classification Categories Phylogenetic Trees Tracing Phylogeny Cladistic Systematics
Outline Classification of Living Things Chapter 20 Mader: Biology 8th Ed. Taxonomy Binomial System Species Identification Classification Categories Phylogenetic Trees Tracing Phylogeny Cladistic Systematics
Phylogenetic Analysis
 Phylogenetic Analysis Aristotle Through classification, one might discover the essence and purpose of species. Nelson & Platnick (1981) Systematics and Biogeography Carl Linnaeus Swedish botanist (1700s)
Phylogenetic Analysis Aristotle Through classification, one might discover the essence and purpose of species. Nelson & Platnick (1981) Systematics and Biogeography Carl Linnaeus Swedish botanist (1700s)
EVOLUTION Unit 1 Part 9 (Chapter 24) Activity #13
 AP BIOLOGY EVOLUTION Unit 1 Part 9 (Chapter 24) Activity #13 NAME DATE PERIOD SPECIATION SPECIATION Origin of new species SPECIES BIOLOGICAL CONCEPT Population or groups of populations whose members have
AP BIOLOGY EVOLUTION Unit 1 Part 9 (Chapter 24) Activity #13 NAME DATE PERIOD SPECIATION SPECIATION Origin of new species SPECIES BIOLOGICAL CONCEPT Population or groups of populations whose members have
C.DARWIN ( )
 C.DARWIN (1809-1882) LAMARCK Each evolutionary lineage has evolved, transforming itself, from a ancestor appeared by spontaneous generation DARWIN All organisms are historically interconnected. Their relationships
C.DARWIN (1809-1882) LAMARCK Each evolutionary lineage has evolved, transforming itself, from a ancestor appeared by spontaneous generation DARWIN All organisms are historically interconnected. Their relationships
Modern Evolutionary Classification. Section 18-2 pgs
 Modern Evolutionary Classification Section 18-2 pgs 451-455 Modern Evolutionary Classification In a sense, organisms determine who belongs to their species by choosing with whom they will mate. Taxonomic
Modern Evolutionary Classification Section 18-2 pgs 451-455 Modern Evolutionary Classification In a sense, organisms determine who belongs to their species by choosing with whom they will mate. Taxonomic
Theory a well supported testable explanation of phenomenon occurring in the natural world.
 Evolution Theory of Evolution Theory a well supported testable explanation of phenomenon occurring in the natural world. Evolution the process by which modern organisms changed over time from ancient common
Evolution Theory of Evolution Theory a well supported testable explanation of phenomenon occurring in the natural world. Evolution the process by which modern organisms changed over time from ancient common
Bio 1B Lecture Outline (please print and bring along) Fall, 2008
 Bio 1B Lecture Outline (please print and bring along) Fall, 2008 B.D. Mishler, Dept. of Integrative Biology 2-6810, bmishler@berkeley.edu Evolution lecture #6 -- Tempo and Mode in Macroevolution -- Nov.
Bio 1B Lecture Outline (please print and bring along) Fall, 2008 B.D. Mishler, Dept. of Integrative Biology 2-6810, bmishler@berkeley.edu Evolution lecture #6 -- Tempo and Mode in Macroevolution -- Nov.
Lecture 6 Phylogenetic Inference
 Lecture 6 Phylogenetic Inference From Darwin s notebook in 1837 Charles Darwin Willi Hennig From The Origin in 1859 Cladistics Phylogenetic inference Willi Hennig, Cladistics 1. Clade, Monophyletic group,
Lecture 6 Phylogenetic Inference From Darwin s notebook in 1837 Charles Darwin Willi Hennig From The Origin in 1859 Cladistics Phylogenetic inference Willi Hennig, Cladistics 1. Clade, Monophyletic group,
How related are organisms?
 The Evolution and Classification of Species Darwin argued for adaptive radiation in which demes spread out in a given environment and evolved How related are organisms? Taonomy the science of classifying
The Evolution and Classification of Species Darwin argued for adaptive radiation in which demes spread out in a given environment and evolved How related are organisms? Taonomy the science of classifying
CLASSIFICATION OF LIVING THINGS. Chapter 18
 CLASSIFICATION OF LIVING THINGS Chapter 18 How many species are there? About 1.8 million species have been given scientific names Nearly 2/3 of which are insects 99% of all known animal species are smaller
CLASSIFICATION OF LIVING THINGS Chapter 18 How many species are there? About 1.8 million species have been given scientific names Nearly 2/3 of which are insects 99% of all known animal species are smaller
Speciation. Today s OUTLINE: Mechanisms of Speciation. Mechanisms of Speciation. Geographic Models of speciation. (1) Mechanisms of Speciation
 Speciation Today s OUTLINE: (1) Geographic Mechanisms of Speciation (What circumstances lead to the formation of new species?) (2) Species Concepts (How are Species Defined?) Mechanisms of Speciation Last
Speciation Today s OUTLINE: (1) Geographic Mechanisms of Speciation (What circumstances lead to the formation of new species?) (2) Species Concepts (How are Species Defined?) Mechanisms of Speciation Last
Organizing Life s Diversity
 17 Organizing Life s Diversity section 2 Modern Classification Classification systems have changed over time as information has increased. What You ll Learn species concepts methods to reveal phylogeny
17 Organizing Life s Diversity section 2 Modern Classification Classification systems have changed over time as information has increased. What You ll Learn species concepts methods to reveal phylogeny
AP Biology. Cladistics
 Cladistics Kingdom Summary Review slide Review slide Classification Old 5 Kingdom system Eukaryote Monera, Protists, Plants, Fungi, Animals New 3 Domain system reflects a greater understanding of evolution
Cladistics Kingdom Summary Review slide Review slide Classification Old 5 Kingdom system Eukaryote Monera, Protists, Plants, Fungi, Animals New 3 Domain system reflects a greater understanding of evolution
Name: Period Study Guide 17-1 and 17-2
 Name: Period Study Guide 17-1 and 17-2 17-1 The Fossil Record (pgs. 417-422) 1. What is the fossil record? 2. What evidence does the fossil record provide? 1. 2. 3. List the 2 techniques paleontologists
Name: Period Study Guide 17-1 and 17-2 17-1 The Fossil Record (pgs. 417-422) 1. What is the fossil record? 2. What evidence does the fossil record provide? 1. 2. 3. List the 2 techniques paleontologists
Phylogenetic Analysis
 Phylogenetic Analysis Aristotle Through classification, one might discover the essence and purpose of species. Nelson & Platnick (1981) Systematics and Biogeography Carl Linnaeus Swedish botanist (1700s)
Phylogenetic Analysis Aristotle Through classification, one might discover the essence and purpose of species. Nelson & Platnick (1981) Systematics and Biogeography Carl Linnaeus Swedish botanist (1700s)
Phylogenetic Analysis
 Phylogenetic Analysis Aristotle Through classification, one might discover the essence and purpose of species. Nelson & Platnick (1981) Systematics and Biogeography Carl Linnaeus Swedish botanist (1700s)
Phylogenetic Analysis Aristotle Through classification, one might discover the essence and purpose of species. Nelson & Platnick (1981) Systematics and Biogeography Carl Linnaeus Swedish botanist (1700s)
Phylogeny and the Tree of Life
 Chapter 26 Phylogeny and the Tree of Life PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from
Chapter 26 Phylogeny and the Tree of Life PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from
PHYLOGENY WHAT IS EVOLUTION? 1/22/2018. Change must occur in a population via allele
 PHYLOGENY EXERCISE 1 AND 2 WHAT IS EVOLUTION? The theory that all living organisms on earth are related and have a common ancestor. These organism have changed over time and are continuing to change. Changes
PHYLOGENY EXERCISE 1 AND 2 WHAT IS EVOLUTION? The theory that all living organisms on earth are related and have a common ancestor. These organism have changed over time and are continuing to change. Changes
AP Biology Review Packet 5- Natural Selection and Evolution & Speciation and Phylogeny
 AP Biology Review Packet 5- Natural Selection and Evolution & Speciation and Phylogeny 1A1- Natural selection is a major mechanism of evolution. 1A2: Natural selection acts on phenotypic variations in
AP Biology Review Packet 5- Natural Selection and Evolution & Speciation and Phylogeny 1A1- Natural selection is a major mechanism of evolution. 1A2: Natural selection acts on phenotypic variations in
This is DUE: Tuesday, Dec 4, 2012 Come prepared to share your findings with your group.
 Biology 160 Reading Guide 13: Ecosystems, Part I NAME: This is DUE: Tuesday, Dec 4, 2012 Come prepared to share your findings with your group. *As before, please turn in only the Critical Thinking questions
Biology 160 Reading Guide 13: Ecosystems, Part I NAME: This is DUE: Tuesday, Dec 4, 2012 Come prepared to share your findings with your group. *As before, please turn in only the Critical Thinking questions
Introduction to characters and parsimony analysis
 Introduction to characters and parsimony analysis Genetic Relationships Genetic relationships exist between individuals within populations These include ancestordescendent relationships and more indirect
Introduction to characters and parsimony analysis Genetic Relationships Genetic relationships exist between individuals within populations These include ancestordescendent relationships and more indirect
Big Idea #1: The process of evolution drives the diversity and unity of life
 BIG IDEA! Big Idea #1: The process of evolution drives the diversity and unity of life Key Terms for this section: emigration phenotype adaptation evolution phylogenetic tree adaptive radiation fertility
BIG IDEA! Big Idea #1: The process of evolution drives the diversity and unity of life Key Terms for this section: emigration phenotype adaptation evolution phylogenetic tree adaptive radiation fertility
PHYLOGENY & THE TREE OF LIFE
 PHYLOGENY & THE TREE OF LIFE PREFACE In this powerpoint we learn how biologists distinguish and categorize the millions of species on earth. Early we looked at the process of evolution here we look at
PHYLOGENY & THE TREE OF LIFE PREFACE In this powerpoint we learn how biologists distinguish and categorize the millions of species on earth. Early we looked at the process of evolution here we look at
Chapter 26: Phylogeny and the Tree of Life
 Chapter 26: Phylogeny and the Tree of Life 1. Key Concepts Pertaining to Phylogeny 2. Determining Phylogenies 3. Evolutionary History Revealed in Genomes 1. Key Concepts Pertaining to Phylogeny PHYLOGENY
Chapter 26: Phylogeny and the Tree of Life 1. Key Concepts Pertaining to Phylogeny 2. Determining Phylogenies 3. Evolutionary History Revealed in Genomes 1. Key Concepts Pertaining to Phylogeny PHYLOGENY
Speciation. Today s OUTLINE: Mechanisms of Speciation. Mechanisms of Speciation. Geographic Models of speciation. (1) Mechanisms of Speciation
 Speciation Today s OUTLINE: (1) Geographic Mechanisms of Speciation (What circumstances lead to the formation of new species?) (2) Species Concepts (How are Species Defined?) Mechanisms of Speciation Last
Speciation Today s OUTLINE: (1) Geographic Mechanisms of Speciation (What circumstances lead to the formation of new species?) (2) Species Concepts (How are Species Defined?) Mechanisms of Speciation Last
Need for systematics. Applications of systematics. Linnaeus plus Darwin. Approaches in systematics. Principles of cladistics
 Topics Need for systematics Applications of systematics Linnaeus plus Darwin Approaches in systematics Principles of cladistics Systematics pp. 474-475. Systematics - Study of diversity and evolutionary
Topics Need for systematics Applications of systematics Linnaeus plus Darwin Approaches in systematics Principles of cladistics Systematics pp. 474-475. Systematics - Study of diversity and evolutionary
4. In light of evolution do individuals evolve or do populations evolve? Explain your answer.
 Chapter 22-26 Homework Questions Chapter 22 - Descent with Modification: A Darwinian View of Life 1. Why was Darwin s theory so controversial? Also, what is the value of a theory in science? 2. List and
Chapter 22-26 Homework Questions Chapter 22 - Descent with Modification: A Darwinian View of Life 1. Why was Darwin s theory so controversial? Also, what is the value of a theory in science? 2. List and
C3020 Molecular Evolution. Exercises #3: Phylogenetics
 C3020 Molecular Evolution Exercises #3: Phylogenetics Consider the following sequences for five taxa 1-5 and the known outgroup O, which has the ancestral states (note that sequence 3 has changed from
C3020 Molecular Evolution Exercises #3: Phylogenetics Consider the following sequences for five taxa 1-5 and the known outgroup O, which has the ancestral states (note that sequence 3 has changed from
Evolution and Darwin
 Evolution and Darwin Evolution The processes that have transformed life on earth from it s earliest forms to the vast diversity that characterizes it today - Darwin Old Theories of Evolution Jean Baptiste
Evolution and Darwin Evolution The processes that have transformed life on earth from it s earliest forms to the vast diversity that characterizes it today - Darwin Old Theories of Evolution Jean Baptiste
Phylogeny is the evolutionary history of a group of organisms. Based on the idea that organisms are related by evolution
 Bio 1M: Phylogeny and the history of life 1 Phylogeny S25.1; Bioskill 11 (2ndEd S27.1; Bioskills 3) Bioskills are in the back of your book Phylogeny is the evolutionary history of a group of organisms
Bio 1M: Phylogeny and the history of life 1 Phylogeny S25.1; Bioskill 11 (2ndEd S27.1; Bioskills 3) Bioskills are in the back of your book Phylogeny is the evolutionary history of a group of organisms
AP Bio Directed Study Summer Assignment Evolution: Chapters 22-26
 1. AP Bio Summer Assignment MANDATORY FOR ALL AP BIOLOGY STUDENTS Students should purchase a copy of the McGraw Hill 5 Steps to a 5 AP Biology (2011-2012 version preferred) available at any book store
1. AP Bio Summer Assignment MANDATORY FOR ALL AP BIOLOGY STUDENTS Students should purchase a copy of the McGraw Hill 5 Steps to a 5 AP Biology (2011-2012 version preferred) available at any book store
In a way, organisms determine who belongs to their species by choosing with whom they will! MODERN EVOLUTIONARY CLASSIFICATION 18-2 MATE
 MODERN EVOLUTIONARY CLASSIFICATION 18-2 In a way, organisms determine who belongs to their species by choosing with whom they will! MATE Taxonomic groups are invented by scientists to group organisms with
MODERN EVOLUTIONARY CLASSIFICATION 18-2 In a way, organisms determine who belongs to their species by choosing with whom they will! MATE Taxonomic groups are invented by scientists to group organisms with
Biology 182: Study Guide
 Biology 182: Study Guide Purpose: This study guide provides a checklist of terms, concepts and topics covered in Bio182. Although arranged by chapters from your text, topics may be presented at various
Biology 182: Study Guide Purpose: This study guide provides a checklist of terms, concepts and topics covered in Bio182. Although arranged by chapters from your text, topics may be presented at various
Chapter 17A. Table of Contents. Section 1 Categories of Biological Classification. Section 2 How Biologists Classify Organisms
 Classification of Organisms Table of Contents Section 1 Categories of Biological Classification Section 1 Categories of Biological Classification Classification Section 1 Categories of Biological Classification
Classification of Organisms Table of Contents Section 1 Categories of Biological Classification Section 1 Categories of Biological Classification Classification Section 1 Categories of Biological Classification
Biodiversity. The Road to the Six Kingdoms of Life
 Biodiversity The Road to the Six Kingdoms of Life How the 6 kingdoms came about At first, only two kingdoms were recognized Then Haeckel proposed a third kingdom Protista (where protists had both plant
Biodiversity The Road to the Six Kingdoms of Life How the 6 kingdoms came about At first, only two kingdoms were recognized Then Haeckel proposed a third kingdom Protista (where protists had both plant
Chapter 10. Classification and Phylogeny of Animals. Order in Diversity. Hierarchy of taxa. Table Linnaeus introduced binomial nomenclature
 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Chapter 10 Classification and Phylogeny of Animals Order in Diversity History Systematic zoologists have three
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Chapter 10 Classification and Phylogeny of Animals Order in Diversity History Systematic zoologists have three
The Origin of New Species
 The Origin of New Species Introduction If microevolution is small changes in gene frequencies What, then would macroevolution be? And how might that work???? The biological species concept emphasizes reproductive
The Origin of New Species Introduction If microevolution is small changes in gene frequencies What, then would macroevolution be? And how might that work???? The biological species concept emphasizes reproductive
Wake Acceleration Academy - Biology Note Guide Unit 6: Evolution & The Diversity of Life
 Wake Acceleration Academy - Biology Note Guide Unit 6: Evolution & The Diversity of Life Extra Resources Website: http://waa-science.weebly.com Module 1: Darwin and Natural Selection Vocabulary Term Charles
Wake Acceleration Academy - Biology Note Guide Unit 6: Evolution & The Diversity of Life Extra Resources Website: http://waa-science.weebly.com Module 1: Darwin and Natural Selection Vocabulary Term Charles
Patterns of Evolution
 Patterns of Evolution A tree that represents an estimate (hypothesis) of evolutionary relatedness is a phylogeny Classifications can be based on groupings within a phylogeny Groupings can be categorized
Patterns of Evolution A tree that represents an estimate (hypothesis) of evolutionary relatedness is a phylogeny Classifications can be based on groupings within a phylogeny Groupings can be categorized
Name: Class: Date: ID: A
 Class: _ Date: _ Ch 17 Practice test 1. A segment of DNA that stores genetic information is called a(n) a. amino acid. b. gene. c. protein. d. intron. 2. In which of the following processes does change
Class: _ Date: _ Ch 17 Practice test 1. A segment of DNA that stores genetic information is called a(n) a. amino acid. b. gene. c. protein. d. intron. 2. In which of the following processes does change
MACROEVOLUTION Student Packet SUMMARY EVOLUTION IS A CHANGE IN THE GENETIC MAKEUP OF A POPULATION OVER TIME Macroevolution refers to large-scale
 MACROEVOLUTION Student Packet SUMMARY EVOLUTION IS A CHANGE IN THE GENETIC MAKEUP OF A POPULATION OVER TIME Macroevolution refers to large-scale evolutionary changes such as speciation events, origin of
MACROEVOLUTION Student Packet SUMMARY EVOLUTION IS A CHANGE IN THE GENETIC MAKEUP OF A POPULATION OVER TIME Macroevolution refers to large-scale evolutionary changes such as speciation events, origin of
1/27/2010. Systematics and Phylogenetics of the. An Introduction. Taxonomy and Systematics
 Systematics and Phylogenetics of the Amphibia: An Introduction Taxonomy and Systematics Taxonomy, the science of describing biodiversity, mainly naming unnamed species, and arranging the diversity into
Systematics and Phylogenetics of the Amphibia: An Introduction Taxonomy and Systematics Taxonomy, the science of describing biodiversity, mainly naming unnamed species, and arranging the diversity into
Classifications can be based on groupings g within a phylogeny
 Patterns of Evolution A tree that represents an estimate (hypothesis) of evolutionary relatedness is a phylogeny Classifications can be based on groupings g within a phylogeny y Groupings can be categorized
Patterns of Evolution A tree that represents an estimate (hypothesis) of evolutionary relatedness is a phylogeny Classifications can be based on groupings g within a phylogeny y Groupings can be categorized
Concept Modern Taxonomy reflects evolutionary history.
 Concept 15.4 Modern Taxonomy reflects evolutionary history. What is Taxonomy: identification, naming, and classification of species. Common Names: can cause confusion - May refer to several species (ex.
Concept 15.4 Modern Taxonomy reflects evolutionary history. What is Taxonomy: identification, naming, and classification of species. Common Names: can cause confusion - May refer to several species (ex.
