Fabrication of Sub-Quarter-Micron Grating Patterns by Employing Lithography
|
|
|
- Delphia French
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 MCROU,!~'O~C ELSEVER Microelectronic Engineering 46 (1999) Fabrication of Sub-Quarter-Micron Grating Patterns by Employing Lithography DUV Holographic L. A. Wang*, C. H. Lin and J. H. Chen nstitute of Electro-Optical Engineering, National Taiwan University, Taipei, Taiwan Sub-quarter-micron grating patterns with period as fine as.22 p.m have been obtained by combining DUV holographic lithography and silylation technique for the first time. A traditional chemical amplified resist (JSR KRF/K2G) originally working for single layer process at 248 nm wavelength was used for silylation. The silylation selectivity was improved by process control and a photoresist pattern with an aspect ration of 4 was obtained. 1. NTRODUCTON Sub-quarter-micron gratings are essential elements for many opto-electronic devices that play key roles in advanced lightwave communication systems. For the ngaasp lasers operating at 1.3 and 1.55 ~m wavelength regions where the transmission losses of an optical fiber are low, the first-order grating periods need to be about.2 and.23 ~tm, respectively. There are several methods such as E-beam[l], X-ray[2] and holographic lithography[3,4] for the fabrication of such gratings. Both E-beam and X-ray lithographies are capable of yielding grating periods well below.1 ~tm with arbitrary patterns. However, the major concern of E- beam lithography is its low throughput owing to the serial nature of pattern writing. For X-ray lithography, mask problems such as pattern distortion, cleaning and repair have not been resolved. Moreover, both E-beam and X-ray lithographies require very expensive equipment. Conversely, for holographic lithography, no mask or stepper is needed for such regular pattern generation. n addition, the setup involved in holographic lithography is relatively simple to implement if the grating period needs to vary frequently. n holographic lithography, it is known that interference between the incoming beam and the one reflected from a substrate produces a standing wave pattern in the photoresist layer. For a positive-tone photoresist, an undercut resist profile results if the maximum of the standing wave occurs at the resist/substrate interface and vice versa. Hence, the photoresist pattern is degraded and may cause more problems when transferred to the substrate. Several methods have been shown to solve this problem. For example, one can apply Cr as mask in oxygen reactive ion etching[5] or employ a trilevel resist process with antireflection coating (ARC) as bottom layer[6]. However, these methods involve complicated processes. Here we employed deep UV holographic lithography and silylation process[7-9] to fabricate sub-quarter-micron grating patterns, which has the following advantages. First, an (KrF or ArF) excimer laser has a shorter wavelength and higher intensity than traditional light sources such as Ar + and He-Cd lasers; therefore, smaller grating periods can be obtained with one or a few pulses. The mechanical stability of exposure system will not become an issue, and a high pattern contrast can be obtained. Second, the silylation process does not Fax: (886-2) ; lon@ccms.ntu.edu.tw /99/$ - see front matter 1999 Elsevier Science B.V. All rights reserved. P: S (99)57-X
2 174 L.A. Wang et al. / Microelectronic Engineering 46 (1999) need multilayer coating and baking as compared with the trilevel resist process. Third, with top surface imaging, the aerial image does not need to be in focus through the entire resist film and resist can be made highly absorbent in order to reduce reflection. Fourth, the processes of liquid-phase silylation and dry development are compatible with the conventional lithography. Therefore, high resolution and wide processing latitude can be obtained. n addition, a vertical sidewall of photoresist pattern can be obtained because of anisotropic oxygen plasma etching. 2. EXPERMENT A KrF excimer laser (Lambda Physik 15T) was utilized as exposure light source which generated pulses of short duration (~ 2 ns) with a rectangular spatial profile (2 x 1 mm2). Since the coherent length of the KrF excimer laser was short (~ 2 mm), the optical path length difference incurred in the exposure setup shown in Fig. 1 needed a careful control. An attenuator was used to reduce the light intensity to about 14 mj/cm 2 before the exposure plane. The incident angle of laser beam, ~, which determines the pattern period can be adjusted by rotating the mirror. The sample under test was located in the exposure plane. The prism and samples were mounted on a translational stage as an assembly which was then aligned with the laser beam. The resist we used was one of the chemical amplified resists working at 248 nm (JSR KRF/K2G)[1]. t was spun on a Si substrate at 4 rpm for 3 sec, resulting in a film thickness of.5 ~tm. The resist-coated substrate was then softbaked at 8 C for 12 sec. After exposure to the laser beams utilizing the setup mentioned previously, the resist film was post-exposure baked and liquidphase silylated at room temperature for 12 sec in a beaker. The liquid phase silylation bath consisted of Bis(dimethylamino)methylsilane (B[DMAMS, 1%) with N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone (N/rP, 3%) as diffusion promoter and xylene as solvent. The OH group in the exposed region reacted with silylation agent, and the reaction is illustrated in Fig. 2. After liquid phase silylation, the sample was rinsed with xylene and spun dry. The silylated region then acted as mask in a subsequent dry development. n contrast to the wet development in a conventional lithography process, an anisotropic 2 plasma etching is then applied to transfer a silylated image. The RF power of the RE system (Plasma Lab) was adjusted to 9 W. The oxygen pressure was held at 3 mtorr, and the flow rate was 3 sccm. An etching rate of-13 nm/min was obtained for the photoresist. B[DMAMS OH H--~i-Me NMe2 Figure 2. Silylation reaction. 3. RESULTS AND DSCUSSON Figure 1. Exposure setup. During the silylation step, Si was selectively incorporated into the exposed resist area. The Si profile inside the silylated resist was obtained by analyzing the Rutherford backscattering spectrum (RBS). RBS was obtained by using a 2 MeV He + beam and a detector at a backscattering angle of 16
3 L.A. Wang et al. / Microelectronic Engineering 46 (1999) degrees. A typical RBS of a silylated resist is shown in Fig. 3. The large signal increase in signal at the low energy end was due to the substrate Si. The energy at which this occurred varied with resist thickness. Fig. 4 shows a series of spectra for different silylation time. t is shown the silicon uptake increases with time. The RBS of the resists silylated for 9 sec at different exposures is shown in Fig. 5. The resist was silylated even in an unexposed region. This is due to the partially protected poly(hydroxystyrene) in our resist, which causes the unexposed resist still to contain the OH group. Because the concentration of OH group is higher for an exposed resist, the silylation agent reacts for a longer time with the top surface of exposed resist and thus diffuses less in the direction of thickness. Therefore, for the resist exposed at 35 mj/cm 2, the concentration of incorporated silicon in the upper portion of resist was found higher than that of the unexposed one, but lower in the lower portion. n contrast, due to the inherent but low concentration of OH group in an unexposed resist, the reaction between OH group and silylation agent quickly finished. Hence, no more OH group could react further and then silylation agent continues to diffuse into the lower portion of resist. Therefore, the silicon distribution was observed in the lower portion of the unexposed resist as shown in Fig. 5. Fig. 4 shows more silicon contents in the lower portion of exposed resist when silylation time was longer. Since it was somewhat silylated in the unexposed resist, the silylation selectivity was not good enough. Therefore, to overcome this problem, we have to expose enough energy, i.e. above 3 mj/cm 2, to ensure a better silylation selectivity Before Silylation... After Silylation E 2 o 1 ~,~l.ojo~,~ r / Substrate Si J ~ Will' o o9 / i i ! Figure 3. RBS of the resist before and after silylation.
4 176 L.A. Wang et al. / Microelectronic Engineering 46 (1999) min 4 ---o---.5 min min... ~ min 3OO o min c- '-'i 2 a d ~?., 't 1 O.9(,,, t ~ ;b o mo n ~ o. ~ ^.x _ " ;o.i o* O" o io o " r4 ~ a o OZ~ ] Figure 4. RBS of the resist for various silylation time. 5,- 4oot [ -- 3s mj/cm~j!!! iiiiii!ili!,31oo ~ 2 E ~J, :i' ~ ~. ~ ~ ' : ":,.~.~.,, Figure 5. RBS of the silylated resists at different exposures. (a) Figure 6. SEM micrographs of sub-quarter-micron L/S resist patterns. Resist was exposed and postexposure baked at (a) 1 C, 12 sec (b) 14 C, 9 sec. (b)
5 L.A. Wang et al. / Microelectronic Engineering 46 (1999) The temperature of pre-silylation bake (PSB) is an important parameter in the process, which affects the silylation selectivity between exposed and unexposed regions. As shown in Fig. 6, a PSB temperature at 1 C led to low silylation selectivity; however, when the temperature was up to 14 C, the pattern exhibited well resolved and had vertical sidewalls. Cross-sectional staining of the silylated regions was done by coating gold on the top surface of the resist in order to prevent erosion during the staining, cleaving the sample cross patterned lines, and applying 2 plasma to the cleaved surface. The silylated profile shown in Fig. 7 was observed by SEM. n the SEM micrographs, we found that it was a little silylated even in the unexposed region. Therefore, we have to apply pre-treatment by using CF4 plasma to etch away the silylated film in the unexposed region before 2 plasma development. Shown in Fig. 8 is the resultant grating with a period as small as.22 ~tm, which can serve as a first order grating for a DFB laser operating at 1.55 ~tm. The linewidth of the photoresist patterns was about.9 ~tm with an aspect ration of 4, currently limited by the uniformity of laser beam and capability of our RE system. 4. CONCLUSON We report for the first time that by combining DUV holographic lithography and silylation, subquarter-micron gratings with periods as small as.22 ~tm can be fabricated. A traditional chemical amplified resist working at the wavelength of 248 nm for single layer process can even be used to perform silylation process region. The RBS analysis indicates that this resist was silylated even in an unexposed resist. Enough energy should be applied to ensure a better silylation selectivity, and CF4 plasma should be applied to etch away the silylated film in the unexposed region before development. REFERENCES Figure 7. SEM micrograph of silylated profiles. Figure 8. SEM micrograph of a resist pattern with.22 9m period and.9 ~tm linewidth. 1. N. Eriksson, M. Hagberg, and A. Larsson, J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B 14 (1996) D.C. Flanders and H.. Smith, Appl. Phys. Lett. 32 (1978) S.H. Zaidi and S. R. J. Brueck, Appl. Opt. 27 (1988) S.H. Zaidi, S. R. J. Brueck, etc., Proc. SPE 348 (1997) Erik H. Anderson, C. M. Horwitz, and Henry. Smith, Appl. Phys. Lett. 43 (1983) M.L. Schattenburg, R. J. Aucoin, and R. C. Fleming, J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B 13 (1995) Katsumi Maeda, Takeshi Ohfuji, Naoaki Aizaki, and Etsuo Hasegawa, Proc. SPE 2438 (1995) K.H Baik, L. Van den hove, and B. Roland, J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B 9 (1991) M.A. Harmey, R. R. Kunz, L. M. Eriksen, Optical Engineering 32 (1993) A. A. Lamola, C. R. Szmanda, J. W. Thackeray, Solid State Technol. 34 (1991) 53.
Introduction. Photoresist : Type: Structure:
 Photoresist SEM images of the morphologies of meso structures and nanopatterns on (a) a positively nanopatterned silicon mold, and (b) a negatively nanopatterned silicon mold. Introduction Photoresist
Photoresist SEM images of the morphologies of meso structures and nanopatterns on (a) a positively nanopatterned silicon mold, and (b) a negatively nanopatterned silicon mold. Introduction Photoresist
Photolithography II ( Part 1 )
 1 Photolithography II ( Part 1 ) Chapter 14 : Semiconductor Manufacturing Technology by M. Quirk & J. Serda Bjørn-Ove Fimland, Department of Electronics and Telecommunication, Norwegian University of Science
1 Photolithography II ( Part 1 ) Chapter 14 : Semiconductor Manufacturing Technology by M. Quirk & J. Serda Bjørn-Ove Fimland, Department of Electronics and Telecommunication, Norwegian University of Science
Photolithography Overview 9/29/03 Brainerd/photoclass/ECE580/Overvie w/overview
 http://www.intel.com/research/silicon/mooreslaw.htm 1 Moore s law only holds due to photolithography advancements in reducing linewidths 2 All processing to create electric components and circuits rely
http://www.intel.com/research/silicon/mooreslaw.htm 1 Moore s law only holds due to photolithography advancements in reducing linewidths 2 All processing to create electric components and circuits rely
Photolithography 光刻 Part II: Photoresists
 微纳光电子材料与器件工艺原理 Photolithography 光刻 Part II: Photoresists Xing Sheng 盛兴 Department of Electronic Engineering Tsinghua University xingsheng@tsinghua.edu.cn 1 Photolithography 光刻胶 负胶 正胶 4 Photolithography
微纳光电子材料与器件工艺原理 Photolithography 光刻 Part II: Photoresists Xing Sheng 盛兴 Department of Electronic Engineering Tsinghua University xingsheng@tsinghua.edu.cn 1 Photolithography 光刻胶 负胶 正胶 4 Photolithography
UNIT 3. By: Ajay Kumar Gautam Asst. Prof. Dev Bhoomi Institute of Technology & Engineering, Dehradun
 UNIT 3 By: Ajay Kumar Gautam Asst. Prof. Dev Bhoomi Institute of Technology & Engineering, Dehradun 1 Syllabus Lithography: photolithography and pattern transfer, Optical and non optical lithography, electron,
UNIT 3 By: Ajay Kumar Gautam Asst. Prof. Dev Bhoomi Institute of Technology & Engineering, Dehradun 1 Syllabus Lithography: photolithography and pattern transfer, Optical and non optical lithography, electron,
Methodology of modeling and simulating line-end shortening effects in deep-uv resist
 Methodology of modeling and simulating line-end shortening effects in deep-uv resist Mosong Cheng*, Ebo Croffie, Andrew Neureuther Electronics Research Laboratory Department of Electrical Engineering and
Methodology of modeling and simulating line-end shortening effects in deep-uv resist Mosong Cheng*, Ebo Croffie, Andrew Neureuther Electronics Research Laboratory Department of Electrical Engineering and
Overview of the main nano-lithography techniques
 Overview of the main nano-lithography techniques Soraya Sangiao sangiao@unizar.es Outline Introduction: Nanotechnology. Nano-lithography techniques: Masked lithography techniques: Photolithography. X-ray
Overview of the main nano-lithography techniques Soraya Sangiao sangiao@unizar.es Outline Introduction: Nanotechnology. Nano-lithography techniques: Masked lithography techniques: Photolithography. X-ray
Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. Vol Materials Research Society
 Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. Vol. 1258 2010 Materials Research Society 1258-Q14-02 Realization of silicon nanopillar arrays with controllable sidewall profiles by holography lithography and a novel single-step
Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. Vol. 1258 2010 Materials Research Society 1258-Q14-02 Realization of silicon nanopillar arrays with controllable sidewall profiles by holography lithography and a novel single-step
High Optical Density Photomasks For Large Exposure Applications
 High Optical Density Photomasks For Large Exposure Applications Dan Schurz, Warren W. Flack, Makoto Nakamura Ultratech Stepper, Inc. San Jose, CA 95134 Microlithography applications such as advanced packaging,
High Optical Density Photomasks For Large Exposure Applications Dan Schurz, Warren W. Flack, Makoto Nakamura Ultratech Stepper, Inc. San Jose, CA 95134 Microlithography applications such as advanced packaging,
A Novel Self-aligned and Maskless Process for Formation of Highly Uniform Arrays of Nanoholes and Nanopillars
 Nanoscale Res Lett (2008) 3: 127 DOI 10.1007/s11671-008-9124-6 NANO EXPRESS A Novel Self-aligned and Maskless Process for Formation of Highly Uniform Arrays of Nanoholes and Nanopillars Wei Wu Æ Dibyendu
Nanoscale Res Lett (2008) 3: 127 DOI 10.1007/s11671-008-9124-6 NANO EXPRESS A Novel Self-aligned and Maskless Process for Formation of Highly Uniform Arrays of Nanoholes and Nanopillars Wei Wu Æ Dibyendu
Supplementary Figure 1 Detailed illustration on the fabrication process of templatestripped
 Supplementary Figure 1 Detailed illustration on the fabrication process of templatestripped gold substrate. (a) Spin coating of hydrogen silsesquioxane (HSQ) resist onto the silicon substrate with a thickness
Supplementary Figure 1 Detailed illustration on the fabrication process of templatestripped gold substrate. (a) Spin coating of hydrogen silsesquioxane (HSQ) resist onto the silicon substrate with a thickness
Nanostructures Fabrication Methods
 Nanostructures Fabrication Methods bottom-up methods ( atom by atom ) In the bottom-up approach, atoms, molecules and even nanoparticles themselves can be used as the building blocks for the creation of
Nanostructures Fabrication Methods bottom-up methods ( atom by atom ) In the bottom-up approach, atoms, molecules and even nanoparticles themselves can be used as the building blocks for the creation of
Three Approaches for Nanopatterning
 Three Approaches for Nanopatterning Lithography allows the design of arbitrary pattern geometry but maybe high cost and low throughput Self-Assembly offers high throughput and low cost but limited selections
Three Approaches for Nanopatterning Lithography allows the design of arbitrary pattern geometry but maybe high cost and low throughput Self-Assembly offers high throughput and low cost but limited selections
Supplementary Information Our InGaN/GaN multiple quantum wells (MQWs) based one-dimensional (1D) grating structures
 Polarized white light from hybrid organic/iii-nitrides grating structures M. Athanasiou, R. M. Smith, S. Ghataora and T. Wang* Department of Electronic and Electrical Engineering, University of Sheffield,
Polarized white light from hybrid organic/iii-nitrides grating structures M. Athanasiou, R. M. Smith, S. Ghataora and T. Wang* Department of Electronic and Electrical Engineering, University of Sheffield,
Lithography and Etching
 Lithography and Etching Victor Ovchinnikov Chapters 8.1, 8.4, 9, 11 Previous lecture Microdevices Main processes: Thin film deposition Patterning (lithography) Doping Materials: Single crystal (monocrystal)
Lithography and Etching Victor Ovchinnikov Chapters 8.1, 8.4, 9, 11 Previous lecture Microdevices Main processes: Thin film deposition Patterning (lithography) Doping Materials: Single crystal (monocrystal)
Swing Curves. T h e L i t h o g r a p h y T u t o r (Summer 1994) Chris A. Mack, FINLE Technologies, Austin, Texas
 T h e L i t h o g r a p h y T u t o r (Summer 1994) Swing Curves Chris A. Mack, FINLE Technologies, Austin, Texas In the last edition of this column, we saw that exposing a photoresist involves the propagation
T h e L i t h o g r a p h y T u t o r (Summer 1994) Swing Curves Chris A. Mack, FINLE Technologies, Austin, Texas In the last edition of this column, we saw that exposing a photoresist involves the propagation
Two-dimensional Bragg grating lasers defined by electron-beam lithography
 Two-dimensional Bragg grating lasers defined by electron-beam lithography Guy A. DeRose a Pasadena, California 91125 and Department of Applied Physics, California Institute of Technology, 1200 E. California
Two-dimensional Bragg grating lasers defined by electron-beam lithography Guy A. DeRose a Pasadena, California 91125 and Department of Applied Physics, California Institute of Technology, 1200 E. California
Robust shadow-mask evaporation via lithographically controlled undercut
 Robust shadow-mask evaporation via lithographically controlled undercut B. Cord, a C. Dames, and K. K. Berggren Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, Massachusetts 02139-4309 J. Aumentado National
Robust shadow-mask evaporation via lithographically controlled undercut B. Cord, a C. Dames, and K. K. Berggren Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, Massachusetts 02139-4309 J. Aumentado National
Chapter 3 : ULSI Manufacturing Technology - (c) Photolithography
 Chapter 3 : ULSI Manufacturing Technology - (c) Photolithography 1 Reference 1. Semiconductor Manufacturing Technology : Michael Quirk and Julian Serda (2001) 2. - (2004) 3. Semiconductor Physics and Devices-
Chapter 3 : ULSI Manufacturing Technology - (c) Photolithography 1 Reference 1. Semiconductor Manufacturing Technology : Michael Quirk and Julian Serda (2001) 2. - (2004) 3. Semiconductor Physics and Devices-
ETCHING Chapter 10. Mask. Photoresist
 ETCHING Chapter 10 Mask Light Deposited Substrate Photoresist Etch mask deposition Photoresist application Exposure Development Etching Resist removal Etching of thin films and sometimes the silicon substrate
ETCHING Chapter 10 Mask Light Deposited Substrate Photoresist Etch mask deposition Photoresist application Exposure Development Etching Resist removal Etching of thin films and sometimes the silicon substrate
Improving resist resolution and sensitivity via electric-field enhanced postexposure baking
 Improving resist resolution and sensitivity via electric-field enhanced postexposure baking Mosong Cheng, a) Lei Yuan, Ebo Croffie, and Andrew Neureuther Electronics Research Laboratory, University of
Improving resist resolution and sensitivity via electric-field enhanced postexposure baking Mosong Cheng, a) Lei Yuan, Ebo Croffie, and Andrew Neureuther Electronics Research Laboratory, University of
Figure 1: Graphene release, transfer and stacking processes. The graphene stacking began with CVD
 Supplementary figure 1 Graphene Growth and Transfer Graphene PMMA FeCl 3 DI water Copper foil CVD growth Back side etch PMMA coating Copper etch in 0.25M FeCl 3 DI water rinse 1 st transfer DI water 1:10
Supplementary figure 1 Graphene Growth and Transfer Graphene PMMA FeCl 3 DI water Copper foil CVD growth Back side etch PMMA coating Copper etch in 0.25M FeCl 3 DI water rinse 1 st transfer DI water 1:10
Lecture 8. Photoresists and Non-optical Lithography
 Lecture 8 Photoresists and Non-optical Lithography Reading: Chapters 8 and 9 and notes derived from a HIGHLY recommended book by Chris Mack, Fundamental Principles of Optical Lithography. Any serious student
Lecture 8 Photoresists and Non-optical Lithography Reading: Chapters 8 and 9 and notes derived from a HIGHLY recommended book by Chris Mack, Fundamental Principles of Optical Lithography. Any serious student
Development of Lift-off Photoresists with Unique Bottom Profile
 Transactions of The Japan Institute of Electronics Packaging Vol. 8, No. 1, 2015 [Technical Paper] Development of Lift-off Photoresists with Unique Bottom Profile Hirokazu Ito, Kouichi Hasegawa, Tomohiro
Transactions of The Japan Institute of Electronics Packaging Vol. 8, No. 1, 2015 [Technical Paper] Development of Lift-off Photoresists with Unique Bottom Profile Hirokazu Ito, Kouichi Hasegawa, Tomohiro
Reactive Ion Etching (RIE)
 Reactive Ion Etching (RIE) RF 13.56 ~ MHz plasma Parallel-Plate Reactor wafers Sputtering Plasma generates (1) Ions (2) Activated neutrals Enhance chemical reaction 1 2 Remote Plasma Reactors Plasma Sources
Reactive Ion Etching (RIE) RF 13.56 ~ MHz plasma Parallel-Plate Reactor wafers Sputtering Plasma generates (1) Ions (2) Activated neutrals Enhance chemical reaction 1 2 Remote Plasma Reactors Plasma Sources
Electric field enhancement in metallic and multilayer dielectric gratings
 Electric field enhancement in metallic and multilayer dielectric gratings B. W. Shore, M. D. Feit, M. D. Perry, R. D. Boyd, J. A. Britten, R. Chow, G. E. Loomis Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory,
Electric field enhancement in metallic and multilayer dielectric gratings B. W. Shore, M. D. Feit, M. D. Perry, R. D. Boyd, J. A. Britten, R. Chow, G. E. Loomis Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory,
Nano fabrication by e-beam lithographie
 Introduction to nanooptics, Summer Term 2012, Abbe School of Photonics, FSU Jena, Prof. Thomas Pertsch Nano fabrication by e-beam lithographie Lecture 14 1 Electron Beam Lithography - EBL Introduction
Introduction to nanooptics, Summer Term 2012, Abbe School of Photonics, FSU Jena, Prof. Thomas Pertsch Nano fabrication by e-beam lithographie Lecture 14 1 Electron Beam Lithography - EBL Introduction
4FNJDPOEVDUPS 'BCSJDBUJPO &UDI
 2010.5.4 1 Major Fabrication Steps in CMOS Process Flow UV light oxygen Silicon dioxide Silicon substrate Oxidation (Field oxide) photoresist Photoresist Coating Mask exposed photoresist Mask-Wafer Exposed
2010.5.4 1 Major Fabrication Steps in CMOS Process Flow UV light oxygen Silicon dioxide Silicon substrate Oxidation (Field oxide) photoresist Photoresist Coating Mask exposed photoresist Mask-Wafer Exposed
DUV Positive Photoresists
 Journal of Photopolymer Science and Technology Volume 5, Number 1(1992) 207-216 Factors Affecting the Performance of Chemically DUV Positive Photoresists Amplified James W. Thackeray, Theodore H. Fedynyshyn,
Journal of Photopolymer Science and Technology Volume 5, Number 1(1992) 207-216 Factors Affecting the Performance of Chemically DUV Positive Photoresists Amplified James W. Thackeray, Theodore H. Fedynyshyn,
Resonator Fabrication for Cavity Enhanced, Tunable Si/Ge Quantum Cascade Detectors
 Resonator Fabrication for Cavity Enhanced, Tunable Si/Ge Quantum Cascade Detectors M. Grydlik 1, P. Rauter 1, T. Fromherz 1, G. Bauer 1, L. Diehl 2, C. Falub 2, G. Dehlinger 2, H. Sigg 2, D. Grützmacher
Resonator Fabrication for Cavity Enhanced, Tunable Si/Ge Quantum Cascade Detectors M. Grydlik 1, P. Rauter 1, T. Fromherz 1, G. Bauer 1, L. Diehl 2, C. Falub 2, G. Dehlinger 2, H. Sigg 2, D. Grützmacher
Kavli Workshop for Journalists. June 13th, CNF Cleanroom Activities
 Kavli Workshop for Journalists June 13th, 2007 CNF Cleanroom Activities Seeing nm-sized Objects with an SEM Lab experience: Scanning Electron Microscopy Equipment: Zeiss Supra 55VP Scanning electron microscopes
Kavli Workshop for Journalists June 13th, 2007 CNF Cleanroom Activities Seeing nm-sized Objects with an SEM Lab experience: Scanning Electron Microscopy Equipment: Zeiss Supra 55VP Scanning electron microscopes
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences. Fall Exam 1
 UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences EECS 143 Fall 2008 Exam 1 Professor Ali Javey Answer Key Name: SID: 1337 Closed book. One sheet
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences EECS 143 Fall 2008 Exam 1 Professor Ali Javey Answer Key Name: SID: 1337 Closed book. One sheet
Chapter 2 On-wafer UV Sensor and Prediction of UV Irradiation Damage
 Chapter 2 On-wafer UV Sensor and Prediction of UV Irradiation Damage Abstract UV radiation during plasma processing affects the surface of materials. Nevertheless, the interaction of UV photons with surface
Chapter 2 On-wafer UV Sensor and Prediction of UV Irradiation Damage Abstract UV radiation during plasma processing affects the surface of materials. Nevertheless, the interaction of UV photons with surface
Micro- and Nano-Technology... for Optics
 Micro- and Nano-Technology...... for Optics U.D. Zeitner Fraunhofer Institut für Angewandte Optik und Feinmechanik Jena Today: 1. Introduction E. Bernhard Kley Institute of Applied Physics Friedrich-Schiller
Micro- and Nano-Technology...... for Optics U.D. Zeitner Fraunhofer Institut für Angewandte Optik und Feinmechanik Jena Today: 1. Introduction E. Bernhard Kley Institute of Applied Physics Friedrich-Schiller
Introduction to Electron Beam Lithography
 Introduction to Electron Beam Lithography Boštjan Berčič (bostjan.bercic@ijs.si), Jožef Štefan Institute, Jamova 39, 1000 Ljubljana, Slovenia 1. Introduction Electron Beam Lithography is a specialized
Introduction to Electron Beam Lithography Boštjan Berčič (bostjan.bercic@ijs.si), Jožef Štefan Institute, Jamova 39, 1000 Ljubljana, Slovenia 1. Introduction Electron Beam Lithography is a specialized
Electron-beam SAFIER process and its application for magnetic thin-film heads
 Electron-beam SAFIER process and its application for magnetic thin-film heads XiaoMin Yang, a) Harold Gentile, Andrew Eckert, and Stanko R. Brankovic Seagate Research Center, 1251 Waterfront Place, Pittsburgh,
Electron-beam SAFIER process and its application for magnetic thin-film heads XiaoMin Yang, a) Harold Gentile, Andrew Eckert, and Stanko R. Brankovic Seagate Research Center, 1251 Waterfront Place, Pittsburgh,
Lithographic Effects Of Acid Diffusion In Chemically Amplified Resists
 INTERFACE '95 This paper was published in the proceedings of the OCG Microlithography Seminar, Interface '95, pp. 217-228. It is made available as an electronic reprint with permission of OCG Microelectronic
INTERFACE '95 This paper was published in the proceedings of the OCG Microlithography Seminar, Interface '95, pp. 217-228. It is made available as an electronic reprint with permission of OCG Microelectronic
Lecture 14 Advanced Photolithography
 Lecture 14 Advanced Photolithography Chapter 14 Wolf and Tauber 1/74 Announcements Term Paper: You are expected to produce a 4-5 page term paper on a selected topic (from a list). Term paper contributes
Lecture 14 Advanced Photolithography Chapter 14 Wolf and Tauber 1/74 Announcements Term Paper: You are expected to produce a 4-5 page term paper on a selected topic (from a list). Term paper contributes
Broadband transmission grating spectrometer for measuring the emission spectrum of EUV sources
 Broadband transmission grating spectrometer for measuring the emission spectrum of EUV sources Extreme ultraviolet (EUV) light sources and their optimization for emission within a narrow wavelength band
Broadband transmission grating spectrometer for measuring the emission spectrum of EUV sources Extreme ultraviolet (EUV) light sources and their optimization for emission within a narrow wavelength band
Techniques for directly measuring the absorbance of photoresists at EUV wavelengths
 Techniques for directly measuring the absorbance of photoresists at EUV wavelengths Manish Chandhok, a Heidi Cao, a Wang Yueh, a Eric Gullikson, b Robert Brainard, c Stewart Robertson c a Intel Corporation,
Techniques for directly measuring the absorbance of photoresists at EUV wavelengths Manish Chandhok, a Heidi Cao, a Wang Yueh, a Eric Gullikson, b Robert Brainard, c Stewart Robertson c a Intel Corporation,
Introduction to Photolithography
 http://www.ichaus.de/news/72 Introduction to Photolithography Photolithography The following slides present an outline of the process by which integrated circuits are made, of which photolithography is
http://www.ichaus.de/news/72 Introduction to Photolithography Photolithography The following slides present an outline of the process by which integrated circuits are made, of which photolithography is
Nanosphere Lithography
 Nanosphere Lithography Derec Ciafre 1, Lingyun Miao 2, and Keita Oka 1 1 Institute of Optics / 2 ECE Dept. University of Rochester Abstract Nanosphere Lithography is quickly emerging as an efficient, low
Nanosphere Lithography Derec Ciafre 1, Lingyun Miao 2, and Keita Oka 1 1 Institute of Optics / 2 ECE Dept. University of Rochester Abstract Nanosphere Lithography is quickly emerging as an efficient, low
Simulation and characterization of surface and line edge roughness in photoresists before and after etching
 Simulation and characterization of surface and line edge roughness in photoresists before and after etching Motivation of this work : Sub 100nm lithographic features often suffer from roughness. Need to
Simulation and characterization of surface and line edge roughness in photoresists before and after etching Motivation of this work : Sub 100nm lithographic features often suffer from roughness. Need to
Industrial Applications of Ultrafast Lasers: From Photomask Repair to Device Physics
 Industrial Applications of Ultrafast Lasers: From Photomask Repair to Device Physics Richard Haight IBM TJ Watson Research Center PO Box 218 Yorktown Hts., NY 10598 Collaborators Al Wagner Pete Longo Daeyoung
Industrial Applications of Ultrafast Lasers: From Photomask Repair to Device Physics Richard Haight IBM TJ Watson Research Center PO Box 218 Yorktown Hts., NY 10598 Collaborators Al Wagner Pete Longo Daeyoung
DQN Positive Photoresist
 UNIVESITY OF CALIFONIA, BEKELEY BEKELEY DAVIS IVINE LOS ANGELES IVESIDE SAN DIEGO SAN FANCISCO SANTA BABAA SANTA CUZ DEPATMENT OF BIOENGINEEING 94720-1762 BioE 121 Midterm #1 Solutions BEKELEY, CALIFONIA
UNIVESITY OF CALIFONIA, BEKELEY BEKELEY DAVIS IVINE LOS ANGELES IVESIDE SAN DIEGO SAN FANCISCO SANTA BABAA SANTA CUZ DEPATMENT OF BIOENGINEEING 94720-1762 BioE 121 Midterm #1 Solutions BEKELEY, CALIFONIA
Chapter 2 FABRICATION PROCEDURE AND TESTING SETUP. Our group has been working on the III-V epitaxy light emitting materials which could be
 Chapter 2 7 FABRICATION PROCEDURE AND TESTING SETUP 2.1 Introduction In this chapter, the fabrication procedures and the testing setups for the sub-micrometer lasers, the submicron disk laser and the photonic
Chapter 2 7 FABRICATION PROCEDURE AND TESTING SETUP 2.1 Introduction In this chapter, the fabrication procedures and the testing setups for the sub-micrometer lasers, the submicron disk laser and the photonic
Gratings in Electrooptic Polymer Devices
 Gratings in Electrooptic Polymer Devices Venkata N.P.Sivashankar 1, Edward M. McKenna 2 and Alan R.Mickelson 3 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Colorado at Boulder, Boulder,
Gratings in Electrooptic Polymer Devices Venkata N.P.Sivashankar 1, Edward M. McKenna 2 and Alan R.Mickelson 3 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Colorado at Boulder, Boulder,
DEPOSITION OF THIN TiO 2 FILMS BY DC MAGNETRON SPUTTERING METHOD
 Chapter 4 DEPOSITION OF THIN TiO 2 FILMS BY DC MAGNETRON SPUTTERING METHOD 4.1 INTRODUCTION Sputter deposition process is another old technique being used in modern semiconductor industries. Sputtering
Chapter 4 DEPOSITION OF THIN TiO 2 FILMS BY DC MAGNETRON SPUTTERING METHOD 4.1 INTRODUCTION Sputter deposition process is another old technique being used in modern semiconductor industries. Sputtering
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences. Professor Ali Javey. Fall 2009.
 UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences EE143 Professor Ali Javey Fall 2009 Exam 1 Name: SID: Closed book. One sheet of notes is allowed.
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences EE143 Professor Ali Javey Fall 2009 Exam 1 Name: SID: Closed book. One sheet of notes is allowed.
3.155J/6.152J Microelectronic Processing Technology Fall Term, 2004
 3.155J/6.152J Microelectronic Processing Technology Fall Term, 2004 Bob O'Handley Martin Schmidt Quiz Nov. 17, 2004 Ion implantation, diffusion [15] 1. a) Two identical p-type Si wafers (N a = 10 17 cm
3.155J/6.152J Microelectronic Processing Technology Fall Term, 2004 Bob O'Handley Martin Schmidt Quiz Nov. 17, 2004 Ion implantation, diffusion [15] 1. a) Two identical p-type Si wafers (N a = 10 17 cm
EE 434 Lecture 7. Process Technology
 EE 434 Lecture 7 Process Technology Quiz 4 How many wafers can be obtained from a 2m pull? Neglect the material wasted in the kerf used to separate the wafers. 2m And the number is. 1 8 3 5 6 4 9 7 2 1
EE 434 Lecture 7 Process Technology Quiz 4 How many wafers can be obtained from a 2m pull? Neglect the material wasted in the kerf used to separate the wafers. 2m And the number is. 1 8 3 5 6 4 9 7 2 1
Spectroscopic Critical Dimension technology (SCD) for Directed Self Assembly
 Spectroscopic Critical Dimension technology (SCD) for Directed Self Assembly Senichi Nishibe a, Thaddeus Dziura a, Venkat Nagaswami a, Roel Gronheid b a KLA-Tencor Corporation, 1 Technology Drive, Milpitas
Spectroscopic Critical Dimension technology (SCD) for Directed Self Assembly Senichi Nishibe a, Thaddeus Dziura a, Venkat Nagaswami a, Roel Gronheid b a KLA-Tencor Corporation, 1 Technology Drive, Milpitas
DUV ( nm ) Characterization of Materials: A new instrument, the Purged UV Spectroscopic Ellipsometer,
 WISE 2000, International Workshop on Spectroscopic Ellipsometry, 8 9 May 2000 DUV (150 350nm ) Characterization of Materials: A new instrument, the Purged UV Spectroscopic Ellipsometer, Pierre BOHER,,
WISE 2000, International Workshop on Spectroscopic Ellipsometry, 8 9 May 2000 DUV (150 350nm ) Characterization of Materials: A new instrument, the Purged UV Spectroscopic Ellipsometer, Pierre BOHER,,
Fabrication Engineering at the Micro- and Nanoscale, by Stephen Campbell, 4 th Edition, Oxford University Press
 Fabrication Engineering at the Micro- and Nanoscale, by Stephen Campbell, 4 th Edition, Oxford University Press Errata, by Chris Mack, chris@lithoguru.com While teaching out of this book at the University
Fabrication Engineering at the Micro- and Nanoscale, by Stephen Campbell, 4 th Edition, Oxford University Press Errata, by Chris Mack, chris@lithoguru.com While teaching out of this book at the University
Sensitization mechanisms of chemically amplified EUV resists and resist design for 22 nm node. Takahiro Kozawa and Seiichi Tagawa
 Sensitization mechanisms of chemically amplified EUV resists and resist design for 22 nm node Takahiro Kozawa and Seiichi Tagawa The Institute of Scientific and Industrial Research, Osaka University, 8-1
Sensitization mechanisms of chemically amplified EUV resists and resist design for 22 nm node Takahiro Kozawa and Seiichi Tagawa The Institute of Scientific and Industrial Research, Osaka University, 8-1
LECTURE 5 SUMMARY OF KEY IDEAS
 LECTURE 5 SUMMARY OF KEY IDEAS Etching is a processing step following lithography: it transfers a circuit image from the photoresist to materials form which devices are made or to hard masking or sacrificial
LECTURE 5 SUMMARY OF KEY IDEAS Etching is a processing step following lithography: it transfers a circuit image from the photoresist to materials form which devices are made or to hard masking or sacrificial
Optical Proximity Correction
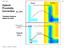 Optical Proximity Correction Mask Wafer *Auxiliary features added on mask 1 Overlay Errors + + alignment mask wafer + + photomask plate Alignment marks from previous masking level 2 (1) Thermal run-in/run-out
Optical Proximity Correction Mask Wafer *Auxiliary features added on mask 1 Overlay Errors + + alignment mask wafer + + photomask plate Alignment marks from previous masking level 2 (1) Thermal run-in/run-out
Plasmonic Hot Hole Generation by Interband Transition in Gold-Polyaniline
 Supplementary Information Plasmonic Hot Hole Generation by Interband Transition in Gold-Polyaniline Tapan Barman, Amreen A. Hussain, Bikash Sharma, Arup R. Pal* Plasma Nanotech Lab, Physical Sciences Division,
Supplementary Information Plasmonic Hot Hole Generation by Interband Transition in Gold-Polyaniline Tapan Barman, Amreen A. Hussain, Bikash Sharma, Arup R. Pal* Plasma Nanotech Lab, Physical Sciences Division,
Techniken der Oberflächenphysik (Techniques of Surface Physics)
 Techniken der Oberflächenphysik (Techniques of Surface Physics) Prof. Yong Lei & Dr. Yang Xu (& Liying Liang) Fachgebiet 3D-Nanostrukturierung, Institut für Physik Contact: yong.lei@tu-ilmenau.de; yang.xu@tu-ilmenau.de;
Techniken der Oberflächenphysik (Techniques of Surface Physics) Prof. Yong Lei & Dr. Yang Xu (& Liying Liang) Fachgebiet 3D-Nanostrukturierung, Institut für Physik Contact: yong.lei@tu-ilmenau.de; yang.xu@tu-ilmenau.de;
Optical Measurements of Critical Dimensions at Several Stages of the Mask Fabrication Process
 Optical Measurements of Critical Dimensions at Several Stages of the Mask Fabrication Process John C. Lam, Alexander Gray n&k Technology, Inc., Santa Clara, CA ABSTRACT Critical dimension (CD) metrology
Optical Measurements of Critical Dimensions at Several Stages of the Mask Fabrication Process John C. Lam, Alexander Gray n&k Technology, Inc., Santa Clara, CA ABSTRACT Critical dimension (CD) metrology
Copyright 1997 by the Society of Photo-Optical Instrumentation Engineers.
 Copyright 1997 by the Society of Photo-Optical Instrumentation Engineers. This paper was published in the proceedings of Advances in Resist Technology and Processing XIV, SPIE Vol. 3049, pp. 706-711. It
Copyright 1997 by the Society of Photo-Optical Instrumentation Engineers. This paper was published in the proceedings of Advances in Resist Technology and Processing XIV, SPIE Vol. 3049, pp. 706-711. It
ECE 695 Numerical Simulations Lecture 35: Solar Hybrid Energy Conversion Systems. Prof. Peter Bermel April 12, 2017
 ECE 695 Numerical Simulations Lecture 35: Solar Hybrid Energy Conversion Systems Prof. Peter Bermel April 12, 2017 Ideal Selective Solar Absorber Efficiency Limits Ideal cut-off wavelength for a selective
ECE 695 Numerical Simulations Lecture 35: Solar Hybrid Energy Conversion Systems Prof. Peter Bermel April 12, 2017 Ideal Selective Solar Absorber Efficiency Limits Ideal cut-off wavelength for a selective
Dielectric Meta-Reflectarray for Broadband Linear Polarization Conversion and Optical Vortex Generation
 Supporting Information Dielectric Meta-Reflectarray for Broadband Linear Polarization Conversion and Optical Vortex Generation Yuanmu Yang, Wenyi Wang, Parikshit Moitra, Ivan I. Kravchenko, Dayrl P. Briggs,
Supporting Information Dielectric Meta-Reflectarray for Broadband Linear Polarization Conversion and Optical Vortex Generation Yuanmu Yang, Wenyi Wang, Parikshit Moitra, Ivan I. Kravchenko, Dayrl P. Briggs,
Stacked Subwavelength Gratings as Circular Polarization Filters
 Brigham Young University BYU ScholarsArchive All Faculty Publications 2001-11-01 Stacked Subwavelength Gratings as Circular Polarization Filters Gregory P. Nordin nordin@byu.edu P. C. Deguzman Follow this
Brigham Young University BYU ScholarsArchive All Faculty Publications 2001-11-01 Stacked Subwavelength Gratings as Circular Polarization Filters Gregory P. Nordin nordin@byu.edu P. C. Deguzman Follow this
An Optimal Substrate Design for SERS: Dual-Scale Diamond-Shaped Gold Nano-Structures Fabricated via Interference Lithography
 Supporting Information An Optimal Substrate Design for SERS: Dual-Scale Diamond-Shaped Gold Nano-Structures Fabricated via Interference Lithography Hyo-Jin Ahn a, Pradheep Thiyagarajan a, Lin Jia b, Sun-I
Supporting Information An Optimal Substrate Design for SERS: Dual-Scale Diamond-Shaped Gold Nano-Structures Fabricated via Interference Lithography Hyo-Jin Ahn a, Pradheep Thiyagarajan a, Lin Jia b, Sun-I
A Novel Approach to the Layer Number-Controlled and Grain Size- Controlled Growth of High Quality Graphene for Nanoelectronics
 Supporting Information A Novel Approach to the Layer Number-Controlled and Grain Size- Controlled Growth of High Quality Graphene for Nanoelectronics Tej B. Limbu 1,2, Jean C. Hernández 3, Frank Mendoza
Supporting Information A Novel Approach to the Layer Number-Controlled and Grain Size- Controlled Growth of High Quality Graphene for Nanoelectronics Tej B. Limbu 1,2, Jean C. Hernández 3, Frank Mendoza
Far IR Gas Lasers microns wavelengths, THz frequency Called Terahertz lasers or FIR lasers At this wavelength behaves more like
 Far IR Gas Lasers 10-1500 microns wavelengths, 300 10 THz frequency Called Terahertz lasers or FIR lasers At this wavelength behaves more like microwave signal than light Created by Molecular vibronic
Far IR Gas Lasers 10-1500 microns wavelengths, 300 10 THz frequency Called Terahertz lasers or FIR lasers At this wavelength behaves more like microwave signal than light Created by Molecular vibronic
IC Fabrication Technology
 IC Fabrication Technology * History: 1958-59: J. Kilby, Texas Instruments and R. Noyce, Fairchild * Key Idea: batch fabrication of electronic circuits n entire circuit, say 10 7 transistors and 5 levels
IC Fabrication Technology * History: 1958-59: J. Kilby, Texas Instruments and R. Noyce, Fairchild * Key Idea: batch fabrication of electronic circuits n entire circuit, say 10 7 transistors and 5 levels
percolating nanotube networks
 Supporting Information for: A highly elastic, capacitive strain gauge based on percolating nanotube networks 0.2 0.18 0.16 0.14 Force (kgf) 0.12 0.1 0.08 0.06 0.04 0.02 Raw Data Mooney-Rivlin (R 2 =0.996)
Supporting Information for: A highly elastic, capacitive strain gauge based on percolating nanotube networks 0.2 0.18 0.16 0.14 Force (kgf) 0.12 0.1 0.08 0.06 0.04 0.02 Raw Data Mooney-Rivlin (R 2 =0.996)
Diamond-like carbon film deposition on PZT ferroelectrics and YBCO superconducting films using KrF excimer laser deposition
 Composites: Part B 30 (1999) 685 689 www.elsevier.com/locate/compositesb Diamond-like carbon film deposition on PZT ferroelectrics and YBCO superconducting films using KrF excimer laser deposition K. Ebihara*,
Composites: Part B 30 (1999) 685 689 www.elsevier.com/locate/compositesb Diamond-like carbon film deposition on PZT ferroelectrics and YBCO superconducting films using KrF excimer laser deposition K. Ebihara*,
Supporting file. Pulse Laser Induced Size-controllable and Symmetrical Ordering of Single Crystal Si
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supporting file Pulse Laser Induced Size-controllable and Symmetrical Ordering of Single Crystal
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supporting file Pulse Laser Induced Size-controllable and Symmetrical Ordering of Single Crystal
Wet and Dry Etching. Theory
 Wet and Dry Etching Theory 1. Introduction Etching techniques are commonly used in the fabrication processes of semiconductor devices to remove selected layers for the purposes of pattern transfer, wafer
Wet and Dry Etching Theory 1. Introduction Etching techniques are commonly used in the fabrication processes of semiconductor devices to remove selected layers for the purposes of pattern transfer, wafer
Improvement of the diffraction properties in holographic polymer dispersed liquid crystal bragg gratings q
 Optics Communications 218 (2003) 27 32 www.elsevier.com/locate/optcom Improvement of the diffraction properties in holographic polymer dispersed liquid crystal bragg gratings q YanJun Liu a, *, Bin Zhang
Optics Communications 218 (2003) 27 32 www.elsevier.com/locate/optcom Improvement of the diffraction properties in holographic polymer dispersed liquid crystal bragg gratings q YanJun Liu a, *, Bin Zhang
Dry Etching Zheng Yang ERF 3017, MW 5:15-6:00 pm
 Dry Etching Zheng Yang ERF 3017, email: yangzhen@uic.edu, MW 5:15-6:00 pm Page 1 Page 2 Dry Etching Why dry etching? - WE is limited to pattern sizes above 3mm - WE is isotropic causing underetching -
Dry Etching Zheng Yang ERF 3017, email: yangzhen@uic.edu, MW 5:15-6:00 pm Page 1 Page 2 Dry Etching Why dry etching? - WE is limited to pattern sizes above 3mm - WE is isotropic causing underetching -
Far IR (FIR) Gas Lasers microns wavelengths, THz frequency Called Terahertz lasers or FIR lasers At this wavelength behaves more like
 Far IR (FIR) Gas Lasers 10-1500 microns wavelengths, 300 10 THz frequency Called Terahertz lasers or FIR lasers At this wavelength behaves more like microwave signal than light Created by Molecular vibronic
Far IR (FIR) Gas Lasers 10-1500 microns wavelengths, 300 10 THz frequency Called Terahertz lasers or FIR lasers At this wavelength behaves more like microwave signal than light Created by Molecular vibronic
Demonstration of Near-Infrared Negative-Index Materials
 Demonstration of Near-Infrared Negative-Index Materials Shuang Zhang 1, Wenjun Fan 1, N. C. Panoiu 2, K. J. Malloy 1, R. M. Osgood 2 and S. R. J. Brueck 2 1. Center for High Technology Materials and Department
Demonstration of Near-Infrared Negative-Index Materials Shuang Zhang 1, Wenjun Fan 1, N. C. Panoiu 2, K. J. Malloy 1, R. M. Osgood 2 and S. R. J. Brueck 2 1. Center for High Technology Materials and Department
XBC300 Gen2. Fully-automated debonder and Cleaner
 XBC300 Gen2 Fully-automated debonder and Cleaner XBC300 Gen2 FULLY AUTOMATED DEBONDER AND CLEANER The SUSS XBC300 Gen2 debonder and cleaner platform is designed for process development as well as high
XBC300 Gen2 Fully-automated debonder and Cleaner XBC300 Gen2 FULLY AUTOMATED DEBONDER AND CLEANER The SUSS XBC300 Gen2 debonder and cleaner platform is designed for process development as well as high
Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory
 Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Title Spatial scaling metrics of mask-induced induced line-edge roughness Permalink https://escholarship.org/uc/item/5rc666c3
Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Title Spatial scaling metrics of mask-induced induced line-edge roughness Permalink https://escholarship.org/uc/item/5rc666c3
Nano fabrication and optical characterization of nanostructures
 Introduction to nanooptics, Summer Term 2012, Abbe School of Photonics, FSU Jena, Prof. Thomas Pertsch Nano fabrication and optical characterization of nanostructures Lecture 12 1 Optical characterization
Introduction to nanooptics, Summer Term 2012, Abbe School of Photonics, FSU Jena, Prof. Thomas Pertsch Nano fabrication and optical characterization of nanostructures Lecture 12 1 Optical characterization
Case Study of Electronic Materials Packaging with Poor Metal Adhesion and the Process for Performing Root Cause Failure Analysis
 Case Study of Electronic Materials Packaging with Poor Metal Adhesion and the Process for Performing Root Cause Failure Analysis Dr. E. A. Leone BACKGRUND ne trend in the electronic packaging industry
Case Study of Electronic Materials Packaging with Poor Metal Adhesion and the Process for Performing Root Cause Failure Analysis Dr. E. A. Leone BACKGRUND ne trend in the electronic packaging industry
Fabrication of micro-optical components in polymer using proton beam micro-machining and modification
 Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B 210 (2003) 250 255 www.elsevier.com/locate/nimb Fabrication of micro-optical components in polymer using proton beam micro-machining and modification
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B 210 (2003) 250 255 www.elsevier.com/locate/nimb Fabrication of micro-optical components in polymer using proton beam micro-machining and modification
Application of the GD-Profiler 2 to the PV domain
 Application of the GD-Profiler 2 to the PV domain GD Profiler 2 RF GDOES permits to follow the distribution of the elements as function of depth. This is an ultra fast characterisation technique capable
Application of the GD-Profiler 2 to the PV domain GD Profiler 2 RF GDOES permits to follow the distribution of the elements as function of depth. This is an ultra fast characterisation technique capable
Surface and line-edge roughness in solution and plasma developed negative tone resists: Experiment and simulation
 Surface and line-edge roughness in solution and plasma developed negative tone resists: Experiment and simulation G. P. Patsis, A. Tserepi, I. Raptis, N. Glezos, and E. Gogolides a) Institute of Microelectronics,
Surface and line-edge roughness in solution and plasma developed negative tone resists: Experiment and simulation G. P. Patsis, A. Tserepi, I. Raptis, N. Glezos, and E. Gogolides a) Institute of Microelectronics,
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure S1. The effect of window size. The phonon MFP spectrum of intrinsic c-si (T=300 K) is shown for 7-point, 13-point, and 19-point windows. Increasing the window
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure S1. The effect of window size. The phonon MFP spectrum of intrinsic c-si (T=300 K) is shown for 7-point, 13-point, and 19-point windows. Increasing the window
A faster, more accurate way of characterizing cube beamsplitters using the Agilent Cary 7000 Universal Measurement Spectrophotometer (UMS)
 A faster, more accurate way of characterizing cube beamsplitters using the Agilent Cary 7000 Universal Measurement Spectrophotometer (UMS) Application note Materials Authors Travis Burt, Chris Colley,
A faster, more accurate way of characterizing cube beamsplitters using the Agilent Cary 7000 Universal Measurement Spectrophotometer (UMS) Application note Materials Authors Travis Burt, Chris Colley,
Direct write electron beam patterning of DNA complex thin films
 Direct write electron beam patterning of DNA complex thin films R. A. Jones, W. X. Li, H. Spaeth, and A. J. Steckl a Nanoelectronics Laboratory, University of Cincinnati, Cincinnati, Ohio 45221-0030 Received
Direct write electron beam patterning of DNA complex thin films R. A. Jones, W. X. Li, H. Spaeth, and A. J. Steckl a Nanoelectronics Laboratory, University of Cincinnati, Cincinnati, Ohio 45221-0030 Received
Far IR (FIR) Gas Lasers microns wavelengths, THz frequency Called Terahertz lasers or FIR lasers At this wavelength behaves more like
 Far IR (FIR) Gas Lasers 10-1500 microns wavelengths, 300 10 THz frequency Called Terahertz lasers or FIR lasers At this wavelength behaves more like microwave signal than light Created by Molecular vibronic
Far IR (FIR) Gas Lasers 10-1500 microns wavelengths, 300 10 THz frequency Called Terahertz lasers or FIR lasers At this wavelength behaves more like microwave signal than light Created by Molecular vibronic
Photomasks. Photolithography Evolution 9/11/2004 ECE580- MPE/MASKS/PHOTOMASKS.PPT
 Photolithography Evolution 1 : Evolution 2 Photomasks Substrates: Type : thermal expansion Chrome Pellicles Mask: OPC and PSM Fabrication: E-Beam or Laser 3 Photomask Information Websites: http://www.photronics.com/internet/corpcomm/publications/basics101/basics.
Photolithography Evolution 1 : Evolution 2 Photomasks Substrates: Type : thermal expansion Chrome Pellicles Mask: OPC and PSM Fabrication: E-Beam or Laser 3 Photomask Information Websites: http://www.photronics.com/internet/corpcomm/publications/basics101/basics.
Au-Ti THIN FILMS DEPOSITED ON GaAs
 Au-Ti THIN FILMS DEPOSITED ON GaAs R. V. GHITA *, D. PANTELICA**, M. F. LAZARESCU *, A. S. MANEA *, C. LOGOFATU *, C. NEGRILA *, V. CIUPINA *** * National Institute of Material Physics, P.O. Box MG7, Mãgurele,
Au-Ti THIN FILMS DEPOSITED ON GaAs R. V. GHITA *, D. PANTELICA**, M. F. LAZARESCU *, A. S. MANEA *, C. LOGOFATU *, C. NEGRILA *, V. CIUPINA *** * National Institute of Material Physics, P.O. Box MG7, Mãgurele,
MICRO AND NANOPROCESSING TECHNOLOGIES
 LECTURE 5 MICRO AND NANOPROCESSING TECHNOLOGIES Introduction Ion lithography X-ray lithography Soft lithography E-beam lithography Concepts and processes Lithography systems Masks and resists Chapt.9.
LECTURE 5 MICRO AND NANOPROCESSING TECHNOLOGIES Introduction Ion lithography X-ray lithography Soft lithography E-beam lithography Concepts and processes Lithography systems Masks and resists Chapt.9.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. DOI: 10.1038/NPHOTON.2016.254 Measurement of non-monotonic Casimir forces between silicon nanostructures Supplementary information L. Tang 1, M. Wang
In the format provided by the authors and unedited. DOI: 10.1038/NPHOTON.2016.254 Measurement of non-monotonic Casimir forces between silicon nanostructures Supplementary information L. Tang 1, M. Wang
Defense Technical Information Center Compilation Part Notice
 UNCLASSIFIED Defense Technical Information Center Compilation Part Notice ADP013351 TITLE: The Effects of Plasma Induced Damage on the Channel Layers of Ion Implanted GaAs MESFETs during Reactive Ion Etching
UNCLASSIFIED Defense Technical Information Center Compilation Part Notice ADP013351 TITLE: The Effects of Plasma Induced Damage on the Channel Layers of Ion Implanted GaAs MESFETs during Reactive Ion Etching
Formation mechanism and Coulomb blockade effect in self-assembled gold quantum dots
 Formation mechanism and Coulomb blockade effect in self-assembled gold quantum dots S. F. Hu a) National Nano Device Laboratories, Hsinchu 300, Taiwan R. L. Yeh and R. S. Liu Department of Chemistry, National
Formation mechanism and Coulomb blockade effect in self-assembled gold quantum dots S. F. Hu a) National Nano Device Laboratories, Hsinchu 300, Taiwan R. L. Yeh and R. S. Liu Department of Chemistry, National
Damage to Molecular Solids Irradiated by X-ray Laser Beam
 WDS'11 Proceedings of Contributed Papers, Part II, 247 251, 2011. ISBN 978-80-7378-185-9 MATFYZPRESS Damage to Molecular Solids Irradiated by X-ray Laser Beam T. Burian, V. Hájková, J. Chalupský, L. Juha,
WDS'11 Proceedings of Contributed Papers, Part II, 247 251, 2011. ISBN 978-80-7378-185-9 MATFYZPRESS Damage to Molecular Solids Irradiated by X-ray Laser Beam T. Burian, V. Hájková, J. Chalupský, L. Juha,
J. Photopolym. Sci. Technol., Vol. 22, No. 5, Fig. 1. Orthogonal solvents to conventional process media.
 originates from the limited number of options regarding orthogonal solvents, i.e. solvents that do not dissolve or adversely damage a pre-deposited organic materials layer. The simplest strategy to achieve
originates from the limited number of options regarding orthogonal solvents, i.e. solvents that do not dissolve or adversely damage a pre-deposited organic materials layer. The simplest strategy to achieve
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Experimental Section Hybrid Nanoparticle Synthesis The hafnium nanoparticles surface-modified with methacrylic acid (MAA, Sigma Aldrich, 99%), trans 2, 3-dimethylacrylic acid
Supplementary Information Experimental Section Hybrid Nanoparticle Synthesis The hafnium nanoparticles surface-modified with methacrylic acid (MAA, Sigma Aldrich, 99%), trans 2, 3-dimethylacrylic acid
X-Rays From Laser Plasmas
 X-Rays From Laser Plasmas Generation and Applications I. C. E. TURCU CLRC Rutherford Appleton Laboratory, UK and J. B. DANCE JOHN WILEY & SONS Chichester New York Weinheim Brisbane Singapore Toronto Contents
X-Rays From Laser Plasmas Generation and Applications I. C. E. TURCU CLRC Rutherford Appleton Laboratory, UK and J. B. DANCE JOHN WILEY & SONS Chichester New York Weinheim Brisbane Singapore Toronto Contents
Analyses of LiNbO 3 wafer surface etched by ECR plasma of CHF 3 & CF 4
 1998 DRY PROCESS SYMPOSIUM VI - 3 Analyses of LiNbO 3 wafer surface etched by ECR plasma of CHF 3 & CF 4 Naoki Mitsugi, Kaori Shima, Masumi Ishizuka and Hirotoshi Nagata New Technology Research Laboratories,
1998 DRY PROCESS SYMPOSIUM VI - 3 Analyses of LiNbO 3 wafer surface etched by ECR plasma of CHF 3 & CF 4 Naoki Mitsugi, Kaori Shima, Masumi Ishizuka and Hirotoshi Nagata New Technology Research Laboratories,
Advanced Texturing of Si Nanostructures on Low Lifetime Si Wafer
 Advanced Texturing of Si Nanostructures on Low Lifetime Si Wafer SUHAILA SEPEAI, A.W.AZHARI, SALEEM H.ZAIDI, K.SOPIAN Solar Energy Research Institute (SERI), Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia (UKM), 43600
Advanced Texturing of Si Nanostructures on Low Lifetime Si Wafer SUHAILA SEPEAI, A.W.AZHARI, SALEEM H.ZAIDI, K.SOPIAN Solar Energy Research Institute (SERI), Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia (UKM), 43600
TARGET INJECTION INTO A GAS-FILLED CHAMBER
 TARGET INJECTION INTO A GAS-FILLED CHAMBER Neil Alexander, Dan Goodin, Abbas Nikroo, Ron Petzoldt, Rich Stephens - (GA) Mike Cherry, Alison Newkirk, Mark Tillack - (UCSD) Presented at ARIES Project Meeting
TARGET INJECTION INTO A GAS-FILLED CHAMBER Neil Alexander, Dan Goodin, Abbas Nikroo, Ron Petzoldt, Rich Stephens - (GA) Mike Cherry, Alison Newkirk, Mark Tillack - (UCSD) Presented at ARIES Project Meeting
