Transport of Electrons on Liquid Helium across a Tunable Potential Barrier in a Point Contact-like Geometry
|
|
|
- Brice Oliver
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Journal of Low Temperature Physics - QFS2009 manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) Transport of Electrons on Liquid Helium across a Tunable Potential Barrier in a Point Contact-like Geometry David Rees Kimitoshi Kono Received: date / Accepted: date Abstract We present transport measurements of electrons bound to the surface of superfluid 4 He in a microchannel of width 10 µm. A set of electrodes 2 µm beneath the Helium surface, fabricated in a split-gate configuration using electron beam lithography, are used to control the current along the microchannel as in a point contact device. As the split-gate bias V SG is swept negative the current decreases to zero. The value of V SG at which the current is suppressed is dependent on the AC driving voltage applied to the electron system. We explain our results using a simple model in which a potential barrier created by the split-gate electrodes must be overcome in order to allow current to flow in the microchannel. The control of electron transport in such confined geometries may offer new possibilities for mesoscopic experiments with electrons on the surface of liquid Helium. Keywords surface-state electron potential barrier quantum wire point contact PACS r b 1 Introduction Surface-state electrons on liquid Helium form an ideal two-dimensional electron system[1]. As the Coulomb interaction between electrons is essentially unscreened, the system has been used to study many phenomena associated with strongly-interacting electron systems such as the transition to the Wigner solid at low temperatures[2]. Recently, it has been proposed that under appropriate conditions electrons on Helium may also be used to study quasi-one-dimensional phenomena such as melting in one dimension and reentrant melting due to structural phase transitions[3]. Recent advances in microfabrication technology have allowed the study of surfacestate electrons in confined geometries using devices such as microchannel arrays[4], David Rees Kimitoshi Kono RIKEN (The Institute of Physical and Chemical Research), Hirosawa 2-1, Wako, Saitama, , Japan Tel.: Fax: drees@riken.jp
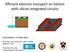
2 2 a) b) Guard Guard Left Reservoir Right Reservoir LR Si RR 0.5 mm 10 µm c) R d) C ~ C Fig. 1 a) Photograph of the device showing the Guard electrode and the microchannel arrays which comprise the left and right reservoirs. b) Scanning electron microscope image of the small central microchannel. The exposed Silicon forms a split-gate electrode. c) Lumped-circuit model in which C is the capacitance of the electron system to the Source or Drain electrodes which are beneath the reservoirs and R is the electron resistance. d) Finite element modelling of the potential profile across the surface of the central channel for V G = 0 mv, V SG = 175 mv, V SD = 350 mv. Here the contour lines are of equipotential; darker regions signify regions of higher potential. single-electron traps[5], field-effect transistors[6] and charge-coupled devices[7]. However, a quantum wire in which the effective width of a conductive channel is less than the thermal wavelength of the electrons has not yet been demonstrated. As a first step towards this goal we have measured the transport properties of electrons in a small microchannel in which the confinement potential along the central axis of the channel may be controlled on the scale of the inter-electron separation (typically 0.5µm). In this article we report preliminary results and discuss factors governing the electron transport properties of the system.
3 3 2 Experimental The sample used in this experiment was fabricated in Gold using multi-layer lithography on a Boron-doped (p-type) Silicon wafer, and is shown in Figure 1a. The surface of the Silicon wafer was covered with a 500 nm insulating oxide layer. As in other similar devices[8], Source and Drain electrodes were fabricated beneath two sets of microchannels, 20 µm wide and 2 µm deep, defined by a Guard electrode, which was isolated from the Source and Drain by a layer of hard-baked photoresist. The two microchannel arrays, denoted Left Reservoir (LR) and Right Reservoir (RR), were connected by a smaller microchannel of width 10 µm and length 20 µm as shown in Figure 1b. At the base of this channel two thin electrodes of width 2 µm, separated by a gap of 200 nm, were fabricated using electron beam lithography. On either side of these thin electrodes the Silicon wafer surface was left exposed. The sample was mounted in an experimental cell which was filled with liquid Helium at 1.25 K until the bulk liquid surface was 0.5 mm below the sample allowing the microchannels to fill by capillary condensation. By applying a DC bias of V G = 0 V to the Guard and a bias of V SD = V to the Source and Drain electrodes, the surface of the Helium in the microchannels was charged by thermionic emission from a small Tungsten filament directly above the sample. The saturated electron density is given by n max = ɛɛ 0 V SD /ed = cm 2 where ɛ, ɛ 0, e and d are the vacuum permittivity, relative permittivity of Helium, the elementary charge and Helium depth respectively. An AC voltage V in of frequency 100 khz was also applied to the Source in order to drive the electron system; the induced current registered at the Drain electrode was measured using a lock-in amplifier. The behaviour of the system was found to be well-described by the lumped-circuit model pictured in Figure 1c. The exposed Silicon wafer formed a split-gate electrode which could be used to control the potential profile for electrons in the thin central channel by applying a voltage V SG to the substrate, as in a point contact device[9]. Figure 1d shows the results of a finite element model analysis which shows that at the center of the channel, at appropriate values for V SG, the potential is approximately uniform in the direction along the channel whilst there is strong confinement in the lateral direction. In the reservoirs the potential is lower than in the channel. To understand the dynamics of the electron system in this region we investigated the dependence of the current through the device on both V SG and V in. 3 Results and Discussion Figure 2 shows the peak AC current I flowing through the device as V SG is varied at several values of V in. As V SG is swept negative I decreases smoothly to zero at a threshold voltage V T ; at negative values of V SG the current may be completely suppressed while at less negative bias electrons may move through the channel. Furthermore, by increasing V in not only the initial value of I but also the magnitude of V T are increased. Initially we assume that the decrease in I corresponds to an increase in R, the resistance of the electron system, which includes components from the reservoirs as well as the central channel, R R and R C. By varying V SG we change only the potential profile of the central channel; any change in resistance must be associated with R C as R R should remain constant. However, the results shown in Figure 2 and those of the
4 mv PP 5 80 mv PP 4 60 mv PP I (na) mv PP mv PP V T V SG (mv) Fig. 2 The current I through the central microchannel versus split-gate voltage V SG. The current is completely suppressed at a threshold voltage V T which depends on the applied AC voltage V in. finite element modelling indicate that setting V SG negative also creates a potential barrier between the two reservoirs; we see that at certain values of V SG at which the resistance is infinite we may induce current flow simply by increasing V in until electrons can pass over the barrier. As the energy of the electron system will surpass that of the barrier for only a fraction of each AC cycle, the measured current is reduced and becomes smaller, and eventually zero, as the barrier height is raised. In future work this effect will be taken into account in order to measure R R and R C explicitly. Figure 3 shows the dependence of the current on the driving amplitude at different gate voltages. Note that here we take into account the voltage dropped across each capacitance C in the lumped-circuit model and calculate the voltage across the resistance R; we denote this voltage V A. The resulting I -V A plot shows that at more positive values of V SG no potential barrier exists and the current increases linearly with increasing voltage. Here the resistance R 2 MΩ which is a typical value for such devices[10]. However, at more negative values of V SG a gap appears in the I -V A plot indicating that current may only flow once the AC voltage applied to the system is large enough for electrons to overcome the resulting potential barrier. The data in Figure 3 allows us to infer the dependence of the barrier height V B on the gate voltage. We assume that the barrier height varies linearly with gate voltage as V B = βv SG + K where β is a scaling factor and K is a constant offset. We take the value of the peak voltage at which current begins to flow as a measure of the barrier height. We find that this threshold voltage varies approximately linearly with V SG in the gap region with β = 0.23 which is in reasonable agreement with the value of 0.28 calculated using the finite element model. The value of K was found to vary from day to day, as may be seen on comparison with Figure 2, probably due to charge accumulation on the Silicon surface as a result of emission from the filament. No significant variation in K was observed between each charging procedure.
5 mv -360 mv -370 mv I (na) mv -390 mv mv V A (mv PP ) Fig. 3 I versus the AC voltage V A applied to the electron system. Labels indicate the respective values of V SG. Thus the barrier height depends rather weakly on V SG, as expected for the region above the thin central electrodes where the screening of other potentials would occur, indicating that the electron system is indeed confined to the area above the thin central electrodes. At the saturated electron density this corresponds to a maximum of 500 electrons being confined in the channel as the current flows. Rousseau et al have recently reported the observation of 1-20 surface-state electrons in a microfabricated trap[11]. By controlling the electron density in the channel by changing V SG, it may be possible to study such small numbers of electrons with the current device. Klier et al have measured the DC current of electrons in a device similar to ours in which a 200 µm wide, 1 mm long channel was defined by a pair of split-gate electrodes[6]. In that experiment the electrons were confined on the surface of a thin Helium film of thickness 100 nm which led to the pinning of electrons due to the roughness of the substrate. Consequently, the current measured was much smaller than in this experiment. However, they also observed that the current decreased as the split-gate voltage was swept negative which they attributed to a change of electron density, and thus mobility, as the effective width of the channel was decreased. We anticipate that by developing a full understanding of the AC electron transport observed in our system, the mechanisms by which the current is suppressed in both devices may be compared. 4 Conclusions We measured the transport of electrons on the surface of liquid Helium through a small microchannel in which the confinement lateral to the direction of electron flow was on a scale comparable to the inter-electron spacing. The current was found to be dependent on a tunable potential barrier formed in the channel by a split-gate electrode beneath
6 6 the Helium surface, as well as the intrinsic resistance of the electron system. Our results are an important step towards the realisation of quasi-one-dimensional electron arrays and quantum wires on the surface of liquid Helium. Acknowledgements We would like to thank C. Marrache-Kikuchi for construction of the experimental apparatus and H. Ikegami and D. Takahashi for useful discussions. References 1. E. Y. Andrei (ed.), Two-Dimensional Electron Systems on Helium and Other Cryogenic Substrates, Kluwer, Dordrecht, Heidelberg (1997) 2. G. C. Grimes, G. Adams, Phys. Rev. Lett. 42, (1979) 3. G. Piacente, I. V. Schweigert, J. J. Betouras, F. M. Peeters, Phys. Rev. B 69, (2004) 4. P. Glasson, V. Dotsenko, P. Fozooni, M. J. Lea, W. Bailey, G. Papageorgiou S. E. Andresen and A. Kristensen, Phys. Rev. Lett. 87, (2001) 5. G. Papageorgiou, P. Glasson, K. Harrabi, V. Antonov, E. Collin, P. Fozooni, P. G. Frayne, M. J. Lea, D. G. Rees, Y. Mukharsky, Appl. Phys. Lett. 86, (2005) 6. J. Klier, I. Doicescu, P. Leiderer, J. of Low Temp. Phys. 121, , (2000) 7. G. Sabouret, S. A. Lyon, Appl. Phys. Lett. 88, (2006) 8. P. Glasson, S. Erfurt Andresen, G. Ensell, V. Dotsenko, W. Bailey, P. Fozooni, A. Kristensen, M. J. Lea, Physica B: Condensed Matter (2000) 9. M. A. Topinka, B. J. LeRoy, S. E. J. Shaw, E. J. Heller, R. M. Westervelt, K. D. Maranowski, A. C. Gossard, Science 289, (2000) 10. H. Ikegami, H. Akimoto, K. Kono, Phys. Rev. Lett. 102, (2009) 11. E. Rousseau, D. Ponarin, L. Hristakos, O. Avenel, E. Varoquaux, Y. Mukharsky, Phys. Rev. B 79, (2009)
Commensurability-dependent transport of a Wigner crystal in a nanoconstriction
 NPCQS2012, OIST Commensurability-dependent transport of a Wigner crystal in a nanoconstriction David Rees, RIKEN, Japan Kimitoshi Kono (RIKEN) Paul Leiderer (University of Konstanz) Hiroo Totsuji (Okayama
NPCQS2012, OIST Commensurability-dependent transport of a Wigner crystal in a nanoconstriction David Rees, RIKEN, Japan Kimitoshi Kono (RIKEN) Paul Leiderer (University of Konstanz) Hiroo Totsuji (Okayama
Electrons on Helium Films
 Electrons on Helium Films Paul Leiderer University of Konstanz Okinawa, 24.04.2012 Experimental Systems B ext colloid sample PS spheres, 5µm superparamagnetic magn. moment µ ~ B ext electrons on liquid
Electrons on Helium Films Paul Leiderer University of Konstanz Okinawa, 24.04.2012 Experimental Systems B ext colloid sample PS spheres, 5µm superparamagnetic magn. moment µ ~ B ext electrons on liquid
Counting Individual Electrons on Liquid Helium
 Counting Individual Electrons on Liquid Helium G. Papageorgiou 1, P. Glasson 1, K. Harrabi 1, V.Antonov 1, E.Collin 2, P.Fozooni 1, P.G.Frayne 1, M.J.Lea 1, Y.Mukharsky 2 and D.G.Rees 1. 1 Department of
Counting Individual Electrons on Liquid Helium G. Papageorgiou 1, P. Glasson 1, K. Harrabi 1, V.Antonov 1, E.Collin 2, P.Fozooni 1, P.G.Frayne 1, M.J.Lea 1, Y.Mukharsky 2 and D.G.Rees 1. 1 Department of
arxiv: v3 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 25 Oct 2018
![arxiv: v3 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 25 Oct 2018 arxiv: v3 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 25 Oct 2018](/thumbs/89/98895882.jpg) Unconventional field-effect transistor composed of electrons floating on liquid helium K. Nasyedkin, H. Byeon, L. Zhang, N.R. Beysengulov, J. Milem, S. Hemmerle, R. Loloee, and J. Pollanen Department of
Unconventional field-effect transistor composed of electrons floating on liquid helium K. Nasyedkin, H. Byeon, L. Zhang, N.R. Beysengulov, J. Milem, S. Hemmerle, R. Loloee, and J. Pollanen Department of
Electron Interferometer Formed with a Scanning Probe Tip and Quantum Point Contact Supplementary Information
 Electron Interferometer Formed with a Scanning Probe Tip and Quantum Point Contact Supplementary Information Section I: Experimental Details Here we elaborate on the experimental details described for
Electron Interferometer Formed with a Scanning Probe Tip and Quantum Point Contact Supplementary Information Section I: Experimental Details Here we elaborate on the experimental details described for
Trapping single electrons on liquid helium
 Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids 66 (2005) 1539 1543 www.elsevier.com/locate/jpcs Trapping single electrons on liquid helium P. Glasson a, G. Papageorgiou a, K. Harrabi a, D.G. Rees a, V. Antonov
Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids 66 (2005) 1539 1543 www.elsevier.com/locate/jpcs Trapping single electrons on liquid helium P. Glasson a, G. Papageorgiou a, K. Harrabi a, D.G. Rees a, V. Antonov
Formation of unintentional dots in small Si nanostructures
 Superlattices and Microstructures, Vol. 28, No. 5/6, 2000 doi:10.1006/spmi.2000.0942 Available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on Formation of unintentional dots in small Si nanostructures L. P. ROKHINSON,
Superlattices and Microstructures, Vol. 28, No. 5/6, 2000 doi:10.1006/spmi.2000.0942 Available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on Formation of unintentional dots in small Si nanostructures L. P. ROKHINSON,
CIRCUIT QUANTUM ELECTRODYNAMICS WITH ELECTRONS ON HELIUM
 CIRCUIT QUANTUM ELECTRODYNAMICS WITH ELECTRONS ON HELIUM David Schuster Assistant Professor University of Chicago Chicago Ge Yang Bing Li Michael Geracie Yale Andreas Fragner Rob Schoelkopf Useful cryogenics
CIRCUIT QUANTUM ELECTRODYNAMICS WITH ELECTRONS ON HELIUM David Schuster Assistant Professor University of Chicago Chicago Ge Yang Bing Li Michael Geracie Yale Andreas Fragner Rob Schoelkopf Useful cryogenics
The Analysis of Nano-Size Inhomogeneities of Substrate by Surface Electrons over Superfluid Helium Film
 Journal of Physical Science and Application 6 (5) (2016) 37-41 doi: 10.17265/2159-5348/2016.05.007 D DAVID PUBLISHING The Analysis of Nano-Size Inhomogeneities of Substrate by Yaroslav Yurievich Bezsmolnyy,
Journal of Physical Science and Application 6 (5) (2016) 37-41 doi: 10.17265/2159-5348/2016.05.007 D DAVID PUBLISHING The Analysis of Nano-Size Inhomogeneities of Substrate by Yaroslav Yurievich Bezsmolnyy,
Supplementary Methods A. Sample fabrication
 Supplementary Methods A. Sample fabrication Supplementary Figure 1(a) shows the SEM photograph of a typical sample, with three suspended graphene resonators in an array. The cross-section schematic is
Supplementary Methods A. Sample fabrication Supplementary Figure 1(a) shows the SEM photograph of a typical sample, with three suspended graphene resonators in an array. The cross-section schematic is
(a) (b) Supplementary Figure 1. (a) (b) (a) Supplementary Figure 2. (a) (b) (c) (d) (e)
 (a) (b) Supplementary Figure 1. (a) An AFM image of the device after the formation of the contact electrodes and the top gate dielectric Al 2 O 3. (b) A line scan performed along the white dashed line
(a) (b) Supplementary Figure 1. (a) An AFM image of the device after the formation of the contact electrodes and the top gate dielectric Al 2 O 3. (b) A line scan performed along the white dashed line
CMPEN 411 VLSI Digital Circuits. Lecture 03: MOS Transistor
 CMPEN 411 VLSI Digital Circuits Lecture 03: MOS Transistor Kyusun Choi [Adapted from Rabaey s Digital Integrated Circuits, Second Edition, 2003 J. Rabaey, A. Chandrakasan, B. Nikolic] CMPEN 411 L03 S.1
CMPEN 411 VLSI Digital Circuits Lecture 03: MOS Transistor Kyusun Choi [Adapted from Rabaey s Digital Integrated Circuits, Second Edition, 2003 J. Rabaey, A. Chandrakasan, B. Nikolic] CMPEN 411 L03 S.1
Nanoelectronics. Topics
 Nanoelectronics Topics Moore s Law Inorganic nanoelectronic devices Resonant tunneling Quantum dots Single electron transistors Motivation for molecular electronics The review article Overview of Nanoelectronic
Nanoelectronics Topics Moore s Law Inorganic nanoelectronic devices Resonant tunneling Quantum dots Single electron transistors Motivation for molecular electronics The review article Overview of Nanoelectronic
New experimental approach on charging technique of helium surface over rectangular electrodes at cryogenic temperature
 New experimental approach on charging technique of helium surface over rectangular electrodes at cryogenic temperature Ram-Krishna Thakur 1,2, * and Paul Leiderer 1 1 Department of Physics, Konstanz University,
New experimental approach on charging technique of helium surface over rectangular electrodes at cryogenic temperature Ram-Krishna Thakur 1,2, * and Paul Leiderer 1 1 Department of Physics, Konstanz University,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Collapse of superconductivity in a hybrid tin graphene Josephson junction array by Zheng Han et al. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION 1. Determination of the electronic mobility of graphene. 1.a extraction from
Collapse of superconductivity in a hybrid tin graphene Josephson junction array by Zheng Han et al. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION 1. Determination of the electronic mobility of graphene. 1.a extraction from
Electronic transport in low dimensional systems
 Electronic transport in low dimensional systems For example: 2D system l
Electronic transport in low dimensional systems For example: 2D system l
MOS CAPACITOR AND MOSFET
 EE336 Semiconductor Devices 1 MOS CAPACITOR AND MOSFET Dr. Mohammed M. Farag Ideal MOS Capacitor Semiconductor Devices Physics and Technology Chapter 5 EE336 Semiconductor Devices 2 MOS Capacitor Structure
EE336 Semiconductor Devices 1 MOS CAPACITOR AND MOSFET Dr. Mohammed M. Farag Ideal MOS Capacitor Semiconductor Devices Physics and Technology Chapter 5 EE336 Semiconductor Devices 2 MOS Capacitor Structure
Fundamentals of the Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor
 Triode Working FET Fundamentals of the Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor The characteristics of energy bands as a function of applied voltage. Surface inversion. The expression for the
Triode Working FET Fundamentals of the Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor The characteristics of energy bands as a function of applied voltage. Surface inversion. The expression for the
Nanomaterials Characterization by lowtemperature Scanning Probe Microscopy
 Nanomaterials Characterization by lowtemperature Scanning Probe Microscopy Stefan Heun NEST, Istituto Nanoscienze-CNR and Scuola Normale Superiore Piazza San Silvestro 12, 56127 Pisa, Italy e-mail: stefan.heun@nano.cnr.it
Nanomaterials Characterization by lowtemperature Scanning Probe Microscopy Stefan Heun NEST, Istituto Nanoscienze-CNR and Scuola Normale Superiore Piazza San Silvestro 12, 56127 Pisa, Italy e-mail: stefan.heun@nano.cnr.it
ECE 340 Lecture 39 : MOS Capacitor II
 ECE 340 Lecture 39 : MOS Capacitor II Class Outline: Effects of Real Surfaces Threshold Voltage MOS Capacitance-Voltage Analysis Things you should know when you leave Key Questions What are the effects
ECE 340 Lecture 39 : MOS Capacitor II Class Outline: Effects of Real Surfaces Threshold Voltage MOS Capacitance-Voltage Analysis Things you should know when you leave Key Questions What are the effects
Black phosphorus: A new bandgap tuning knob
 Black phosphorus: A new bandgap tuning knob Rafael Roldán and Andres Castellanos-Gomez Modern electronics rely on devices whose functionality can be adjusted by the end-user with an external knob. A new
Black phosphorus: A new bandgap tuning knob Rafael Roldán and Andres Castellanos-Gomez Modern electronics rely on devices whose functionality can be adjusted by the end-user with an external knob. A new
Operation and Modeling of. The MOS Transistor. Second Edition. Yannis Tsividis Columbia University. New York Oxford OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS
 Operation and Modeling of The MOS Transistor Second Edition Yannis Tsividis Columbia University New York Oxford OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS CONTENTS Chapter 1 l.l 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 Chapter 2 2.1 2.2
Operation and Modeling of The MOS Transistor Second Edition Yannis Tsividis Columbia University New York Oxford OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS CONTENTS Chapter 1 l.l 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 Chapter 2 2.1 2.2
Chapter 4 Field-Effect Transistors
 Chapter 4 Field-Effect Transistors Microelectronic Circuit Design Richard C. Jaeger Travis N. Blalock 5/5/11 Chap 4-1 Chapter Goals Describe operation of MOSFETs. Define FET characteristics in operation
Chapter 4 Field-Effect Transistors Microelectronic Circuit Design Richard C. Jaeger Travis N. Blalock 5/5/11 Chap 4-1 Chapter Goals Describe operation of MOSFETs. Define FET characteristics in operation
Ideal Discrete Energy Levels in Synthesized Au. Nanoparticle for Chemically Assembled. Single-Electron Transistors
 Ideal Discrete Energy Levels in Synthesized Au Nanoparticle for Chemically Assembled Single-Electron Transistors Shinya Kano,, Yasuo Azuma,, Kosuke Maeda,, Daisuke Tanaka,, Masanori Sakamoto,,, Toshiharu
Ideal Discrete Energy Levels in Synthesized Au Nanoparticle for Chemically Assembled Single-Electron Transistors Shinya Kano,, Yasuo Azuma,, Kosuke Maeda,, Daisuke Tanaka,, Masanori Sakamoto,,, Toshiharu
Indium arsenide quantum wire trigate metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistor
 JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS 99, 054503 2006 Indium arsenide quantum wire trigate metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistor M. J. Gilbert a and D. K. Ferry Department of Electrical Engineering and
JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS 99, 054503 2006 Indium arsenide quantum wire trigate metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistor M. J. Gilbert a and D. K. Ferry Department of Electrical Engineering and
Quantum-dot cellular automata
 Quantum-dot cellular automata G. L. Snider, a) A. O. Orlov, I. Amlani, X. Zuo, G. H. Bernstein, C. S. Lent, J. L. Merz, and W. Porod Department of Electrical Engineering, University of Notre Dame, Notre
Quantum-dot cellular automata G. L. Snider, a) A. O. Orlov, I. Amlani, X. Zuo, G. H. Bernstein, C. S. Lent, J. L. Merz, and W. Porod Department of Electrical Engineering, University of Notre Dame, Notre
The Low Temperature Physics of Thin Films Superconducting Tin and Monolayer Graphene
 The Low Temperature Physics of Thin Films Superconducting Tin and Monolayer Graphene Abstract: The aim of this project was to investigate how the electrical resistance of a conductor changes if it is deposited
The Low Temperature Physics of Thin Films Superconducting Tin and Monolayer Graphene Abstract: The aim of this project was to investigate how the electrical resistance of a conductor changes if it is deposited
Zeeman splitting of single semiconductor impurities in resonant tunneling heterostructures
 Superlattices and Microstructures, Vol. 2, No. 4, 1996 Zeeman splitting of single semiconductor impurities in resonant tunneling heterostructures M. R. Deshpande, J. W. Sleight, M. A. Reed, R. G. Wheeler
Superlattices and Microstructures, Vol. 2, No. 4, 1996 Zeeman splitting of single semiconductor impurities in resonant tunneling heterostructures M. R. Deshpande, J. W. Sleight, M. A. Reed, R. G. Wheeler
Traps in MOCVD n-gan Studied by Deep Level Transient Spectroscopy and Minority Carrier Transient Spectroscopy
 Traps in MOCVD n-gan Studied by Deep Level Transient Spectroscopy and Minority Carrier Transient Spectroscopy Yutaka Tokuda Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, Aichi Institute of Technology,
Traps in MOCVD n-gan Studied by Deep Level Transient Spectroscopy and Minority Carrier Transient Spectroscopy Yutaka Tokuda Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, Aichi Institute of Technology,
Fig The electron mobility for a-si and poly-si TFT.
 Fig. 1-1-1 The electron mobility for a-si and poly-si TFT. Fig. 1-1-2 The aperture ratio for a-si and poly-si TFT. 33 Fig. 1-2-1 All kinds defect well. (a) is the Dirac well. (b) is the repulsive Columbic
Fig. 1-1-1 The electron mobility for a-si and poly-si TFT. Fig. 1-1-2 The aperture ratio for a-si and poly-si TFT. 33 Fig. 1-2-1 All kinds defect well. (a) is the Dirac well. (b) is the repulsive Columbic
Graphene photodetectors with ultra-broadband and high responsivity at room temperature
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NNANO.2014.31 Graphene photodetectors with ultra-broadband and high responsivity at room temperature Chang-Hua Liu 1, You-Chia Chang 2, Ted Norris 1.2* and Zhaohui
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NNANO.2014.31 Graphene photodetectors with ultra-broadband and high responsivity at room temperature Chang-Hua Liu 1, You-Chia Chang 2, Ted Norris 1.2* and Zhaohui
Low-dimensional electron transport properties in InAs/AlGaSb mesoscopic structures
 Superlattices and Microstructures, Vol 21, No 1, 1997 Low-dimensional electron transport properties in InAs/AlGaSb mesoscopic structures M Inoue, T Sugihara, T Maemoto, S Sasa, H Dobashi, S Izumiya Department
Superlattices and Microstructures, Vol 21, No 1, 1997 Low-dimensional electron transport properties in InAs/AlGaSb mesoscopic structures M Inoue, T Sugihara, T Maemoto, S Sasa, H Dobashi, S Izumiya Department
Semiconductor Nanowires: Motivation
 Semiconductor Nanowires: Motivation Patterning into sub 50 nm range is difficult with optical lithography. Self-organized growth of nanowires enables 2D confinement of carriers with large splitting of
Semiconductor Nanowires: Motivation Patterning into sub 50 nm range is difficult with optical lithography. Self-organized growth of nanowires enables 2D confinement of carriers with large splitting of
To Quantum Dots and Qubits with electrons on helium
 To Quantum Dots and Qubits with electrons on helium CEA-DRECAM Service de Physique de l Etat Condensé CEA-Saclay France E. Rousseau D. Ponarine Y. Mukharsky E.Varoquaux O. Avenel J.M. Richomme Confine
To Quantum Dots and Qubits with electrons on helium CEA-DRECAM Service de Physique de l Etat Condensé CEA-Saclay France E. Rousseau D. Ponarine Y. Mukharsky E.Varoquaux O. Avenel J.M. Richomme Confine
single-electron electron tunneling (SET)
 single-electron electron tunneling (SET) classical dots (SET islands): level spacing is NOT important; only the charging energy (=classical effect, many electrons on the island) quantum dots: : level spacing
single-electron electron tunneling (SET) classical dots (SET islands): level spacing is NOT important; only the charging energy (=classical effect, many electrons on the island) quantum dots: : level spacing
Supplementary Figure 1. Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of another locally gated PN junction based on boron
 Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of another locally gated PN junction based on boron nitride and few-layer black phosphorus (device S1). (a) Optical micrograph of device S1.
Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of another locally gated PN junction based on boron nitride and few-layer black phosphorus (device S1). (a) Optical micrograph of device S1.
Sample Exam # 2 ECEN 3320 Fall 2013 Semiconductor Devices October 28, 2013 Due November 4, 2013
 Sample Exam # 2 ECEN 3320 Fall 203 Semiconductor Devices October 28, 203 Due November 4, 203. Below is the capacitance-voltage curve measured from a Schottky contact made on GaAs at T 300 K. Figure : Capacitance
Sample Exam # 2 ECEN 3320 Fall 203 Semiconductor Devices October 28, 203 Due November 4, 203. Below is the capacitance-voltage curve measured from a Schottky contact made on GaAs at T 300 K. Figure : Capacitance
Metallic: 2n 1. +n 2. =3q Armchair structure always metallic = 2
 Properties of CNT d = 2.46 n 2 2 1 + n1n2 + n2 2π Metallic: 2n 1 +n 2 =3q Armchair structure always metallic a) Graphite Valence(π) and Conduction(π*) states touch at six points(fermi points) Carbon Nanotube:
Properties of CNT d = 2.46 n 2 2 1 + n1n2 + n2 2π Metallic: 2n 1 +n 2 =3q Armchair structure always metallic a) Graphite Valence(π) and Conduction(π*) states touch at six points(fermi points) Carbon Nanotube:
Supporting Information for: Electrical probing and tuning of molecular. physisorption on graphene
 Supporting Information for: Electrical probing and tuning of molecular physisorption on graphene Girish S. Kulkarni, Karthik Reddy #, Wenzhe Zang, Kyunghoon Lee, Xudong Fan *, and Zhaohui Zhong * Department
Supporting Information for: Electrical probing and tuning of molecular physisorption on graphene Girish S. Kulkarni, Karthik Reddy #, Wenzhe Zang, Kyunghoon Lee, Xudong Fan *, and Zhaohui Zhong * Department
MOS Transistor Properties Review
 MOS Transistor Properties Review 1 VLSI Chip Manufacturing Process Photolithography: transfer of mask patterns to the chip Diffusion or ion implantation: selective doping of Si substrate Oxidation: SiO
MOS Transistor Properties Review 1 VLSI Chip Manufacturing Process Photolithography: transfer of mask patterns to the chip Diffusion or ion implantation: selective doping of Si substrate Oxidation: SiO
META-STABILITY EFFECTS IN ORGANIC BASED TRANSISTORS
 META-STABILITY EFFECTS IN ORGANIC BASED TRANSISTORS H. L. Gomes 1*, P. Stallinga 1, F. Dinelli 2, M. Murgia 2, F. Biscarini 2, D. M. de Leeuw 3 1 University of Algarve, Faculty of Sciences and Technology
META-STABILITY EFFECTS IN ORGANIC BASED TRANSISTORS H. L. Gomes 1*, P. Stallinga 1, F. Dinelli 2, M. Murgia 2, F. Biscarini 2, D. M. de Leeuw 3 1 University of Algarve, Faculty of Sciences and Technology
Quantum Computing with Electrons on Liquid Helium
 Turk J Phys 27 (2003), 383 393. c TÜBİTAK Quantum Computing with Electrons on Liquid Helium İsmail Dept. of Physics, Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, OH 44106, USA Received 12.09.2003 Abstract
Turk J Phys 27 (2003), 383 393. c TÜBİTAK Quantum Computing with Electrons on Liquid Helium İsmail Dept. of Physics, Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, OH 44106, USA Received 12.09.2003 Abstract
Semi-Conductors insulators semi-conductors N-type Semi-Conductors P-type Semi-Conductors
 Semi-Conductors In the metal materials considered earlier, the coupling of the atoms together to form the material decouples an electron from each atom setting it free to roam around inside the material.
Semi-Conductors In the metal materials considered earlier, the coupling of the atoms together to form the material decouples an electron from each atom setting it free to roam around inside the material.
Supporting Online Material for
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/320/5874/356/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Chaotic Dirac Billiard in Graphene Quantum Dots L. A. Ponomarenko, F. Schedin, M. I. Katsnelson, R. Yang, E. W. Hill,
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/320/5874/356/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Chaotic Dirac Billiard in Graphene Quantum Dots L. A. Ponomarenko, F. Schedin, M. I. Katsnelson, R. Yang, E. W. Hill,
Solid State Device Fundamentals
 Solid State Device Fundamentals ENS 345 Lecture Course by Alexander M. Zaitsev alexander.zaitsev@csi.cuny.edu Tel: 718 982 2812 Office 4N101b 1 Outline - Goals of the course. What is electronic device?
Solid State Device Fundamentals ENS 345 Lecture Course by Alexander M. Zaitsev alexander.zaitsev@csi.cuny.edu Tel: 718 982 2812 Office 4N101b 1 Outline - Goals of the course. What is electronic device?
CHAPTER 5 EFFECT OF GATE ELECTRODE WORK FUNCTION VARIATION ON DC AND AC PARAMETERS IN CONVENTIONAL AND JUNCTIONLESS FINFETS
 98 CHAPTER 5 EFFECT OF GATE ELECTRODE WORK FUNCTION VARIATION ON DC AND AC PARAMETERS IN CONVENTIONAL AND JUNCTIONLESS FINFETS In this chapter, the effect of gate electrode work function variation on DC
98 CHAPTER 5 EFFECT OF GATE ELECTRODE WORK FUNCTION VARIATION ON DC AND AC PARAMETERS IN CONVENTIONAL AND JUNCTIONLESS FINFETS In this chapter, the effect of gate electrode work function variation on DC
Free-standing Organic Transistors and Circuits. with Sub-micron thickness
 Supplementary Information Free-standing Organic Transistors and Circuits with Sub-micron thickness Kenjiro Fukuda 1,2,3,4 (*), Tomohito Sekine 1, Rei Shiwaku 1, Takuya Morimoto 5, Daisuke Kumaki 1, and
Supplementary Information Free-standing Organic Transistors and Circuits with Sub-micron thickness Kenjiro Fukuda 1,2,3,4 (*), Tomohito Sekine 1, Rei Shiwaku 1, Takuya Morimoto 5, Daisuke Kumaki 1, and
Circuit QED with electrons on helium:
 Circuit QED with electrons on helium: What s the sound of one electron clapping? David Schuster Yale (soon to be at U. of Chicago) Yale: Andreas Fragner Rob Schoelkopf Princeton: Steve Lyon Michigan State:
Circuit QED with electrons on helium: What s the sound of one electron clapping? David Schuster Yale (soon to be at U. of Chicago) Yale: Andreas Fragner Rob Schoelkopf Princeton: Steve Lyon Michigan State:
GaN based transistors
 GaN based transistors S FP FP dielectric G SiO 2 Al x Ga 1-x N barrier i-gan Buffer i-sic D Transistors "The Transistor was probably the most important invention of the 20th Century The American Institute
GaN based transistors S FP FP dielectric G SiO 2 Al x Ga 1-x N barrier i-gan Buffer i-sic D Transistors "The Transistor was probably the most important invention of the 20th Century The American Institute
Supplementary Figure S1. AFM images of GraNRs grown with standard growth process. Each of these pictures show GraNRs prepared independently,
 Supplementary Figure S1. AFM images of GraNRs grown with standard growth process. Each of these pictures show GraNRs prepared independently, suggesting that the results is reproducible. Supplementary Figure
Supplementary Figure S1. AFM images of GraNRs grown with standard growth process. Each of these pictures show GraNRs prepared independently, suggesting that the results is reproducible. Supplementary Figure
Demonstration of a functional quantum-dot cellular automata cell
 Demonstration of a functional quantum-dot cellular automata cell Islamshah Amlani, a) Alexei O. Orlov, Gregory L. Snider, Craig S. Lent, and Gary H. Bernstein Department of Electrical Engineering, University
Demonstration of a functional quantum-dot cellular automata cell Islamshah Amlani, a) Alexei O. Orlov, Gregory L. Snider, Craig S. Lent, and Gary H. Bernstein Department of Electrical Engineering, University
Anisotropic spin splitting in InGaAs wire structures
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Physics Physics Procedia Procedia 3 (010) 00 (009) 155 159 000 000 14 th International Conference on Narrow Gap Semiconductors and Systems Anisotropic spin splitting
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Physics Physics Procedia Procedia 3 (010) 00 (009) 155 159 000 000 14 th International Conference on Narrow Gap Semiconductors and Systems Anisotropic spin splitting
Single ion implantation for nanoelectronics and the application to biological systems. Iwao Ohdomari Waseda University Tokyo, Japan
 Single ion implantation for nanoelectronics and the application to biological systems Iwao Ohdomari Waseda University Tokyo, Japan Contents 1.History of single ion implantation (SII) 2.Novel applications
Single ion implantation for nanoelectronics and the application to biological systems Iwao Ohdomari Waseda University Tokyo, Japan Contents 1.History of single ion implantation (SII) 2.Novel applications
From nanophysics research labs to cell phones. Dr. András Halbritter Department of Physics associate professor
 From nanophysics research labs to cell phones Dr. András Halbritter Department of Physics associate professor Curriculum Vitae Birth: 1976. High-school graduation: 1994. Master degree: 1999. PhD: 2003.
From nanophysics research labs to cell phones Dr. András Halbritter Department of Physics associate professor Curriculum Vitae Birth: 1976. High-school graduation: 1994. Master degree: 1999. PhD: 2003.
A. Optimizing the growth conditions of large-scale graphene films
 1 A. Optimizing the growth conditions of large-scale graphene films Figure S1. Optical microscope images of graphene films transferred on 300 nm SiO 2 /Si substrates. a, Images of the graphene films grown
1 A. Optimizing the growth conditions of large-scale graphene films Figure S1. Optical microscope images of graphene films transferred on 300 nm SiO 2 /Si substrates. a, Images of the graphene films grown
Scaling Issues in Planar FET: Dual Gate FET and FinFETs
 Scaling Issues in Planar FET: Dual Gate FET and FinFETs Lecture 12 Dr. Amr Bayoumi Fall 2014 Advanced Devices (EC760) Arab Academy for Science and Technology - Cairo 1 Outline Scaling Issues for Planar
Scaling Issues in Planar FET: Dual Gate FET and FinFETs Lecture 12 Dr. Amr Bayoumi Fall 2014 Advanced Devices (EC760) Arab Academy for Science and Technology - Cairo 1 Outline Scaling Issues for Planar
Energy position of the active near-interface traps in metal oxide semiconductor field-effect transistors on 4H SiC
 Energy position of the active near-interface traps in metal oxide semiconductor field-effect transistors on 4H SiC Author Haasmann, Daniel, Dimitrijev, Sima Published 2013 Journal Title Applied Physics
Energy position of the active near-interface traps in metal oxide semiconductor field-effect transistors on 4H SiC Author Haasmann, Daniel, Dimitrijev, Sima Published 2013 Journal Title Applied Physics
Quantum Phenomena & Nanotechnology (4B5)
 Quantum Phenomena & Nanotechnology (4B5) The 2-dimensional electron gas (2DEG), Resonant Tunneling diodes, Hot electron transistors Lecture 11 In this lecture, we are going to look at 2-dimensional electron
Quantum Phenomena & Nanotechnology (4B5) The 2-dimensional electron gas (2DEG), Resonant Tunneling diodes, Hot electron transistors Lecture 11 In this lecture, we are going to look at 2-dimensional electron
Supporting information. Gate-optimized thermoelectric power factor in ultrathin WSe2 single crystals
 Supporting information Gate-optimized thermoelectric power factor in ultrathin WSe2 single crystals Masaro Yoshida 1, Takahiko Iizuka 1, Yu Saito 1, Masaru Onga 1, Ryuji Suzuki 1, Yijin Zhang 1, Yoshihiro
Supporting information Gate-optimized thermoelectric power factor in ultrathin WSe2 single crystals Masaro Yoshida 1, Takahiko Iizuka 1, Yu Saito 1, Masaru Onga 1, Ryuji Suzuki 1, Yijin Zhang 1, Yoshihiro
Device 3D. 3D Device Simulator. Nano Scale Devices. Fin FET
 Device 3D 3D Device Simulator Device 3D is a physics based 3D device simulator for any device type and includes material properties for the commonly used semiconductor materials in use today. The physical
Device 3D 3D Device Simulator Device 3D is a physics based 3D device simulator for any device type and includes material properties for the commonly used semiconductor materials in use today. The physical
Universal Mobility-Field Curves For Electrons In Polysilicon Inversion Layer
 International Journal of Engineering & Computer Science IJECS-IJENS Vol:13 No:5 36 Universal Mobility-Field Curves For Electrons In Polysilicon Inversion Layer M. I. Idris 1, Faiz Arith 2, S. A. M. Chachuli
International Journal of Engineering & Computer Science IJECS-IJENS Vol:13 No:5 36 Universal Mobility-Field Curves For Electrons In Polysilicon Inversion Layer M. I. Idris 1, Faiz Arith 2, S. A. M. Chachuli
Gold Nanoparticles Floating Gate MISFET for Non-Volatile Memory Applications
 Gold Nanoparticles Floating Gate MISFET for Non-Volatile Memory Applications D. Tsoukalas, S. Kolliopoulou, P. Dimitrakis, P. Normand Institute of Microelectronics, NCSR Demokritos, Athens, Greece S. Paul,
Gold Nanoparticles Floating Gate MISFET for Non-Volatile Memory Applications D. Tsoukalas, S. Kolliopoulou, P. Dimitrakis, P. Normand Institute of Microelectronics, NCSR Demokritos, Athens, Greece S. Paul,
Charge spectrometry with a strongly coupled superconducting single-electron transistor
 PHYSICAL REVIEW B, VOLUME 64, 245116 Charge spectrometry with a strongly coupled superconducting single-electron transistor C. P. Heij, P. Hadley, and J. E. Mooij Applied Physics and Delft Institute of
PHYSICAL REVIEW B, VOLUME 64, 245116 Charge spectrometry with a strongly coupled superconducting single-electron transistor C. P. Heij, P. Hadley, and J. E. Mooij Applied Physics and Delft Institute of
The Devices: MOS Transistors
 The Devices: MOS Transistors References: Semiconductor Device Fundamentals, R. F. Pierret, Addison-Wesley Digital Integrated Circuits: A Design Perspective, J. Rabaey et.al. Prentice Hall NMOS Transistor
The Devices: MOS Transistors References: Semiconductor Device Fundamentals, R. F. Pierret, Addison-Wesley Digital Integrated Circuits: A Design Perspective, J. Rabaey et.al. Prentice Hall NMOS Transistor
Electric Field-Dependent Charge-Carrier Velocity in Semiconducting Carbon. Nanotubes. Yung-Fu Chen and M. S. Fuhrer
 Electric Field-Dependent Charge-Carrier Velocity in Semiconducting Carbon Nanotubes Yung-Fu Chen and M. S. Fuhrer Department of Physics and Center for Superconductivity Research, University of Maryland,
Electric Field-Dependent Charge-Carrier Velocity in Semiconducting Carbon Nanotubes Yung-Fu Chen and M. S. Fuhrer Department of Physics and Center for Superconductivity Research, University of Maryland,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 1.138/NNANO.213.24 Detecting the translocation of DNA through a nanopore using graphene nanoribbons F. Traversi 1, C.Raillon 1, S. M. Benameur 2, K.Liu 1, S. Khlybov 1, M.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 1.138/NNANO.213.24 Detecting the translocation of DNA through a nanopore using graphene nanoribbons F. Traversi 1, C.Raillon 1, S. M. Benameur 2, K.Liu 1, S. Khlybov 1, M.
Woo Jin Hyun, Ethan B. Secor, Mark C. Hersam, C. Daniel Frisbie,* and Lorraine F. Francis*
 Woo Jin Hyun, Ethan B. Secor, Mark C. Hersam, C. Daniel Frisbie,* and Lorraine F. Francis* Dr. W. J. Hyun, Prof. C. D. Frisbie, Prof. L. F. Francis Department of Chemical Engineering and Materials Science
Woo Jin Hyun, Ethan B. Secor, Mark C. Hersam, C. Daniel Frisbie,* and Lorraine F. Francis* Dr. W. J. Hyun, Prof. C. D. Frisbie, Prof. L. F. Francis Department of Chemical Engineering and Materials Science
1 Name: Student number: DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS AND PHYSICAL OCEANOGRAPHY MEMORIAL UNIVERSITY OF NEWFOUNDLAND. Fall :00-11:00
 1 Name: DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS AND PHYSICAL OCEANOGRAPHY MEMORIAL UNIVERSITY OF NEWFOUNDLAND Final Exam Physics 3000 December 11, 2012 Fall 2012 9:00-11:00 INSTRUCTIONS: 1. Answer all seven (7) questions.
1 Name: DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS AND PHYSICAL OCEANOGRAPHY MEMORIAL UNIVERSITY OF NEWFOUNDLAND Final Exam Physics 3000 December 11, 2012 Fall 2012 9:00-11:00 INSTRUCTIONS: 1. Answer all seven (7) questions.
Class 05: Device Physics II
 Topics: 1. Introduction 2. NFET Model and Cross Section with Parasitics 3. NFET as a Capacitor 4. Capacitance vs. Voltage Curves 5. NFET as a Capacitor - Band Diagrams at V=0 6. NFET as a Capacitor - Accumulation
Topics: 1. Introduction 2. NFET Model and Cross Section with Parasitics 3. NFET as a Capacitor 4. Capacitance vs. Voltage Curves 5. NFET as a Capacitor - Band Diagrams at V=0 6. NFET as a Capacitor - Accumulation
Final Examination EE 130 December 16, 1997 Time allotted: 180 minutes
 Final Examination EE 130 December 16, 1997 Time allotted: 180 minutes Problem 1: Semiconductor Fundamentals [30 points] A uniformly doped silicon sample of length 100µm and cross-sectional area 100µm 2
Final Examination EE 130 December 16, 1997 Time allotted: 180 minutes Problem 1: Semiconductor Fundamentals [30 points] A uniformly doped silicon sample of length 100µm and cross-sectional area 100µm 2
Semiconductor Physics fall 2012 problems
 Semiconductor Physics fall 2012 problems 1. An n-type sample of silicon has a uniform density N D = 10 16 atoms cm -3 of arsenic, and a p-type silicon sample has N A = 10 15 atoms cm -3 of boron. For each
Semiconductor Physics fall 2012 problems 1. An n-type sample of silicon has a uniform density N D = 10 16 atoms cm -3 of arsenic, and a p-type silicon sample has N A = 10 15 atoms cm -3 of boron. For each
Part 5: Quantum Effects in MOS Devices
 Quantum Effects Lead to Phenomena such as: Ultra Thin Oxides Observe: High Leakage Currents Through the Oxide - Tunneling Depletion in Poly-Si metal gate capacitance effect Thickness of Inversion Layer
Quantum Effects Lead to Phenomena such as: Ultra Thin Oxides Observe: High Leakage Currents Through the Oxide - Tunneling Depletion in Poly-Si metal gate capacitance effect Thickness of Inversion Layer
Choice of V t and Gate Doping Type
 Choice of V t and Gate Doping Type To make circuit design easier, it is routine to set V t at a small positive value, e.g., 0.4 V, so that, at V g = 0, the transistor does not have an inversion layer and
Choice of V t and Gate Doping Type To make circuit design easier, it is routine to set V t at a small positive value, e.g., 0.4 V, so that, at V g = 0, the transistor does not have an inversion layer and
Impact of disorder and topology in two dimensional systems at low carrier densities
 Impact of disorder and topology in two dimensional systems at low carrier densities A Thesis Submitted For the Degree of Doctor of Philosophy in the Faculty of Science by Mohammed Ali Aamir Department
Impact of disorder and topology in two dimensional systems at low carrier densities A Thesis Submitted For the Degree of Doctor of Philosophy in the Faculty of Science by Mohammed Ali Aamir Department
Lecture 2. Introduction to semiconductors Structures and characteristics in semiconductors. Fabrication of semiconductor sensor
 Lecture 2 Introduction to semiconductors Structures and characteristics in semiconductors Semiconductor p-n junction Metal Oxide Silicon structure Semiconductor contact Fabrication of semiconductor sensor
Lecture 2 Introduction to semiconductors Structures and characteristics in semiconductors Semiconductor p-n junction Metal Oxide Silicon structure Semiconductor contact Fabrication of semiconductor sensor
There's Plenty of Room at the Bottom
 There's Plenty of Room at the Bottom 12/29/1959 Feynman asked why not put the entire Encyclopedia Britannica (24 volumes) on a pin head (requires atomic scale recording). He proposed to use electron microscope
There's Plenty of Room at the Bottom 12/29/1959 Feynman asked why not put the entire Encyclopedia Britannica (24 volumes) on a pin head (requires atomic scale recording). He proposed to use electron microscope
ECE 342 Electronic Circuits. Lecture 6 MOS Transistors
 ECE 342 Electronic Circuits Lecture 6 MOS Transistors Jose E. Schutt-Aine Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Illinois jesa@illinois.edu 1 NMOS Transistor Typically L = 0.1 to 3 m, W = 0.2
ECE 342 Electronic Circuits Lecture 6 MOS Transistors Jose E. Schutt-Aine Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Illinois jesa@illinois.edu 1 NMOS Transistor Typically L = 0.1 to 3 m, W = 0.2
How a single defect can affect silicon nano-devices. Ted Thorbeck
 How a single defect can affect silicon nano-devices Ted Thorbeck tedt@nist.gov The Big Idea As MOS-FETs continue to shrink, single atomic scale defects are beginning to affect device performance Gate Source
How a single defect can affect silicon nano-devices Ted Thorbeck tedt@nist.gov The Big Idea As MOS-FETs continue to shrink, single atomic scale defects are beginning to affect device performance Gate Source
Section 12: Intro to Devices
 Section 12: Intro to Devices Extensive reading materials on reserve, including Robert F. Pierret, Semiconductor Device Fundamentals Bond Model of Electrons and Holes Si Si Si Si Si Si Si Si Si Silicon
Section 12: Intro to Devices Extensive reading materials on reserve, including Robert F. Pierret, Semiconductor Device Fundamentals Bond Model of Electrons and Holes Si Si Si Si Si Si Si Si Si Silicon
Metal Deposition. Filament Evaporation E-beam Evaporation Sputter Deposition
 Metal Deposition Filament Evaporation E-beam Evaporation Sputter Deposition 1 Filament evaporation metals are raised to their melting point by resistive heating under vacuum metal pellets are placed on
Metal Deposition Filament Evaporation E-beam Evaporation Sputter Deposition 1 Filament evaporation metals are raised to their melting point by resistive heating under vacuum metal pellets are placed on
EE C245 / ME C218 INTRODUCTION TO MEMS DESIGN FALL 2009 PROBLEM SET #7. Due (at 7 p.m.): Thursday, Dec. 10, 2009, in the EE C245 HW box in 240 Cory.
 Issued: Thursday, Nov. 24, 2009 PROBLEM SET #7 Due (at 7 p.m.): Thursday, Dec. 10, 2009, in the EE C245 HW box in 240 Cory. 1. Gyroscopes are inertial sensors that measure rotation rate, which is an extremely
Issued: Thursday, Nov. 24, 2009 PROBLEM SET #7 Due (at 7 p.m.): Thursday, Dec. 10, 2009, in the EE C245 HW box in 240 Cory. 1. Gyroscopes are inertial sensors that measure rotation rate, which is an extremely
MICRO-SCALE SHEET RESISTANCE MEASUREMENTS ON ULTRA SHALLOW JUNCTIONS
 MICRO-SCALE SHEET RESISTANCE MEASUREMENTS ON ULTRA SHALLOW JUNCTIONS Christian L. Petersen, Rong Lin, Dirch H. Petersen, Peter F. Nielsen CAPRES A/S, Burnaby, BC, Canada CAPRES A/S, Lyngby, Denmark We
MICRO-SCALE SHEET RESISTANCE MEASUREMENTS ON ULTRA SHALLOW JUNCTIONS Christian L. Petersen, Rong Lin, Dirch H. Petersen, Peter F. Nielsen CAPRES A/S, Burnaby, BC, Canada CAPRES A/S, Lyngby, Denmark We
Quantum Hall circuits with variable geometry: study of the inter-channel equilibration by Scanning Gate Microscopy
 *nicola.paradiso@sns.it Nicola Paradiso Ph. D. Thesis Quantum Hall circuits with variable geometry: study of the inter-channel equilibration by Scanning Gate Microscopy N. Paradiso, Advisors: S. Heun,
*nicola.paradiso@sns.it Nicola Paradiso Ph. D. Thesis Quantum Hall circuits with variable geometry: study of the inter-channel equilibration by Scanning Gate Microscopy N. Paradiso, Advisors: S. Heun,
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences. EECS 130 Professor Ali Javey Fall 2006
 UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences EECS 130 Professor Ali Javey Fall 2006 Midterm 2 Name: SID: Closed book. Two sheets of notes are
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences EECS 130 Professor Ali Javey Fall 2006 Midterm 2 Name: SID: Closed book. Two sheets of notes are
EECS130 Integrated Circuit Devices
 EECS130 Integrated Circuit Devices Professor Ali Javey 10/30/2007 MOSFETs Lecture 4 Reading: Chapter 17, 19 Announcements The next HW set is due on Thursday. Midterm 2 is next week!!!! Threshold and Subthreshold
EECS130 Integrated Circuit Devices Professor Ali Javey 10/30/2007 MOSFETs Lecture 4 Reading: Chapter 17, 19 Announcements The next HW set is due on Thursday. Midterm 2 is next week!!!! Threshold and Subthreshold
Simple and accurate modeling of the 3D structural variations in FinFETs
 Simple and accurate modeling of the 3D structural variations in FinFETs Donghu Kim Electrical Engineering Program Graduate school of UNIST 2013 Simple and accurate modeling of the 3D structural variations
Simple and accurate modeling of the 3D structural variations in FinFETs Donghu Kim Electrical Engineering Program Graduate school of UNIST 2013 Simple and accurate modeling of the 3D structural variations
Meta-stability effects in organic based transistors
 Meta-stability effects in organic based transistors H. L. Gomes *a, P. Stallinga a, M. Murgia b, F. Biscarini b T. Muck c, V. Wagner c E. Smits d and. M. de Leeuw d a University of Algarve, Faculty of
Meta-stability effects in organic based transistors H. L. Gomes *a, P. Stallinga a, M. Murgia b, F. Biscarini b T. Muck c, V. Wagner c E. Smits d and. M. de Leeuw d a University of Algarve, Faculty of
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature12036 We provide in the following additional experimental data and details on our demonstration of an electrically pumped exciton-polariton laser by supplementing optical and electrical
doi:10.1038/nature12036 We provide in the following additional experimental data and details on our demonstration of an electrically pumped exciton-polariton laser by supplementing optical and electrical
Metal Semiconductor Contacts
 Metal Semiconductor Contacts The investigation of rectification in metal-semiconductor contacts was first described by Braun [33-35], who discovered in 1874 the asymmetric nature of electrical conduction
Metal Semiconductor Contacts The investigation of rectification in metal-semiconductor contacts was first described by Braun [33-35], who discovered in 1874 the asymmetric nature of electrical conduction
EE 3329 Electronic Devices Syllabus ( Extended Play )
 EE 3329 - Electronic Devices Syllabus EE 3329 Electronic Devices Syllabus ( Extended Play ) The University of Texas at El Paso The following concepts can be part of the syllabus for the Electronic Devices
EE 3329 - Electronic Devices Syllabus EE 3329 Electronic Devices Syllabus ( Extended Play ) The University of Texas at El Paso The following concepts can be part of the syllabus for the Electronic Devices
Retract. Press down D RG MG LG S. Recess. I-V Converter VNA. Gate ADC. DC Bias. 20 mk. Amplifier. Attenuators. 0.
 a Press down b Retract D RG S c d 2 µm Recess 2 µm.5 µm Supplementary Figure 1 CNT mechanical transfer (a) Schematics showing steps of pressing down and retracting during the transfer of the CNT from the
a Press down b Retract D RG S c d 2 µm Recess 2 µm.5 µm Supplementary Figure 1 CNT mechanical transfer (a) Schematics showing steps of pressing down and retracting during the transfer of the CNT from the
Supporting information
 Supporting information Design, Modeling and Fabrication of CVD Grown MoS 2 Circuits with E-Mode FETs for Large-Area Electronics Lili Yu 1*, Dina El-Damak 1*, Ujwal Radhakrishna 1, Xi Ling 1, Ahmad Zubair
Supporting information Design, Modeling and Fabrication of CVD Grown MoS 2 Circuits with E-Mode FETs for Large-Area Electronics Lili Yu 1*, Dina El-Damak 1*, Ujwal Radhakrishna 1, Xi Ling 1, Ahmad Zubair
Transistors - a primer
 ransistors - a primer What is a transistor? Solid-state triode - three-terminal device, with voltage (or current) at third terminal used to control current between other two terminals. wo types: bipolar
ransistors - a primer What is a transistor? Solid-state triode - three-terminal device, with voltage (or current) at third terminal used to control current between other two terminals. wo types: bipolar
Efficient electron transport on helium with silicon integrated circuits
 Efficient electron transport on helium with silicon integrated circuits - - + - - Forrest Bradbury 1 and Maika Takita 1, Kevin Eng 2, Tom M Gurrieri 2, Kathy J Wilkel 2, Stephen A Lyon 1 1 Princeton University
Efficient electron transport on helium with silicon integrated circuits - - + - - Forrest Bradbury 1 and Maika Takita 1, Kevin Eng 2, Tom M Gurrieri 2, Kathy J Wilkel 2, Stephen A Lyon 1 1 Princeton University
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Monolithically Integrated Flexible Black Phosphorus Complementary Inverter Circuits Yuanda Liu, and Kah-Wee Ang* Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering National University
Supporting Information Monolithically Integrated Flexible Black Phosphorus Complementary Inverter Circuits Yuanda Liu, and Kah-Wee Ang* Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering National University
Fig. 8.1 : Schematic for single electron tunneling arrangement. For large system this charge is usually washed out by the thermal noise
 Part 2 : Nanostuctures Lecture 1 : Coulomb blockade and single electron tunneling Module 8 : Coulomb blockade and single electron tunneling Coulomb blockade and single electron tunneling A typical semiconductor
Part 2 : Nanostuctures Lecture 1 : Coulomb blockade and single electron tunneling Module 8 : Coulomb blockade and single electron tunneling Coulomb blockade and single electron tunneling A typical semiconductor
Resistance Thermometry based Picowatt-Resolution Heat-Flow Calorimeter
 Resistance Thermometry based Picowatt-Resolution Heat-Flow Calorimeter S. Sadat 1, E. Meyhofer 1 and P. Reddy 1, 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, 48109 Department
Resistance Thermometry based Picowatt-Resolution Heat-Flow Calorimeter S. Sadat 1, E. Meyhofer 1 and P. Reddy 1, 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, 48109 Department
Energetic particles and their detection in situ (particle detectors) Part II. George Gloeckler
 Energetic particles and their detection in situ (particle detectors) Part II George Gloeckler University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI University of Maryland, College Park, MD Simple particle detectors Gas-filled
Energetic particles and their detection in situ (particle detectors) Part II George Gloeckler University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI University of Maryland, College Park, MD Simple particle detectors Gas-filled
Graphene Canada Montreal Oct. 16, 2015 (International Year of Light)
 Luminescence Properties of Graphene A. Beltaos 1,2,3, A. Bergren 1, K. Bosnick 1, N. Pekas 1, A. Matković 4, A. Meldrum 2 1 National Institute for Nanotechnology (NINT), 11421 Saskatchewan Drive, Edmonton,
Luminescence Properties of Graphene A. Beltaos 1,2,3, A. Bergren 1, K. Bosnick 1, N. Pekas 1, A. Matković 4, A. Meldrum 2 1 National Institute for Nanotechnology (NINT), 11421 Saskatchewan Drive, Edmonton,
Design Considerations for Integrated Semiconductor Control Electronics for a Large-scale Solid State Quantum Processor
 Design Considerations for Integrated Semiconductor Control Electronics for a Large-scale Solid State Quantum Processor Hendrik Bluhm Andre Kruth Lotte Geck Carsten Degenhardt 1 0 Ψ 1 Quantum Computing
Design Considerations for Integrated Semiconductor Control Electronics for a Large-scale Solid State Quantum Processor Hendrik Bluhm Andre Kruth Lotte Geck Carsten Degenhardt 1 0 Ψ 1 Quantum Computing
